Rice blast resistant gene RMg1, RMg2 or RMg3, and its application
A rice blast resistance gene and rice technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of cumbersome and time-consuming breeding process, and achieve the effects of broadening the resistance spectrum, enhancing the resistance and shortening the breeding cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
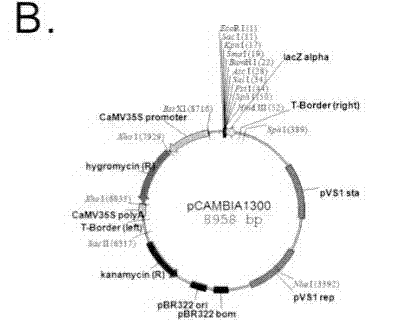
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment one: Cloning and Identification of Rice Blast Resistance Gene RMg1 (Os02g27540-GM)
[0029] 1. Determination of the candidate site RMg1 for rice blast resistance: (1) It mostly exists in the form of gene families and gene clusters, and there are two similar copies in each of Nipponbare and 93-11; (2) In its LRR region, especially Yes xxLxLxx region has a higher Ka / Ks value;
[0030] 2. Isolation and cloning of rice blast resistance gene RMg1: Using public database sequencing varieties Nipponbare (Nipponbare) and 93-11 as reference sequences, design primers (both ends of the primers have enzyme cutting sites AscI). Refer to the sequence listing for the primer sequence, the forward primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:10; the reverse primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:11.
[0031] Using disease-resistant rice varieties Tetep, Gumei 2 and Q2436 as templates, long-segment PCR (Long-PCR) was used to amplify candidate gene fragments. The PCR program was as ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment two: Cloning and Identification of Rice Blast Resistance Gene RMg2 (Os05g23990-Tetep)
[0040] 1. Determination of the candidate site RMg2 for resistance to rice blast: (1) It exists in the form of a single gene, and there is one copy in each of Nipponbare and 93-11; (2) It has a higher LRR region, especially the xxLxLxx region Ka / Ks value;
[0041] 2. Isolation and cloning of rice blast resistance gene RMg2: Using public database sequencing varieties Nipponbare (Nipponbare) and 93-11 as reference sequences, design primers (both ends of the primers have enzyme cutting sites AscI). The primer sequences are listed in the sequence table, the forward primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 12; the reverse primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 13.
[0042] Using disease-resistant rice varieties Tetep, Gumei 2 and Q2436 as templates, long-segment PCR (Long-PCR) was used to amplify candidate gene fragments. The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment three: Cloning and Identification of Rice Blast Resistance Gene RMg3 (Os08g01580-Q2436)
[0050] 1. Features of the rice blast resistance candidate locus RMg3: (1) It exists as a single gene, with one copy in each of Nipponbare and 93-11; (2) It has a high Ka in its LRR region, especially in the xxLxLxx region / Ks value;
[0051] 2. Isolation and cloning of rice blast resistance gene RMg3: Using public database sequencing varieties Nipponbare (Nipponbare) and 93-11 as reference sequences, design primers (both ends of the primers have enzyme cutting sites AscI). The primer sequence is listed in the sequence table, the forward primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 14; the reverse primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 15.
[0052]Using disease-resistant rice varieties Tetep, Gumei 2 and Q2436 as templates, long-segment PCR (Long-PCR) was used to amplify candidate gene fragments. The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, denatu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com