Insertion mutation detection method and system based on new-generation sequencing data
A technology for sequencing data and variant detection, applied in genomics, instrumentation, proteomics, etc., can solve the problems of wrong detection results, large deviation of repeated sequences, assembly errors, etc., to achieve a good detection effect and solve the effect of inaccurate judgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
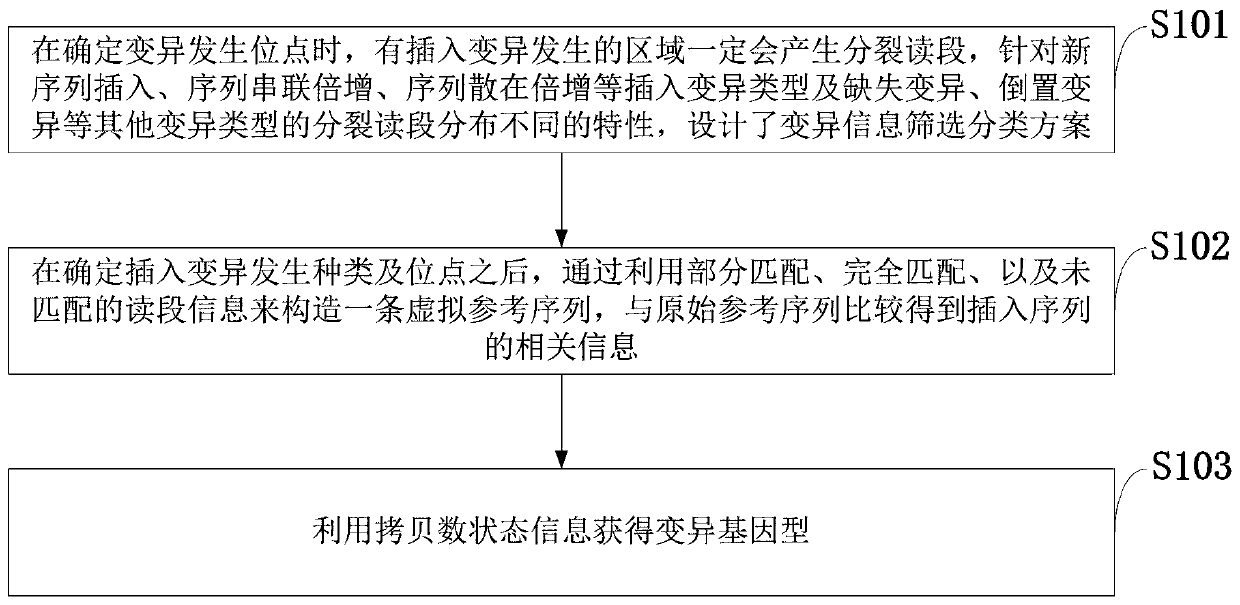
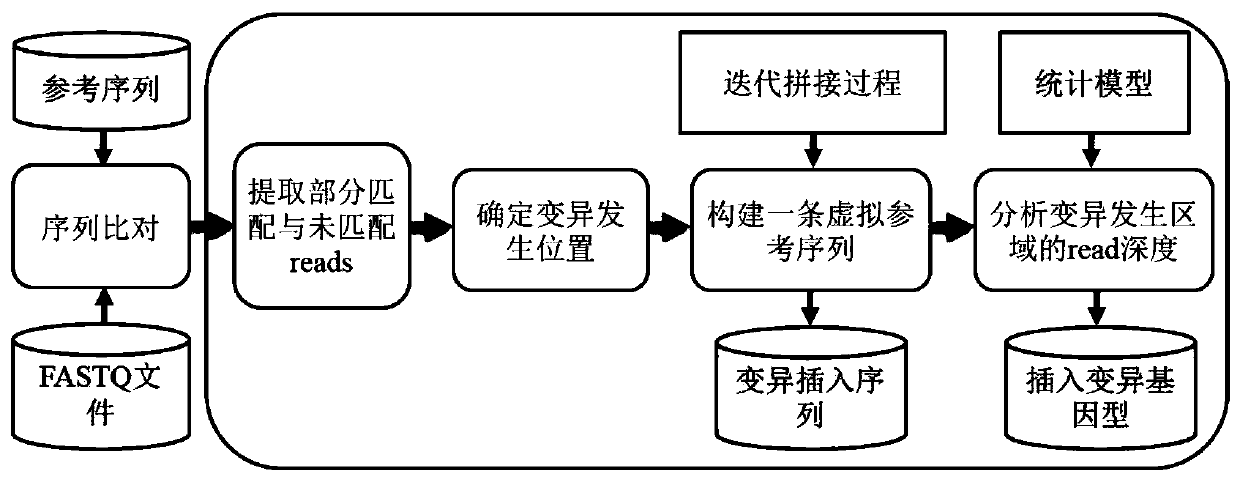
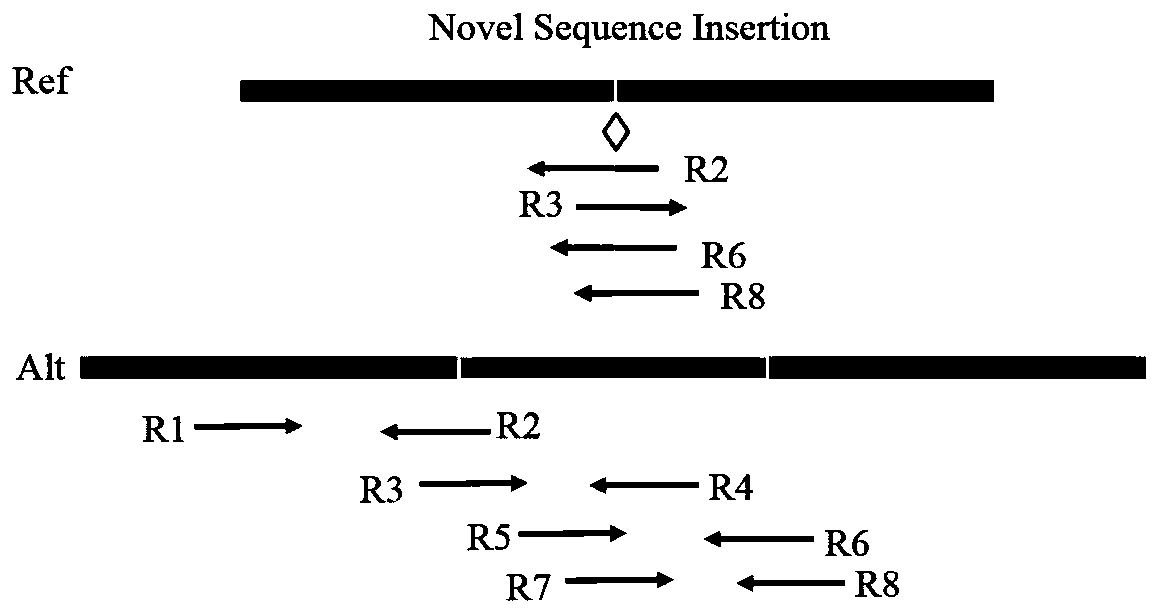
[0052] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
[0053] In view of the fact that the existing technology does not meet the situation of various types of insertion mutations in cancer samples, it greatly limits the ability of cancer diagnosis and targeted drug selection; the ability to detect large-scale insertion mutations is insufficient; the problem of obtaining wrong mutation detection results . The present invention uses the split read and insert size information of the paired-end read-end to accurately target the site and type of insertion variation. The present invention technically uses an insertion sequence iterative splicing method to detect and extract insertio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com