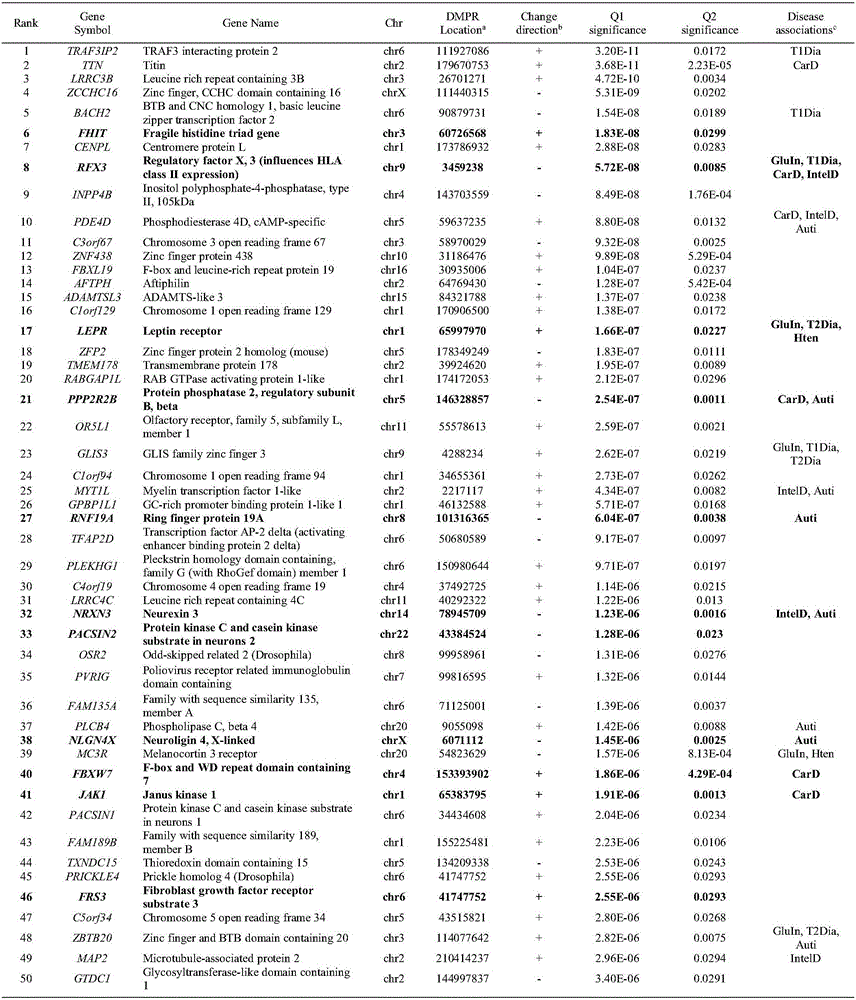
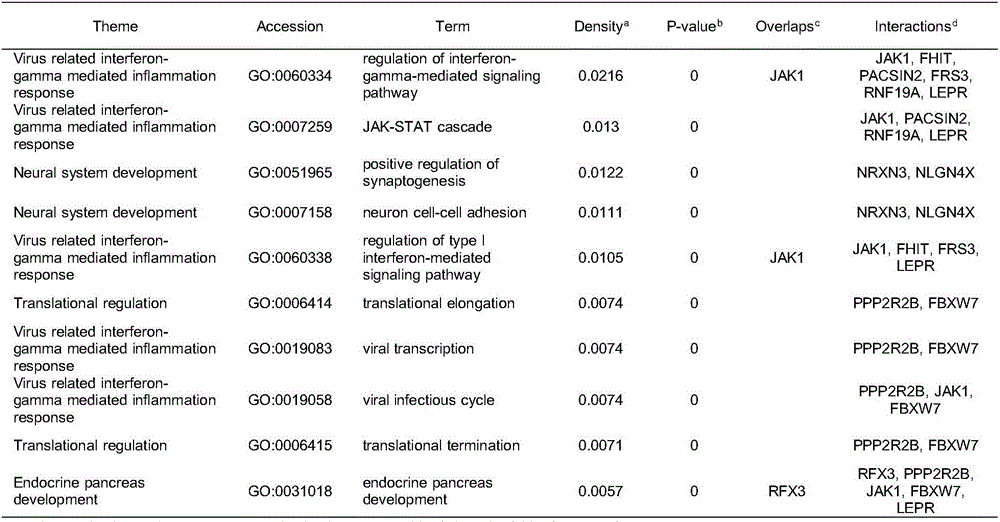
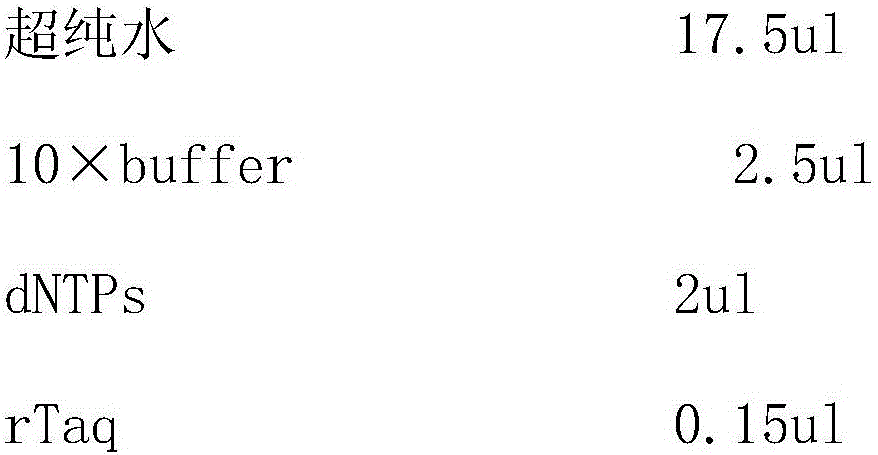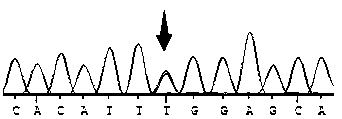Patents
Literature
70 results about "Genetic divergence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic divergence is the process in which two or more populations of an ancestral species accumulate independent genetic changes (mutations) through time, often after the populations have become reproductively isolated for some period of time. In some cases, subpopulations living in ecologically distinct peripheral environments can exhibit genetic divergence from the remainder of a population, especially where the range of a population is very large (see parapatric speciation). The genetic differences among divergent populations can involve silent mutations (that have no effect on the phenotype) or give rise to significant morphological and/or physiological changes. Genetic divergence will always accompany reproductive isolation, either due to novel adaptations via selection and/or due to genetic drift, and is the principal mechanism underlying speciation.
Hppd-inhibitor herbicide tolerance
ActiveUS20110185445A1Negatively impactingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePlant cell
This invention relates generally to the detection of genetic differences among soybeans. More particularly, the invention relates to soybean quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tolerance or sensitivity to HPPD-inhibitor herbicides, such as mesotrione and isoxazole herbicides, to soybean plants possessing these QTLs, which map to a novel chromosomal region, and to genetic markers that are indicative of phenotypes associated with tolerance, improved tolerance, susceptibility, or increased susceptibility. Methods and compositions for use of these markers in genotyping of soybean and selection are also disclosed, as are methods and compositions for use of these markers in selection and use of herbicides for weed control. Also disclosed are isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to such tolerance or sensitivity and methods of introgressing such tolerance into a plant by breeding or transgenically or by a combination thereof. Plant cells, plants, and seeds produced are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
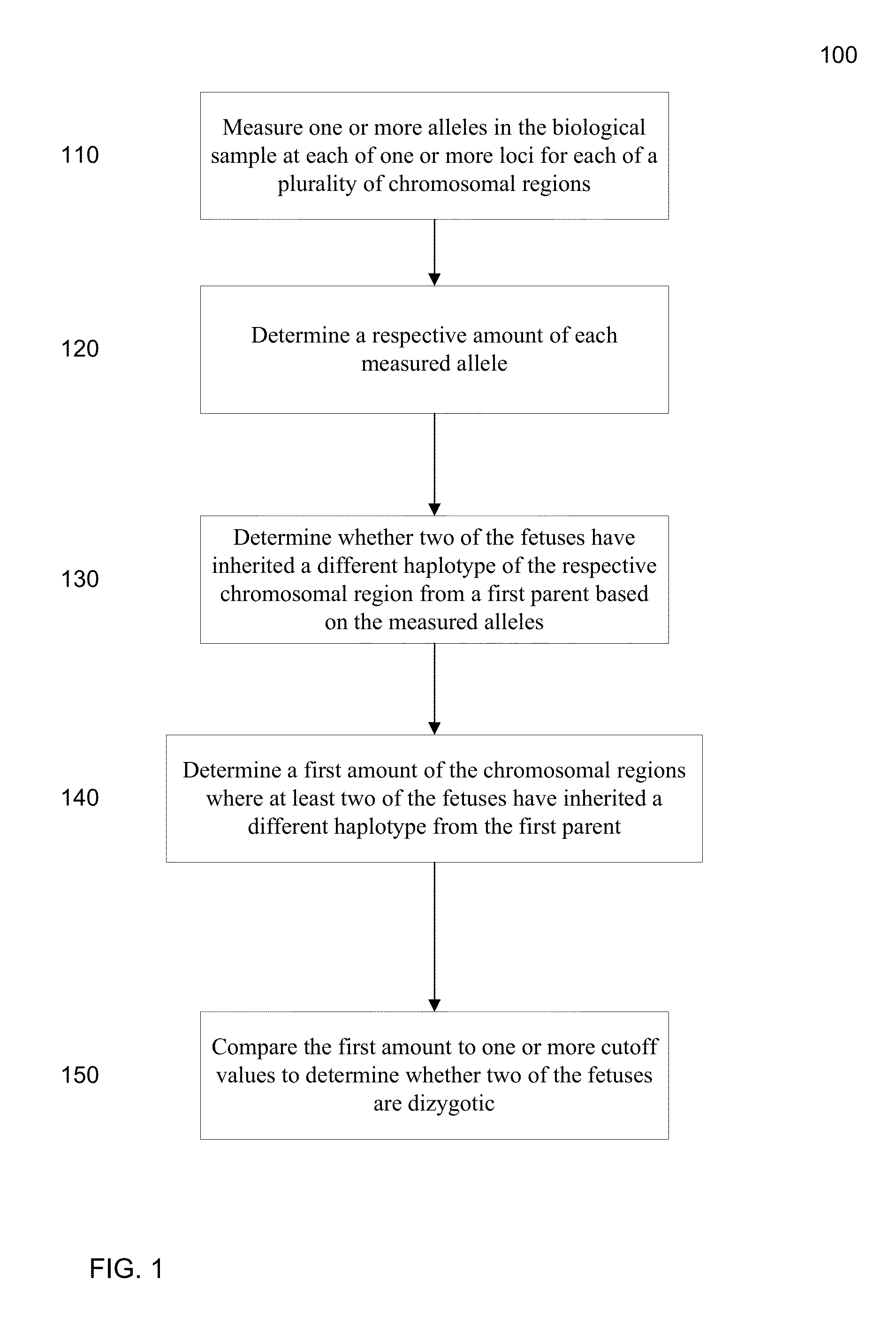
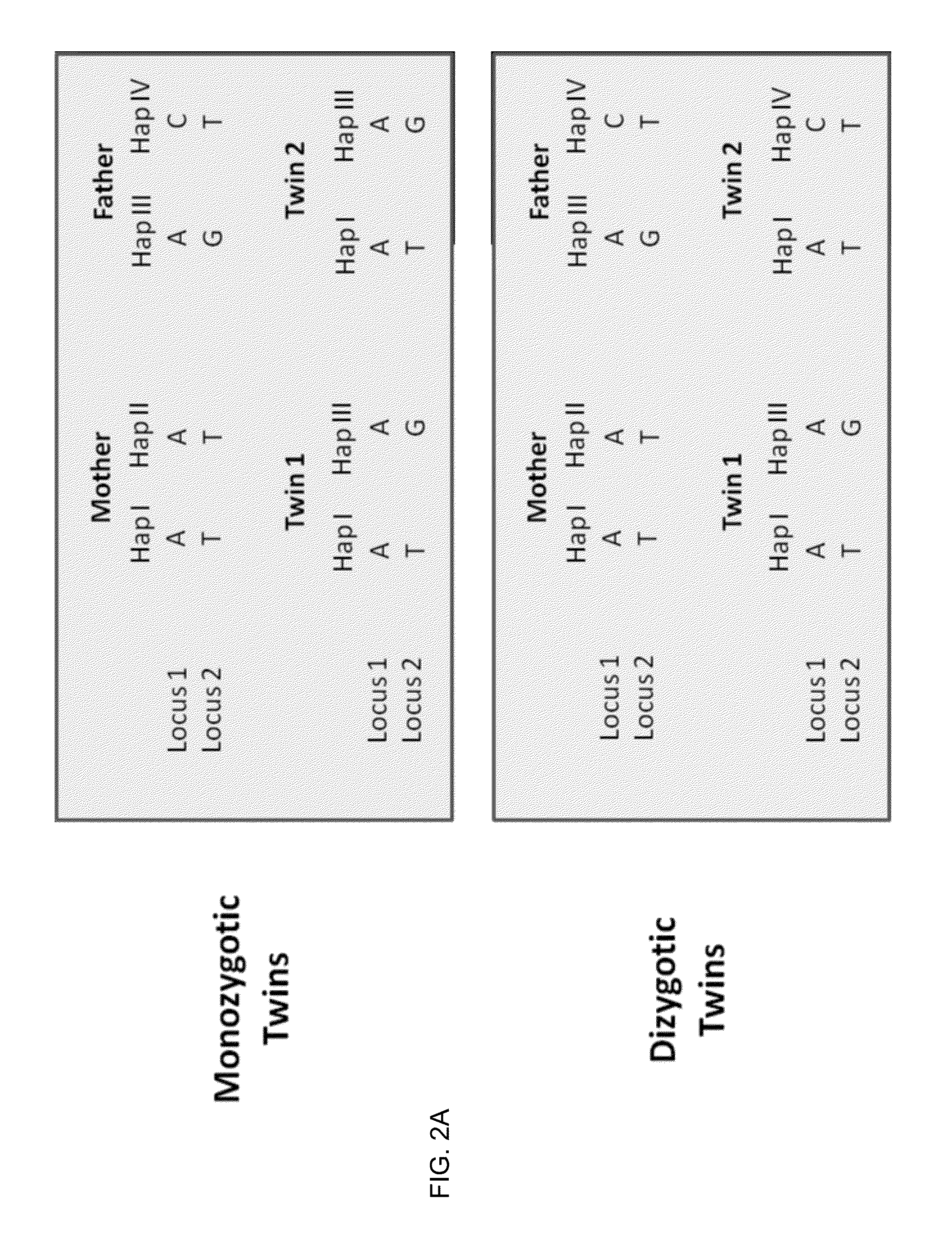
Molecular testing of multiple pregnancies
ActiveUS20130059733A1Non invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSpecific chromosomeGenetic divergence
Methods, systems, and apparatus are provided for determining zygosity of a multiple-fetus pregnancy using a biological sample taken from the mother. The fetal and maternal DNA in the sample (e.g. plasma) can be analyzed for a particular chromosomal region to identify genetic differences in the fetuses. For example, a normalized parameter for the measure of a primary or secondary allele can show variances for different chromosomal regions when fetuses are dizygotic. Such a variance can be determined relative to an expected value if the fetuses were genetically identical. Statistical methods are provided for analyzing the variation of the normalized parameters to determine fetal DNA concentration and the maternal-fetal mixed genotype at various loci. Parental genotype and haplotype information can also be used to identify inheritance of different parental haplotypes to indicate genetic differences among the fetuses.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Screening method and application of Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken genome SNP molecular marker
PendingCN109295238AComprehensive and effective germplasm analysisPromote development and utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementEggshellScreening method
Relating to the field of genetics, the invention specifically provides a screening method and application of a Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken genome SNP molecular marker. The screening method includes: conducting high-throughput sequencing detection, then calculating the genetic statistics, then analyzing the genetic difference between Dongxiang blue-eggshell chickens and other chicken breed groups, and finally screening out the Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken SNP molecular marker. The screening method has the technical effects of efficient and rapid screening of Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken molecular marker, the selected gene of the screened Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken serves as the molecular marker for identifying the Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken germplasm, has the characteristics of low cost, abundant data and high detection precision, alleviates the technical problems of high genetic differentiation research cost and low accuracy caused by lack of efficient molecular biological method and genetic marker in current Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken genetic differentiation identification. And application of the Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken genome SNP molecular markeralleviates the technical problem of lack of efficient molecular biological marker in the genetic differentiation research of Dongxiang blue-eggshell chicken.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Hybrid breeding method for sea cucumber
A hybridization method between Chinese spiny sea cucumber and Russian (or korean) one for preparing the hybrid one with high growth speed, stress resistance, survival rate and nutritive value includes such steps as using special culture technique to make them mature symultaneously, artificial oxytocia to obtain their spermatozoa and ova, artificial fertilization, and culturing fertilizer ova until they become laval plankton.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying prunus persica plant species based on SSR molecular markers
InactiveCN105512513APromote healthy developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic divergenceGenetic similarity
The invention relates to a method for identifying prunus persica plant species based on SSR molecular markers. According to the method, SSR primers with high polymorphism are selected for carrying out the SSR-PCR amplified reaction, electrophoresis detection and system analysis on 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials. The result shows that 10 pairs of primers, with high polymorphism, screened from 100 pairs of SSR primers are used for carrying out SSR-PCR amplification on genome DNA of the prunus persica plant specie materials, 63 amplified bands are amplified together, the number of polymorphic bands is 60, the polymorphic rate is 95.2%, and the better amplification result is obtained. Similarity coefficient and cluster analysis is carried out, the genetic similarity coefficient is 0.4133-0.9600, and the average similarity coefficient is 0.6867; the genetic difference among the 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials shows that the different species and the genetic distances among the different species are different, when the similarity coefficient is smaller than 0.68, most cultivated varieties are clustered into one cluster, and most cultivated varieties in the same provenance can be clustered together. An important way is provided for further distinguishing the genetic relationship among the prunus persica plant specie resources.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method of developing polymorphic EST-SSR marker by utilizing complete genome and EST data
InactiveCN104673884AImprove development efficiencyThere is little difference between the tested samplesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGenetic divergenceSequencing data
The invention discloses a method of developing a polymorphic EST-SSR marker by utilizing a complete genome and EST data and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a genomic sequence and the EST data firstly; then searching an SSR site in the complete genome, and identifying and screening a single SSR site in the complete genome; then designing a comparison primer of the single SSR site, and carrying out comparison with EST sequence data as a template; counting a comparison result, and screening the SSR site with more than two stimulation amplified products and the polymorphism in the EST template; and finally, designing a polymorphic EST-SSR site primer to obtain the polymorphic EST-SSR marker. The method is capable of efficiently, simply and conveniently developing the EST-SSR marker and preventing the EST-SSR marker with potential utilizable value from weeding out caused by insufficient genomic sequence or genetic diversity of an experimental material. The developed EST-SSR marker is tightly related to a single gene and has high genetic and breeding values.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Personalized genetic typing guidance body building and weight losing method and equipment application thereof
InactiveCN105821136AEasy to useHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationPersonalizationHuman DNA sequencing
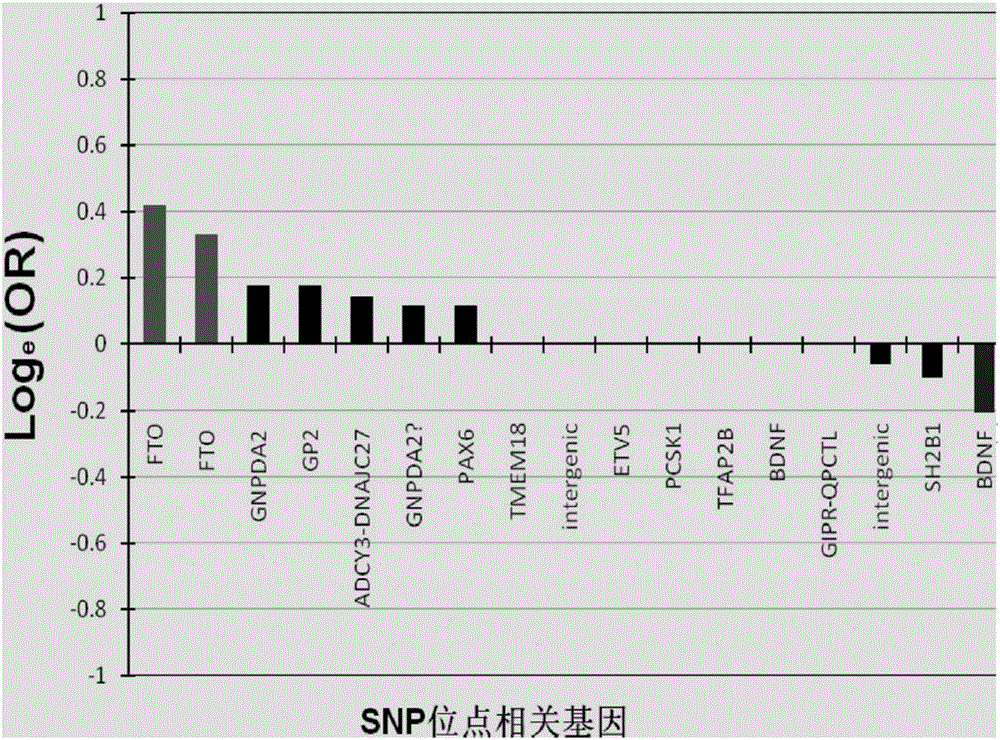
The invention relates to data related to influences of different kinds of fat intake on obesity and influences of different types of sports on weight reduction and blood glucose reduction in disclosed human genome single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data. According to genetic differences between individuals, a method suitable for determining main reasons of obesity and making personalized diet schemes or giving suggestions about lifestyles is built, and the method is applied to development of wearable mobile devices and application software. The invention further relates to preparation and application of genetic chips related to detection. The personalized weight losing and body building schemes can reasonably, efficiently and selectively use modern sports exercise means and diet regulation according to personal gene characteristics, so that individuals achieve the aims of diet regulation and exercise planning more scientifically and more quickly.
Owner:SHANGHAI MIJIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for identifying varieties of lilium brownii by adopting SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marking technology
InactiveCN104263835AHigh polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmPetal
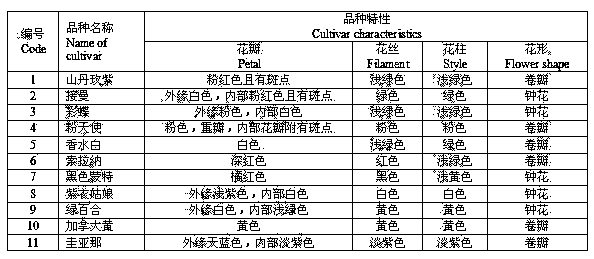
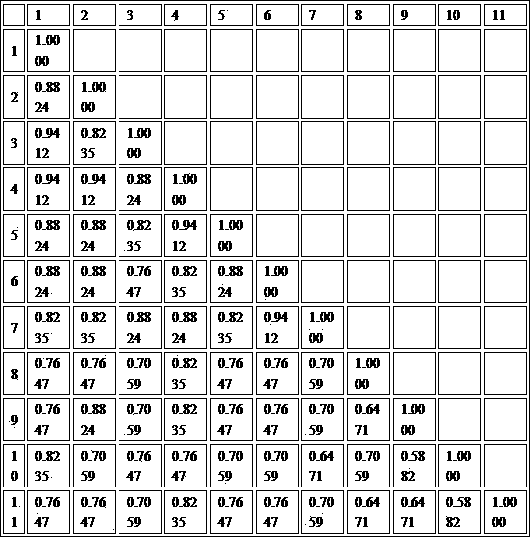
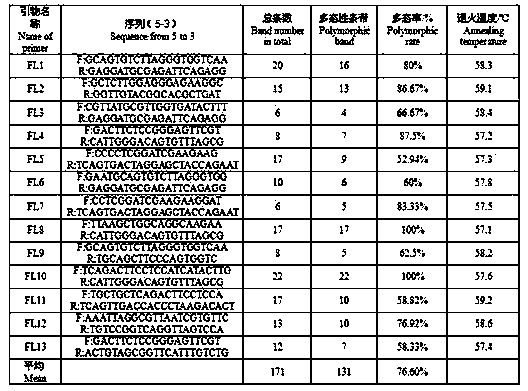
The invention relates to the method for identifying the varieties of lilium brownii by adopting an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marking technology. A result shows that: two pairs of high-polymorphism and high-repeatability primers are screened from 13 pairs of primers for detecting 171 fragments comprising 131 polymorphic fragments, 4 to 22 fragments can be detected by each pair of primers with the sizes of 100 to 250bp, 1.69 bands are amplified by each pair of primers, and the polymorphism rate is 76.70 percent; NTSYS-pc2.11 is used for similarity coefficient and cluster analysis, the genetic similarity coefficient is 0.5882 to 09412, and the average similarity coefficient is 0.7647; materials are divided into six major classes by cluster analysis, the genetic differences between 11 lilium brownii germplasms are irrelevant to varietal characteristics, flower forms, the colors of filaments and styluses, but have certain correlation with the colors of petals, flower genes can better reflect genetic relationships between the lilium brownii germplasms, different varieties have different colors, and the primers can be designed by controlling related genes of flowers to provide an important means for further distinguishing the genetic relationships.
Owner:KAILI UNIV
Gene function association network-based method for discovering chronic disease mechanism and early warning intervention policy thereof
ActiveCN106126893AShow validityEpigenetic far-reachingHealth-index calculationProteomicsDisease riskCrowds
The present invention discloses a gene function association network-based method for discovering a chronic disease mechanism and an early warning intervention policy thereof. The method can be applied to the field of related research and application of biology, medicine and pharmacy. Epigenetic changes of the high-risk groups surveyed and discovered according to epidemiology before disease attack are detected, the epigenetic changes before the disease is associated with indicator gene changes of the disease through gene function network analysis, then a long-term molecular mechanism contributing to the disease risk is discovered, and risk early warning for the group, risky diagnosis for an individual, and indicators and methods for preventive intervention are provided. According to the method, a long-term steady biological path or biological function change may leave a mark on related gene epigenetic inheritance, and a chronic disease biological path or biological function level mechanism may be found through analysis of the synergistic effect of epigenetic differences.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Molecular marker primer and method for identifying Shao's Sillago and Sillago sihama
ActiveCN106434977AAmplification results are consistentThe result is stableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSillago sihamaGermplasm
A molecular marker primer for identifying Shao's Sillago and Sillago sihama belongs to the technical field of biology, and sequences of the primer include L5979: 5'-TTTAGTATTCGGAGCCTGAG-3' and H6241: 5'-CCTCAACACCTGATGAGGCC-3'. The invention also provides a method for identifying Shao's Sillago and Sillago sihama by using the primer, comprising the steps of extracting DNA from Shao's Sillago and Sillago sihama, using DNAs of the two species as templates to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, purifying and sequencing amplification results, and comparing sequencing results to determine that intraspecific genetic difference is not greater than 1%; molecular marker sequence of Shao's Sillago is SEQ NO. 3 and molecular marker sequence of Sillago sihama is SEQ NO. 4; the method of the invention helps solve the problem of germplasm mixing of Sillago fishes, and is simple to perform, easy to master and high in accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Screening method for species group with heterosis of germany mirror carp
InactiveCN101403006AScreening results are accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteCyprinus
The invention relates to a screening method of dominant hybridization species of German mirror carps and discloses a screening method of the dominant hybridization species of carps. The invention provides an effective screening method of the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps so as to ensure the genetic diversity of hybrids thereof, thus reducing the workloads, shortening the breeding period, decreasing the breeding cost and improving the success rate of selective breeding. The screening method includes the following steps: 1. morphological marker; 2. microsatellite molecular maker; and 3. data analysis. The method screens the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps by combining the morphological marker and the microsatellite molecular marker. The genetic differences between the species are dually tested and the screening results are more accurate.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Uses and method for polymorphic point genetype for predicting sulfaurea drugs effect
InactiveCN101008032AHigh amplification efficiencyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBeta-cell FunctionSide effect
The invention relates to the prediction of sulfonylureas drug effect by measuring polymorphism site genetype of sulfonylureas recepted gene, and the method. It predicts the effect of sulfonylureas drug in reducing blood sugar, improving and restoring Langer-hans' insula beta cell function and / or intensifying insulin sensitive function by measuring polymorphism site genetype of sulfonylureas recepted gene; and predicts the effect of sulfonylureas drug in reducing blood sugar, improving and restoring Langer-hans' insula beta cell function and / or intensifying insulin sensitive function by making use of polymorphism parting oligonucleotide to detect polymorphism site genetype of sulfonylureas recepted gene in biological sample. The invention can indicate doctor to choose medicine according to individual gentic difference, increase the effective rate of clinical medicine treating and safty of clinical midicine usage, reduce toxic and side effect of medicine and economical load, and reduce diabetes complication generation.
Owner:BEIJING HUAANFO BIOMEDICAL RES CENT +1
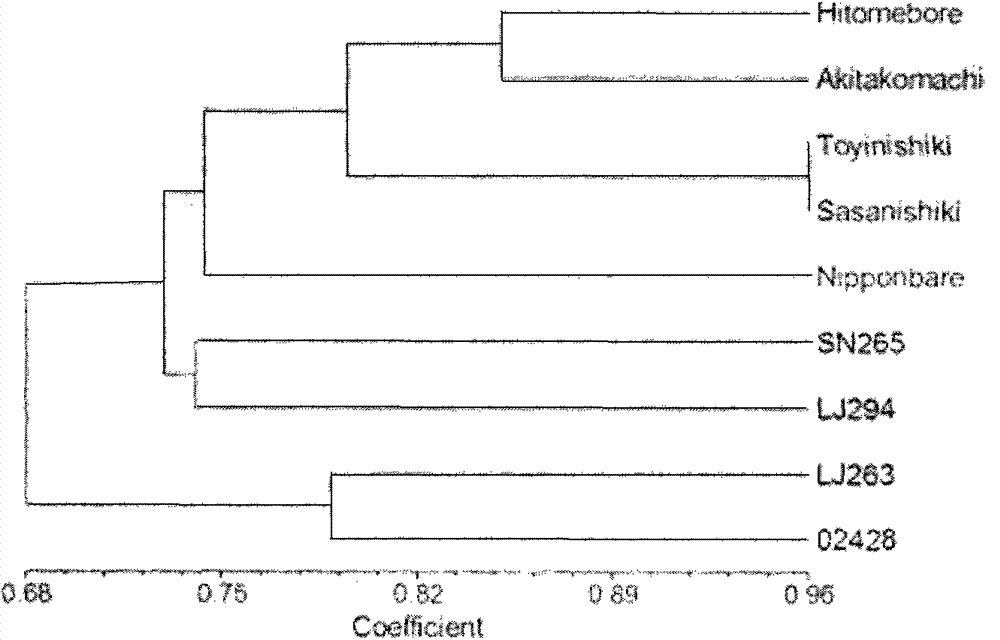
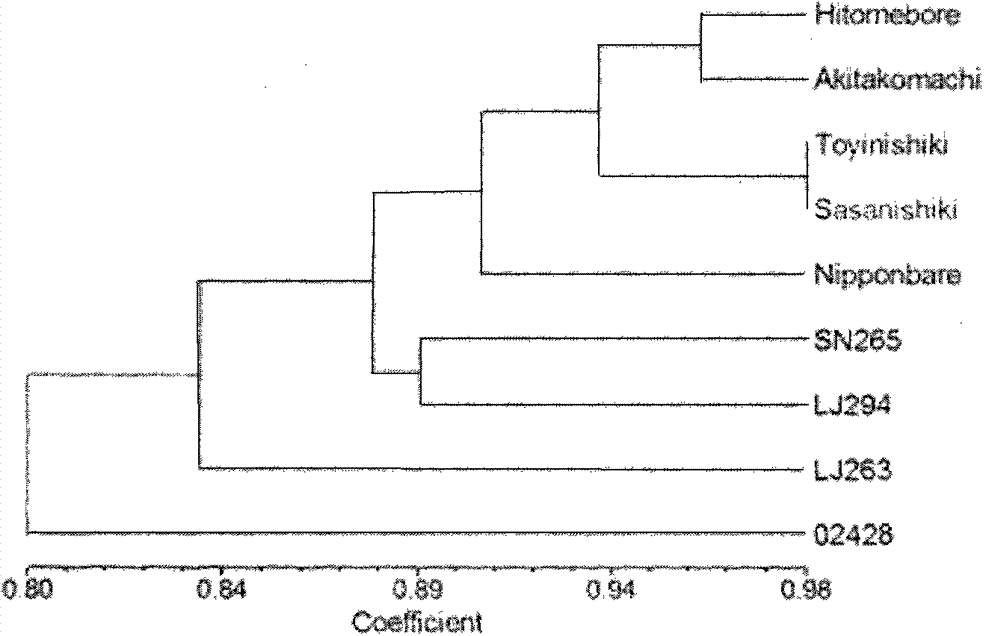
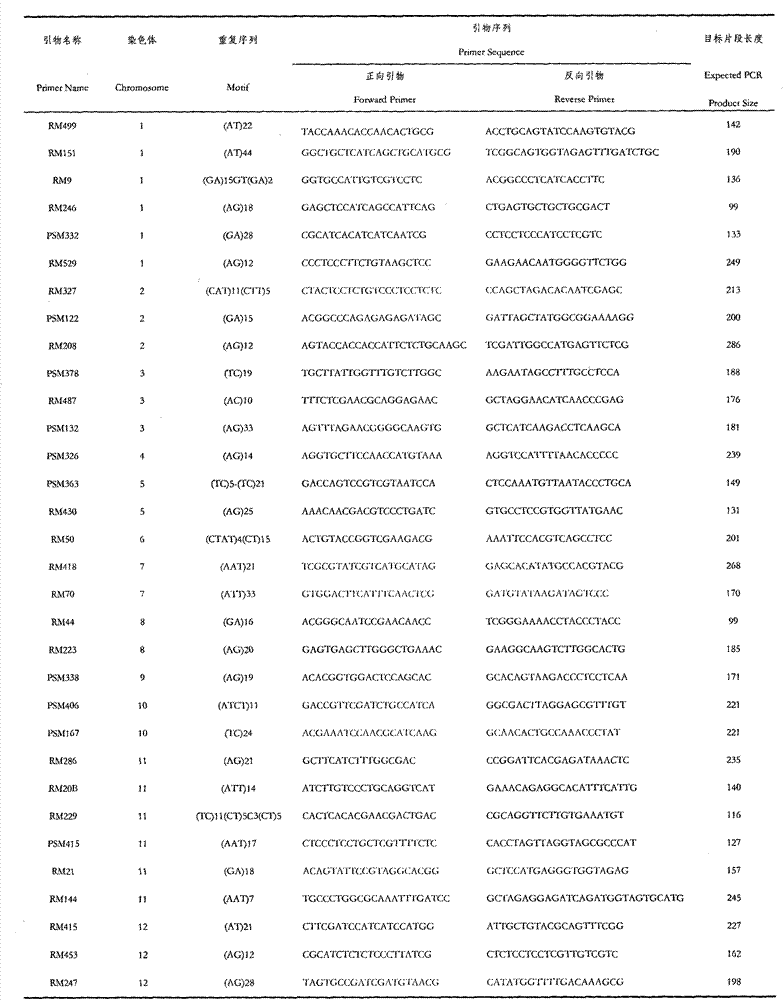
Molecular marker for japonica rice genetic diversity analysis and authentication method for molecular marker
InactiveCN103789308AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic divergence
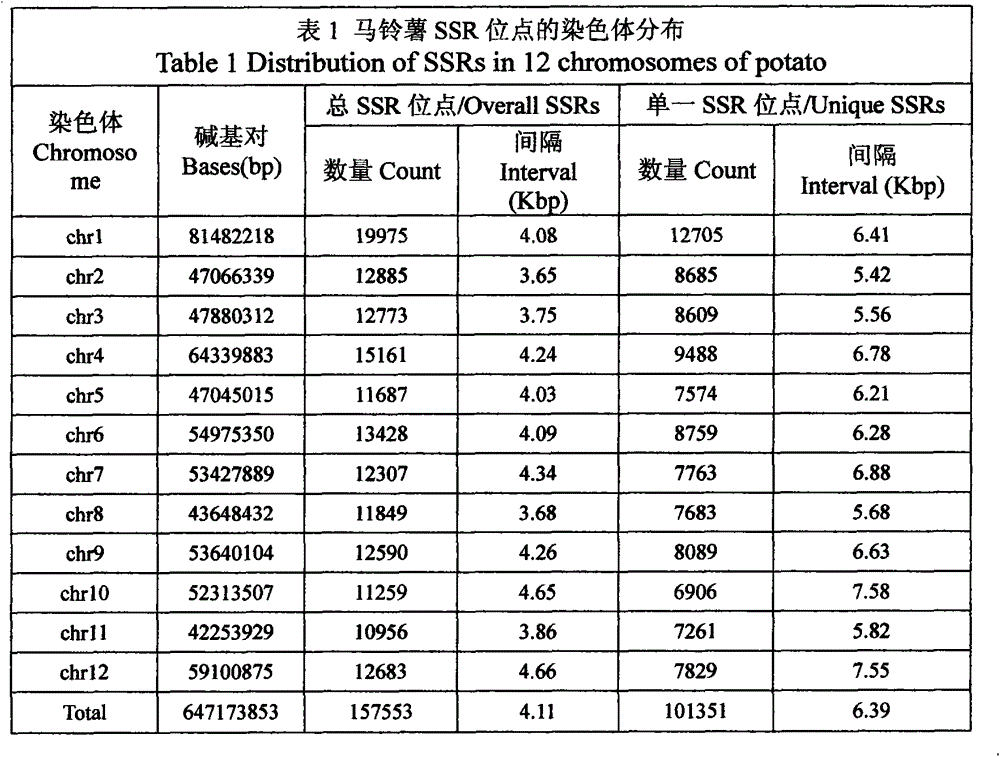
The invention relates to a molecular marker for japonica rice genetic diversity analysis and an authentication method for the molecular marker. The molecular marker comprises 32 pairs of SSR markers covering 12 chromosomes of paddy rice; each of the fourth, sixth and ninth chromosomes has one marker, each of the fifth, seventh, eighth and tenth chromosomes has two markers; each of the second, third and twelfth chromosomes has three markers; and each of the first and eleventh chromosomes has six markers. The authentication method comprises the steps of a, DNA extraction; b, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification: a PCR reaction system is 15 microlitres and contains 50mM of KCl, 10mM of Tris-HCl(pH8.8), 0.1 percent of Triton-X, 1.5mM of MgCl2, 200mu M of each of NTPs, 0.2mu M of each primer, 5 percent (v / v) dimethyl sulfoxide and 0.5UT of aq DNA polymerase; c, PCR product detection; and d, statistical analysis. According to the molecular marker for japonica rice genetic diversity analysis and the authentication method for the molecular marker, the genetic diversity of a japonica rice material to be detected and genetic difference can be detected, and the molecular markers for the japonica rice genetic diversity analysis are screened.
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
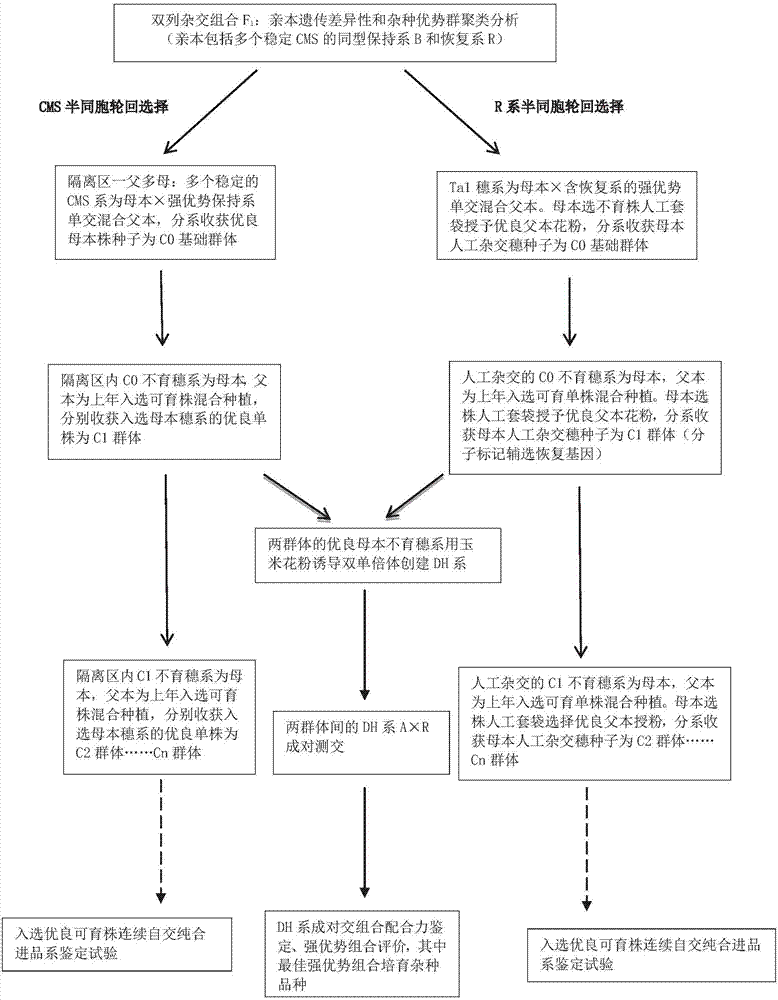
Recurrent selection method for dominant germplasm population of hybrid wheat
ActiveCN107568057AImprove matching efficiencyPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention relates to a recurrent selection method for a dominant germplasm population of hybrid wheat. The recurrent selection method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out half-sibling ear line phenotype recurrent selection on a CMS sterile line population and an R restoring line population; carrying out clustering analysis of genetic difference and heterotic group on diallel cross F1 combinations and parents thereof, wherein the parents comprise maintainer lines and restoring lines of male sterile lines CMS of wheat cells; carrying out CMS line half-slib recurrent selection by taking CMS sterile lines as female parents and B lines as male parents, selecting excellent sterile lines subjected to recurrent selection, and carrying out double haploid induction to obtainmale sterile DH lines; carrying out R line half-slib recurrent selection by taking dominant genic sterile Tal ear lines as female parents and R lines as male parents, selecting excellent sterile plants subjected to recurrent selection, and carrying out the double haploid induction to obtain fertile DH lines with restoring genes; carrying out test cross on the sterile DH lines and the fertile DH lines, selecting heterosis crosses of the lines according to the test cross result, and cultivating wheat hybrid varieties.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Screening method and application of Bian chicken molecular marker
ActiveCN109295239AImprove detection accuracyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyScreening method
Relating to the field of genetics, the invention provides a screening method and application of a Bian chicken molecular marker. The screening method of a Bian chicken molecular marker includes: conducting high-throughput sequencing detection on SNP marker, calculating genetic statistics, analyzing and comparing the genetic difference of Bianji group and other chicken breed groups, and screening out a Bian chicken molecular marker. The method provided by the invention alleviates the technical problems of high Bian chicken genetic differentiation research cost and low accuracy caused by lack ofefficient molecular biological method in existing Bian chicken breed conservation effect evaluation process, and reaches the technical effect of efficient and rapid screening of a molecular marker for Bian chicken breed conservation effect evaluation. The invention also provides a screening method of the Bian chicken molecular marker and application of the screened molecular marker, and alleviates the technical problems of lack of efficient molecular biological marker and screening method in Bian chicken research.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
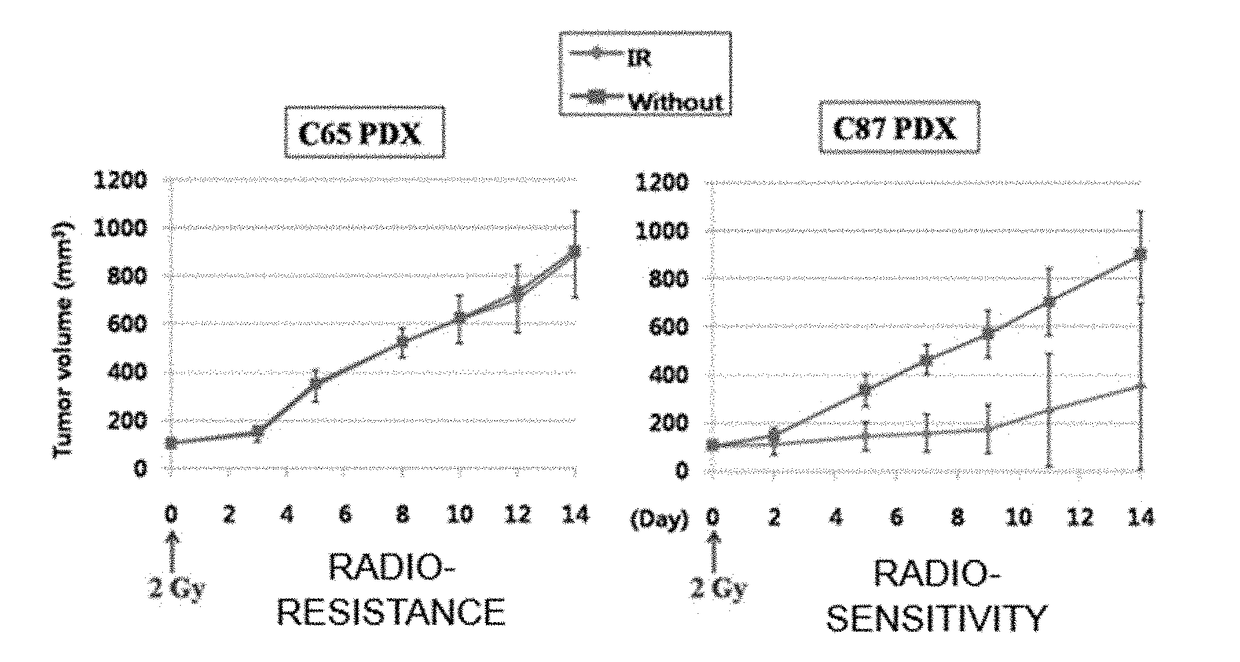
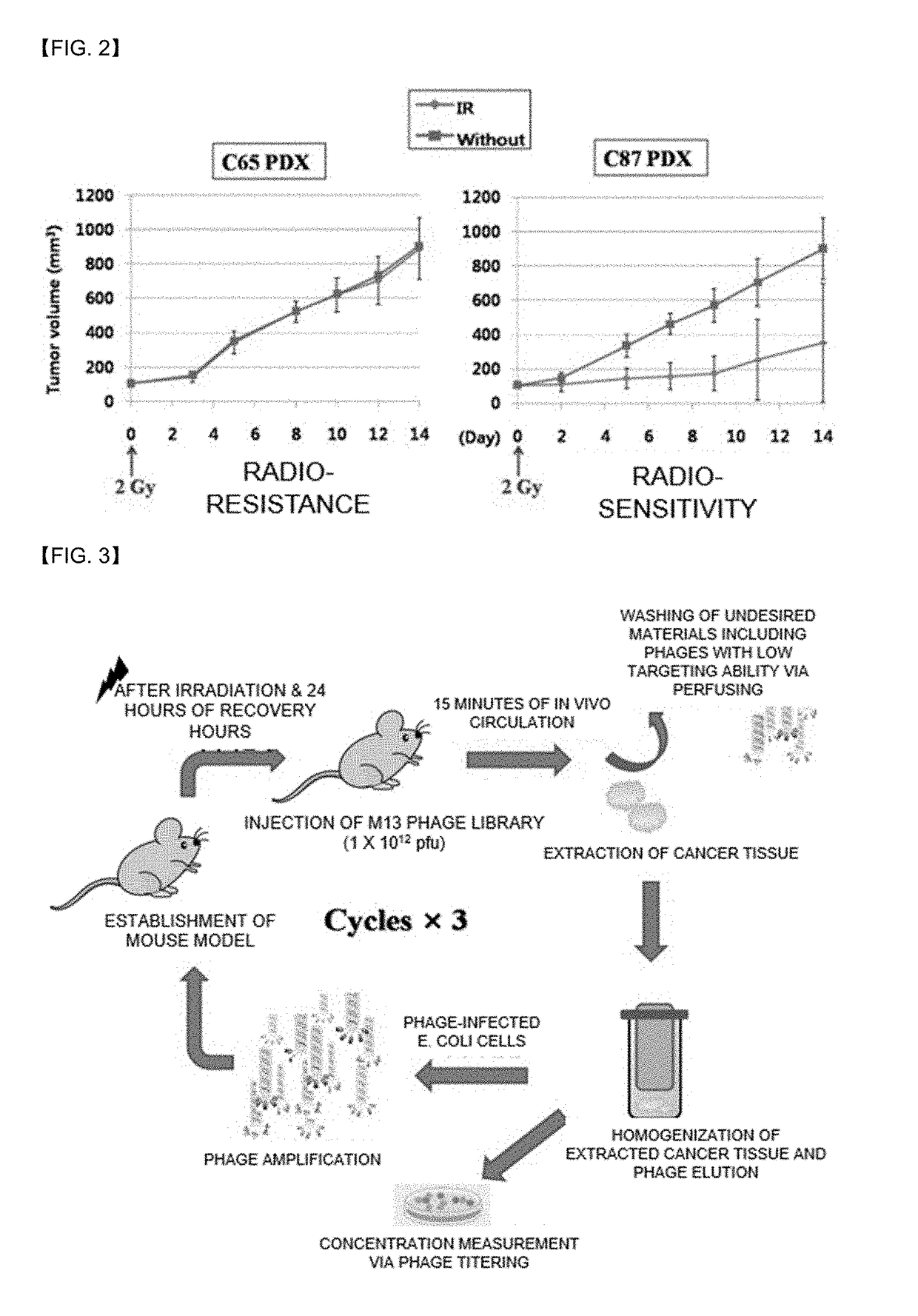
Peptides for targeting gastric cancer, and medical use tehreof
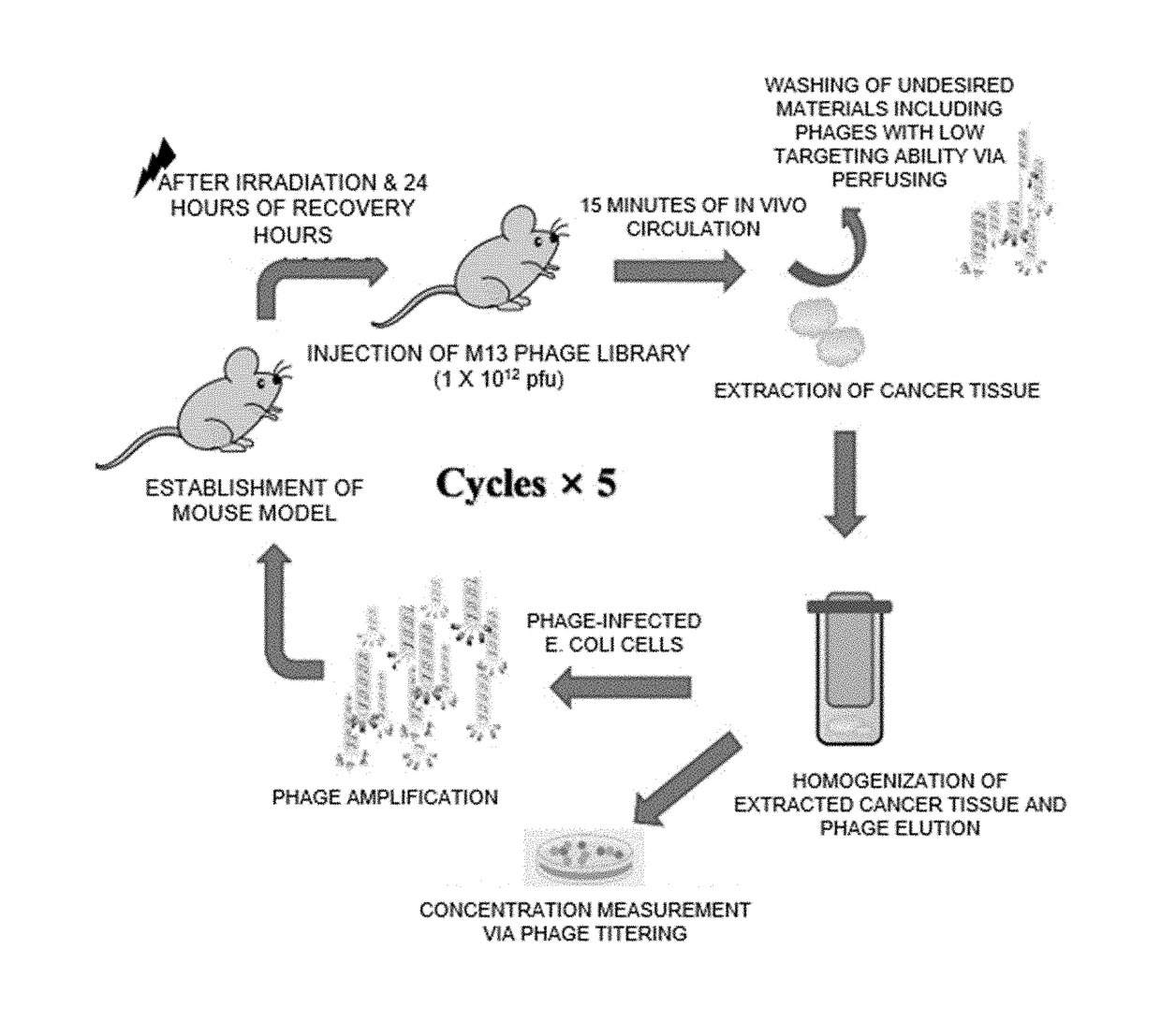
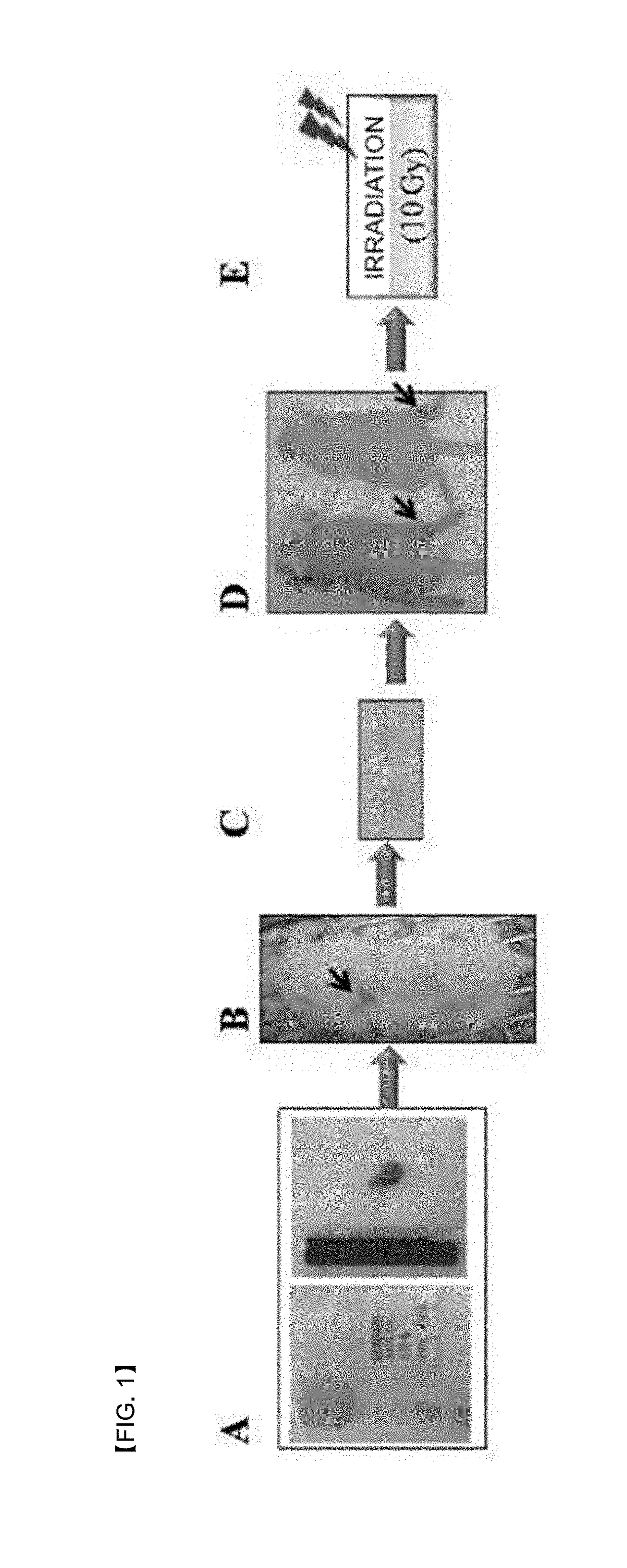
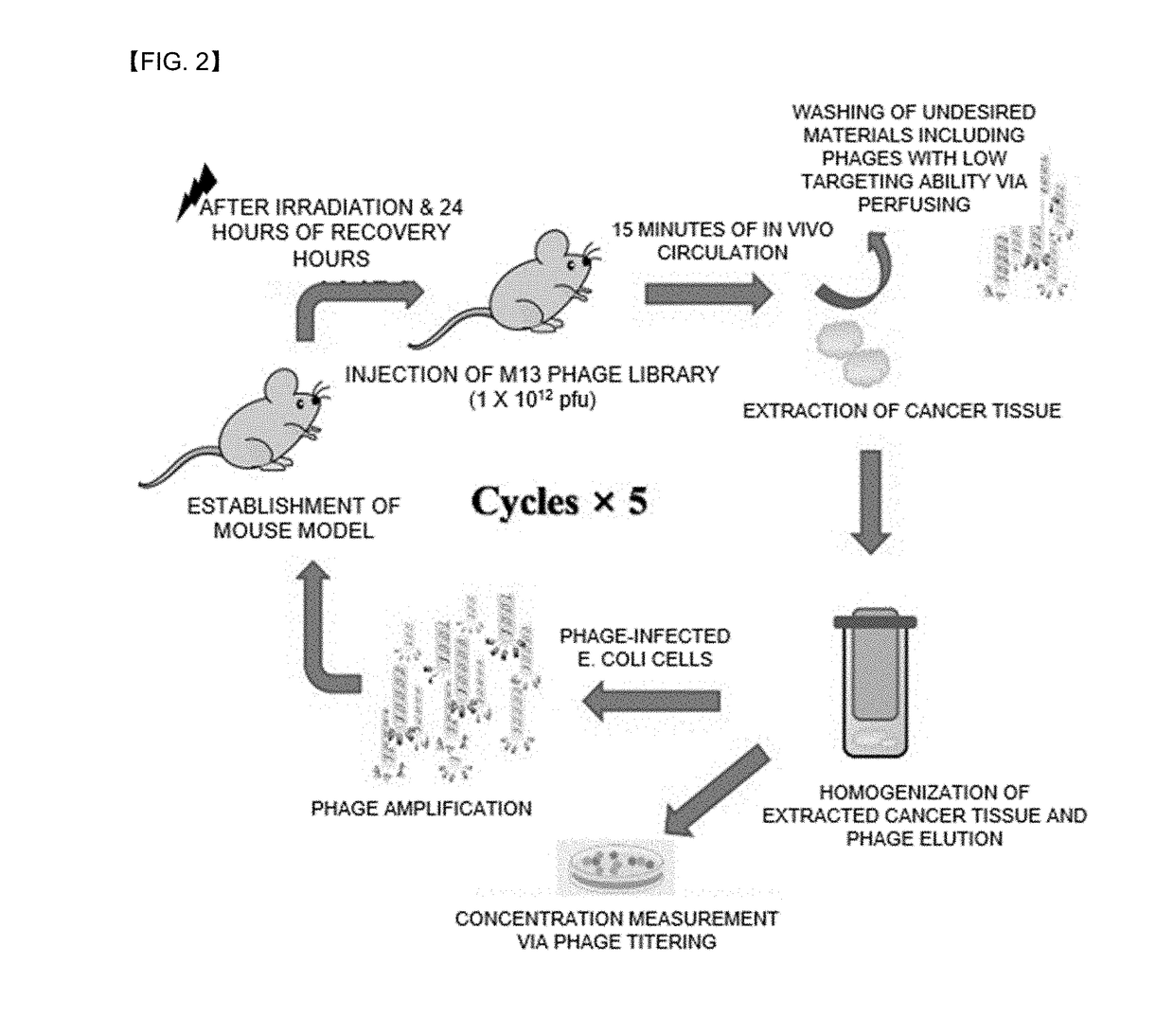
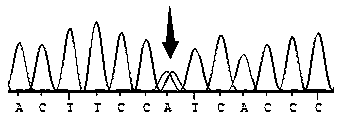
Provided is a peptide for targeting gastric cancer, a composition for diagnosing radioresponsiveness-dependent gastric cancer using the peptide, and a drug delivery use of the peptide, wherein a functional peptide capable of targeting cancer has been discovered so as to implement personalized diagnosis and treatment for individual patients having cancer, consideration of problems occurring during treatment in which treatment cases of respective patients differ due to different therapeutic responses resulting from genetic differences in the individual patients.
Owner:UNIV OF ULSAN FOUND FOR IND COOPERATION
Method for breeding high-quality high-yield silkworm breed suitable for industrial breeding
The invention relates to the technical field of silkworm breed cultivation, in particular to a method for breeding a high-quality high-yield silkworm breed suitable for industrial breeding. The method includes: adopting a single moth area breeding method, a gradual improving and selecting technique and a molecular marker technology to acquire moth areas and individual breeds which are stabile in hereditary and good in artificial feed eating; adopting a China-Japan series breeder seed genetic complement principle and a molecular marker genetic polymorphism and genetic difference analysis technique to generate a good hybridized combination generation by mating and acquire the high-quality high-yield silkworm breed according with industrial production; adjusting breeding temperature, feed amount, feed shape and breeding facility and adopting a silkworm disease prevention technique unique in pertinence and a temperature and humidity remote controlling technique to systematically set up an artificially-fed silkworm breeding technology and a hybridized combination generation artificial feeding and industrial feeding technology. The good breed which is high in feed consumption and suitable for industrial breeding is selected by means of the hybridization technique, orderliness and robustness in development are promoted, diseases and environmental hazards are reduced, and safety in silkworm breeding is guaranteed.
Owner:XINYUAN COCOON SILK GROUP
Aspirin individualized drug gene detection kit and detection method
PendingCN109207583APrecision therapyPrevention of cardiovascular eventsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetic divergence
Owner:中科基因生物科技(江苏)有限公司
Methods for identifying anatomical and molecular targets for analgesic therapy
InactiveUS20060253014A1Suitable for usePromote generationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineGenetic divergence
This invention features methods for identifying targets for analgesic therapy by comparing the results of functional magnetic resonance imaging in non-human test subjects having genetically-based differences in their neural responses to painful stimuli.
Owner:MCLEAN HOSPITAL THE
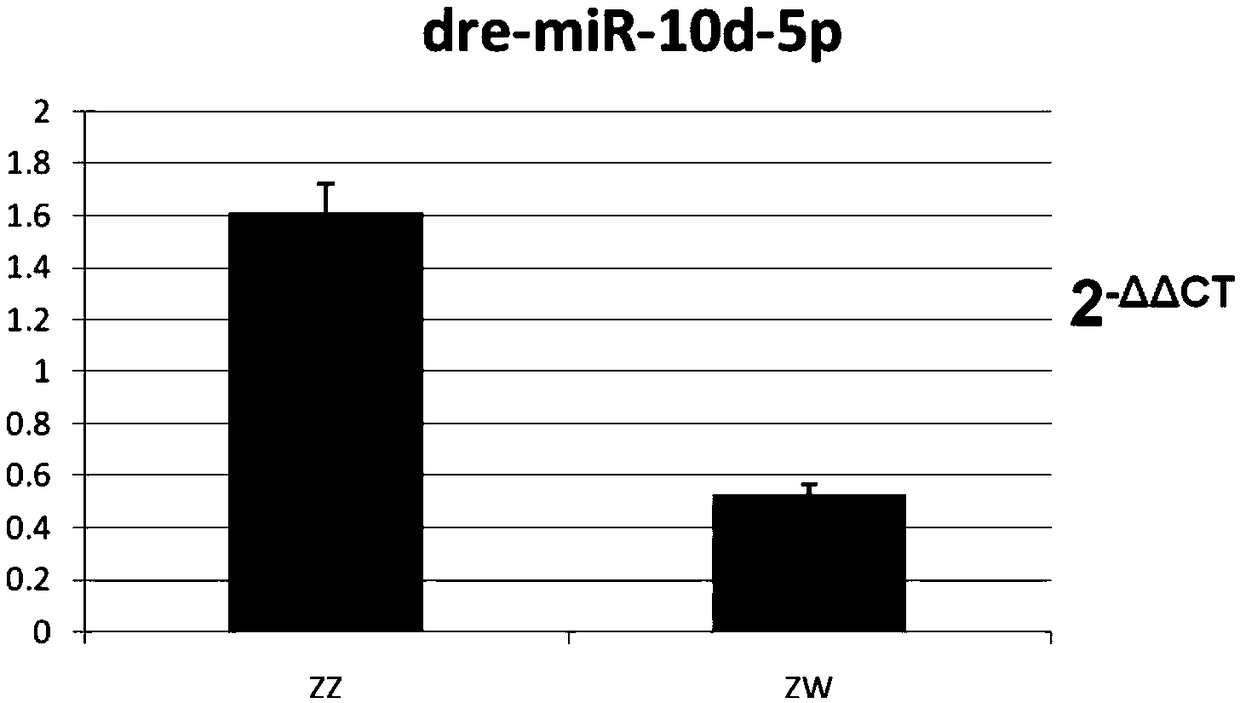
Cynoglossus semilaevis exosome gender difference expression label and kit
InactiveCN109055520ACause traumaAccurate and reliable identification resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementReproductive geneticsExosome
The invention relates to a cynoglossus semilaevis exosome gender difference expression label and a kit, belonging to the field of fish biotechnology. A micro ribonucleic acid (miRNA) gender label is dre-miR-10d-5p, and a sequence is TACCCTGTAGAACCGAATGTGTG; the problem of distinguishing reproductive genetic differences between male cynoglossus semilaevis and female pseudo-male cynoglossus semilaevis is solved. The marker miRNAs have the characteristic of significant difference expression of male fish and female pseudo-male fish, and are specific molecular recognition markers.
Owner:TIANJIN BOHAI SEA FISHERIES RES INST
Cold region hybrid japonica rice breeding method
InactiveCN106332770AGenetically stableHigh sterile threshold temperaturePlant genotype modificationDiseaseTest sample
The invention relates to the field of hybrid rice genetic breeding, and especially relates to a cold region hybrid japonica rice breeding method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out backcross breeding with Yannong S carrying out an inverse temperature-sensitive sterile gene as a donor parent and cold region japonica rice R1 with excellent comprehensive properties as a recurrent parent, and cultivating to obtain an inverse temperature-sensitive sterile line R1S reserving the basic characteristics of the R1; 2, carrying out massive crossing hybridization combination with the R1S as a female parent and cold region japonica rice R2 with excellent comprehensive properties as a male parent to obtain R1S / R2; and 3, evaluating the comprehensive properties of the R1S / R2 with test sample species in the same ecologic region, and screening to obtain cold region hybrid japonica rice, wherein the comprehensive properties comprise but not be limited to one or more of the output, the cold resistance, the disease resistance and the rice quality, and the cold region japonica rice R2 and the cold region japonica rice R1 have genetic differences. The cold region hybrid japonica rice breeding method has the characteristics of high critical sterility inducing temperature, stable hereditary potency, high yield, high quality, good cold and disease resistance, and inverse temperature-sensitive sterility.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT +1
Primer for identifying coilia ectenes and coilia brachygnathus and molecular biological method
ActiveCN106434642AImprove identification efficiencySimple resultMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenetic divergenceCoilia
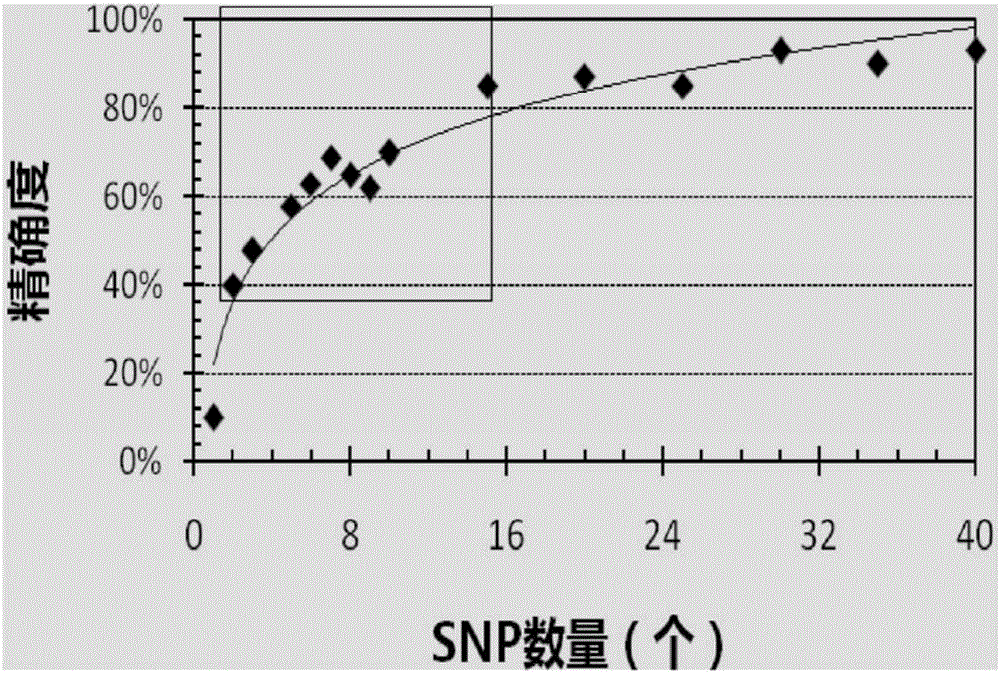
The invention provides a primer for identifying coilia ectenes and coilia brachygnathus and a molecular biological method. The primer contains an amplified primer group and an extended primer group. A nucleotide sequence of the amplified primer group is shown as SEQ ID NO:1-16, a nucleotide sequence of the extended primer group is shown as SEQ ID NO:17-24. The primer combination can be effectively used for identifying the coilia ectenes and the coilia brachygnathus. The molecular biological method comprises the steps that a to-be-tested coilia ectenes and coilia brachygnathus SNP locus area nucleic acid sequencing library is established, sequencing is conducted on the library to obtain a sequencing result; based on the sequencing result, a coilia ectenes and coilia brachygnathus SNP locus area nucleic acid sequence is determined; then Structure2.3.2 software is utilized to draw a column diagram of population genetic differences and a column diagram of individual genetic differences, and species are judged by utilizing analysis. The method includes simple and convenient steps and is accurate, efficient and low in cost.
Owner:XINYANG AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Hybrid breeding method for sea cucumber
A hybridization method between Chinese spiny sea cucumber and Russian (or korean) one for preparing the hybrid one with high growth speed, stress resistance, survival rate and nutritive value includes such steps as using special culture technique to make them mature symultaneously, artificial oxytocia to obtain their spermatozoa and ova, artificial fertilization, and culturing fertilizer ova until they become laval plankton.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Use and method for predicting serotonin re-uptake inhibitor medicine effect by polymorphic site
InactiveCN101029337AImprove efficiencyImprove securityNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementSerotoninDepressant
A method for determining HTR1A gene polymorphism site gene and predicting 5-hydroxytrytamine re-ingestion inhibitor medicinal effect and its use are disclosed. It can predict therapeutical effect and acting time by polymorphism site oligonucleotide inspecting biological sample. It's safe, cheap and non-toxic and can be used for thymoleptic and medicine in treatment of sexual disorders.
Owner:BEIJING HUAANFO BIOMEDICAL RES CENT +1
SNP marker for analyzing rice genetic diversity and identifying varieties, primers and application
ActiveCN107868839AImprove versatilityEasy to controlMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly discloses an SNP marker for analyzing rice genetic diversity and identifying varieties, loci of the SNP marker in rice, primers obtaining the SNP marker as well as related application. The SNP marker has good generality and does not need large-sized equipment instrument. The SNP marker disclosed by the invention canbe used for accurately distinguishing genotypes of to-be-detected varieties, genetic difference among the varieties and difference among the loci with close genetic distance; after the primer of certain locus is designed, a plurality of individuals can be researched for the locus, so that the cost is well controlled.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular markers linked to PPO inhibitor tolerance in soybeans
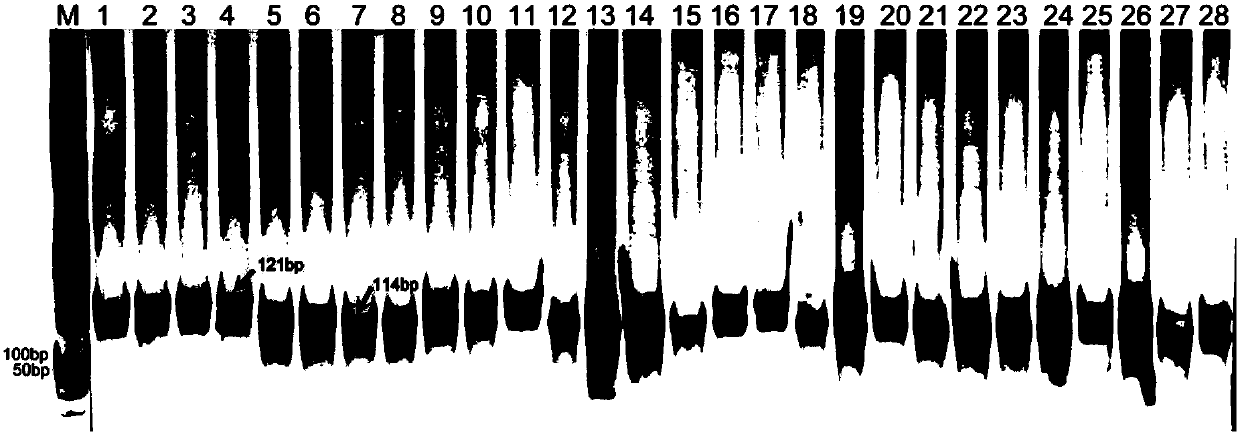
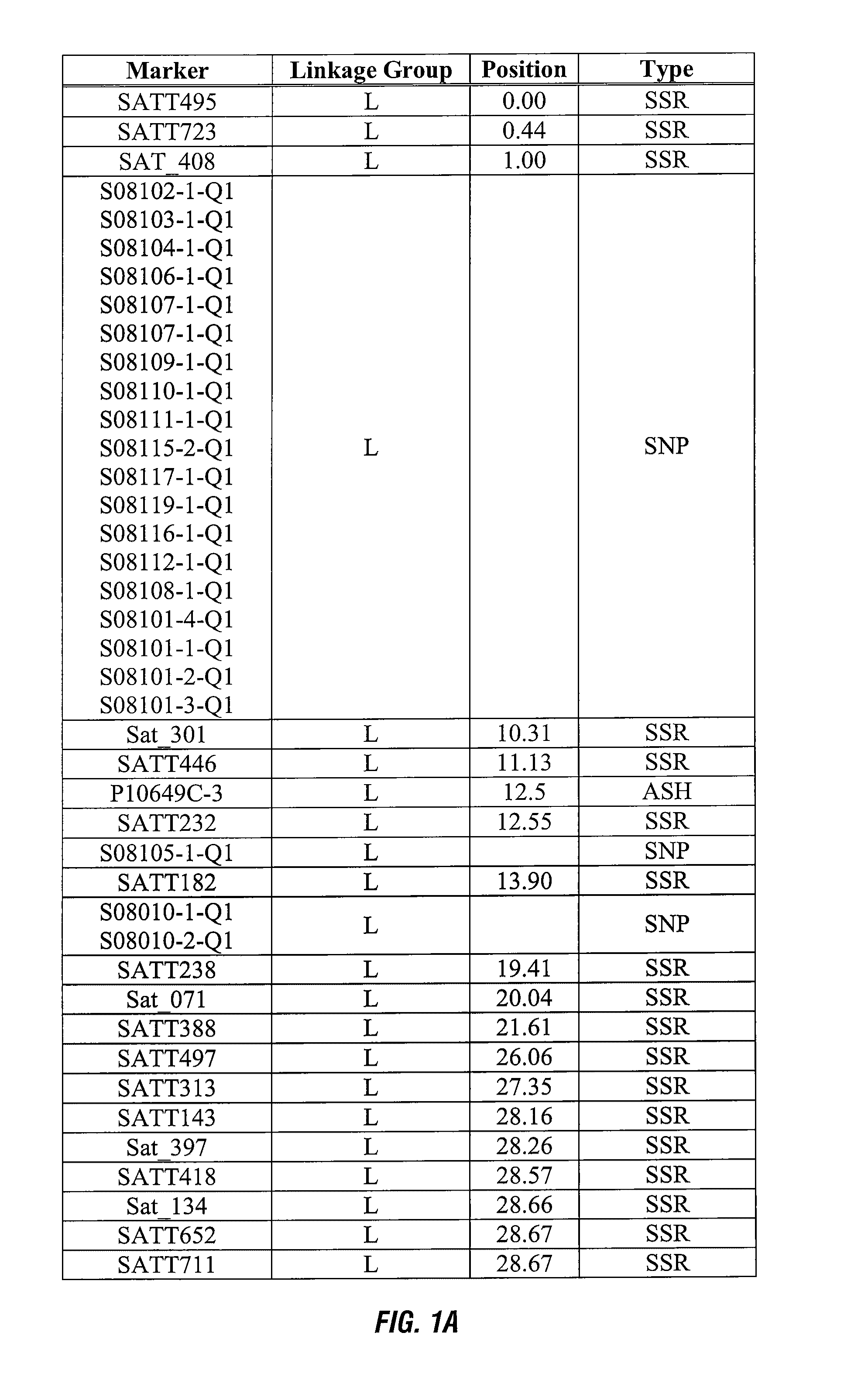
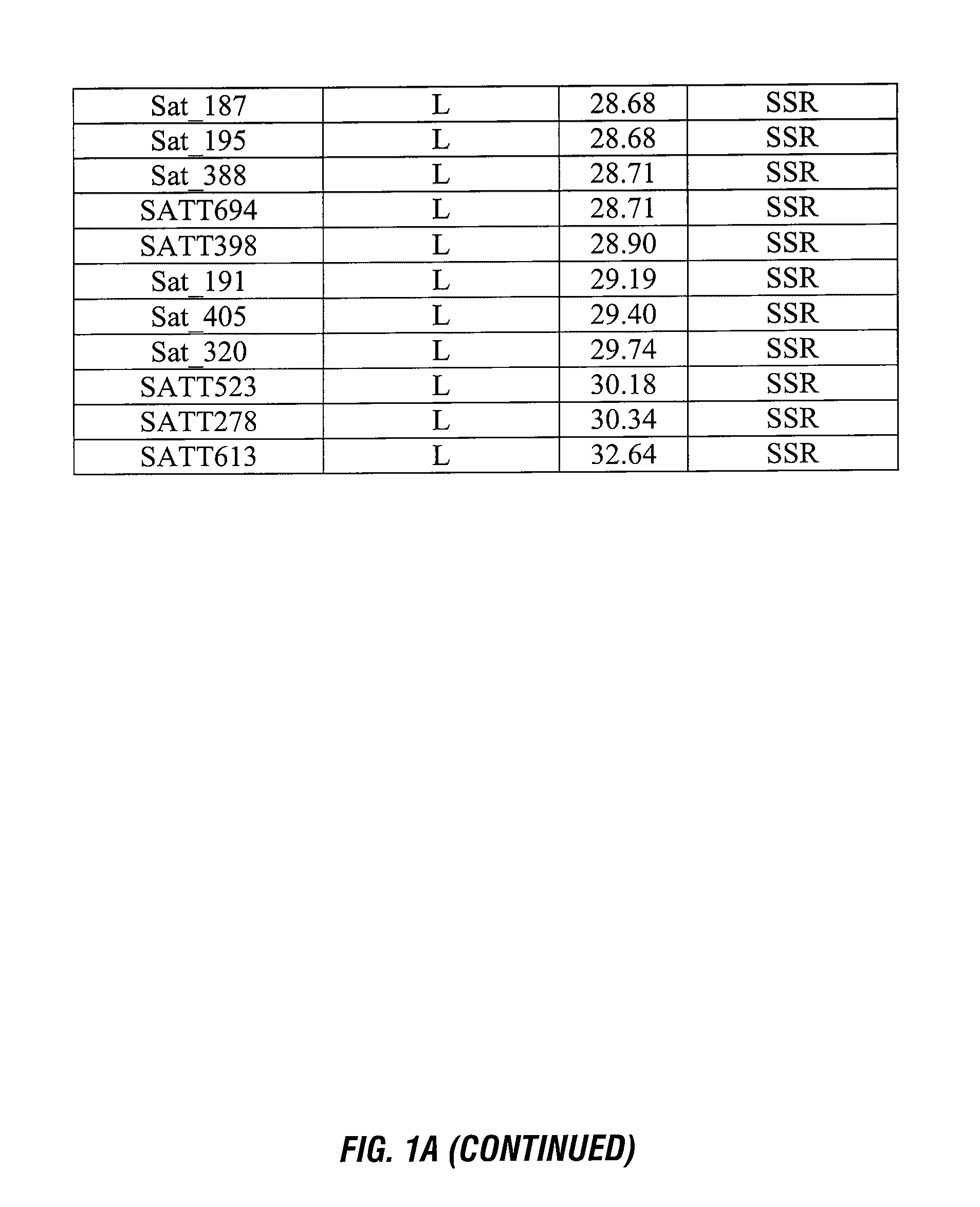
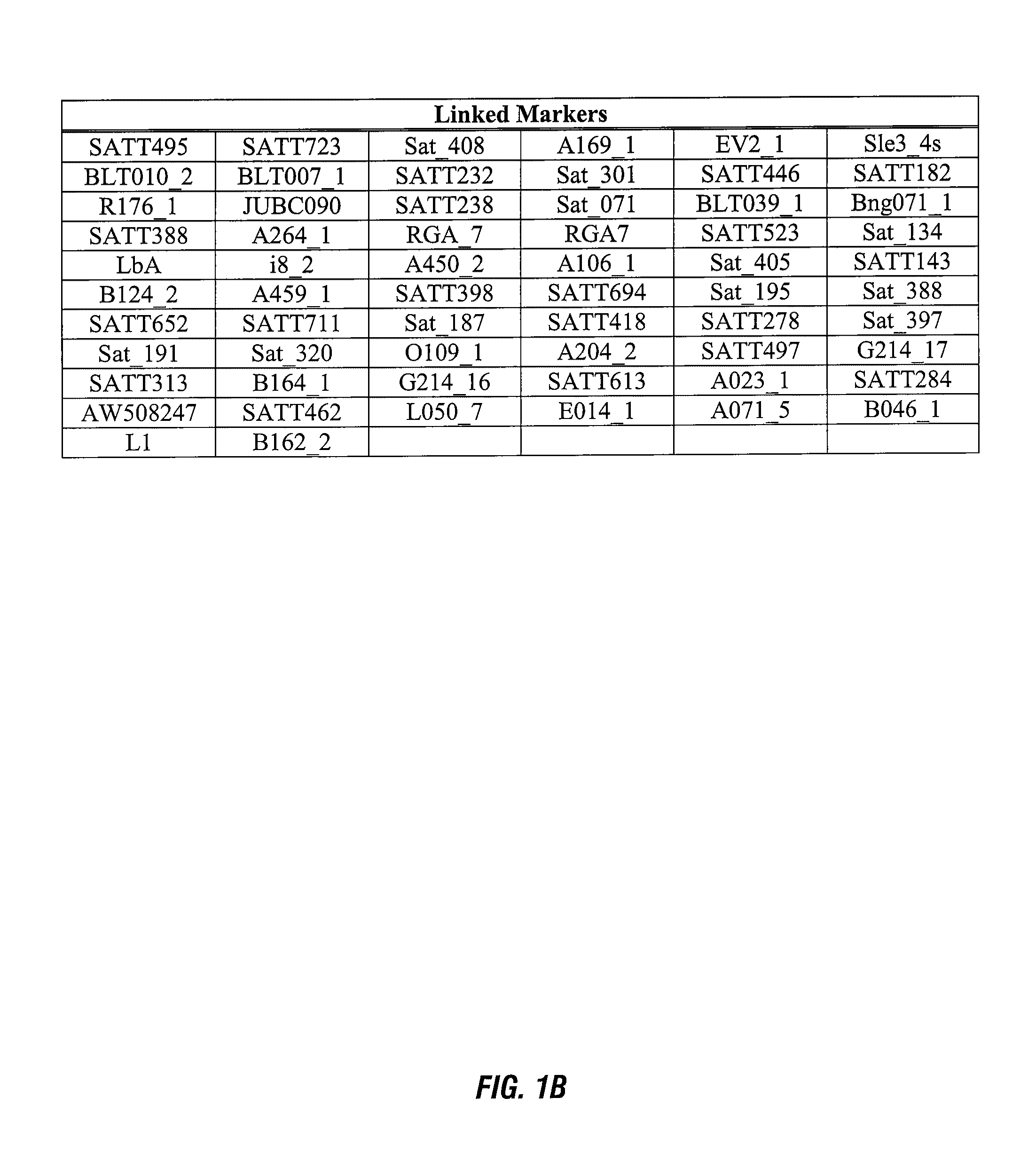
ActiveUS8748695B2Negatively impactingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic divergenceGenotyping
This invention relates generally to the detection of genetic differences among soybeans. More particularly, the invention relates to soybean quantitative trait loci (QTL) for tolerance to protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors, to soybean plants possessing these QTLs, which map to a novel chromosomal region, and to genetic markers that are indicative of phenotypes associated with protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor tolerance. Methods and compositions for use of these markers in genotyping of soybean and selection are also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for screening molecular marker of Jinhu black-bone chickens and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN109321665ALow costRich dataMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGenetic divergence
The invention provides a method for screening a molecular marker of Jinhu black-bone chickens and application of the molecular marker and relates to the field of genetics. The method for screening themolecular marker of the Jinhu black-bone chickens comprises the steps of detecting an SNP marker through high-pass sequencing, calculating genetic statistics, and analyzing and comparing genetic differences between Jinhu black-bone chicken colonies and other chicken colonies, thereby screening out the molecular marker of the Jinhu black-bone chickens. The technical problem that the research on genetic differentiation of the Jinhu black-bone chickens is high in cost and low in accuracy due to the fact that a process of evaluation on a Jinhu black-bone chicken breed conservation effect is lackof efficient molecular biology methods at present is solved, and the technical effect of efficiently and rapidly screening out the molecular marker for evaluating the Jinhu black-bone chicken breed conservation effect is achieved. The invention further provides the method for screening the molecular marker of the Jinhu black-bone chickens and application of the screened molecular marker. The technical problem that researches on the Jinhu black-bone chickens are lack of molecular biological markers and screening methods is solved.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Application of cynoglossus semilaevis gender difference indication label
ActiveCN109055521ACause traumaAccurate and reliable identification resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementReproductive geneticsGenetic divergence
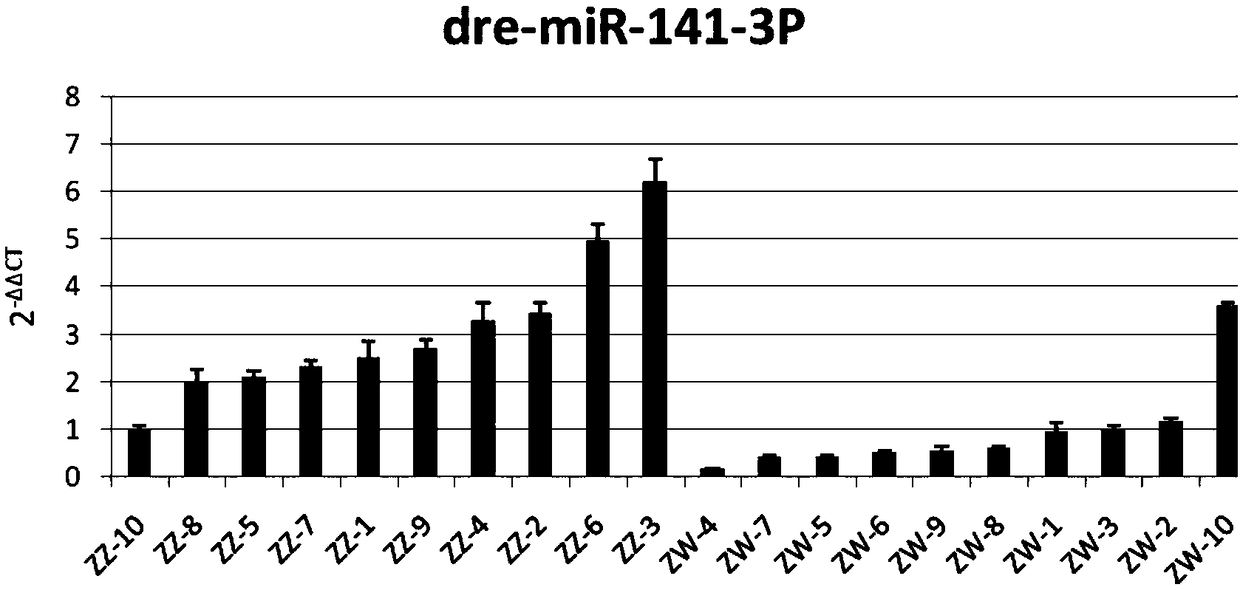
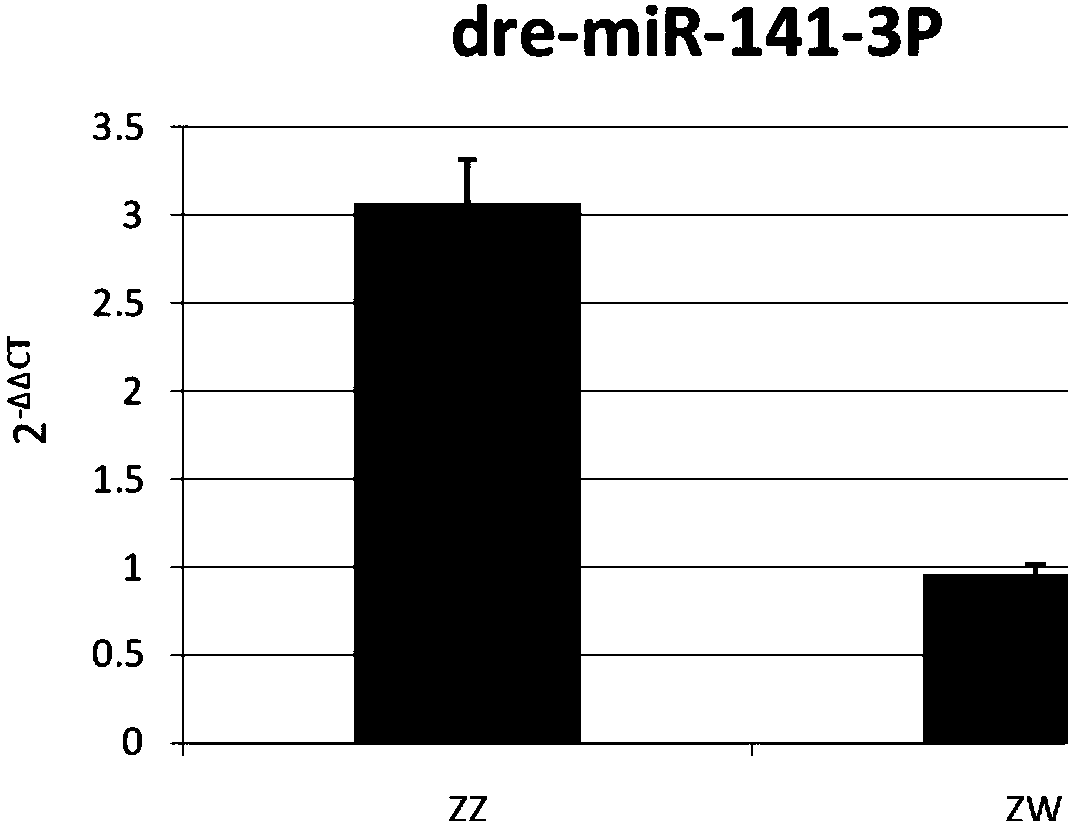
The invention relates to application of a cynoglossus semilaevis gender difference indication label, belonging to the field of fish biotechnology. A micro ribonucleic acid (miRNA) gender label is sdre-miR-141-3p, and a sequence is TAACACTGTCTGGTAACGATGC; the problem of distinguishing reproductive genetic differences between male cynoglossus semilaevis and female pseudo-male cynoglossus semilaevisis solved. The marker miRNAs have the characteristic of significant difference expression of male fish and female pseudo-male fish, and are specific molecular recognition markers.
Owner:TIANJIN BOHAI SEA FISHERIES RES INST
Primer group for identifying sika deer, red deer and hybrid deer, kit and application
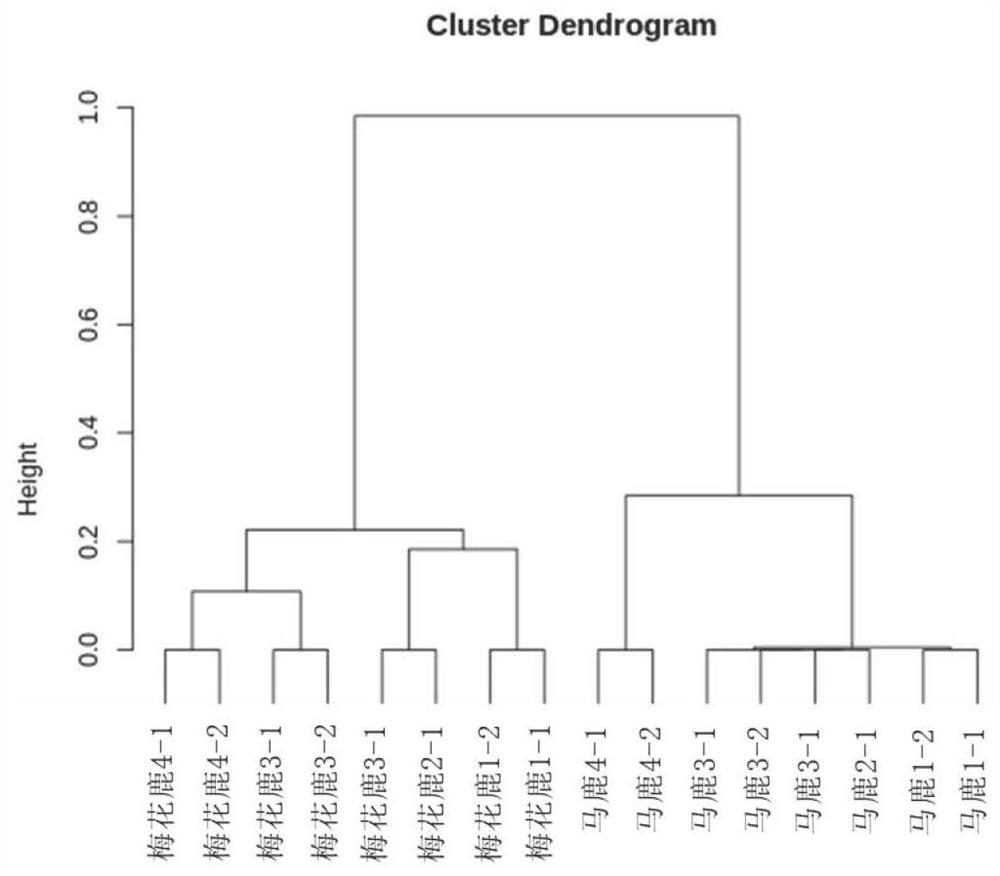
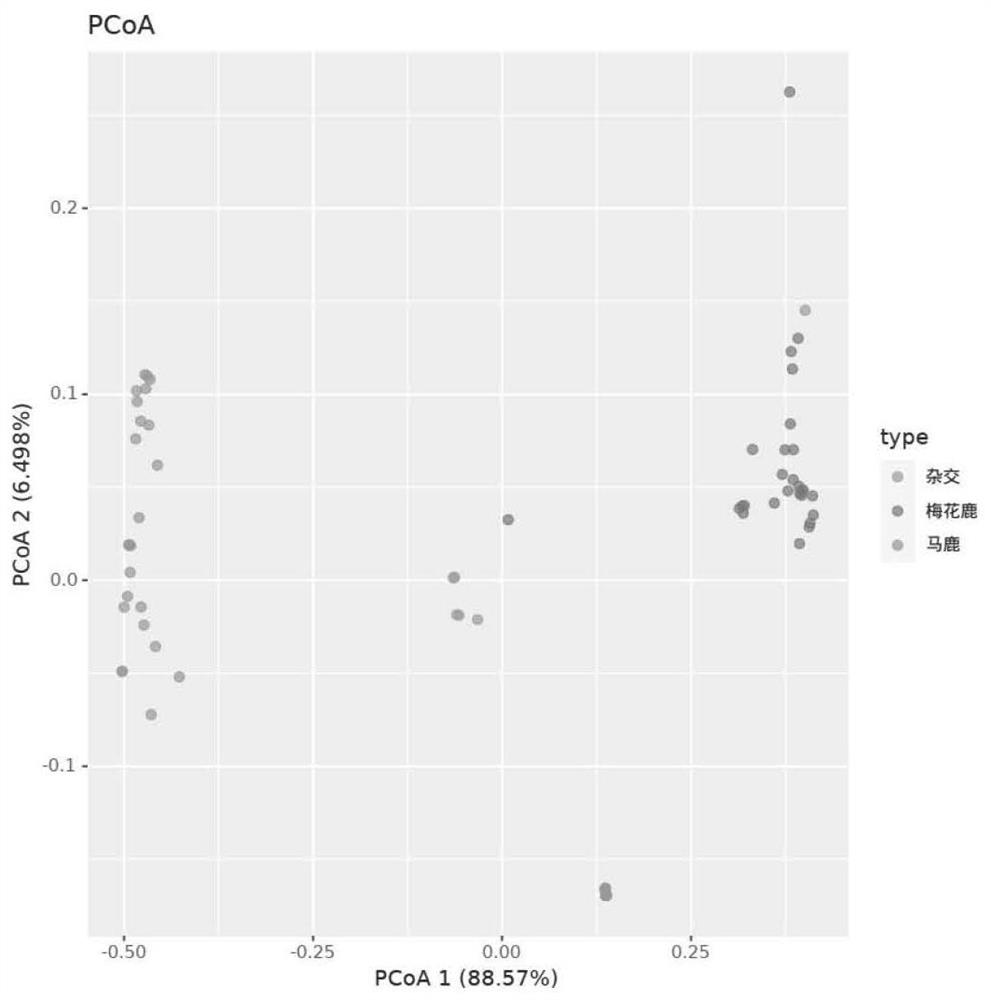
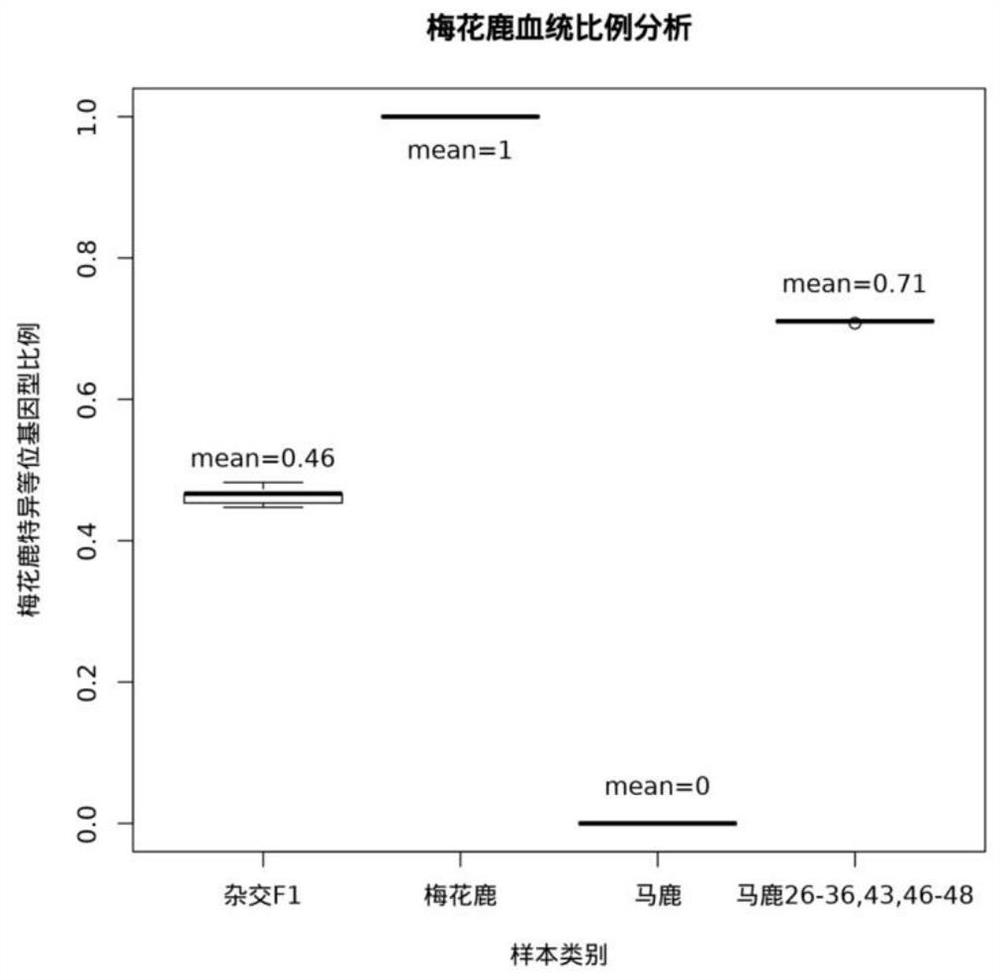
ActiveCN113832236AImprove accuracyHigh individual discriminationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a primer group for identifying the sika deer, the red deer and the hybrid deer, a kit and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The primer group comprises primers as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 400 in a sequence table. According to the application of MNP marker sites, 200 MNP marker sites shown in Table 1 in the specification are used for genetic difference analysis of the sika deer, the red deer and the hybrid deer and blood line analysis of the sika deer, the red deer and the hybrid deer. The primer group provided by the embodiment of the invention has good distinction degree, reproducibility and accuracy, the kit using the primer group can simultaneously have the advantages, and the detection accuracy can be effectively ensured.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY +2
Peptides for targeting colorectal cancer, and medical use thereof
ActiveUS20170328906A1Compounds screening/testingRadioactive preparation carriersCancer targetingGenetic divergence
Provided is a peptide for targeting colorectal cancer, a composition for diagnosing radioresponsiveness-dependent prognosis of colorectal cancer using the peptide, and a drug delivery use of the peptide, wherein a functional peptide capable of targeting cancer has been discovered so as to implement personalized diagnosis and treatment for individual patients having cancer, in consideration of problems occurring during treatment in which treatment cases of respective patients differ due to different therapeutic responses resulting from genetic differences in the individual patients.
Owner:UNIV OF ULSAN FOUND FOR IND COOPERATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com