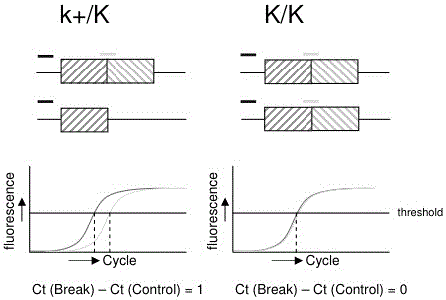
Method for detecting slow-feathering mutation genotypes of cocks
A technology for mutant genes and roosters, applied in the field of detection of rooster slow-feather mutant genotypes, can solve the problems of inability to determine slow-feather alleles, complicated processes, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieves the effect of short cycle, few links, and less error-prone effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
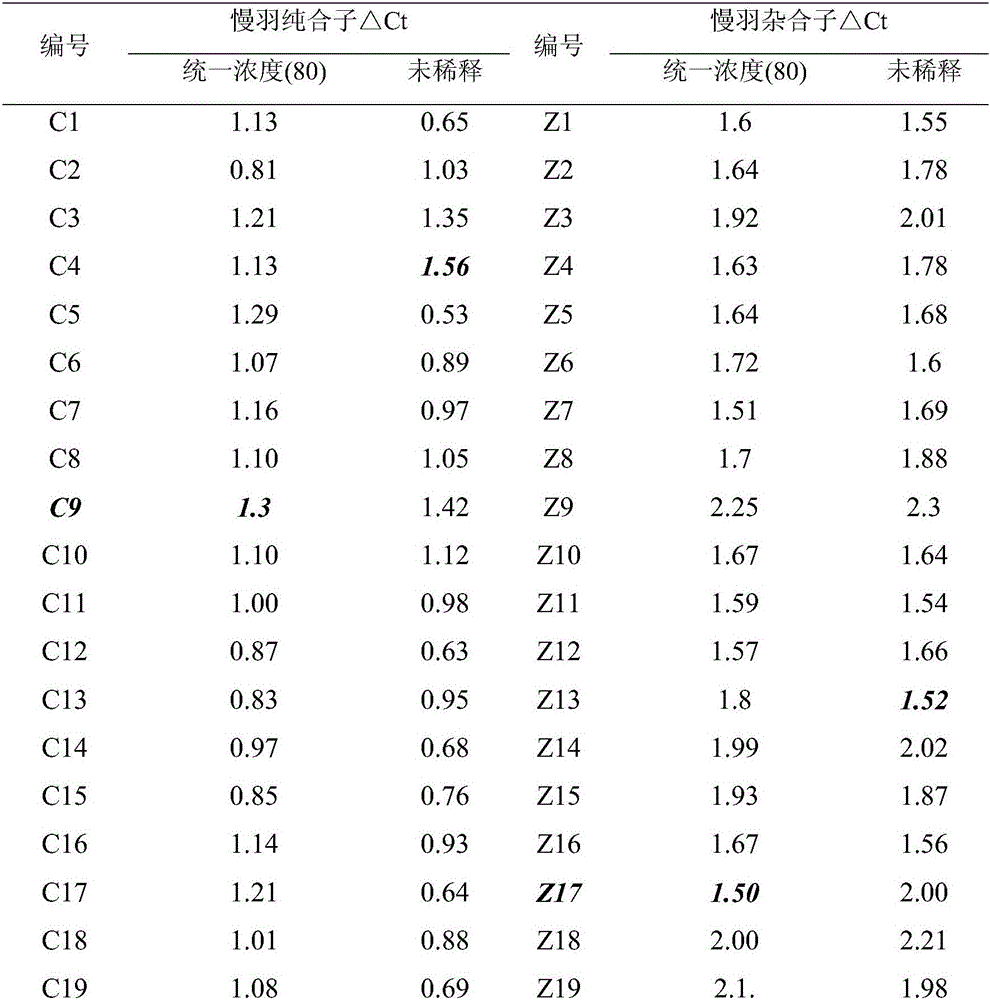
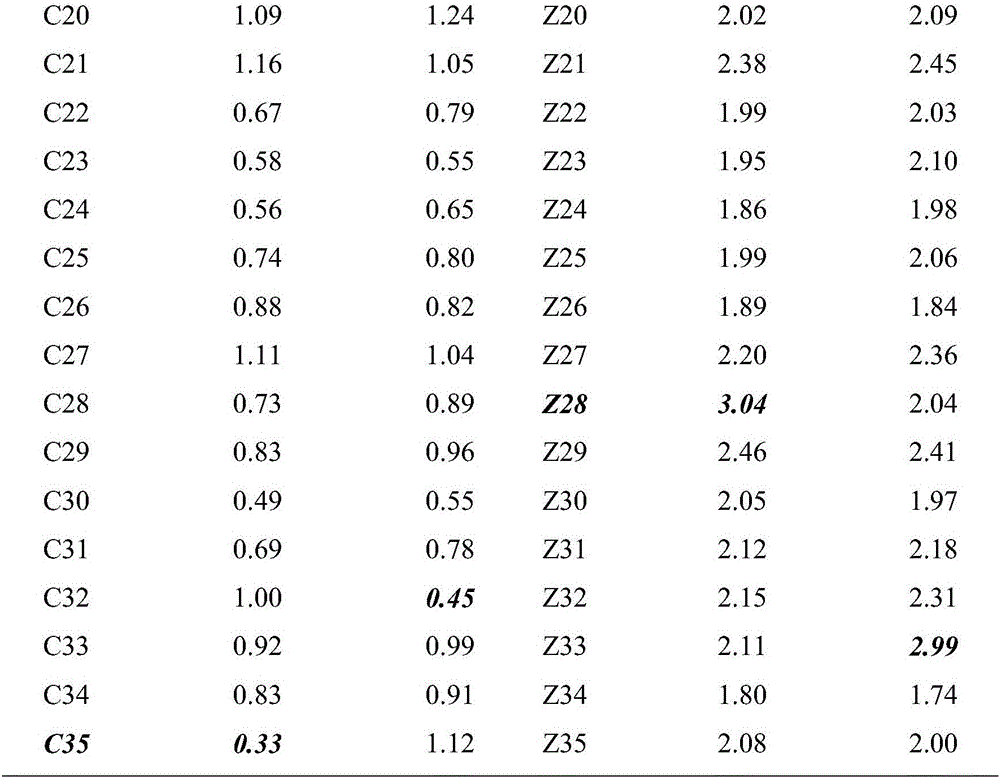
[0016] Example 1 Effect of different concentrations of DNA on detection results
[0017] The animal materials used in this embodiment are 35 rooster individuals known to be homozygous for slow plumage, and 35 individual roosters known to be heterozygous for slow feather.
[0018] A method for detecting rooster slow feather mutation genotype, comprising the steps:
[0019] S1. DNA extraction: Use a disposable syringe to extract about 1 mL of blood from the vein under the chicken wing, inject it into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube that has been sterilized by high pressure and filled with about 200 μL of 2% sterile EDTA anticoagulant, and shake it gently , record the wing number, and store at -20°C for future use.
[0020] Genomic DNA was extracted using phenol-chloroform extraction (Osper F et al., 1998):
[0021] (1) Take 30 μL of whole blood and place in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 470 μL of 1×SET buffer, 12.5 μL of 20% SDS and 6 μL of 10 mg / mL proteinase K, mix well and place i...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 The Influence of Two Different Types of Real-time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Instruments on the Detection Results
[0039] The animal materials used in this example were 35 individual roosters known to be homozygous for slow plumage, and 35 individual roosters known to be heterozygous for slow feathering; the fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument models were ABI 7300 and Bio-rad CFX96.
[0040]A method for detecting rooster slow feather mutation genotype, comprising the steps:
[0041] S1. DNA extraction: Use a disposable syringe to extract about 1 mL of blood from the vein under the chicken wing, inject it into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube that has been sterilized by high pressure and filled with about 200 μL of 2% sterile EDTA anticoagulant, and shake it gently , record the wing number, and store at -20°C for future use.
[0042] Genomic DNA was extracted using phenol-chloroform extraction (Osper F et al., 1998):
[0043] (1) Take 30 μL of whole blood and ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Influence of different real-time fluorescent quantitative reagents on detection results
[0059] The animal materials used in this example were 35 individual roosters known to be homozygous for slow plumage, and 35 individual roosters known to be heterozygous for slow feathering; the model of the fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument was Bio-rad CFX96.
[0060] A method for detecting the genotype of the rooster's slow-feather mutation, the specific steps are the same as those in Example 1, and the only different fluorescent quantitative reagents used are Bio-rad SYBR Green Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Mix or KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Master Mix. It was found that the reagents of KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Master Mix could not amplify the results at all.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com