Human DPP4 gene knock-in mouse model and production method and use thereof
A gene knock-in, mouse model technology, applied in other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, biochemical equipment and methods, genetic engineering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
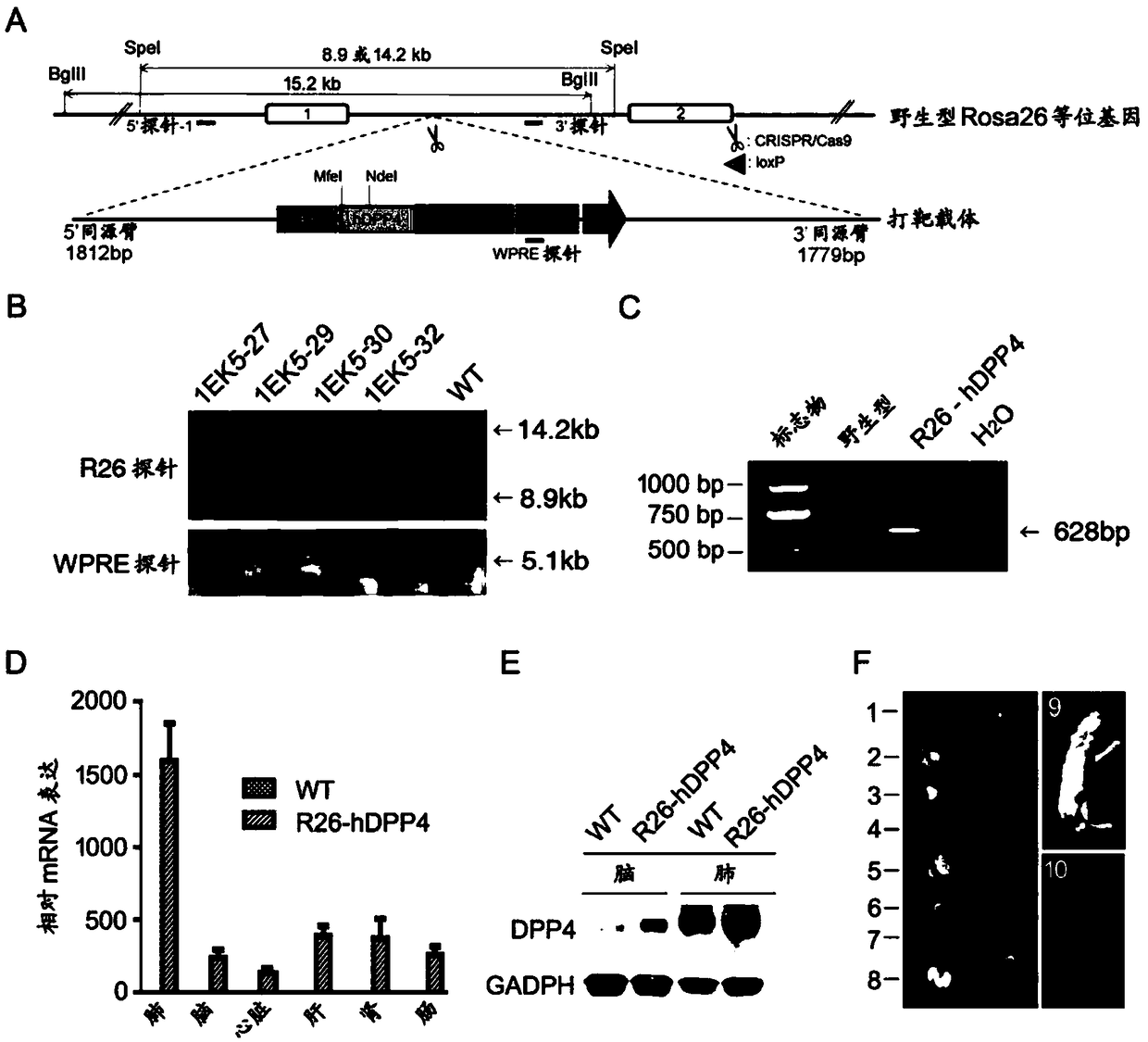
[0146] Example 1. Construction of targeting vector comprising hDPP4 gene
[0147]Human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (hDPP4) is the receptor of MERS-CoV, which has the ability to mediate the infection of hosts by MERS-CoV. Mouse dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (mDPP4) is not a functional receptor for MERS-CoV, therefore, MERS-CoV cannot infect mice via mDPP4.
[0148] In this example, a targeting vector containing the hDPP4 gene was constructed for knocking the hDPP4 gene into the Rosa26 locus of the mouse genome and expressing the hDPP4 protein, aiming to obtain gene knock-in mice capable of infecting MERS-CoV.
[0149] The targeting vector contains 5' homology arm, splicing acceptor (splicing acceptor, SA), hDPP4 gene, internal ribosome entry site (IRES) sequence, tdTomato reporter gene, woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element (woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE)), poly A sequence, 3' homology arm; wherein said 5' homology arm a...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2. Generation of mice with targeted knock-in of the hDPP4 gene at the target site of the Rosa26 locus
[0154] The targeting vector comprising the hDPP4 gene constructed in Example 1, the sgRNA efficiently targeting the Rosa26 locus (comprising the nucleotide sequence TAGGCCGCACCCTTCTCCGG shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 and the nucleotide sequence AAACCCGGAGAAGGGTGCGG shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 ) and Cas9 mRNA sequences known in the prior art (for example, the Cas9 mRNA sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6) were microinjected into 294 C57BL / 6 mouse zygotes, and then the zygotes were implanted Pseudo-pregnant surrogate mice were pregnant in KM mice or ICR mice, and offspring were born from surrogate mice. A total of 41 offspring were obtained.
[0155] For 41 offspring of surrogate mice, the primer hDpp4 forward primer: 5'-CTGCAGTACCCAAAGACTGTACGGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4); hDpp4 reverse primer: 5'-GACACCTTTTCCGGATTCAGCTCACA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5) Genotyping wa...
Embodiment 3
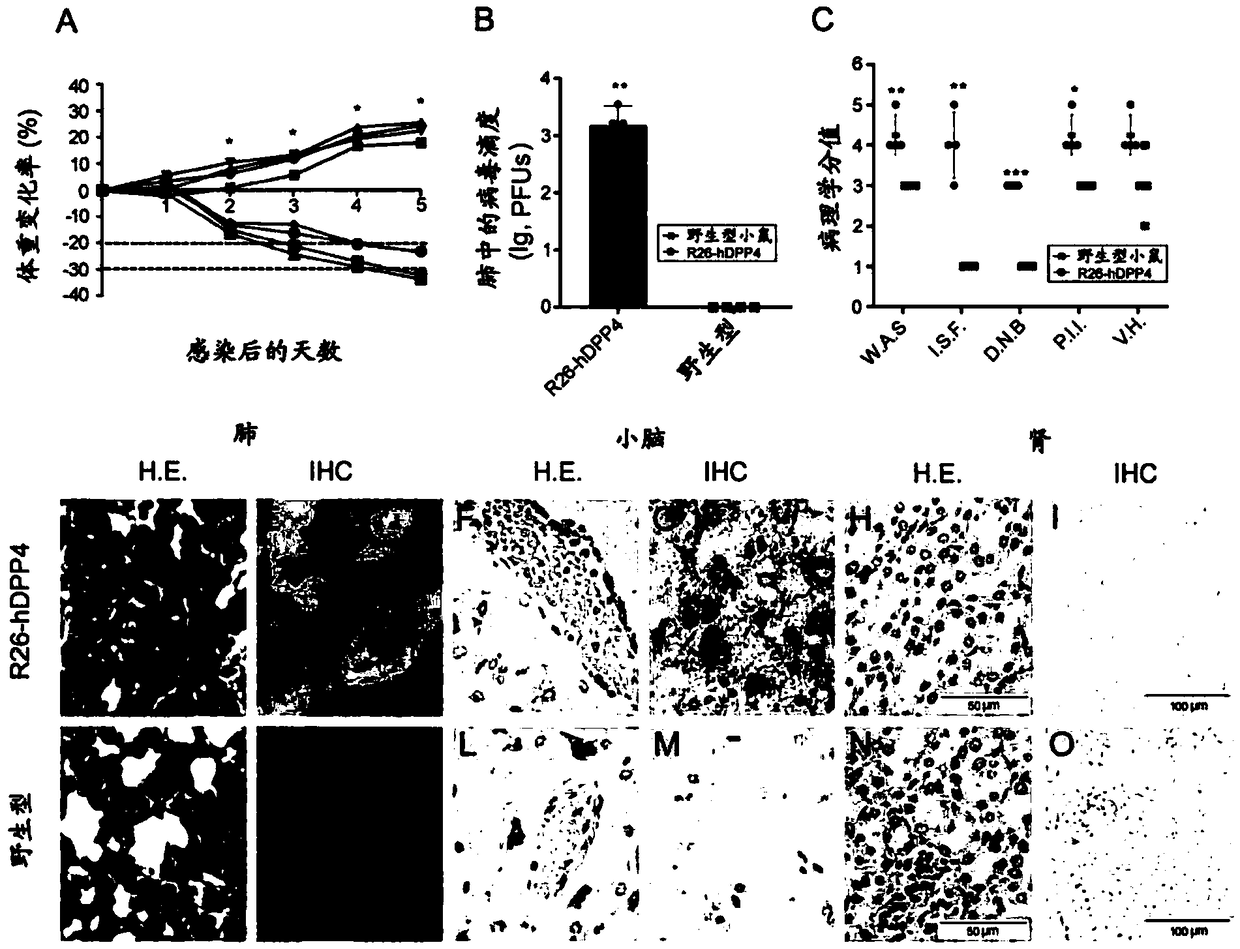
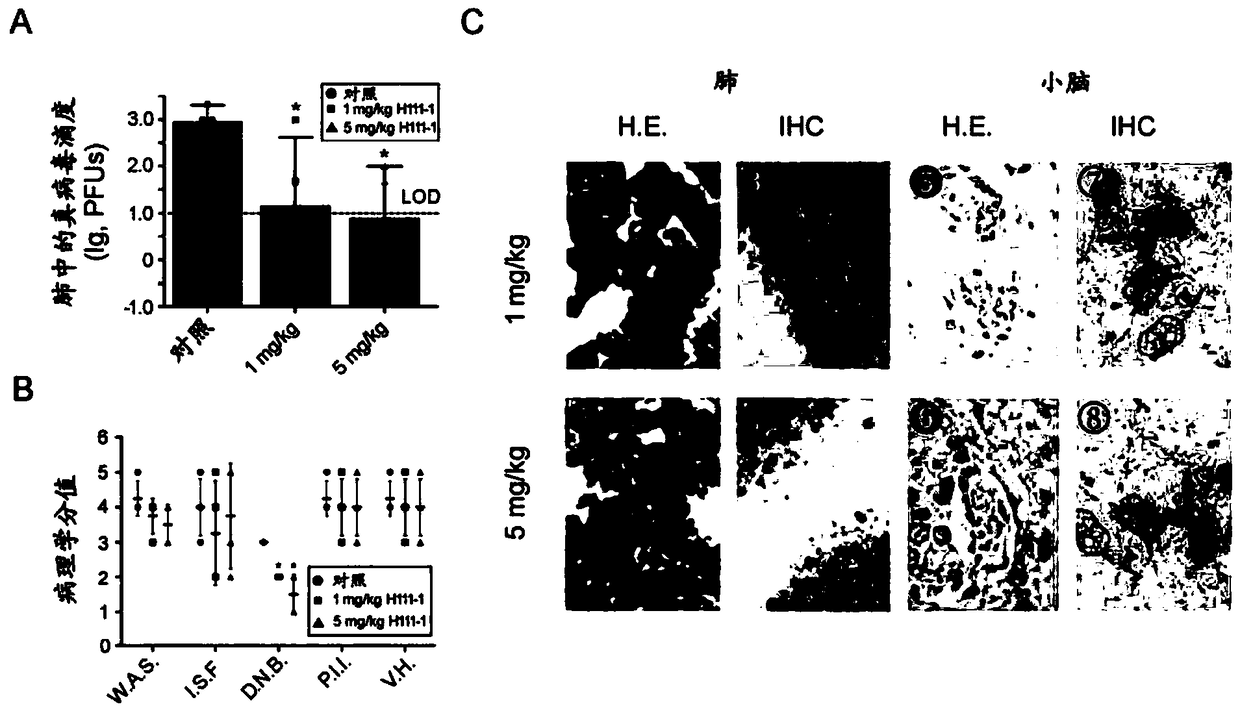
[0158] Example 3. Detection of hDPP4 gene expression and immune system detection in R26-hDPP4 mice
[0159] The expression of hDPP4mRNA in R26-hDPP4 mice was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). figure 1 D shows that significant expression of hDPP4 mRNA can be detected in lung, brain, heart, liver, kidney, and intestine. Western blotting of lung and brain tissues confirmed the expression of hDPP4 protein ( figure 1 E). The R26-hDPP4 mice of the present invention have the highest expression of hDPP4 in the lung. Benefiting from the tdTomato gene inserted after the hDPP4 gene, the expression pattern of hDPP4 in mouse tissue and whole body was visualized by bioluminescent imaging (BLI) ( figure 1 F).
[0160] The expressions of IL-12, TNF-α, INF-γ, MCP-1, IL-10 and IL-6 in R26-hDPP4 mice were detected by flow cytometry and the corresponding cytokines in wild-type C57BL / 6 mice expression was comparable, suggesting that insertion of human DPP4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com