Patents
Literature
581results about How to "Non-invasive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
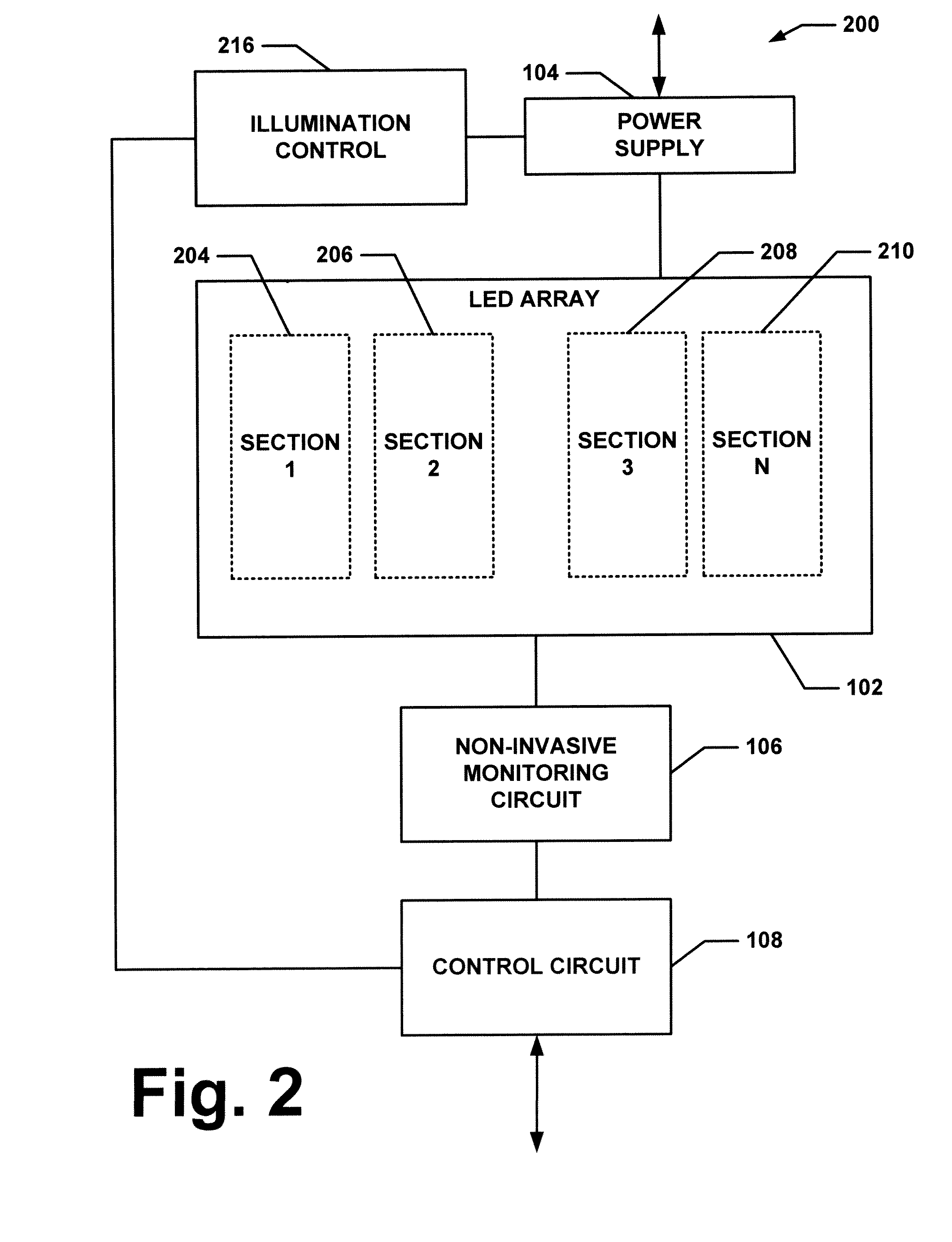
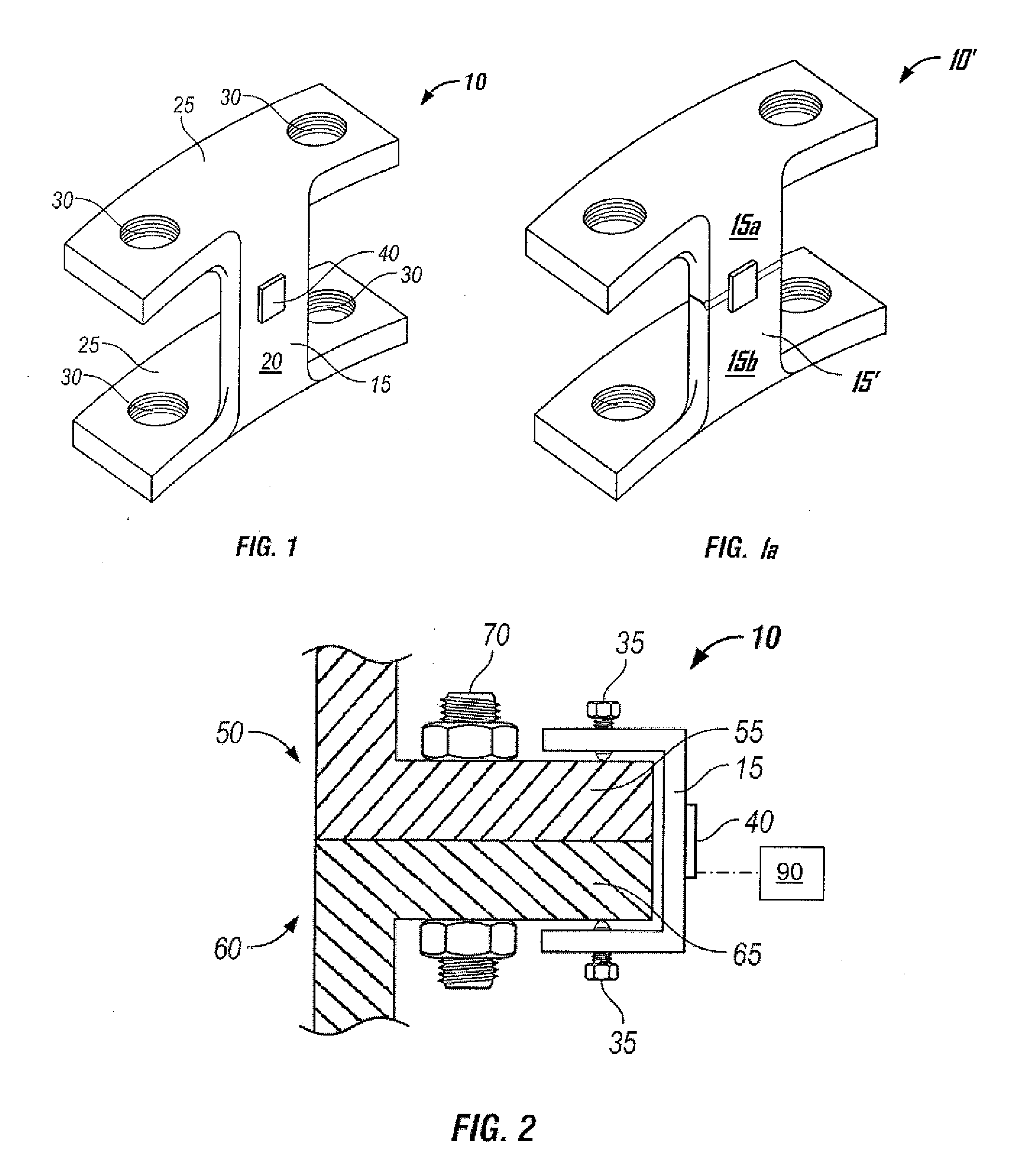
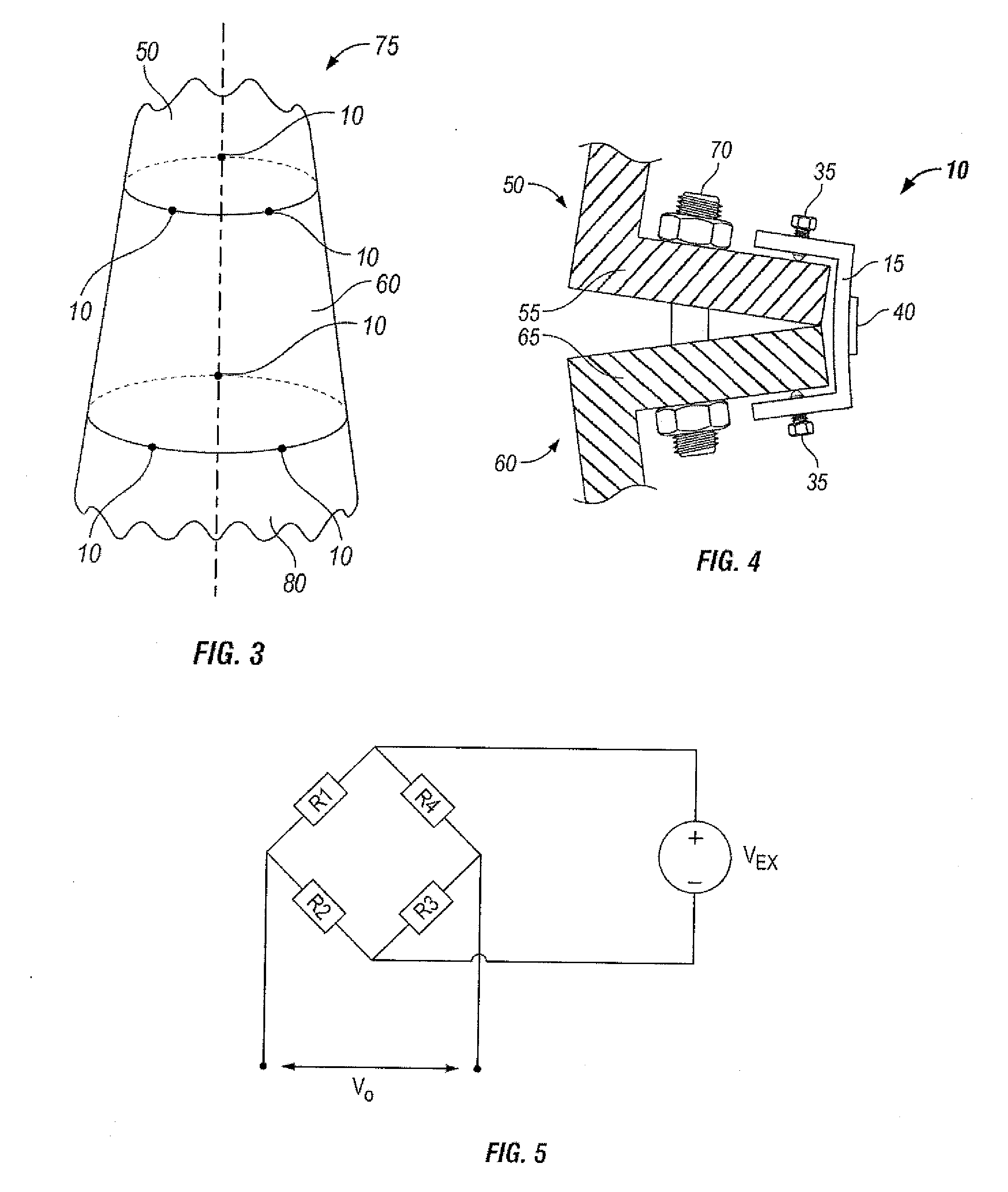
External Defibrillator
ActiveUS20080033495A1Minimal maintenancePrevent implantationHeart defibrillatorsElectricityElectrical battery
An external defibrillator having a battery; a capacitor electrically communicable with the battery; at least two electrodes electrically communicable with the capacitor and with the skin of a patient; a controller configured to charge the capacitor from the battery and to discharge the capacitor through the electrodes; and a support supporting the battery, capacitor, electrodes and controller in a deployment configuration, the defibrillator having a maximum weight per unit area in the deployment configuration of 0.1 lb / in2 and / or a maximum thickness of 1 inch. The support may be a waterproof housing.
Owner:ELEMENT SCI
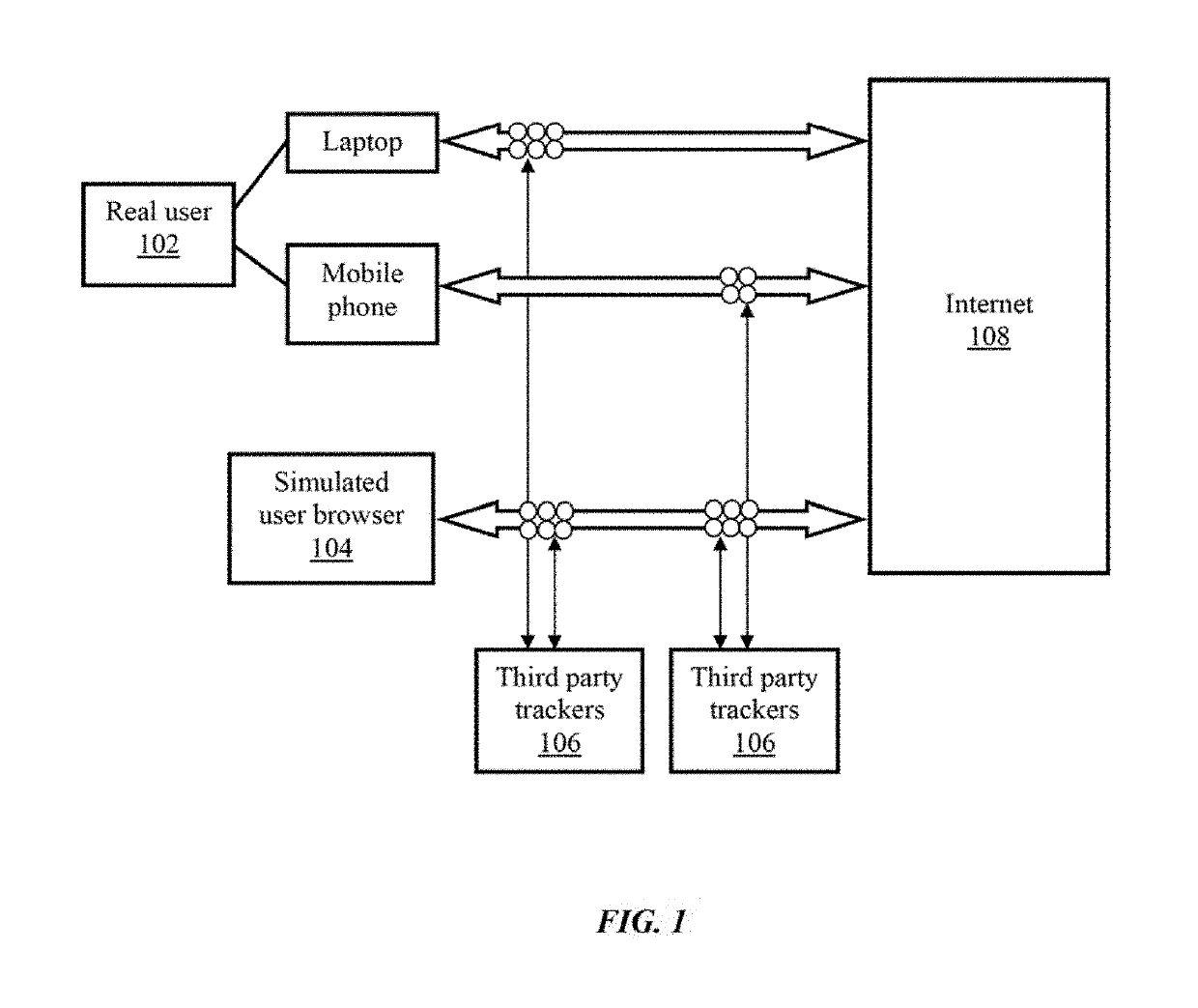
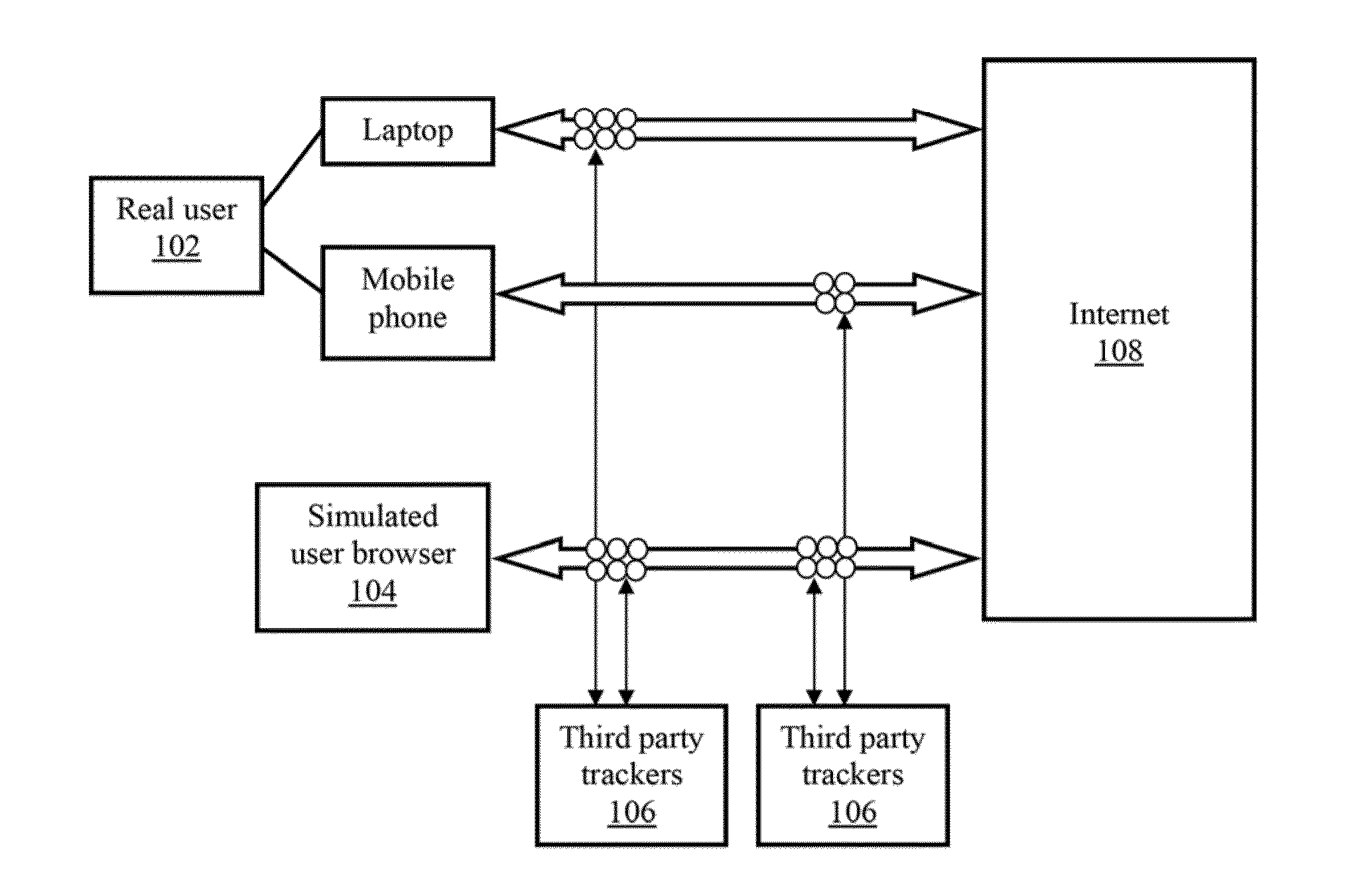
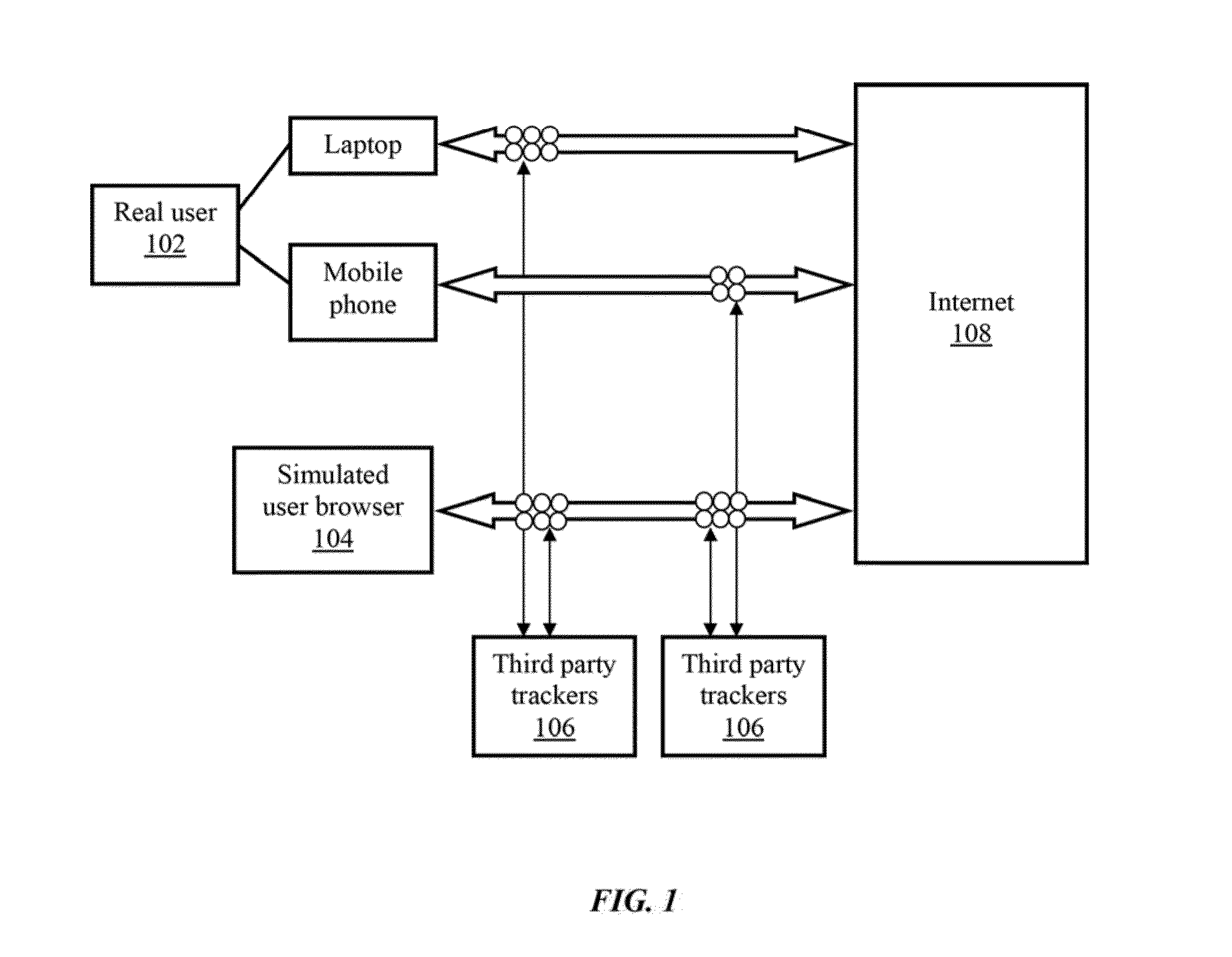
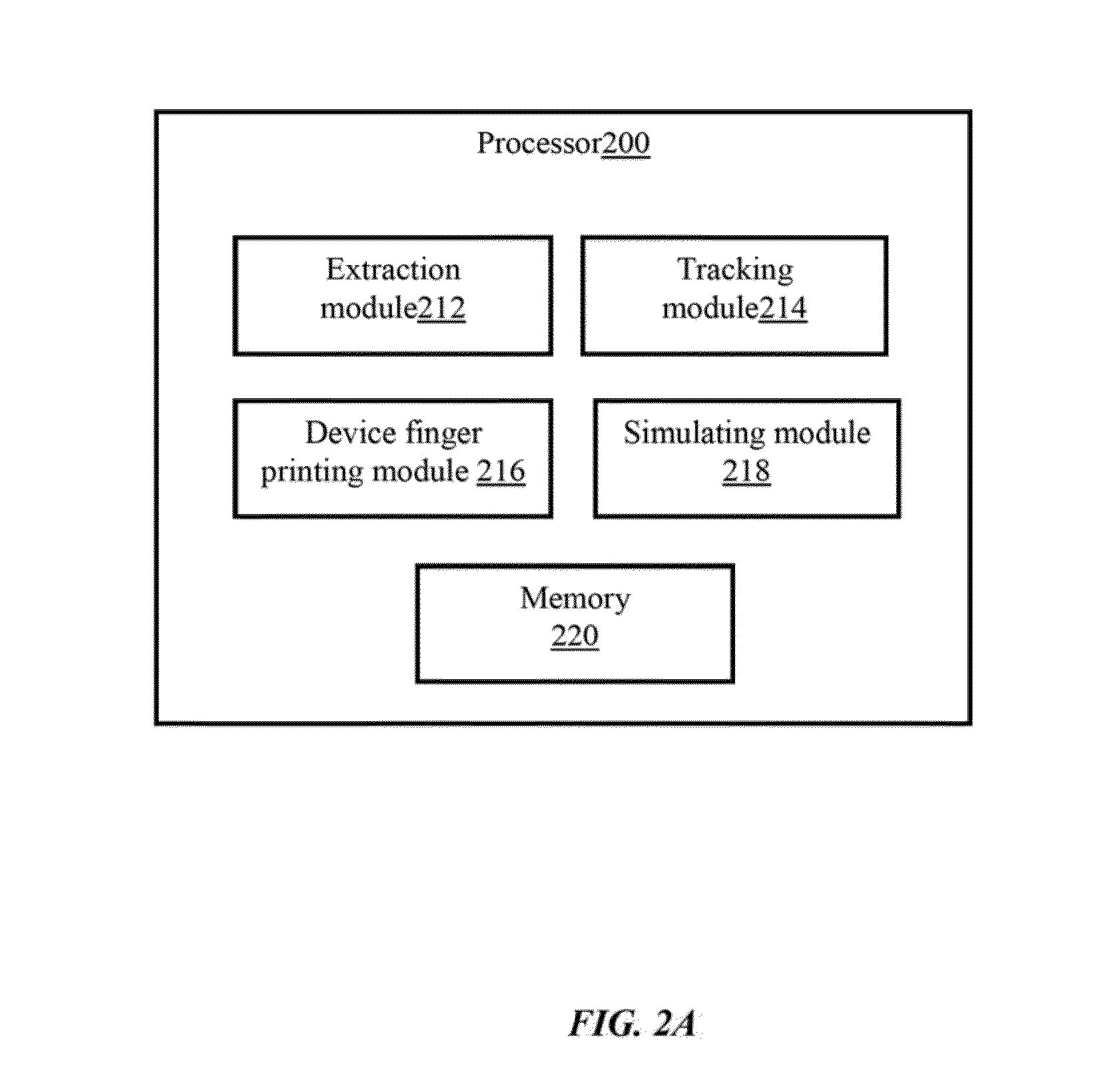
System and method for simulating internet browsing system for user without graphical user interface
ActiveUS10346186B2Non-invasiveDigital data protectionTransmissionVirtual userGraphical user interface
The embodiments herein provide a system and a method of simulating internet browsing system without a graphical user interface. The method comprises the steps of extracting browser characteristics of a real user browser. The internet browsing system is simulated without graphical user interface by including the browser character of a real user browser within the simulated virtual user browser to makes the simulated virtual user digitally identical to the real user browser. Further, the tracking elements of the real user browser are shared with the simulated virtual user browser to divert the internet trackers away from the real user browser. Further, a fingerprint on the real user browser is duplicated in the simulated virtual user browser. The method uses an algorithm to simulate the simulated virtual user browser. The algorithm is intent to sell and purchase goods and services, thereby misguiding the internet trackers.
Owner:KALYANPUR ROHAN
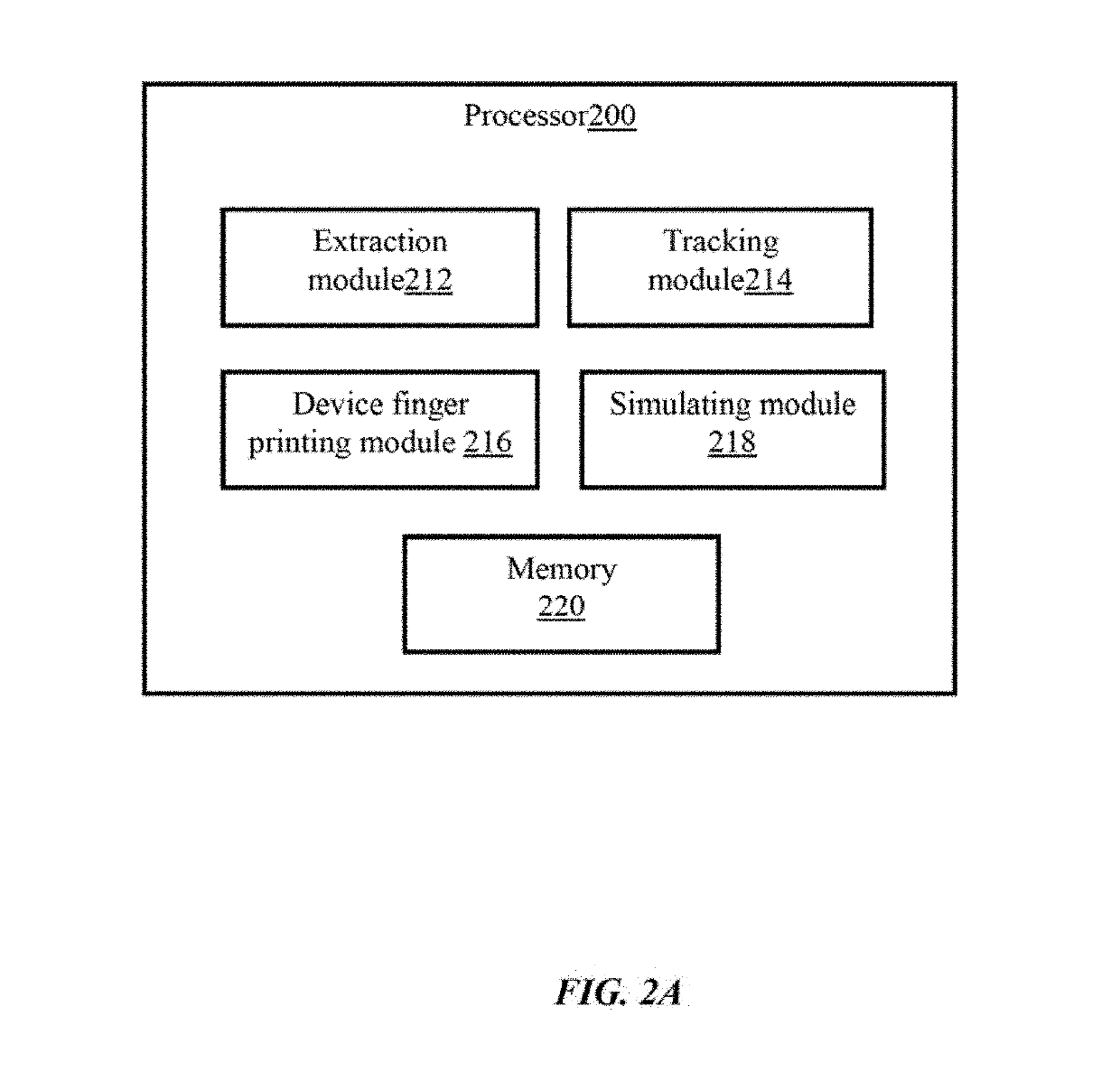
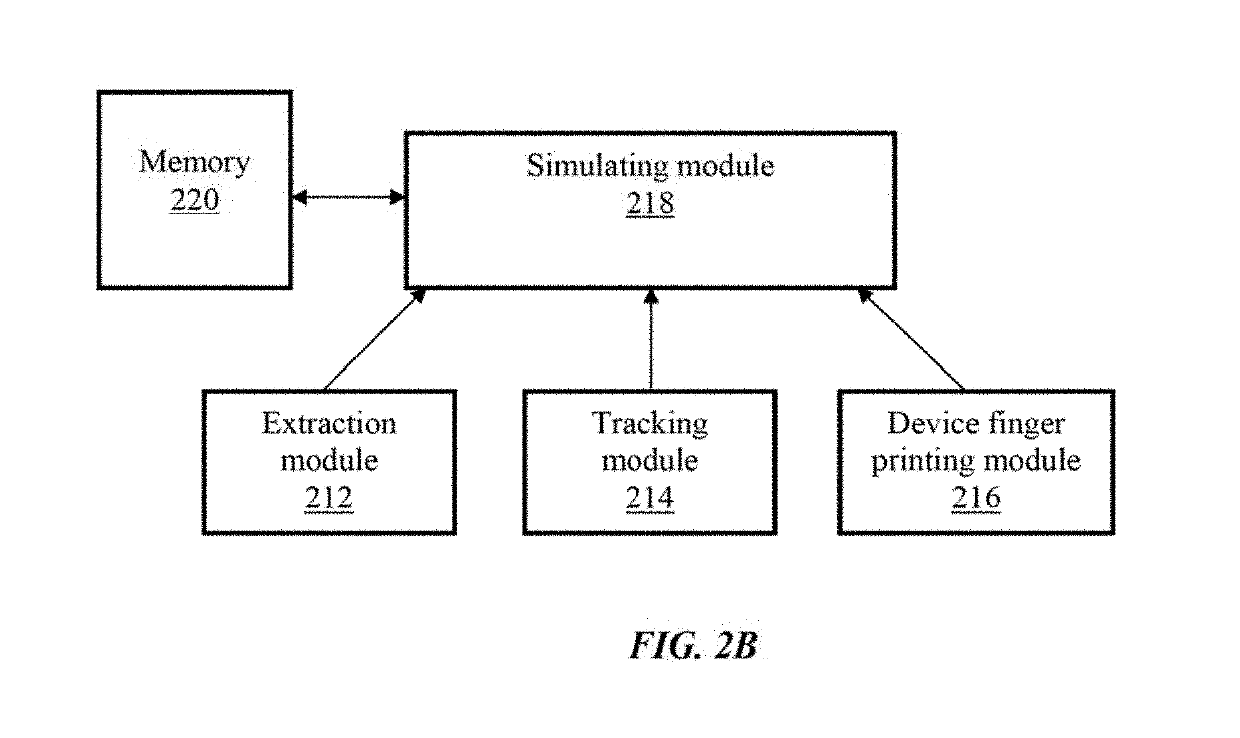
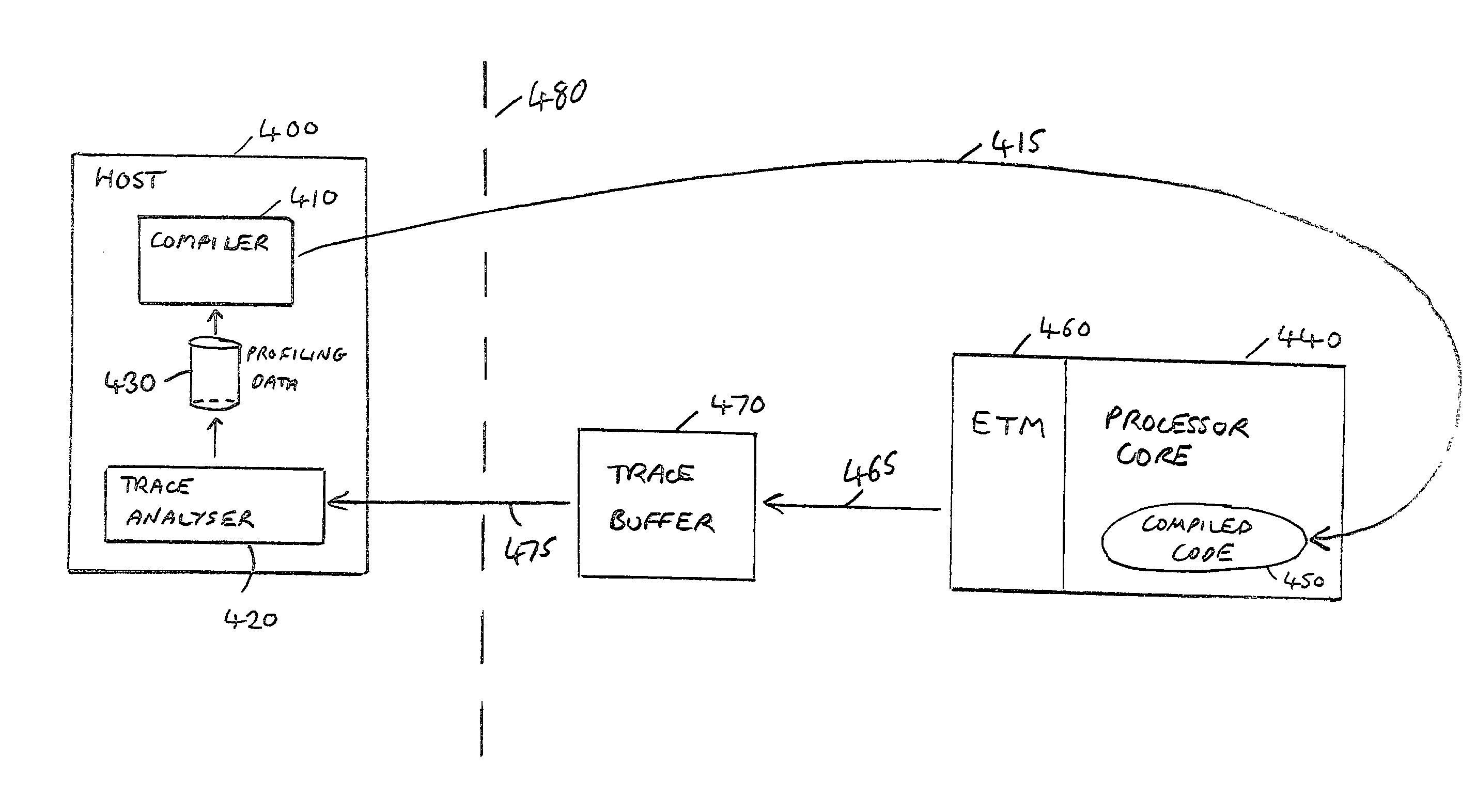
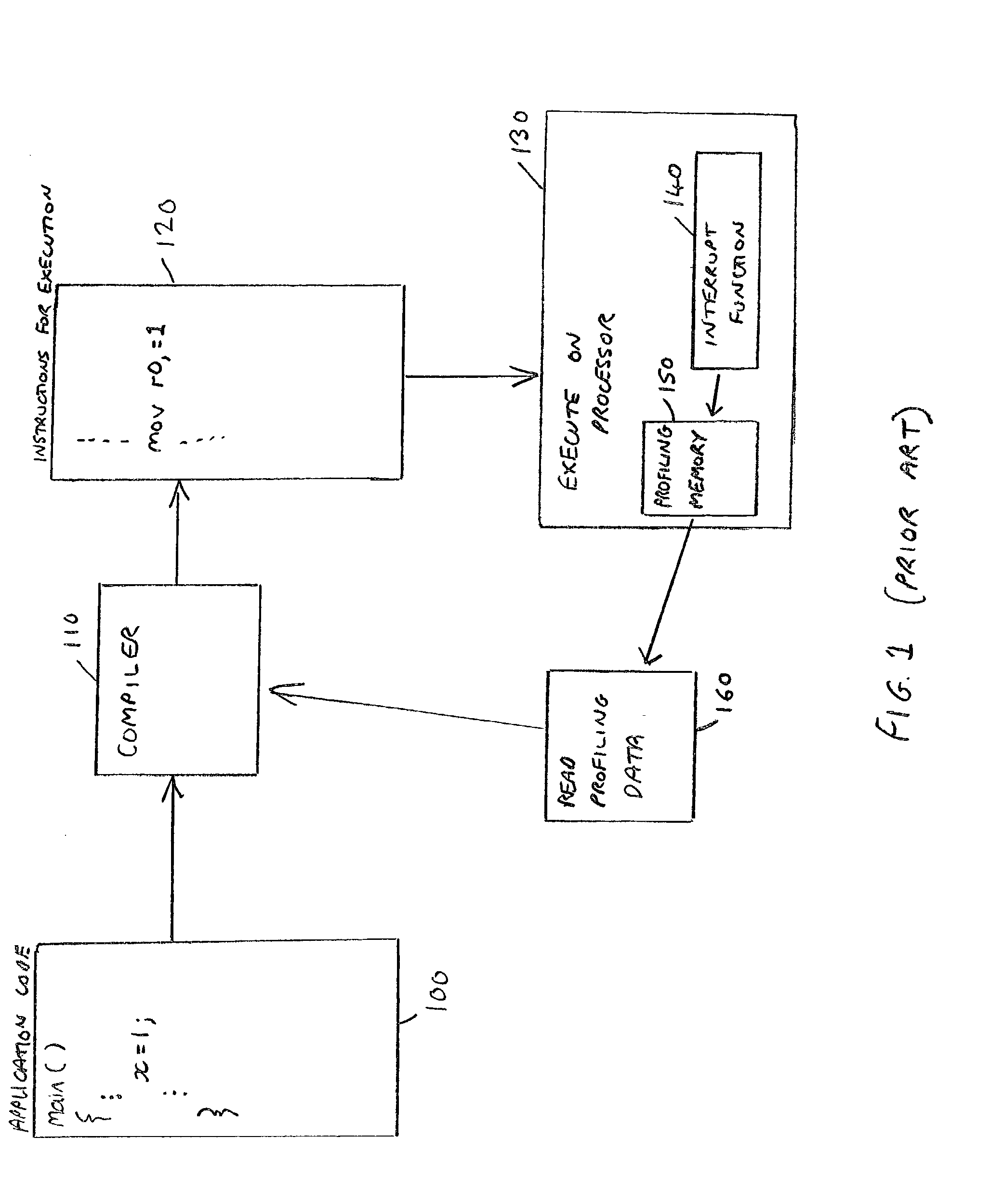
Compilation of application code in a data processing apparatus
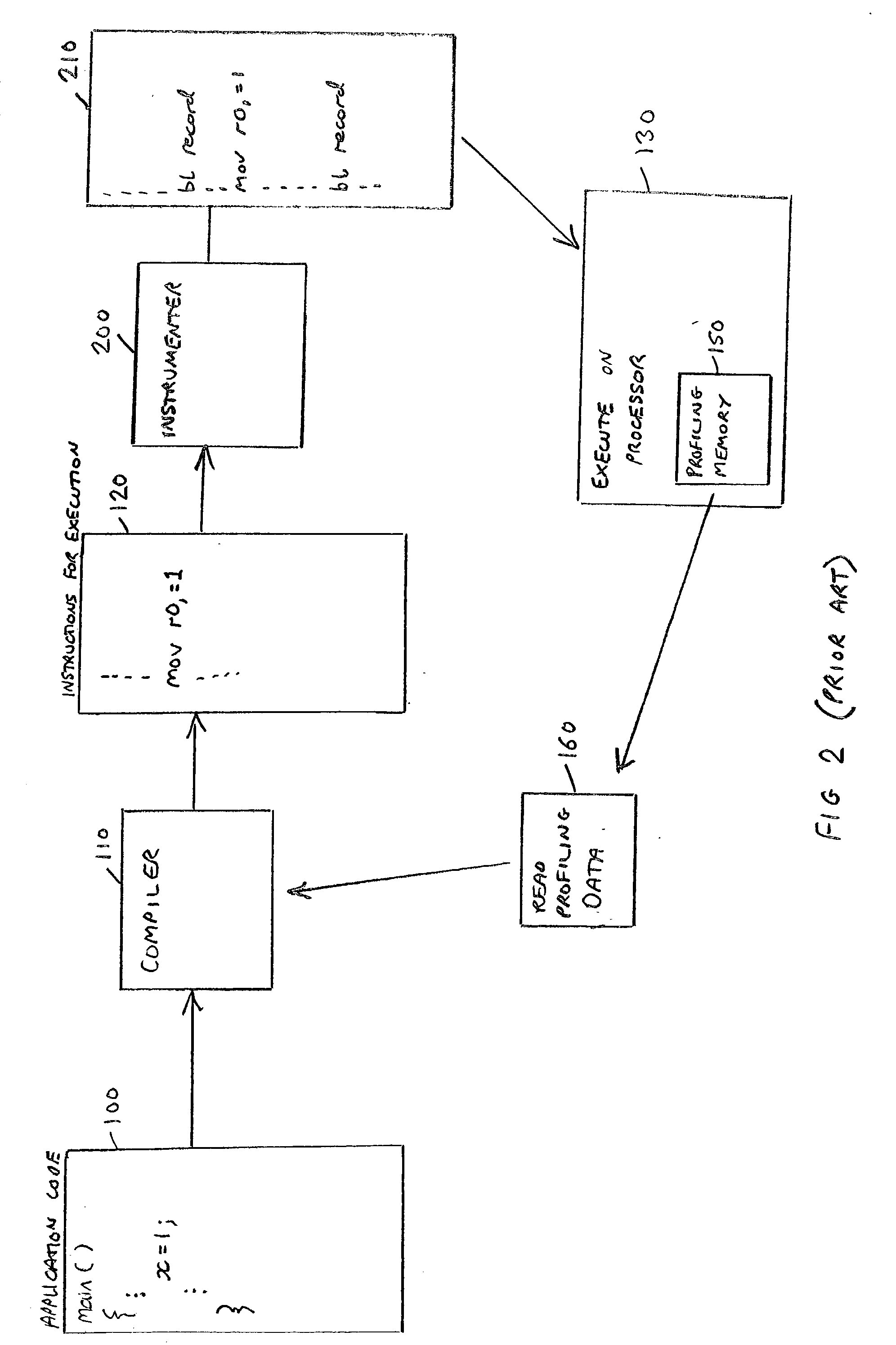
ActiveUS20040019886A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceSoftware engineeringHardware monitoringProgram codeComputer engineering
The present invention relates to a data processing apparatus and method for compiling application code. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor, and a compiler for compiling application code to generate instructions for execution by the processor. Furthermore, a non-invasive trace unit is coupled to the processor for generating, from input signals received from the processor, trace signals indicative of the instructions being executed by the processor. The compiler is then arranged to control the compilation of the application code dependent on the trace signals. The non-invasive nature of the trace unit enables it to generate trace signals that can be used to produce profiling information for use by the compiler without altering the behaviour of the code being executed by the processor, and accordingly provides a significantly improved technique for obtaining profiling information for use in feedback driven optimisation compilation techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
Devices and methods for treatment of incontinence
InactiveUS6964643B2Increase blood flowPrevent involuntary contractionPneumatic massageDiagnosticsGenital regionGynecology
Therapeutic devices and methods according to embodiments of the invention alleviate e.g. urinary incontinence in female and male patients. Suction or vacuum, for example, is applied to the genital region, clitoris or clitoral region, the external urethral orifice, and / or other designated areas, e.g. physically stimulating the sacral / pudendal nerves and / or nerve roots and alleviating incontinence. Such embodiments also can encourage or cause clitoral engorgement, or otherwise promote blood flow in the genital region. Vacuum or suction applied to e.g. the clitoris creates a negative pressure in the clitoris that is lower than the systolic blood pressure, tending to promote engorgement of the clitoris with blood. Aspects of the invention are applicable not only to treatment of urinary and fecal incontinence, but also to the treatment of female sexual dysfunction. Aspects of the invention are also applicable to treatment of male incontinence and male erectile dysfunction.
Owner:NUGYN
System and method for photoacoustic imaging and monitoring of laser therapy
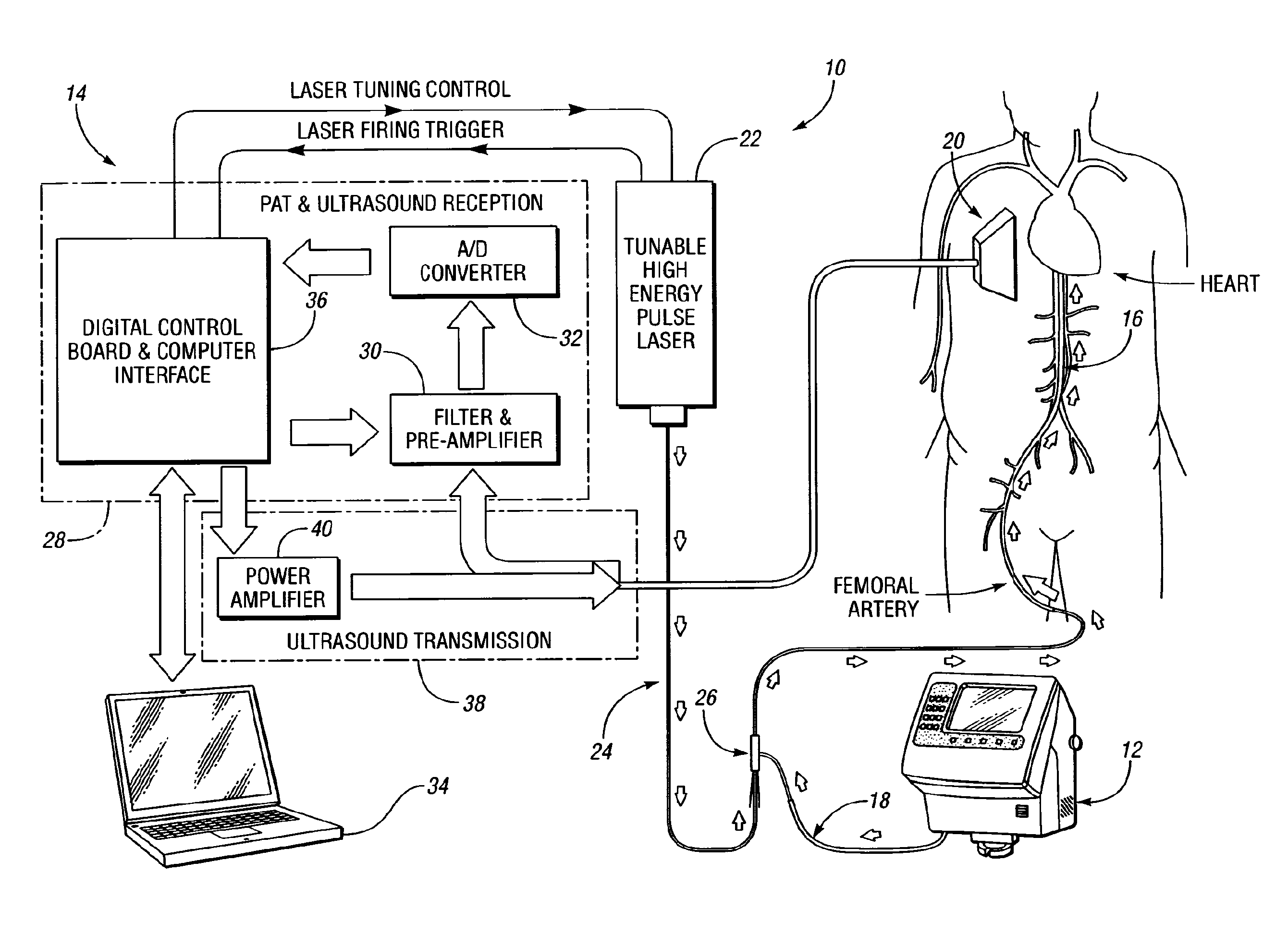
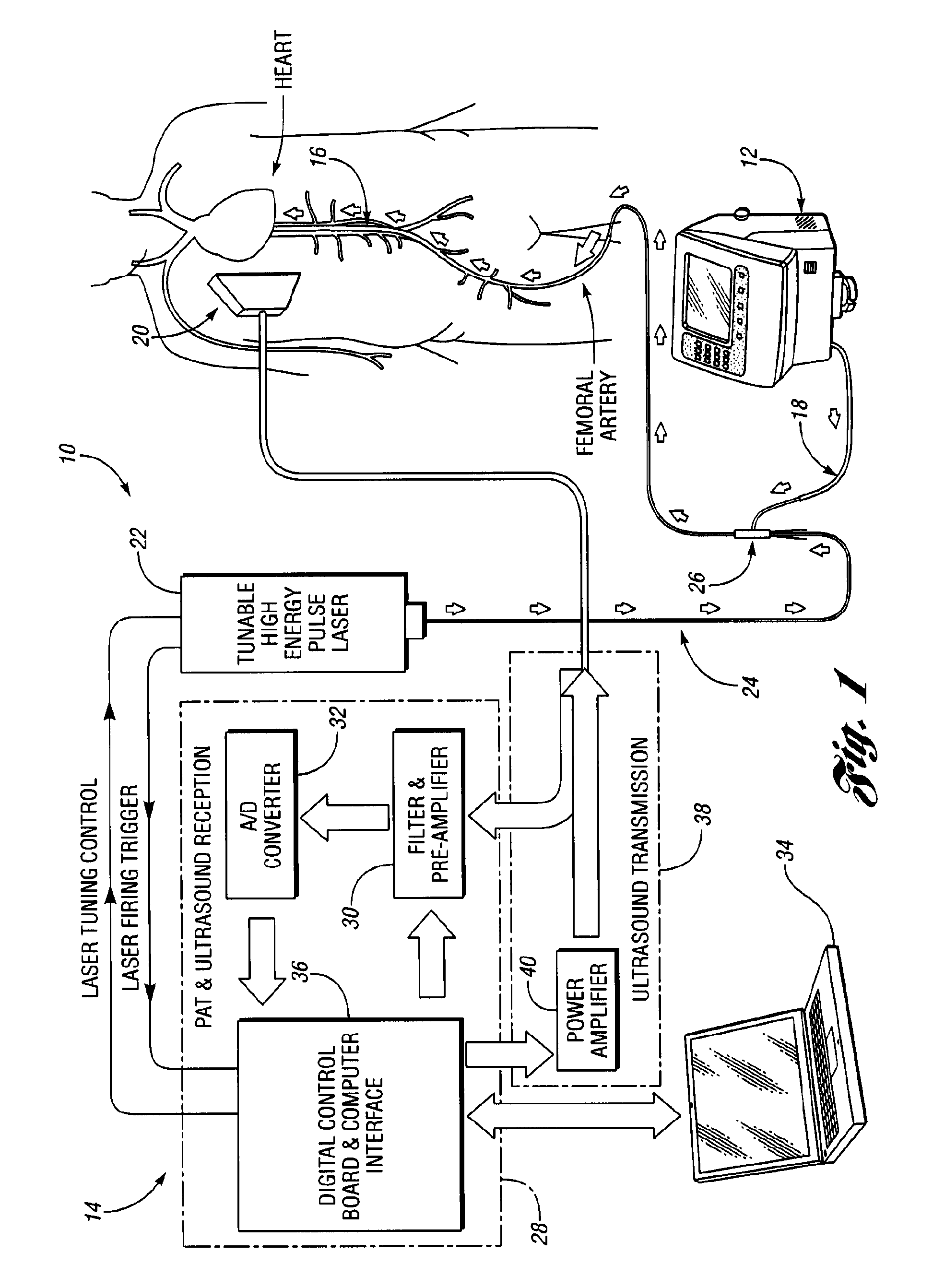
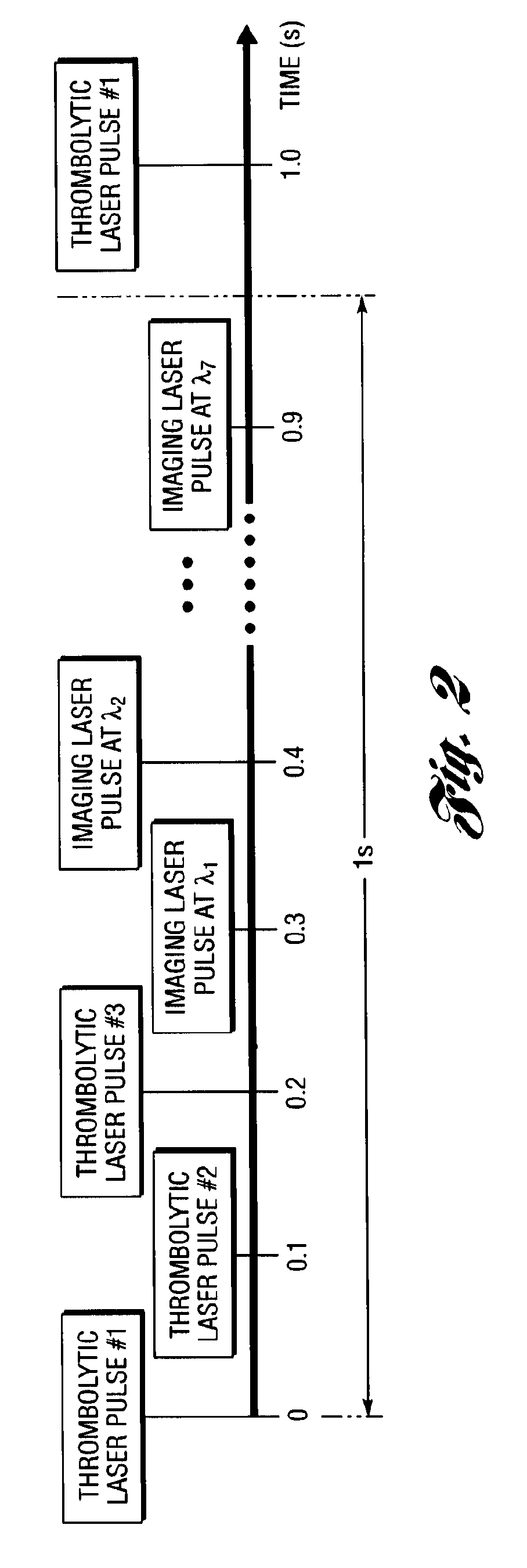
InactiveUS20090227997A1Control damageEasy to controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTherapy controlTomographic image
A system and method for monitoring laser therapy of a target tissue include a therapeutic control unit having a first light source configured to deliver light to the target tissue for therapy, an ultrasonic transducer for receiving photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of light energy by the target tissue, and a monitoring control unit in communication with the ultrasonic transducer for reconstructing photoacoustic tomographic images from the received photoacoustic signals to provide an optical energy deposition map of the target tissue. A second light source utilized for imaging may also be provided.
Owner:THE RGT OF THE UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Non-invasive characterization of a physiological parameter
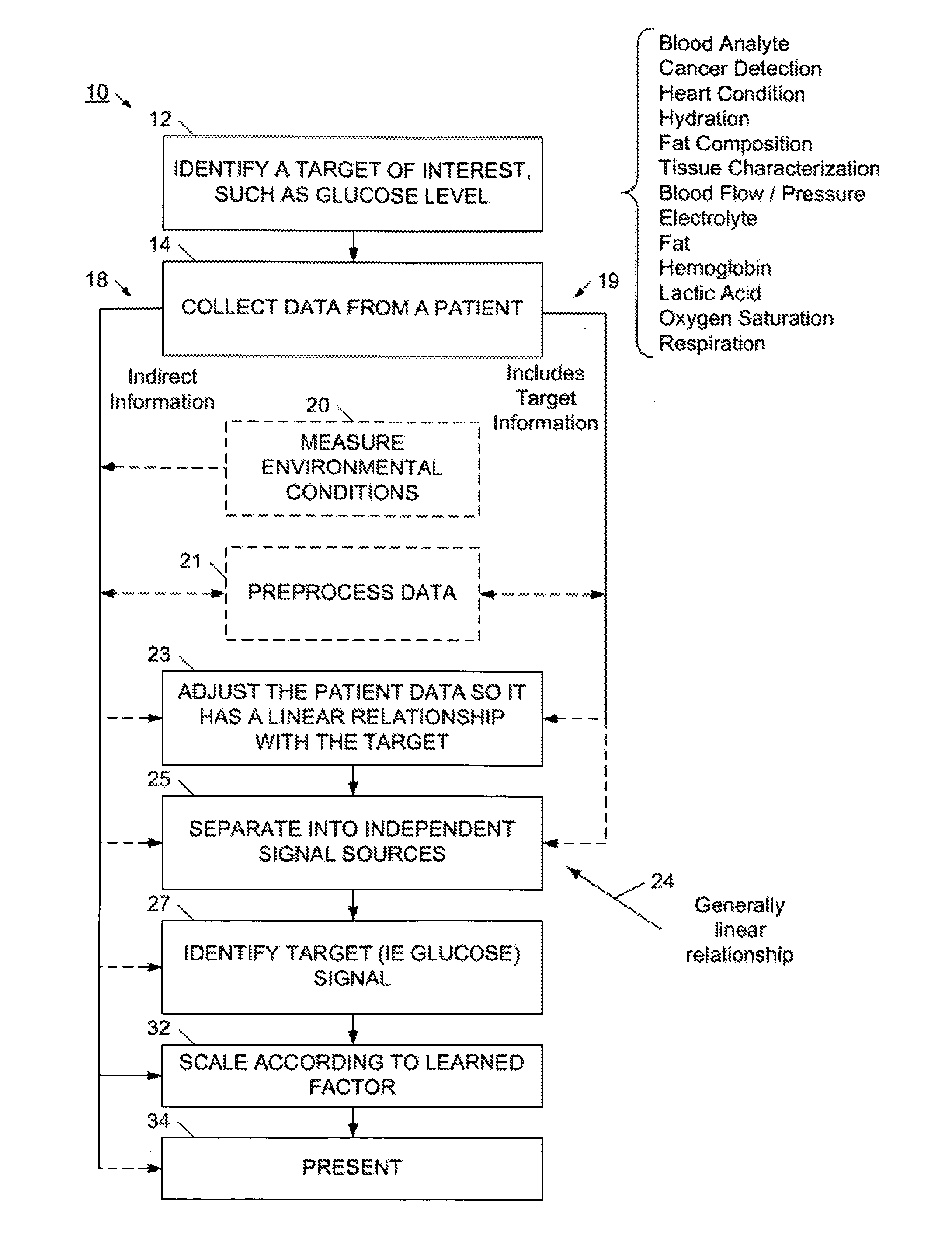
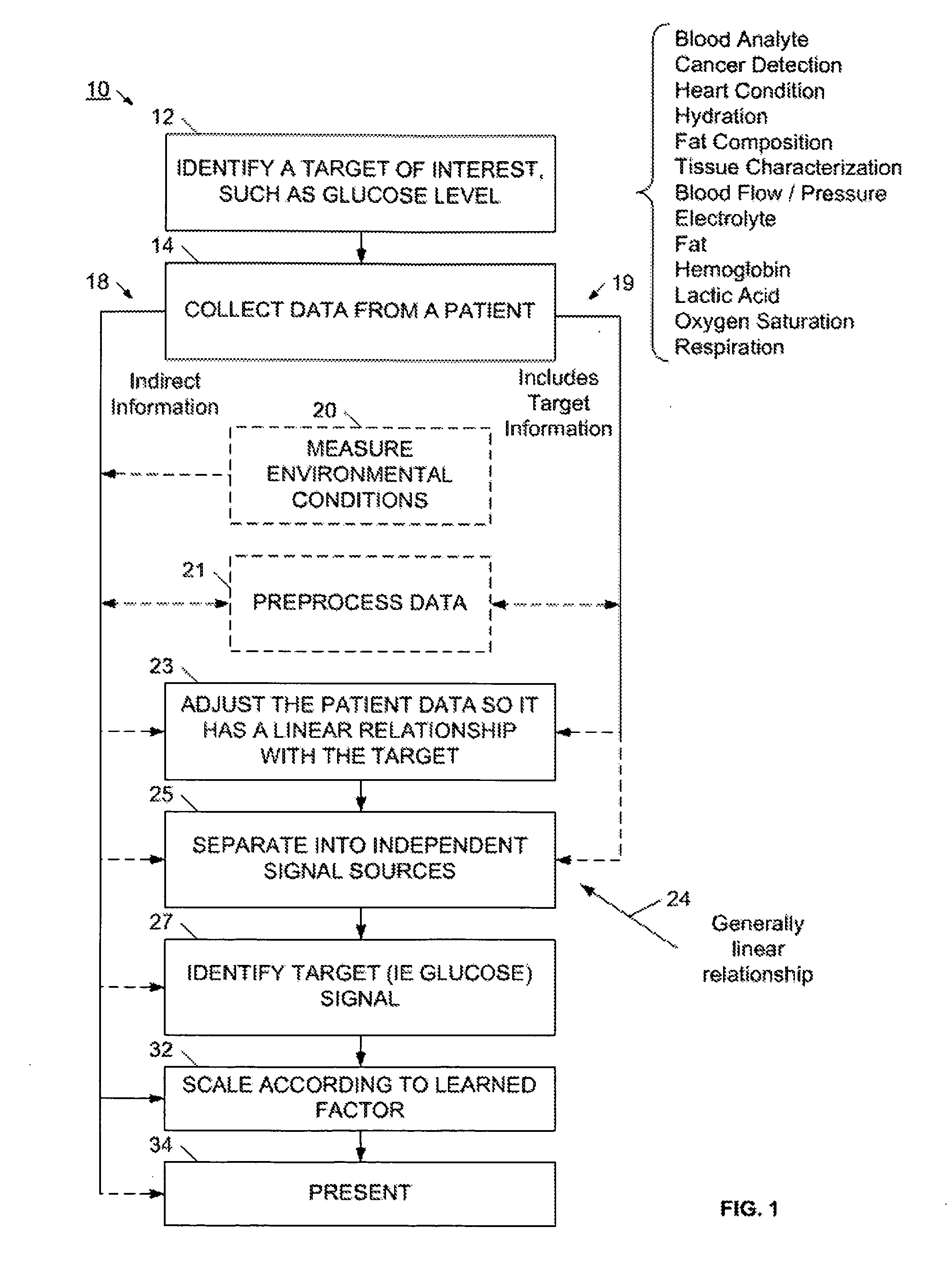
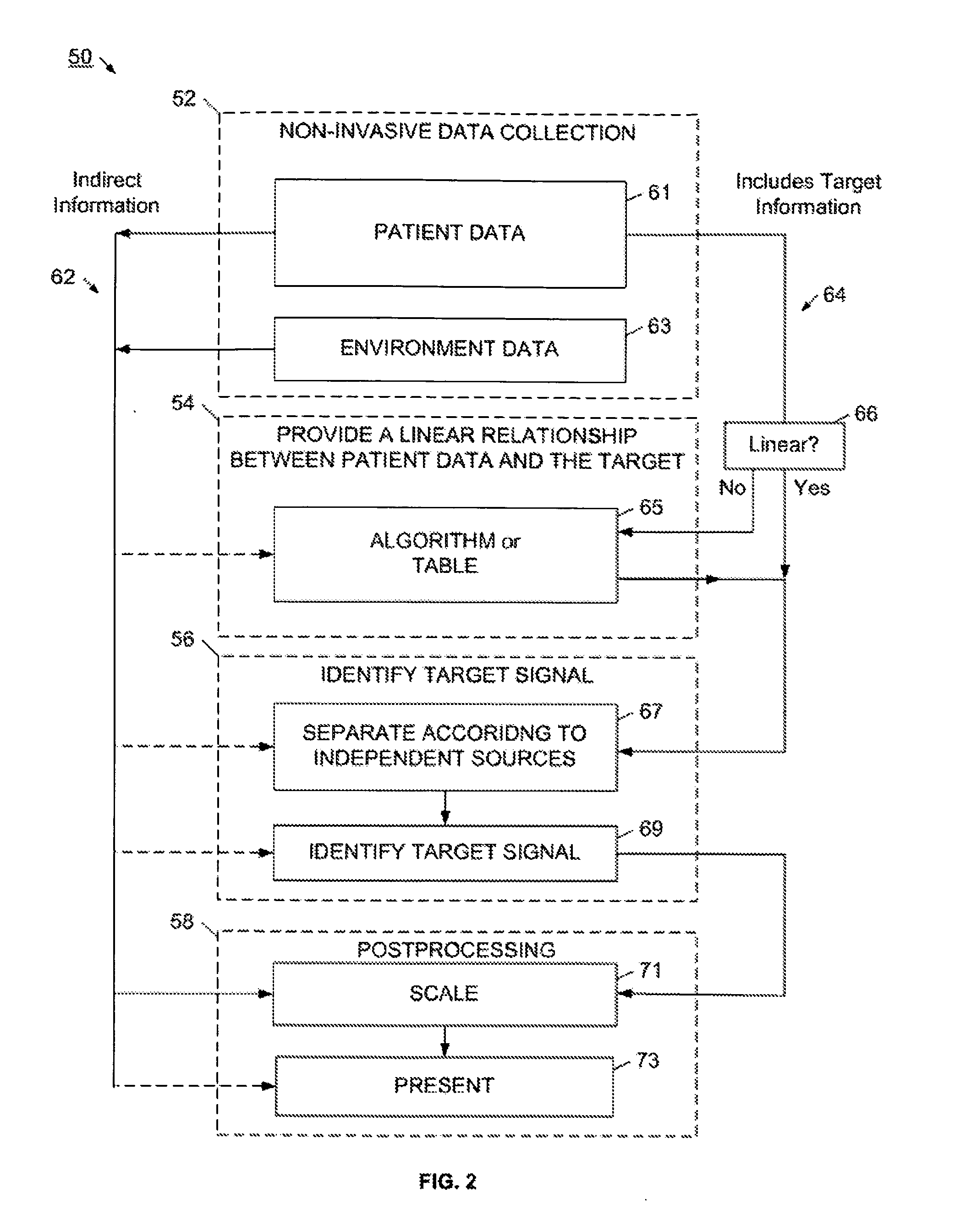
InactiveUS20100324398A1Insensitive to fluctuating patientInsensitive to environment conditionSensorsBlood characterising devicesData setPatient data
The present invention provides a method and device for characterizing a physiological parameter. The method, in one application, uses one or more non-invasive sensors to collect patient data, and may also collect data on environmental conditions. At least some of the patient data has a direct relationship with the physiological parameter, that is, a change in the physiological parameter is reflected in the data set, although the magnitude of the physiological parameter may masked by noise, interference, or other environmental or patient influences. The direct patient data preferably has a generally linear relationship with the physiological parameter, and if not, the patient data is linearized according to an algorithm, table, or other adjustment process. These linearizing processes may be predefined, and may adaptively learn or adjust. A blind signal source process is applied to the linearized data to generate separated signals, and the signal associated with the physiological parameter is identified. The identified signal is scaled or further processed, and the characterization result is presented. Although the method and device are described for use with a human, they may be advantageously used on animals.
Owner:TZYY PING JUNG
Method and apparatus for treatment of skin using RF and ultrasound energies
ActiveUS7955262B2Improve conductivityNon-invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundTransducer
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Devices and methods for treatment of incontinence
InactiveUS20020120219A1Inexpensive and easy to useReducing incontinencePneumatic massageDiagnosticsGenital regionGynecology
Therapeutic devices and methods according to embodiments of the invention alleviate e.g. urinary incontinence in female and male patients. Suction or vacuum, for example, is applied to the genital region, clitoris or clitoral region, the external urethral orifice, and / or other designated areas, e.g. physically stimulating the sacral / pudendal nerves and / or nerve roots and alleviating incontinence. Such embodiments also can encourage or cause clitoral engorgement, or otherwise promote blood flow in the genital region. Vacuum or suction applied to e.g. the clitoris creates a negative pressure in the clitoris that is lower than the systolic blood pressure, tending to promote engorgement of the clitoris with blood. Aspects of the invention are applicable not only to treatment of urinary and fecal incontinence, but also to the treatment of female sexual dysfunction. Aspects of the invention are also applicable to treatment of male incontinence and male erectile dysfunction.
Owner:NUGYN
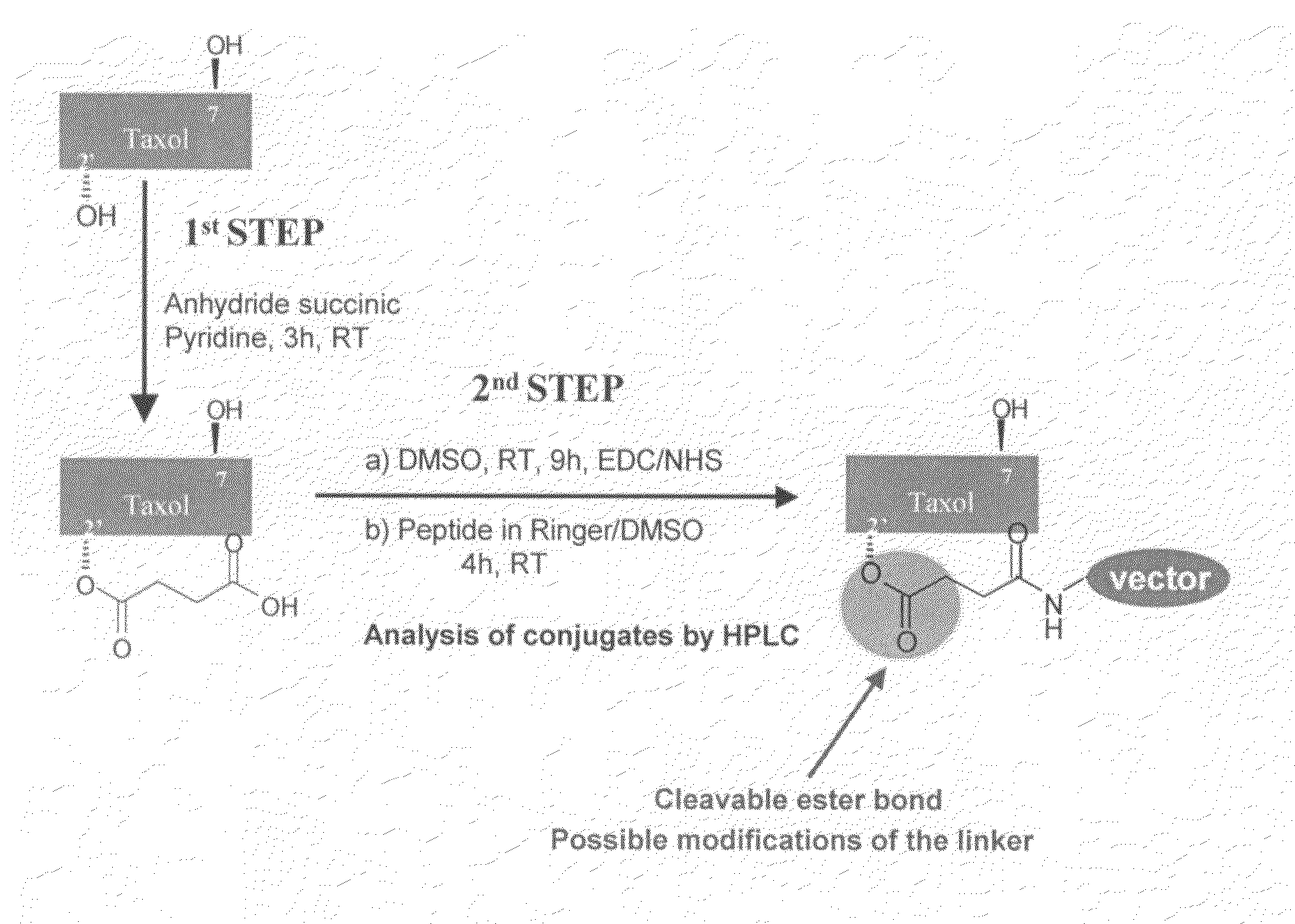
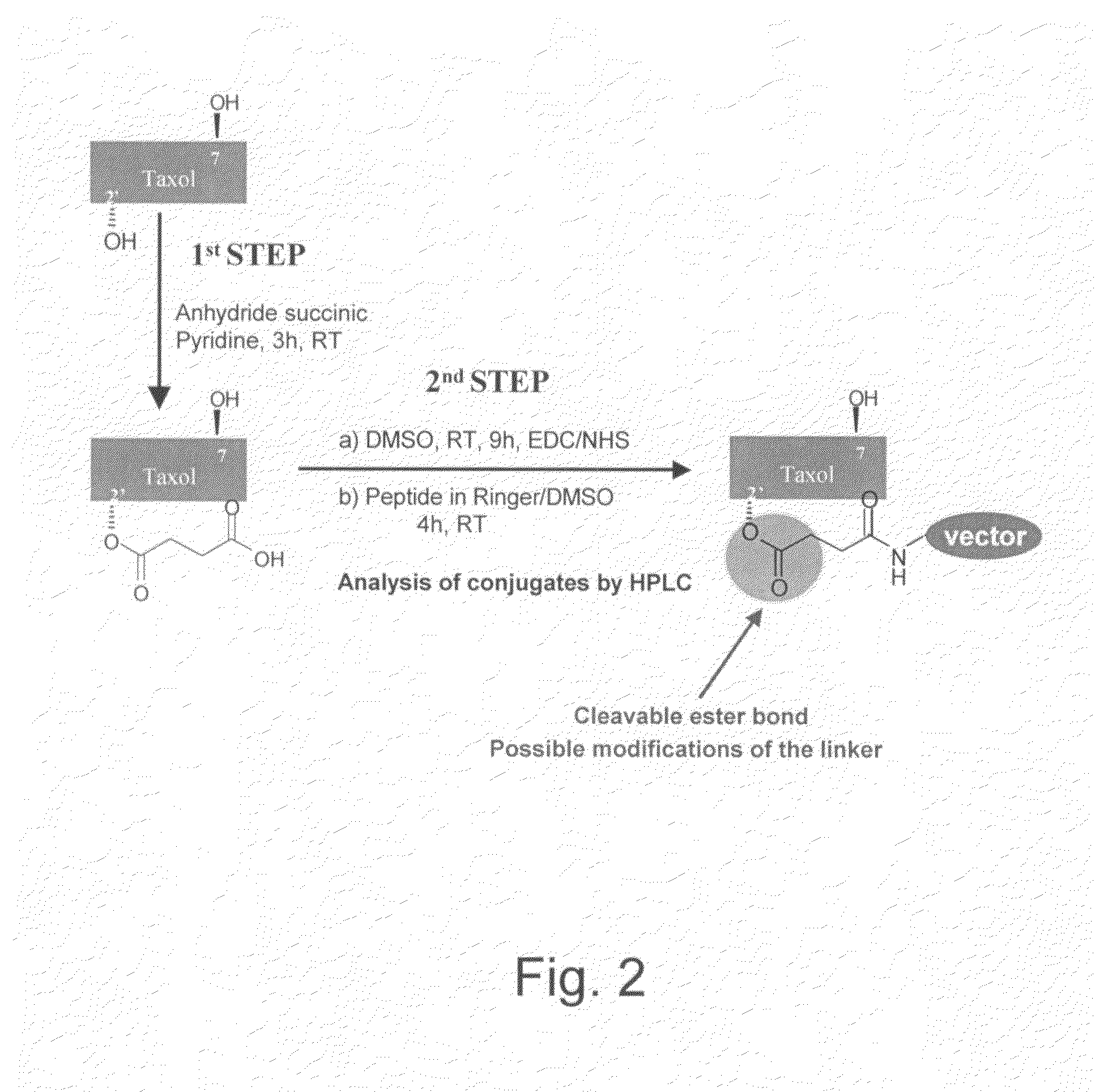
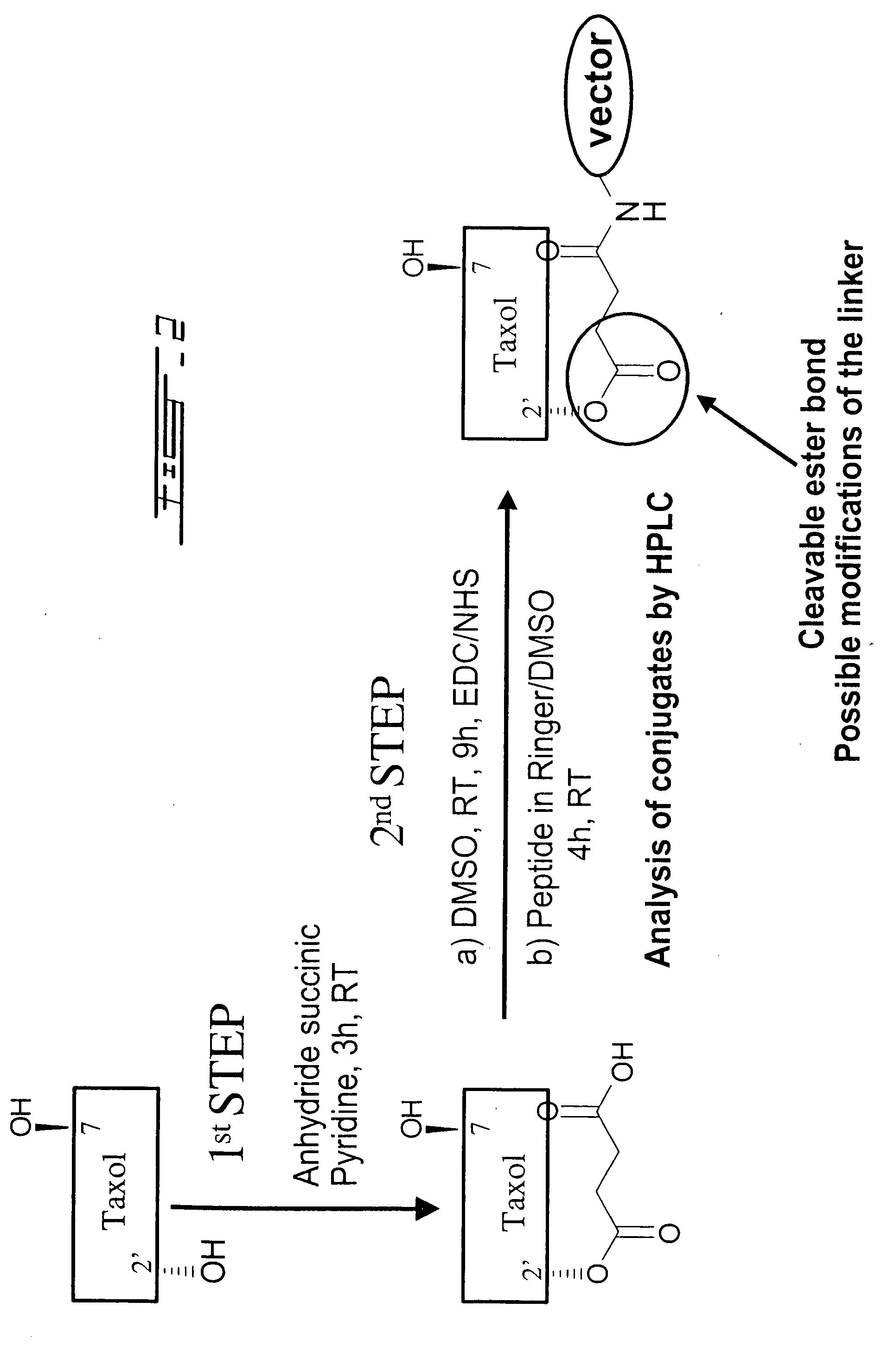
Method for transporting a compound across the blood-brain barrier
ActiveUS20060182684A1Disease reliefRelieve symptomsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugBiochemistry
The present invention relates to improvements in the field of drug delivery. More particularly, the invention relates to a non-invasive and flexible method and carrier for transporting a compound or drug across the blood-brain barrier of an individual. In particular the present invention relates to a carrier for transporting an agent attached thereto across a blood-brain barrier, wherein the carrier is able to cross the blood-brain barrier after attachment to the agent and thereby transport the agent across the blood-brain barrier. The present invention relates to improvements in the field of drug delivery. More particularly, the invention relates to a non-invasive and flexible method and carrier for transporting a compound or drug across the blood-brain barrier of an individual. In particular the present invention relates to a carrier for transporting an agent attached thereto across a blood-brain barrier, wherein the carrier is able to cross the blood-brain barrier after attachment to the agent and thereby transport the agent across the blood-brain barrier.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
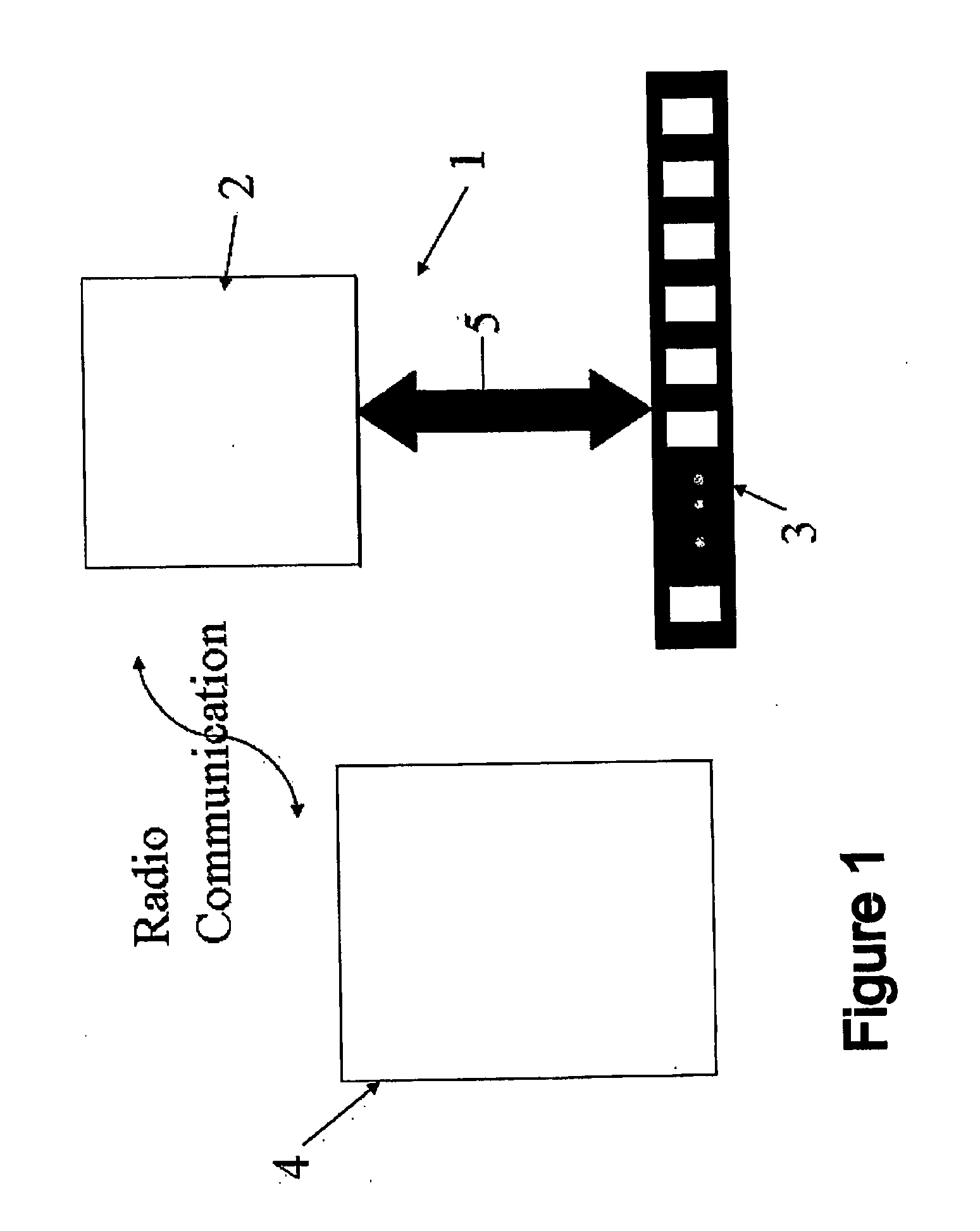
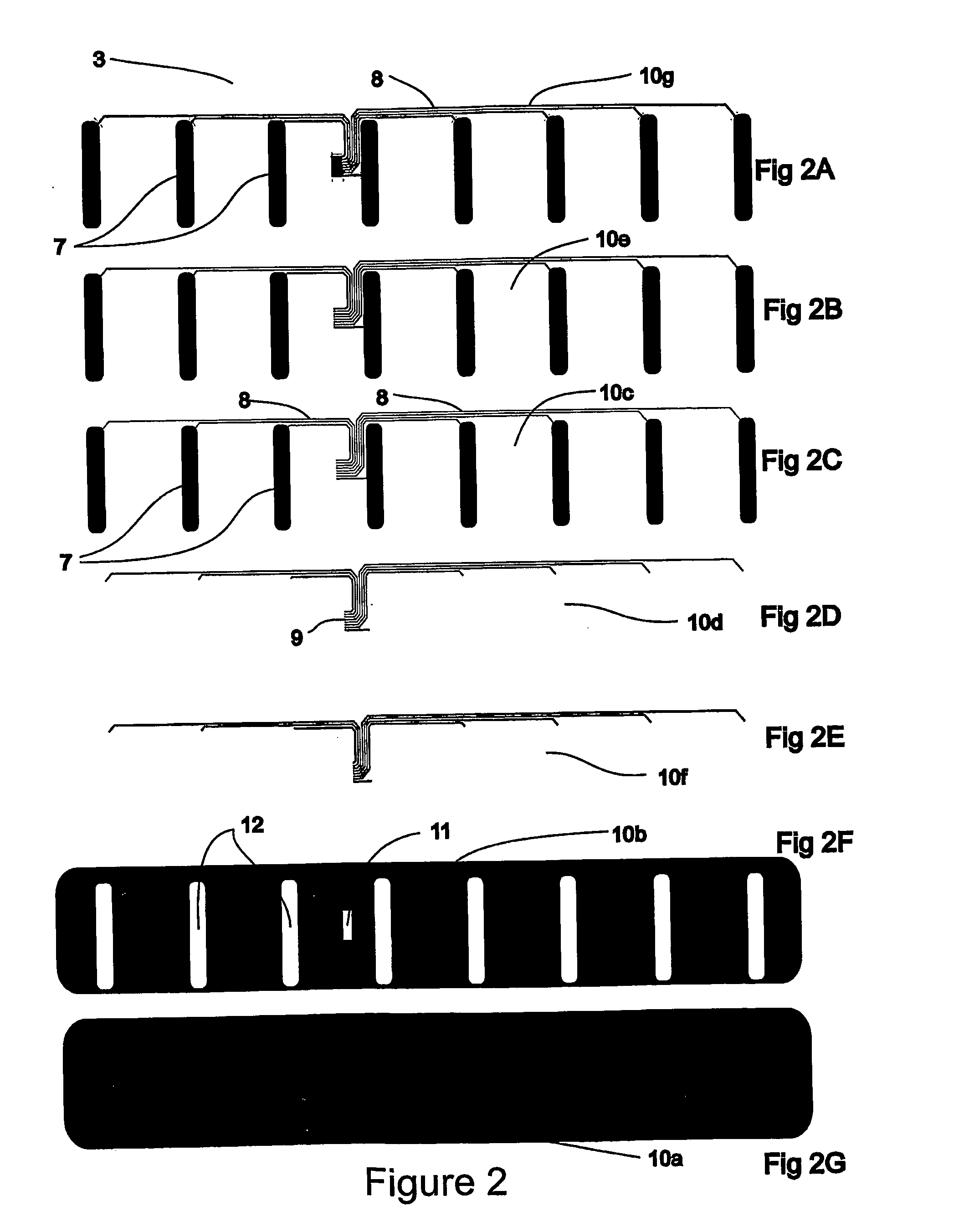
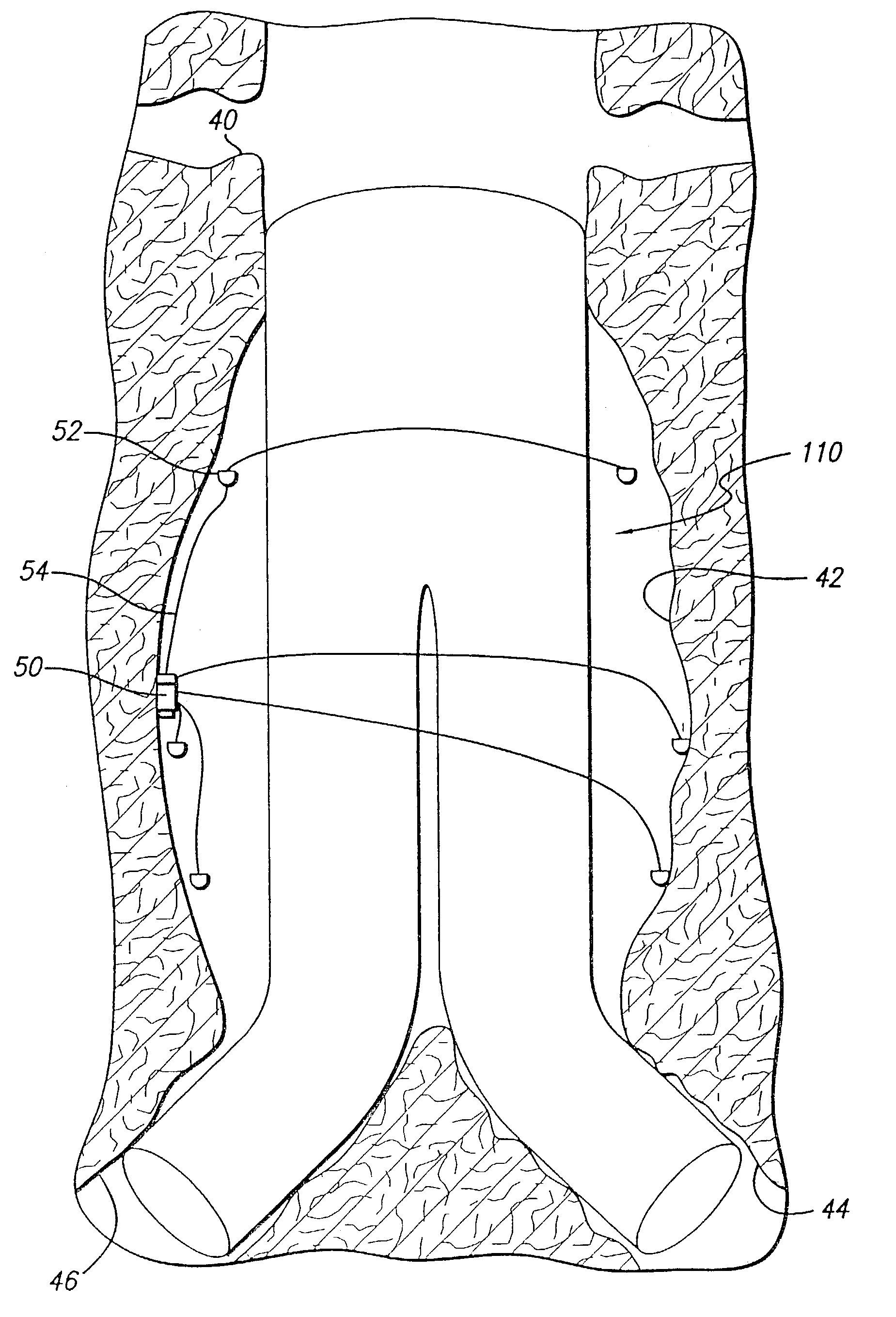
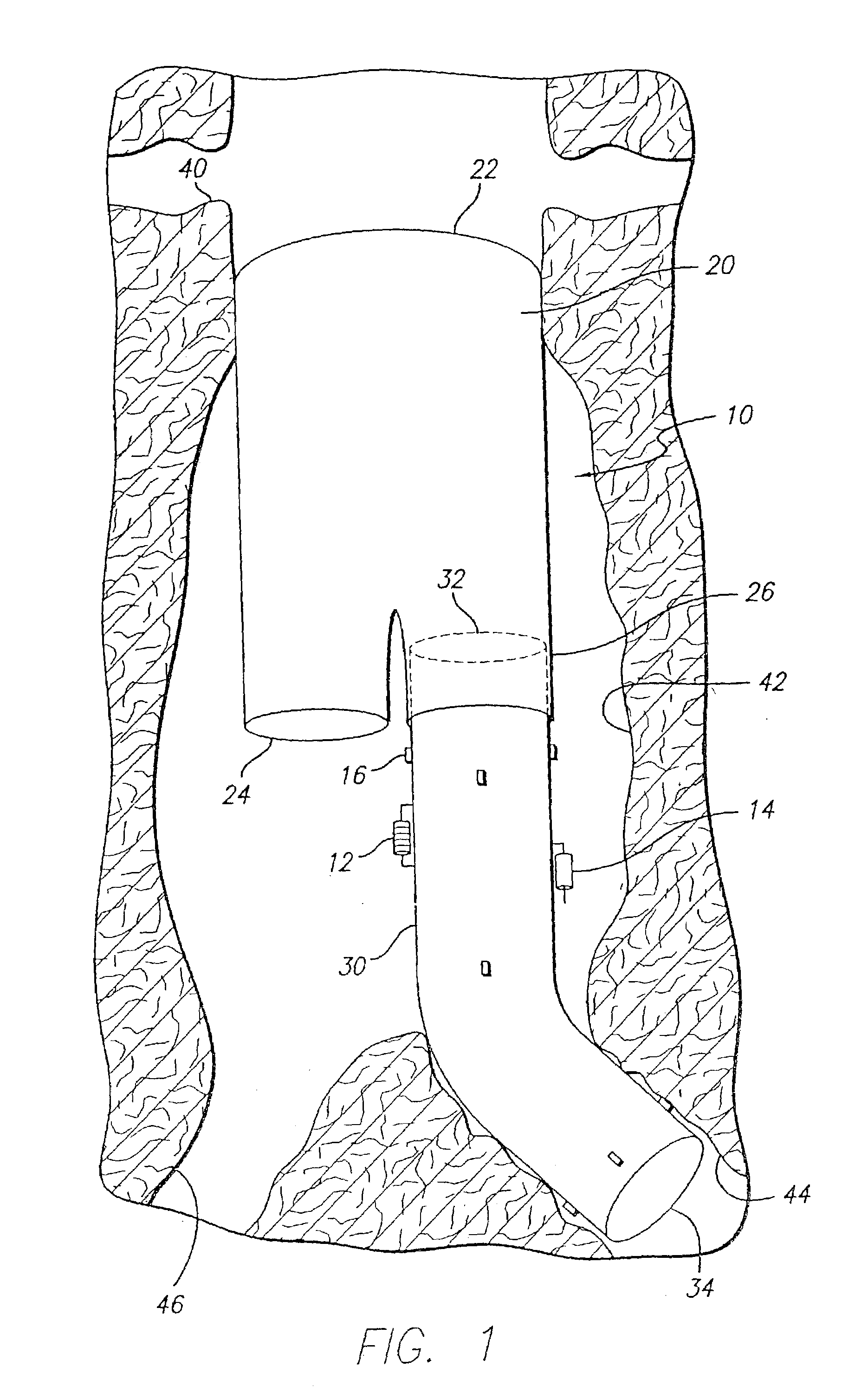
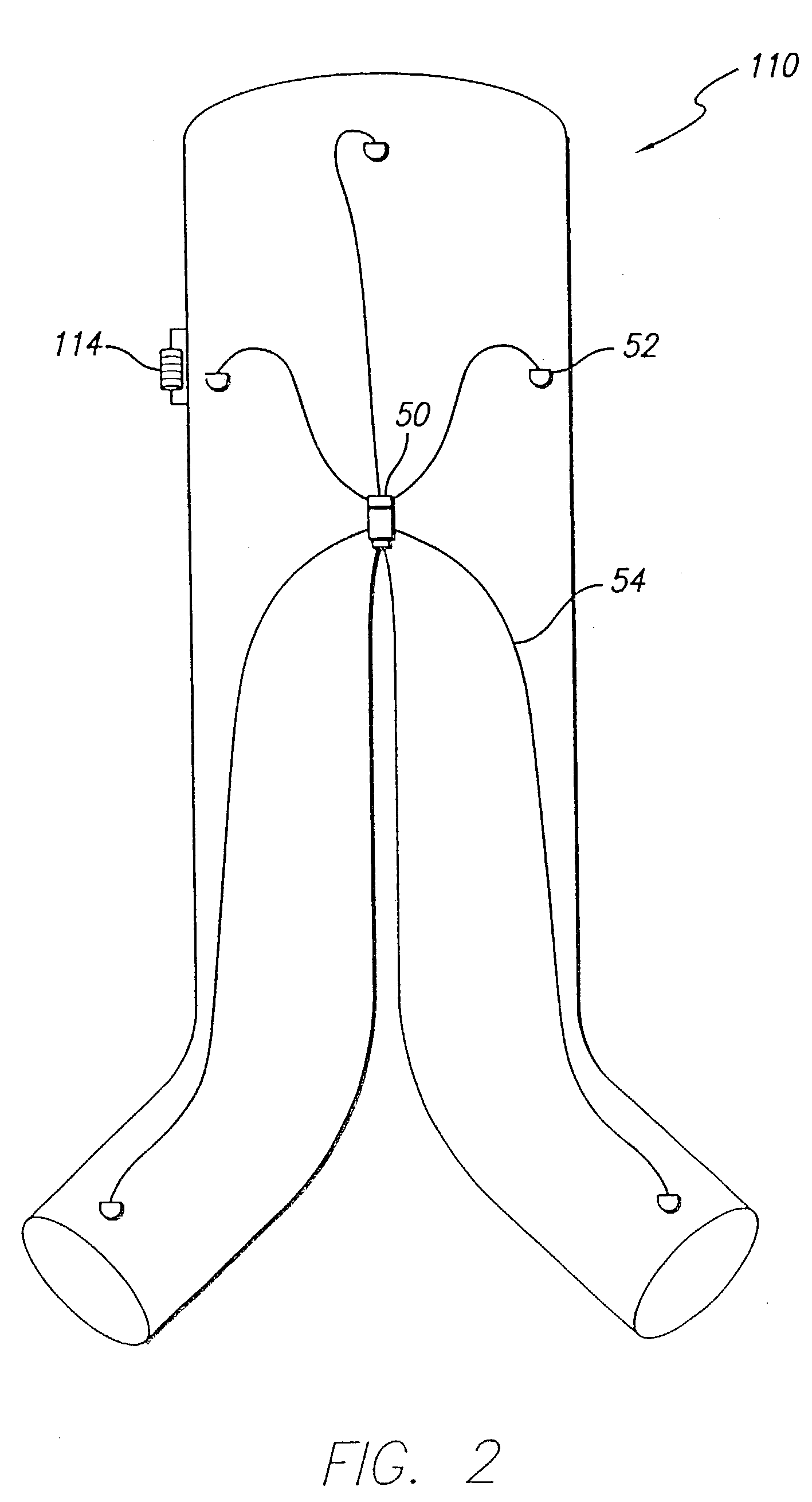
Internal Bleeding Detection Apparatus
Abstract: An EIT system (1) adapted to detect internal bleeding in a body portion, the EIT system (1) comprising a plurality of electrodes (3) adapted in use to extend in a substantially linear orientation across one side only of the body portion and to be applied in electrical contact with the skin of the body portion, a current source adapted to cyclically apply an electric current between one pair of the electrodes (3), a voltage measuring means to measure the voltage across each of the other pairs of the electrodes resulting from the current, a data collection system (2) and a data analysis system (4) to analyse data resulting from the voltages that are measured by the voltage measuring means, wherein the analysis system (4) is configured to obtain quantitative information related to amounts and rates of conductive tissue changes occurring in the body, based on an EIT analysis equivalent to that obtained from data derived from electrodes spaced around the full perimeter of the body portion. Also disclosed is an electrode belt suitable for bioelectrical use and in particular for detection of change of volume of tissue in a body portion.
Owner:EUROPEAN INSTITUTE OF INNOVATION AND TECHNOLOGY
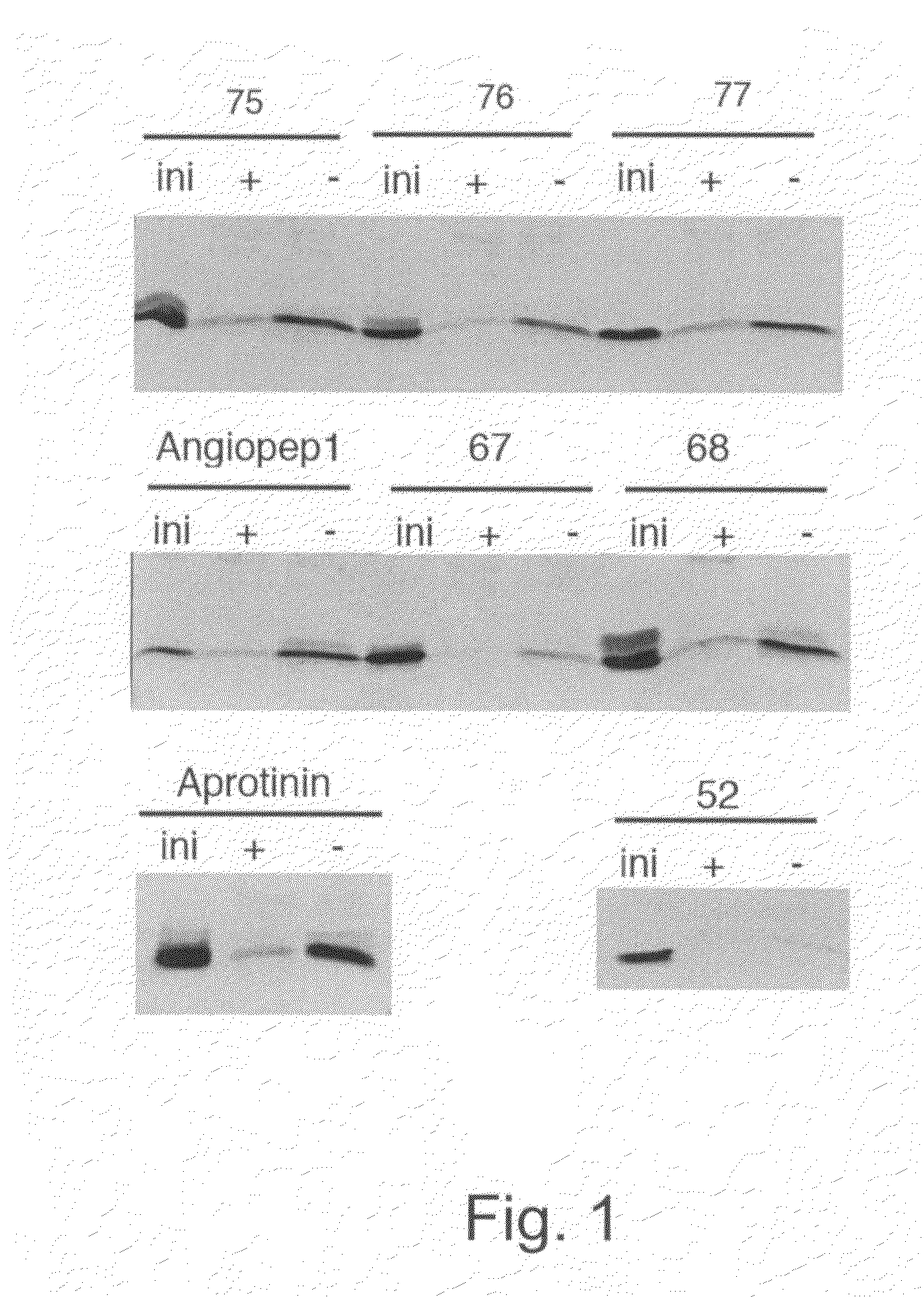
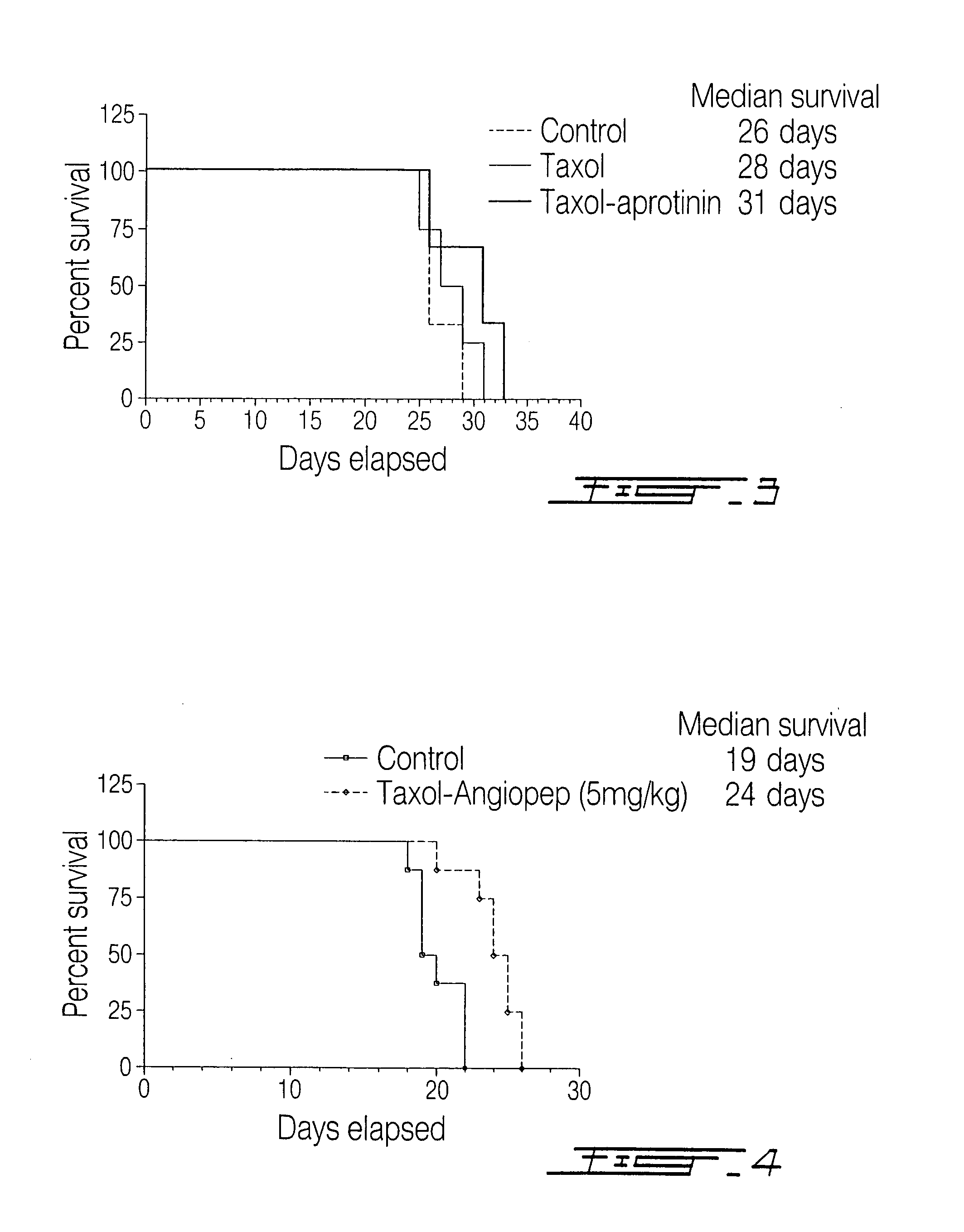
Delivery of antibodies to the central nervous system
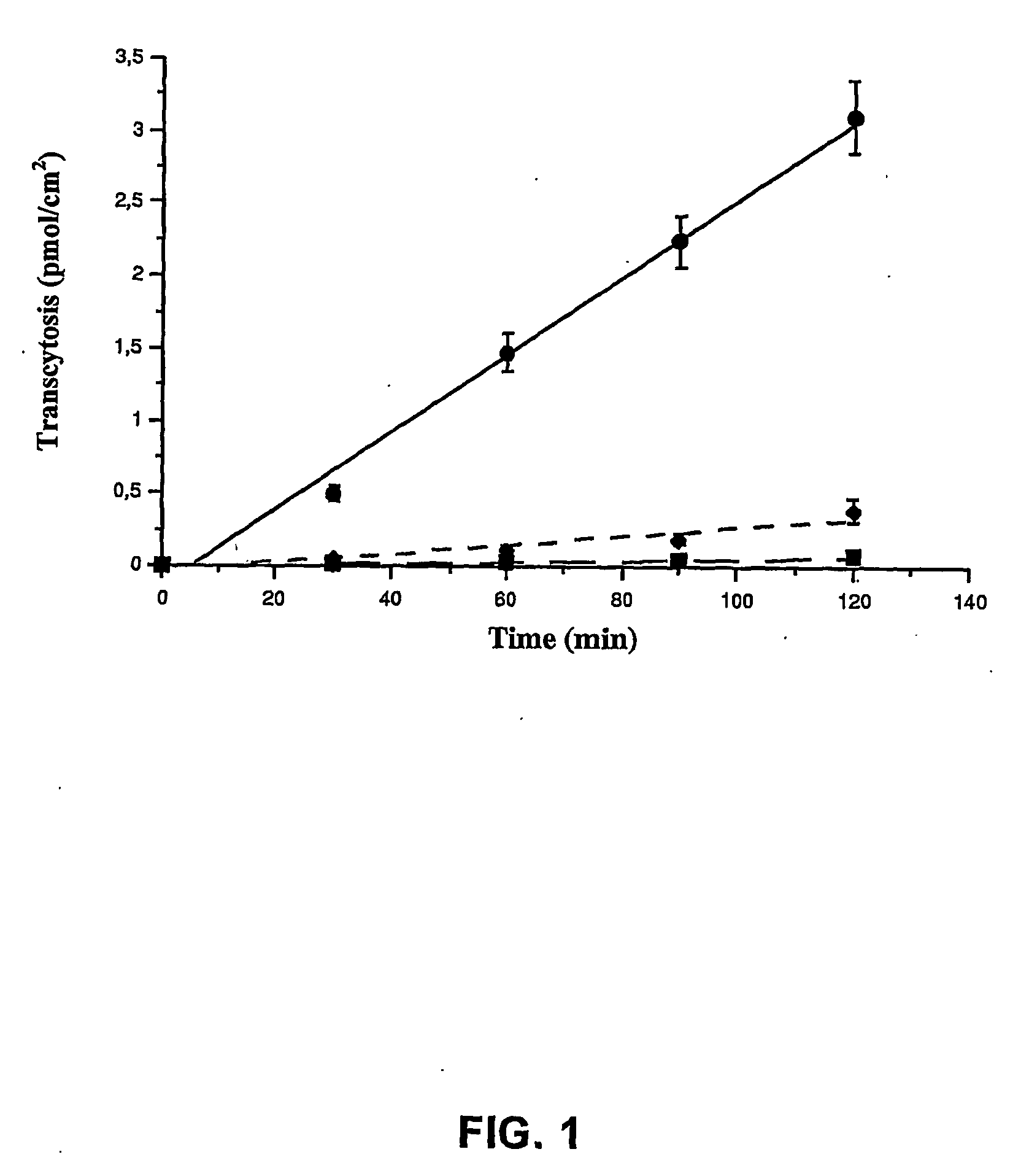
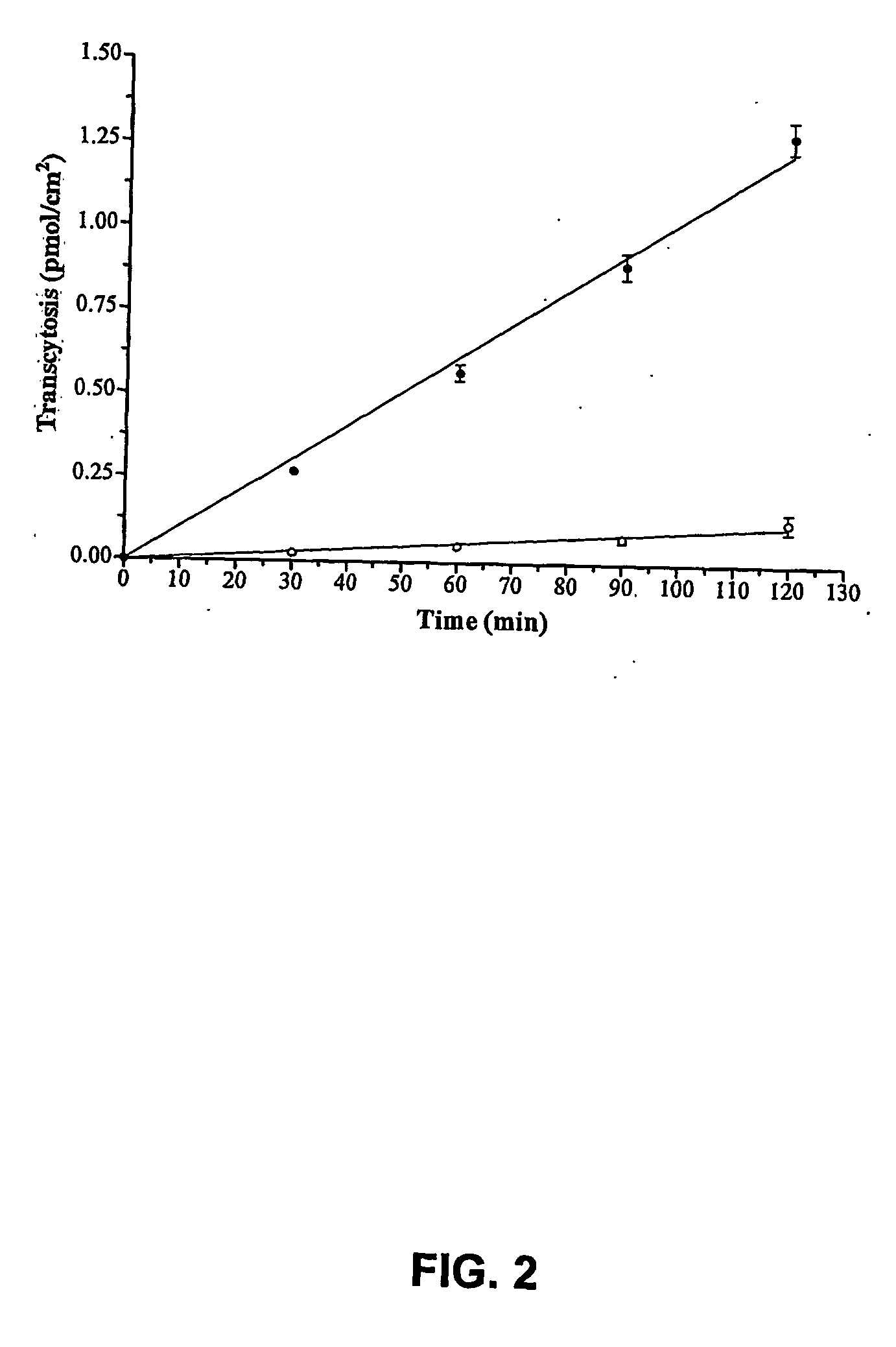
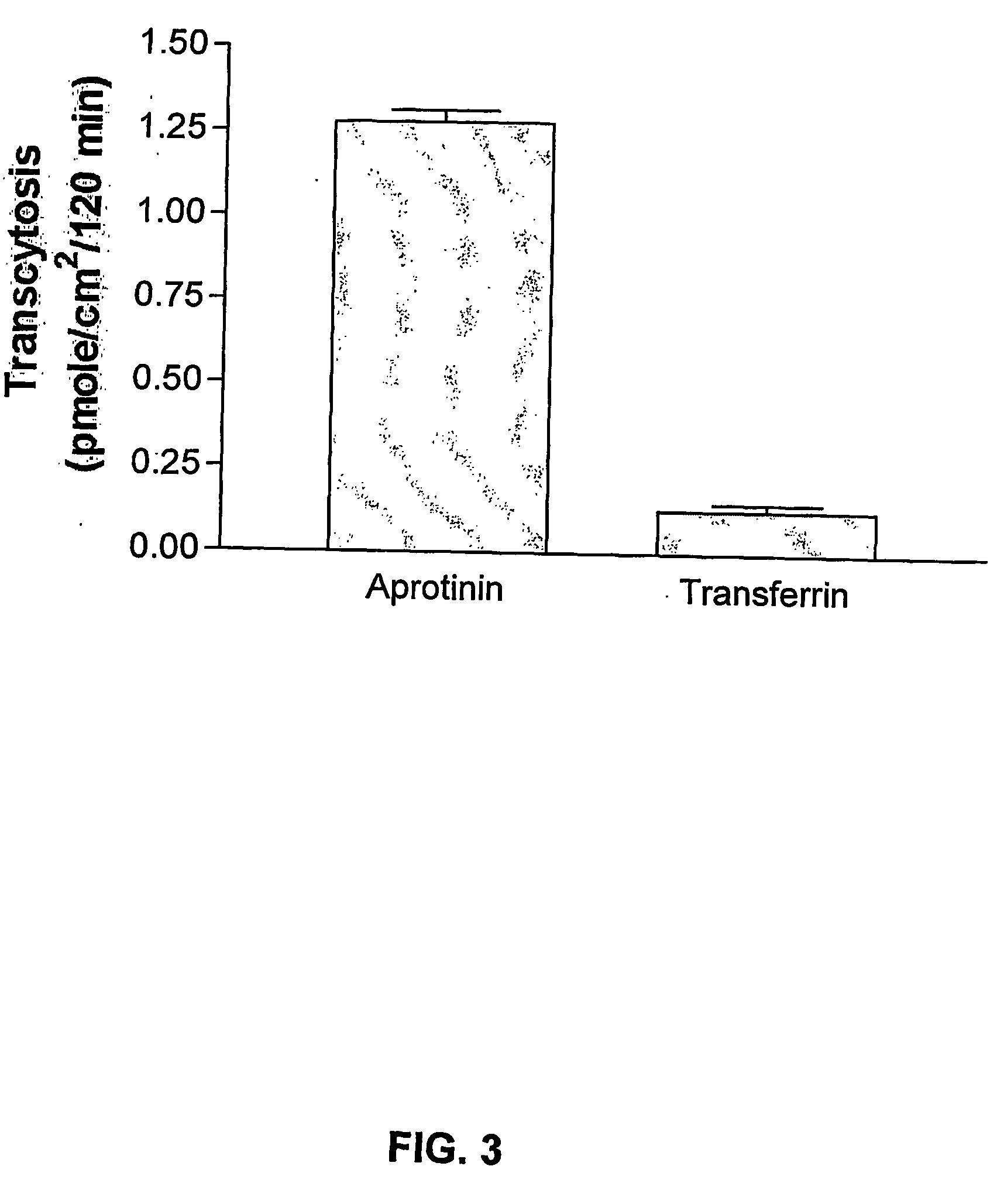
InactiveUS20090016959A1Improve biological activityNon-invasiveCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderDiseaseAprotinin
The invention relates to improvements in the field of drug delivery. More particularly, the invention relates to polypeptide derived from aprotinin and from aprotinin analogs as well as conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions comprising these polypeptides. The present invention also relates to the use of these polypeptide for transporting an antibody or antibody fragment across the blood-brain barrier of an individual and in the treatment and diagnosis of neurological diseases.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Mixing bag with integral sparger and sensor receiver
A mixing bag for use in bioprocessing in which a fluid is received and agitated using an internal fluid-agitating element driven by an external motive device is disclosed. The bag may include an integral sparger and sensor receiver. Related methods are also disclosed.
Owner:PALL TECH UK
Molecules for transporting a compound across the blood-brain barrier
ActiveUS20060189515A1Non-invasiveImprove biological activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDisease causeProtein C
The invention relates to improvements in the field of drug delivery. More particularly, the invention relates to polypeptide derived from aprotinin and from aprotinin analogs as well as conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions comprising these polypeptides. The present invention also relates to the use of these polypeptide for transporting a compound or drug across the blood-brain barrier of an individual and in the treatment and diagnosis of neurological diseases.
Owner:UNIV DU QUEBEC A MONTREAL +1
Method and apparatus for treatment of skin using RF and ultrasound energies
ActiveUS20070038156A1Improve conductivityNon-invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundTransducer
A system and method for treating skin. The System comprises one or more ultrasound transducers and one or more pairs of RF electrodes. The ultrasound transducers are adapted to focus ultrasound energy at one or more focal volumes in the skin. The RF electrodes are adapted to deliver RF energy to the one or more focal volumes. The method comprises heating the skin to a first temperature at one or more focal volumes in the skin by focusing ultrasound energy at the one or more focal volumes. The focal regions are then heated to a second temperature, the second temperature being higher than the first temperature, by generating an RF current in a region of the skin containing the focal regions.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
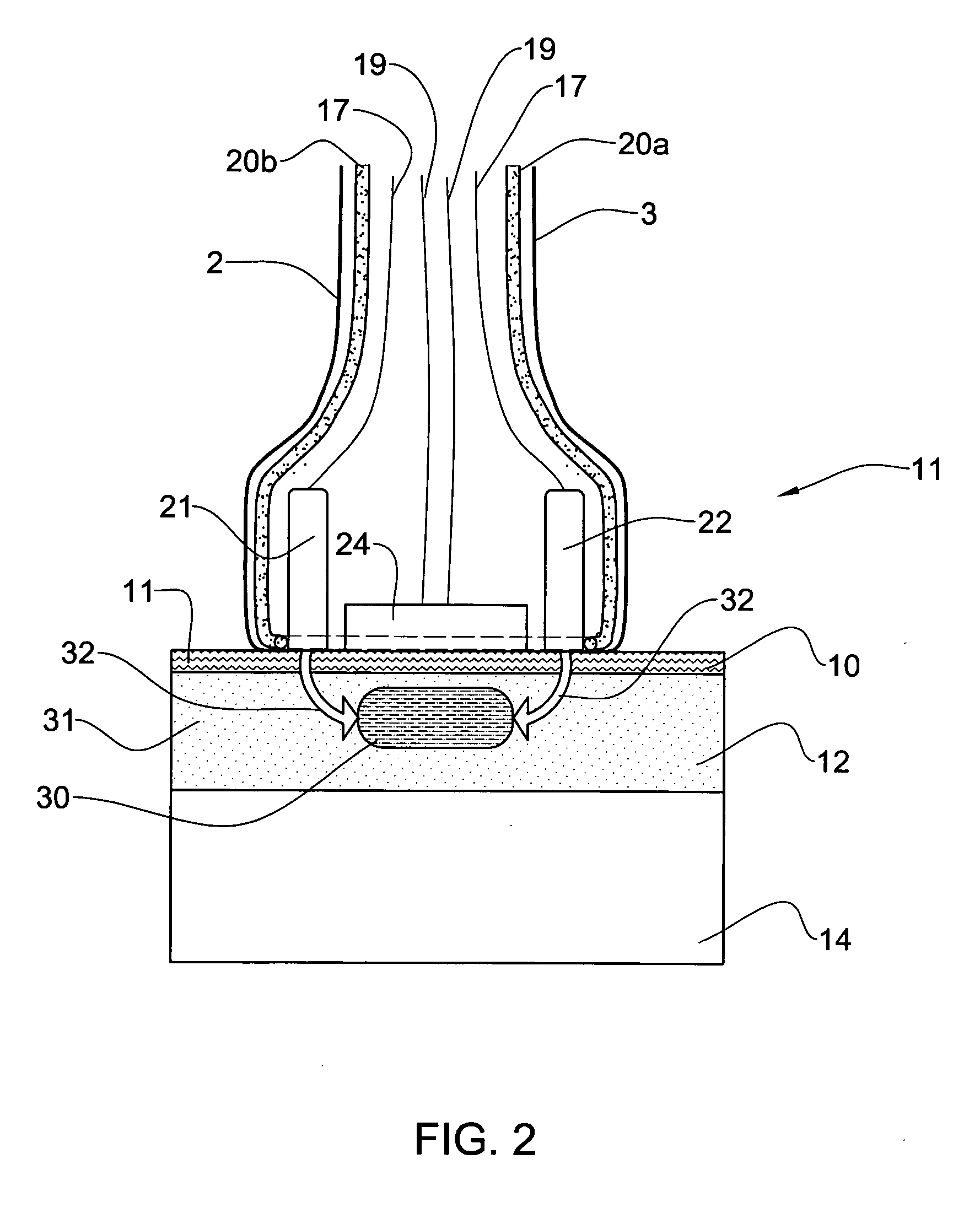
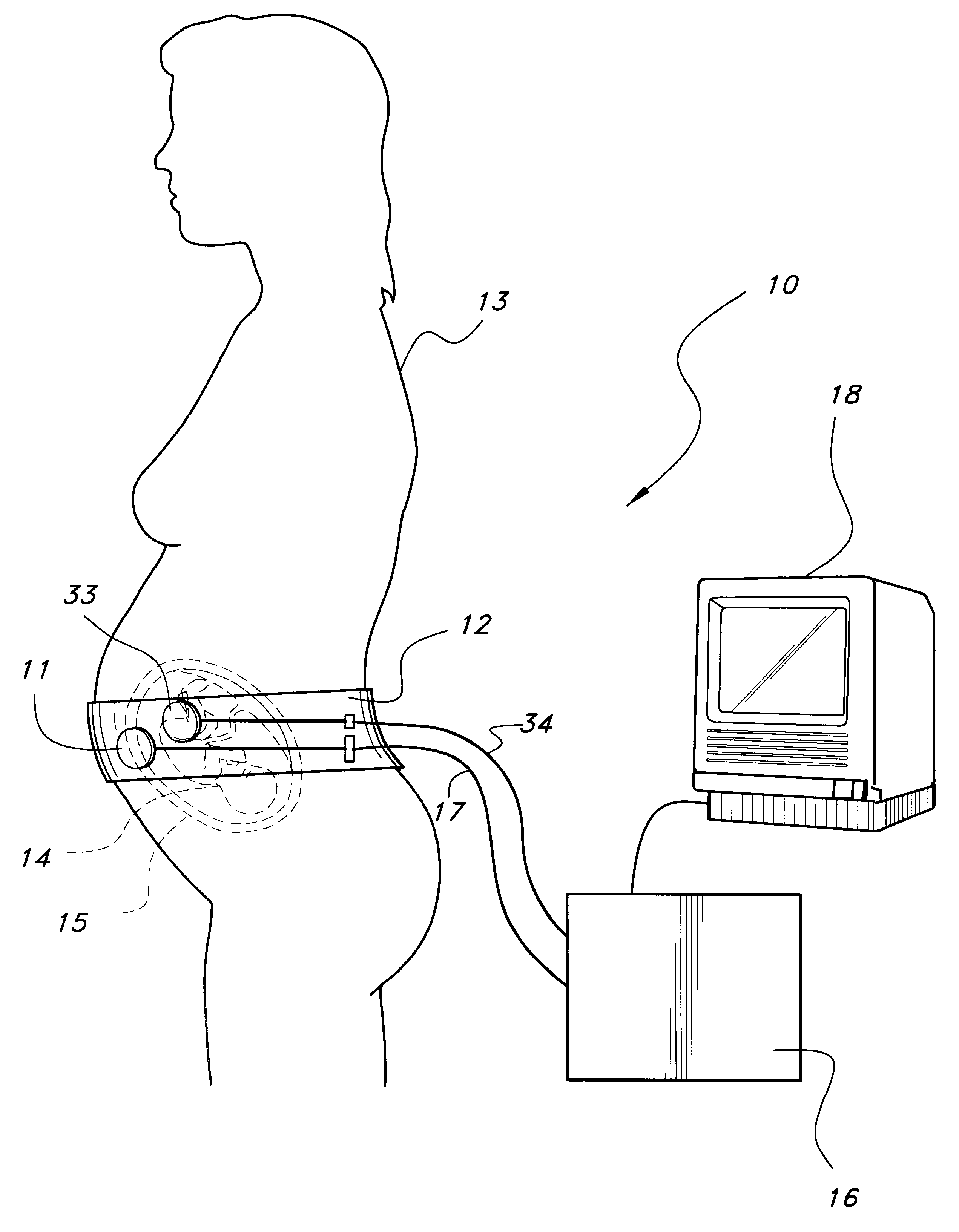
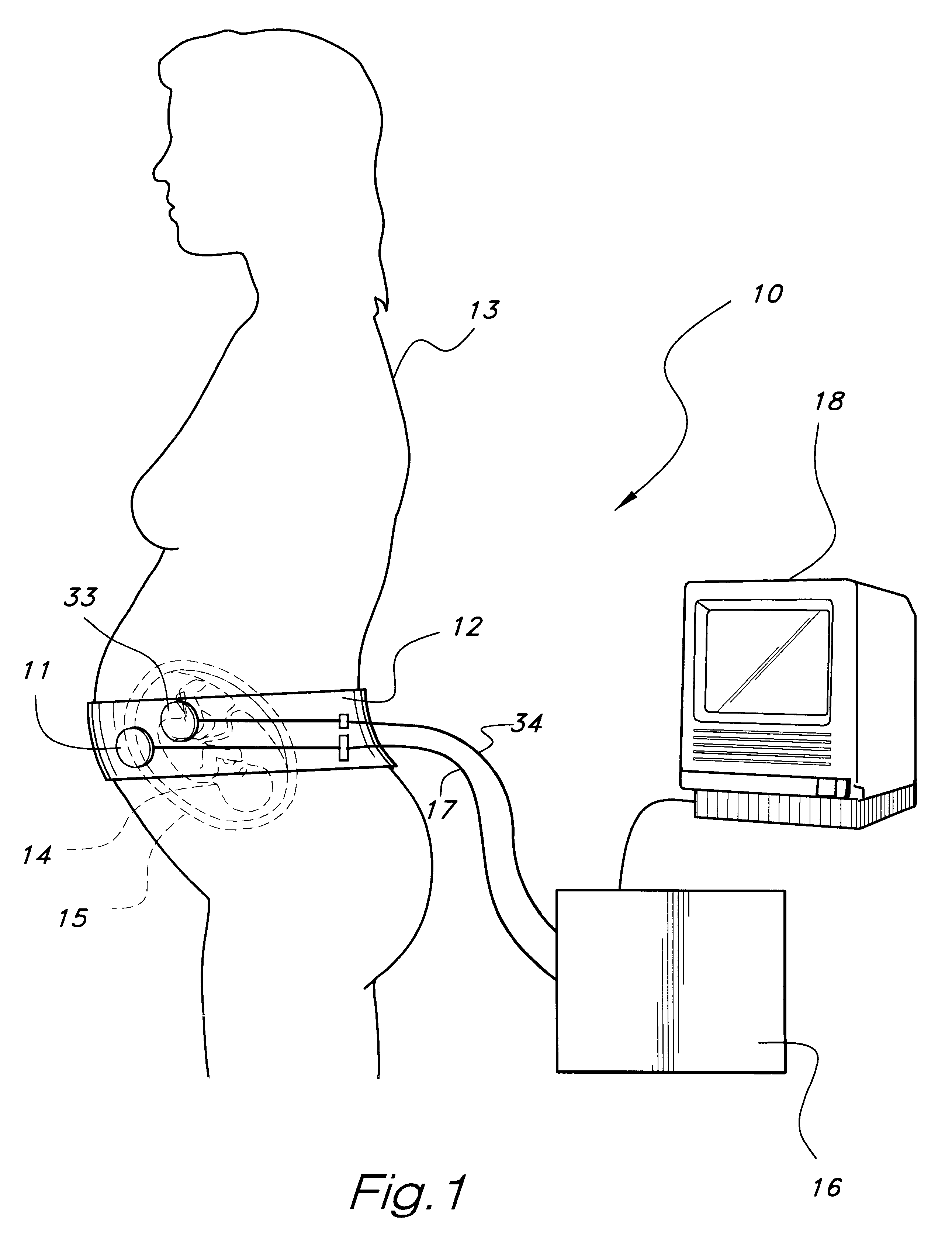
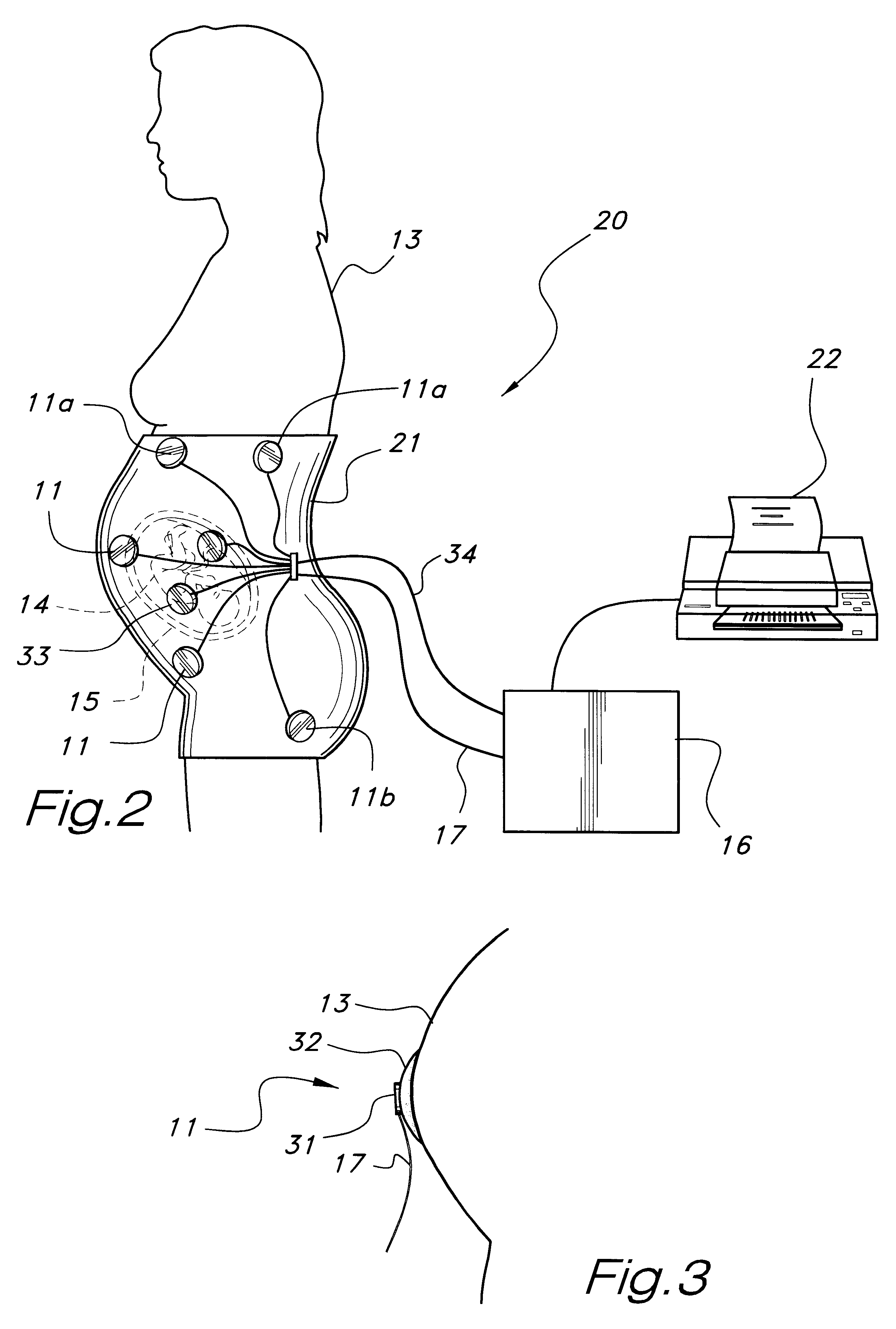
Foetal circulatory impedance monitor
A device and method for monitoring a foetus over a period of time. The device includes an electrocardiograph for receiving and processing signals generated by the foetal heart and received from an electrode attached to the abdomen of the mother. The device also includes a second signal receiving and processing means for signals generated by a pressure or acceleration detector that is also attached to the abdomen of the pregnant mammalian animal. The pressure detector produces signals representative of the sounds of foetal heartbeat. The device also includes a comparator means to compare the respective sets of signals, and output means to produce an output indicative of the comparison between the two sets of signals.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF +1
Endovascular graft with separable sensors
InactiveUS7399313B2Quickly and easily obtainedNon invasiveStentsCatheterMedicineBiomedical engineering
A endovascular graft having sensing devices attached thereto to facilitate measurement of pertinent parameters within the vasculature into which the graft is implanted. Power sources and transmitters may be attached to the graft to facilitate transmission of measurements to a receiving device outside the patient's body. The sensing devices, may be electrically passive or integrated devices with measurement and transmission capability. The sensing devices may be attached to specific locations on the graft material or attached to the lumen, thereby providing pertinent parameters from critical points inside the vasculature, or may be dispersed over the surface of the graft material or within the lumen to provide a profile of pertinent parameters. The sensing devices may be attached to the graft material with one suture using a running stitch to minimize graft bulk and may be coated with a material to inhibit or control tissue growth. A bio-reabsorbable or hard wire tether or suture may be employed to attach devices to one or more graft components.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
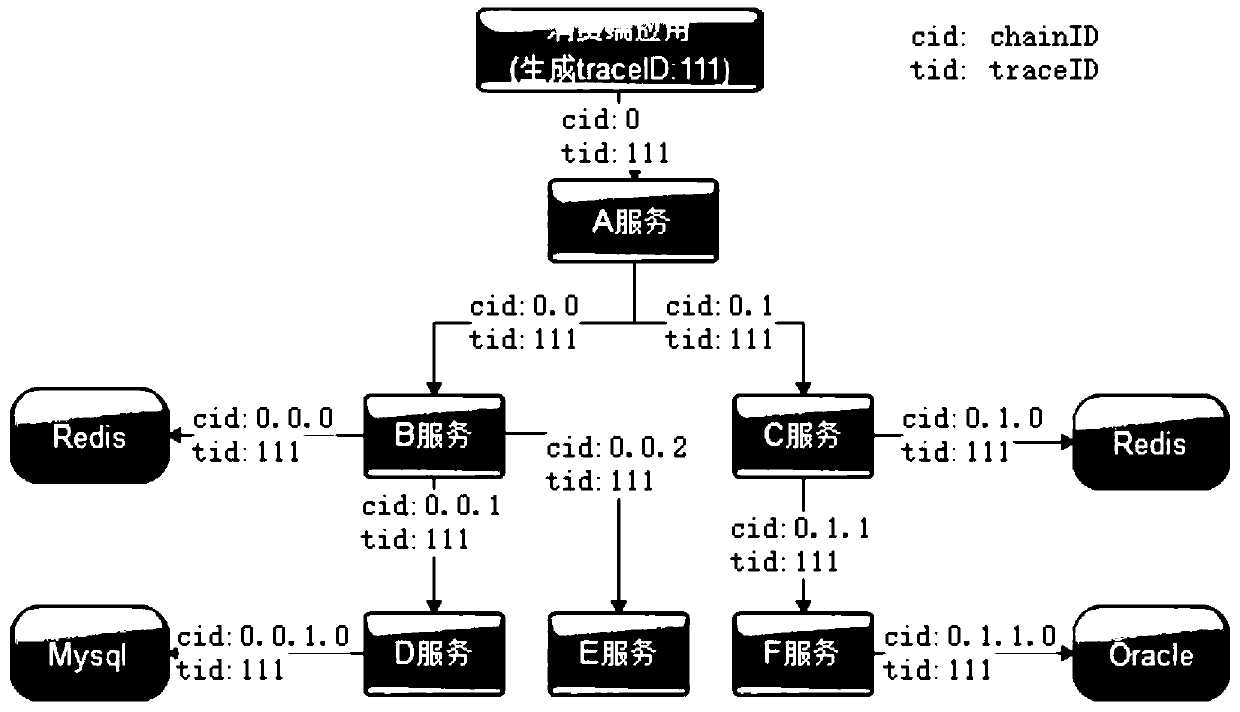
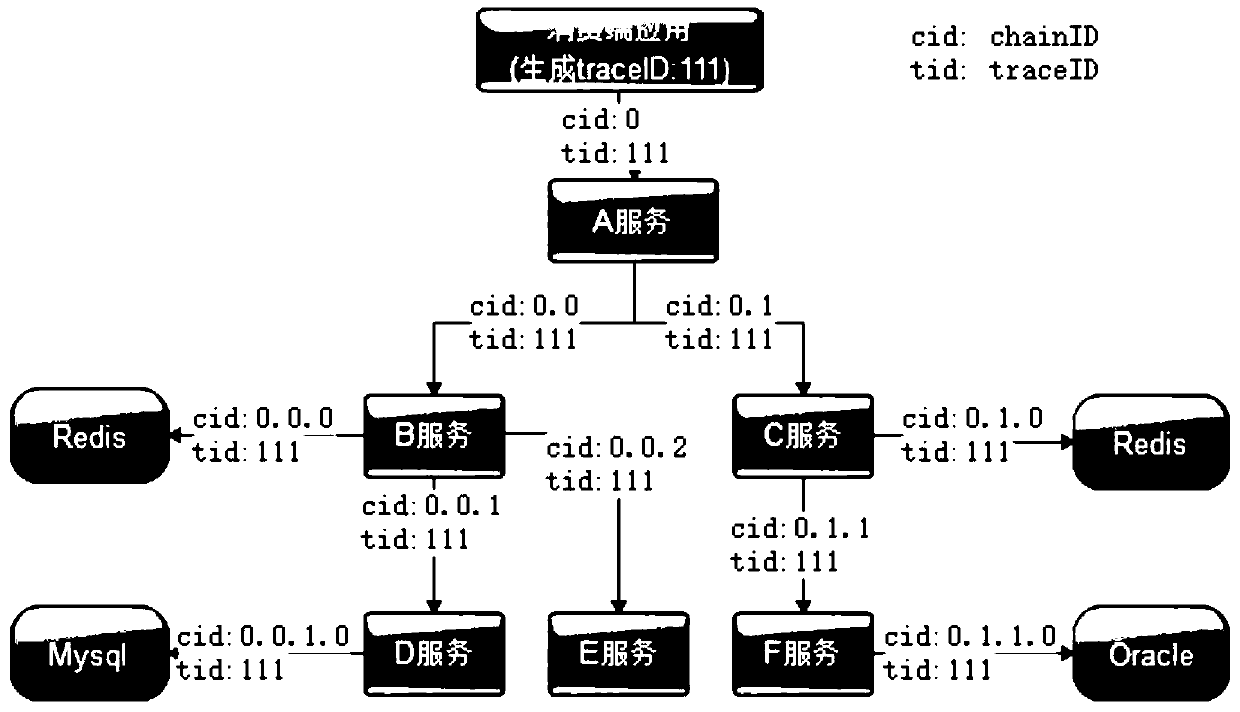
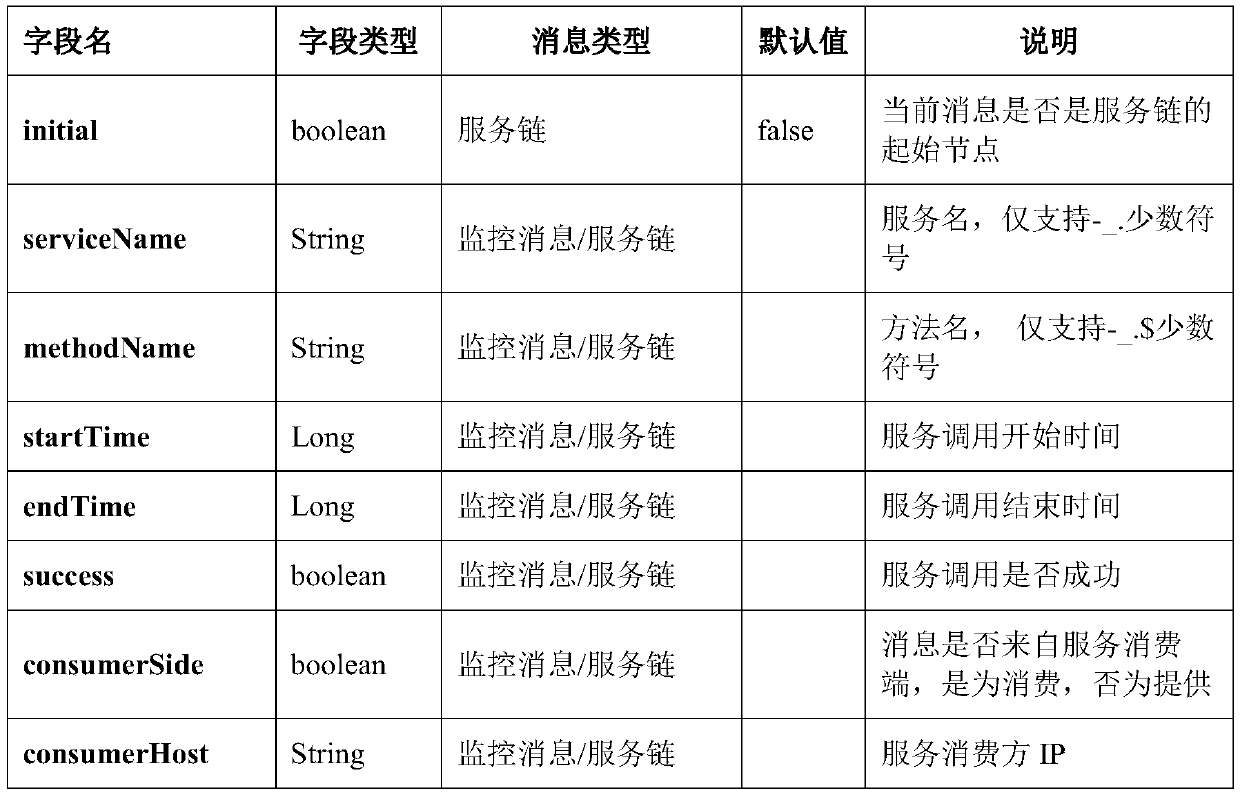
A real-time calling chain tracking method based on micro-service
InactiveCN109921927AImprove the efficiency of locating production problemsImprove efficiencyData switching networksDistributed cacheChain system
The invention discloses a real-time call chain tracking method based on micro-service. According to the method, a calling relation data structure is adopted, a distributed cache and database client monitoring are incorporated into a micro-service calling chain system, a trace ID is implanted into a business log, business information of a calling chain is connected in series, and the method is usedfor clearly sorting calling nesting relations one by one in complex calling. Through the system, the efficiency of positioning production problems can be greatly improved, and the understanding capability of development, operation and maintenance personnel on the system can be improved by analyzing the performance information of each link on the micro-service calling chain, so that the system canbe better optimized and improved.
Owner:苏州人之众信息技术有限公司
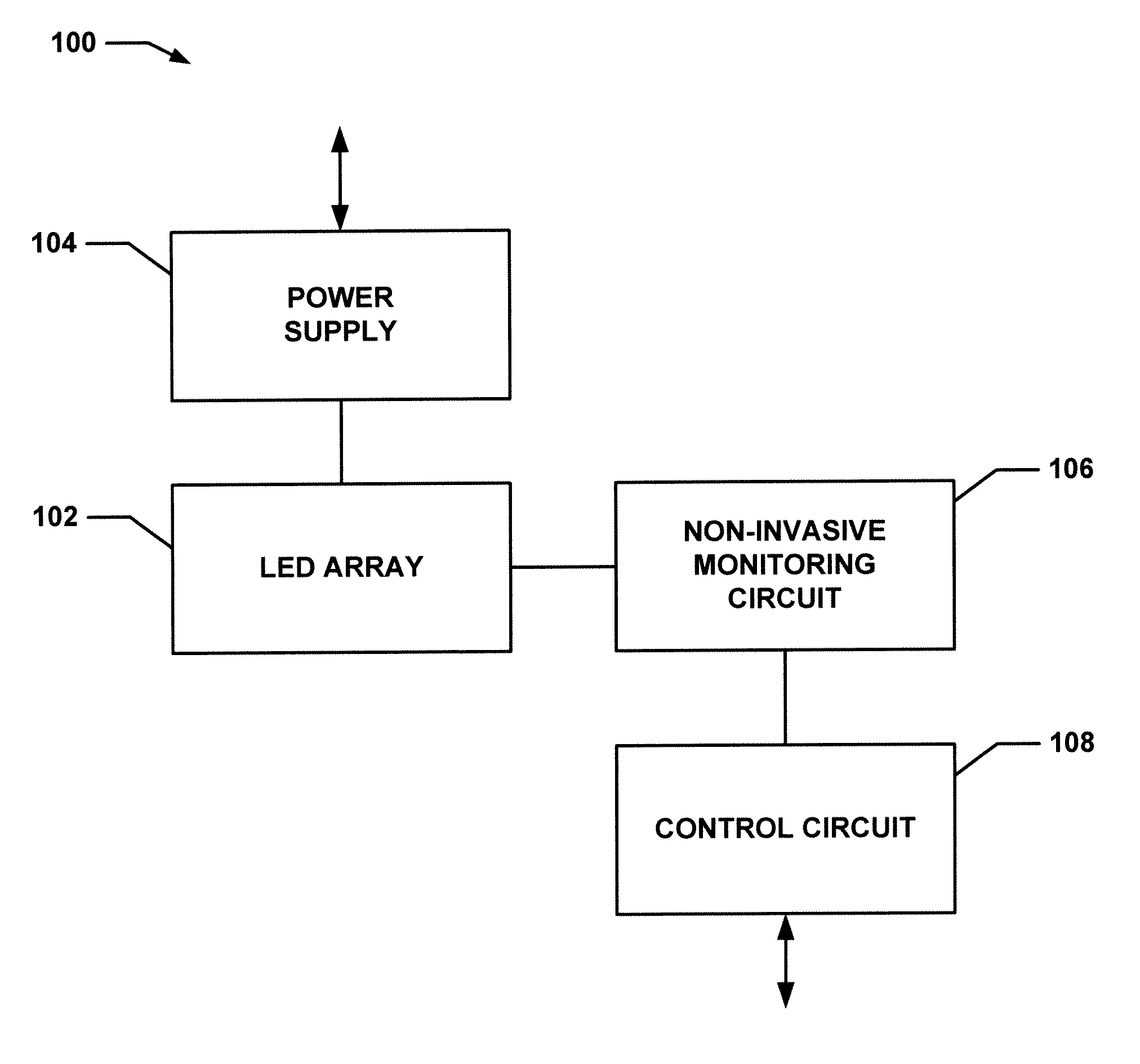
LED chain failure detection
InactiveUS20080204029A1Non invasiveDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesLuminous intensityEngineering
The system consists of an LED failure detection circuit to provide protection against individual LED catastrophic failure. When LED clusters are arranged in a series-parallel configuration, it is important to detect individual LED failure in order to avoid uncontrolled luminous intensity reduction and / or light uniformity degradation. The circuit compares the voltage levels on LEDs with similar position but situated in different chains. In normal conditions, the voltage levels are substantially similar to one another. In case of individual or multiple LED failure, open or shortcircuit, the circuit sends a signal to the automatic turn off circuit that initiates the lamp forced turn off sequence.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Method and devices to increase craniofacial bone density
InactiveUS20100092916A1Increase bone densityCost-effectiveDental implantsGum massagePeak valueHigh frequency
The present invention relates to a method for increasing bone growth in teeth and / or other craniofacial regions of a subject. This method includes administering to the jaw and / or teeth of the subject a mechanical vibration having a frequency of 10 to 1000 Hz with an acceleration peak of 0.1 to 2.00 g and that can produce a low magnitude strain of 1 to 50 microstrain in the jaw and / or teeth. The present invention also relates to devices that deliver high frequency, low magnitude force to the teeth.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Methods for modulating osteochondral development using bioelectrical stimulation
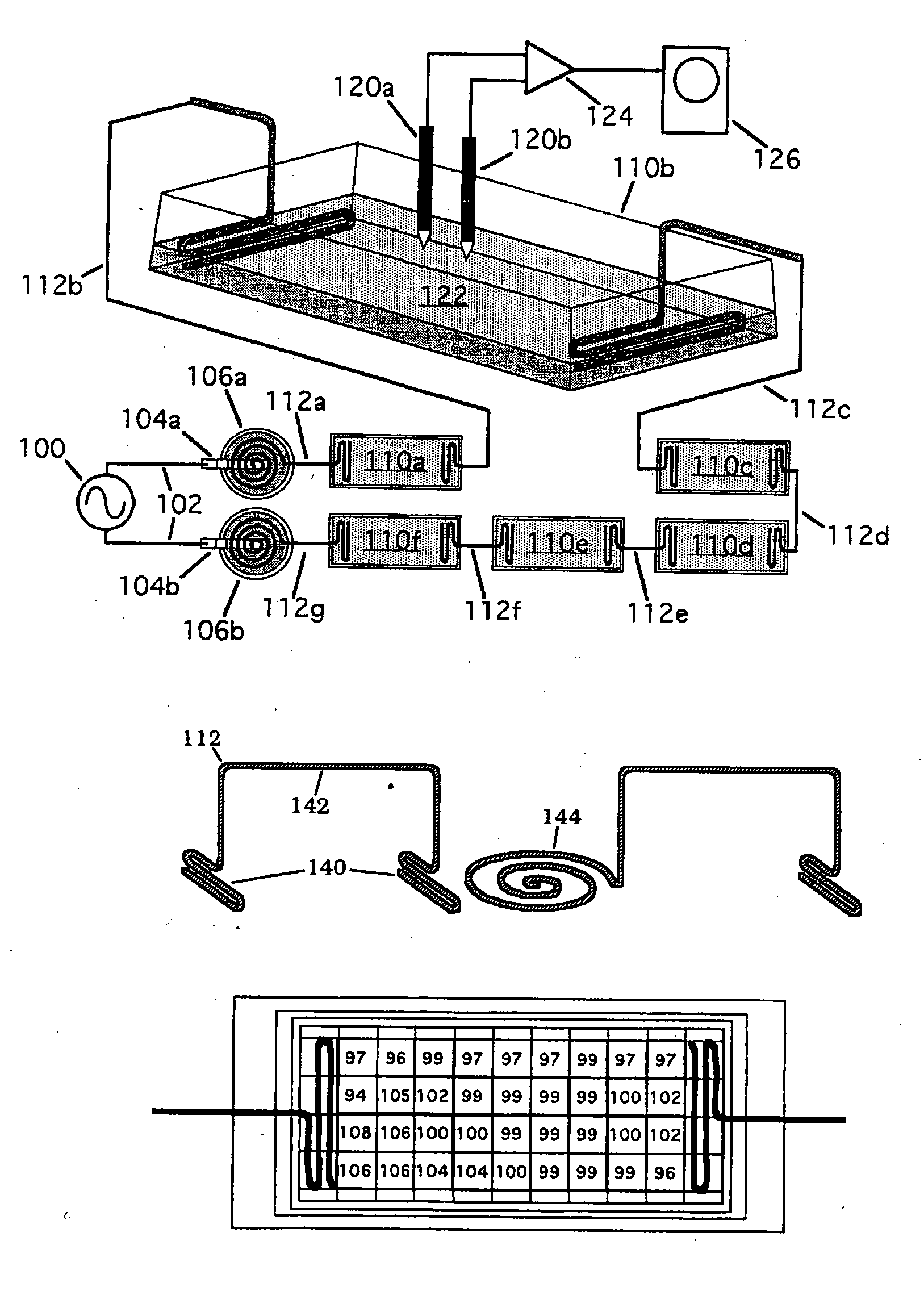
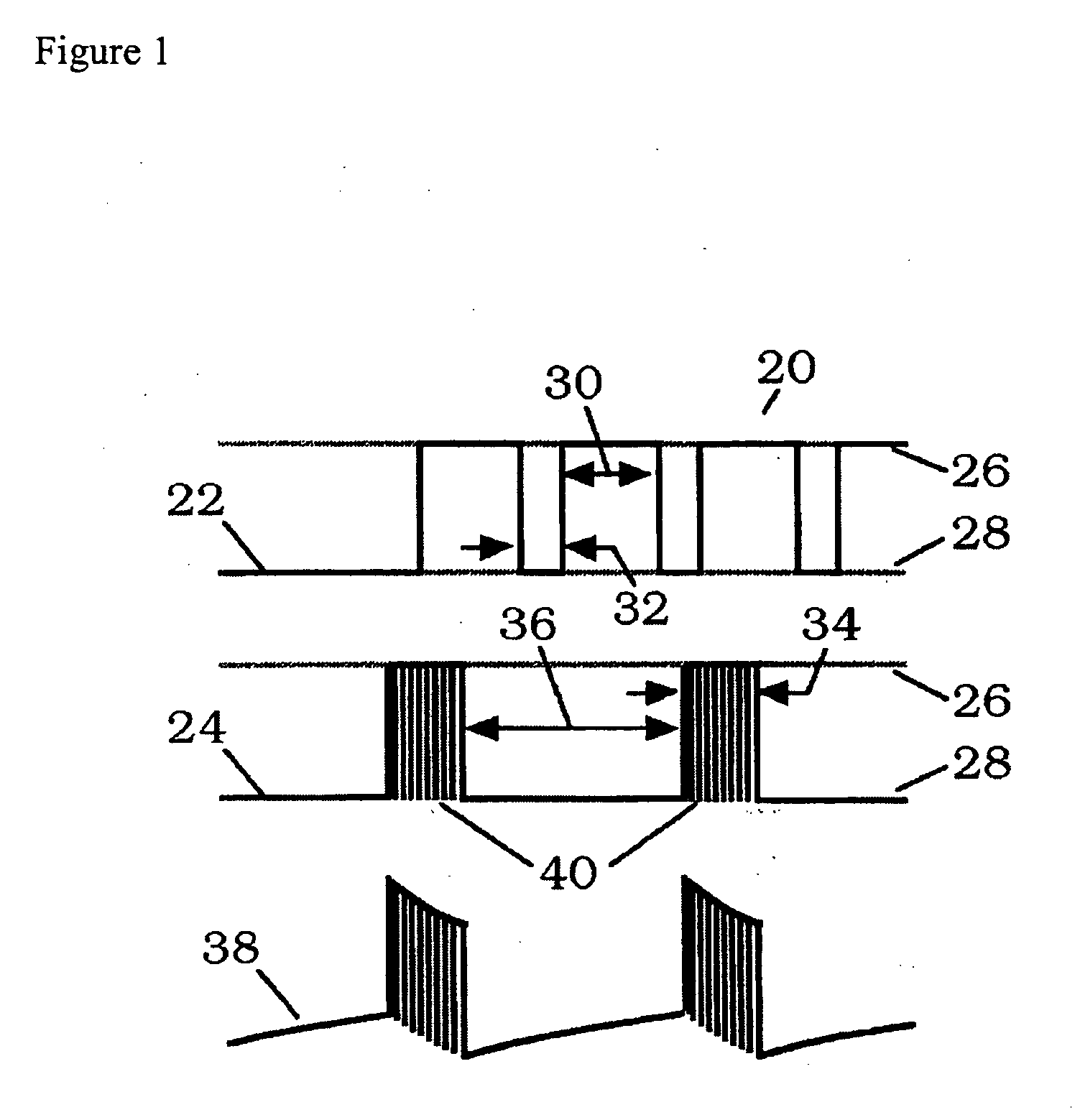
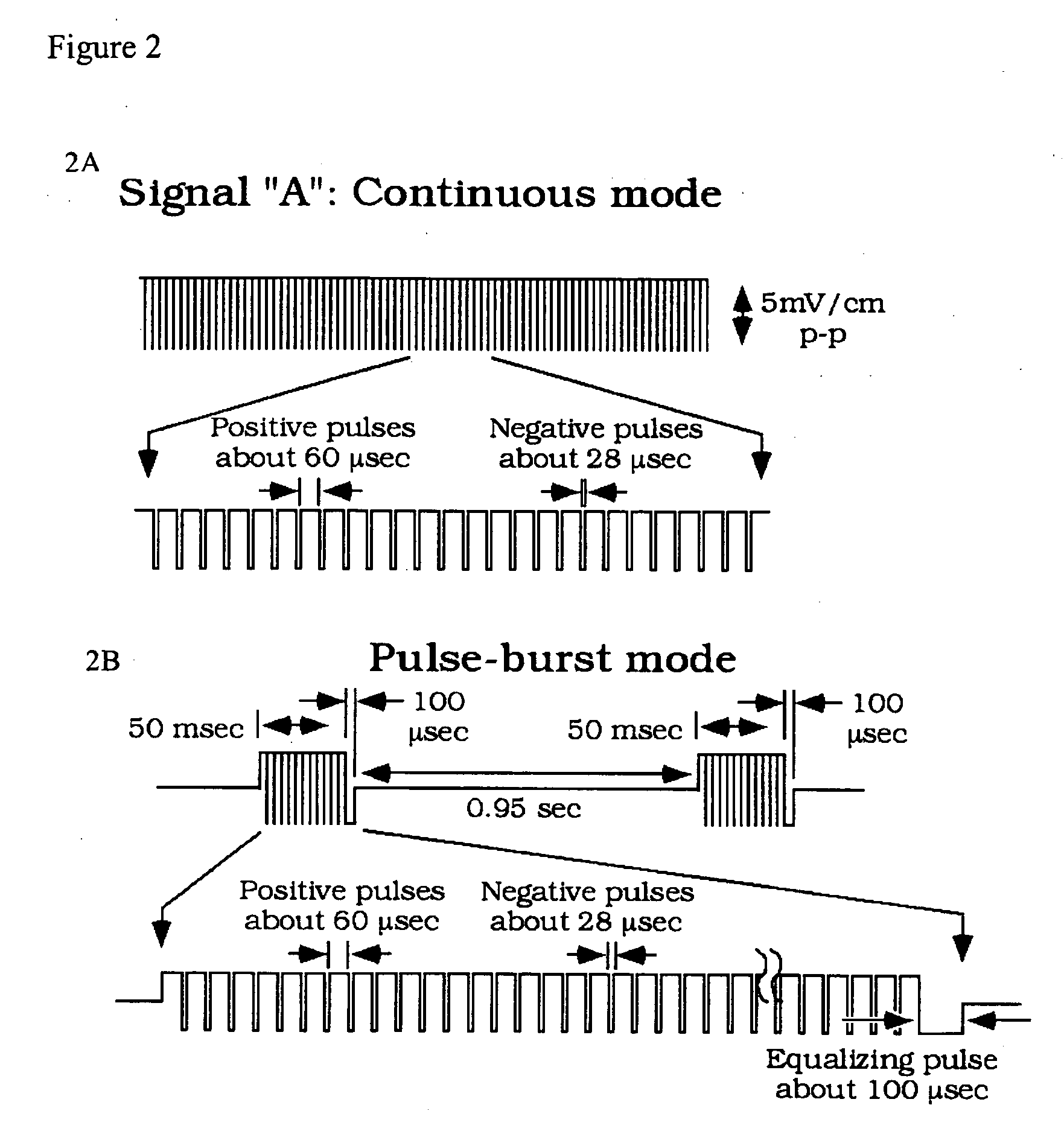
ActiveUS20060293724A1Maximize utilizationMaximize applicationElectrotherapyStress based microorganism growth stimulationCo administrationOsteoblast
Compositions and methods are provided for modulating the growth, development and repair of bone, cartilage or other connective tissue. Devices and stimulus waveforms are provided to differentially modulate the behavior of osteoblasts, chondrocytes and other connective tissue cells to promote proliferation, differentiation, matrix formation or mineralization for in vitro or in vivo applications. Continuous-mode and pulse-burst-mode stimulation of cells with charge-balanced signals may be used. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by nitric oxide release through electrical stimulation and may be modulated through co-administration of NO donors and NO synthase inhibitors. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by release of BMP-2 and BMP-7 in response to electrical stimulation to promote differentiation of cells. The methods and devices described are useful in promoting repair of bone fractures, cartilage and connective tissue repair as well as for engineering tissue for transplantation.
Owner:MEDRELIEF
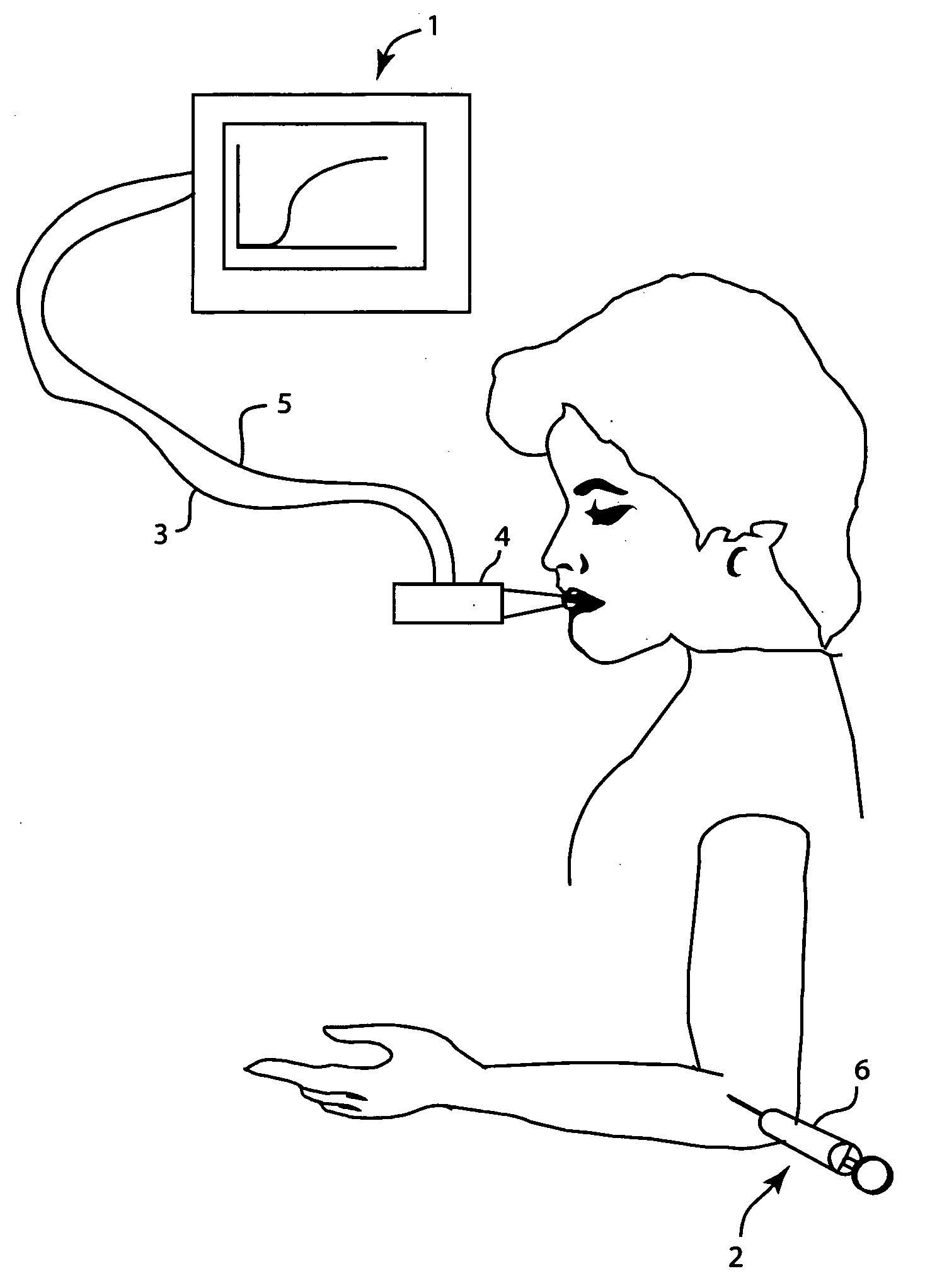
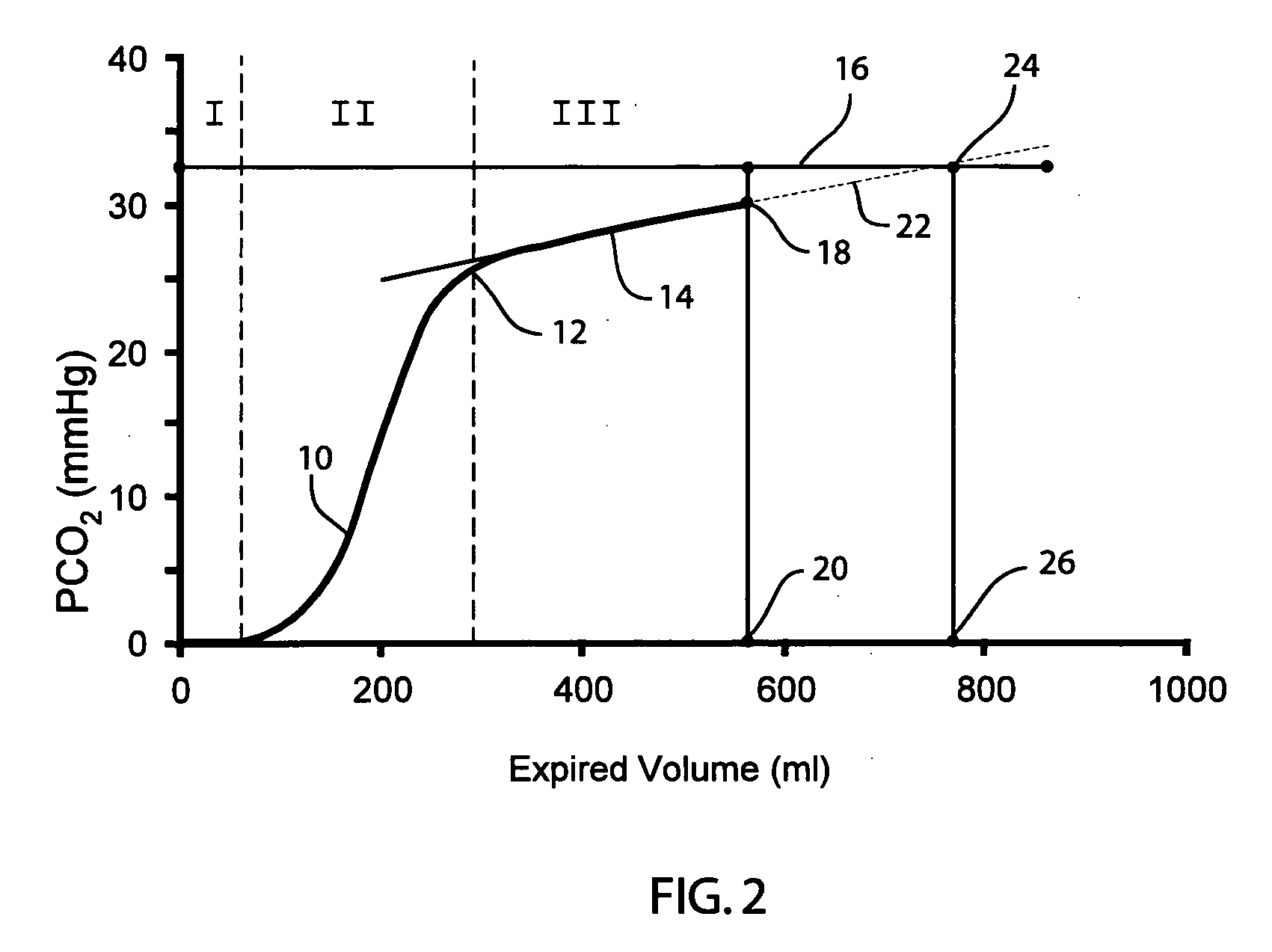
Method and apparatus for indicating the absence of a pulmonary embolism in a patient
ActiveUS20070129646A1Avoid dependenceReduce in quantityRespiratorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBreathing gasIntensive care medicine
A method and apparatus for determining the presence or absence of a pulmonary embolism (PE) in a patient. The breathing gas CO2 partial pressure (PCO2) during the expiration of breathing gases by the patient, the end tidal (EtCO2), CO2 partial pressure, and the CO2 partial pressure (PaCO2) of the blood are measured. The volume (V) of breathing gases expired during the expiration of breathing gases by the patient is also measured and a relationship between changes in breathing gas CO2 partial pressure (PCO2) and changes in breathing gas volume (V) in an alveolar expiration phase of patient expiration is determined. The difference between the blood CO2 partial pressure (PaCO2) and the end expiration CO2 partial pressure is divided by the relationship between PCO2 and V produce a quantity which is compared to a threshold value. If the quantity is below the threshold value, the absence of a pulmonary embolism is indicated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
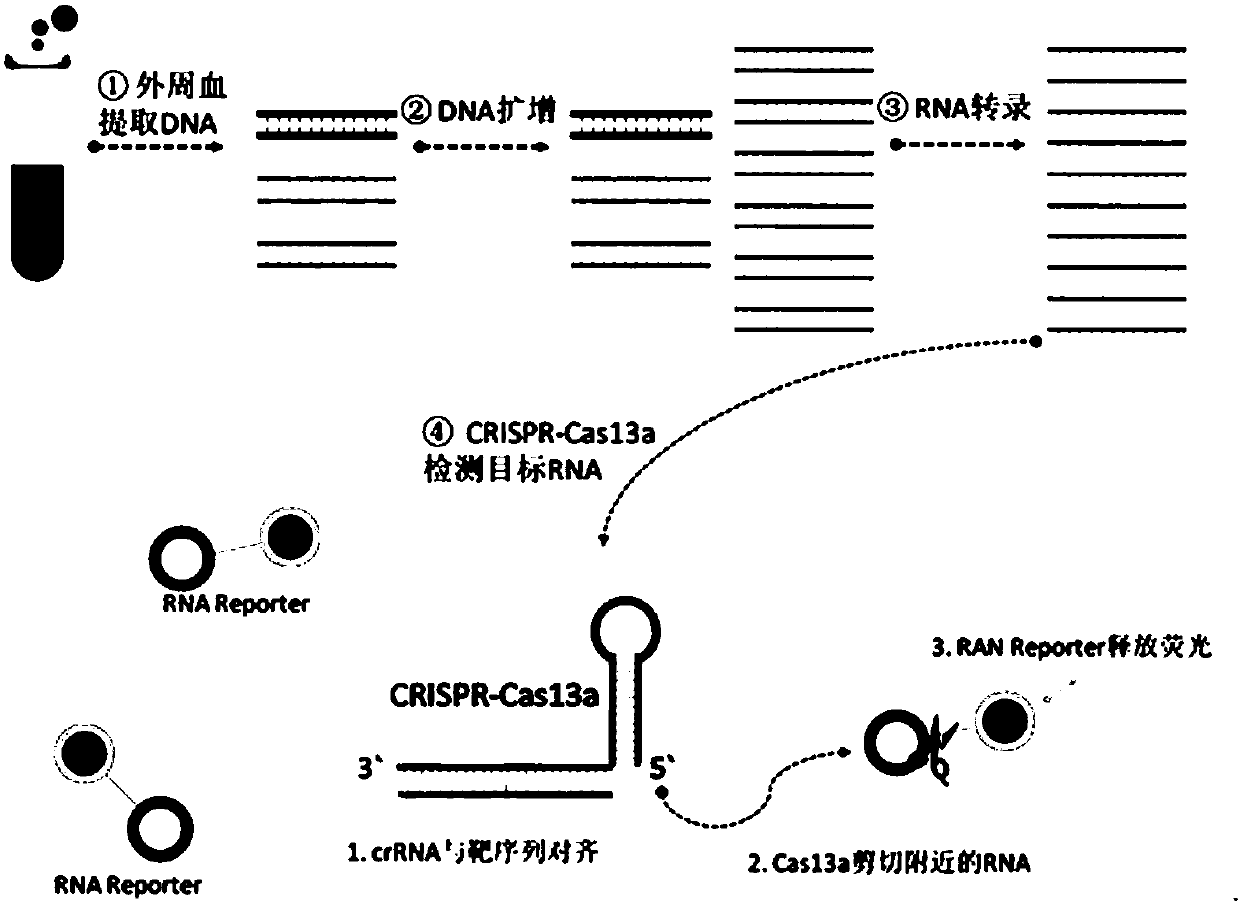
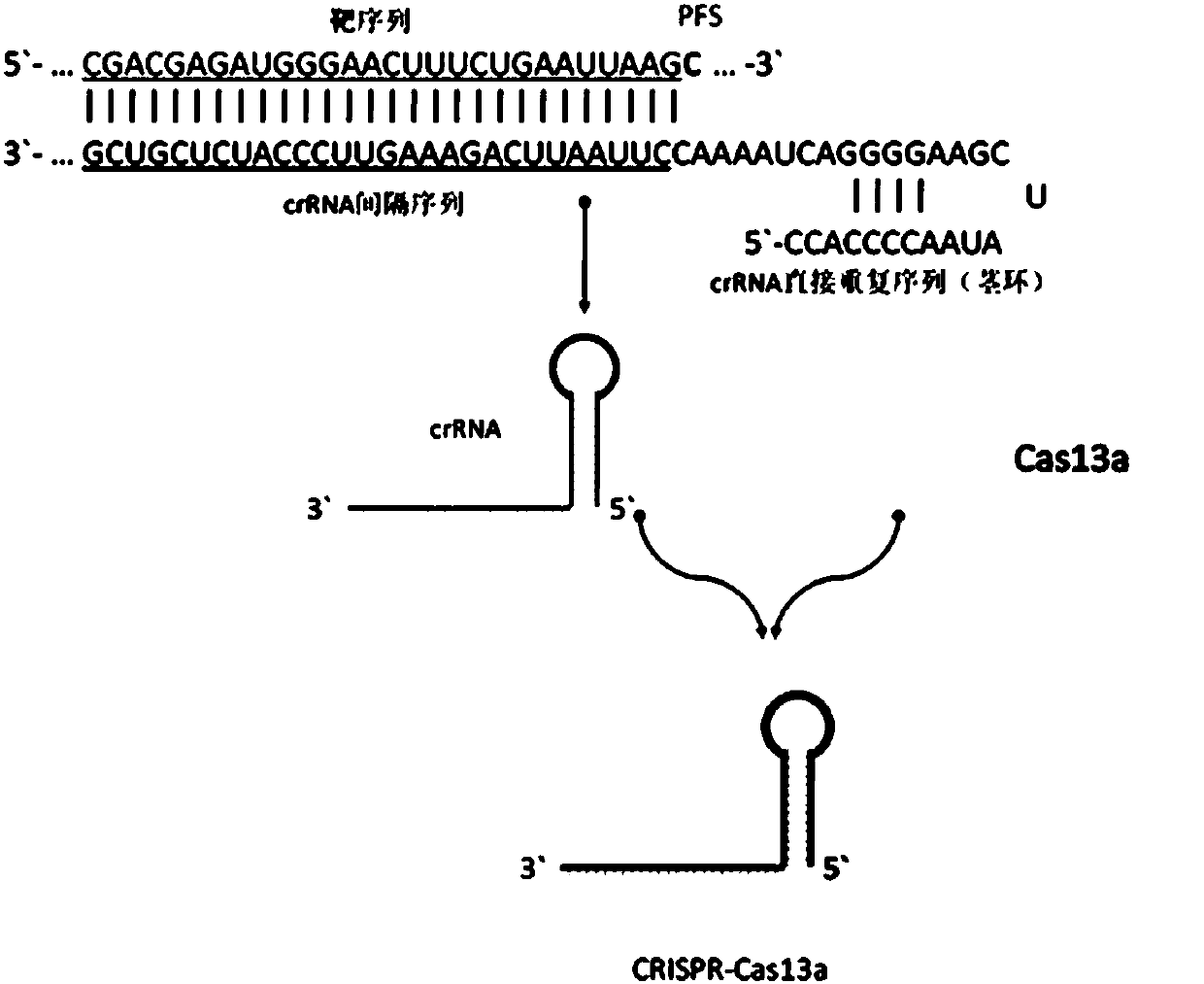
CrRNA specifically targeting toward human RSPO2 gene in CRISPR-Cas13a system and system and application
ActiveCN108048466AConducive to commercial promotionSuitable for large-scale applicationsHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh fluxFluorescence
The invention discloses crRNA specifically targeting toward a human RSPO2 gene in a CRISPR-Cas13a system and a system and an application. The crRNA can establish a CRISPR-Cas13a system for specific targeting toward a human RSPO2 gene. A trace of a RSPO2 gene is specifically detected in a body fluid. The system is non-invasive, can perform frequent detection, and is fast in detection speed. Compared with liquid biopsy in the prior art, the system can detect a trace of a RSPO2 gene in the body liquid via fluorescent reading. The system doesn't require high-flux sequencing, is low in cost, high in detection speed, and suitable for clinic large-scale application.
Owner:JIAXING NO 1 HOSPITAL
Sorter and sorting method for separating cells and particles
ActiveCN102019277ARich feature informationNon-invasiveNanoparticle analysisPreparing sample for investigationParticle sortingFluorescence
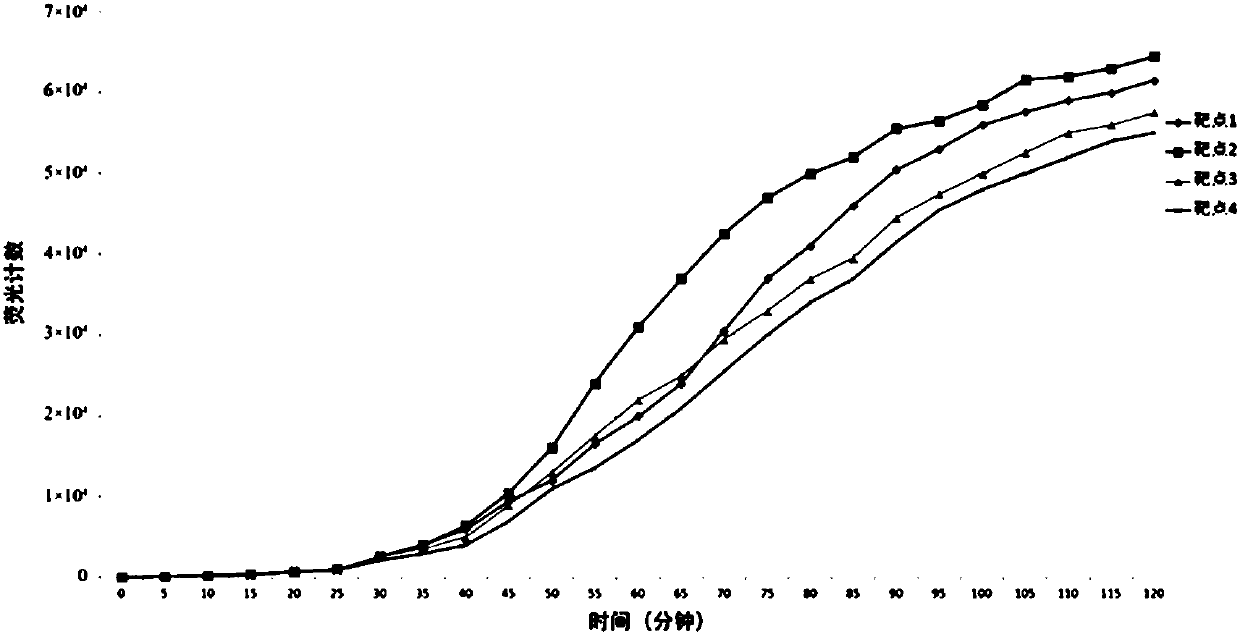
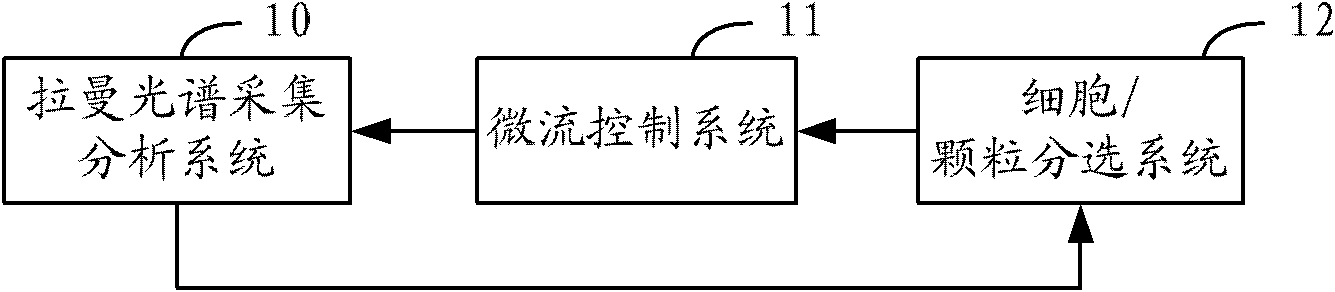
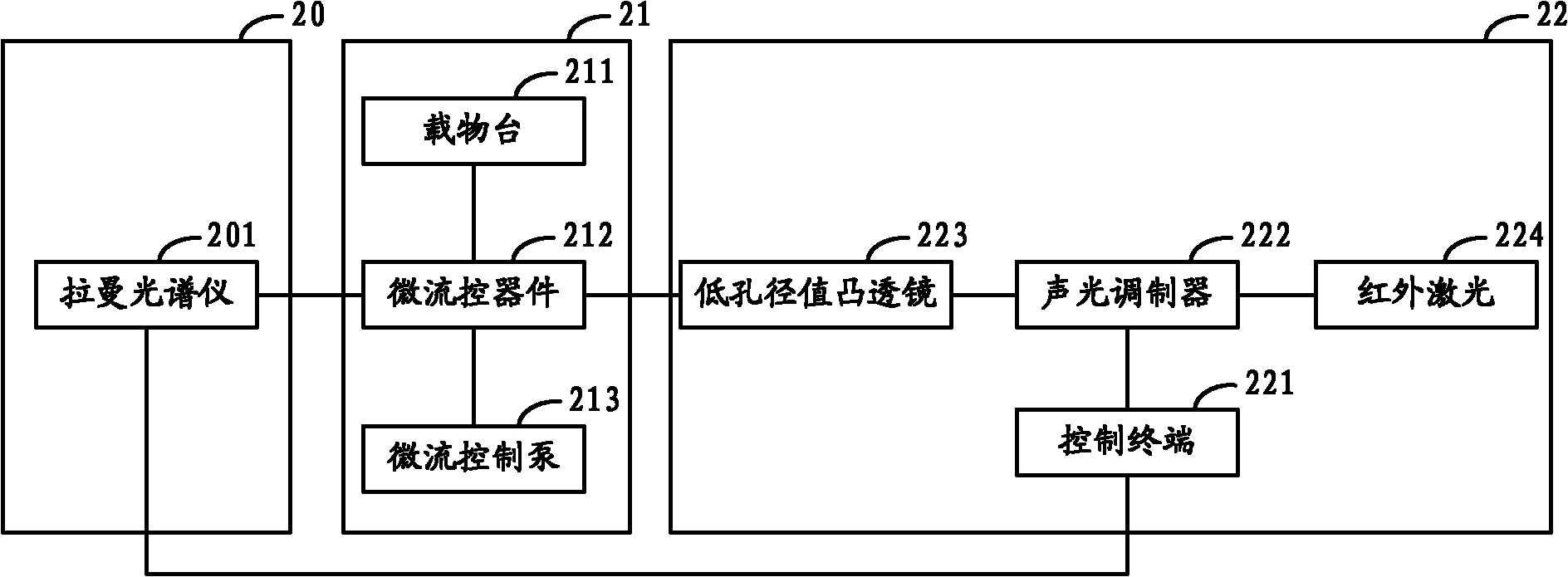
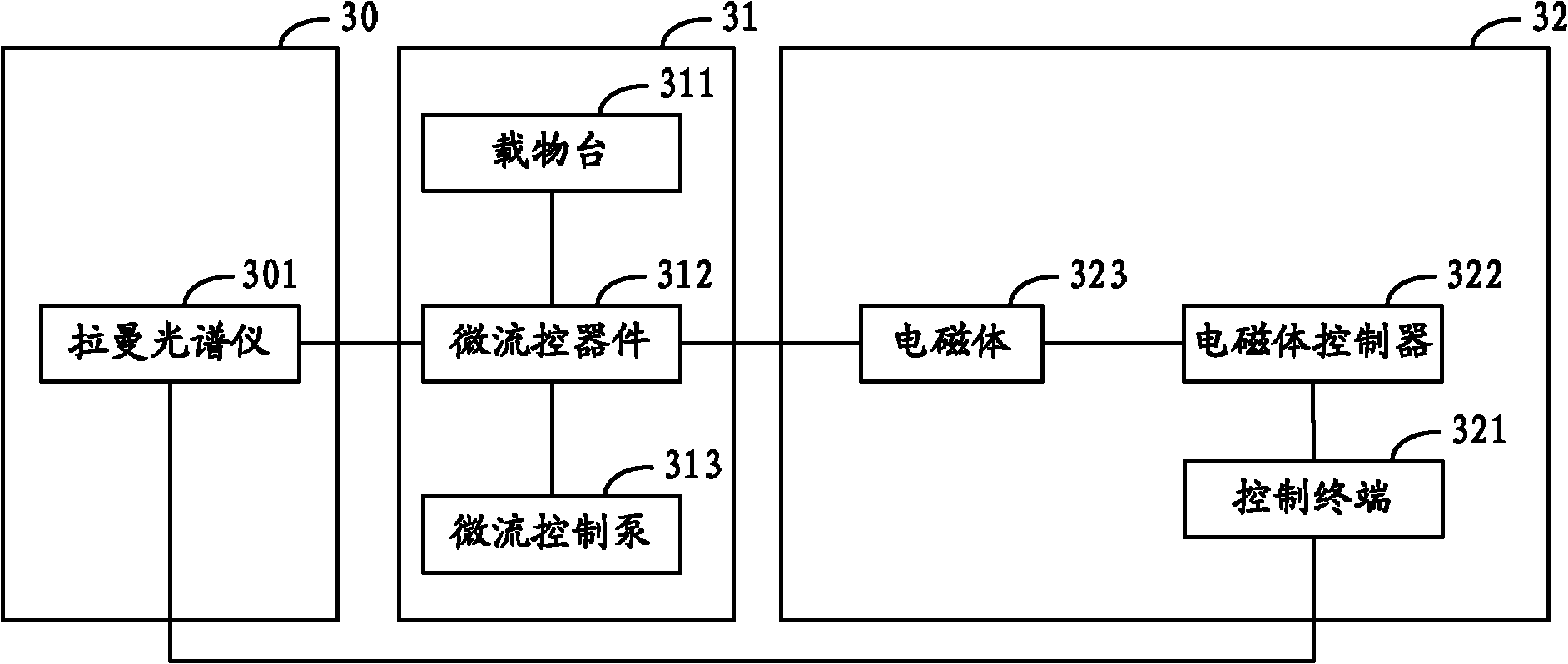
The invention relates to a sorter and a sorting method for separating cells and particles. The sorter comprises a Raman spectrum acquisition analysis system, a micro-flow control system and a cell / particle sorting system, wherein the micro-flow control system is connected with the Raman spectrum acquisition analysis system; the Raman spectrum acquisition analysis system is connected with the cell / particle sorting system; and the cell / particle sorting system is connected with the micro-flow control system. The invention also provides a sorting method for separating the cells and the particles.The sorter can effectively identify and sort nanometer-micron sized cells, nano materials, particles and cell contents, and because the Raman spectrum has the characteristics of high speed, non-invasive property, high information content and the like, the sorting method provides richer characteristic information of the cells or the particles in the same time period compared with methods of fluorescence or radio isotope labeling and the like.
Owner:长春长光辰英生物科学仪器有限公司
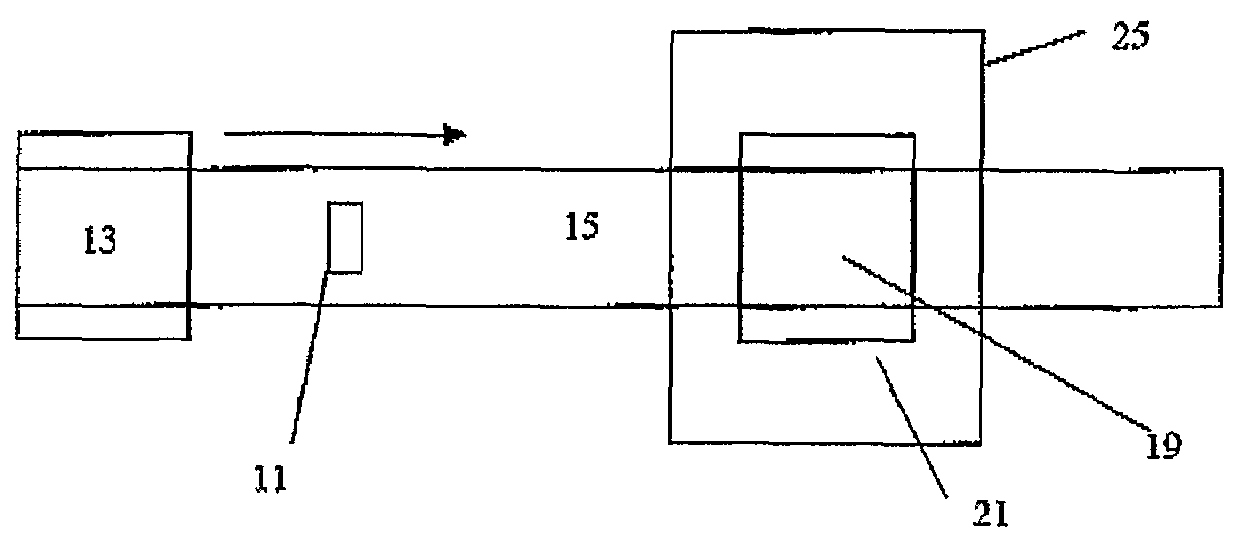
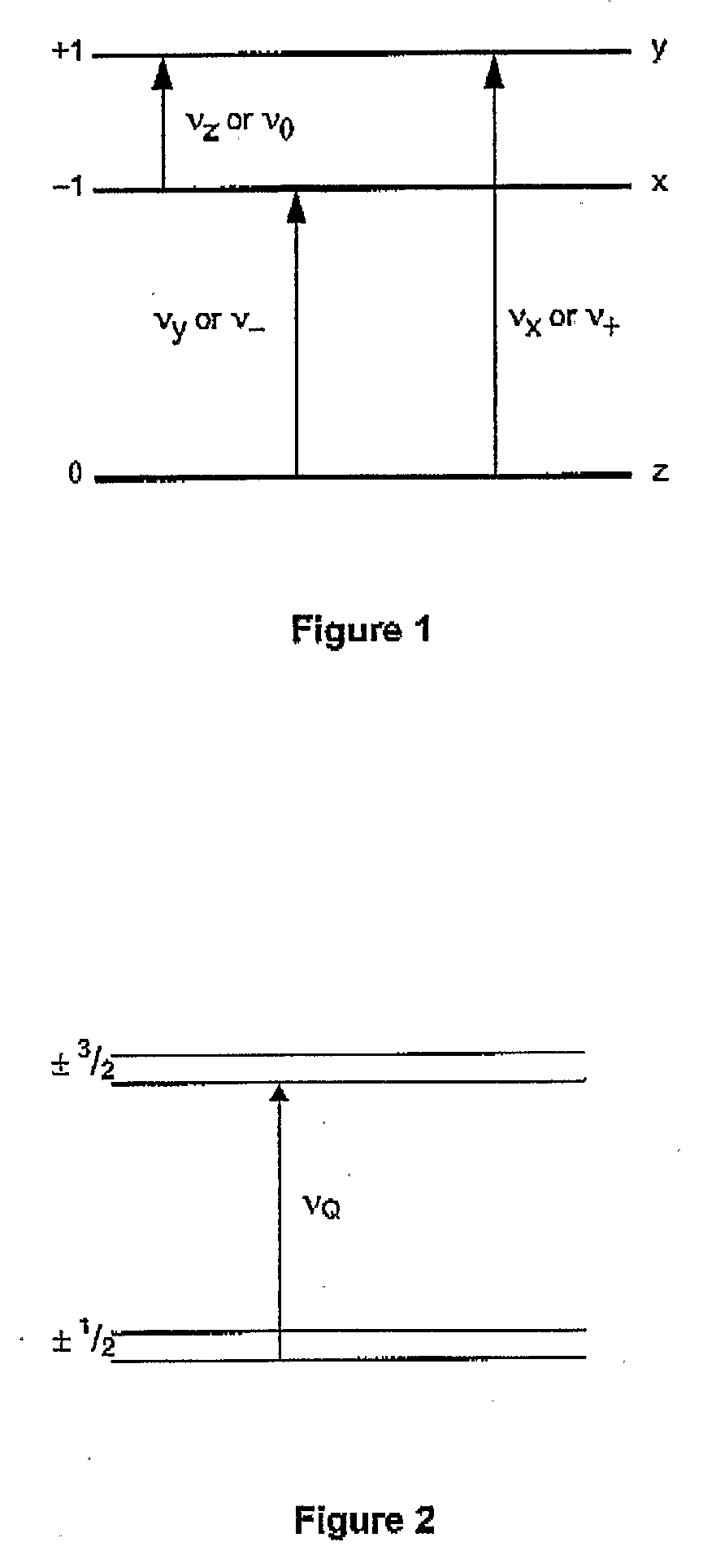
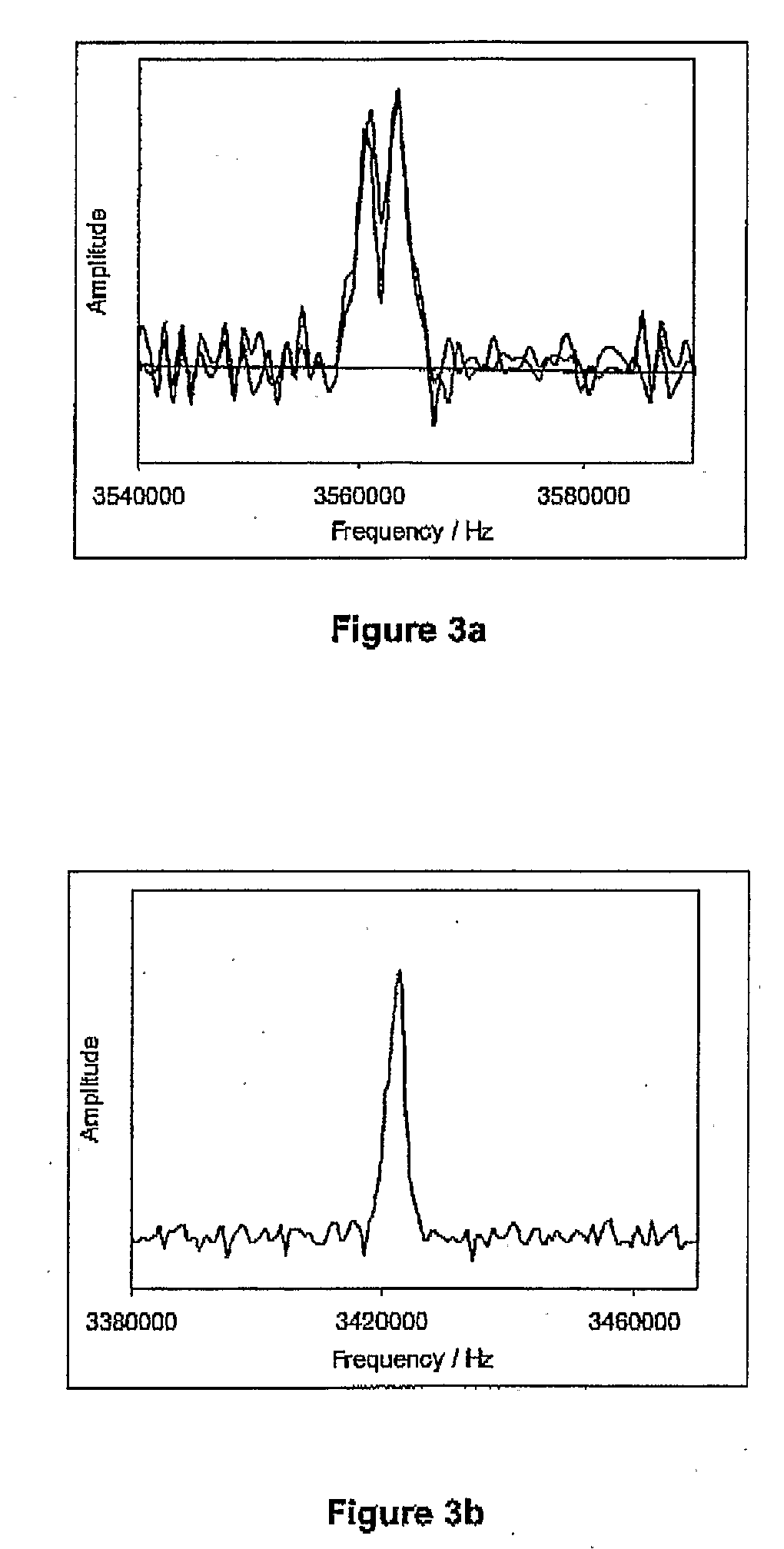
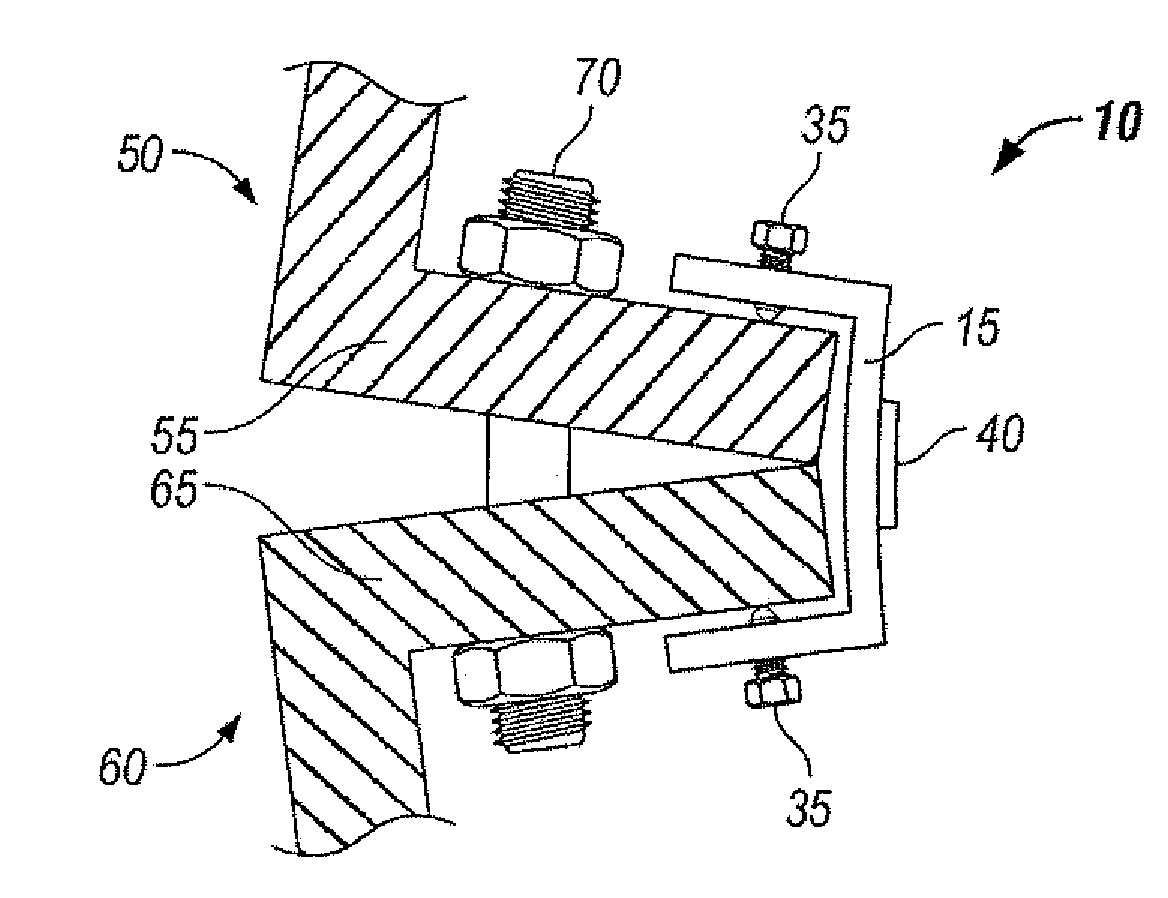
System and Method for Improving the Analysis of Chemical Substances Using Nqr
InactiveUS20080309339A1Improve analysisEasy to analyzeMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCHEMISTRY METHODSAmount of substance
A method for analysing a chemical substance containing quadrupolar nuclei to determine a measurable characteristic of the substance. The method includes irradiating the substance with RF energy in a prescribed manner to stimulate NQR of certain quadrupolar nuclei within the substance. Then receiving and processing a signal emitted from the substance to isolate an NQR signal therefrom. Thereafter analysing the NQR signal to obtain a measure of the characteristic of the substance; and providing an output indicative of the measure for analytical purposes. Specific methods for analysing a chemical substance during production thereof to determine a characteristic of the substance indicative of the quality thereof, and for searching for chemicals together with specific systems are also described.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Wind Turbine Tower Monitoring Device
InactiveUS20100126115A1Non invasiveImprove installation speedEngine fuctionsForce measurementRelative motionTower
A wind turbine installation monitoring device, for detecting relative movement between two adjacent components of a wind turbine installation is provided. The device comprises a deformable member together with a securing device. The securing device is configured to enable the device to be connectable to a wind turbine installation, in use. The deformable member is located across an interface between the adjacent components of a wind turbine installation. Further, a detection device is provided and configured to detect deflection of the deformable member and thereby to detect relative movement between the two components.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Mobile phase treatment for chromatography
InactiveUS20060054558A1Convenient temperature programmingThe process is convenient and fastIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationDead volumeContact time
A convenient and efficient method for heating or cooling the mobile phase fluid of a chromatographic system prior to its entry into the chromatographic column is described. The “preheating” or “precooling” process is carried out using an apparatus containing a short length of tubing where the mobile phase is heated or cooled. The heating or cooling is performed using a heating or cooling element that is in intimate thermal contact with the exterior of the tubing. The temperature change of the mobile phase is measured downstream by a non-invasive, low-mass sensing element on the exterior of the tubing. With a low mass heating or cooling element, the device can be very responsive and allows for rapid equilibration and convenient temperature programming of the mobile phase. This configuration also requires only a short mobile phase contact time, is non-invasive, adds no dead volume, and allows for use of columns over a wide range of internal diameter, flow rates and temperatures.
Owner:SELERITY TECH
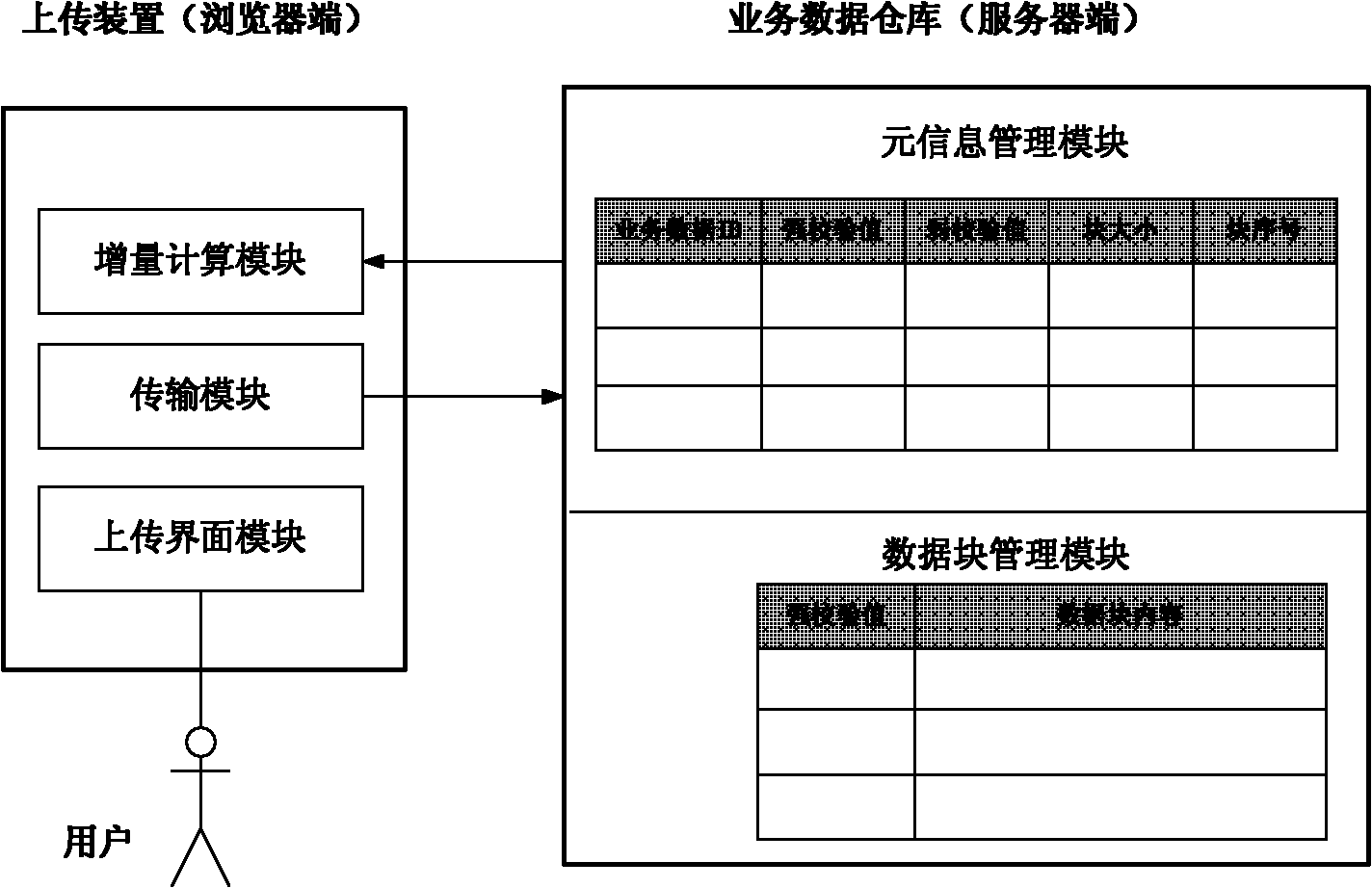
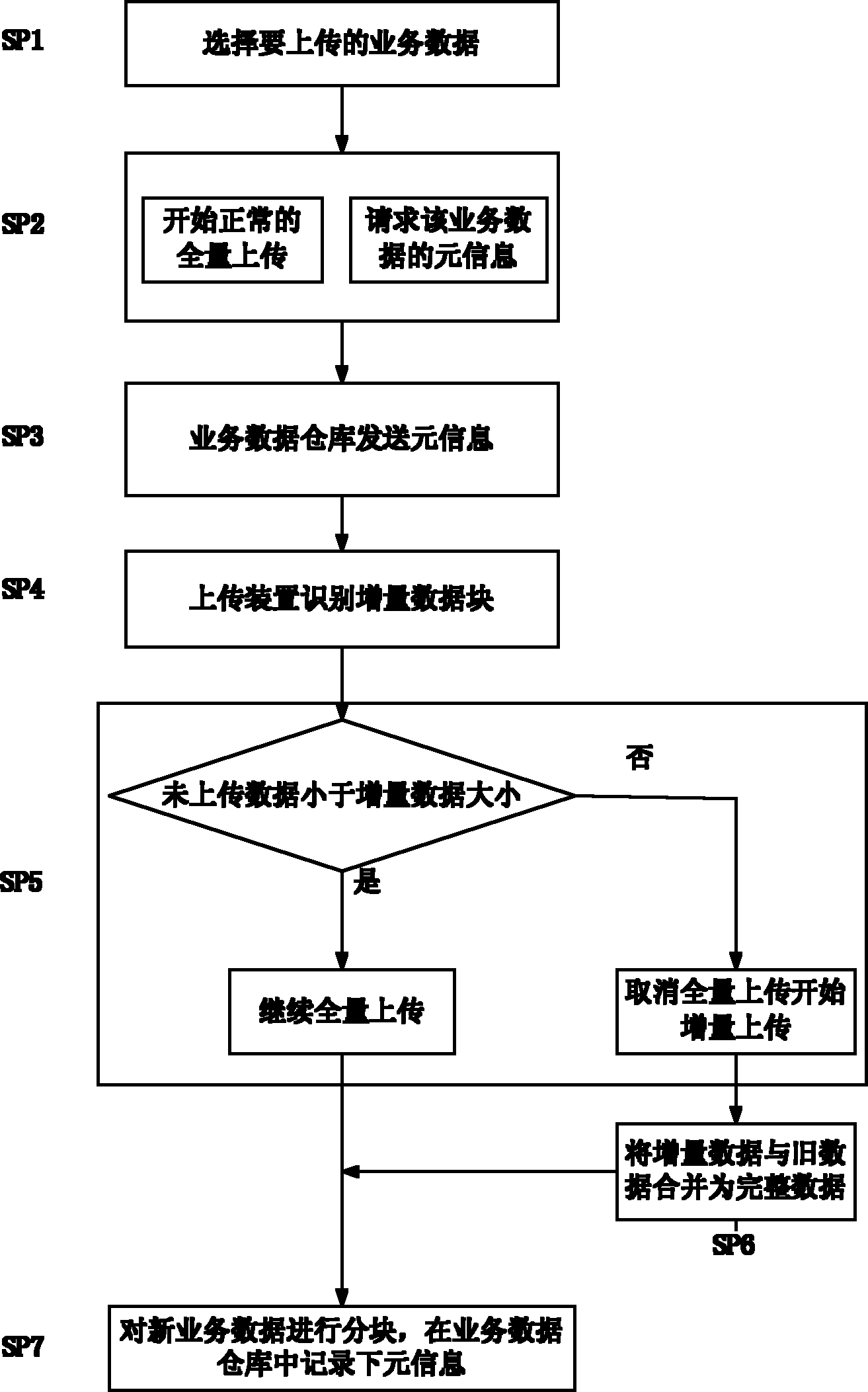
Flow service data uploading system and method
ActiveCN102163308AReduce consumptionImprove efficiencyTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsData warehouseData storing
The invention provides a flow service data uploading system which comprises a service data warehouse positioned at a server terminal and an uploading device positioned at a client, wherein the service data warehouse is used for storing the meta information and data block of service data and providing the meta information of the required service data for the uploading device; and the uploading device is used for obtaining the meta information of the service data which is stored in the service data warehouse and corresponds to the to-be-uploaded service data, then identifying the incremental data of the to-be-uploaded service data with respect to the corresponding service data stored by the service data warehouse according the meta information of the corresponding service data, and uploading the incremental data to the service data warehouse. The invention further provides a corresponding flow service data uploading method. By using the uploading system and method provided by the invention, the transmitted data volume can be reduced, the integral flow operation efficiency is improved, the use ratio of a disk is improved, and the disk quota loss to a tenant is reduced.
Owner:国信电子票据平台信息服务有限公司
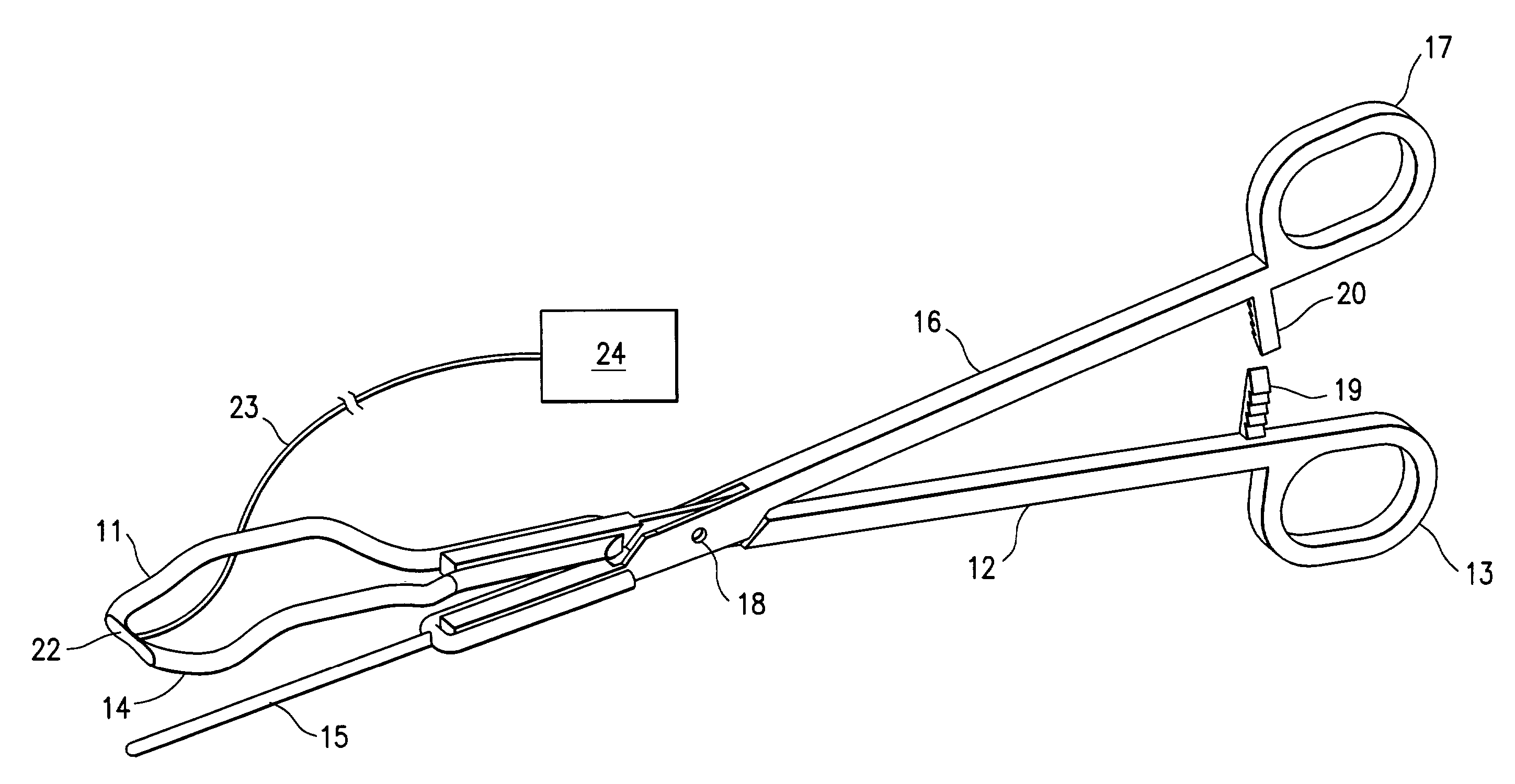
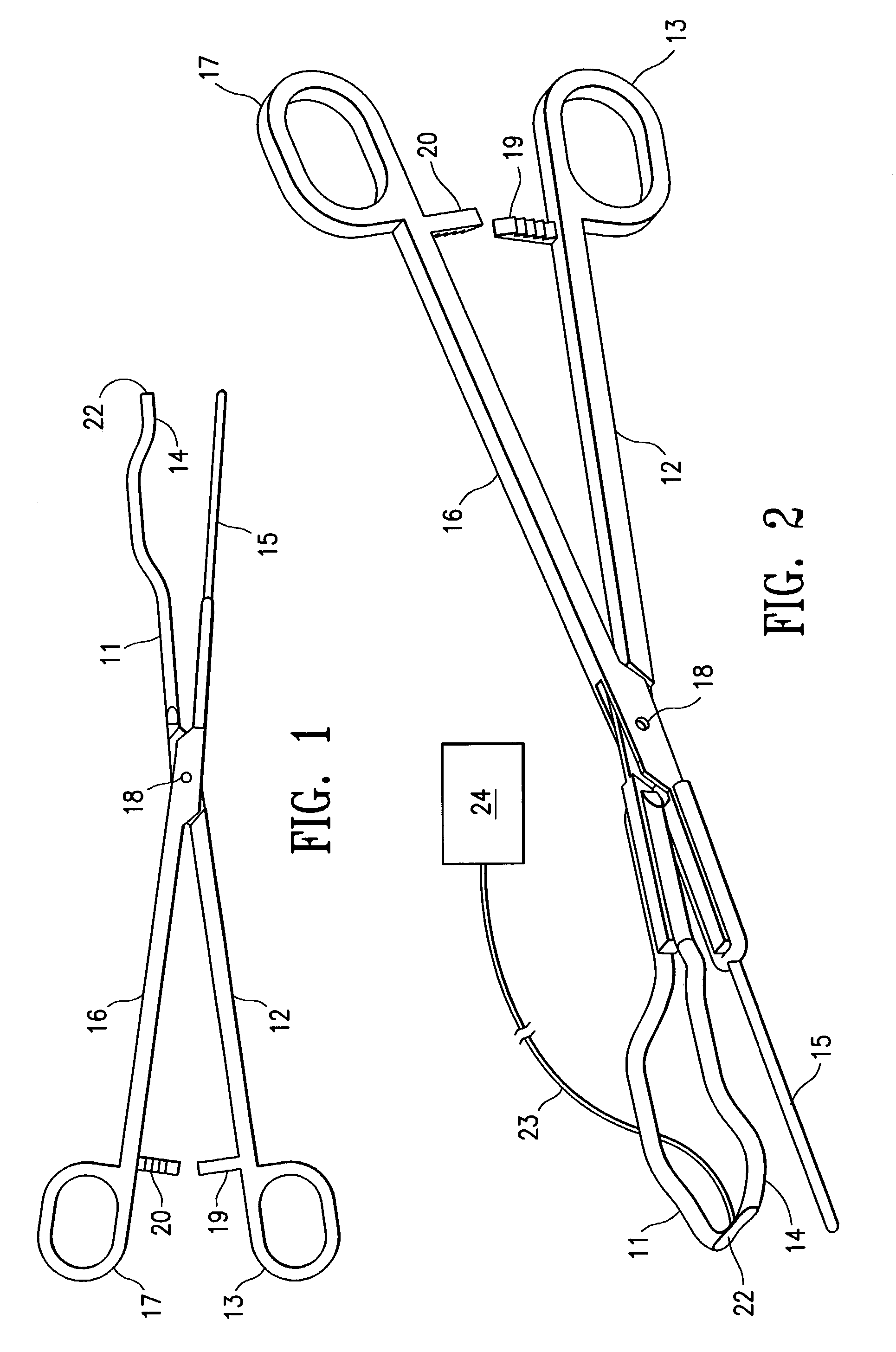
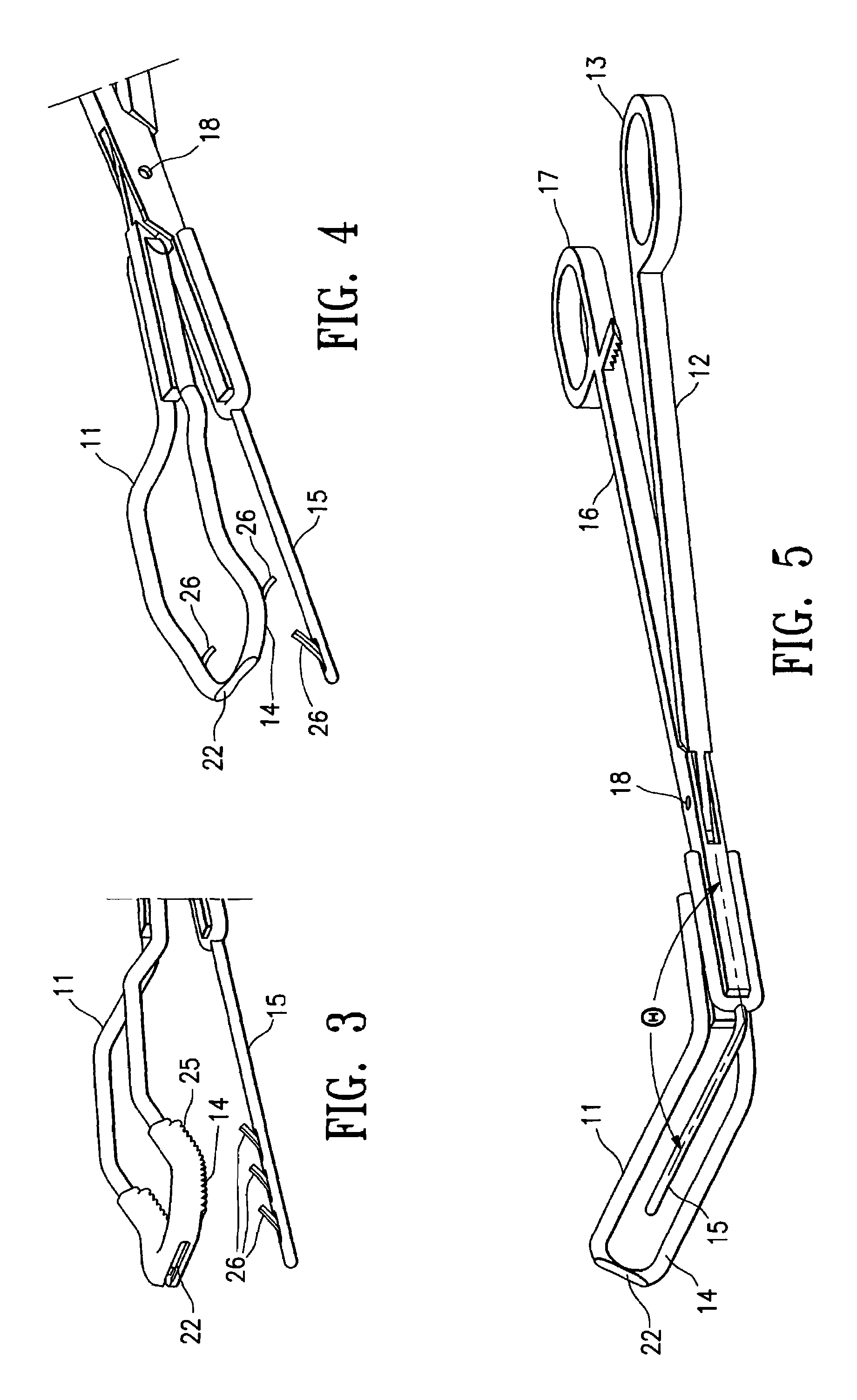
Uterine artery occlusion clamp
InactiveUS7329265B2Reducing and terminating blood flowNon invasiveDiagnosticsObstetrical instrumentsUterine DisorderDisease
Owner:VASCULAR CONTROL SYST
System and method for simulating internet browsing system for user without graphical user interface
ActiveUS20160170778A1Non-invasiveDigital data protectionArtificial lifeGraphicsGraphical user interface
The embodiments herein provide a system and a method of simulating internet browsing system without a graphical user interface. The method comprises the steps of extracting browser characteristics of a real user browser. The interne browsing system is simulated without graphical user interface by including the browser character of a real user browser within the simulated virtual user browser to makes the simulated virtual user digitally identical to the real user browser. Further, the tracking elements of the real user browser are shared with the simulated virtual user browser to divert the interne trackers away from the real user browser. Further, a fingerprint the real user browser is duplicated in the simulated virtual user browser. The method uses an algorithm to simulate the simulated virtual user browser. The algorithm is intent to sell and purchase goods and services, thereby misguiding the internet trackers.
Owner:KALYANPUR ROHAN
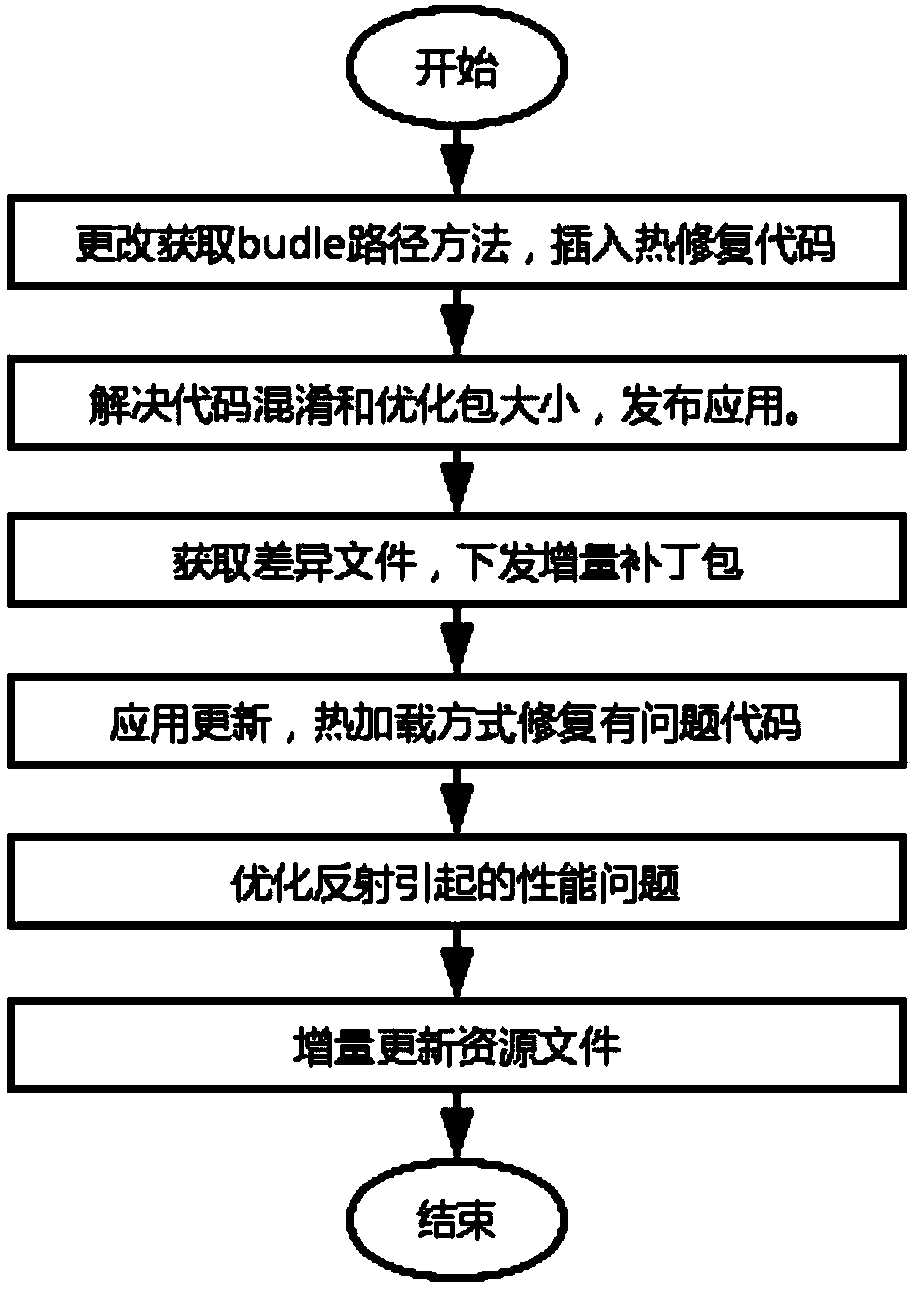
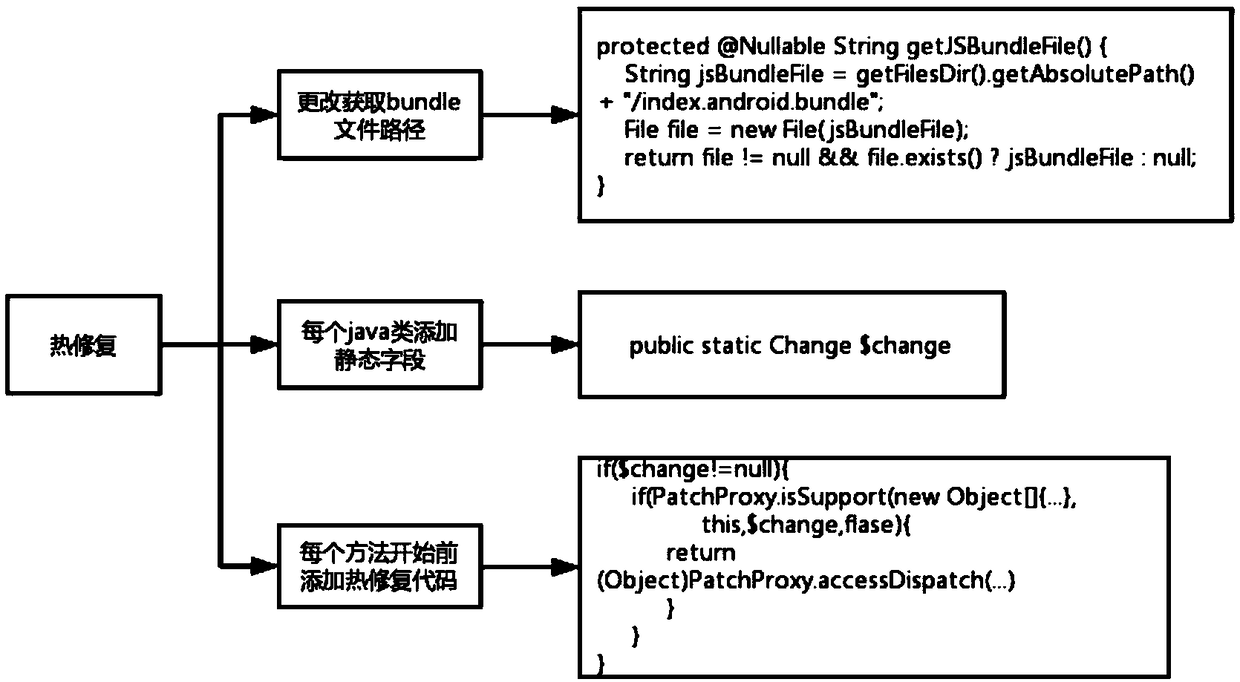
Incremental updating method of an integrated Android application
ActiveCN109491695AReduce trafficImprove application experienceCode compilationProgramming languageComputer compatibility
The invention discloses an incremental updating method of an integrated Android application, which is based on React Native, adds a static field to all classes in an Android native code serving as anapplication, inserts a skip code at an entrance of the method, and comprises condition judgment on the static field; in addition, the method for reading the bundle path is changed, and the bsdiff is used for achieving incremental updating of the application. According to the invention, the existing thermal remediation technology is optimized; a hot repair framework which is higher in compatibilityand can take effect in real time without restarting is achieved, online bugs can be repaired at any time without releasing a new version, resource files can be updated, discovered problems can be quickly repaired, great help is provided for developers, and great significance is achieved for improving the application use experience.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com