Patents
Literature
394 results about "Naphthoic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
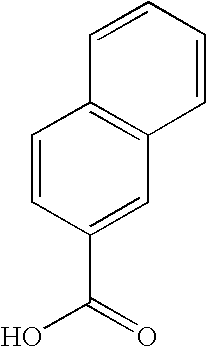
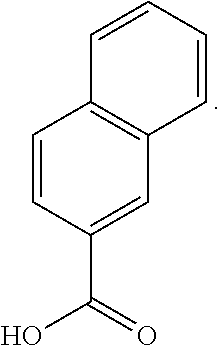
1-naphthoic acid is a naphthoic acid carrying a carboxy group at position 1. It has a role as a fungal xenobiotic metabolite and a bacterial xenobiotic metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a 1-naphthoate.
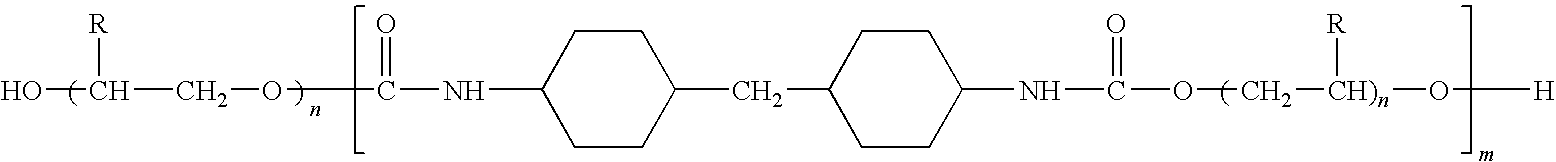
Nicotine salts, co-crystals, and salt co-crystal complexes
The invention provides certain nicotine salts, co-crystals, and salt co-crystals and provides novel polymorphic forms of certain nicotine salts. In particular, nicotine salts with mucic acid, 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and crystalline polymorphic forms of nicotine 4-acetamidobenzoate, nicotine gentisate, and nicotine 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate are described. The invention further provides methods of preparation and characterization of such nicotine salts, co-crystals, and salt co-crystals and polymorphic forms thereof. In addition, tobacco products, including smoking articles, smokeless tobacco products, and electronic smoking articles comprising nicotine salts, co-crystals, and / or salt co-crystals are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
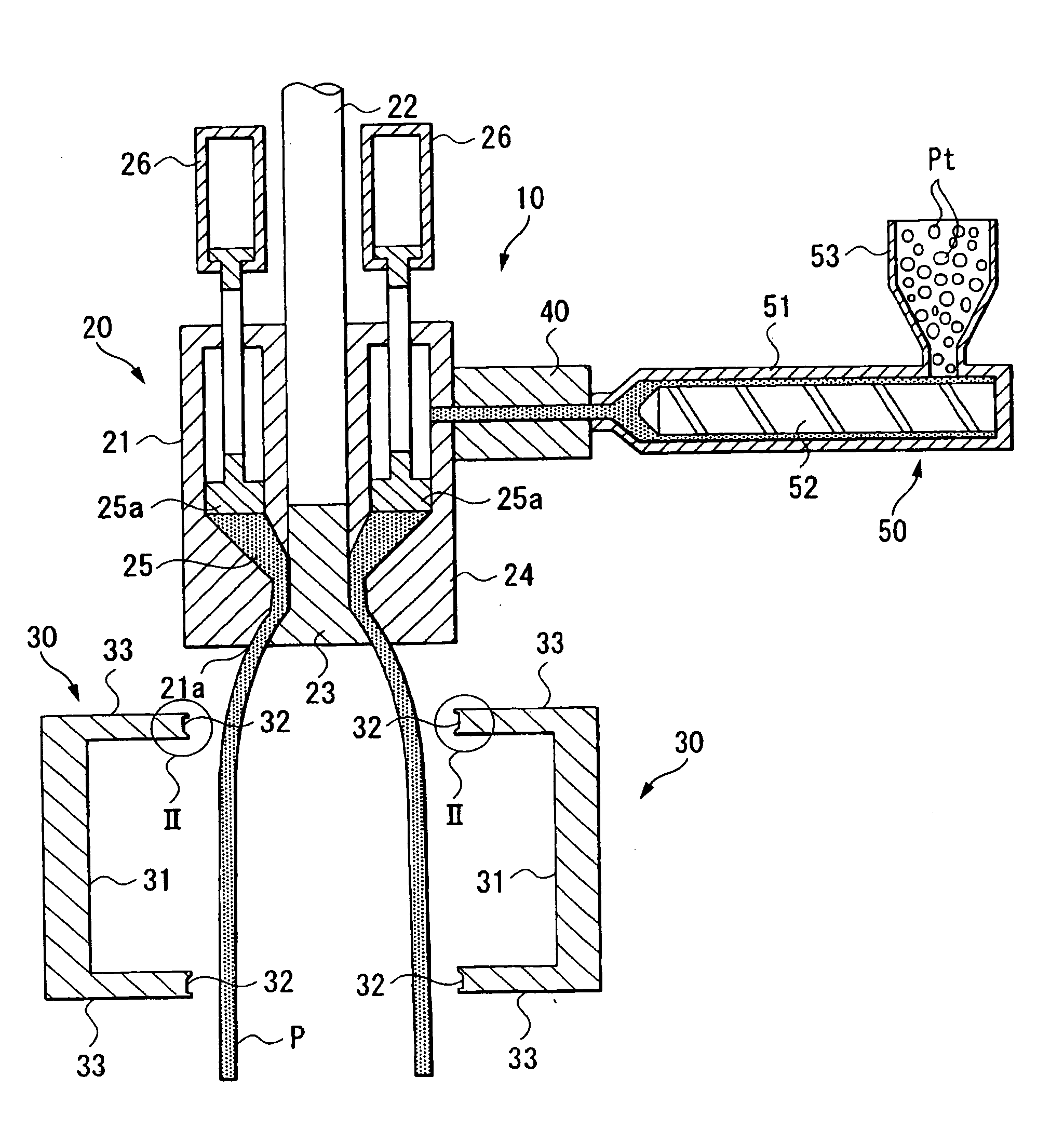
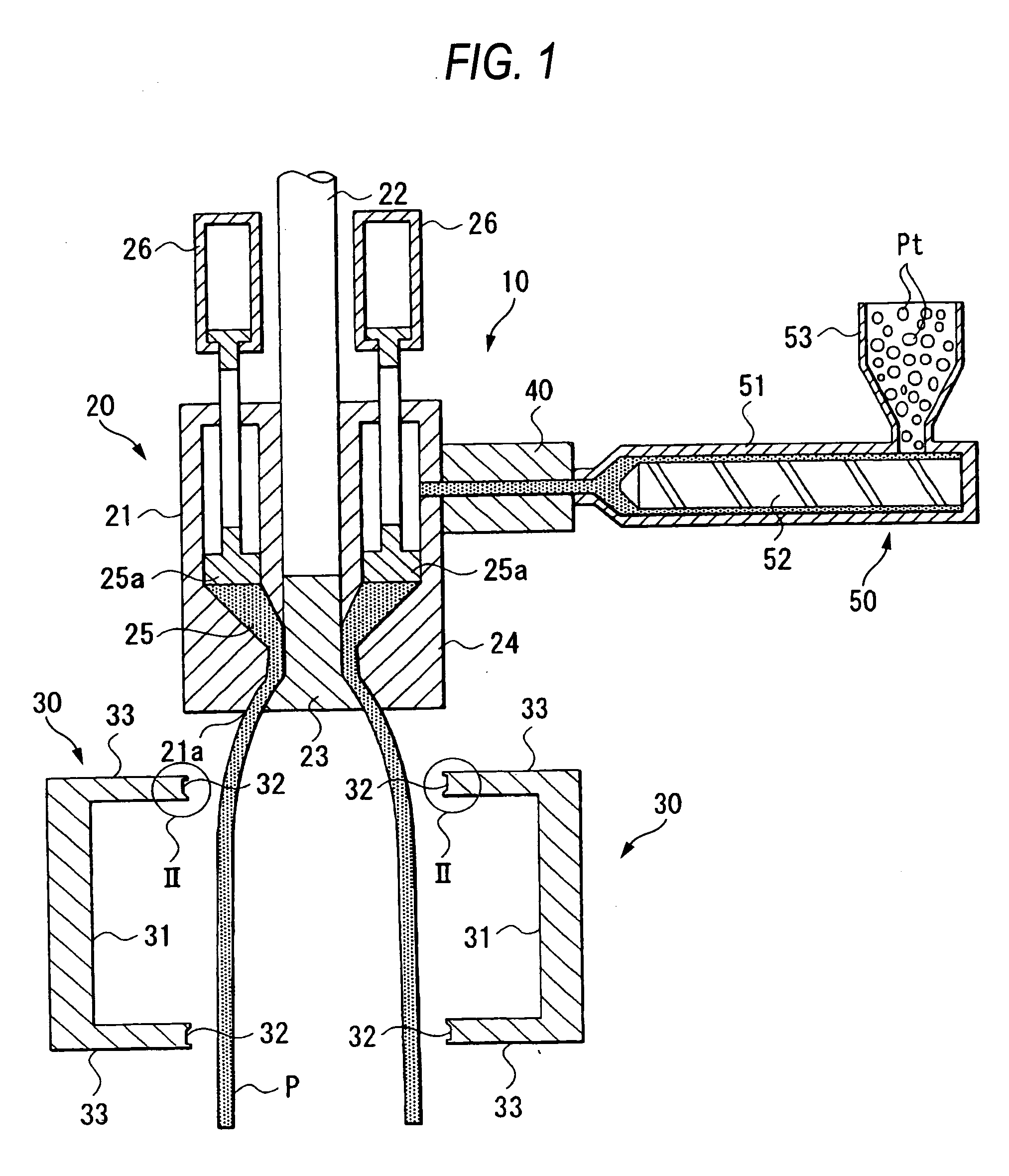
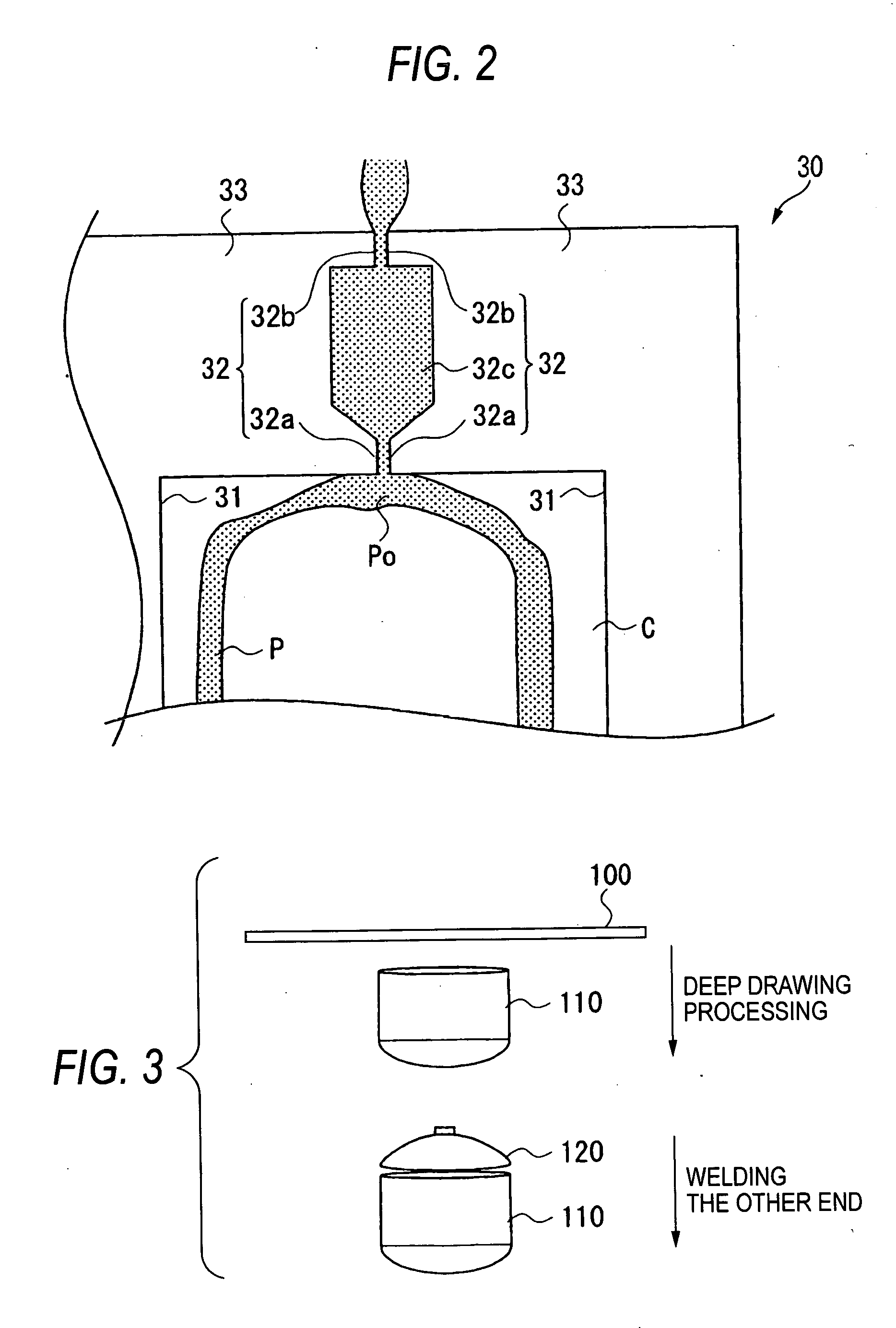
Method for manufacturing liner for pressure resistant container and liner made of liquid crystal resin
InactiveUS20050260372A1Favorable blow molding characteristicExcellent gas barrier propertiesLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingPolyesterPolymer science
A wholly aromatic polyester amide liquid crystal resin including repeating units of: (I) a 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid residue: 1 to 15 mol %, (II) a 4-hydroxybenzoic acid residue: 40 to 70 mol %, (III) an aromatic diol residue: 5 to 28.5 mol %, (IV) a 4-aminophenol residue: 1 to 20 mol %, and (V) an aromatic dicarboxylic acid residue: 6 to 29.5 mol %, and having a melting point of 270° C. to 370° C., and having a melt viscosity of 60 Pa.s to 200 Pa.s at a shear rate of 1000 / sec at a temperature higher by 10° C. to 20° C. than this melting point is molten at a temperature of the melting point +40° C., and extruded at a rate of 0.3 kg / min or more and less than 5 kg / min to form a parison. A pair of molds arranged with the parison interposed there between are closed under a prescribed mold closing pressure, so that air is blown into the interior of the parison.
Owner:SUBARU CORP +1
Aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester and film thereof
ActiveUS7063892B2Small dielectric lossSmallLiquid crystal compositionsLayered product treatmentLiquid crystallinePolyester
An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester having a small dielectric loss in a wide frequency region is provided. An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester is provided that can manufacture a film having a small volume expansion by heating. An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester substantially comprising a repeating structural unit originating in 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid 30 to 80 mol %, a repeating structural unit originating in aromatic diol 35 to 10 mol %, and a repeating structural unit originating in aromatic dicarboxylic acid 35 to 10 mol %.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Dermatological/pharmaceutical compositions comprising benzoyl peroxide, at least one naphthoic acid compound and at least one polyurethane polymer
InactiveUS20100143285A1Improve permeabilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsDERMATOLOGY/SKINPolymer science
Topically applicable, dermatological / pharmaceutical compositions contain, formulated into a physiologically acceptable medium, benzoyl peroxide, at least one naphthoic acid compound and at least one compound of the polyurethane polymer type or derivatives thereof, wherein the benzoyl peroxide and the at least one naphthoic acid compound are dispersed therein.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
Liquid crystalline polyester resin composition
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions
InactiveCN105753662AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationMolecular fluorescenceFluorescent quenching
The invention provides a pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex.Copolymerized pillar[5]arene serves as a subject, 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid serves as an object, C-H......pi and electrostatic attraction serve as driving force, partial 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid provided with negative charges is included into a cavity of pillararene in an alkaline environment, the assembling process of the subject and the object is completed, and the stable pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex is formed.Iron ions are added to an alkaline aqueous solution of the complex, and the subject and the object are subjected to fluorescence quenching; fluorine ions are added, a complex is formed by the fluorine ions and the iron ions, so that the iron ions are separated from the cavity of copolymerized pillar[5]arene, and molecular fluorescence of the complex is reopened.Therefore, Fe<3+> can be determined through the pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex, and F<-> can be continuously identified through fluorescence quenching of the solution.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
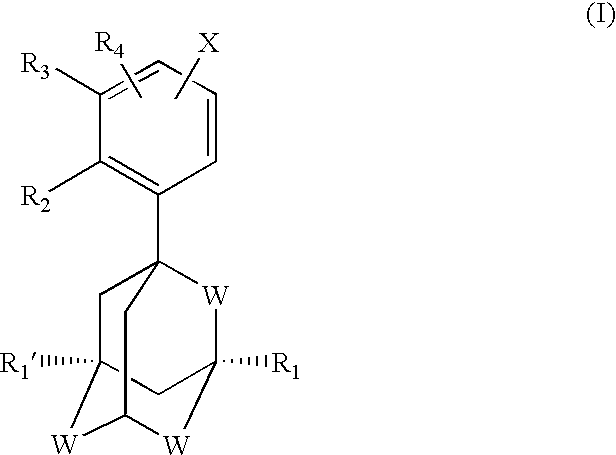
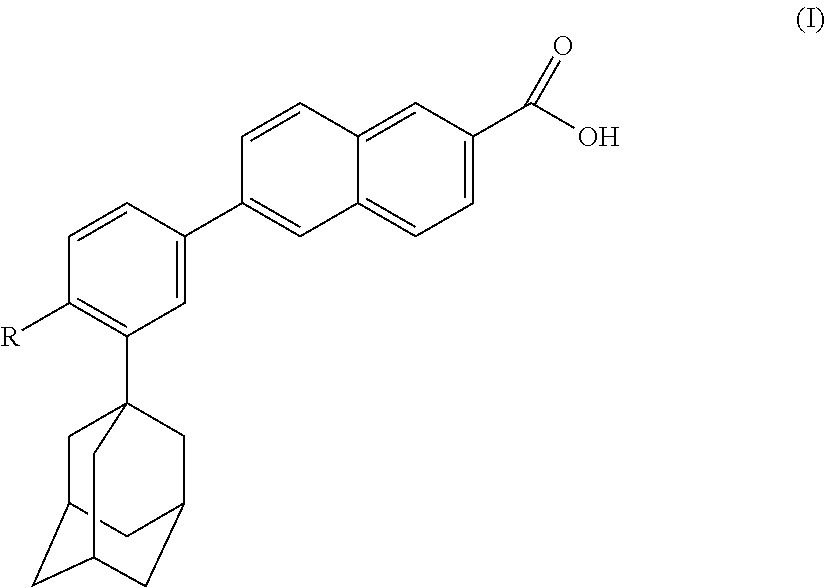
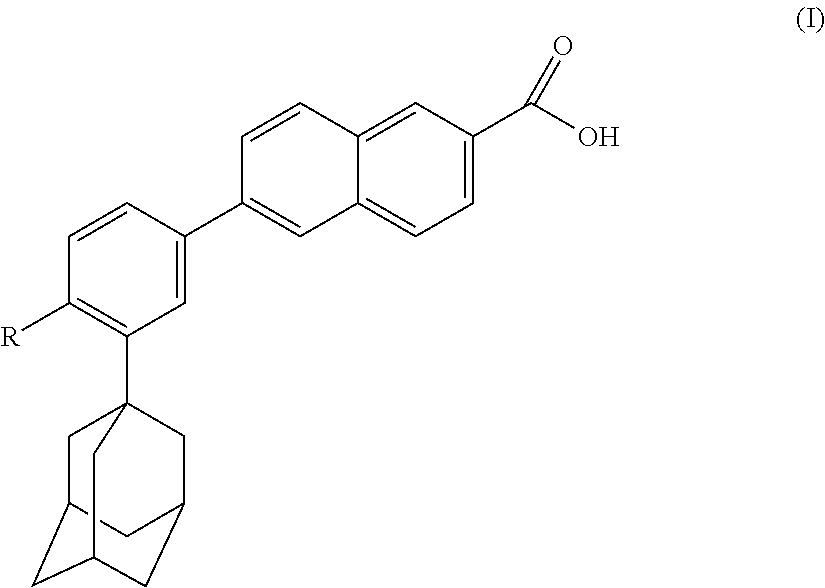
Apoptosis inducing adamantyl derivatives and their usage as anti-cancer agents, especially for cervical cancers and dysplasias
InactiveUS6462064B1Easy to convertCombating the greasy appearance of the skin orBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsCancer preventionRetinoid
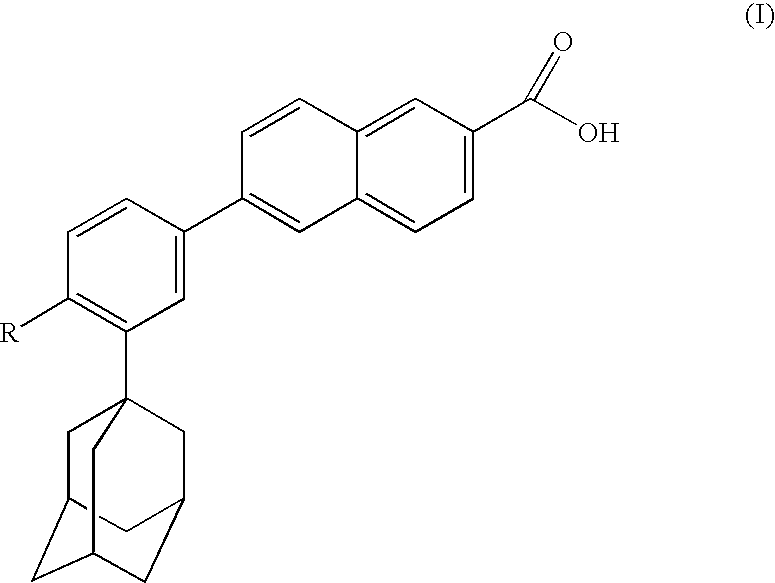
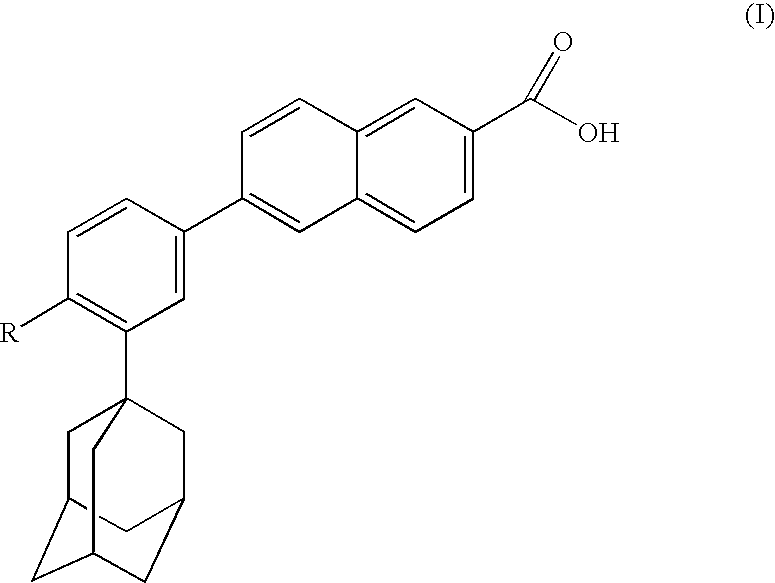
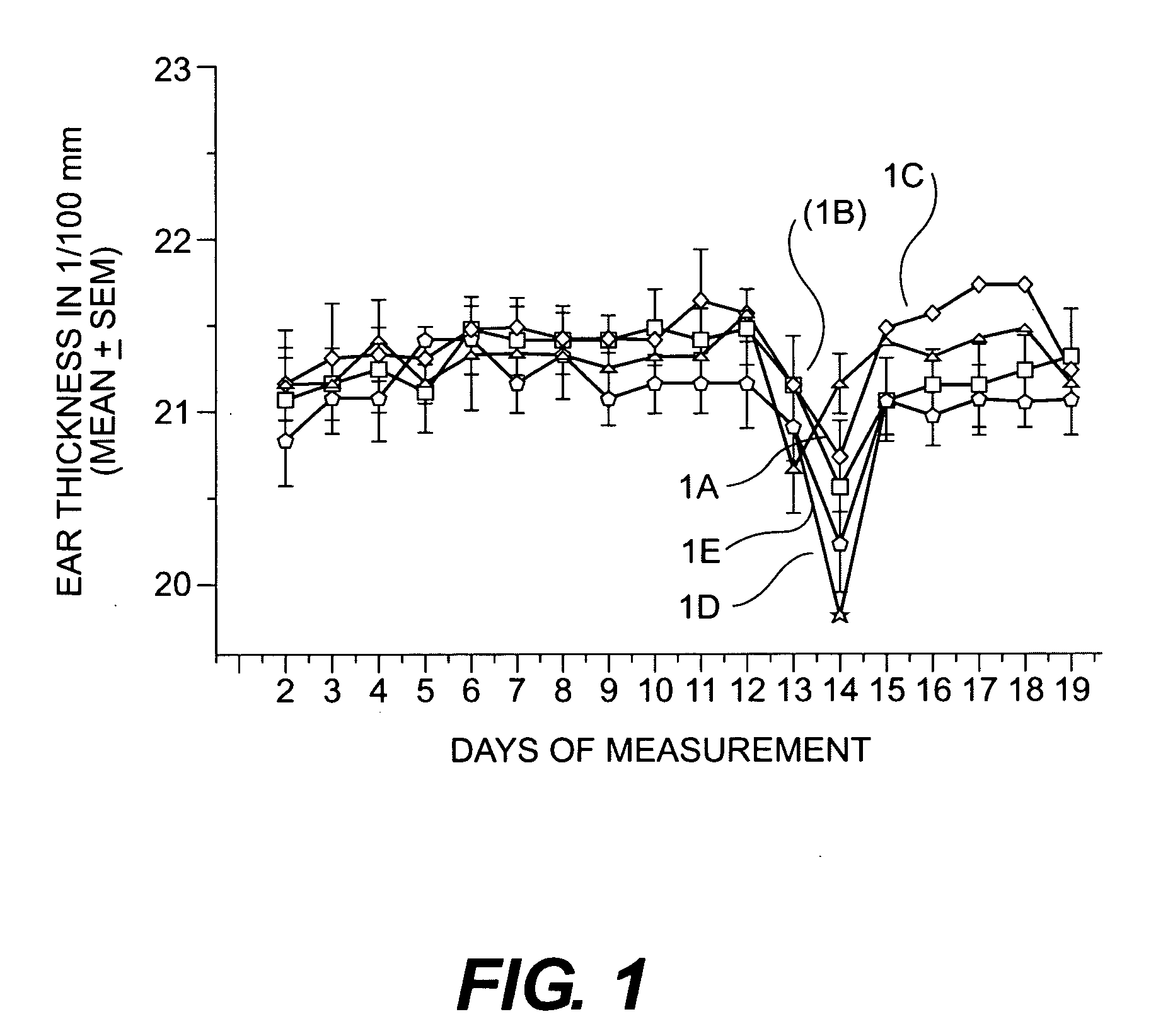
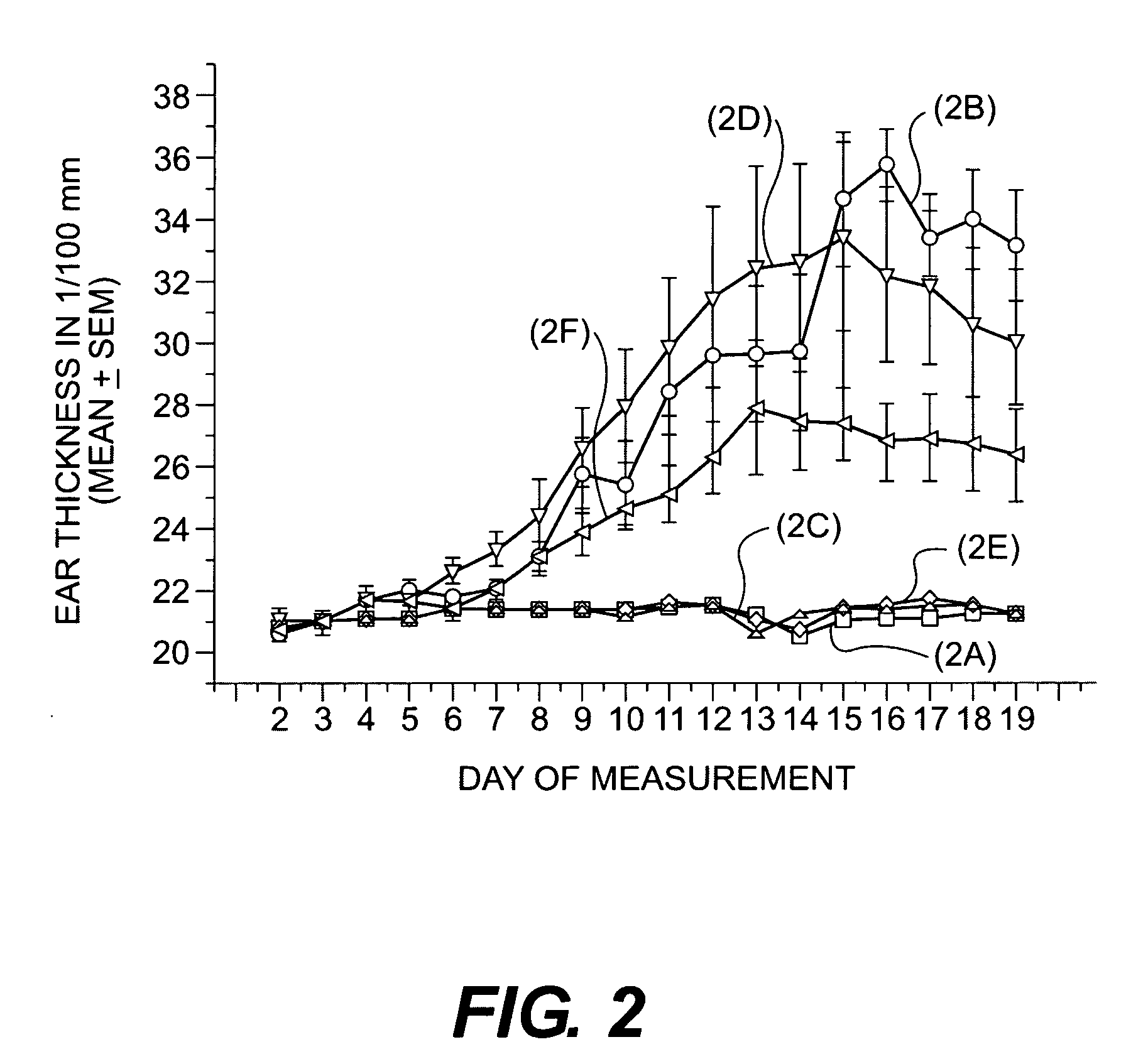
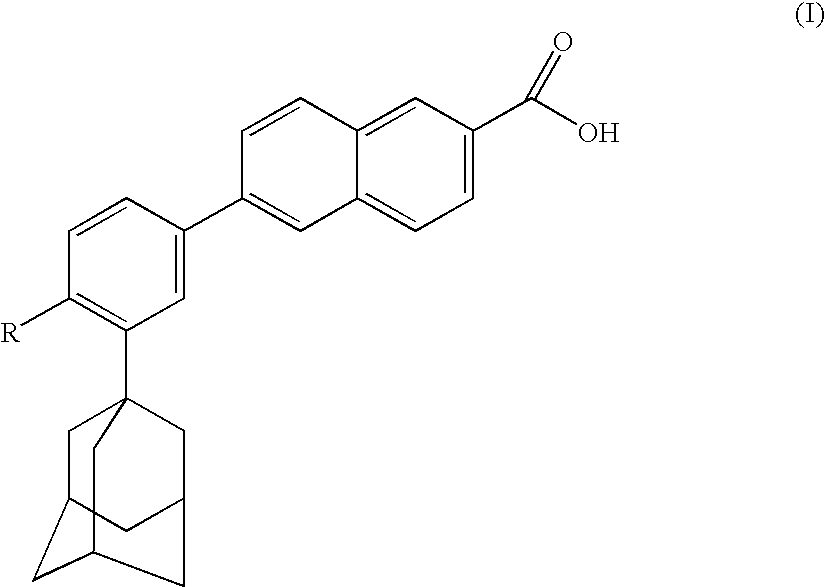
The invention relates to the discovery that specific adamantyl or adamantyl group derivatives containing retinoid-related compounds induce apoptosis of cancer cells and therefore may be used for the treatment of cancer, including advanced cancer. Also, the present invention relates to novel adamantyl or adamantyl group derivatives containing retinoid compounds and their usage for treatment and / or prevention of cancer, keratinization disorders, dermatological conditions, and other therapies More specifically, it has been shown that such adamantyl compounds, e.g., 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid, 2-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-5-benzimidazole carboxylic acid, and 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4,5-methylenedioxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid, can be used to treat or prevent cervical cancers and precancers such as cervical dysplasias, including high grade and low grade dysplasias.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC +1
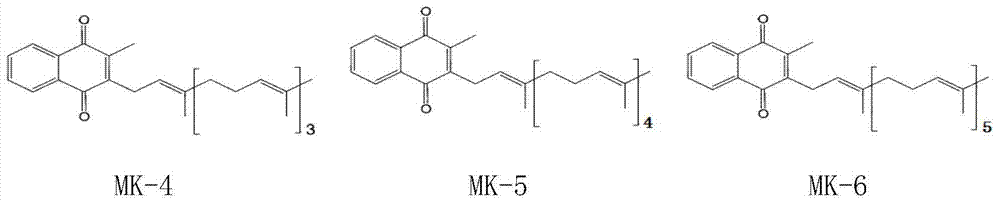
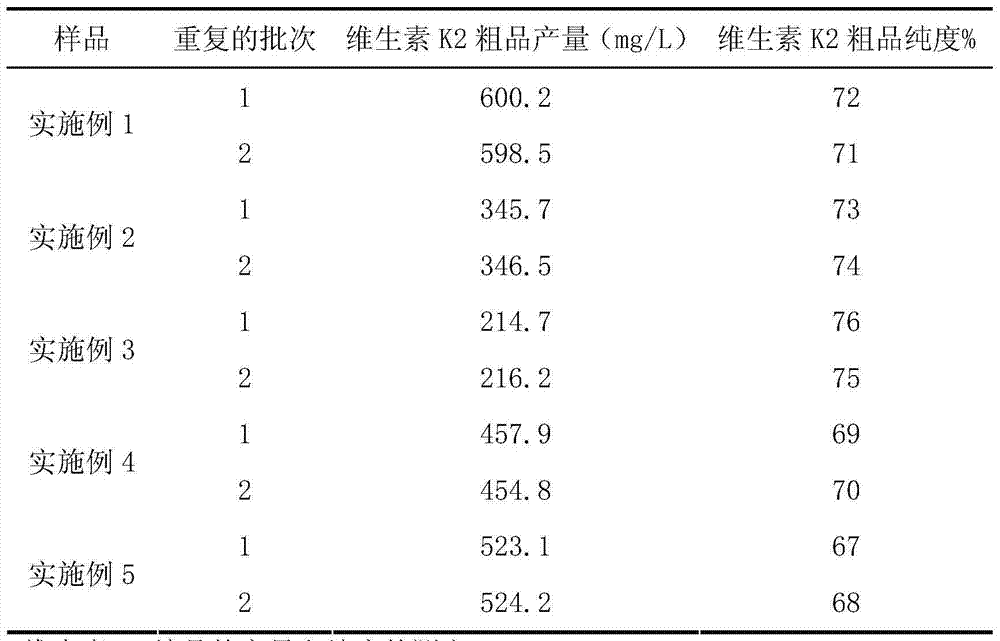
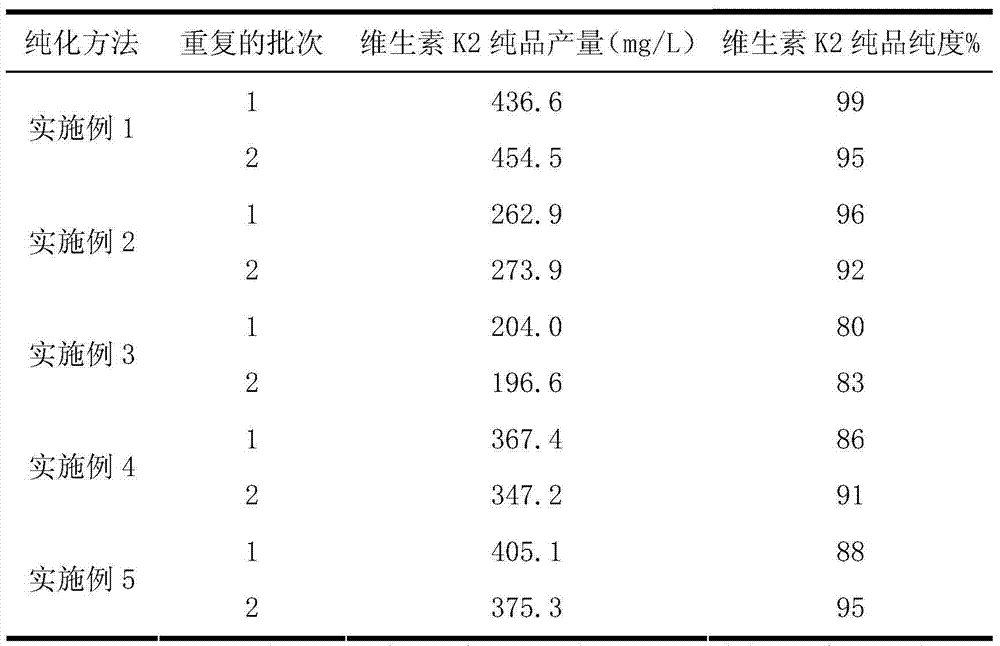
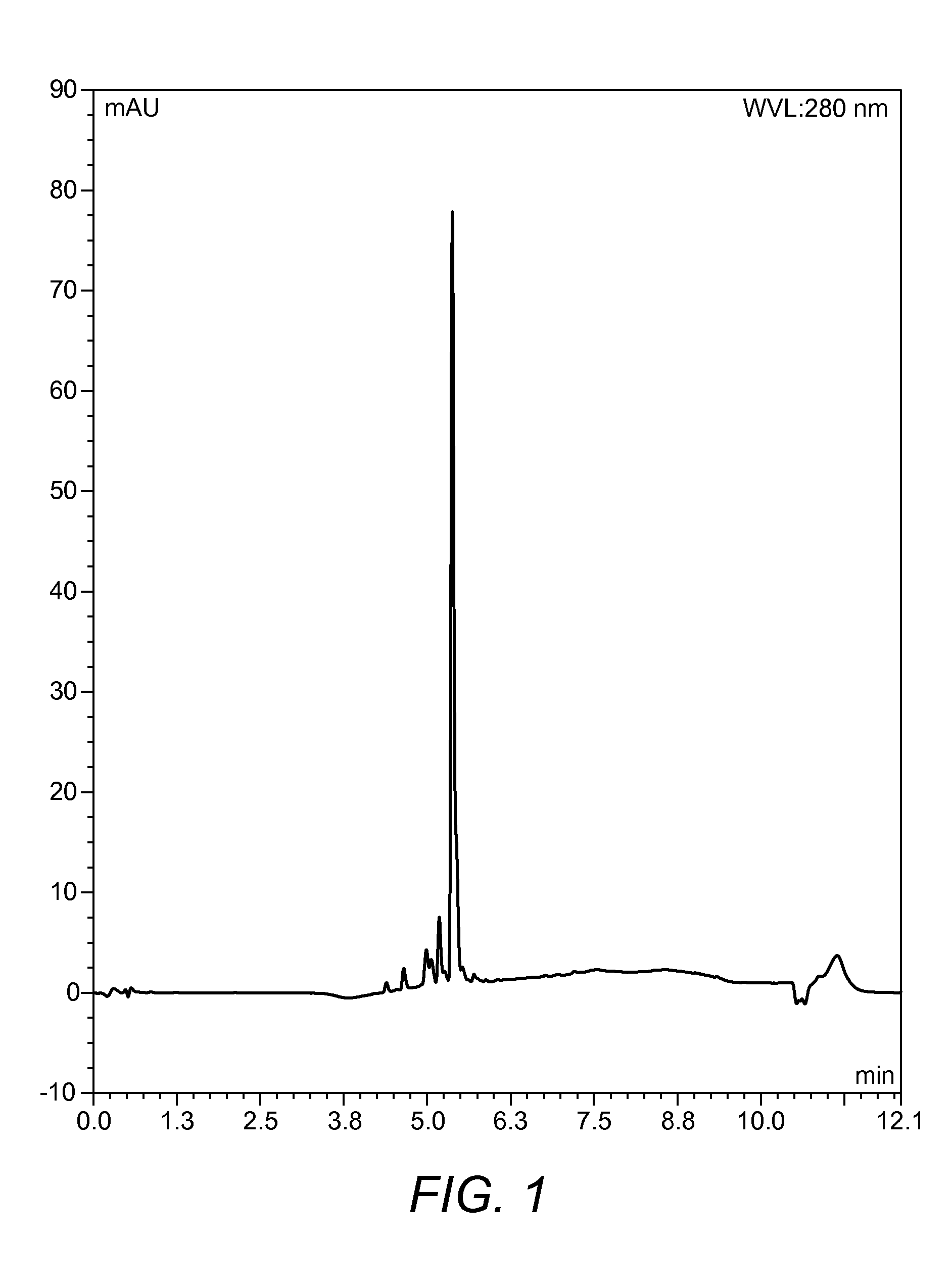
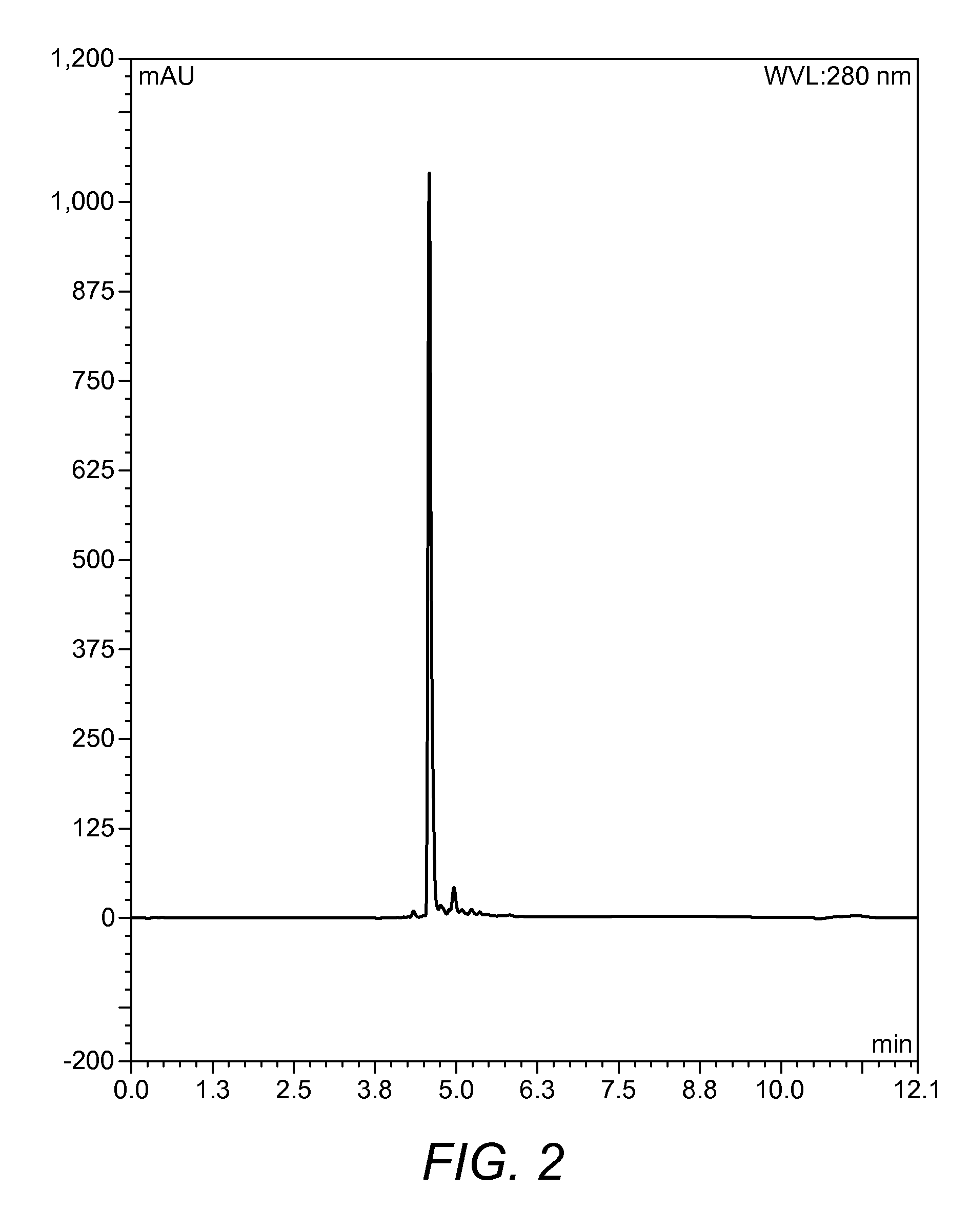
Vitamin K2 and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN103571897AHigh purityIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationVitamin K2Organic solvent
The invention discloses a vitamin K2 and preparation process thereof. According to the process, 1-hydroxyl-2-naphthoic acid resistant flavobacterium strain HNA12-D is fermented and cultured, and vitamin K2 efficiently metabolizes in the strain through the batch feeding of glycerin serving as the carbon source, peptone serving as the nitrogen source and precursor substances, and is extracted by using organic solvents and separated by macroporous resin, and the yield and purity of the product are improved. The total output of the vitamin K2 crude product is 200-600 mg / L after the flavobacterium strain HNA12-D of the invention is fermented and cultured for 120-144 hours, and the product purity reaches 80-99 percent after absorption chromatography; compared with the prior art, the yield output and the product purity are greatly improved, and the product can be used in industrial production.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Controlled release composition and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20030134800A1Suppressing initial excess releaseStable releasing speed for a long period of timeNervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsControlled release3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid
A controlled release composition containing a physiologically active substance in high content, suppressing the initial excess release, and achieving a stable release speed over a long period of time is provided. A controlled release composition comprising (1) a physiologically active substance or salt thereof in an amount of about 14% (w / w) to about 24% (w / w) based on the total composition weight, (2) hydroxynaphthoic acid selected from the group consisting of 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid and 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid or salt thereof, and (3) a lactic acid polymer or salt thereof having a weight-average molecular weight of 15000 to 50000 in which the content of polymers having molecular weights of 5000 or less is about 5% by weight or less, wherein the molar ratio of said hydroxynaphthoic acid or salt thereof to said physiologically active substance or salt thereof is from 3:4 to 4:3.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Peptide clearing agents
InactiveUS20130053543A1Easy to removeReduce molecular weightPeptide sourcesNanomedicineDipeptideReactive site
A peptide clearing agent is provided for clearance of a conjugate of an enzyme and a binding molecule which binds specifically at a target location from a non-target location in a subject. The peptide clearing agent binds the active site of the enzyme. The peptide also binds to the asialoglycoprotein receptor expressed by hepatic cells to facilitate clearance through the liver. The peptide may be glycosylated to facilitate clearance through the liver by binding to hepatic cells expressing an asialoglyco-protein receptor. Typically, the peptide prevents or inhibits enzyme activity upon binding to the enzyme and is not substantially modified by the enzyme activity. The peptide may be based upon the dipeptide amino-naphthoic acid (ANA)-glutamate (GIu) and may comprise the amino acid sequence serine (Ser)-Alanine (Ala)-amino-naphthoic acid (ANA)-glutamate (GIu). In such cases, the enzyme of interest is typically CPG2.
Owner:MOLOGIC LTD
Preparation method of graphene/thermotropic liquid crystal wholly aromatic polyester composite material
ActiveCN103333324AEvenly dispersedImprove conductivityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolymer scienceResin-Based Composite
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene / thermotropic liquid crystal wholly aromatic polyester composite material. According to the invention, 6-alkyl-2-naphthoic acid non-covalent bond modified graphene oxide is obtained through the pi-pi interaction of the naphthalene ring structure of 6-alkyl-2-naphthoic acid and graphene oxide, and the modified graphene oxide is subjected to hot reduction in the polycondensation process of a wholly aromatic polyester monomer to generate graphene, so that the graphene is uniformly dispersed in the thermotropic liquid crystal wholly aromatic polyester resin, thus overcoming the problems that the graphene is difficult to disperse and the lamellar structure is easy to agglomerate when the graphene is directly blended with the thermotropic liquid crystal wholly aromatic polyester. After being processed into fiber, the prepared composite resin has favorable conductivity and mechanical performance. Tests prove that the composite material has stable mechanical performance, the strength of the fiber formed by spinning the composite material is increased by 60% or so in comparison with the simple thermotropic liquid crystal wholly aromatic polyester, the fiber has favorable conductivity, and the mechanical performance of the fiber is even superior to that of the simple TLCP (thermotropic liquid crystal polymer) fiber.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide composition
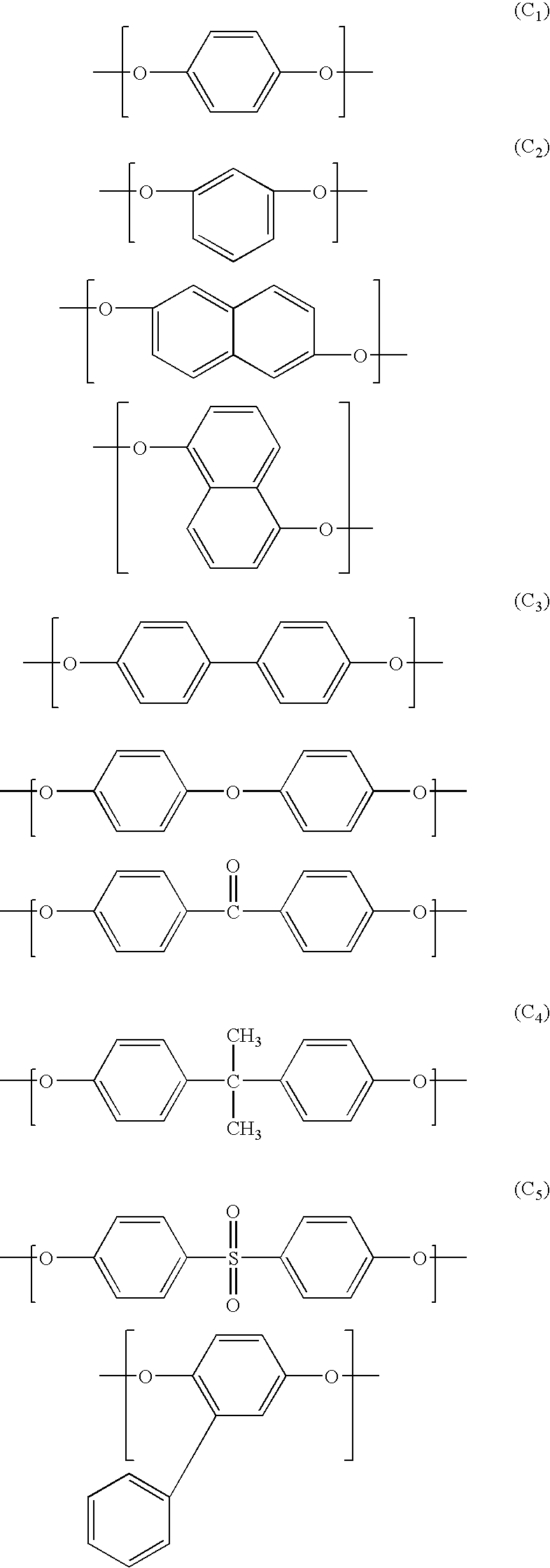
InactiveUS20060073306A1Improve tensile propertiesImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolyesterPolyolefin
The present invention is to provide an amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide composition which has an excellent stretching property and a good adhesion to a heterogeneous polymer and thereby can be in particular suitably used for a multilayer film, or a multilayer sheet, a multilayer blow formed product and the like. That is, (the first invention) an amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide composition obtained by blending 1 to 30% by weight of a modified polyolefin resin or a polyamide resin having a melting point of 230° C. or lower or being amorphous with an amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide exhibiting an optical anisotropy at softening and flowing and being a wholly aromatic polyester amide obtained by copolymerizing (A) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, (B) 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid, (C) an aromatic aminophenol and (D) an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, wherein (1) the ratio of (C) the aromatic aminophenol is from 7 to 35% by mol, (2) the ratio of the bending monomer(s) among the starting monomers is from 7 to 35% by mol, (3) the ratio ((A) / (B)) between (A) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and (B) 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid is from 0.15 to 4.0, (4) the ratio of isophthalic acid is at least 35% by mol in (D) the aromatic dicarboxylic acid, (5) any melting point is not found by DSC measurement at a temperature rising rate of 20° C. / min and (6) the glass transition temperature is from 100 to 180° C., and (the second invention) an amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide composition obtained by blending 1 to 30% by weight of a modified polyolefin resin or a polyamide resin having a melting point of 230° C. or lower or being amorphous with an amorphous wholly aromatic polyester amide exhibiting optical anisotropy at softening and flowing and being a wholly aromatic polyester amide obtained by copolymerizing (A) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, (B) 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid, (C)′ an aromatic diamine and (D) an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, wherein (1) the ratio of (C)′ the aromatic diamine is from 3 to 15% by mol, (2) the ratio of the bending monomer(s) is from 7 to 35% by mol in the starting monomers, (3) the ratio ((A) / (B)) between (A) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and (B) 2-hydroxy-4-naphthoic acid is from 0.15 to 4.0, (4) any melting point is not found by DSC measurement at a temperature rising rate of 20° C. / min and (5) the glass transition temperature is from 100 to 180° C.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Reduced-irritant dermatological compositions comprising at least one naphthoic acid compound and benzoyl peroxide and treatment of keratinization disorders therewith
InactiveUS20090191245A1Improve permeabilityReduce skin irritationPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsDiseaseBenzoyl peroxide
Topically applicable, reduced-irritant dermatological / cosmetic compositions useful for the prevention / treatment of a variety of keratinization disorders, for example acne vulgaris, contain at least one naphthoic acid compound and an amount of benzoyl peroxide encapsulated in a polymeric system of porous particles for increasing cutaneous penetration of the at least one naphthoic acid compound, are formulated into topically applicable, physiologically acceptable media therefor.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
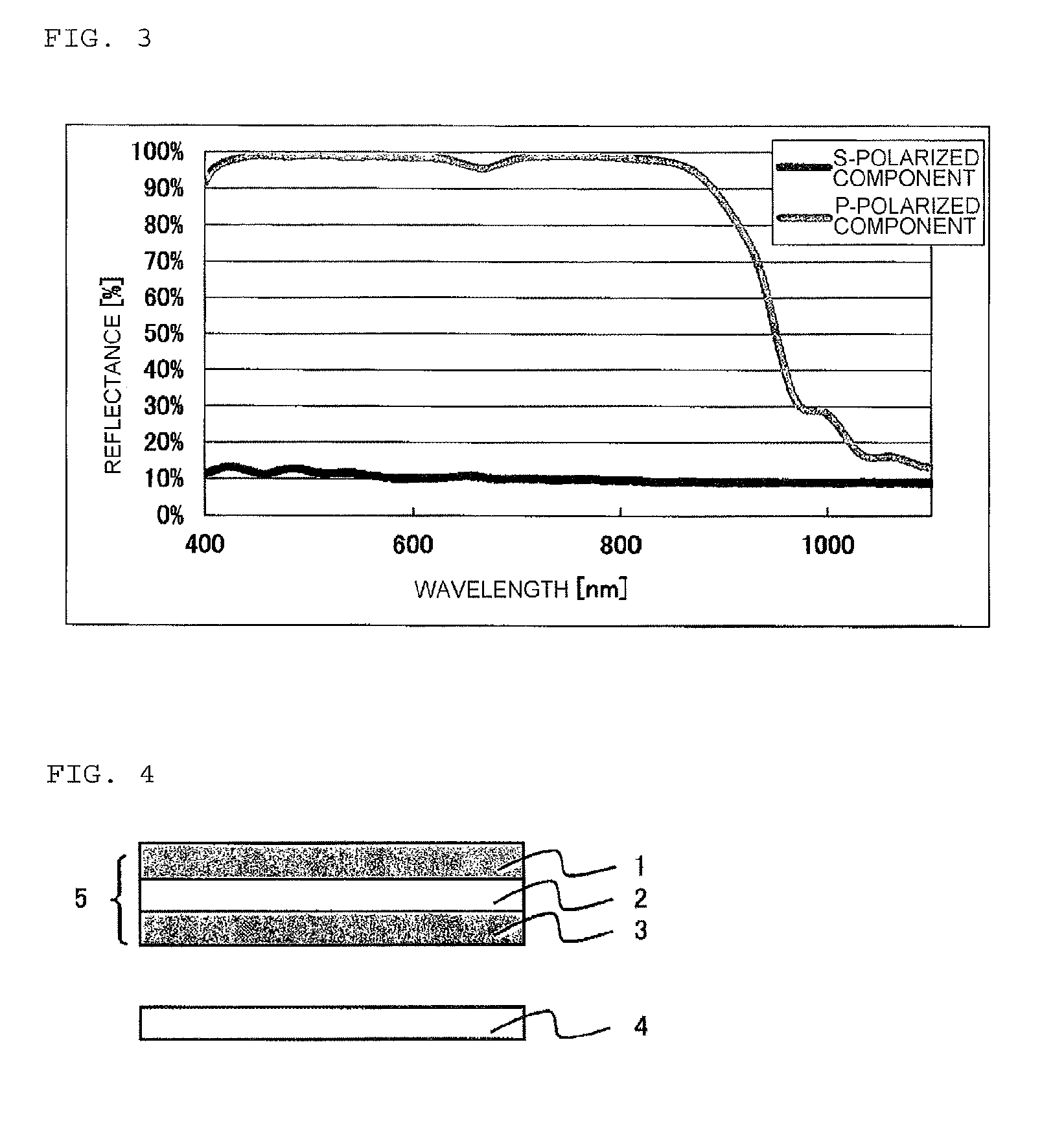
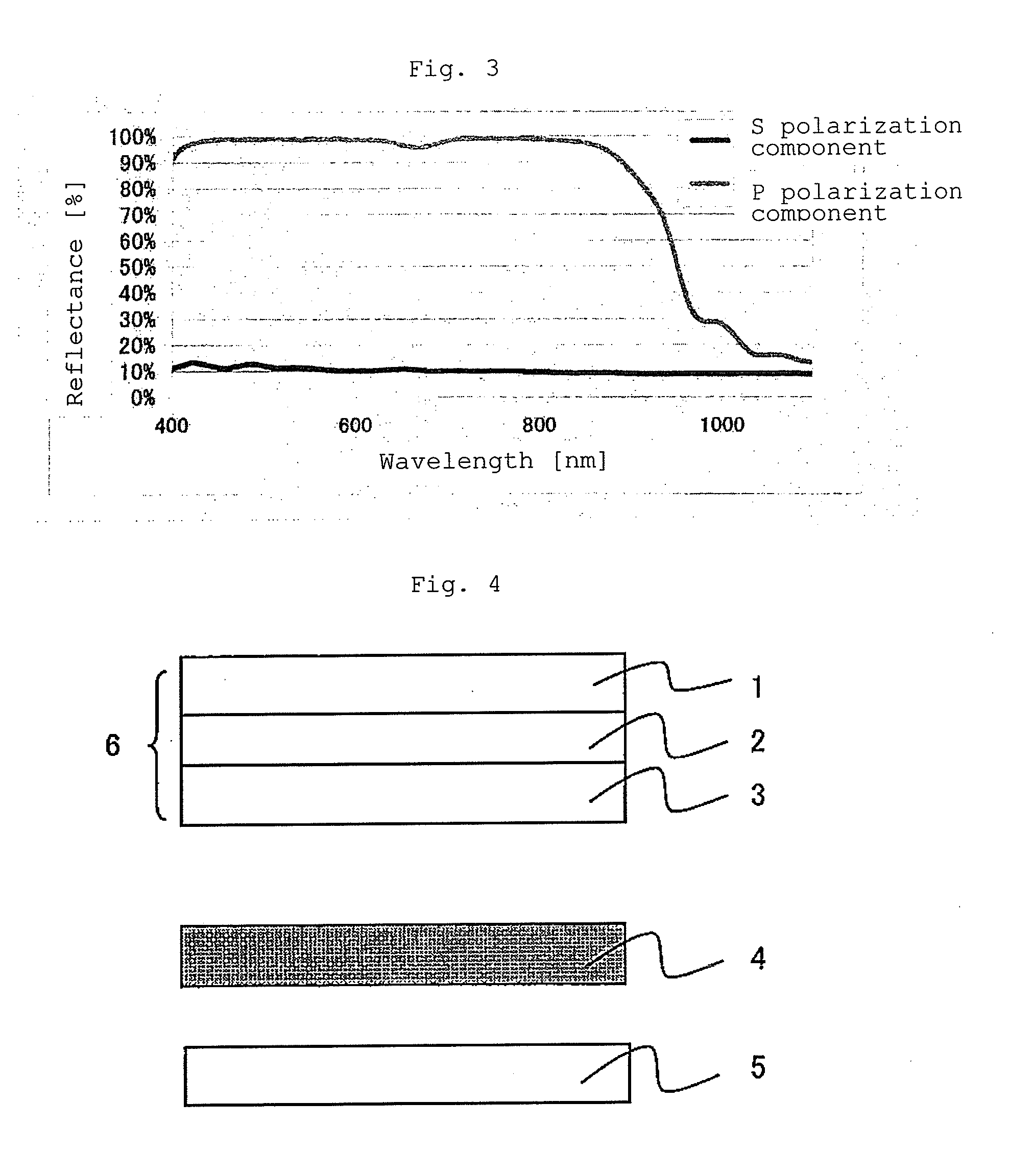
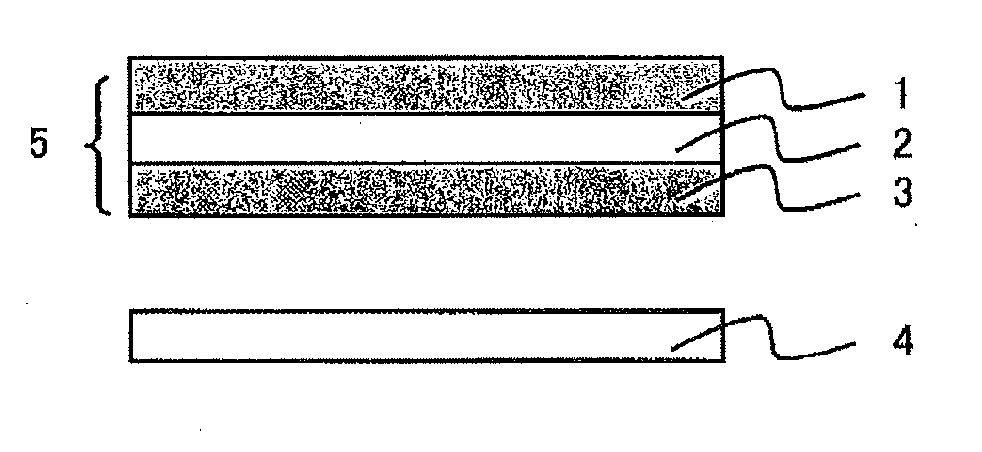
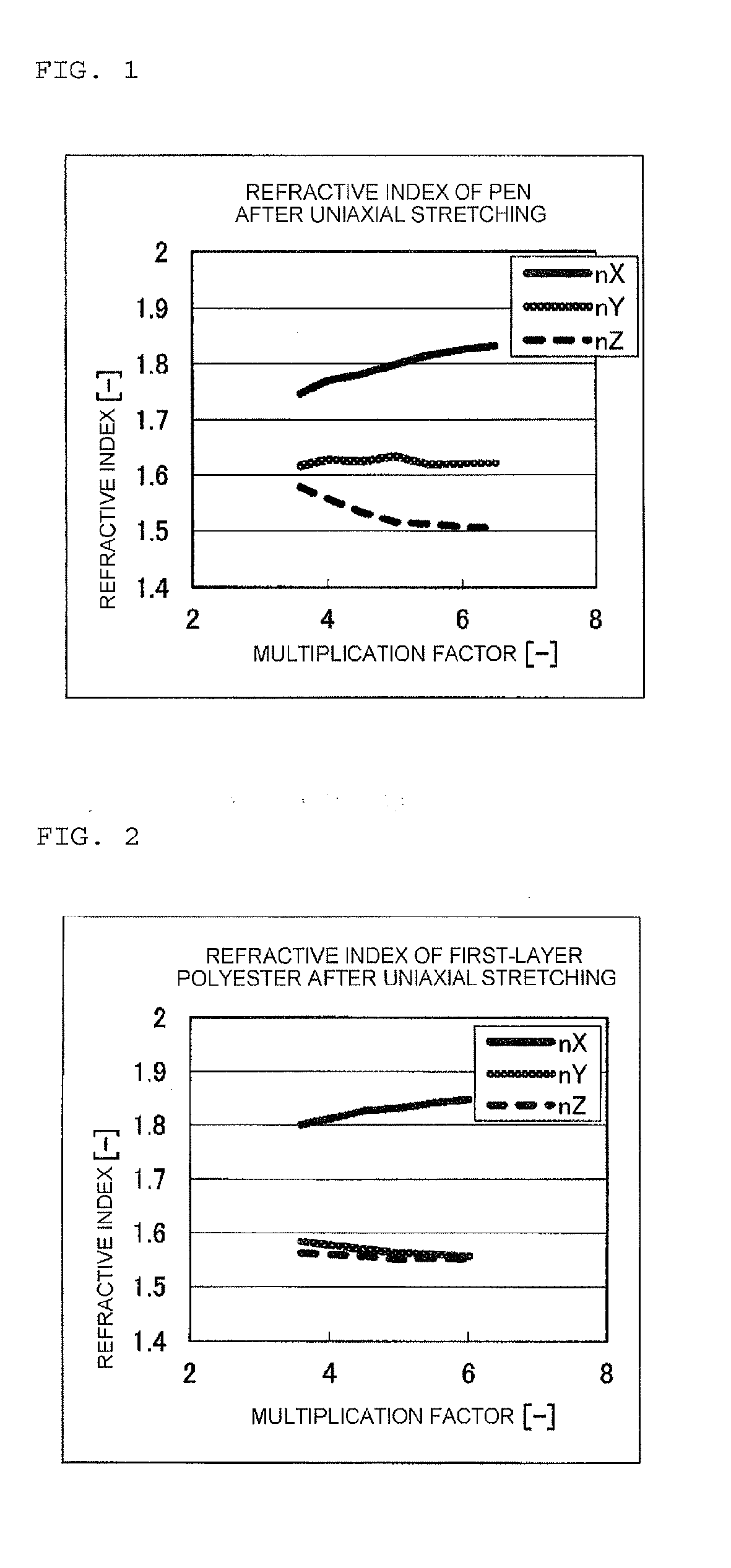
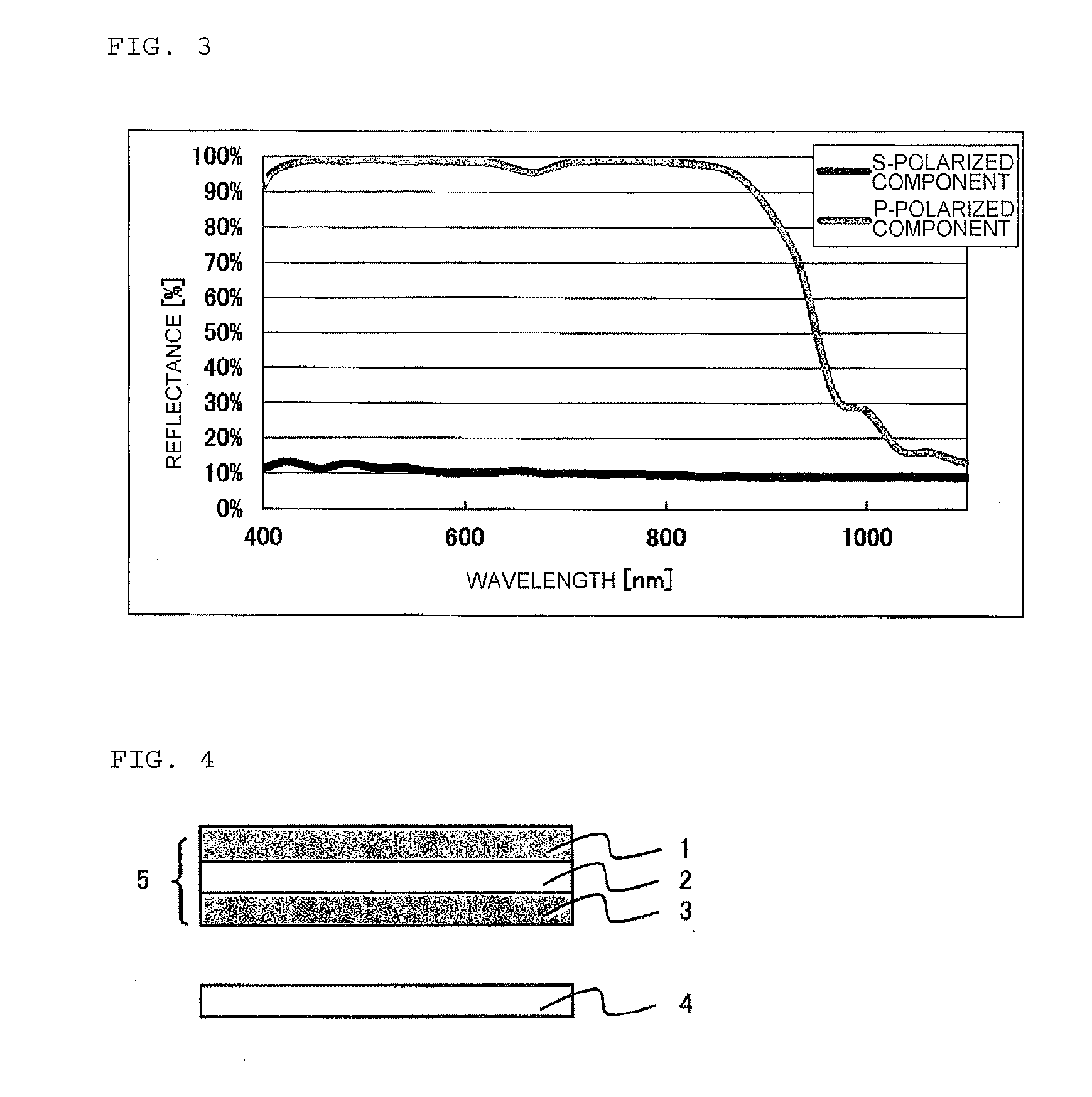
Reflective polarizing film, and optical member for liquid crystal display device, and liquid crystal display device formed from same
ActiveUS9405048B2Improve polarization performanceLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsPolyesterCrystallography
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Highly thermal-conductive resin composition
ActiveUS20050256291A1Improve thermal conductivityConductive materialOrganic conductorsHydroquinone CompoundPhthalic acid
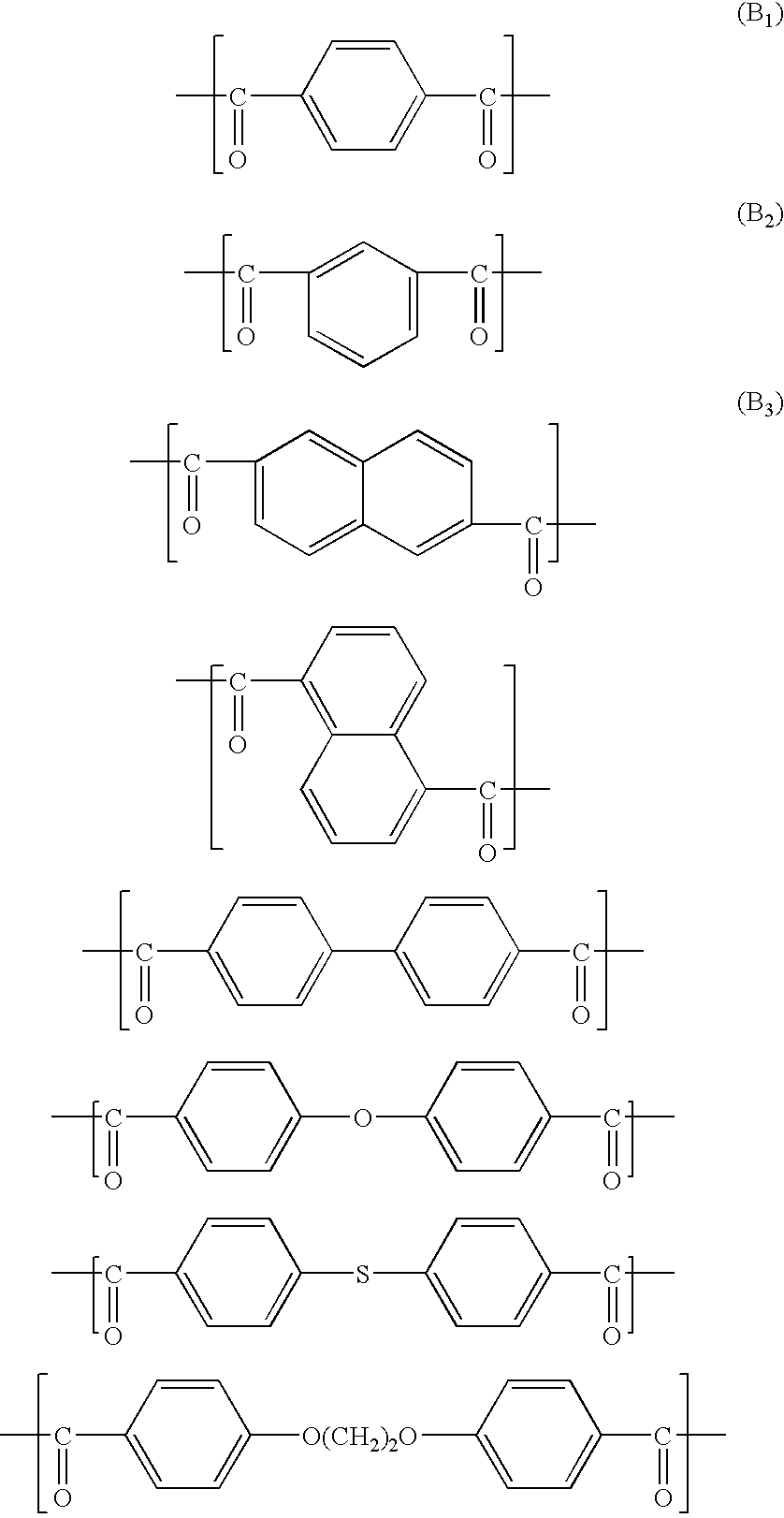
A resin composition comprising an inorganic material with a thermal conductivity of 10 W / mK or higher at a temperature of 20° C. and an aromatic polyester is provided. The aromatic polyester may have structural units derived from (I) 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid, (II) a compound selected from hydroquinone, 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl and 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, (III) naphthalenedicarboxylic acid and (IV) a compound selected from terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid and phthalic acid.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
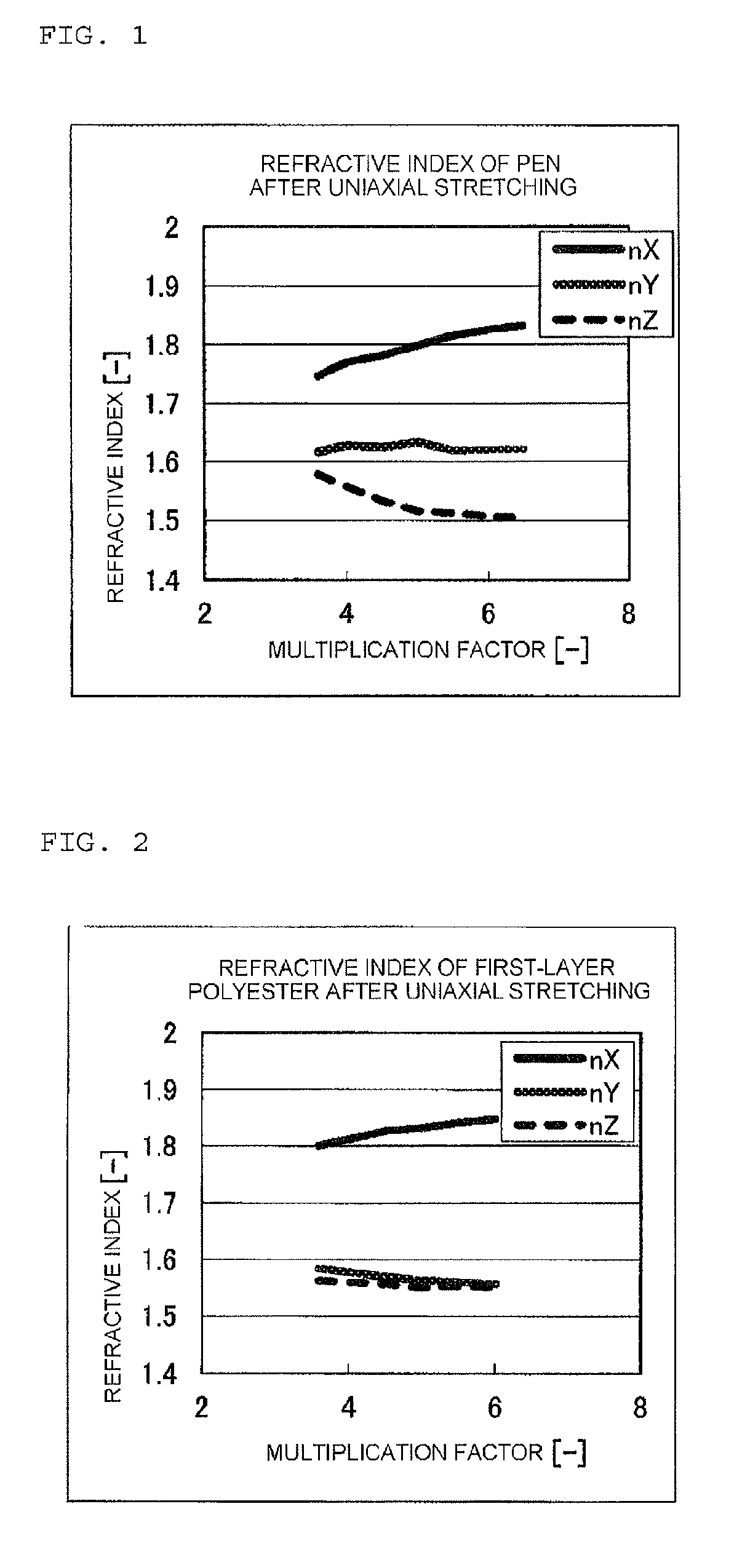
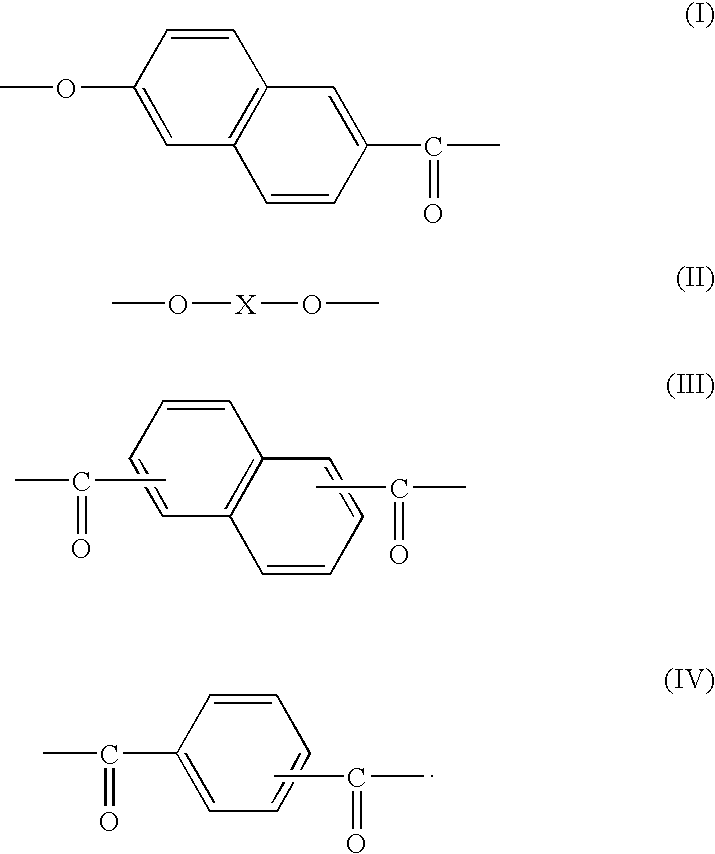
Multi-layer stretched film
ActiveUS20120249935A1Improve polarization performanceRefractive index differenceSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsPolyesterPolymer science
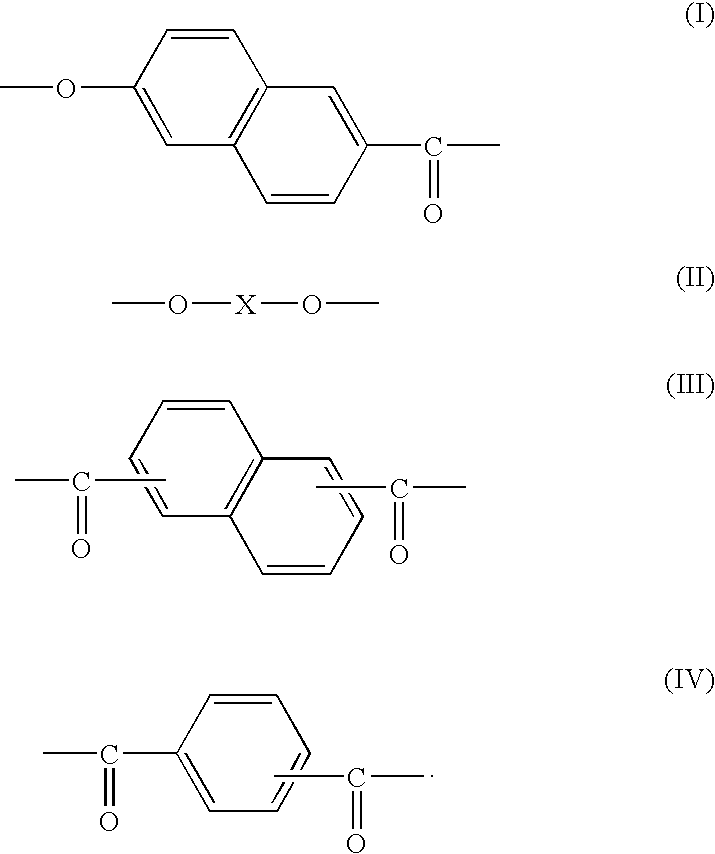
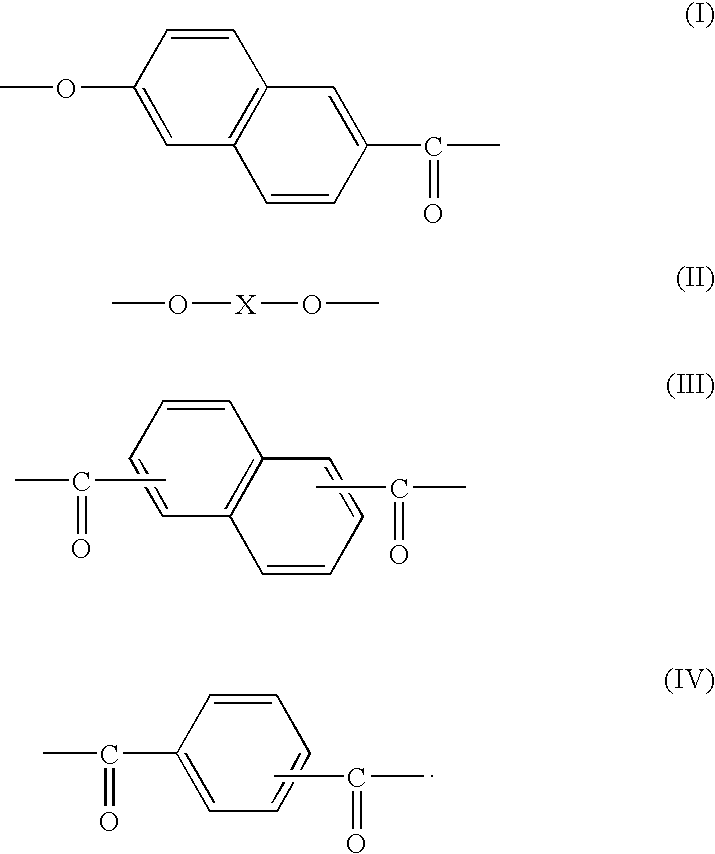
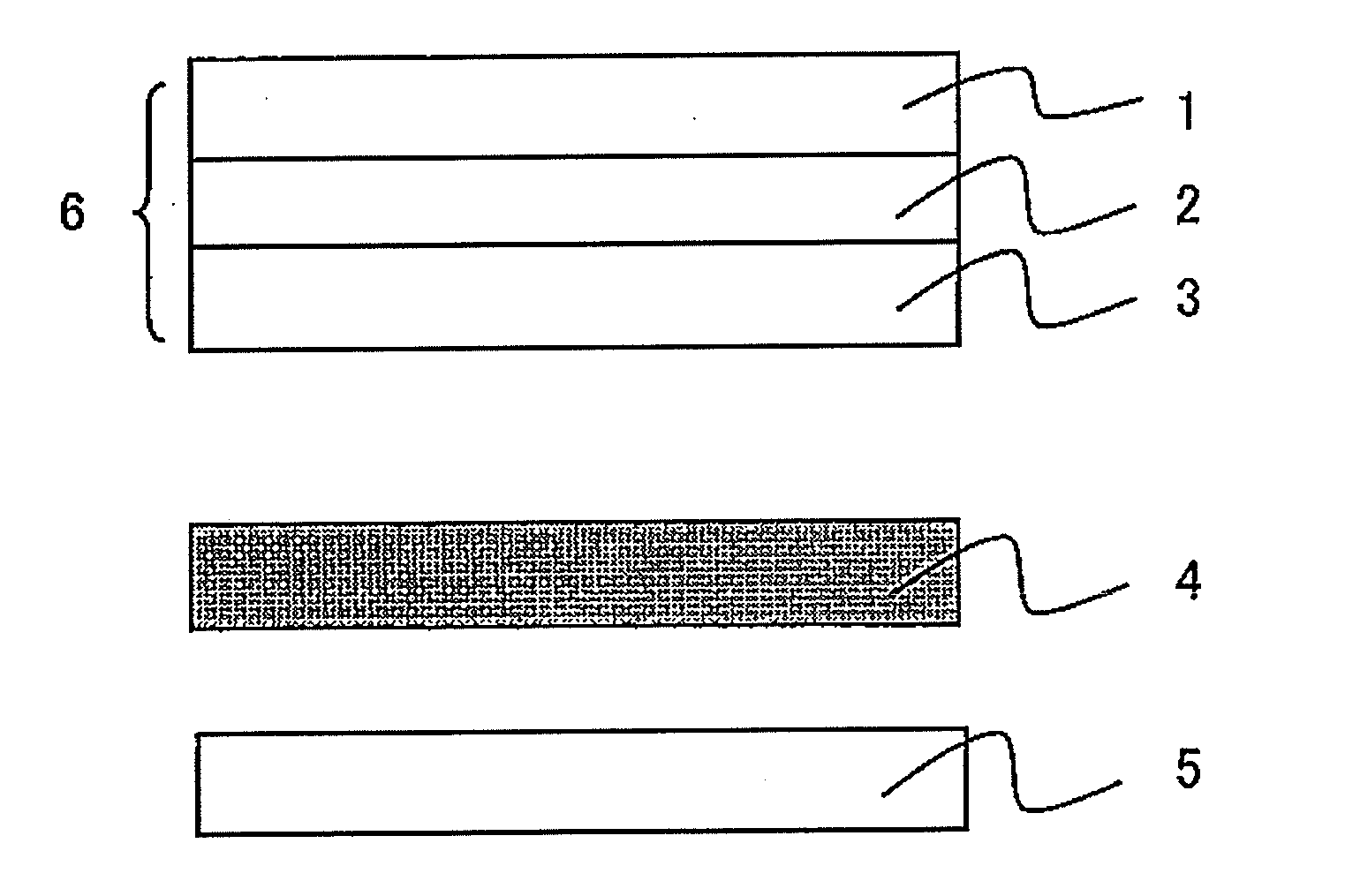
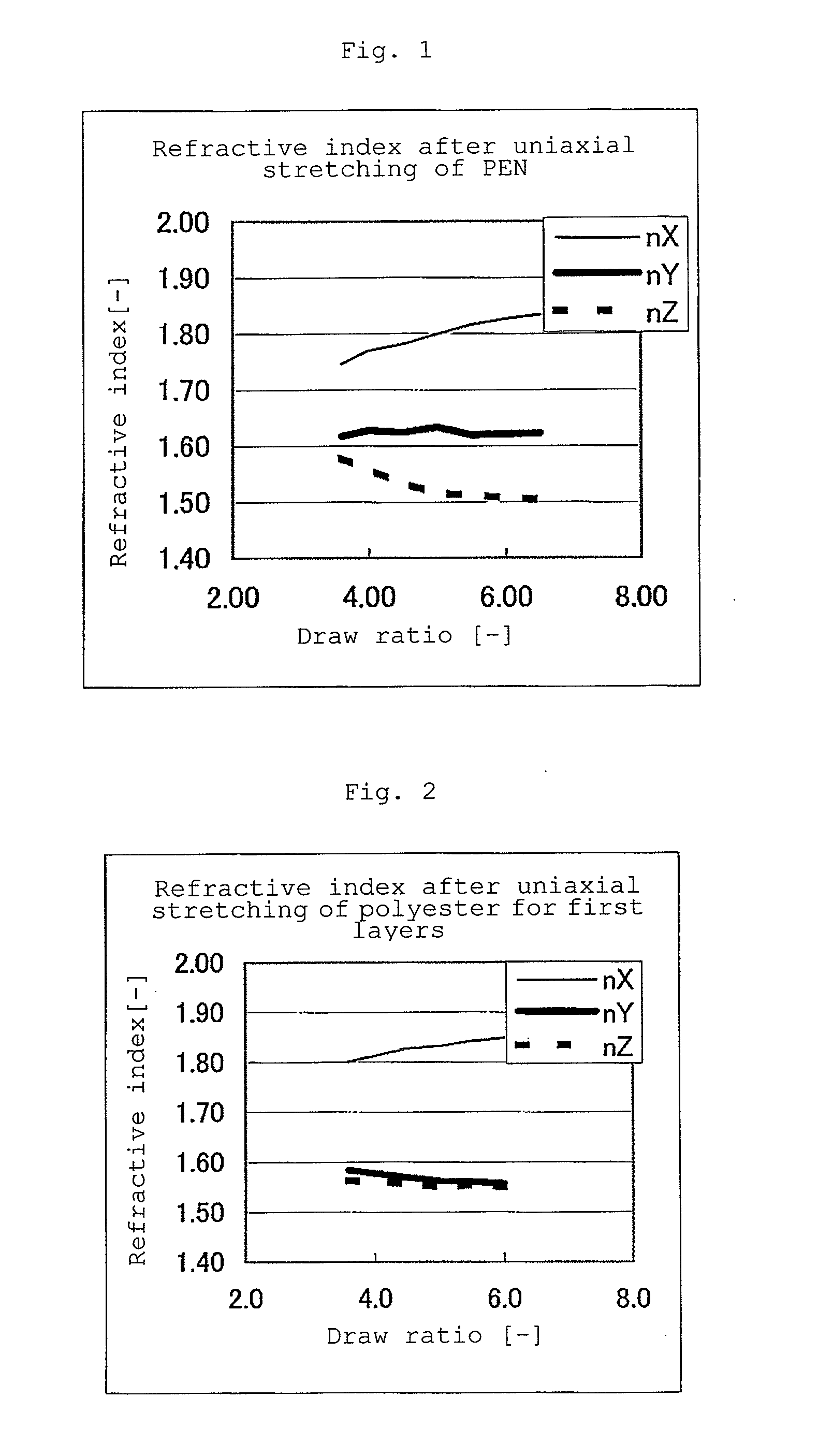
A multi-layer stretched film has 251 or more alternating layers which consist of first layers and second layers, wherein the first layers are made of a polyester which contains (i) 5 to 50 mol % of a naphthoic acid component as a dicarboxylic acid component and (ii) a diol having an alkylene group with 2 to 10 carbon atoms as a diol component; and the second layers are made of a thermoplastic resin having an average refractive index of 1.50 to 1.60 and differences in refractive index among a uniaxial stretching direction, a direction orthogonal to the uniaxial stretching direction and a film thickness direction of 0.05 or less before and after stretching, and the film has specific reflectance characteristics for a P polarization component and an S polarization component.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Liquid crystalline polyester compositions
ActiveUS20110233462A1High molar massHigh melting pointLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineTerephthalic acid
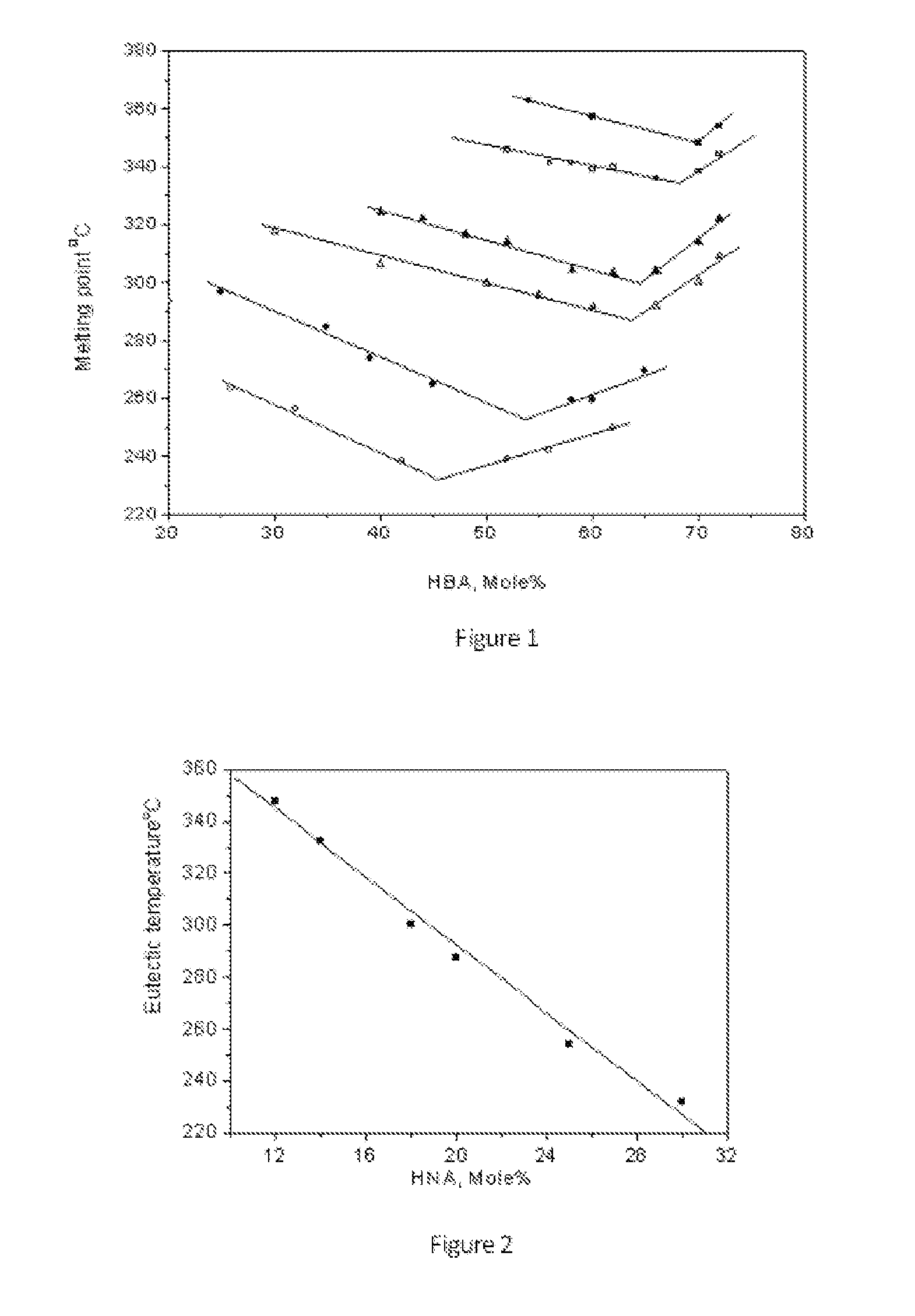
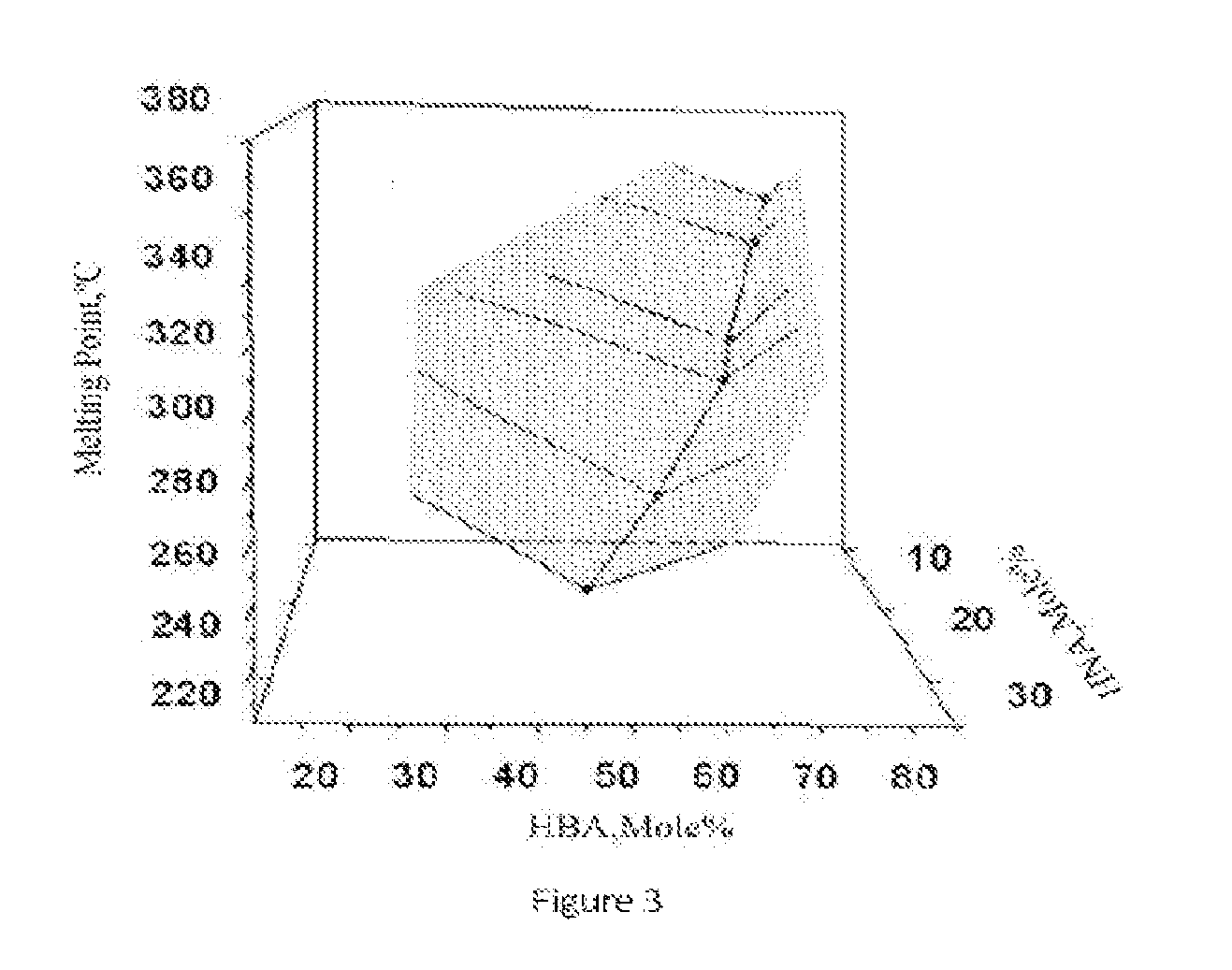
The present invention provides a class of thermotropic liquid crystalline polyesters (TLCPs) and molding compositions comprising the polyesters and glass fiber. The TLCPs consist essentially of repeat units derived from p-hydroxybenzoic acid (HBA), 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (HNA), terephthalic acid (TA), and hydroquinone (HQ), and the mole percent of HBA, HNA, TA and HQ is 34-72%, 12-26%, 4-21% and 4-21%, respectively. The TLCPs have a melting temperature equal to or below 355° C., an inherent viscosity of 4.0-10.0 dL / g and a Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) in the range of 260-285° C. when compounded with 30% by weight glass fiber. The optimum compositions, selected from the above-mentioned compositional ranges exhibit a relatively low melting temperature and a relatively high HDT. Specified compositions, selected from the above-mentioned compositional ranges have low melting point, which are useful to blend with conventional polymers such as poly (ethylene terephthalate) and nylon etc.
Owner:WANG XIUZHEN +2
Reflective polarizing film, and optical member for liquid crystal display device, and liquid crystal display device formed from same
ActiveUS20140132897A1Improve polarization performanceIncreased polarizationPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolyesterDevice form
A multilayered reflective polarizing film is provided that has high polarization performance comparable to that of an absorption-type polarizing plate, and is preferred as a polarizing plate attached to a liquid crystal cell. An optical member for liquid crystal display devices, and a liquid crystal display device formed from such a multilayered reflective polarizing film are also provided. Specifically, the reflective polarizing film includes a uniaxially stretched multilayered film in which a specific aromatic polyester containing (alkylenedioxy)di-2-naphthoic acid as a part of dicarboxylic acid components is used as a first layer, and an optically isotropic polyester having an average refractive index of 1.50 to 1.60 is used as a second layer, and that has a predetermined refractive index difference between the layers. The reflective polarizing film has an angle of orientation of 2 degrees or less.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Resin composition for extrusion molding and extrusion-molded article
InactiveUS7776410B2Specific melt viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterEpoxy
A purpose of the present invention is to obtain a hollow extruded article by easy blow molding or extrusion molding to give a draw down resistance and a uniform wall thickness of the article without damaging low gas permeability which is a characteristic property of a liquid-crystalline polymer. A resin composition for extrusion molding which is prepared by melting and kneading 99-70 wt. % of wholly aromatic polyester amide liquid crystal resin (A) having a melting point of 270-370° C. and a melt viscosity at 1000 / sec. shear rate of 20-60 Pa·s at Temperature T1 which is higher than 20° C. from said melting point, and containing (I) 1-15 mole % of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid residue, (II) 40-70 mole % of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid residue, (III) 5-28.5 mole % of aromatic diol residue, (IV) 1-20 mole % of 4-aminophenol residue, and (V) 6-29.5 mole % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid residue; and 1-30 wt. % of epoxy modified polyolefin type resin (B), and has a melt viscosity at 1000 / sec. shear rate of 60-4000 Pa·s at said Temperature T1, and a melt tensile strength of 20 mN or more at 14.8 m / min. draw rate is used.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Preparation method for C.I. paratonere 49:1
The invention relates to a preparation method for C.I. paratonere 49:1 and belongs to the field of organic pigments. According to the preparation method, in the preparation of diazonium liquid, a second diazonium component 2-naphthylamine-1,5-disulfonic acid and a non-ionic surface active agent are added; in the preparation of coupling liquid, a second coupling component 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid is added; and in color lake reaction, a polyoxyalkylene amine pigment modifying agent and a second color lake agent aluminum chloride are added. Specifically, the preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the diazonium liquid; preparing the coupling liquid; performing coupled reaction; and performing color lake reaction and after-treatment. The C.I. paratonere 49:1 prepared according to the preparation method has lower viscosity and higher tinting power and gloss.
Owner:宇虹颜料股份有限公司
Luminescent material of naphthoic acid functionalized polymer and rare earth complex and preparation method of luminescent material
InactiveCN102775981AGood mechanical propertiesImprove thermal stabilityLuminescent compositionsPolymer substrateRare earth ions
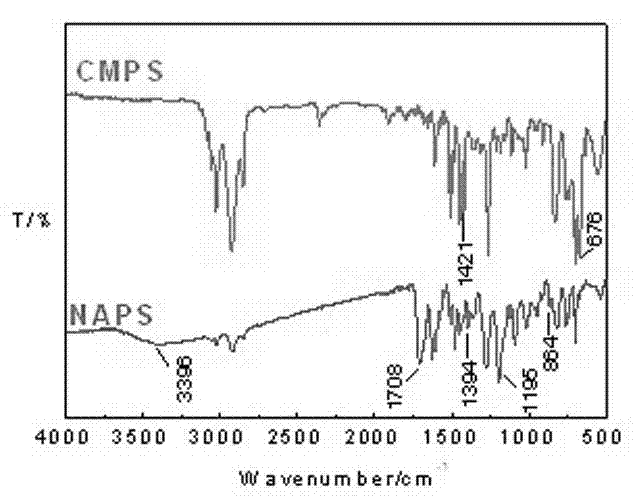
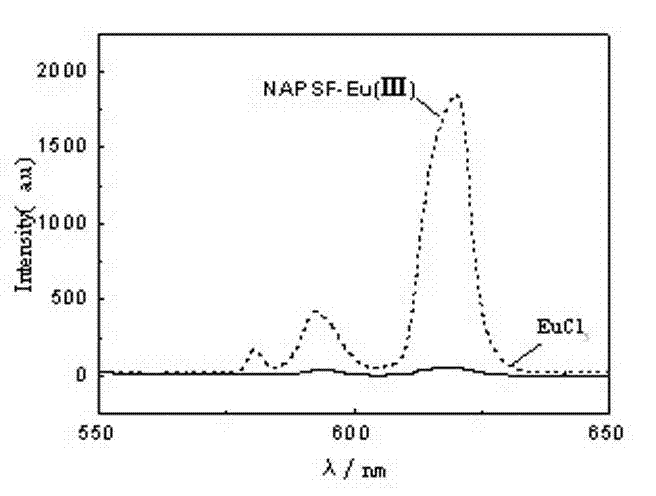
The invention belongs to the field of a rare earth-polymer composite luminescent material, and specifically relates to a luminescent material of naphthoic acid functionalized polymer and rare earth complex and a preparation method of the luminescent material. In the preparation method, a naphthalene acid ligand with coordination and sensitization dual-function roles on rare earth ions is introduced into a polymer side group; and the ligand not only can form stable polymer-rare earth complex together with the rare earth ions, but also has a large conjugate rigid plane, can greatly enhance energy transfer action of the polymer ligand on the rare earth ions, and enhances the luminescence property. The method disclosed by the invention not only is easy to achieve, but also solves the problems that the rare earth complex in the prior art has dispersion inequality and poor polymer substrate performance.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Synthesizing method of nafcillin sodium-hydrate
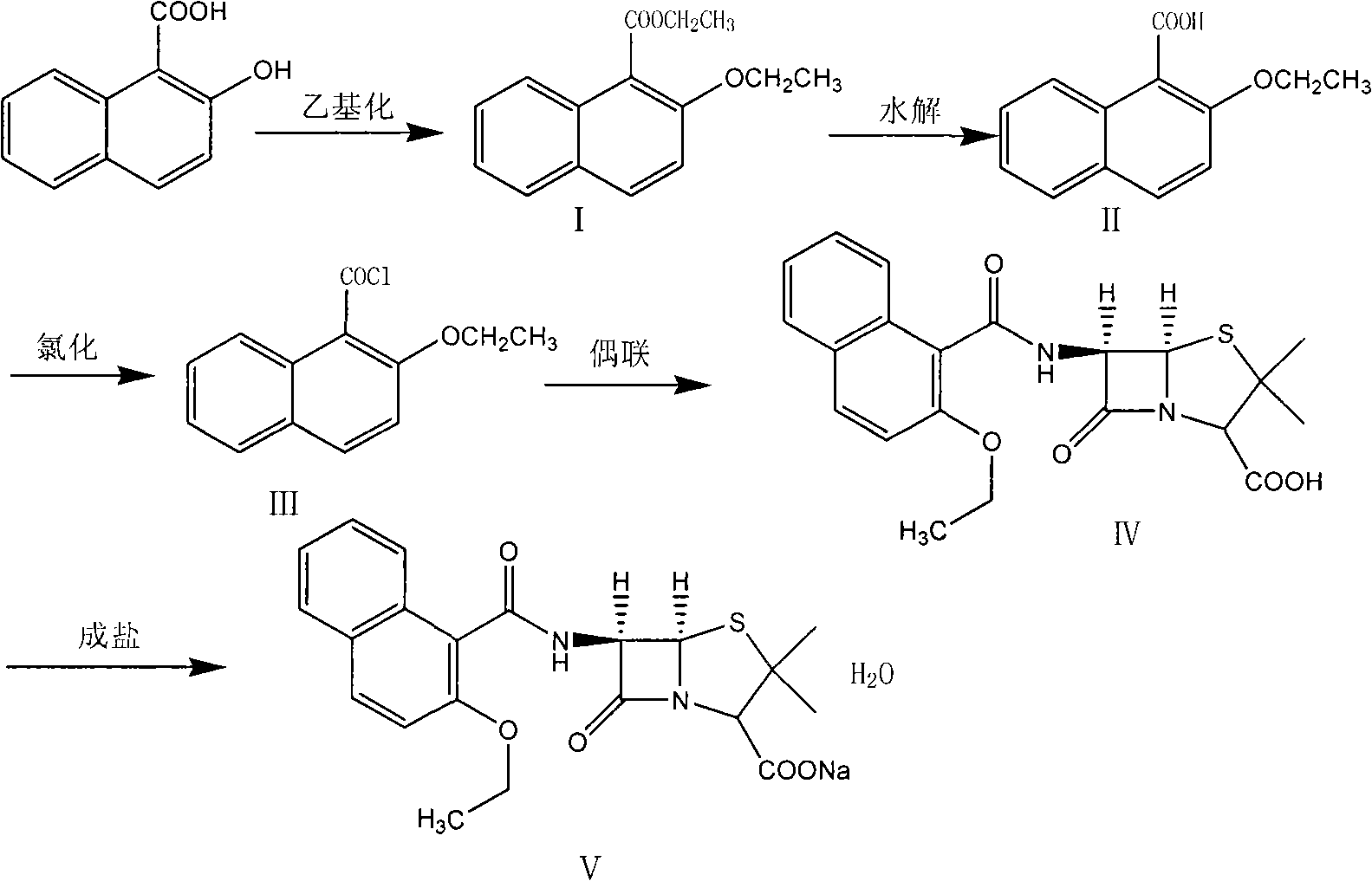
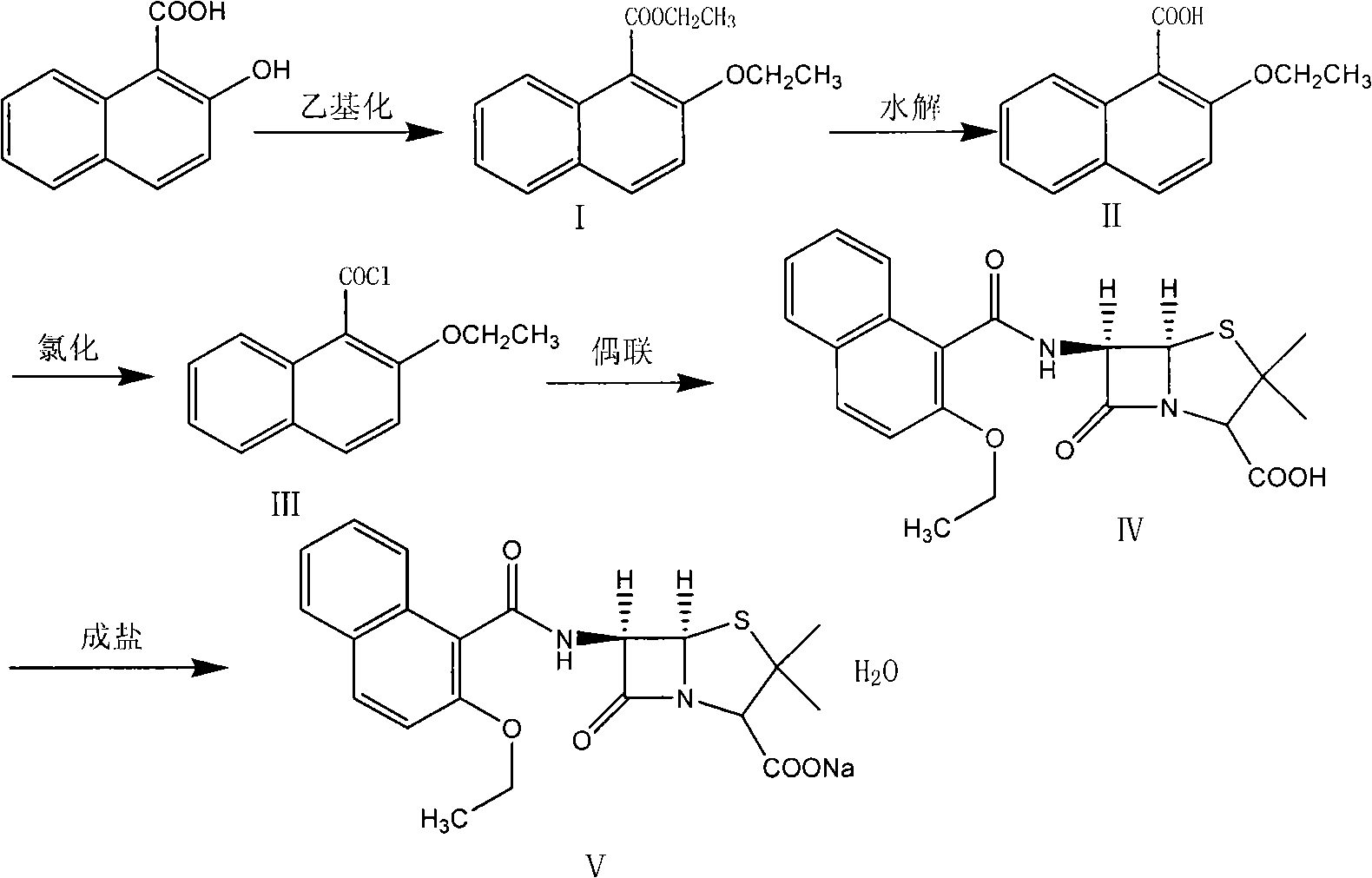
The invention relates to a synthesizing method of nafcillin sodium-hydrate. 2-hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid is adopted as the initial raw material to be ethylized to obtain 2-ethyoxyl-1-ethyl naphthalene, the 2-ethyoxyl-1-ethyl naphthalene is hydrolyzed, chloridized and is coupled with 6-APA to obtain the nafcillin acid, and the nafcillin acid is salified in the mixed solution of acetone of sodium bicarbonate or sodium carbonate to directly prepare the target product nafcilin sodium-hydrate. The product prepared with the method has low cost, is easy to obtain the raw materials, has simple process, and is easy to control the residual solvent. The content is me than 99.5 percent. The product is applicable to the industrialized production.
Owner:北京紫萌医药科技有限公司
Liquid-crystal polyester resin
InactiveUS6984712B2Good coloring effectImprove heat resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineHeat resistance
The present invention provides a liquid-crystalline polyester resin which comprises monomer units derived from 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid and / or 2-hydroxynaphthalene-3,6-dicarboxylic acid in an amount of 1-5000 mmol % based on the total monomer components of the resin and an alkaline metal compound in an amount of 10-3000 ppm as alkaline metal based on the total monomer components of the resin. The liquid-crystalline polyester resin of the present invention has good colorability, improved heat resistance and good mechanical properties.
Owner:UENO FINE CHEM IND LTD
Liquid potting composition
InactiveUS6562482B1Improve insulation performanceShort potting timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEpoxyGallic acid ester
A liquid potting composition, a semiconductor device manufactured using such composition and a process for manufacturing a semiconductor device using such composition. The liquid potting composition comprises: (a) a liquid epoxy resin; (b) a hardener comprising a multi-hydroxy aromatic compound containing at least two hydroxy groups and at least one carboxyl group; and (c) an accelerator. Suitable hardening agents include 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid; 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid; 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid; 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid; gallic acid; 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid; 3,5-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid; phenolphthaline; diphenolic acid and mixtures thereof.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Pharmaceutical/cosmetic, e.g., Anti-acne compositions comprising at least one naphthoic acid compound, benzoyl peroxide and at least one film-forming agent
ActiveUS20110135584A1Stable and less irritantLess irritatingBiocideCosmetic preparationsBenzoyl peroxideDibenzoyl Peroxide
Stable pharmaceutical / cosmetic compositions for topical application, notably for the treatment of acne vulgaris include, formulated into a physiologically acceptable medium, at least one naphthoic acid compound, benzoyl peroxide and at least one film-forming agent, the at least one naphthoic acid compound and the benzoyl peroxide advantageously being in a dispersed form therein.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
Aromatic liquid crystal polyester and its film
An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester having a small dielectric loss in a wide frequency region is provided. An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester is provided that can manufacture a film having a small volume expansion by heating. An aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester substantially comprising a repeating structural unit originating in 2-hydroxy-6-naphthoic acid 30 to 80 mol %, a repeating structural unit originating in aromatic diol 35 to 10 mol %, and a repeating structural unit originating in aromatic dicarboxylic acid 35 to 10 mol %.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Bonding type polymer-rare earth ternary complex luminescent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103013494AGood chemical stabilityEasy to processLuminescent compositionsTernary complexRare earth ions
The invention belongs to the field of rare earth-macromolecule complex luminescent materials, and particularly relates to a bonding type polymer-rare earth ternary complex luminescent material and a preparation method thereof. The bonding type polymer-rare earth ternary complex luminescent material is prepared by coordinating rare earth ions with polymer of bonded naphthoic acid ligand serving as a macromolecule ligand and any one of naphthoic acid, phenanthroline, and 2,2'-diphridyl serving as a micromolecule ligand. Not only is the method easily realized, but also the performances of the material prepared can be greatly improved, the problems in the prior art that the rare earth complex are uneven to disperse, poor in performances of polymer matrix and the like can be solved, and the bonding type polymer-rare earth ternary complex luminescent material and the preparation method thereof can develop a new way for preparing novel rare earth-macromolecule complex luminescent materials.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
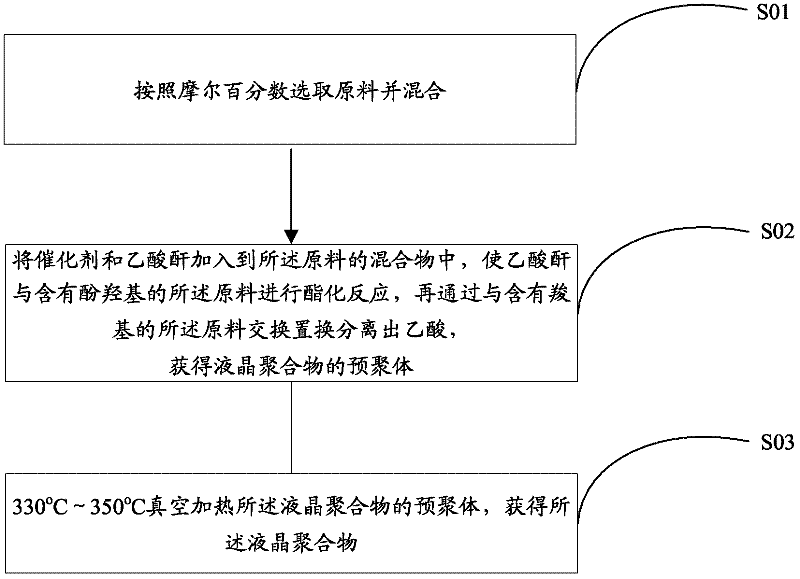
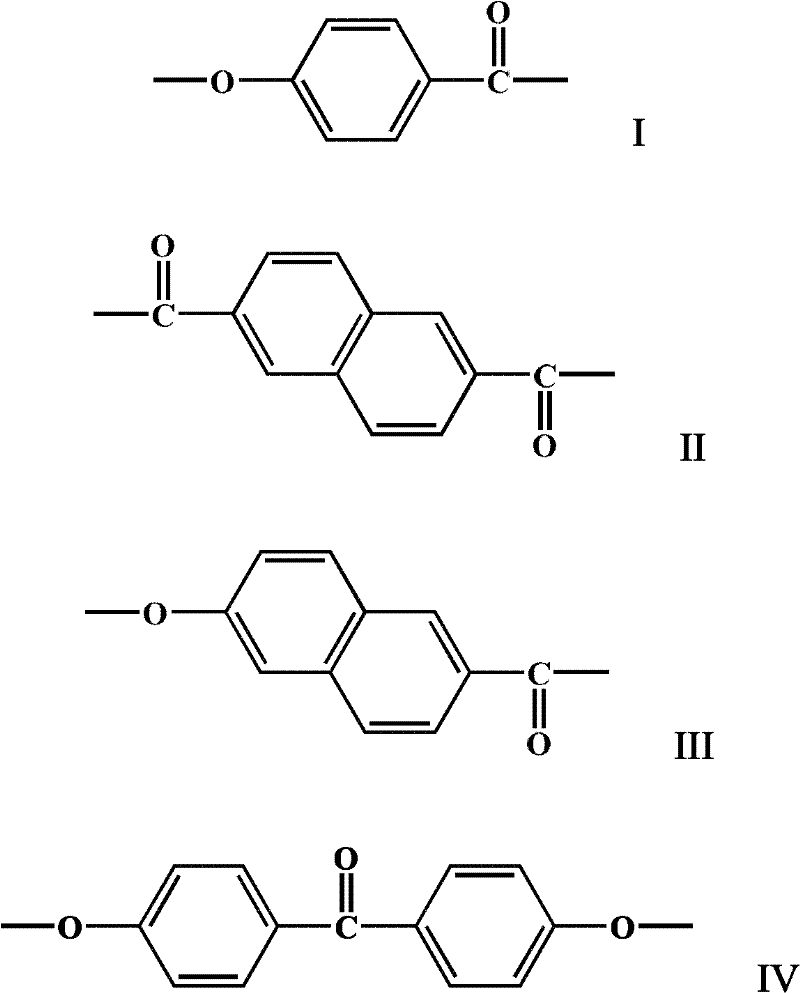
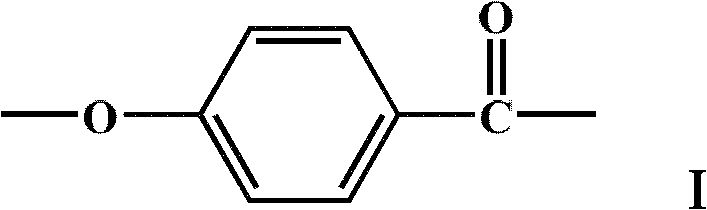
Liquid crystal polymer and preparation method thereof, and liquid crystal polymer composite materials
InactiveCN102643415ALow melting pointIncreased processing temperature rangeLiquid crystal compositionsCrystallographyPolymer composites
The invention provides a liquid crystal polymer which is prepared by polycondensing para-hydroxybenzoic acid, 2,6-naphthalic acid, 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid and 4,4-dihydroxybenzophenone. The invention also provides a preparation method of the liquid crystal polymer. Besides, the invention also provides liquid crystal polymer composite materials containing the liquid crystal polymer. The melting point of the liquid crystal polymer is moderate, and the processing temperature range is widened; and ketone characteristic groups are introduced into the polymer chain, thereby enhancing the comprehensive mechanical properties of the polymer. Further more, the preparation method of the liquid crystal polymer is simple, has the advantage of easily controlled reaction end point, and can ensure the reproducibility of the polymer quality. In addition, the liquid crystal polymer can be used as a resin for preparing multiple liquid crystal polymer composite materials.
Owner:SHENZHEN LINKCONN ELECTRONICS
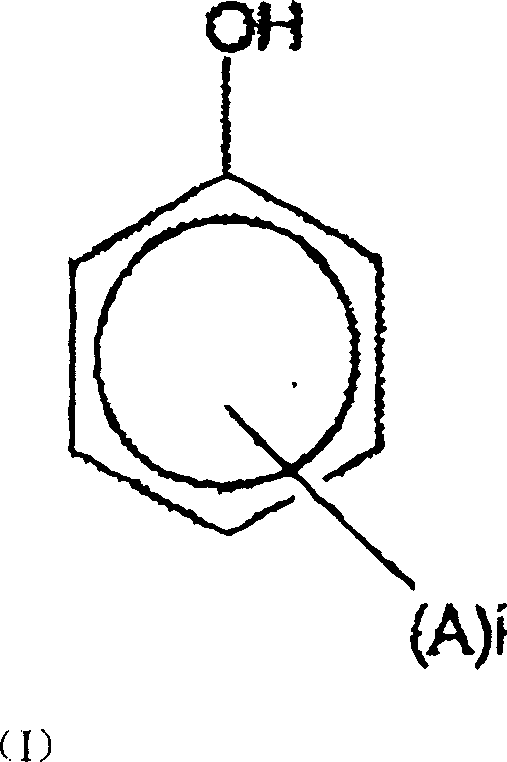
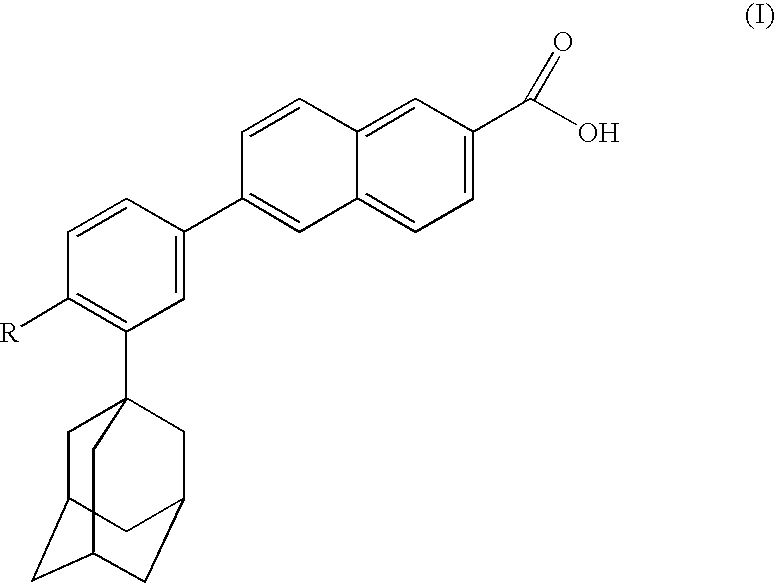
Dermatological compositions comprising at least one retinoid compound, an Anti-irritant compound and benzoyl peroxide
InactiveUS20100160439A1Improve toleranceOvercome problemsCosmetic preparationsBiocideRetinoidIsotretinoin
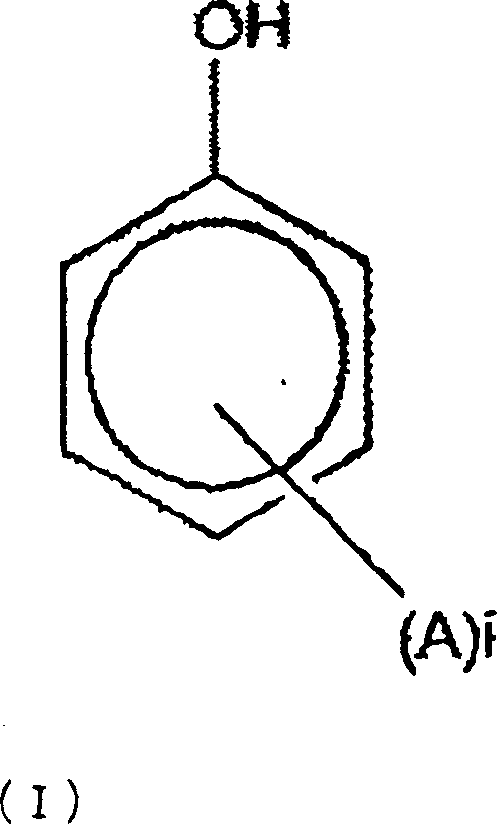
Dermatological compositions contain, formulated into a physiologically acceptable medium, at least one retinoid compound selected from among all-trans retinoic acid, isotretinoin, motretinide, and naphthoic acid compounds of formula (I), and salts and esters thereof:wherein R is a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl radical, a branched or unbranched alkyl radical having from 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy radical having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms, or a cycloaliphatic radical which is substituted or unsubstituted, and benzoyl peroxide, and also at least one anti-irritant compound selected from among 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid, and its salts and derivatives thereof.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
Cosmetic/dermatological compositions comprising naphthoic acid compounds and polyurethane polymers
ActiveUS20080253986A1Increase topical penetrationPromote topical penetrationOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsPolymerChemistry
Cosmetic / dermatological compositions for topical application and useful for the treatment, e.g., of acne, contain, formulated into a physiologically acceptable medium, at least one naphthoic acid compound and at least one polyurethane polymer or derivative thereof, the at least one naphthoic acid compound being dispersed therein.
Owner:GALDERMA RES & DEV SNC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
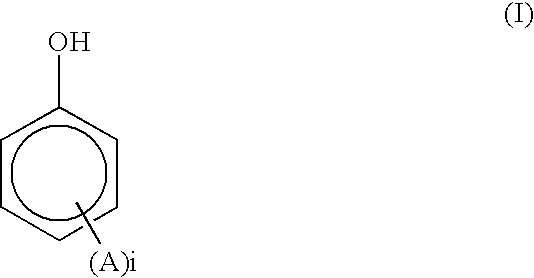
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111727.PNG)
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111731.PNG)
![Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions Pillar[5]arene and 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid complex and preparation thereof and application in detecting iron ions and fluorine ions](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9701a422-70b5-4870-9f49-92bcf764c7de/160401111735.PNG)