Patents
Literature
186 results about "Virosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A virosome is a drug or vaccine delivery mechanism consisting of unilamellar phospholipid membrane (either a mono- or bi-layer) vesicle incorporating virus derived proteins to allow the virosomes to fuse with target cells. Viruses are infectious agents that can replicate in their host organism, however virosomes do not replicate. The properties that virosomes share with viruses are based on their structure; virosomes are essentially safely modified viral envelopes that contain the phospholipid membrane and surface glycoproteins. In clinically designed virosomes, the viral genetic material are substituted with therapeutic agents. As a drug or vaccine delivery mechanism they are biologically compatible with many host organisms and are also biodegradable. The use of reconstituted virally derived proteins in the formation of the virosome allows for the utilization of what would otherwise be the immunogenic properties of a live-attenuated virus, but is instead a safely killed virus. A safely killed virus can serve as a promising vector because it won’t cause infection and the viral structure allows the virosome to recognize specific components of its target cells.
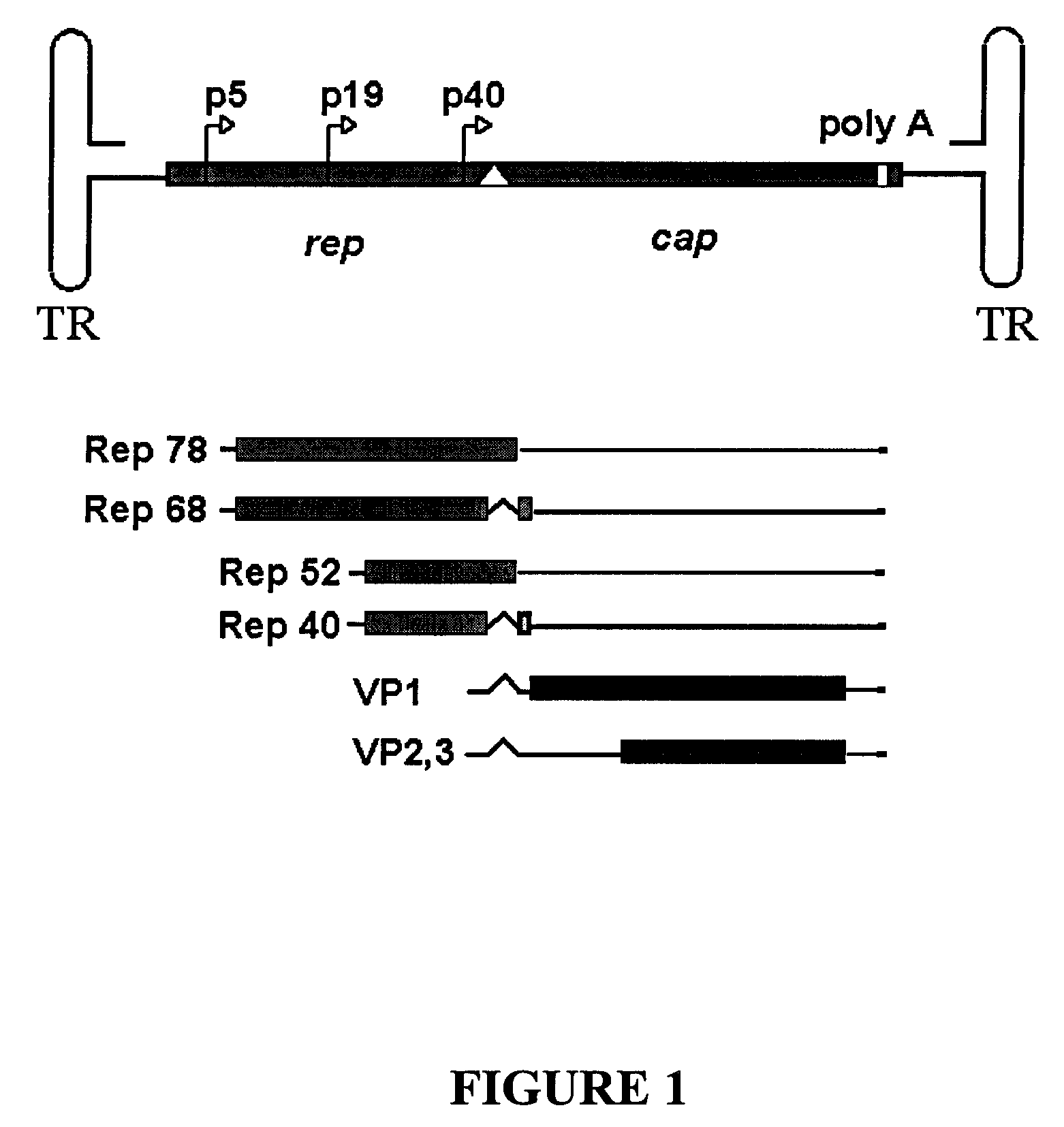
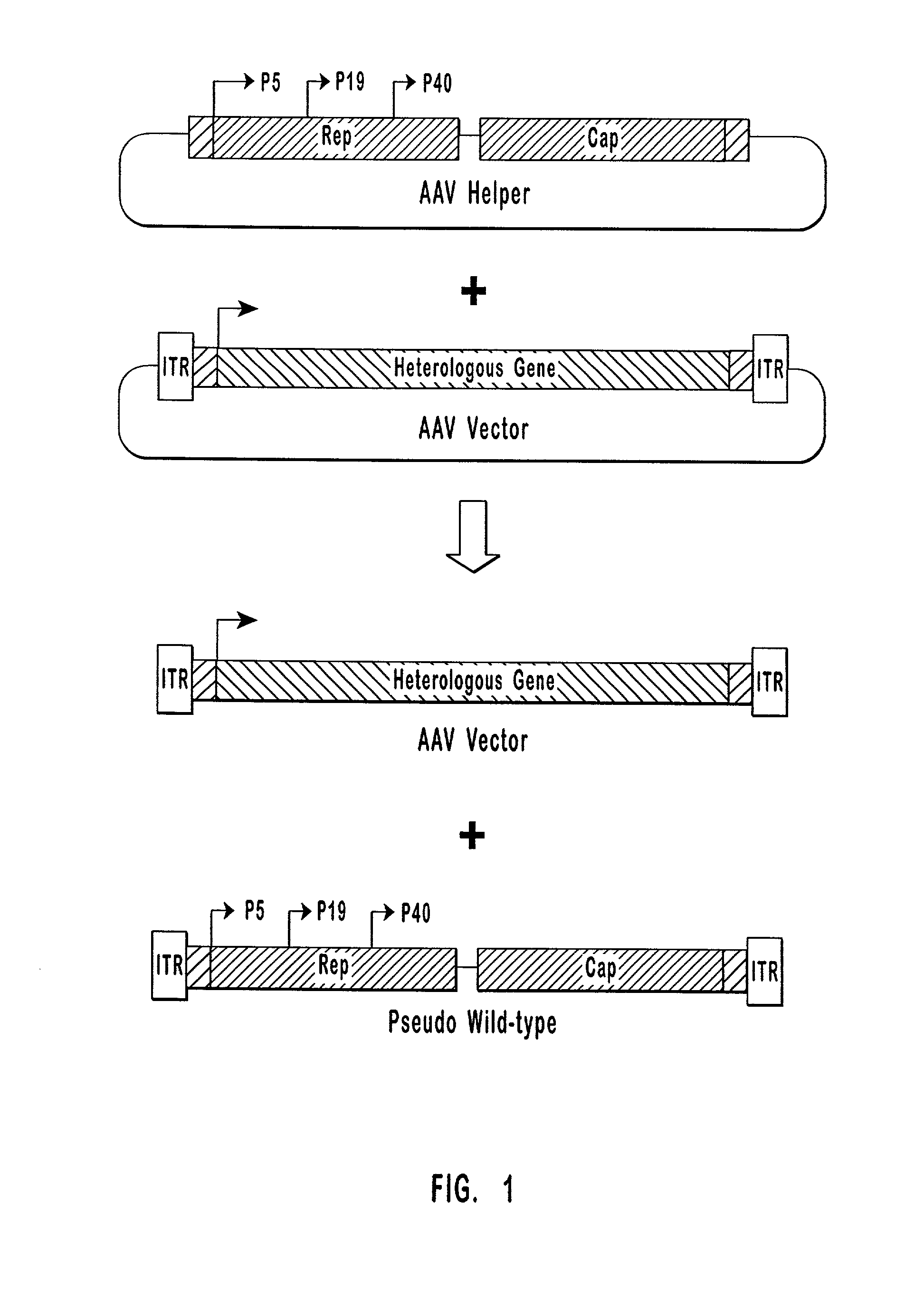
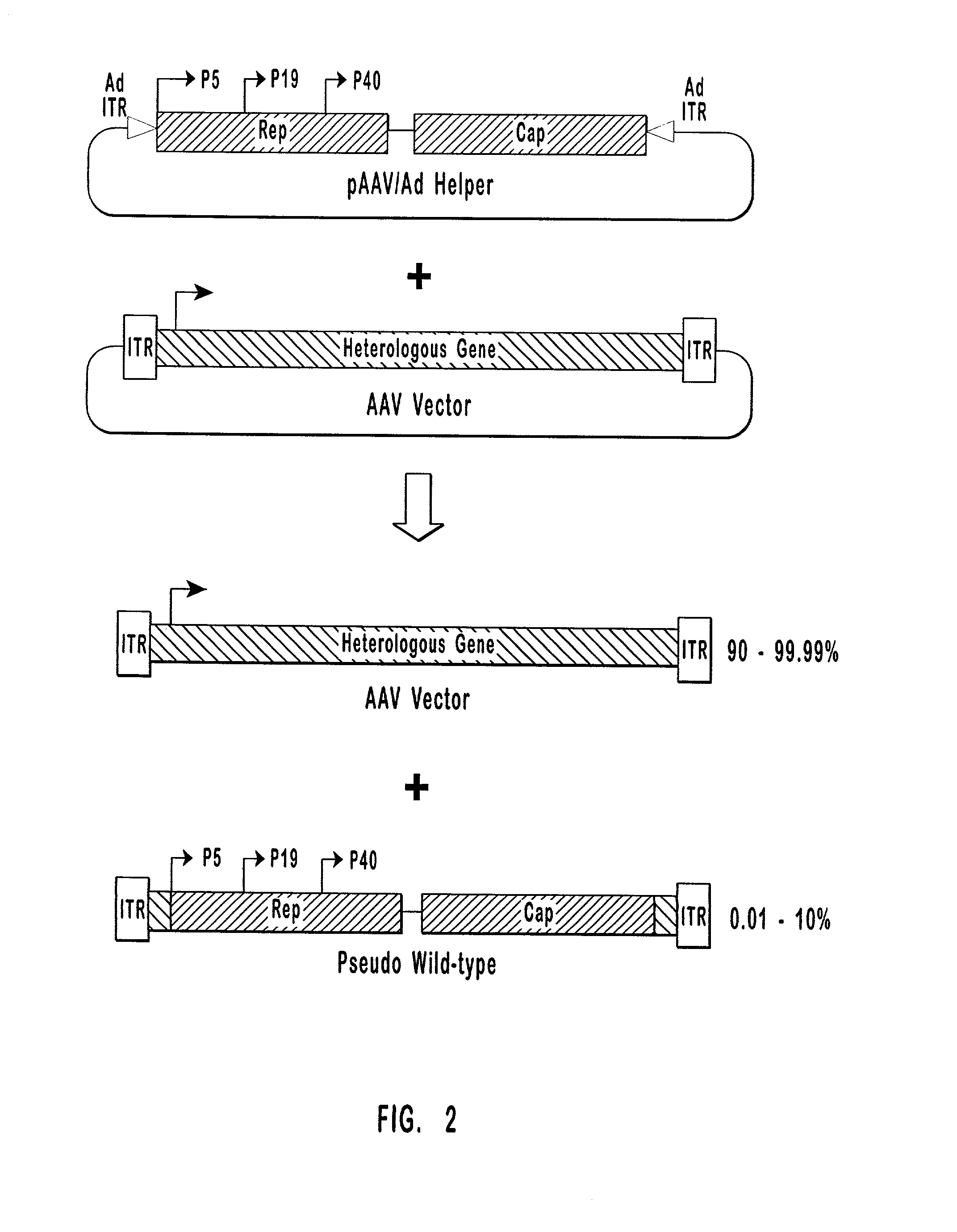
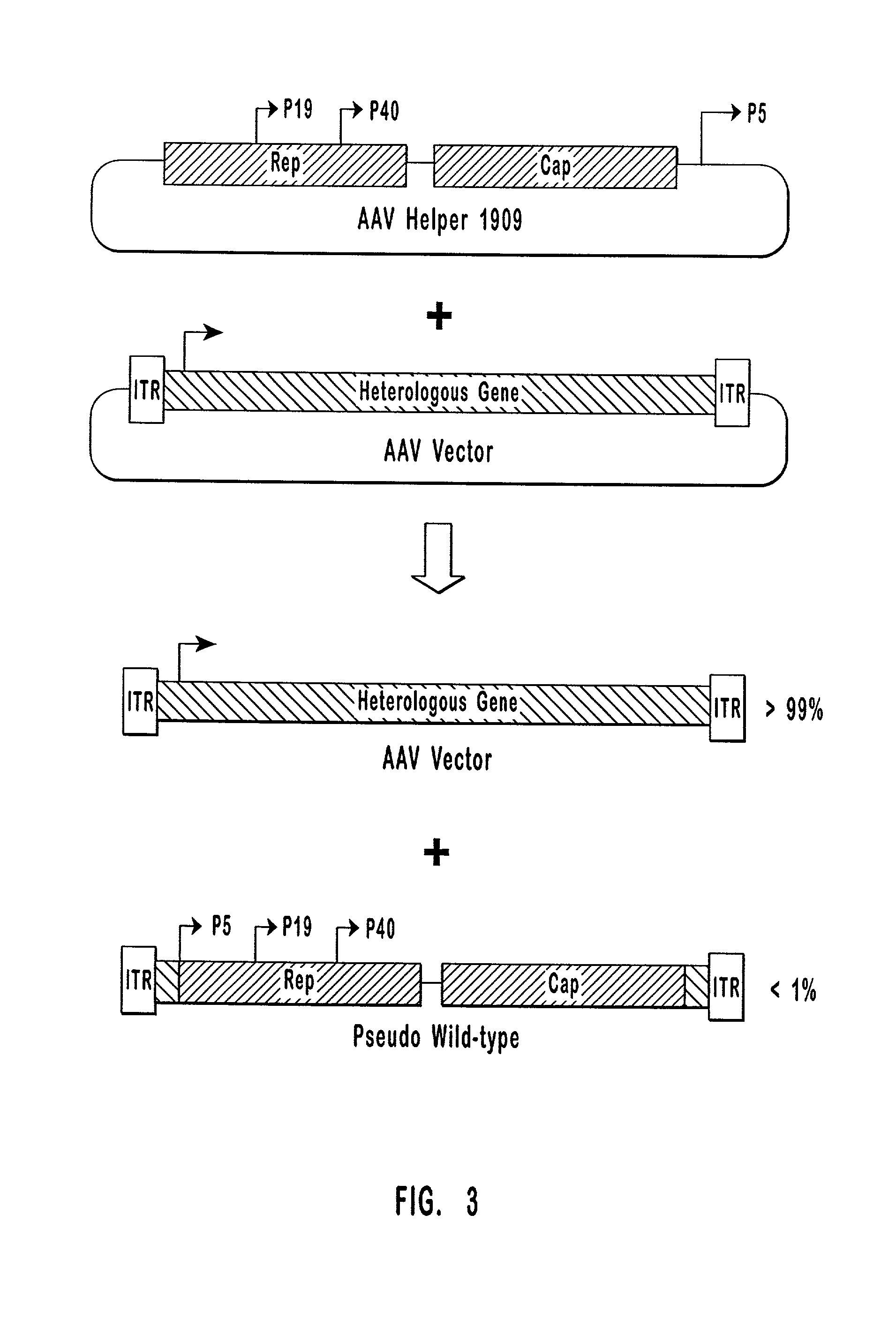
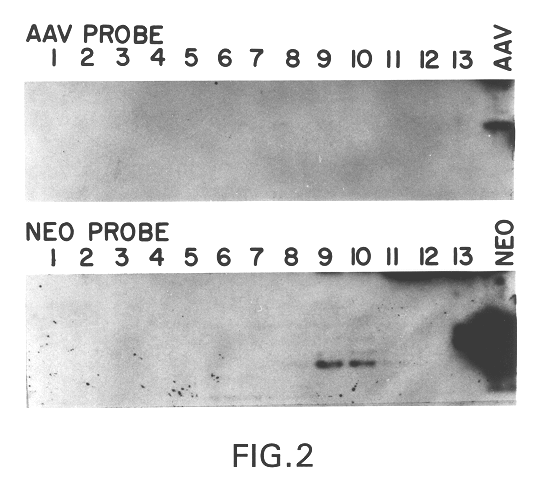
Production of pseudotyped recombinant AAV virions
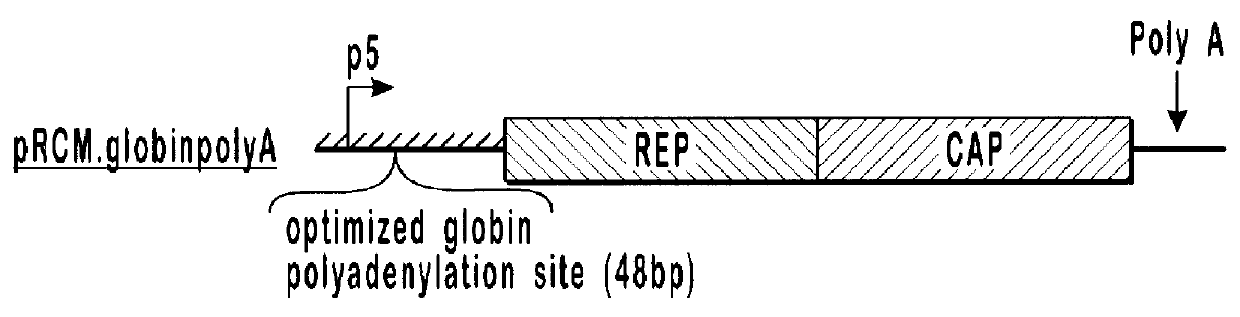
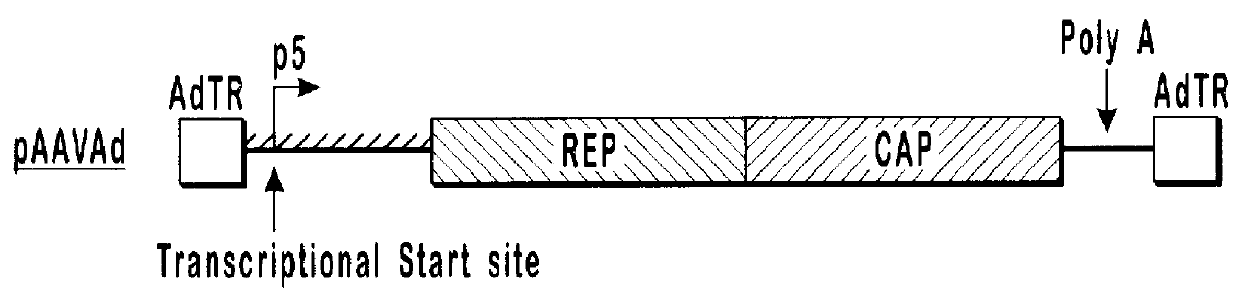
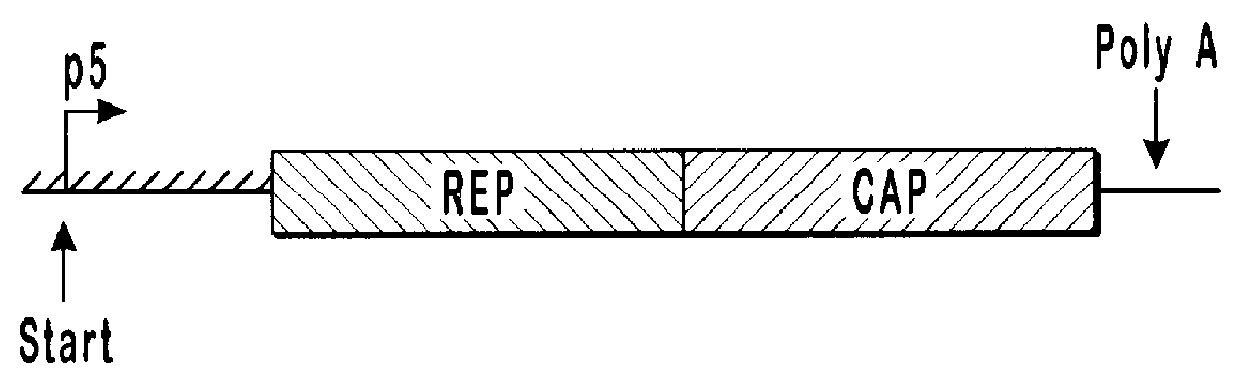
InactiveUS7094604B2Highly purified and concentratedEfficient and large-scale productionVectorsSugar derivativesPurification methodsSerotype
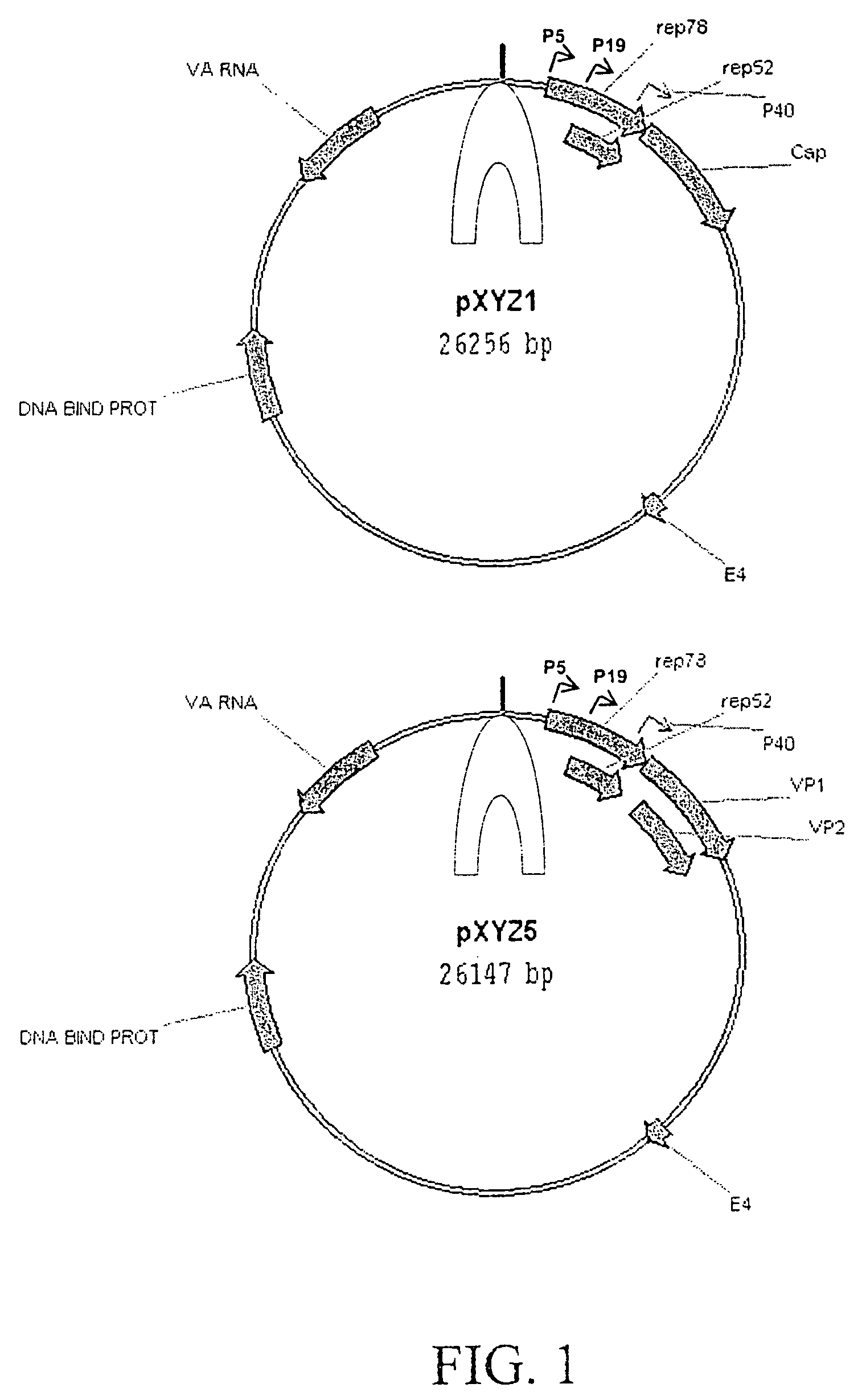
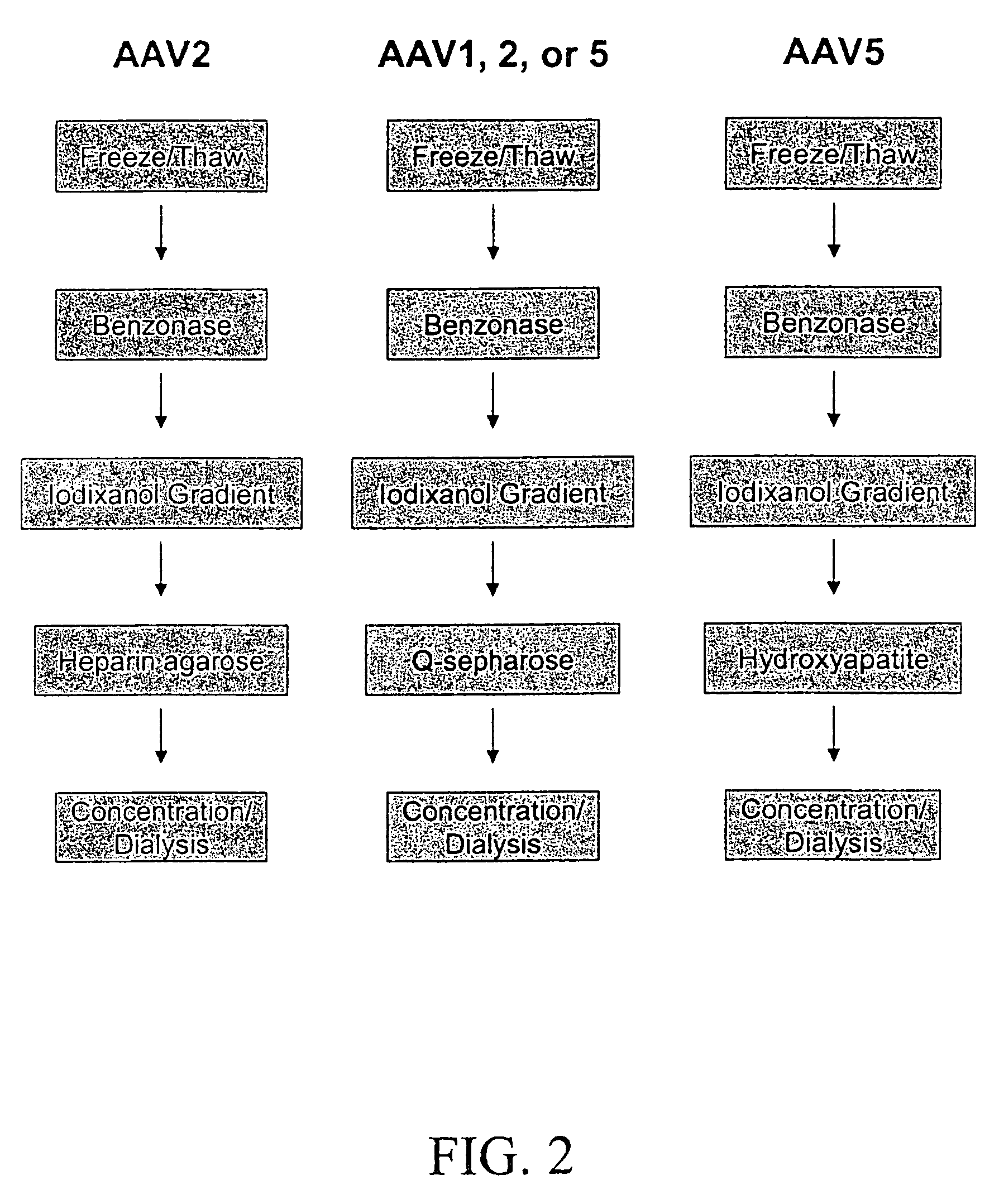
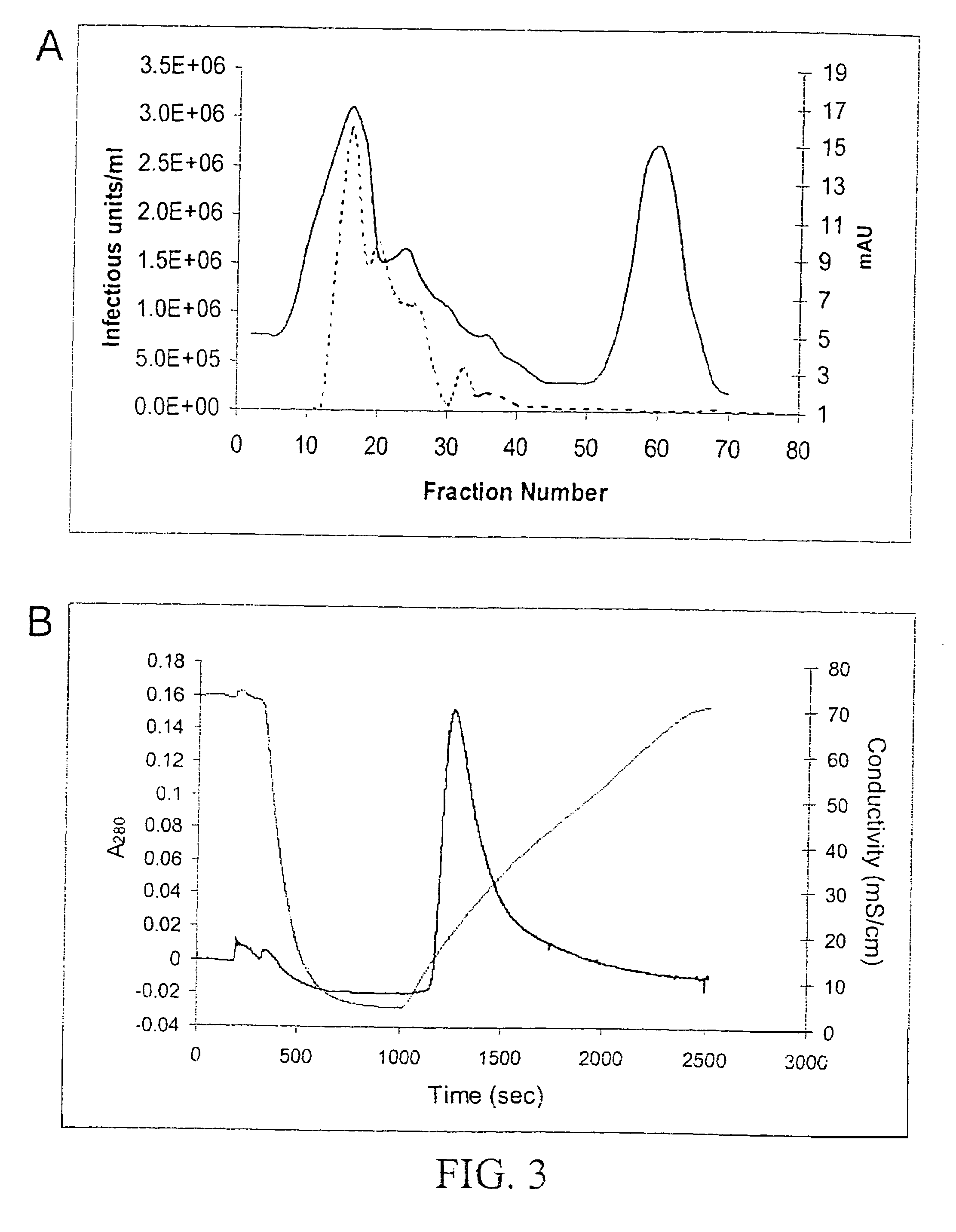
Vectors that encode Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Rep and Cap proteins of different serotypes and Adenovirus transcription products that provide helper functions were used to produce pseudotyped recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions. Purification methods generated pseudotyped rAAV virion stocks that were 99% pure with titers of 1×1012–1×1013 vector genomes / ml.
Owner:UNIVIRSITY OF FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
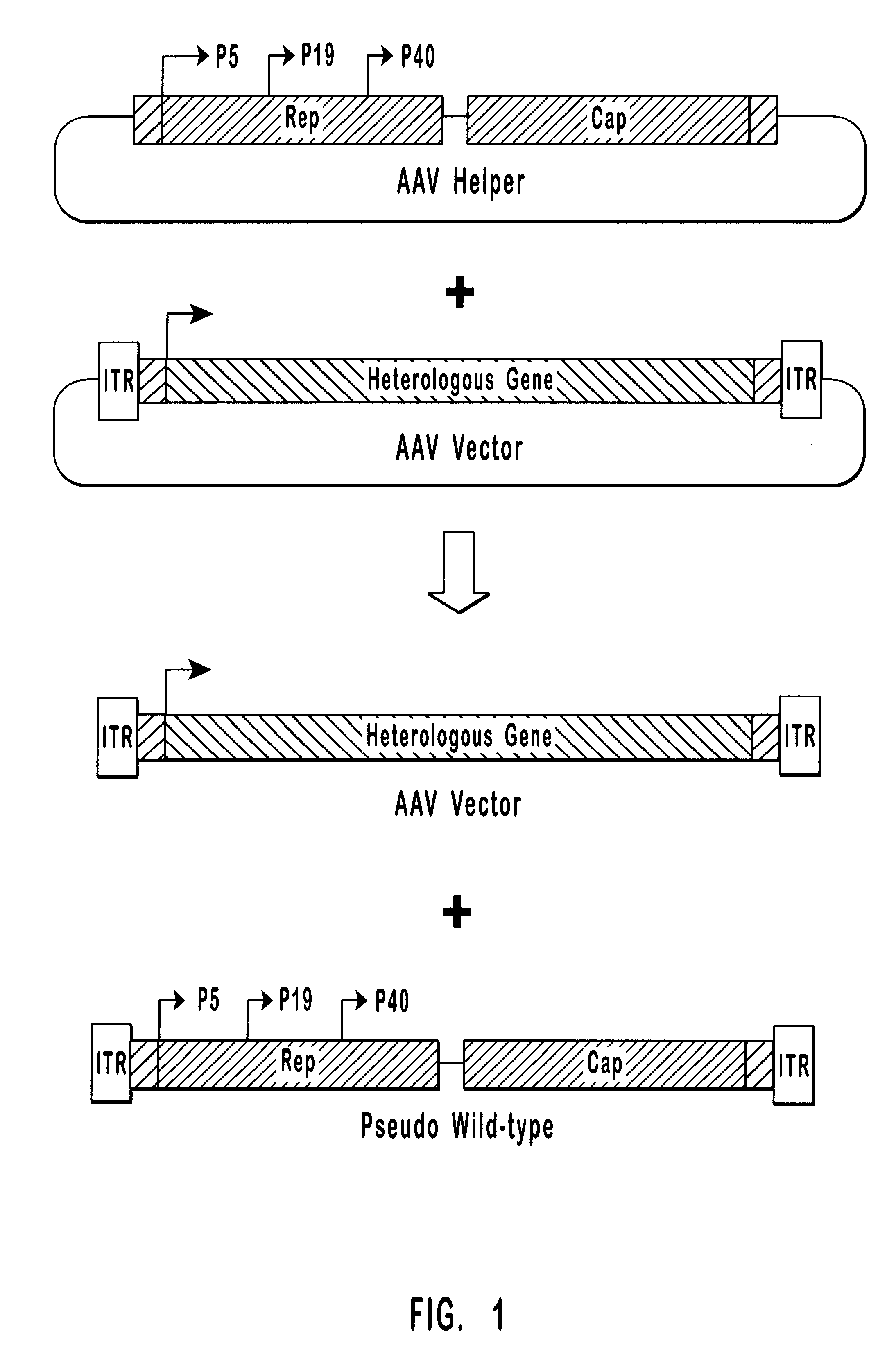
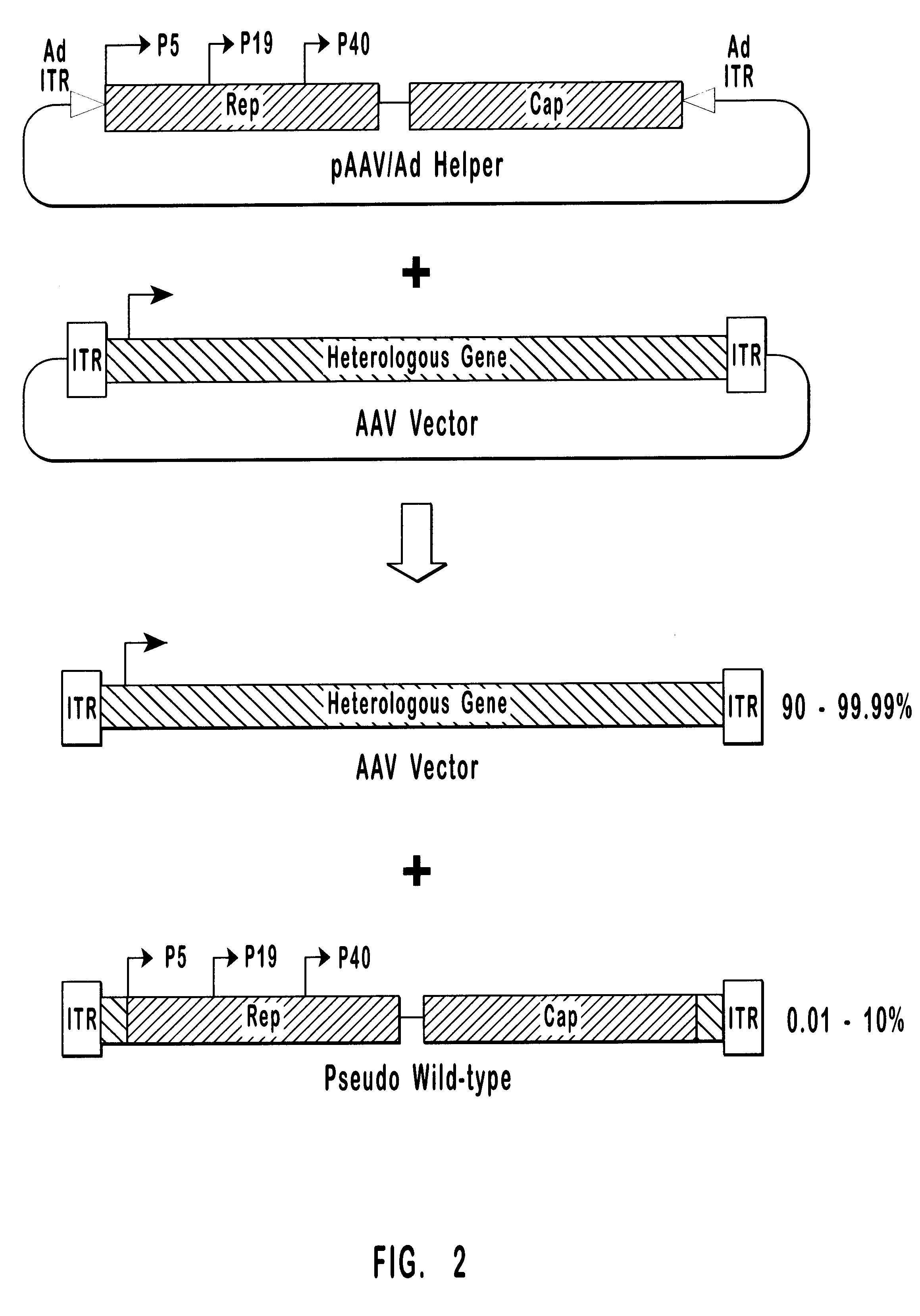
High-efficiency wild-type-free AAV helper functions
InactiveUS6376237B1Efficient productionEliminate productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesWild typeNucleic acid
The present invention provides methods and compositions for producing high titer, wild-type-free preparations of recombinant AAV ("rAAV") virions. The compositions of the present invention include novel nucleic acids encoding AAV helper functions and AAV helper function vectors. The present invention also includes host cells transfected by the claimed nucleic acids, methods of using the claimed vectors, and rAAV virions produced by such methods.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
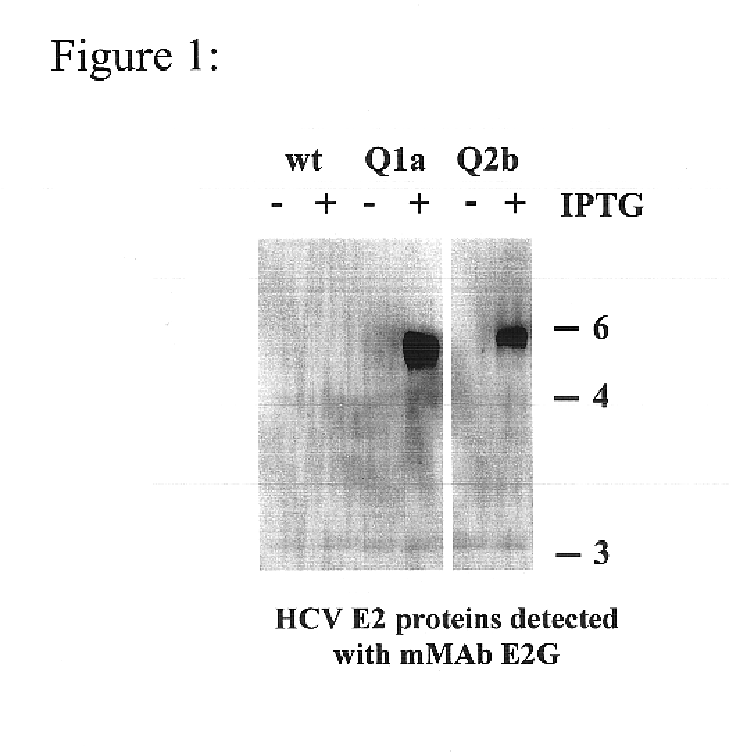
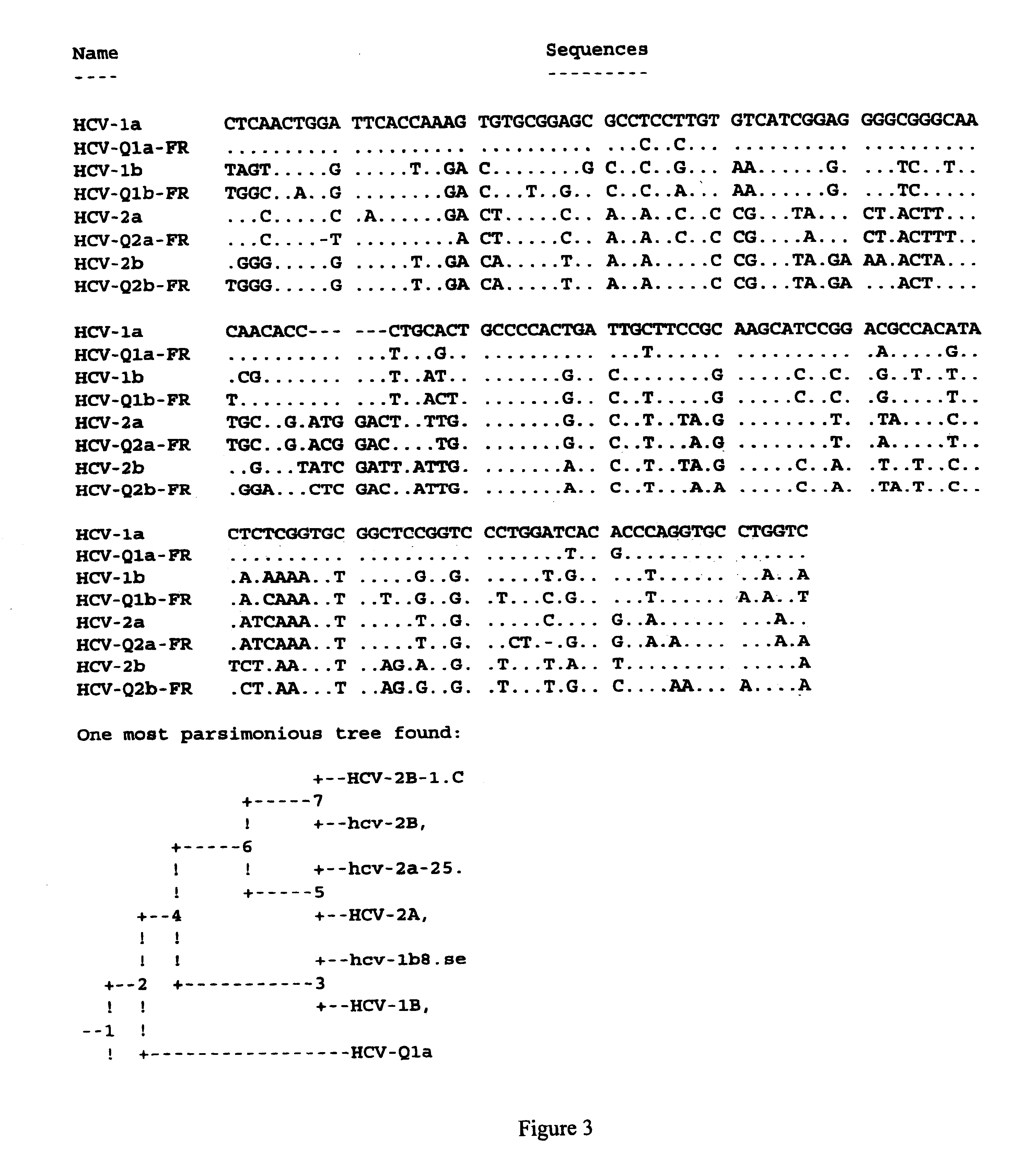
Prevention and treatment of HCV infection employing antibodies that inhibit the interaction of HCV virions with their receptor
Human monoclonal antibodies binding to epitopes common to type 1 and 2 HCV are provided, as well as conformationally conserved HCV E2 2a and 2b proteins. Compositions comprising the antibodies find use in diagnosis and therapy. The antibodies recognize conformational epitopes that are conserved across multiple genotypes of HCV. Thus the antibodies have the potential to be useful in the prevention and treatment of the majority of HCV infections. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2, CBH-5, CBH-7, CBH-8C, CBH-8E, and CBH-11) have the ability to prevent the binding of HCV E2 proteins of multiple genotypes to human CD81, a possible co-receptor for HCV infection. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2 and CBH-5) have been shown to inhibit the binding of HCV virions (as opposed to purified E2 protein) to human CD81. A further subset of the antibodies (CBH-4D, CBH4B, CBH-8C, and CBH-9) have been shown to prevent HCV envelope mediated fusion using an HCV psuedotype system.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050053922A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityAntibacterial agentsVirusesReassortant VirusesNeutralizing antibody
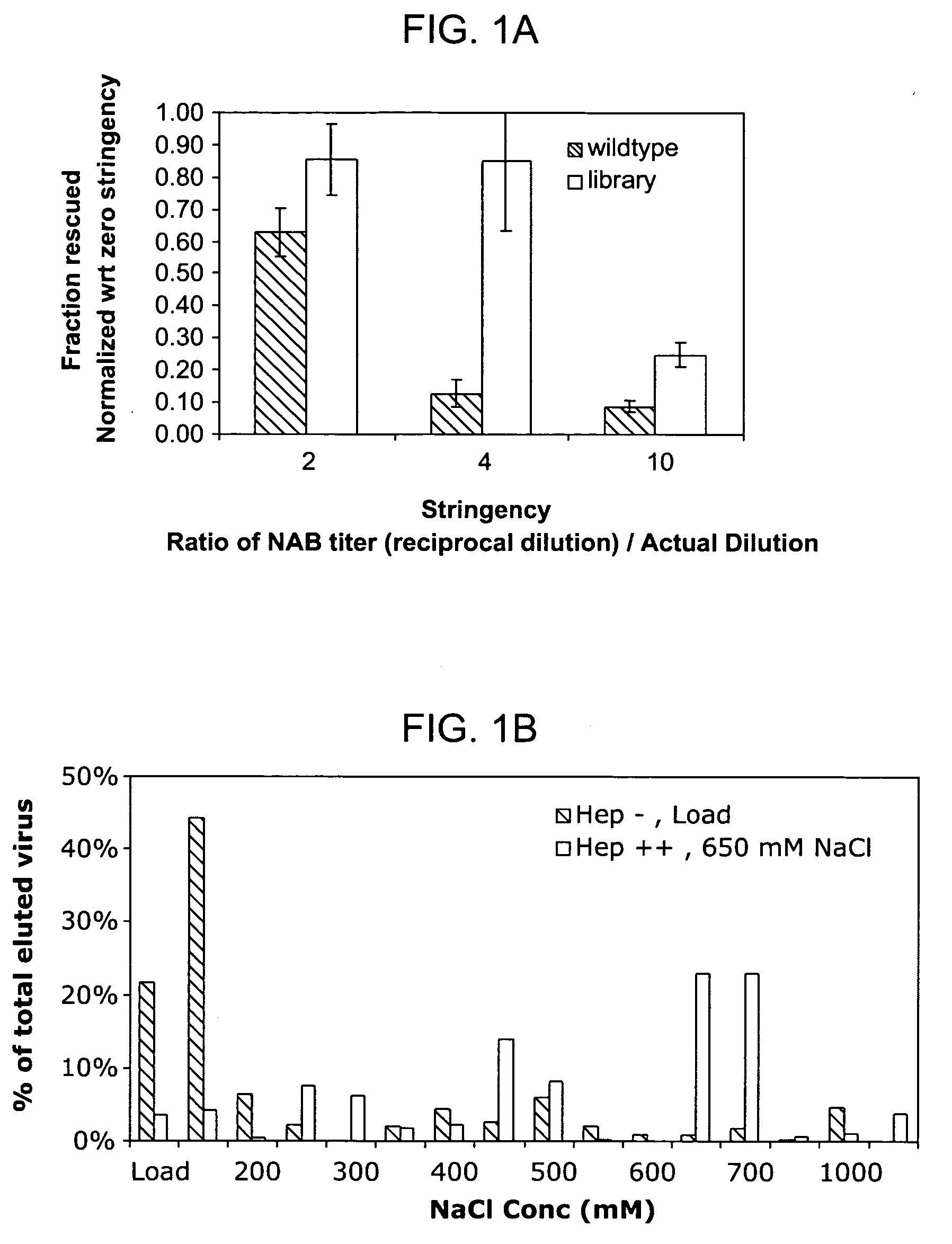
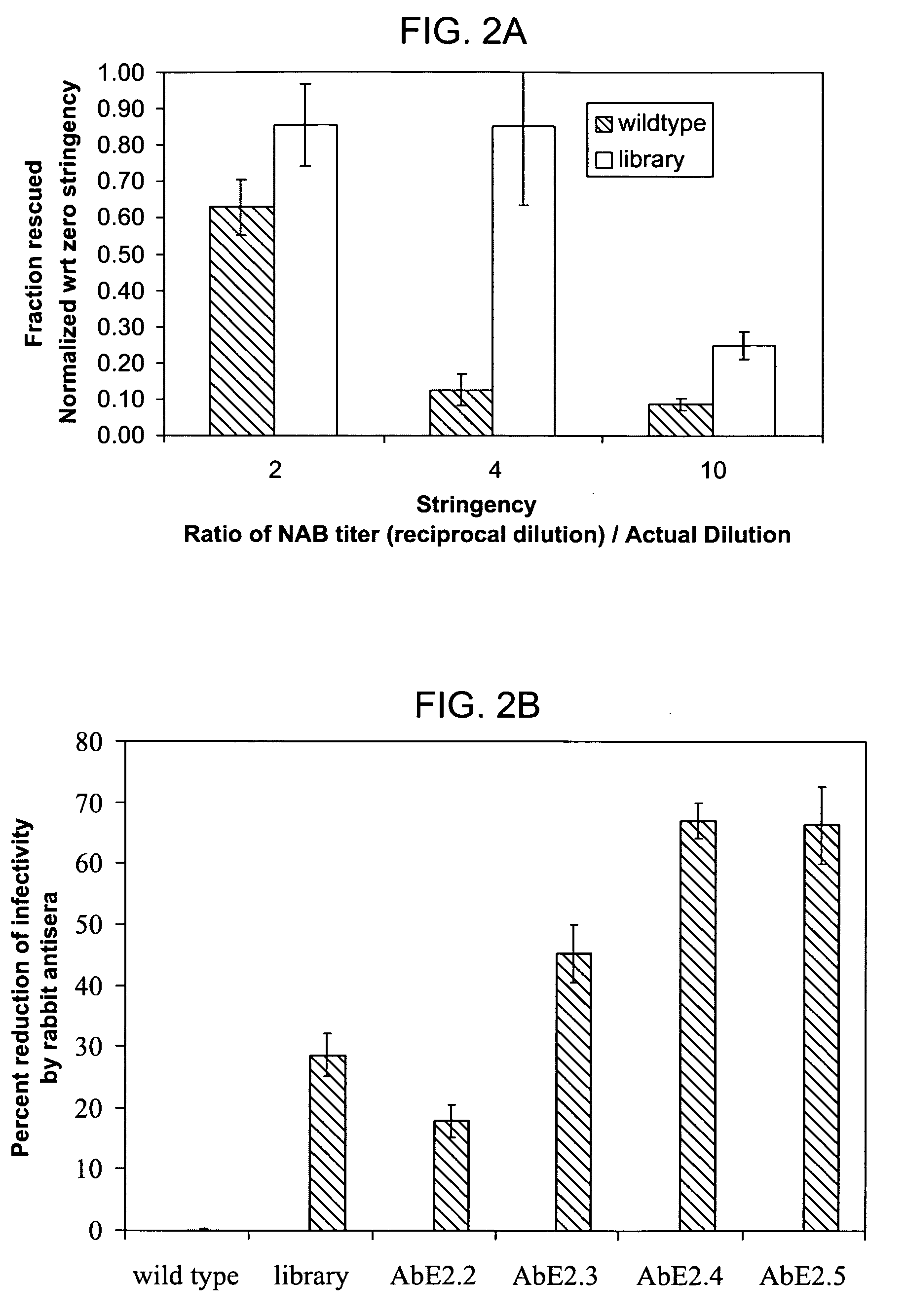
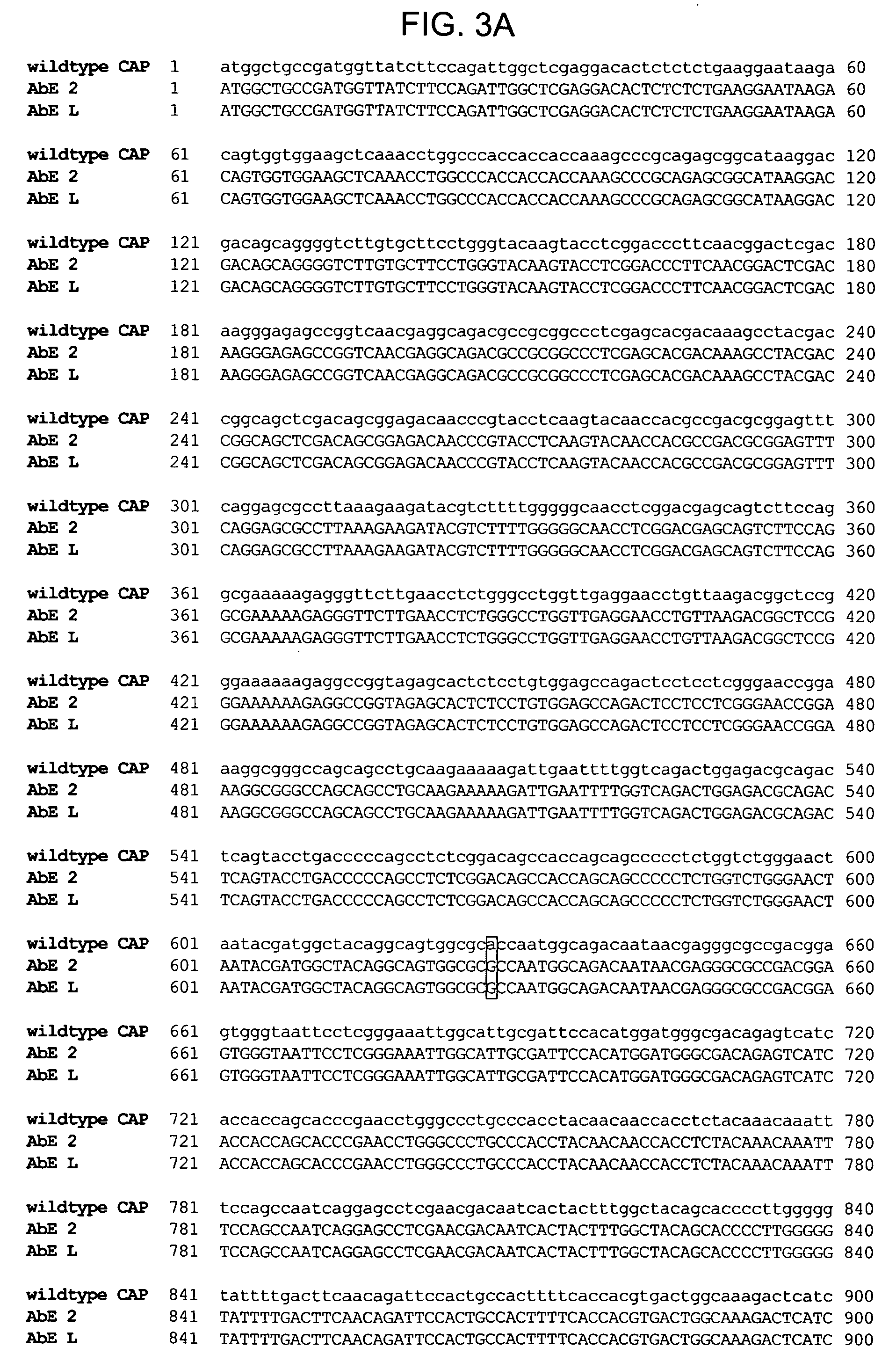
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
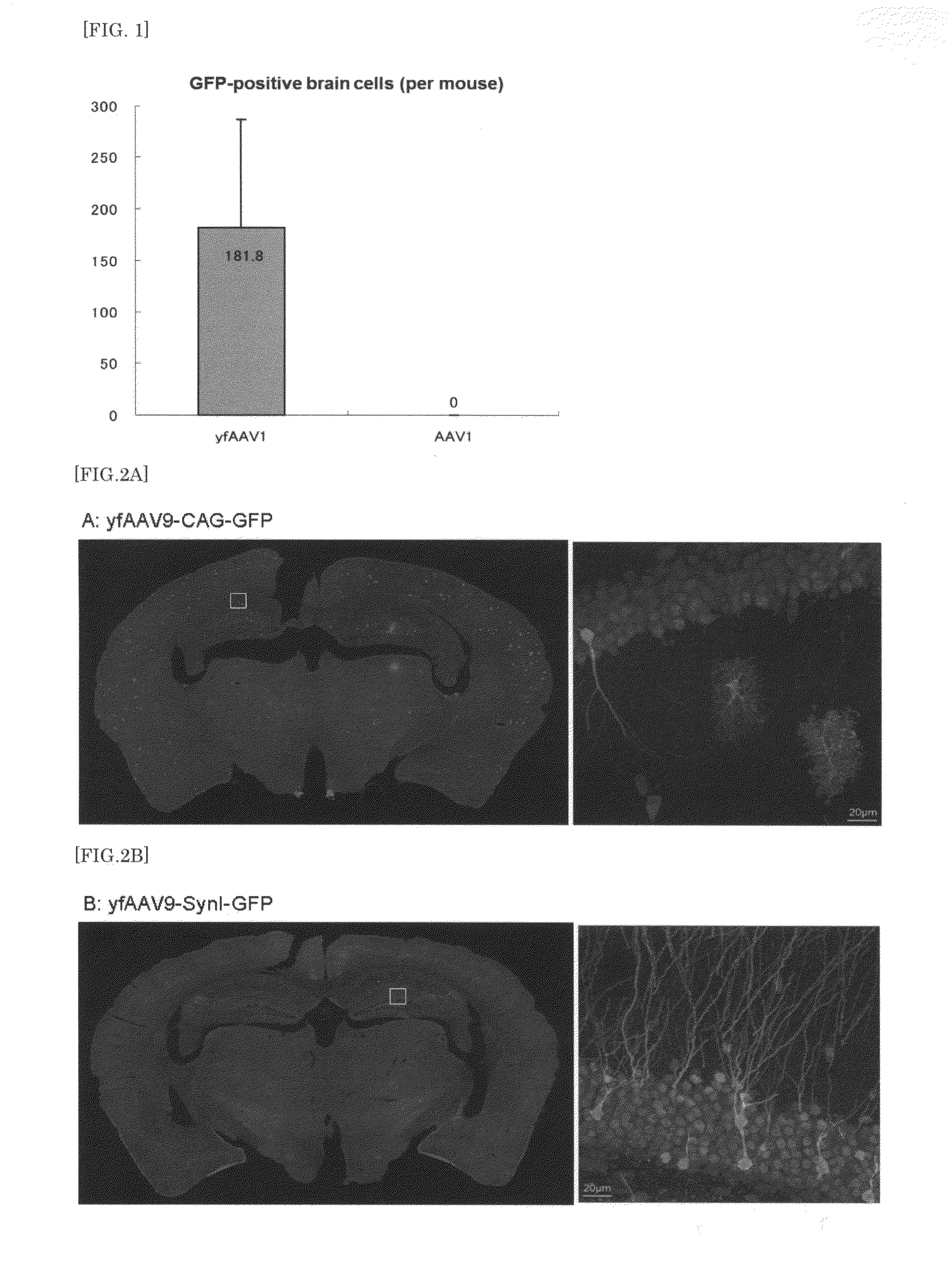
Adeno-Associated Virus Virion for Gene Transfer to Nervous System Cells
ActiveUS20130224836A1Improve efficiencyLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderSpecial deliveryNervous systemAdeno associate virus
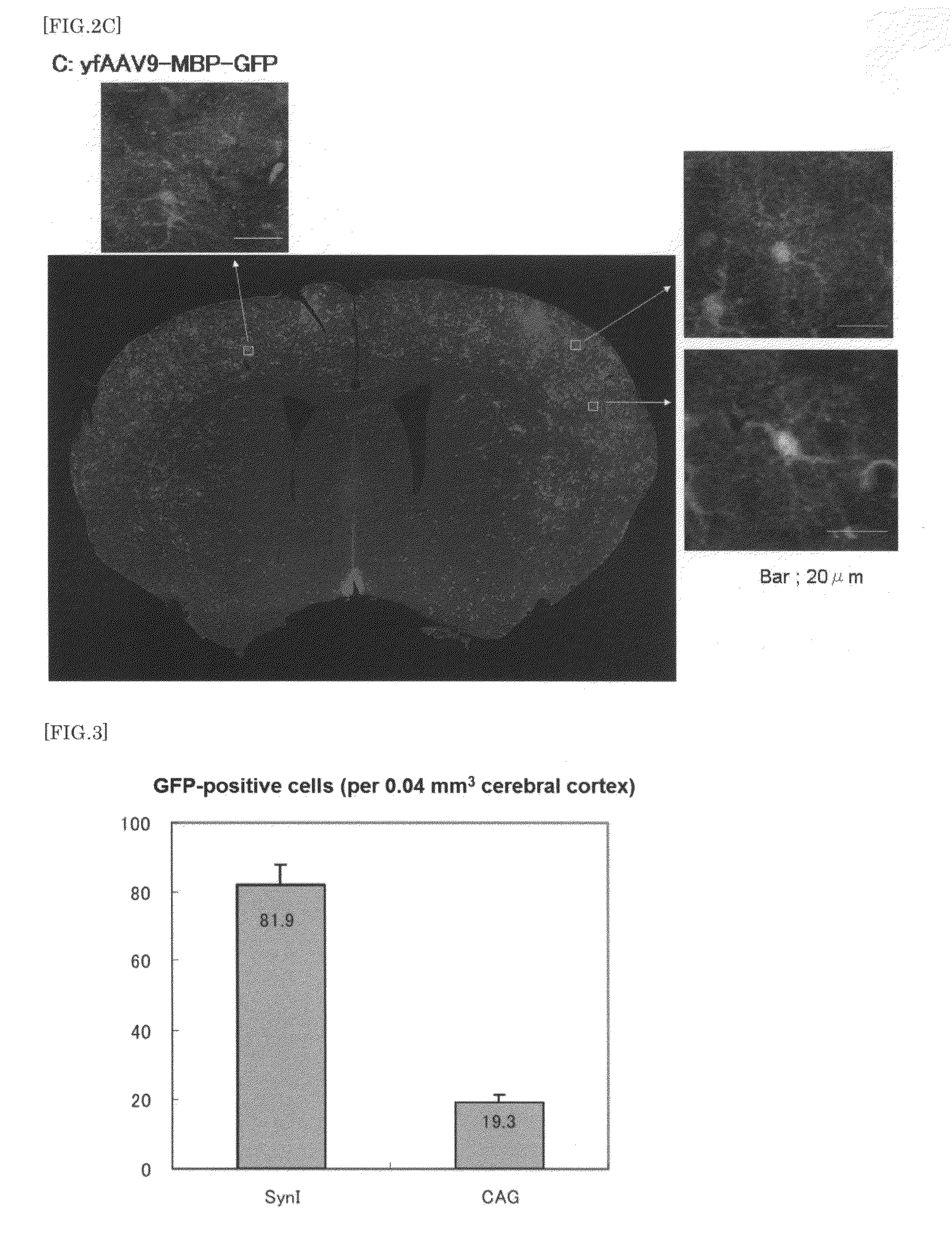
The present invention provides a means for transferring a therapeutic gene of interest into a nervous system cell by a highly-efficient and simpler means. More specifically, the present invention provides a recombinant vector that uses an adeno-associated virus (AAV), a method for manufacturing the recombinant vector, and a method for using the recombinant vector. More specifically, recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, which are capable of passing through the brain-brain barrier, for transferring a therapeutic genes of interest into a nervous system cell in a highly-efficient manner, a drug composition containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, a method for manufacturing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, and a kit or the like are provided.
Owner:JICHI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
AAV vectors for gene delivery to the lung
ActiveUS7427396B2Efficient transductionDecreased immunoreactivityPowder deliveryBiocideGene deliveryVirosome
Owner:AVIGEN
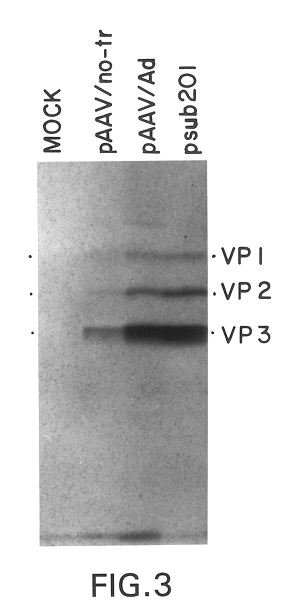
Parvoviral capsid with incorporated gly-ala repeat region
InactiveUS20110171262A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid sequencingCapsid
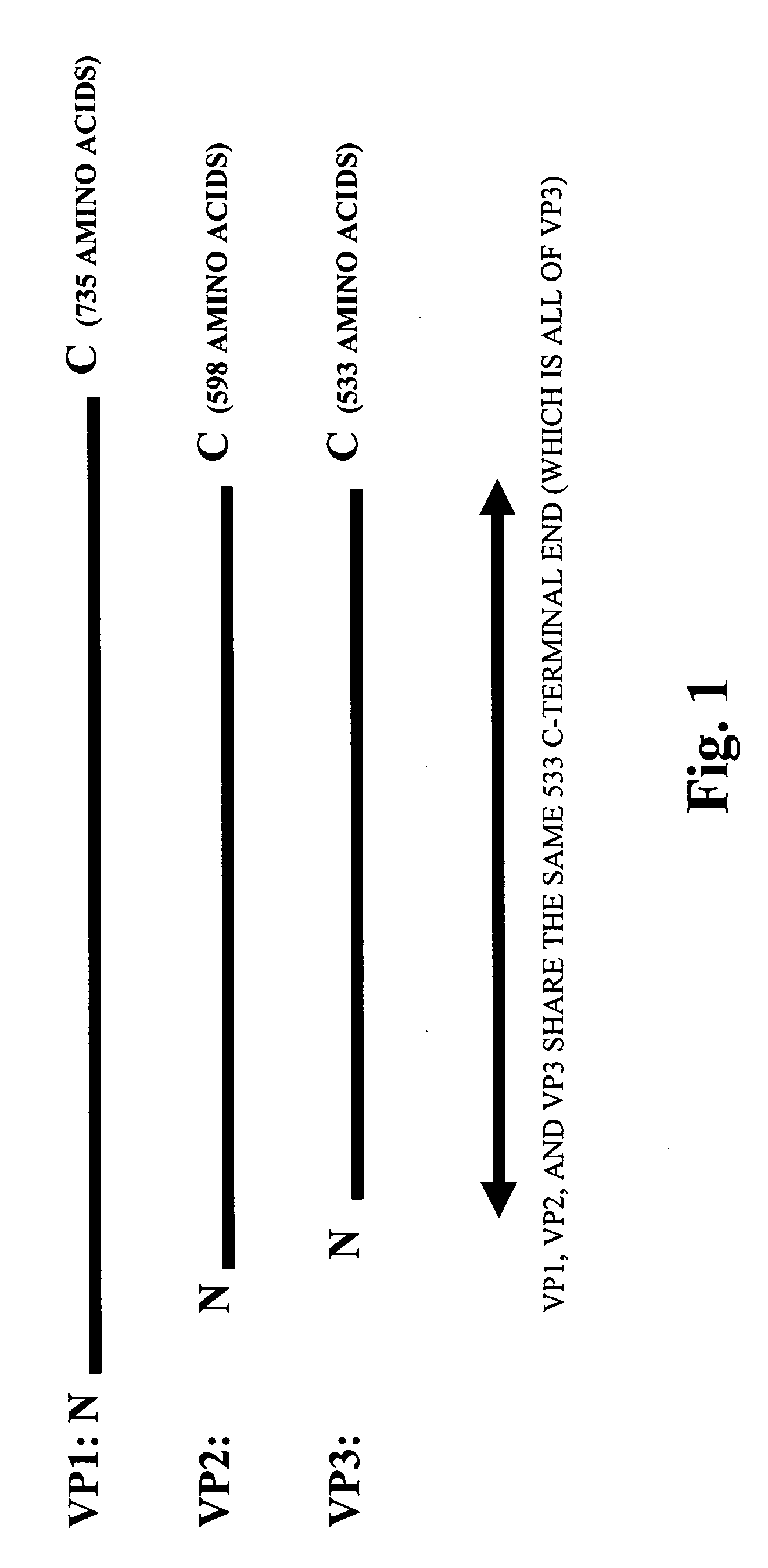
Parvoviral capsid with incorporated Gly-Ala repeat region The present invention provides a nucleic acid construct comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a parvoviral VP1, VP2 and VP3 capsid proteins comprising an immuno evasion repeat sequence. In addition, the present invention provides a cell comprising such construct, a parvoviral virion comprising a capsid protein that comprises an immune evasion repeat sequence, use of that parvoviral virion in gene therapy and a pharmaceutical composition comprising such parvoviral virion.
Owner:AMSTERDAM MOLECULAR THERAPEUTICS
Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vectors
InactiveUS20020141980A1Efficient deliveryEfficient expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseConvection-Enhanced Delivery
Methods of delivering viral vectors, particularly recombinant AAV virions, to the CNS are provided. Also provided are methods of treating Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Adeno-associated virus virions with variant capsid and methods of use thereof
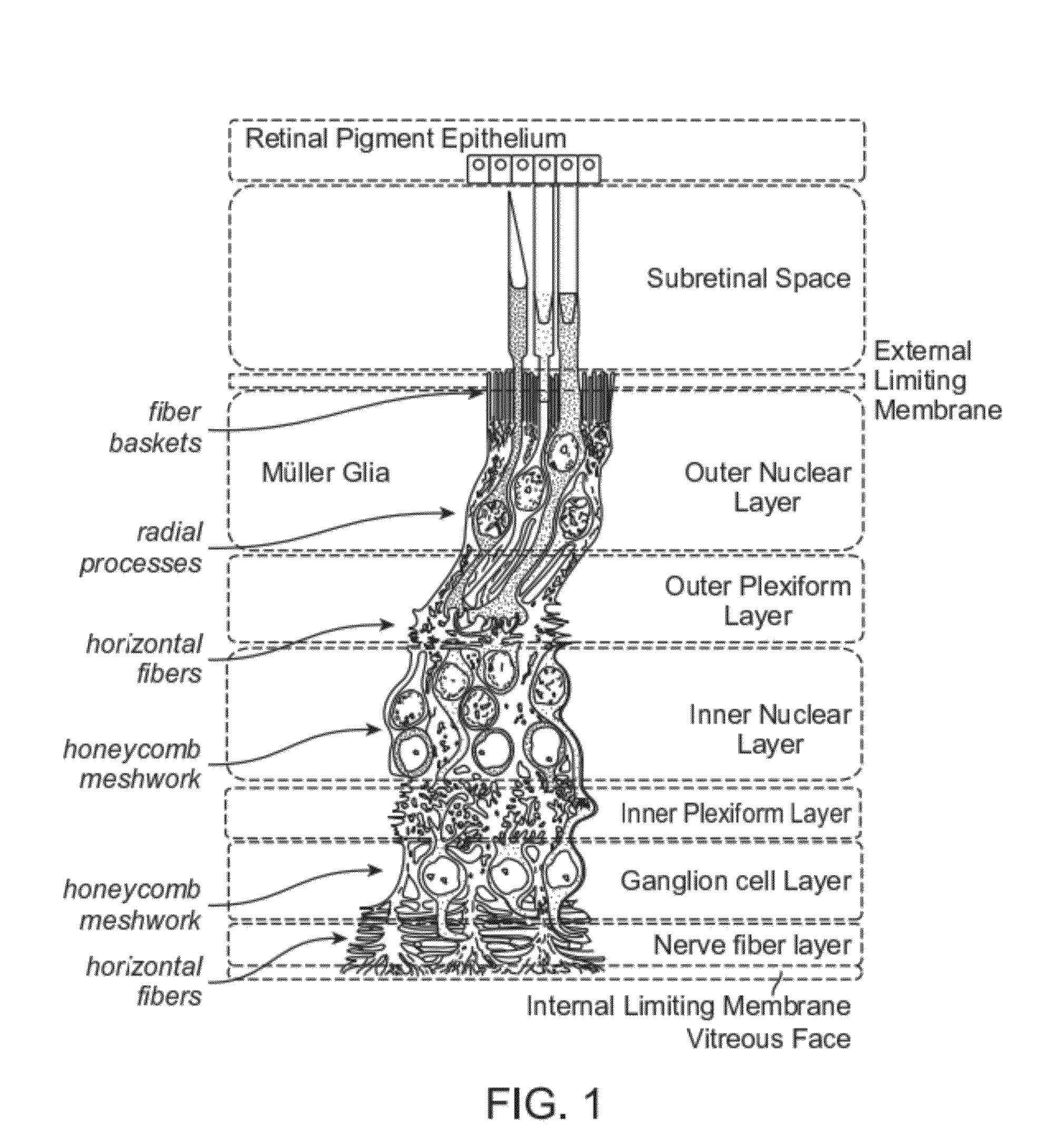
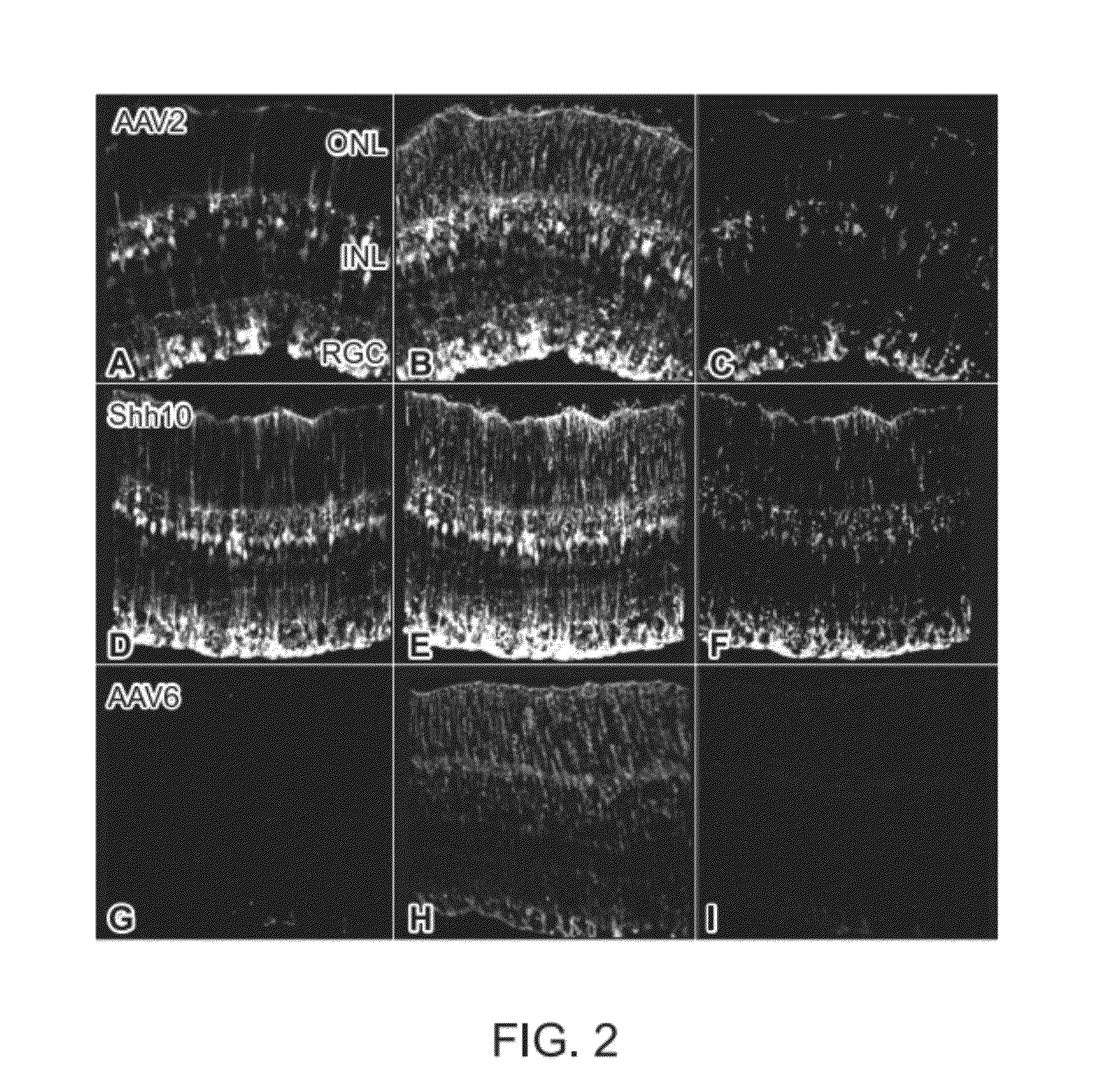
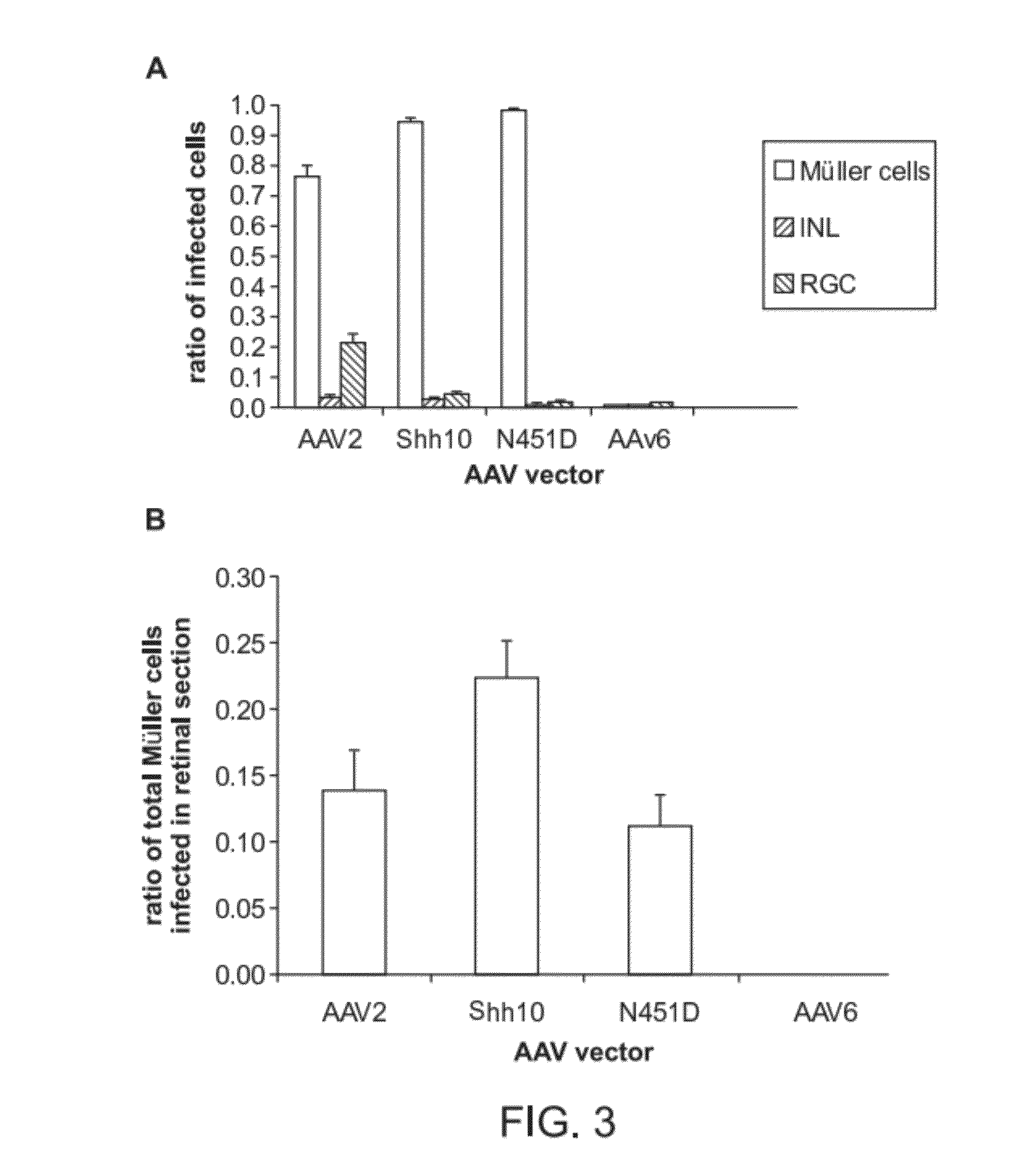
The present disclosure provides adeno-associated virus (AAV) virions with altered capsid protein, where the AAV virions exhibit greater infectivity of retinal cells compared to wild-type AAV. The present disclosure further provides methods of delivering a gene product to a retinal cell in an individual, and methods of treating ocular disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production of recombinant AAV virions
ActiveUS7927585B2Simple working processCost effective productionBiocideSugar derivativesYeastVirosome
Stocks of infectious rAAV are generated using yeast strains, bacterial strains, and bacteriophages engineered to express the required AAV proteins and harboring rAAV vector sequences. Stocks of rAAV virions of all serotypes and pseudotypes can be generated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells using the methods described herein.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Modified AAV
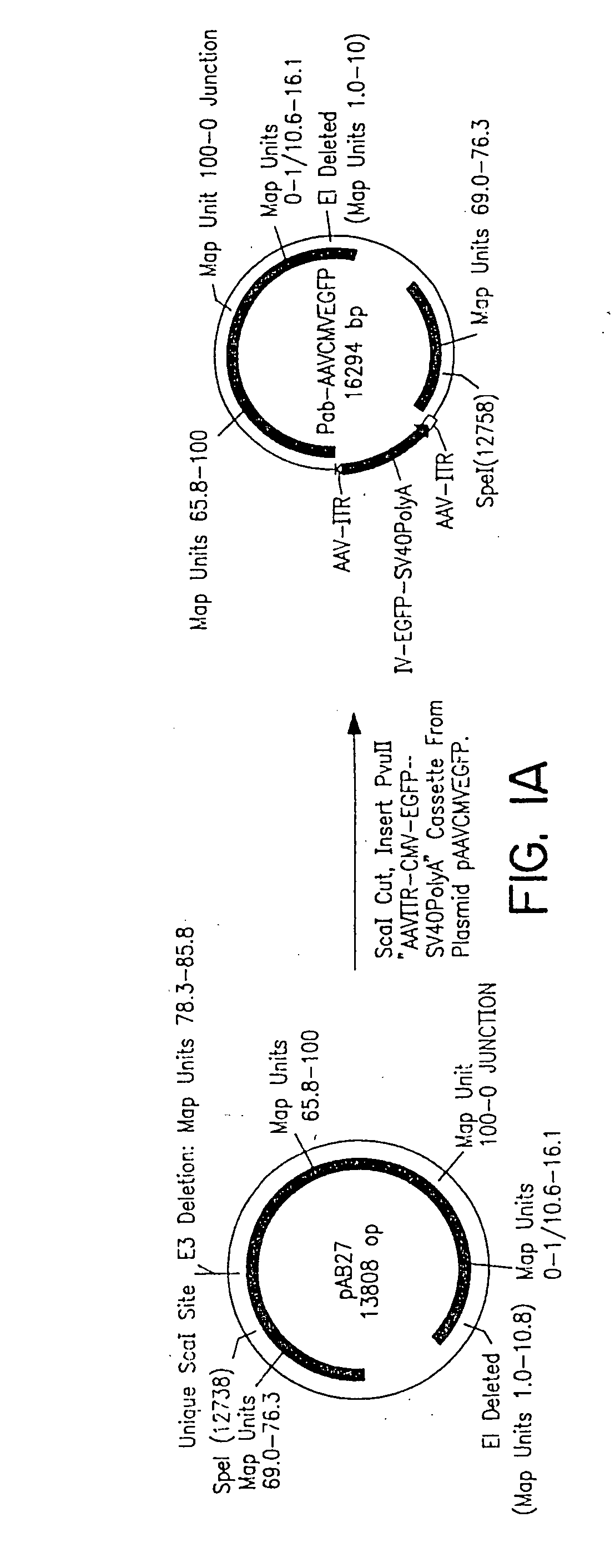
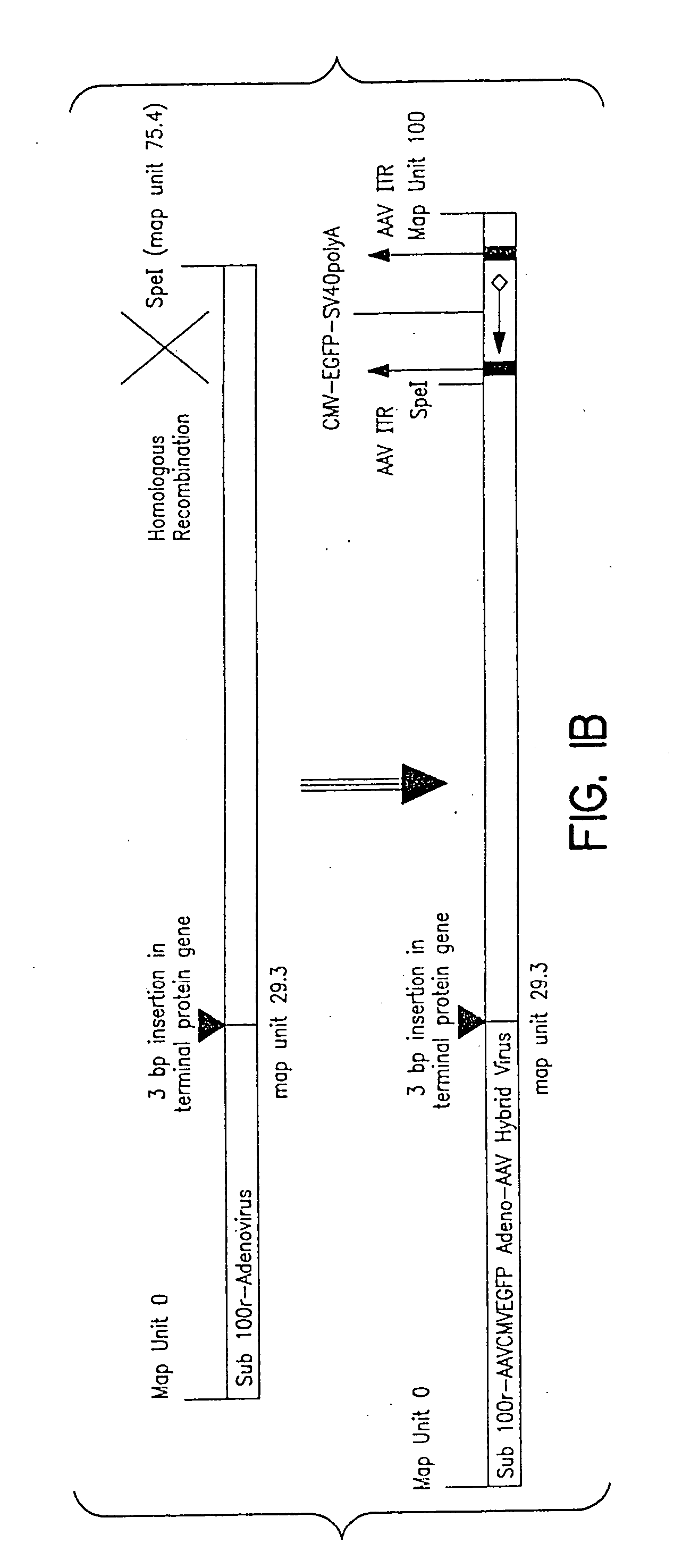
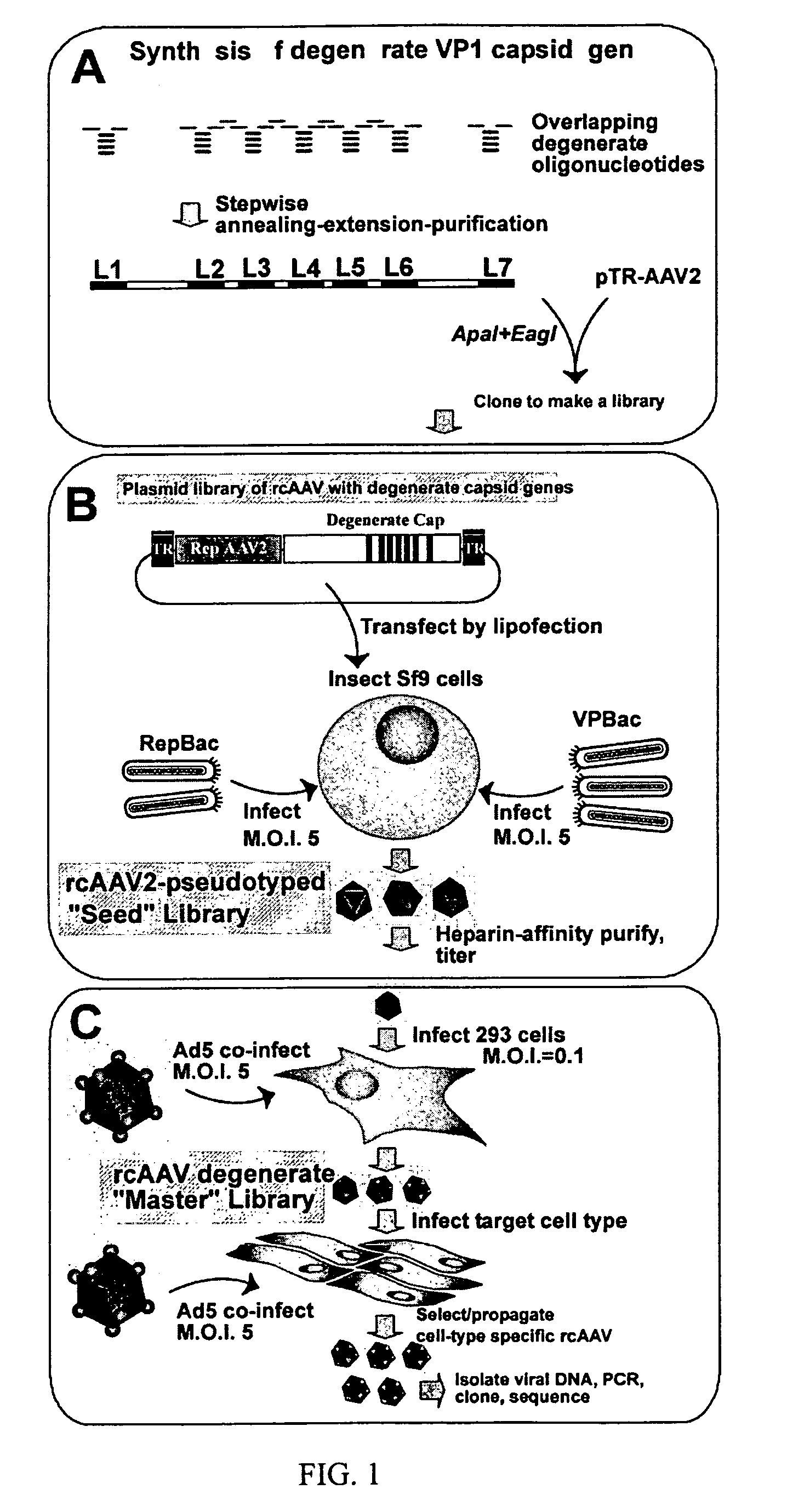
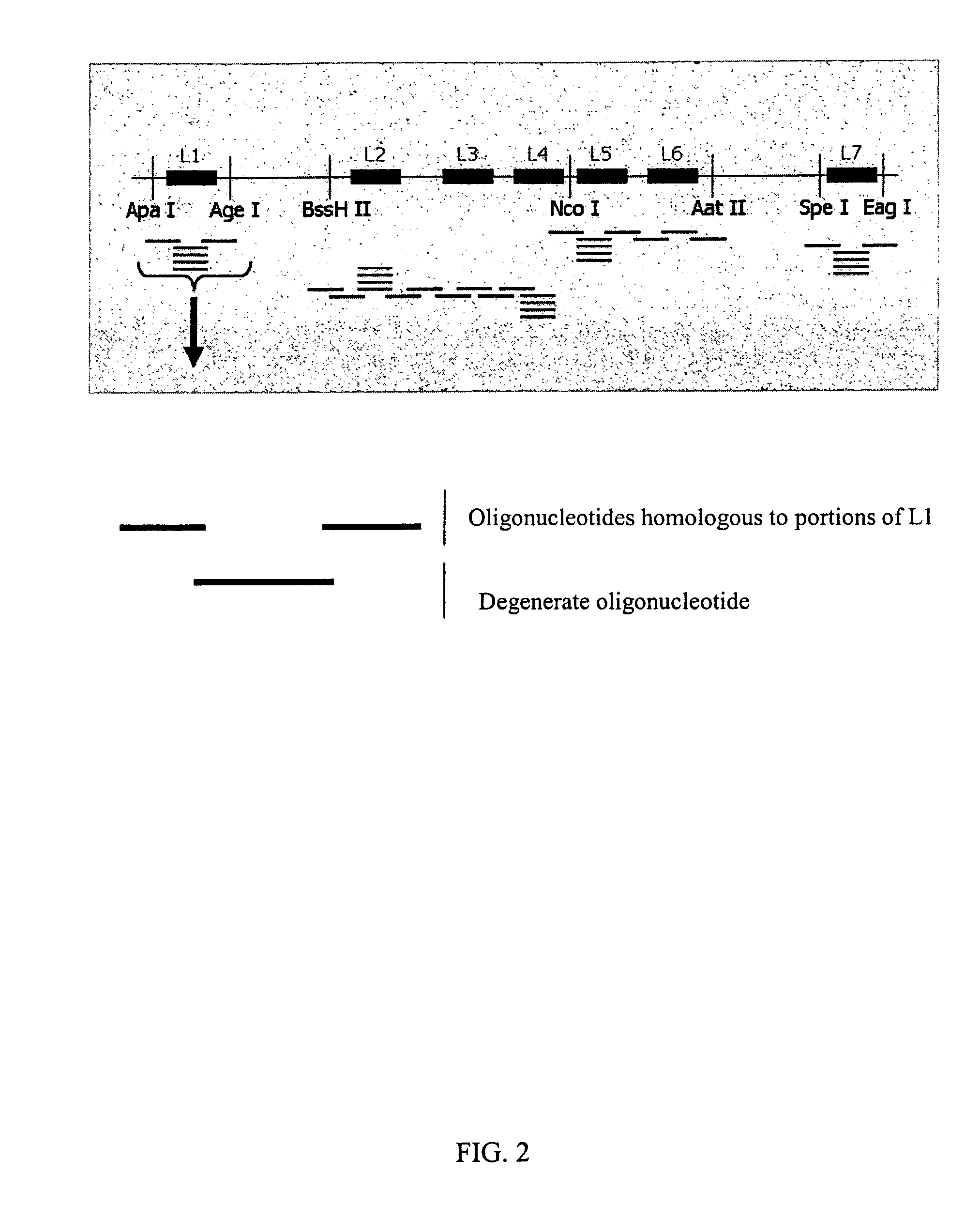
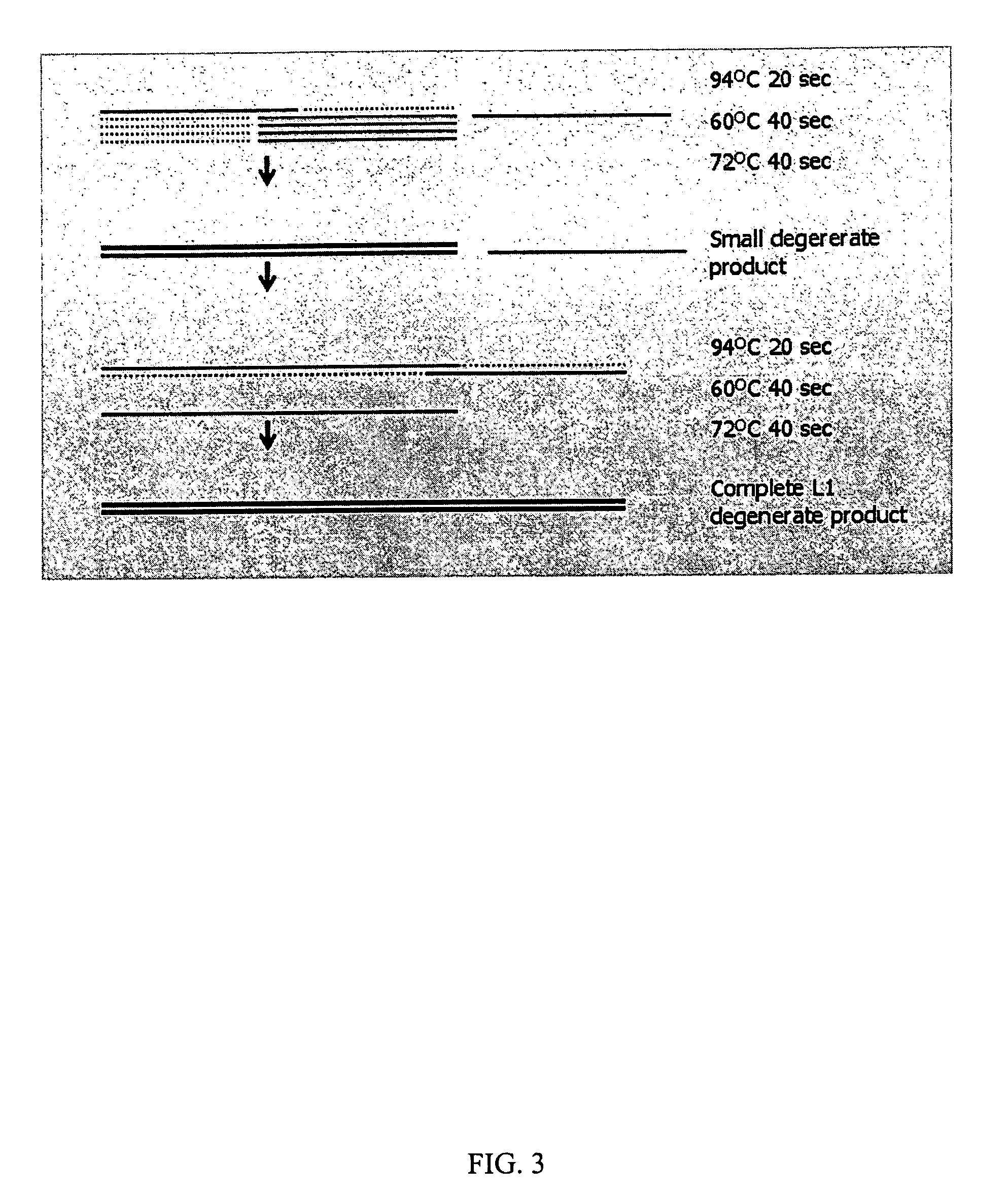
InactiveUS7220577B2Facilitates AAV replicationVectorsSugar derivativesENCODEDegenerate oligonucleotide
Libraries of modified AAV cap genes are generated by synthesizing modified cap genes using degenerate oligonucleotides. Combinatorial libraries of virions composed of modified (e.g., chimeric), replication-competent AAV vectors and modified Cap proteins are also produced. Helper vectors are described that encode AAV Rep protein, modified Cap proteins, and Ad proteins. The helper vectors are used to produce stocks of virions composed of modified (e.g., chimeric) capsids and rAAV vectors.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
AAV vectors for gene delivery to the lung
ActiveUS20080292595A1Efficient transductionDecreased immunoreactivityBiocideVectorsGene deliveryVirosome
Owner:GENZYME CORP
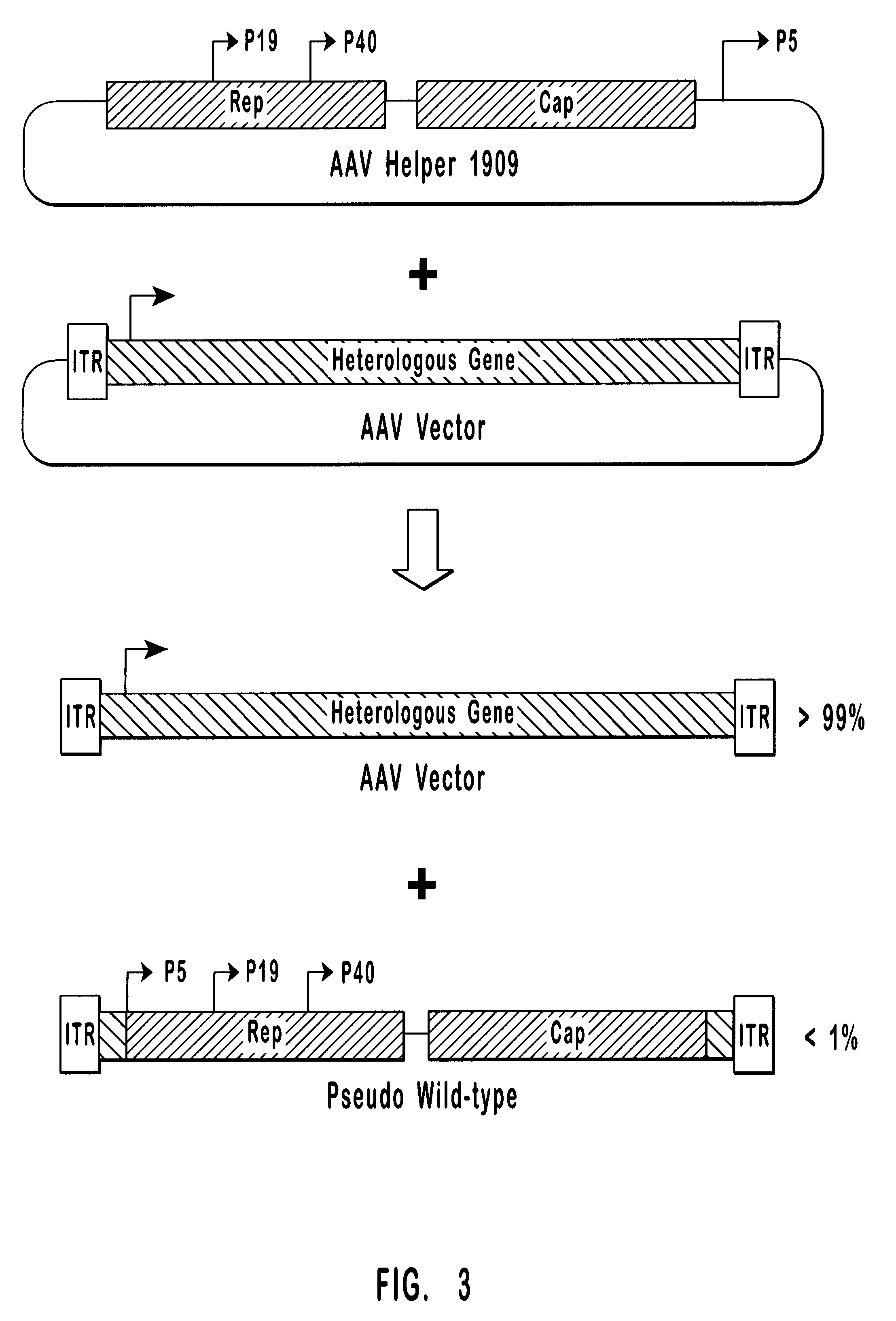
High-efficiency AA V helper functions
The present invention provides methods and compositions for producing high titer preparations of recombinant AAV ("rAAV") virions. The compositions of the present invention include AAV helper function systems and host cells. The present invention also includes methods of using AAV helper function vectors that effect the production of only small amounts of the long forms of Rep protein, and rAAV virions produced by such methods.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
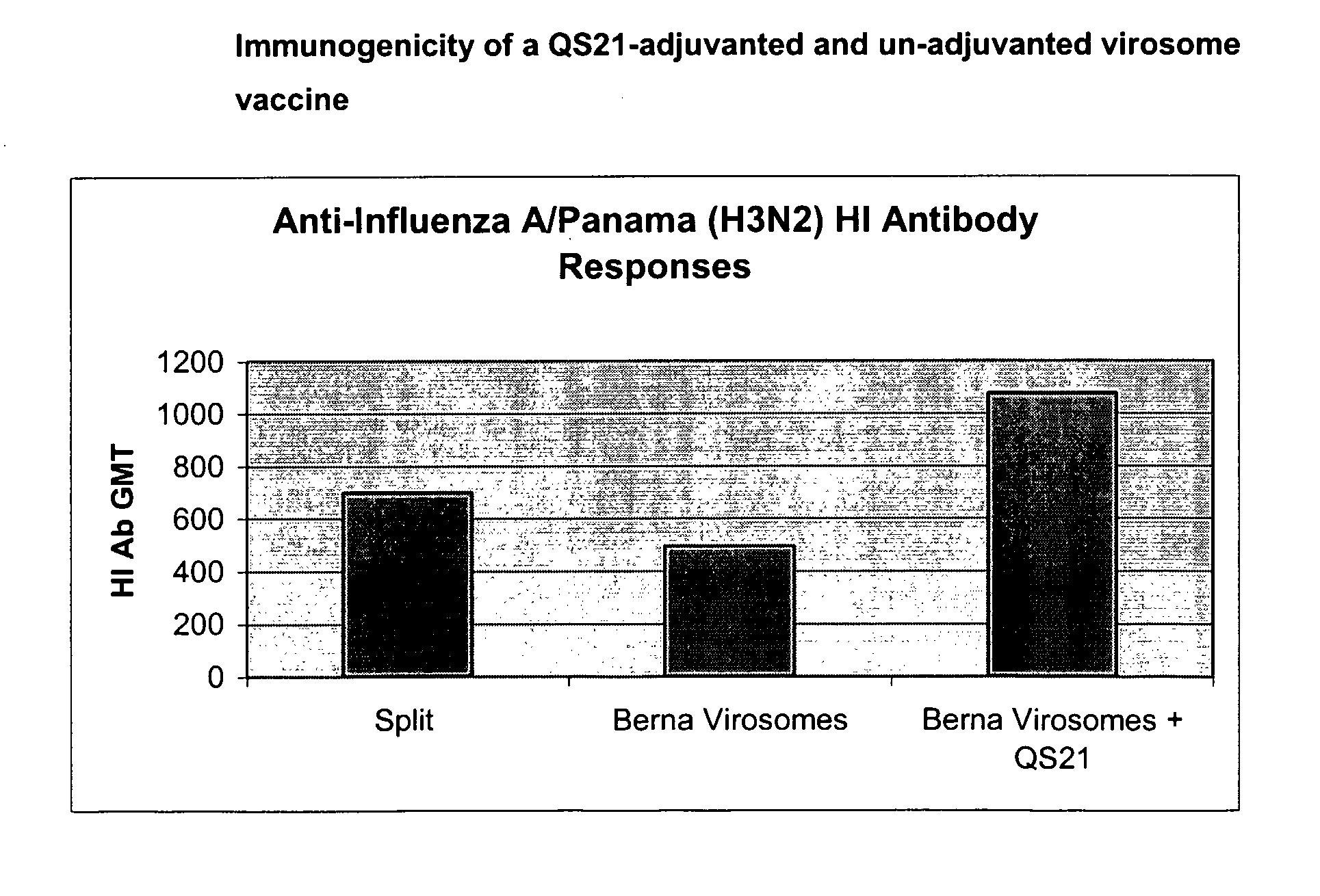
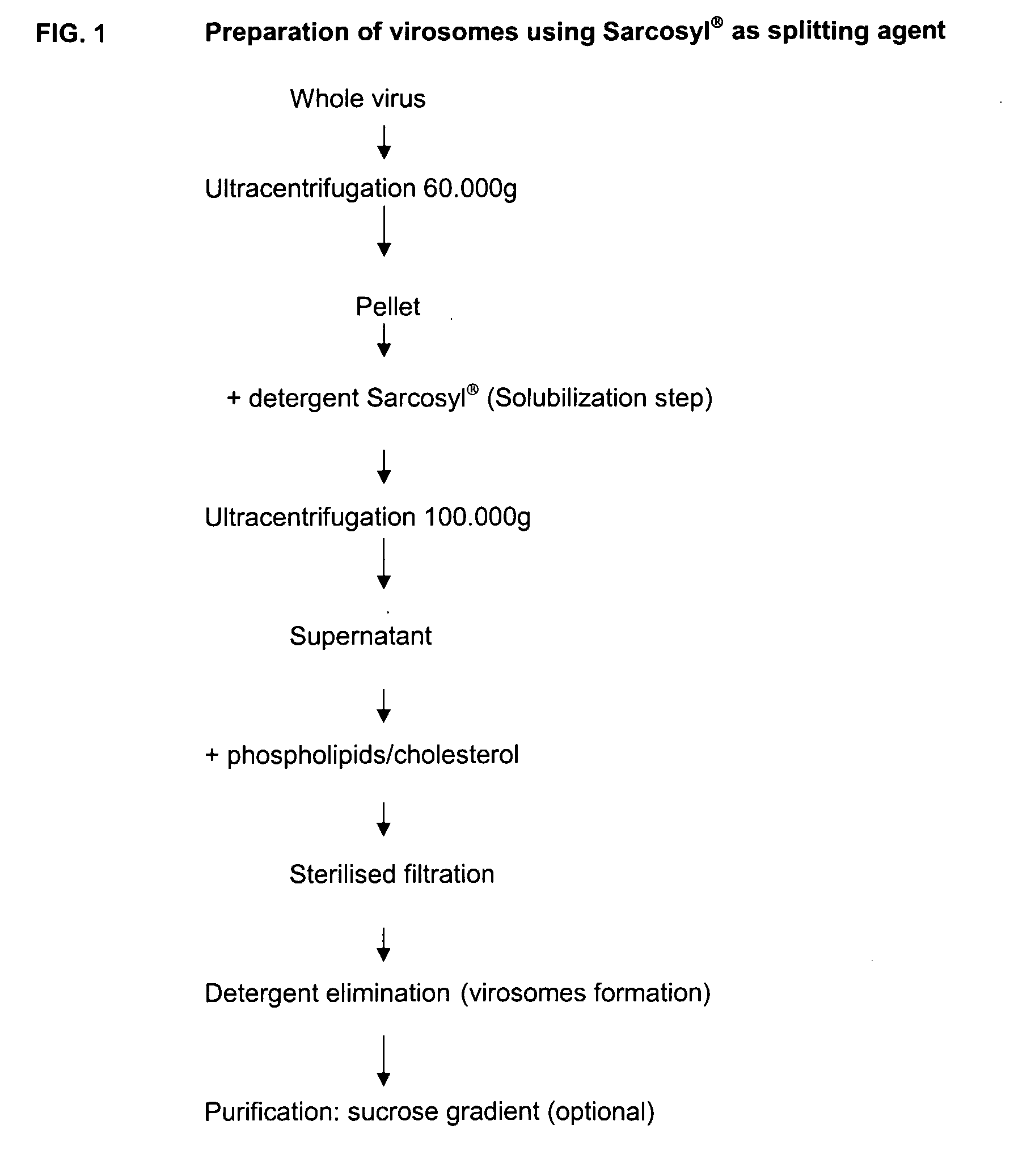
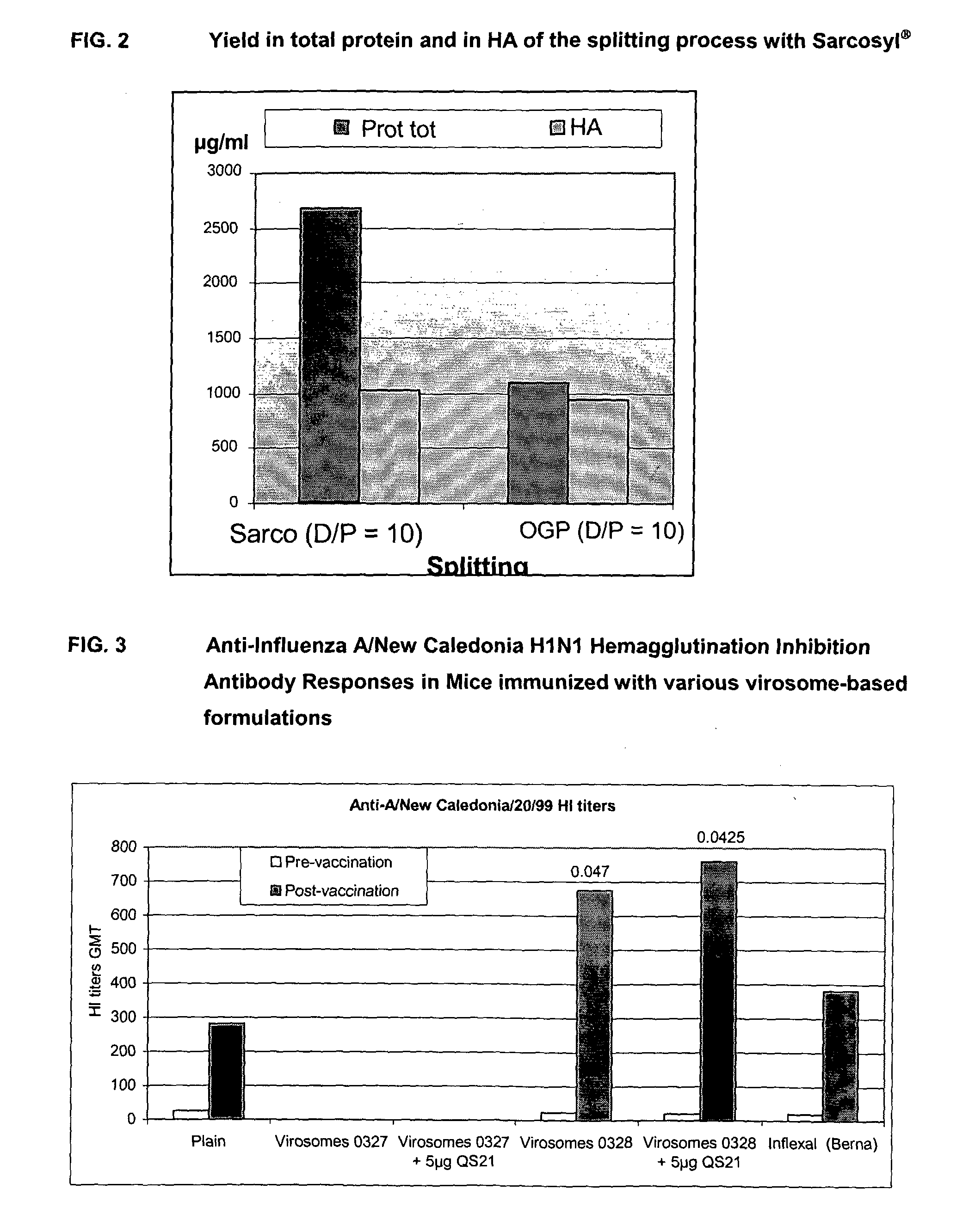
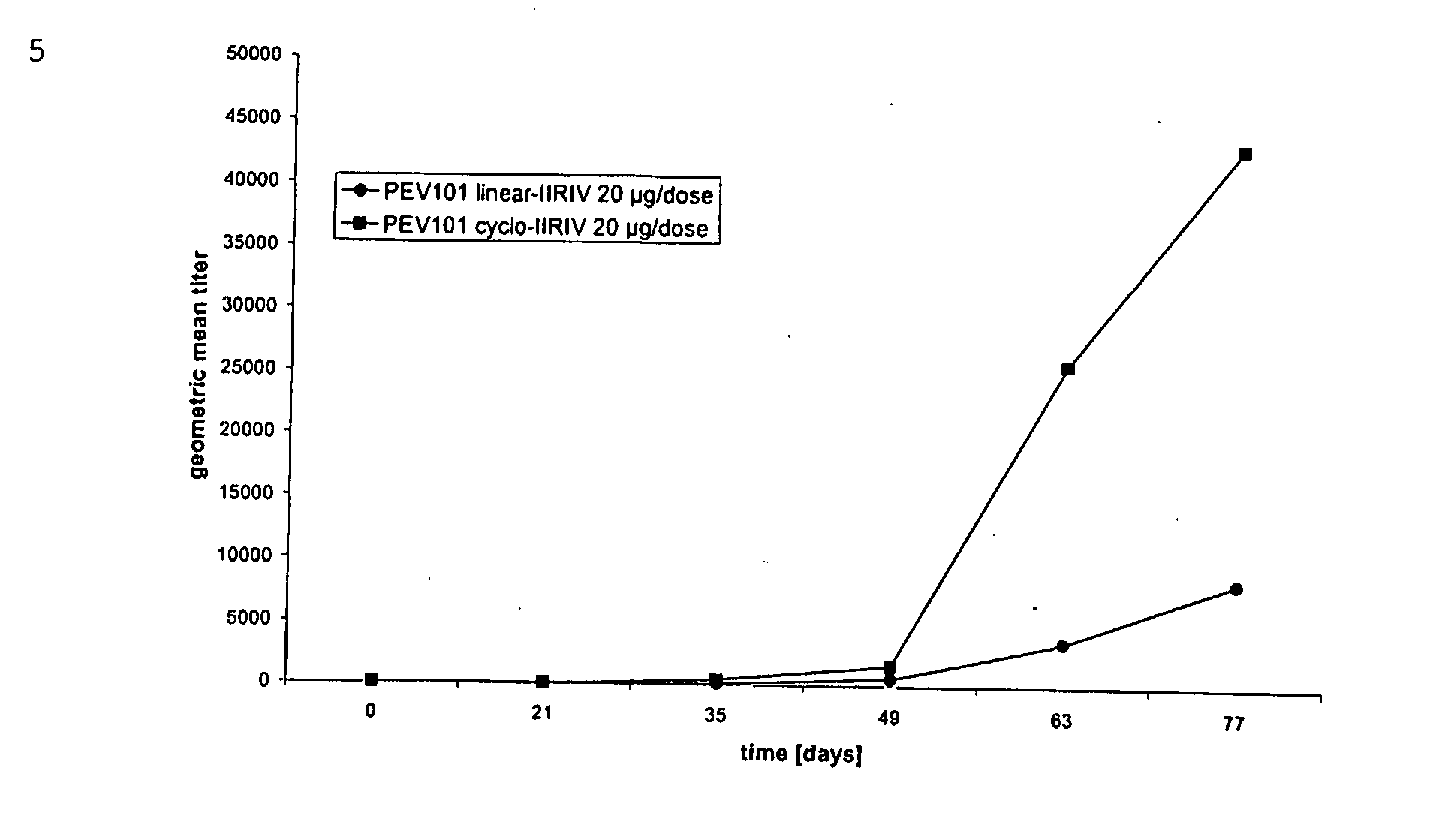
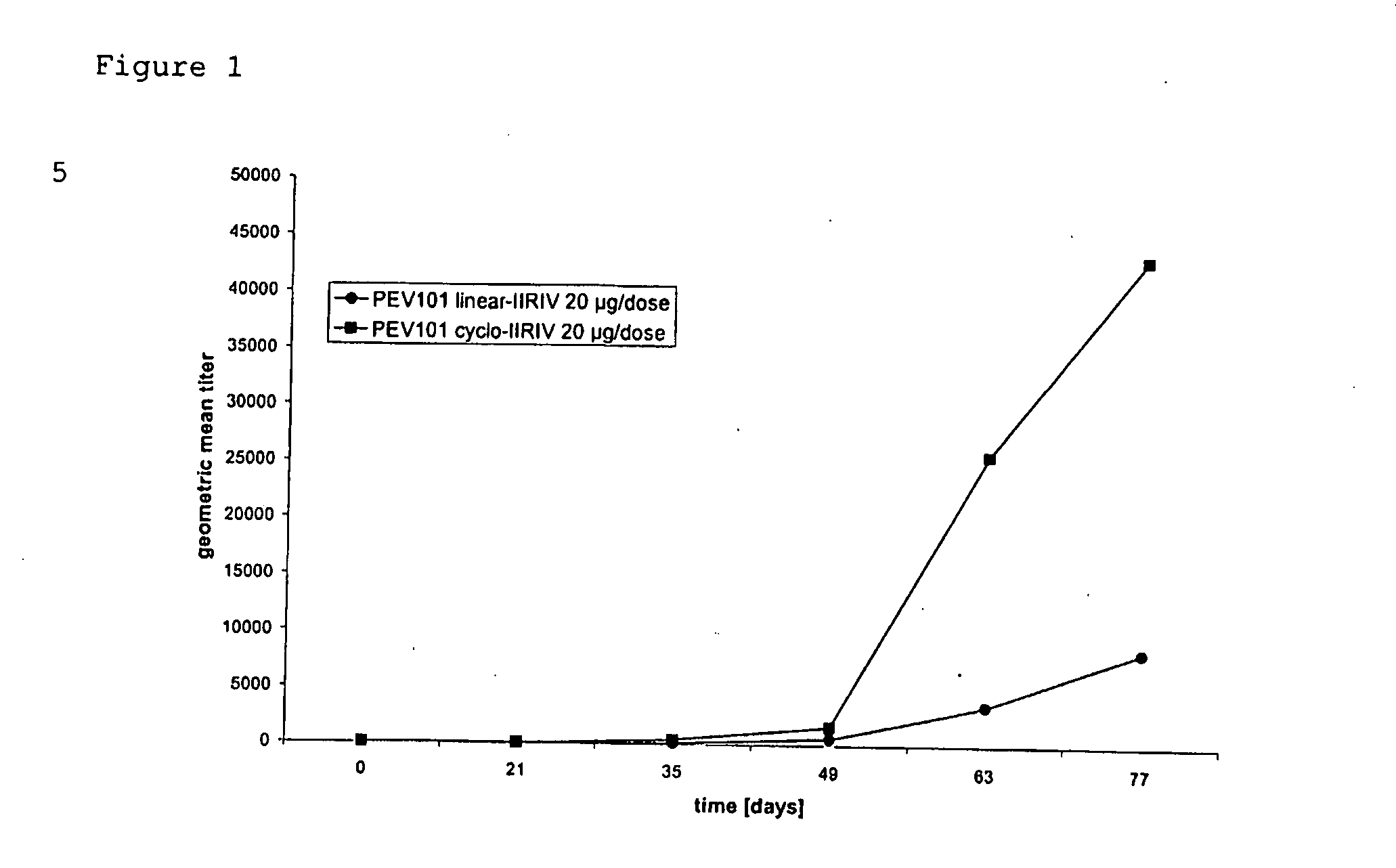
Vaccine Compositions Comprising Virosomes and a Saponin Adjuvant
InactiveUS20090263470A1Enhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsSterolVirosome
This invention provides virosome preparations from an enveloped virus, in particular from influenza virus, containing from said virus, and a saponin adjuvant. In particular the invention provides a virosome preparation from influenza virus an influenza antigen a QS21, optionally with a sterol. The invention also provides vaccine compositions containing said virosome preparations, methods of preparing said virosome preparations and vaccine containing them.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Optimization of expression of parvoviral rep and cap proteins in insect cells
The present invention relates to the improved production of recombinant parvoviral virions in insect cells. In particular, the invention relates to an improved process for the production of recombinant parvoviral virions in insect cells, wherein the full / empty parvoviral virion ratio is increased. The invention also relates to the production of parvoviral vectors that may be used in gene therapy and to improvements in expression of the viral Rep proteins that increase the productivity of parvoviral vectors.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
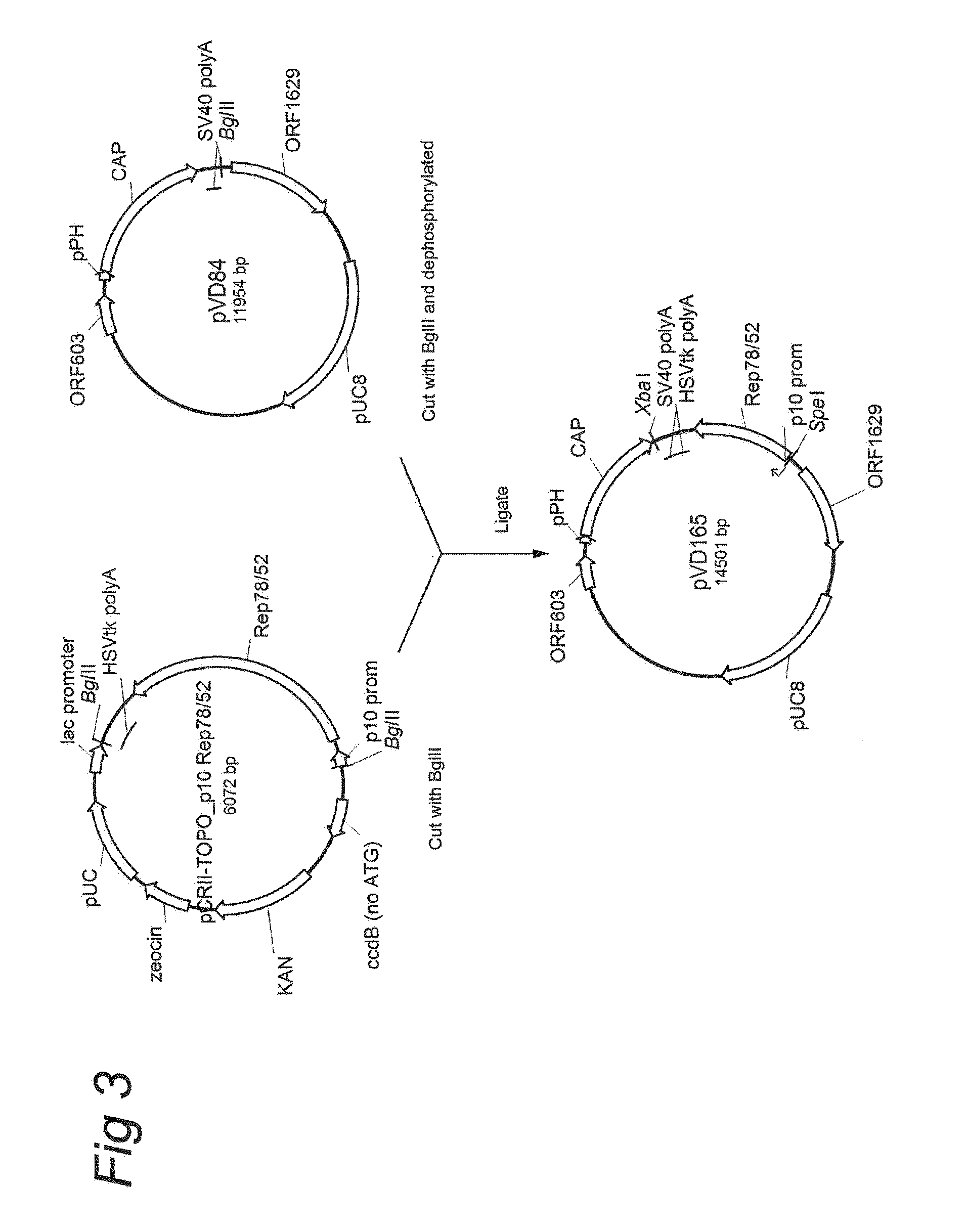
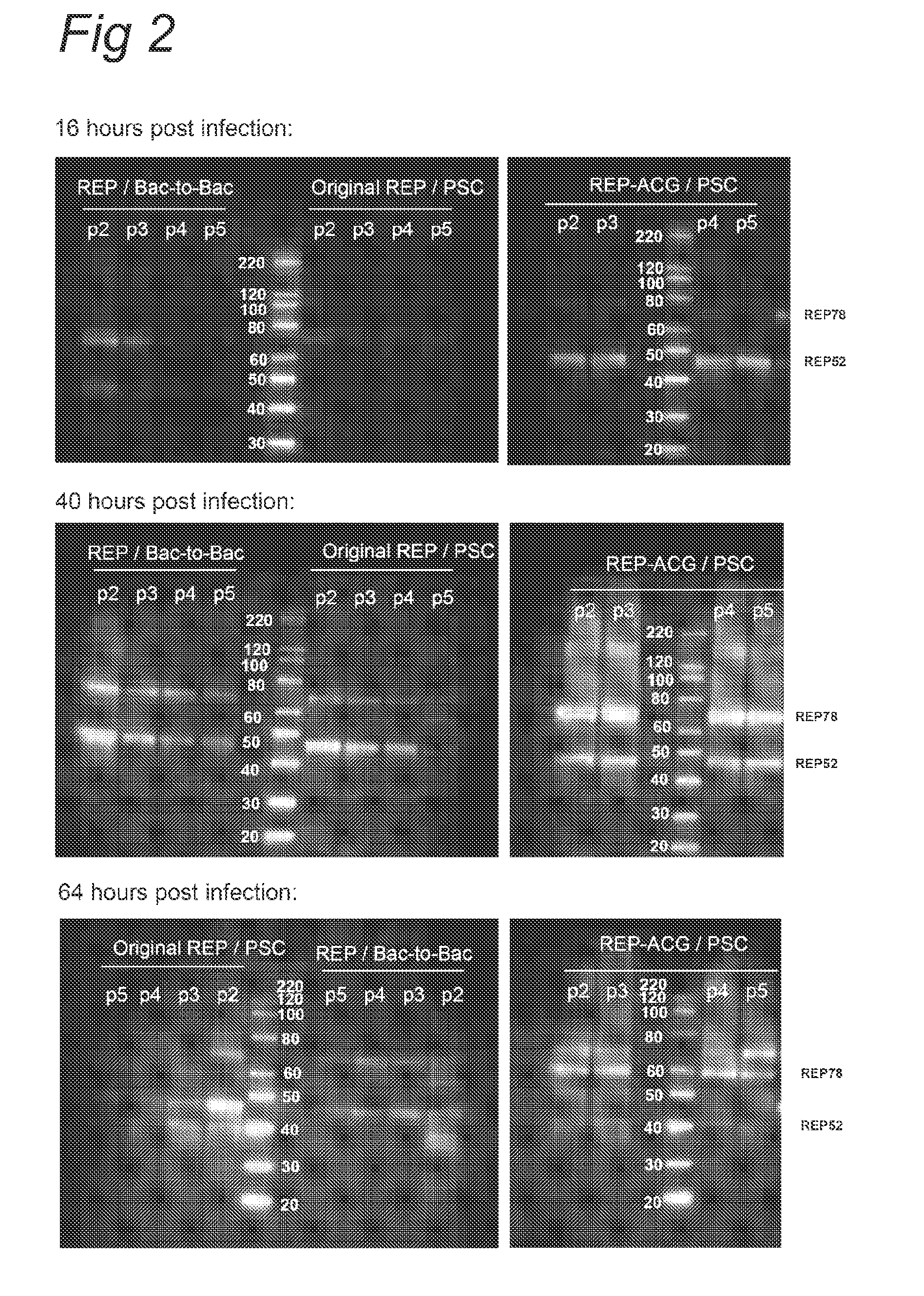
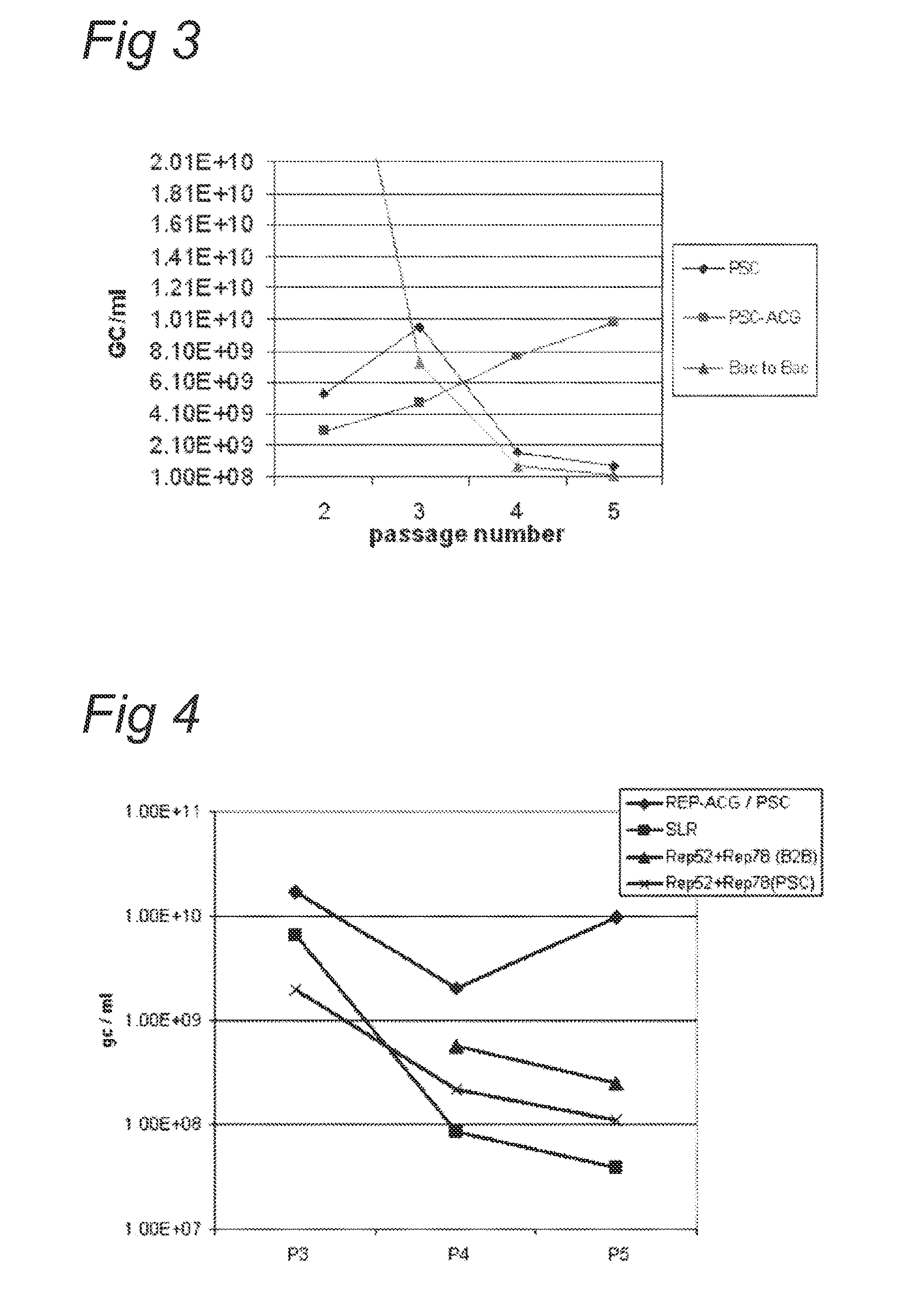
Vectors with modified initiation codon for the translation of aav-rep78 useful for production of aav
ActiveUS20130296532A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelVirus peptidesNucleic acid vectorNucleotideCapsid
The present invention relates nucleic acid constructs for the production of recombinant parvoviral (e.g. adeno-associated viral) vectors in insect cells, to insect cells comprising such constructs and to methods wherein the cells are used to produce recombinant parvoviral virions. The insect cells preferably comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the parvoviral rep proteins whereby the initiation codon for translation of the parvoviral Rep78 protein is a suboptimal initiation codon that effects partial exon skipping upon expression in insect cells. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one parvoviral (AAV) inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence and a third nucleotide sequence comprising a sequences coding for the parvoviral capsid proteins.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Adeno-associated virus variant capsids and methods of use thereof
Provided herein are variant adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins having one or more modifications in amino acid sequence relative to a parental AAV capsid protein, which, when present in an AAV virion, confer increased infectivity of one or more types of retinal cells as compared to the infectivity of the retinal cells by an AA V virion comprising the unmodified parental capsid protein. Also provided are recombinant AAV virions and pharmaceutical compositions thereof comprising a variant AAV capsid protein as described herein, methods of making these rAAV capsid proteins and virions, and methods for using these rAAV capsid proteins and virions in research and in clinical practice, for example in, e.g., the delivery of nucleic acid sequences to one or more cells of the retina for the treatment of retinal disorders and diseases.
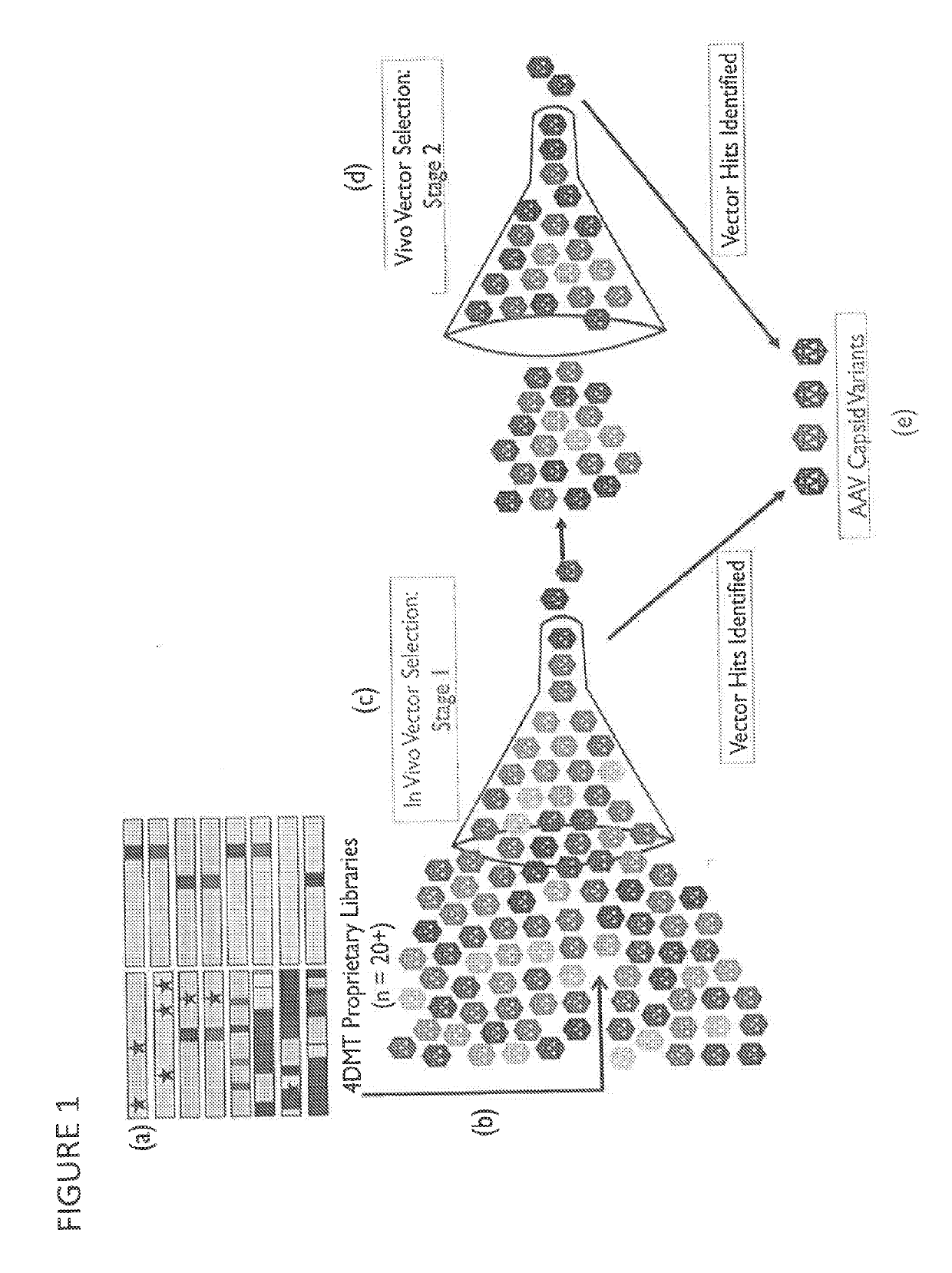
Owner:4D MOLECULAR THERAPEUTICS INC
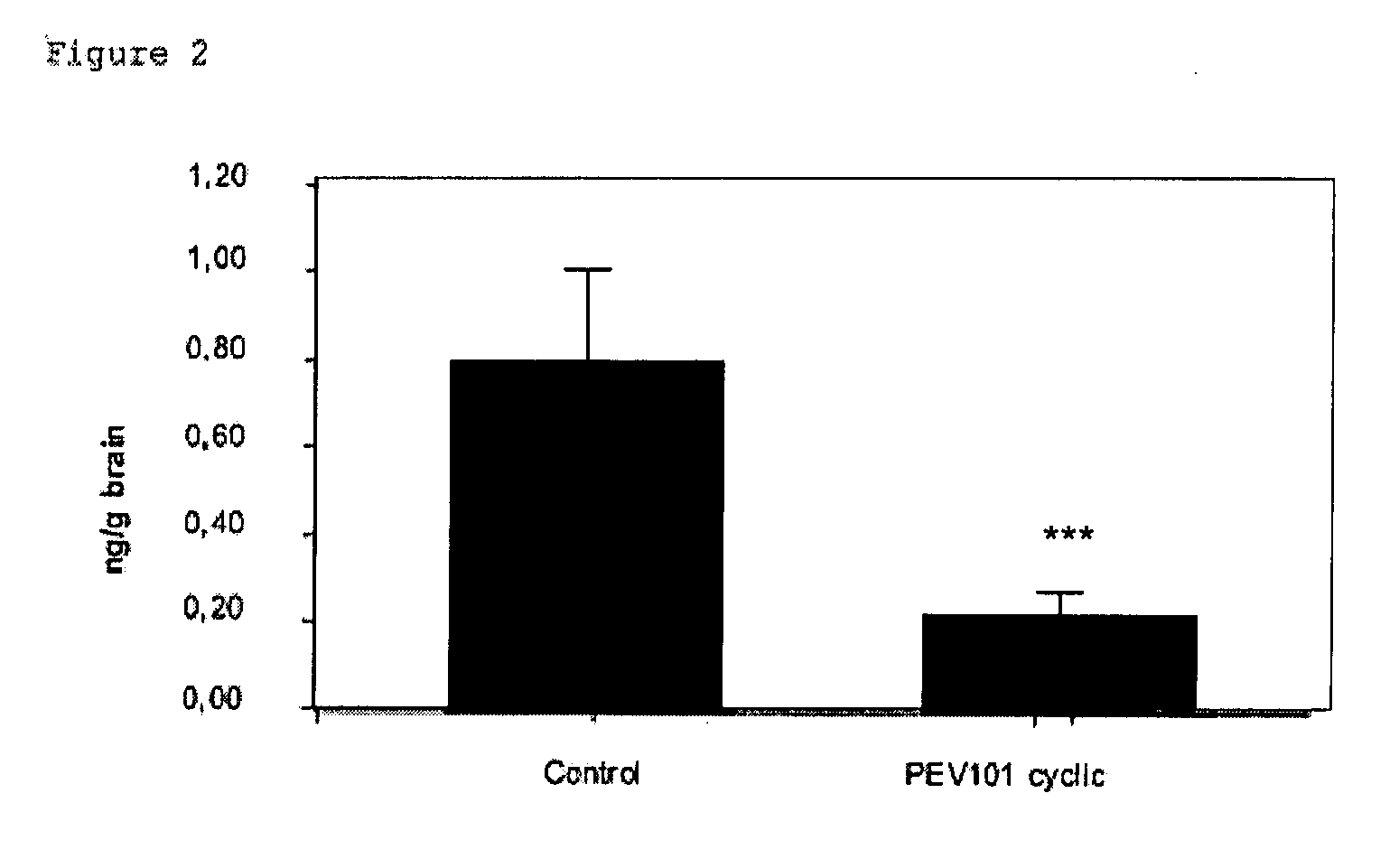
Immunogenic compositions of cyclic peptides derived from the beta-amyloid peptide
InactiveUS20080107649A1Inhibition formationReduce chancePeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsCyclic peptideAdjuvant
Owner:PEVION BIOTECH
AAV virions with decreased immunoreactivity and uses therefor
ActiveUS20080008690A1Decreased immunoreactivityEfficient transductionVirusesHydrolasesVirosomeSerotype
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Methods and compositions for the synergistic activation of latent HIV
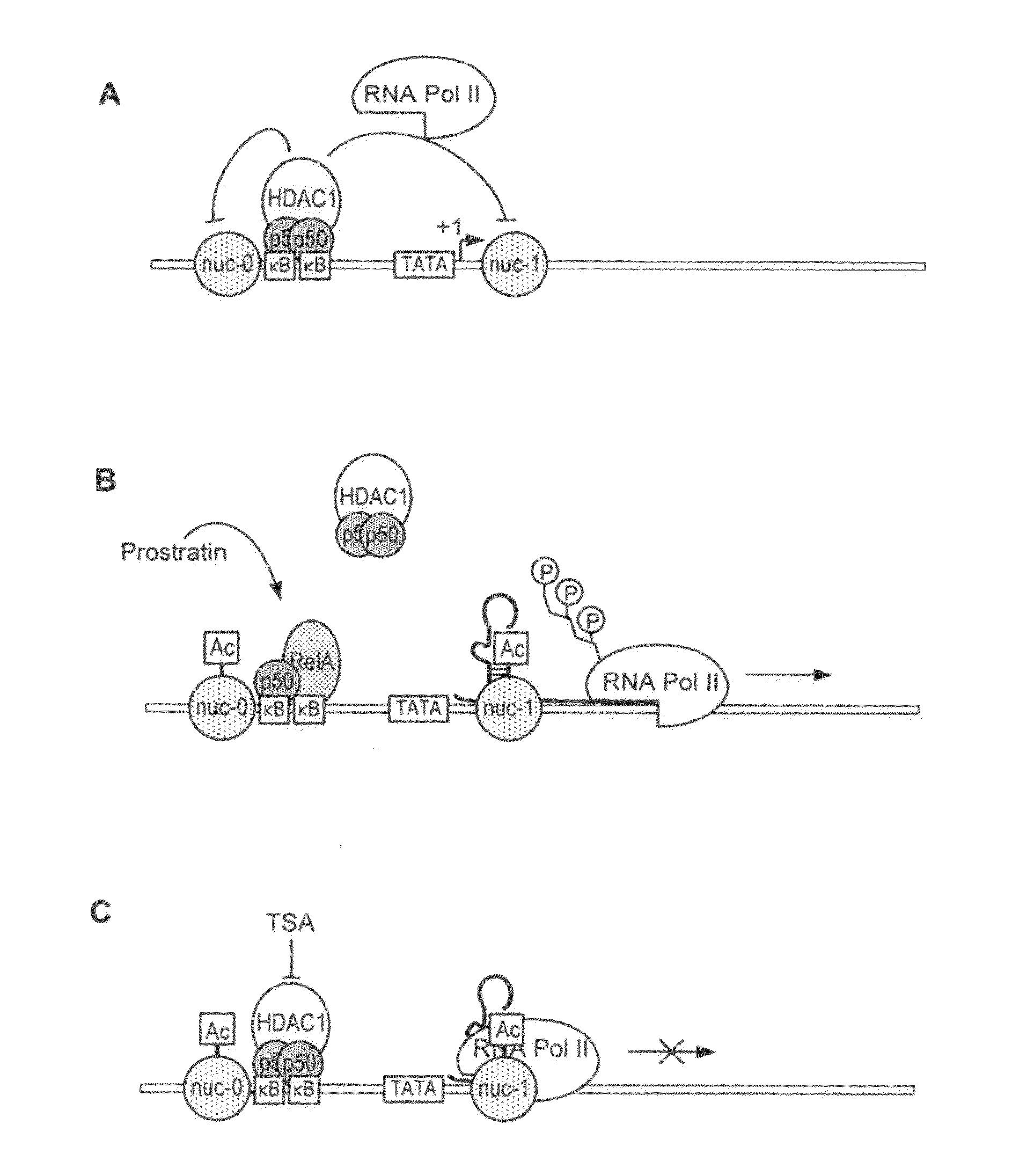
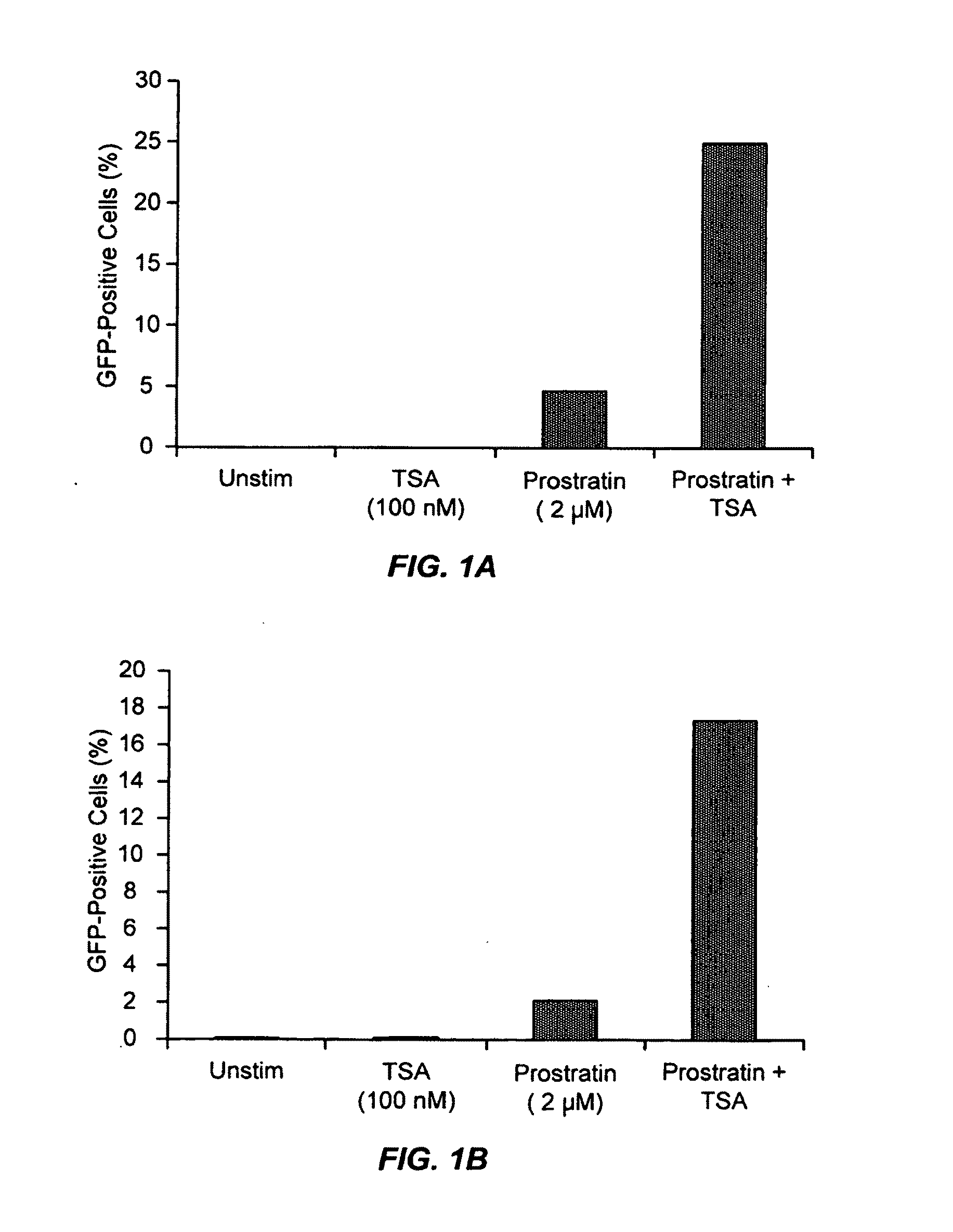
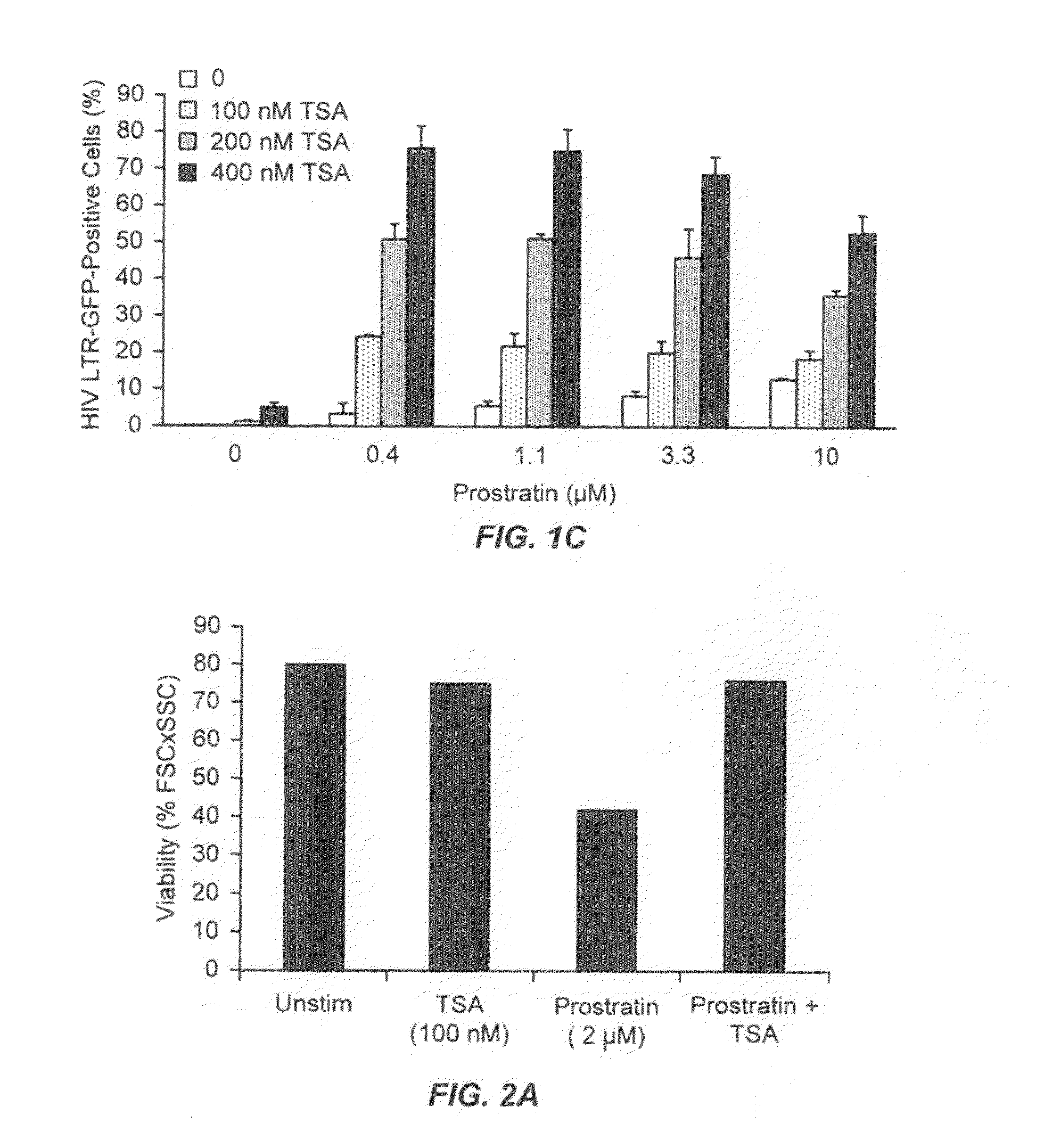
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful for the elimination of latent HIV reservoirs that persist despite HAART. The methods and compositions overcome this latent barrier by inducing the replication of HIV in latently infected T cells while preventing the spread of the newly produced virions to uninfected cells by providing HAART simultaneously. Compositions of the invention comprise an activator of latent HIV expression, such as prostratin, and an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, such as TSA. A surprising finding of this invention is that the inhibitor of the histone deacetylase synergizes the effect of prostratin thus, allowing administering to a patient a lower, non-toxic dose of prostratin.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Nanoscale particles synthesized within an assembled virion
Virion-constrained nanoparticles comprising a shell of virion coat protein(s) surrounding an organic, inorganic and / or organo-metallic non-viral nanoparticle and methods of making and using.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
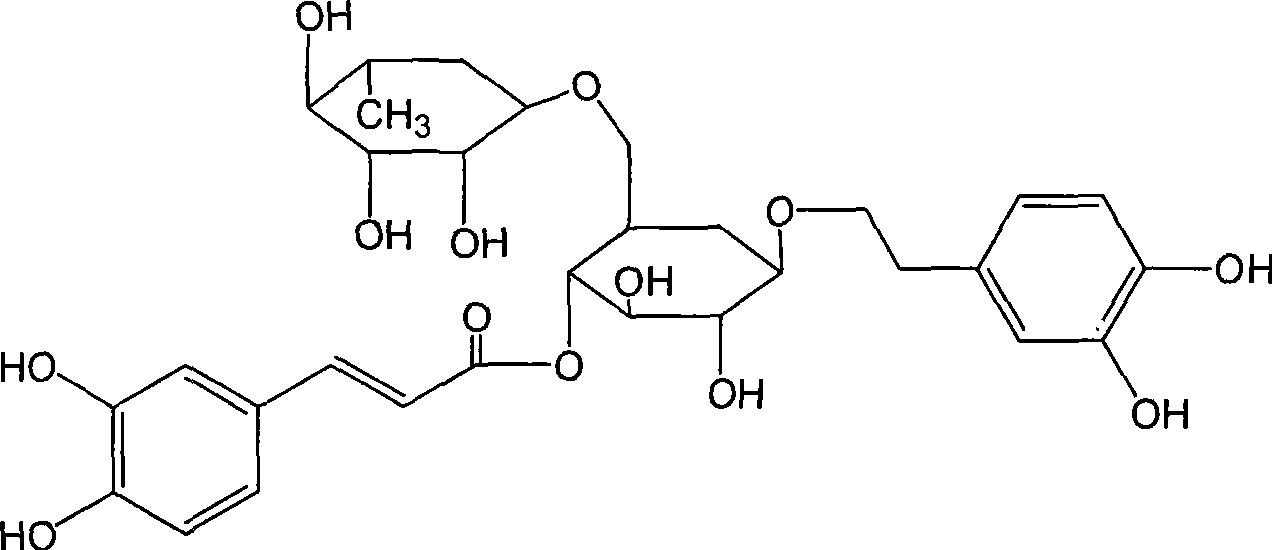
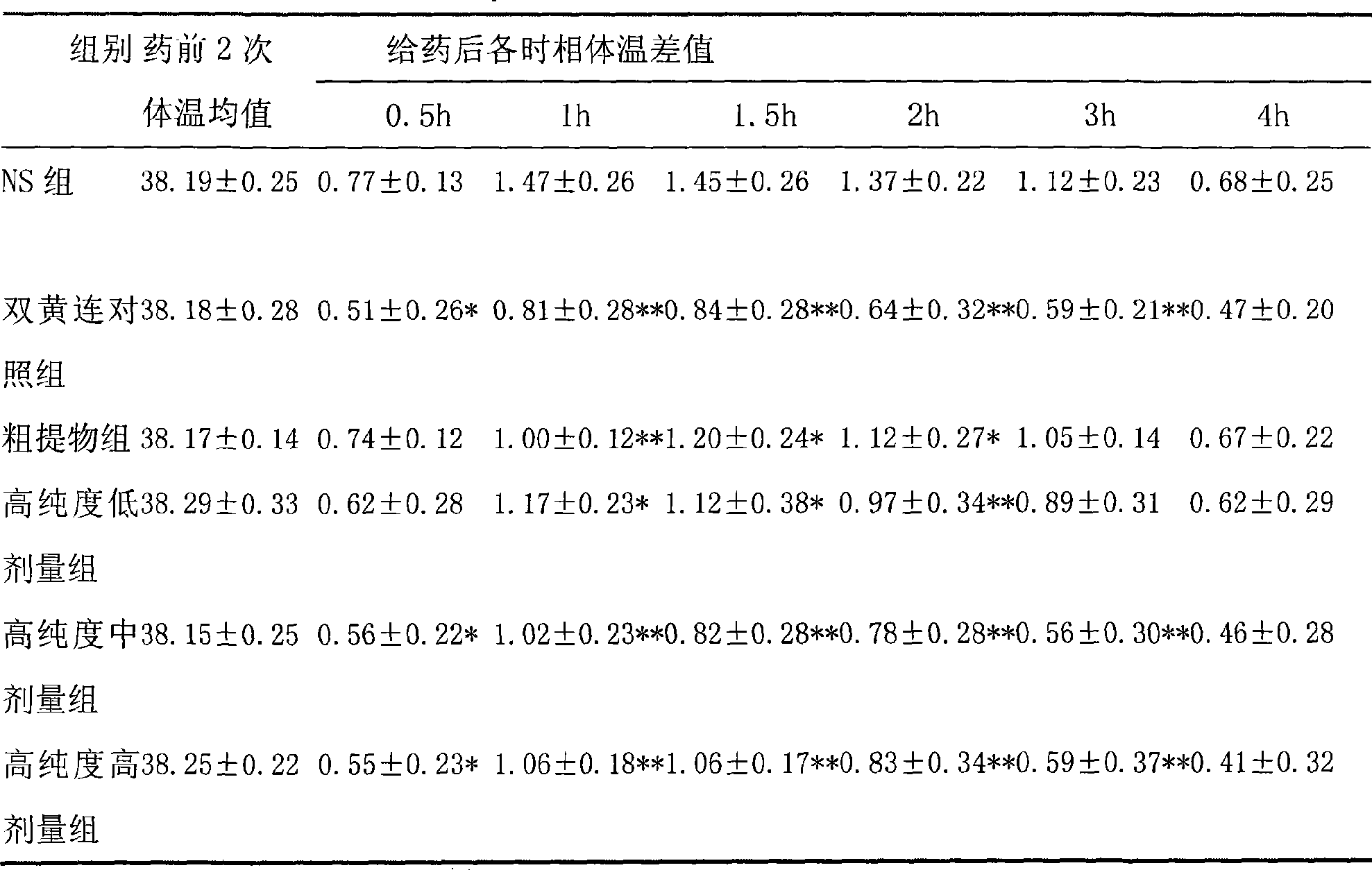
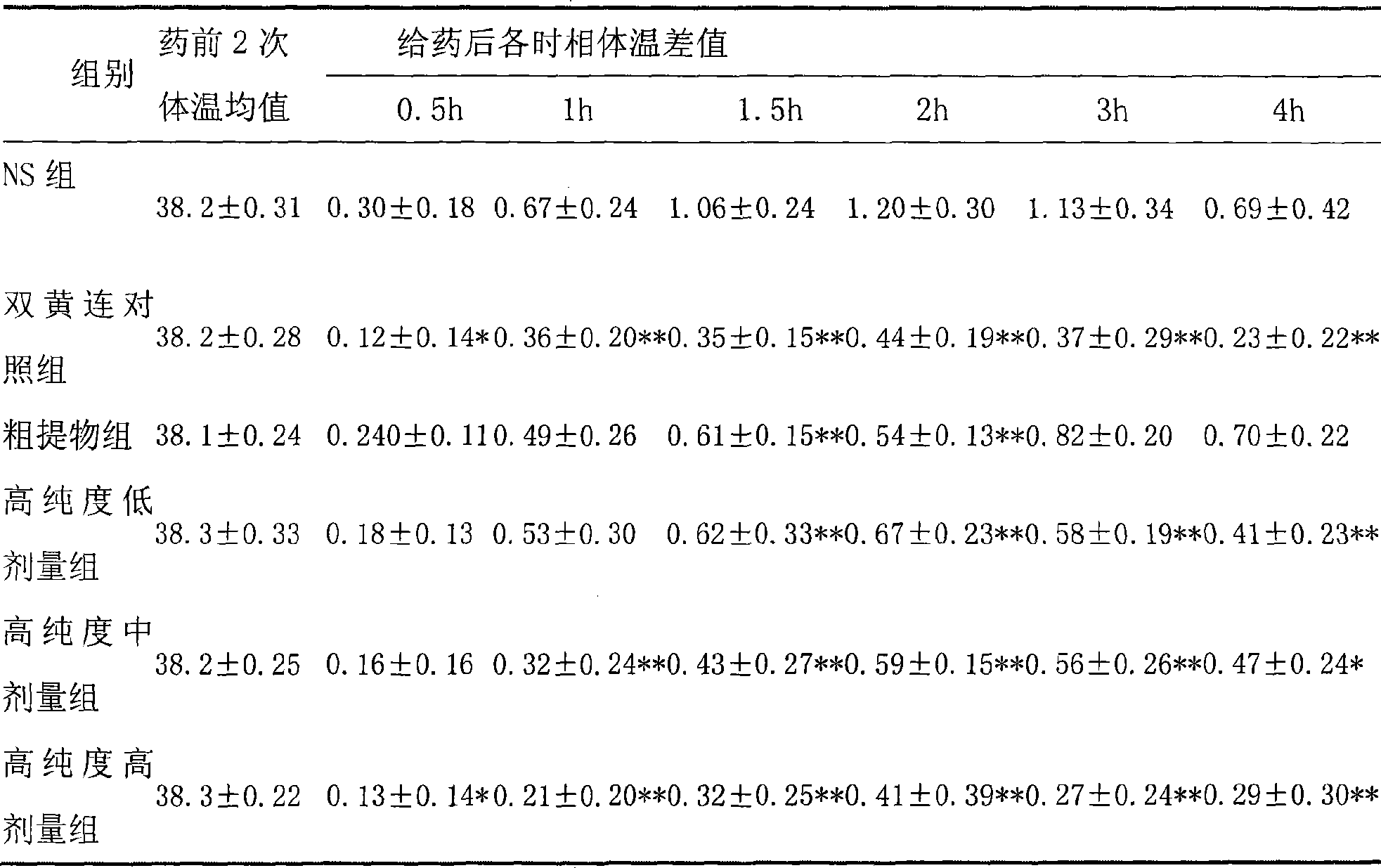
Use of high-purity forsythin in preparing bacteriostasis, antivirus and other medicine
ActiveCN101390869AIncrease contentEasy to removeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAnti virusBeta-hemolytic streptococcus
The invention belongs to the medical technical field and discloses the application of high-purity in the preparation of antibacterial medicine, antiviral medicine and other medicines. The invention proves the antipyretic, anti-inflammation, immunity enhancement, antibacterial and anti-virus effects of high-purity forsythiaside through the following experiments: (1) the experiment that high-purity forsythiaside has antipyretic effect on fever rats; (2) the experiment that high-purity forsythiaside inhibits xylene-induced mice ear edema, xylene-reduced capillary permeability of mice; (3) the experiment that high-purity forsythiaside increases carbon clearance ability of mice and increases the lymphocyte transformation rate; (4) the experiment that high-purity forsythiaside has vitro anti-influenza A type virus effect and in-vivo anti-respiratory syncytial virus effect; (5) the experiment that high-purity forsythiaside has vitro inhibition effects on beta-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus viridans and staphylococcus epidermidis.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA
High-efficiency wild-type-free AAV helper functions
The present invention provides methods and compositions for producing high titer, wild-type-free preparations of recombinant AAV ("rAAV") virions. The compositions of the present invention include novel nucleic acids encoding AAV helper functions and AAV helper function vectors. The present invention also includes host cells transfected by the claimed nucleic acids, methods of using the claimed vectors, and rAAV virions produced by such methods.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
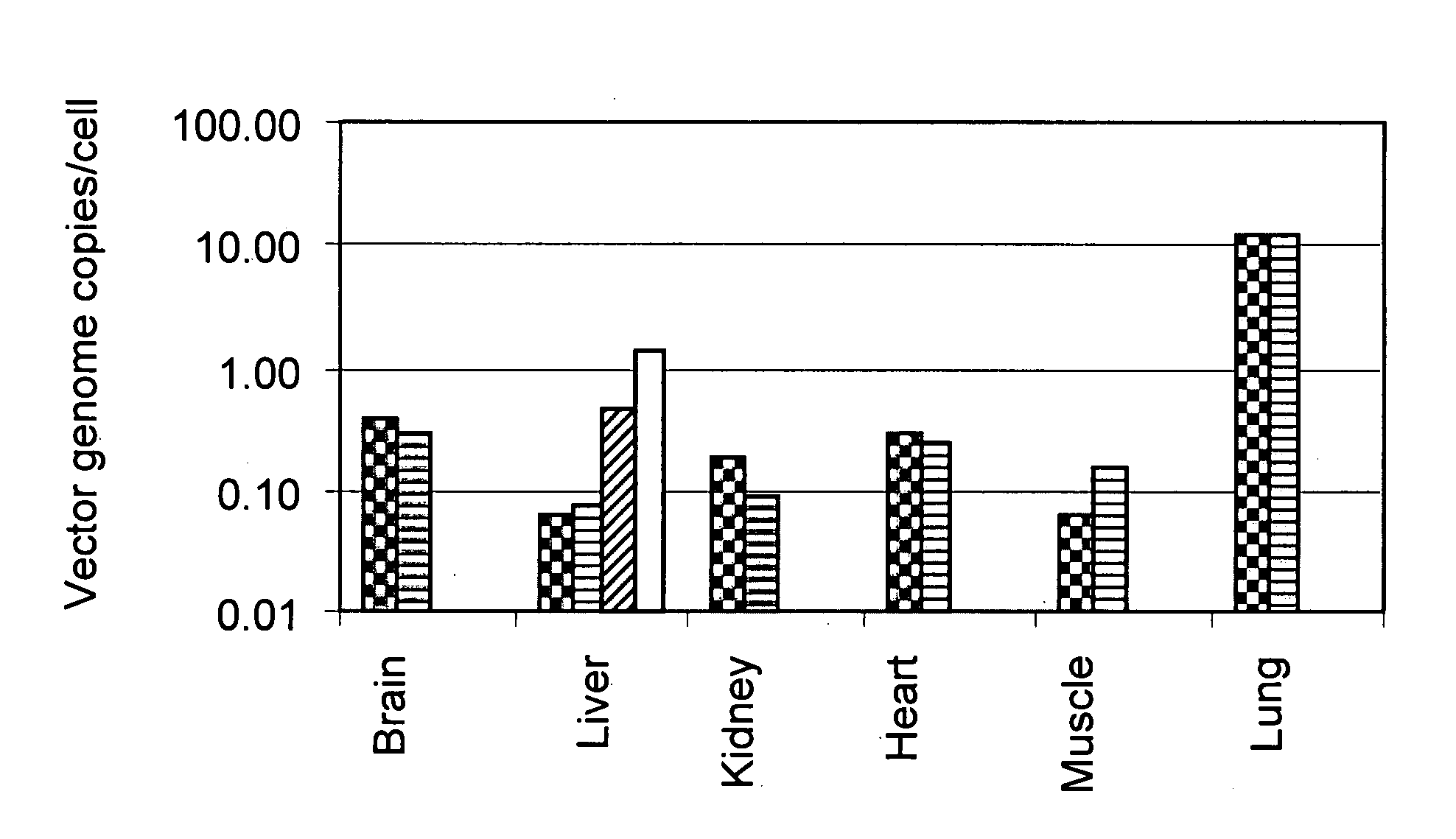
Methods for delivering recombinant adeno-associated virus virions to the liver of a mammal
Methods for introducing recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virions into the liver of a mammal are provided. In these methods, the liver is partially or completely isolated from its blood supply, a catheter is introduced into the liver via a peripheral blood vessel, and rAAV virions are then infused through the catheter to the liver. The methods described herein may be used, for example, to deliver heterologous genes encoding therapeutic proteins to the hepatocytes of humans. This can be accomplished, for example, by introducing the catheter into a femoral artery, threading the catheter into the hepatic artery, and infusing rAAV virions through the catheter and into the liver. Exemplary examples of heterologous genes include those coding for blood coagulation factors.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Virosomes comprising hemagglutinin derived from an influenza virus produced in a cell line, compositions, methods of manufacturing, use thereof
InactiveUS8367077B2Improved fusion activityImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininVirosome
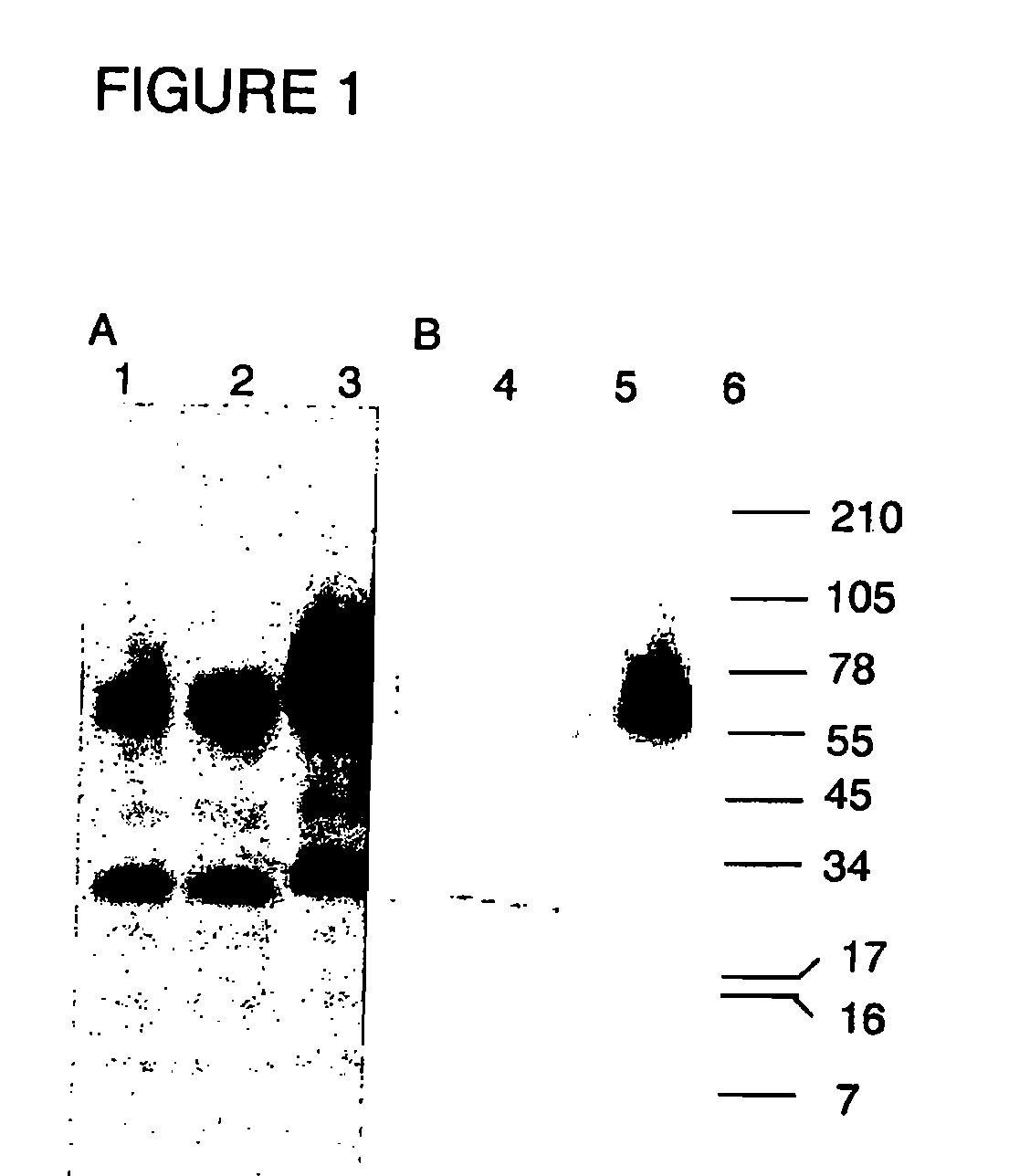
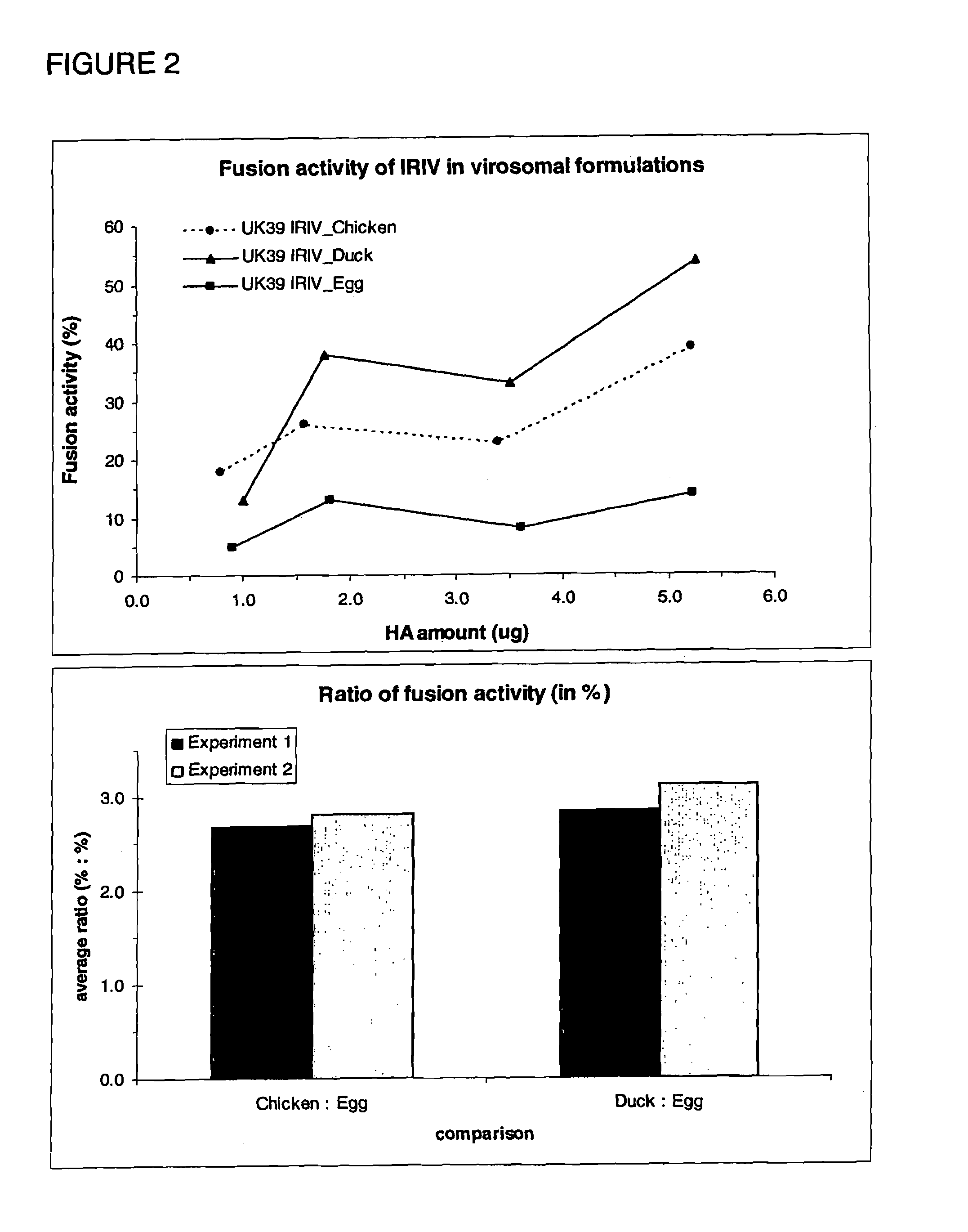
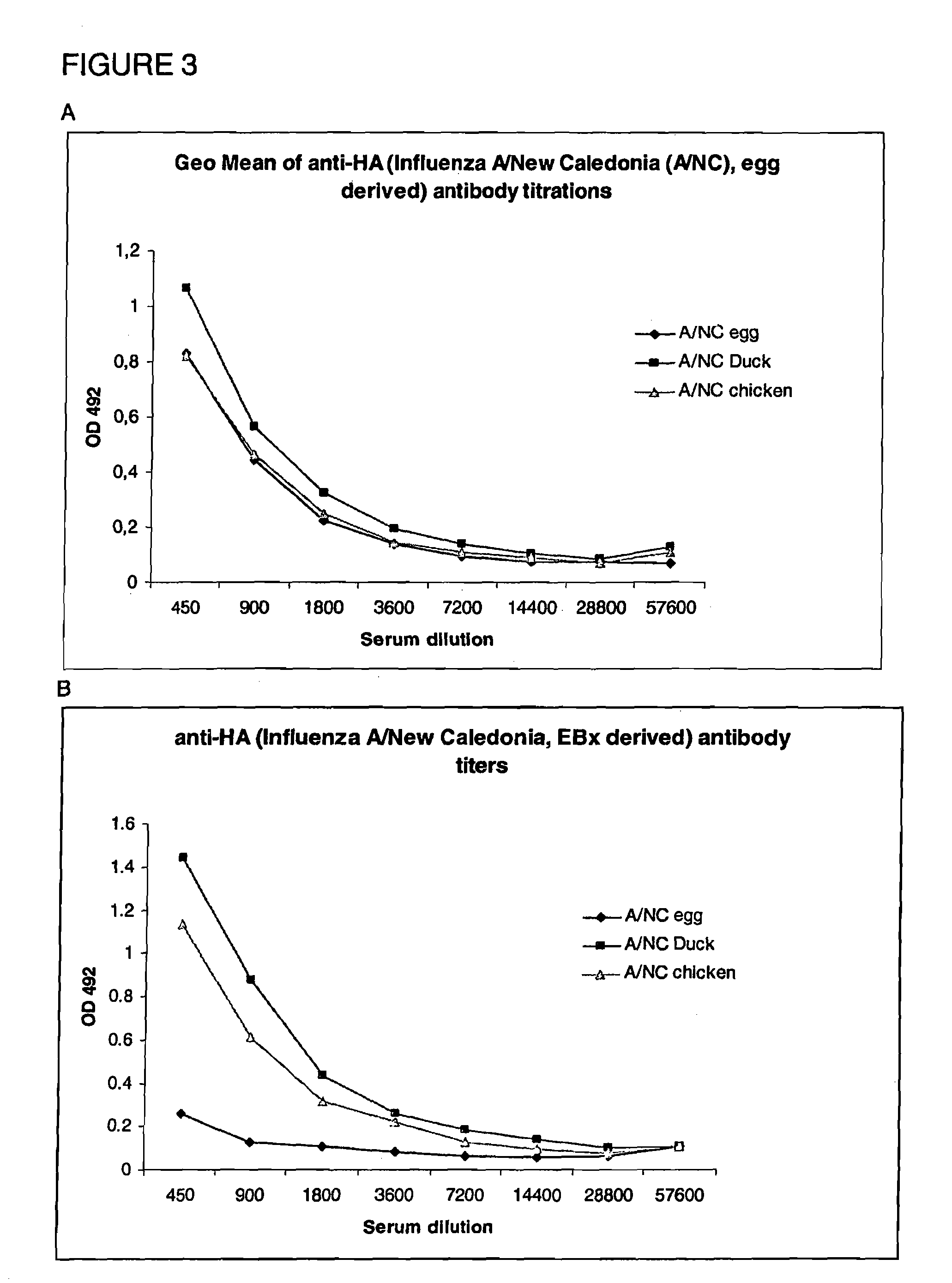
The present invention relates to virosomes comprising hemagglutinin (HA) with improved fusion activity. Preferably, the HA comprised in said virosomes was derived from influenza virus produced in a cell line. The present invention also relates to compositions and a kit comprising the virosomes according to the invention. Further, the present invention relates to uses and methods involving said virosomes, as well as to a method for preparing same.
Owner:PEVION BIOTECH
Helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS6489162B1Efficient yieldImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWild typeViral vector
The present invention relates to a method for producing helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) which can be used to efficiently and stably transduce foreign genes into host cells or organisms. The method comprises the cotransfection of eukaryotic cells with rAAV and with helper AAV DNA in the presence of helper virus (e.g. adenovirus or herpesvirus) such that the helper AAV DNA is not associated with virion formation. The crux of the invention lies in the inubility of the helper AAV DNA to recombine with rAAV vector, thereby preventing the generation of wild-type virus. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the vector comprises a recombinant AAV genome containing only the terminal regions of the AAV chromosome bracketing a non-viral gene, and the helper AAV DNA comprises a recombinant AAV genome containing that part of the AAV genome which is not present in the vector, and in which the AAV terminal regions are replaced by adenovirus sequences. In a further embodiment of the invention, cell lines are created which incorporate helper AAV DNA which can directly produce substantially pure recombinant AAV virus. The pure stocks of recombinant AAV produced according to the invention provide an AAV viral expression vector system with increased yield of recombinant virus, improved efficiency, higher definition, and greater safety than presently used systems.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Kit for fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of main porcine viruses
ActiveCN104263853AImprove the level of detection technologyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementClassical swine feverPseudorabies
The invention relates to a kit which utilizes a probe fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, is divided into two systems and can fast obtain and detect a variety of viruses causing porcine reproductive disorders and diarrheal diseases from clinical samples, wherein the A system is used for detecting porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2), porcine parvovirus (PPV) and pseudorabies virus (PRV); the B system is used for detecting porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) and classical swine fever virus (CSFV). The detection kit is reasonable in design, simple in a using method, fast, accurate and high in sensitivity, is suitable for port inspection and quarantine management, livestock farming, animal protection and other departments, and simultaneously has extensive scientific research values and commercial prospects.
Owner:广州中科基因检测服务有限公司
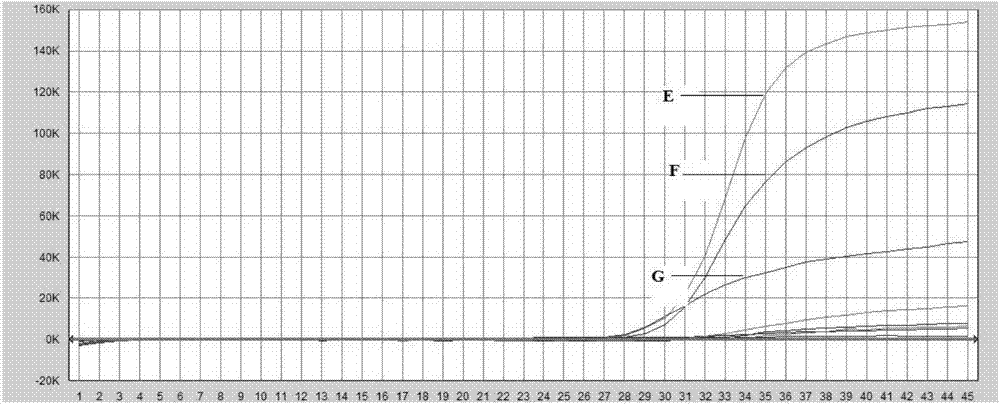
AAV (adeno-associated virus) virion with mutated capsid and application of AAV virion
ActiveCN109897831AHigh transduction efficiencyLow transduction efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesAdeno-associated virusMutation
The invention discloses an AAV (adeno-associated virus) virion with a mutated capsid and an application of the AAV virion. The AAV virion with the mutated capsid has mutated AAV6 capsid protein, and endows enhanced retina Muller (shown in the description) cells with infectivity; compared with corresponding parent AAV6 capsid protein, 663-poisiton serine in the amino acid sequence of the mutated AAV6 capsid protein is mutated into leucine; pharmaceutical composition contains the AAV virion and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. By means of site-directed mutation of amino acid of encoded AAV6 capsid, an AAV vector for specifically and efficiently transducing the Muller (shown in the description) cells is obtained, and is suitable for carrying exogenous therapeutic gene transduced Muller (shown in the description) cells to treat retinopathy.
Owner:苏州吉脉基因药物生物科技有限公司
Helper dependent adenoviral vector system and methods for using the same
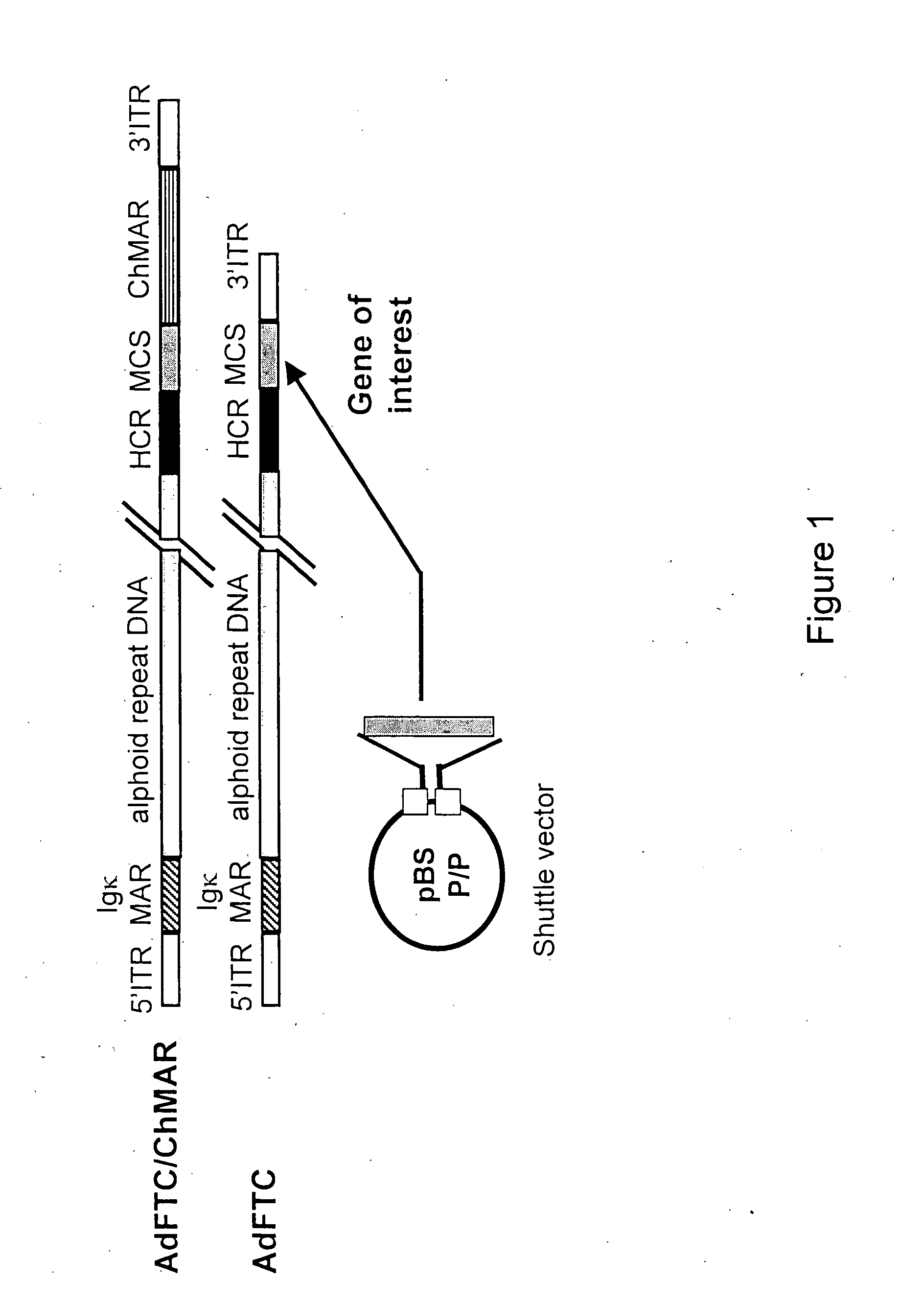
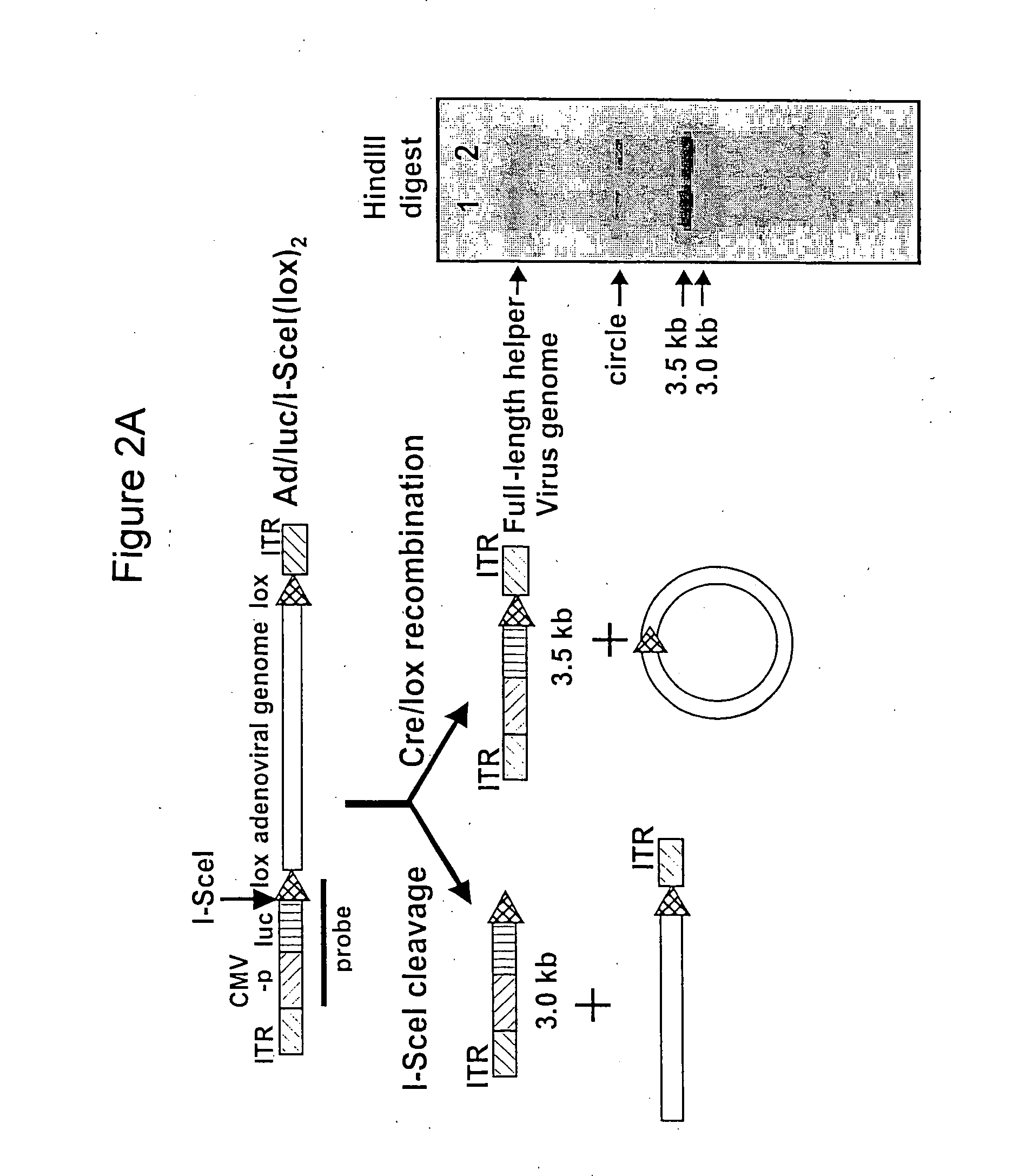
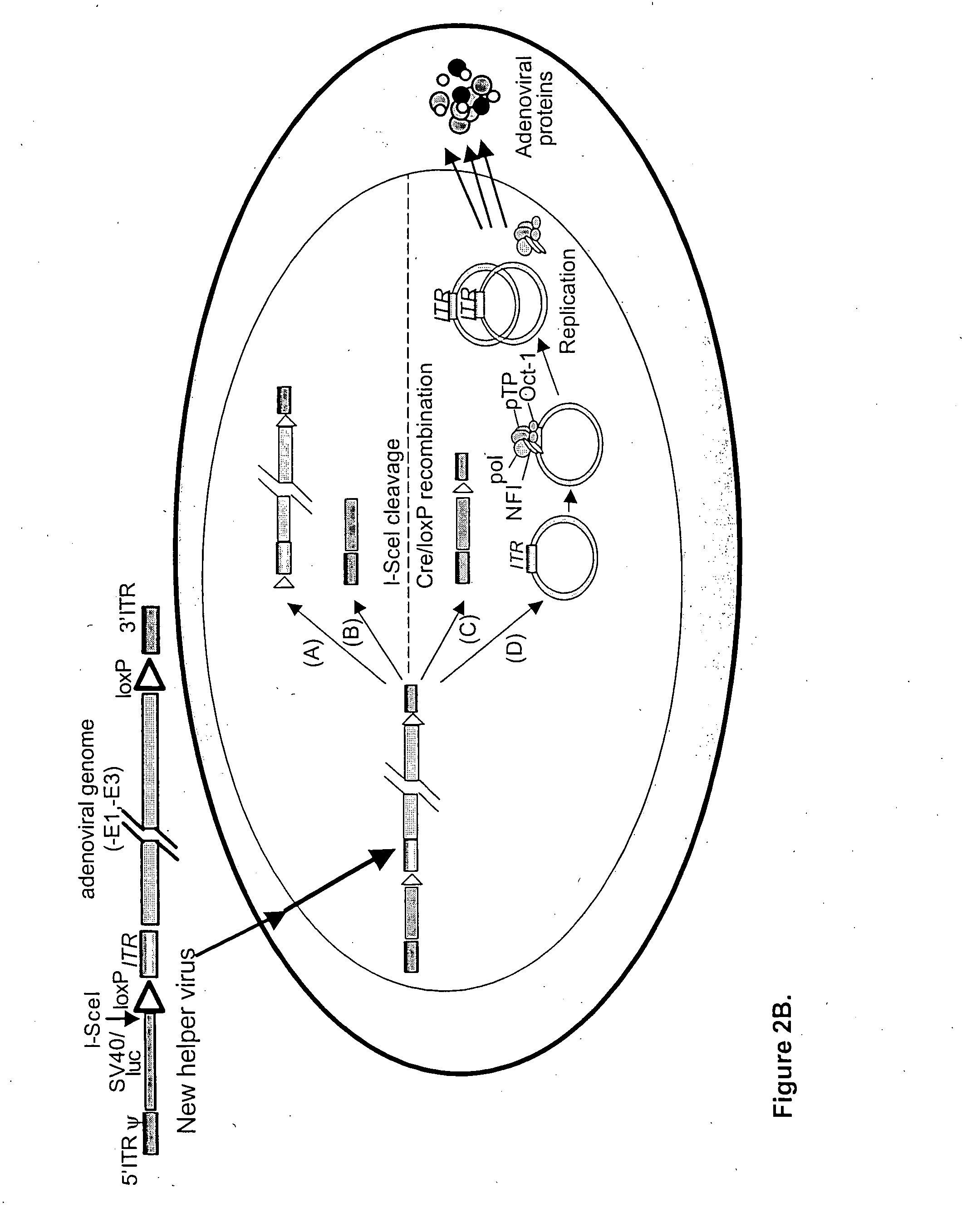
A helper dependent adenoviral vector system is provided. The subject helper dependent adenoviral vector system is made up of: (1) a "gutless" adenoviral vector, which in certain embodiments includes cis-acting human stuffer DNA that provides for in vivo long term, high level expression of a coding sequence present on the vector, where in certain embodiments the vector includes an integrating domain; (2) an adenoviral helper vector that is characterized by having an adenoviral genome region flanked by recombinase recognition sites, where the helper vectors further include a non-mammalian endonuclease recognition site positioned outside of the adenoviral genome region and in certain embodiments a third adenoviral inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequence positioned between first and second terminal ITRs; and (3) a mammalian cell that expresses the corresponding recombinase and endonuclease, as well as the adenoviral preterminal and polymerase proteins. Also provided are methods of using the subject systems to produce virions having the subject helper dependent adenoviral vectors encapsulated in an adenoviral capsid. In addition, kits for use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com