A Simulation Method of Refracting Stars
A simulation method and technology of refracting stars, applied in astronomical navigation, navigation calculation tools, etc., can solve problems such as large gaps, and achieve the effect of low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] Step 1: Scan the star catalog to determine whether the current star is a refracting star; if it is judged to be a refracting star, go to step 2, otherwise continue scanning;
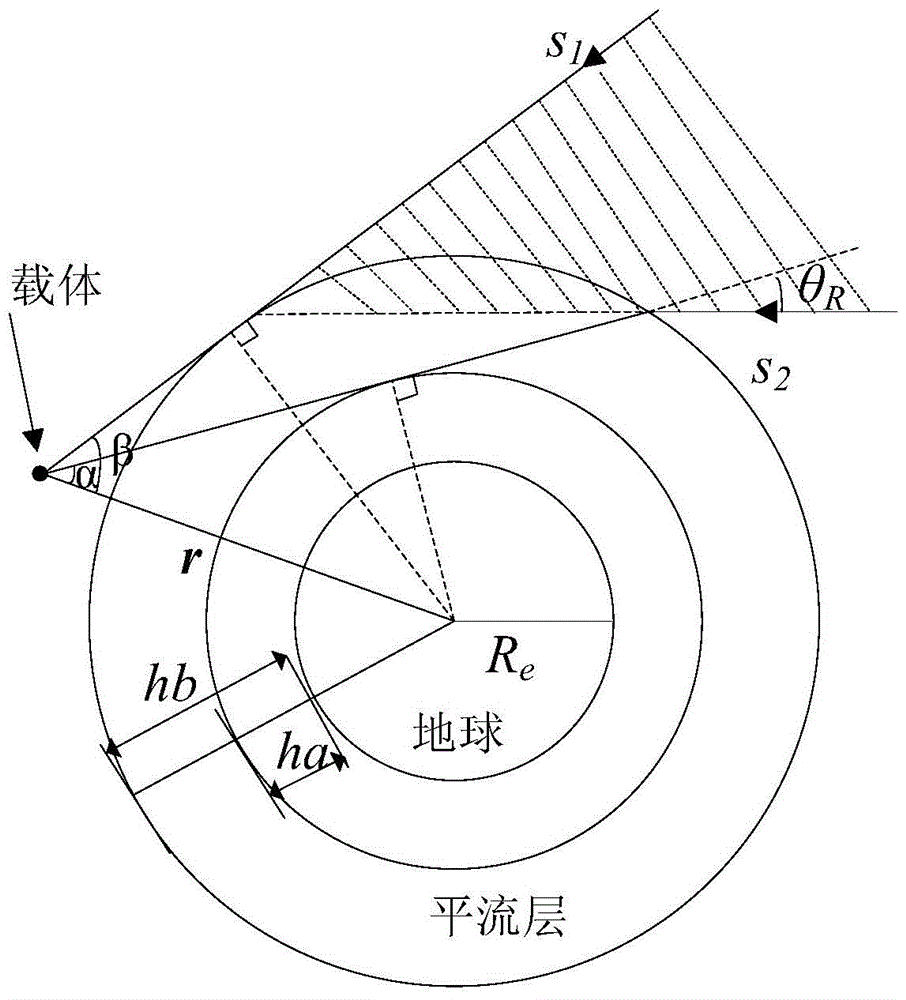
[0045] figure 1 Middle: ha-minimum refraction height 20km, hb-maximum refraction height 50km, r-carrier position vector, Re-earth radius s 1 , s 2 - Direction vector of stellar starlight, θ R - Angle of starlight refraction at a refraction altitude of 20km.
[0046] When using the refraction star for navigation, the refraction height is generally selected to be 20km-50km according to the thickness of the stratosphere, that is, figure 1 In ha=20km, hb=50km; assuming that the direction vector of the starlight of a certain star is s, then by figure 1 A star that satisfies the following equation can be selected as a refractor star
[0047]
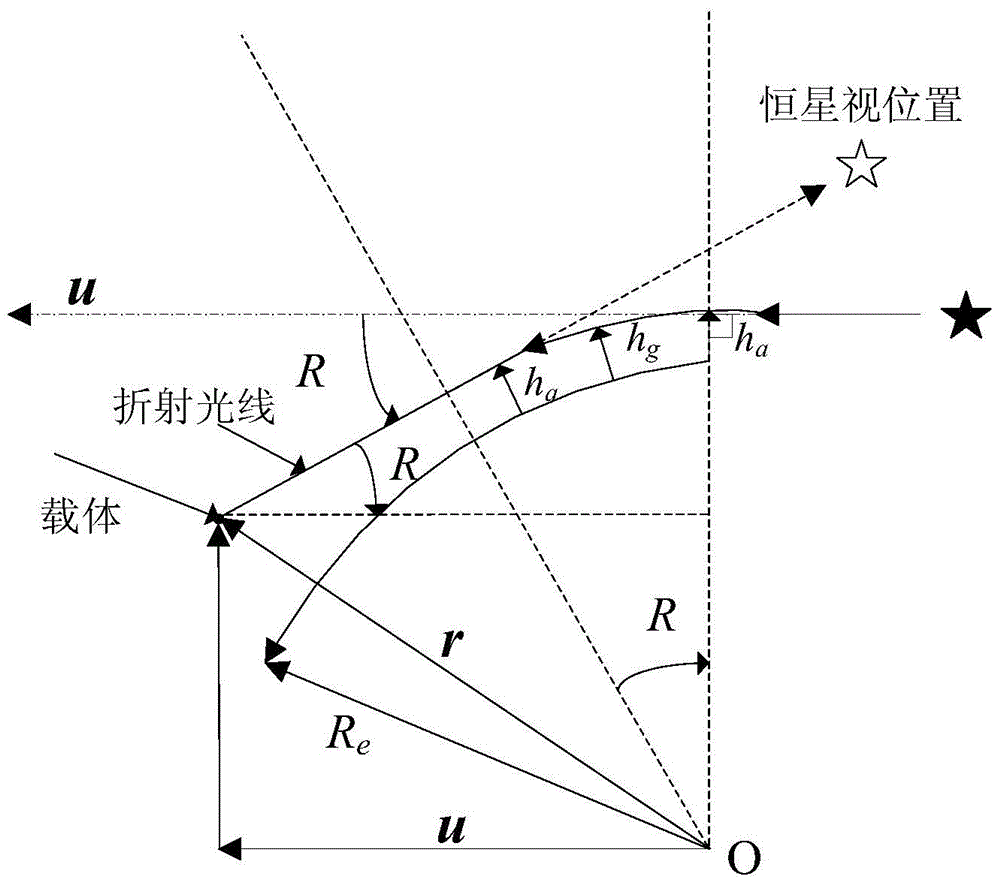
[0048] Among them, θ Ris the corresponding starlight refraction angle when the refraction height is 20km, which can be calculated by the atmospheric refr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com