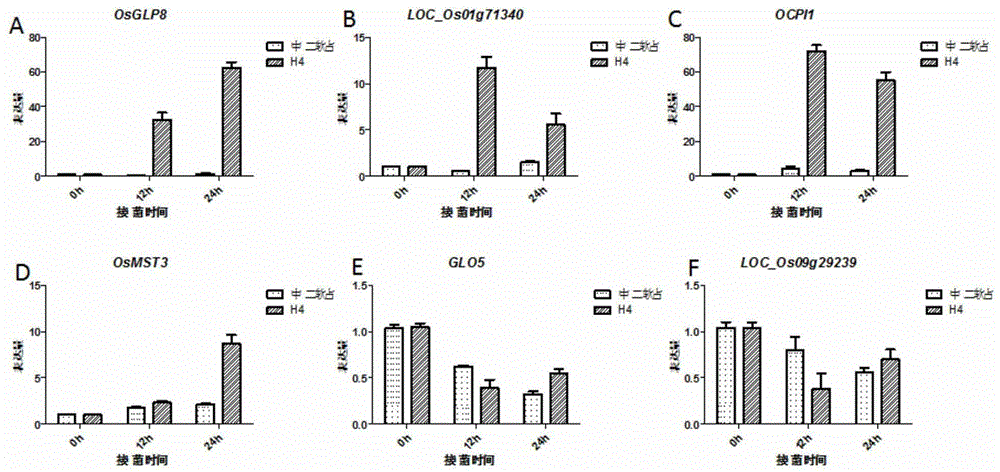
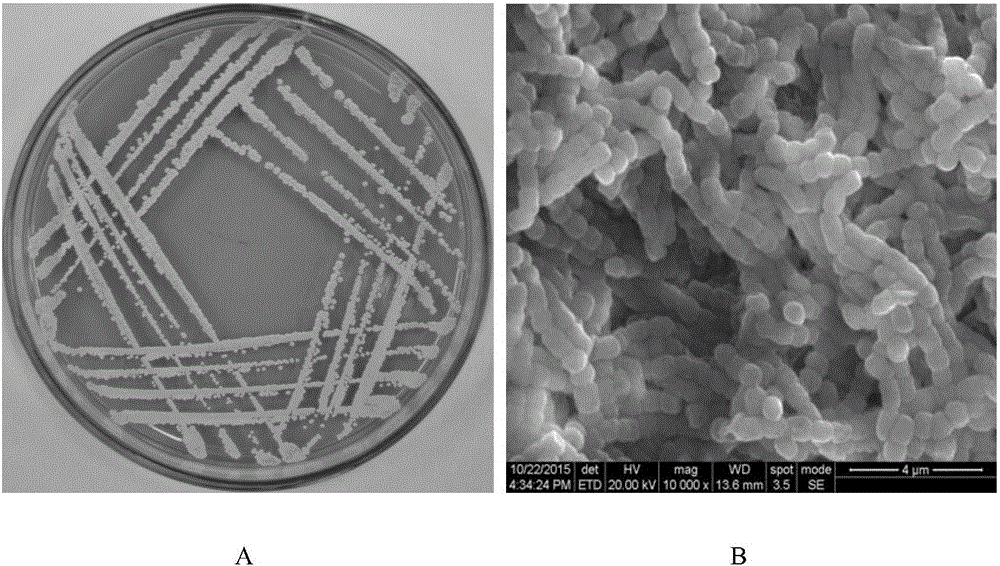
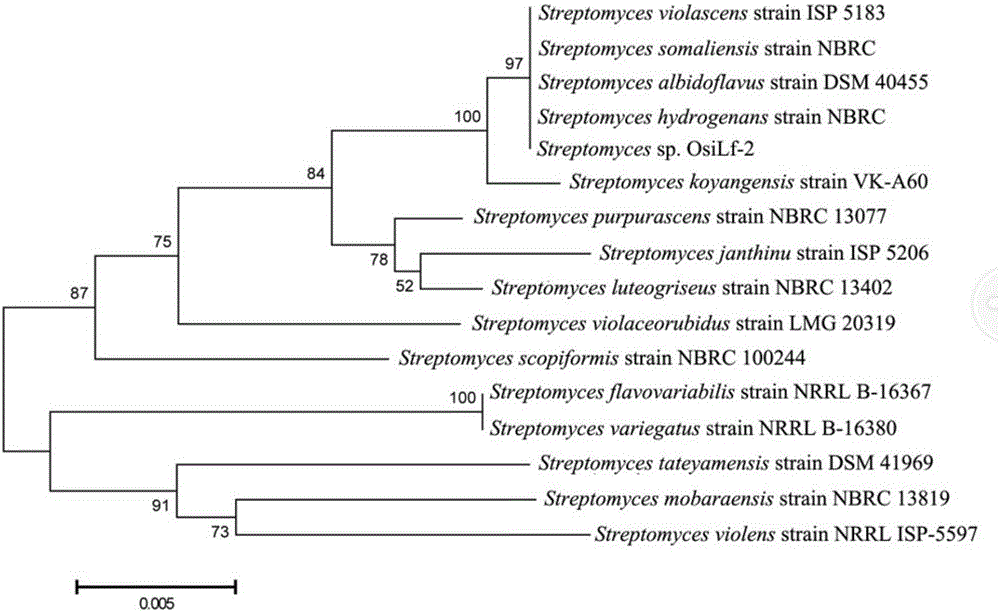
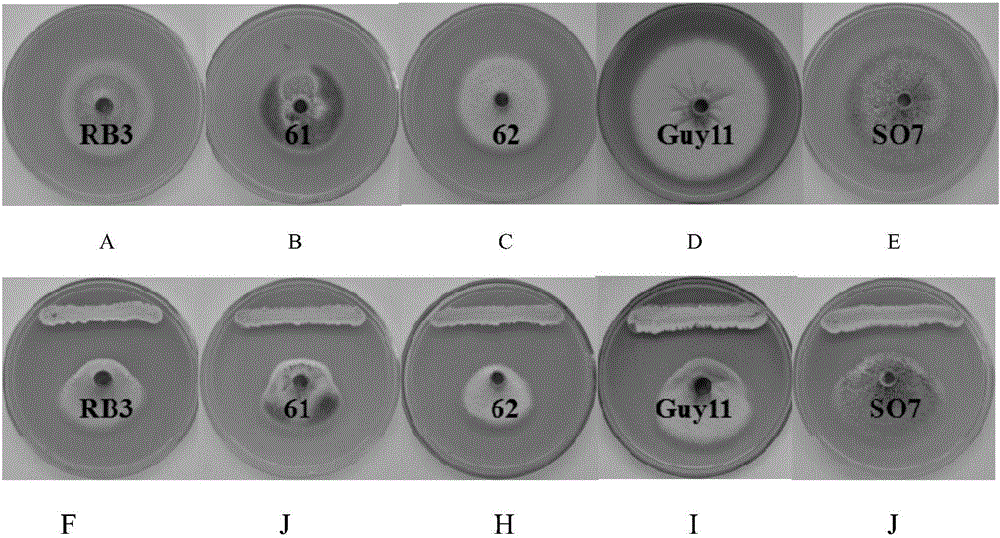
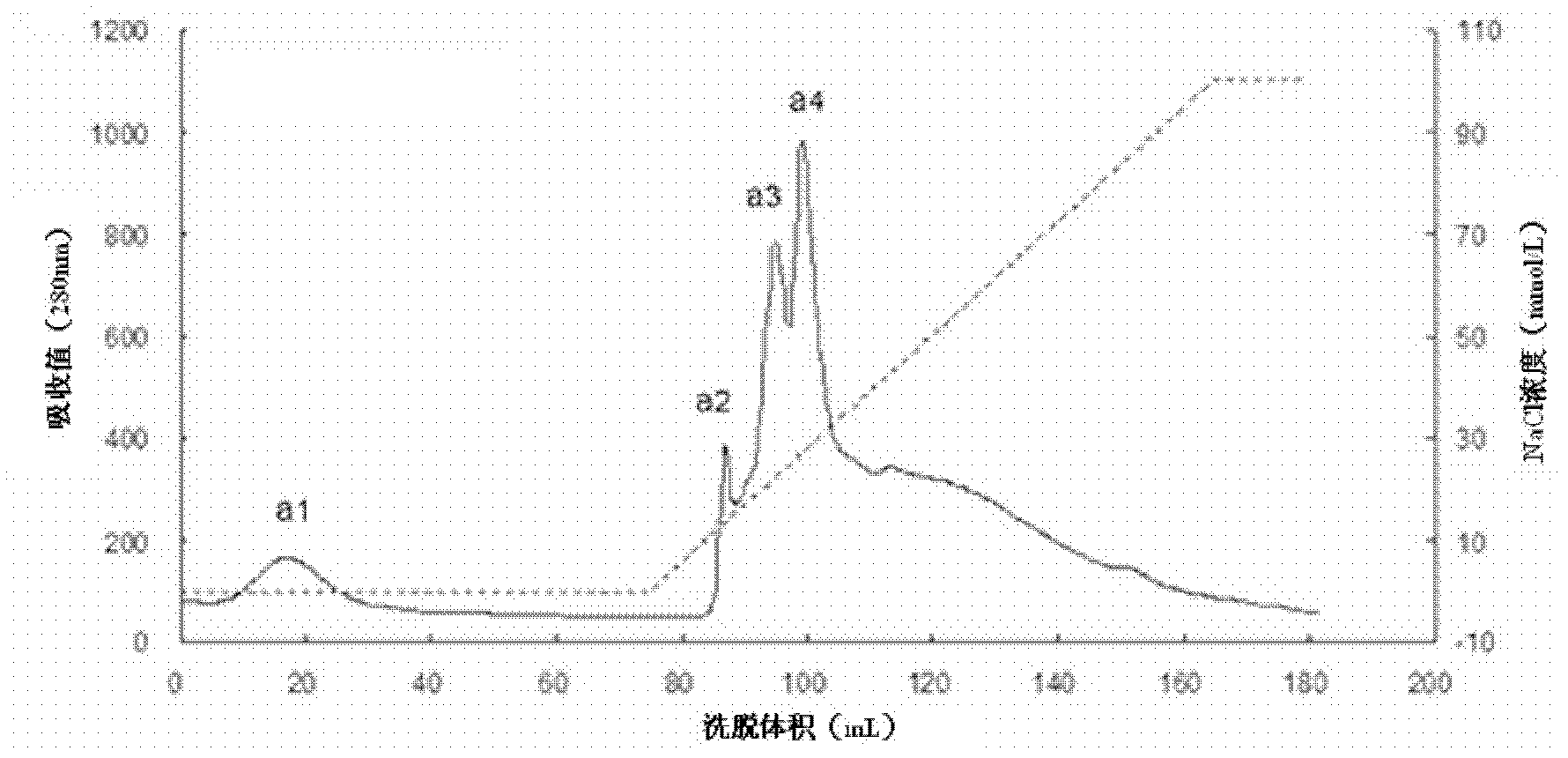
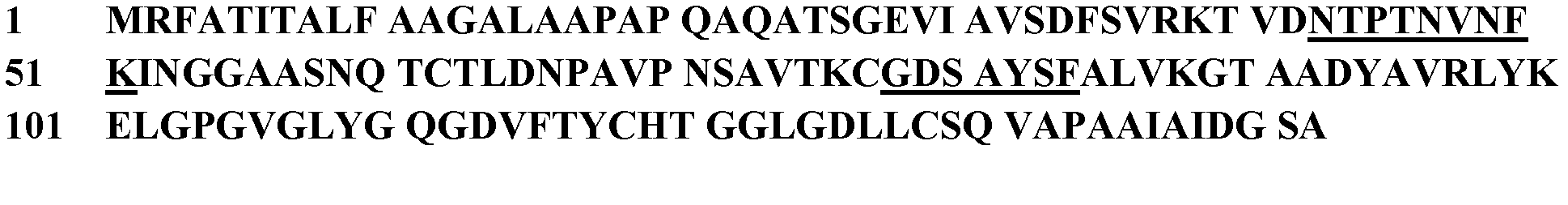Patents
Literature
291 results about "Magnaporthe oryzae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnaporthe oryzae (anamorph: Pyricularia grisea) also known as rice blast fungus is an important plant pathogen isolated from rice and a variety of other rice field weeds. It affects all growth stages of the plant with severe damage during the seedling stage.
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof
InactiveCN102816725AGood control effectHigh antibacterial activityBiocideBacteriaSnow moldAntibacterial activity
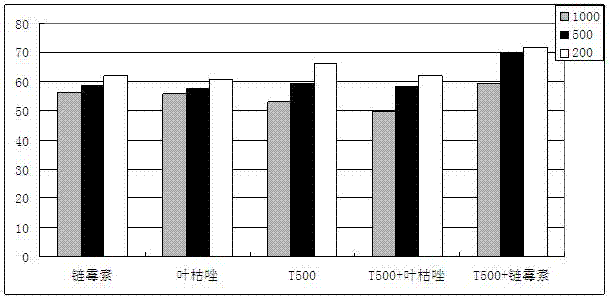
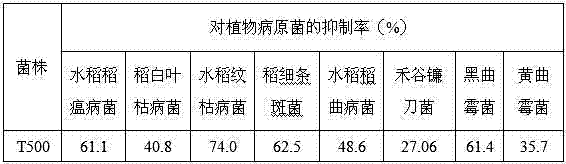
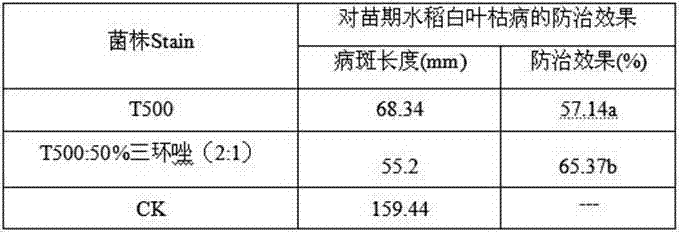
The invention relates to a Bacillus subtilis T-500. The Bacillus subtilis T-500 has been preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection), and the preservation number is CGMCC NO:6058. The Bacillus subtilis T-500 can be used as a biological pesticide for preventing and treating multiple plant diseases, and can also be used as a biological fertilizer for promoting the yield increase of crops. The Bacillus subtilis T-500 has higher antibacterial activity on Magnaporthe oryzae, Pellicularia sasakii, Xanthomonas oryzae, Ustilaginoidea virens, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, Fusarium graminearum, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger and other pathogenic bacteria, and has better prevention and control effects on diseases caused by the pathogenic bacteria. The Bacillus subtilis T-500 can prevent and treat rice leaf diseases when being diluted 200-500 times on the leaves of rice, can prevent and treat bakanae diseases of rice after seed soaking, and can prevent and treat soil-borne diseases of vegetables and the like after root irrigation.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
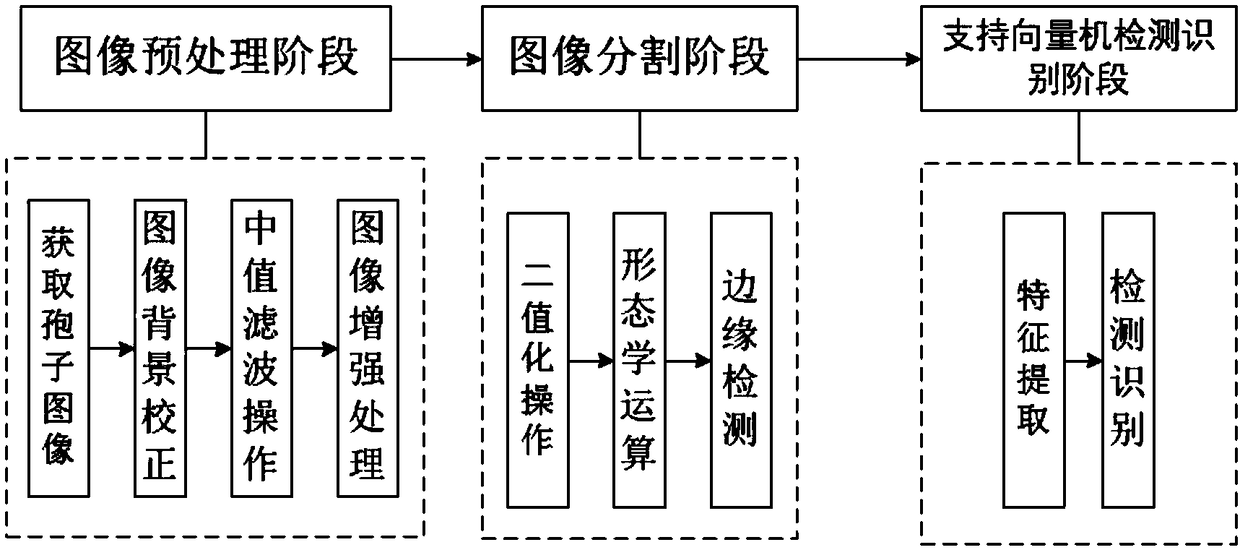
Microscopic image detection and recognition method for rice blast fungus spore based on support vector machine
InactiveCN108564124ASolve the detection accuracyResolving Analysis ResultsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDisease
The invention discloses a microscopic image detection and recognition method for a rice blast fungus spore based on a support vector machine. The method comprises the steps of (1) image preprocessingincluding image background correction, median filtering processing and image enhancement processing, (2) image segmentation including binarization operation, morphological operation and edge detectionof a preprocessed image and the obtainment of a graph contour of a suspected rice blast fungus spore, and (3) support vector machine detection and identification including the extraction of most representative shape feature parameters and texture feature parameters from the graph contour of a suspected rice blast fungus spore, the training of a support vector machine classifier model with the shape feature parameters and texture feature parameters as input vectors, and the detection and identification of the rice blast fungus spore by using the trained support vector machine classifier model.According to the method, the rapid and accurate identification of the rice blast fungus spore can be achieved, and a technical support can be provided for the early detection and the discrimination of a disease degree of a rice blast disease.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microbial bactericide and application thereof
ActiveCN102604864AGood antibacterial effectBroad spectrumBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses an antibiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with powerful bacteriostasis and wide bactericidal spectrum. The strain has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and the taxonomy name of the strain is: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with preservation number CGMCCNo.4777. The antibiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has powerful bacteriostasis, wide bactericidal spectrum, high inhibition rate up to above 93.5% on the rice blast fungus, the Botrytis cinerea and the Phytophthora parasitica; the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens also has very strong stress resistance, and very strong resistance to the acid and alkali, and is suitable to be used as microbial bactericide.
Owner:LONGDENG CHEM XIAN
Method for identifying rice blast resistance of rice
InactiveCN102487742AIncrease concentrationEasy to inoculateHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
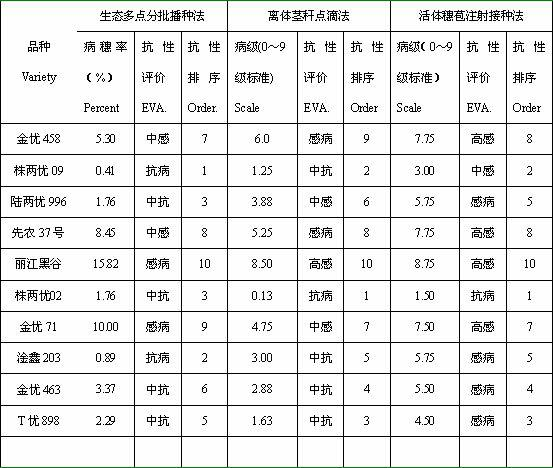
A method for identifying rice blast resistance of rice comprises the steps of scissoring three rice stems in a large bract period from a rice growing field, bringing the rice stems back to a laboratory, scissoring 2cm from the upper portion of each stem section and 5-6cm from the lower portion of each stem section to obtain one rice stem with the whole length of approximate 7-8cm, putting the three rice stems into culture dishes with two layers of filter paper, adding sterile water of 1mL into each culture dish, washing cultivated rice blast fungus spores with the sterile water, obtaining concentration of 106 pcs / ml, dropping spore suspending liquid of 8 muL to stem section sites of each rice stem through a liquid moving gun, putting the culture dishes into a illuminating incubator at the temperature of 26 DEG C, wrapping the culture dishes with transparent films to keep humidity in the culture dishes, cultivating for ten days in light and dark alternating modes to survey disease conditions, dividing survey disease levels into three levels, regarding the first level as disease-resistant cultivars, regarding the second level as susceptible cultivars, and regarding the third level as highly susceptible cultivars. The method optimizes the concentration and inoculation amount of inoculated rice blast fungus spores and establishes simple, convenient and accurate grading standards.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
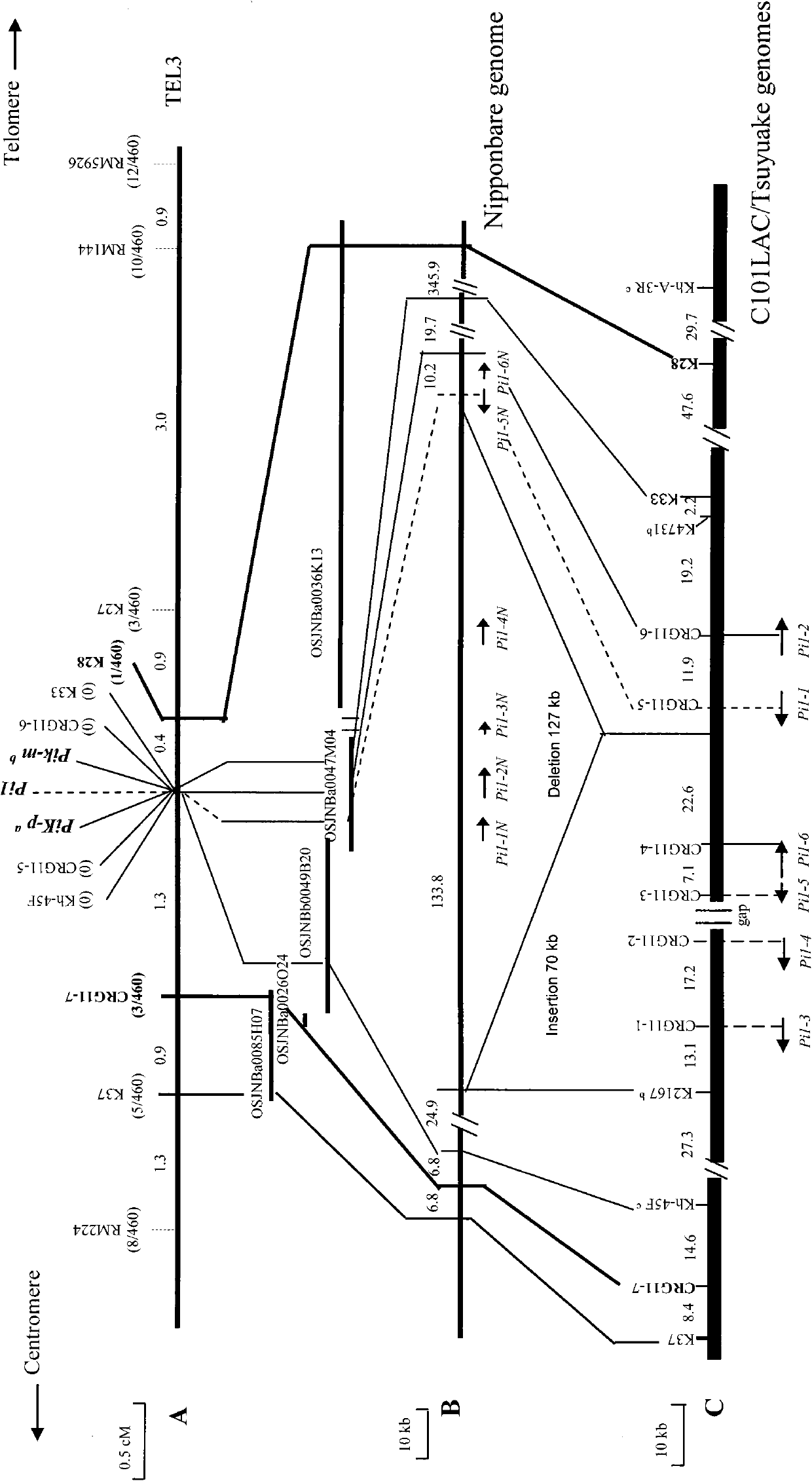
Rice blast resistance gene Pi1 and application thereof
InactiveCN101906427ADoes not create linkage problems with bad genesNo cascading problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses clone and application of rice blast resistance gene Pi1. The rice blast resistance gene Pi1 comprises gene Pi1-1, or Pi1-2, or tandem sequence of the Pi1-1 and the Pi1-2, the nucleotide sequence of the Pi1-1 is shown as SEQIDNO:1, the nucleotide sequence of the Pi1-2 is shown as SEQIDNO:2, and the nucleotide sequence of the tandem sequence is shown as SEQIDNO:3. The two genes of Pi1-1 and Pi1-2 belong to members of CC-NBS-LRR resistance gene family and are constitutive expression genes. The rice blast resistance gene Pi1 can endue plants with specific disease resistance response to disease caused by rice blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae), and is suitable for the plants sensitive to pathogens. By connecting the Pi1 gene sequence with plants transformation carriers to be introduced to plant cells, genetically modified resistant varieties can be obtained so as to be applied to farm production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of researching change of proteome of rice responding rice blast bacterial infection through iTRAQ technology
InactiveCN104820103AQuick and effective screeningStrong disease resistanceBiological testingDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method of researching the change of a proteome of rice responding rice blast bacterial infection through an iTRAQ technology and belongs to the field of plant biotechnology. The method includes following steps: A. extracting a plant materials and leaf protein; B. performing further FASP enzymolysis, peptide fragment marking, SCX classification and LC-MS analysis to the protein sample obtained in the step A; C. performing data query and quantitative analysis to the result after the LC-MS analysis to obtain the change situation of the whole proteome during an interaction process between rice and rice blast bacteria. The method can quickly and effectively screening a candidate gene relative to disease resistance of rice, can be used for researching the candidate gene relative to the disease resistance of the rice well with the proteomics researching method, iTRAQ, which is high-throughput and accurate, can be widely used for researching and developing the characters of plant disease resistance and breeding new plant varieties being strong in disease resistance with combination of the transgenic technology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Indoor rice variety Magnaporthe oryzae resistance identification method
The invention discloses an indoor rice variety Magnaporthe oryzae resistance identification method, comprising the steps of firstly performing spray inoculation indoors, recording susceptible varieties in a classifying way, and ending a test under the situation of susceptible contrasting with LTH; growing seedlings again for nosotropic varieties, then performing indoor in vitro leaf segment liquid dripping inoculation, recording susceptible varieties in the classifying way, and ending a test; growing seedlings again for nosotropic varieties, then performing liquid dripping inoculation, and timely recording morbidity conditions after a disease state is stable. The technology set of resistance screening, combining three inoculation methods, avoids the defect of a single inoculation method and saves manpower and material resources, finally the indoor Magnaporthe oryzae-resisting capability of a rice variety can be really shown, and test results can lay a stable and reliable foundation for the excavating of field popularized varieties and variety resistance gene, and the like.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Streptomyces hydrogenans OsiLf-2 capable of effectively antagonizing magnaporthe oryzae in vitro
ActiveCN106434409AStrong antagonistic effectIncreased growth inhibition rateBiocideBacteriaAntibacterial activityMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses streptomyces hydrogenans OsiLf-2 capable of effectively antagonizing magnaporthe oryzae in vitro. The strain is collected in CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center), with the collection number of CGMCC No. 11673. Streptomyces hydrogenans OsiLf-2 has a good antagonistic effect on magnaporthe oryzae of at least five different physiological races in vitro. Fermentation broth of streptomyces hydrogenans OsiLf-2 also has a relatively high antagonistic effect on magnaporthe oryzae, and the antibacterial activity is very stable. Streptomyces hydrogenans OsiLf-2 and the fermentation broth have great application potential in biological prevention of rice blast, development of novel, safe, nontoxic and environment-friendly pesticides and the like.
Owner:湖南新长山农业发展股份有限公司
Anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103724407ABroad-spectrum inhibitionStrong cracking abilityBiocidePeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyGaeumannomyces
The invention discloses an anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology and biological pesticides. The amino acid sequence of the anti-bacterial protein PBR1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The anti-bacterial protein PBR1 has a superior effect on preventing and curing plant diseases such as cruciferous plasmodiophoromycetes, paddy rice magnaporthe oryzae, curvularia lunata, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. dianthi, fusarium oxysporum vasinfectum, konjac foot rot bacteria, panax notoginseng root rot pathogen, pomegranate wilt pathogen, gaeumannomyces gramini, cylindrosporium pomi brooks, alternaria alternata and / or botrytis cinerea. A pesticide taking the anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as an active ingredient is a novel environment-friendly biological pesticide, is safe to people and livestock, protects the environment, and has a favorable development prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biocontrol Bacillus velezensis SF259 and application thereof
ActiveCN111154688AHas antagonistic activityHas antagonistic effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyConiella castaneicola
The invention relates to biocontrol Bacillus velezensis SF259 and application thereof. The Bacillus velezensis strain is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on September20, 2019, with the collection name of Bacillus velezensis SF259 and the collection number of CCTCCM 2019735. The Bacillus velezensis has a significant inhibition effect on xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), also shows broad-spectrum bacteriostatic activity for xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), X. campestris pv. musacearum, X. axonopodis pv. vignicola, X. campestris pv. malvacearum, botrytis cinerea and magnaporthe oryzae, and has important biocontrol application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Novel protein, genes encoding the same and method of using the same
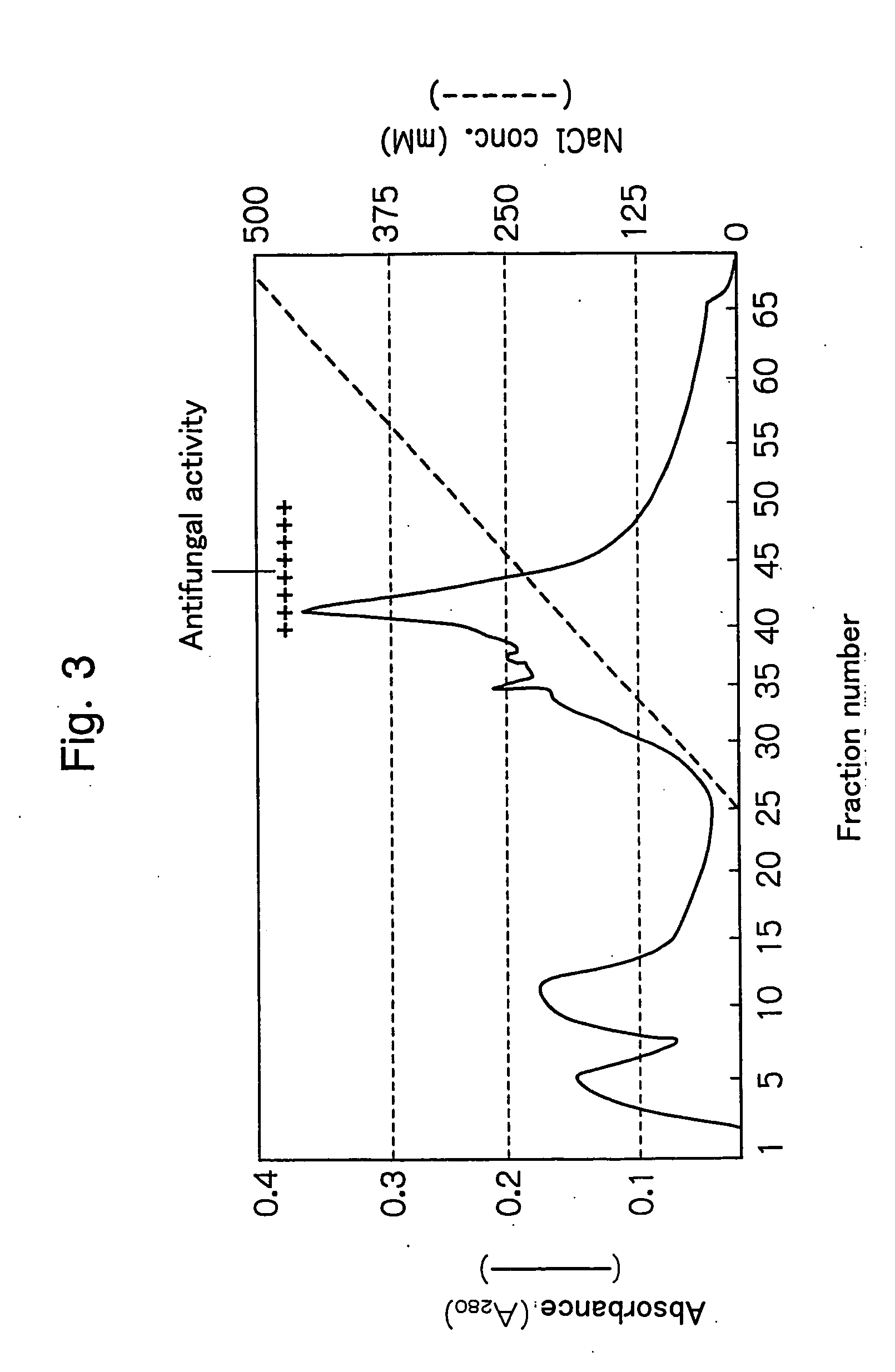
An object of the present invention is to search and identify novel antifungal proteins capable of inhibiting the growth of plant pathogenic microorganisms including Magnaporthe grisea and Rhizoctonia solani causing two major rice diseases at relatively low concentrations, and further to clone a gene for said protein. The present invention provides an antifungal protein which can be obtained from fraction(s) precipitated by ammonium sulfate precipitation using an aqueous extract from Pleurotus cornucopiae, wherein said protein has an antifungal activity against at least rice blast, and exhibits existence of a component having a molecular weight of about 15 kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE method; a gene encoding said protein and uses thereof.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Quinoline compound and preparation method and application thereof to prevention of plant diseases
InactiveCN108477170AEnhanced inhibitory effectGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsBiocideSclerotiniaQuinoline
The invention discloses a quinoline compound and a preparation method and application thereof to prevention of plant diseases. The test result shows that the compound has the excellent prevention effects on plant diseases caused by cotton oxysporum, gibberella saubinetii, sclerotinia scleotiorum, rhizoctonia solani and rice blast and pumpkin powdery mildew and cucumber powdery mildew. The quinoline compound is simple in preparation technology, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the product purity is high, and the quinoline compound can be hopefully developed as a new bactericide.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
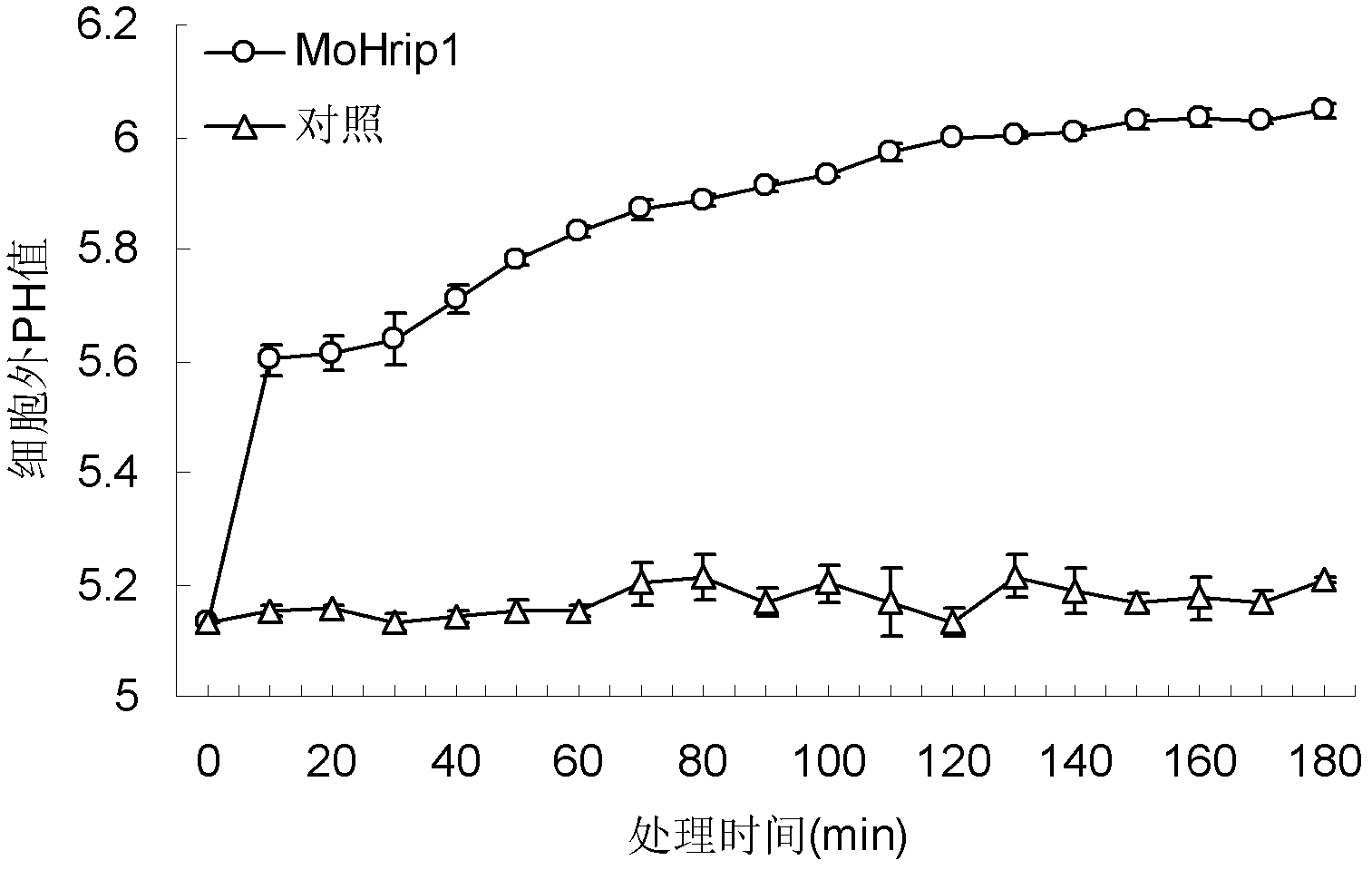
Magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein for improving plant resistance and inducing defense reaction of plant and gene and application of magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein
The invention discloses a magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein and gene thereof as well as a nucleotide sequence for applying peptide with 20 amino acids and coding a peptide segment and application of the nucleotide sequence. According to the magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein, the plant resistance can be improved, the defense reaction of the plant can be induced, and the resistance of the plant can be remarkably improved by the magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein; the magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein is low in concentration and quick in onset of action; and rice leaves are treated by using a 10muMHis-MoHrip1 solution for 3 days and then the treated rice leaves are inoculated to magnaporthe oryzae, and the inhibition rate for pathogenesis can reach 63.89 percent. The amino acid sequence of the magnaporthe oryzae isolated protein is shown as SEQIDNO.2. The invention also relates to a gene for coding the protein. The amino acid sequence of the gene is shown as SEQIDNO.1.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
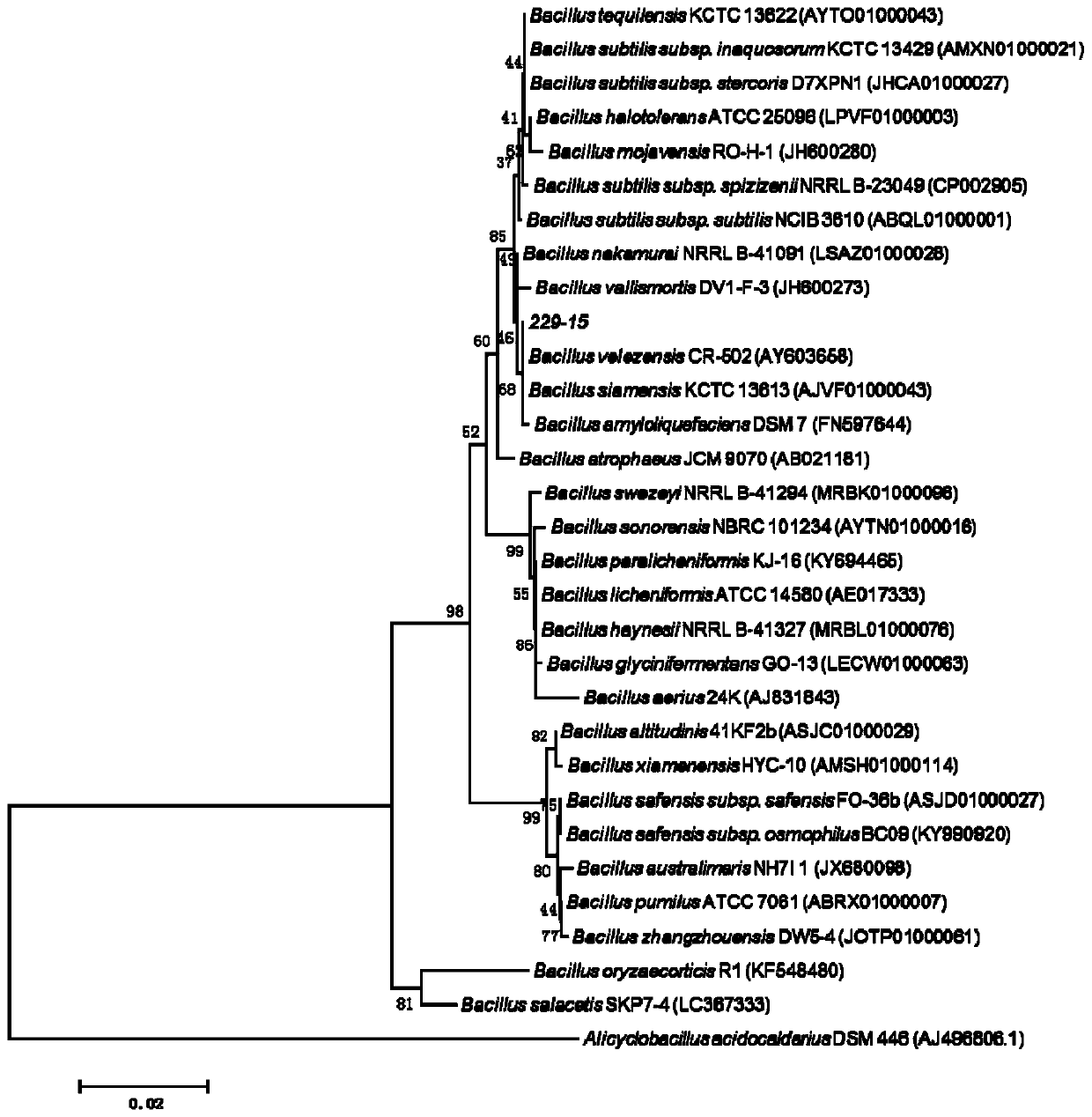
Bacillus velezensis 229-15 and application thereof
ActiveCN111254093AStrong antagonistic effectBroad-spectrum antibacterialBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to Bacillus velezensis 229-15 and application thereof. The Bacillus velezensis is preserved in the Chinese Type Culture Collection on September 20, 2019, the sample name is Bacillus 229-15 Bacillus sp. 229-15, the preservation number is CCTCC No: CCTCC M 2019734, and the strain is isolated from a campus soil sample in Gansu Agricultural University, Anning District, Gansu Province in China. The Bacillus velezensis 229-15 has a bacteriostatic effect on Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae, Xoo and Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzicola, Xoc, and also has bacteriostatic effects on X.campestris pv.musacearum, X.axonopodis pv.vignicola, X.campestris pv.phaseoli and Magnaporthe oryzae, Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium graminearum and other pathogenic fungi at the same time. It is shown throughresults that the strain has a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic ability, good biocontrol resources are provided for prevention and control of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae, Xoo and Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzicola, Xoc, and a foundation is laid for development of novel microbial agents.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
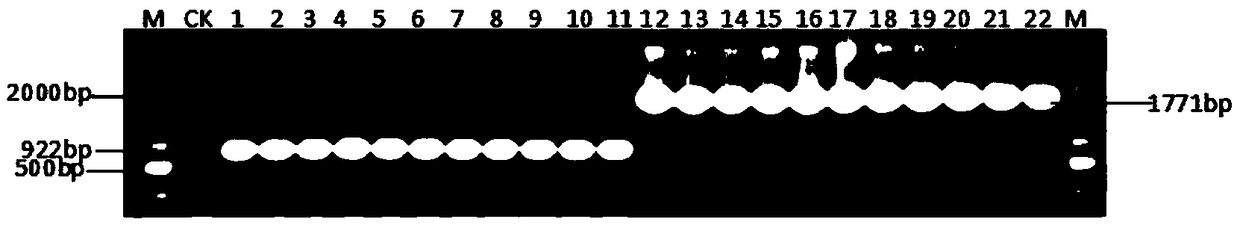
PCR detection and identification method capable of distinguishing pyricularia grise and magnaporthe oryzae
ActiveCN108707687AQuick and easy identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesElectrophoresisDNA extraction
The invention discloses a PCR detection and identification method capable of distinguishing pyricularia grise and magnaporthe oryzae and belongs to the technical field of plant fungus molecule biological detection. The PCR detection and identification method includes the steps of A, extracting DNA, to be specific, respectively extracting DNA of pyricularia grise and magnaporthe oryzae; B, designing primers, to be specific, designing a pair of specific primers Mol3-F / Mol3-F by inserting two ends of the retrotransposon of 849bp into a coding region of avirulence gene PWL3 of pyricularia grise; C, performing PCR, to be specific, performing PCR amplification by taking the extracted total DNA of pyricularia grise and magnaporthe oryzae as a template, so as to obtain an amplification product; D,determiningresults, to be specific, subjecting the amplification product to electrophoresis detection, if a target band of 1771bp is detected, then determining the product as pyricularia grise; if aband of 922bp is detected, then determining the product as magnaporthe oryzae. The PCR detection and identification method can rapidly accurately distinguish pyricularia grise and magnaporthe oryzae which are difficult to distinguish, and has a great significance in field spreading, breeding and evolving of Pyricularia on natural conditions.
Owner:GRAIN RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Molecular marker for rice blast resistance gene Pita and application thereof
InactiveCN104789654AImprove detection efficiencyImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant biology, and particularly discloses a molecular marker for a rice blast resistance gene Pita and application thereof. The molecular marker consists of a pair of outer primers Pita-O-F and Pita-O-R and a pair of inner primers Pita-T-F and Pita-C-R, wherein the primer sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4. The rice blast resistance gene Pita genotype is authenticated by utilizing the marker; rice blast resistance genes can be genotyped to distinguish a rice blast fungus resistant rice variety from a susceptible variety only through simple PCR without sequencing; auxiliary selection of the molecular marker of a rice blast can be realized; according to the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, the Pita gene detecting efficiency can be improved; the molecular marker is suitable for the molecular marker auxiliary selection of a rice improvement segregation population; the breeding efficiency is improved; the requirement on large-scale molecular breeding is met.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rice blast resistance gene RMg41 and applications thereof
ActiveCN104372011AOvercoming the Difficulty of Distant HybridizationShorten the breeding cycleBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyDisease
The present invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a rice blast resistance gene RMg41 and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the nucleotide sequence and the amino acid polypeptide sequence encoded by the gene of the new rice blast resistance gene RMg41 are disclosed, and the gene belongs to the member of the NBS-LRR type resistance gene family; and the rice blast resistance gene RMg41 is cloned from the rice strain exhibiting high resistance on the rice blast bacteria, the rice blast resistance gene RMg41 is transformed into the rice blast bacterial susceptible variety, and the rice blast bacterial infection method is adopted to evaluate the disease resistance so as to finally determine the resistance of the gene on the rice blast.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Bacillus velezensis LJBV19 and application thereof
ActiveCN113151062AHas a disease prevention effectHas a growth-promoting effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses bacillus velezensis LJBV19 separated from rhizosphere soil of grapes. The strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on April 2, 2021 and has an accession number of CGMCC No. 21804. The invention further discloses a broad-spectrum disease-preventing growth-promoting bacterium agent and application thereof in prevention and treatment of plant diseases caused by phytopathogens. The bacillus velezensis LJBV19 disclosed by the invention has broader-spectrum disease preventing and growth promoting effects and can be used for effectively controlling the plant diseases caused by paddy pathogens, grape pathogens, Solanaceae crop pathogens and wood pathogens, and the average inhibiting rate of the bacillus velezensis LJBV19 to Magnaporthe oryzae reaches up to 75.75%; and the bacillus velezensis LJBV19 can also be used for promoting growth of plants, improving crop yield, improving fruit quality, improving resistance of crops, developing agricultural economy and pushing agricultural development.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Rice blast bacterium nontoxic gene Avr-Pib and application
InactiveCN101240282AAvoid infectionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNon toxicity
A rice blast bacterium innocuity gene Avr-Pib is obtained by separation and appraising in T-DNA insertion mutation. The out-knocking mutant of the gene can cause susceptibility of rice breed variety containing Pib disease-resistant gene. The out-knocking mutant and field susceptibility individual plant can recover non-toxicity by function complementation experiment and the breed variety is disease-resistant. The gene can be used as molecule target of newly pesticides and paddy rice disease-resistant genetic engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Separation method of magnaporthe oryzae
The invention discloses a separation method of magnaporthe oryzae. According to the method, a special spore slippery filament is adopted, and a single conidium is directly separated from a rice blast standard sample and is cultured to form a rice blast bacteria strain with a single genetic composition. The implementation and operation steps of the isolated culture are as follows: 1) collecting a rice blast standard sample; (2) treating a magnaporthe oryzae standard sample; (3) preparing spore slippery filaments; (4) preparing a spore dispersing plate; (5) dispersing the conidia; (6) cutting the spore-carrying sliding scattering plate; and 7) culturing conidia and forming a monospore strain. The method has the following advantages: 1) a key appliance for separating spores is simple and easy to manufacture, and the separation operation is simple and easy; 2) single spore strains can be separated and obtained at one time; 3) the separation work consumes less time and labor; and 4) the working efficiency of separating the magnaporthe oryzae and the reliability of a separation result can be obviously improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Botanical fungicide for preventing and treating rice blast
InactiveCN107114416AHarm reductionReduce usageBiocideDead animal preservationFungicideCynanchum komarovii
The invention discloses a botanical fungicide for preventing and treating rice blast. The botanical fungicide is prepared from the following component of ethanol extract of sophora alopecuroides powder and cynanchum komarovii powder, wherein the ethanol extract is prepared by smashing the sophora alopecuroides powder and the cynanchum komarovii powder, both of which have the fineness of 80 meshes, matching the sophora alopecuroides powder and the cynanchum komarovii powder according to a proportion of (1 to 9) to (9 to 1) in parts by weight, uniformly stirring and carrying out twice extracting and mixing through an ethanol solution of which the concentration is 95 percent. The botanical fungicide for preventing and treating the rice blast, disclosed by the invention, can be sprayed to rice leaves during a rice crevasse stage and a full heading stage, magnaporthe oryzae can be killed, spot expansion can be inhibited, and occurrence and harm of the rice blast can be reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT HUAIYIN AGRI SCI RES INST
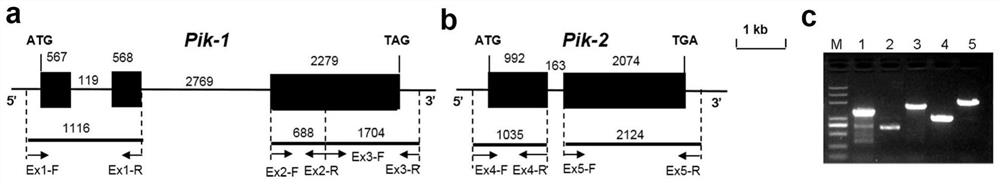
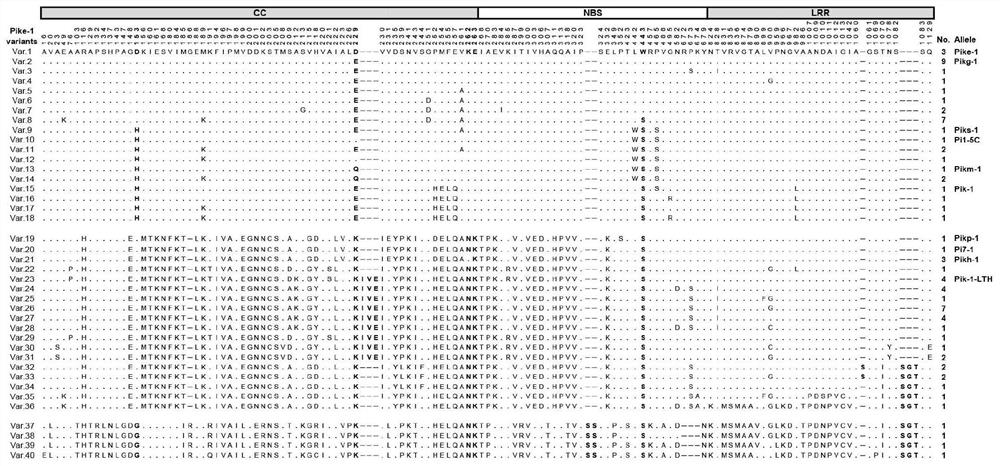
Rice blast resistance gene Pikg, encoding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN111978387AEnhanced or broadened resistanceGenetic improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a rice blast resistance gene Pikg, encoding protein and application thereof, and belongs to the field of rice disease resistance breeding. The rice blast resistance gene Pikg comprises Pikg<-1> and Pikg<-2>, and the nucleotide sequence of a coding region and the amino acid sequence of coding protein of the rice blast resistance gene Pikg are respectively shown in a sequencetable. The gene and the protein can be used for improving the resistance of rice plants to magnaporthe griseat.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for researching oryza sativa and pathogen interaction mode
ActiveCN104911261AQuick and effective screeningStrong disease resistanceComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTotal rna
The invention discloses a method for researching an oryza sativa and pathogen interaction mode, and belongs to the field of plant biotechnology. The method for researching the interaction mode of oryza sativa in response to pathogen infection through integrated application of a transtriptome, a proteome and a miRNA group comprises the concrete steps: A, respectively taking oryza sativa leaf blade total RNAs, Small RNAs and total proteins of a disease-resistant material and a susceptible material at different time points before and after pathogen inoculation; B, respectively carrying out differential-expression spectrum analysis, differential proteomics analysis and miRNA identification and target gene analysis; and C, integrating and associating differential genes, proteins and miRNA target genes identified by the three ways, to reveal disease-resistant and susceptible reaction paths activated or inhibited in the oryza sativa and pathogen interaction process, so as to relatively systematically illuminate an oryza sativa-magnaporthe oryzae interaction mechanism. The method can quickly and effectively screen candidate genes associated with oryza sativa disease resistance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
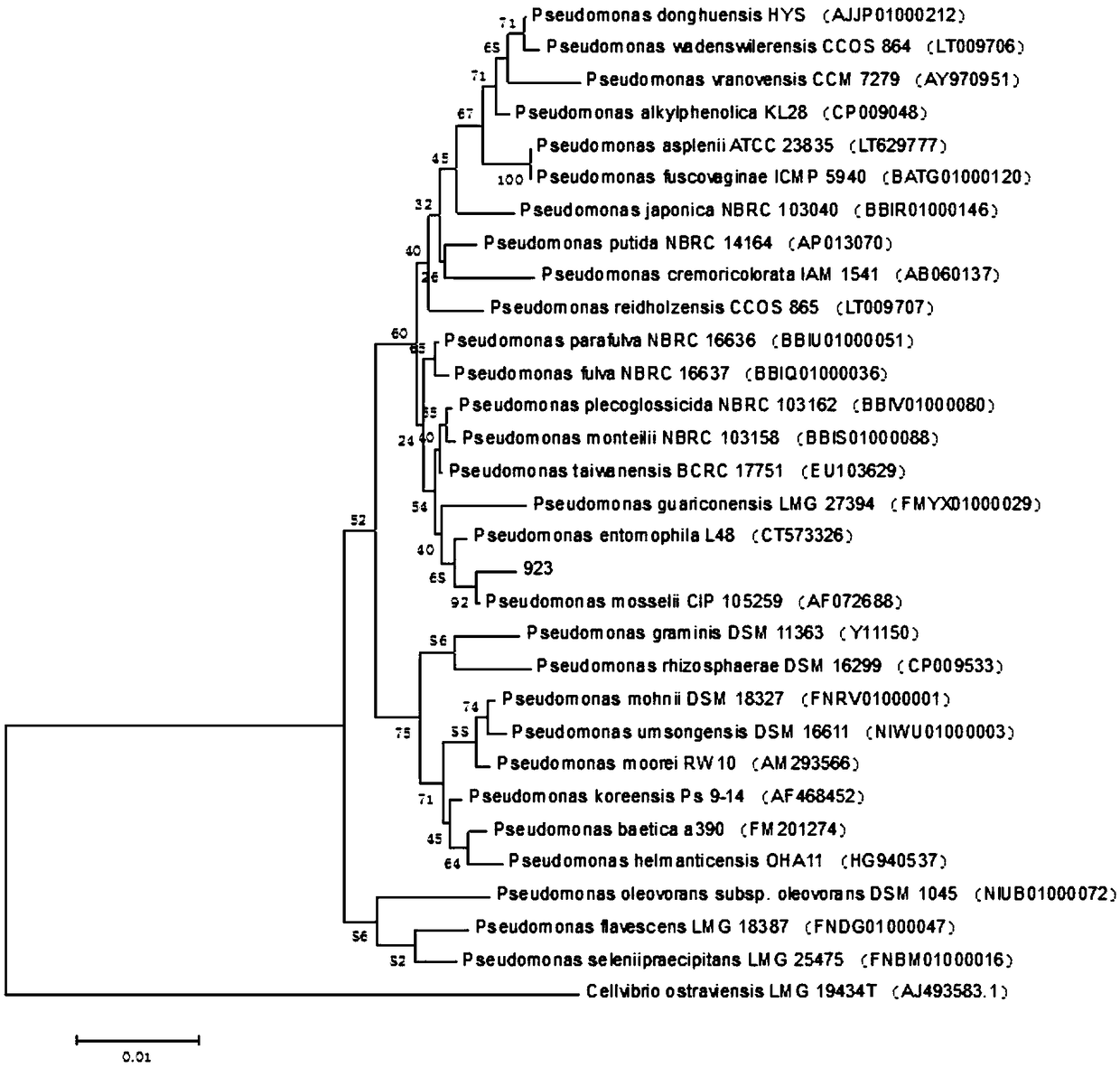
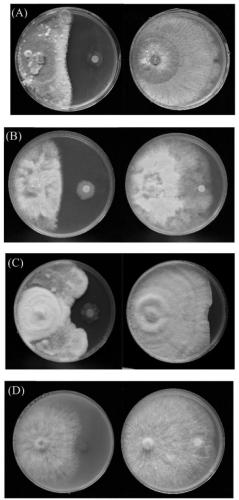
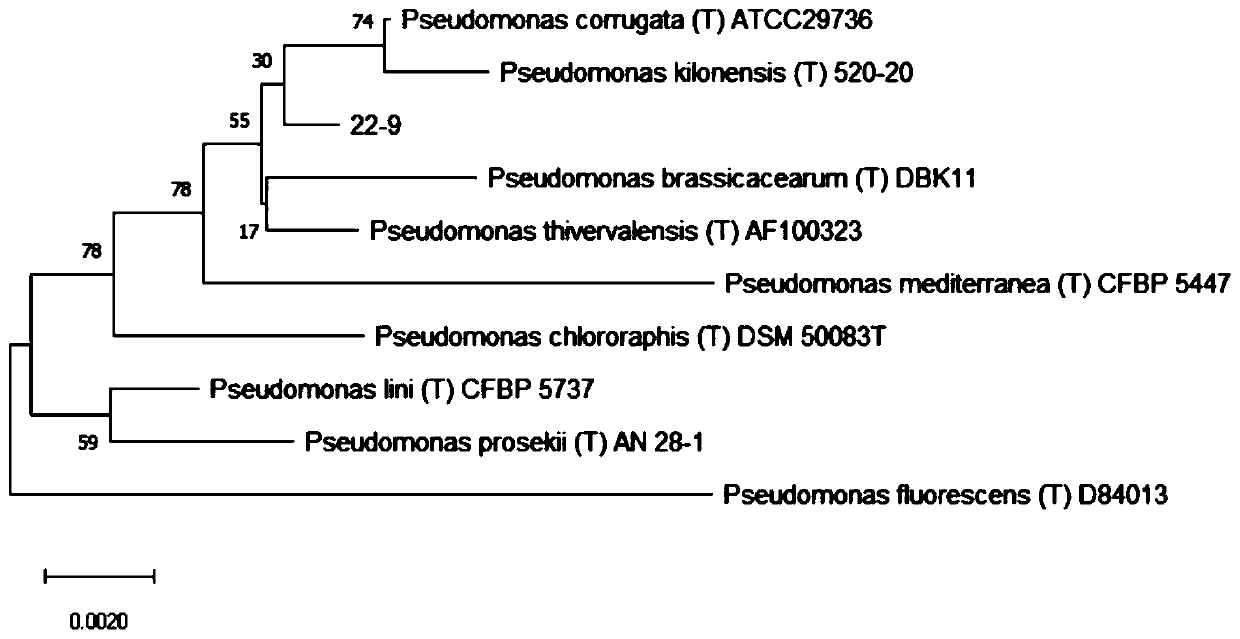
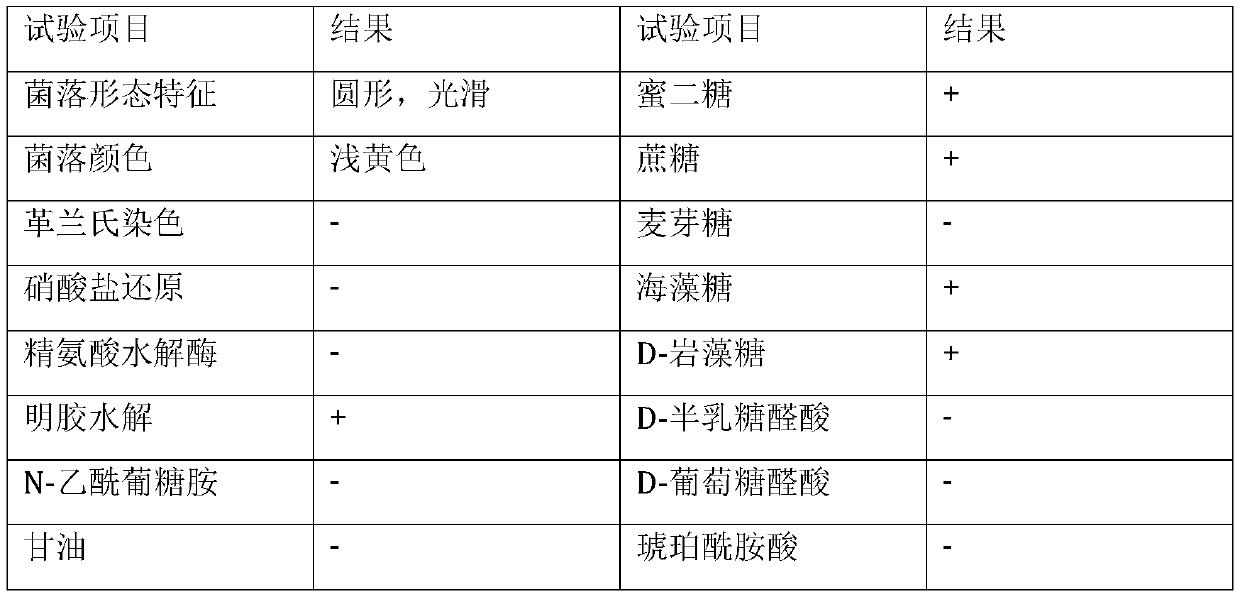
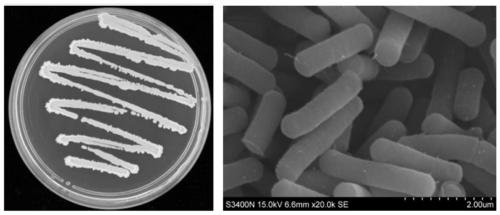
Pseudomonas having antagonistic action against Xanthomonas oryzae and magnaporthe oryzae and application of pseudomonas
ActiveCN108998389AStrong antagonistic effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBacilli
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to a strain of pseudomonas having significant antagonistic action against Xanthomonas oryzae and magnaporthe oryzae and application of the pseudomonas. The strain is isolated from rice rhizosphere soil of Fengxian District, Shanghai; the pseudomonas provided by the invention was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2018, the preservation name is Pseudomonas mosselii 923, and the preservation number is CCTCC No:M 2018252. The pseudomonas provided by the invention has a significant inhibitory effect on Xanthomonas oryzae, has relatively strong inhibitory capacity against other plant pathogenic bacteria and magnaporthe oryzae of Xanthomonas, and has biological control application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Rice blast resistant gene RMg1, RMg2 or RMg3, and its application
ActiveCN102732530AOvercoming the Difficulty of Distant HybridizationShorten the breeding cycleBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyDisease
The invention which belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering concretely relates to a rice blast resistant gene RMg1, RMg2 or RMg3, and its application. The invention discloses nucleotide sequences of the new rice blast resistant genes RMg1, RMg2 and RMg3, and amino acid polypeptide sequences coded by the nucleotide sequences. The three genes belong to an NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich-repeat) type disease resistant gene family. The three rice blast resistant genes of the invention are cloned from a rice line highly resisting rice blast pathogens, and are converted to lines which can suffer from the rice blast pathogens, and the disease resistances of the lines are assessed through using a rice blast pathogen invasion method, so a case that the three genes have resistances to the rice blast is finally determined.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Novel wide-spectrum bacillus resisting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi and application thereof
InactiveCN103087939ABroad antifungal spectrumGood antibacterial effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBacterial strain
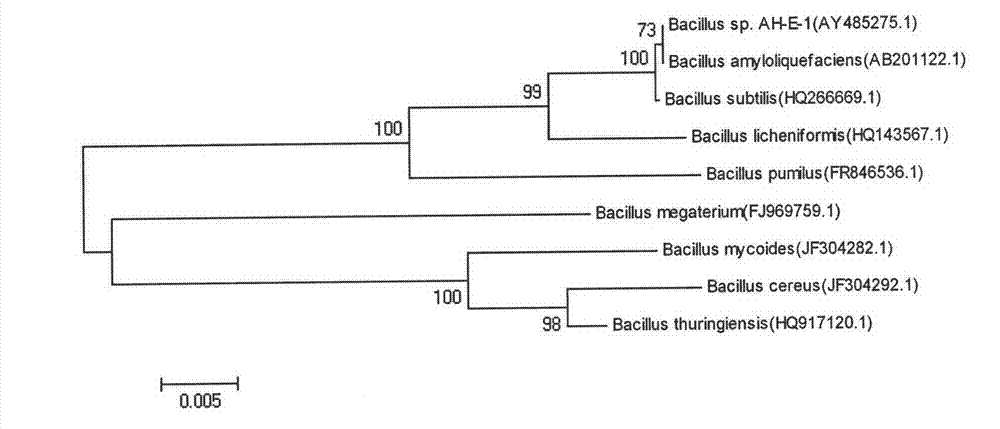
The invention relates to a novel wide-spectrum bacterial strain Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 inhibiting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi, and an application thereof. The main content comprises: (1) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 is a newly-discovered bacillus strain or subspecies; (2) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can produce anti-fungus substances after fermentation under appropriate conditions; (3) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 20 clinical pathogenic fungi such as aspergillus flavus, aspergillus fumigates, trichophyton rubrum, trichophyton mentagrophyte, candida glabrata, cryptococcus neoformans, and the like; (4) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 13 plant pathogenic fungi such as staphylococcus, magnaporthe oryzae, rhizopusstolonife, and the like. The invention provides an excellent novel anti-fungus substance producing bacterial strain which has the advantages of wide fungus-inhibiting spectrum, obvious effect, and the like.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Cultivating method and seedling planting method of cross-year regrowing rice seeds
ActiveCN103782857AIncrease productionWon't dieClimate change adaptationPlant genotype modificationOryza rufipogonCold resistance
The invention provides a cultivating method of cross-year regrowing rice seeds. According to the cultivating method, wild rice containing cold-resisting and root-flourishing genes is adopted as a male parent, DS89-1 glutinous rice is adopted as a female parent, 3-5 times of recrossing is carried out, and then the cross-year regrowing rice seeds can be obtained. The invention further provides a seedling planting method of the cross-year regrowing rice seeds. Rice which is grown from the cross-year regrowing rice seeds obtained through the cultivating method and is planted according to the seedling planting method has the advantages of being high in yield and milled rice rate, good in rice quality, capable of regrowing in the next year and strong in cold resistance, drought resistance, lodging resistance and Magnaporthe oryzae resistance.
Owner:胡代书
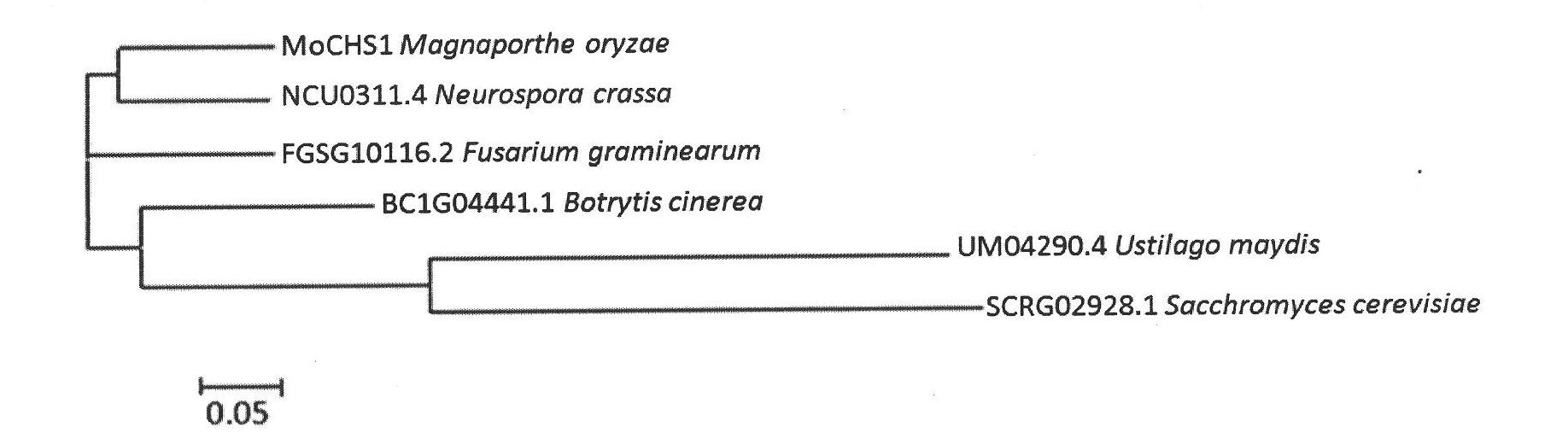
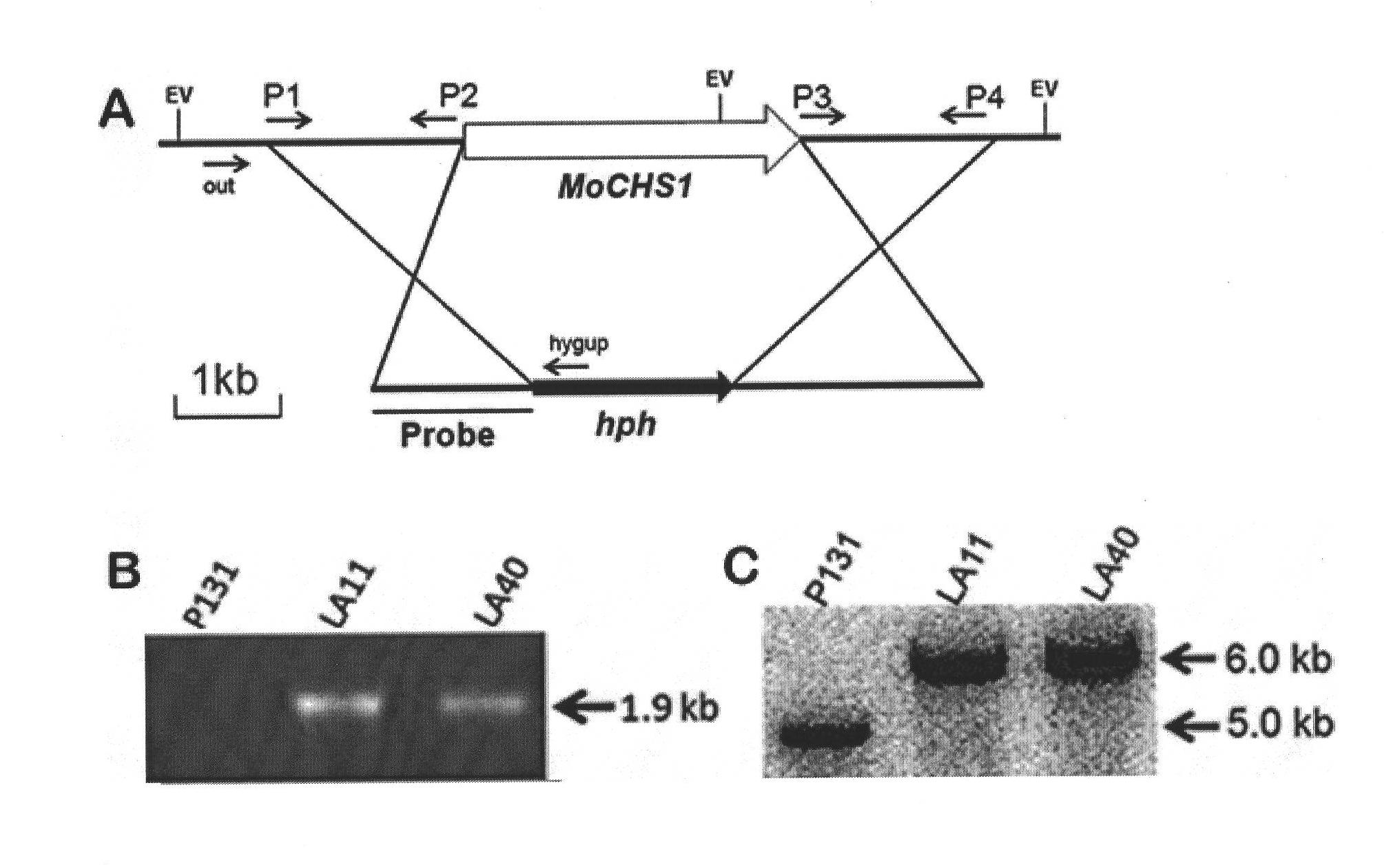
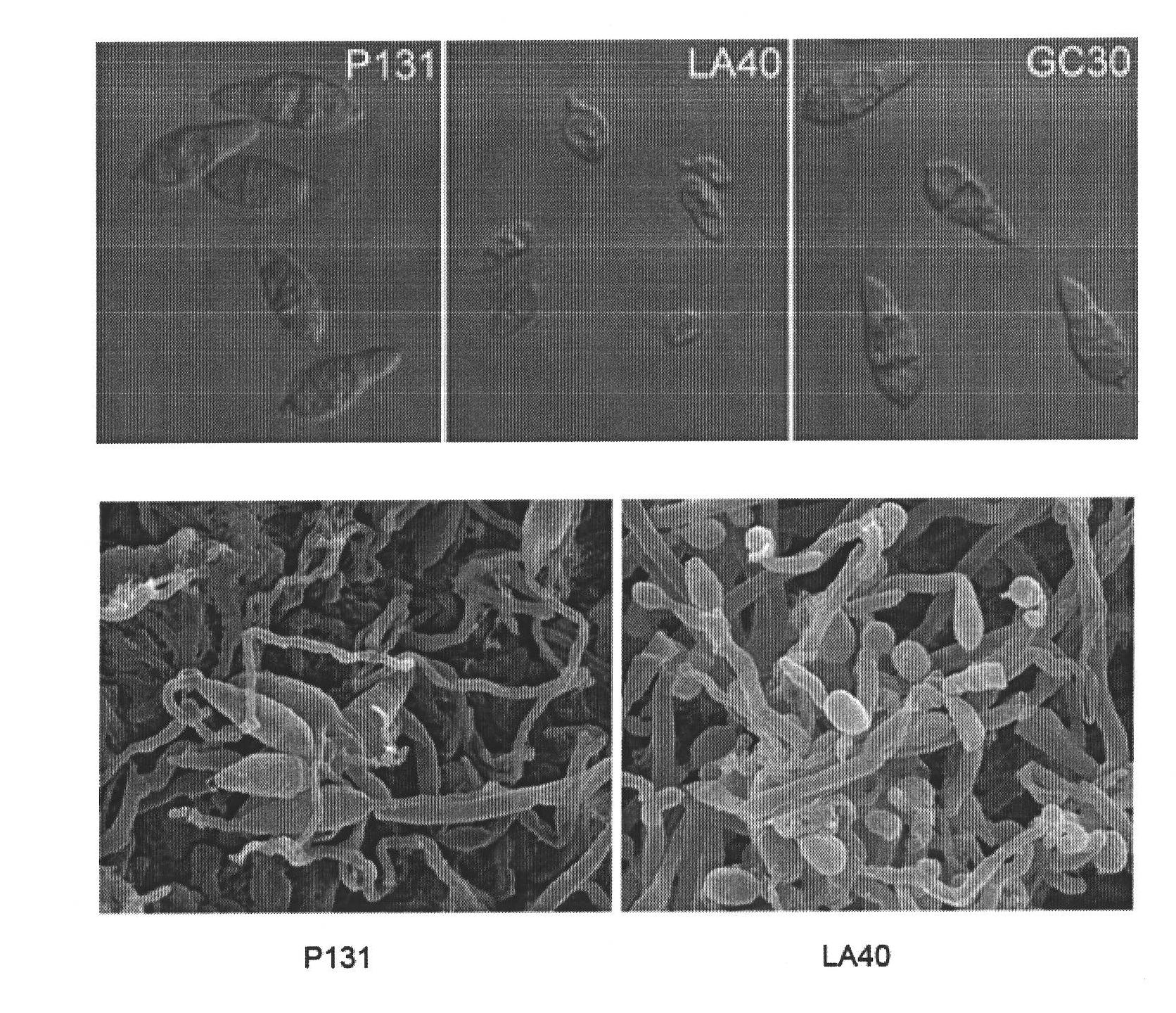
Function and usage of magnaporthe oryzae MoCHS1 gene and coded protein thereof
InactiveCN102021185AReduce incidenceReduce formation rateDepsipeptidesFermentationNucleotideAntifungal drug
The invention discloses the function and the usage of a magnaporthe oryzae MoCHS1 gene and a coded protein thereof. The gene controls the conidium form, the conidium yield, the appressorium formation rate and the pathogenicity of magnaporthe oryzae. The gene as well as the cDNA and the coded protein thereof respectively comprise nucleotide or amino acid sequences SEQ ID No: 1, No: 2 and No: 3 in the sequence list. The knockout of the MoCHS1 gene causes the change of the form establishment of the magnaporthe oryzae conidium; the conidium is reduced and has no diaphragm or has only one diaphragm; the yield of the conidium is decreased to 2% of wild type bacterial strains; the formation rate of the appressorium is decreased to 60% of the wide type bacterial strains; and the infestation capability on rice vanes is obviously decreased. The protein coded by MoCHS1 or / and the expression or the modification of the homologous protein in other pathogenic fungi can be taken as important candidate targets and can be used for designing and screening novel antifungal drugs.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Biocontrol pseudomonas sp. and application thereof
ActiveCN111187741AEnhanced inhibitory effectConducive to green and pollution-free productionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMagnaporthe grisea
The invention relates to a biocontrol pseudomonas sp. and an application thereof, specifically to a biocontrol strain GZ9 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 20191037. The strain has a significant inhibition effect on botrytis cinerea, and shows a good inhibition effect on phytophthora capsici, magnaporthe grisea and gibberella zeae. The fermentation liquor of the strain has a good control effect on tomato gray mold, and can reach a control effect of 78.66%. Thus, the strain has good biocontrol application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JT68 and application thereof in prevention and control of tea anthracnose
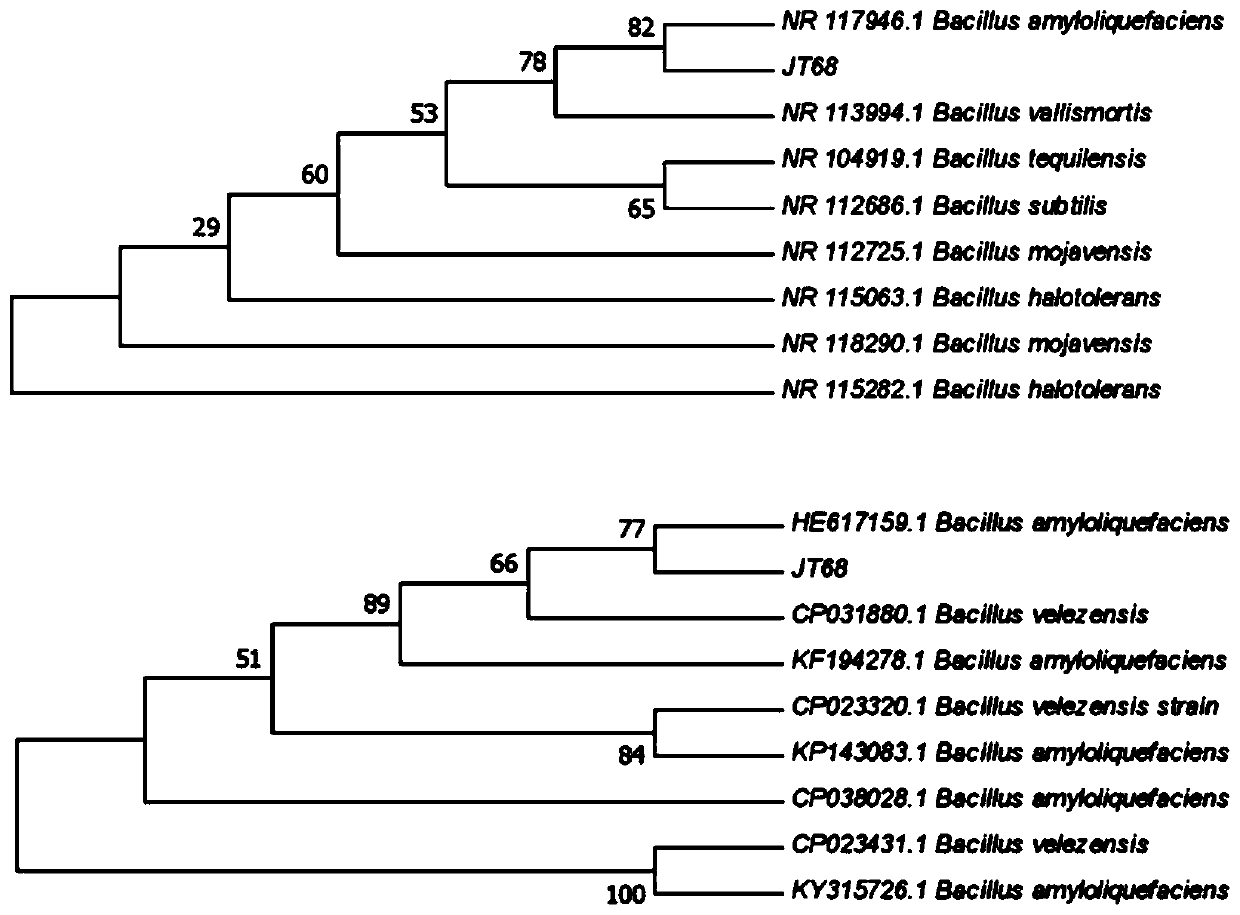
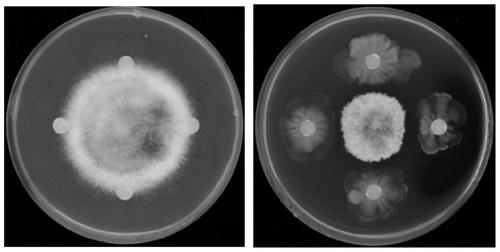
ActiveCN110317747AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of germinationBiocideBacteriaSpore germinationPesticide residue
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens JT68 and application thereof in prevention and control of tea anthracnose. The screened bacillus amyloliquefaciens JT68 can significantly inhibit themycelial growth and spore germination of Gloeosporium theae-sinensis Miyake and reduce disease indexes, has a very good inhibitory effect on the Gloeosporium theae-sinensis Miyake, and is expected tobe used for preventing and controlling tea anthracnose and reducing the occurrence of tea anthracnose. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens is derived from Guangdong province and has a higher application value in prevention and control of local tea anthracnose, especially for local tea gardens suffering tea anthracnos at a high incidence rate. At the same time, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens JT68 alsohas a good inhibitory effect on rice blast fungi, brassica parachinensis anthracnose fungi, banana wilt fungi, pepper anthracnose fungi, cotton fusarium wilt fungi and the like, and has a prospect indevelopment of a fungicide for inhibiting plant pathogenic fungi and prevention and control of tea anthracnose. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens can not only reduce the use of chemical pesticides but also reduce the pesticide residues of tea, and a new way is provided for gradually replacing chemical prevention and control with biological prevention and control.
Owner:海峡两岸农业科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com