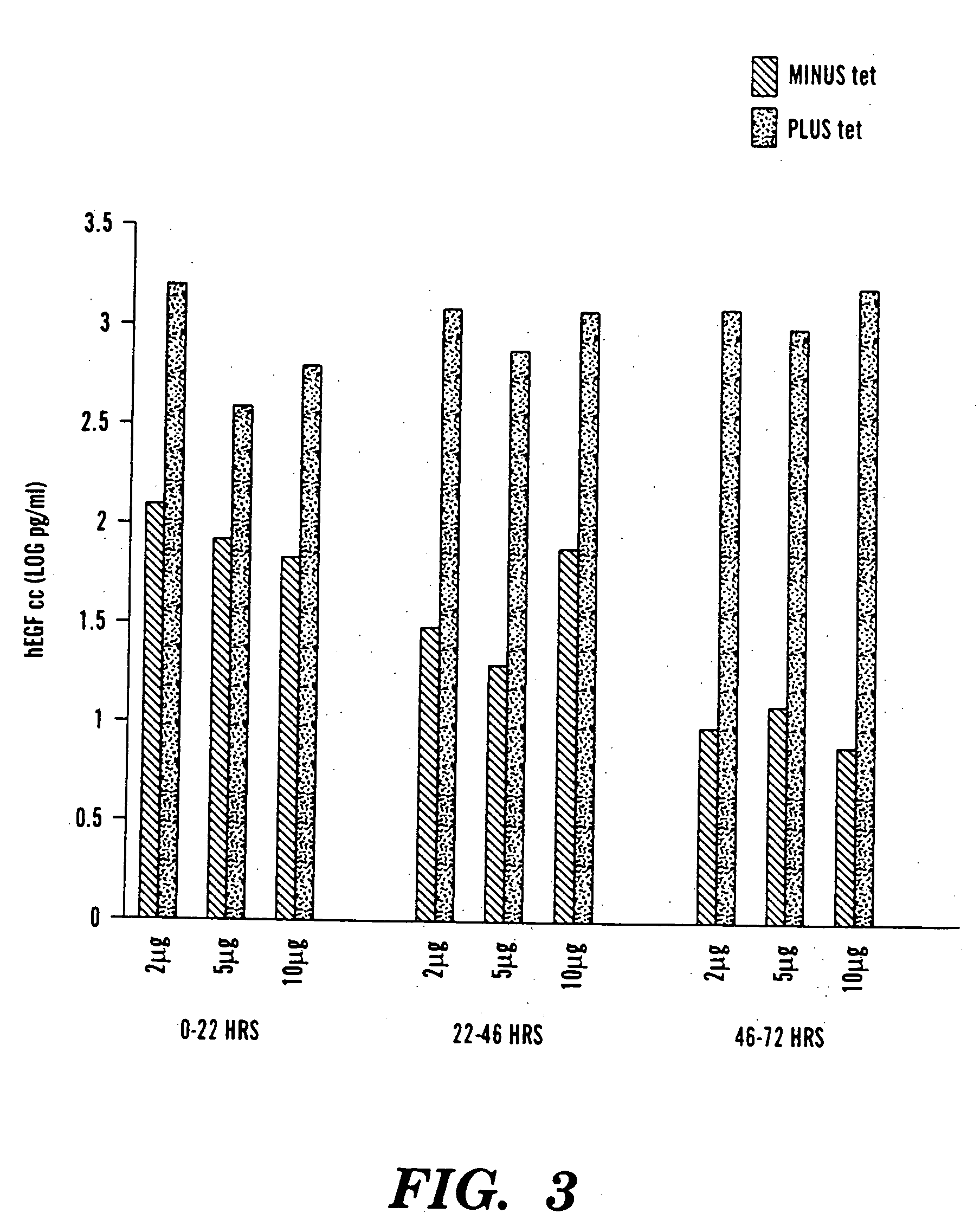
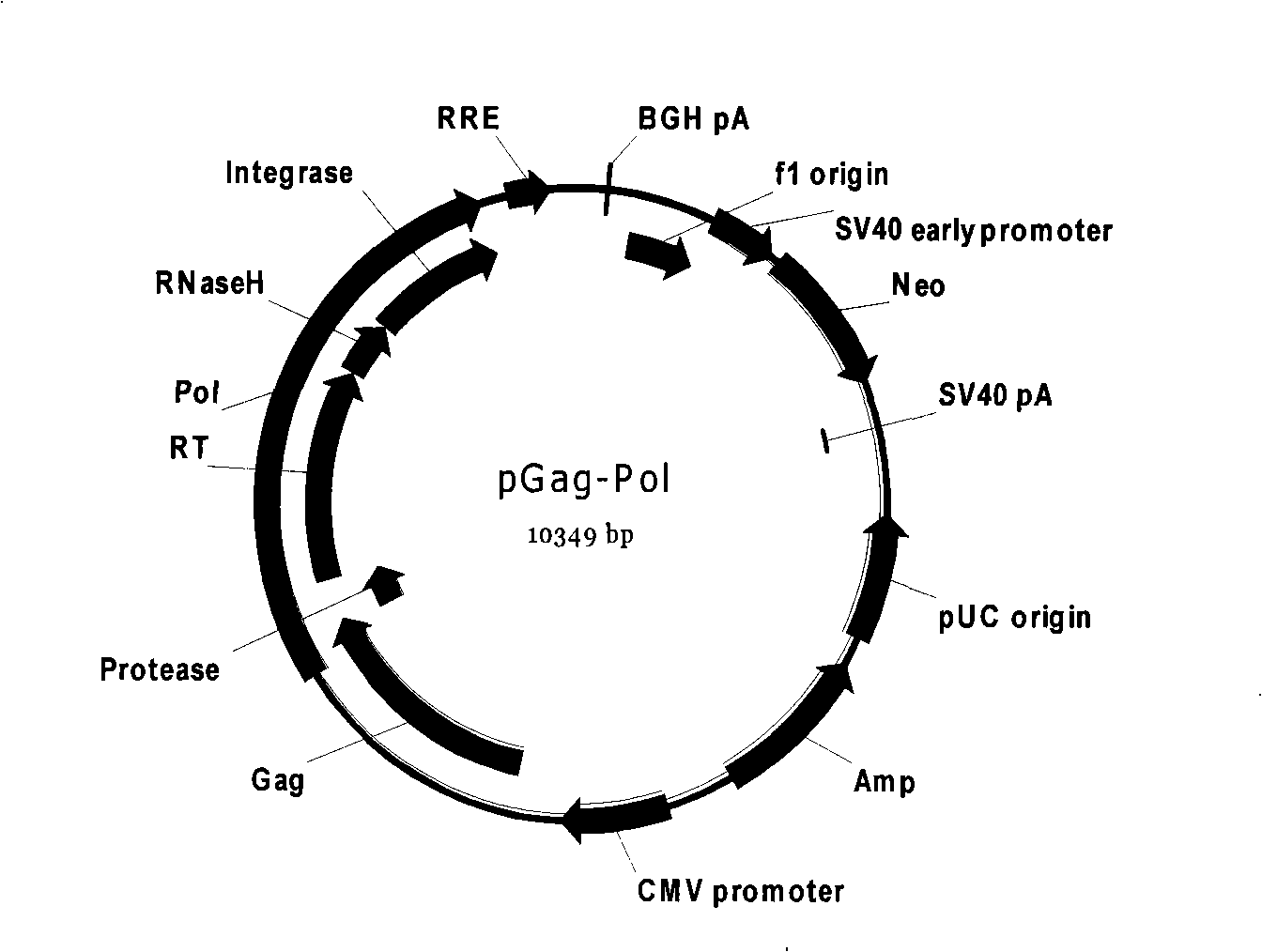
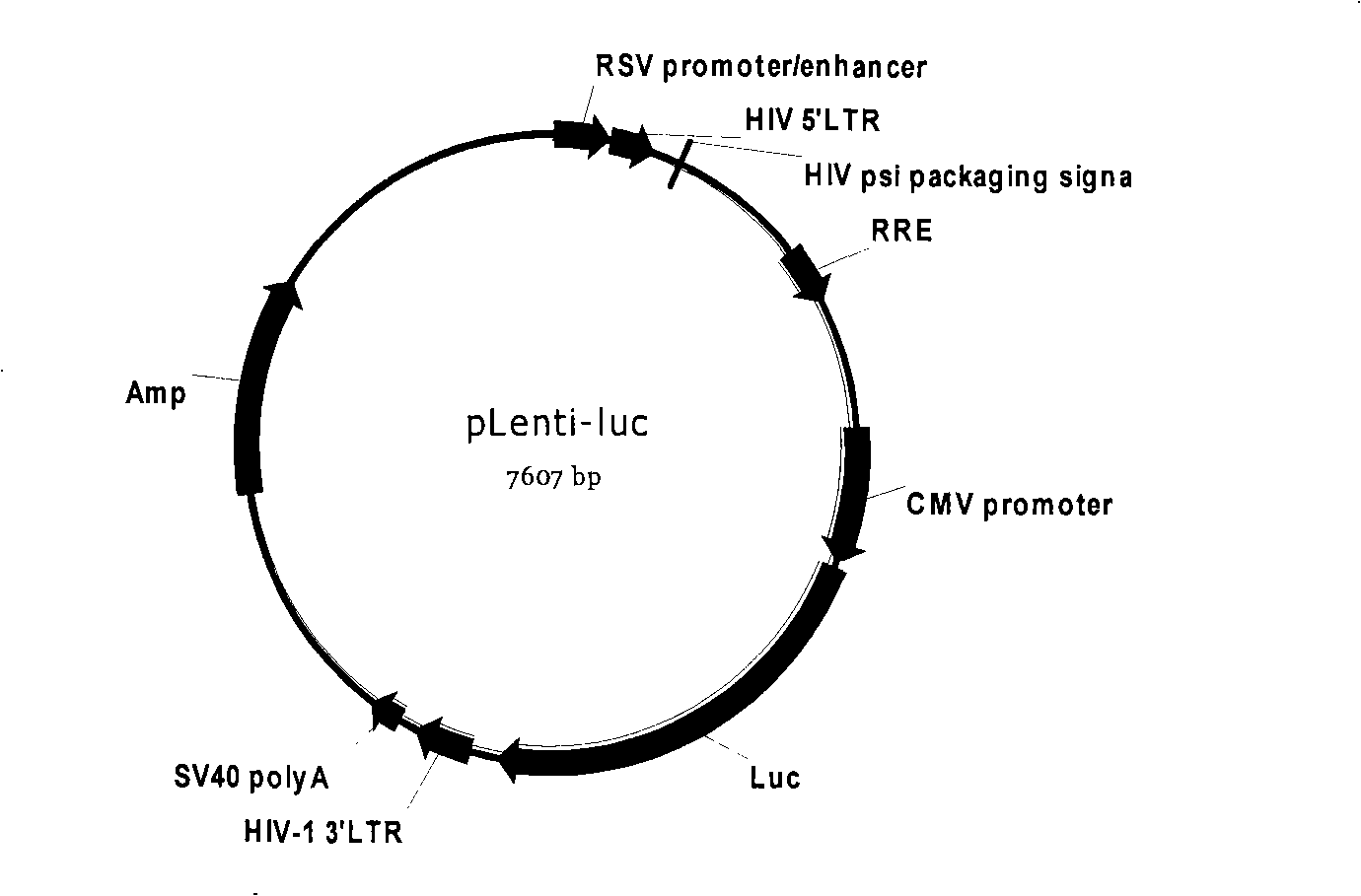
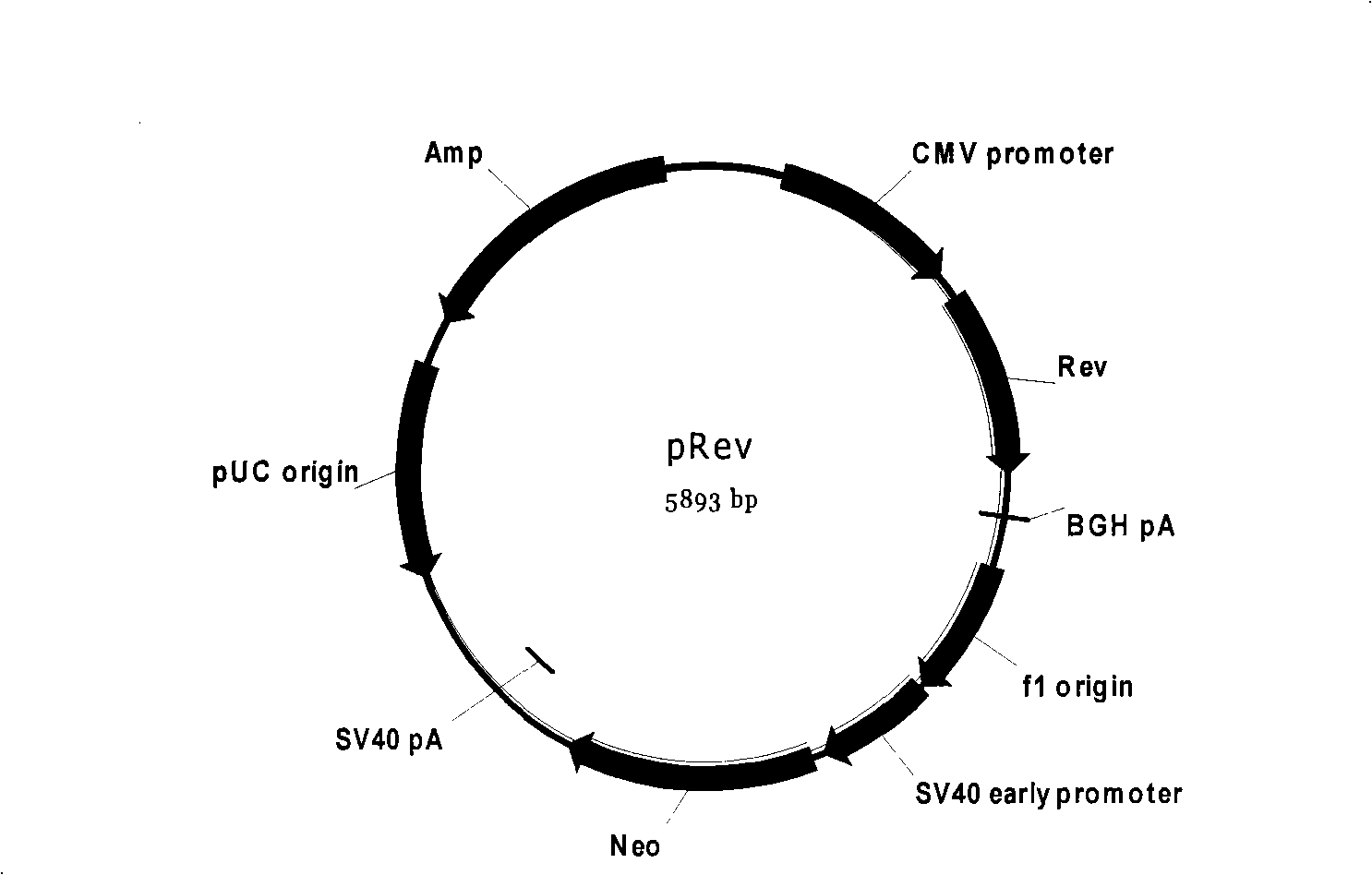
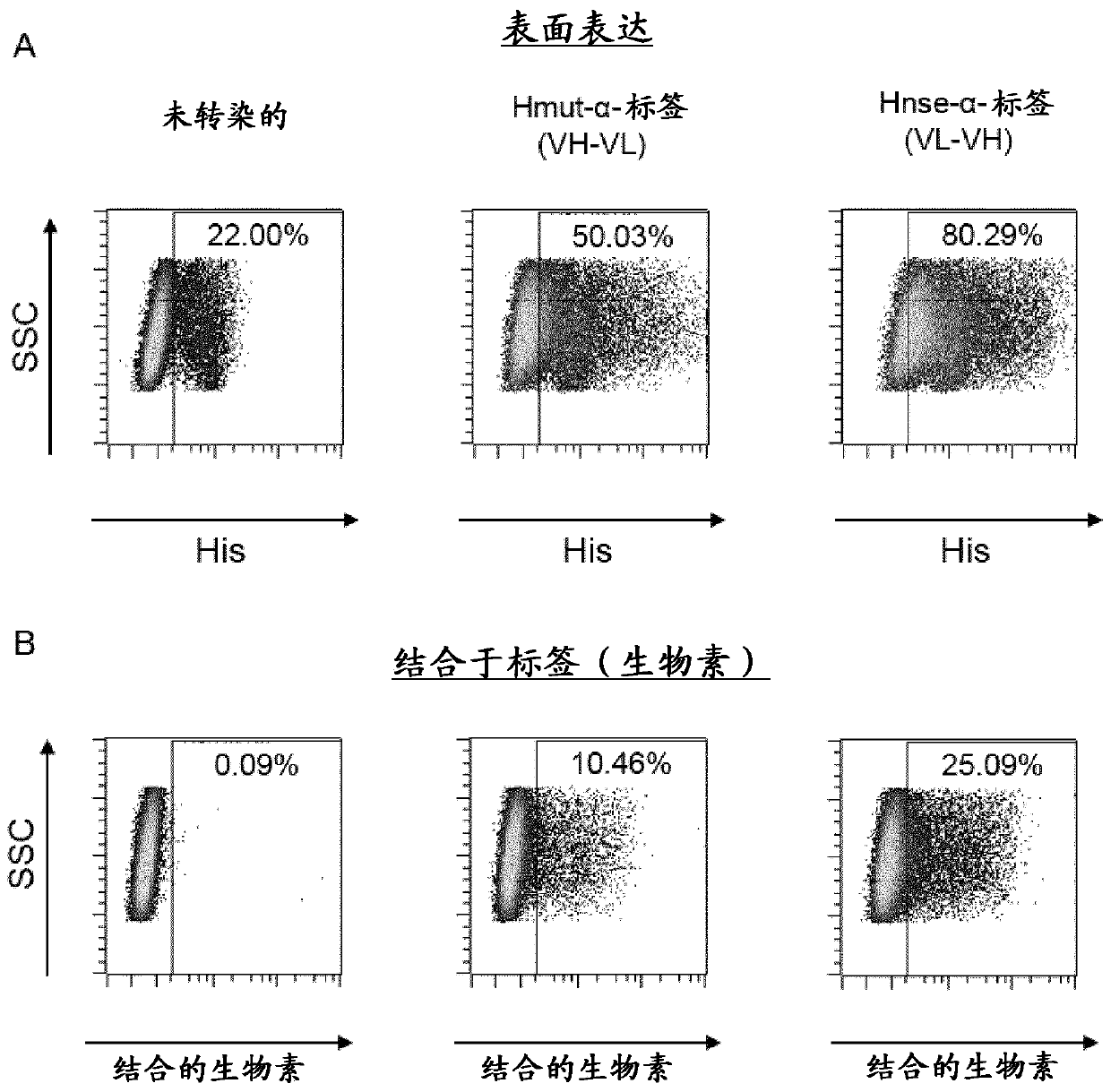
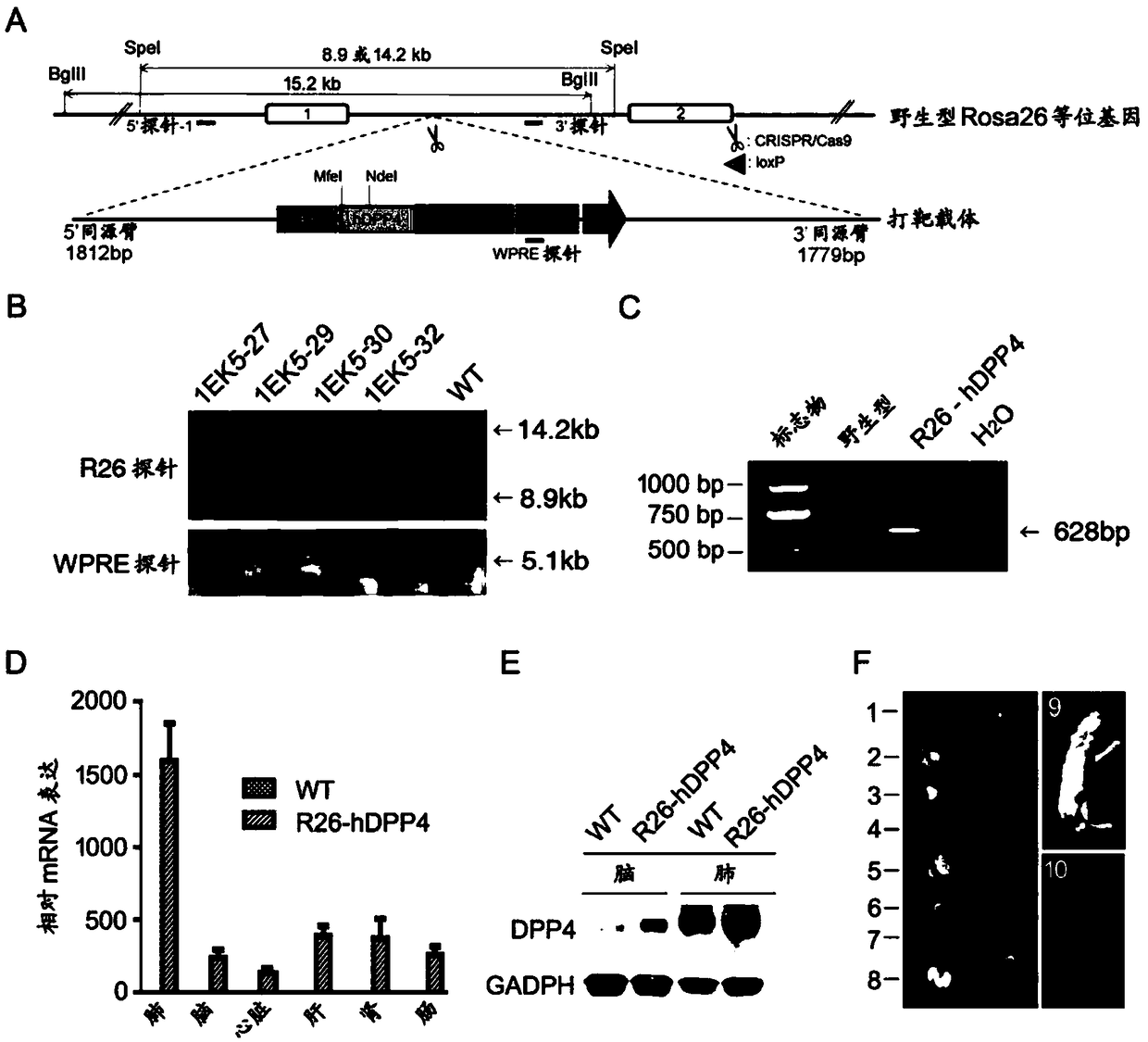
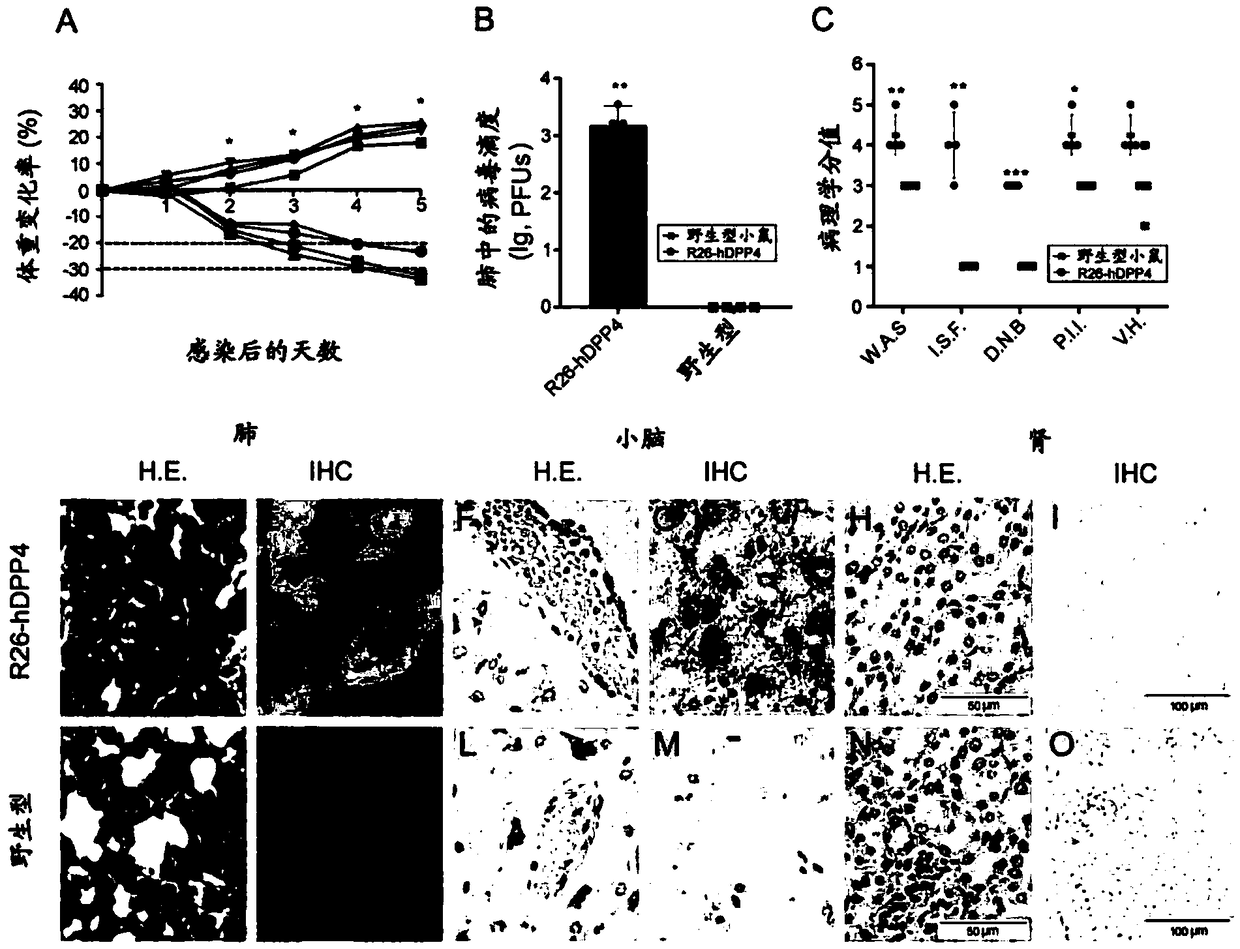
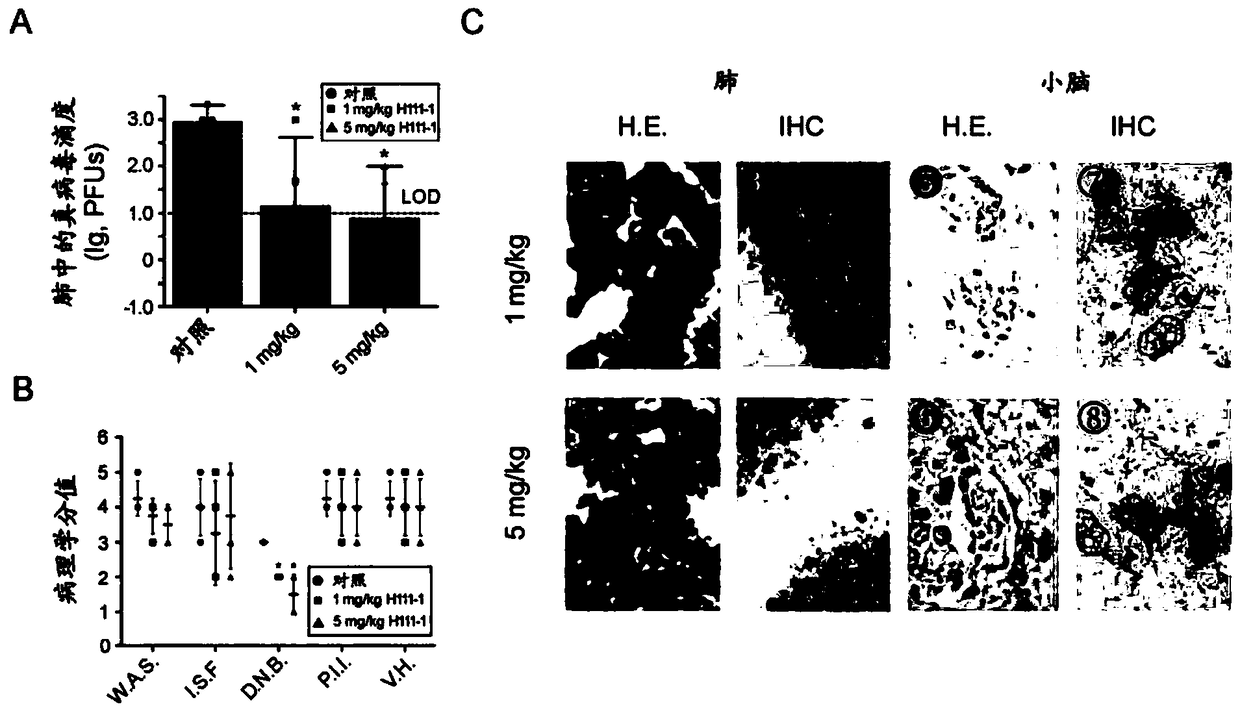
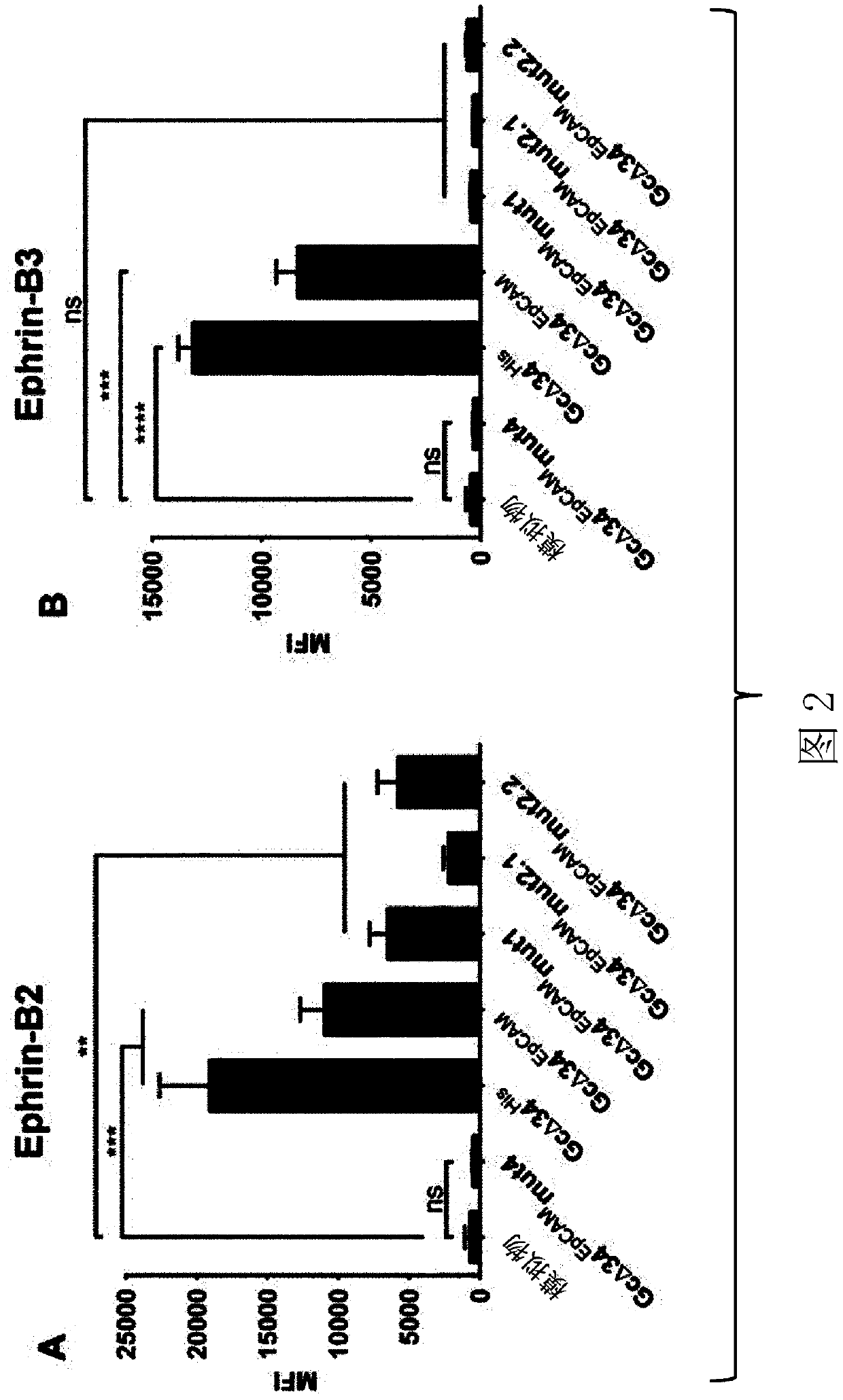
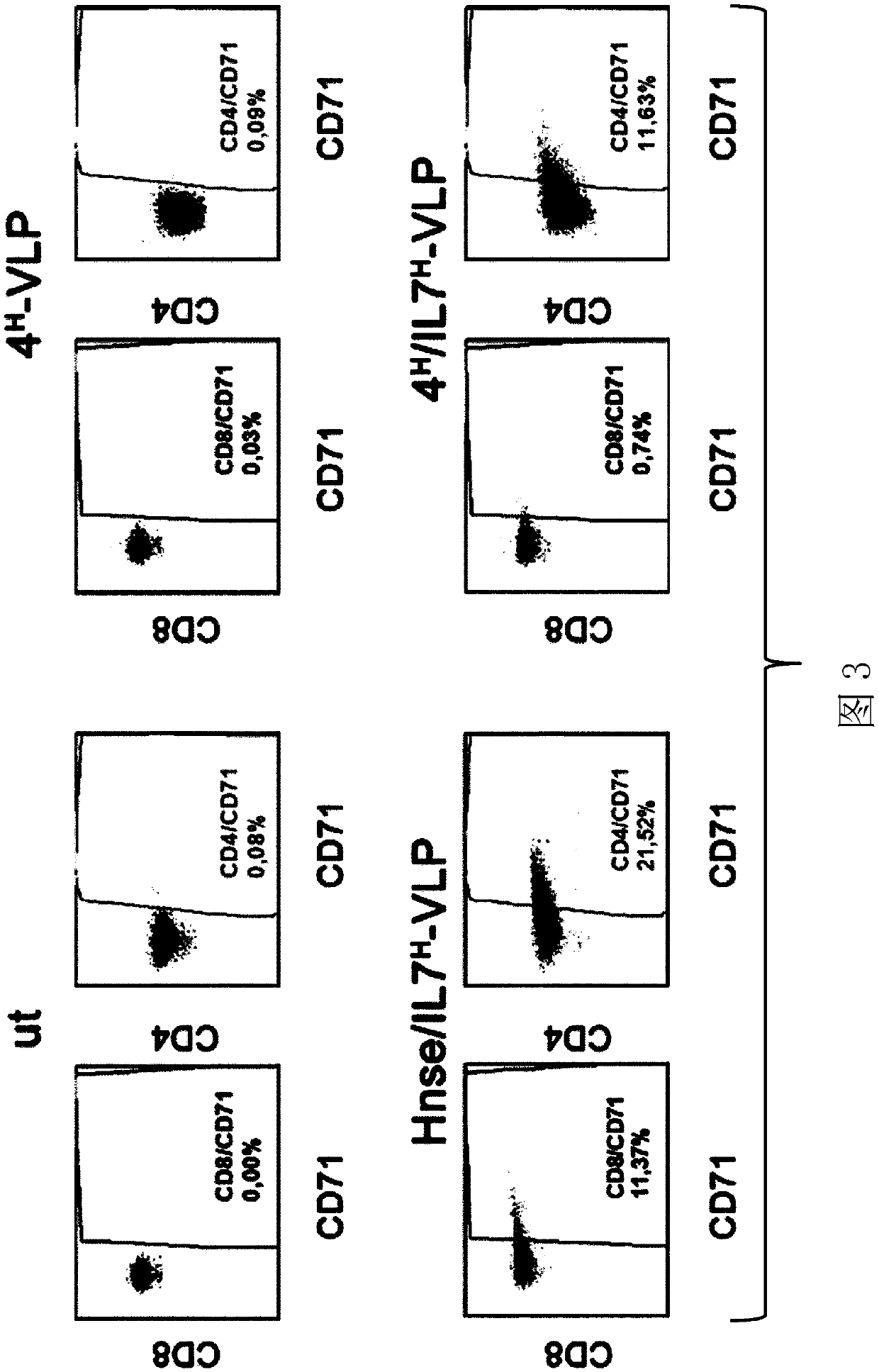
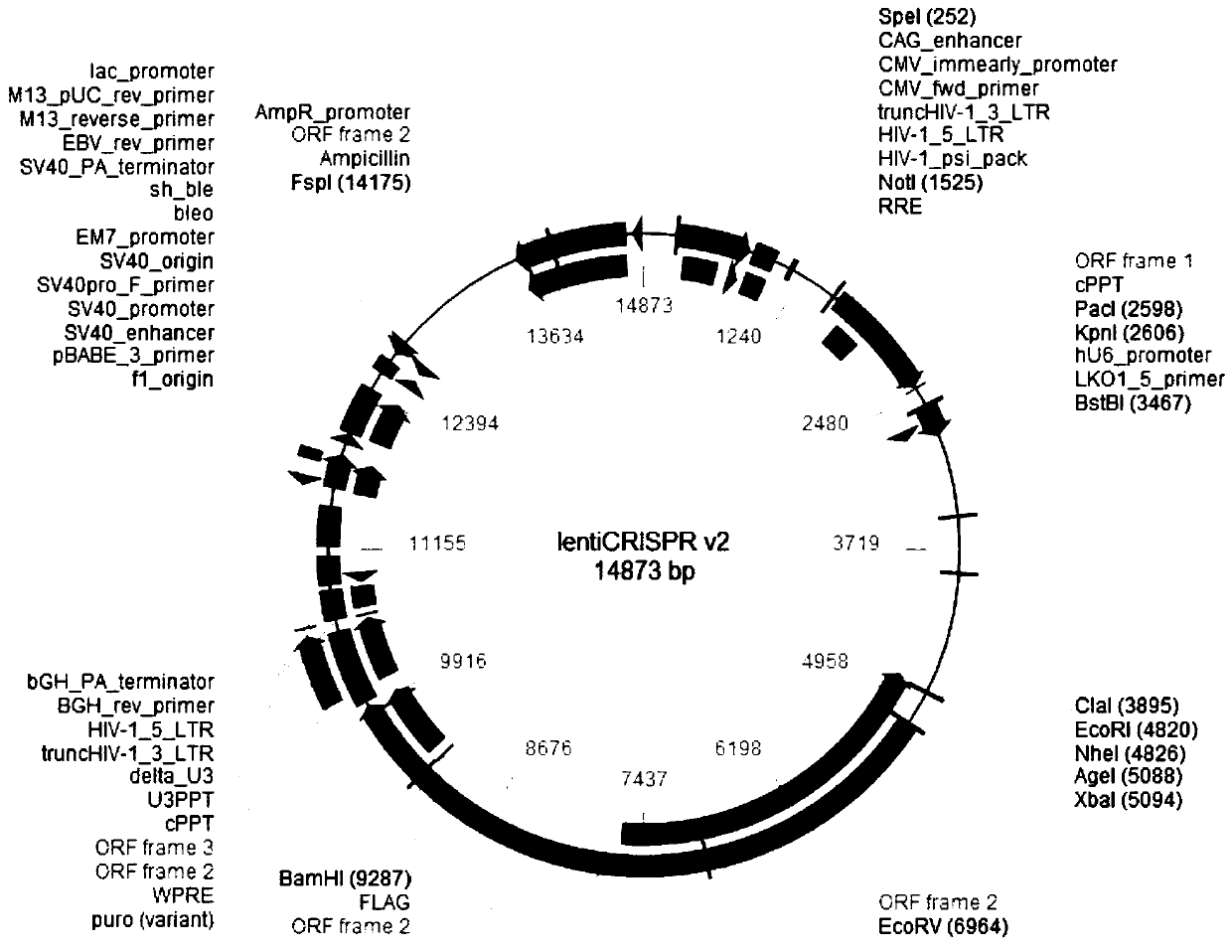
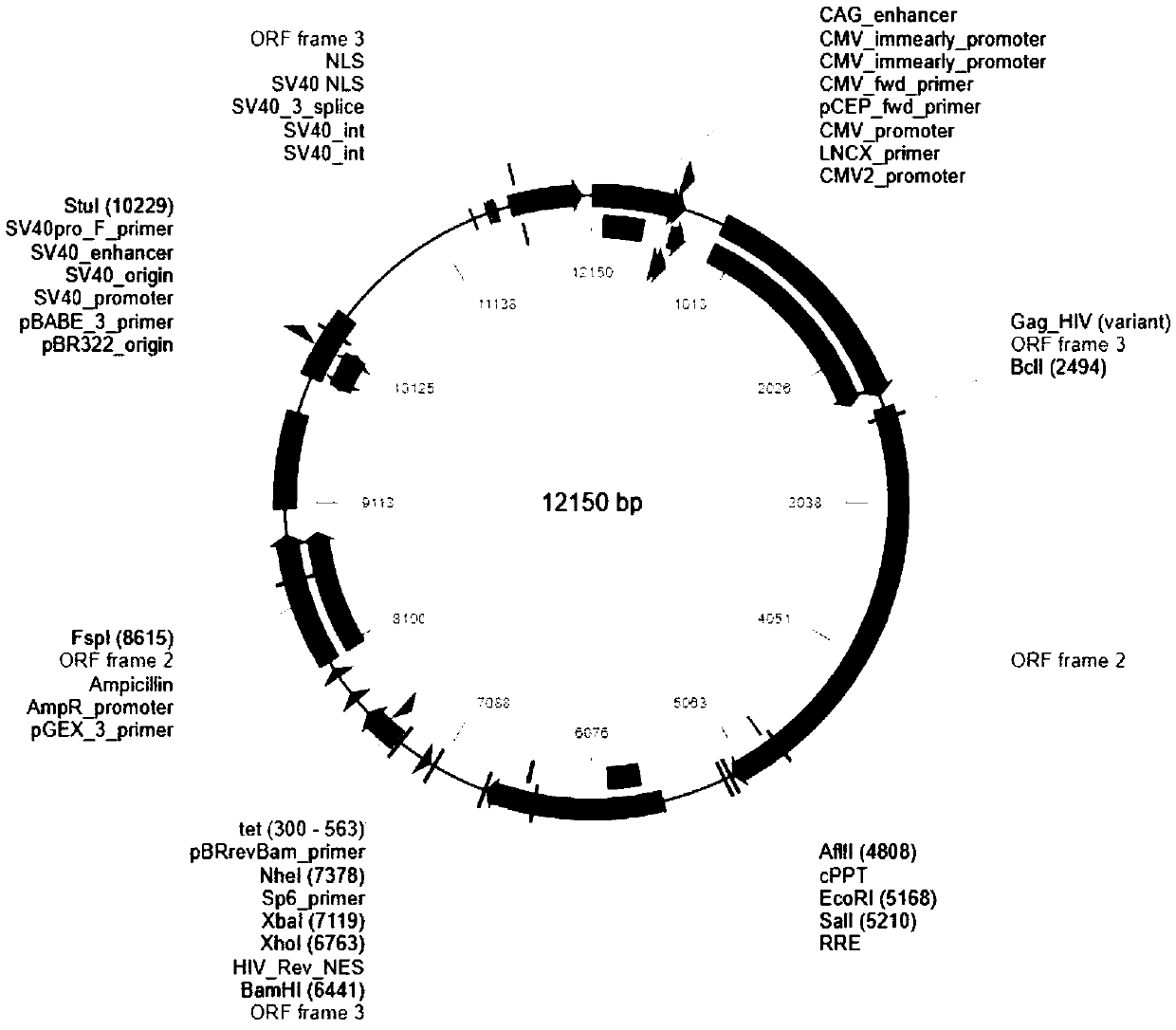
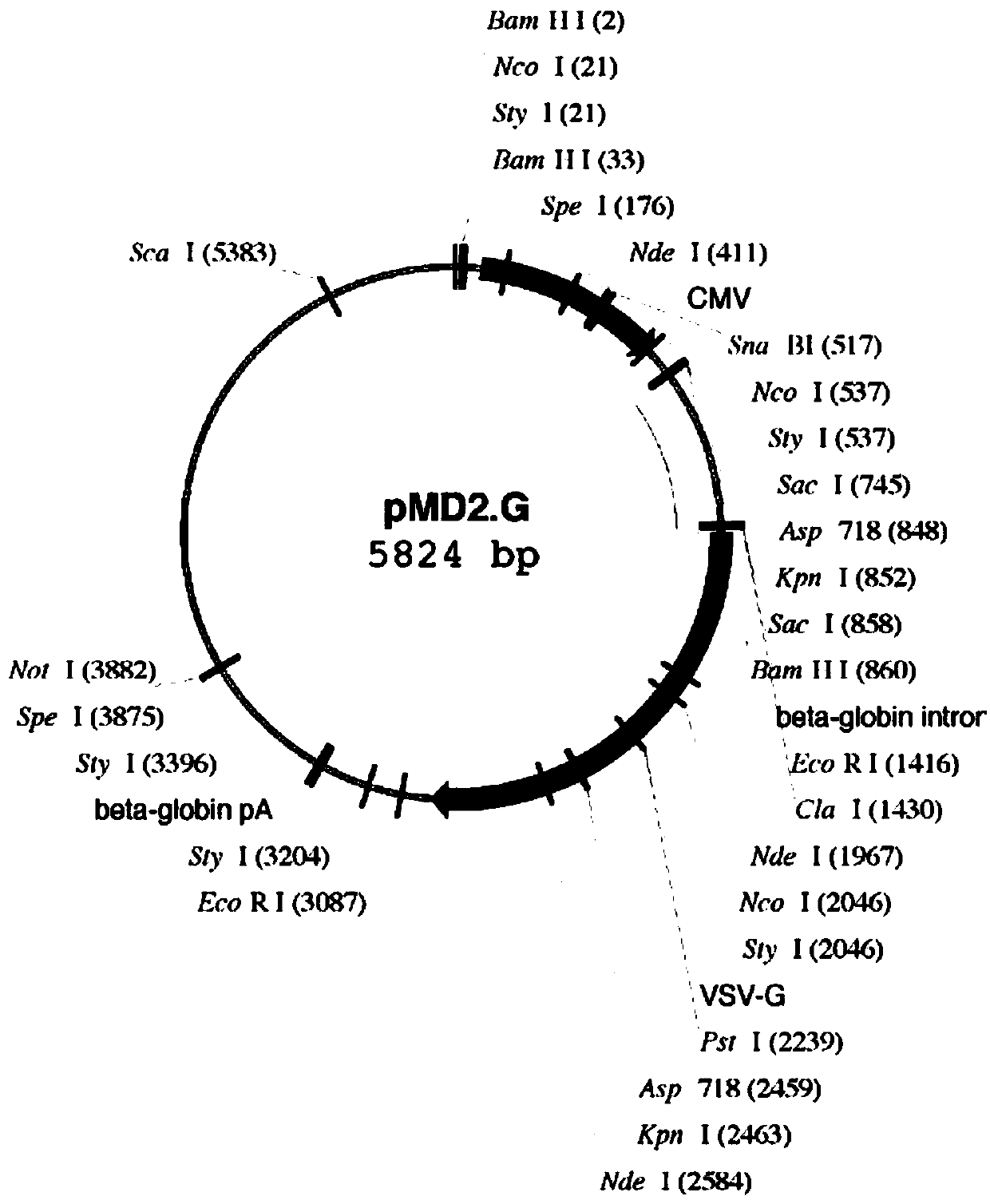
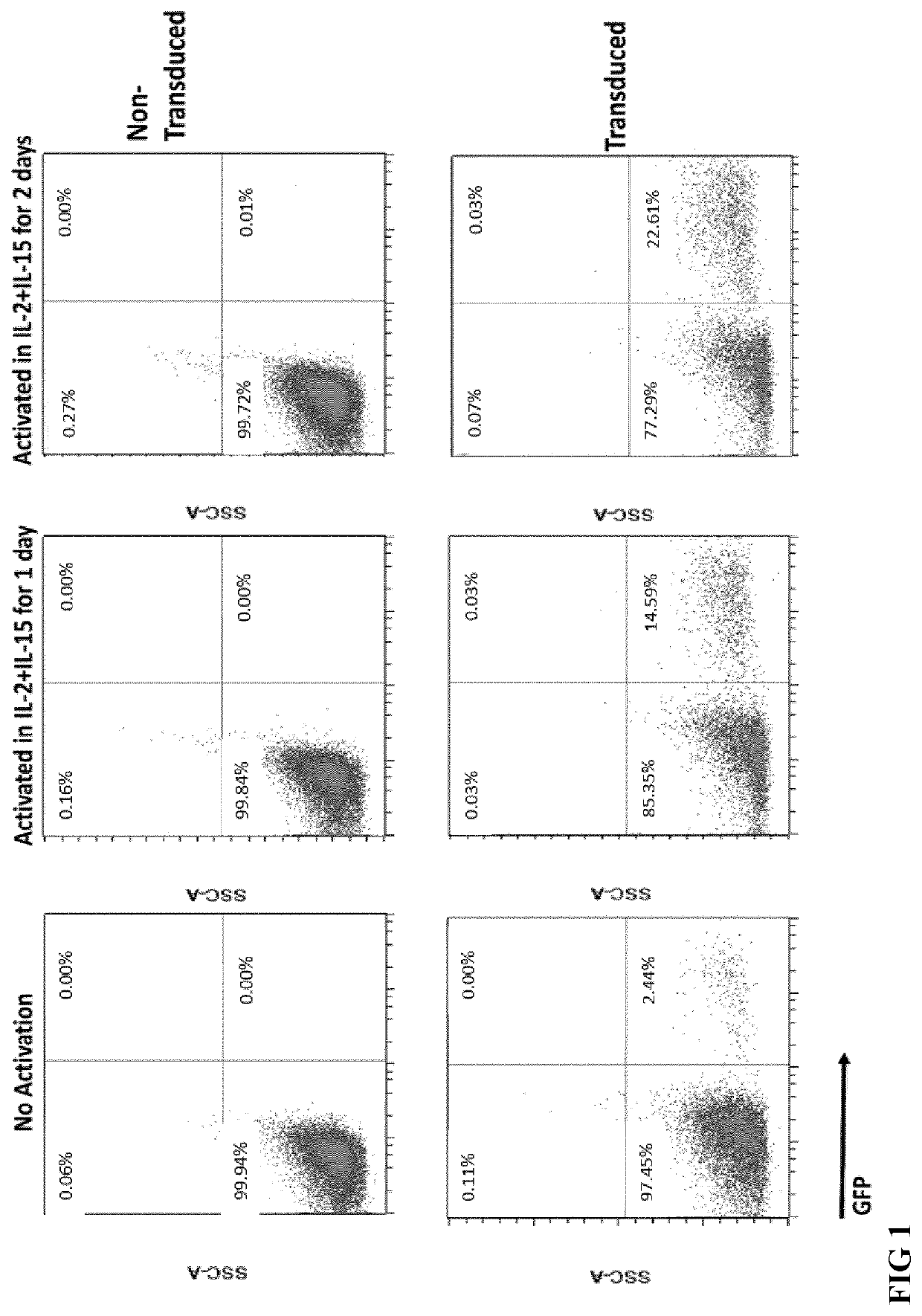
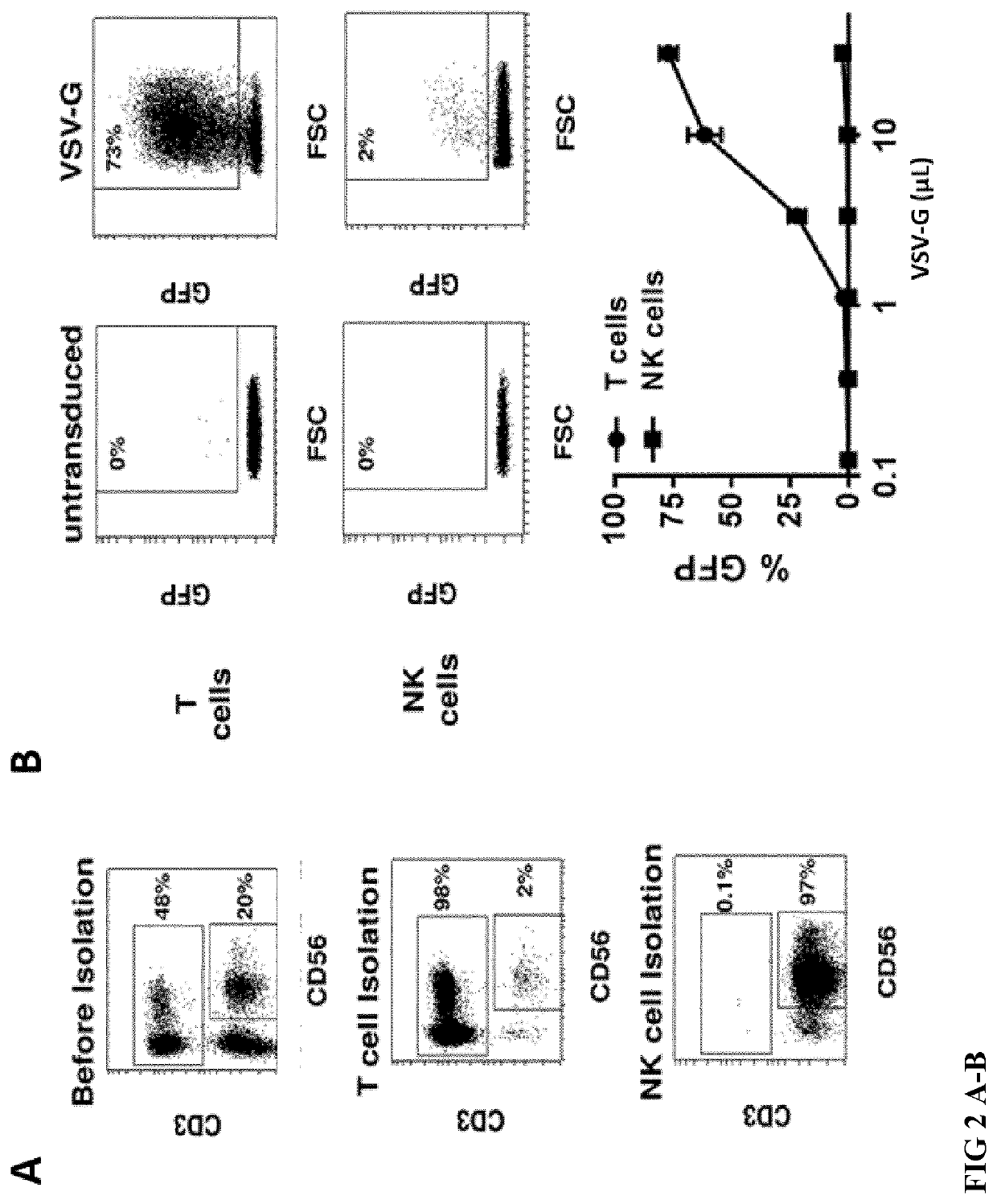
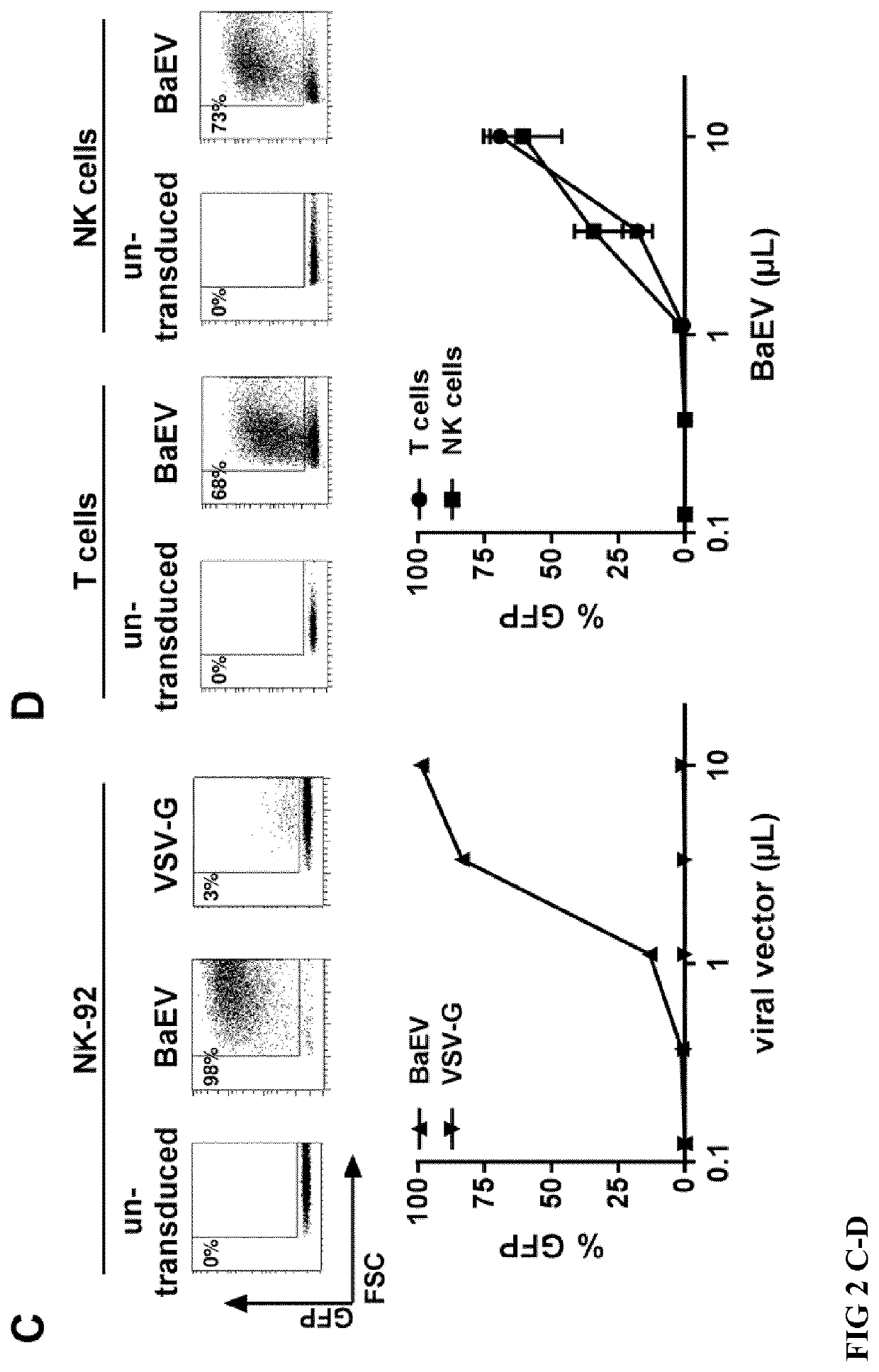
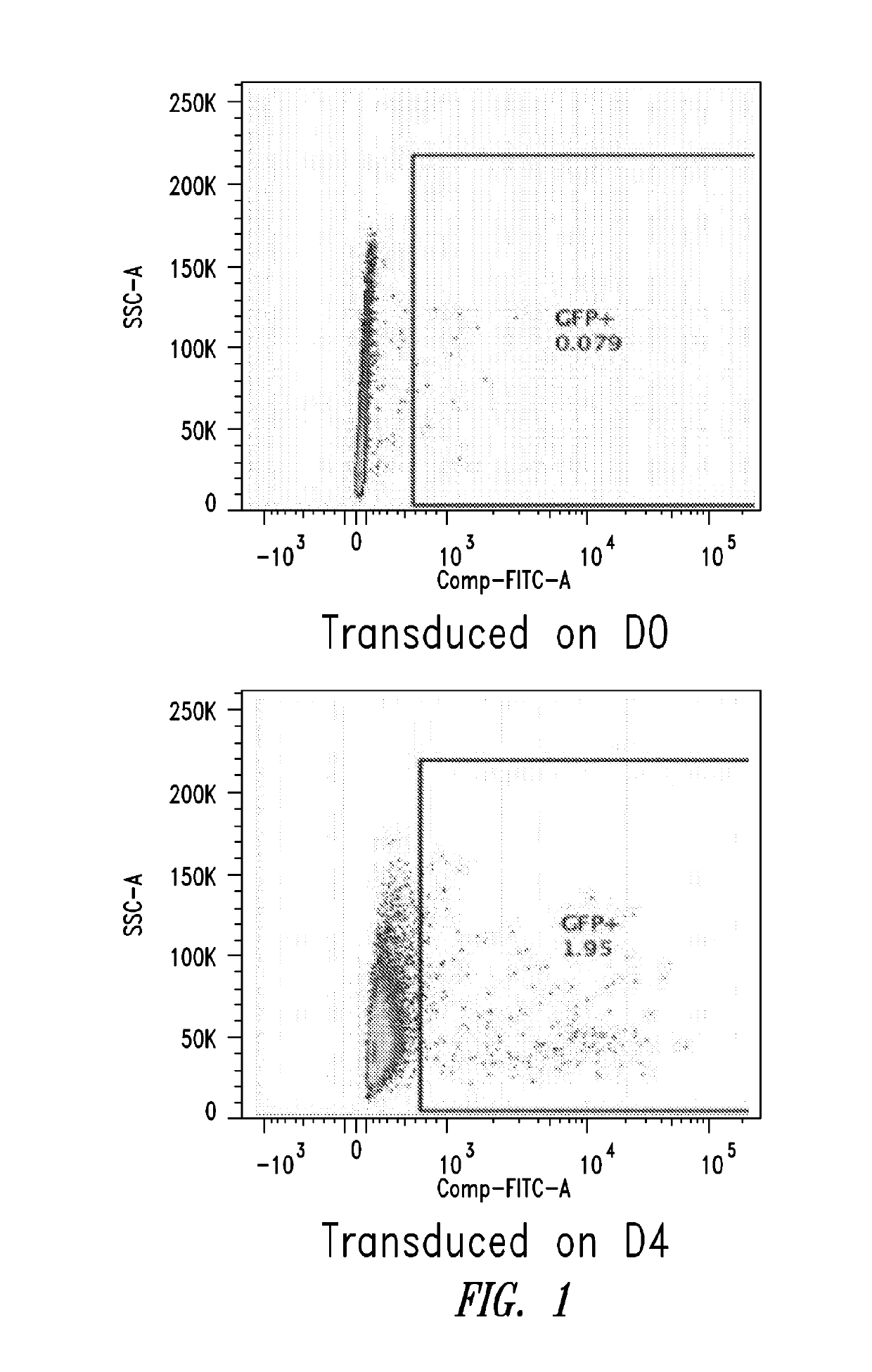
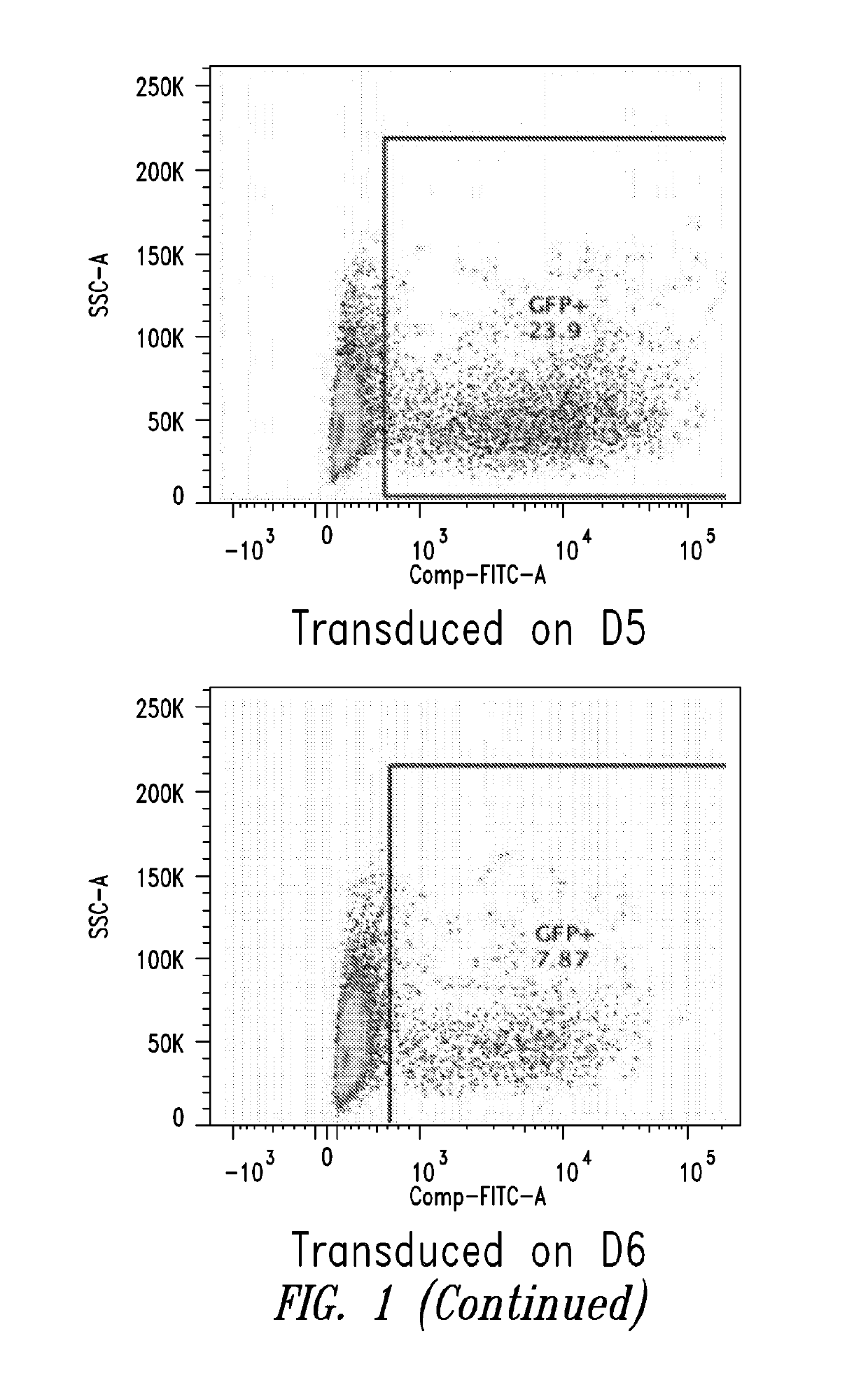
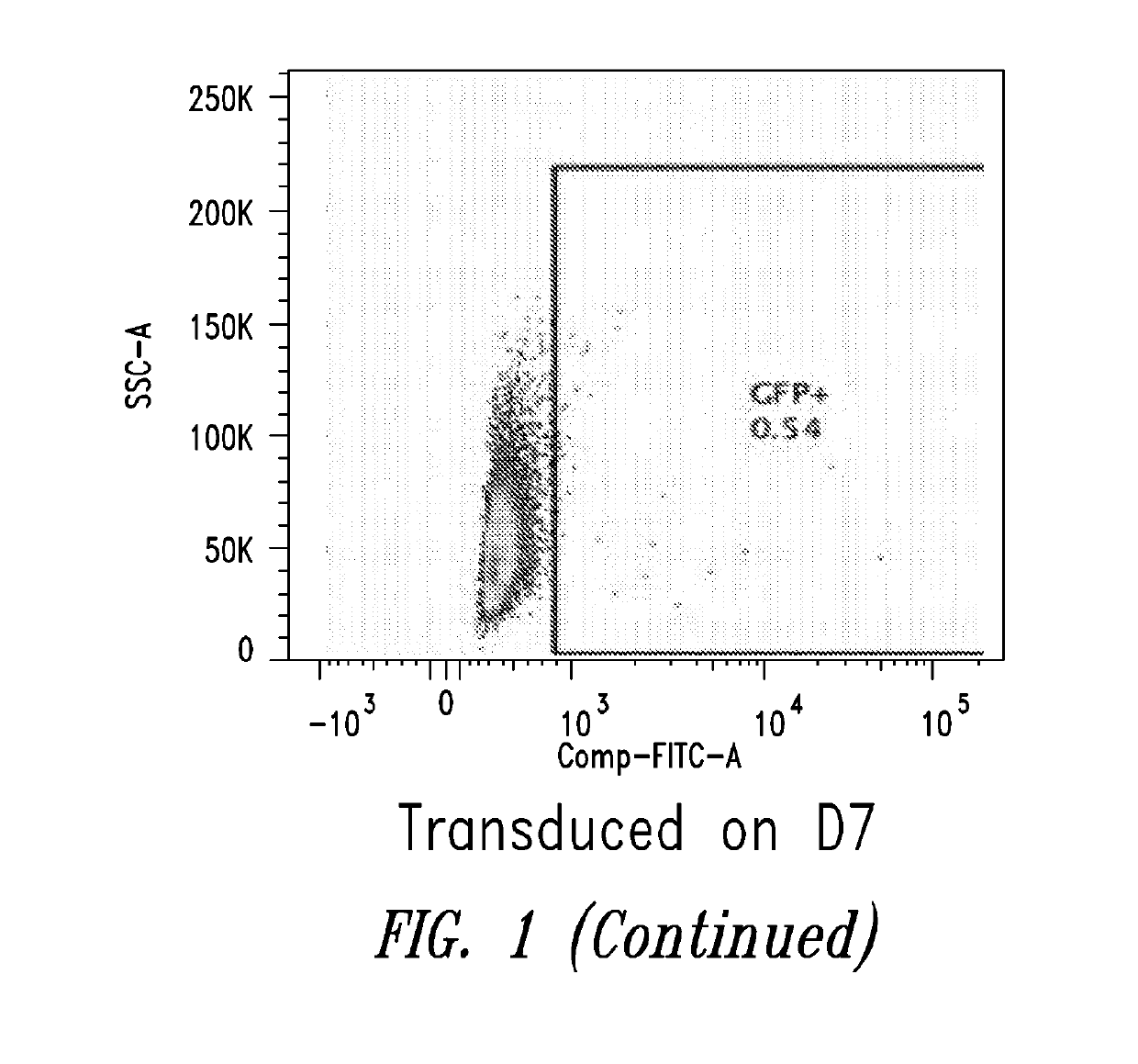
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Pseudotyping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
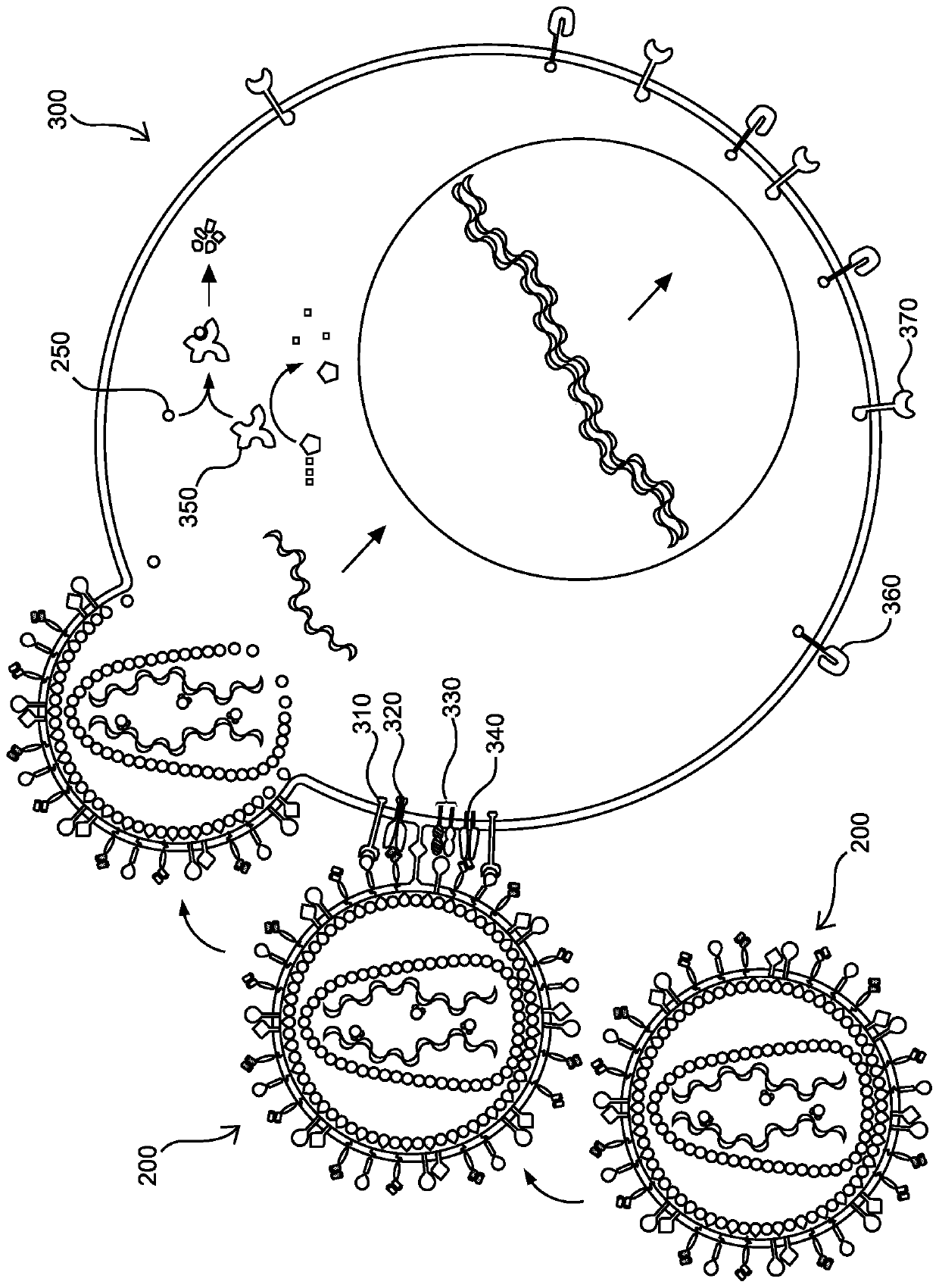
Pseudotyping is the process of producing viruses or viral vectors in combination with foreign viral envelope proteins. The result is a pseudotyped virus particle. With this method, the foreign viral envelope proteins can be used to alter host tropism or an increased/decreased stability of the virus particles. Pseudotyped particles do not carry the genetic material to produce additional viral envelope proteins, so the phenotypic changes cannot be passed on to progeny viral particles.
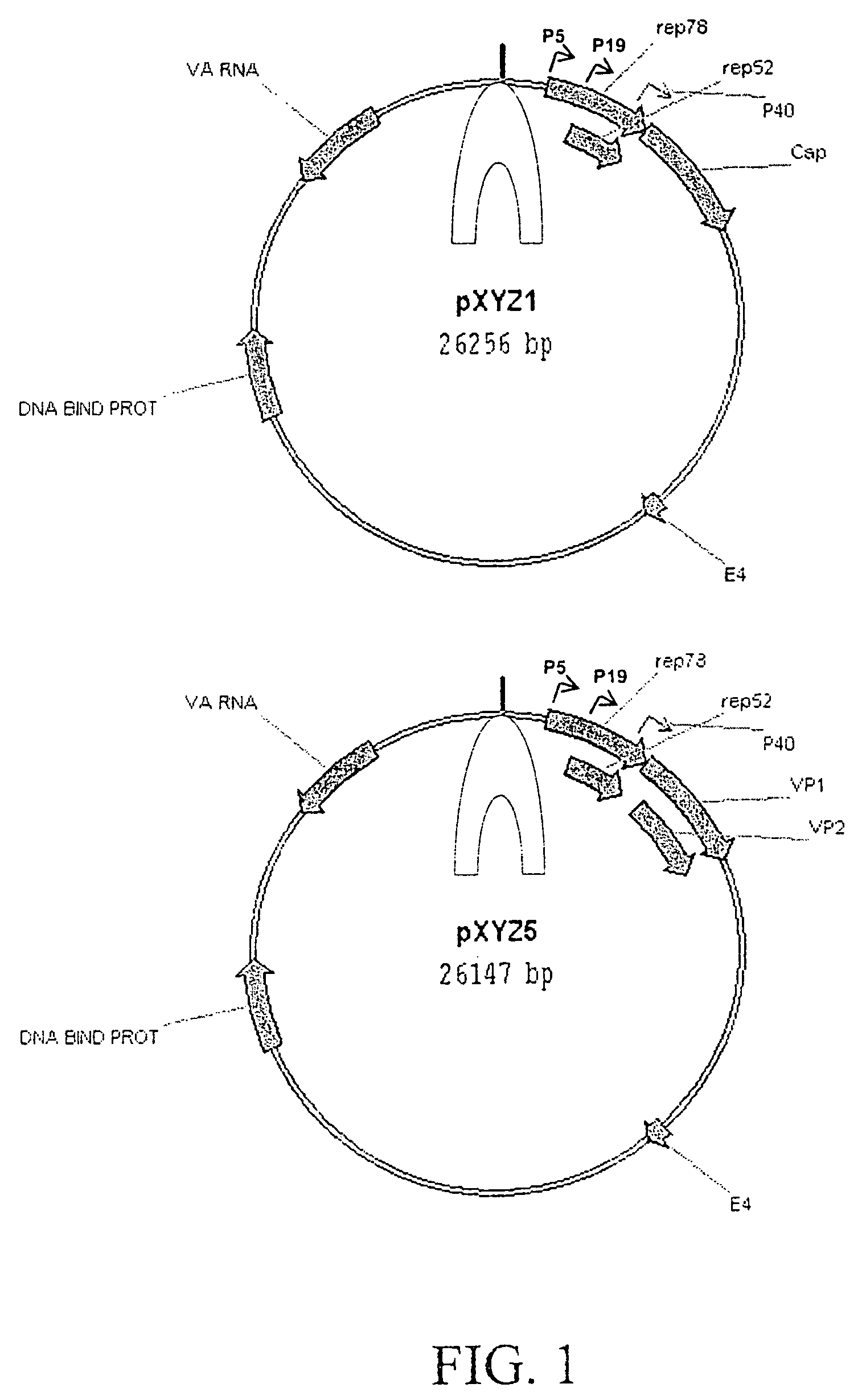
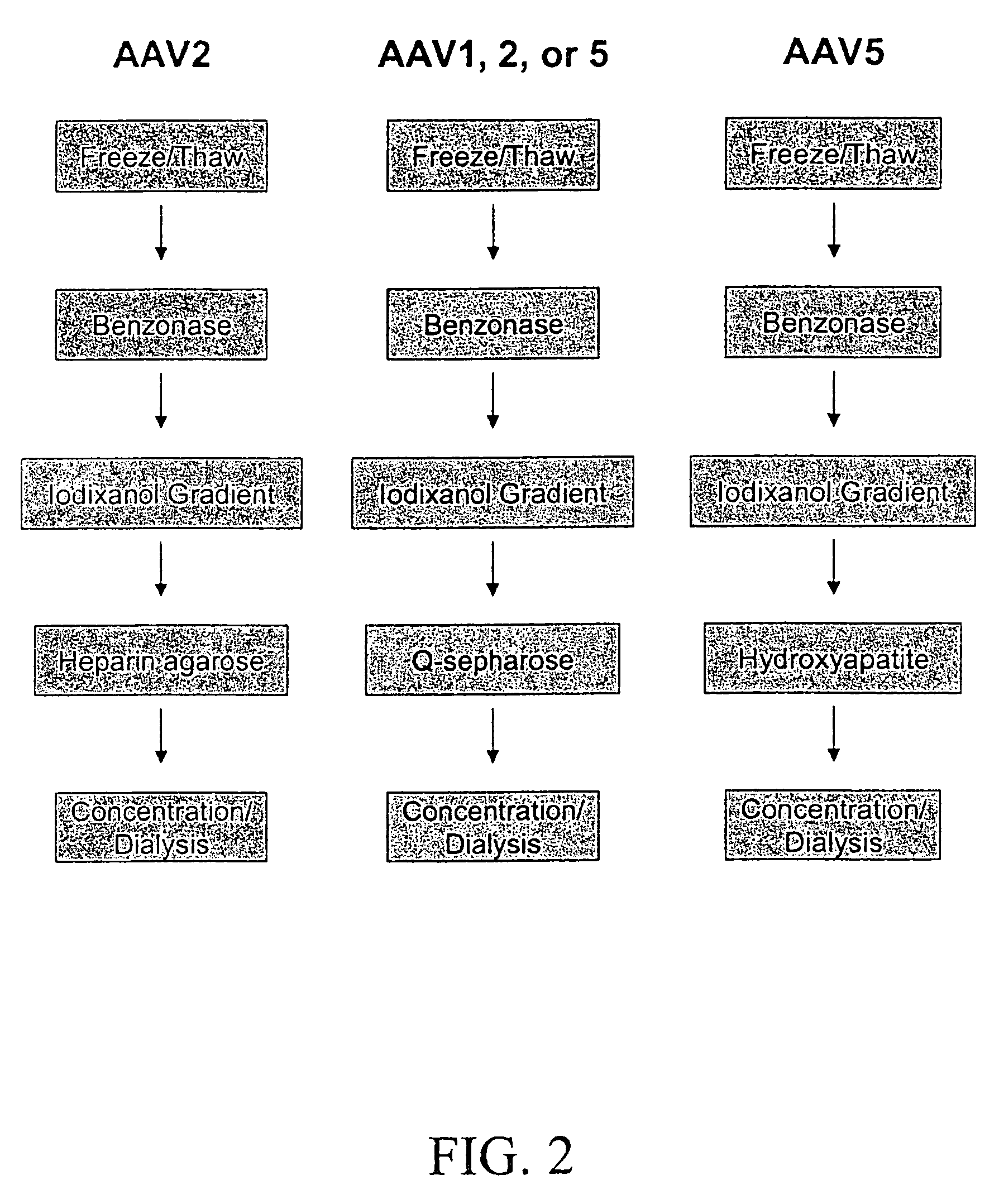
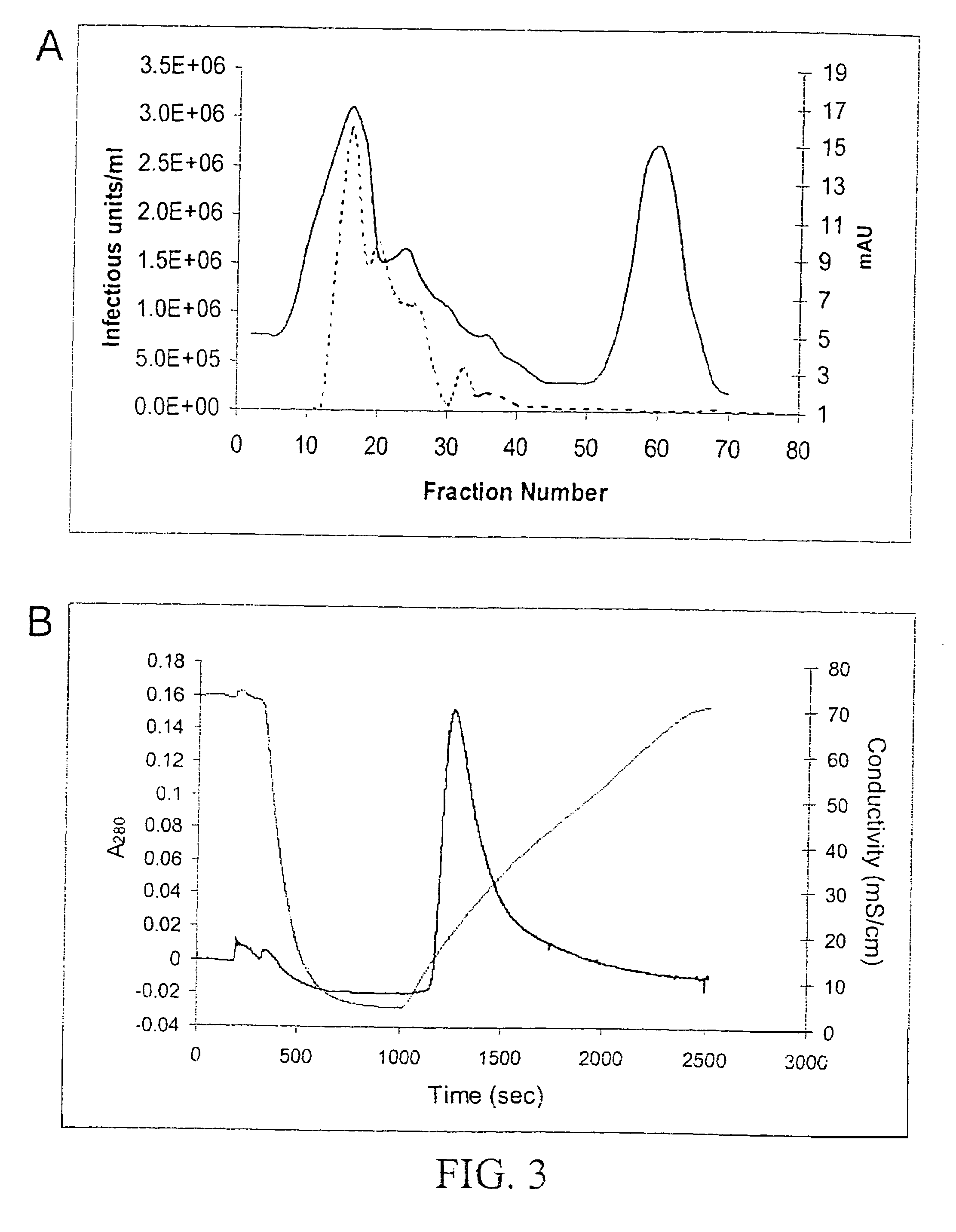
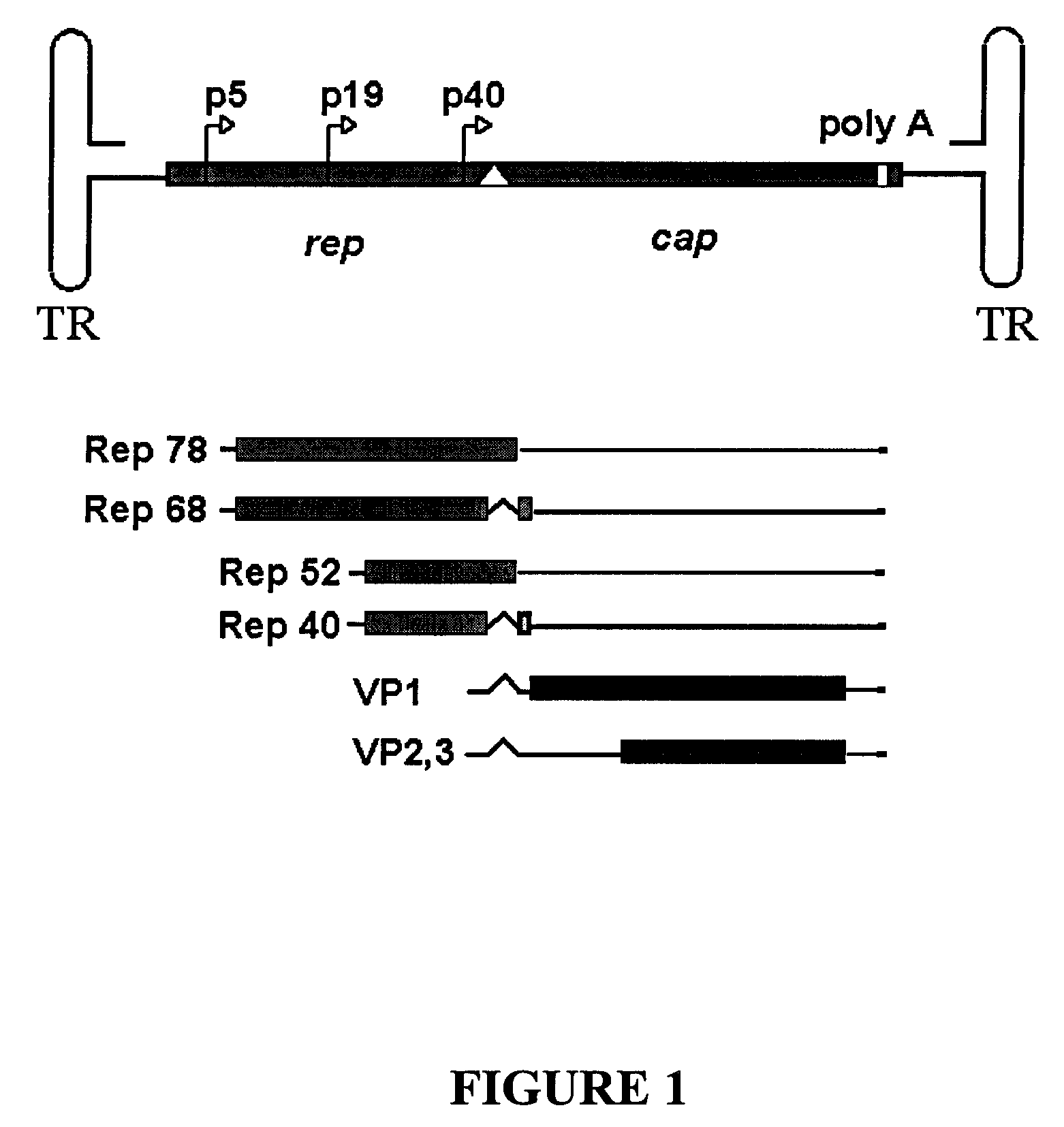
Production of pseudotyped recombinant AAV virions
InactiveUS7094604B2Highly purified and concentratedEfficient and large-scale productionVectorsSugar derivativesPurification methodsSerotype
Vectors that encode Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Rep and Cap proteins of different serotypes and Adenovirus transcription products that provide helper functions were used to produce pseudotyped recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions. Purification methods generated pseudotyped rAAV virion stocks that were 99% pure with titers of 1×1012–1×1013 vector genomes / ml.
Owner:UNIVIRSITY OF FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
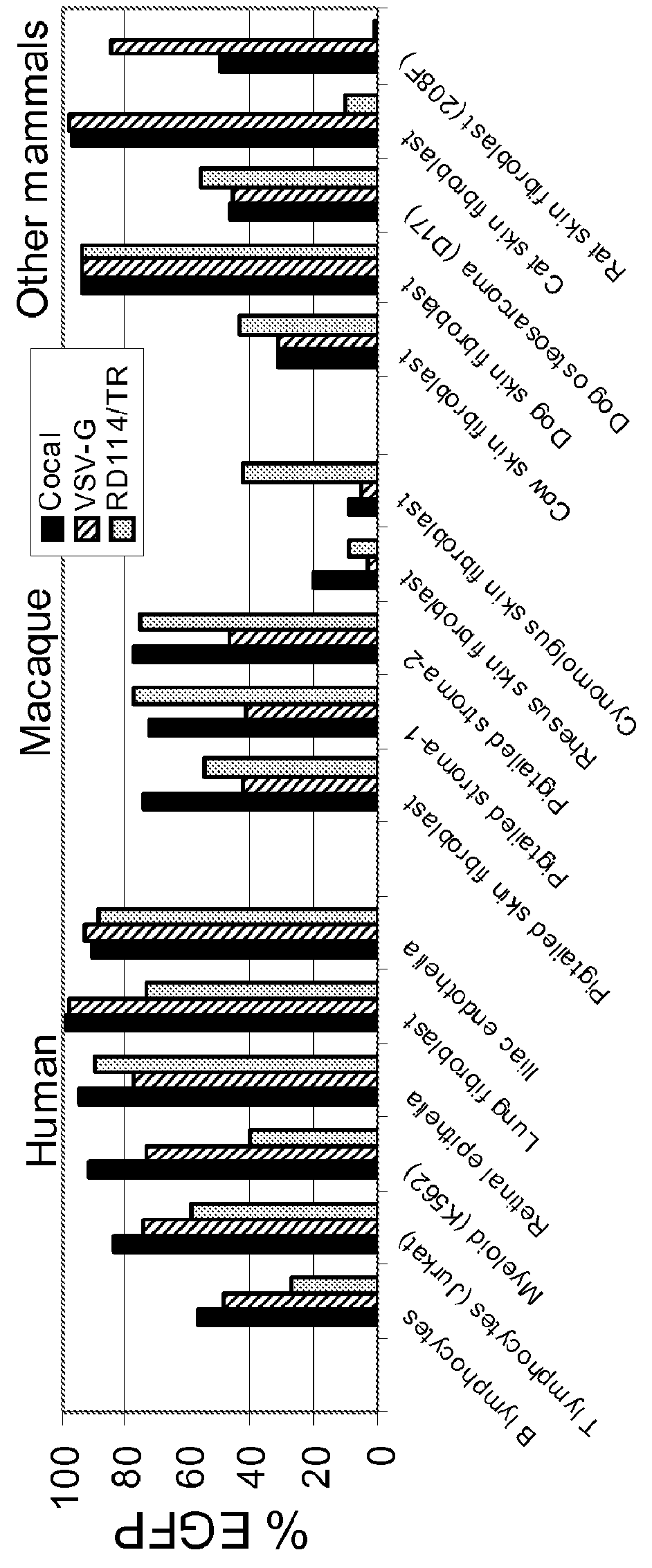
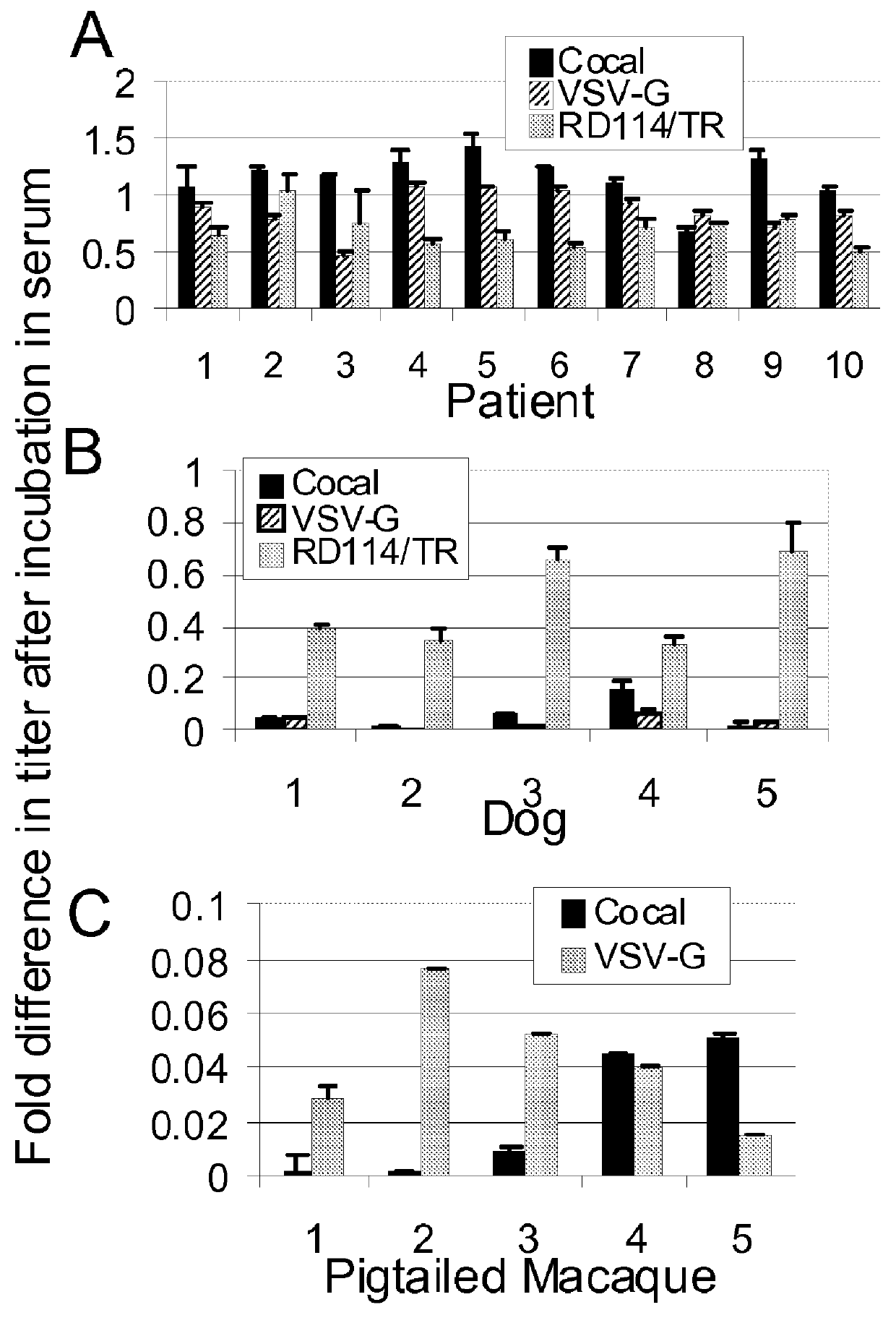
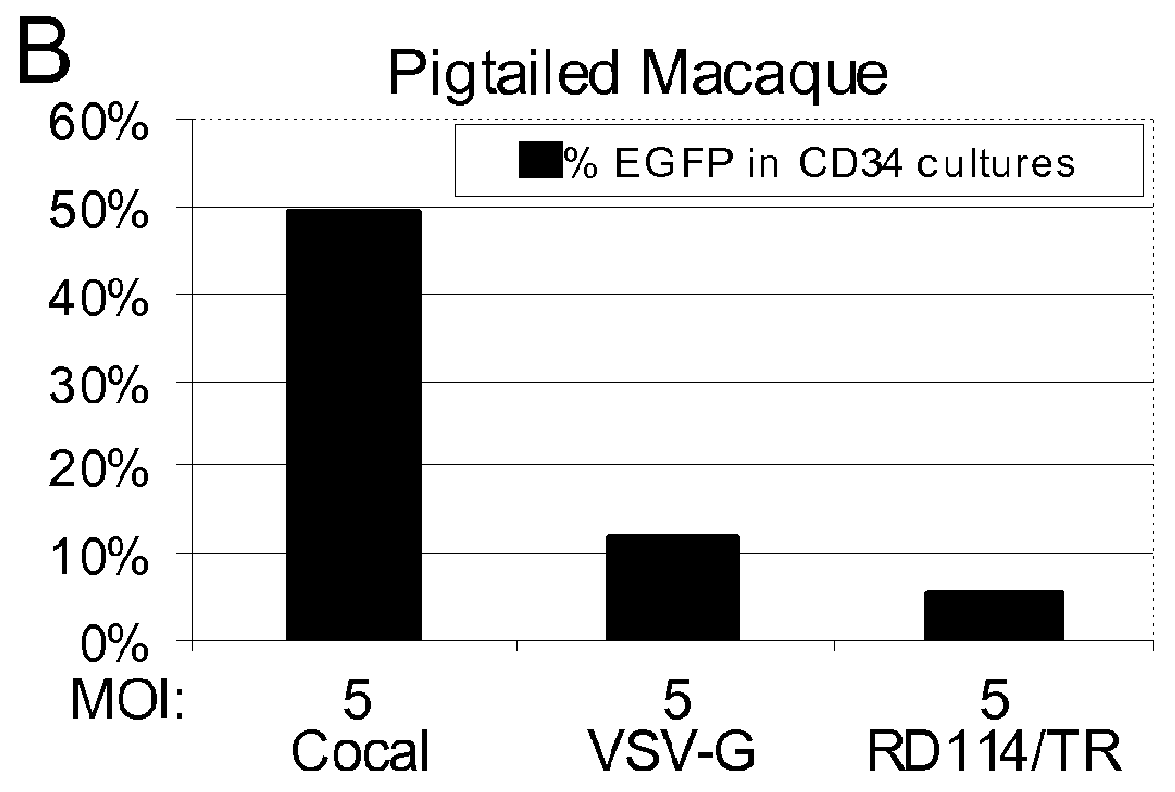
Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors
InactiveUS20120164118A1Increase serum stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideCocal vesiculovirusVirus-Retrovirus
Provided herein are Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors that exhibit high titers, broad species and cell-type tropism, and improved serum stability. Disclosed Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors may be suitably employed for gene therapy applications and, in particular, for the ex vivo and in vivo delivery of a gene of interest to a wide variety of target cells.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
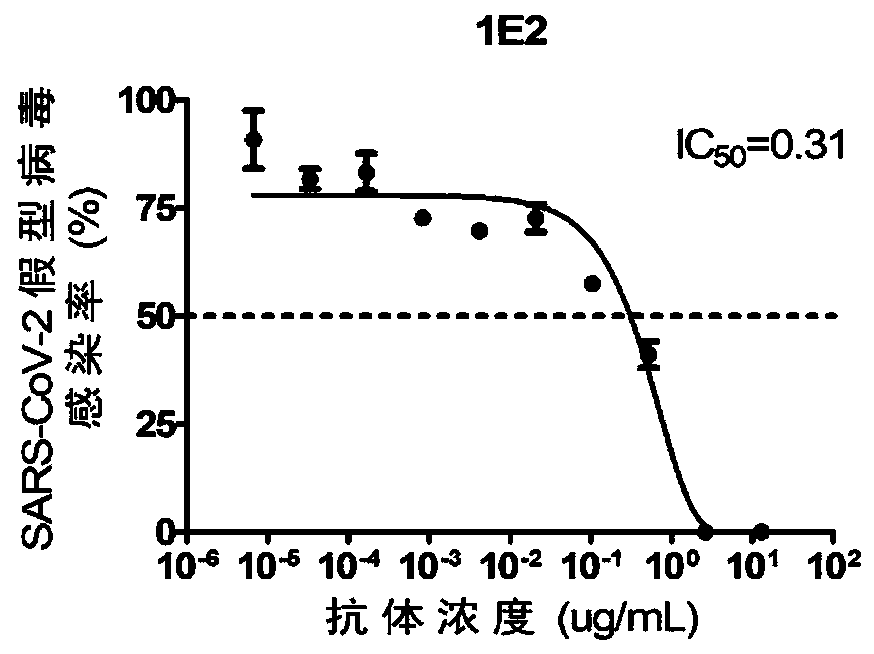
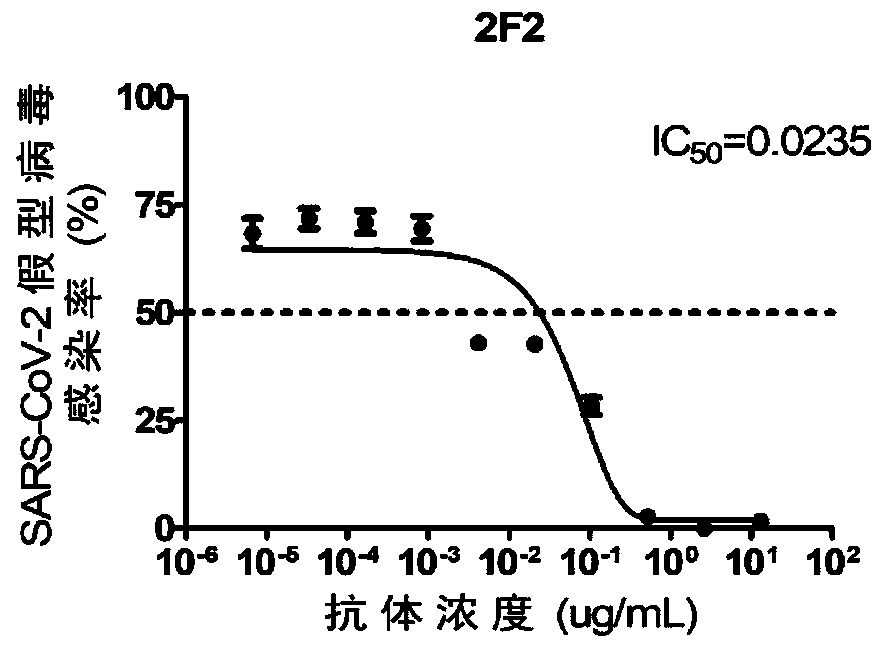
Single-domain antibodies for novel coronavirus and application of single-domain antibodies
ActiveCN111303279AHigh affinityAnd high activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenReceptor
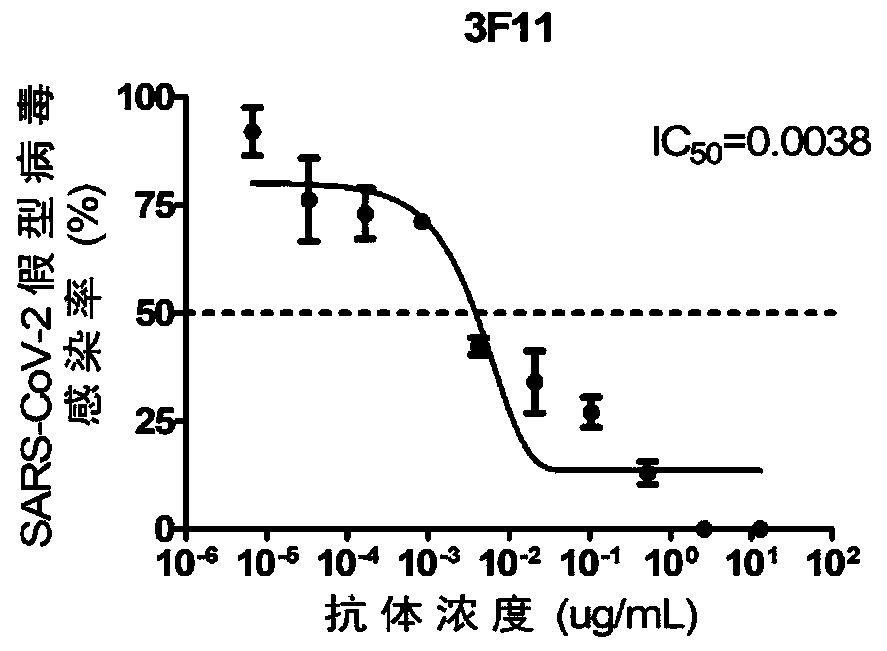
The invention discloses humanized single-domain antibodies for a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and an application of the humanized single-domain antibodies. The invention protects the single-domain antibodies described in any one of SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.5. Experimental results show that the single-domain antibodies provided by the invention have good affinity with receptor binding domain (RBD)antigens and have high neutralization activity on SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus. The humanized single-domain antibodies have important scientific significance and application prospect for prevention and clinical treatment of the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and for development of diagnostic reagents of the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.
Owner:BEIJING KAWIN TECH SHARE HLDG
Production of recombinant AAV virions
ActiveUS7927585B2Simple working processCost effective productionBiocideSugar derivativesYeastVirosome
Stocks of infectious rAAV are generated using yeast strains, bacterial strains, and bacteriophages engineered to express the required AAV proteins and harboring rAAV vector sequences. Stocks of rAAV virions of all serotypes and pseudotypes can be generated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells using the methods described herein.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Modified baculovirus expression system for production of pseudotyped rAAV vector
InactiveUS20060166363A1Reduce lossesEfficient and high productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesBaculovirus expressionHelper virus
The invention provides modifications to a baculovirus-based recombinant adeno associated virus (AAV) system including enhancement of the helper virus stability and construction of novel baculovirus vectors for rAAV pseudotyping. The modified system extends the flexibility of rAAV vector production and promotes the utility of AAV as, a clinically applicable gene therapy vector.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Antiviral agents and vaccines against influenza
InactiveUS20090208531A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsHemagglutininPrime boost
These vaccines target H5N1, H1, H3 and other subtypes of influenza and are designed to elicit neutralizing antibodies, as well as cellular immunity. The DNA vaccines express hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleoprotein (NP) proteins from influenza which are codon optimized and / or contain modifications to protease cleavage sites of HA which affect the normal function of the protein. Adenoviral constructs expressing the same inserts have been engineered for prime boost strategies. Protein-based vaccines based on protein production from insect or mammalian cells using foldon trimerization stabilization domains with or without cleavage sites to assist in purification of such proteins have been developed. Another embodiment of this invention is the work with HA pseudotyped lentiviral vectors which would be used to screen for neutralizing antibodies in patients and to screen for diagnostic and therapeutic antivirals such as monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Pseudotyping of retroviral vectors, methods for production and use thereof for targeted gene transfer and high throughput screening
ActiveUS20100189690A1Increase in titer and transduction efficiencyHigh transduction efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideSurface markerMorbillivirus
The invention relates to the pseudotyping of retroviral vectors with heterologous envelope proteins derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, genus Morbillivirus, and various uses of the resulting vector particles. The present invention is based on the unexpected and surprising finding that the incorporation of morbillivirus F and H proteins having truncated cytoplasmic tails into lentiviral vector particles, and the complex interaction of these two proteins during cellular fusion, allows for a superior and more effective transduction of cells. Moreover, these pseudotyped vector particles allow the targeted gene transfer into a given cell type of interest by modifying a mutated and truncated H protein with a single-chain antibody or ligand directed against a cell surface marker of the target cell.
Owner:BUNDESREPUBLIK DEUTLAND LETZTVERTRETEN DURCH DEN PRASIDENTEN DES PAUL EHRLICH INSTITUTS
Method for preparing retrovirus vector for gene therapy
InactiveUS6743620B1High recovery rateStably produced at a high titerVectorsSugar derivativesPol genesA-DNA
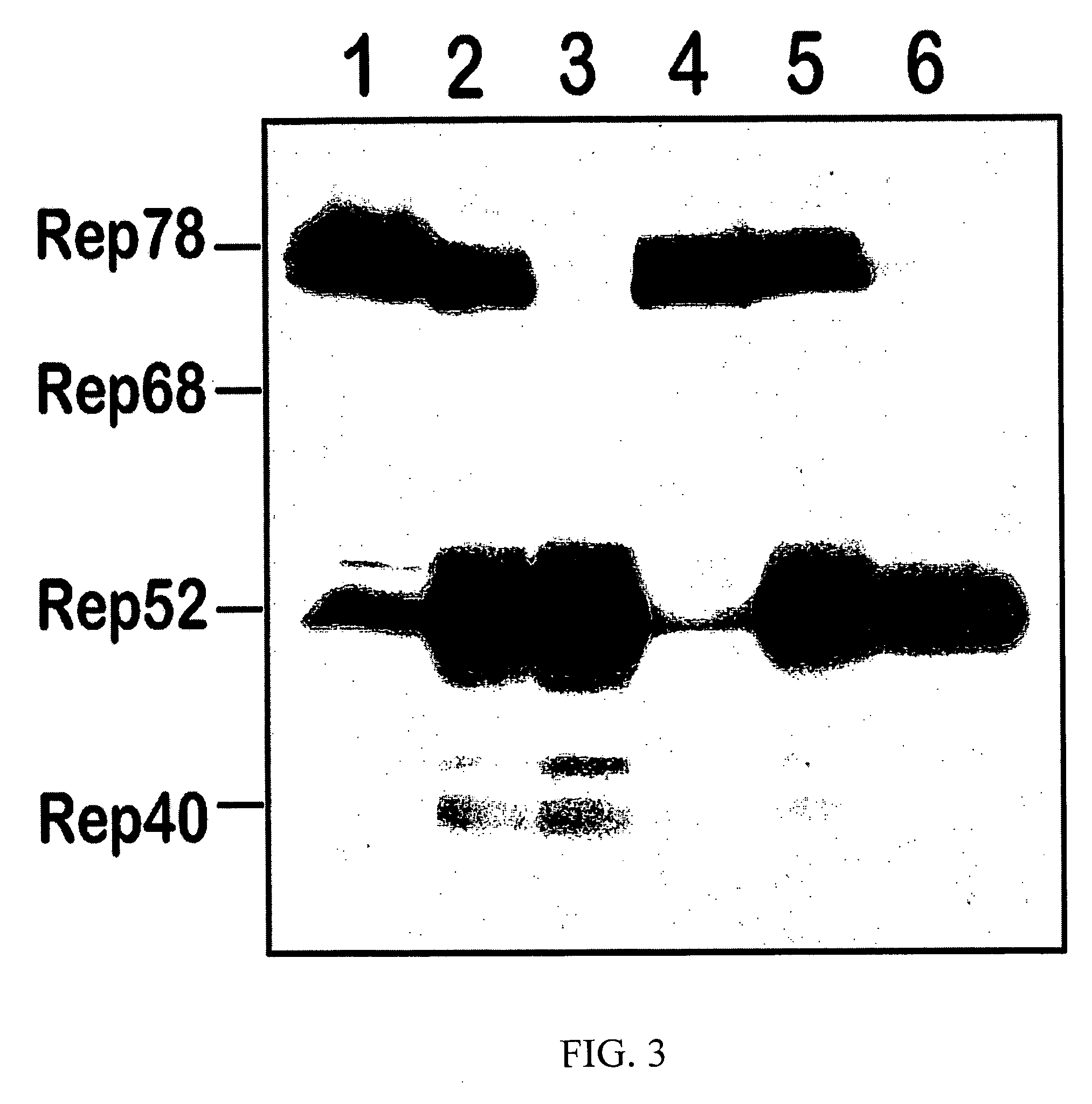
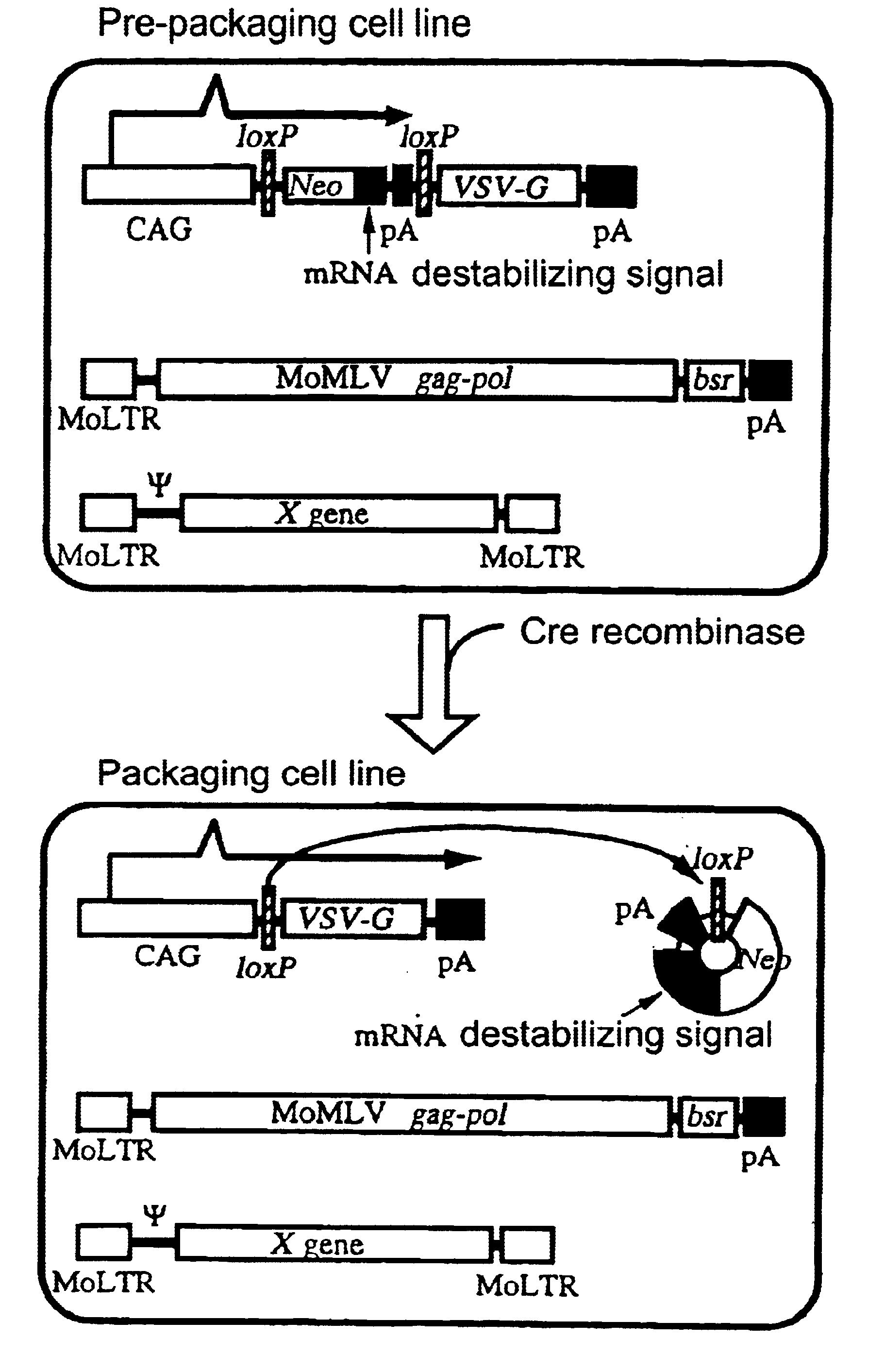
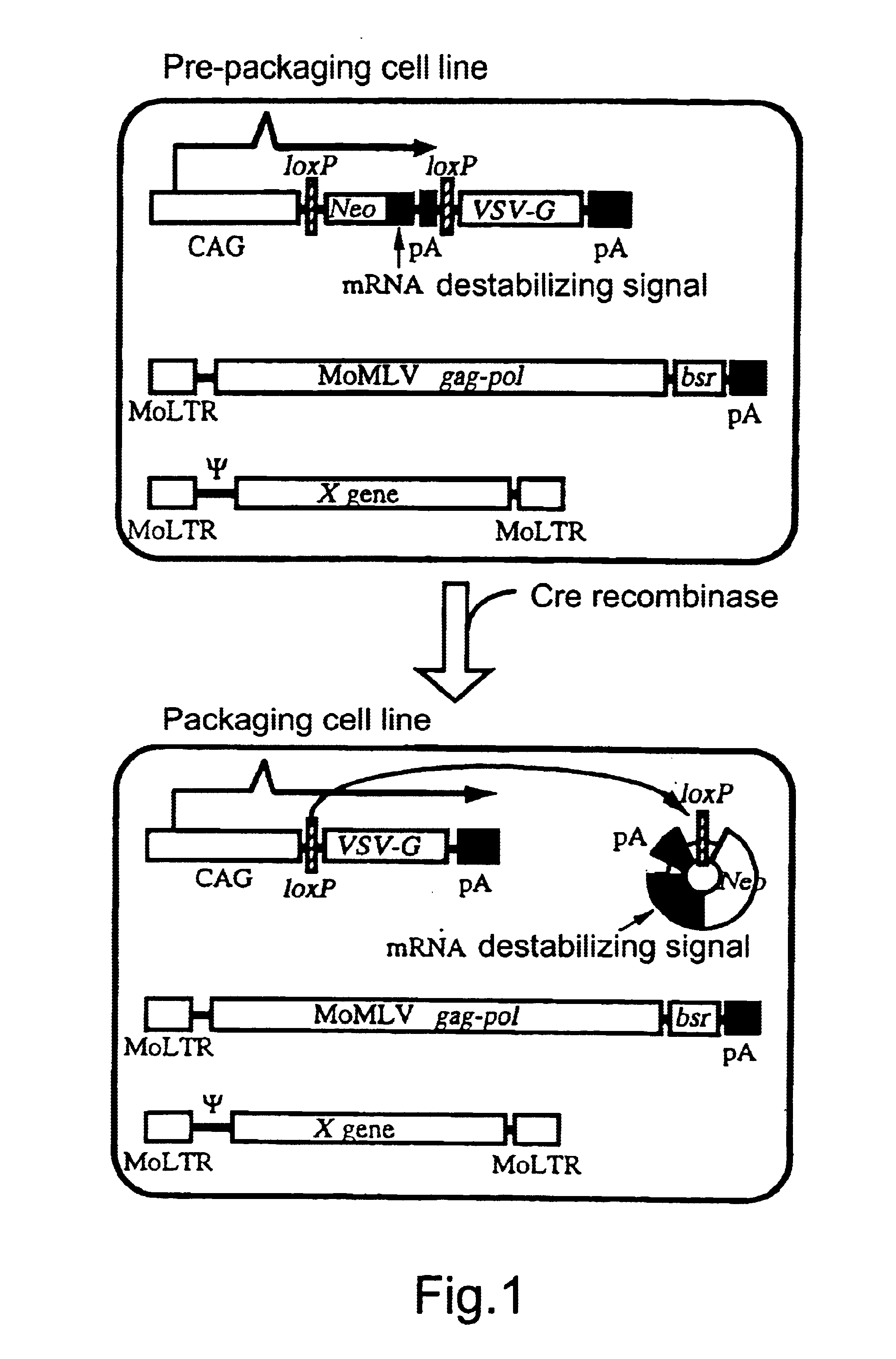
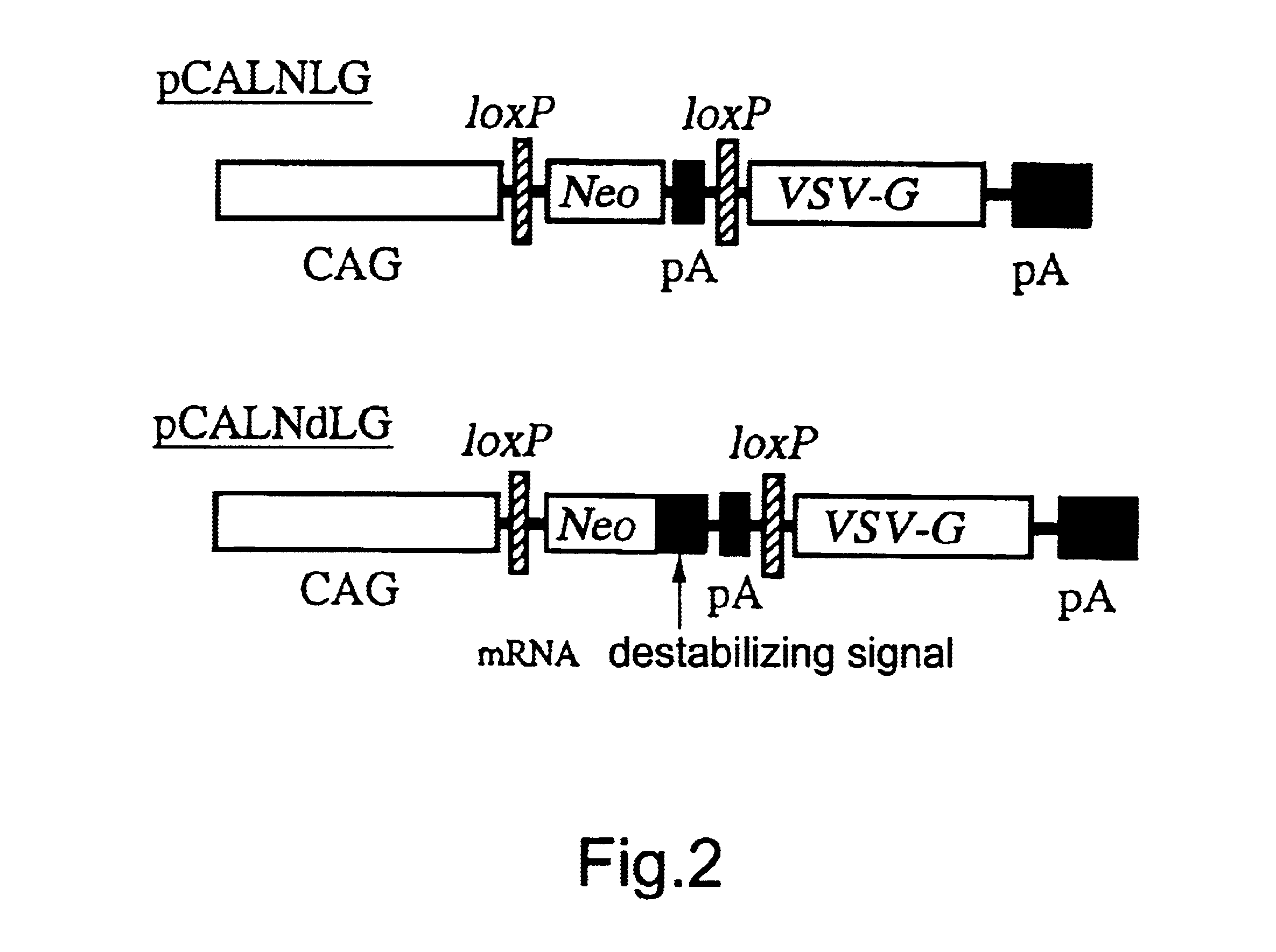
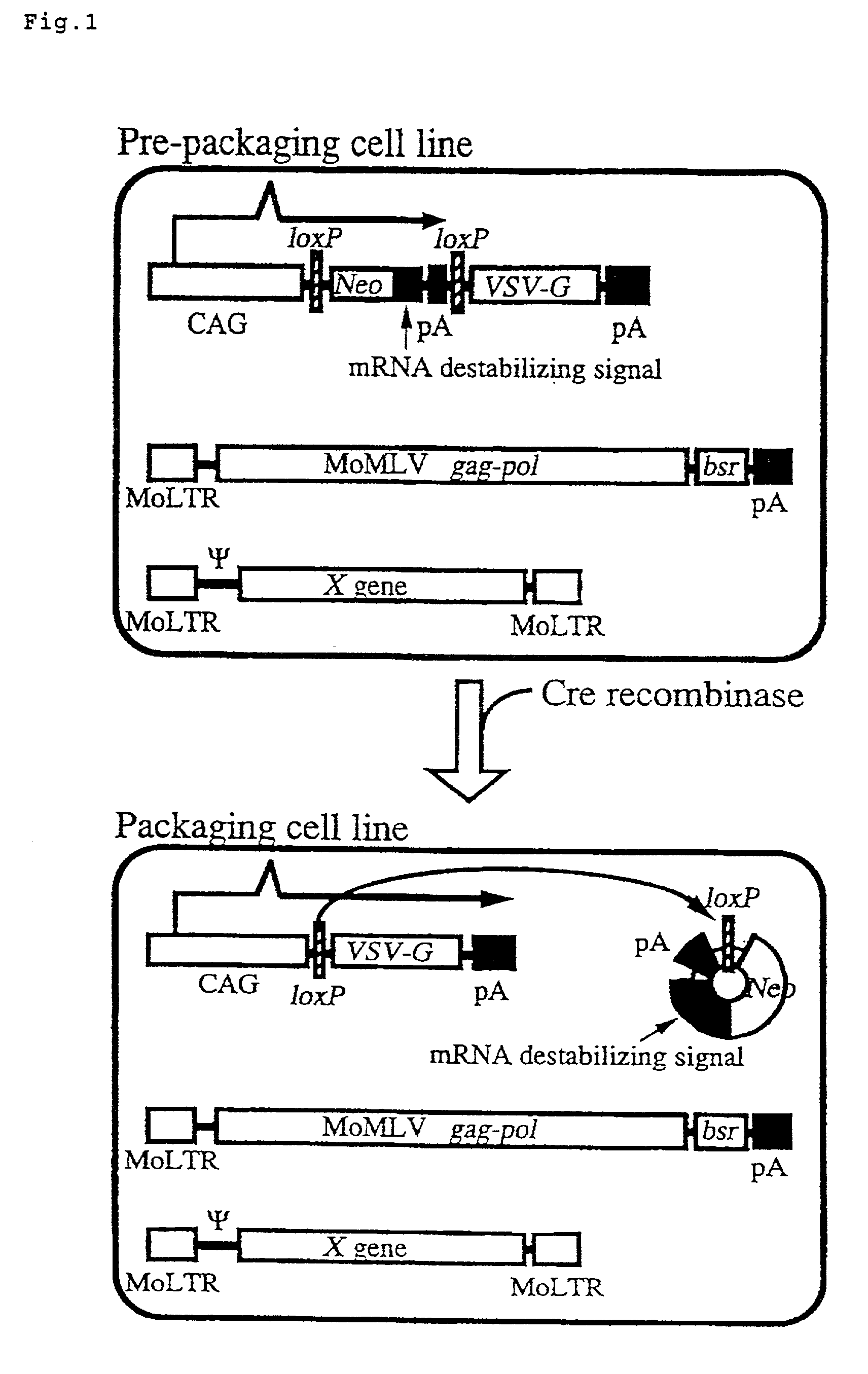
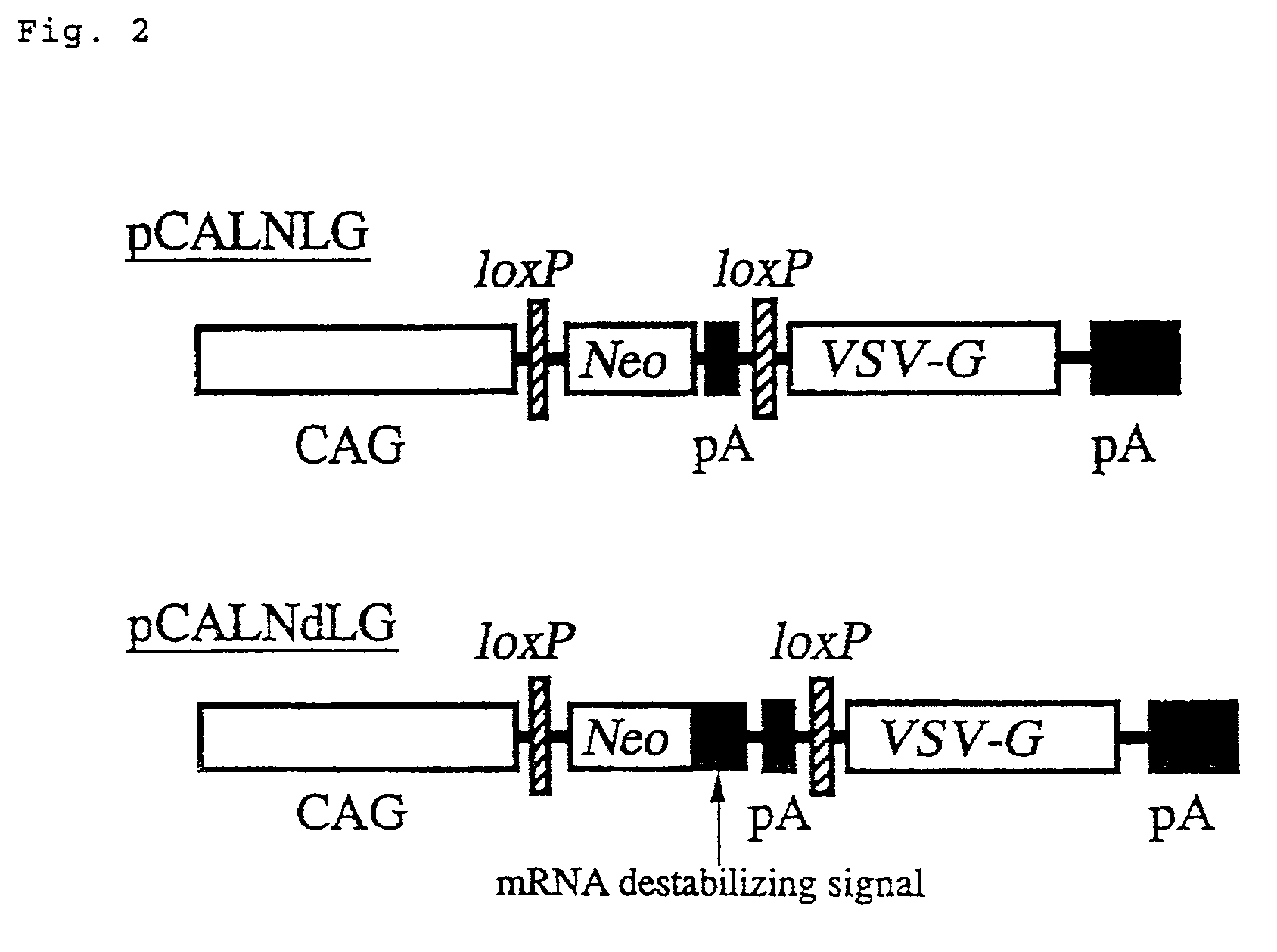
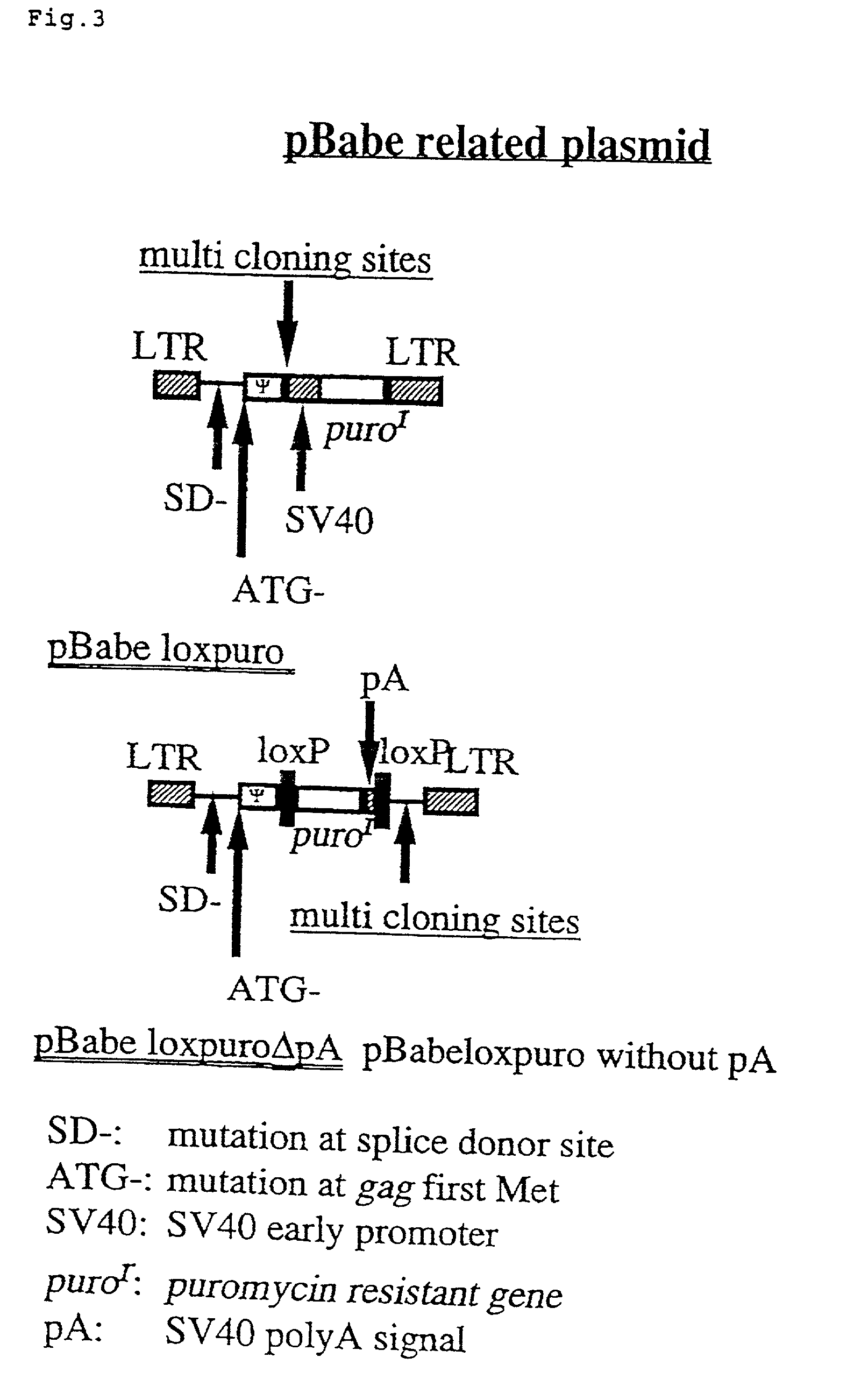
The present invention provides a process for preparing a retrovirus to be expressed at a high titer by specifically transferring a desired foreign gene into target cells. A pseudotyped retrovirus vector having a high titer can be prepared by transferring a DNA construction wherein a promoter, an loxP sequence, a VSV-G gene and a polyA addition signal are arranged in this order is transferred into cells carrying the retrovirus gag and pol gene expression systems, and then transferring a retrovirus vector containing the desired foreign gene thereinto, followed by treatment with a recombinase.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Pseudotyped lentiviral vectors and uses thereof
InactiveUS7078031B2Increase ratingsEasy to superviseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideVector systemViral vector
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Process for preparing retrovirus vector for gene therapy
InactiveUS20010018203A1High recovery rateStably produced at a high titerVectorsGenetic material ingredientsPol genesA-DNA
The present invention provides a process for preparing a retrovirus to be expressed at a high titer by specifically transferring a desired foreign gene into target cells. A pseudotyped retrovirus vector having a high titer can be prepared by transferring a DNA construction wherein a promoter, an loxP sequence, a VSV-G gene and a polyA addition signal are arranged in this order is transferred into cells carrying the retrovirus gag and pol gene expression systems, and then transferring a retrovirus vector containing the desired foreign gene thereinto, followed by the treatment with a recombinase.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Pseudotyped oncolytic viral delivery of therapeutic polypeptides
InactiveCN109983121ASsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMedicinePharmaceutical drug
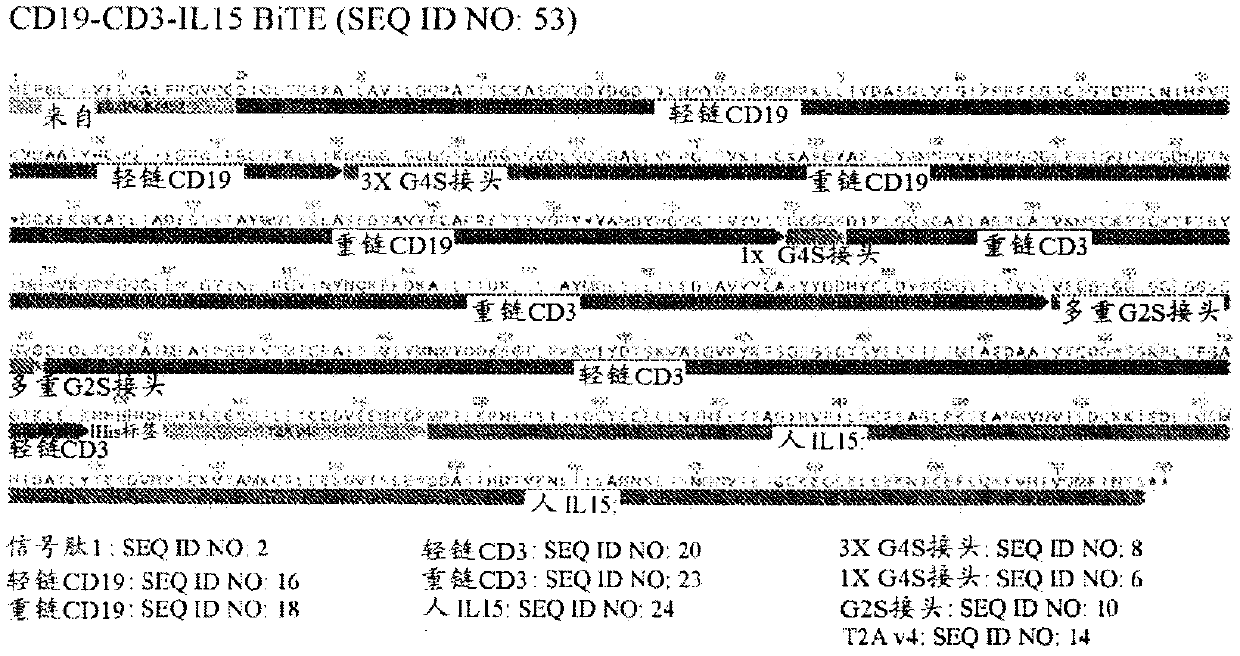
Described herein are pseudotyped oncolytic viruses comprising nucleic acids encoding an engager molecule. In some embodiments, the pseudotyped oncolytic viruses comprises nucleic acids encoding an engager molecule and one or more therapeutic molecules. Pharmaceutical compositions containing the pseudotyped oncolytic virus and methods of treating cancer using the pseudotyped oncolytic viruses are further provided herein.
Owner:ONCORUS INC
Methods for producing and using in vivo pseudotyped retroviruses
The present invention provides novel pseudotyped retroviral vectors that can transduce human and other cells. Vectors are provided that are packaged efficiently in packaging cells and cell lines to generate high titer recombinant virus stocks expressing novel envelope glycoproteins. The present invention further relates to compositions for gene therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Pseudotyped lentiviral vectors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050003505A1Increase ratingsEasy to superviseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideVector systemViral vector
A vector system that will produce a pseudotyped lentiviral vector that can be used to deliver a desired gene is disclosed. The vector constructs that are described include a number of modifications that enhance the safety of the vector. The vector can be used to more specifically target cells for expression of certain genes.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
HIV medicament screening cell model and special pseudotype lentivirus therefor
InactiveCN101353666AIncreased sensitivityImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesPol genesHerpetic stomatitis
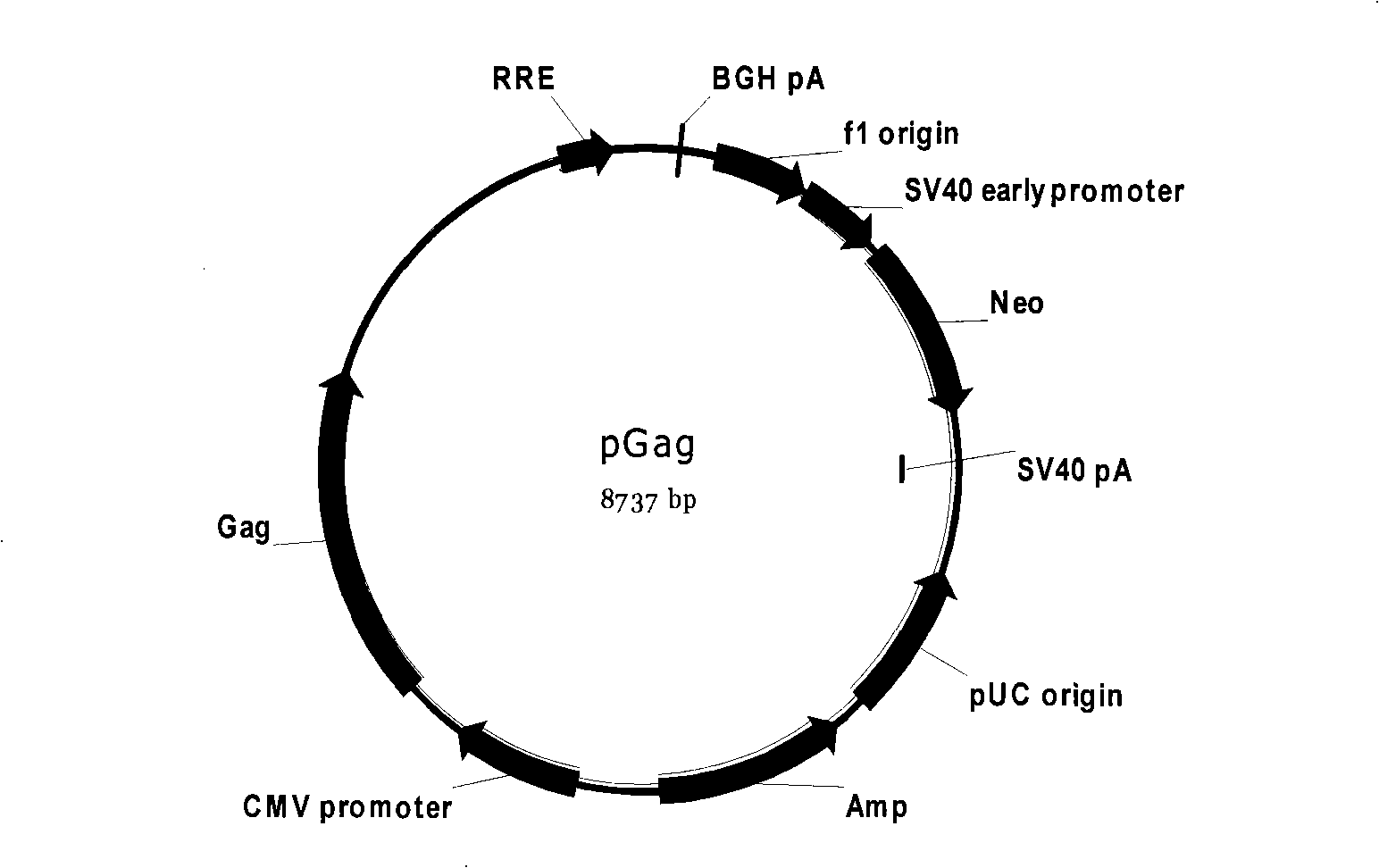
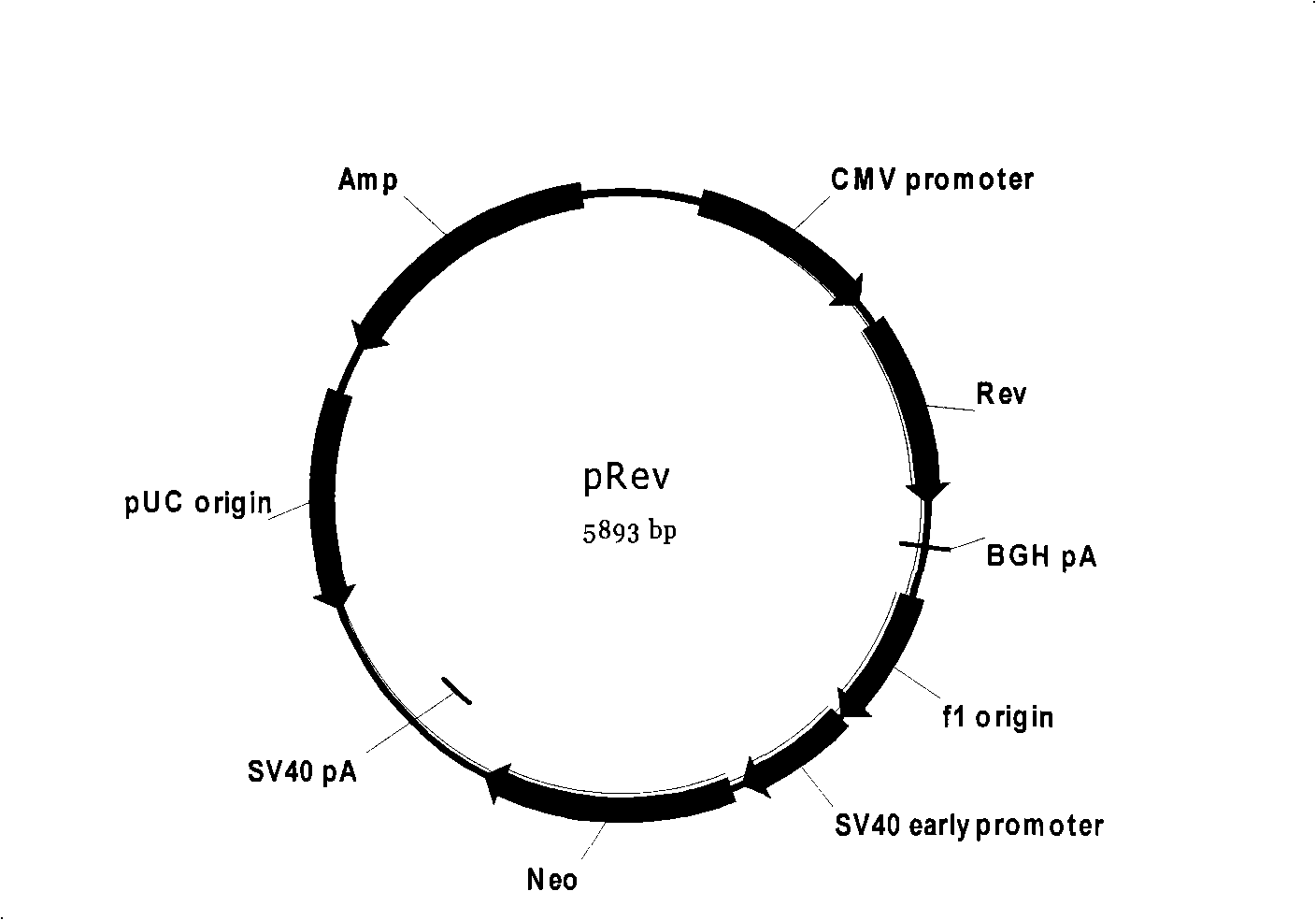
The invention discloses an HIV drug screening cell model and special pseudotype slow virus thereof; the invention constructs recombinant plasmid for expressing Gag gene and Pol gene of HIV, recombinant slow-virus plasmid for expressing reporter gene and recombinant plasmid for expressing Rev gene of HIV; the three plasmids and recombinant plasmid for expressing glycoprotein gene of capsid G of herpetic stomatitis are transfected in the cells of mammals so as to obtain pseudotype slow virus; the pseudotype slow virus is used for infecting the cells of mammals, thus obtaining the HIV drug screening cell model based on the reporter gene. The HIV drug screening cell model provided by the invention uses the virus with one-time infection with good safety and the reporter gene leads the cell model to have super high sensitivity.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
HIV stain drug-resistant phenotype analytical cell model and special pseudotype lentivirus therefor
InactiveCN101353667ARapid Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisSafety Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesPhenotypic resistanceReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis and special pseudotype slow virus thereof; the invention constructs plasmid for expressing Gag protein of HIV, recombinant slow-virus plasmid for expressing reporter gene and helper plasmid for expressing Rev protein of HIV; under the effect of the helper plasmid pVSV-G, the three plasmid and HIV reverse transcriptase and the gene fragment of protease which are amplified from strain can obtain the pseudotype slow virus of the HIV reverse transcriptase and protease gene containing strain. The pseudotype slow virus is used for infecting the cells of mammals, thus obtaining the strain phenotypic resistance cell model based on the reporter gene. The cell model of the invention can carry out phenotypic resistance analysis to the strain, the reporter gene leads the cell model to have super high sensitivity, and the cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis is applicable to the phenotypic drug resistance analysis of HIV strain in Chinese population.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
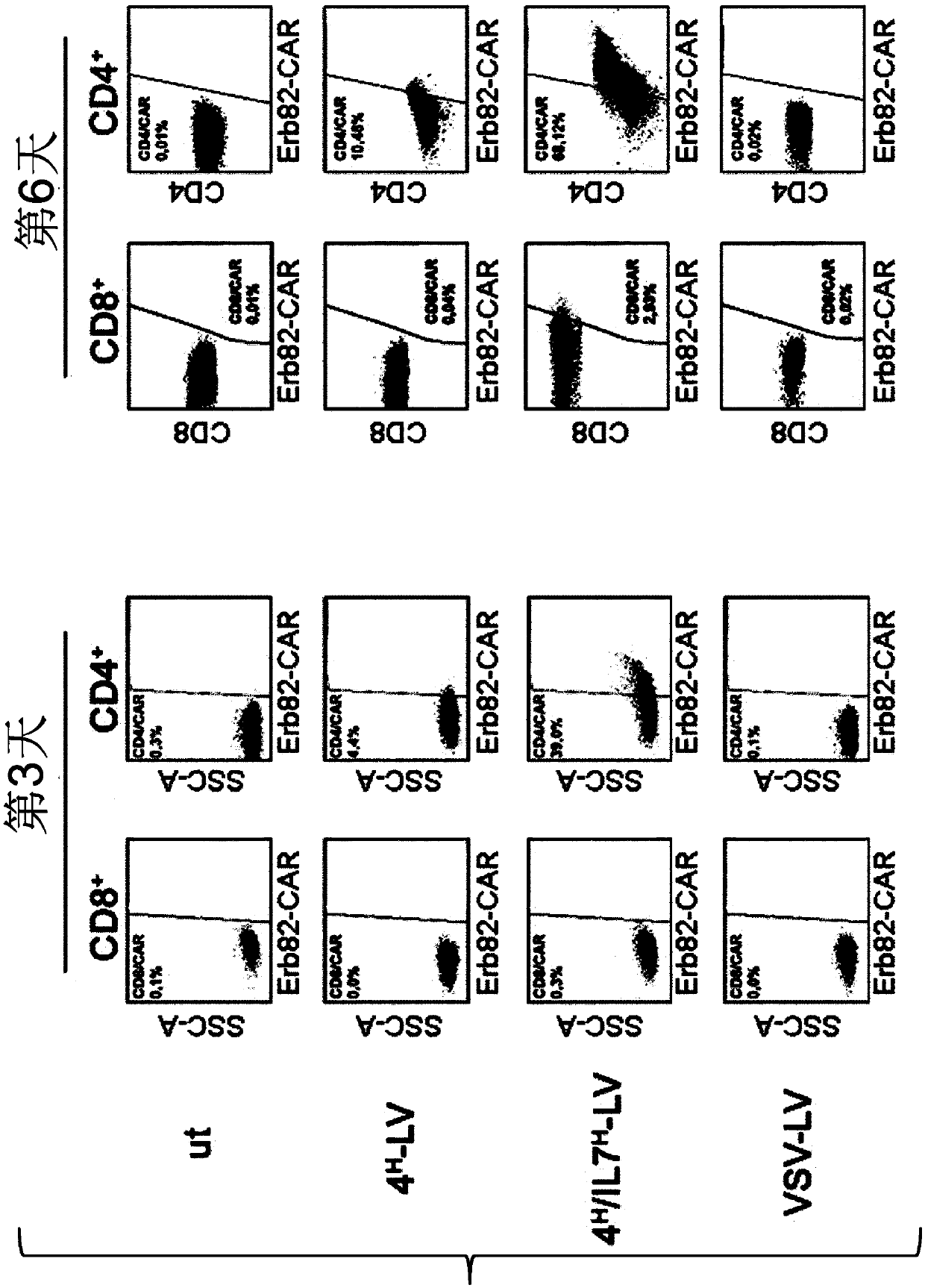
Methods and compositions for genetically modifying and expanding lymphocytes and regulating the activity thereof
PendingCN111479921AFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsT cell
The present disclosure provides methods and compositions for genetically modifying lymphocytes and related methods that include genetically modifying T cells and / or NK cells. The methods use replication incompetent recombinant retroviral particles that comprise a pseudotyping element on their surface and optionally a membrane-bound T cell activation element, such as an anti-CD3, and encode one ormore engineered signaling polypeptides that can include a lymphoproliferative element, and / or a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). The methods can include contacting PBMCs with replication incompetent recombinant retroviral particles for various exemplary time periods, such as less than 24 hours or in some illustrative embodiments less than 15 minutes. Illustrative chimeric lymphoproliferative elements that are capable of promoting survival and / or proliferation of T cells or NK cells in culture without adding IL-2, are provided. Furthermore, additional regulatory elements are provided, such as inhibitory RNA molecules.
Owner:埃克苏马生物技术公司
Adapter-based retroviral vector system for the selective transduction of target cells
PendingCN111315761ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntigen bindingEctodomain
The present invention provides a composition comprising i) a pseudotyped retroviral vector particle or virus-like particle thereof comprising a) one envelope protein with antigen-binding activity, wherein said envelope protein is a recombinant protein that does not interact with at least one of its native receptor(s) and is fused at its ectodomain to a polypeptide comprising an antigen binding domain specific for a tag of a tagged polypeptide, and wherein said envelope protein is protein G, HN or H derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, and b) one envelope protein with fusion activity derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, and ii) said tagged polypeptide, wherein said tagged polypeptide binds specifically to an antigen expressed on the surface of a target cell, thereby transducing thetarget cell with said retroviral vector particle or thereby inducing uptake of the virus-like particle into the target cell. A pharmaceutical composition thereof and an in vitro method for transduction of targets cells with said vector particle are also disclosed.
Owner:ミルテニイビオテックベーファーウントコーカーゲー
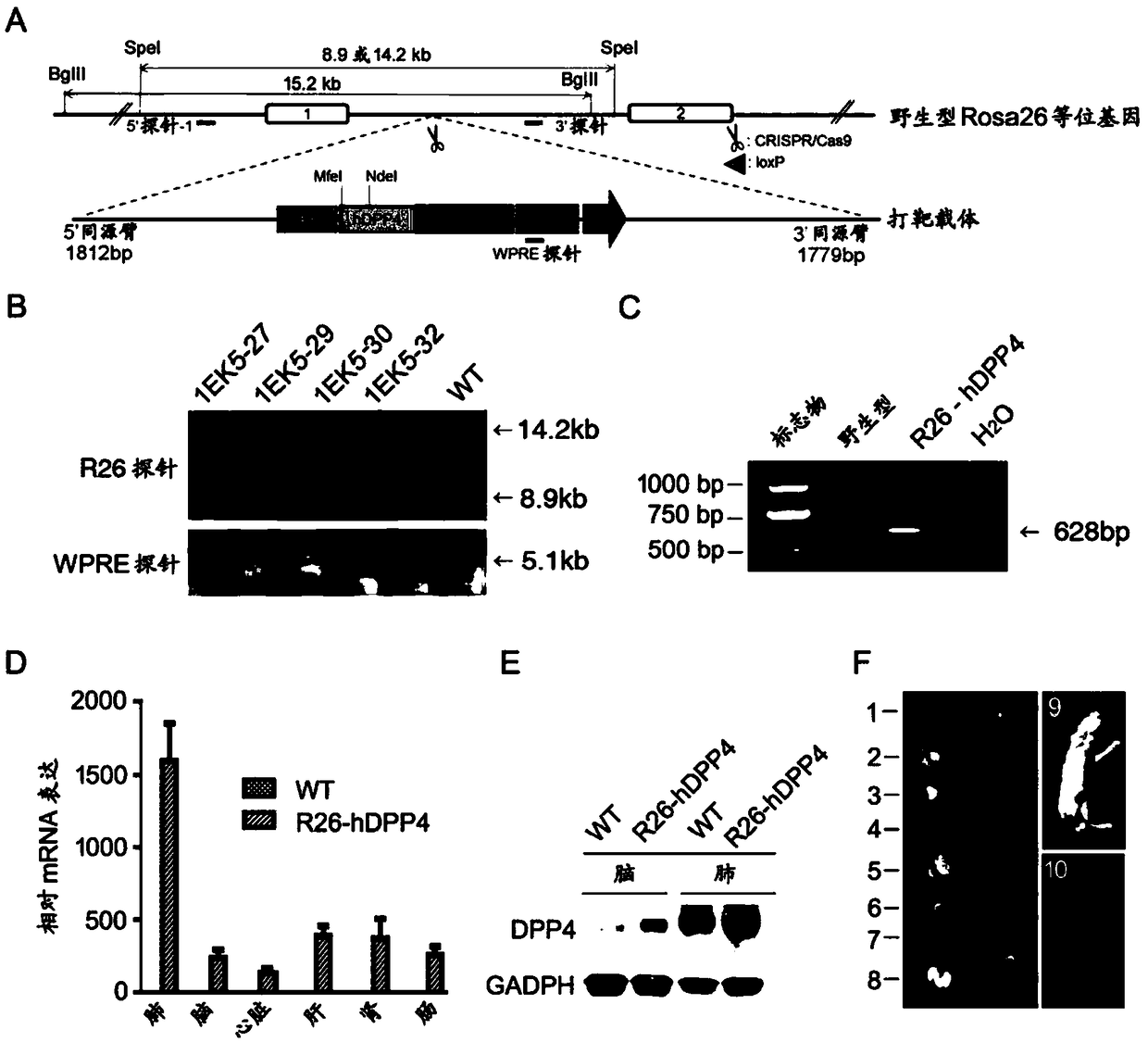
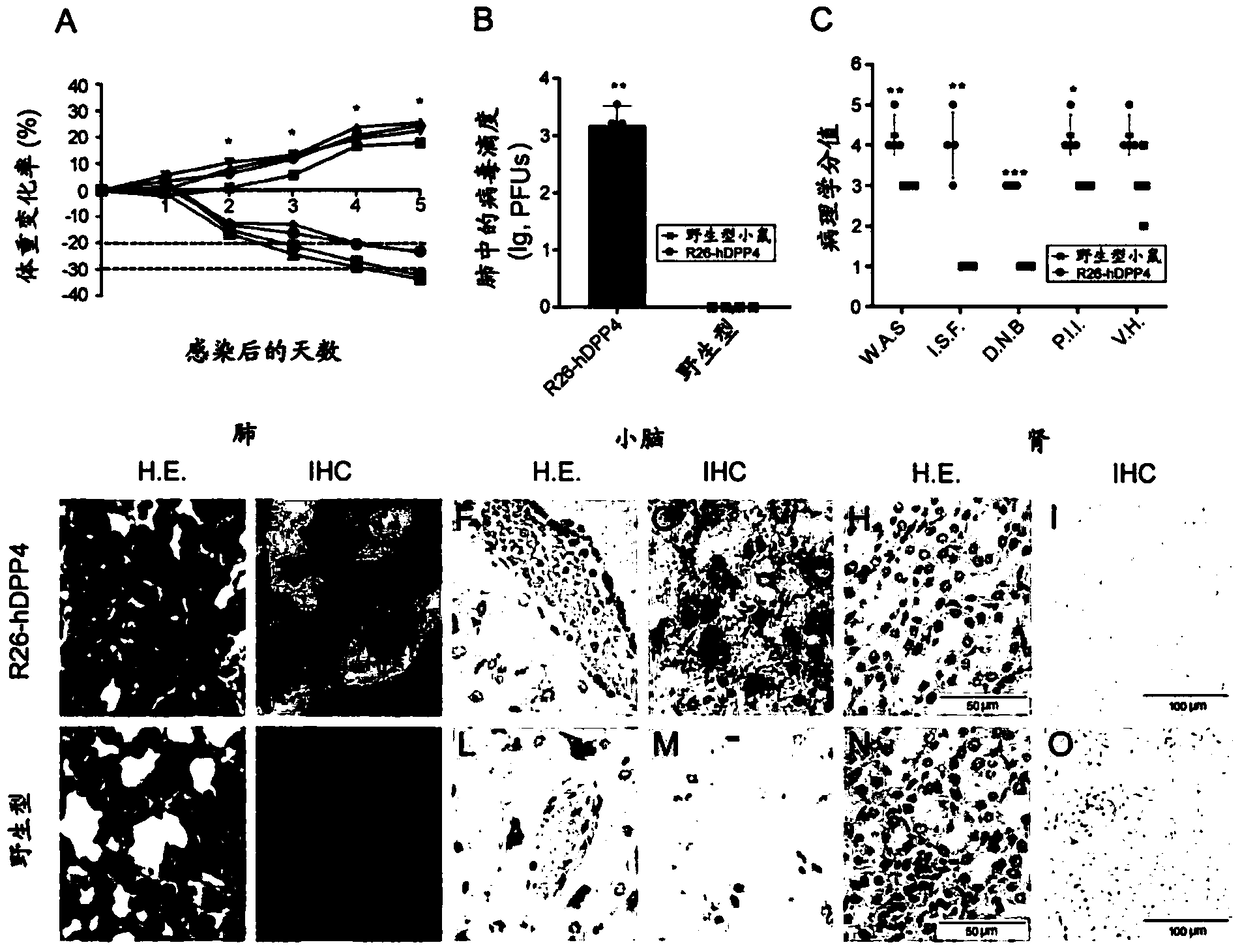
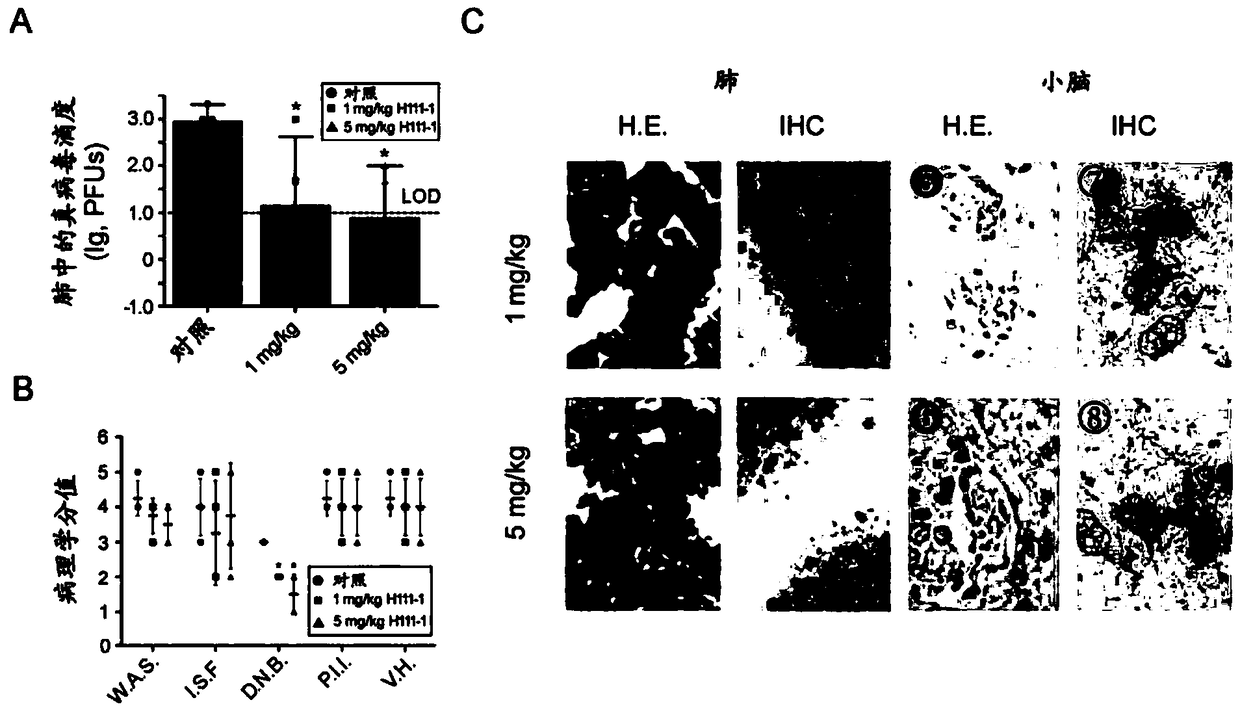
Human DPP4 gene knock-in mouse model and production method and use thereof
The present invention provides a human DPP4 gene knock-in mouse model and a production method and use thereof. Specifically, human DPP4 is accurately inserted into a safe harbor locus of a mouse genome without changing mouse DPP4 function to establish a novel homozygous mouse model in which a human DPP4 gene is knocked into the mouse safe harbor locus. The invention also provides the use of the mouse model in which the human DPP4 gene is knocked into the genome in infection of a mouse with a low dose MERS-CoV euvirus in a BSL-3 facility and evaluation of the in-vivo efficacy of anti-MERS-CoV antiviral agents and vaccines or infection of the mouse with pseudotype MERS-CoV virus in a biological laboratory lacking the BSL-3 facility and evaluation of the in-vivo efficacy of the anti-MERS-CoVantiviral agents and vaccines.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Pseudo MERS-CoV virus of infected animal, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a pseudo MERS-CoV virus packaging system, a method for preparing pseudo MERS-CoV viruses by in-vitro transfection of cells using the pseudo MERS-CoV virus packaging system, and a mouse model with knock-in of a hDPP4 (human dipeptidyl peptidase 4) gene infected by the pseudo MERS-CoV viruses in a biological laboratory lack of BSL-3 (biological safety level 3), so as to evaluate the in-vivo effects of an anti-virus agent and a vaccine.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Methods for selectively modulating the activity of distinct subtypes of cells
PendingCN109642243AStable and constant stimulusImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSsRNA viruses negative-senseVaccinationImmune therapy
The present invention relates to pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors comprising both engineered envelope glycoproteins derived from a virus of the Paramyxoviridae family fusedto a cell targeting domain and fused to a functional domain. The present invention also relates to the use of said pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors to selectively modulate the activity of specific subsets of cells, in particular of specific immune cells. These pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors are particularly useful for gene therapy, immune therapy and / or vaccination.
Owner:ECOLE NORMALE SUPERIEURE DE LYON +3
Pseudotyping of retroviral vectors, methods for production and use thereof for targeted gene transfer and high throughput screening
ActiveUS9862971B2Increase in titer and transduction efficiencyHigh transduction efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideSurface markerSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention relates to the pseudotyping of retroviral vectors with heterologous envelope proteins derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, genus Morbillivirus, and various uses of the resulting vector particles. The present invention is based on the unexpected and surprising finding that the incorporation of morbillivirus F and H proteins having truncated cytoplasmic tails into lentiviral vector particles, and the complex interaction of these two proteins during cellular fusion, allows for a superior and more effective transduction of cells. Moreover, these pseudotyped vector particles allow the targeted gene transfer into a given cell type of interest by modifying a mutated and truncated H protein with a single-chain antibody or ligand directed against a cell surface marker of the target cell.
Owner:BUNDESREPUBLIK DEUTLAND LETZTVERTRETEN DURCH DEN PRASIDENTEN DES PAUL EHRLICH INSTITUTS
Method for specifically knocking out fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 and specific sgRNA
PendingCN111100876AKnockout fastKnockout precisionHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyLentivirus
The invention relates to a method for specifically knocking out a fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 and specific sgRNA. The method is applied to specifically knock out theFAH gene of pigs and rabbits and comprises the following specific steps: S1: selection and design of a sgRNA target sequence; S2: construction of a CRISPR-Cas9 vector of the FAH gene; S3: obtaining ofa pseudotype lentivirus expressing FAH sgRNA and Cas9 protein; and S4: infection of a target cell and detection of an FAH gene knockout effect. The target sequence of the specific sgRNA on the FAH genes of the pigs and rabbits conforms to a sequence arrangement law of 5'-N(20)NGG-3'. The specific sgRNA is applied to the method for specifically knocking out the FAH gene of the pigs and rabbits byusing the CRISPR-Cas9, can rapidly, accurately, efficiently and specifically knock out the FAH gene of the pigs and rabbits respectively, and effectively solves the technical problems of long period and high cost in construction of pigs and rabbits with the FAH gene knocked out.
Owner:立沃生物科技(深圳)有限公司
Method for nk cell transduction
PendingUS20200390812A1Efficient transductionPracticalFusion with RNA-binding domainViral antigen ingredientsHematopoietic cellNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The present invention discloses an in-vitro method for transferring biological material into activated NK cells with a pseudotyped retroviral vector particle or a virus-like particle thereof, comprising the steps a) activation of NK cells, and b) addition of said pseudotyped retroviral vector particle or virus-like particle thereof to said activated NK cells, wherein said pseudotyped retroviral vector particle or virus-like particle thereof comprises a modified baboon endogenous retrovirus (BaEV) envelope glycoprotein that is able of binding to and fusing with a hematopoietic cell membrane, thereby transferring biological material into said activated NK cells. Preferentially, the activating of NK cells is performed by the addition of a IL-1 family cytokine to the NK cells.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
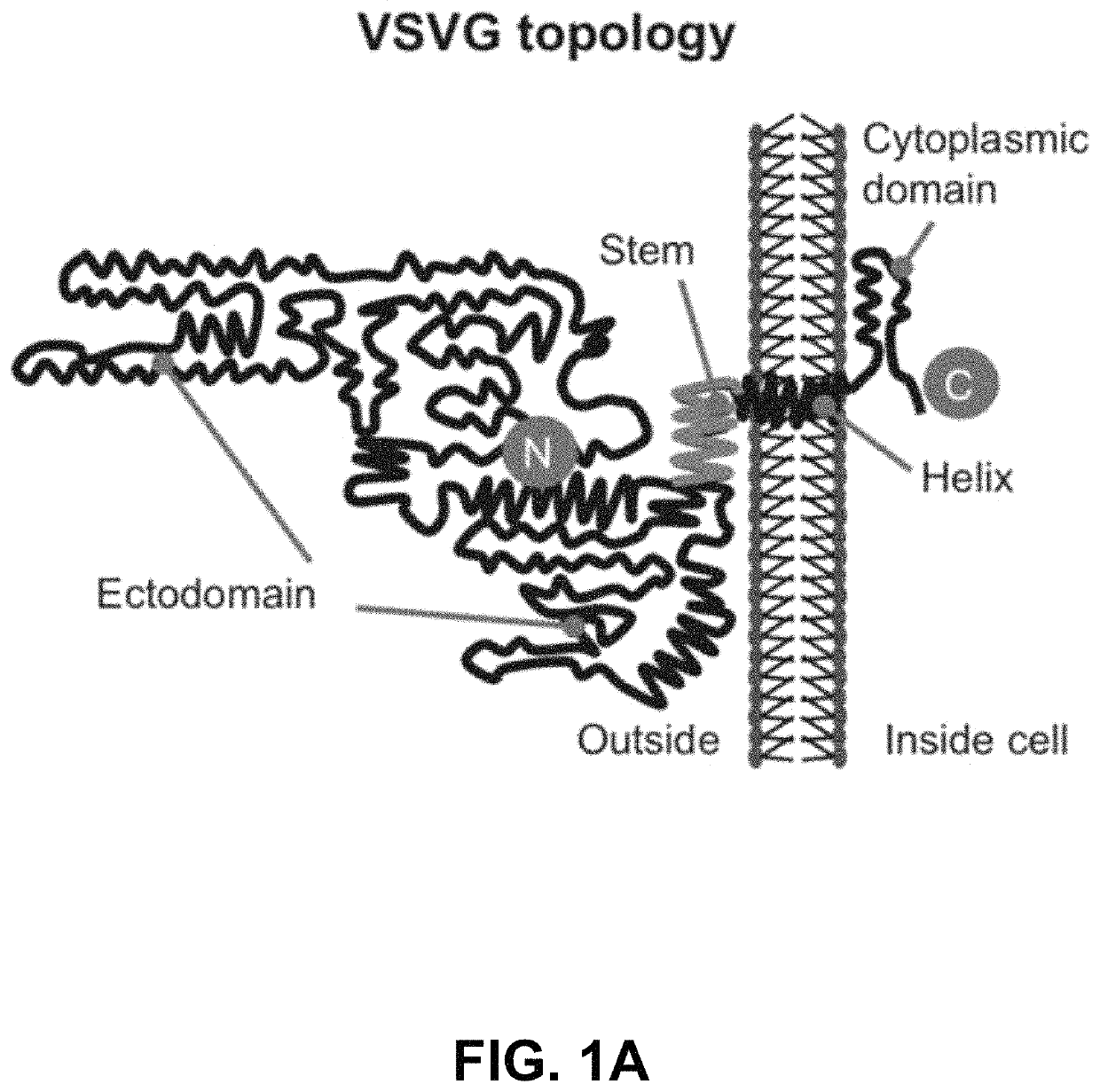
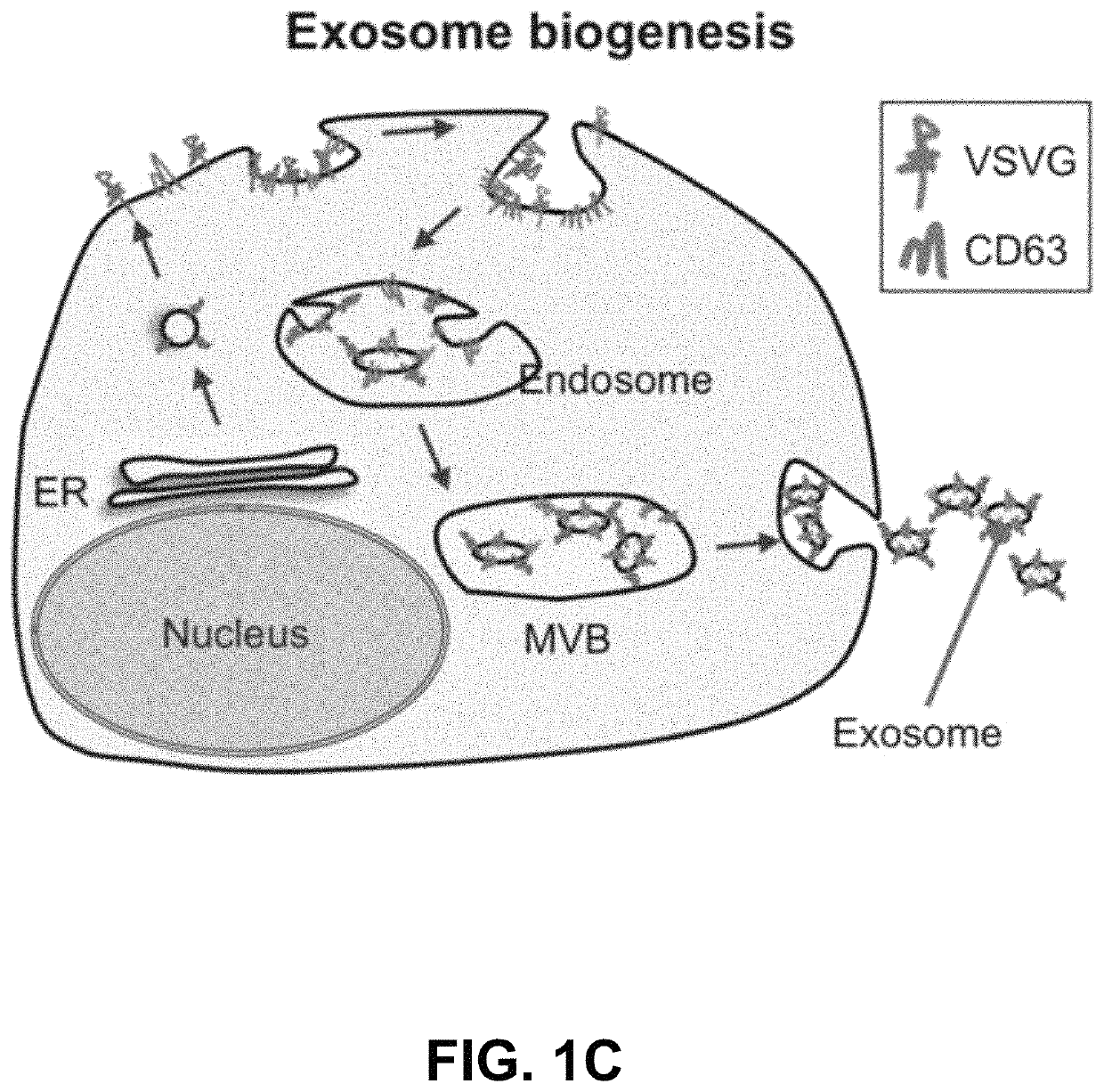
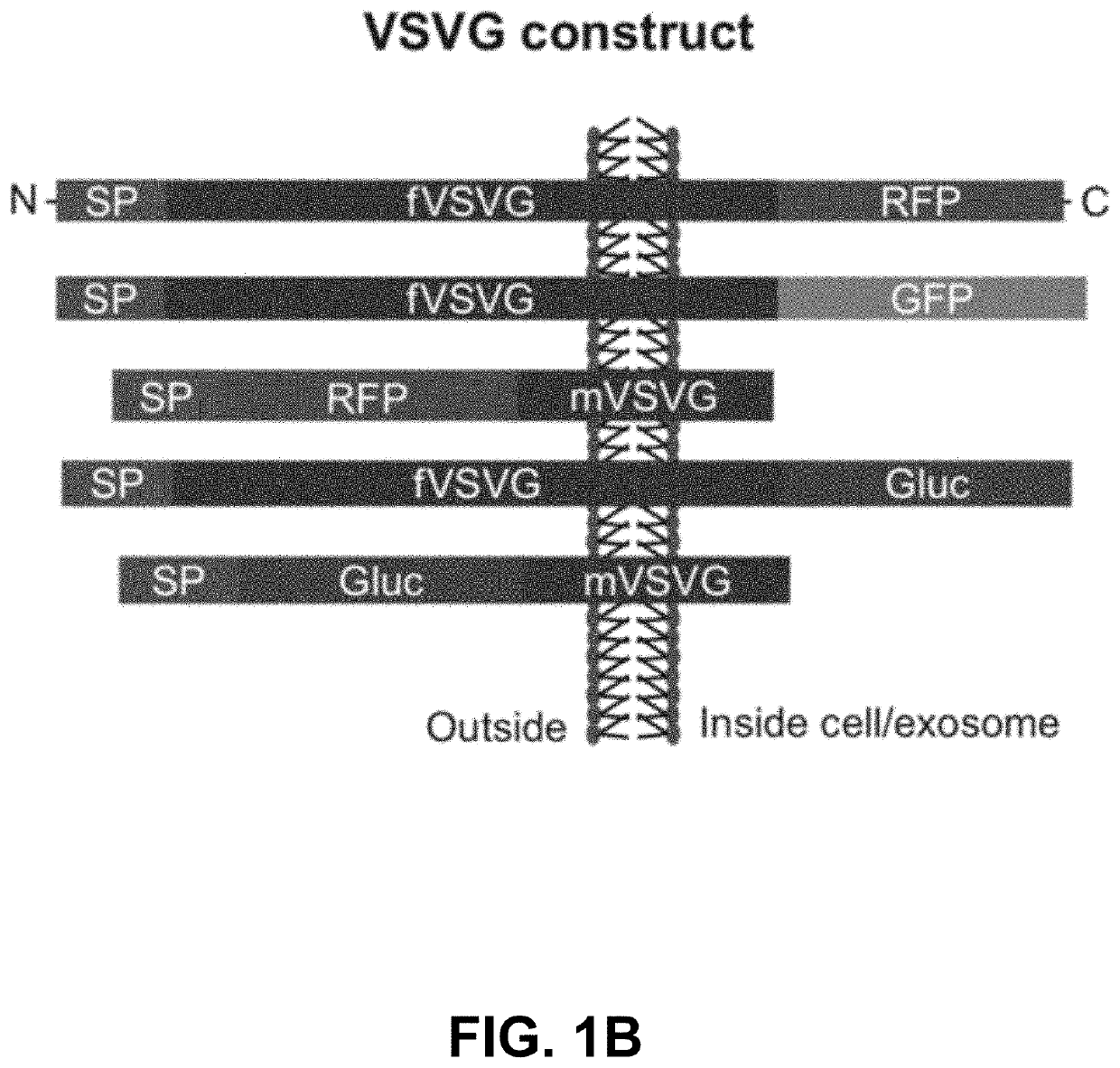
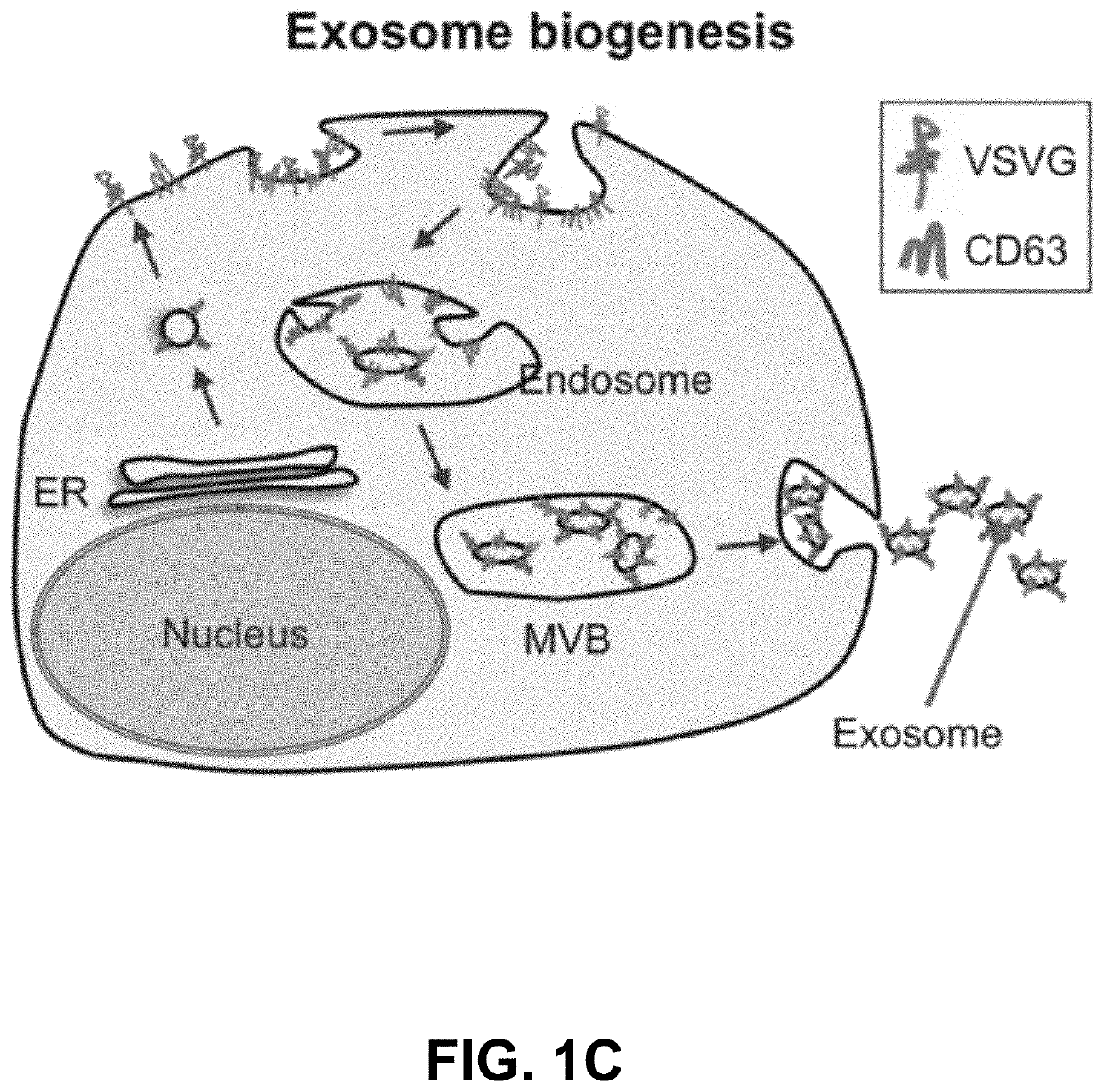
Engineered exosomes for the delivery of bioactive cargo using transmembrane VSV-G
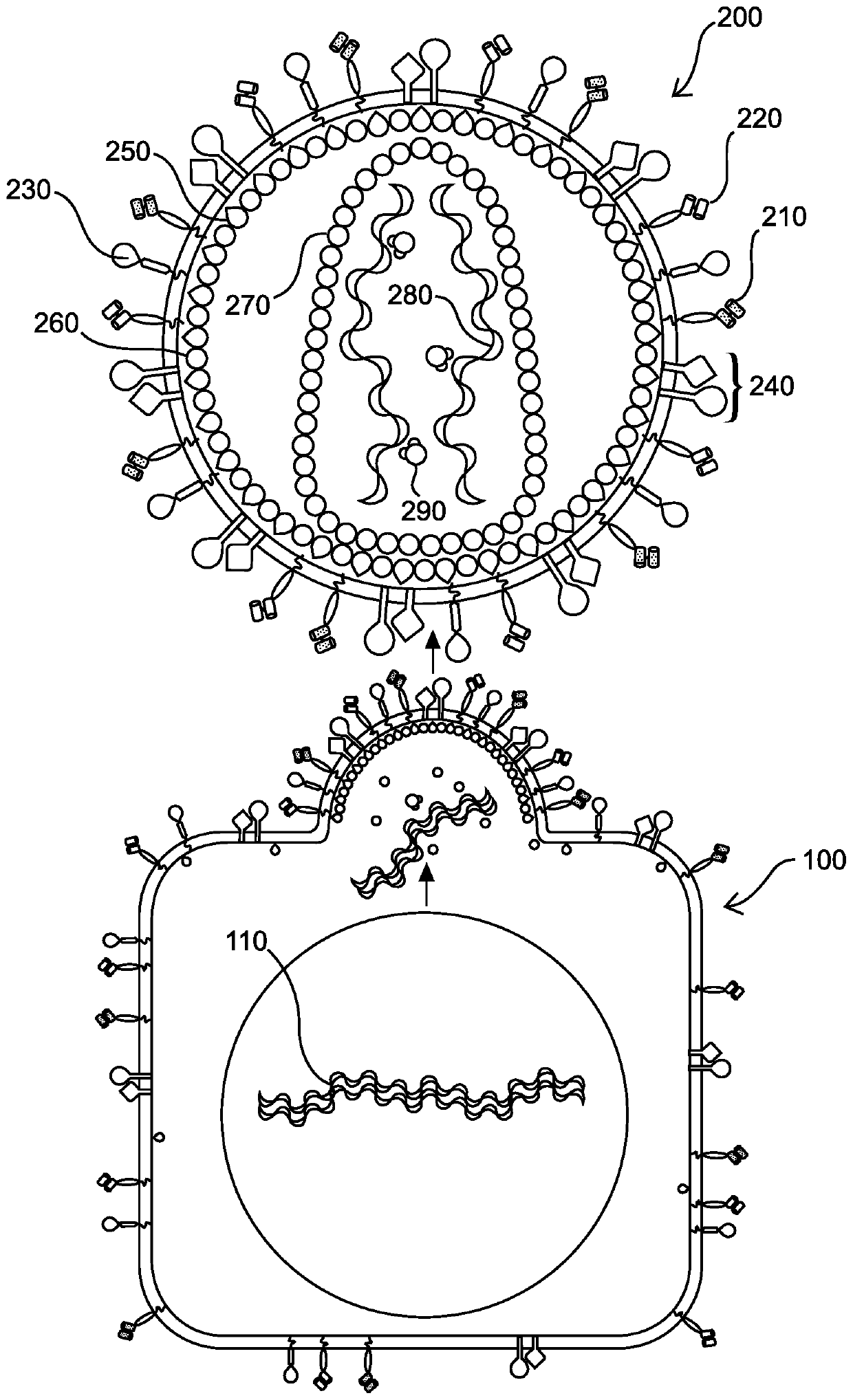
ActiveUS10758486B2Increase infectionEfficient loadingAerosol deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsTherapeutic proteinSomatic cell
Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVG) can both load protein cargo onto exosomes and increase their delivery ability via a pseudotyping mechanism. By fusing a set of fluorescent and luminescent reporters with VSVG, we show the successful targeting and incorporation of VSVG fusions into exosomes by gene transfection and fluorescence tracking. VSVG pseudotyping of exosomes does not affect the size or distributions of the exosomes, and both the full-length VSVG and the VSVG without the ectodomain integrate into the exosomal membrane, suggesting that the ectodomain is not required for protein loading. Finally, exosomes pseudotyped with full-length VSVG are internalized by multiple-recipient cell types to a greater degree compared to exosomes loaded with VSVG without the ectodomain, confirming a role of the ectodomain in cell tropism. This invention provides a new genetically encoded pseudotyping platform to load and enhance the intracellular delivery of therapeutic proteins via exosome-based vehicles to target cells.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
Engineered Exosomes for the Delivery of Bioactive Cargo Using Transmembrane VSV-G
InactiveUS20200306297A1Increase infectionEffective protein loadingSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsTherapeutic proteinSomatic cell
Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVG) can both load protein cargo onto exosomes and increase their delivery ability via a pseudotyping mechanism. By fusing a set of fluorescent and luminescent reporters with VSVG, we show the successful targeting and incorporation of VSVG fusions into exosomes by gene transfection and fluorescence tracking. VSVG pseudotyping of exosomes does not affect the size or distributions of the exosomes, and both the full-length VSVG and the VSVG without the ectodomain integrate into the exosomal membrane, suggesting that the ectodomain is not required for protein loading. Finally, exosomes pseudotyped with full-length VSVG are internalized by multiple-recipient cell types to a greater degree compared to exosomes loaded with VSVG without the ectodomain, confirming a role of the ectodomain in cell tropism. This invention provides a new genetically encoded pseudotyping platform to load and enhance the intracellular delivery of therapeutic proteins via exosome-based vehicles to target cells.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
Pseudotype insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns, virus, construction method and application
ActiveCN111378689AImprove packaging efficiencyImproving Cytotropism of PenaeusSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBaculovirus expressionPrawn
The invention relates to a pseudotype insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns, a virus, a construction method and an application, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering.The pseudotype insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns disclosed by the invention comprises a Bac-to-Bac insect baculovirus expression system, prawn virus envelope protein gene expression plasmids and insect packaging cells. The pseudotype insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns disclosed by the invention can stably and efficiently transfer and express exogenous genes in prawn tissue and cells.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Methods for in vitro memory B cell differentiation and transduction with VSV-G pseudotyped viral vectors
ActiveUS10240125B2Less timeHigh transduction efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsGenetically modified cellsMemory B-cell differentiationPlasma cell
The present disclosure relates to the in vitro differentiation of memory B cells to plasmablasts or plasma cells and genetic modification of these cells to express a protein of interest, such as a specific antibody or other protein therapeutic.
Owner:IMMUSOFT CORP
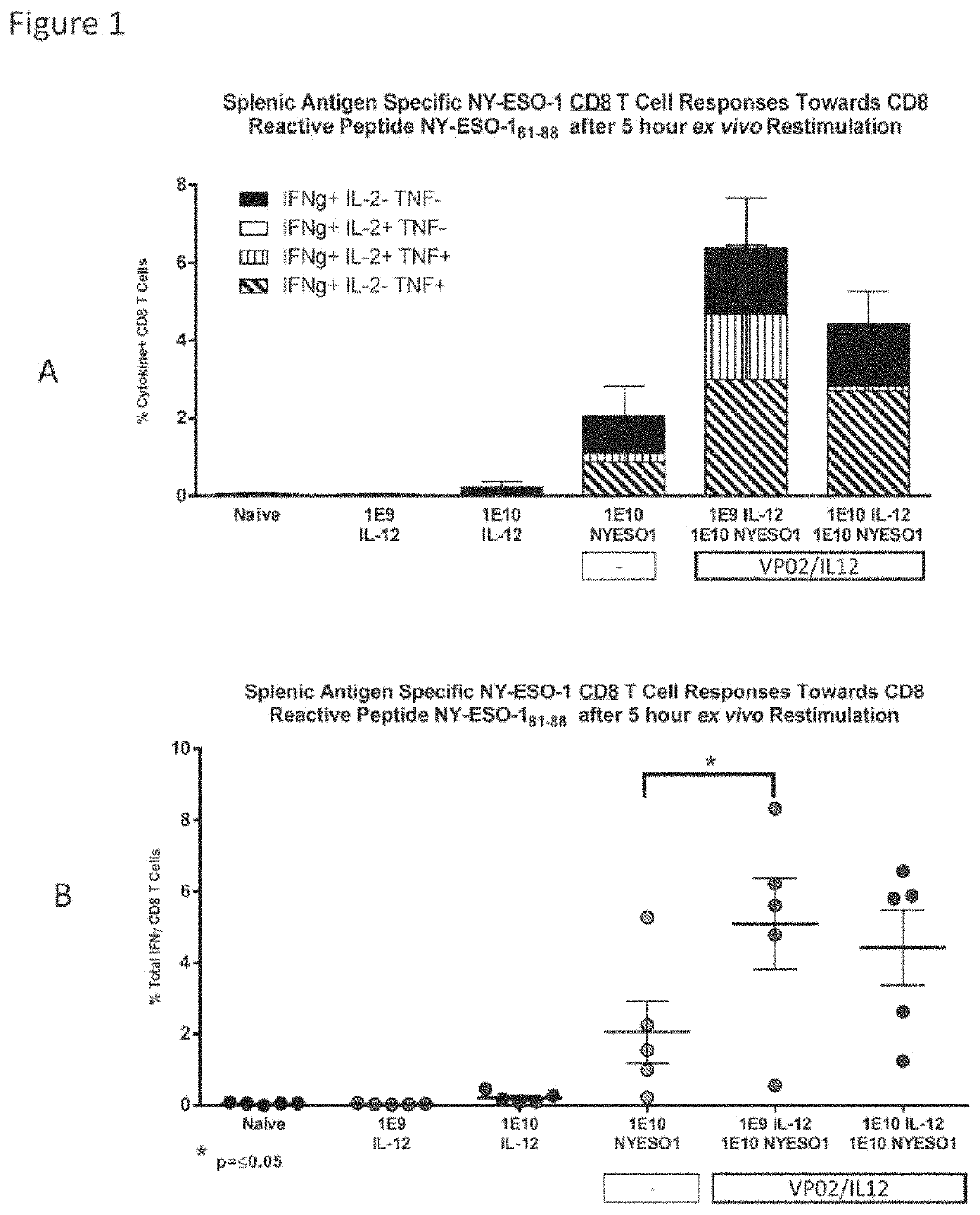
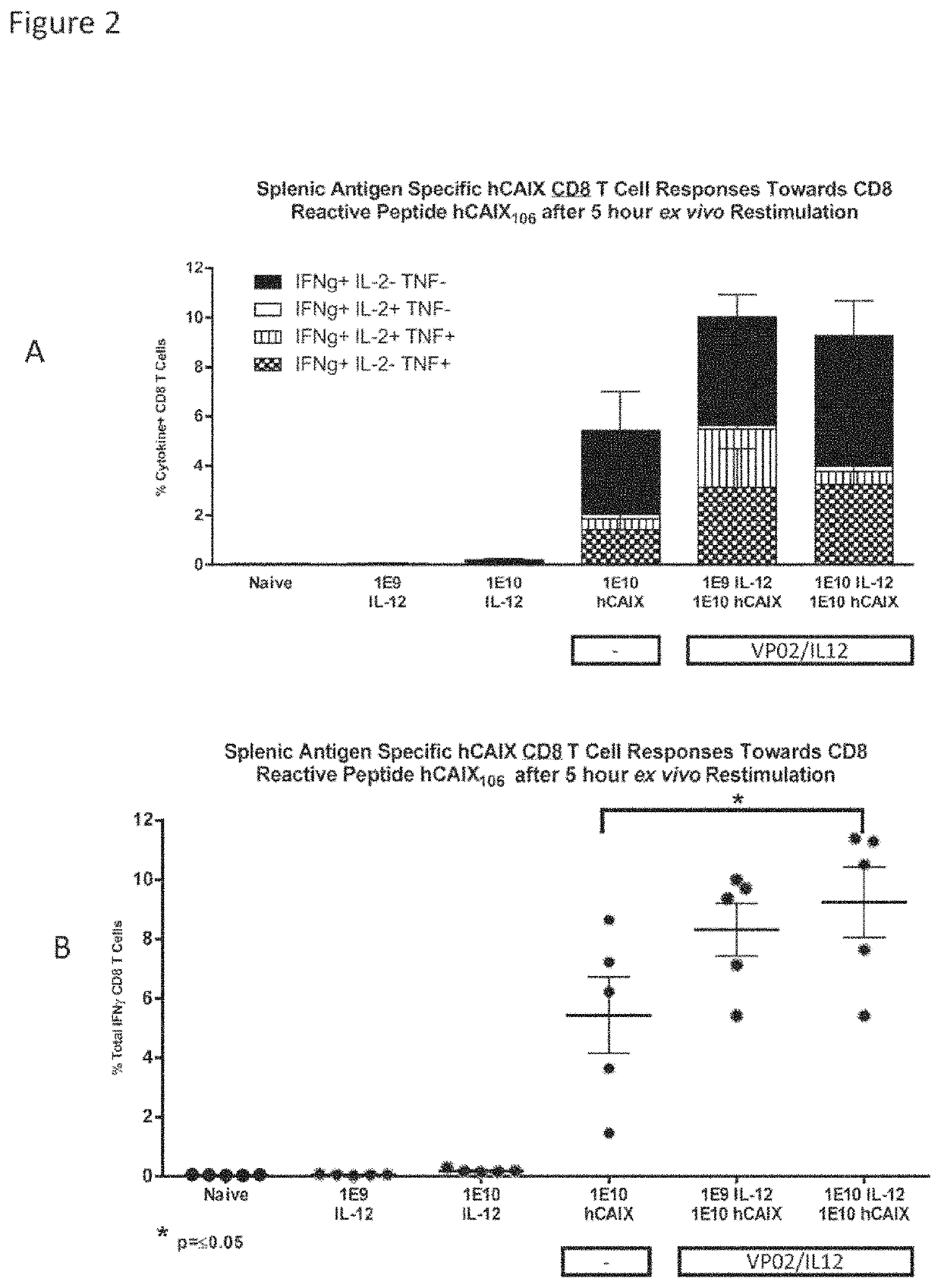
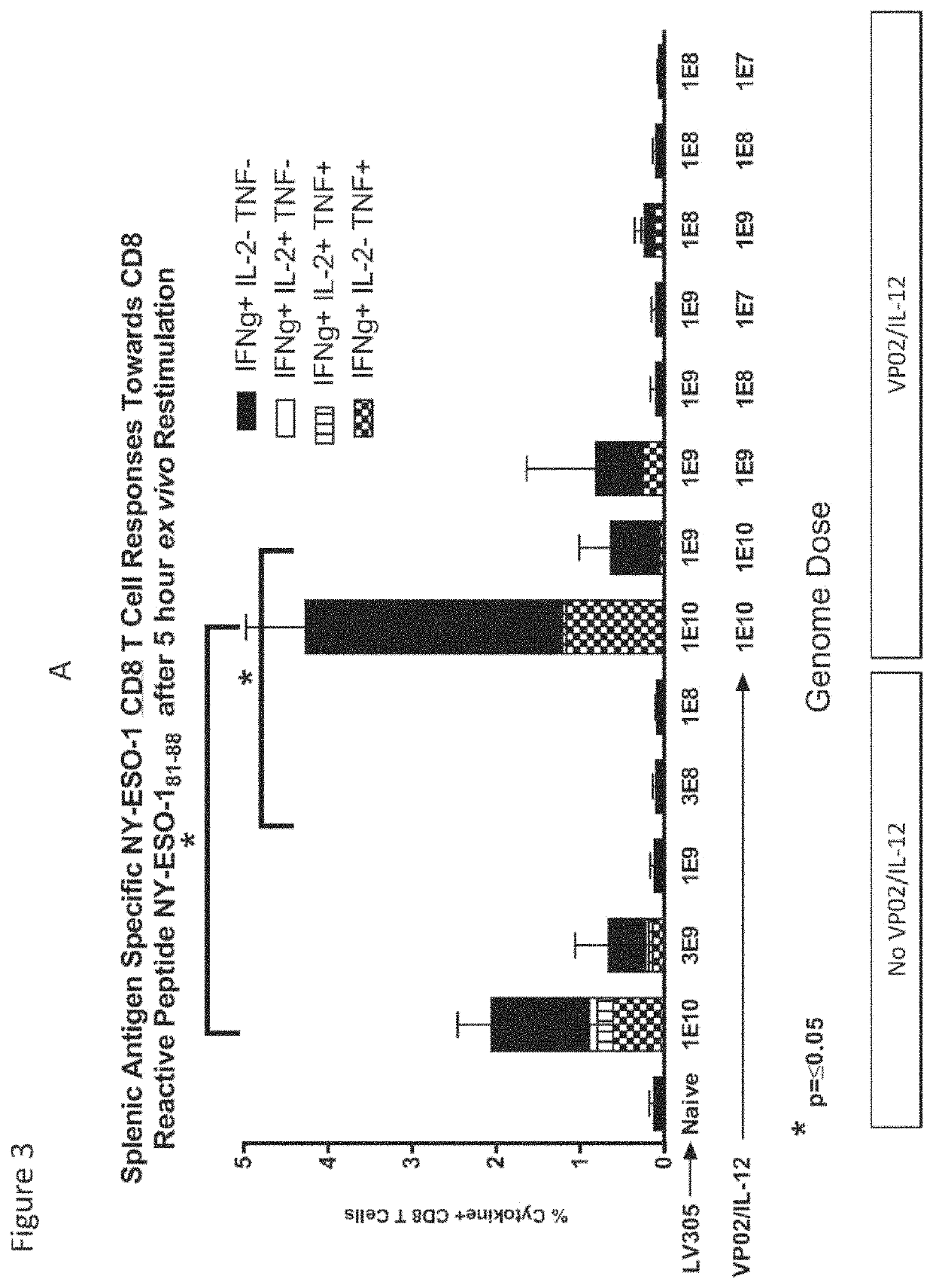
Compositions comprising lentiviral vectors expressing IL-12 and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS11365230B2Improve survivalSlow tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsLentivirusOncology
Owner:IMMUNE DESIGN CORP
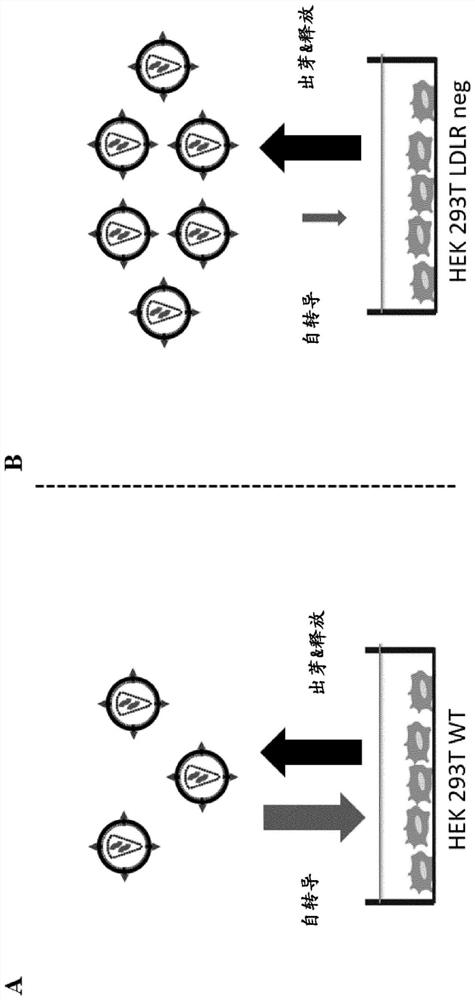
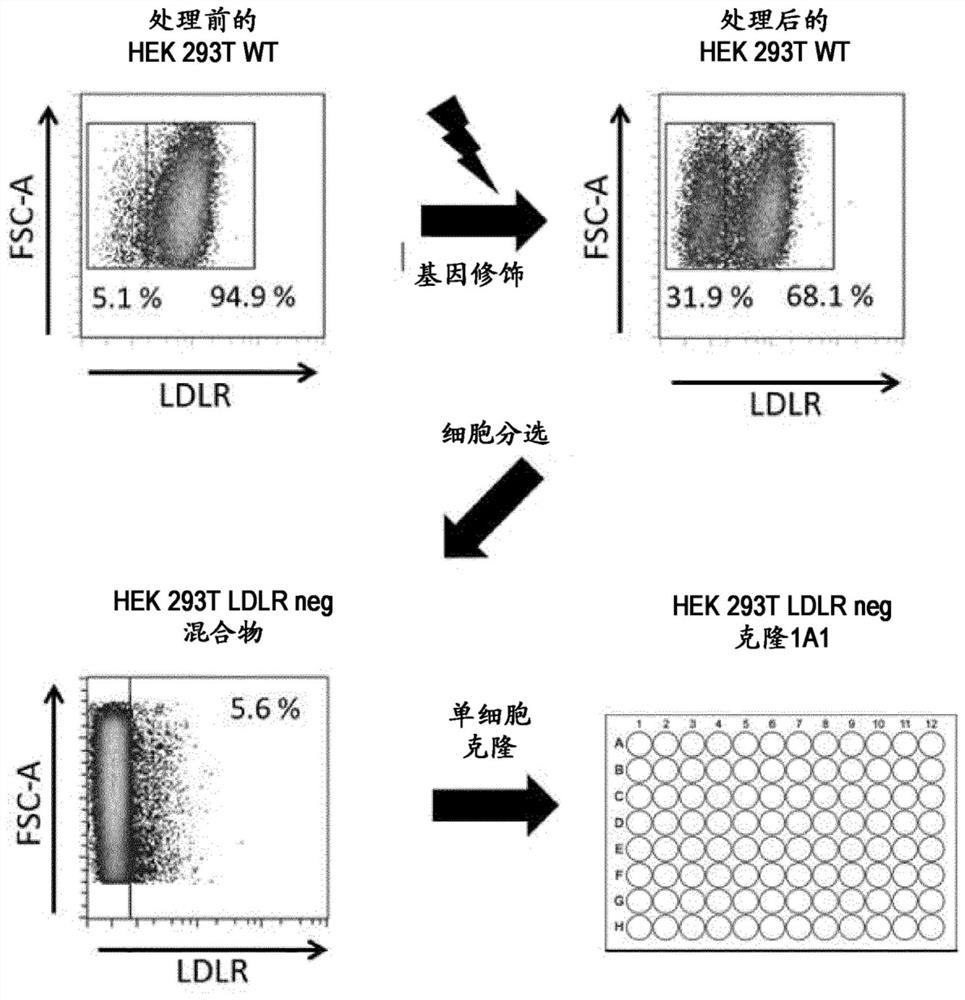
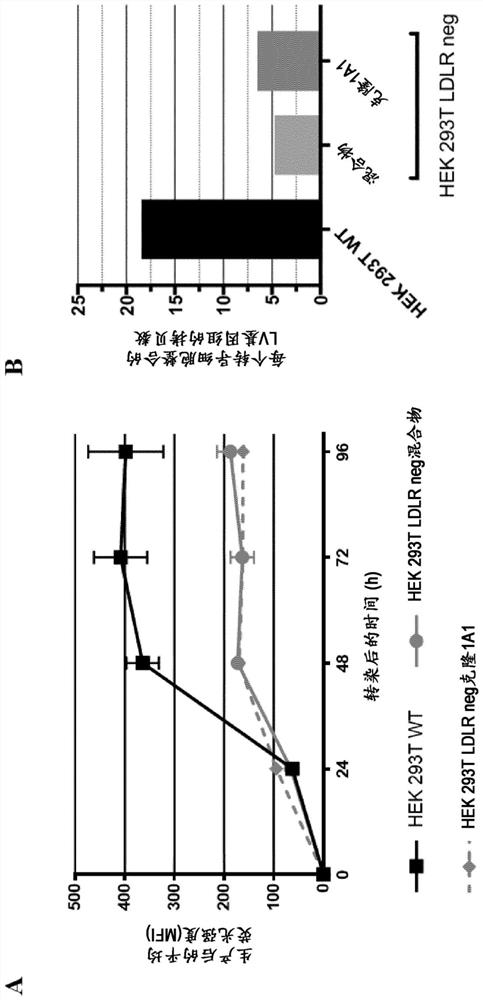
Ldlr negative packaging cell line for the production of vsv-g pseudotyped retroviral vector particles or virus particles thereof
The present invention provides the use of a packaging cell line for the production of VSV-G pseudotyped retroviral vector particles or virus like particles thereof, wherein said packaging cell line is negative for Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR), optionally said packaging cell line stably expresses VSV-G. A method for producing said VSV-G pseudotyped retroviral vector particles or virus like particles thereof is disclosed as well as said particles obtained by said method.
Owner:ミルテニイビオテックベーファーウントコーカーゲー
A pseudotyped insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns, virus and its construction method and application
ActiveCN111378689BImprove packaging efficiencyImproving Cytotropism of PenaeusSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBaculovirus expressionPrawn
The invention relates to a pseudotyped insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns, a virus and a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The pseudotyped insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns of the present invention includes a Bac-to-Bac insect baculovirus expression system, a prawn virus envelope protein gene expression plasmid and insect packaging cells. The pseudotyped insect baculovirus gene transfer system for prawns of the invention can stably and efficiently transfer and express exogenous genes in prawn tissues and cells.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com