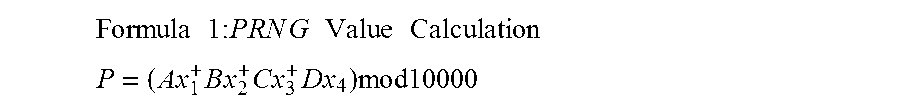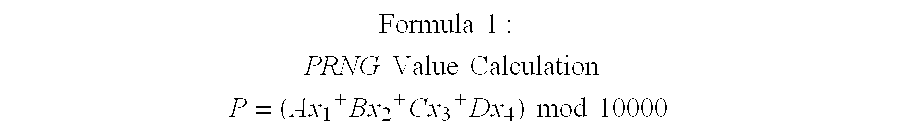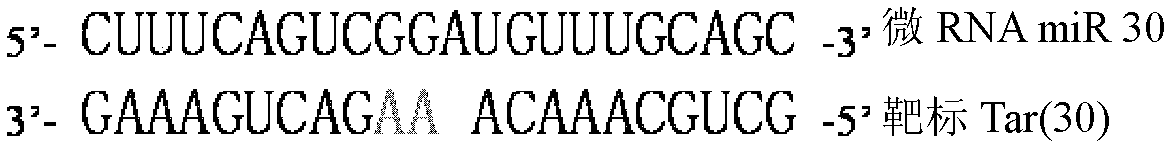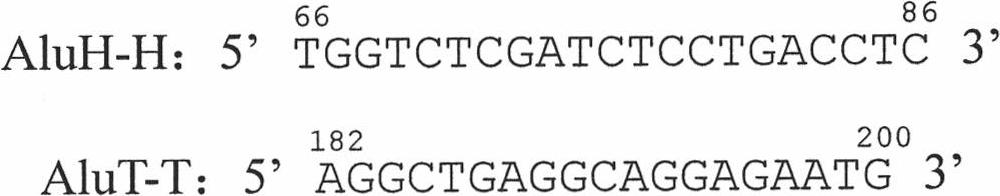Patents
Literature
50 results about "Sequence Insertions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
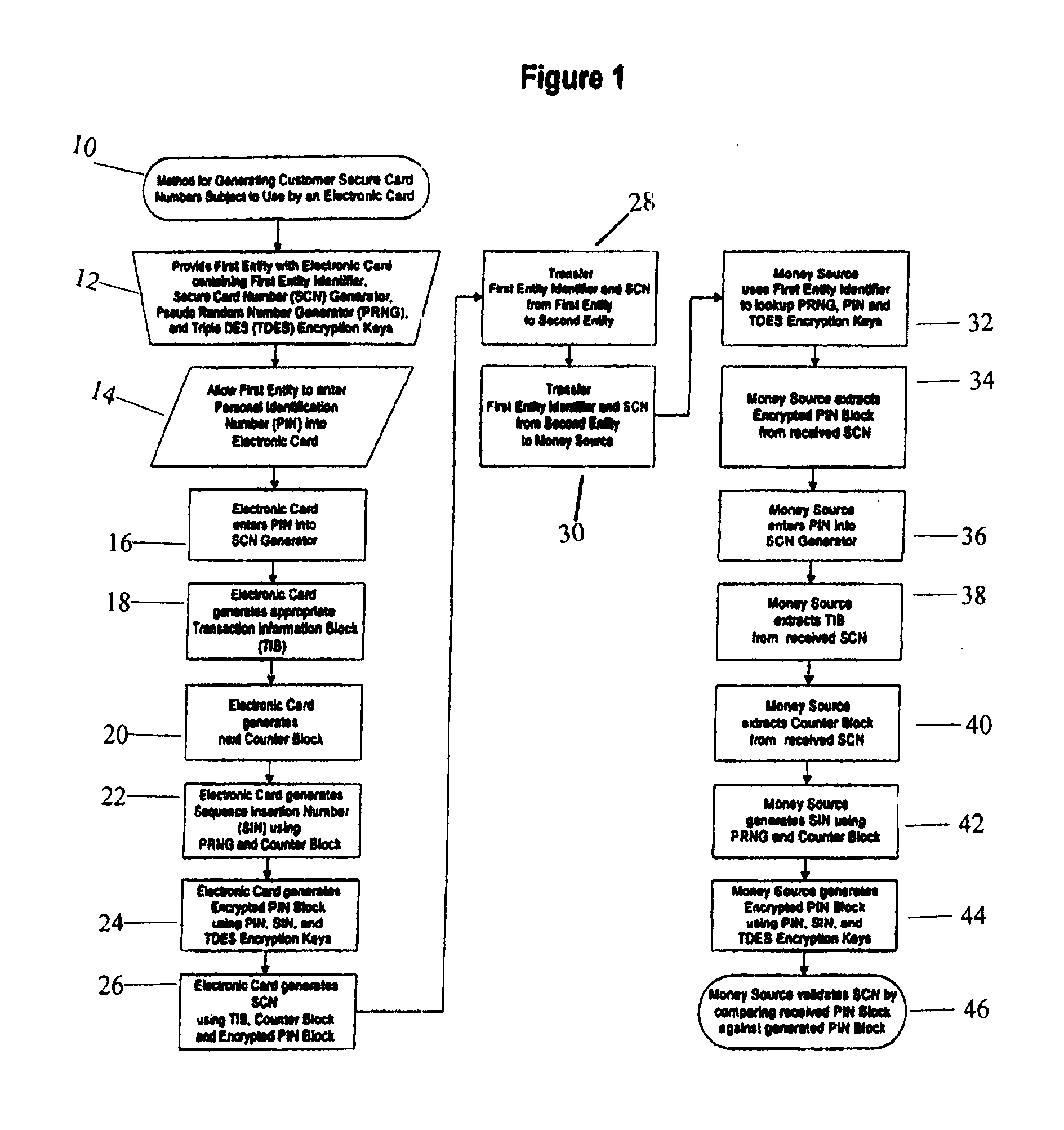
Method for generating customer secure card numbers
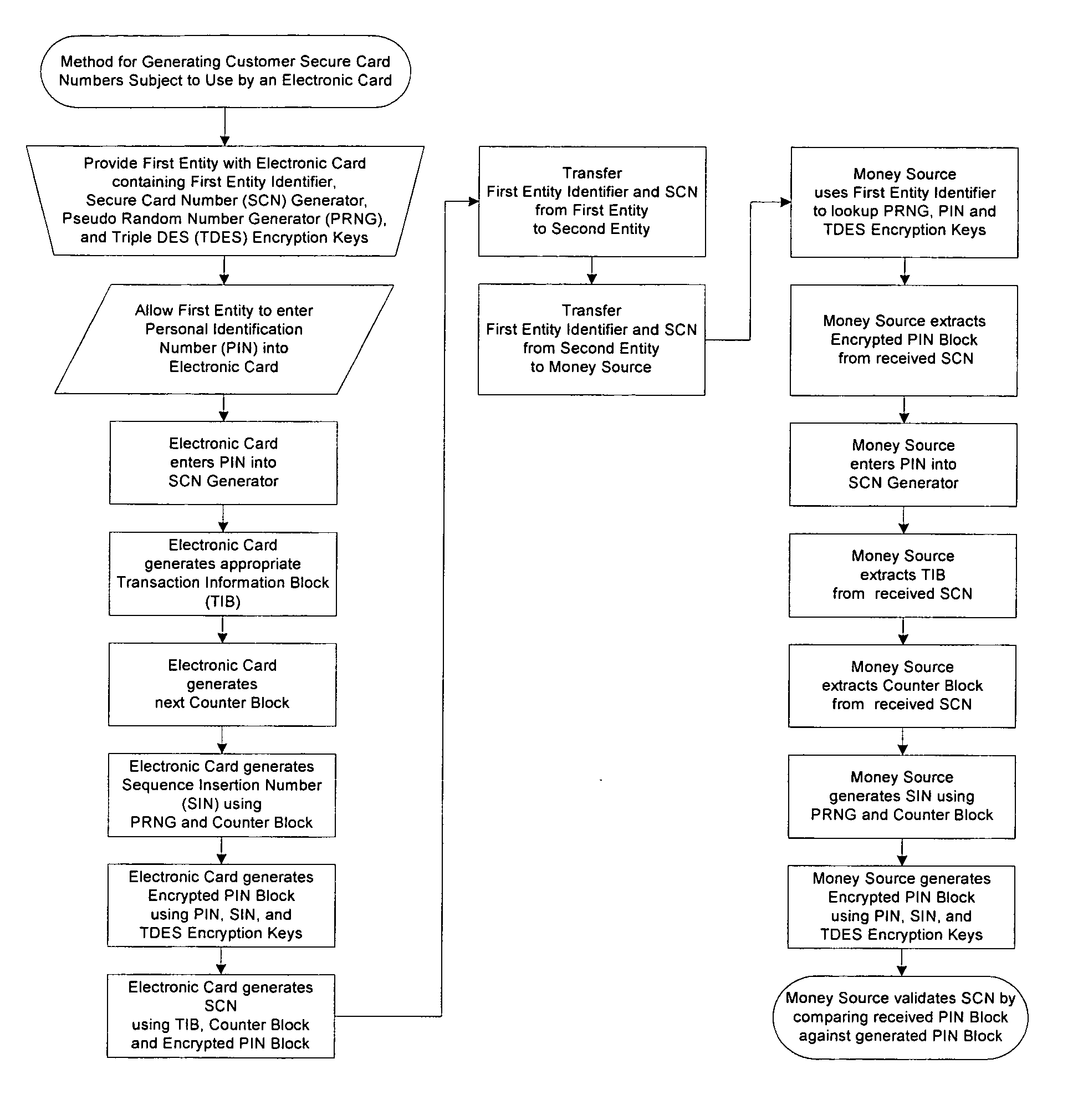
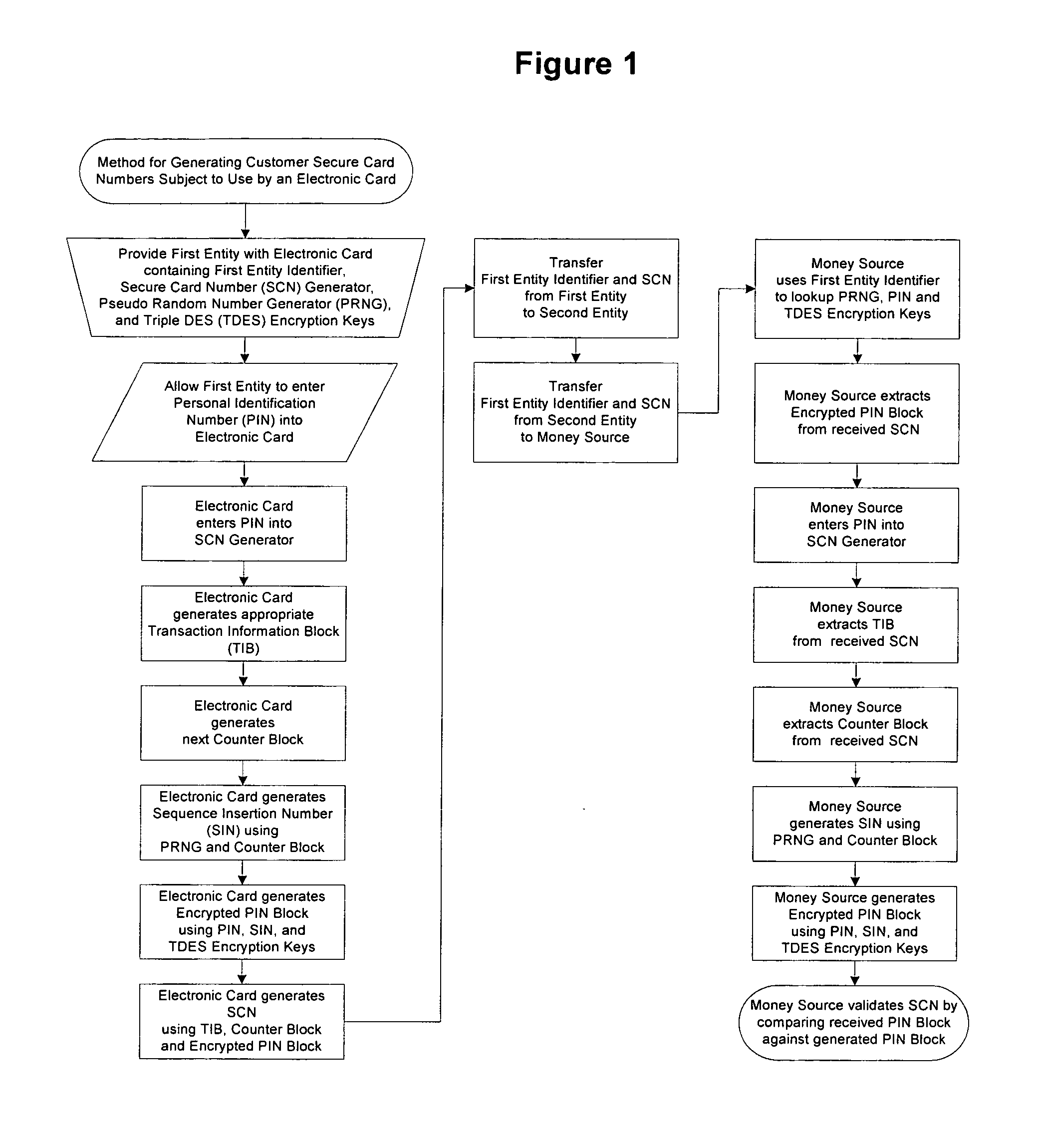
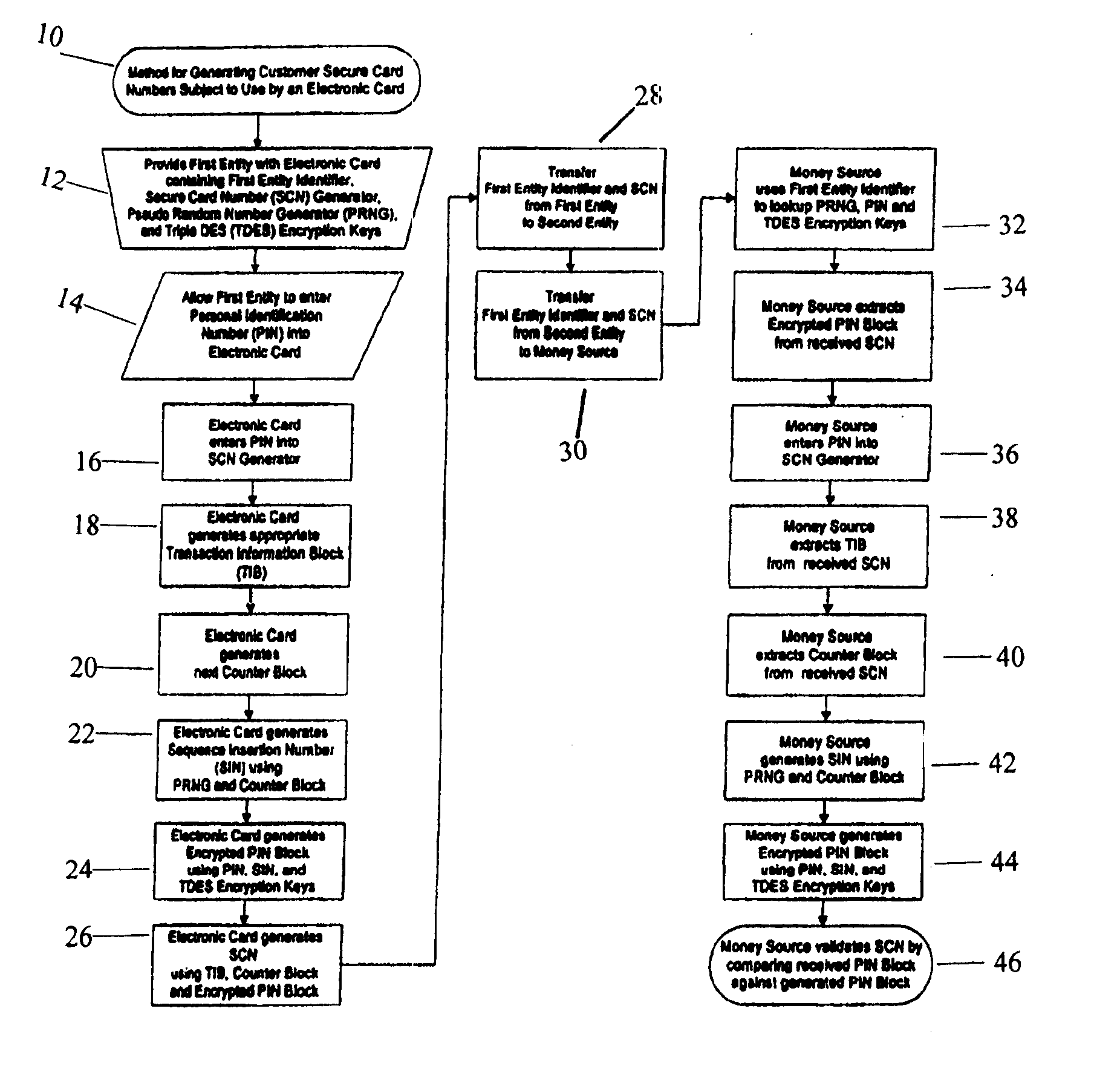
A method for providing secure transactions generates a Secure Card Number (“SCN”) for a first entity that is transferred with a first entity identifier to a second entity and then to a money source that verifies that the transaction is valid by use of the first entity identifier and the SCN. The SCN includes a 0Transaction Information Block (“TIB”), a Counter Block, and an encrypted Personal Identification Number (“PIN”) Block. The SCN is transferred to the money source in an account number or a non-account data field. The money source can use the TIB to determine whether the SCN should be used once or multiple times or to identify one of several physical devices, all of which are issued to the first entity, used to generate the SCN. The money source validates the SCN by duplicating the encryption process used to create an encrypted PIN Block and comparing the result to the encrypted PIN Block received with the transaction. A Triple Data Encryption Standard algorithm encrypts a PIN Block generated from a PIN, a Sequence Insertion Number (“SIN”) and a known starting value. The SIN can be a combination of three seed values and a random value generated by a Pseudo Random Number Generator (“PRNG”) initialized with the seed values. A Counter value is associated with the Counter Block and the seed values.
Owner:PRIVASYS
Method for Generating Customer Secure Card Numbers
InactiveUS20070215688A1Complete banking machinesFinancePersonal identification numberEntity identifier
A method for providing secure transactions generates a Secure Card Number (“SCN”) for a first entity that is transferred with a first entity identifier to a second entity and then to a money source that verifies that the transaction is valid by use of the first entity identifier and the SCN. The SCN includes a Transaction Information Block (“TIB”), a Counter Block, and an encrypted Personal Identification Number (“PIN”) Block. The SCN is transferred to the money source in an account number or a non-account data field. The money source can use the TIB to determine whether the SCN should be used once or multiple times or to identify one of several physical devices, all of which are issued to the first entity, used to generate the SCN. The money source validates the SCN by duplicating the encryption process used to create an encrypted PIN Block and comparing the result to the encrypted PIN Block received with the transaction. A Triple Data Encryption Standard algorithm encrypts a PIN Block generated from a PIN, a Sequence Insertion Number (“SIN”) and a known starting value. The SIN can be a combination of three seed values and a random value generated by a Pseudo Random Number Generator (“PRNG”) initialized with the seed values. A Counter value is associated with the Counter Block and the seed values.
Owner:PRIVASYS
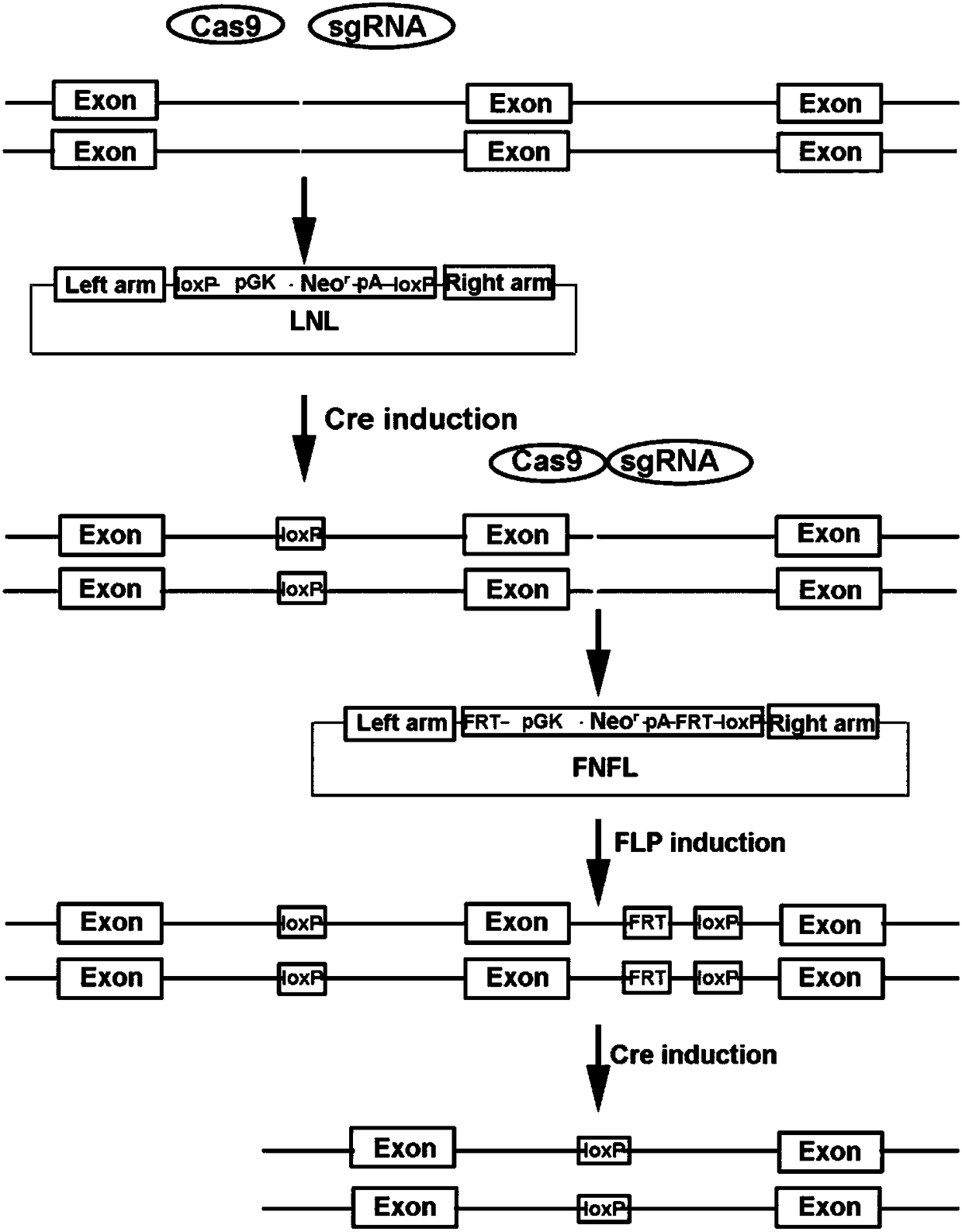
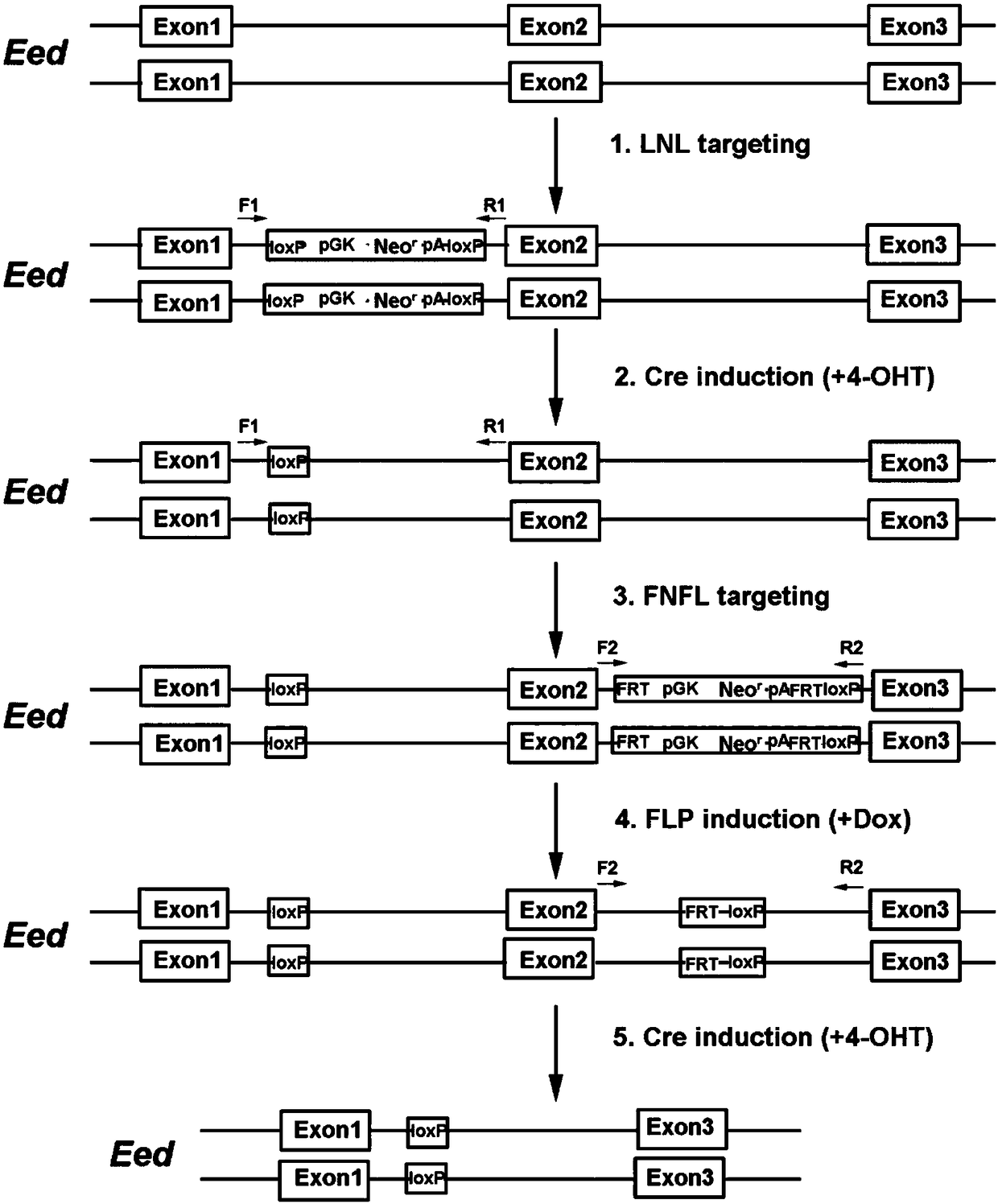
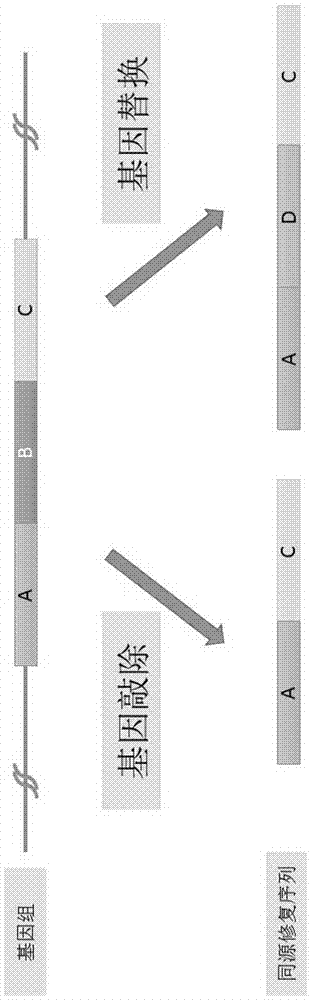
Conditional gene knockout method constructed by using CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN108441520AImprove recombination efficiencySave time and costHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEnzyme digestionSequence Insertions
The invention relates to a conditional gene knockout method constructed by using a CRISPR / Cas9 system. LoxP-antibiotic-LoxP and FRT-antibiotic-FRT-LoxP sequence insertion sites are selected from leftand right sides of a to-be-knocked-out area respectively; left and right homologous arms are selected from upstream and downstream positions of to-be-inserted sites, amplification, purification, enzyme digestion, linking and conversion are performed, and left and right targeting plasmids are obtained; Cas9 plasmid, the left or right targeting plasmid of the knockout area and corresponding gRNA expression plasmids are sequentially or simultaneously introduced into cells, screening is performed with antibiotics after transfection, and target cells with left and right targeting sequences insertedare screened out simultaneously; 4-OHT and DOX are used for inducing Cre-LoxP and FLP-FRT medicated homologous recombination, so that loxp sites are introduced in left and right sides of the to-be-knocked-out area; 4-OHT is used for inducing Cre-LoxP medicated homologous recombination, and cloning of target fragment knockout is obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
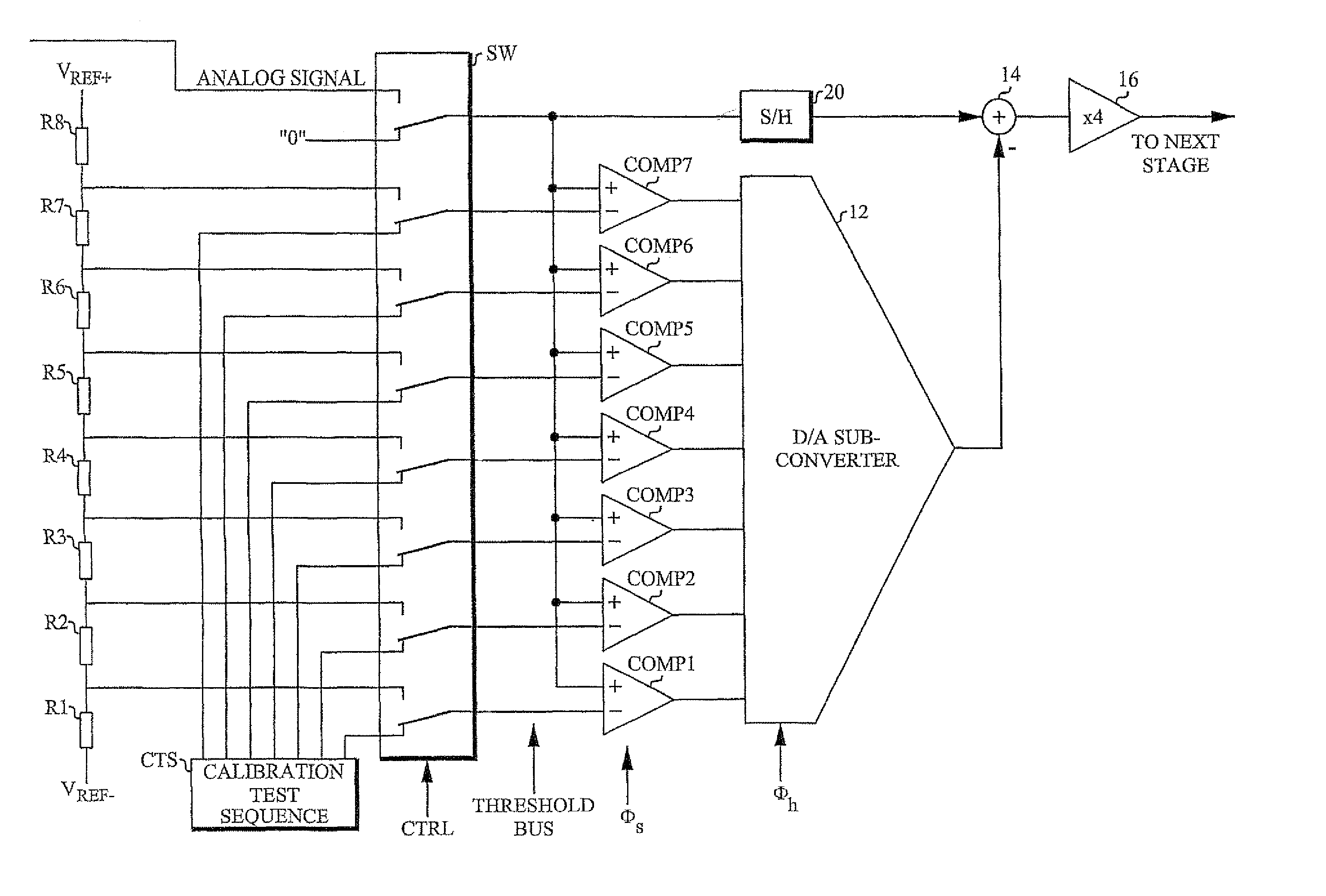
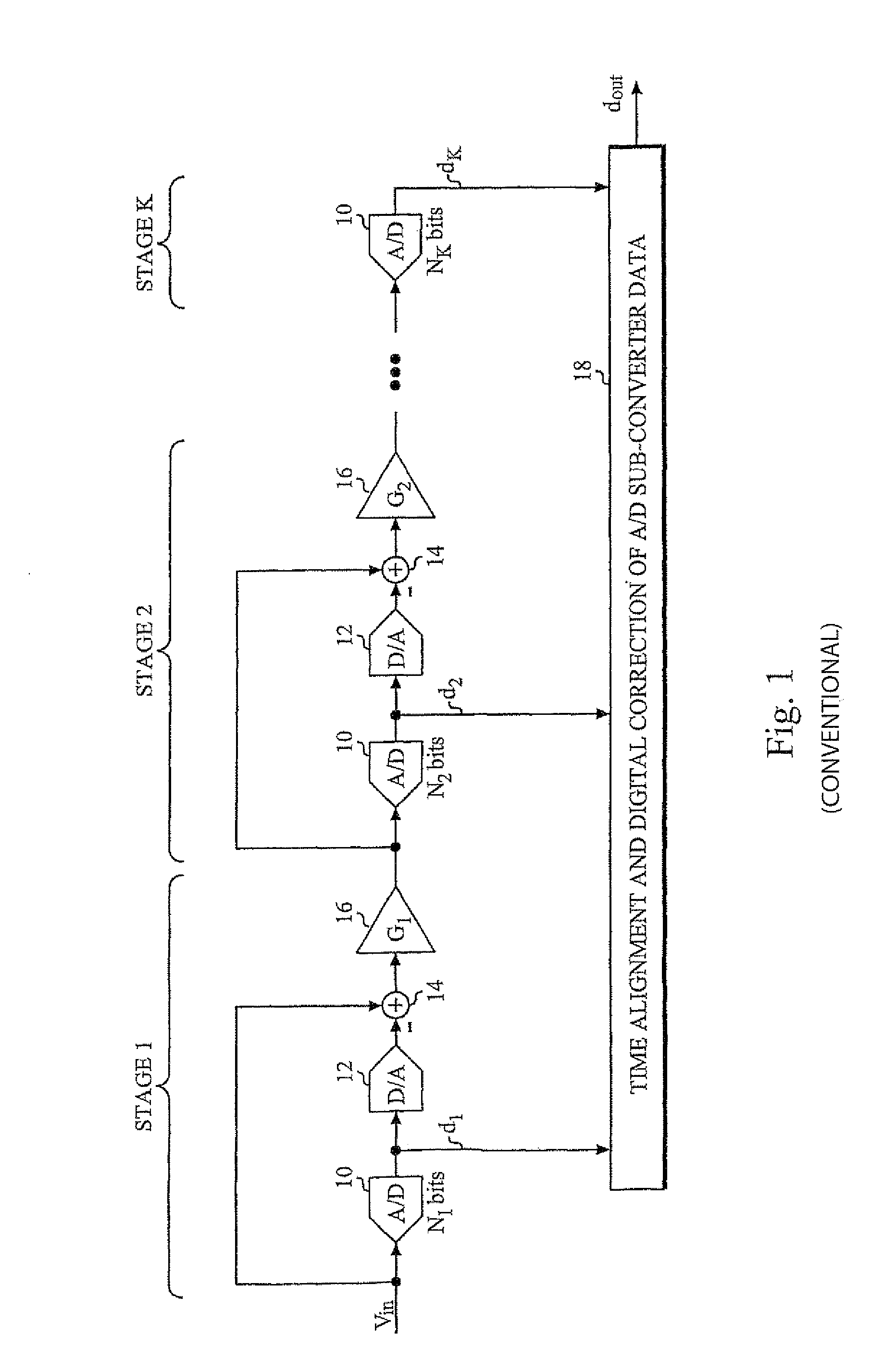
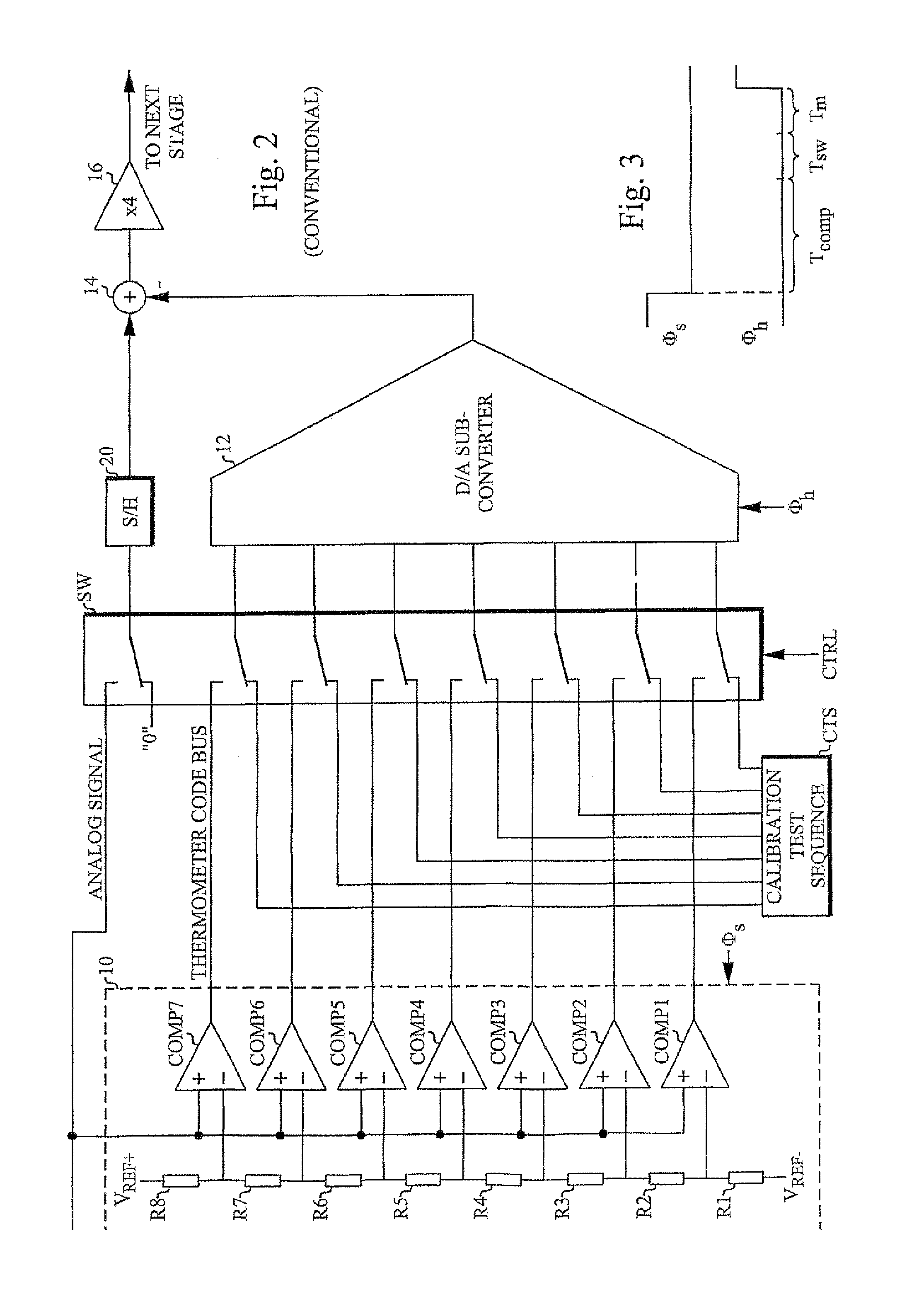
A/D converter calibration test sequence insertion
InactiveUS7405681B2Increasing attainable sample rateEliminate delaysElectric signal transmission systemsElectrical measurementsSequence InsertionsA d converter
An A / D converter stage including an A / D sub-converter connected to a D / A sub-converter (12) is calibrated by a method that inserts a calibration test sequence into the D / A sub-converter. This is accomplished by forcing (SW) the comparators (COMP1-COMP7) of the A / D sub-converter to generate and insert the sequence into the D / A sub-converter.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Gene editing technique taking Argonaute nuclease as core
InactiveCN105483118ASimple designThe dosage is easy to controlDNA preparationGenome editing3-deoxyribose
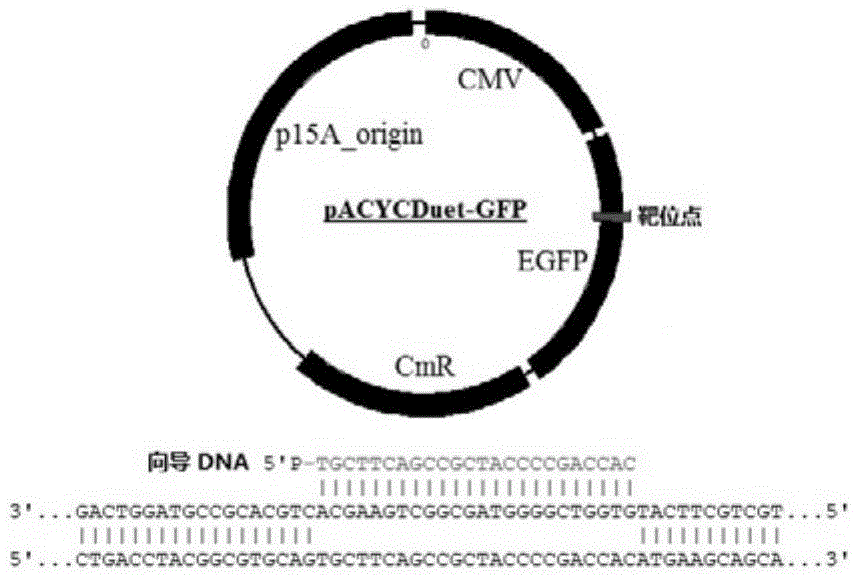
The invention discloses a gene editing technique taking Argonaute nuclease as a core. In the presence of guide DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), Argonaute endonuclease can cut any locus of a targeted DNA sequence, including a genome of a mammal to cause breakage of DNA double chains, thereby fulfilling an editing aim. Editing means include incision, deletion, mutagenesis induction, exogenous sequence insertion, fragment substitution and the like. Editing effects include gene inactivation, gene mutation, exogenous gene induction and the like. The protein can serve as an important tool for genome editing. A gene editing tool taking the protein as the core has the characteristics of easiness in operation, high efficiency, low target missing rate and high fidelity. Moreover, almost any genome locus can be effectively targeted and cut by the Argonaute nuclease. By using the technique, high-specificity and high-efficiency genome targeted editing is helpfully realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
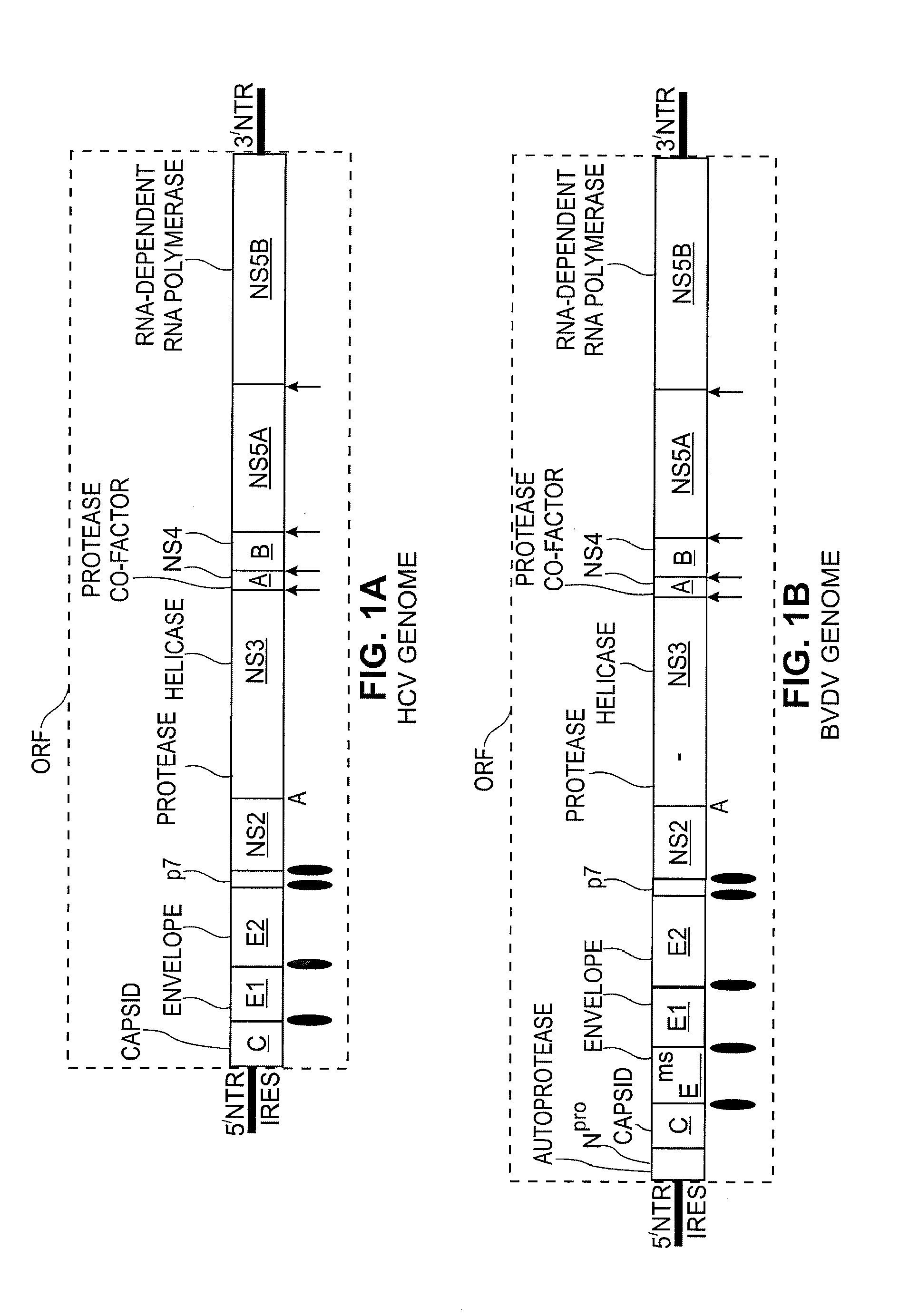
Replication Stable and RNase Resistant Chimeras of Pestivirus with Insertion in 3' Nontranslated Region (3'NTR)
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid amplification, particularly to quality control materials for use in viral RNA assays. It specifically relates to the construction of a recombinant Pestivirus by the identification of a region in the 3′NTR of the viral RNA genome where additional sequence elements can be stably inserted. Chimeric Pestivirus with sequence insertions in the 3′ nontranslated region (3′NTR) of the viral RNA genome were stable in replication and capable of forming infectious, RNase resistant virus particles. This chimeric Pestivirus with a 3′NTR insertion can be utilized as a quality control material in analytical assays for RNA targets, including external, internal controls, quantitative standards in PCR and NAT nucleic acid assays.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Mutant type Tn5 transposase and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106754811AChange combinationChange dependenciesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesTn5 transposaseSequence Insertions
Disclosed are a mutant type Tn5 transposase and a preparation method and application thereof. The mutant type Tn5 transposase has the advantages that an existing EK / LP Tn5 transposase is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis for lowing DNA preference, site-directed mutagenesis refers to mutagenesis in at least two of D97E, D188E and E326D and improves a protein sequence and a conformation of the Tn5 transposase, and a reaction system is subjected to fine adjustment, so that preference of the Tn5 transposase to DNA target sequence insertion is improved, DNA library construction uniformity is improved remarkably, library construction results have better coverage degree, and requirements of high-throughput sequencing library construction are met.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Encoding and decoding method for improving decoding efficiency by pilot frequency information and device thereof
InactiveCN101534127AFast convergenceImprove decoding performanceCode conversionCoding detailsTime delaysError correcting
The invention discloses an encoding and decoding method for improving decoding efficiency by pilot frequency information and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: pilot frequency sequences are evenly inserted into an information sequence before encoding, and the information sequence is subjected to error correction encoding by an error correcting code; the encoded information sequence is generated into an OFDMA symbol after IFFT conversion, and is transmitted to a receiving end; the receiving end carries out FFT conversion on the received information sequence to obtain soft information corresponding to the information sequence which is encoded by a transmitting end; the positions of the pilot frequency sequences inserted into the information sequence are set into corresponding soft information values according to values of the pilot frequency sequences; and the information is subjected to error correcting decoding to obtain transmitting information of the transmitting end. The method and the device can improve the velocity of convergence and decoding performance of an error correcting decoder, reduce the times of decoding iteration, reduce decoding time delay, and simplify the process of decoding.
Owner:西安新邮通信设备有限公司
Efficient Method of Preparing Dna Inverted Repeat
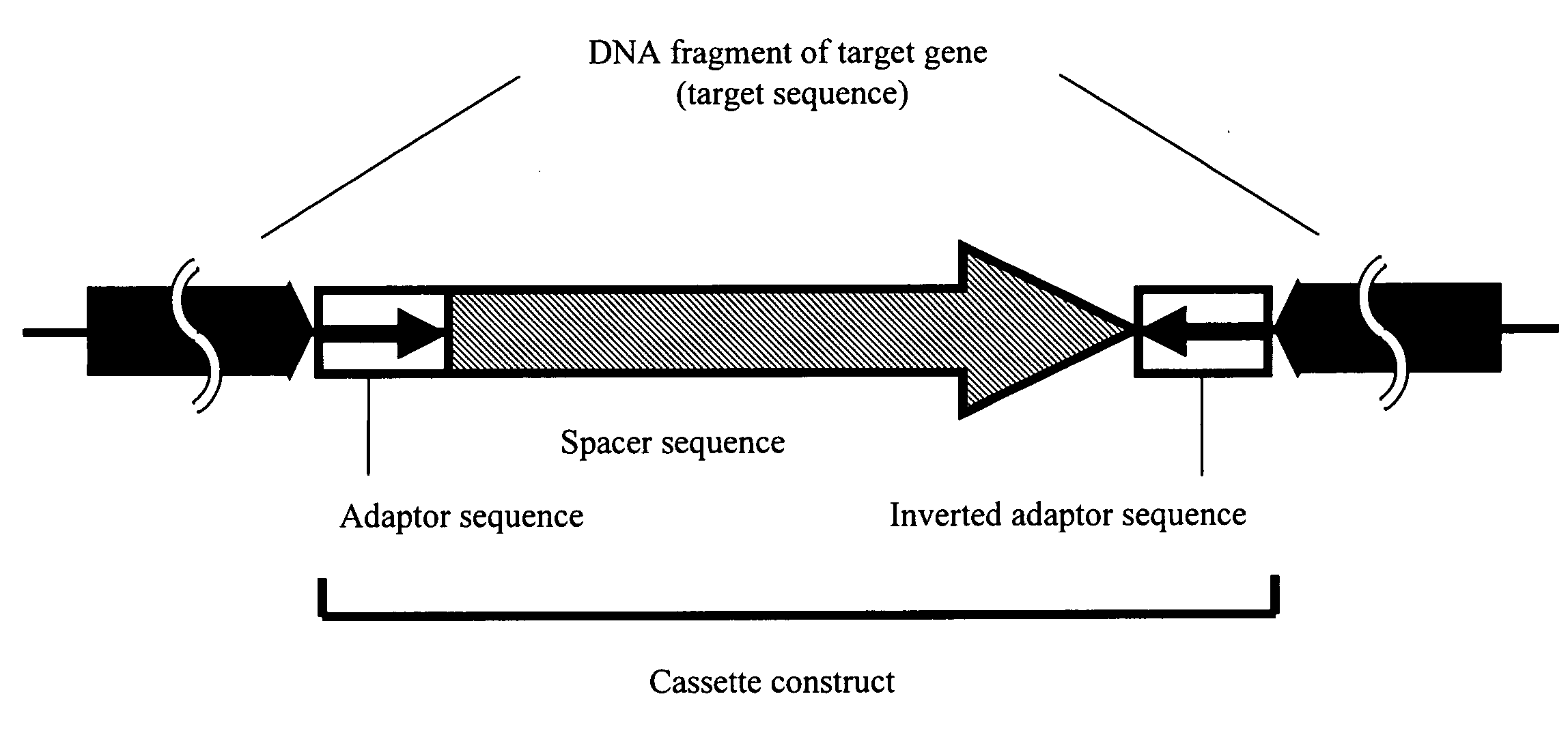
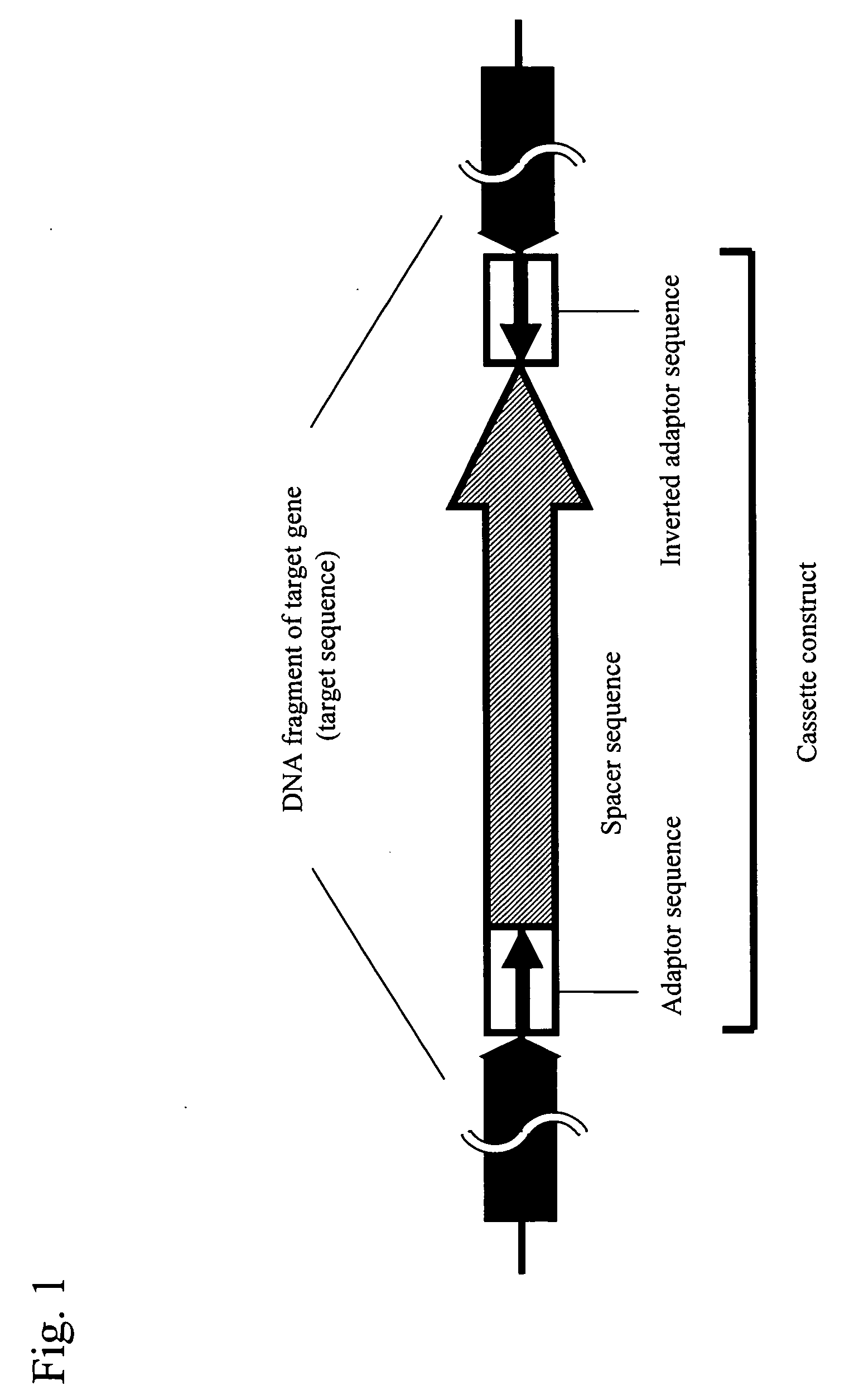
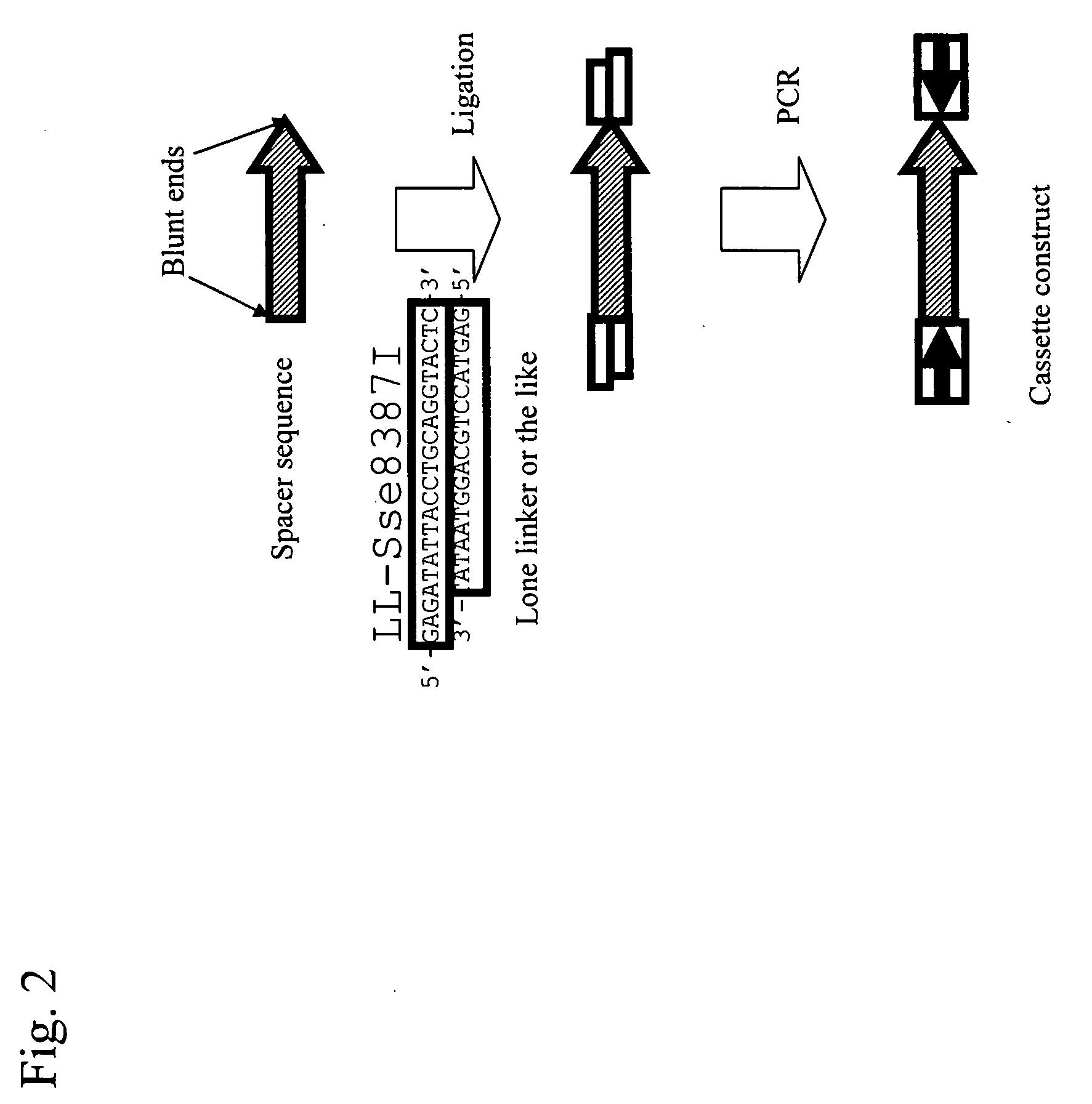
Conventional techniques for preparing a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence of a target sequence suffer from complications since a target sequence is inserted into 2 sites on a vector in sense and antisense orientations, and restriction enzyme recognition sequences must be independently provided at an insertion site of a vector and both ends of the target sequence.In this invention, a cassette construct comprising an arbitrary adaptor sequence and an inverted adaptor sequence separated by an arbitrary spacer sequence or a plasmid vector comprising such cassette construct incorporated therein is prepared, a target sequence is ligated to either or both ends of the cassette construct, or a target sequence is inserted into one end of the cassette construct on the plasmid vector, followed by PCR. Thus, a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence is prepared.
Owner:RIKEN
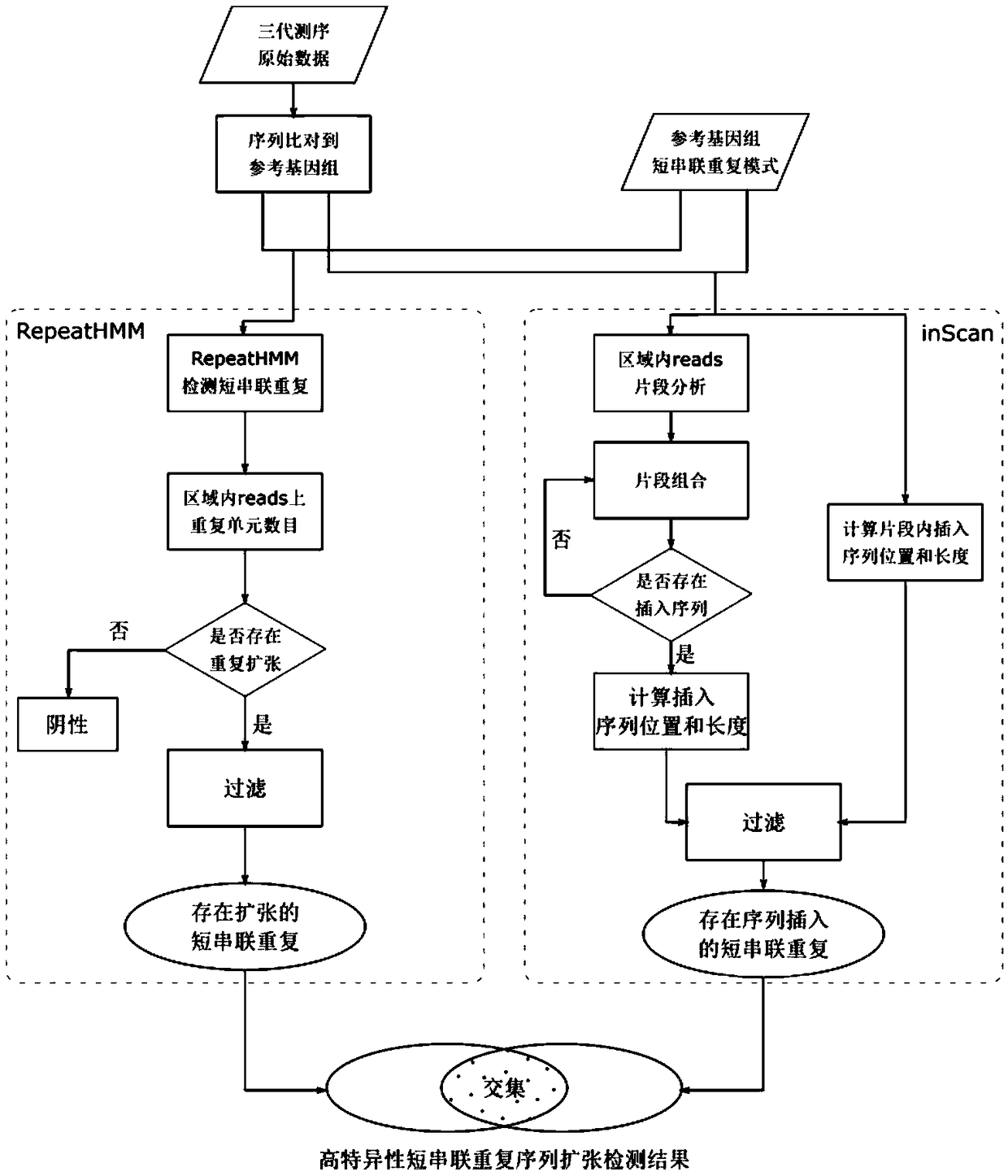
Method for detecting expansion of short tandem repeat
ActiveCN108660200AStrong specificityReduce false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence InsertionsThird generation sequencing
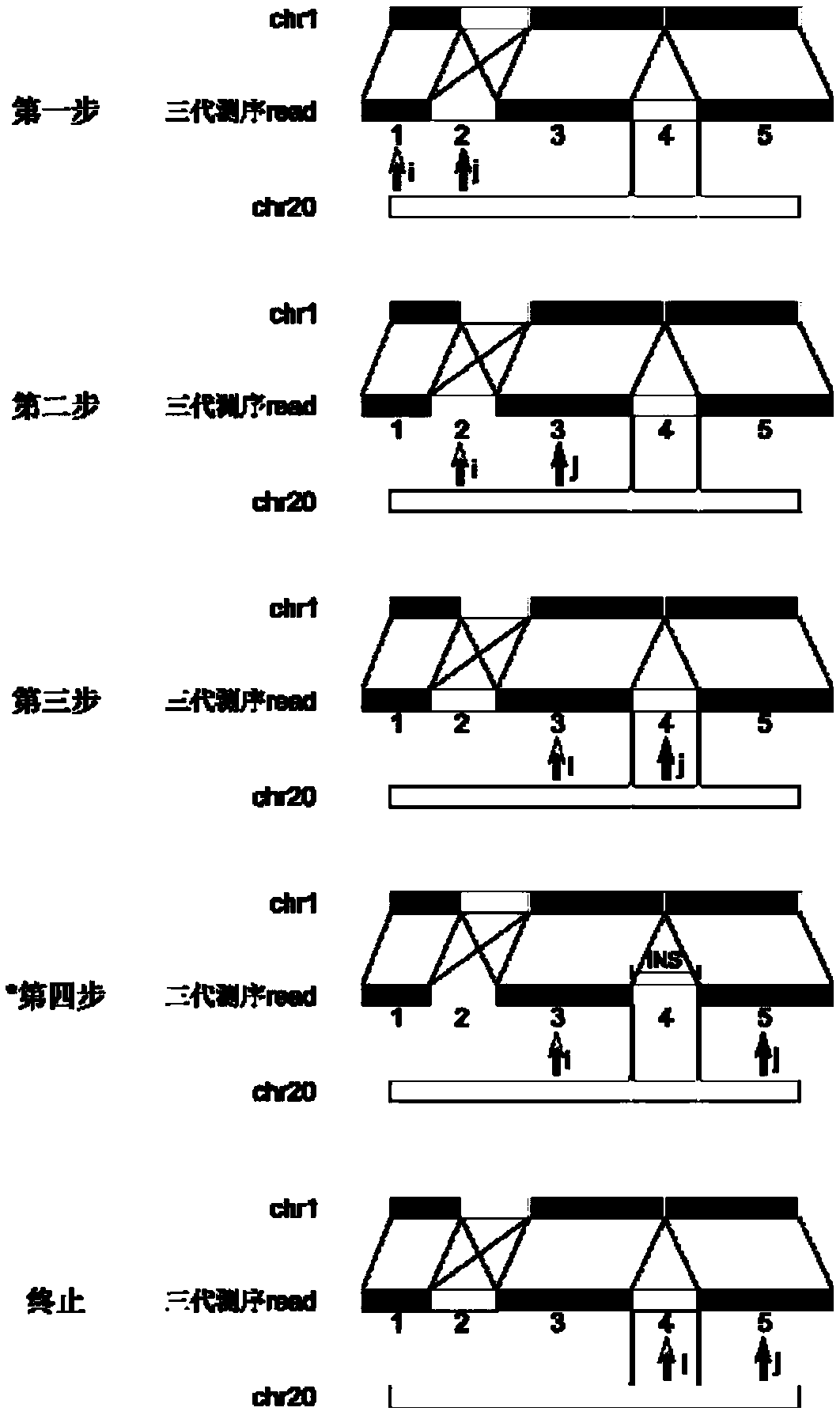
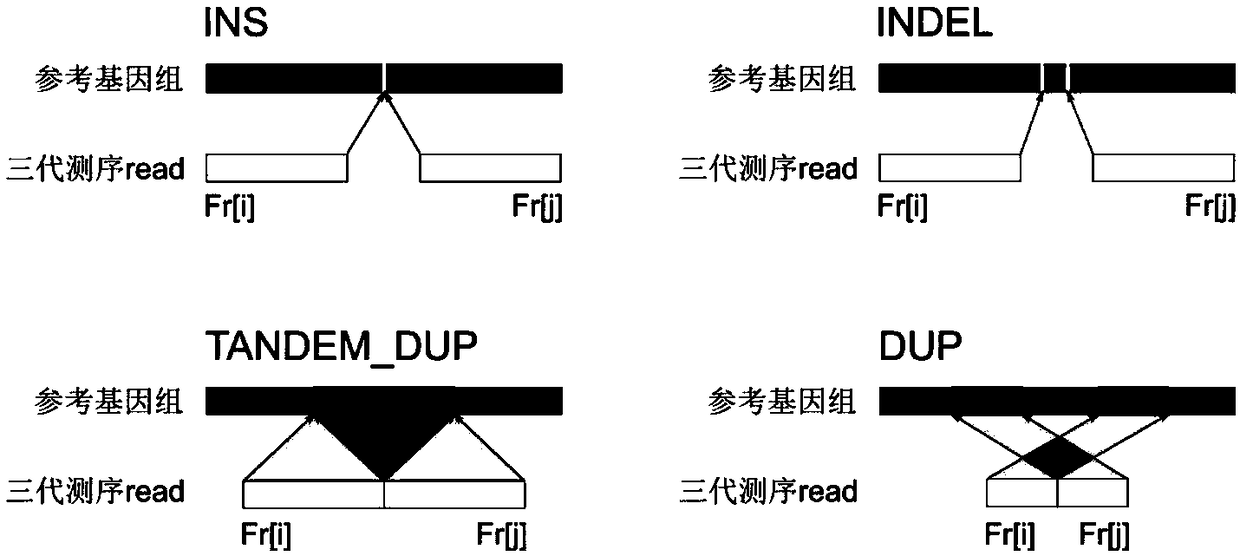
The invention provides a method for detecting expansion of a short tandem repeat. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out sequence alignment; secondly, detecting short tandem repeat of third-generation sequencing data by RepeatHMM; thirdly, detecting sequence insertion of a short tandem repeat area by inScan; fourthly, calculating an intersection of RepeatHMM detection results and sequence insertion detection results of the short tandem repeat area. According to the method provided by the invention, the results of the sequence insertion and RepeatHMM short tandem repeatdetection are combined, so that the specificity of detecting the expansion of the short tandem repeat is improved.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH +1
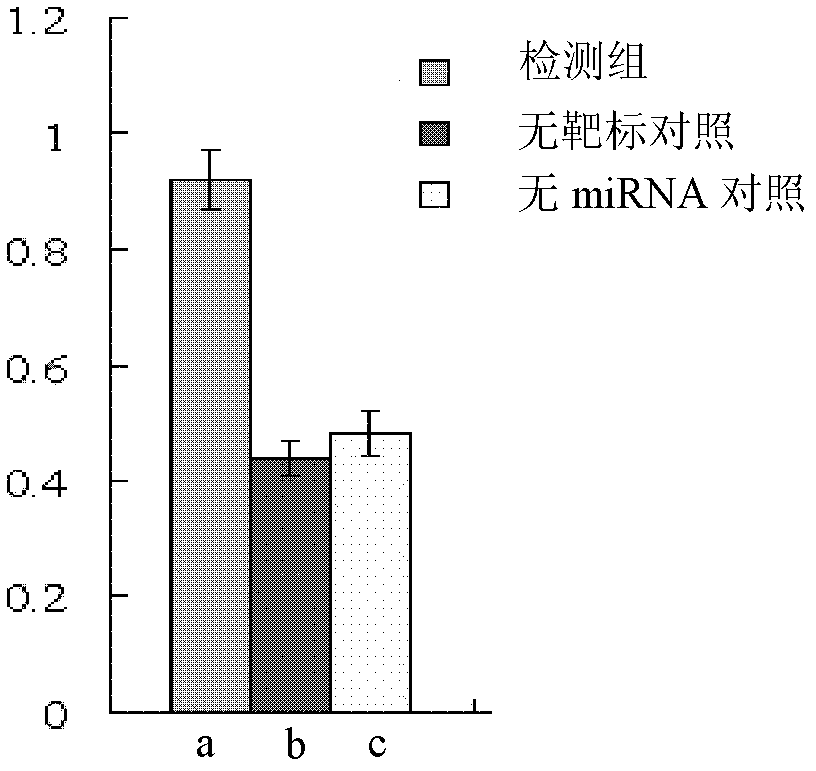
Preparation method and application for dual-fluorescence reporting system with micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid) function
InactiveCN102443595AJudgment inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReporting systemEnhanced green fluorescent protein
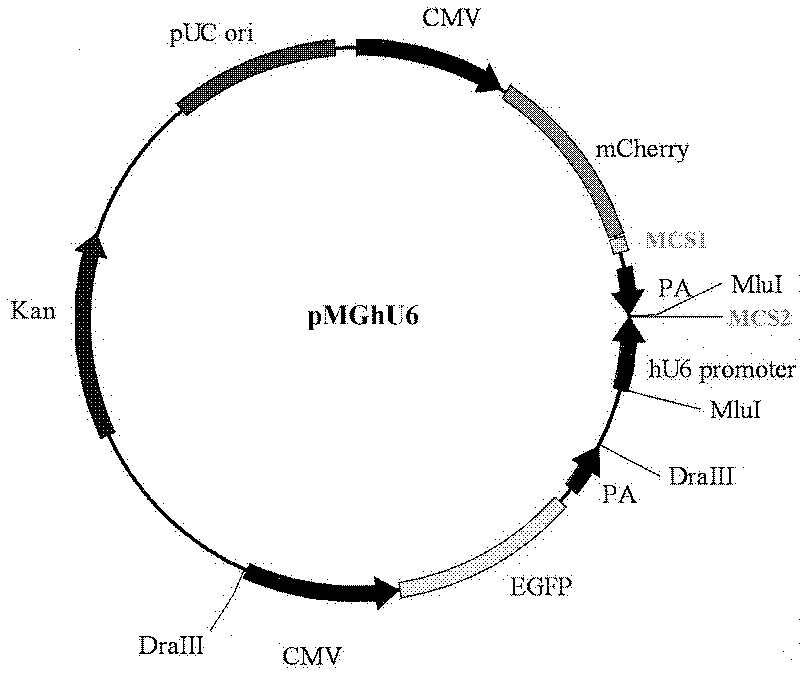
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application for a dual-fluorescence reporting system for detecting a micro-RNA (ribonucleic acid) function, wherein the preparation method comprises the following preparation steps of: A, obtaining a mCherry gene sequence via a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, inserting a rho EGFP-C1 carrier to replace the EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) sequence of the mCherry gene sequence, and constructing a carrier rho mCherry-C1; B, using a RNAi-Ready rho SIREN-RetroQ plasmid as a template, obtaining a human U6 promoter gene via a PCR amplification, and inserting the carrier rho mCherry-C1 to obtain a plasmid rho hU6-mCherry-C1; and C, obtaining a gene sequence carried with a CMV (cytomegalovirus) promoter and an EGFP expression dialog sequence in an interval of 358 to 1944 on a plasmid rho Adtrack-CMV, and inserting the sequence in the plasmid rho hU6-mCherry-C1 to obtain a plasmid rho MGhU6. The plasmid rho MGhU6 is a dual-fluorescence reporting system simultaneously containing a mCherry reporting gene, an internal reference EGFP, a micro-RNA and the target sequence insertion site thereof. The reporting system can be used for detecting the inhibition function of the micro-RNA to the target sequence expression. The detection method is easy, as well as simple and convenient in operation; and a function detection for the micro-RNA can be realized by transfecting one plasmid only. The system also can be used for visually detecting the inhibition function of a micro-RNA in a single living cell to the target thereof by the aid of fluorescence microscopic imaging.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
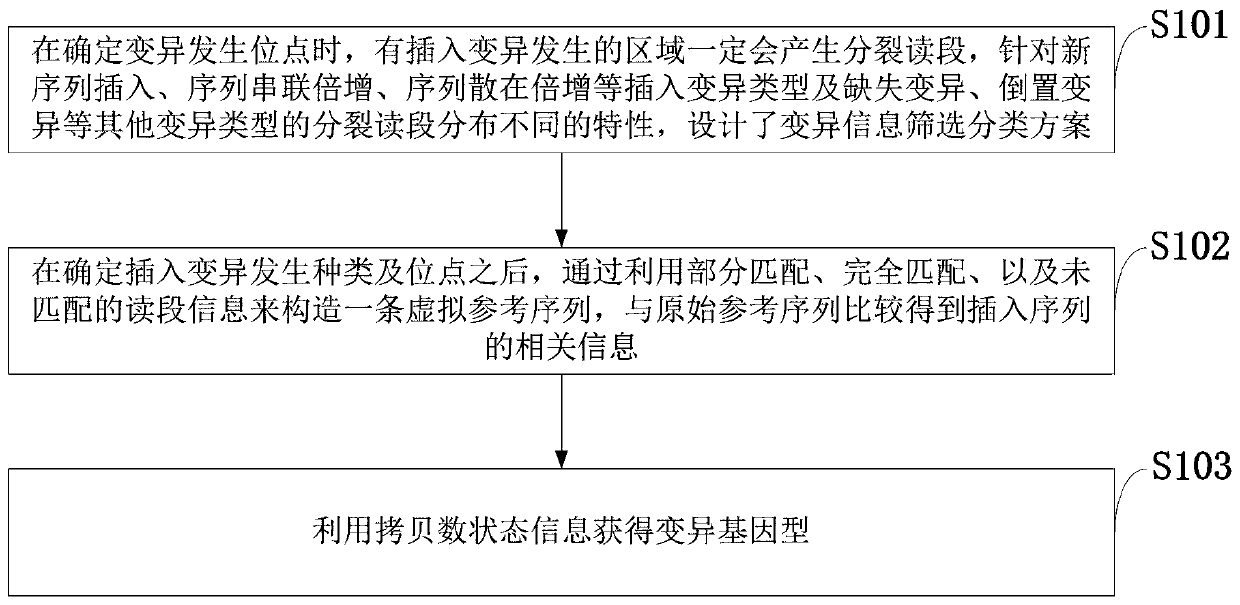
Insertion mutation detection method and system based on new-generation sequencing data
ActiveCN110299185ASolve the problem of inaccurate judgmentSolve the problem of detection errorProteomicsGenomicsGenomic sequencingRelevant information
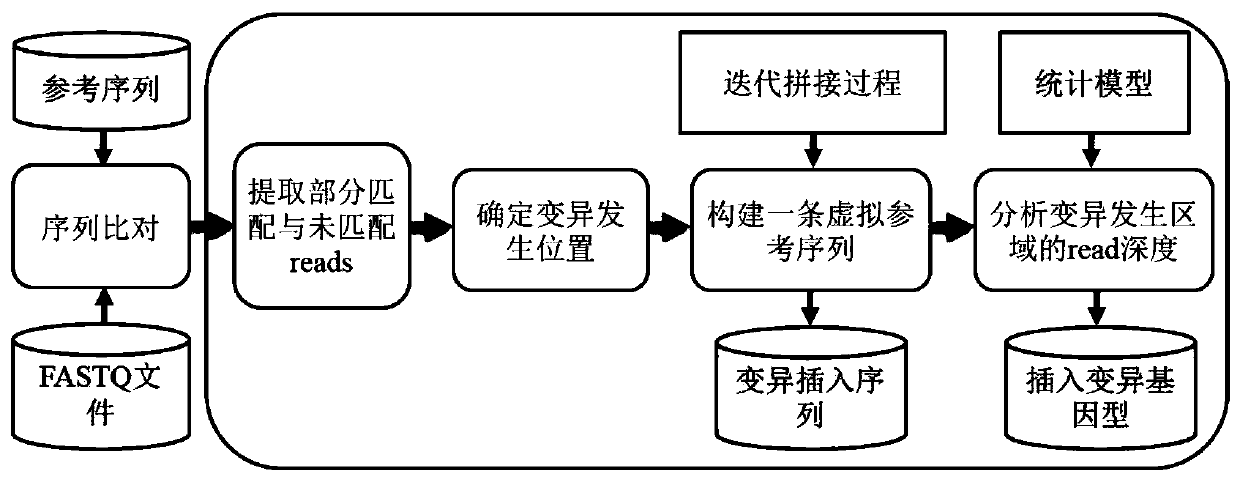
The invention belongs to the technical field of genome sequencing, and discloses an insertion mutation detection method based on new-generation sequencing data. The method comprises the steps: when amutation generation site is determined, a region where insertion mutation occurs certainly generates a split reading section, aiming at the characteristics that insertion variation types such as new sequence insertion, sequence series multiplication and sequence dispersion multiplication are different in distribution of missing variation and inverted mutation split reading sections, constructing avirtual reference sequence by utilizing partial matching, complete matching and unmatched read segment information after determining the insertion mutation generation type and site, and comparing thevirtual reference sequence with the original reference sequence to obtain related information of the insertion sequence; and obtaining a mutant genotype by utilizing the copy number state information. According to the invention, the problem of inaccurate insertion mutation point judgment can be solved; the problem of omission caused by insertion mutation detection of an SR method can be solved; the problem that in the prior art, repeated sequences may cause detection errors can be solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Polypeptide, lipoprotein-like nano particle and application thereof
ActiveCN106831997AAchieve multi-functionalityStable formationApolipeptidesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCancer cellAlpha helix
The invention discloses a polypeptide, a lipoprotein-like nano particle (LNP) and application thereof. The LNP contains at least one phospholipid and at least one polypeptide. A polypeptide series helix-ring-helix structure polypeptide contains at least two amphiphilic alpha helixes, and the two amphiphilic alpha helixes are connected through at least one connecting peptide containing a cyclic structure. The helix part of the polypeptide is imbedded into a lipoprotein-like nano particle surface layer, stable formation of lipid nano particles with uniform size and relatively small particle diameters can be promoted, meanwhile cyclic sequences stretch out of the surfaces of the lipoprotein-like nano particles, and functional sequence insertion is further facilitated, so that multi-functionalization of the LNP is realized. Moreover, the application of the LNP can be further expanded by using an LNP packaged lyophobically functional substance, and for example, the LNP can be used as a drug delivery system; the drug delivery system has the characteristics of being low in toxicity and high in stability, facilitating functionalization and the like, and a simple, convenient and effective means is provided for target killing of cancer cells and cell and tissue imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for detecting characteristics of gene region based on inter-alu polymerase chain reaction
The invention relates to a method for centralized expanding and detecting the gene region of a genome DNA, which aims to verify the characteristics of the gene area in the genome. The characteristics comprise single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), point mutuation, sequence insertion / deletion and the levels of dideoxy nucleotide (DNA) methylated CpG sites. With an Alu family, particularly an AluY subfamily common sequence as the main oligonucleotide primer, the method expands the DNA and copies all gene regions which are mostly concentrated in the genome with the oligonucleotide primer inter-alu PCR expanded genome DNA. The method is characterized in that the inter-Alu PCR can filter some non-gene sequences, so that a novel generation of sequencing technology detects the SNP, the point mutuation, the sequence insertion / deletion and the levels of DNA methylated CpG sites of the gene region in a centralized way, so as to save the consumption of the genome DNA required by the sequencing.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HKUST FOK YING TUNG RES INST
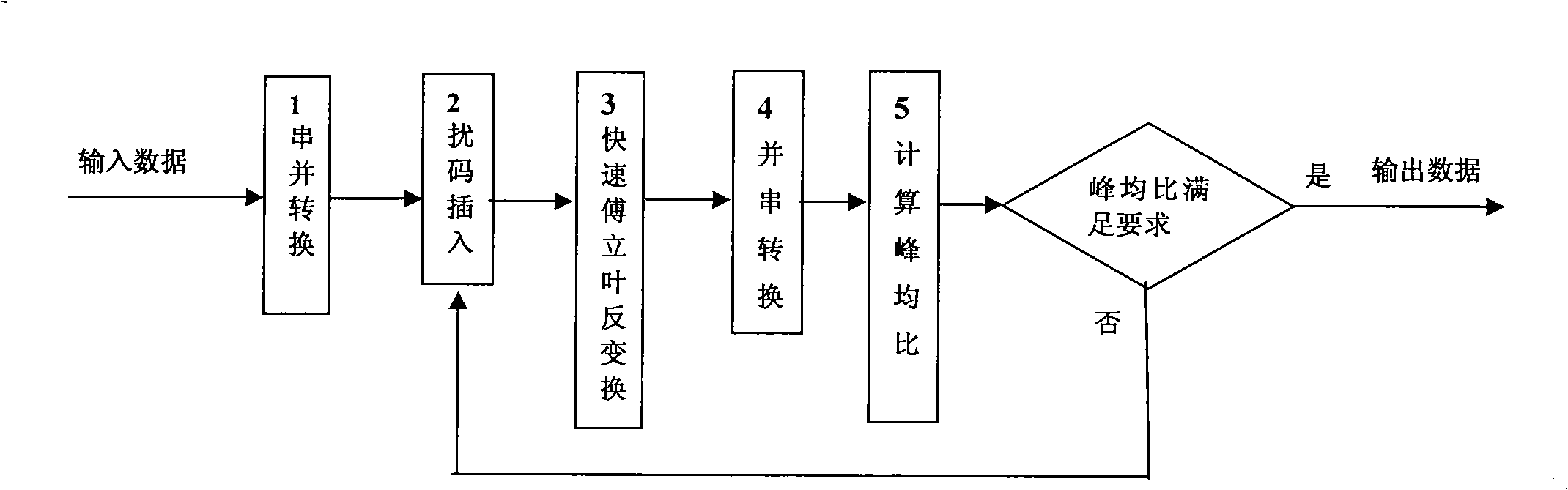
Method for reducing PAR of OFDM system
InactiveCN101304398AReduce the peak-to-average ratio of the signalImprove bit error performanceMulti-frequency code systemsRound complexityComputer architecture
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
OFDM transmitter and method for inserting pilot frequency into OFDM signal
InactiveCN1466292AEasy to getCode division multiplexOrthogonal multiplexFrequency spectrumSequence Insertions
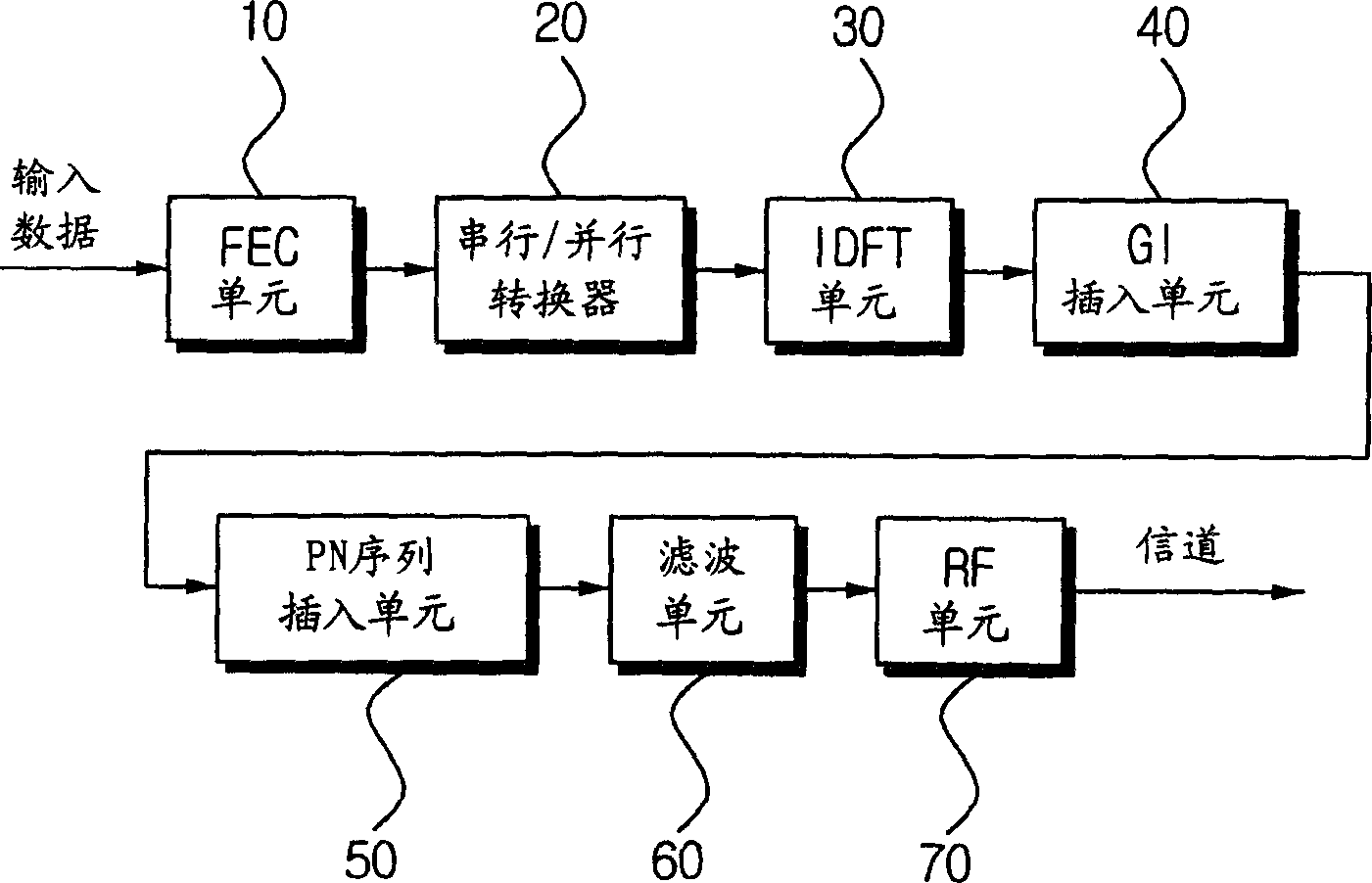
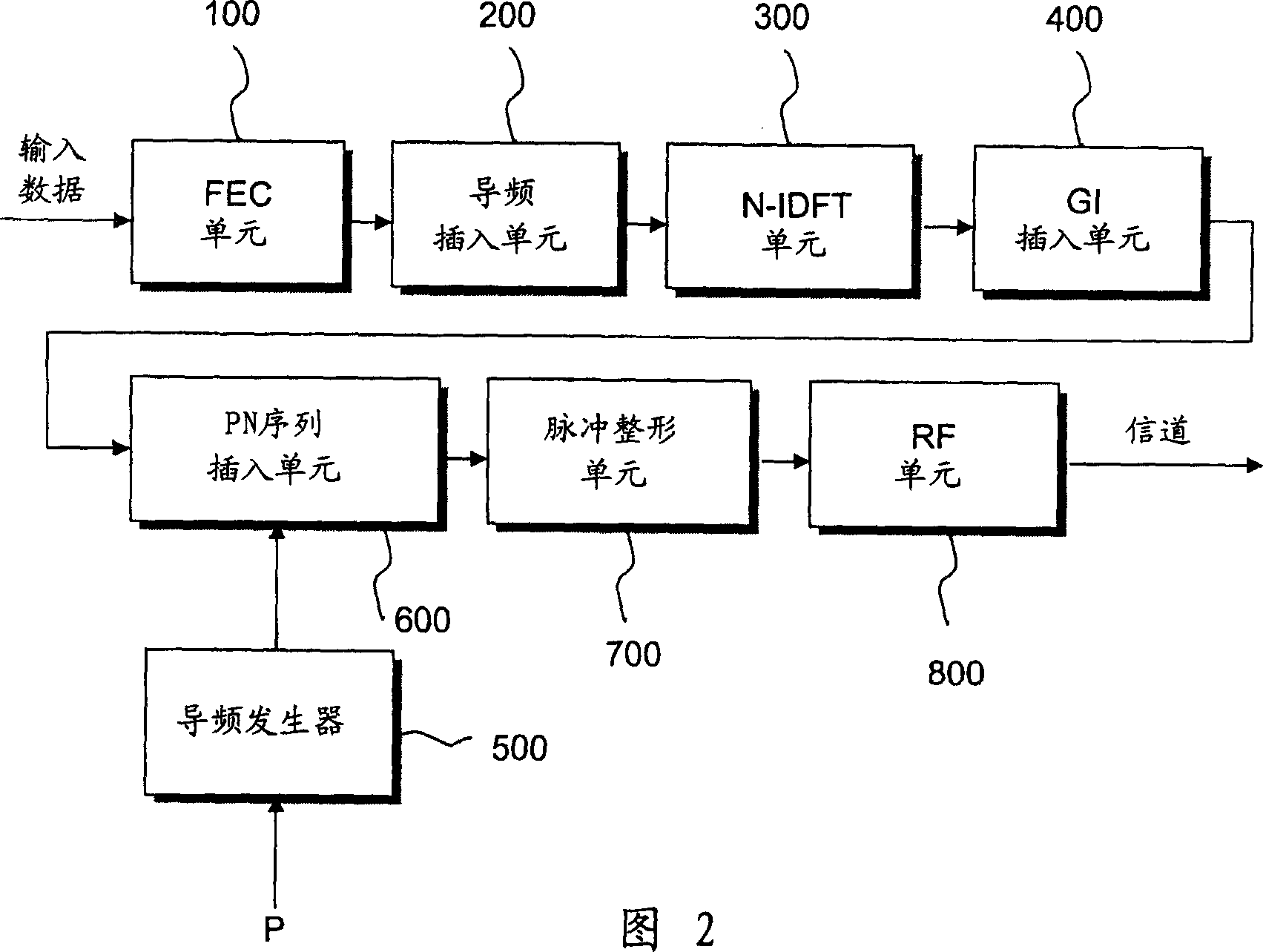
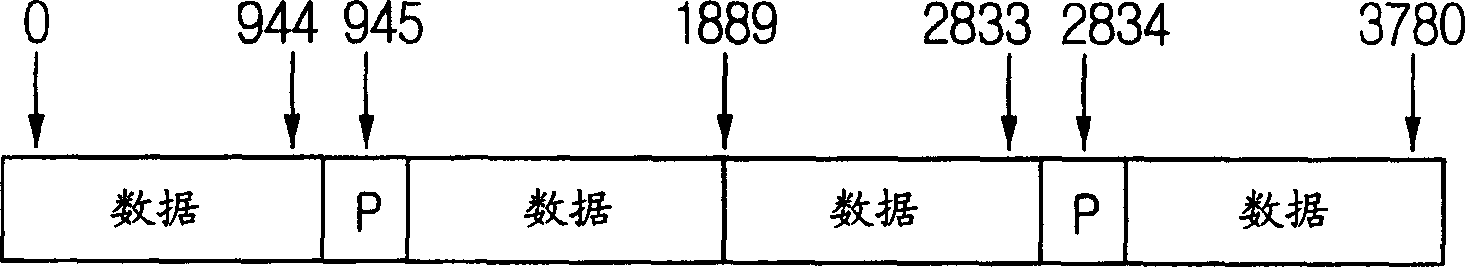
An OFDM transmitter comprises a FEC unit used for encoding the input data to correct the errors occuring at the receiving machine during the data transmission; a pilot insertion unit used for inserting at least two pilot data to the effective data; an IDFT unit used for modulating the encoded data which have pilot data and are defined as OFDM code elements; a guard interval (GI) insertion unit used for insertion of GI for barrage jamming between OFDM code elements;a pseudo noise (PN) sequence insertion unit used for inserting PN sequences and pilot signals into the OFDM code elements, wherein the pilot signals correspond to the pilot data inserted into the OFDM code elements; a pulse shaping filtering unit used for filtering the OFDM code elements; and a RF unit used for upconversing the OFDM signals into RF signals and transmitting them to channels. Herein, at least two pilot signal of continuance phase are inserted into the OFDM code element frequency spectrum and the entire PN sequence, then the receiving side can easily realize the synchronization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
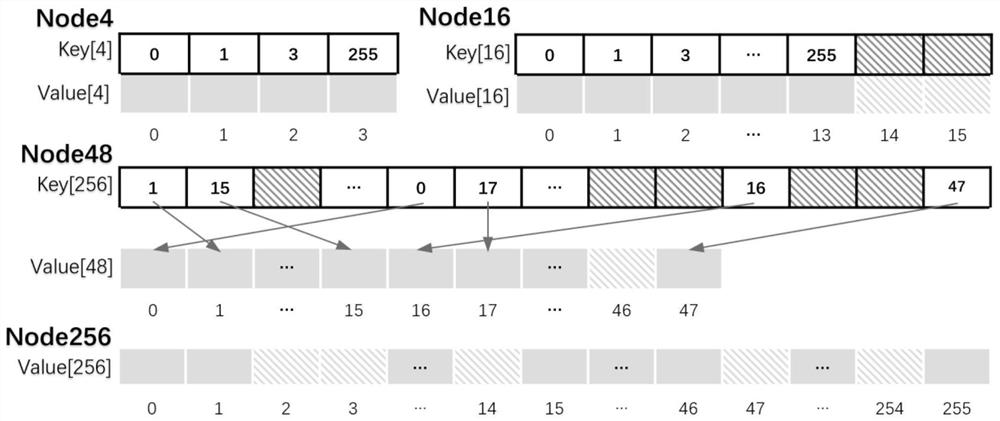
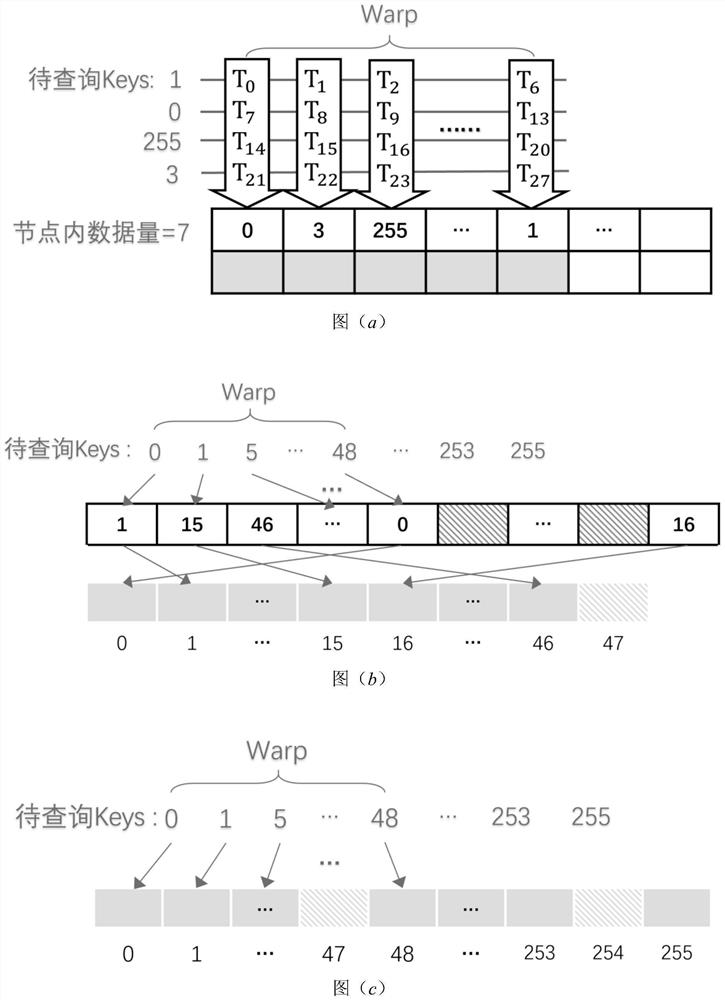
Adaptive cardinal number tree dynamic indexing method based on GPU parallelism
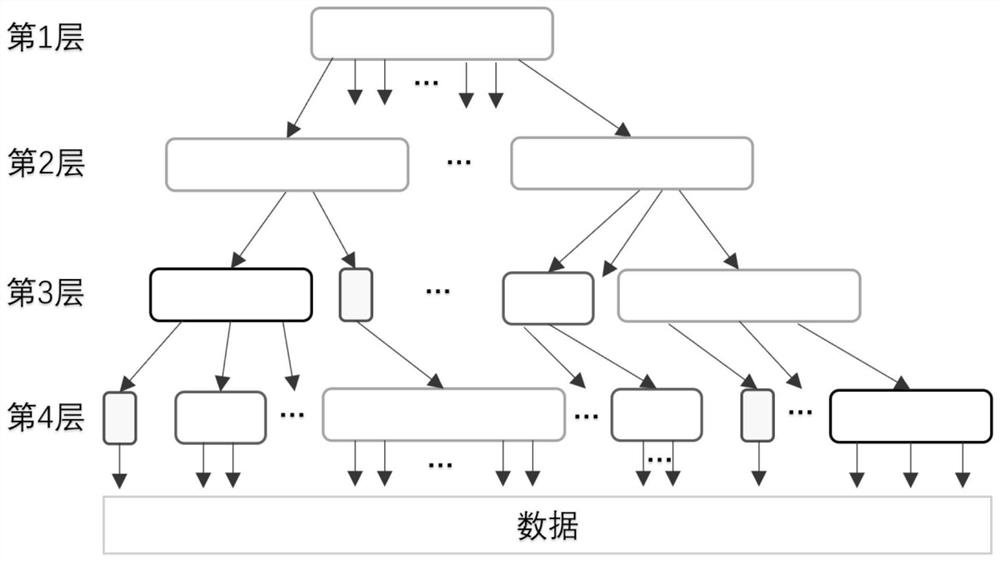
ActiveCN112000847AOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceConcurrent computation
The invention provides an adaptive cardinal number tree dynamic indexing method based on GPU parallelism. Firstly, an adaptive cardinal number tree data structure is constructed; the first two layerscreate tree nodes of the Node256 type; a cardinal number sequencing method based on high-order priority is created for the third layer and the fourth layer; tree nodes capable of accommodating corresponding sizes are created according to the number of the branches; the creation of a dynamic data structure is realized; it can be ensured that the latest update in the original batch of data is stillbehind the old update after sorting; and de-duplication is performed, redundant old updates are removed, latest updates are reserved, each section of sequence without duplicate data is inserted into anode corresponding to the section after duplicate removal to finish the establishment of the whole self-adaptive cardinal number tree, and secondly, data insertion, query and deletion operations canbe performed in parallel based on GPU parallel computing capability.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
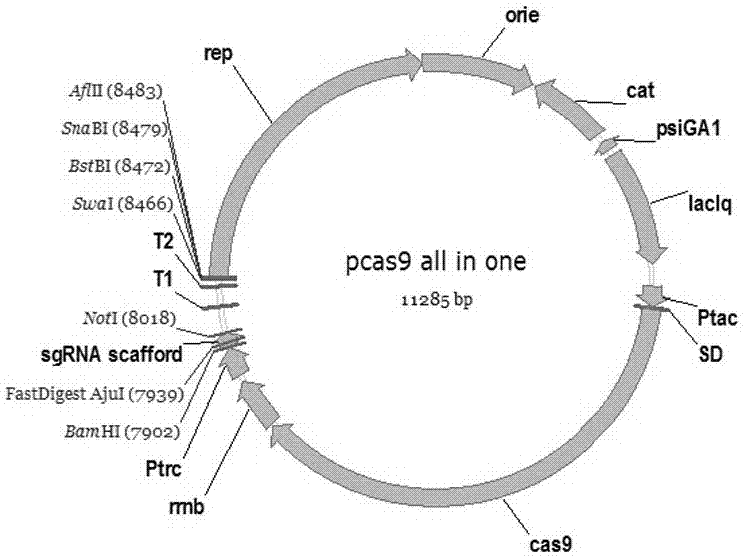
Gene editing vector for corynebacterium glutamicum, preparation method, system and application thereof
InactiveCN107384951AShort cycleCost efficientHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionResistant genesSequence Insertions
The invention provides a gene editing vector for corynebacterium glutamicum. The gene editing vector has higher gene editing efficiency. The gene editing vector comprises a Cas9 expression element, an sgRNA expression element, a replicon element and a homologous repairing sequence insertion site, wherein the Cas9 expression element comprises a resistance gene, an operon, a promoter, a SD sequence, a cas9 sequence and a terminator; the cas9 sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.5; the SD sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.6; the sgRNA expression element comprises a promoter, an sgRNA scaffold sequence and a terminator; the sgRNA scaffold sequence comprises trancrRNA and crRNA insertion sites; the sgRNA scaffold sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.7; AND the replicon element comprises a corynebacterium glutamicum replicon repA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
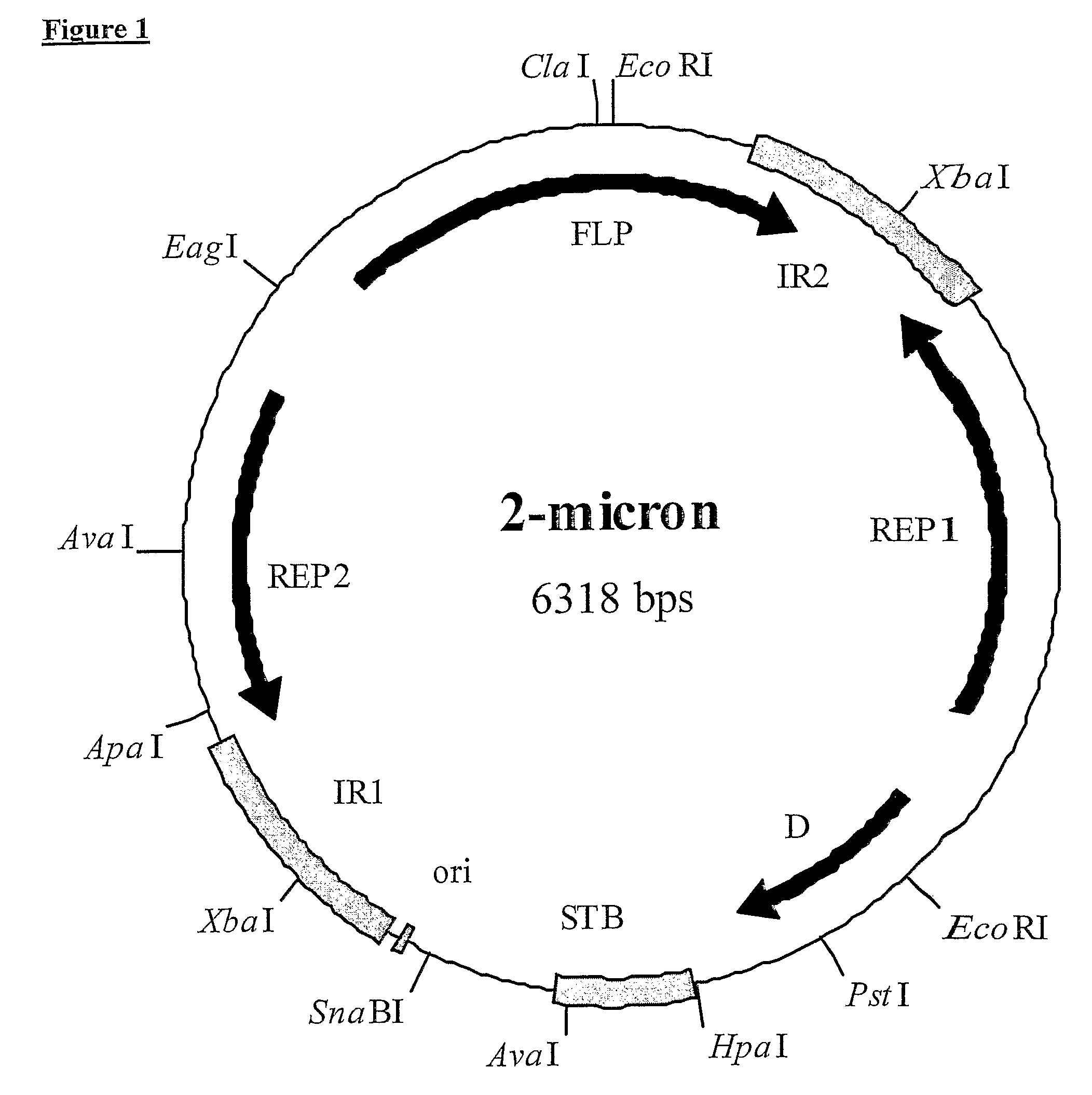
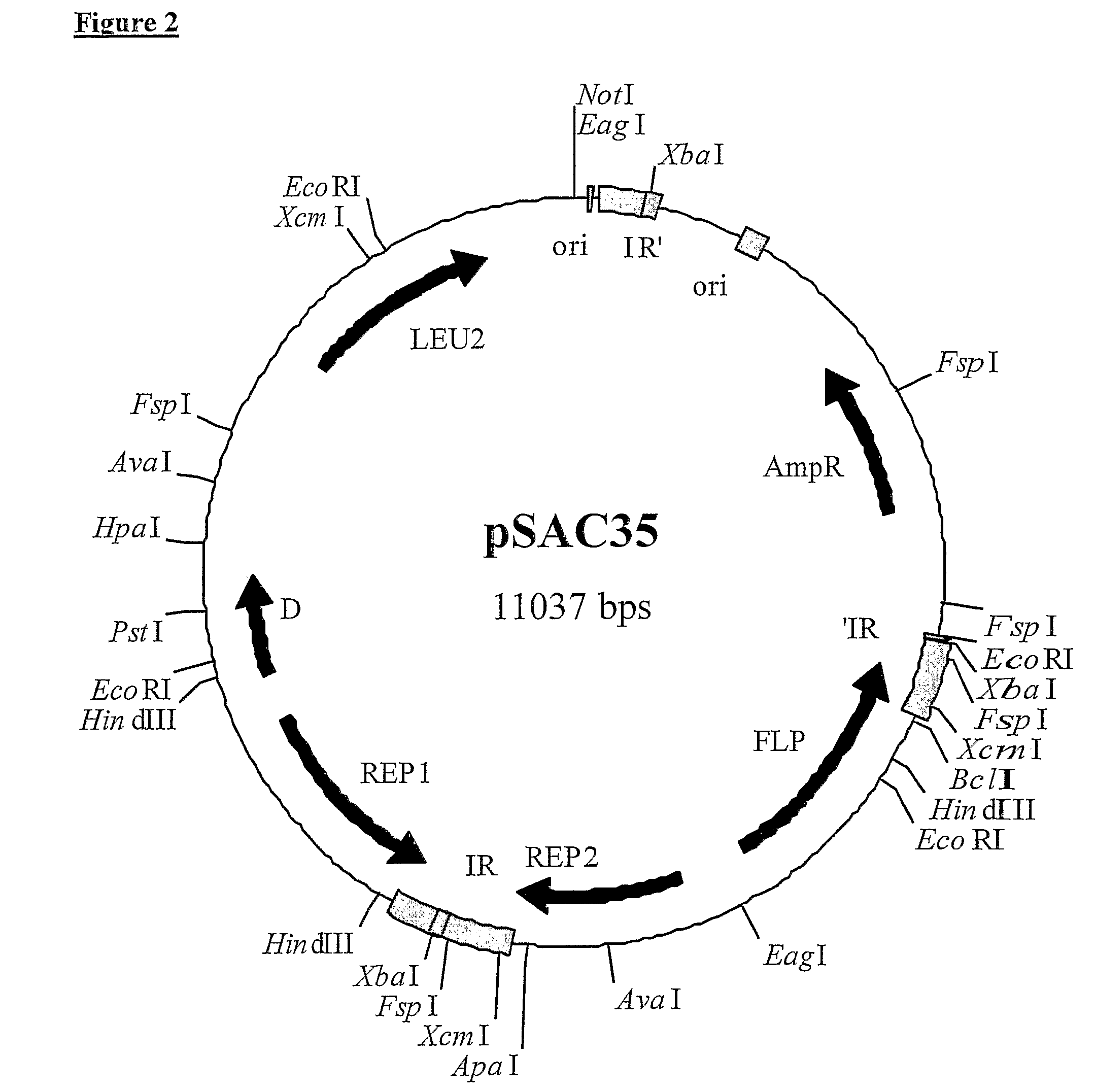
2-micron family plasmid and use thereof
InactiveUS8252551B2Loss of stability of plasmidIncrease productionMicroorganismsDermatological disorderSequence InsertionsPolynucleotide
The present invention provides a 2 μm-family plasmid comprising a polynucleotide sequence insertion, deletion and / or substitution between the first base after the last functional codon of at least one of either a REP2 gene or an FLP gene and the last base before the FRT site in an inverted repeat adjacent to said gene.
Owner:ALBUMEDIX LIMITED
Chimeric pestivirus with insertion in 3' nontranslated region (3' NTR) with stable replication and rnase resistance
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
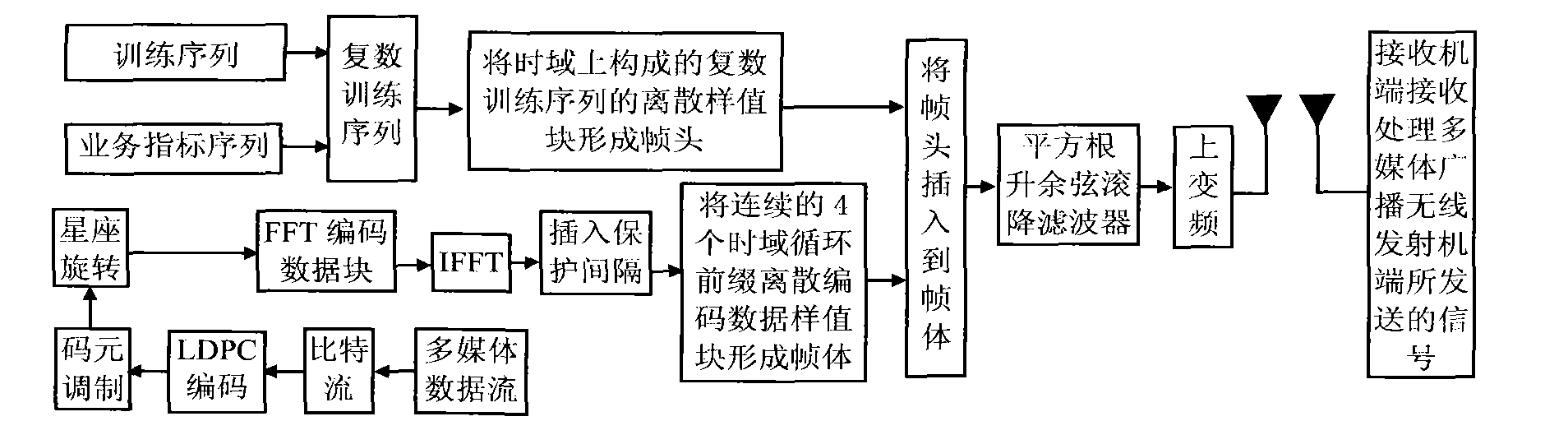
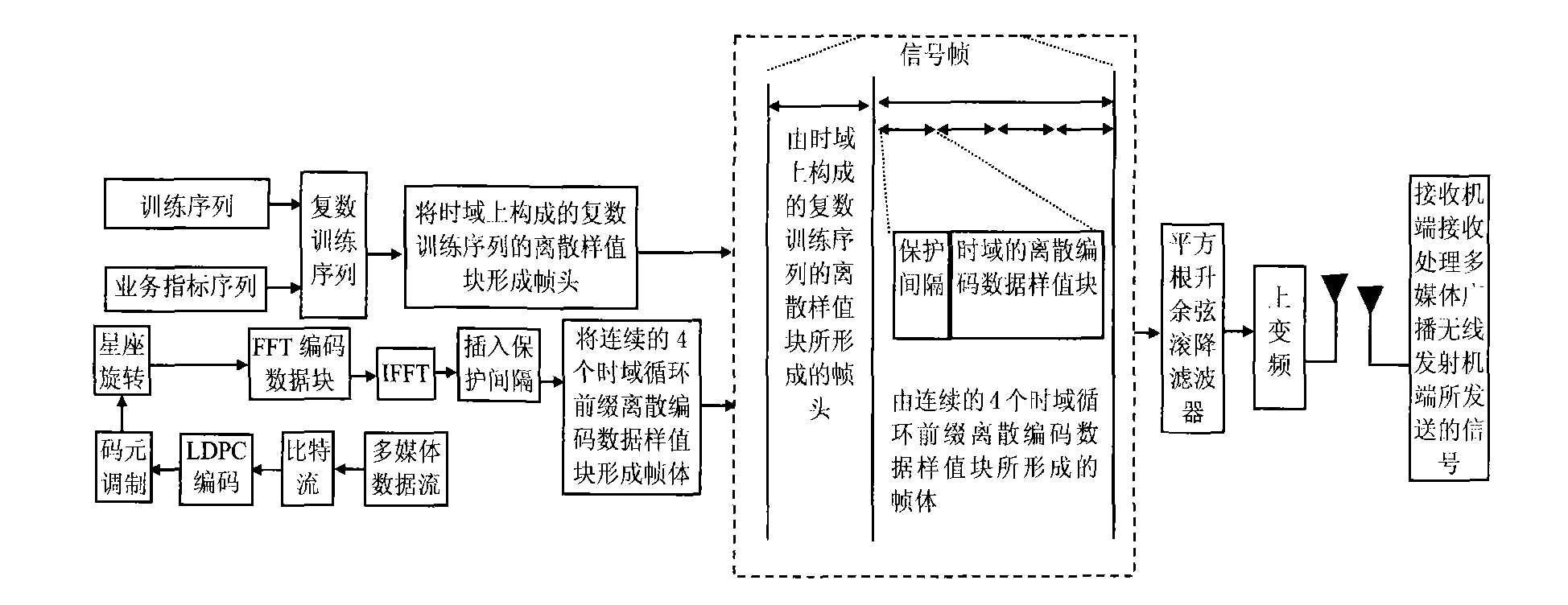
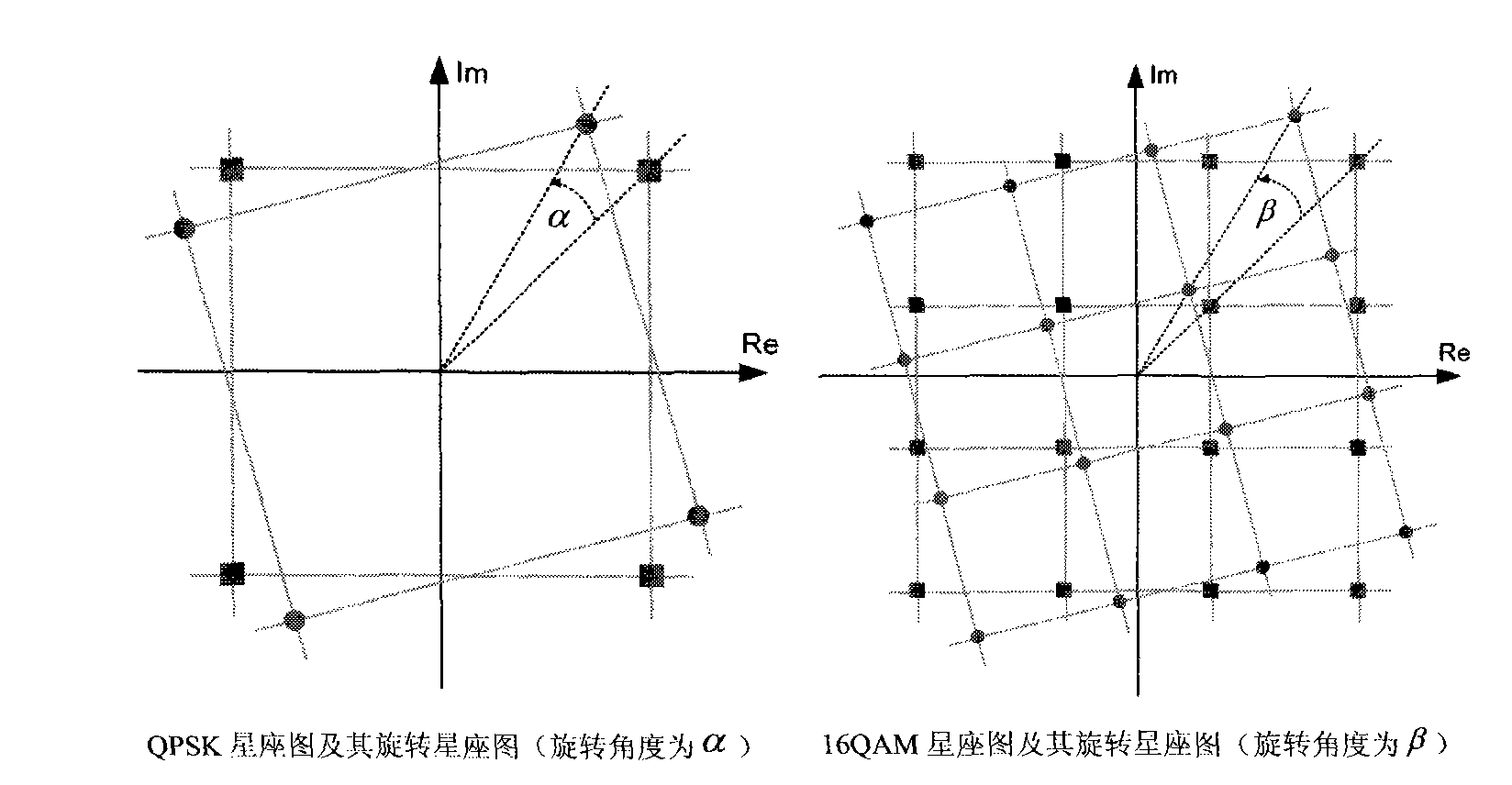
Multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-noise transmission method
InactiveCN101783893AHas pseudorandom propertiesReduce the impact of interferenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCarrier signalCoded element
The invention discloses a multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-noise transmission method; in the multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-noise transmission method, the multimedia broadcasting wireless signal is at the multimedia broadcasting wireless transmitter terminal, a multimedia data stream is processed by media data processing, bit stream LDPC coding, code element modulation, constellation rotating, frame body formation, time domain training sequence insertion framing, pulse formation and up-conversion to carrier wave to form a radio-frequency signal which is transmitted to an air wireless information channel, and the signal transmitted by the multimedia broadcasting wireless transmitter terminal is received and processed by a receiver terminal; the multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-noise transmission method has the advantages of short receiving synchronization time, high transmission efficiency and controllable multi-service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
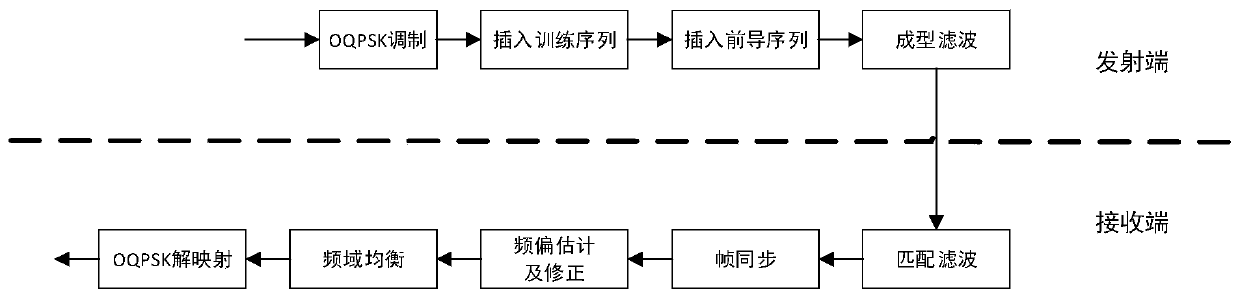
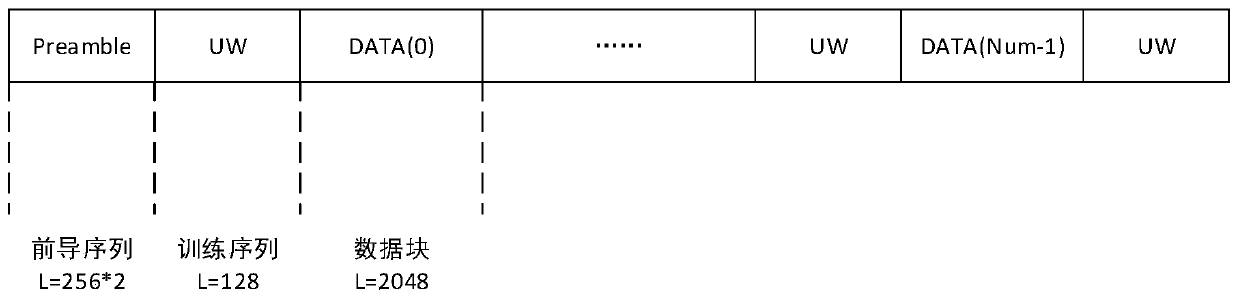
An OQPSK frequency domain equalization wireless data transmission system and method
ActiveCN109861939AReduce design requirementsReduce design costModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultipath interferenceEqualization
The invention provides an OQPSK frequency domain equalization wireless data transmission system and method. The OQPSK frequency domain equalization wireless data transmission system comprises a transmitting end and a receiving end, and the transmitting end comprises an OQPSK modulation module, a training sequence insertion module, a leader sequence insertion module and a forming filtering module;The receiving end comprises a matching filtering module, a frame synchronization module, a frequency offset estimation and correction module, an equalization module and an OQPSK demapping module. An OQPSK module is arranged, and OQPSK is a constant envelope technology and has the advantages of being small in PAPR, high in frequency band utilization rate, high in power and the like, the design requirement of a transmitting end power amplifier is lowered, and meanwhile the design cost of the power amplifier is lowered. And an equalization module is arranged to remove intersymbol interference andprovide multipath interference resistance, and meanwhile, compared with direct expansion communication with the same anti-interference capability, the system has a higher information transmission rate, and can meet the high-speed + multipath interference resistance wireless communication requirement at the same time.
Owner:西安思丹德信息技术有限公司
9B/10B encoding and decoding methods
ActiveCN112838868AEliminate DC componentPromote recoveryIndividual digits conversionDecoding methodsSequence Insertions
Owner:NOREL SYST
Gene editing method based on Vcre-Vloxp recombinase system and application of gene editing method
ActiveCN111705079AReduce the efficiency of the seriesGood efficiency in seriesMicroinjection basedNucleic acid vectorSequence InsertionsDouble strand
The invention provides a gene editing method based on the Vcre-Vloxp recombinase system and application of the gene editing method. The gene editing method includes the following steps that (1) a Vloxp sequence is connected to the 5' tail end or 3' tail end of a double-stranded DNA, or the Vloxp sequence is inserted between the functional regions of the double-stranded DNA; and (2) the double-stranded DNA, a Vcre protein and a gene editing reaction solution are mixed, and then transferred into a target cell to complete the gene editing. When the double-stranded DNA is repeatedly connected during an integration process, the double-stranded DNA is cut under the action of the Vcre protein, finally only one double-stranded DNA is left, no matter how many double-stranded DNAs are in tandem connection, the Vcre protein can cut all repetitive fragments from the first Vloxp sequence to the last Vloxp sequence, and therefore, the gene editing method can significantly reduce the tandem duplication phenomenon of recombinant DNA fragments in the integration process.
Owner:上海药康生物科技有限公司
High-throughput identification method for genome insulator
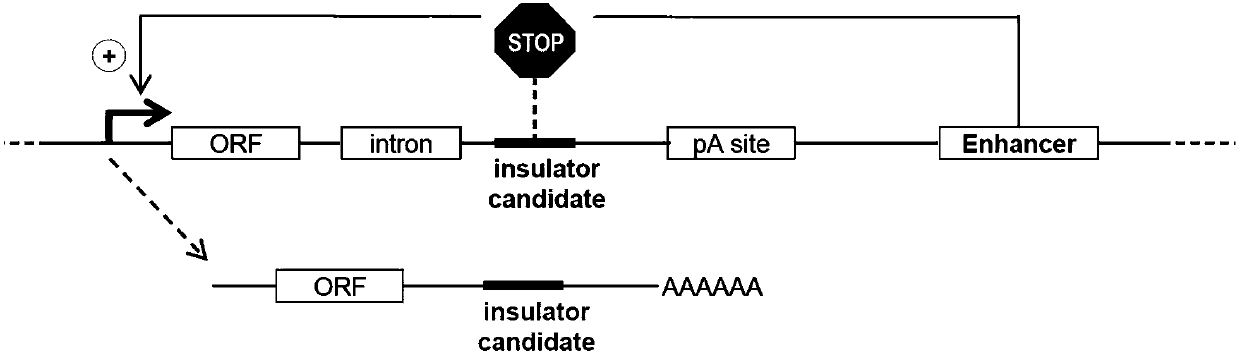
The invention discloses a high-throughput identification method for a genome insulator. The high-throughput identification method for the genome insulator includes the steps of (1) building a reportervector, specifically, the reporter vector sequentially comprises a promoter, an ORF region, an intron, an insulator candidate sequence insertion region and an enhancer, the enhancer is used for enhancing expression of an upstream sequence, and an insulator candidate sequence is inserted in the insulator candidate sequence insertion region; (2) expressing and transcribing the reporter vector; and(3) detecting the transcribing condition of the edited transcribing sequence, and determining whether the insulator candidate sequence is the insulator or not. A reporter vector library built by the method can cover 90-99% of genome noncoding regions, protein position information is not needed, and overall analysis is achieved; the built library is transferred into a cell, whether nearly the wholegenomic sequence has insulator activity or not can be detected at the same time, large-scale parallel analysis can be carried out, and single and small-quantity analysis is avoided; and since the built library covers nearly all sites, zones of ignorance can be also detected and analyzed.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Method for amplifying target region of nucleic acid, library building and sequencing methods and kit
PendingCN112824534AAvoid wastingLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence InsertionsGene
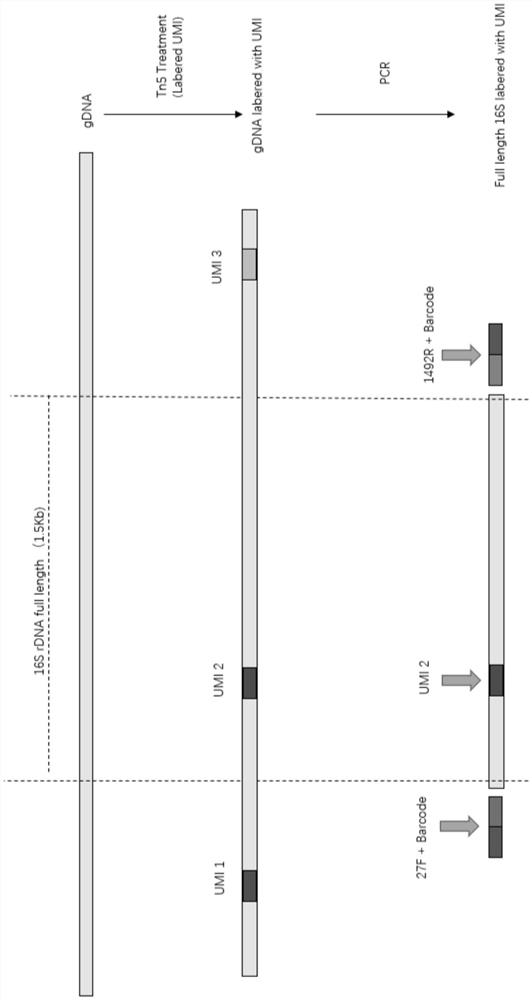
The invention relates to the field of gene sequencing, in particular to a method for amplifying a target area of nucleic acid and library building and sequencing methods. The provided method for amplifying the target region of the nucleic acid comprises the following steps of (1) inserting a UMI sequence into the nucleic acid by using transposase so as to obtain a fusion product which contains the UMI sequence and a target region sequence; and (2) amplifying the fusion product by using a primer so as to obtain an amplification product containing the target region sequence and the UMI sequence. The invention also provides the library building method for the target region of the nucleic acid and the sequencing method. According to the method provided by the invention, the time of library building and sequencing can be shortened; and the production cost can be reduced, and the data utilization rate is effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
9B/10B encoding and decoding method suitable for low-pass and band-pass channels
ActiveCN114598579AEliminate DC componentPromote recoveryPulse conversionSynchronous/start-stop systemsDecoding methodsSequence Insertions
Owner:NOREL SYST
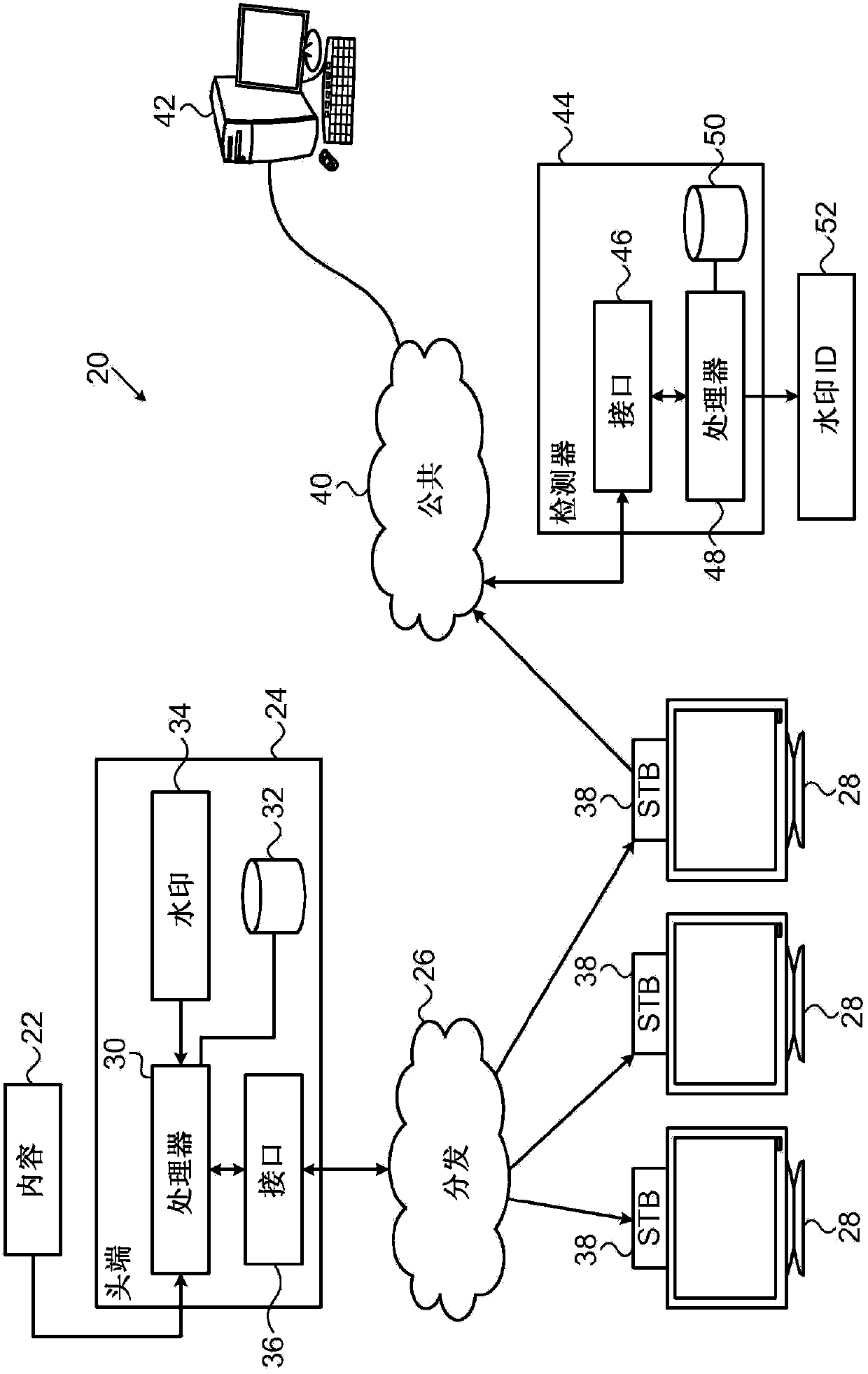
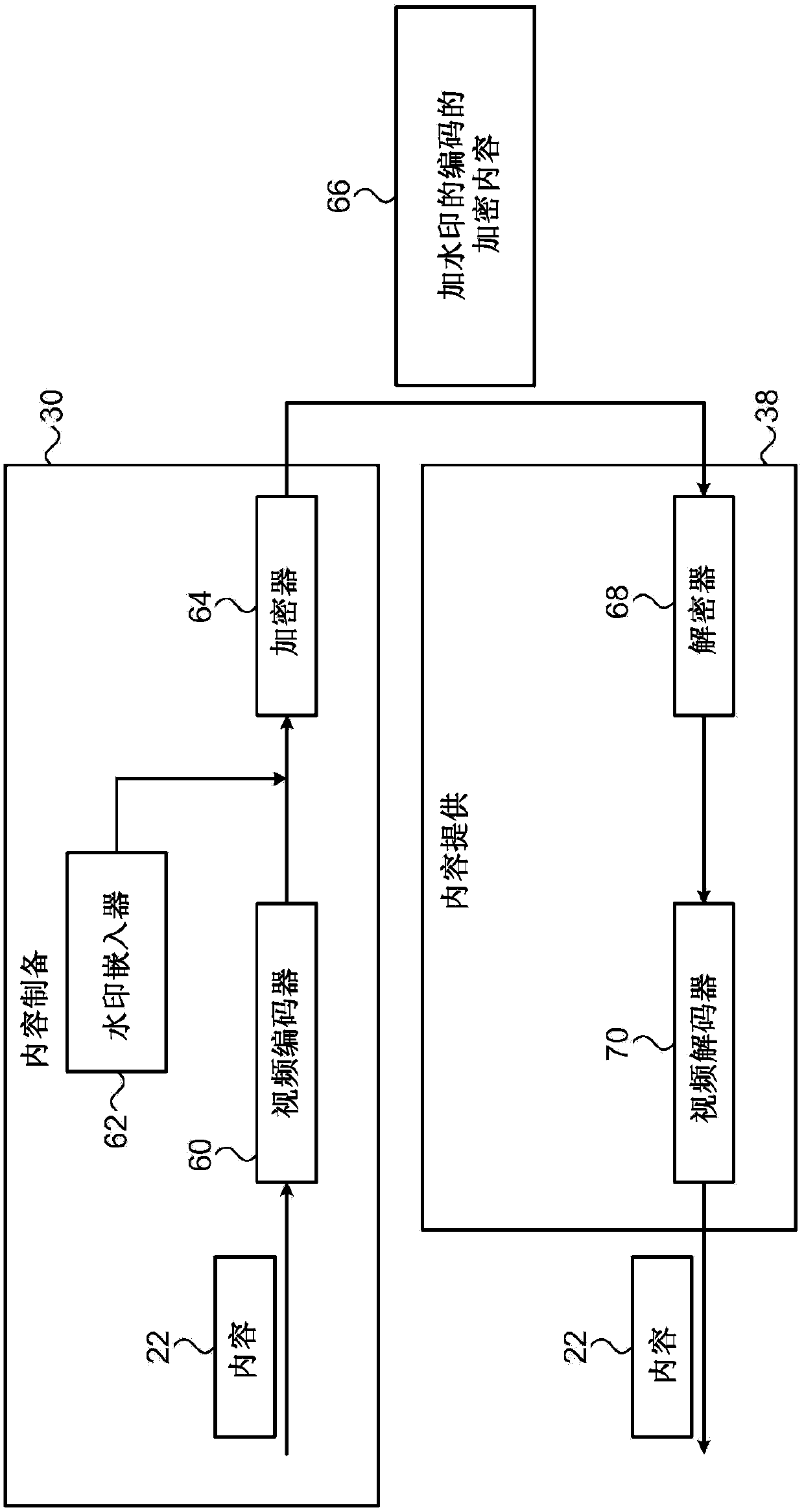
Encryption-resistant watermarking
ActiveCN104272748AImage data processing detailsSelective content distributionDigital dataSequence Insertions
A method and system for providing encryption resistant watermarking of data is described. The method and system comprises encoding a string of symbols, each having a respective symbol value, as a sequence of vectors where each vector includes a respective number of repetitions of a sub-vector of a predefined length, such that the respective number of the repetitions in each vector in the sequence is indicative of the respective symbol value of a corresponding symbol in the string. This sequence of vectors is then inserted into the item of content including digital data to apply a watermark to the item of content. This insertion process may involve interleaving the vectors with gaps of known lengths containing arbitrary data and may involve insertion prior to the vector sequence a marker comprising a concatenation of a number of copies of a marker vector. The length of the sub-vector may be chosen to be an integer divisor of a block size of a block cipher that is to be applied to the item of content after application of the watermark thereto.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
Method for determining the sequence, insertion position and marginal sequence of exogenous dna fragments in transgenic organisms
ActiveCN107630079BDetecting the hitchhiking effectAccurate detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSequence InsertionsExogenous DNA
The present invention discloses a method for determining the sequence, the insertion position and the boundary sequence of an exogenous DNA fragment in a transgenic organism. The method comprises: sequencing the whole genome of a transgenic organism, comparing a sequence A to the whole genome sequence of the transgenic organism, and determining the sequence, the insertion position and the boundarysequence of the exogenous DNA fragment in the transgenic organism, wherein an acceptor organism is treated by a vector containing the exogenous DNA fragment to obtain the transgenic organism, and thesequence A is the following a1), a2) or a3): a1) the full-length sequence of the vector, a2) the sequence of any one DNA fragment derived from the vector and containing the exogenous DNA fragment, and a3) the sequence of the exogenous DNA fragment or any one fragment thereof. According to the present invention, the method can break through the limitation in species, is not limited by the target gene for constructing the transgenic organism, and can rapidly and precisely detect the insertion position, the boundary sequence and even the copy number of the transgenic gene.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A variation detection method and device based on genome assembly
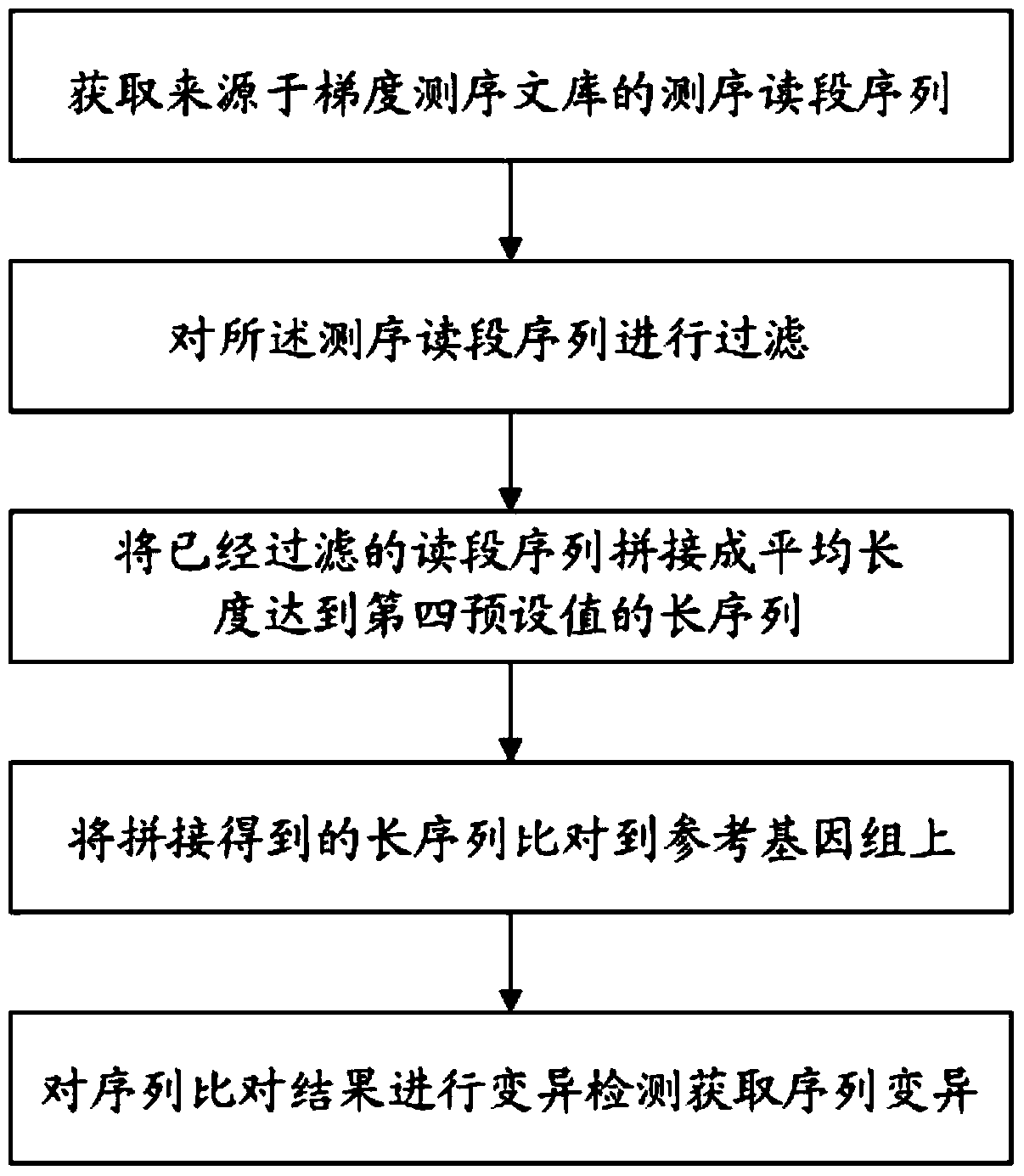
ActiveCN105989246BRealize detectionSpecial data processing applicationsSequence InsertionsSequence variation
The invention discloses a variation detection method and device assembled based on genomes. The method comprises following steps: obtaining sequencing and section-reading sequences from a gradient sequencing library; filtering the sequencing and section-reading sequences; splicing the filtered sequencing and section-reading sequence to long sequences with average length up to fourth pre-set value; comparing the spliced long sequences to a reference genome; and carrying out variation detection on sequence comparison results in order to obtain sequence variation. The variation detection method and device assembled based on genomes helps effectively solve the detection difficulty such as 'dark areas',long sequence insertion and complex designability for variation detection.
Owner:深圳市华大智造软件技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com