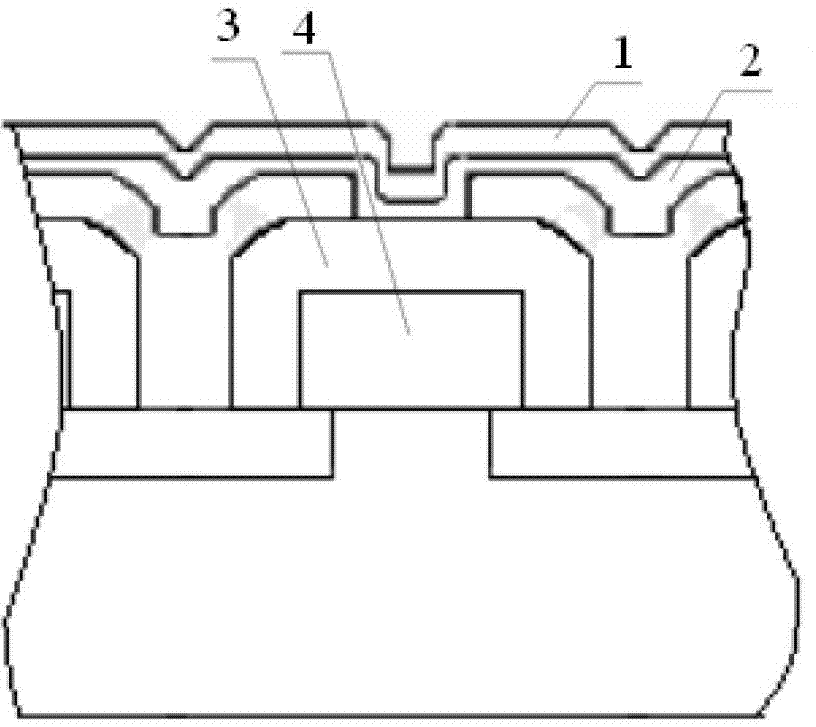
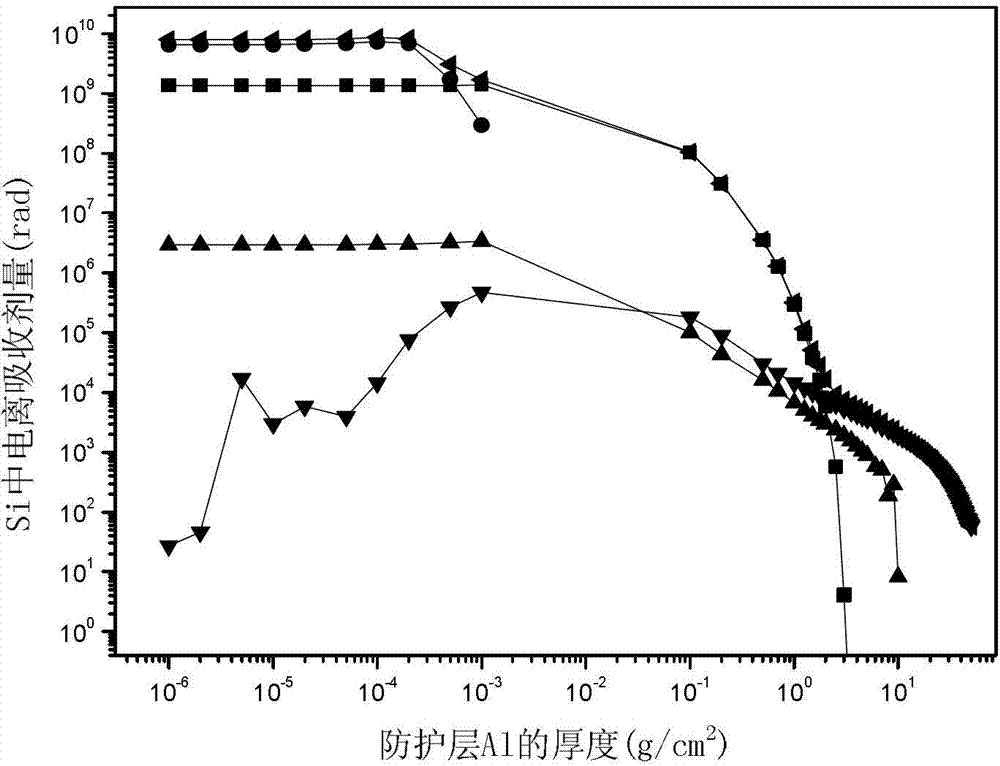
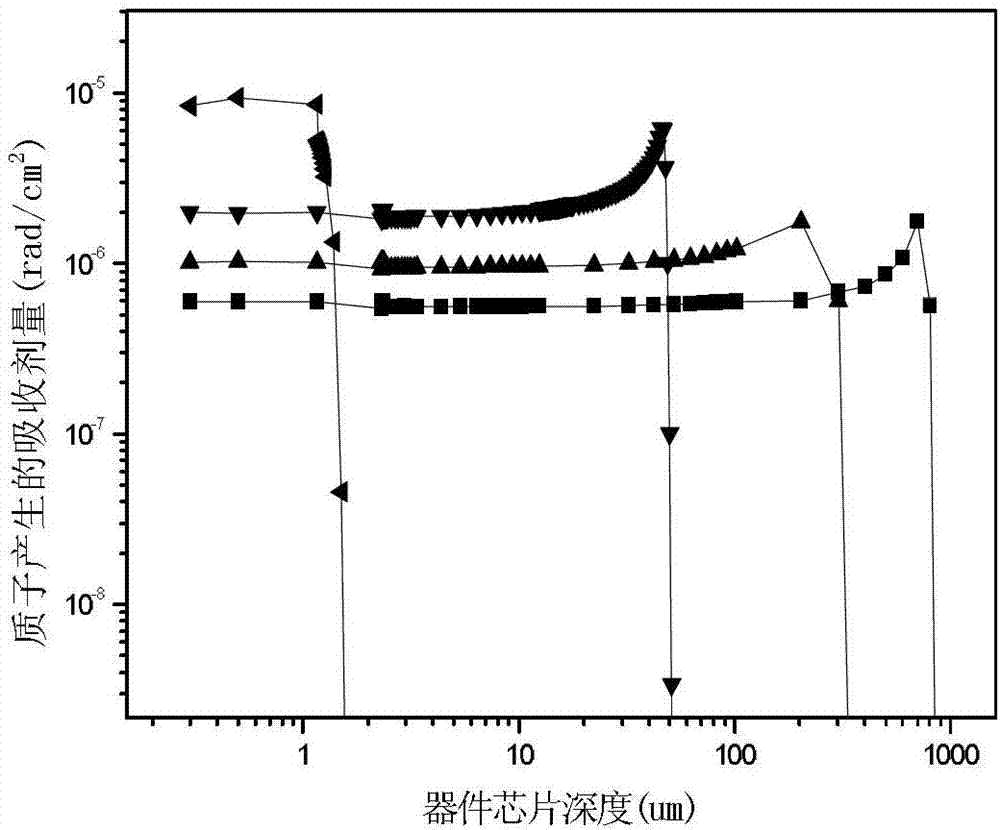
Ground equivalent fluence calculating method for electronic component charged particle irradiation effect
A technology for electronic components and charged particles is applied in the field of ground equivalent fluence calculation of the irradiation effect of charged particles of electronic components, and can solve the problems of large errors in the ground simulation test of the irradiation effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0021] Specific implementation mode 1: The method for calculating the ground equivalent fluence of charged particle radiation effect of electronic components in this implementation mode is carried out according to the following steps:
[0022] 1. According to the service orbit and service period of electronic components, calculate the orbital charged particle energy spectrum of electronic components. The orbital charged particle energy spectrum includes the proton energy spectrum of the earth radiation belt, the electron energy spectrum of the earth radiation belt, and the proton energy spectrum and galactic cosmic ray proton spectrum;
[0023] 2. According to the orbital charged particle energy spectrum obtained in step 1, use the Monte-Carlo method or GEANT4 program to calculate the on-orbit ionization and displacement absorbed dose D1 that reaches the surface of the electronic component after passing through the protective layer, and the unit of the absorbed dose is rad;
...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the orbital charged particle energy spectrum is the earth radiation belt proton energy spectrum, the earth radiation belt electron energy spectrum, the solar cosmic ray proton energy spectrum or the galactic cosmic ray proton energy spectrum . Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the type of particles in Step 4 is high-energy electron source, proton source, heavy ion source, neutron or Co-60 source. Others are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
[0031] Verify beneficial effect of the present invention with following test:
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com