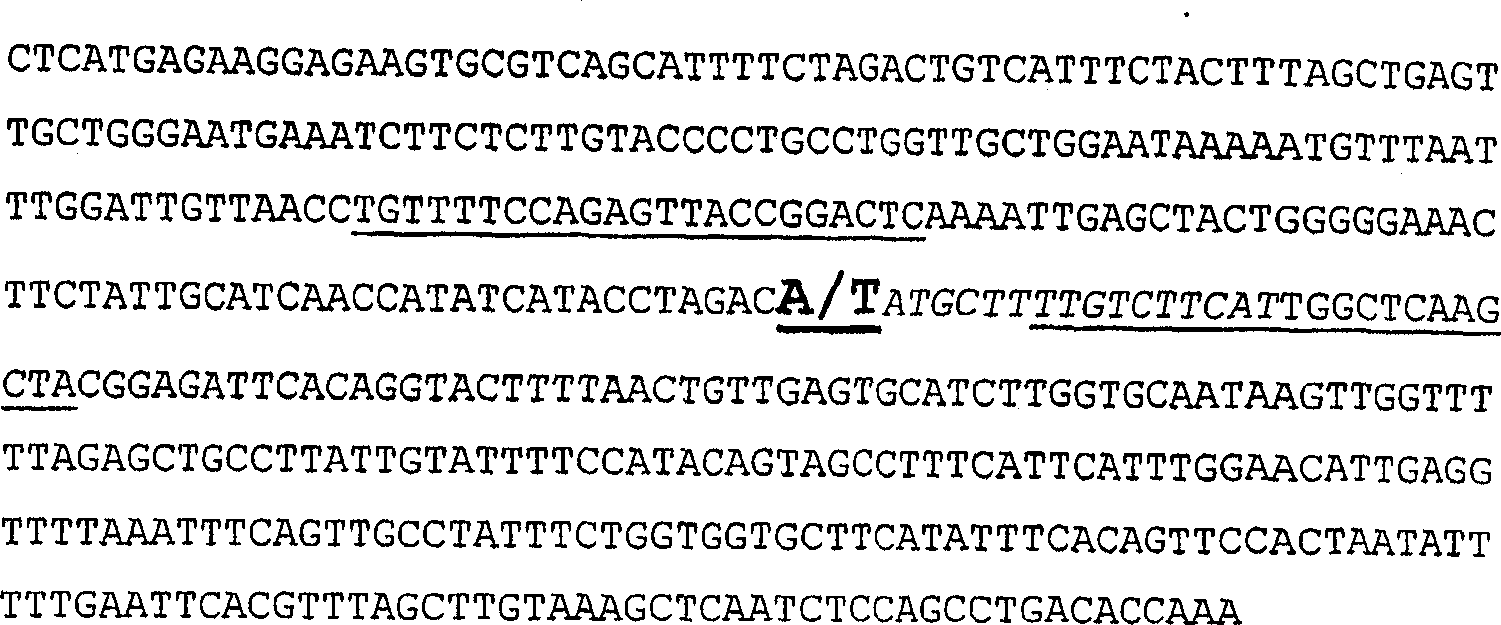Isolated nucleotide sequences responsible for the tomato high pigment-1 mutant phenotypes (hp-1 and hp-1w) and uses thereof
A nucleotide sequence and nucleotide technology, applied in the fields of applications, chemical instruments and methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of 9 base pair deletions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Identification and cloning of DDB1 tomato homologues
[0088] The DDB1 protein is a heterodimer composed of two subunits, DDB1 and DDB2. Unlike rice, chicken, human, mouse, Drosophila and Schizosaccharomycespombe, the A. thaliana genome has two highly homologous copies of the DDB1 gene (Schroeder et al. 2002; Zolezzi et al. 2002 ; Fu et al.2003; Ishibashi et al.2003): DDB1A and DDB1B, both 1088 amino acids in length (Genbank protein accession numbers NP_192451 and NP_193842, respectively). When each of these two protein accession numbers was used as a query for tblastn analysis in the TIGR database (http: / / www.tigr.org / ) containing the tomato expressed sequence tags (ESTs), both revealed Two highly homologous sequences: TC117371 (394bp) and TC117372 (2206bp). A. thaliana accession number NP_192451 was found to be 87 and 86% identical to tomato TC117371 and TC117372 accession numbers, respectively. On the other hand, accession number NP_193842 has 87 and 83% identit...
Embodiment 2
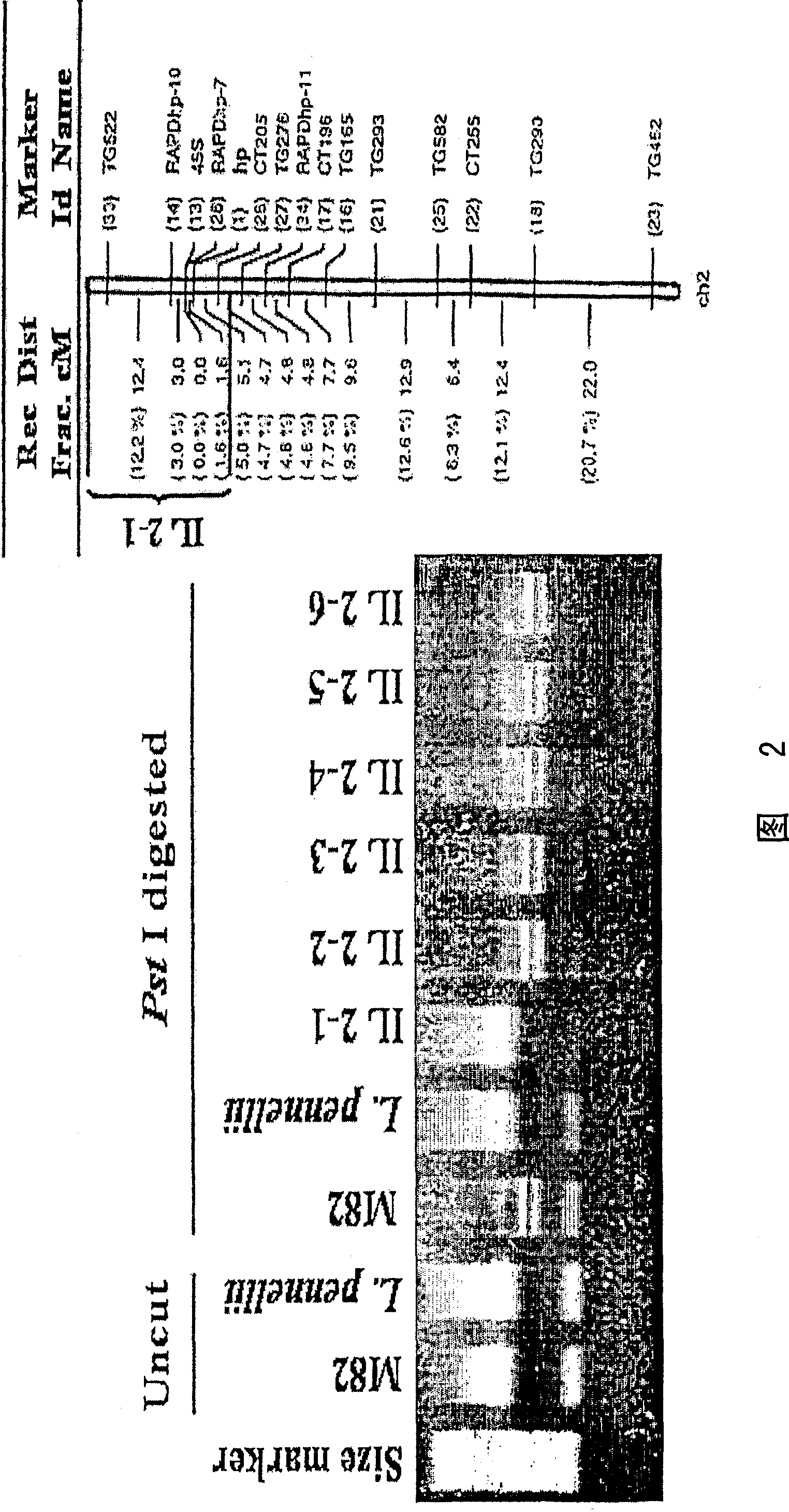
[0090] Mapping of Tomato DDB1 Gene
[0091] Part of the mapping results, including the approximate location of the tomato DDB1 gene, is shown in Figure 2. These results indicate that DDB1 is located on tomato chromosome 2 in introgressed varieties with the HP-1 gene (Yen et al. 1997).
Embodiment 3
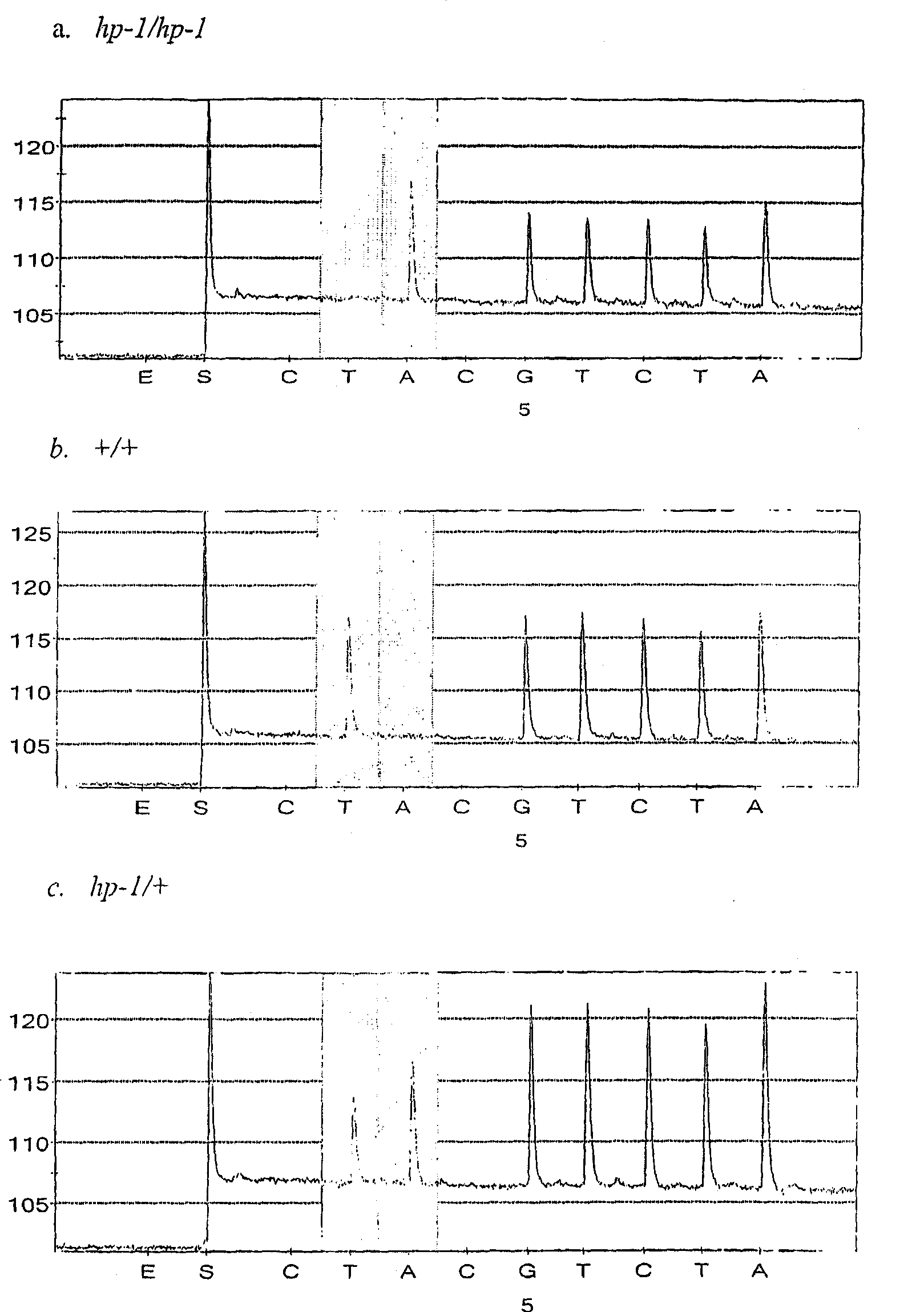
[0093] hp-1 and hp-1 w Sequence characterization of tomato DDB1 in mutants
[0094] Several forward and reverse primers (Table 1) complementary to the 3' region of the tomato DDB1 gene (TIGR Accession No. TC117372) were used for direct cDNA preparation from seedling leaves of hp-1 and normal plants of the Ailsa Craig background. sequencing. No polymorphisms between hp-1 and normal plants were acquired in this region. Therefore, the 5' region of the DDB1 gene in the two genotypes was also cloned and fully sequenced. In silico translation of all sequences revealed that tomato DDB1 is a 1090 amino acid protein. Sequence analysis of the DDB1 coding sequence from hp-1 and its near-isogenic normal genotype revealed the presence of a single A in the coding sequence of the DDB1 gene in mutant hp-1 plants 931 to T 931 base transversion. Asparagine 311 to tyrosine 311 replacement (Figure 4).
[0095] Based on the sequence information obtained in the background of Ailsa Crai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com