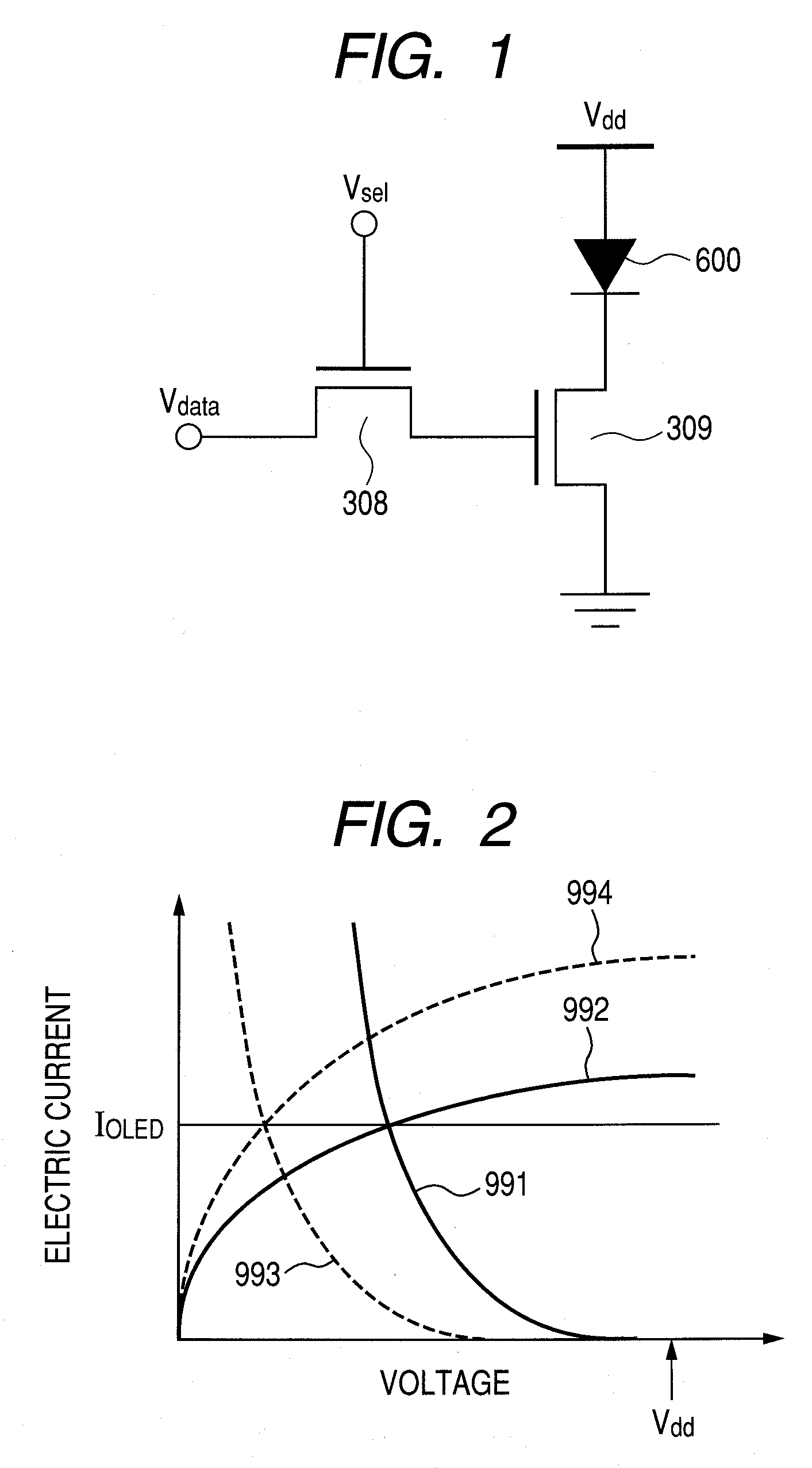
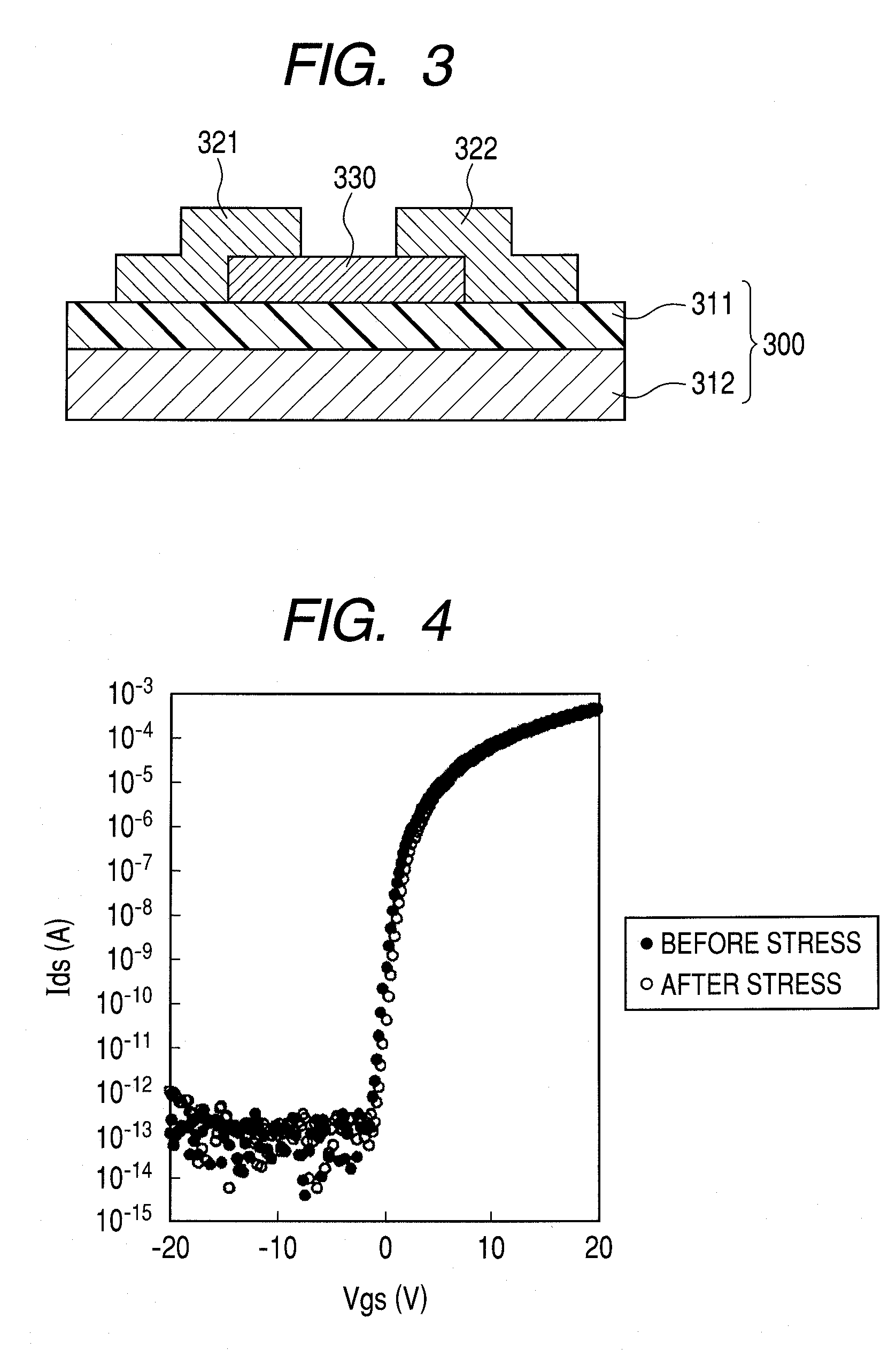
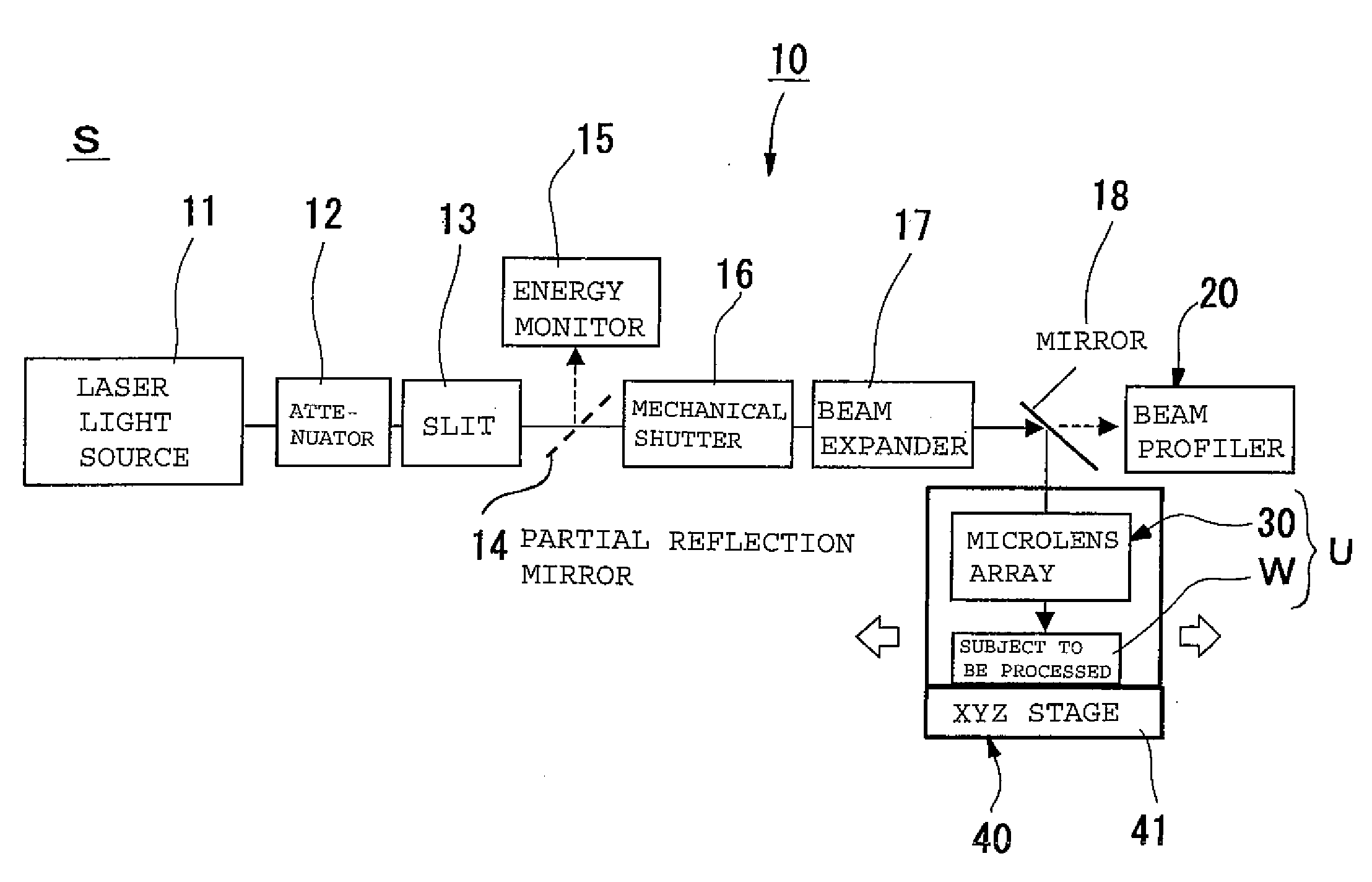
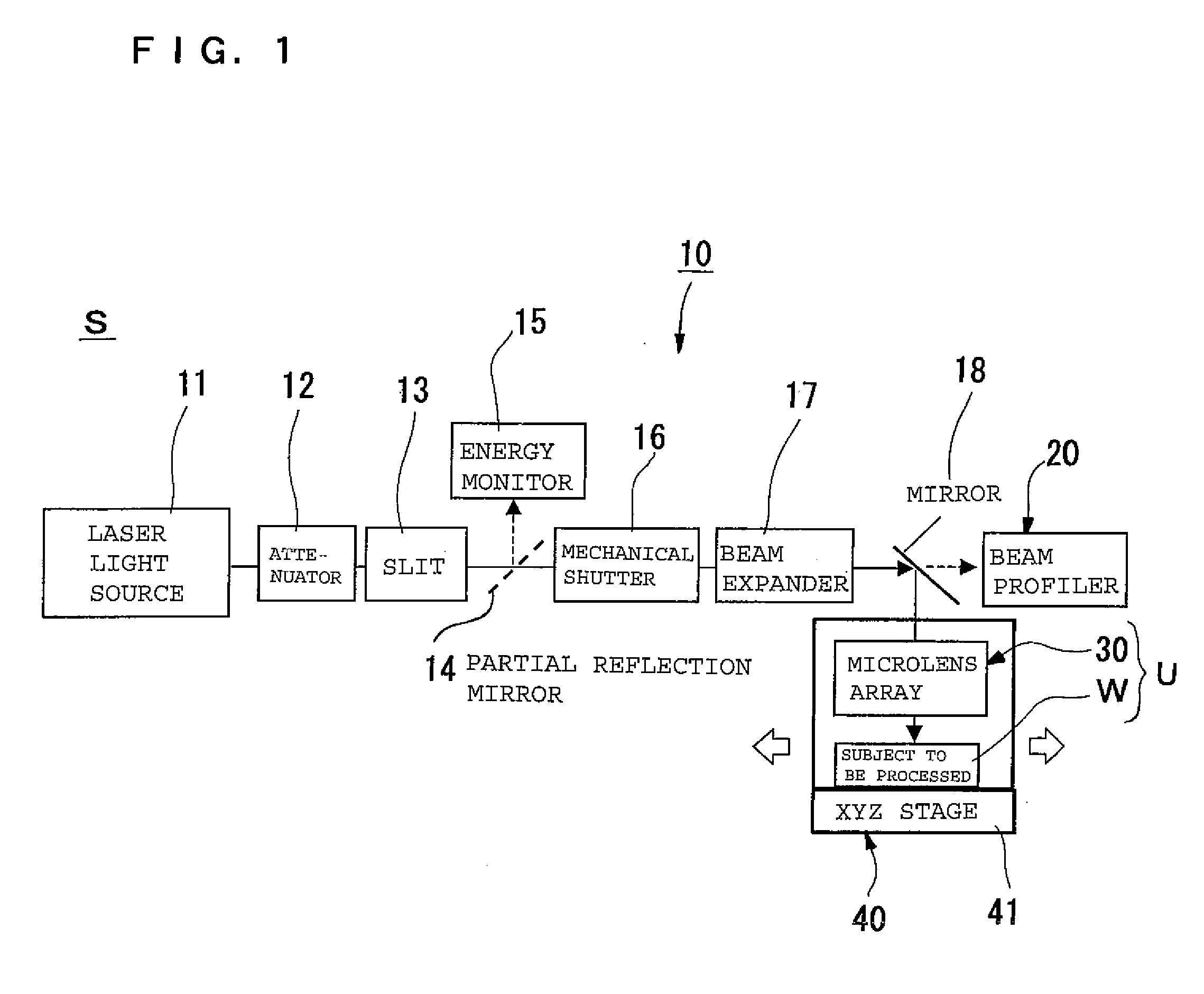
Patents
Literature
863 results about "Irradiation time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
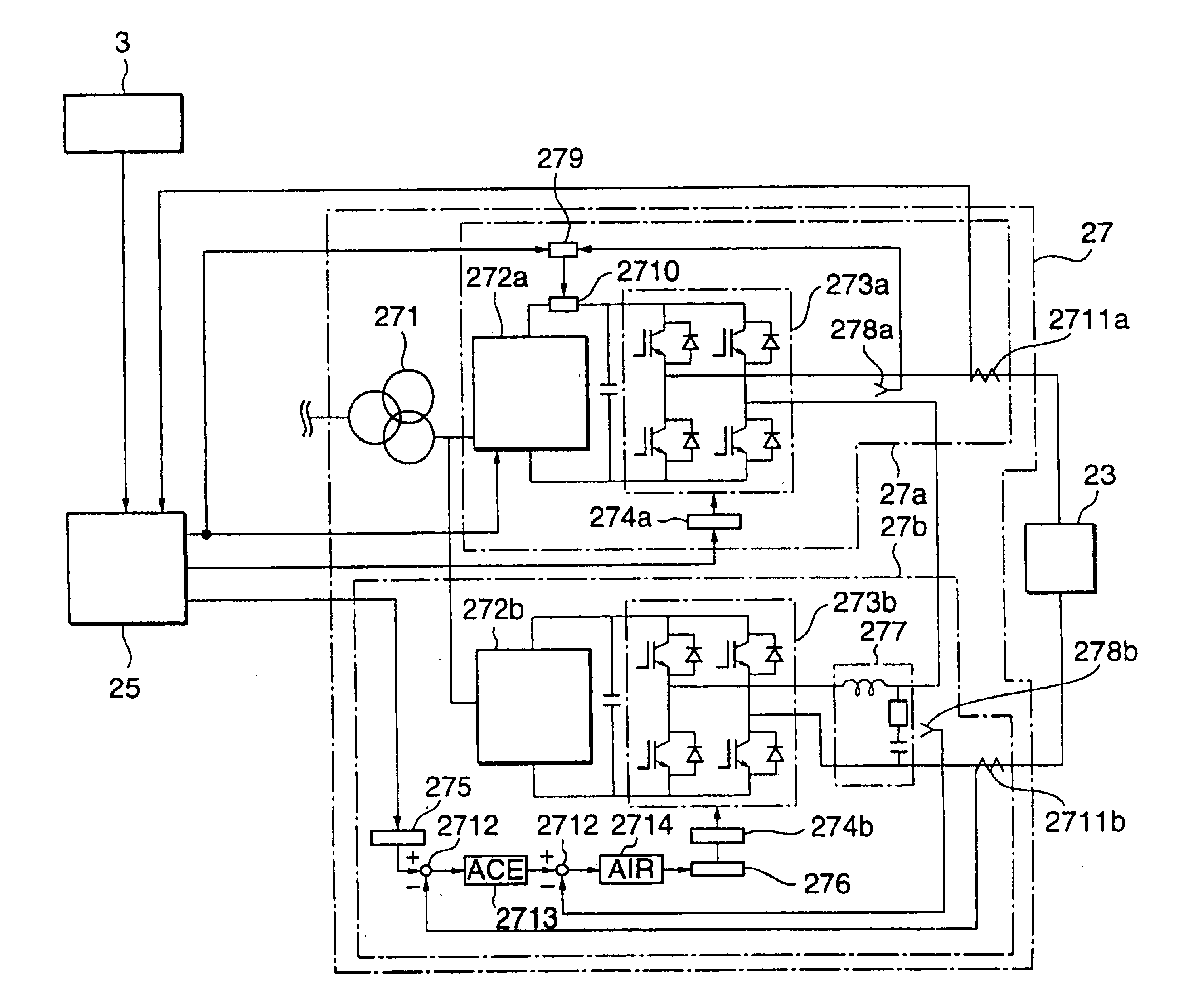
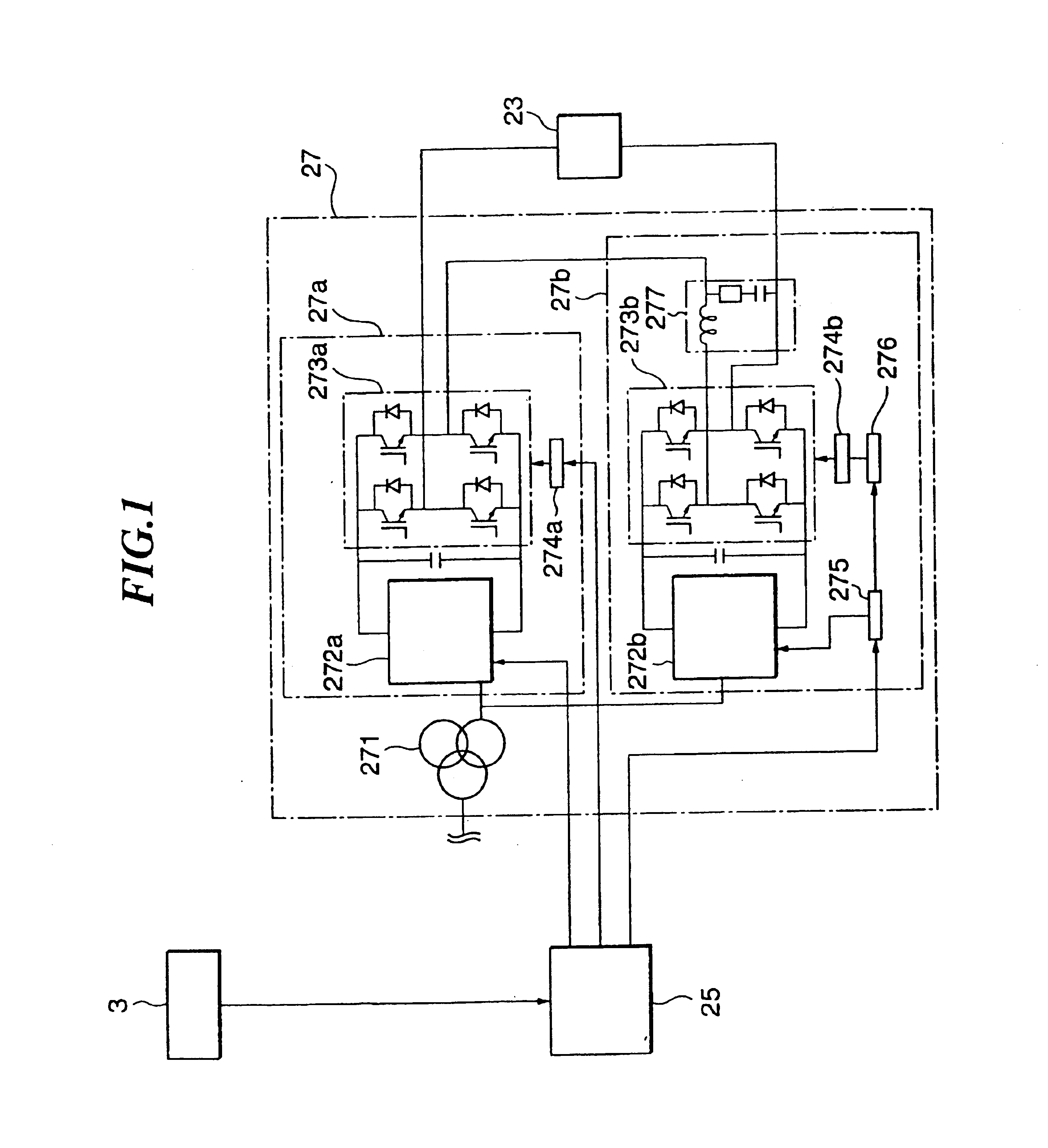
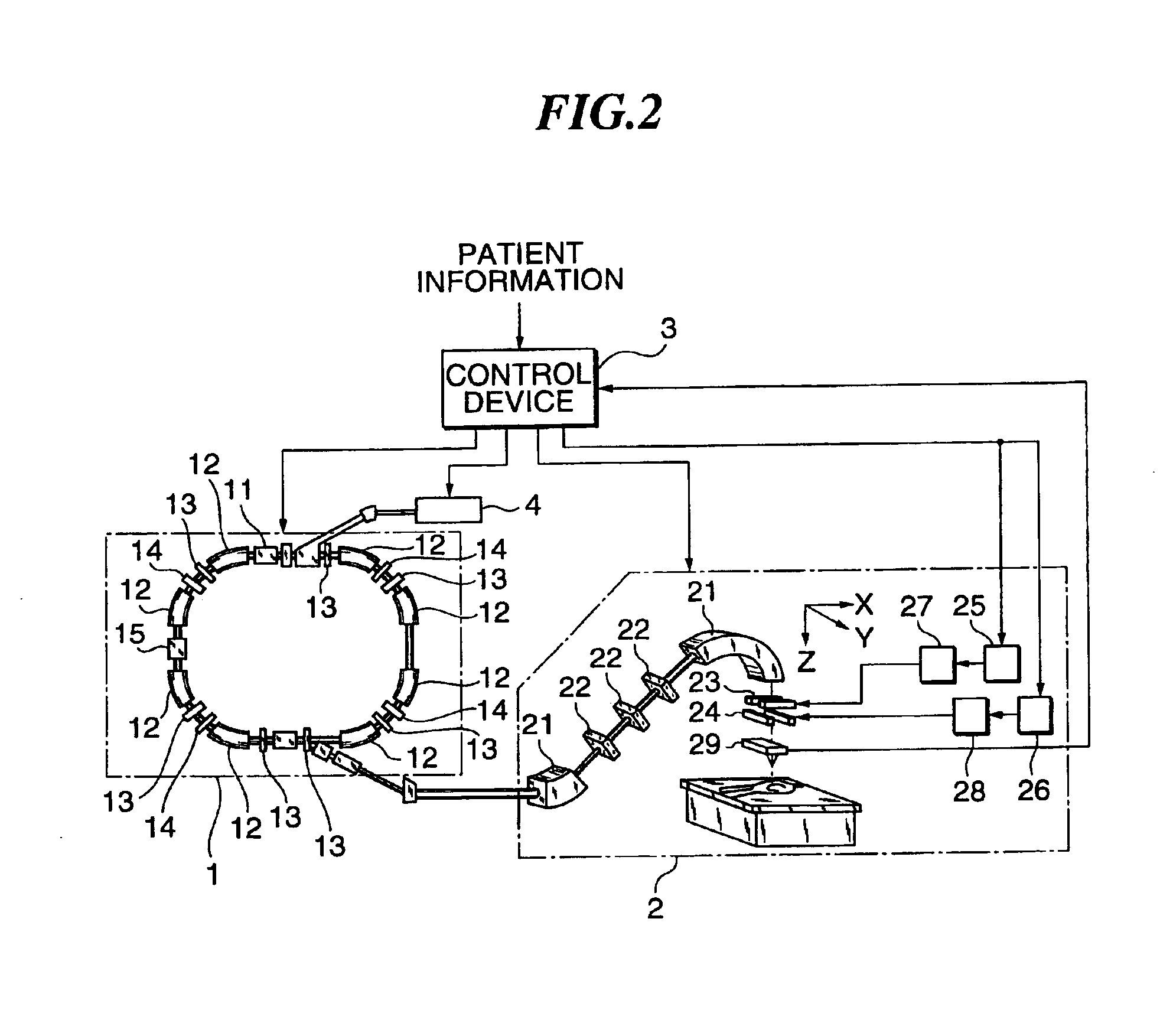
Charged particle beam irradiation equipment and control method thereof
InactiveUS6881970B2Short timeIrradiation time can be shortenedThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle physicsElectrical current
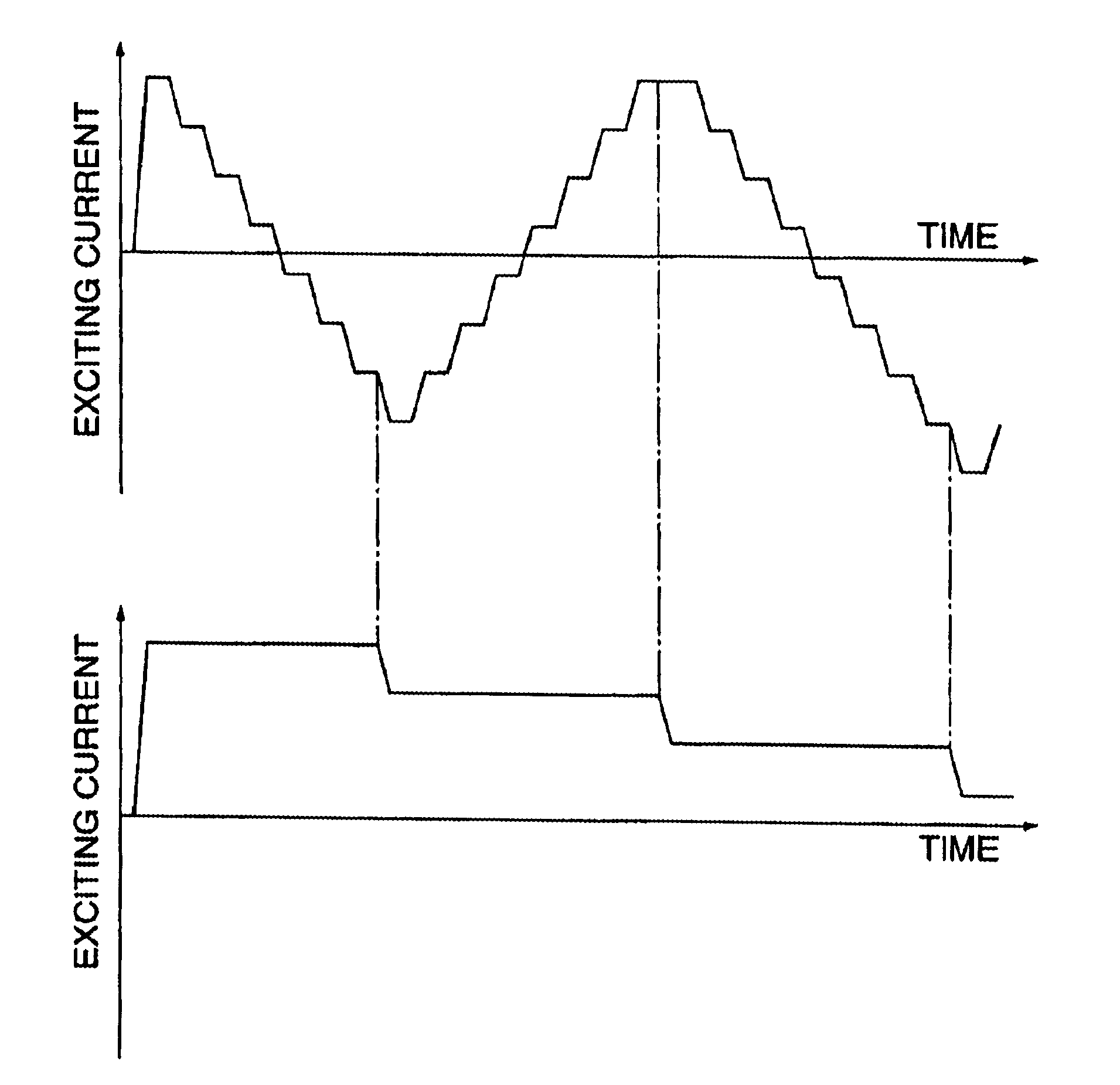
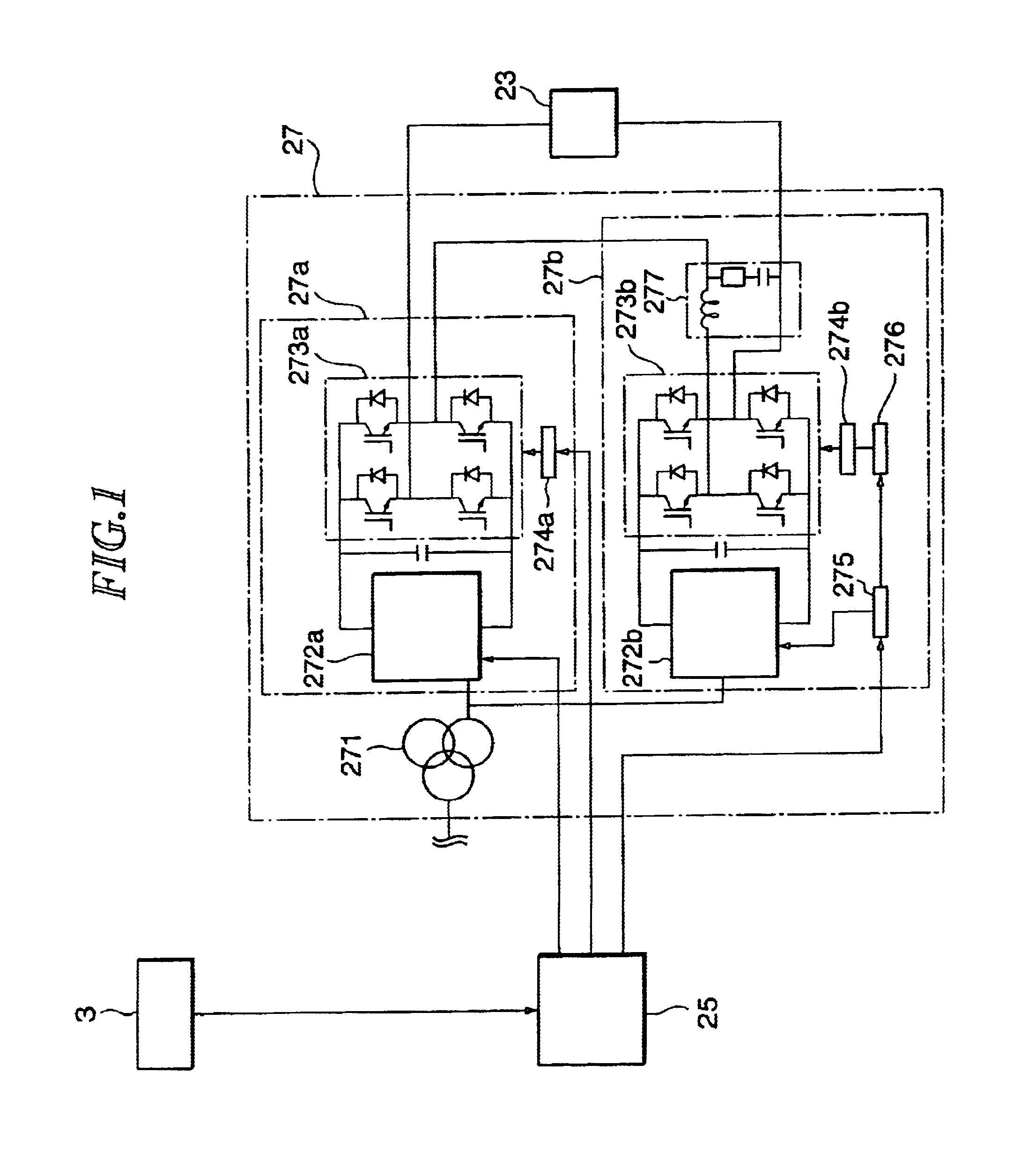
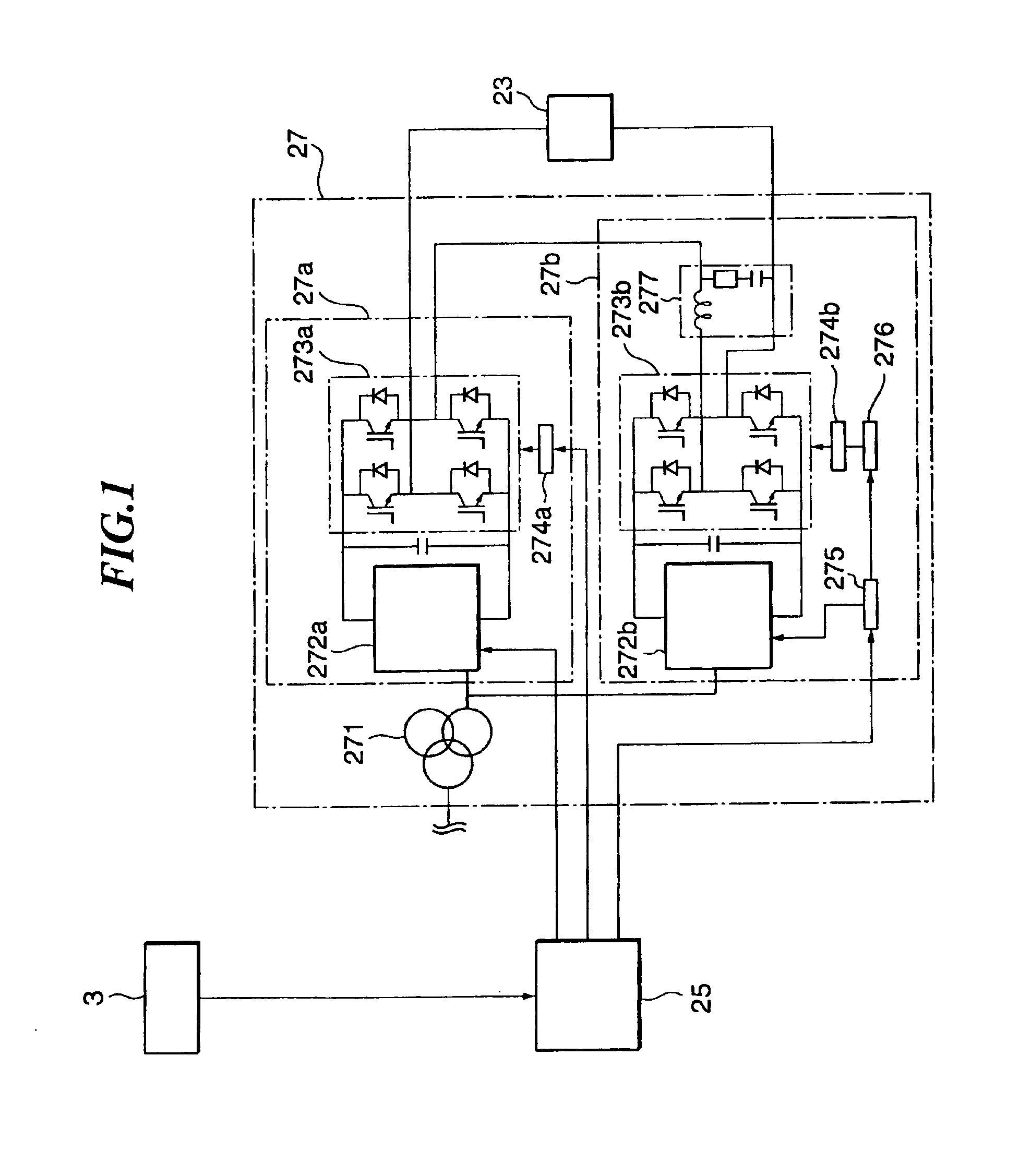
A power supply for applying a voltage to a scanning electromagnet for deflecting a charged particle beam has a first power supply unit having no filter and a second power supply unit having a filter. When an irradiation position of the charged particle beam in an irradiation object is moved, the first power supply unit, namely a power supply unit having no filter, is used to apply the voltage to the scanning electromagnet, so that an exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be changed in a short time. Further, when the irradiation position of the charged particle beam is maintained, the second power supply is used to apply a voltage whose pulsating component was removed to the scanning electromagnet, so that the exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be controlled precisely. Consequently, the charged particle beam can be applied uniformly to the irradiation object and an irradiation time of the charged particle beam to the irradiation object can be curtailed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Charged particle beam irradiation equipment having scanning electromagnet power supplies
InactiveUS6903351B1Irradiation time can be shortenedShort timeThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersExcitation currentElectrical current
A power supply for applying a voltage to a scanning electromagnet for deflecting a charged particle beam has a first power supply unit having no filter and a second power supply unit having a filter. When an irradiation position of the charged particle beam in an irradiation object is moved, the first power supply unit, namely a power supply unit having no filter, is used to apply the voltage to the scanning electromagnet, so that an exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be changed in a short time. Further, when the irradiation position of the charged particle beam is maintained, the second power supply is used to apply a voltage whose pulsating component was removed to the scanning electromagnet, so that the exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be controlled precisely. Consequently, the charged particle beam can be applied uniformly to the irradiation object and an irradiation time of the charged particle beam to the irradiation object can be curtailed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Charged particle beam irradiation equipment and control method thereof
InactiveUS6900446B2Irradiation time can be shortenedShort timeStability-of-path spectrometersStatic indicating devicesParticle physicsElectrical current
A power supply for applying a voltage to a scanning electromagnet for deflecting a charged particle beam has a first power supply unit having no filter and a second power supply unit having a filter. When an irradiation position of the charged particle beam in an irradiation object is moved, the first power supply unit, namely a power supply unit having no filter, is used to apply the voltage to the scanning electromagnet, so that an exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be changed in a short time. Further, when the irradiation position of the charged particle beam is maintained, the second power supply is used to apply a voltage whose pulsating component was removed to the scanning electromagnet, so that the exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be controlled precisely. Consequently, the charged particle beam can be applied uniformly to the irradiation object and an irradiation time of the charged particle beam to the irradiation object can be curtailed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
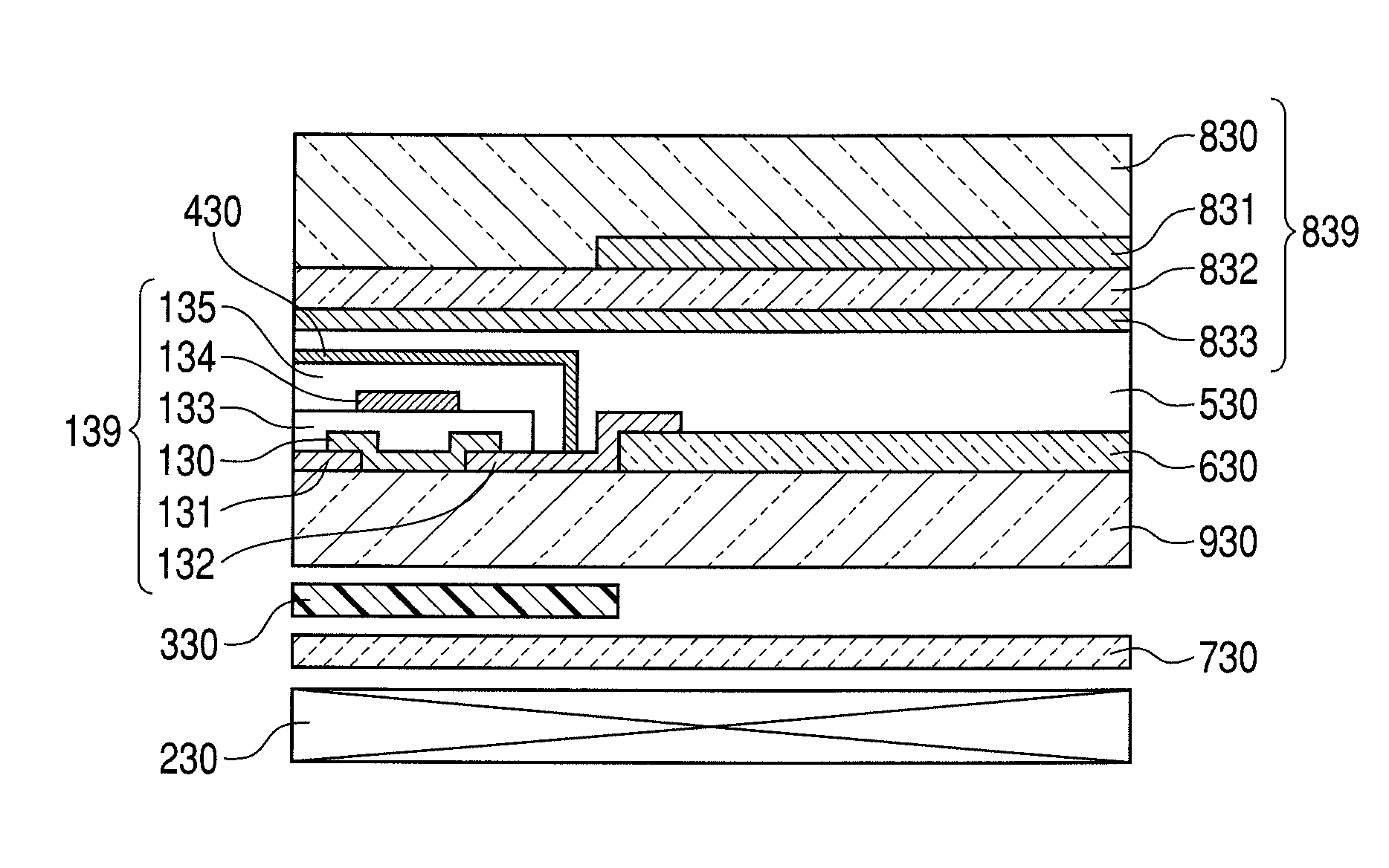
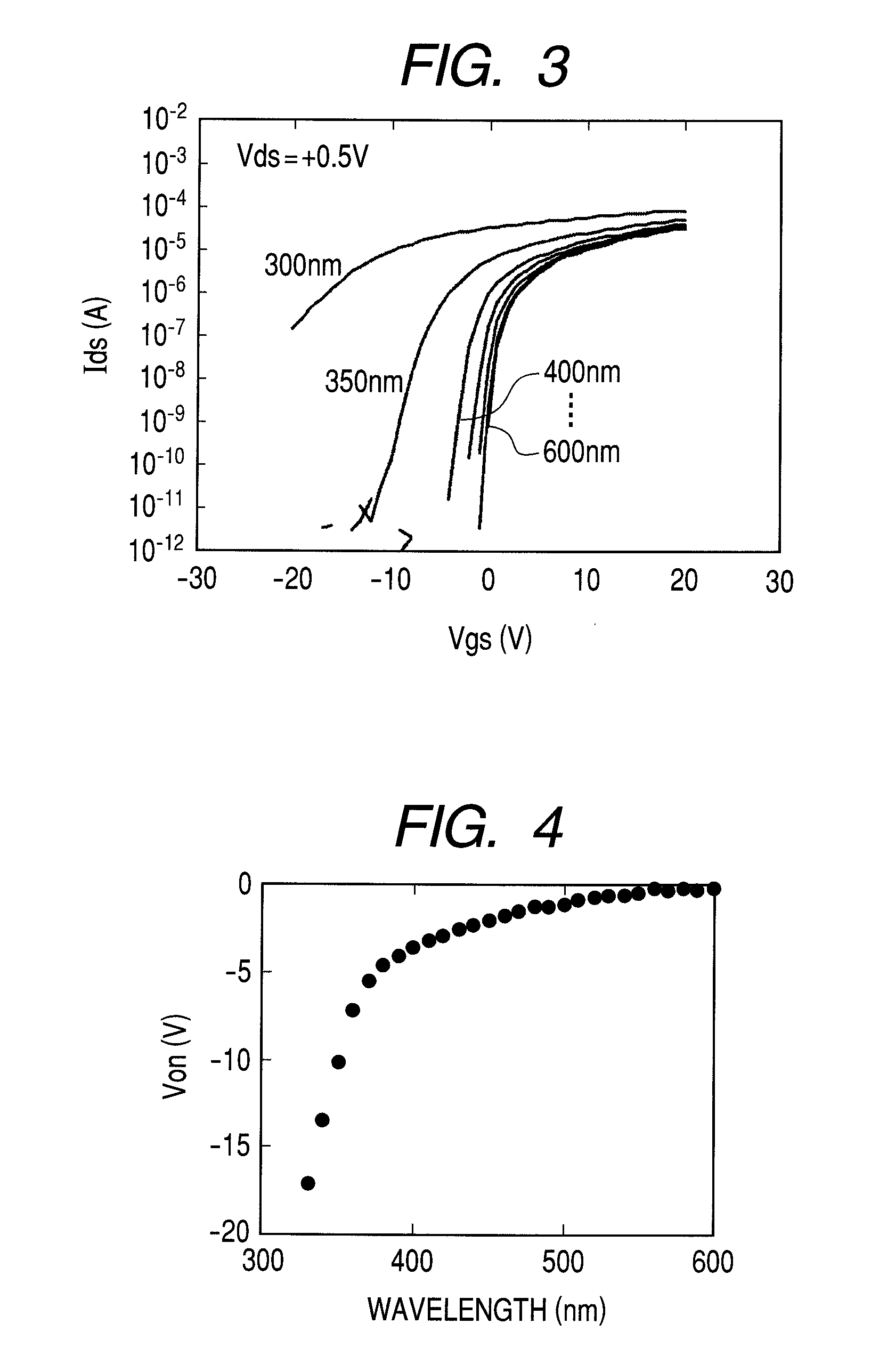
Method for controlling threshold voltage of semiconductor element
ActiveUS8530246B2Accurate operationComplicates the entire circuitSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThreshold voltageVoltage
A method for controlling the threshold voltage of a semiconductor element having at least a semiconductor as a component is characterized in including a process to measure one of a threshold voltage and a characteristic value serving as an index for the threshold voltage; a process to determine one of the irradiation intensity, irradiation time, and wavelength of the light for irradiating the semiconductor based on one of the measured threshold voltage and the measured characteristic value serving as the index for the threshold voltage; and a process to irradiate light whose one of the irradiation intensity, irradiation time, and wavelength has been determined onto the semiconductor; wherein the light irradiating the semiconductor is a light having a longer wavelength than the wavelength of the absorption edge of the semiconductor, and the threshold voltage is changed by the irradiation of the light.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods for uniformly treating biological samples with electromagnetic radiation
ActiveUS20050202395A1Effective pathogen reductionUnified processingElectrotherapyDead animal preservationBlood componentMedicine
Methods, devices and device components are presented for uniformly treating fluids undergoing mixing with electromagnetic radiation. In one aspect, the present invention provides methods of treating a fluid undergoing continuous fluid mixing wherein net radiant energies necessary to provide uniform treatment of the fluid samples with electromagnetic radiation are calculate on the basis of the volume, mass or mixing rate of the fluid or any combination of these variables. In another aspect, the present invention provides algorithms for determining net radiation energies, radiant powers, and / or illumination times necessary for providing uniform treatment of fluid samples. The present invention provides methods for uniformly reducing pathogens in biological fluids, including blood and blood components.
Owner:TERUMO BCT BIOTECH
Method for controlling threshold voltage of semiconductor element
ActiveUS20110076790A1Fluctuation of threshold voltageSuppress fluctuationsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLength wave
A method for controlling the threshold voltage of a semiconductor element having at least a semiconductor as a component is characterized in including a process to measure one of a threshold voltage and a characteristic value serving as an index for the threshold voltage; a process to determine one of the irradiation intensity, irradiation time, and wavelength of the light for irradiating the semiconductor based on one of the measured threshold voltage and the measured characteristic value serving as the index for the threshold voltage; and a process to irradiate light whose one of the irradiation intensity, irradiation time, and wavelength has been determined onto the semiconductor; wherein the light irradiating the semiconductor is a light having a longer wavelength than the wavelength of the absorption edge of the semiconductor, and the threshold voltage is changed by the irradiation of the light.
Owner:CANON KK
Laser Processing Apparatus and Laser Processing Method
A laser processing apparatus for processing a multitude of portions to be processed in an area to be processed in a subject W to be processed, including a laser device, a focusing or imaging means for laser beams provided by the laser device, and an arranging means for arranging the subject W to be processed, in which the subject W to be processed and the focusing or imaging means are fixed, and the subject to be processed is processed while relatively shifting the laser beams and the focusing or imaging means so that the focusing or imaging means is irradiated from different areas in the laser beam, inside and outside the area to be processed, and that cumulative laser beam irradiation time during the processing of each of the multitude of portions to be processed is equalized.
Owner:PHOETON CORP
Systems and methods for collapsing air lines in nanostructured optical fibers
InactiveUS20090199597A1Heating evenlyGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesLine tubingMid infrared
Systems and methods of collapsing the air lines in the air line-containing region of a nanostructure optical fiber are disclosed. One method includes initiating irradiation of a portion of the nanostructure optical fiber from essentially opposite directions with at least first and second laser beams having substantially equal power and essentially the same mid-infrared wavelength. The method includes continuing the irradiation for an irradiation time t1 so as to bring the optical fiber portion to a softening temperature TS at which the air lines in the optical fiber portion collapse into the adjacent cladding. Exemplary optical systems for carrying out the air- line-collapsing methods of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
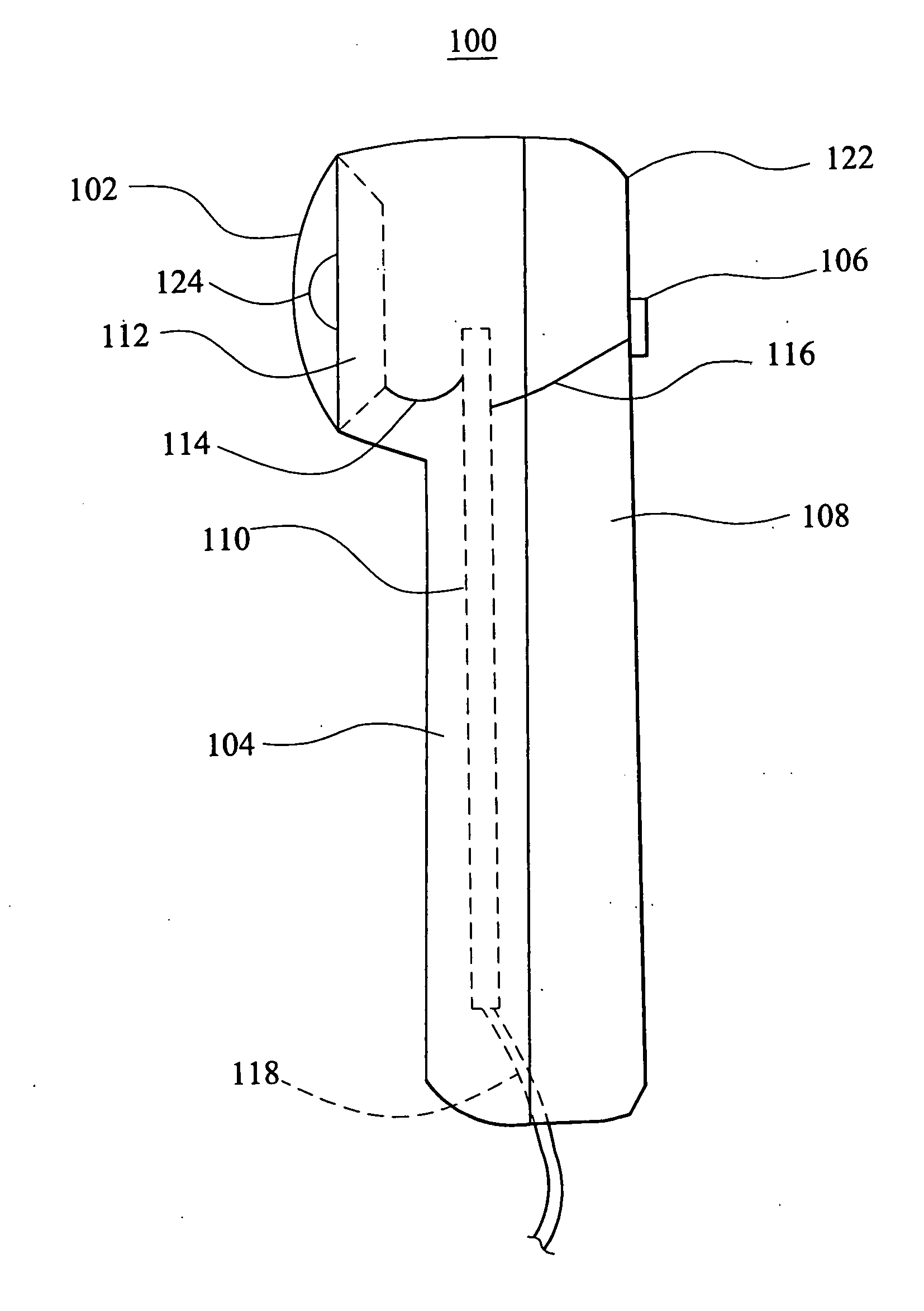
Portable infrared device
InactiveUS20050065579A1Not hurt or burn the skin being treatedEasy to operateElectrotherapyLight therapyInfraredEngineering
Disclosed is a portable IR device for the treatment of skin. The device comprises a handle, a light-emitting assembly including one or more replaceable light-emitting elements formed of either the same LED for emitting IR rays of a predetermined wavelength or different LEDs for emitting IR rays of different wavelengths, and a controller assembly coupled to the light-emitting assembly for controlling irradiation time, wavelength of IR rays, and light-emitting mode of each light-emitting element. Holding the handle and activating the device will cause the light-emitting elements to emit IR rays for treating the skin in close proximity therewith.
Owner:CHEN GEORGE C C +1
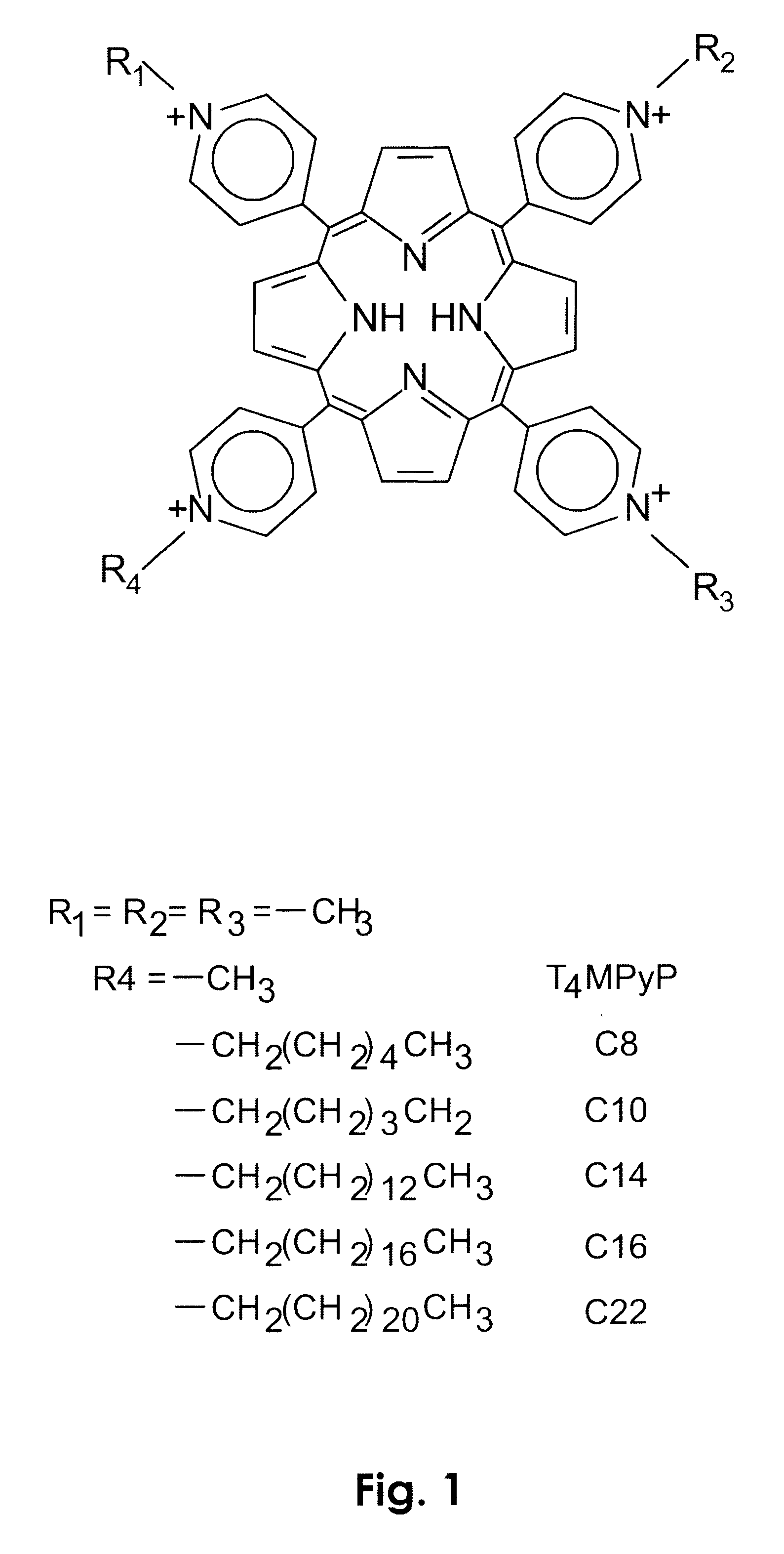
Photodynamic porphyrin antimicrobial agents
A series of novel positively-charged porphyrins is disclosed which exhibit a markedly increased efficiency in photosensitizing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria to the action of visible light, causing death to such bacteria when present at much lower concentrations and much shorter irradiation times than those porphyrins taught in the prior art. These porphyrins are characterized by the presence of up to four positive charges in the peripheral substituents and at least one hydrophobic tail comprising between 6 and 22 carbons inclusive, originating at one or more of the charged sites.
Owner:FRONTIER SCI INC
A kind of glass transparent thermal insulation coating and preparation method thereof
A glass transparent heat-insulating coating and its preparation method, the coating contains cesium tungsten bronze powder with a general formula of Cs0.1-3.5WO3, the crystal phase composition of the powder is Cs0.2WO3 or Cs0.32WO3, the powder The particle size is 100-1300nm, and the specific surface area is 7-50m2 / g. The glass transparent heat-insulating coating of the present invention has the functions of visible light transmission and near-infrared shielding, and has the function of light self-regulation, that is, with the extension of light intensity and light time, the effects of visible light transmission and near-infrared shielding will be further enhanced , so it is especially suitable for preparing transparent thermal insulation film on the surface of glass. It is an intelligent transparent thermal insulation coating for glass and has broad application prospects in the fields of thermal insulation of architectural window glass and automotive glass. The coating has simple components and is suitable for large-scale industrial production and practical application.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Pulsed laser beam machining method and apparatus for machining a wiring board at multiple locations
InactiveUS20050184035A1Rapidly and accurately be machinedLaser beam welding apparatusEtching metal masksLaser beam machiningLight beam
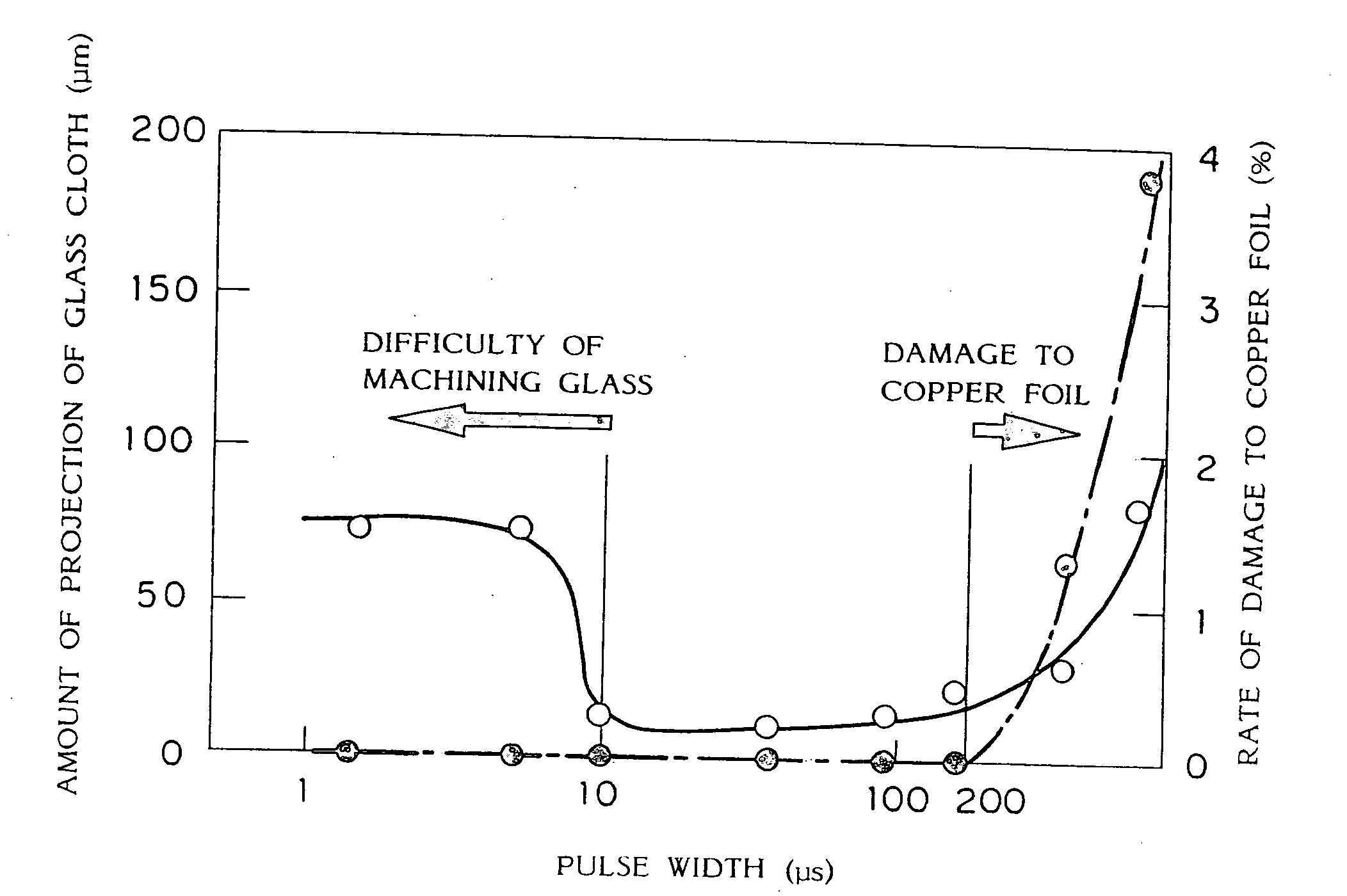
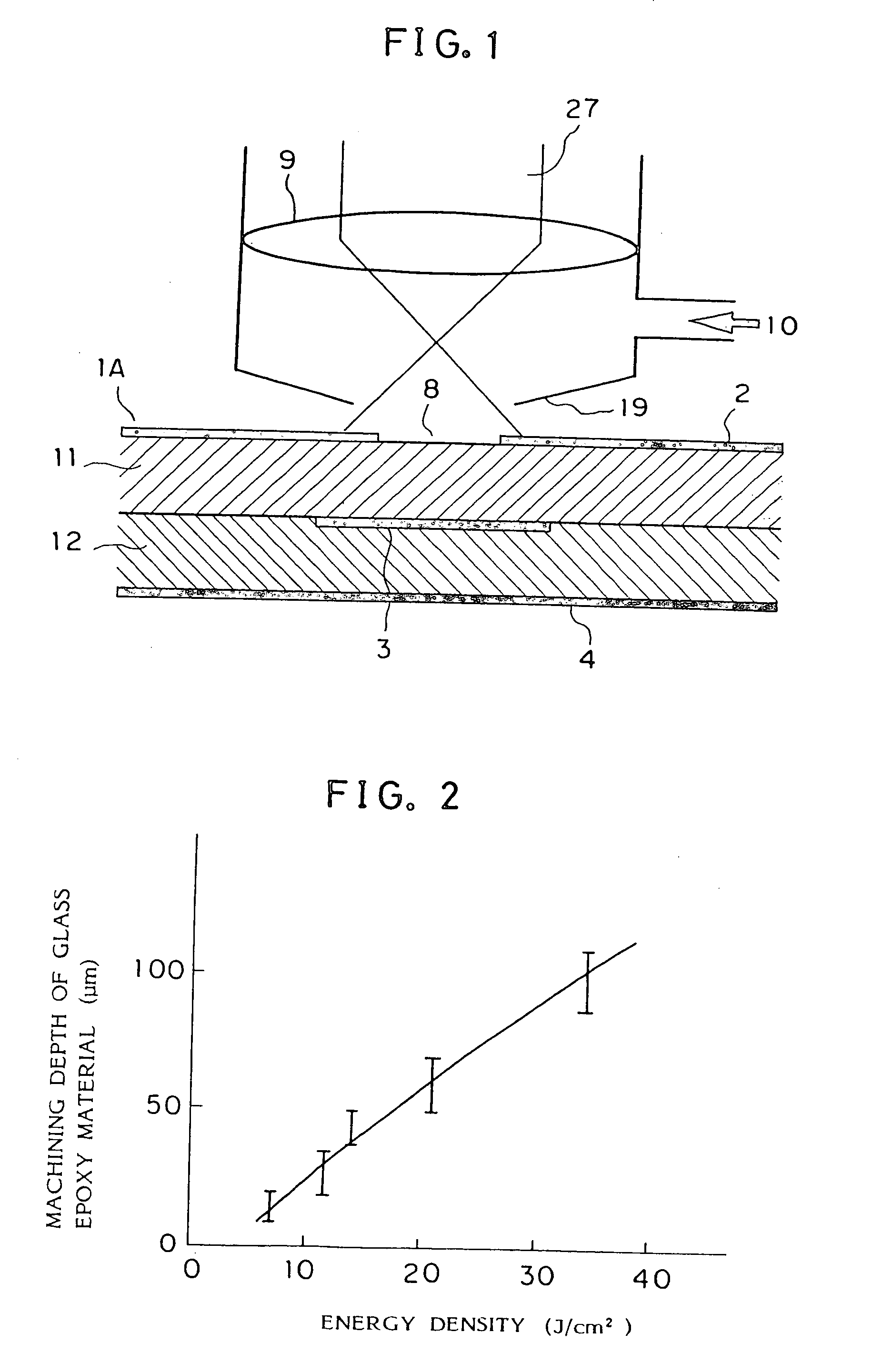
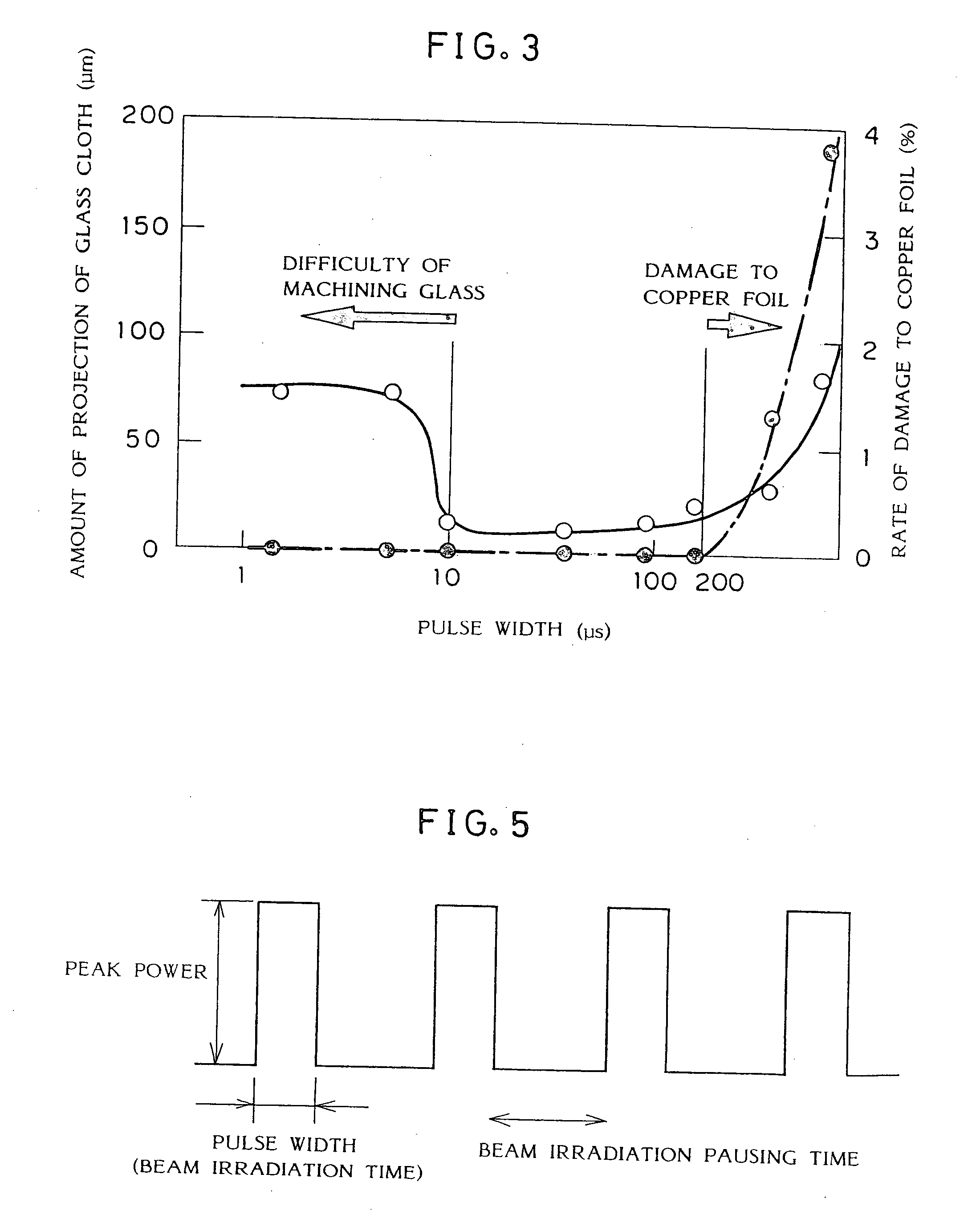
In a laser beam machining method for a wiring board, a machined portion of the wiring board is irradiated with a pulsed laser beam for a beam irradiation time ranging from about 10 to 200 μs and with energy density of about 20 J / cm2 or more, thereby machining the wiring board, for example, drilling for a through-hole and a blind via hole, grooving, and cutting for an outside shape. The laser beam operates at a frequency of more than 67 Hz, and the spot of the laser beam is sequentially moved to different drilling positions for each pulse. After all of many drilling positions in the range of a scan vision are irradiated with the laser beam pulse by pulse, or after the elapse of a time of 15 ms or more from irradiation of the first drilling position, the laser spot is returned to the first drilling position. The spot is sequentially moved once again, and the movement is repeated several times. A pause of 15 ms or more is required between pulses directed to the same drilling position to avoid formation of a thick char layer and projection of glass cloth into the hole.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Methods of manufacturing electron-emitting device, electron source, and image display apparatus
InactiveUS6896571B2Save power consumptionImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage/pattern display tubesElectron sourcePolymer
In a process of reducing a resistivity of a polymer film for carbonization in a surface conduction electron-emitting device, by irradiating an energy beam onto the polymer film, when an energy intensity of the beam given in a unit area in a unit time is assumed to be W W / m2, W satisfies a formula W≧2×T×(ρsub·Csub·λsub / τ)1 / 2, where T is defined as a temperature ° C. at which the polymer film is heated for one hour in a vacuum degree of 1×10−4 Pa to reduce a resistivity of the polymer film to 0.1 Ω·cm, Csub is a specific heat J / kg·K of the substrate, ρsub is a specific gravity kg / m3 of the substrate, λsub is a heat conductivity W / m·K of the substrate, and τ is an irradiation time in the range of 10−9 sec to 10 sec.
Owner:CANON KK
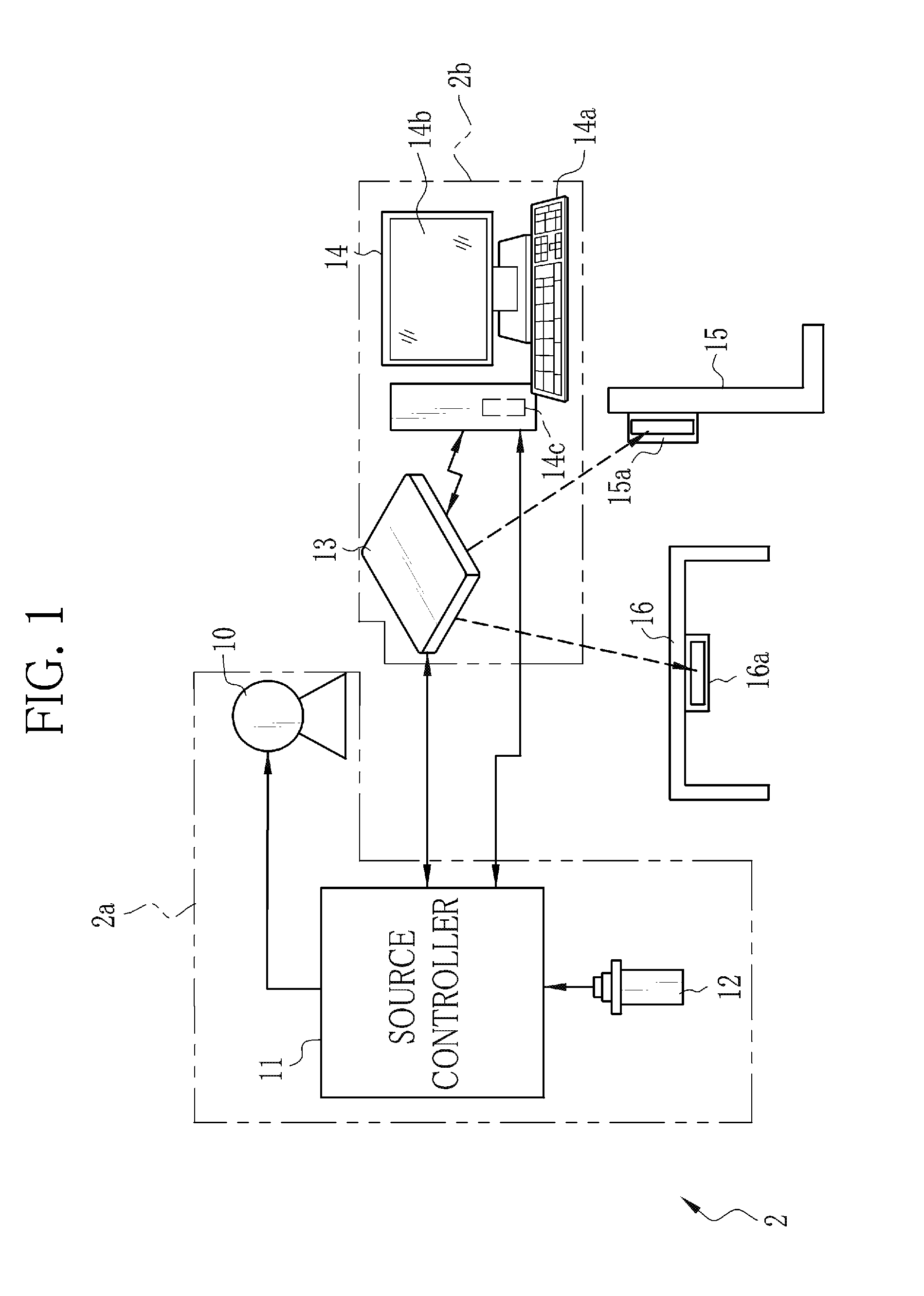
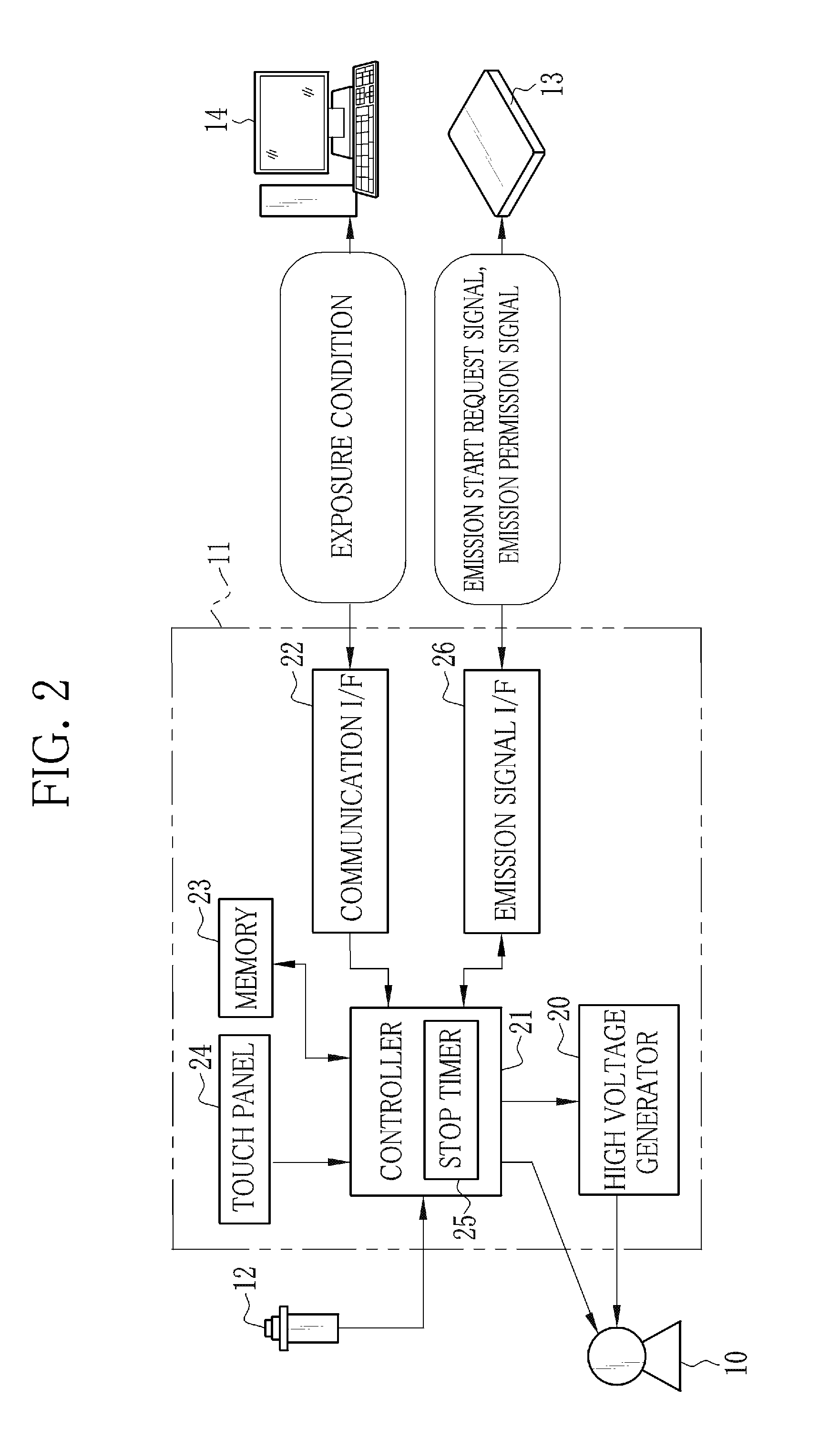
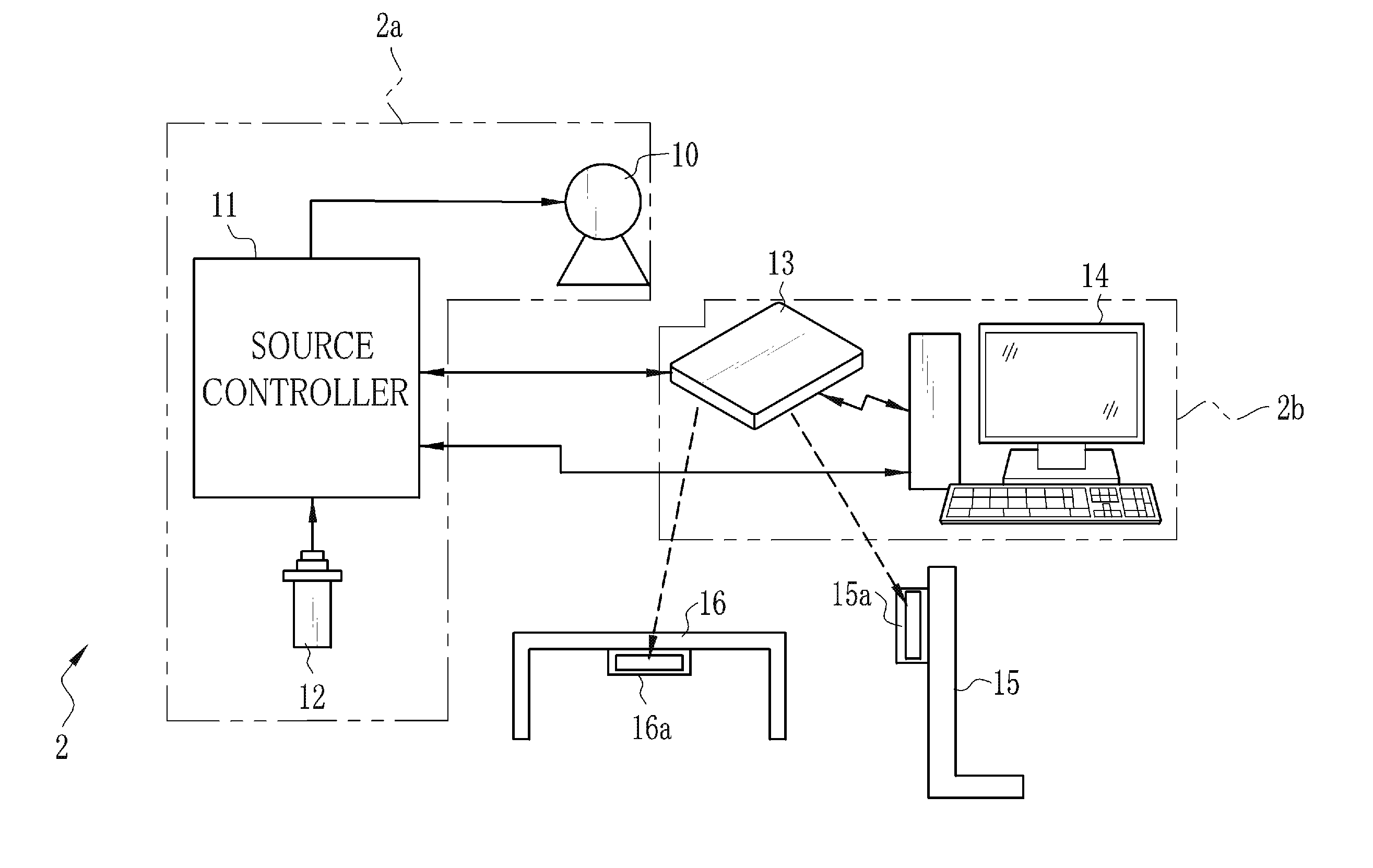
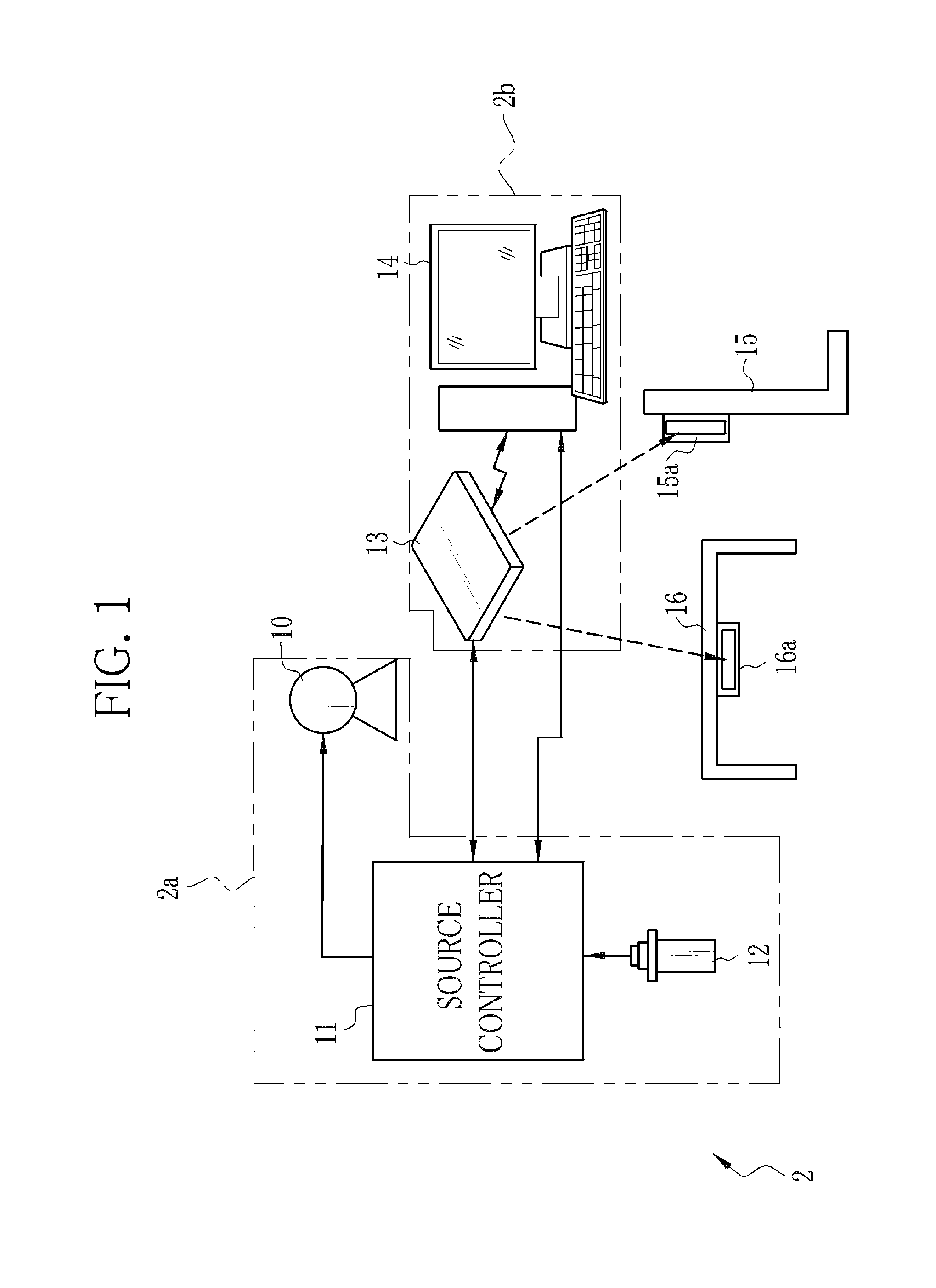
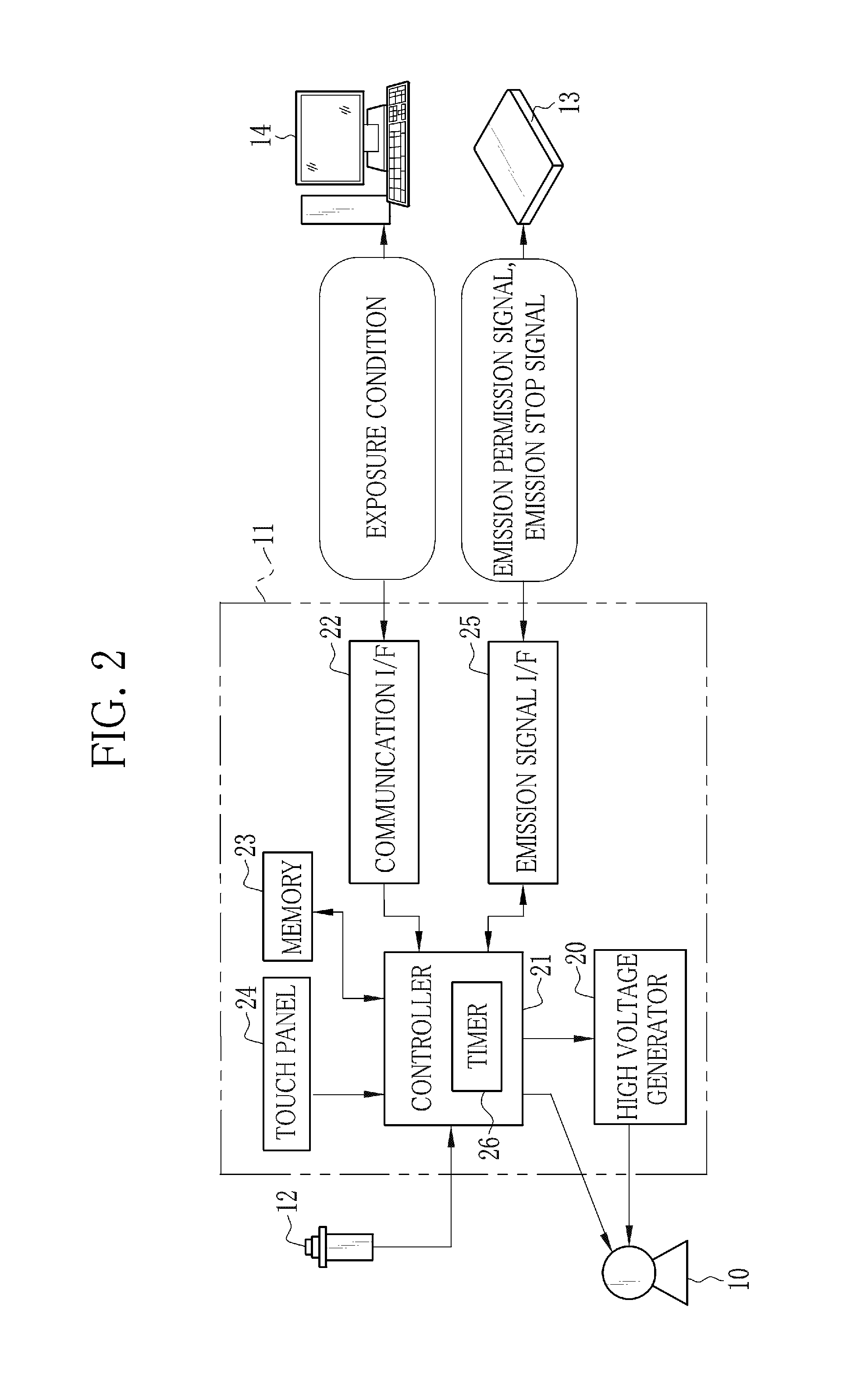
Radiation imaging apparatus and operation method thereof
InactiveUS20130148782A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation imagingExposure
An X-ray imaging system performs pre-exposure and main exposure to take a single X-ray image. In the pre-exposure, an AEC circuit reads out a dose detection signal outputted from a detection pixel, and compares an integral value of the dose detection signal with a threshold value. When the integral value has reached the threshold value, the AEC circuit stops X-ray emission. A main exposure condition determination unit determines main irradiation time, being one item of a main exposure condition, based on irradiation time in the pre-exposure, an integral dose in the pre-exposure, and a necessary dose required for production of the X-ray image. After that, the main exposure is performed immediately with the determined main irradiation time. Normal pixels perform a charge accumulation operation continuously from the start of the pre-exposure to the end of the main exposure, and the X-ray image is produced from accumulated electric charge.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
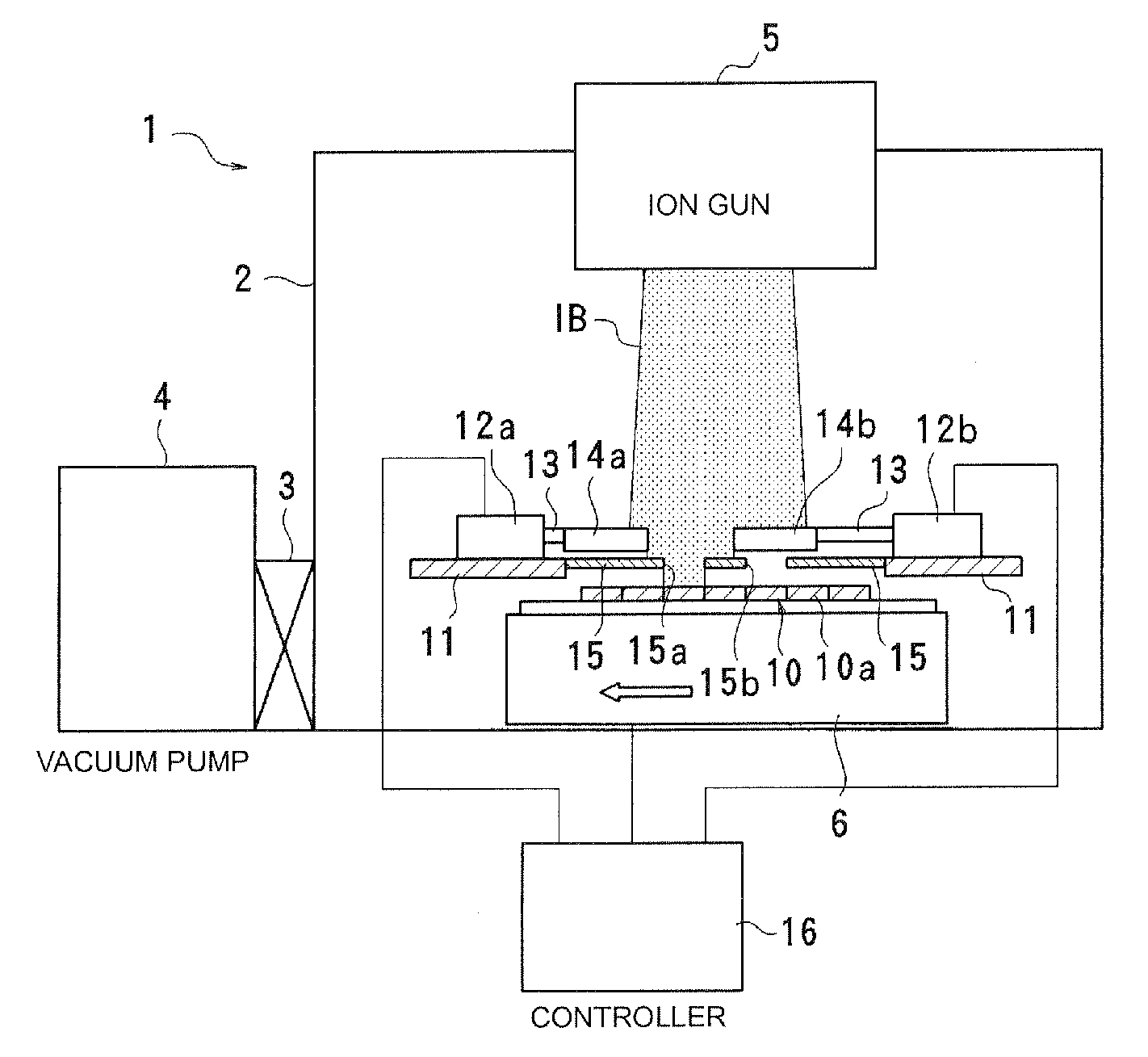
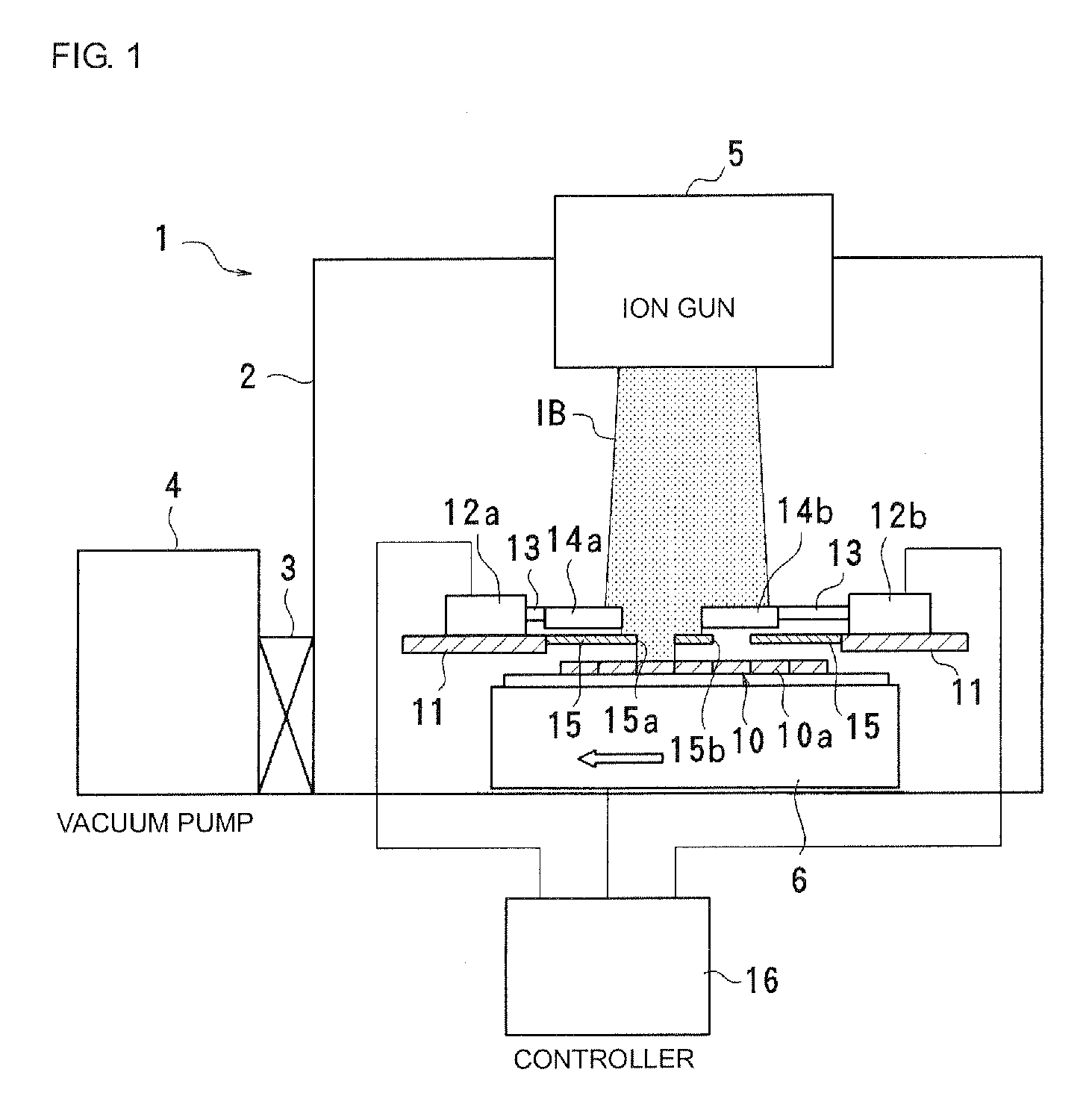
Frequency adjusting apparatus
A wafer having a plurality of elements closely arranged thereon is irradiated with an ion beam while being conveyed in one direction by a conveying unit. Each of shutters adjusts an irradiation time during which a target area of the wafer is irradiated with the ion beam. Thus, a frequency in the target area is adjusted. Each of a plurality of mask holes in a pattern mask disposed between the wafer and the shutters corresponds to one area of the wafer. The mask holes are alternately displaced in a wafer conveying direction in which the wafer is conveyed, and are arranged in a plurality of columns perpendicular to the wafer conveying direction. To individually open and close the mask holes, the shutters are arranged to correspond to the respective mask holes. Thus, frequency adjustment, for areas in one column perpendicular to the wafer conveying direction, is performed in multiple steps.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Lighting system for preventing plant disease damage
InactiveUS20110163246A1Suppress manufacturing costAdditional componentElectrical apparatusSaving energy measuresDiseaseEffect light
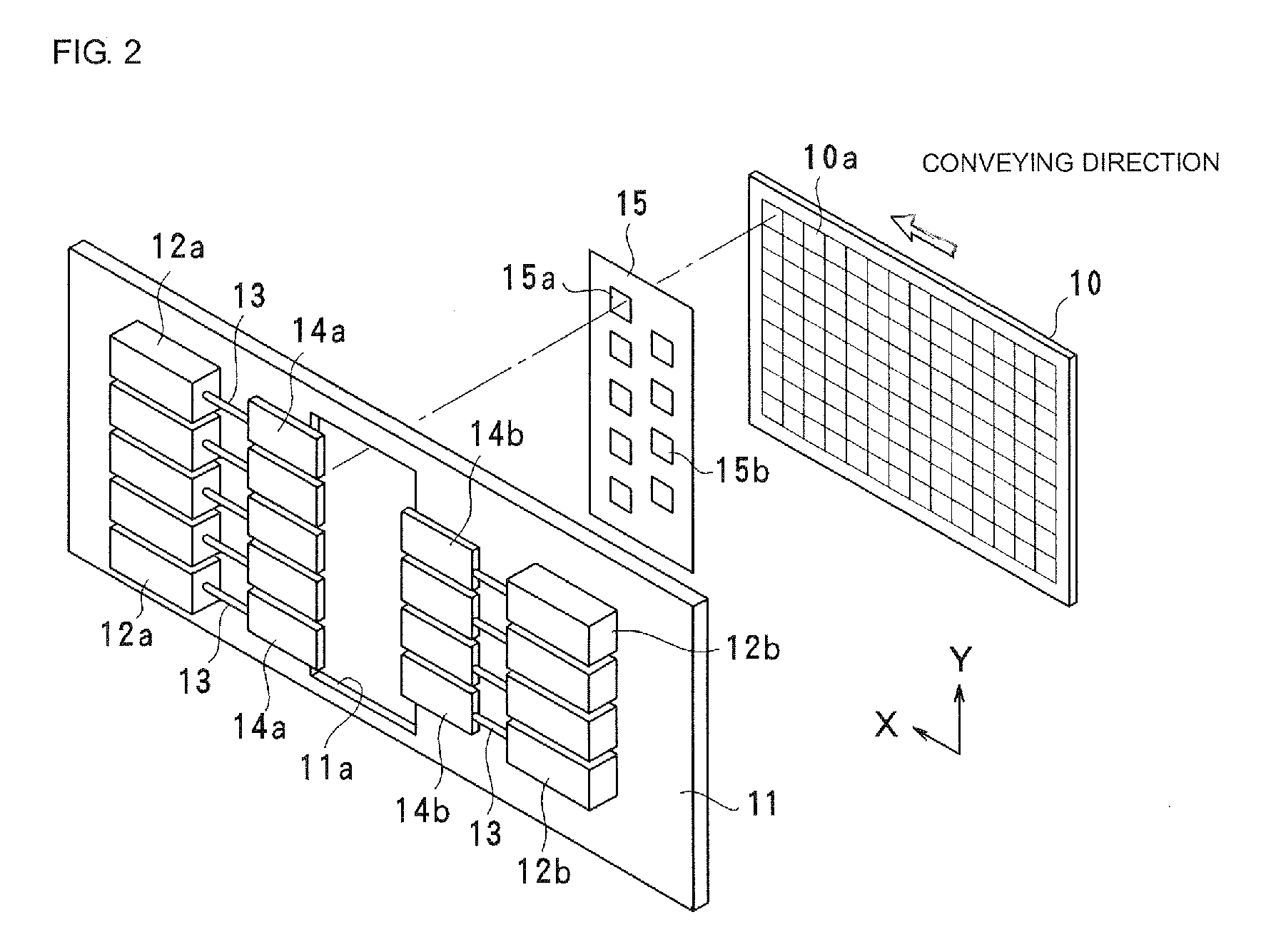
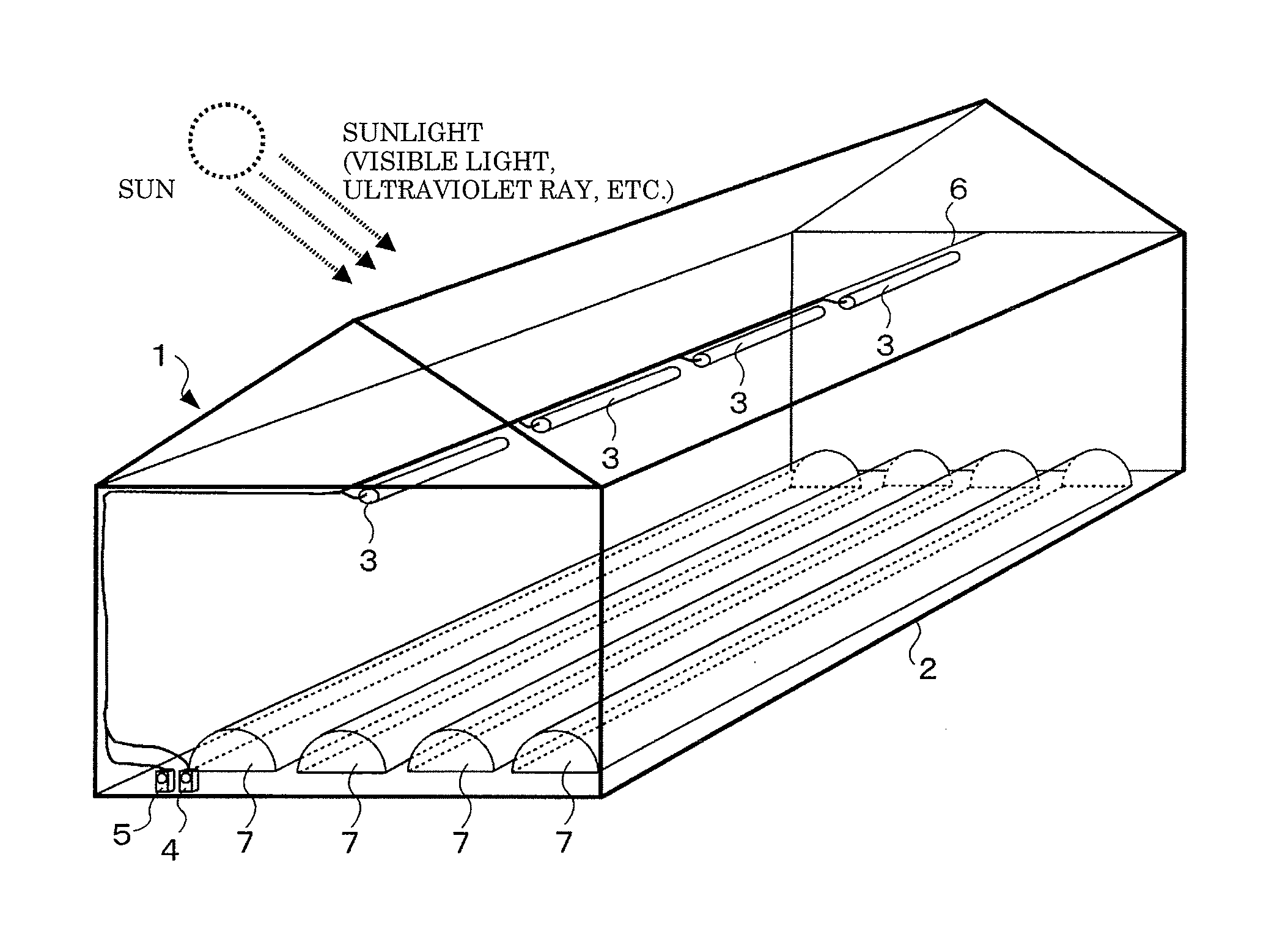
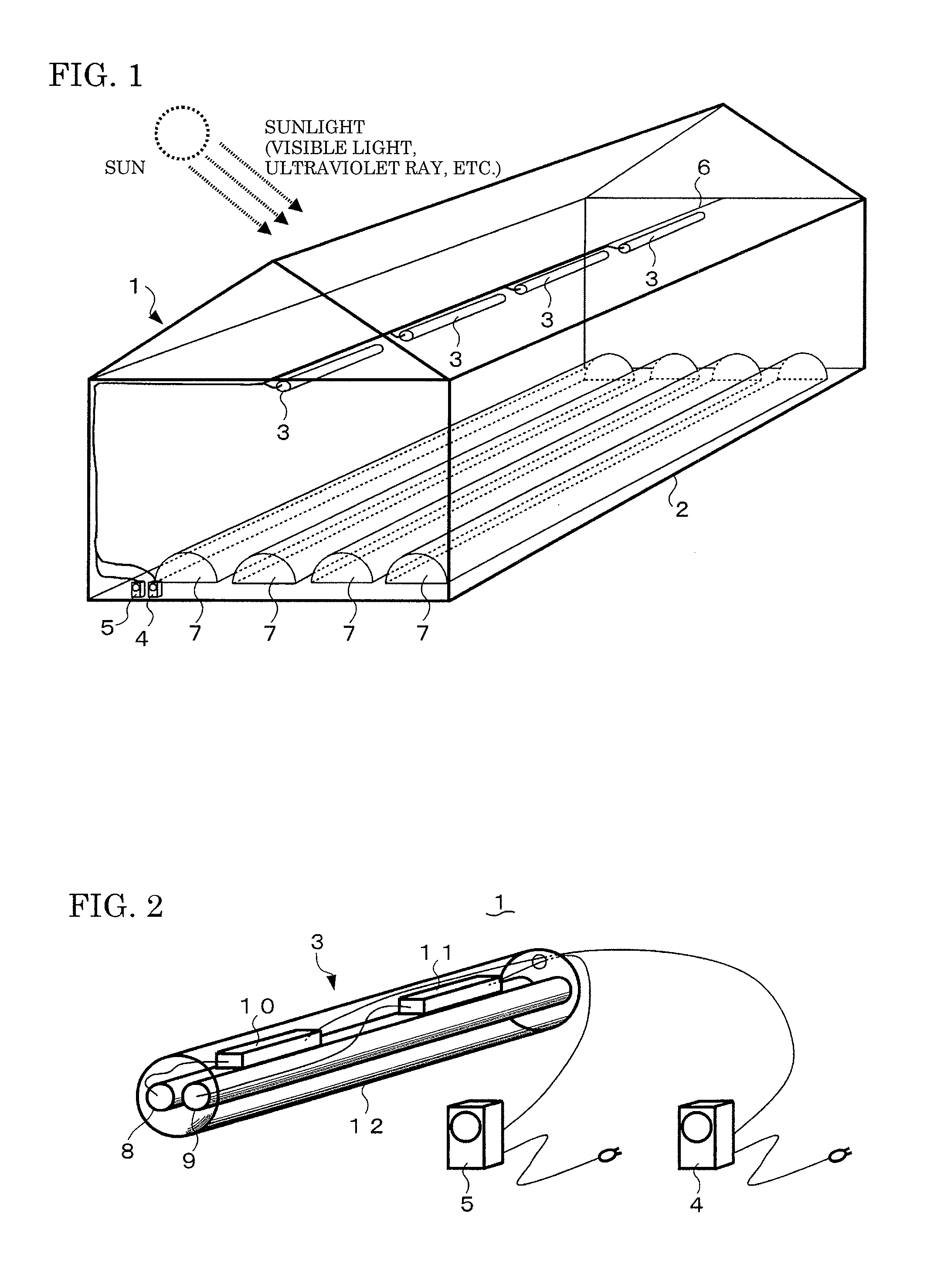
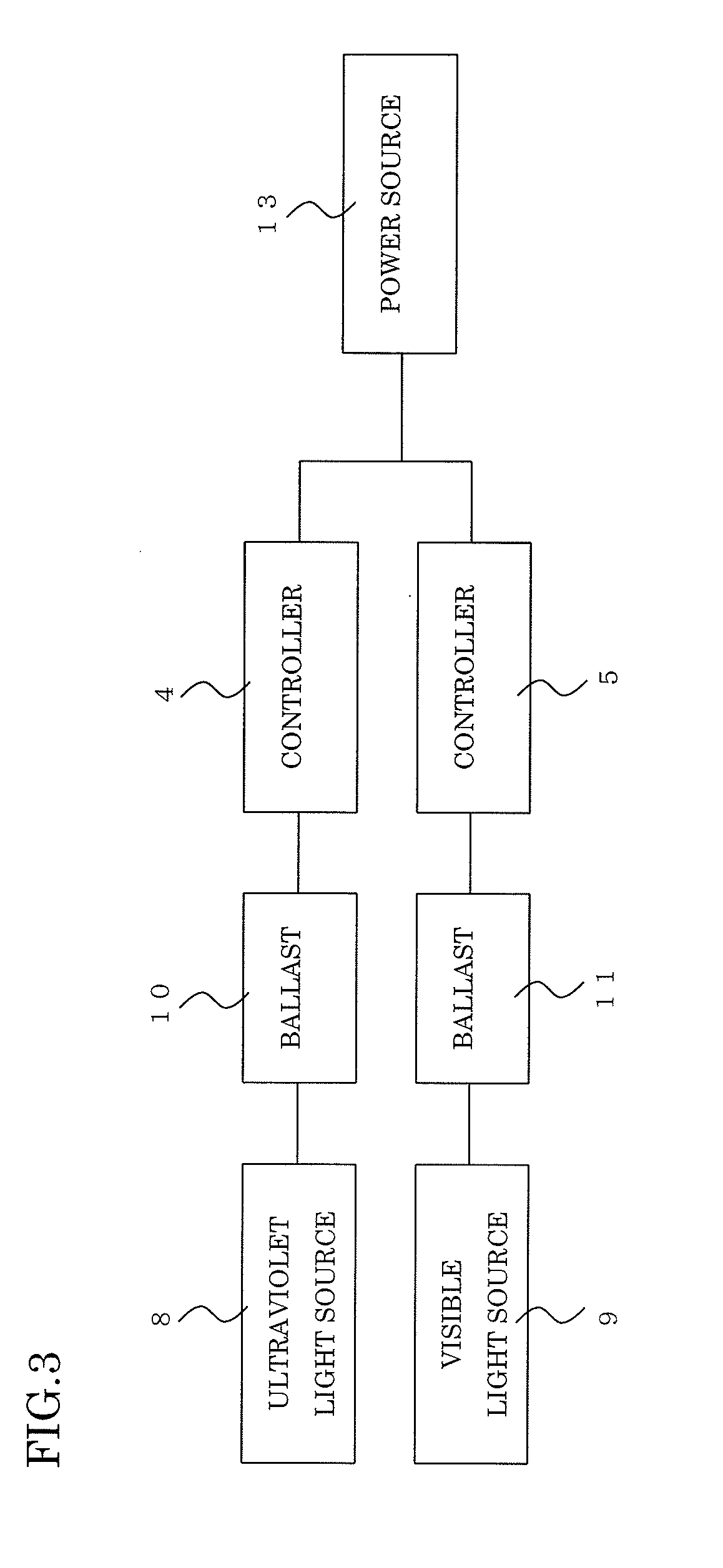
A lighting system for preventing a plant disease damage is provided with an ultraviolet light source which emits ultraviolet ray including UV-B in a wavelength region of 255 to 340 nm, a visible light source which emits visible light, and controllers which control a lighting of the ultraviolet light source and the visible light source. The controller controls the lighting of the ultraviolet light source so that a horizontal irradiance on a canopy surface of a plant is 50 μW / cm2 or less during a predetermined daytime period. The controller controls the lighting of the visible light source so that a horizontal illuminance on a canopy surface of a plant is 10 lux or less during a predetermined nighttime period. The lighting system promotes a component change of the plant effectively by a stimulation by the UV-B irradiation and the prolonged irradiation time of the visible light which is associated with a vegetative growth, so that a nutritional component of the plant can stably be increased. Moreover, the lighting of the ultraviolet light source and the visible light source is controlled by the controllers, thus a user effort is reduced and efficiency is achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and display apparatus
Provided is a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element including at least a semiconductor as a component characterized by including: a mechanism for irradiating the semiconductor with light having a wavelength longer than an absorption edge wavelength of the semiconductor; and a dimming mechanism, provided in a part of an optical path through which the light passes, for adjusting at least one factor selected from an intensity, irradiation time and the wavelength of the light, wherein a threshold voltage of the semiconductor element is varied by the light adjusted by the dimming mechanism.
Owner:CANON KK
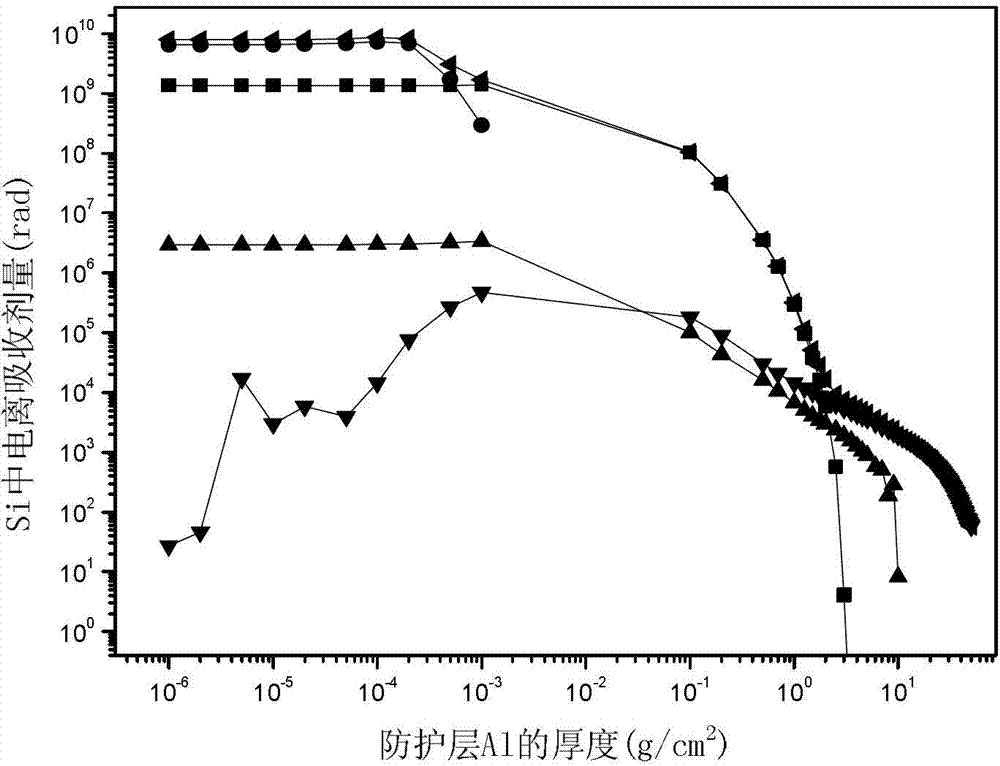
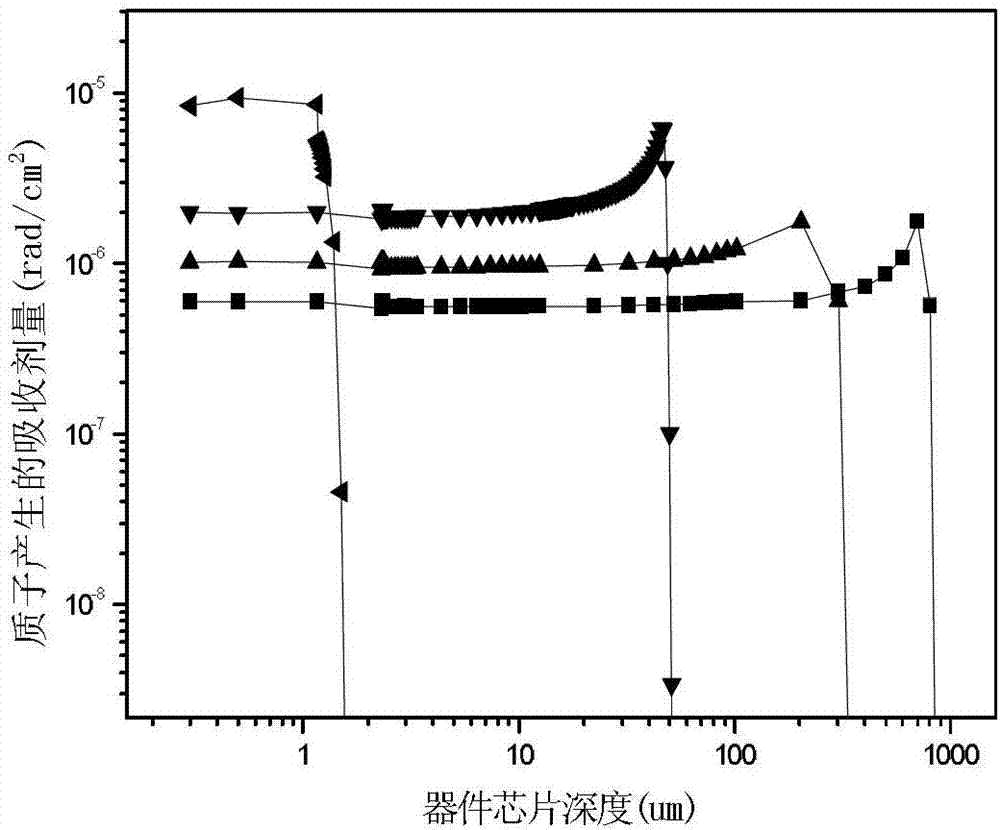
Ground equivalent fluence calculating method for electronic component charged particle irradiation effect
InactiveCN103116176ASolve the technical problem of large error in simulation testThe calculations are realisticDosimetersProtection layerElectron
The invention relates to a simulating test method of an electronic component and discloses a ground equivalent fluence calculating method for an electronic component charged particle irradiation effect. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect aims to solve the technical problem that a ground simulation test of the irradiation effect of the existing electronic component is large in experimental error. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect comprises the following steps: measuring the energy spectrum of orbit charged particles received by the electronic component; utilizing the method of Monte-Carlo or the program of GEANT4 to calculate the in-orbit lonization and the displacement absorbed dose D1 which pass through a protection layer and reach the surface of the electronic component; determining the thickness of a sensitive area of the electronic component; determining the types and energy of particles under the selected condition of the test, calculating the lonization and the displacement absorbed dose D2 of the sensitive area under the condition of the test through the method of Monte-Carlo or the program of GEANT4; and calculating the equivalent fluence phi and the irradiation time t under the condition of a laboratory according to D1=D2. The ground equivalent fluence calculating method for the electronic component charged particle irradiation effect is used for a simulation test of the electronic component.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Methods for uniformly treating biological samples with electromagnetic radiation
ActiveUS8296071B2Effective pathogen reductionUnified processingDead animal preservationLavatory sanitoryBlood componentMedicine
Methods, devices and device components are presented for uniformly treating fluids undergoing mixing with electromagnetic radiation. In one aspect, the present invention provides methods of treating a fluid undergoing continuous fluid mixing wherein net radiant energies necessary to provide uniform treatment of the fluid samples with electromagnetic radiation are calculate on the basis of the volume, mass or mixing rate of the fluid or any combination of these variables. In another aspect, the present invention provides algorithms for determining net radiation energies, radiant powers, and / or illumination times necessary for providing uniform treatment of fluid samples. The present invention provides methods for uniformly reducing pathogens in biological fluids, including blood and blood components.
Owner:TERUMO BCT BIOTECH
Irradiation device and collimator
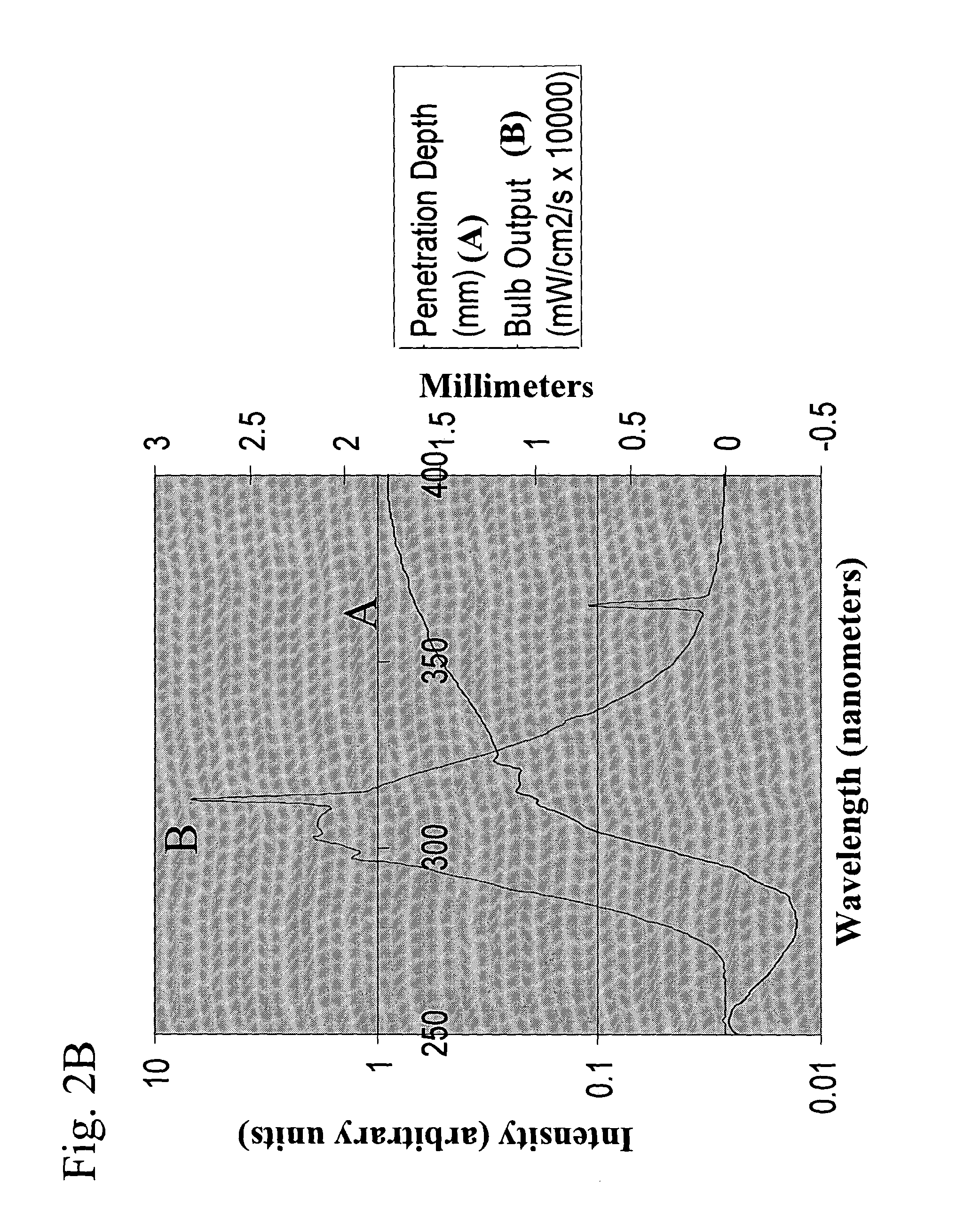
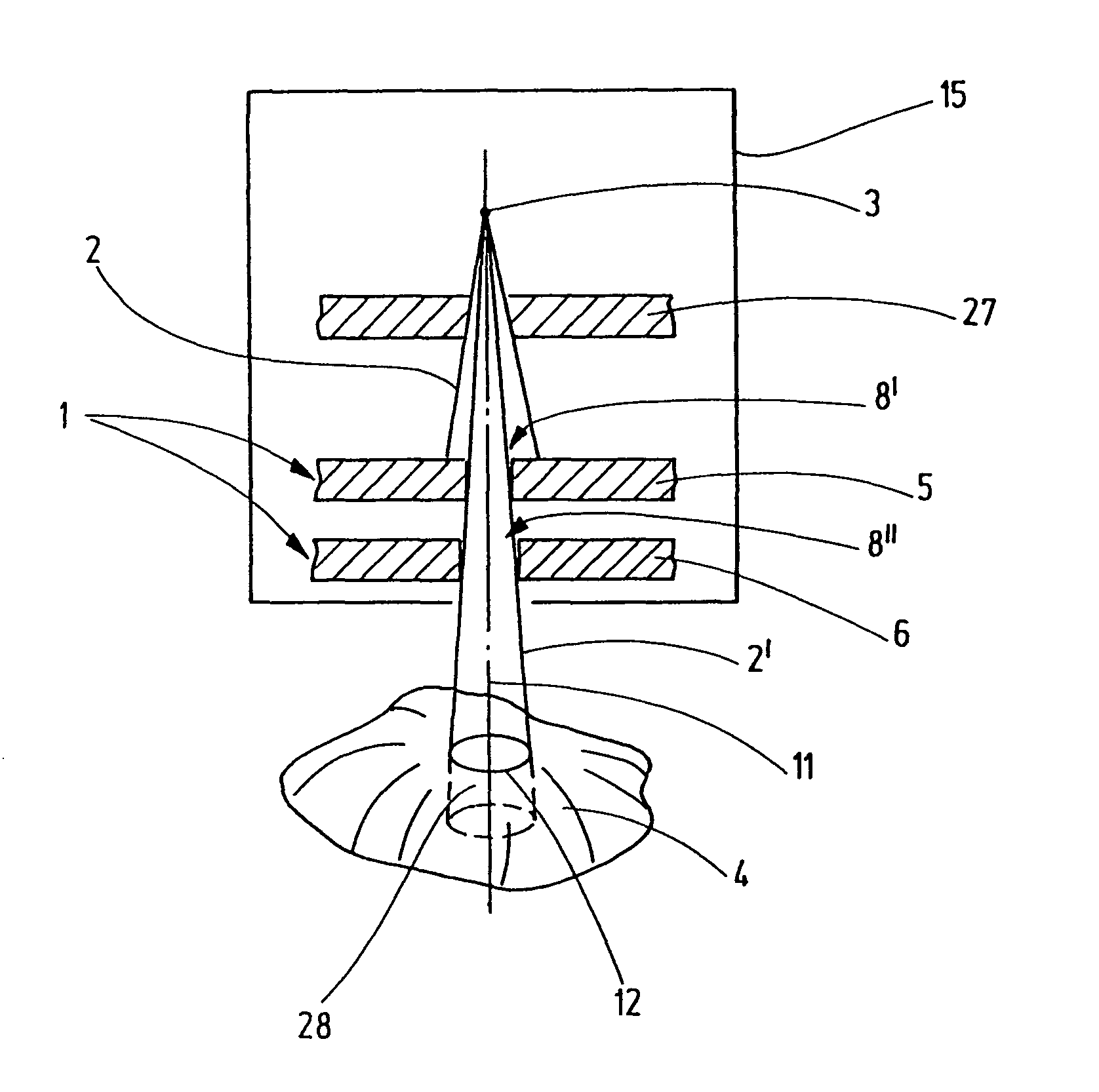
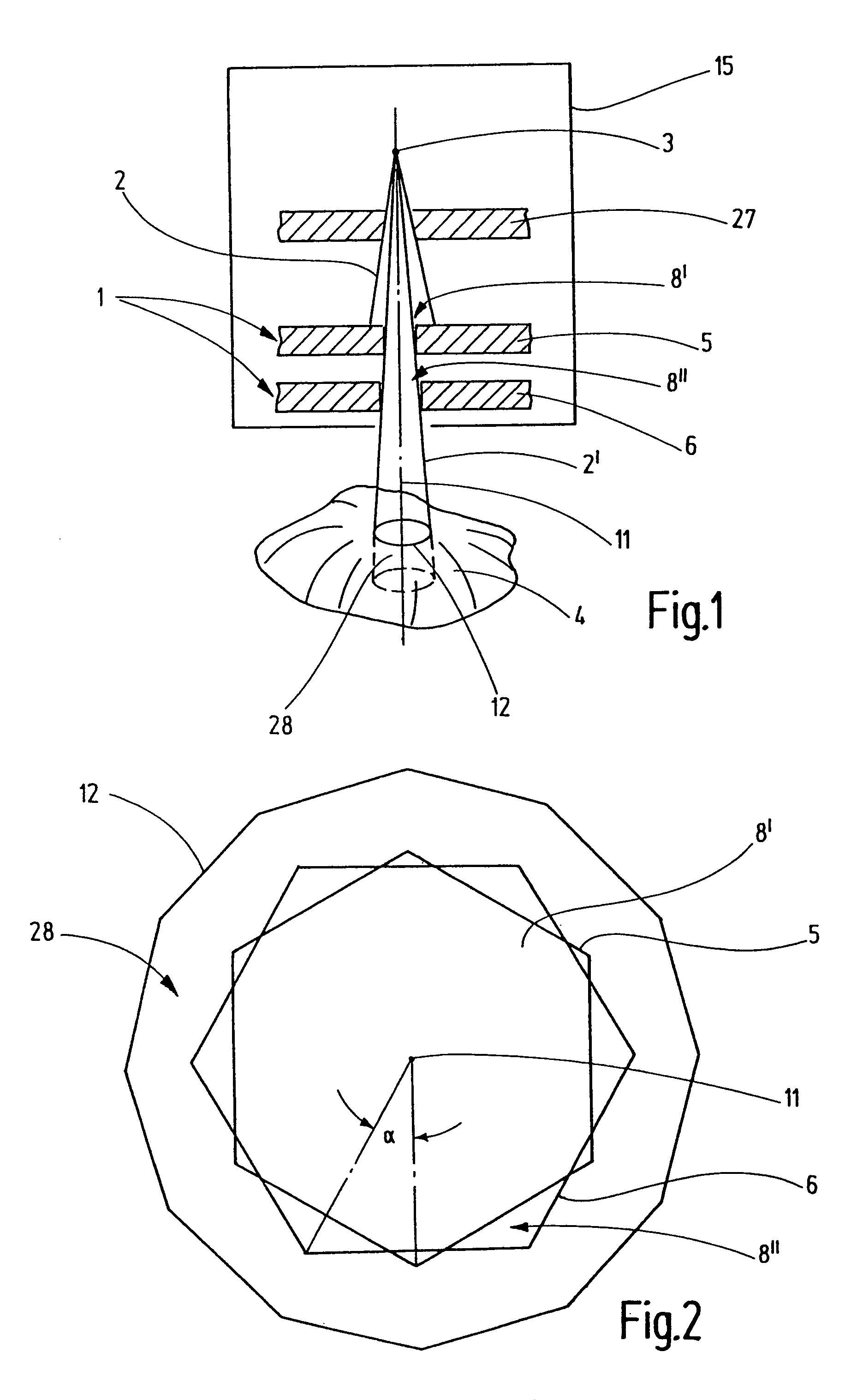
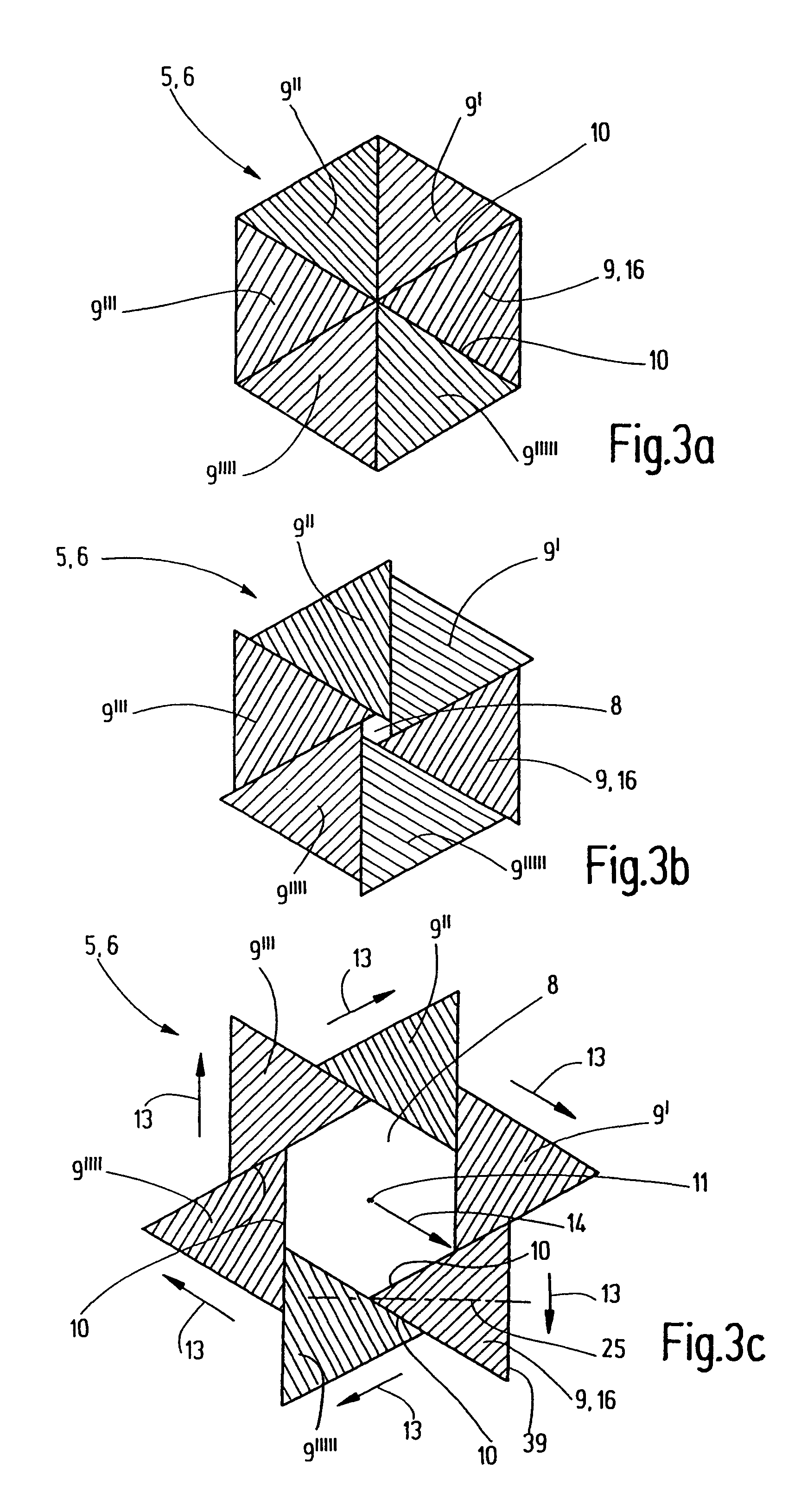
ActiveUS7783007B2Easy to observeIncrease the intensity of irradiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHigh energyLight beam
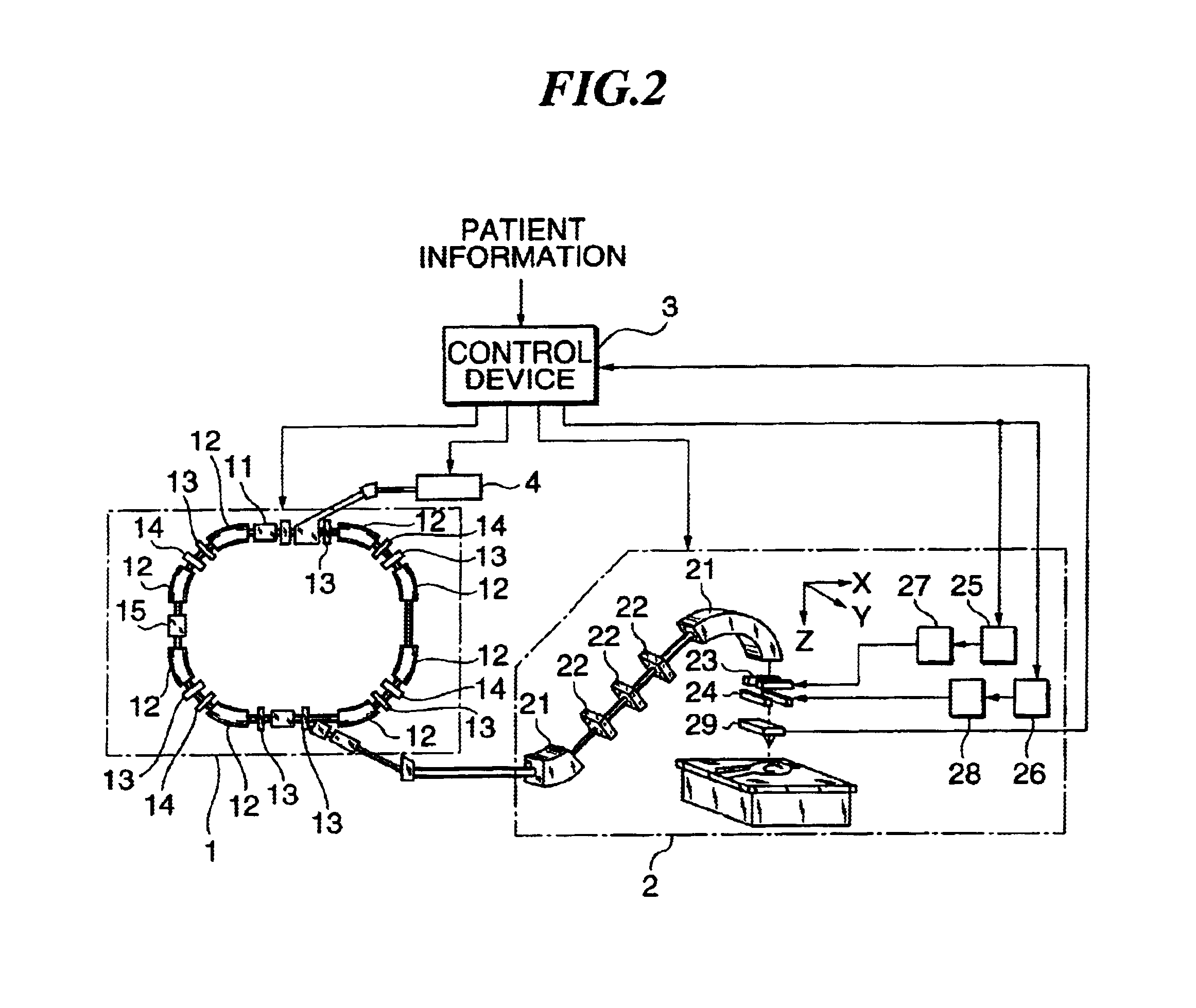
An irradiation device for radiation treatment and a collimator (1) are used to define a beam of high-energy rays (2) with beam limitation by means of an iris diaphragm (5) having adjusting elements (7), and a mechanism that is used to direct the beams (2′) limited by the collimator (1) to the object to be treated (4) from all sides, wherein the parameters for direction, surface area, intensity and time of irradiation can be specified with the help of a control mechanism. An exact three-dimensional irradiation profile is produced, while keeping the costs and efforts regarding mechanical engineering, computation and irradiation time low. This is achieved by using at least one further iris diaphragm (6) located in coaxial alignment in the optical path, whereby the leaves (9, 9′, 9″, 9′″, 9″″, 9′″″) of the iris diaphragms (5, 6) are arranged in a staggered manner and in a rotational sense around their axis (11), so that the beam limited by the collimator (1) has the cross-section of a polygon (12), the number of corners of which complies with the number of the leaves of all iris diaphragms (5, 6), so that the leaves (9, 9′, 9″, 9′″, 9″″, 9′″″) allow for linear adjustment movements (13), the control mechanism being suitable to enable the irradiation of an irregular space through the overlaying and adjoining of many irradiated spaces (28).
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method thereof, and radiation imaging system
ActiveUS20130121464A1Minimum time and effortEliminate needX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayRadiation imaging
Besides normal pixels, a plurality detection pixels are arranged in an imaging surface of an FPD. In preliminary imaging, X-rays are emitted to an imaged body portion of a patient. The detection pixels receive the X-rays passed through the body portion, and output AEC detection signals. If an integral value of the AEC detection signals has reached a threshold value, X-ray emission is stopped and the preliminary imaging is completed. A main exposure condition determination unit determines a main irradiation time, being an irradiation time with the X-rays during the main imaging, based on an irradiation time with the X-rays during the preliminary imaging and the integral value of the AEC detection signals. The main imaging is performed using the main irradiation time. The normal pixels continue a charge accumulation operation over the preliminary imaging and the main imaging to produce an X-ray image for use in diagnosis.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
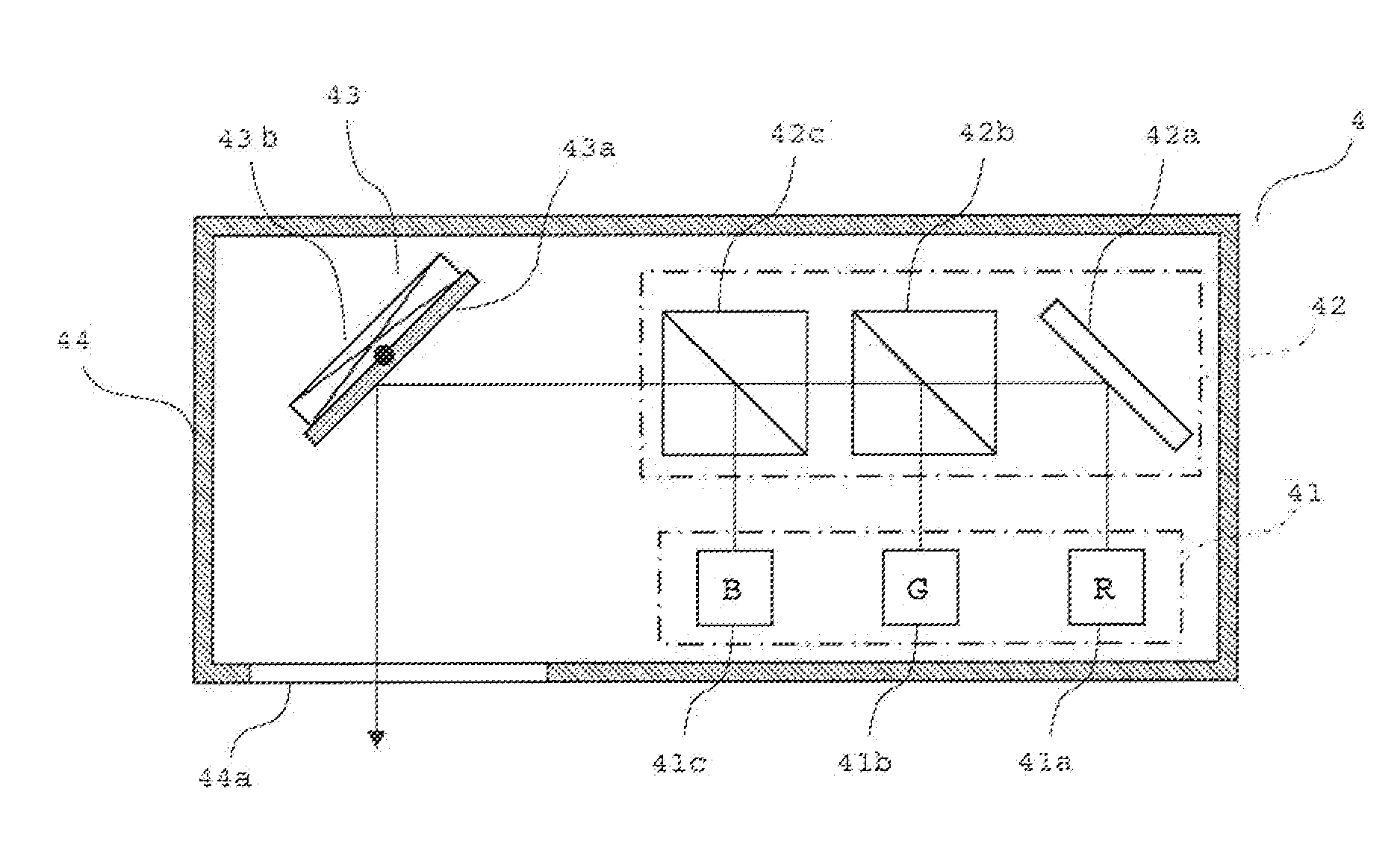
Projection Device
InactiveUS20100265473A1Project time is substantially increasedEasy to operateProjectorsColor television detailsLaser lightActuator
[Object]To provide a scan-type projection device that can lengthen a projecting time during a battery-powered operation.[Constitution] If a battery 600 is sufficiently charged, an actuator control part 120 drives a movable mirror 43 so as to form a normal turning angle, and an image signal processing part 130 drives a light source part 41 so as to irradiate laser lights with predetermined gradations to one pixel region for a normal irradiation time t1. Accordingly, an image with a normal screen size is displayed on a projection plane. Meanwhile, if the battery becomes low in remaining level, the actuator control part 120 drive the movable mirror 43 so as to form a small turning angle, and the image signal processing part 130 drives the light source part 41 so as to irradiate laser lights with predetermined gradations to one pixel region for a short irradiation time t2. Accordingly, an image with a reduced screen size is displayed on a projection plane.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Multiplexed / pathlength resolved noninvasive analyzer apparatus and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20150045636A1Material analysis by optical meansAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyMultiplexingAnalyte
A noninvasive analyzer apparatus and method of use thereof is described using a plurality of time resolved sample illumination zones coupled to at least one two-dimensional detector array monitoring a plurality of detection zones. Control of illumination times and / or patterns along with selected detection zones yields pathlength resolved groups of spectra. Sectioned pixels and / or zones of the detector are optionally filtered for different light throughput as a function of wavelength. The pathlength resolved groups of spectra are subsequently analyzed to determine an analyte property. Optionally, in the mapping and / or collection phase, incident light is controllably varied in time in terms of any of: sample probe position, incident light solid angle, incident light angle, depth of focus, energy, intensity, and / or detection angle. Optionally, one or more physiological property and / or model property related to a physiological property is used in the analyte property determination.
Owner:ZYOMED
Watt level full solid state ultraviolet laser cleaning machine and laser cleaning method
InactiveCN101219430AImprove adhesionEfficient removalCleaning using gasesNonlinear optical crystalUltraviolet
The invention discloses a Watt-level all-solid ultraviolet laser cleaner and a laser cleaning method, which pertains to the optical energy cleaning technology field and are applied to cleaning micro electronic substrate such as the integrated circuit. The power of the cleaner is connected with a laser resonance chamber; two non-linear optical crystals, a selective microscope and a reflector are positioned in the light path of pulsed laser from the laser resonance chamber; a rotating mirror drum is fixed above one side of the reflector; a work piece to be cleaned is arranged on a convey belt; a blower is positioned at one side of the convey belt and a cleaner is arranged at the other side. By adopting the method, substrates to be cleaned can be continuously or discontinuously conveyed to go through the laser which is Watt-level pulse laser with about 266nm and comes from the all-solid laser; proper laser intensity, pulse frequency and irradiation time can be controlled to effectively remove micron and submicron particles, organics, oily contamination, etc. on the surface of the substrate. The adhesion of the coating after cleaning and the product yield rate are greatly improved and the warp or spalling of the coating rarely happens.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Preparation method of transparent conducting material based on 3D printing technology
ActiveCN104409170AGood light transmissionImprove conductivitySpecial data processing applicationsCable/conductor manufactureLiquid jetModeling software
The invention relates to a preparation method of a transparent conducting material based on a 3D printing technology. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1) modeling; designing a model of a strip transparent conducting electrode by utilizing computer modeling software, and converting a software command of the model to a mechanical equipment directive of 3D printing so as to control the moving path, the movement speed and the liquid jet velocity of each 3D printing head as well as the moving path, the movement speed and the laser irradiation time of each laser head; and 2) printing the strip transparent conducting electrode. The transparent conducting electrode prepared by the invention has the advantages of good light transmittance and good electrical conductivity and overcomes the defect of poor adhesiveness of between a carbon nano-tube film layer and a substrate and between a graphene film layer and the substrate; and by adopting the method, the thickness and the width of the transparent conducting electrode are precisely controlled.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Apparatus for and method of capturing radiation image
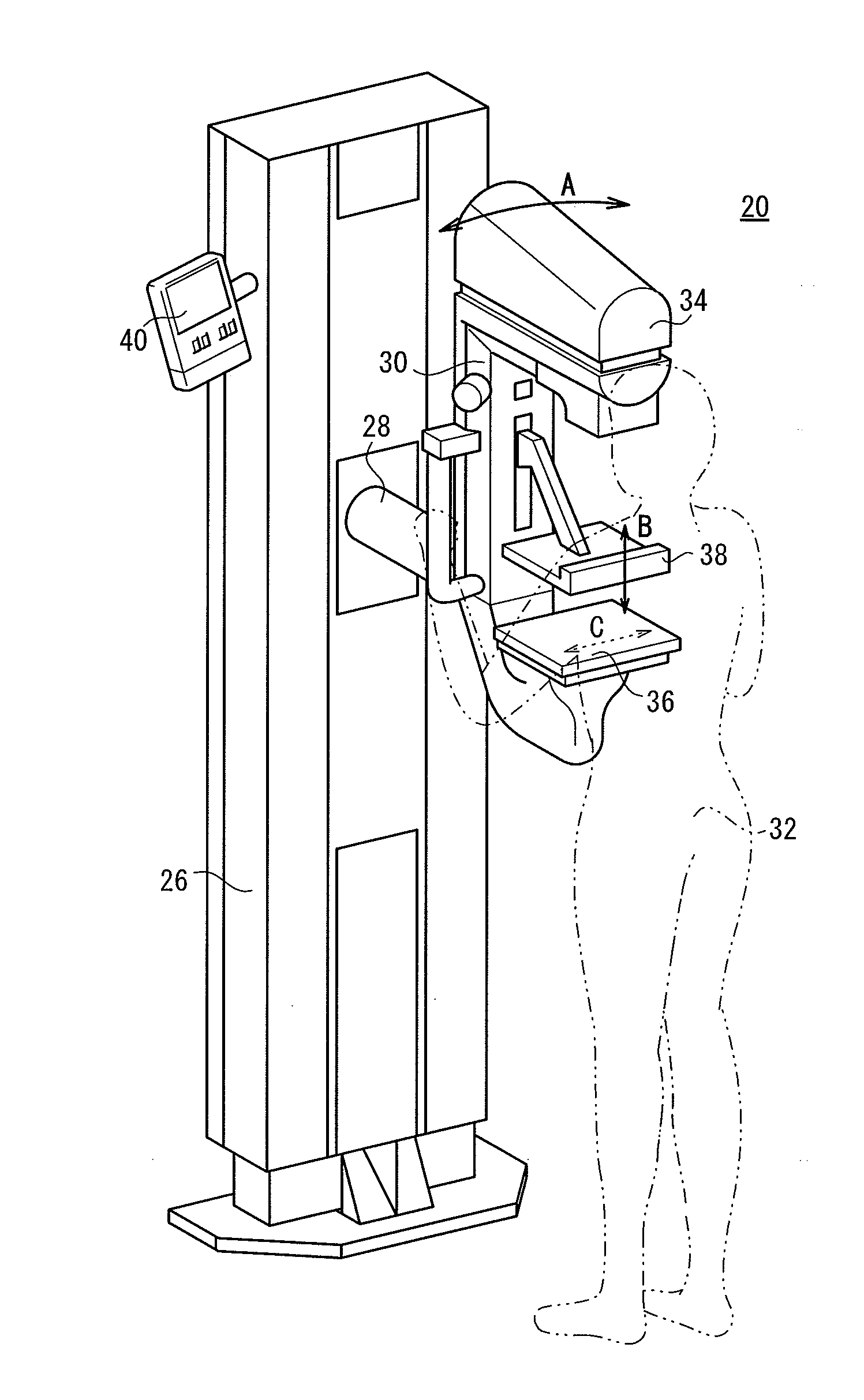
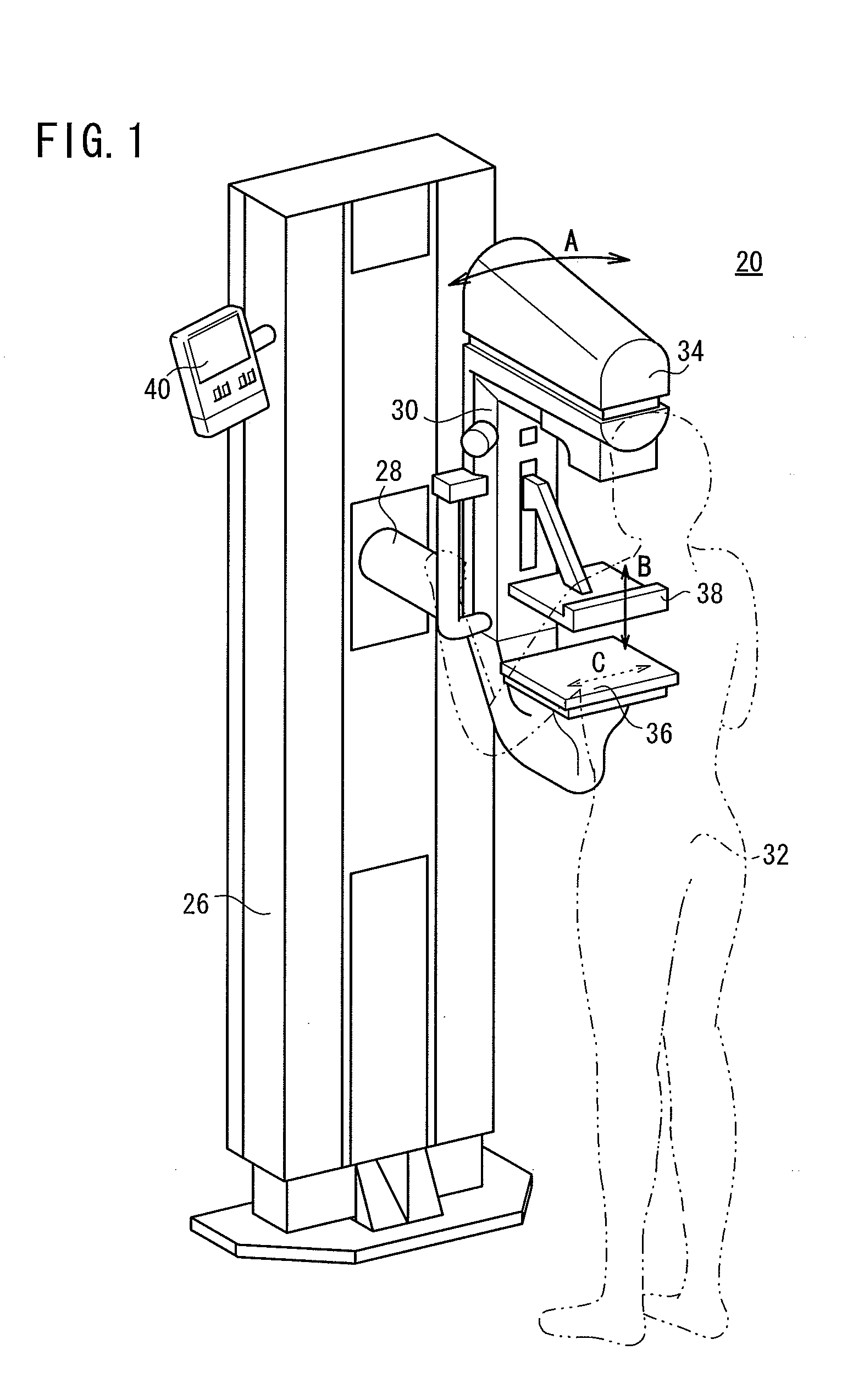
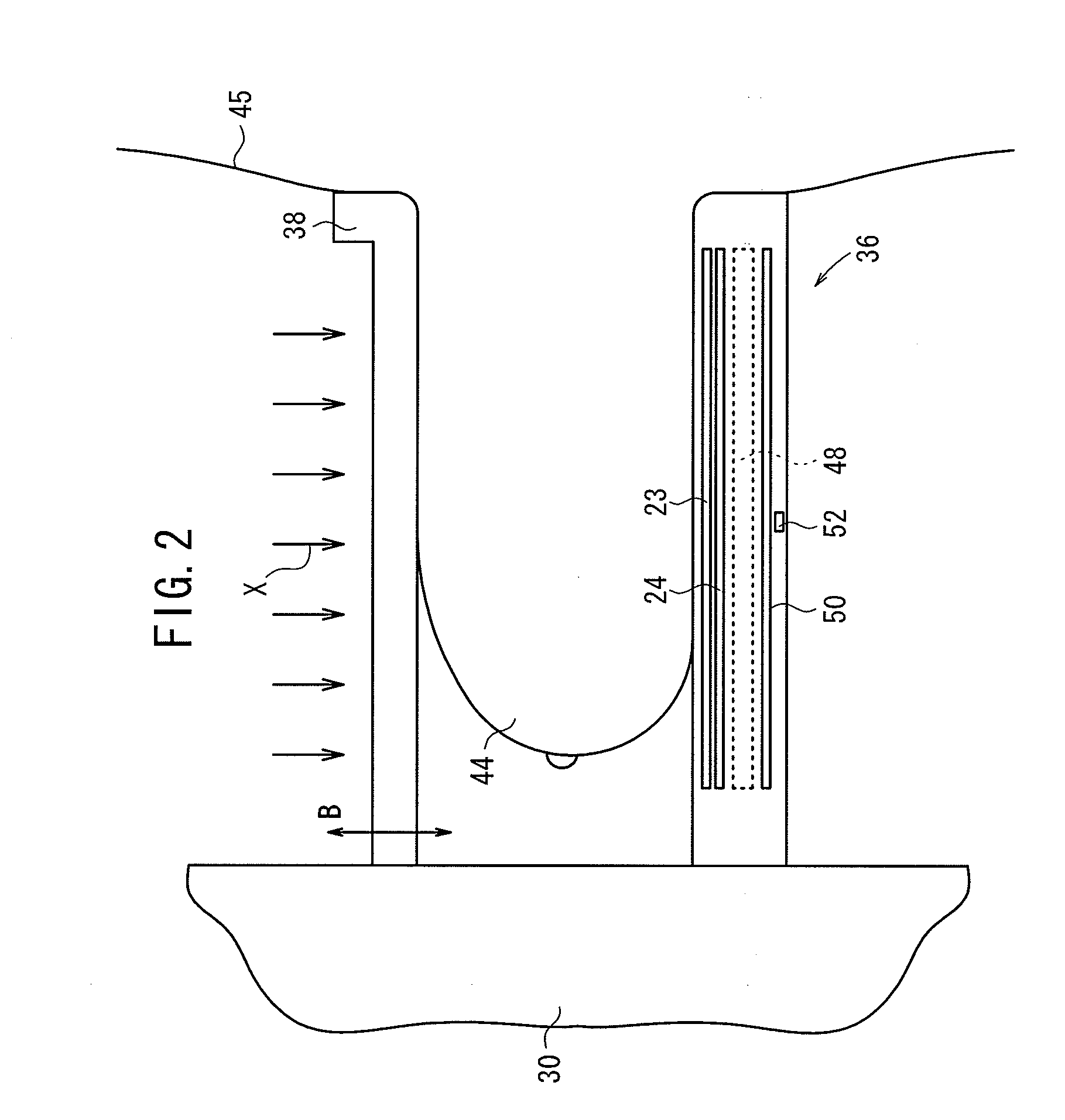
ActiveUS20090022273A1Accurate calculationPreventing the breast from being irradiatedPatient positioning for diagnosticsMammographyCalculatorRadiation dose
An irradiation dose calculator calculates a pre-exposure-mode-required irradiation dose using the thickness of a breast which measured by a thickness measuring unit, as a parameter, and the irradiation time of a pre-exposure mode is controlled to apply a radiation to the breast in the pre-exposure mode. According to the dose of the radiation detected by a dose detecting sensor in the pre-exposure mode, the irradiation dose calculator calculates a main-exposure-mode-required irradiation dose, and the irradiation time of a main exposure mode is controlled to apply the radiation to the breast in the main exposure mode, thereby capturing a radiation image of the breast.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and device for forming plastic part microstructure based on laser heating
InactiveCN102962583AHigh processing flexibilityFast absorption of laser energyLaser beam welding apparatusLine heatingLaser heating
The invention discloses a method and a device for forming a plastic part microstructure based on laser heating, and relates to the field of formation of the plastic part microstructure, in particular to the method and the device for forming the plastic part microstructure based on laser heating. The surface of a base body of a plastic part with microstructure characteristics is quickly heated and molten by utilizing the heat effect of laser on a polymer and accurately controlling laser power and irradiation time as well as irradiation mode, and the plastic part microstructure is formed and processed through a laser heating extrusion forming device. The method and the device have the advantages of high forming precision, large scale range, good flexibility, high efficiency and low cost, are suitable for large-batch automatic forming and processing of the plastic part microstructure, and have higher application values.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
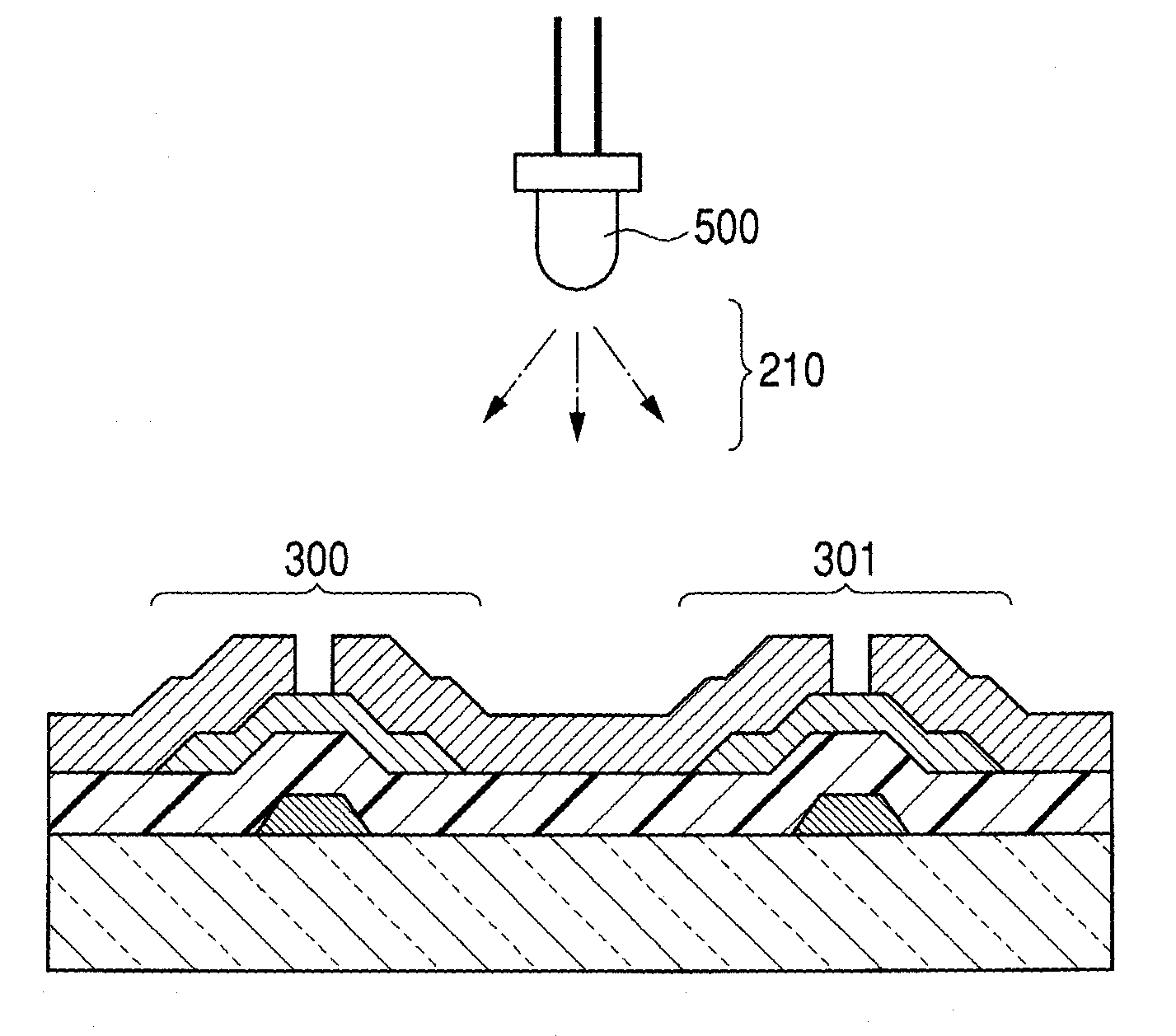
Heat treatment apparatus and method for heating substrate by light irradiation
ActiveUS20090263112A1Avoid damagePossible damageDomestic stoves or rangesDrying solid materials with heatLight irradiationSemiconductor
In light-irradiation heating with a total irradiation time of one second or less, two-stage irradiation is performed, including a first stage of light irradiation of a semiconductor wafer, which irradiation produces an output waveform that reaches a peak at a given emission output; and a second stage of supplemental light irradiation of the semiconductor wafer, which irradiation is started after the peak, producing an emission output smaller than the above given emission output. The emission output in the second stage is two thirds or less than the above given emission output at the peak. The first-stage light-irradiation time is between 0.1 and 10 milliseconds, and the second-stage light-irradiation time is 5 milliseconds or more. This allows the temperature of the semiconductor wafer even at a somewhat greater depth below the surface to be raised to some extent while allowing the surface temperature to be maintained at a generally constant processing temperature.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Finishing method for improving hydrophilicity of polyester fabric
InactiveCN102061610ANo emissionsThe grafting reaction is completePhysical treatmentFibre typesPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to a finishing method for improving the hydrophilicity of a polyester fabric. Polyethylene glycol serving as a graft monomer is subjected to grafting reaction on a polyester fiber under the initiation of low temperature plasma treatment. The method comprises the following three steps of: impregnating the graft monomer, performing grafting treatment, and performing aftertreatment, wherein in the step of impregnating the graft monomer, the concentration of aqueous solution of polyethylene glycol is 5 to 30 percent, the impregnating temperature is between 20 and 30 DEG C, the impregnating time is 1 to 1.5 hours, and the bath ratio is 1:30-1:50; the grafting treatment is the low temperature plasma treatment, the irradiation atmosphere is argon, the irradiation intensity is 50 to 200W, the irradiation time is 1 to 5 minutes, and the vacuum degree is 20 to 80Pa; and the aftertreatment step comprises washing and drying. By the finishing method, the performance of the hydrophobic polyester fabric is obviously improved, the moisture absorption and moisture transfer performance of the polyester fabric is improved, and the effect that the polyester fabric is comfortable to wear and use is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF CLOTHING TECHNOLOGY
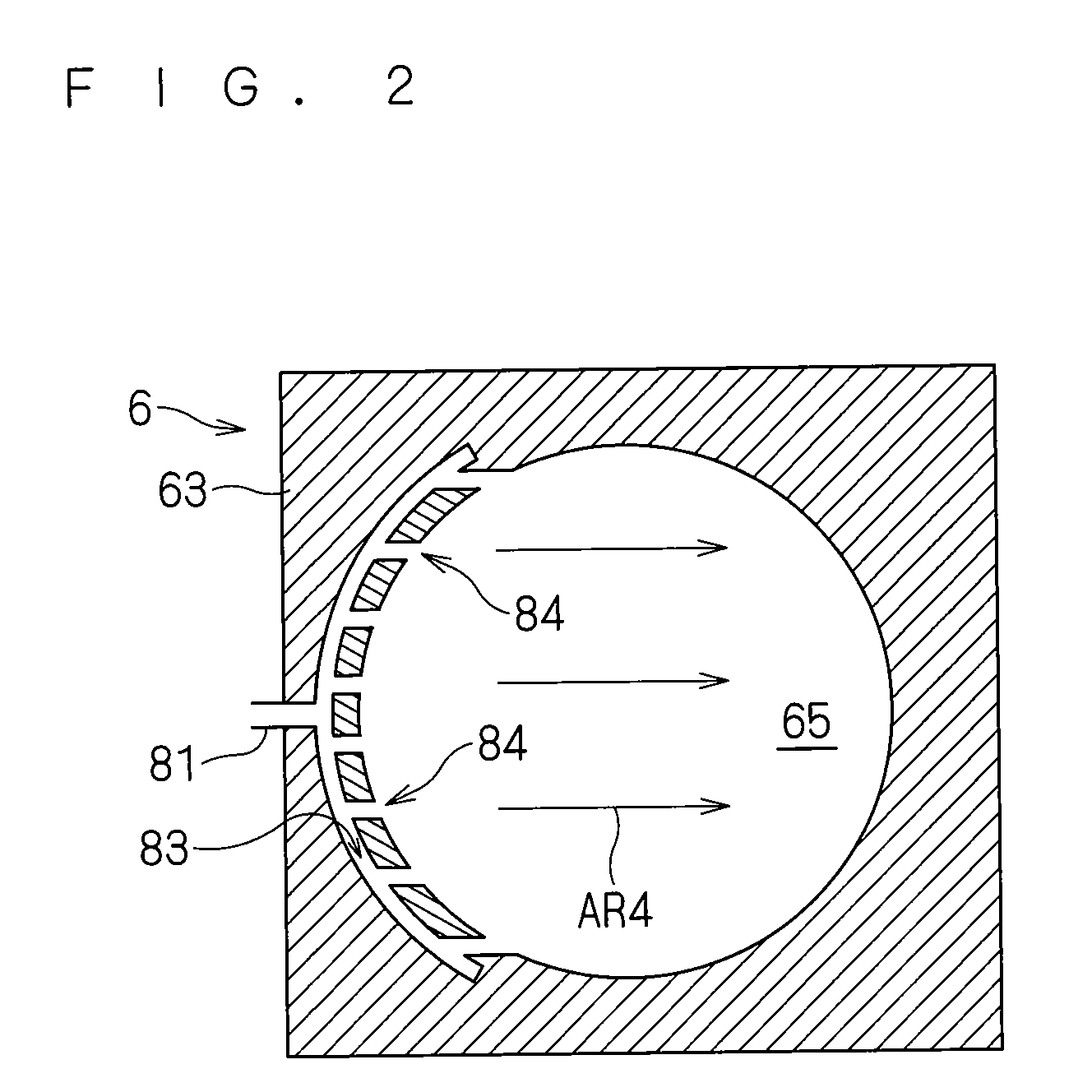
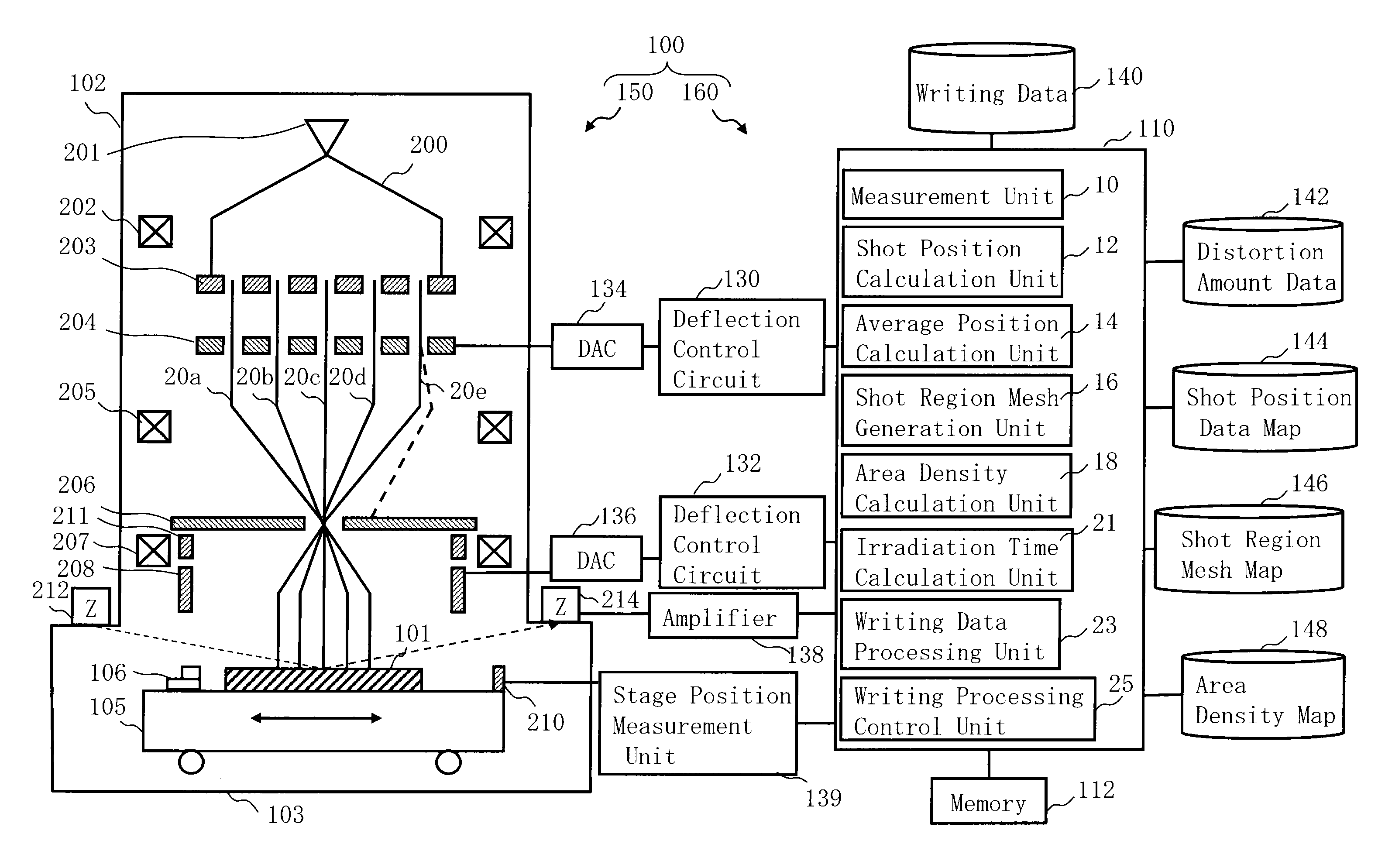
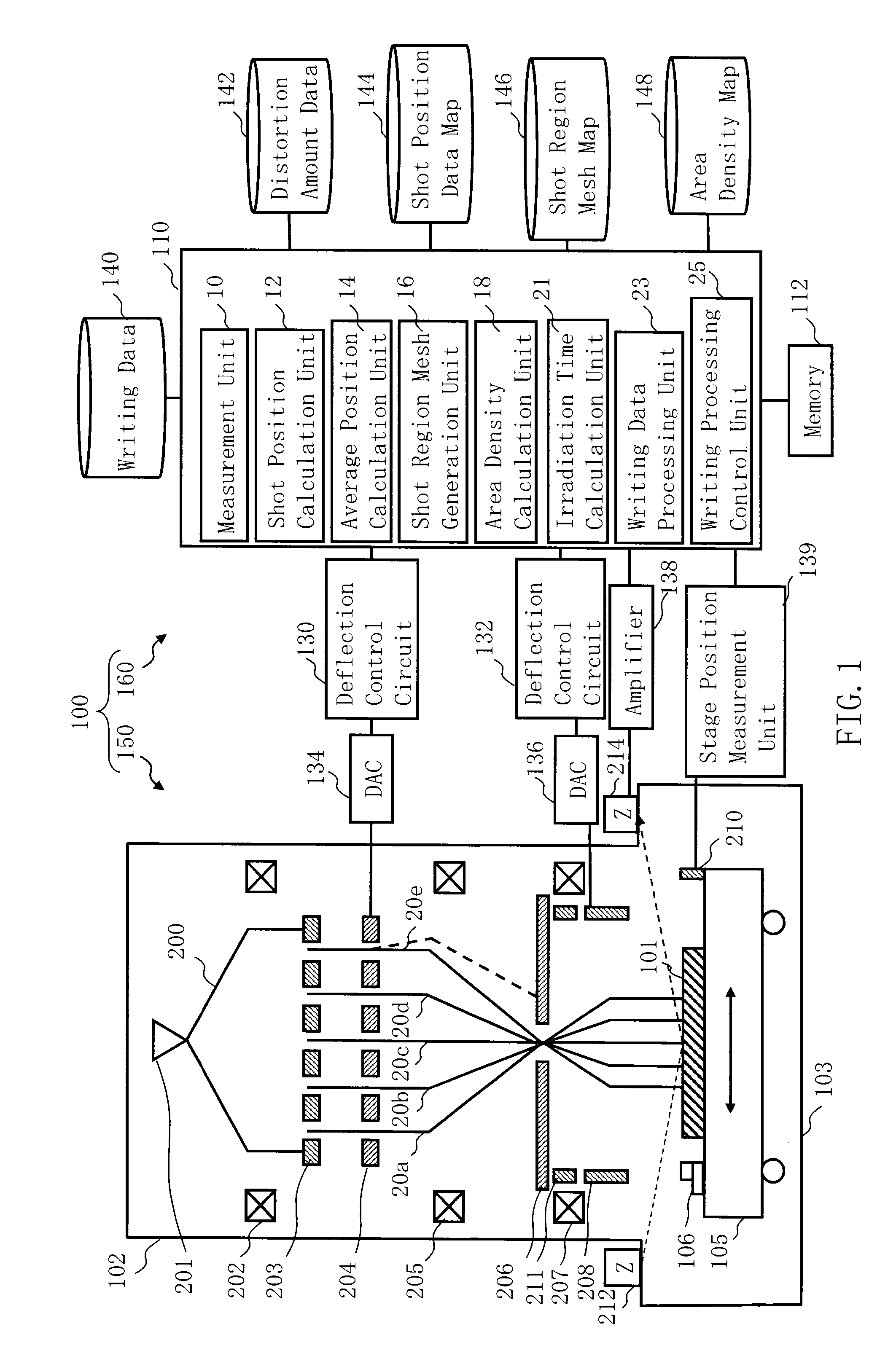
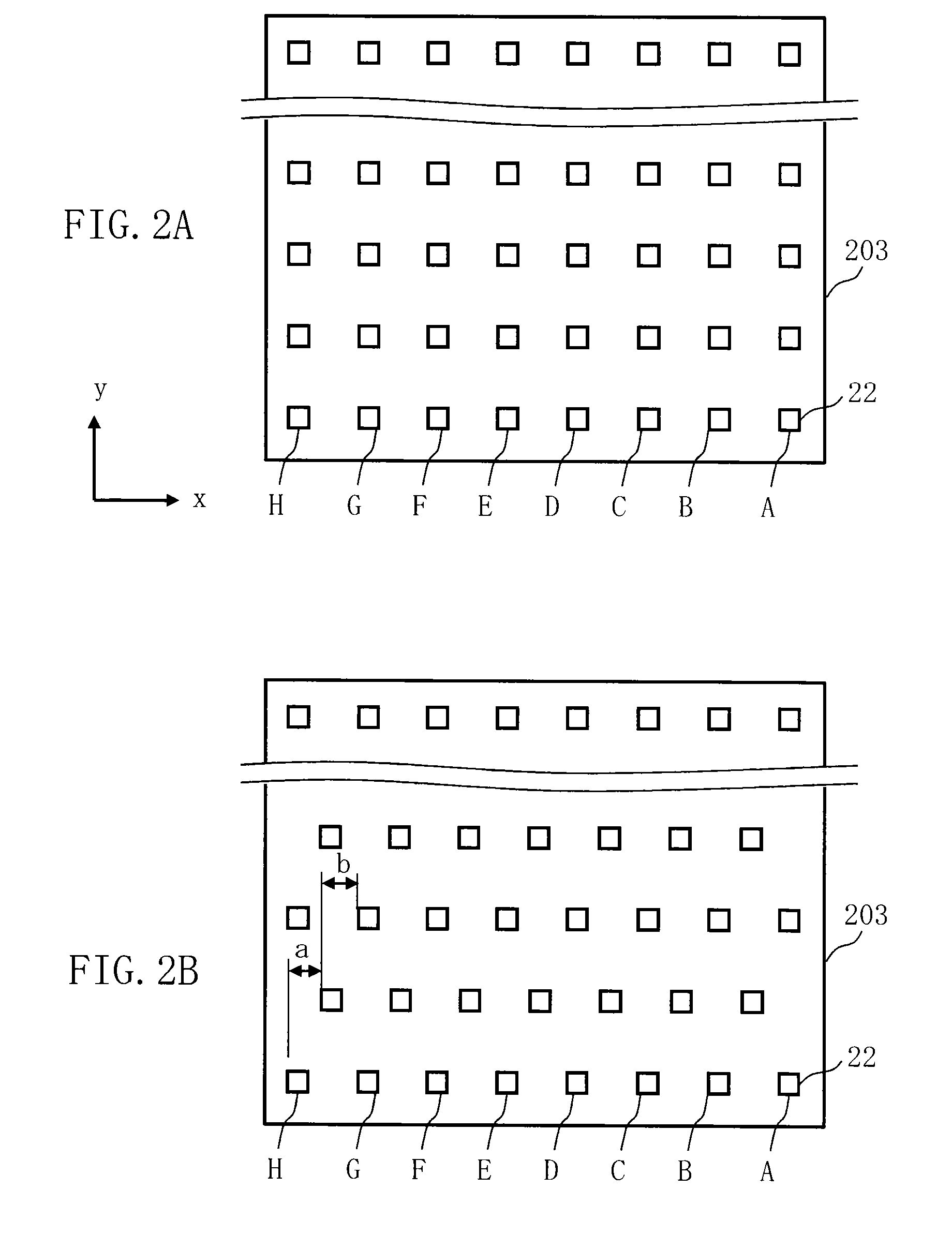
Multi charged particle beam writing method and multi charged particle beam writing apparatus
ActiveUS20130320230A1Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamArea density
A multi charged particle beam writing method includes calculating first shot positions of multiple beams, each of which includes a distortion amount of an irradiating corresponding beam, in a case of irradiating each beam, based on control grid intervals, calculating first condition positions based on a pre-set condition, each of which is arranged in a corresponding first region surrounded by closest second shot positions of 2×2 in length and width of the first shot positions, calculating, for each of second regions respectively surrounded by closest second condition positions of the first condition positions, an area density of a figure pattern in overlapping with a second region concerned, calculating an irradiation amount or an irradiation time of each beam whose corresponding first shot position is in a corresponding second region, based on an area density, and writing a pattern by irradiating a beam of the calculated irradiation amount or time.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com