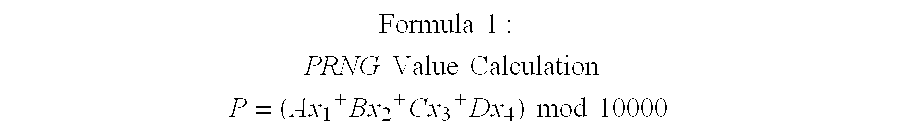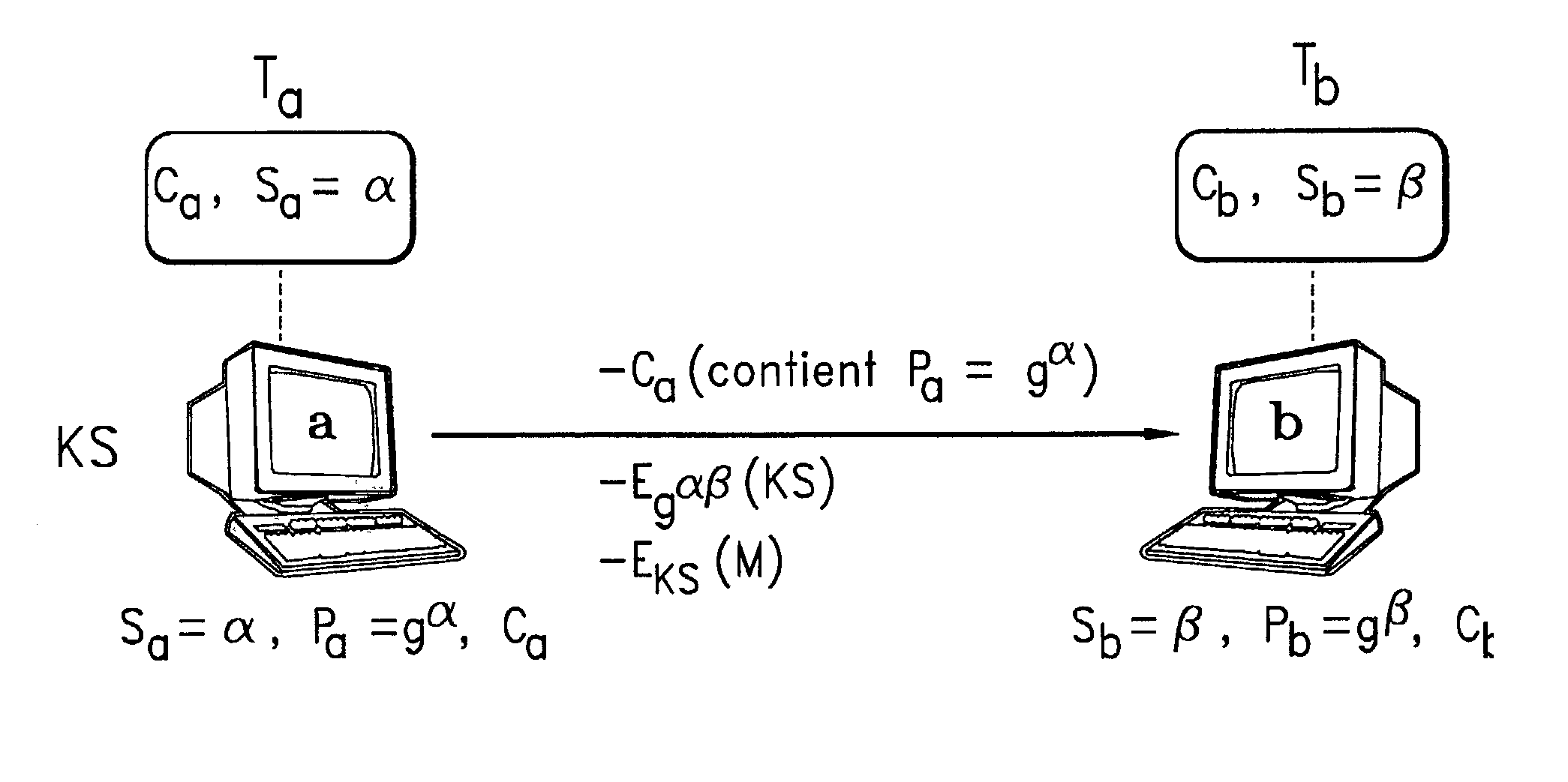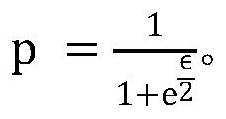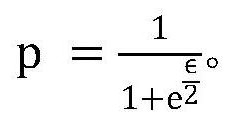Patents
Literature
88 results about "Pseudorandom generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
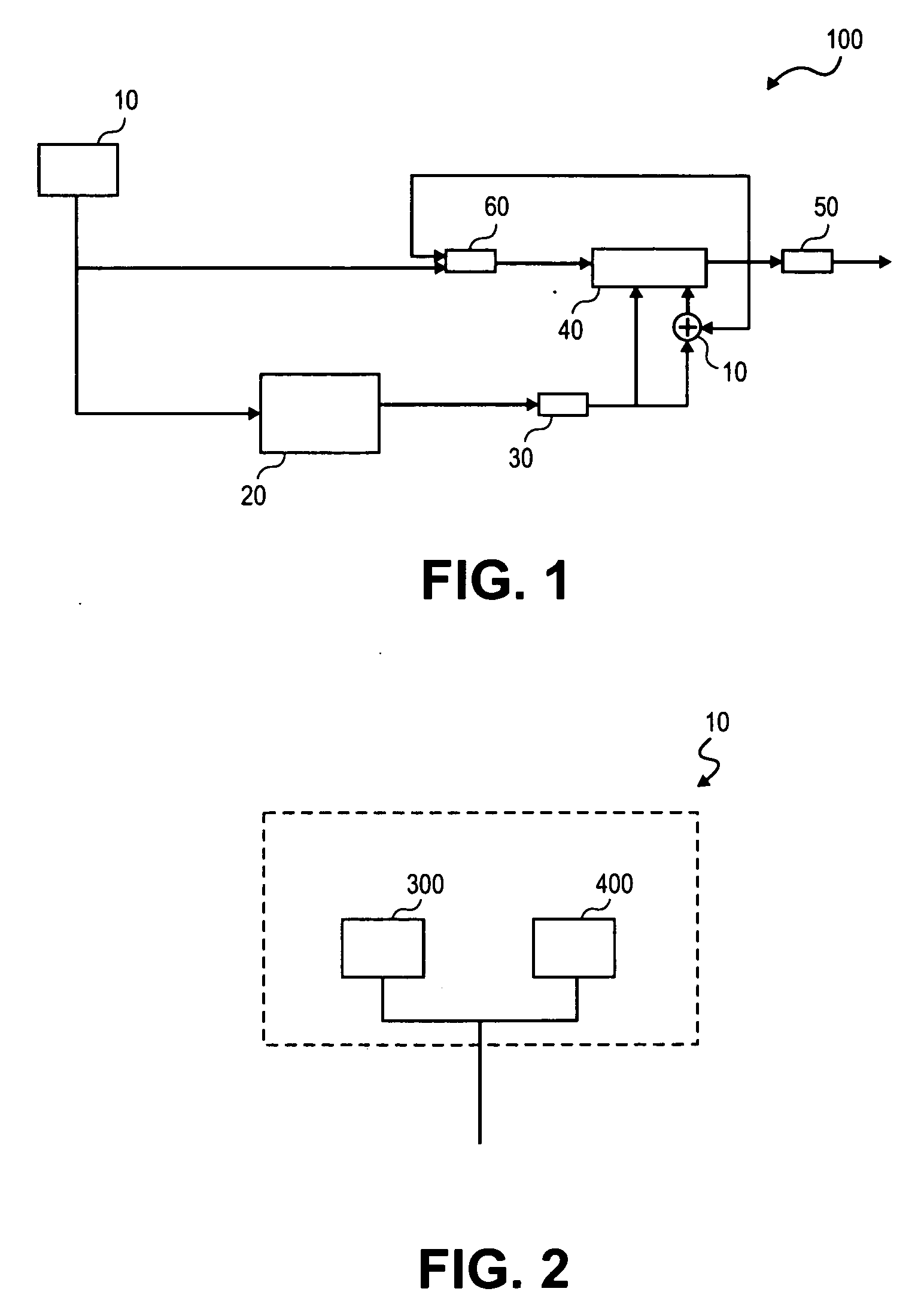
In theoretical computer science and cryptography, a pseudorandom generator (PRG) for a class of statistical tests is a deterministic procedure that maps a random seed to a longer pseudorandom string such that no statistical test in the class can distinguish between the output of the generator and the uniform distribution. The random seed is typically a short binary string drawn from the uniform distribution.
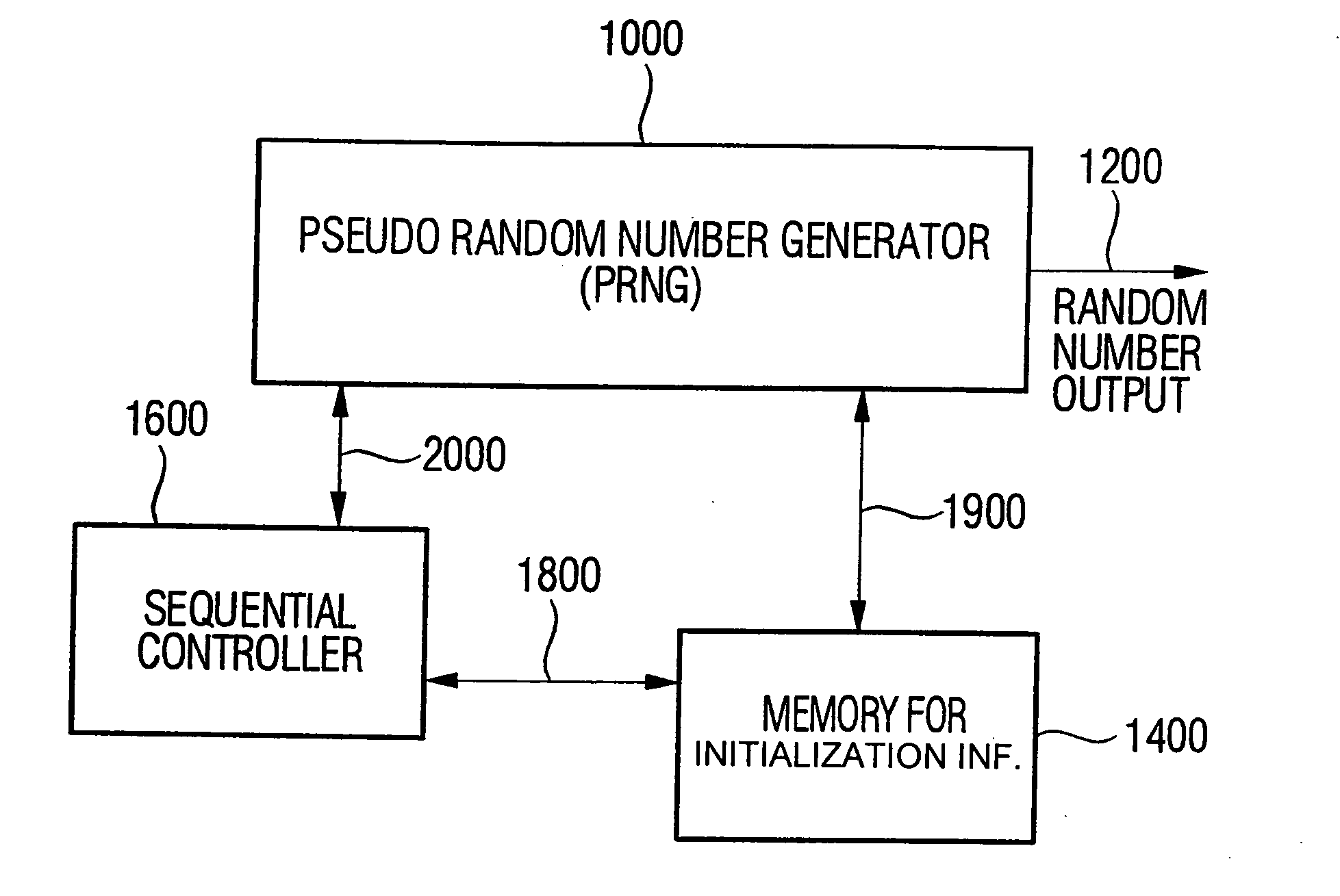
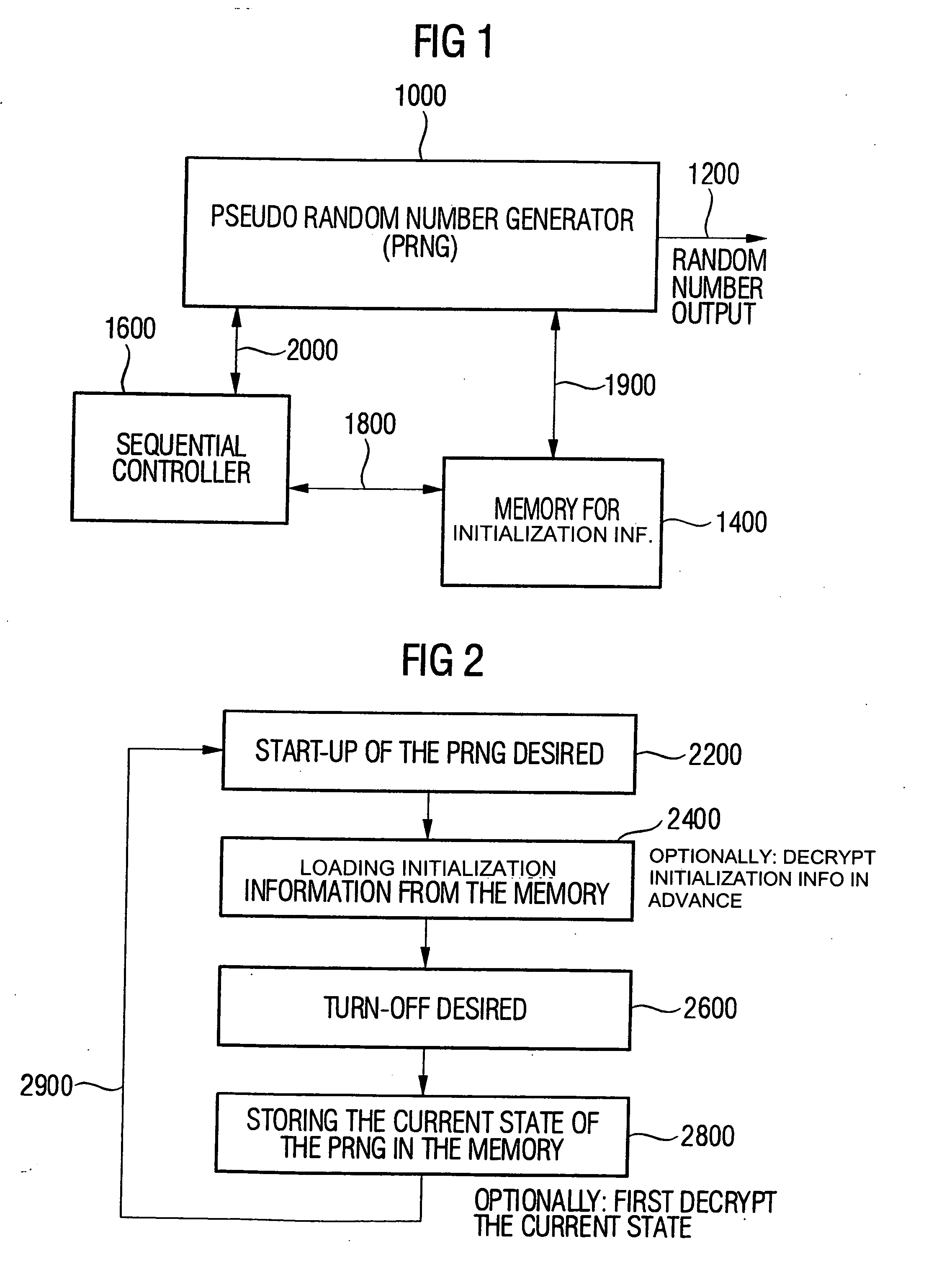
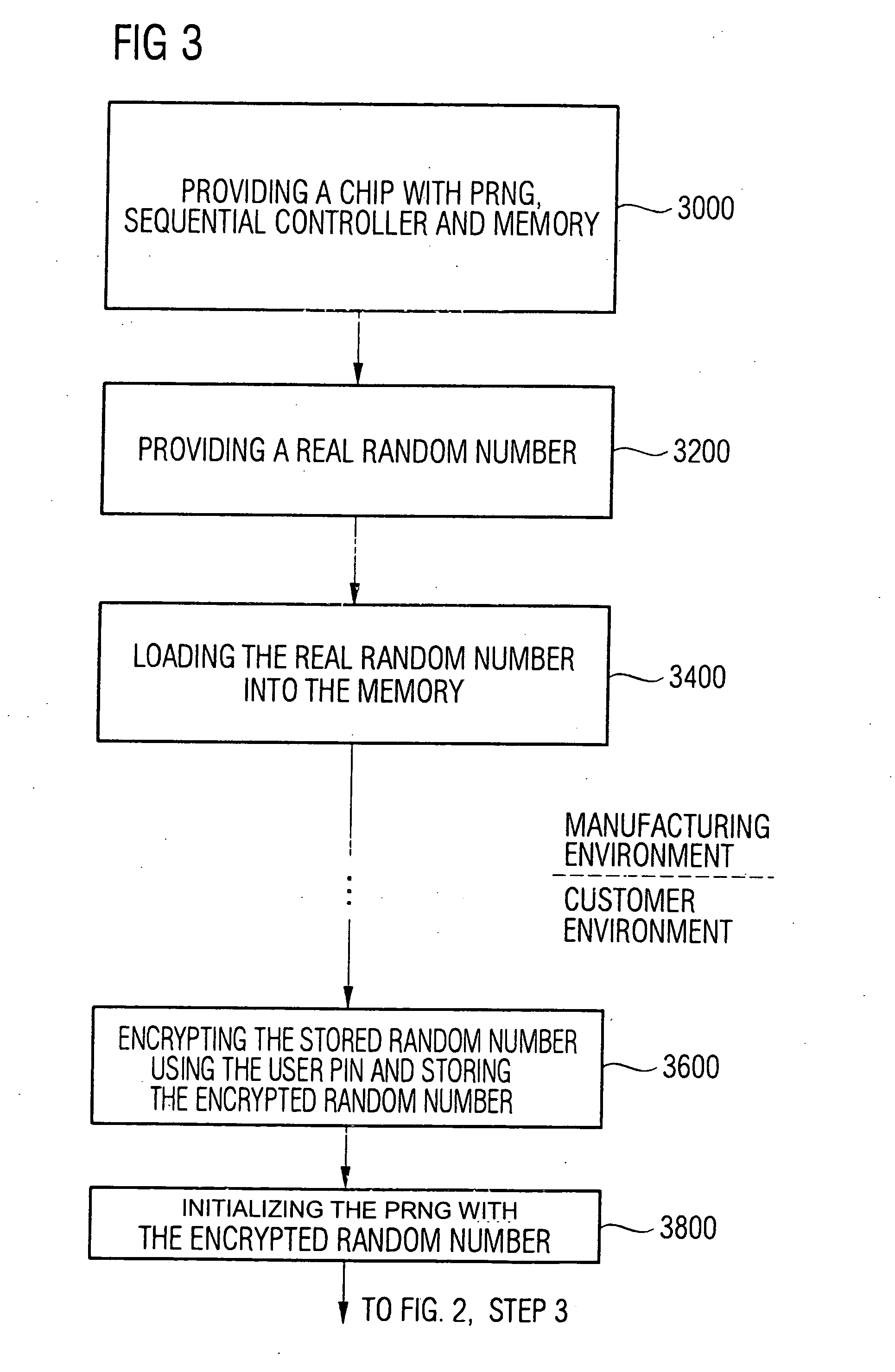
Device and method for generating random numbers using a pseudo random number generator
InactiveUS20050129247A1Simpler and more practicableQuality improvementKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsIntermediate stateNumber generator
Device for generating random numbers having a pseudo random number generator, a memory and a sequential controller. The pseudo random number generator generates a deterministic random number sequence after an initialization using an initialization value. The memory stores initialization information, wherein the initialization information is derived from a true random number or corresponds to the true random number. The sequential controller initializes the pseudo random number generator at start-up using the initialization information or the information derived from the initialization information, stores an intermediate state of the pseudo random number generator or information derived from the intermediate state in the memory at a turn-off of the pseudo random number generator, and uses the intermediate state or the information derived from the intermediate state for an initialization of the pseudo random number generator at a renewed start-up.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
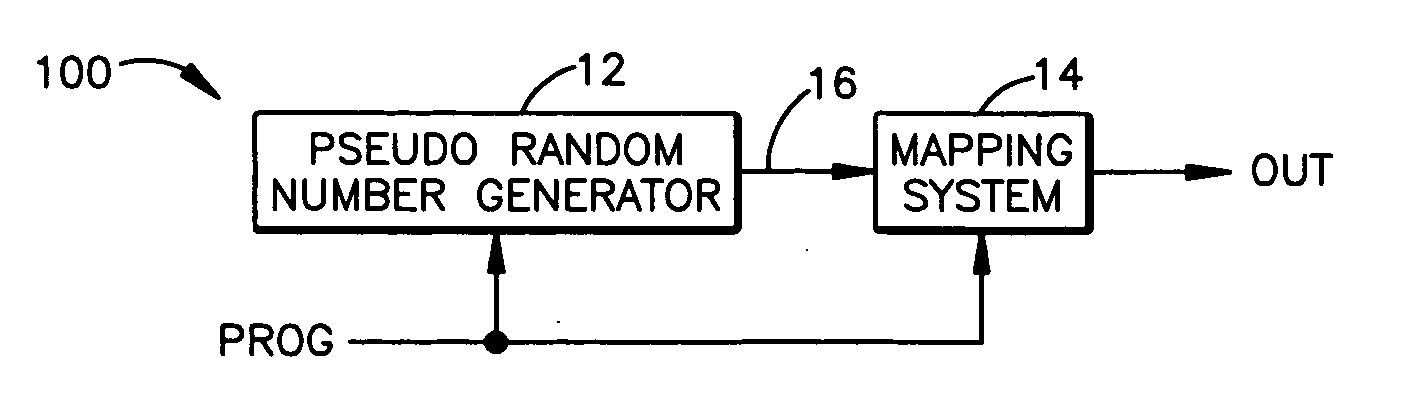
System and method for generating pseudorandom numbers
ActiveUS20050207574A1Random number generatorsSecuring communicationTheoretical computer scienceSystematic mapping
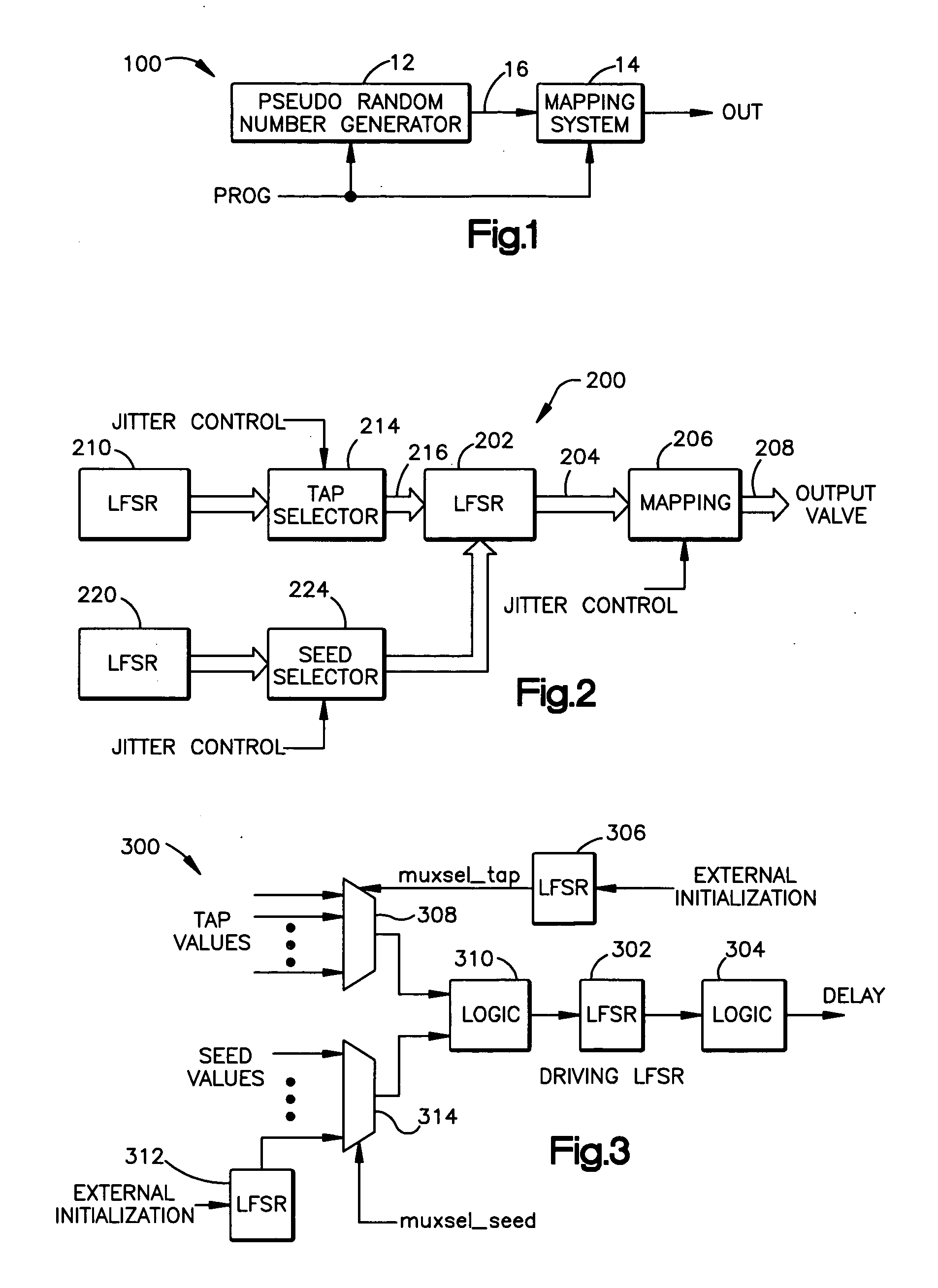
A system that has a pseudorandom number generator and a mapping system. The pseudorandom number generator generates a random number that is mapped by the mapping system to an output value that is selected from a set of predetermined output values. To increase the randomness of the sequence of numbers generated by the pseudorandom number generator, a tap and / or seed value of the pseudorandom number generator can be varied.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
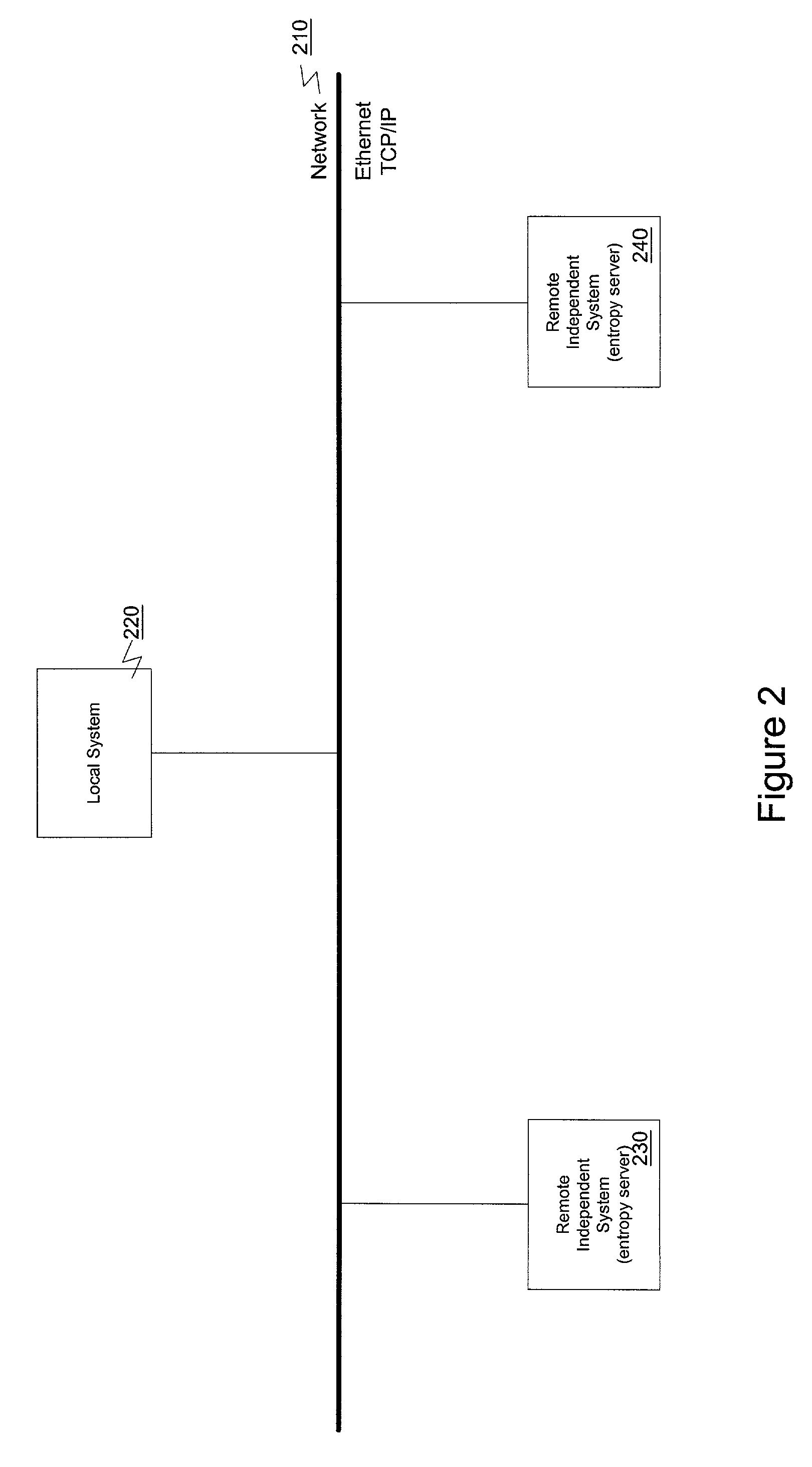
Enhancing entropy in pseudo-random number generators using remote sources
InactiveUS20060072747A1Random number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationNumber generatorComputer science
A system, apparatus, and method are provided for enhancing entropy in a pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) using remote sources. According to one embodiment of the present invention, first, the PRNG's internal state is initialized. Local seeding information is then obtained from a local host. For added security, additional seeding information is obtained from one or more remote entropy servers operating independently to each maintain a constantly updated state pool. Finally, the PRNG is stirred based upon the local seeding information, and the additional seeding information.
Owner:INTEL CORP
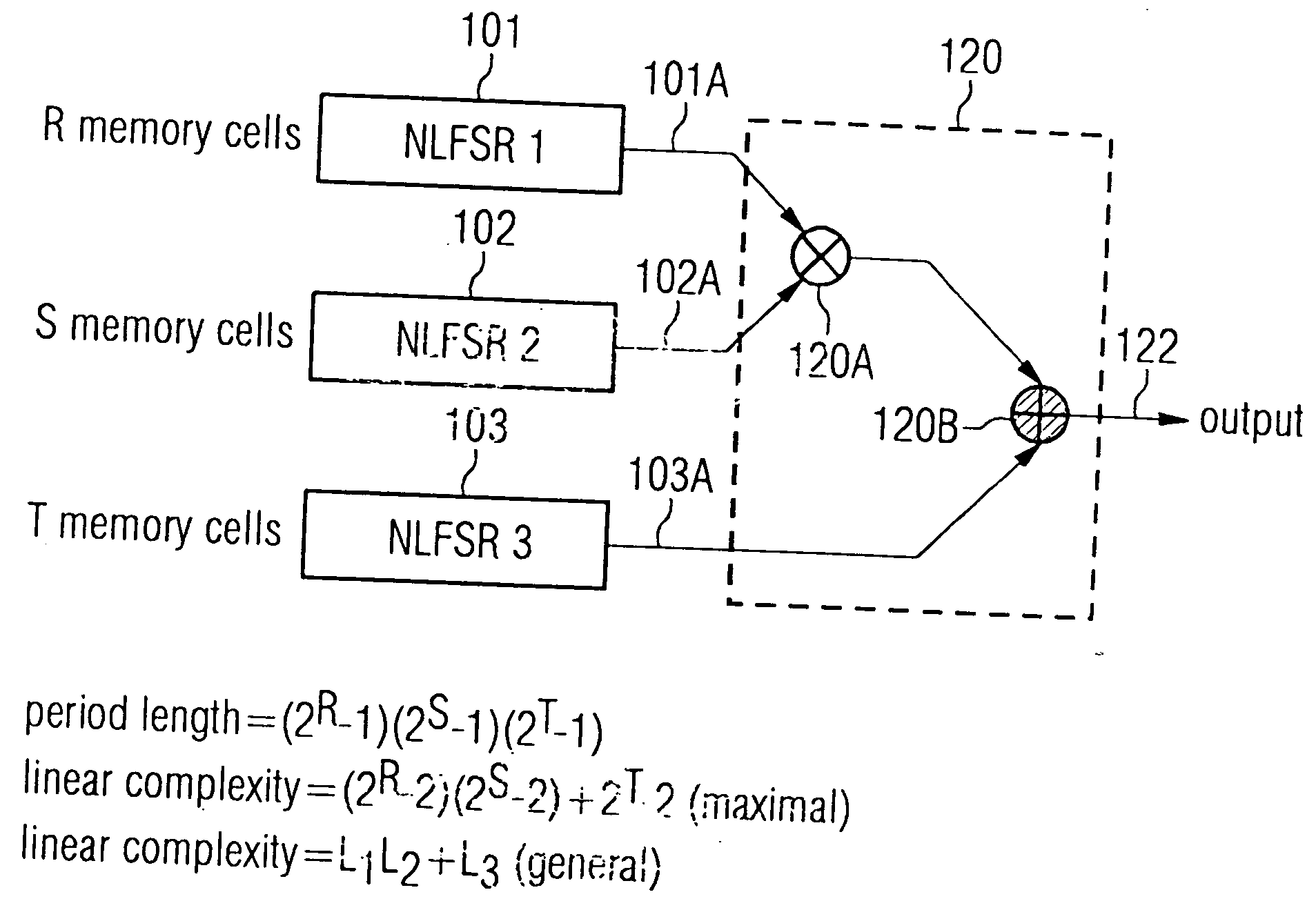
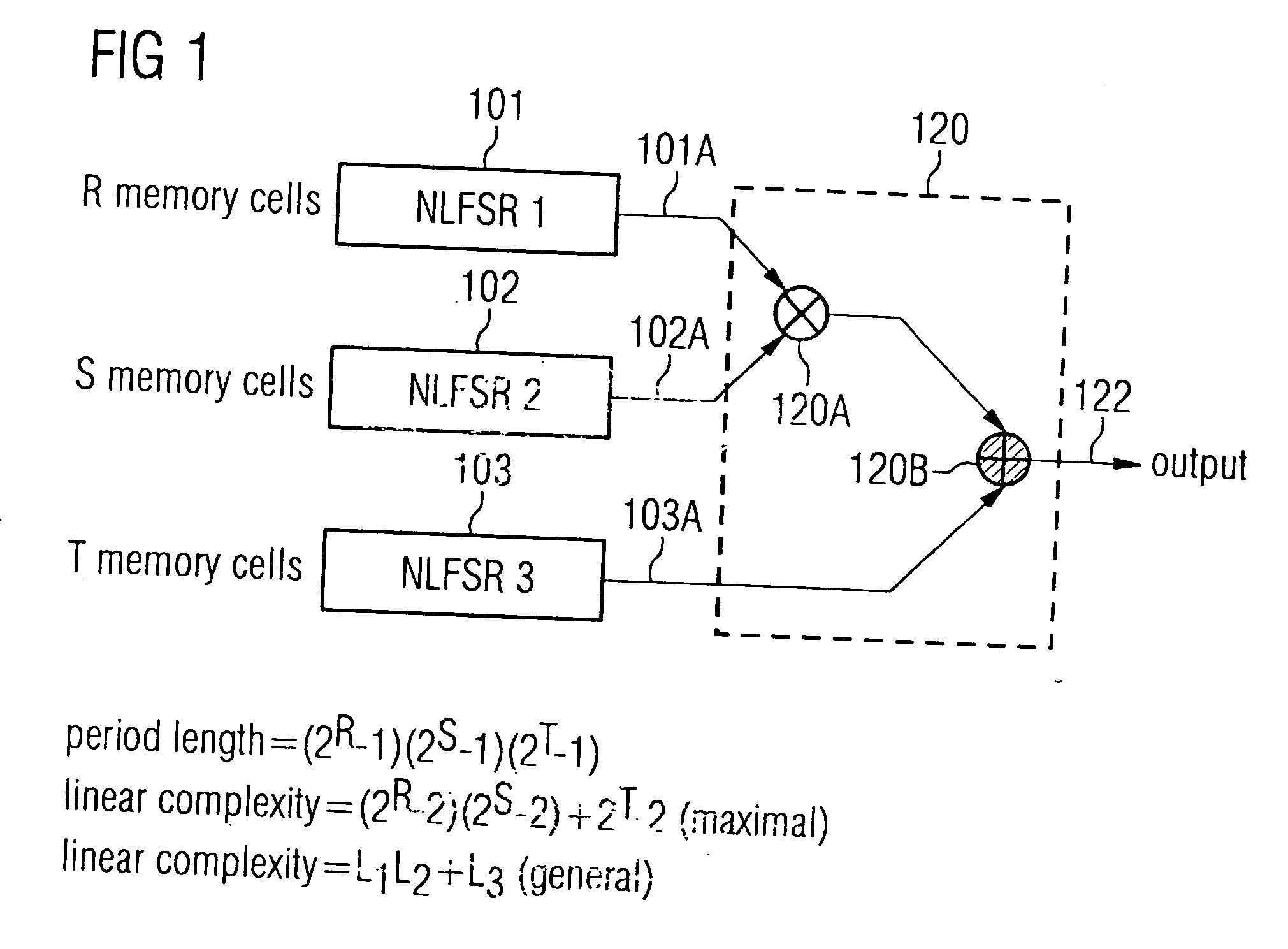
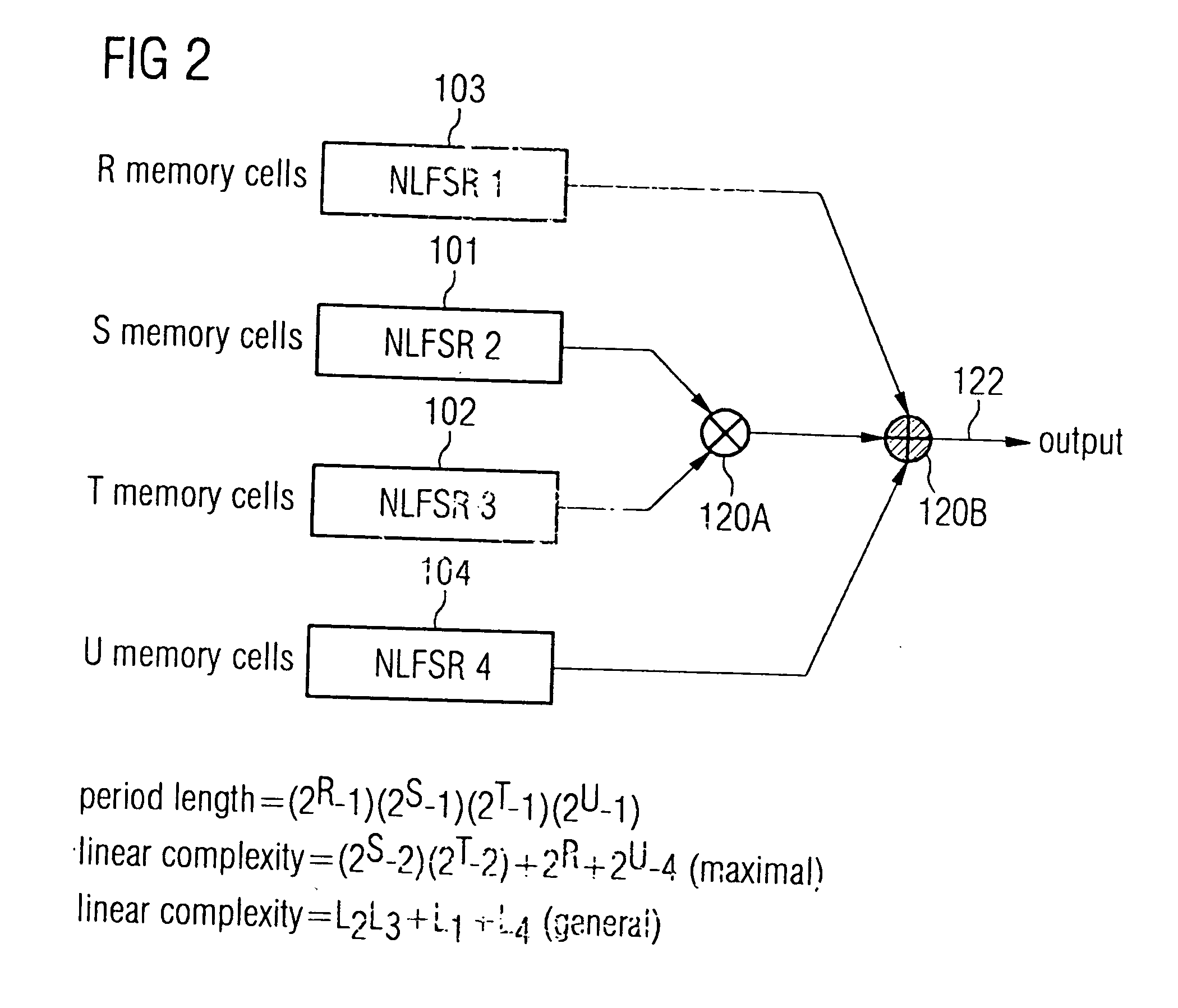
Pseudorandom number generator
InactiveUS20050097153A1Flexible usage of hardware resourceHigh complexityRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsProcessor registerLinear complexity
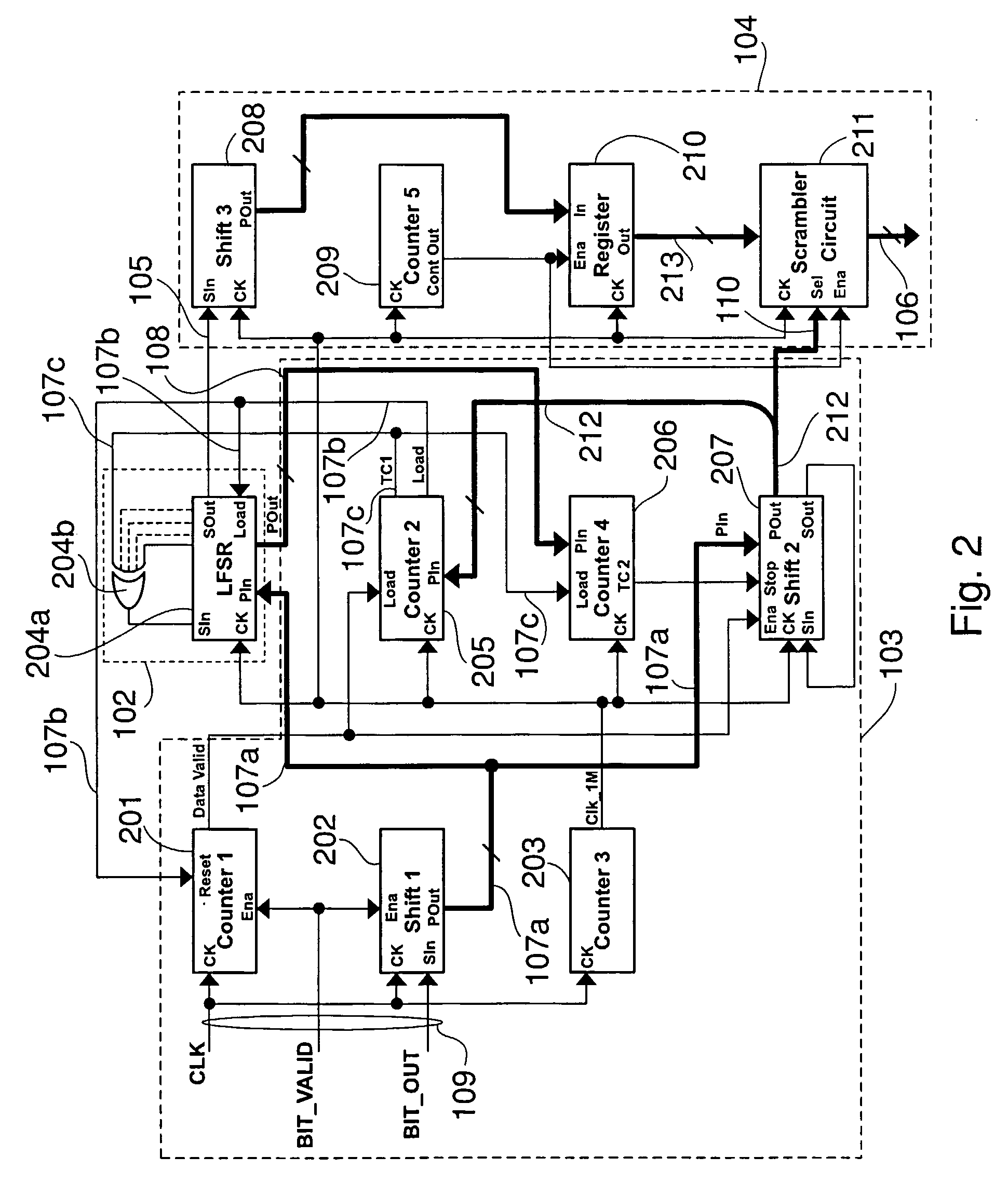
A pseudorandom number generator includes a first elemental shift register having a non-linear feedback feature, a second elemental shift register and combiner for combining signals at an output of the first elemental shift register and the second elemental shift register to obtain a combined signal representing a pseudorandom number. The combination of individual non-linear elemental shift registers allows a safe and flexible implementation of random number generators, the output sequences of which include a high linear complexity and a high period length.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
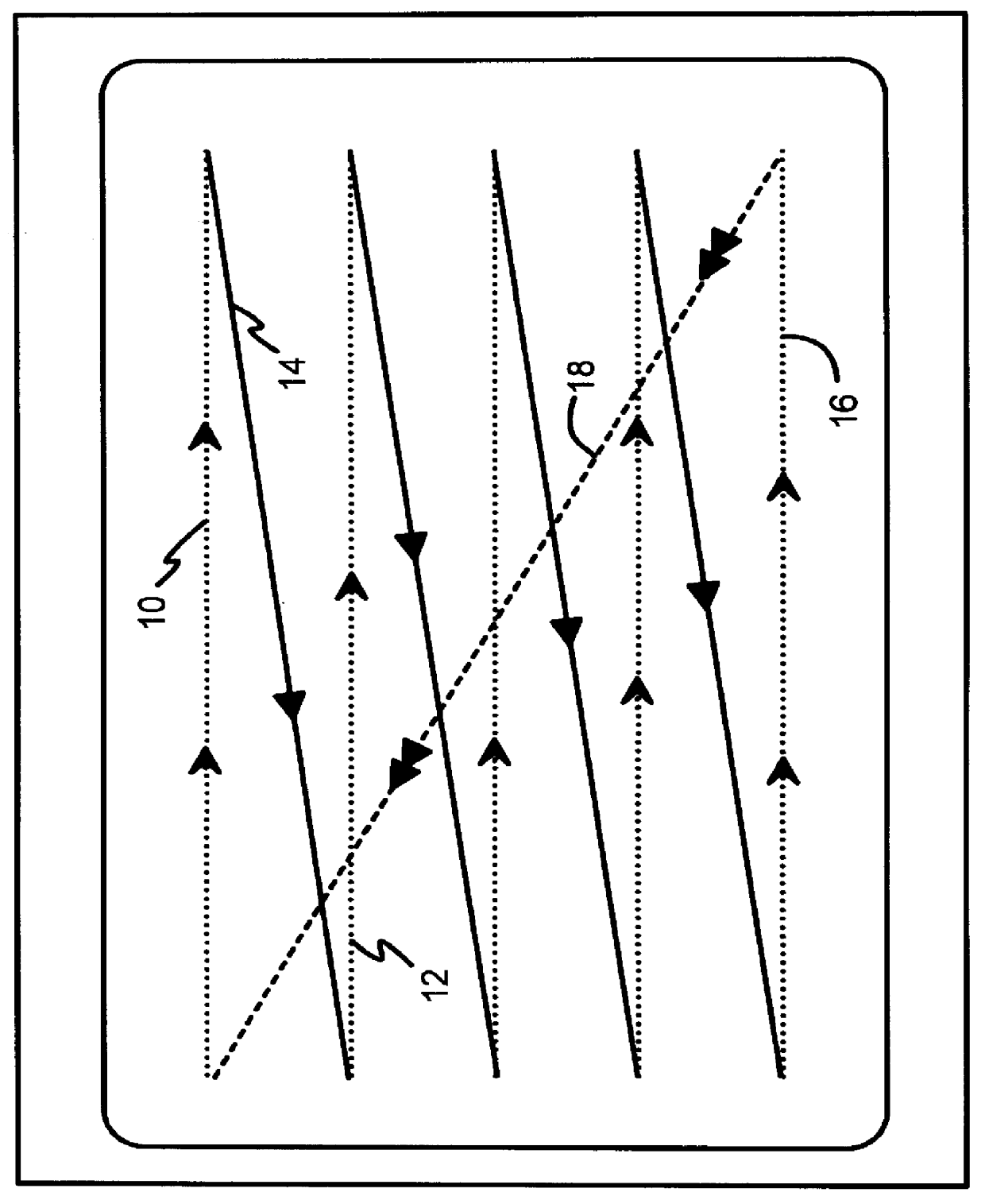
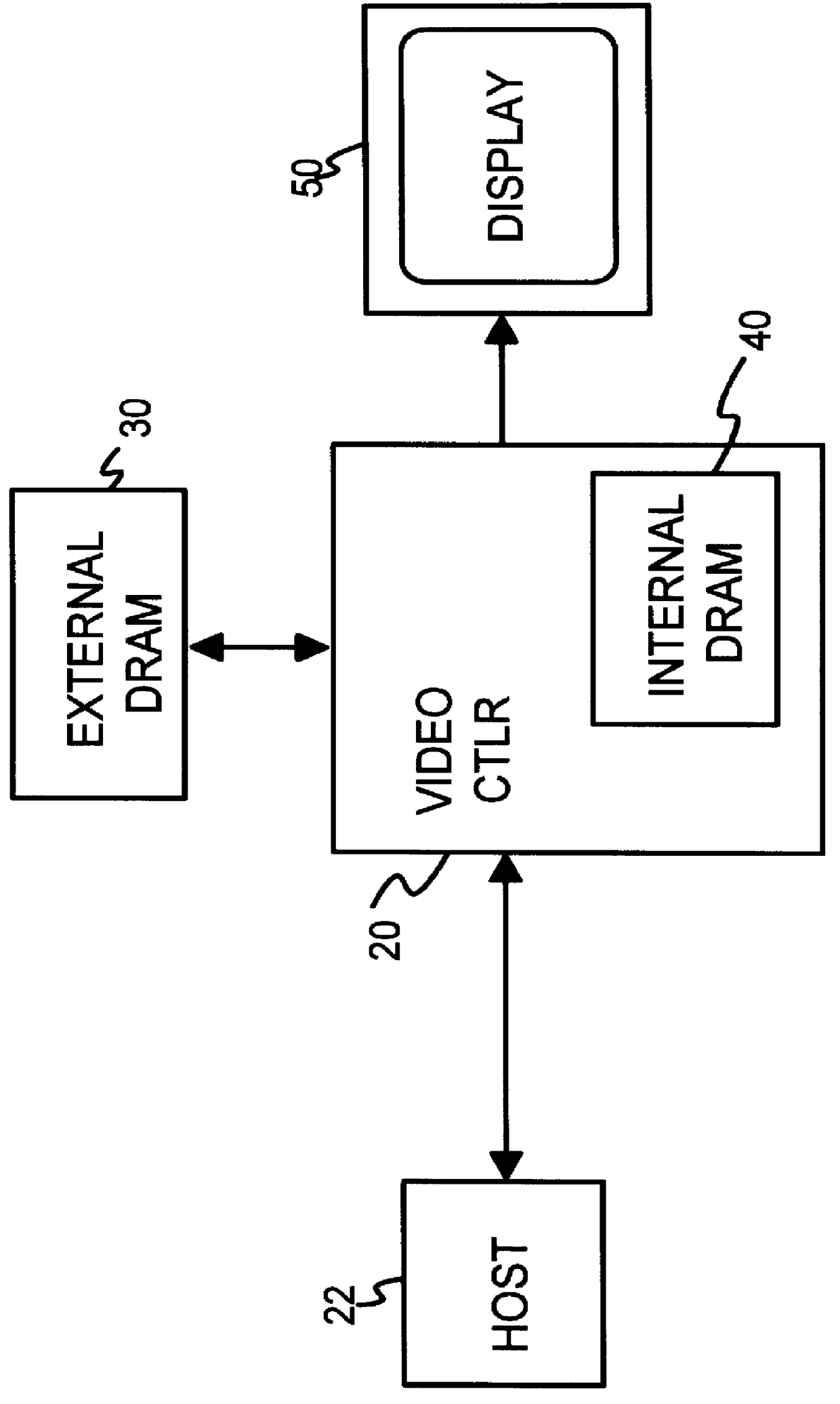
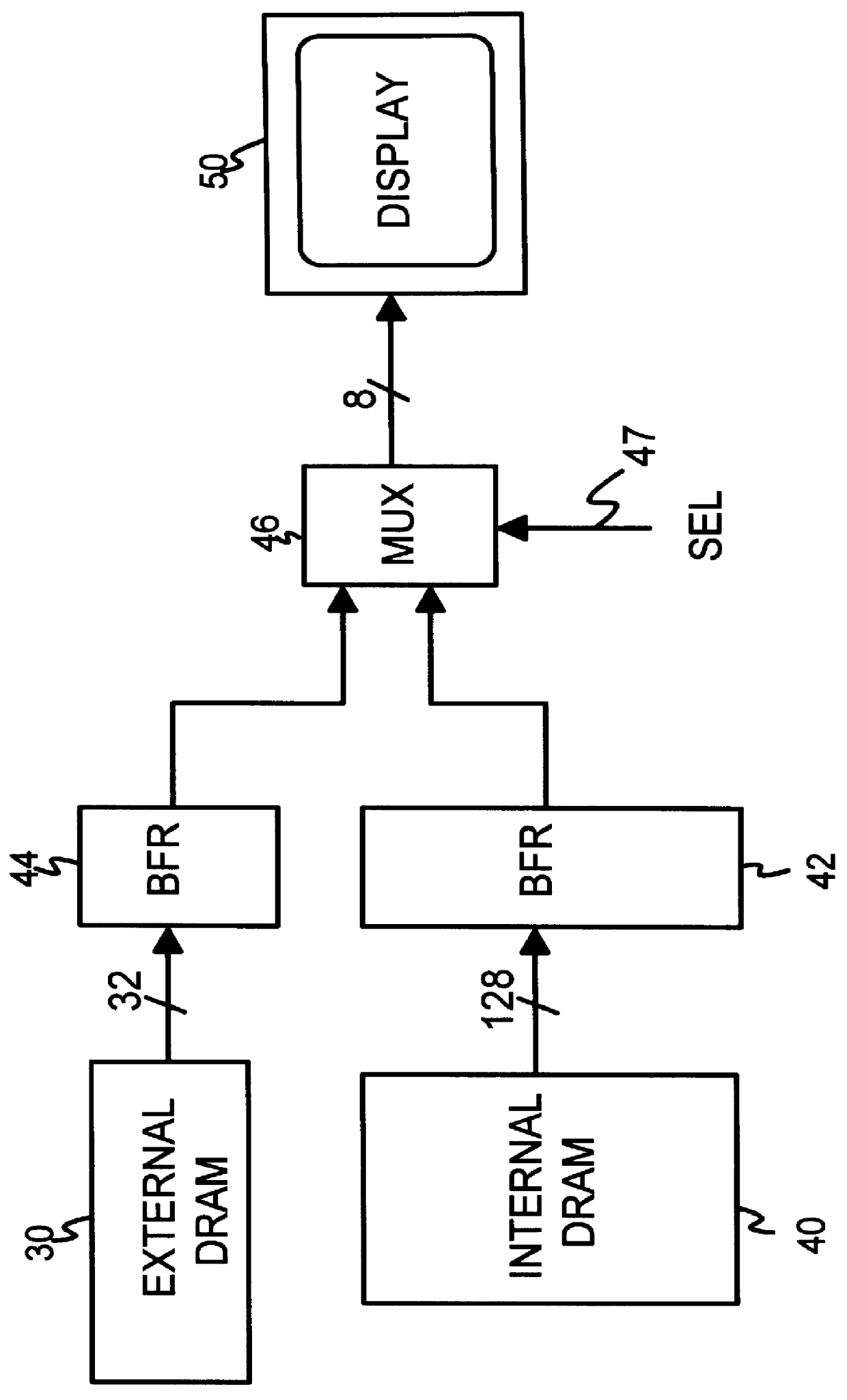
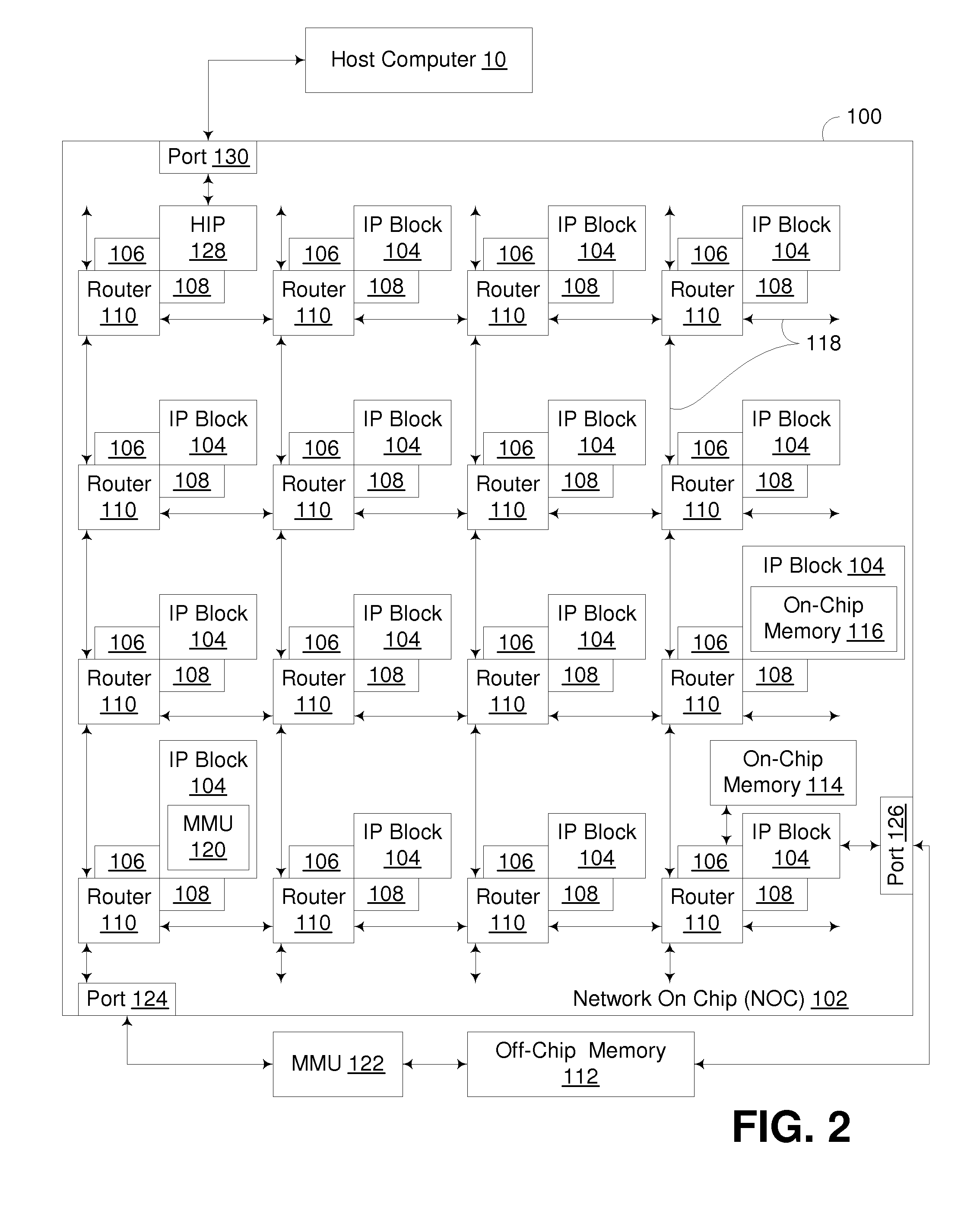
Testable interleaved dual-DRAM architecture for a video memory controller with split internal/external memory
A video sub-system features reduced power consumption by integrating a video memory onto the same chip as the video memory controller. The video memory is preferably a small DRAM sufficiently large to store all pixel data for lower resolutions, but insufficient for higher resolutions. At higher resolutions, an external DRAM supplements the internal DRAM. The amount of external DRAM needed depends upon the resolution to be supported. The internal DRAM has a wide data bus and thus high bandwidth, since no external I / O pins are needed. The external DRAM is narrow to minimize pincount and power consumption. Since the external DRAM is slower and lower in bandwidth, pixel data from both internal and external DRAMs are interleaved together for each horizontal scan line. Thus the lower bandwidth of the external DRAM is masked by the high bandwidth of the wide internal DRAM. Either the internal or the external DRAM, or both, are automatically tested with a pseudo-random number generator that writes pseudo-random numbers to the DRAM while simultaneously supplying pixel data to the graphics data path for display. A checksum of the pixel data output from the graphics data path is generated for the first screen of pixels or frame, while on the second frame the pseudo-random number generator is disabled and the DRAM supplies the same pixel data that was written to it by the pseudo-random number generator during the first frame. The checksums for the first and second frames should match if the DRAM is free of faults.
Owner:FAUST COMMUNICATIONS LLC
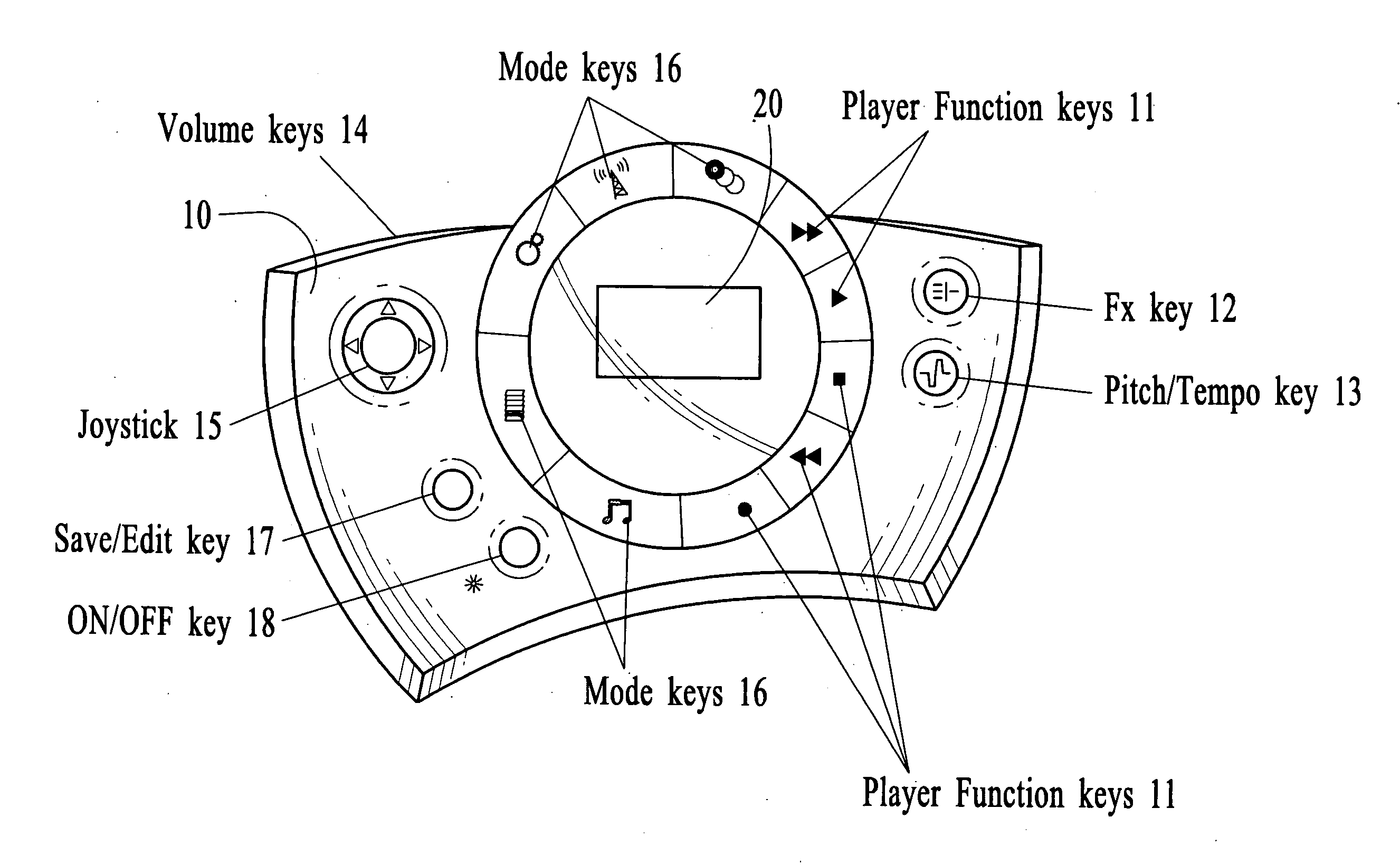
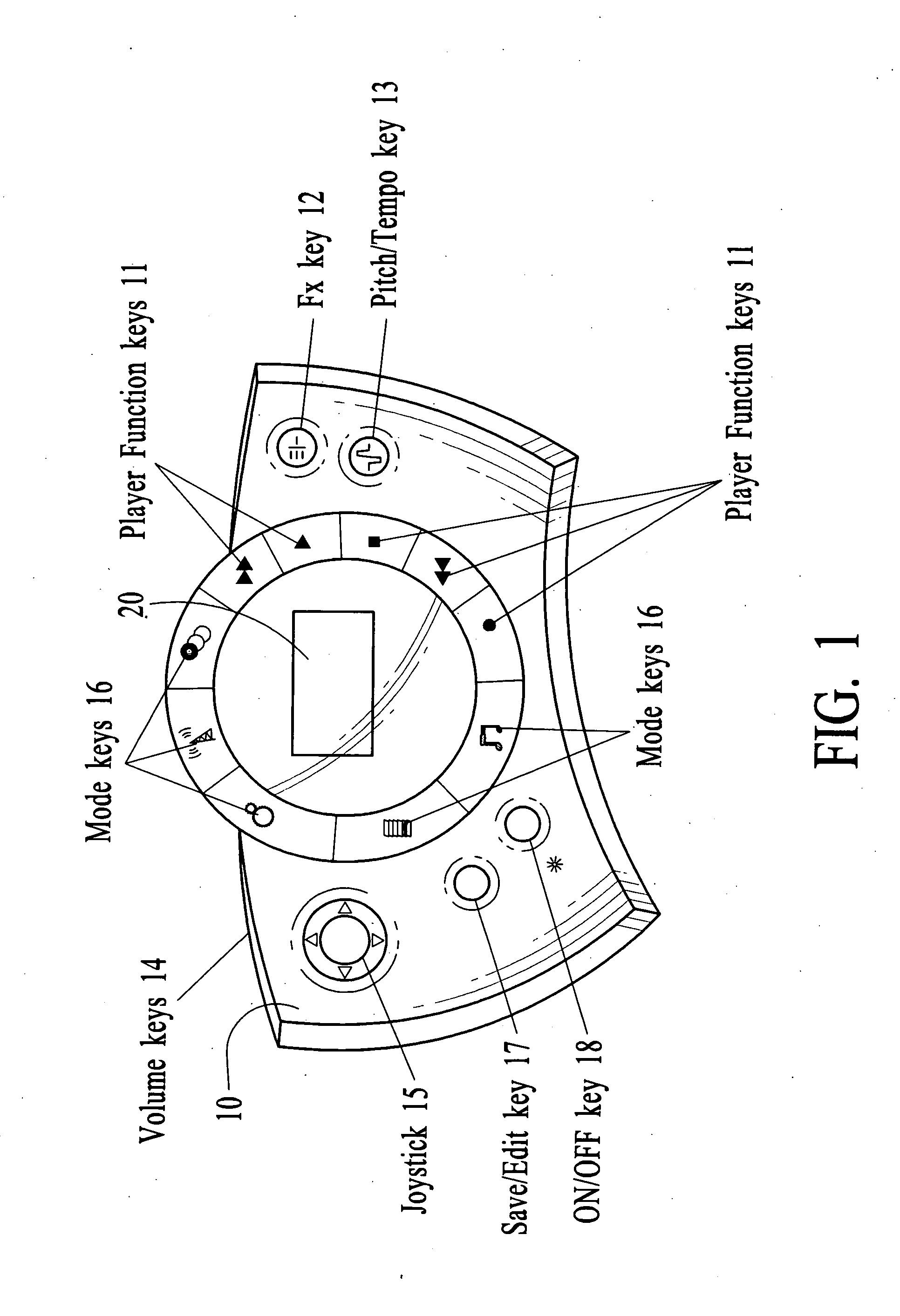
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing musical compositions
InactiveUS20070186752A1Easy to useIncrease user enjoymentGearworksMusical toysData fileDisplay device
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing music are provided, particularly systems and methods employing a top-down process, where the user is provided with a musical composition that may be modified and interacted with and played and / or stored (for later play). The system preferably is provided in a handheld form factor, and a graphical display is provided to display status information, graphical representations of musical lanes or components which preferably vary in shape as musical parameters and the like are changed for particular instruments or musical components such as a microphone input or audio samples. An interactive auto-composition process preferably is utilized that employs musical rules and preferably a pseudo random number generator, which may also incorporate randomness introduced by timing of user input or the like, the user may then quickly begin creating desirable music in accordance with one or a variety of musical styles, with the user modifying the auto-composed (or previously created) musical composition, either for a real time performance and / or for storing and subsequent playback. In addition, the present invention makes use of node-based music generation as part of a system and method to broadcast and receive music data files, which are then used to generate and play music. By incorporating the music generation process into a node / subscriber unit, the bandwidth-intensive systems of conventional techniques can be avoided. Consequently, the bandwidth can preferably be also used for additional features such as node-to-node and node-to-base music data transmission. The present invention is characterized by the broadcast of relatively small data files that contain various parameters sufficient to describe the music to the node / subscriber music generator.
Owner:MEDIALAB SOLUTIONS
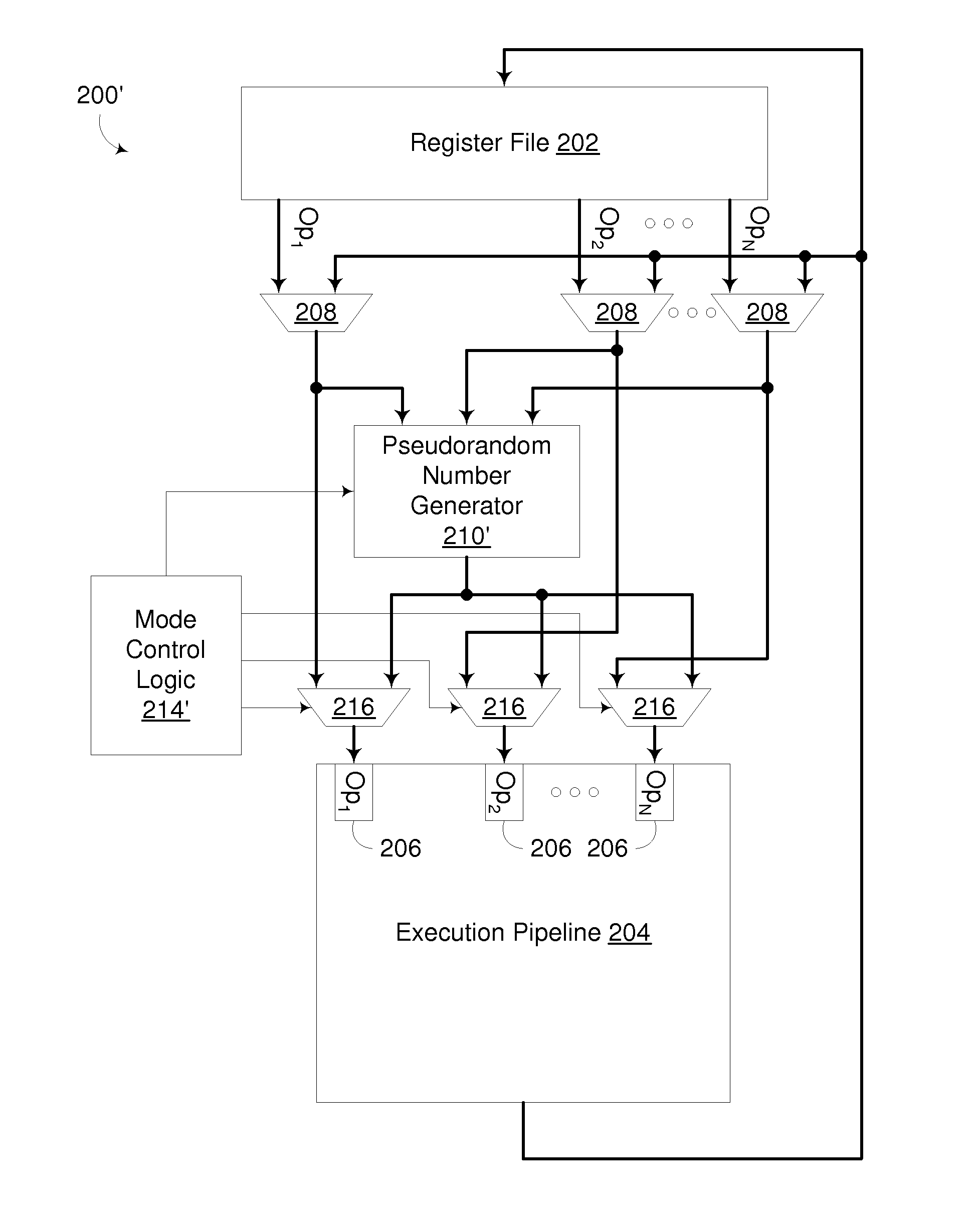
Execution Unit With Inline Pseudorandom Number Generator
A circuit arrangement and method couple a hardware-based pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) to an execution unit in such a manner that pseudorandom numbers generated by the PRNG may be selectively output to the execution unit for use as an operand during the execution of instructions by the execution unit. A PRNG may be coupled to an input of an operand multiplexer that outputs to an operand input of an execution unit so that operands provided by instructions supplied to the execution unit are selectively overridden with pseudorandom numbers generated by the PRNG. Furthermore, overridden operands provided by instructions supplied to the execution unit may be used as seed values for the PRNG. In many instances, an instruction executed by an execution unit may be able to perform an arithmetic operation using both an operand specified by the instruction and a pseudorandom number generated by the PRNG during the execution of the instruction, so that the generation of the pseudorandom number and the performance of the arithmetic operation occur during a single pass of an execution unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
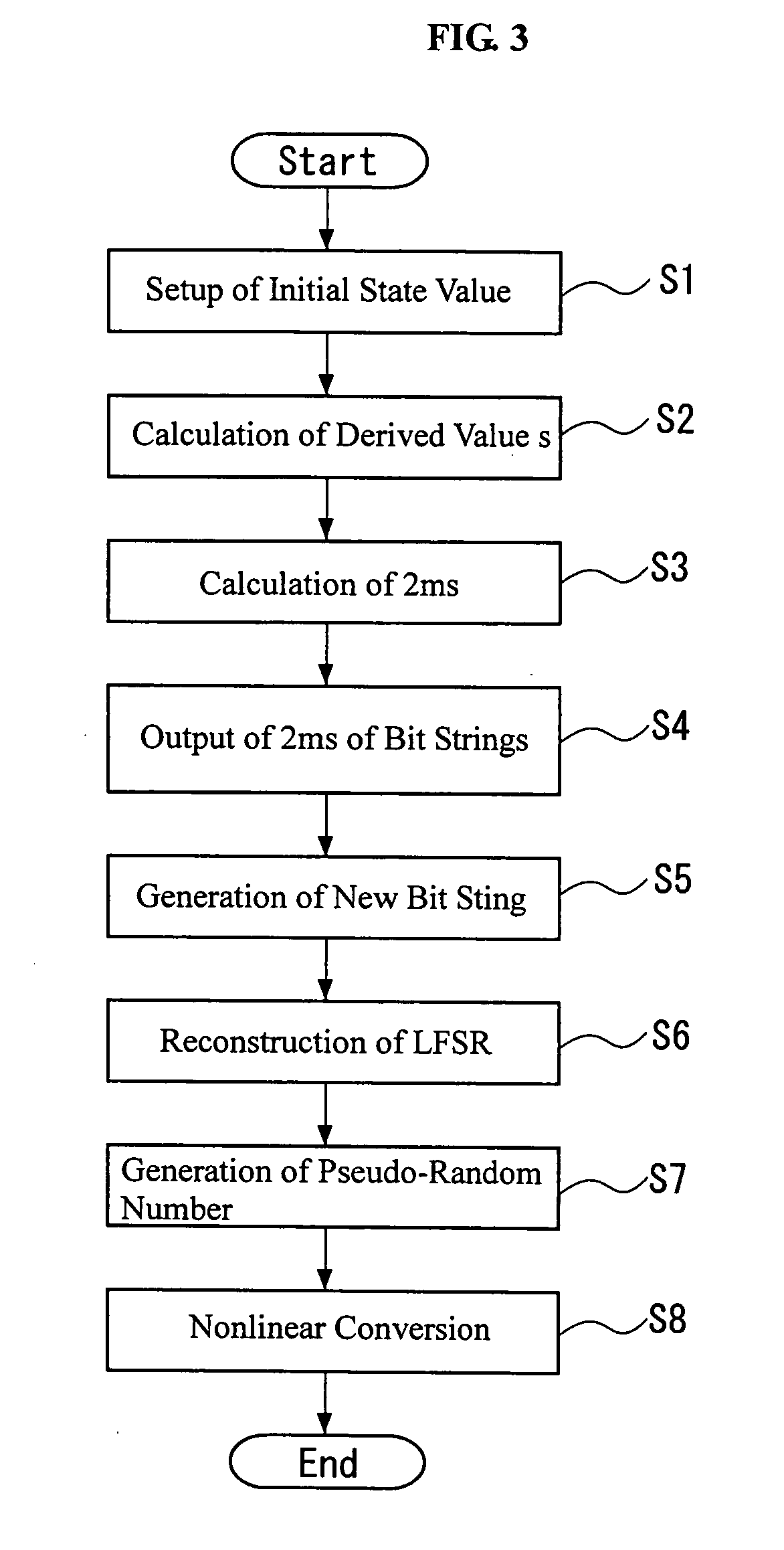
Pseudo-random number generation method and pseudo-random number generator
InactiveUS20060039558A1Easy to changeHigh encryption strengthRandom number generatorsCoding/ciphering apparatusLinearityNumber generator
A bit string obtained by sampling, every the number s, bits of a bit string whose output sequence is M sequence, when the bit number per one cycle of the M sequence is prime to the derived value, constitutes M sequence of a linear feedback shift register having other construction. Further, the linear feedback shift register can be determined from bits corresponding to at least two cycles by Berlekamp-Massay algorithm, whereby the linear feedback shift register 11 can be easily and dynamically reconstructed based on the initial state value.
Owner:KOBAYASHI AKIRA +1
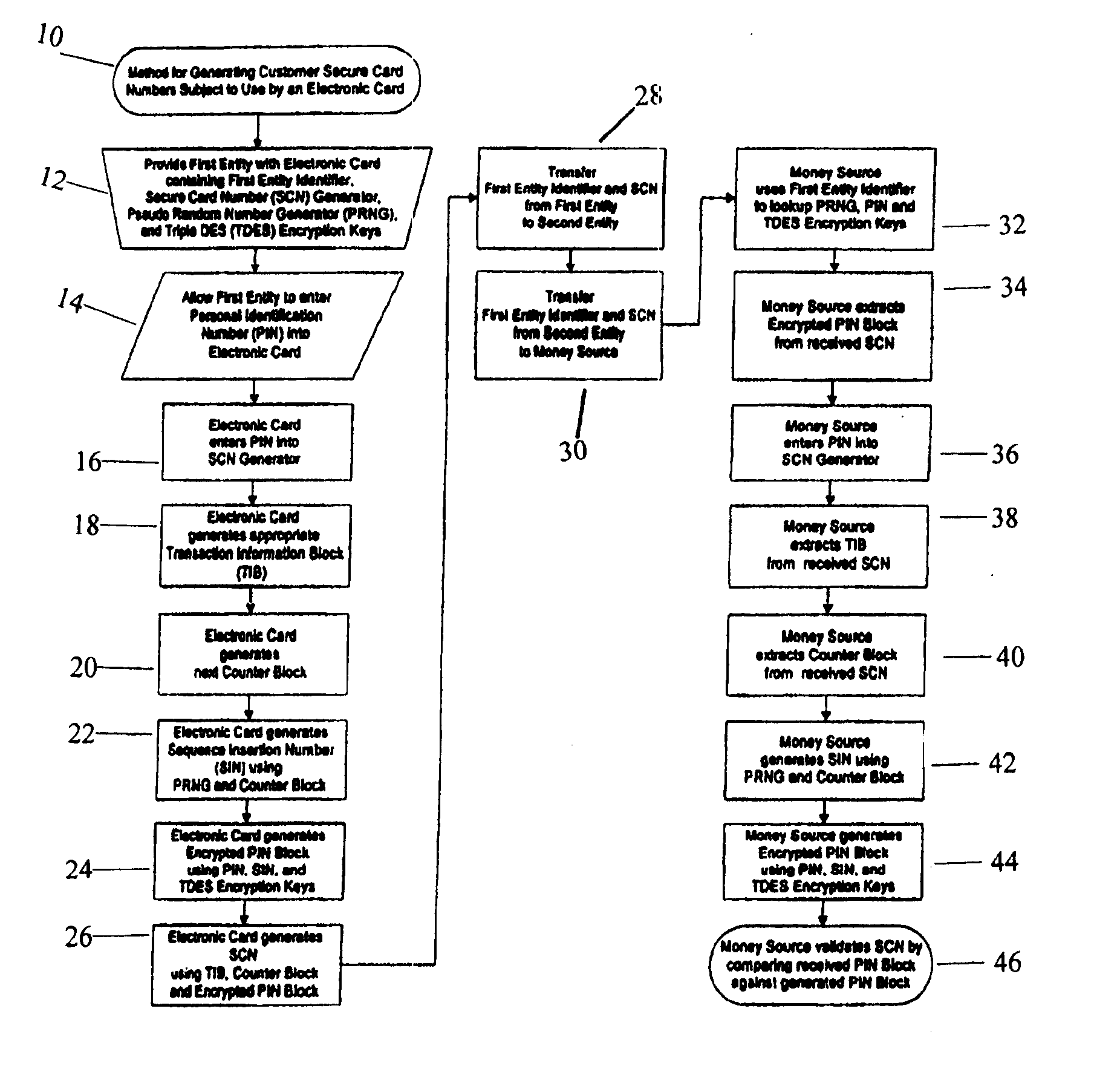
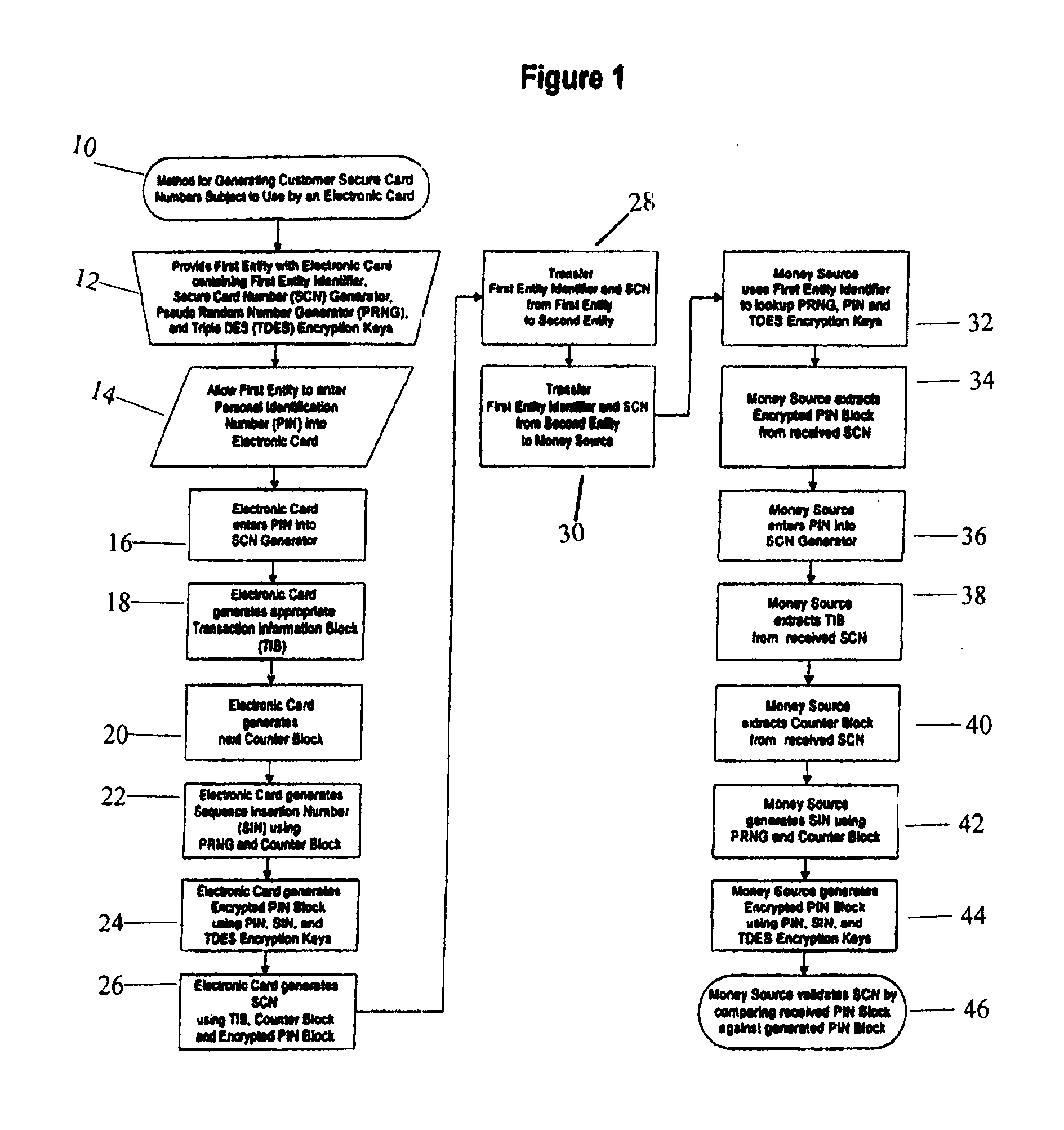
Method for Generating Customer Secure Card Numbers
InactiveUS20070215688A1Complete banking machinesFinancePersonal identification numberEntity identifier
A method for providing secure transactions generates a Secure Card Number (“SCN”) for a first entity that is transferred with a first entity identifier to a second entity and then to a money source that verifies that the transaction is valid by use of the first entity identifier and the SCN. The SCN includes a Transaction Information Block (“TIB”), a Counter Block, and an encrypted Personal Identification Number (“PIN”) Block. The SCN is transferred to the money source in an account number or a non-account data field. The money source can use the TIB to determine whether the SCN should be used once or multiple times or to identify one of several physical devices, all of which are issued to the first entity, used to generate the SCN. The money source validates the SCN by duplicating the encryption process used to create an encrypted PIN Block and comparing the result to the encrypted PIN Block received with the transaction. A Triple Data Encryption Standard algorithm encrypts a PIN Block generated from a PIN, a Sequence Insertion Number (“SIN”) and a known starting value. The SIN can be a combination of three seed values and a random value generated by a Pseudo Random Number Generator (“PRNG”) initialized with the seed values. A Counter value is associated with the Counter Block and the seed values.
Owner:PRIVASYS
System and method for generating pseudo-random numbers
ActiveUS20070230693A1Random number generatorsSecuring communicationCryptographic hash functionNumber generator
A process and system for generating a pseudo-random number is presented. Input data having entropy is gathered in an Entropy Pool and transformed once by a cryptographic hash function. The transformed data forms the internal state of the pseudo-random number generator. The generator forms the output by applying a second cryptographic hash function to this internal state. Finally, the generator updates the internal state by inputting the current internal state and data from the Entropy Pool into a third cryptographic hash function. The output of the third hash function forms the new internal state of the pseudo-random number generator.
Owner:SAP AG
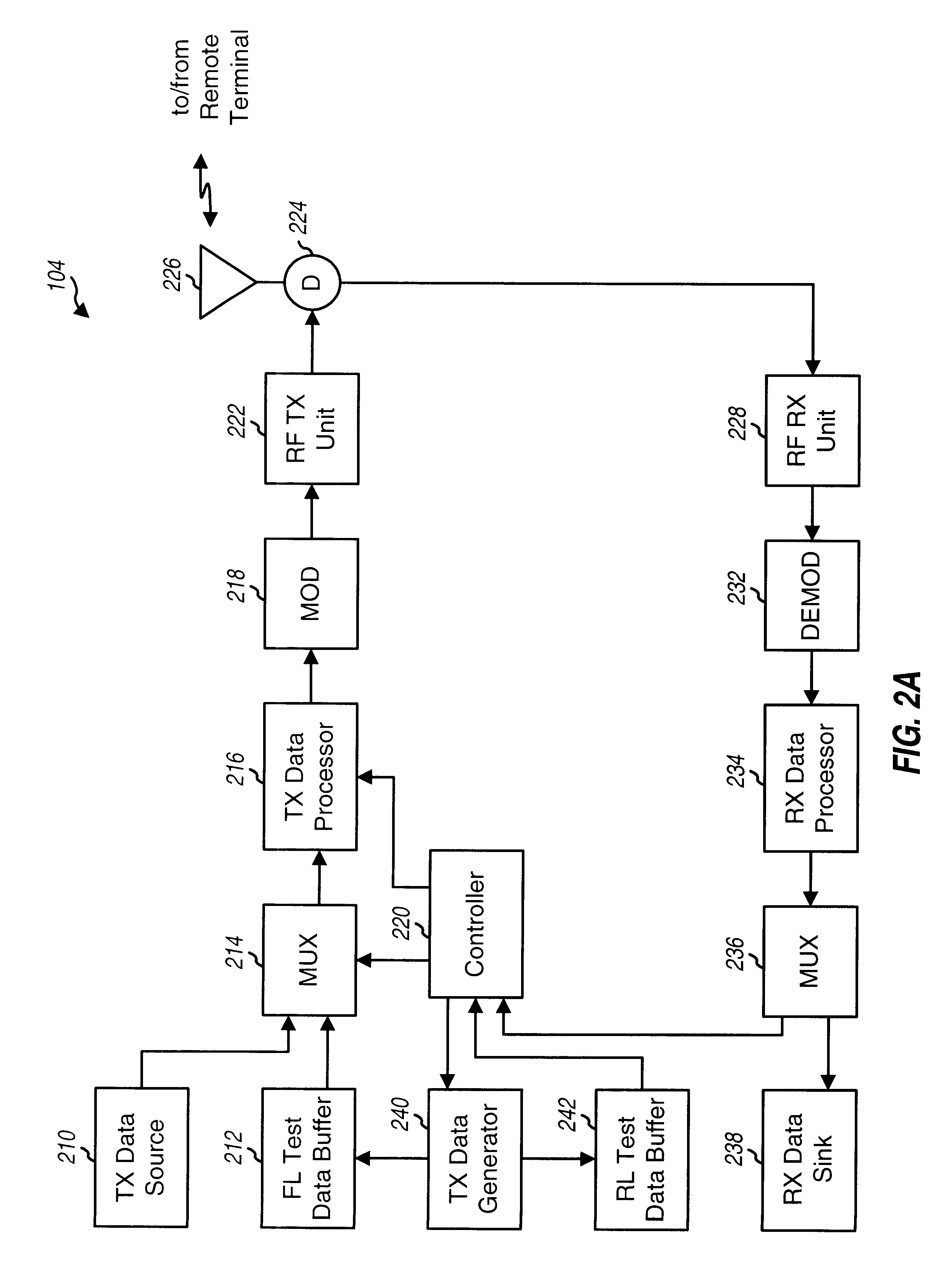
Method and apparatus for testing wireless communication channels
InactiveUS6542538B2Correct operation testingFrequency-division multiplex detailsState markov chainCommunication link
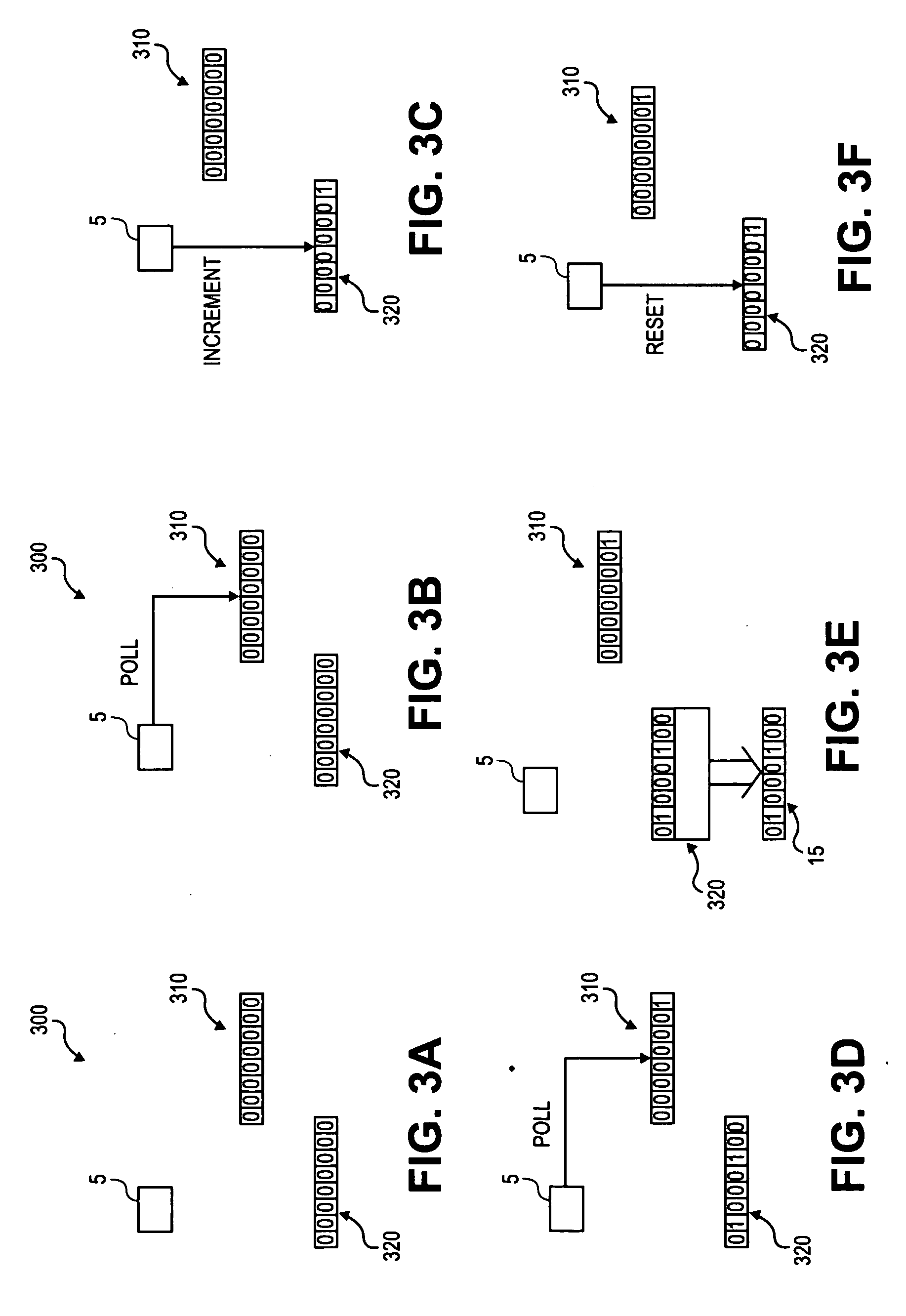
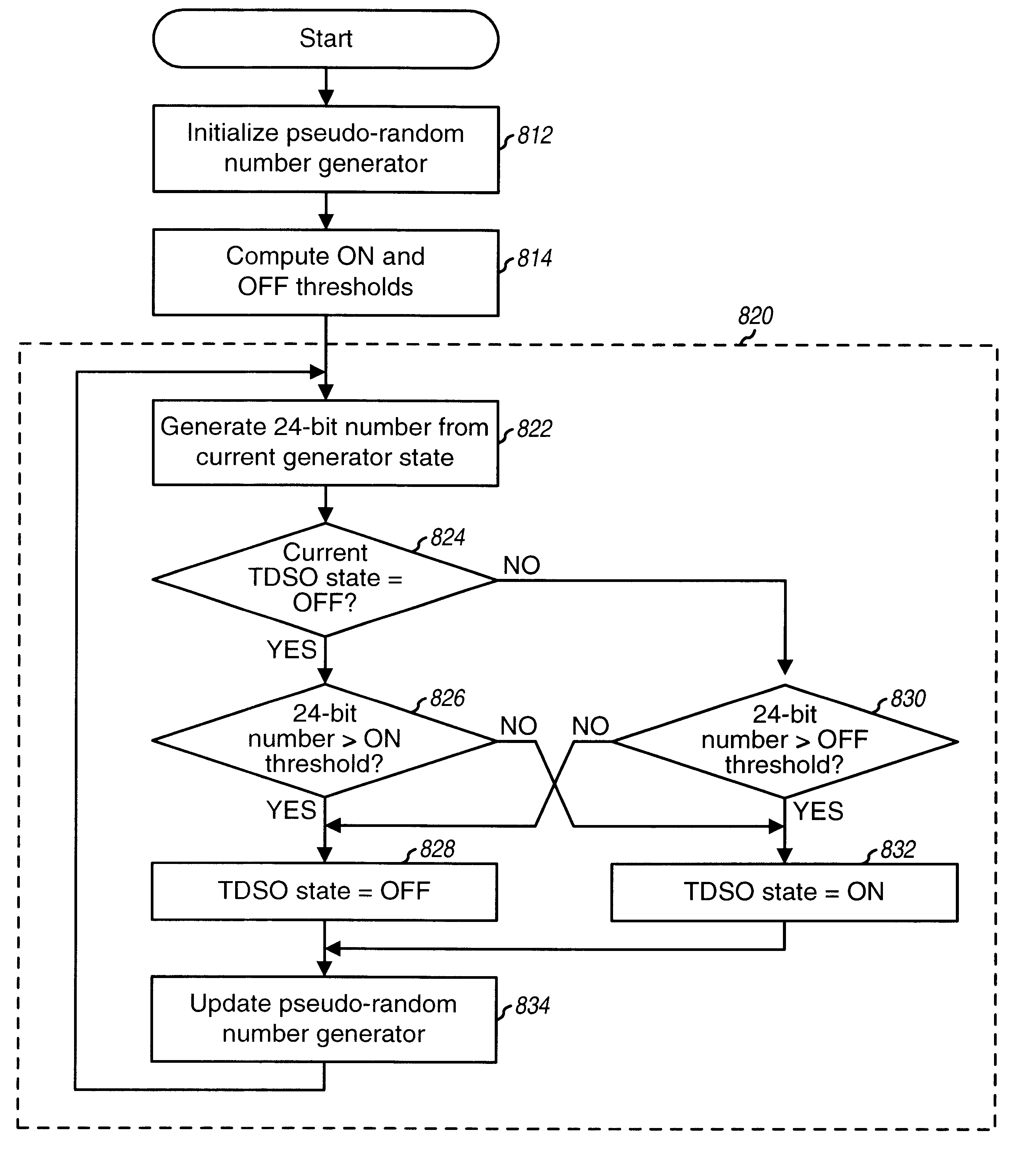
Techniques to test a wireless communication link. A traffic channel is tested via a test data service option (TDSO) that may be negotiated and connected similar to other services. Test parameters values may be proposed, accepted or rejected, and negotiated. Test data for a channel is generated based on a defined data pattern or a pseudo-random number generator. Sufficient test data may be generated based on the generator for a test interval, stored to a buffer, and thereafter retrieved from a particular section of the buffer to form data block(s) for each "active" frame. The traffic channel may be tested using discontinuous transmission. A two-state Markov chain determines whether or not to transmit test data for each frame. The average frame activity and average burst length are defined by selecting the probabilities for transitioning between the ON / OFF states of the Markov chain, which may be driven by a second generator.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
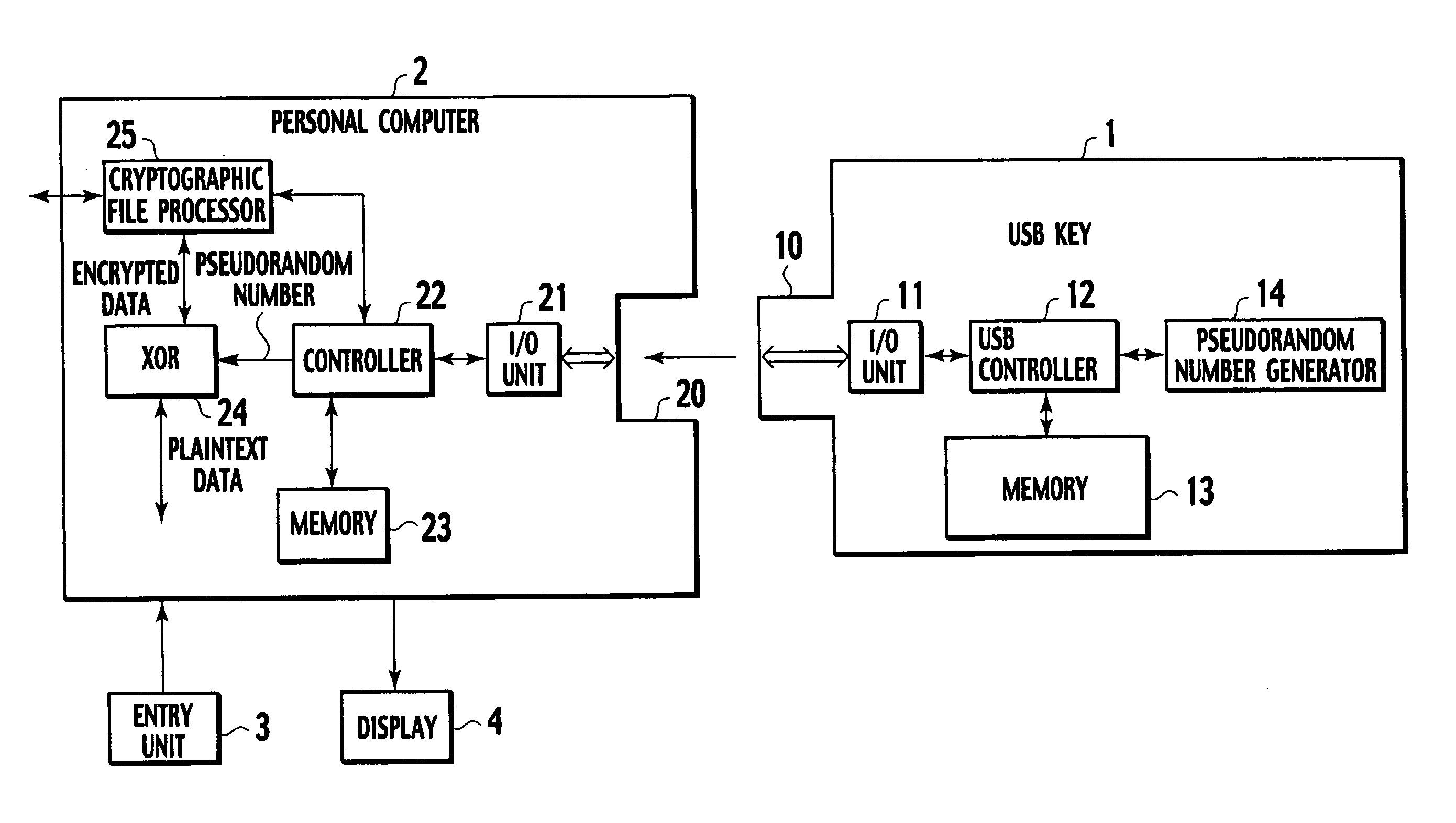
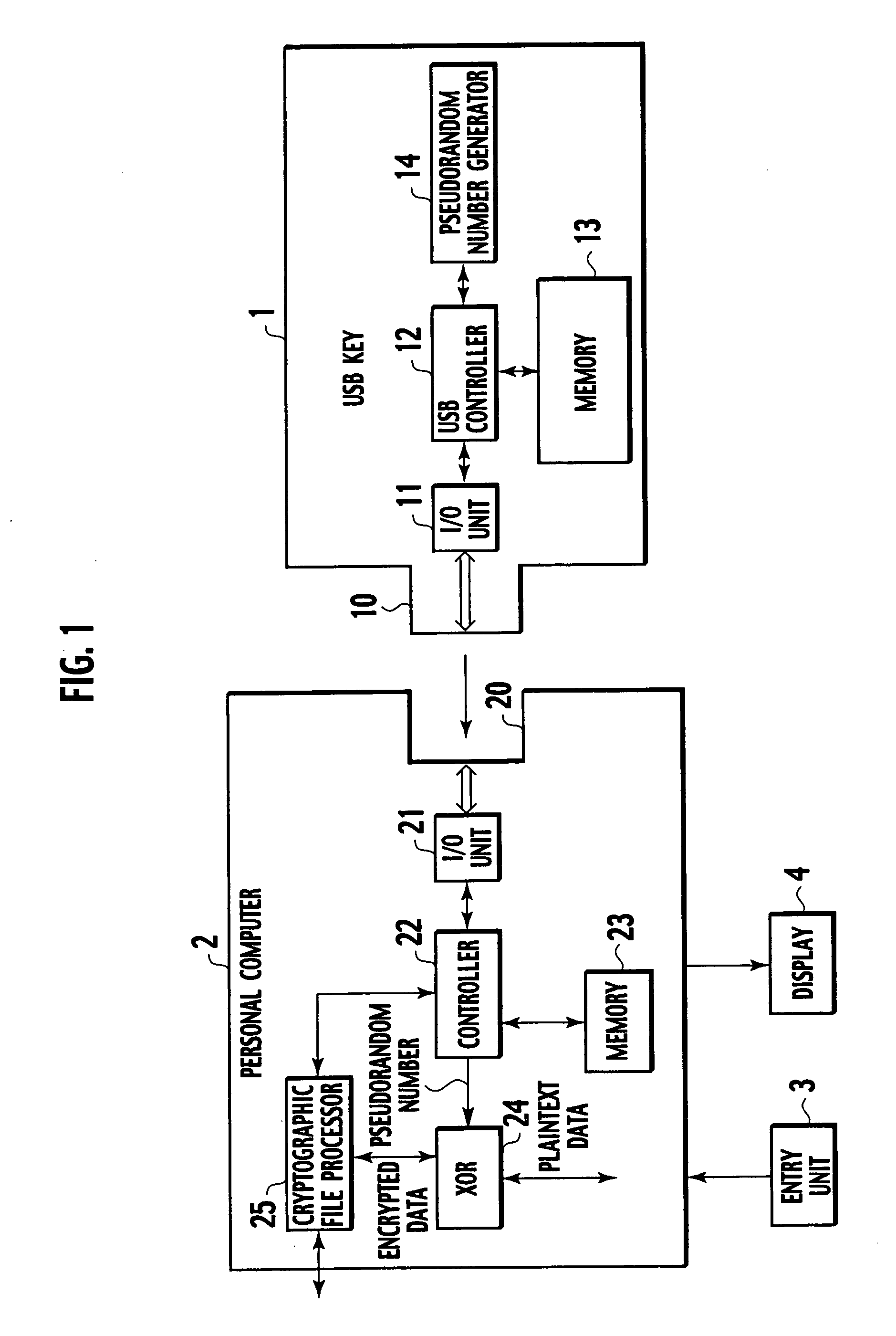
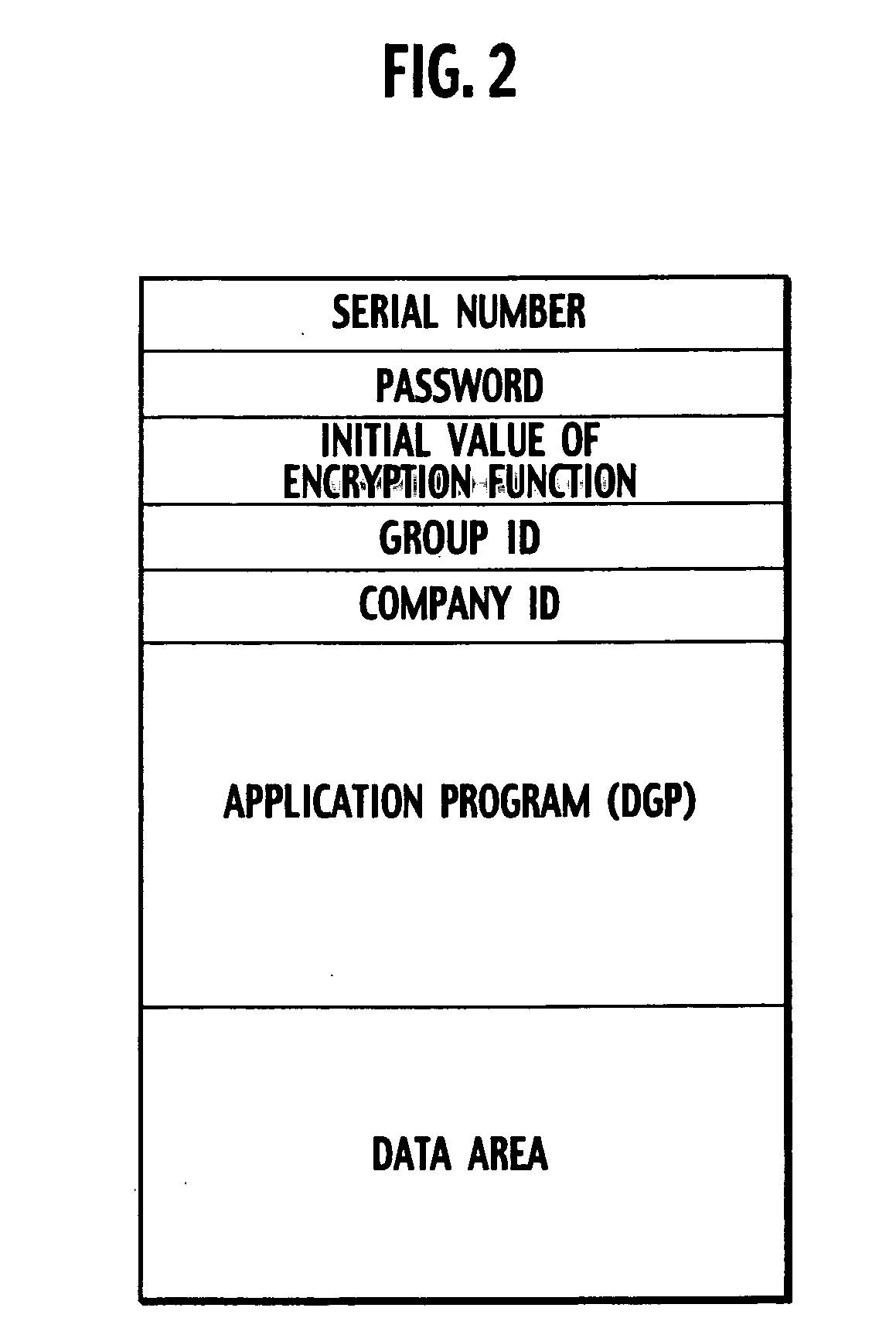
Encryption key device, encryption device and decryption device
InactiveUS20050175182A1Easy to operateImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareInformation processor
An encryption key device can be freely attached to and detached from an information processor encrypting or decrypting data and includes a memory, a pseudorandom number generator, and a controller. The memory stores an application program to operate the encryption key device and a group ID specifying permission for use of the encryption key device. The pseudorandom number generator generates a pseudorandom number according to an encryption function using the group ID stored in the memory as an initial value of the encryption function. The controller causes the pseudorandom number generator to generate the pseudorandom number according to data size received from the information processor operating according to the application program and sends the generated pseudorandom number and the group ID read from the memory to the information processor.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
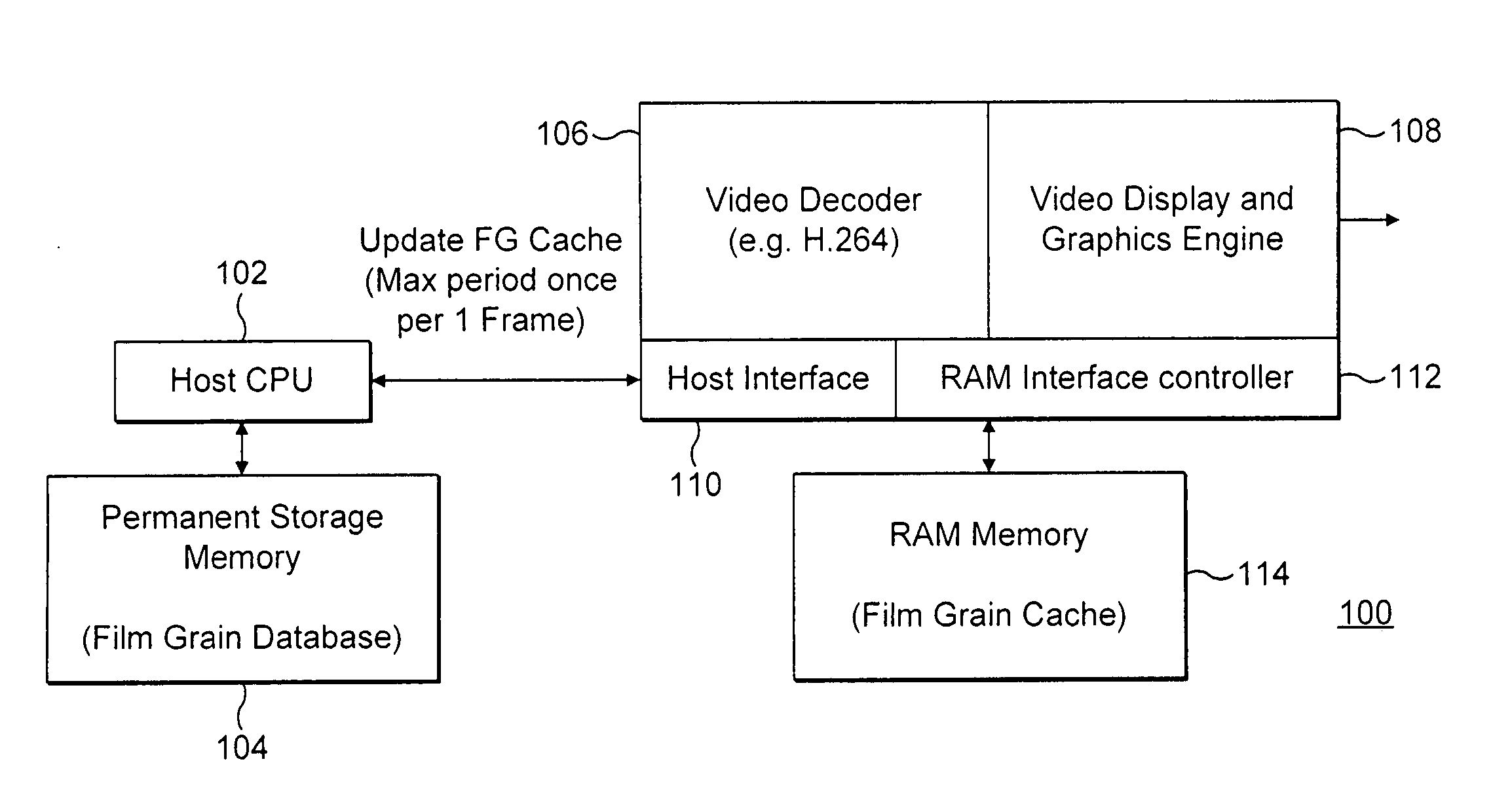
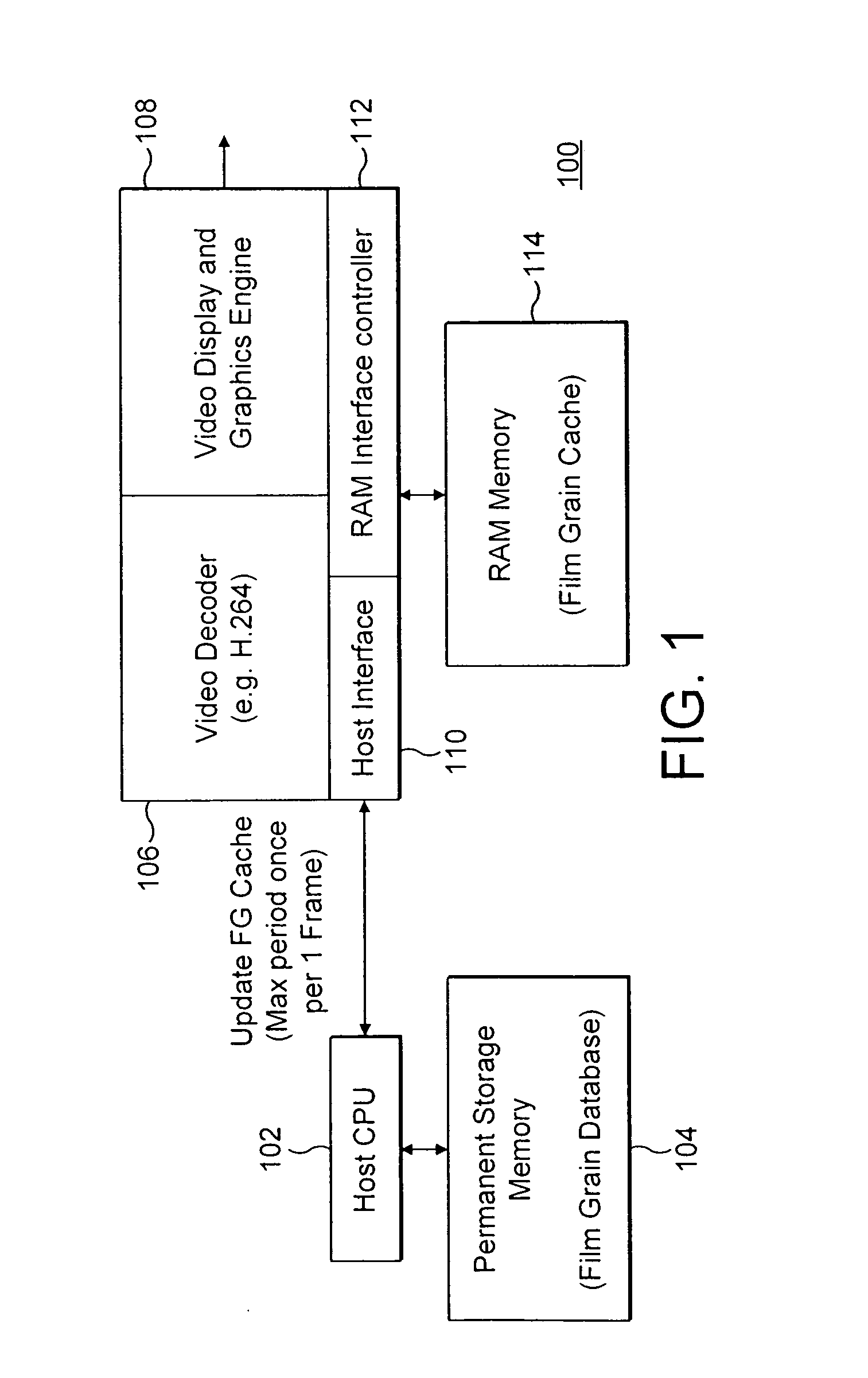
Method and apparatus for reading film grain patterns in a raster order in film grain simulation
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for reading film grain patterns in a raster order in film grain simulation including establishing a pseudo-random starting position, repeating the pseudo-random starting position for each line of a group of film grain blocks, and using a different pseudo-random starting position for each display line of a next group of film grain blocks. In various embodiments of the present invention, the different pseudo-random starting positions are triggered by resetting at least one seed value of a pseudo-random number generator implemented to determine said pseudo-random starting positions.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Random number generator
InactiveUS20060047735A1Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsNumber generatorComputer science
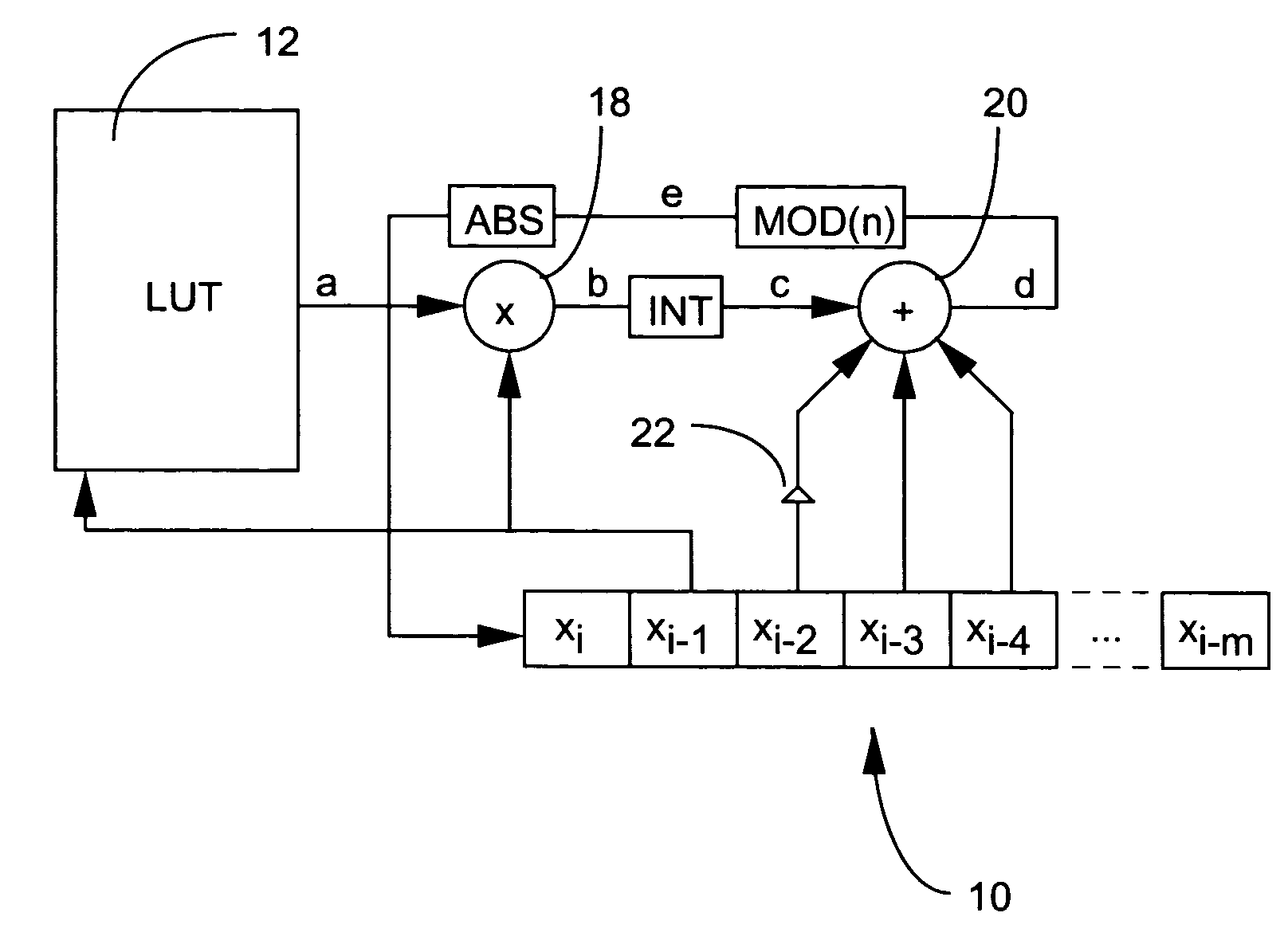
A pseudo-random number generator employs a value in an existing sequence of numbers as an index into a table of irrational numbers. The value that is retrieved from the table is used to derive another value that is combined with multiple other values in the sequence to generate the next number in the sequence. The resulting values are shown to be more random than those generated by other known generators.
Owner:NUNES RYAN J
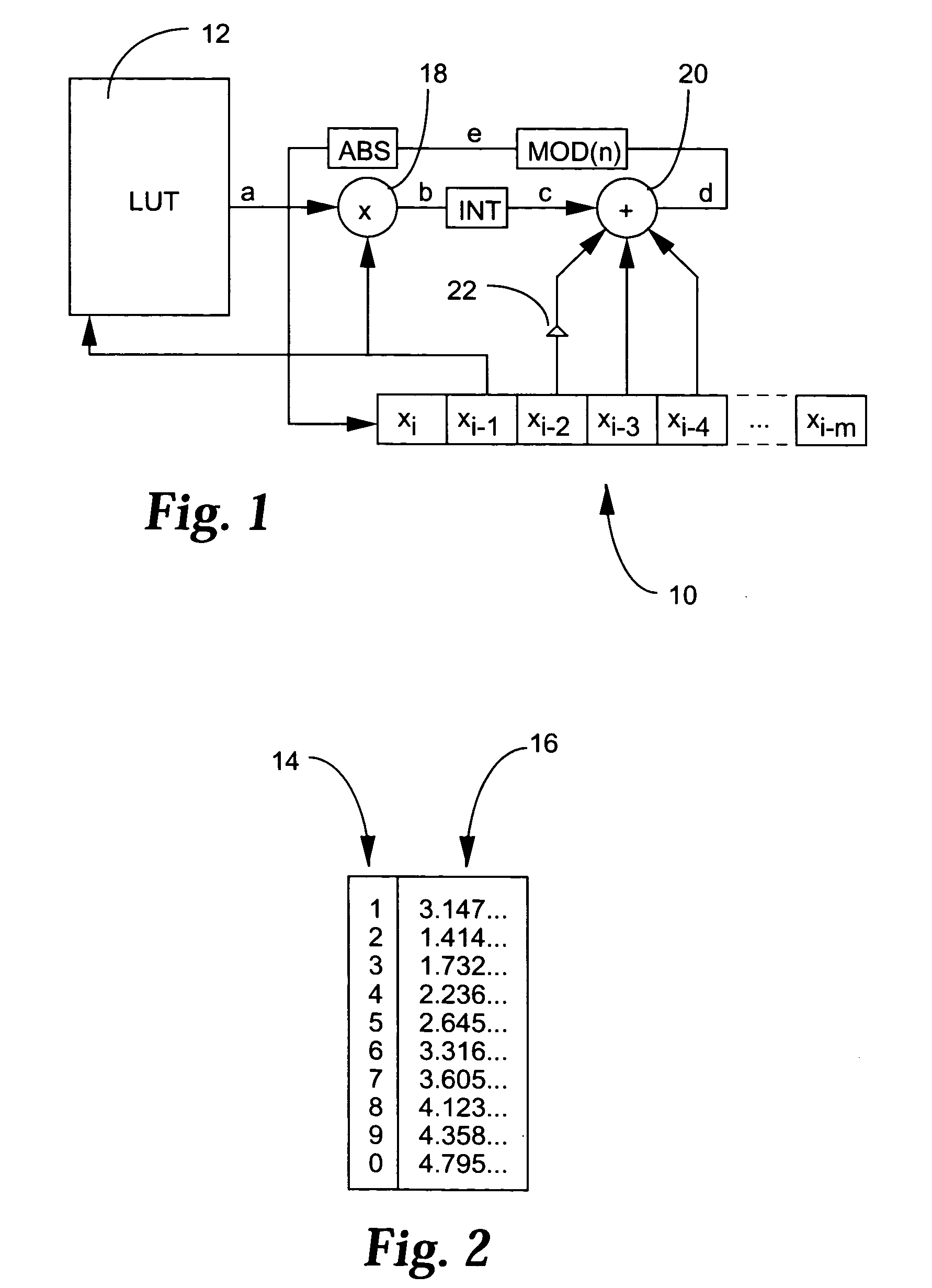
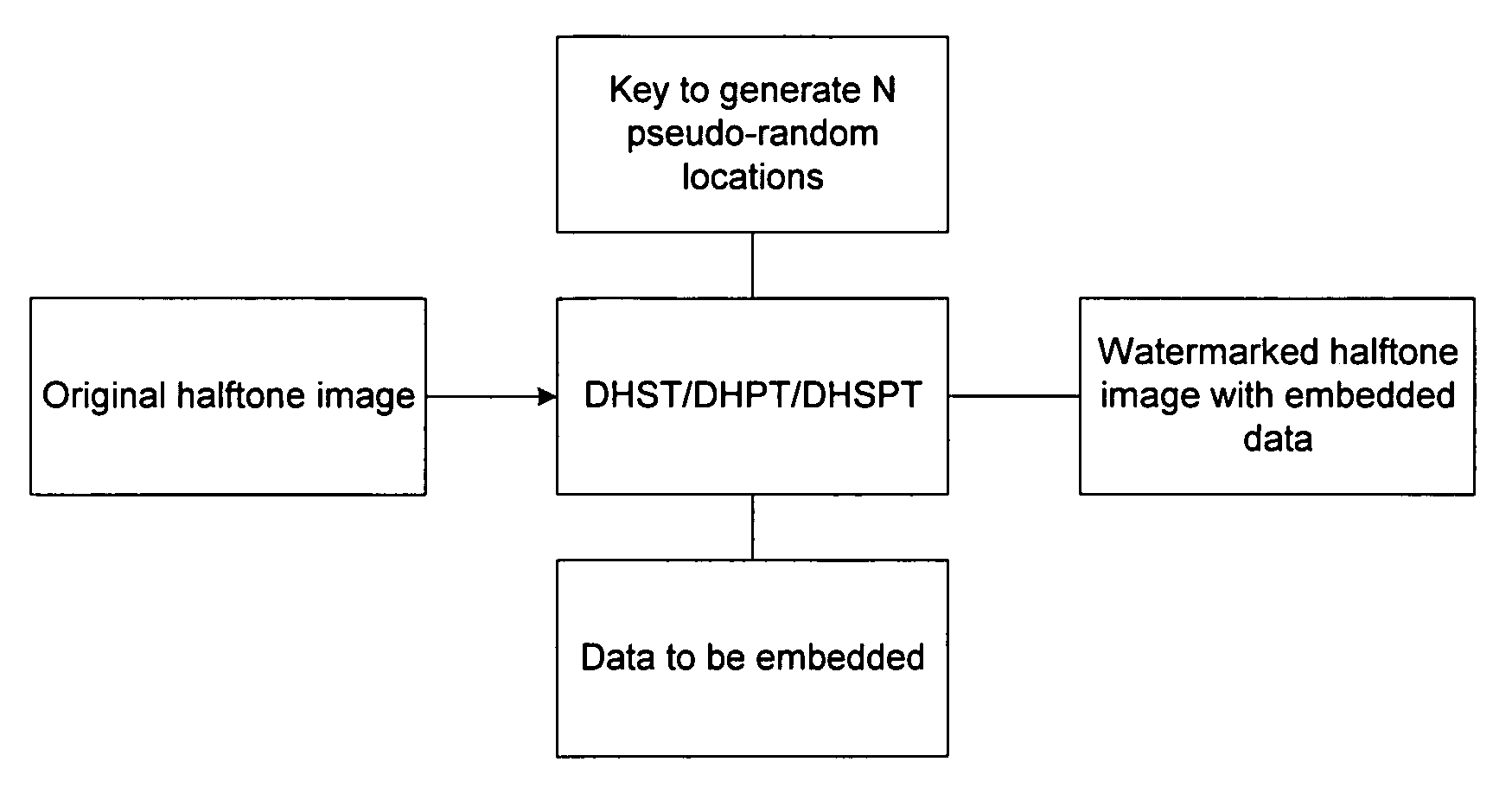
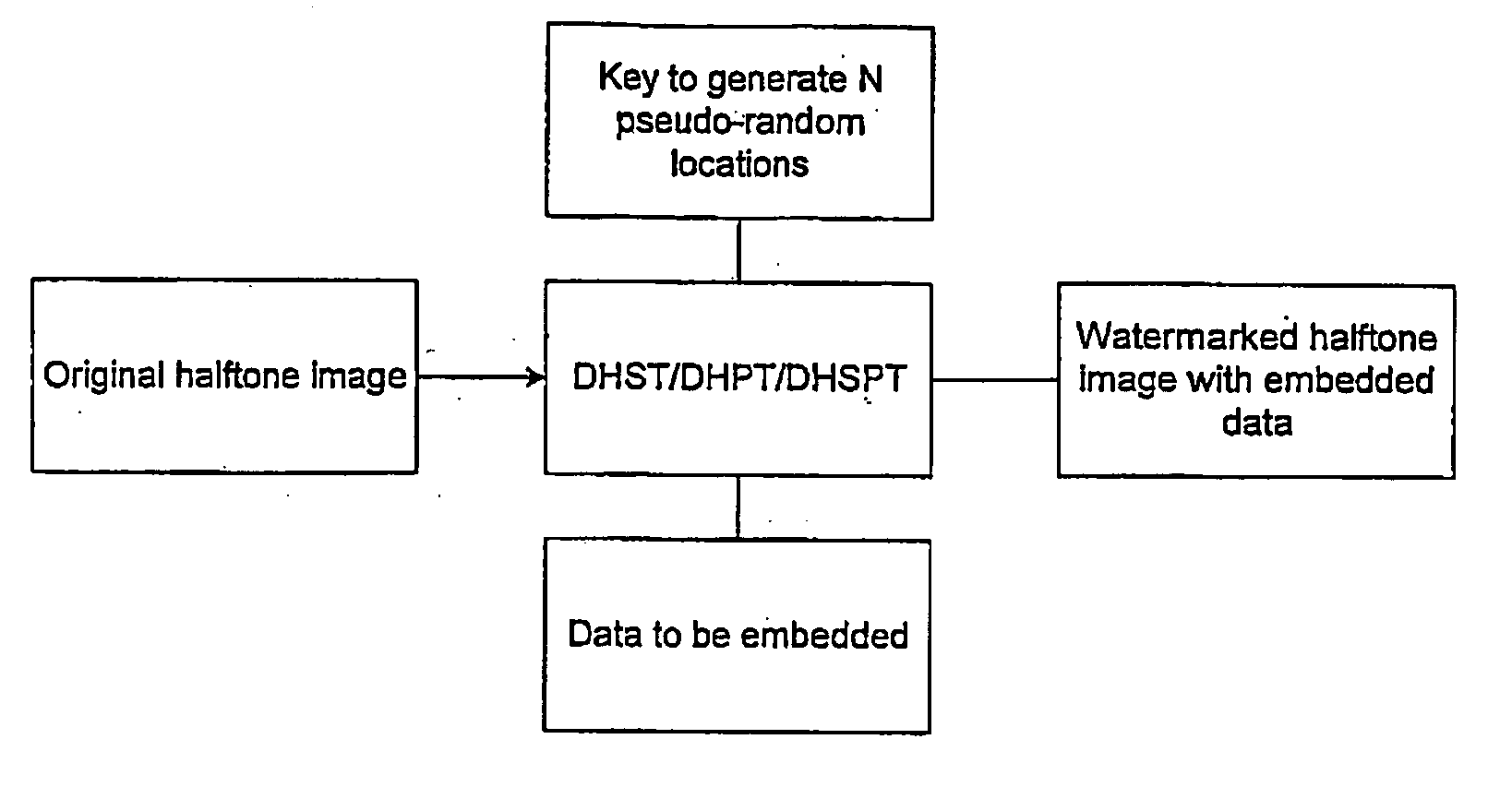
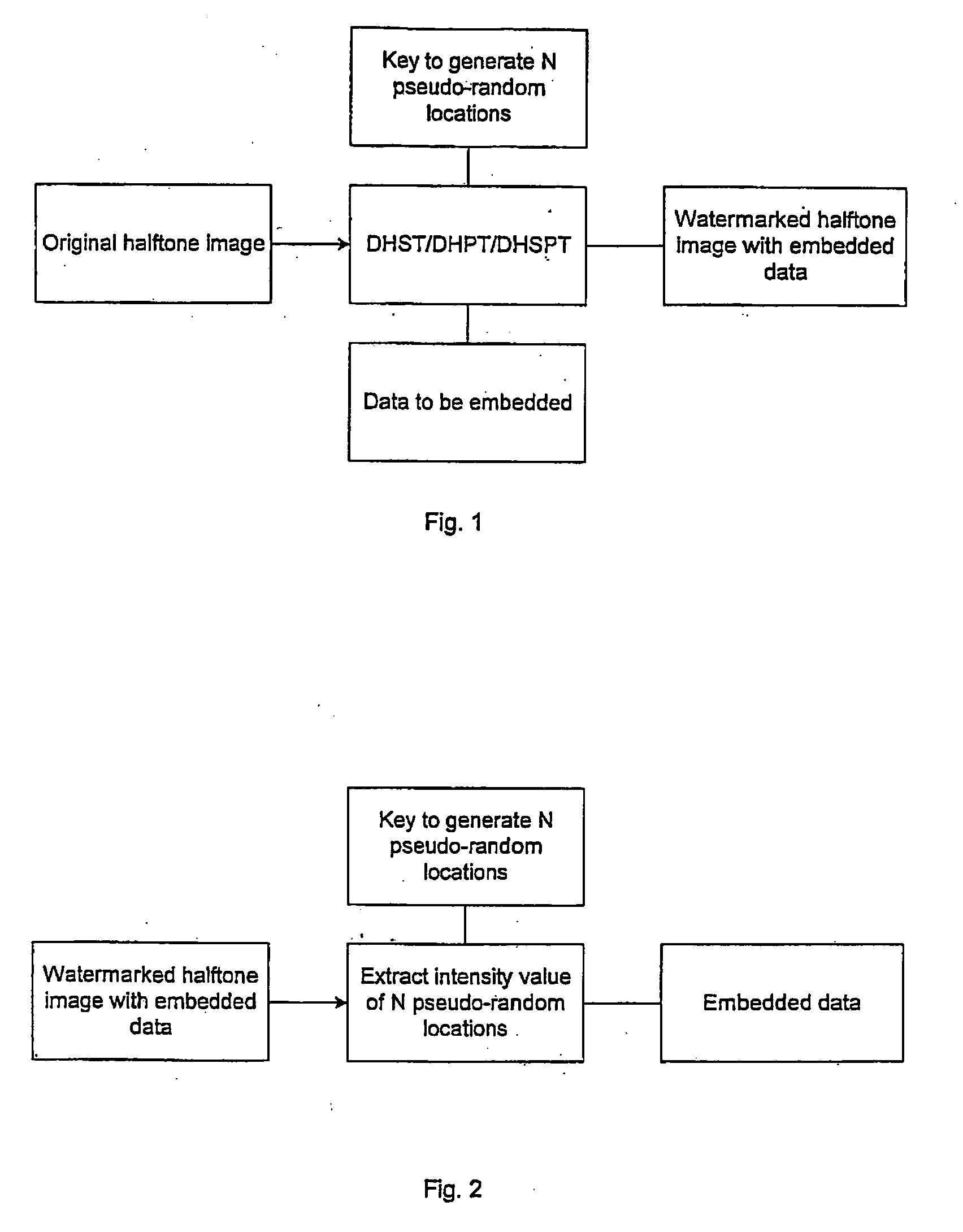
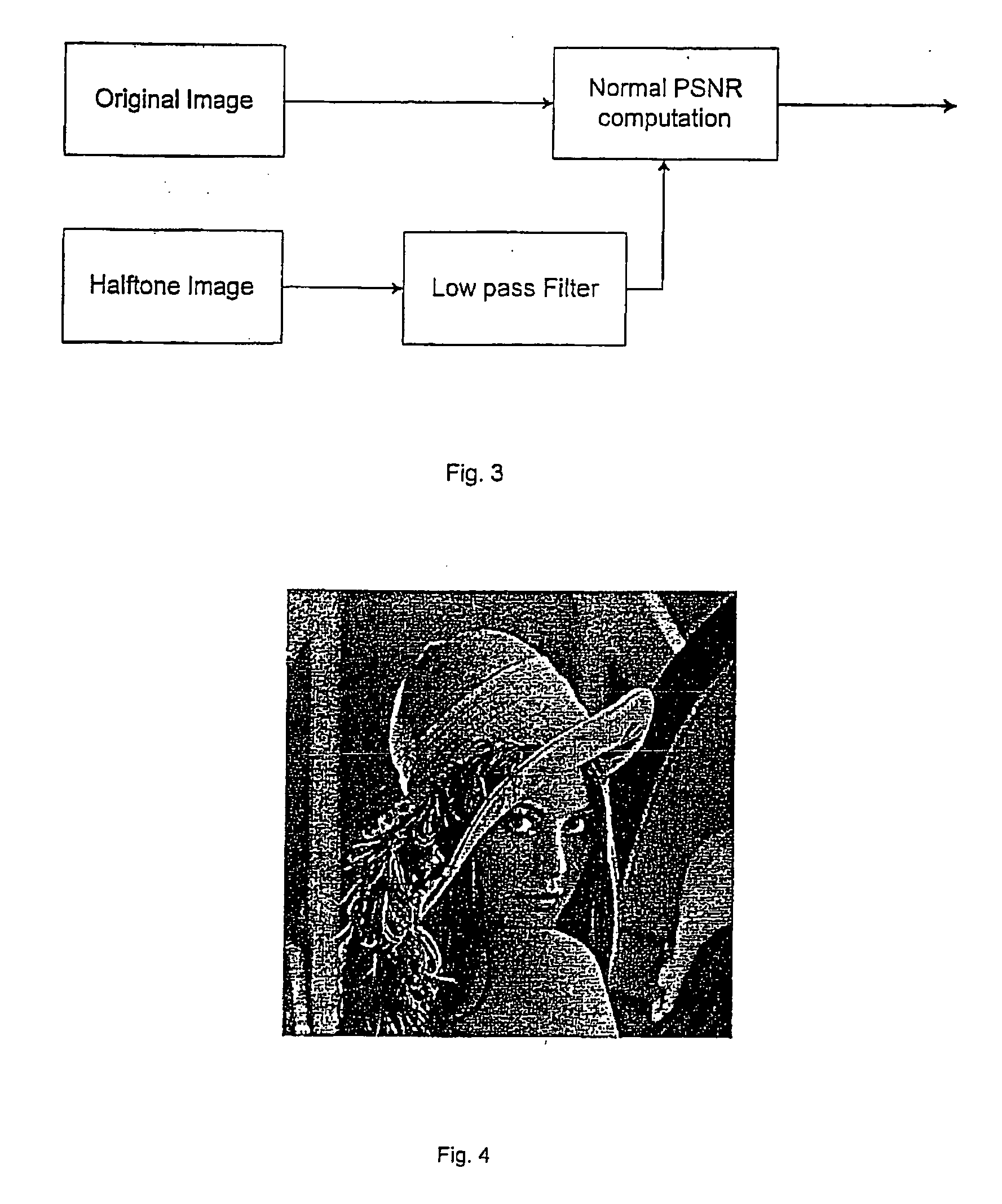
Methods and apparatus for hiding data in halftone images
InactiveUS7058199B1A large amountPreserving the local average intensityCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual presentationPattern recognitionHidden data
We propose methods for generating a halftone image, in which each pixel takes one of two tone values. The generated image contains hidden data, which is present at data storage pixels chosen using a pseudo-random number generator. In a first case, the data is hidden within an existing halftone image by reversing the tone value at certain of the data storage pixels, and at pixels neighboring the data storage pixels. In a second case, the halftone image is generated from a grey-scale image, and data is hidden during this conversion process.
Owner:SCI & TECH HONG KONG UNIV OF THE
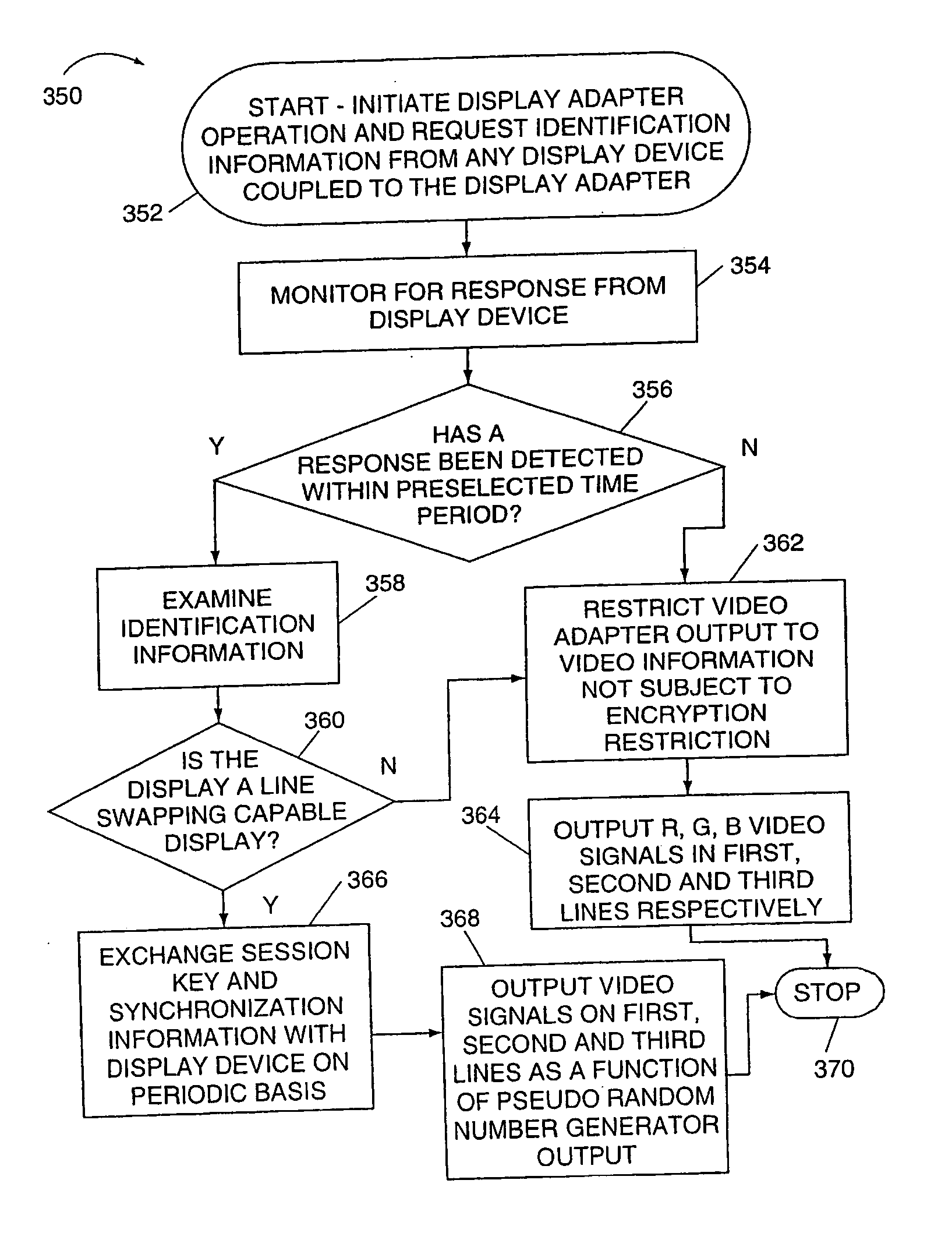
Methods and apparatus for protecting signals transmitted between a source and destination device over multiple signal lines
InactiveUS20050207577A1Improve protectionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDisplay deviceAnalog signal
Methods and apparatus for protecting copyrighted information, e.g., video signals, from unauthorized use are described. Encrypted video signals are transmitted from a source device, e.g., display adapter, to a display device, e.g., monitor, over analog signal lines after the identity of the destination device is confirmed by receipt of a certificate assigned to the destination device. A session key, used for encrypting the analog signals, is generated and exchanged between the source and destination devices. The source and destination devices each include a pseudo-random number generator driven by the session key. As part of the encryption process a false video signal is generated. The false video signal and R, G, B video signals are transmitted to the display device over four lines. The lines used to transmit the R, G, B and false video signals are periodically swapped as a function of the output of the pseudo random number generator to encrypt, e.g., scramble, the video signals. To avoid having to provide an additional line between the display adapter and the display device beyond those used in conventional displays, horizontal synchronization information is combined with, e.g., modulated on, one or more of the other signals transmitted to the display. The horizontal sync line is then used to convey one of the four video signals. The display device extracts the horizontal timing information from the received video signals and decrypts the signals using the output of its pseudo random number generator to reverse the scrambling process used to encrypt the transmitted video signals.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and circuit for generating random numbers, and computer program product therefor
ActiveUS20070140485A1Improve securityRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationRandom seedNumber generator
A random number generator uses the output of a true random generator to alter the behavior of a pseudo-random number generator. The alteration is performed by a mixing logic that builds a random seed for the pseudo-random number generator and includes a generator of an alteration signal, the generation of which exploits the random instant of arrival of the bits outgoing from the true random generator. The alteration signal is obtained by processing the seed by means of the pseudo-random sequence.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Methods and apparatus for generating authenticated error correcting codes
ActiveUS9496897B1Overcome problemsSecurity permitJoint error correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareBlock code
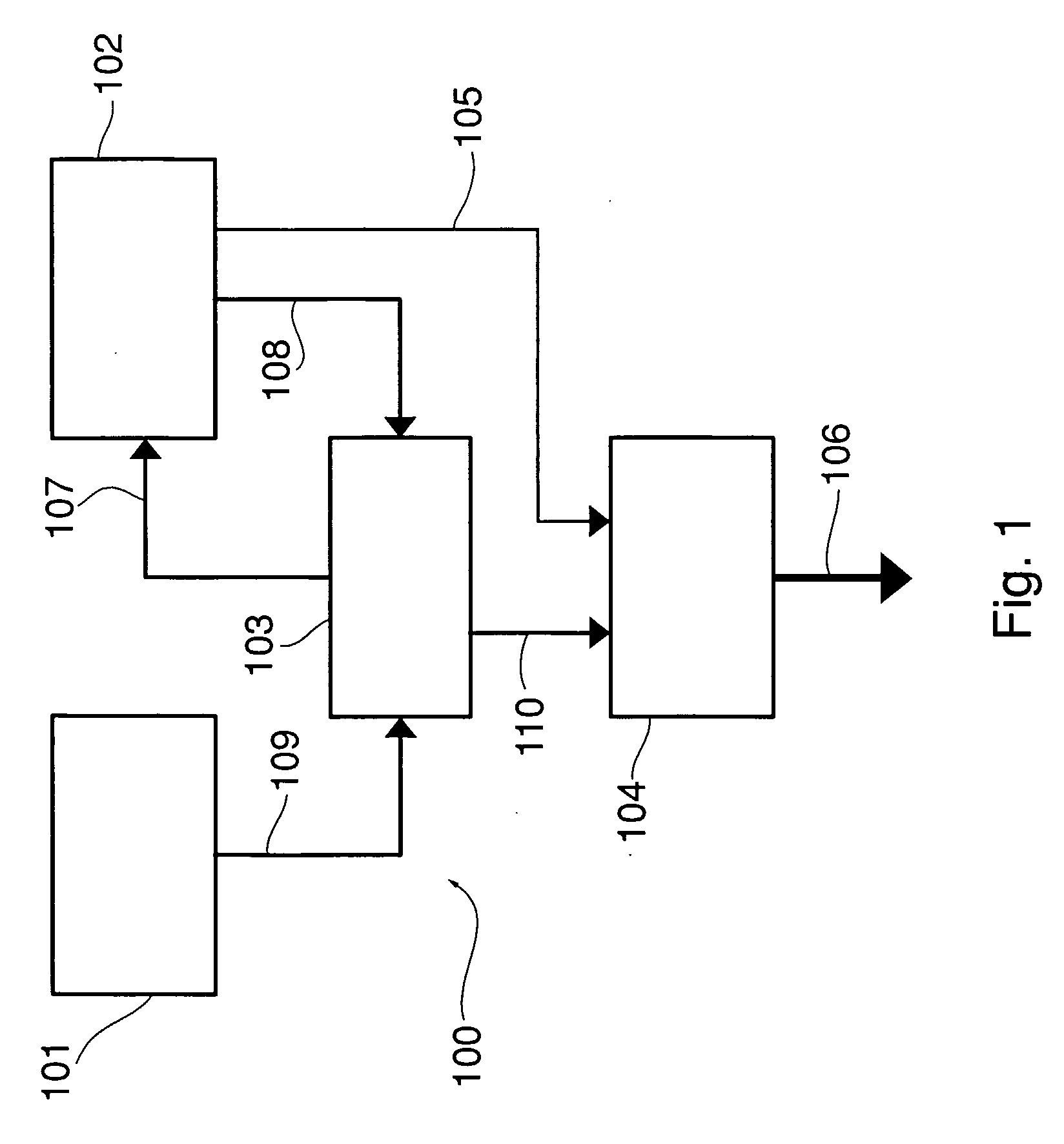
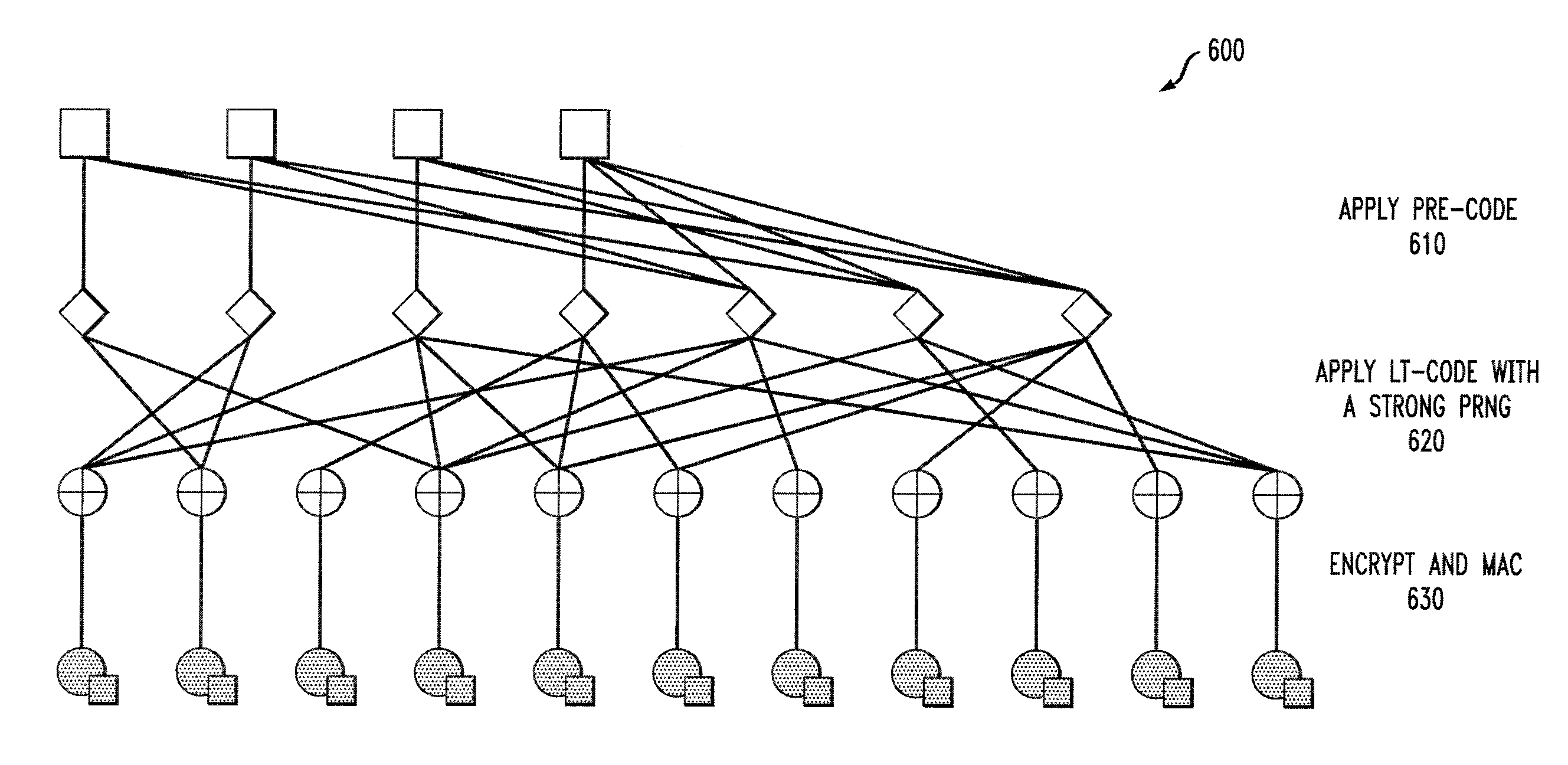
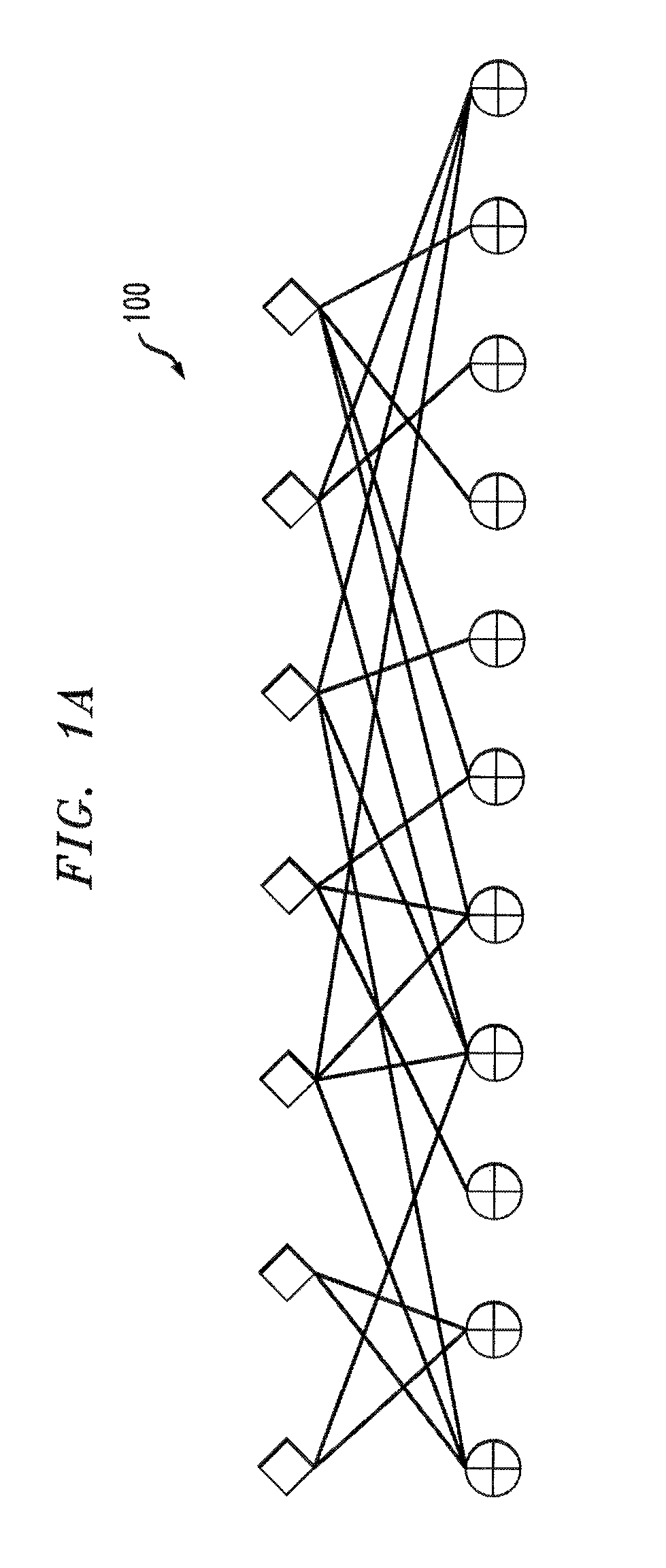
Methods and apparatus are provided for encoding and decoding via authenticated error correcting codes, such as secure LT codes, secure Raptor codes, block codes and / or rateless codes. Encoded symbols are generated via an authenticated error correcting code by applying a Luby Transform (LT) code to a plurality of message symbols to produce one or more intermediate symbols using a pseudo random number generator (PRNG) to select the plurality of message symbols to combine to produce the intermediate symbols; encrypting the intermediate symbols to produce encrypted symbols; computing an authentication value, such as a message authentication code (MAC), over one or more of the one or more encrypted symbols; and appending the authentication value to the corresponding encrypted symbols to form the encoded symbols. Block scalable and random scalable constructions are also provided, as well as decoding techniques for all of the constructions.
Owner:EMC CORP
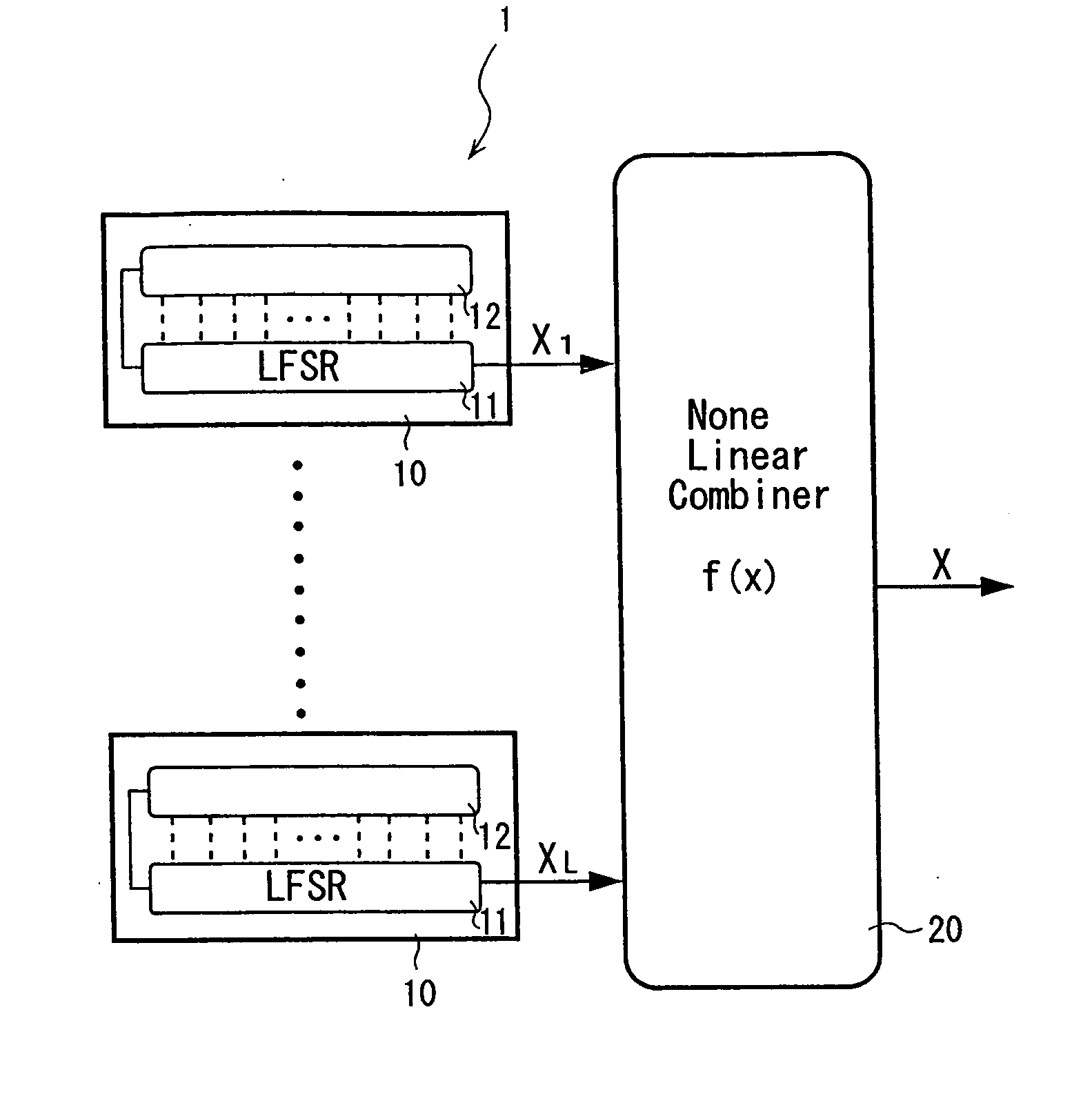
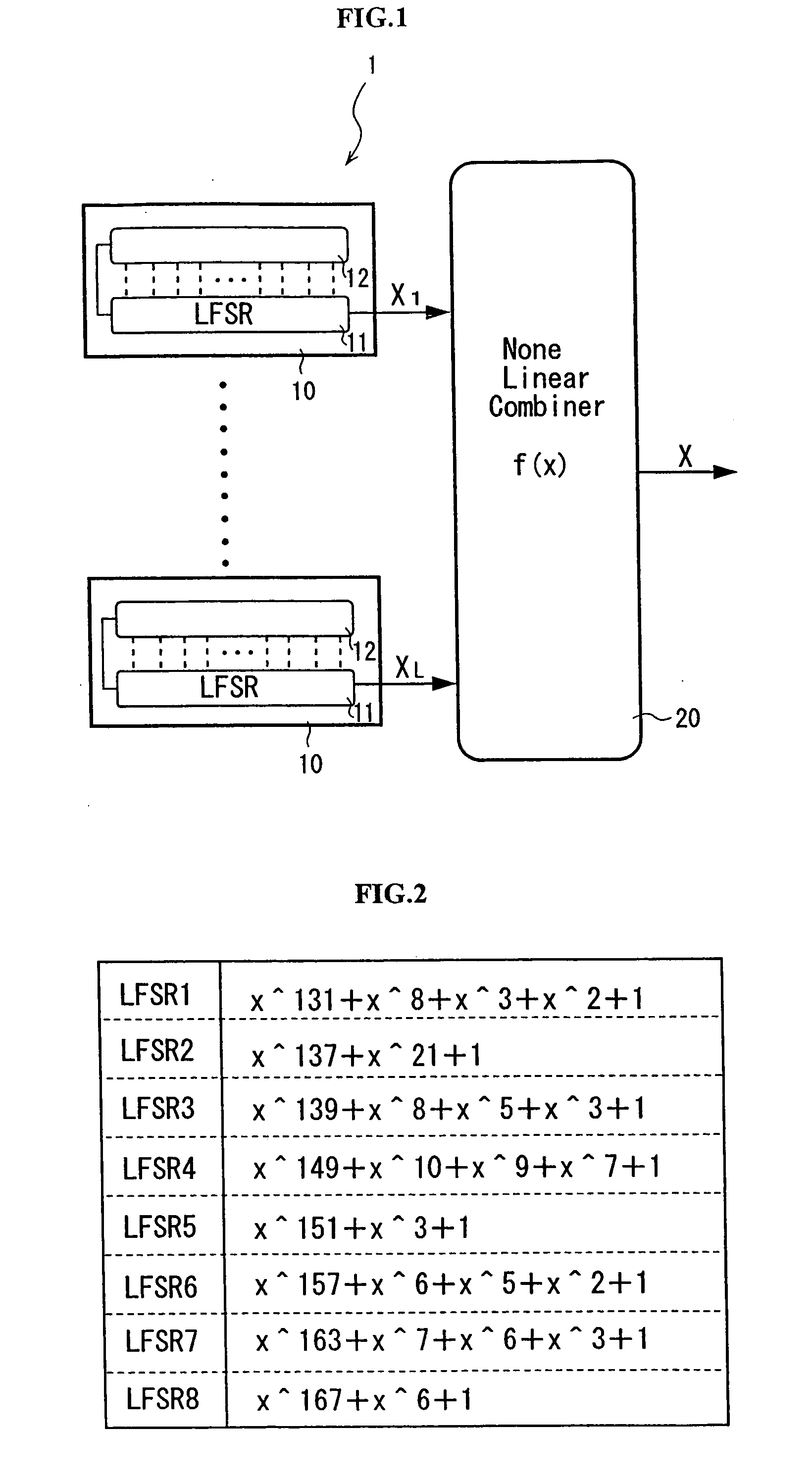
Pseudorandom number generator for a stream cipher
ActiveUS20050120065A1Random number generatorsSecuring communicationStream cipherPseudorandom generator
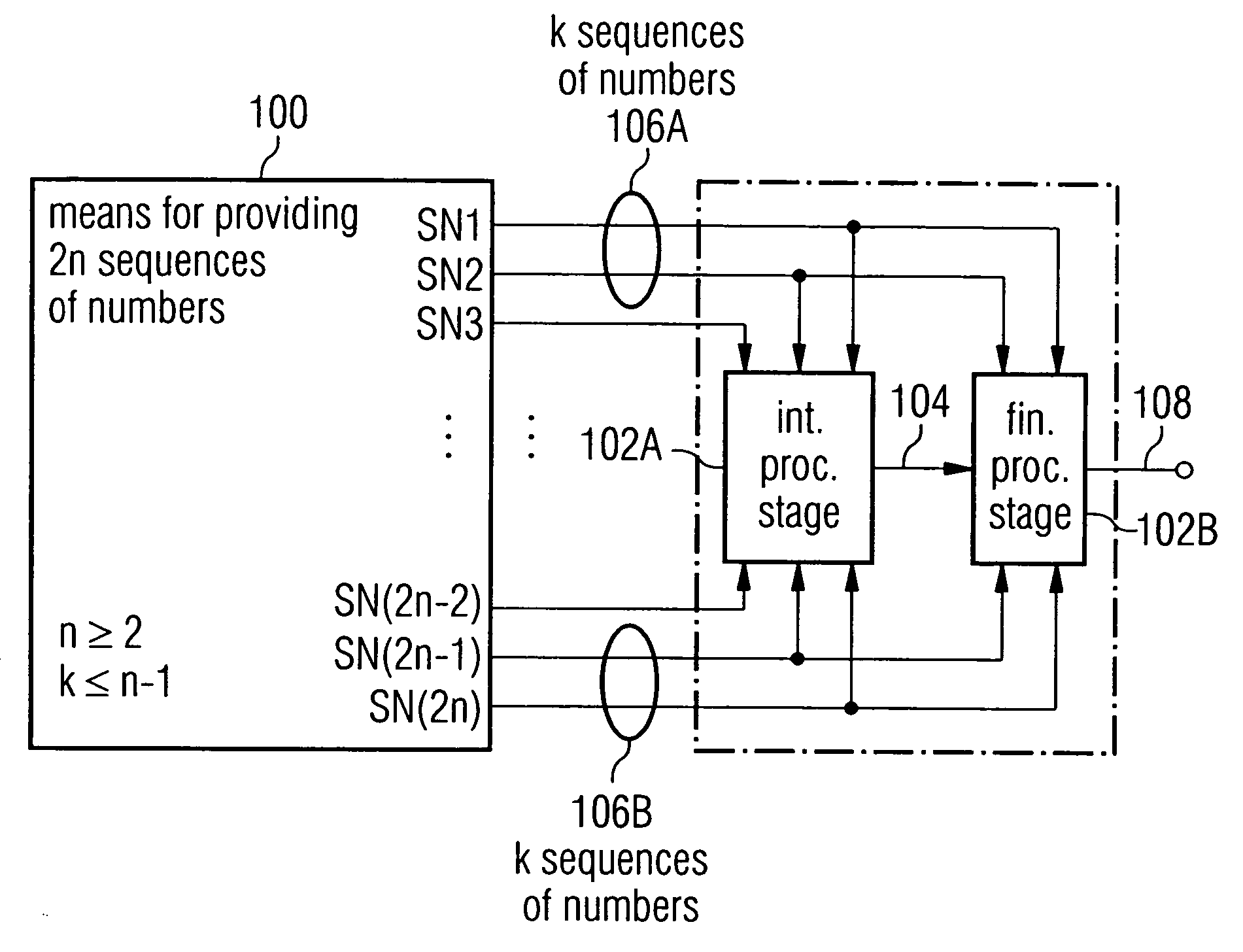
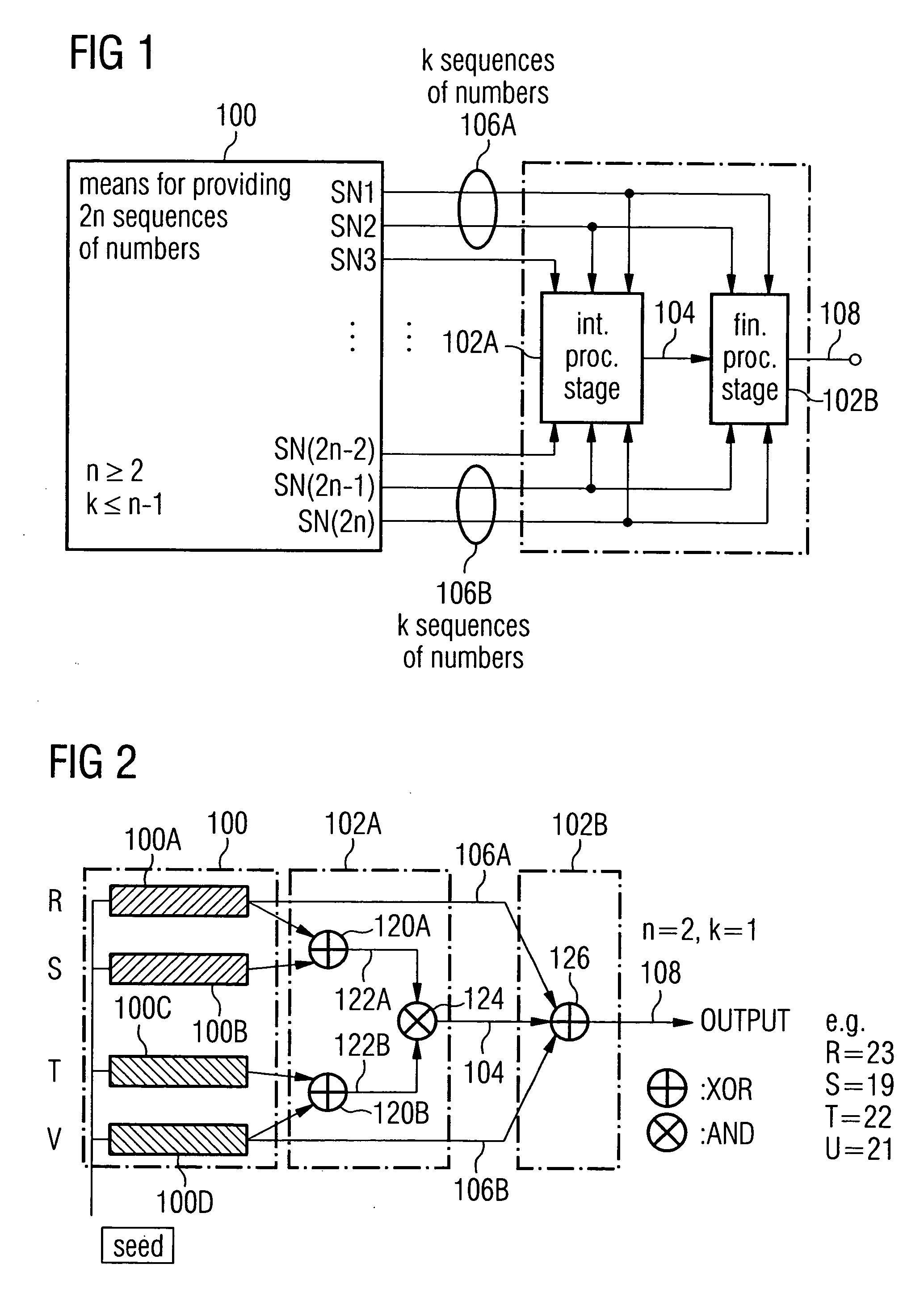
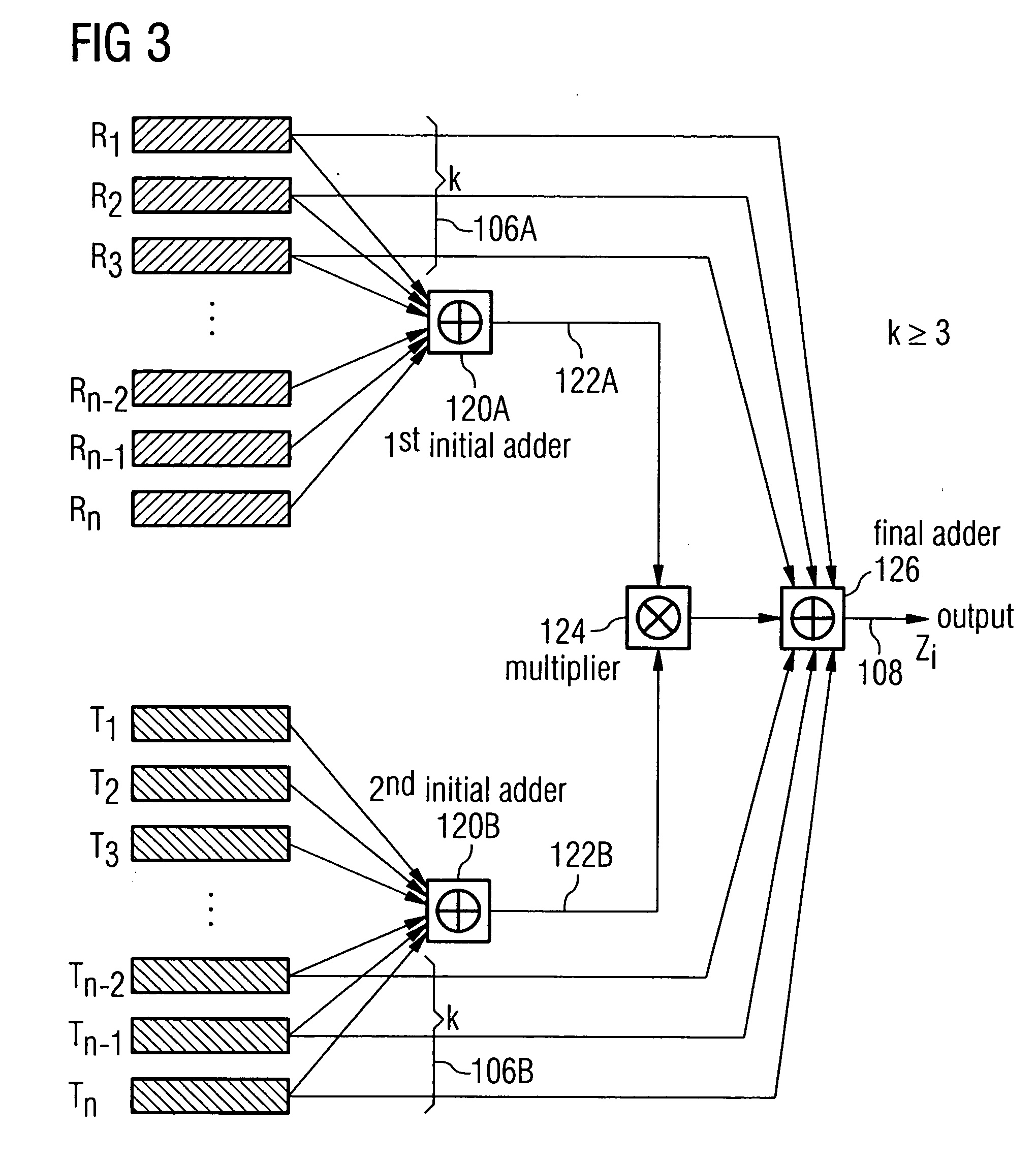
A pseudorandom number generator includes a unit for providing a number of 2n sequences of numbers, n being greater than or equal to 2. The sequences of numbers are combined by a unit such that at first all the sequences of numbers are combined with one another in an intermediate processing stage to obtain an intermediate processing sequence, and that subsequently a subgroup of k sequences of numbers is combined with the intermediate processing sequence in a final processing stage to obtain the output sequence.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Hardware device for genetic algorithms
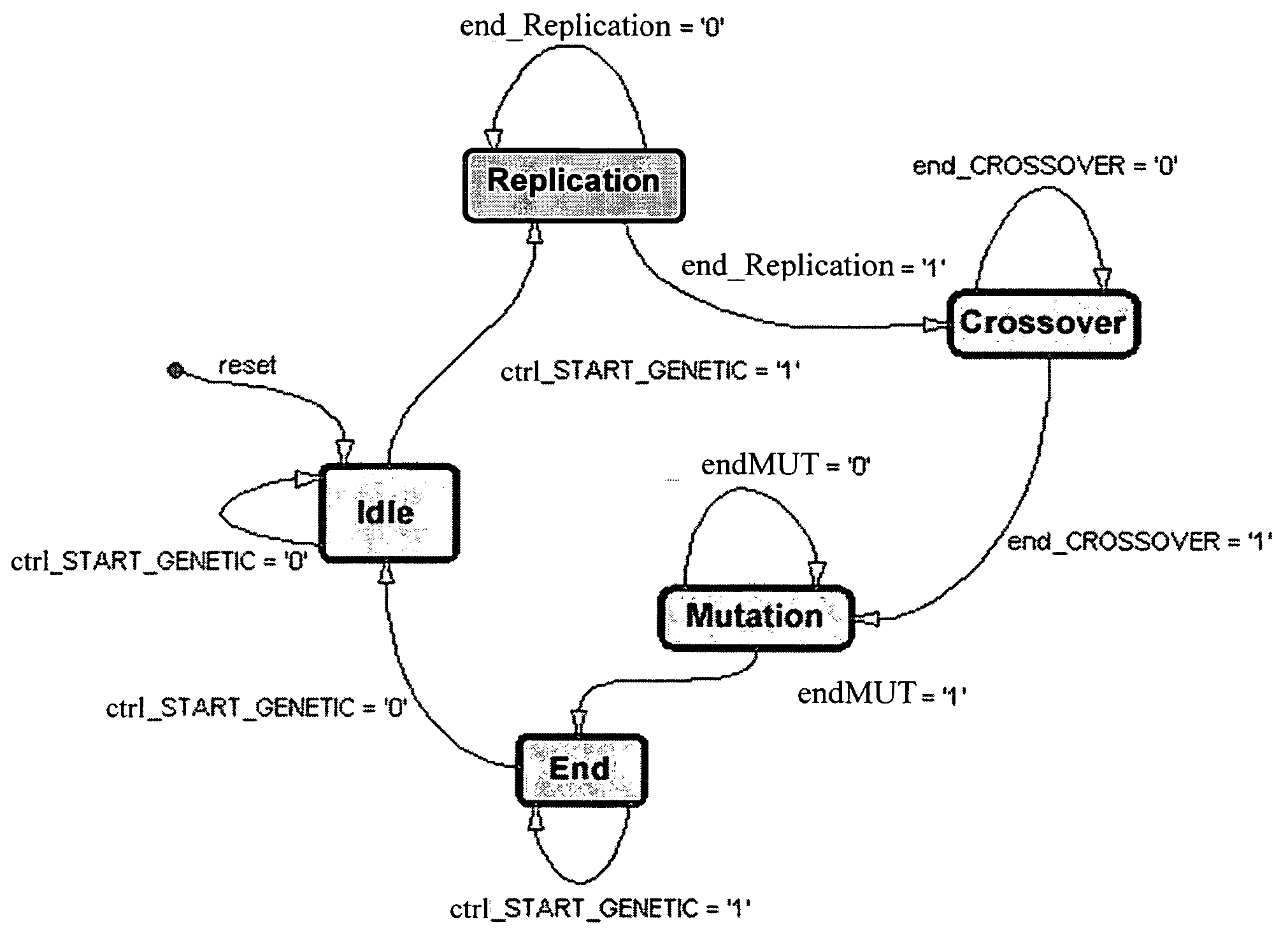
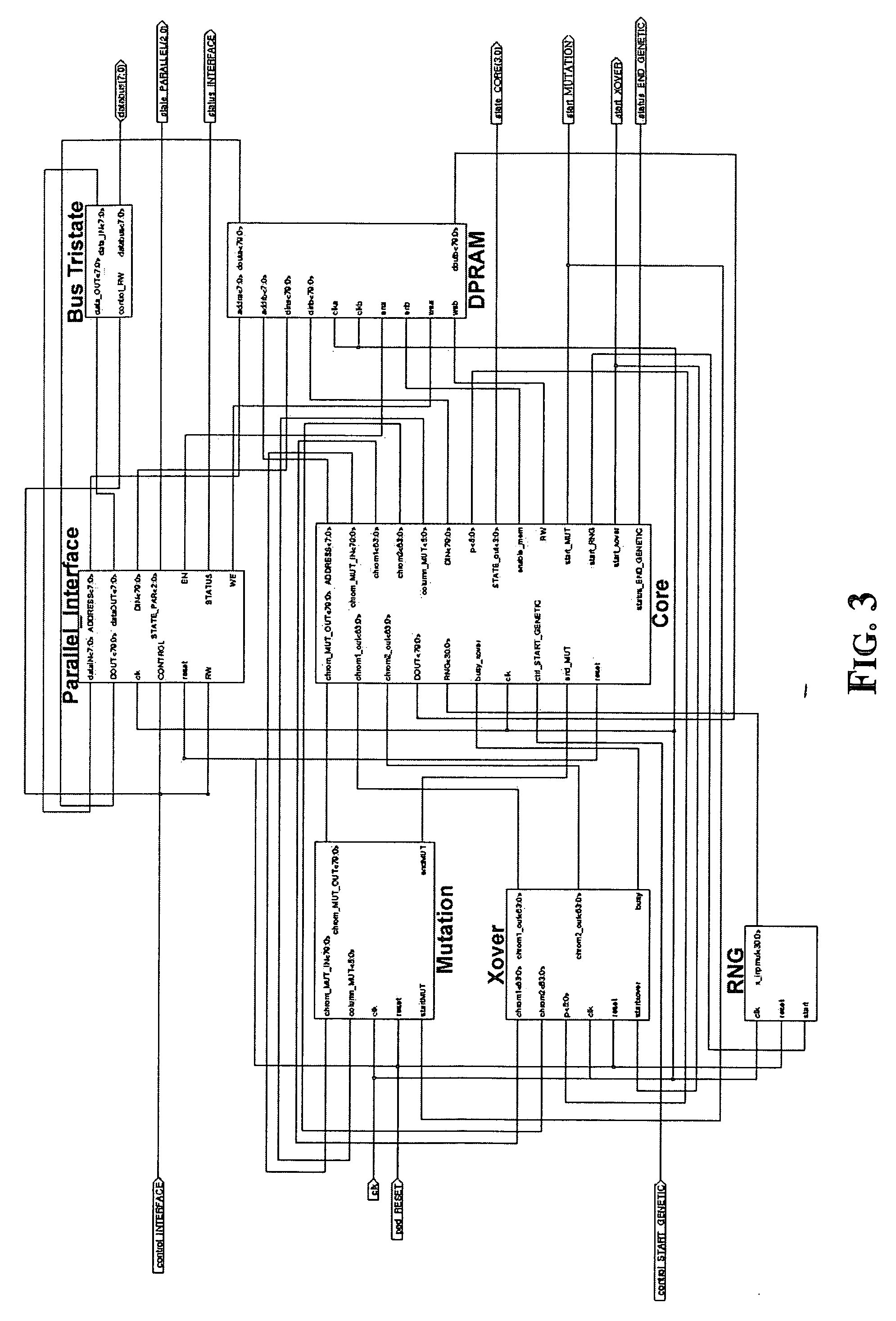
A hardware device is for performing crossover and mutation operations based upon a genetic algorithm. The hardware device may include a random or pseudo-random number generator, and a crossover block, conditioned with a random crossover index, for generating output crossover bit-strings from current bit-strings. The device may also include a mutation block, conditioned with a random mutation index, for generating output bit-strings by switching at least one bit of each input bit-string pointed to by the mutation index. A memory may temporarily store the current bit-strings and the output bit-strings. In addition, the hardware device may include a control unit, interfaced with the random number generator, the crossover block, the mutation block and the memory and managing their functioning by generating respective control signals therefor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
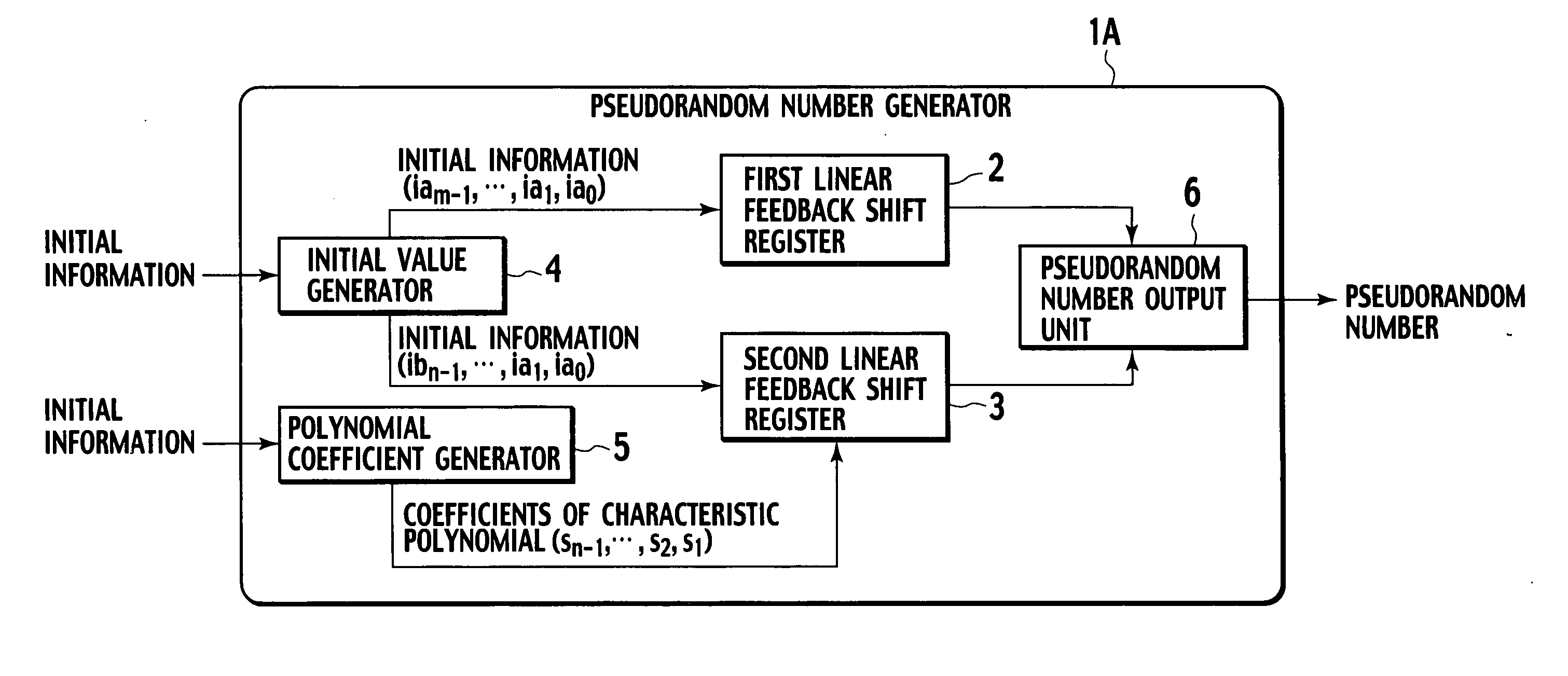
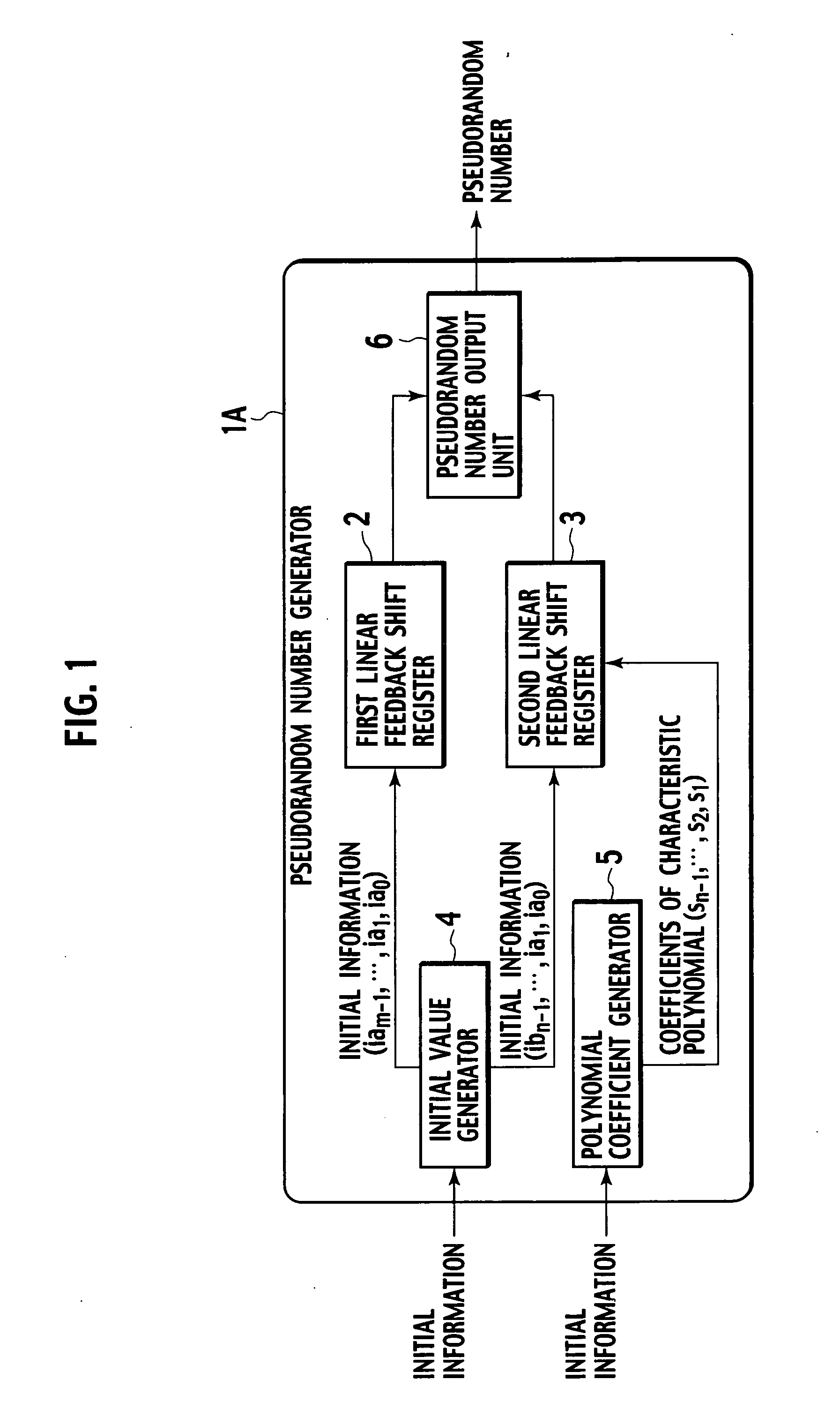
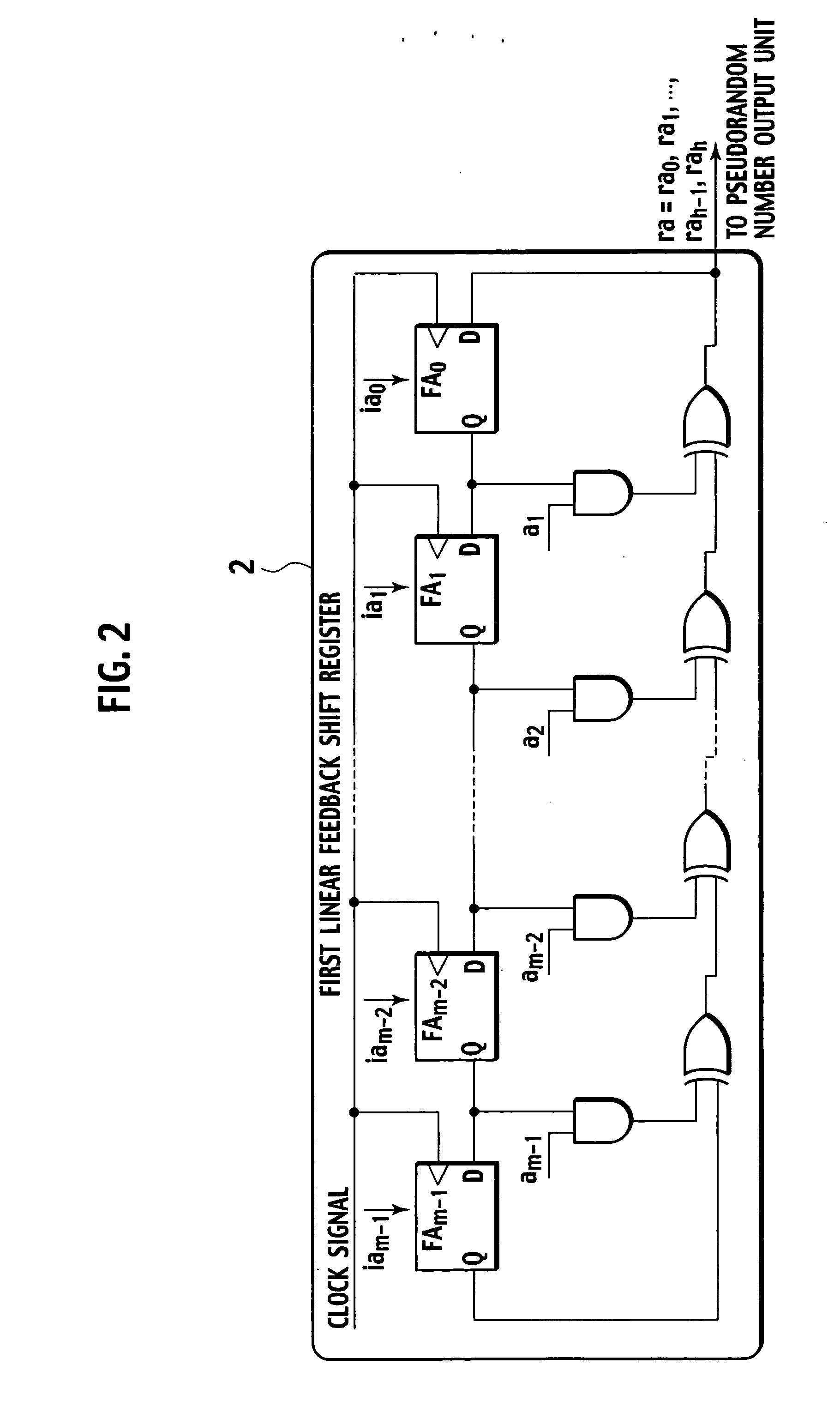
Pseudorandom number generator and pseudorandom number generation program
A pseudorandom number generator (1) has a first linear feedback shift register (2), a second linear feedback shift register (3), an initial value generator (4), a polynomial coefficient generator (5), and a pseudorandom number output unit (6). The initial value generator (4) generates initial values and supplies the same to the first linear feedback shift register (2) and second linear feedback shift register (3). The polynomial coefficient generator (5) generates coefficients of a characteristic polynomial and supplies the same to the second linear feedback shift register (3). The pseudorandom number output unit (6) carries out exclusive-OR operations on bits sequentially provided by the first linear feedback shift register (2) and second linear feedback shift register (3), generates a pseudorandom number sequence, and outputs the same.
Owner:VICTOR CO OF JAPAN LTD
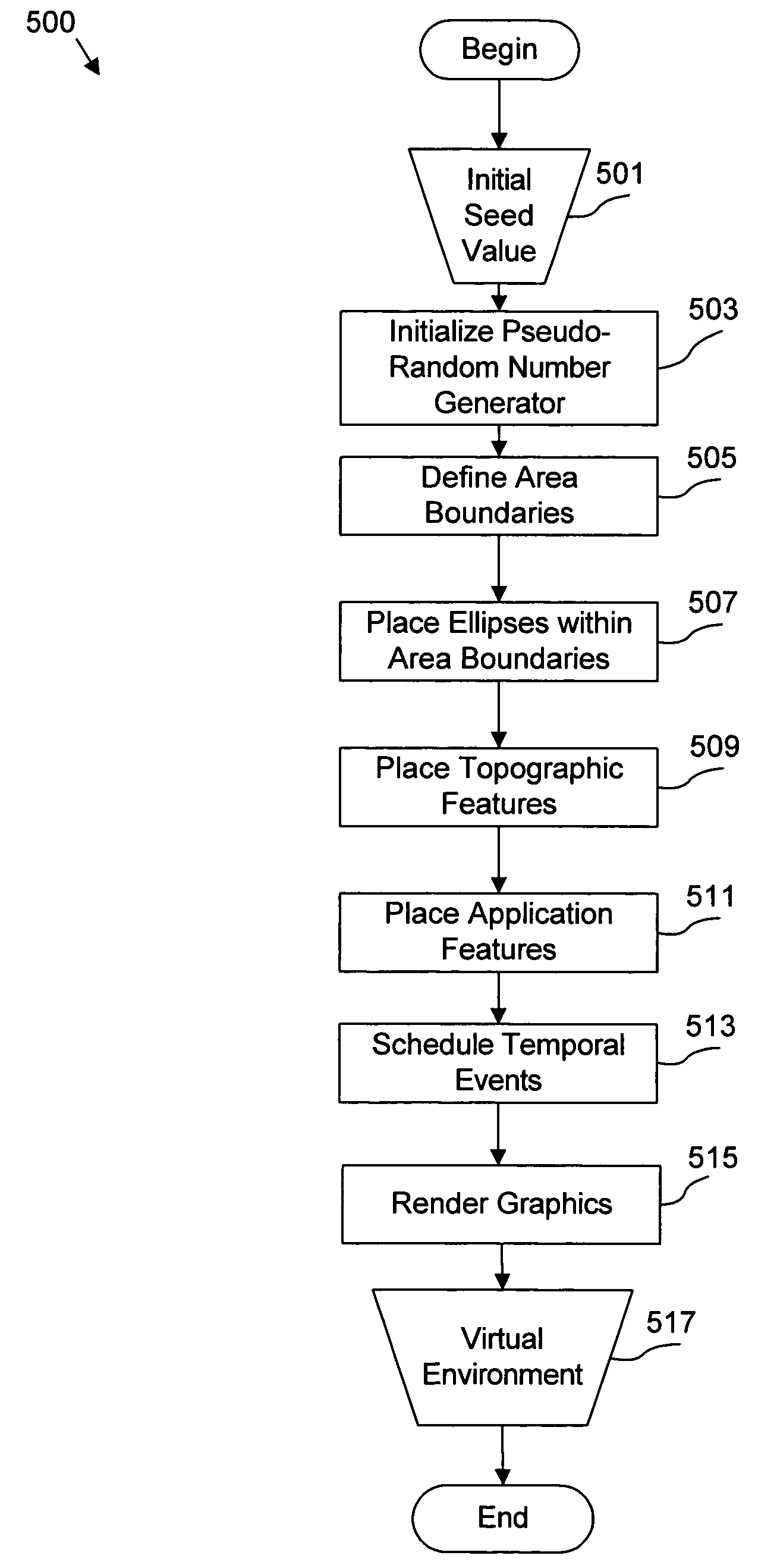
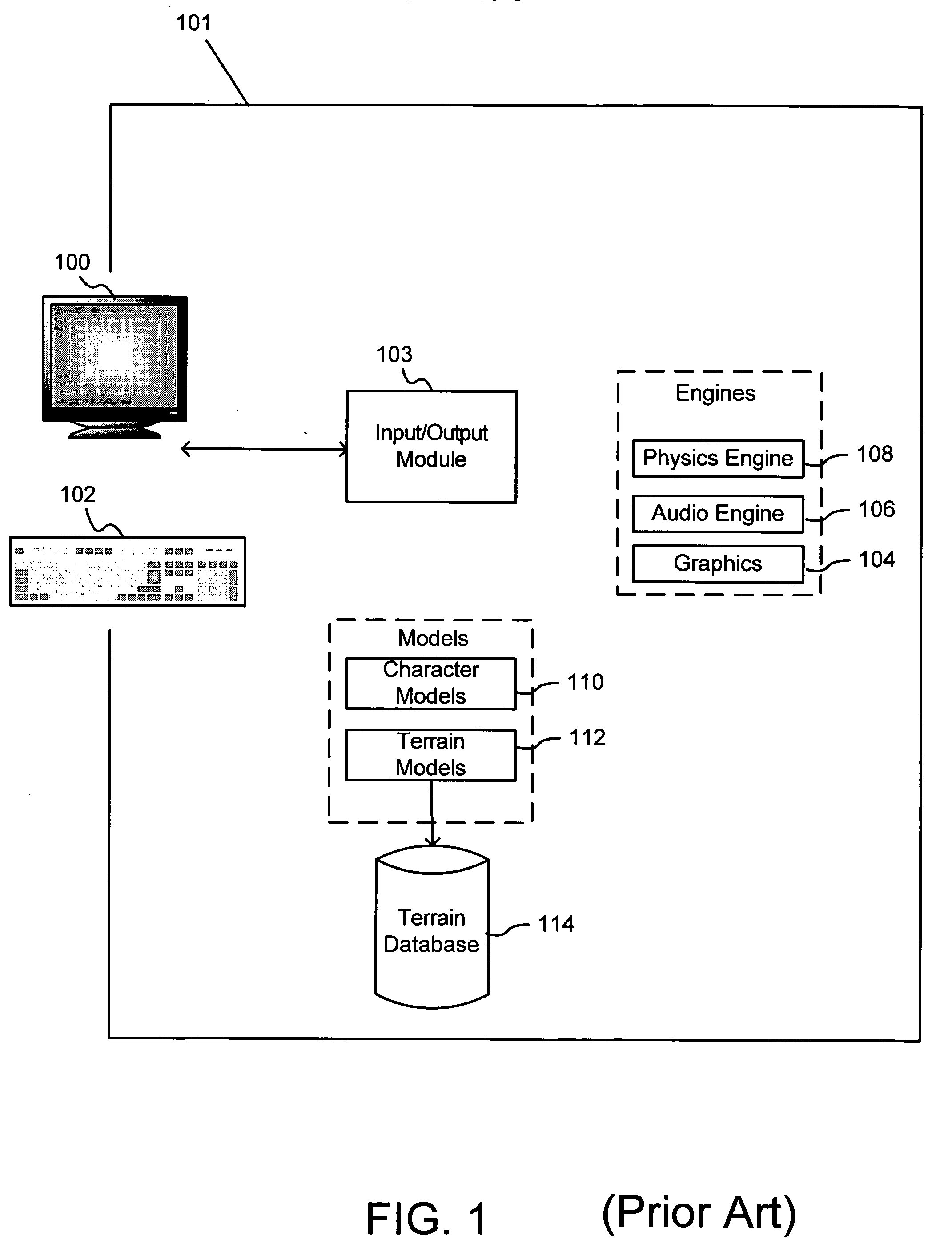
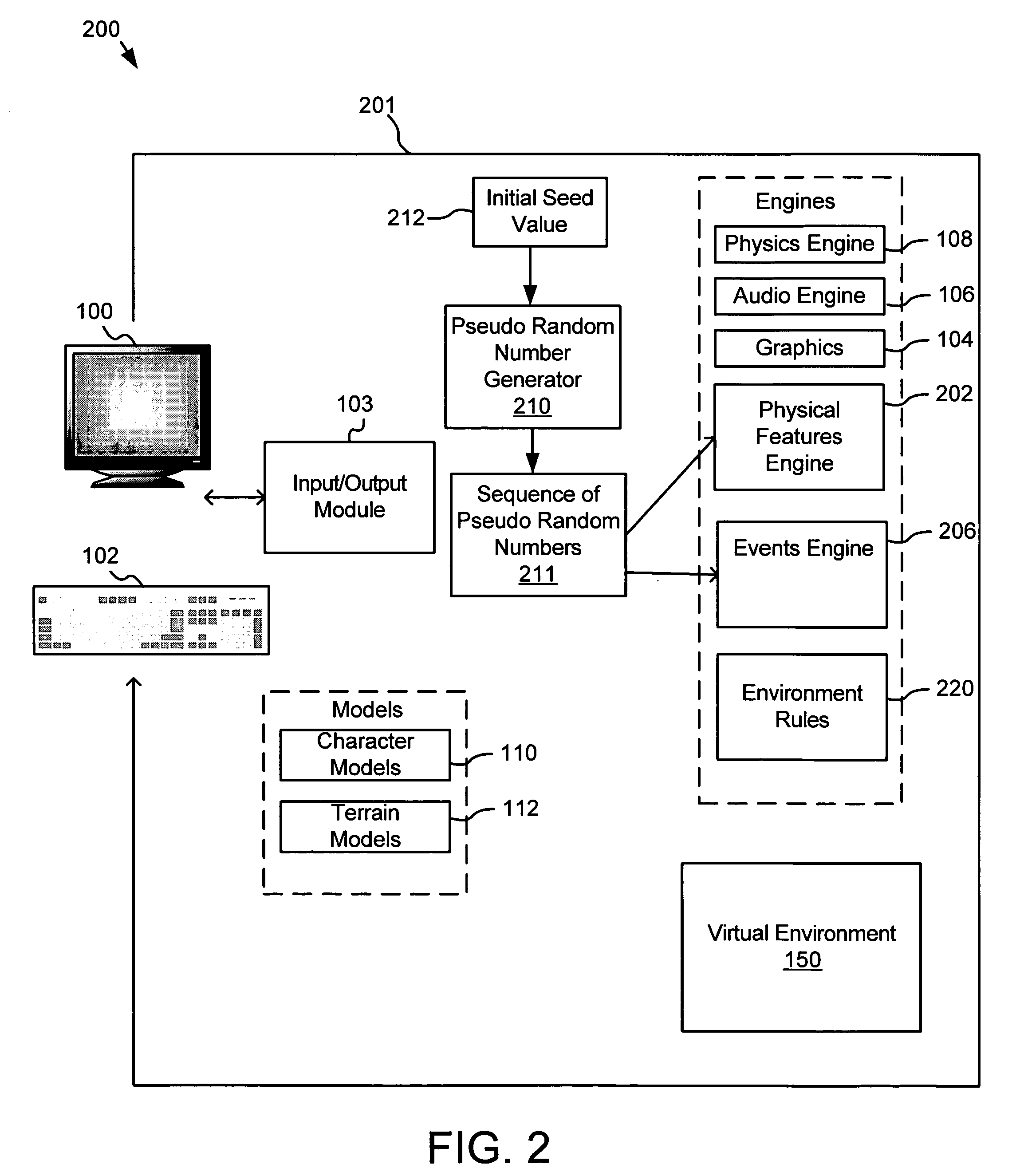
Apparatus, system, and method for automated generation of a virtual environment for software applications
InactiveUS20060030405A1Video gamesSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringAdemetionine
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for generating a reproducible virtual environment in a computer software program. This invention describes a method of generating a realistic virtual environment dependent on a sequence of pseudo-random numbers generated by a pseudo-random number generator initialized by a seed value that may be created by the user. If a user starts with the same initial seed, the same virtual environment is created each time the program is run. However, if a new seed is used, a new virtual environment will be created.
Owner:ROBERTSON ALAN
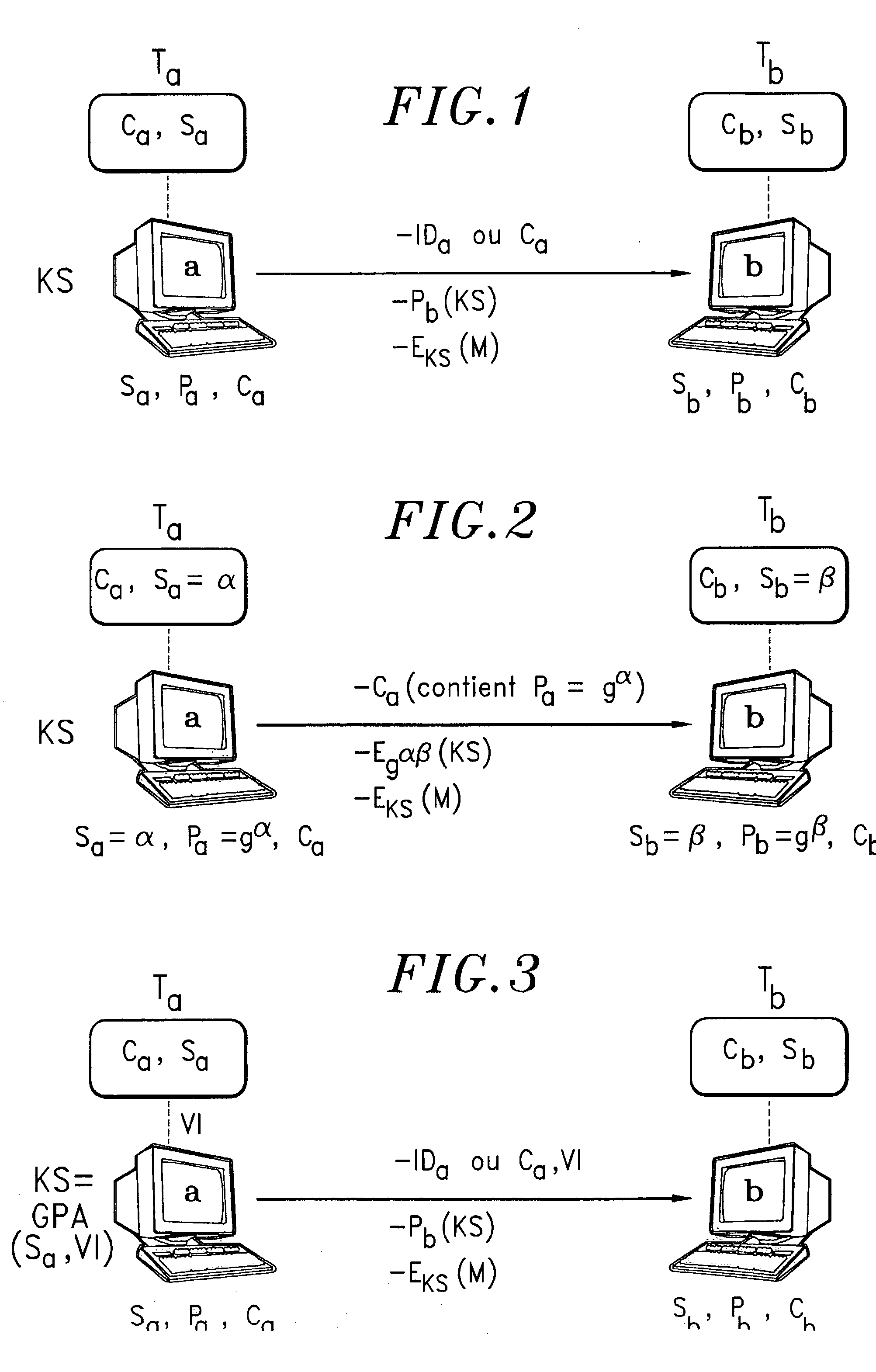
Communication method with encryption key escrow and recovery
InactiveUS20030012387A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageInternet privacySecret code
Communication process with key encryption escrow and recovery systems. The entity participating in a communication session generates a session key (SK) through a pseudorandom generator that is initiated by the entity's secret key and an initial value (IV). The session key codes the message. The escrow authority that files the secret code may recover the message and the initial value (IV). Application to secure communication systems.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Methods and apparatus for hiding data in halftone images
InactiveUS20060034483A1Preserving local average intensityBig amount of dataCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionHidden data
We propose methods for generating a halftone image, in which each pixel takes one of two tone values. The generated image contains hidden data, which is present at data storage pixels chosen using a pseudo-random number generator. In a first case, the data is hidden within an existing halftone image by reversing the tone value at certain of the data storage pixels, and at pixels neighbouring the data storage pixels. In a second case, the halftone image is generated from a grey-scale image, and data is hidden during this conversion process.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
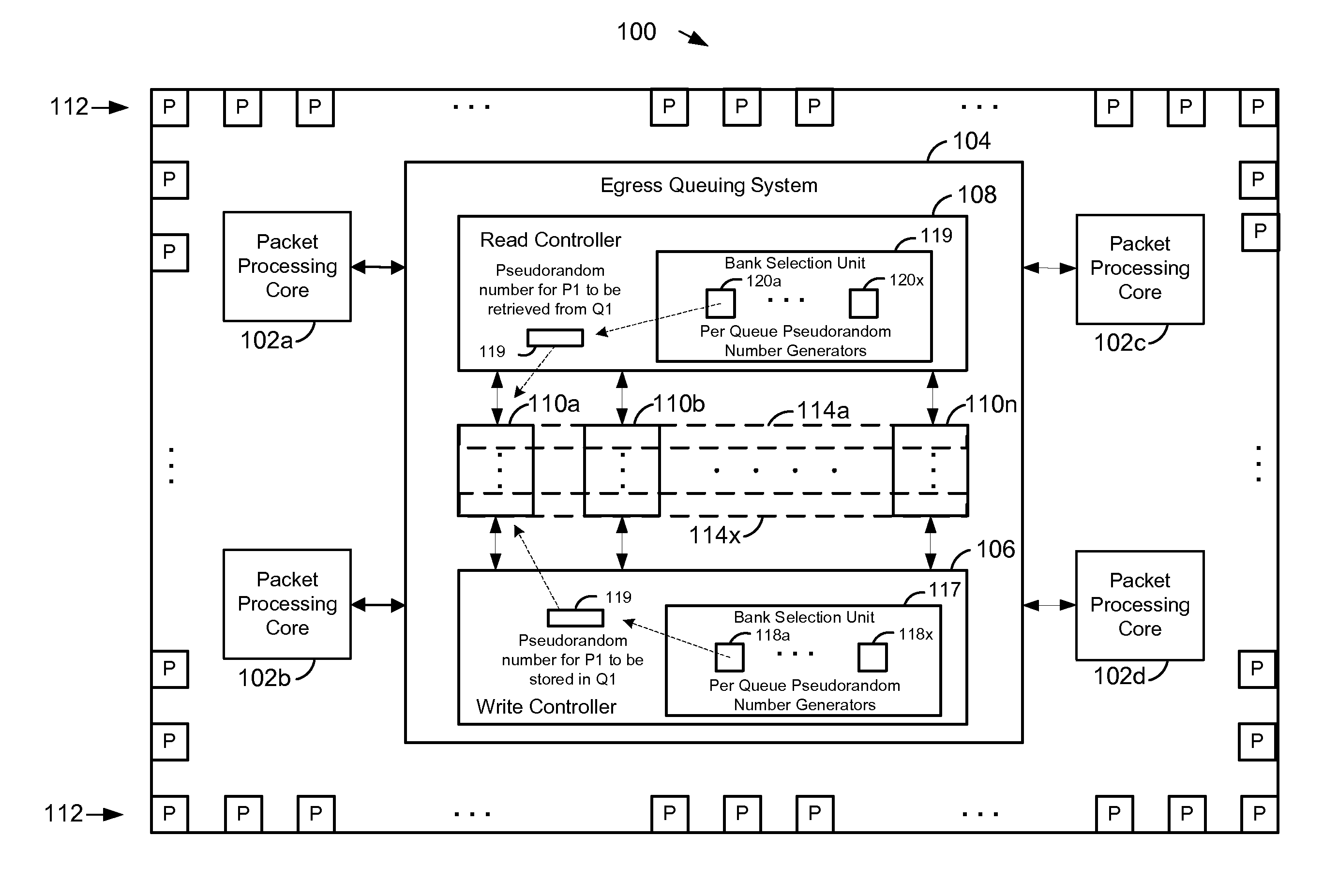
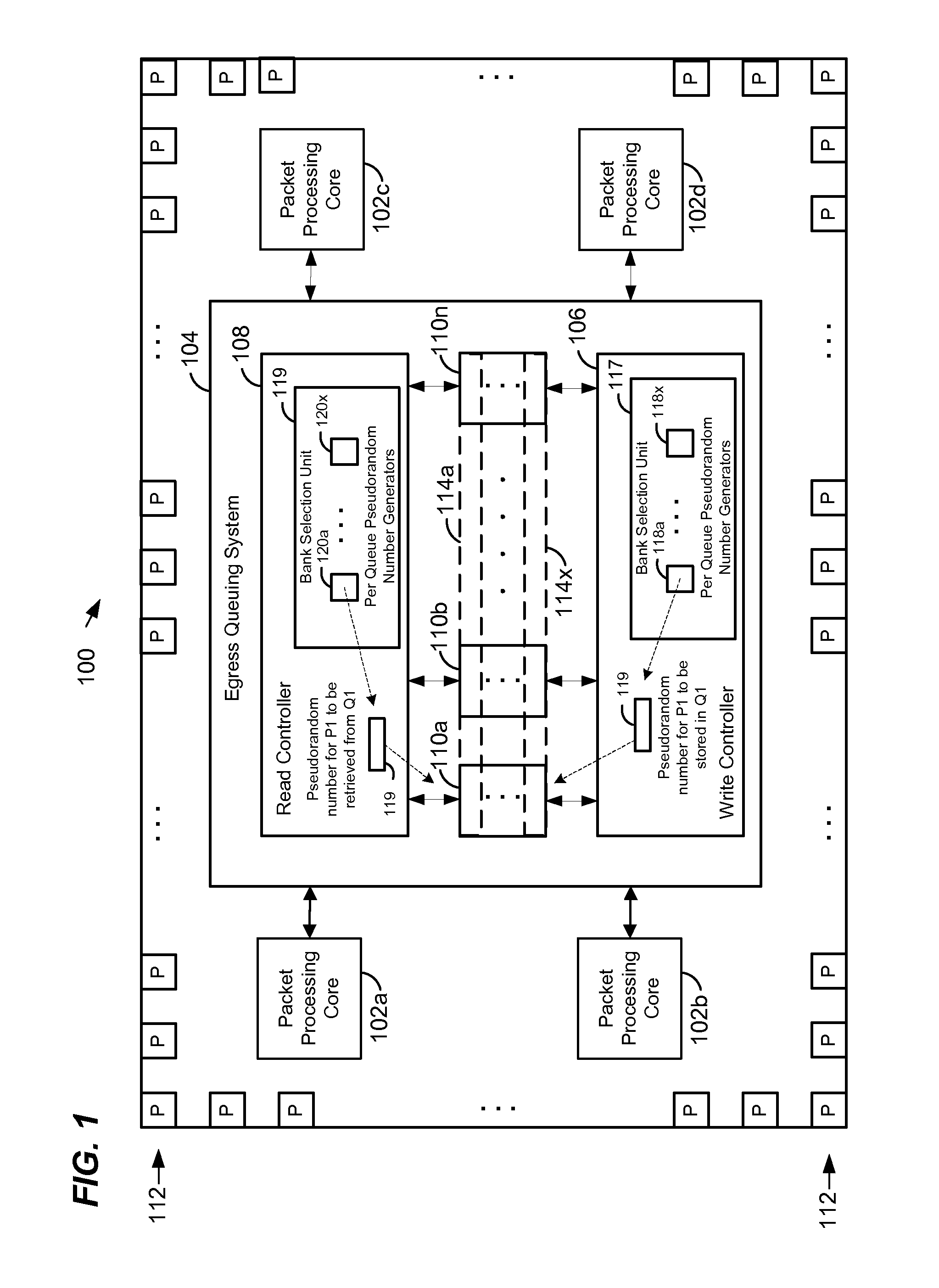
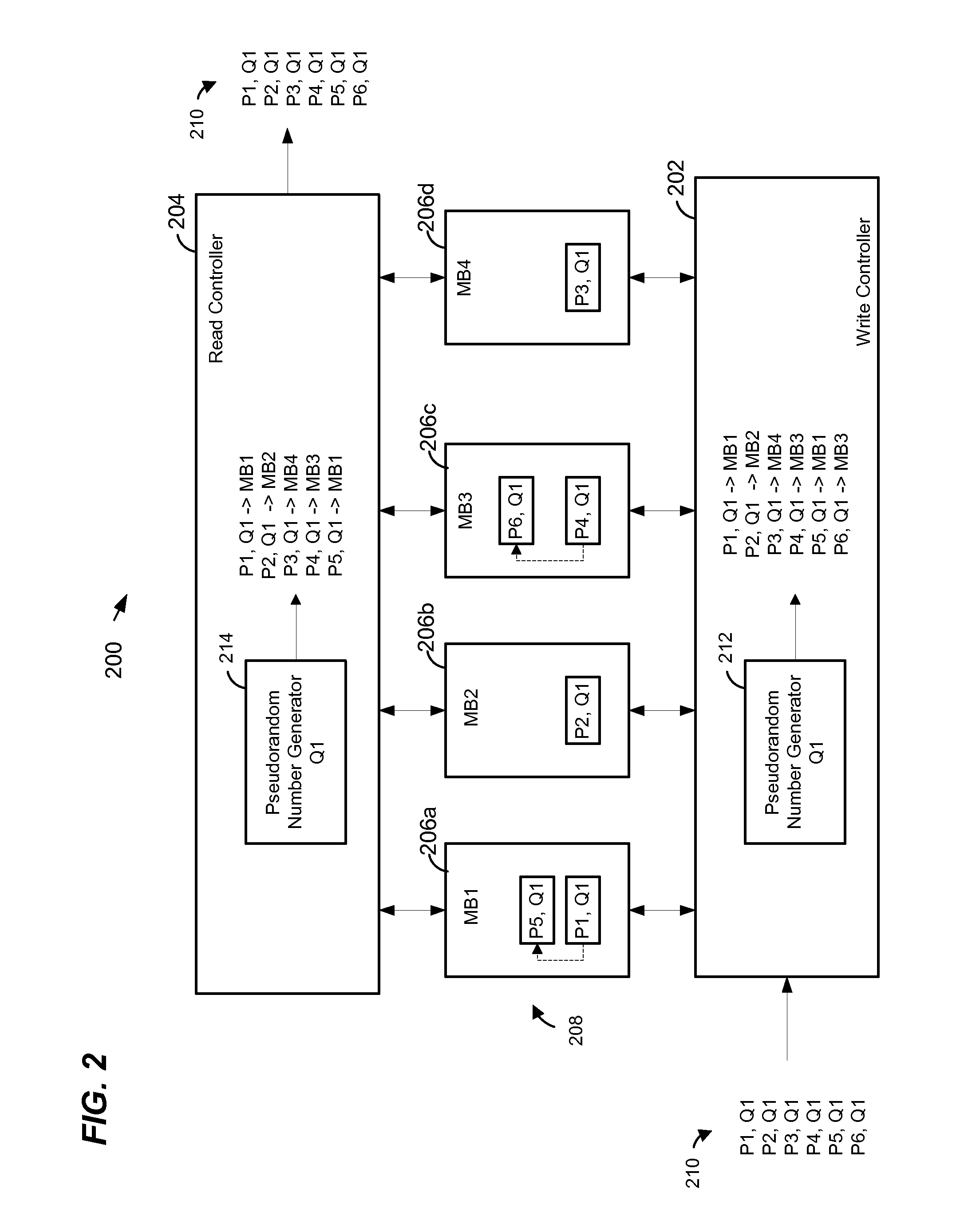
Multibank egress queuing system in a network device
ActiveUS9306876B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsMemory bankNetwork Access Device
In a method of managing queues in an egress queuing system in a network device, a plurality of packets to be stored in a first egress queue are received. The first egress queue is distributed among a plurality of memory banks. The packets are distributed among the plurality of memory banks. Memory banks in which to store the packets are selected based on pseudorandom numbers generated for the packets. The pseudorandom numbers are generated using a first pseudorandom number generator initialized with a first seed. Subsequently, the packets are retrieved from the plurality of memory banks. Memory banks from which to retrieve the packets are selected based on pseudorandom numbers regenerated for the packets. The pseudorandom numbers are regenerated using a second pseudorandom number generator initialized with the first seed.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
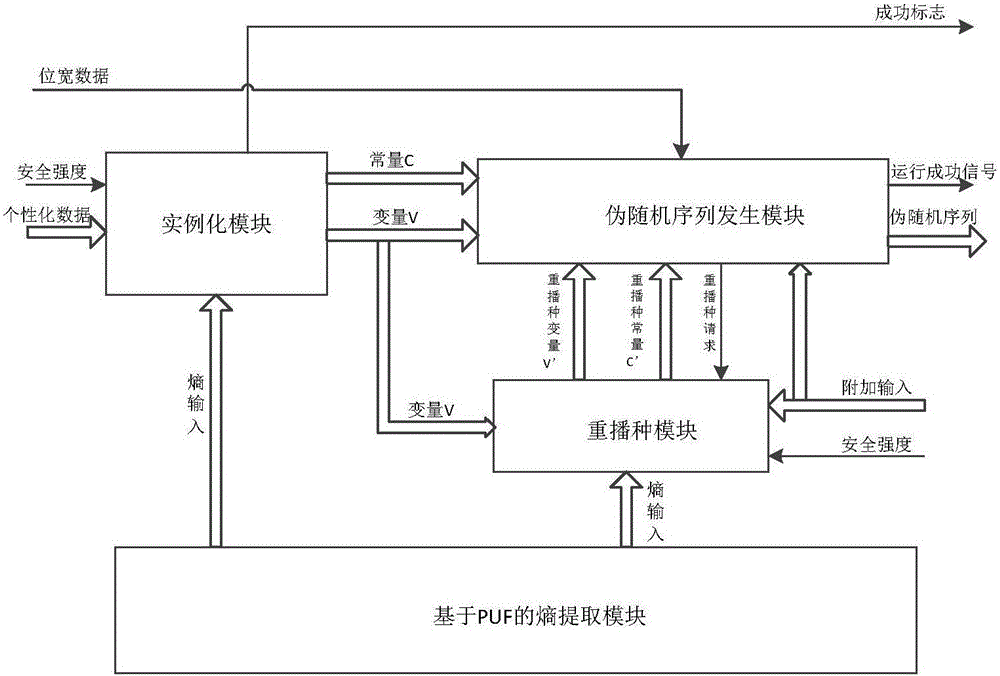
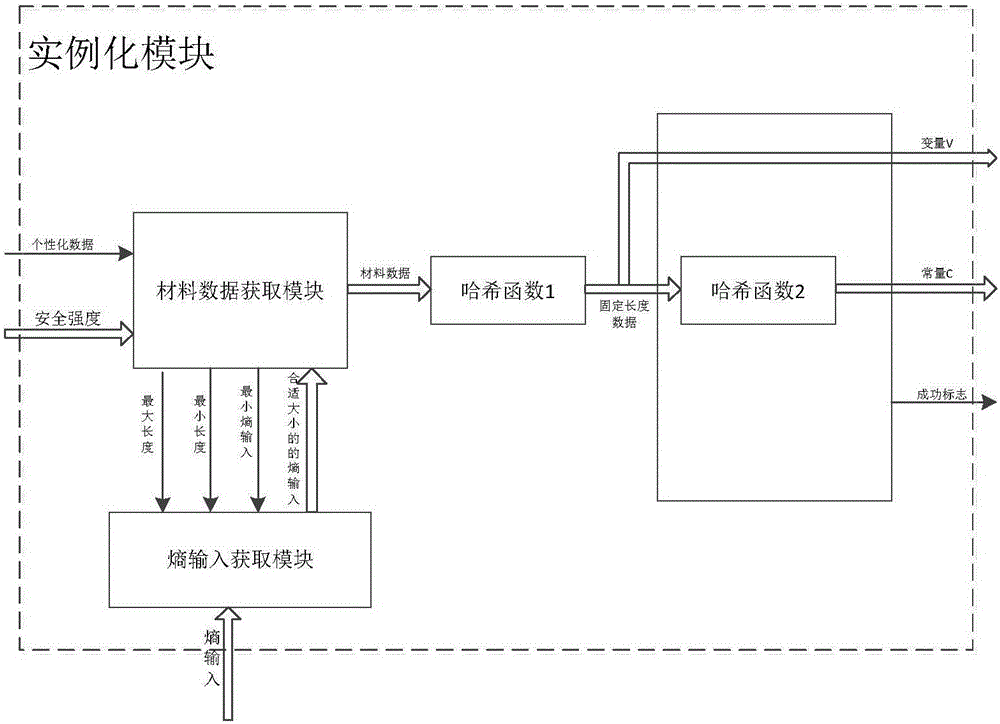
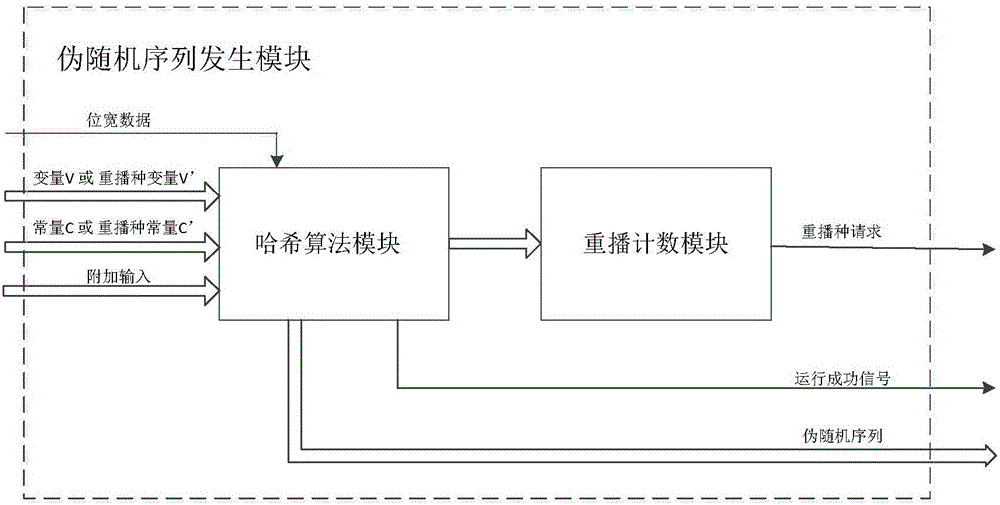
Pseudorandom sequence generator based on PUF
ActiveCN106020771APhysically UnclonableIncrease randomnessRandom number generatorsComputer sciencePseudorandom sequence
The invention provides a pseudorandom sequence generator based on PUF. The pseudorandom sequence generator comprises an entropy extracting module based on the PUF, an instantiation module, a reseeding module and a pseudorandom sequence generating module. A true random number is generated in a PUF mode to serve as entropy input, and pseudorandom sequences are generated by selecting different PUF implementation methods according to the characteristics of the pseudorandom sequences needing to be generated. When the bits of the sequences cannot meet the requirement, the generator can continue conducting iterative operation by generating a reseeding variable V' and a reseeding constant C' until the bits of the generated pseudorandom sequences meet the requirement. According to the pseudorandom sequence generator based on the PUF, the characteristic that the PUF cannot be cloned is fully utilized, and the pseudorandom sequences are generated by extracting the true random number as a seed through the irreversibility of a Hash algorithm. Compared with an existing pseudorandom sequence generator, the pseudorandom sequences generated by the pseudorandom sequence generator are low in cost and high in randomness and safety.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Synthesizable pseudorandom verification method and device for high-speed buffer memory
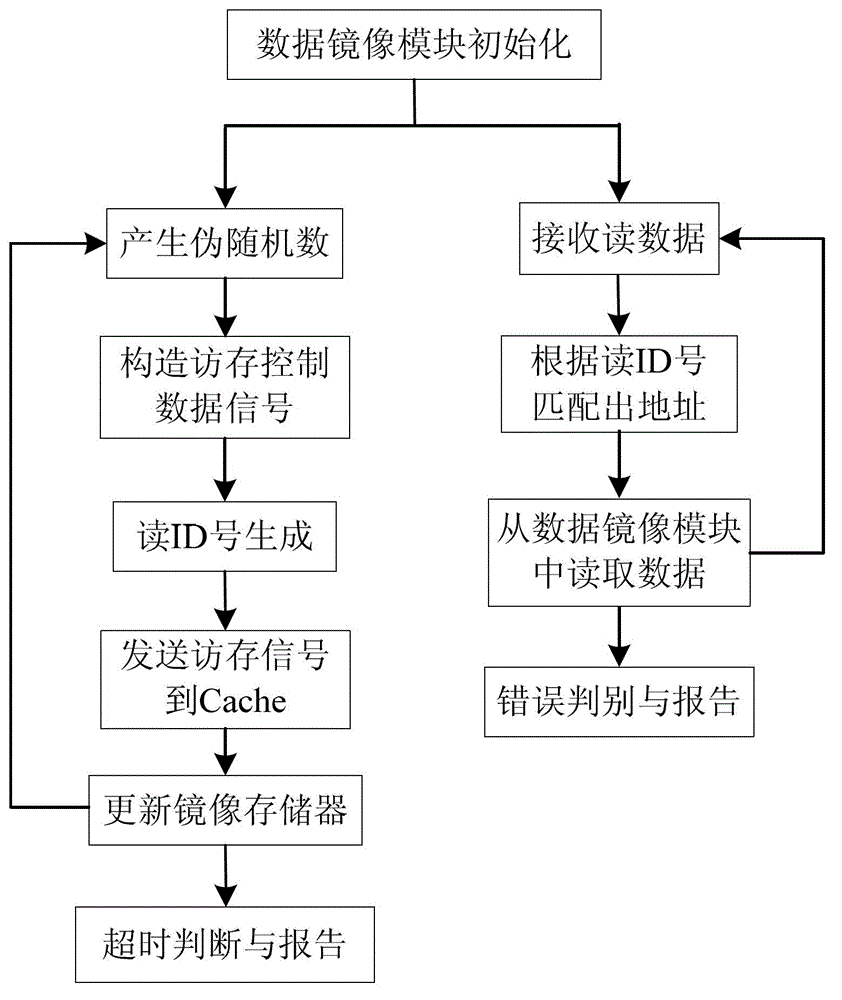
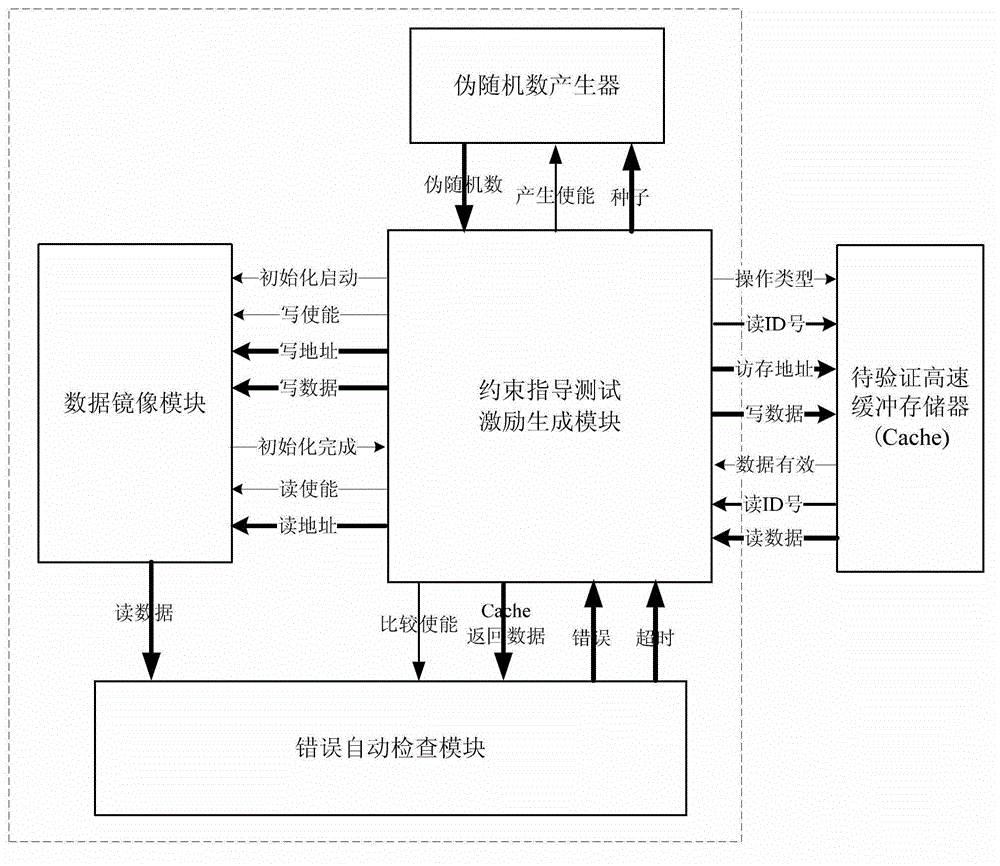
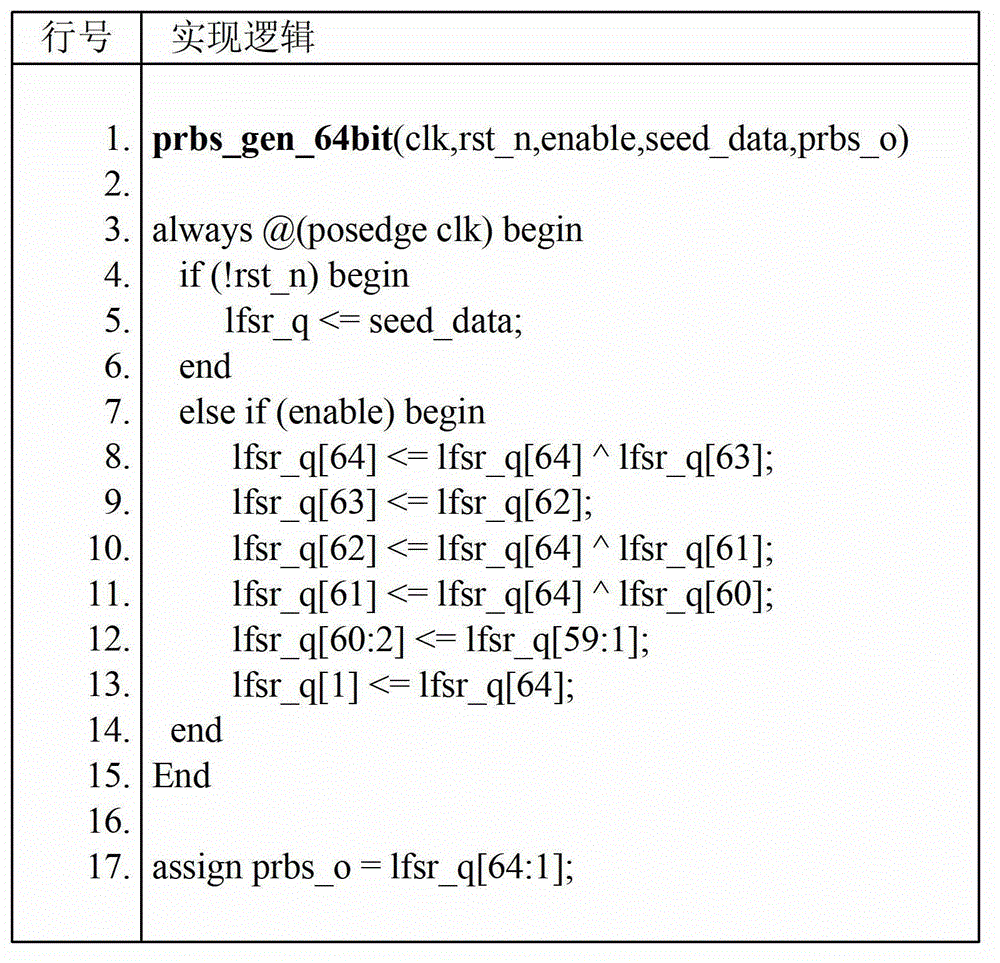
ActiveCN103150228AGuaranteed correctnessIncrease coverageFunctional testingRedundant data error correctionError checkingComputer architecture
The invention discloses a synthesizable pseudorandom verification method and device for a high-speed buffer memory. The method comprises the following steps: (1) setting and initializing a data mirroring module; and (2) generating pseudorandom numbers, structuring a fetching control data signal, sending the fetching control data signal to the high-speed buffer memory, meanwhile, starting an overtime counter, and reporting an overtime error in case of a timeout; and when receiving read data and read identification (ID) numbers, which are returned by the high-speed buffer memory, comparing the returned read data with the data mirroring module, judging whether the access of the high-speed buffer memory fails or not, and meanwhile, judging whether an ID is mistakenly read and an error correcting code is mistakenly checked. The device comprises a data mirroring module, a pseudorandom number generator, a restriction, guidance, testing, excitation and generation module and an automatic error checking module. The synthesizable pseudorandom verification method and device have the advantages of high verification efficiency, high verification coverage and good verification quality.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
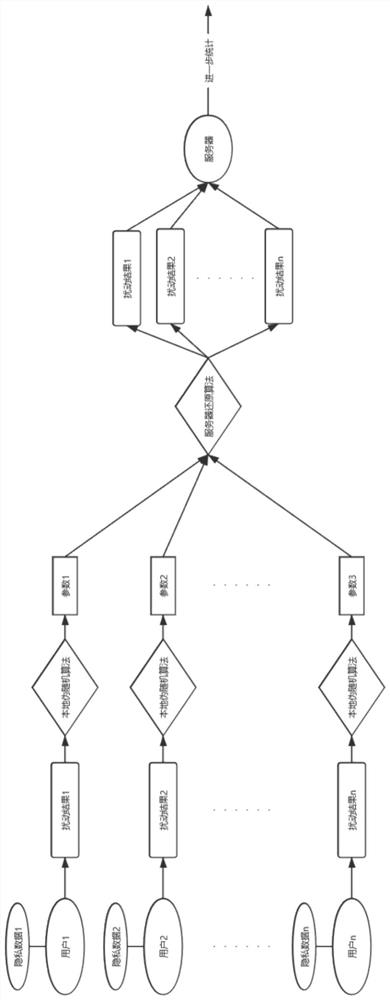
Localized differential private data exchange method and storage medium
ActiveCN111669366AReduce overheadHigh transmission accuracyKey distribution for secure communicationOriginal dataDifferential privacy
The invention discloses a localized differential privacy data exchange method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, defining a pseudo random number generation algorithm G, a differential privacy budget parameter epsilon and a data range L, enabling the client to disturb the one-hot vector V of the original data x according to the differential privacy budget parameter epsilon, recording the bit index with the value of 1 in V as Info, and recording the bit with the value of 1 after disturbance as N, selecting N different random numbers which are uniformly distributed from the L pieces of data by utilizing the algorithm G to obtain an array Indexes, adding random numbers offset which are uniformly distributed on [0, L-1] to each element to obtain a disturbance sequence, and sending a triple (seed, N, offset) to a server, and enabling the server to access a pseudo-random number generator G(seed) and restoring the disturbance vector according to an algorithm. The invention further discloses a computer storage medium based on the method. According to the method, the transmission and operation expenditure is greatly reduced while the privacy data transmission precision isguaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
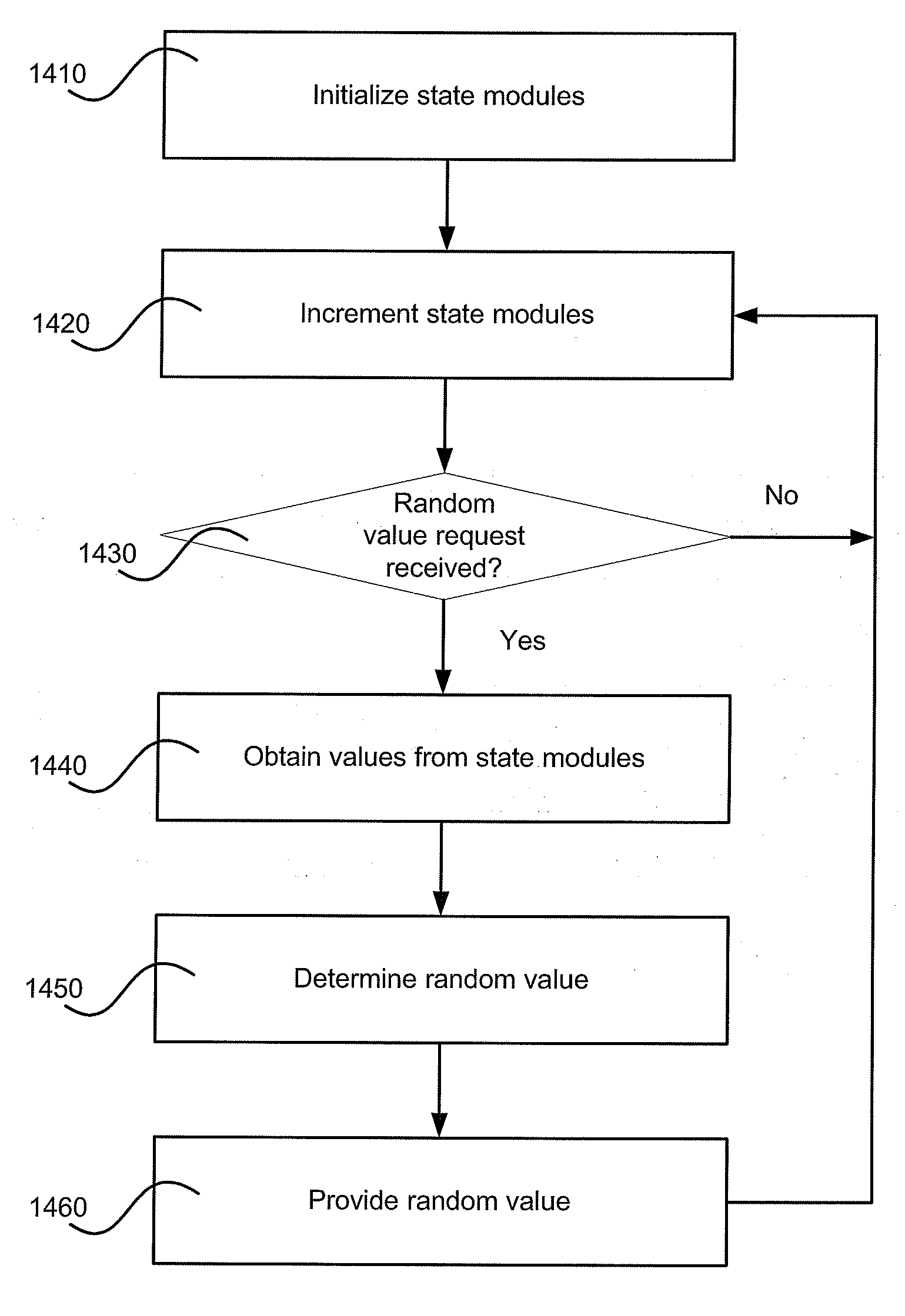
Pseudorandom Number Generation
ActiveUS20090106338A1Well formedRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationTheoretical computer scienceLimit value
A system and method of for obtaining a pseudorandom number generator are disclosed. A set of state modules, each with a limit value, may be provided. In an embodiment, each of the limit values may be relatively prime to the other limit values. In response to one or more events, the values of the state modules are incremented. At some frequency that may be statistically independent from the occurrence of the one or more events, the values of the state modules are obtained and combined to form a random number. The values may be combined as desired and, if desired, may be combined modulo 2w, where 2w represents the number of possible random values.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Uniform random number generation method for encoding deep-space communication protocol
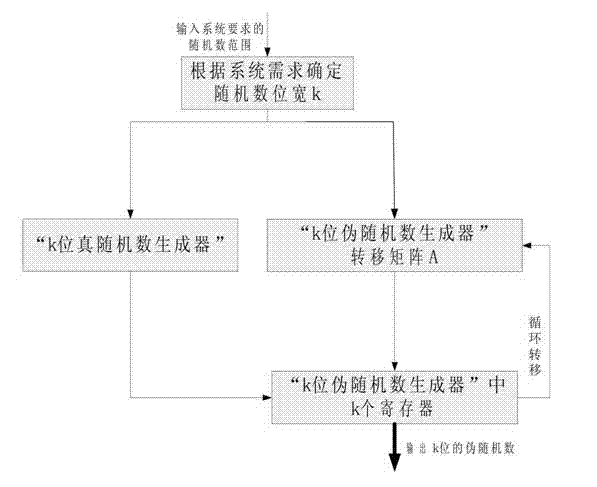
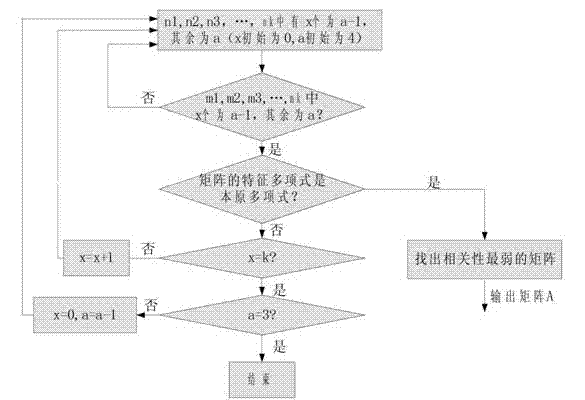
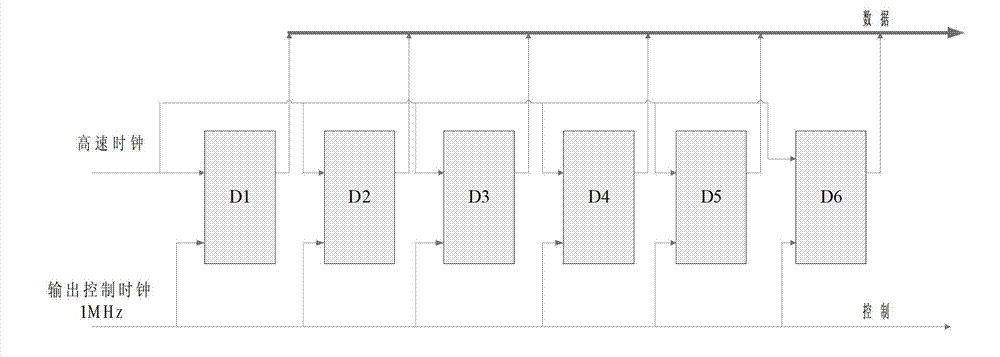
InactiveCN103197912AIncrease randomnessMeet the requirements of variable bit widthRandom number generatorsCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a uniform random number generation method for encoding a deep-space communication protocol, belonging to the technical field of deep-space communication and communication signal processing. According to the invention, a k*k dimension pseudo-random number generation matrix is designed, so that the generated pseudo-random number reaches the maximum period and the random performance of the random number is improved; and the bit width of the generated random number is k, and thus the requirement that the bit width is variable is met when the deep-space communication protocol is realized. In addition, a true random number is generated as a seed of a pseudo-random number generator, and thus a true random number which is not limited by the period is obtained and better output random characteristics of the random number are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com