Method of developing polymorphic EST-SSR marker by utilizing complete genome and EST data
A genome-wide, polymorphic technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of insufficient representation, mis-elimination of polymorphic SSR markers, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, and achieve the goal of improving development efficiency, high genetics and breeding value Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
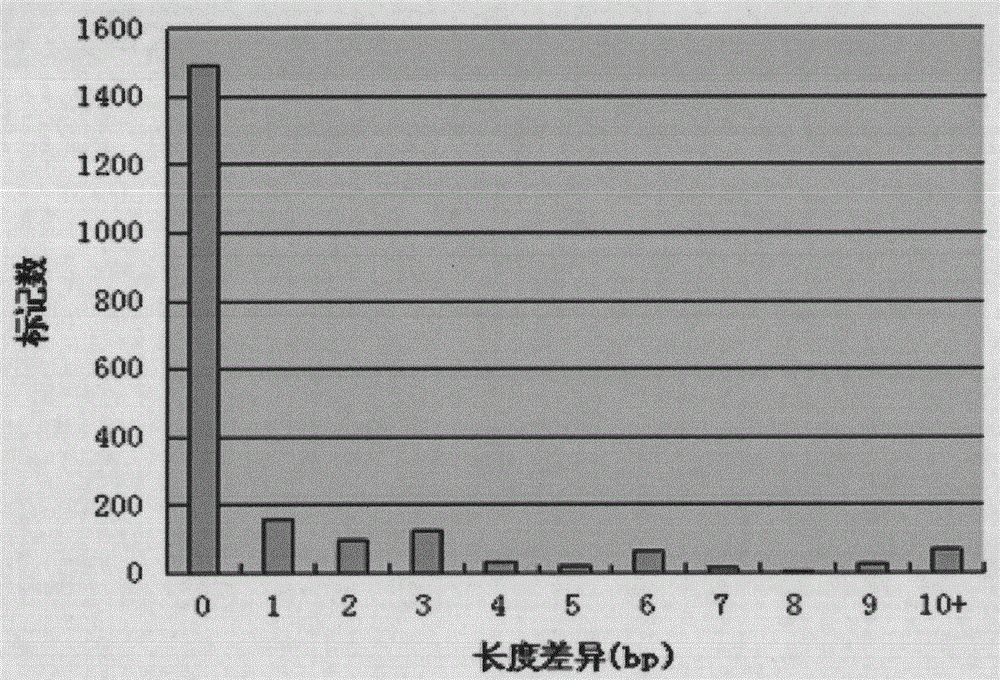
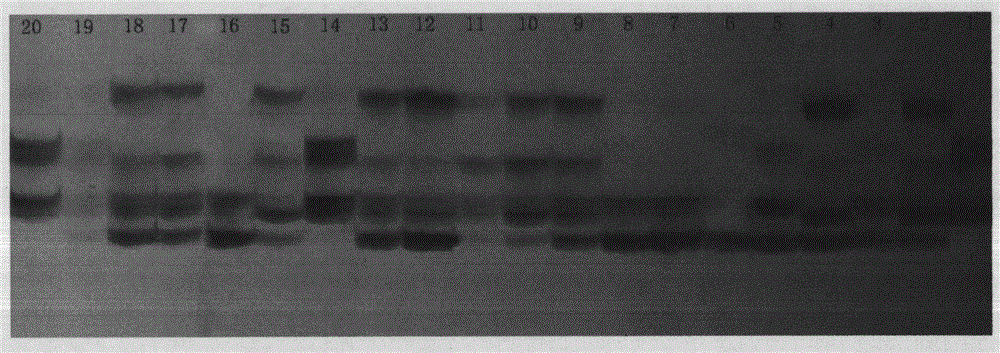
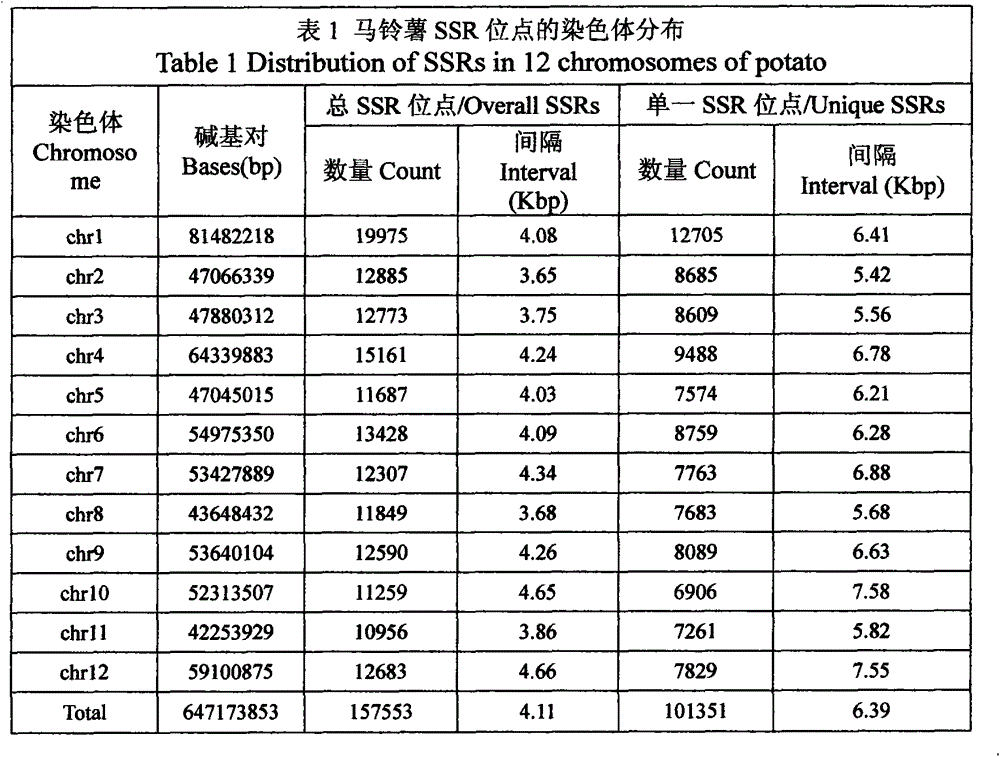
[0022] Example: Development and Validation of Potato EST-SSR Markers
[0023] Development of EST-SSR markers using genome-wide and EST data
[0024] 1.1 Obtain potato genome sequence and EST data:
[0025] The potato genome sequence data (PGSC_DM_v3_2.1.11_pseudomolecules) and corresponding gene annotation information (PGSC_DM_v3.4) were downloaded from the public database (http: / / solanaceae.plantbiology.msu.edu / ). Download potato EST data from NCBI (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ), a total of more than 260,000 (as of April 2013).
[0026] Exon and Intron sequences were analyzed using the genome annotation information, and the first 2000 bp of the gene TSS transcription start site was selected as the promoter sequence.
[0027] 1.2 Search and analysis of SSR loci in potato genome:
[0028] Use the MISA program (http: / / pgrc.ipk-gatersleben.de / misa / ) to scan the 12 chromosomal DNA sequences of the whole potato genome, search and analyze the SSR sites contained in the genome seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com