Function and usage of magnaporthe oryzae MoCHS1 gene and coded protein thereof
A rice blast fungus and protein technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, application, etc., can solve the problems of gene cloning and few molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
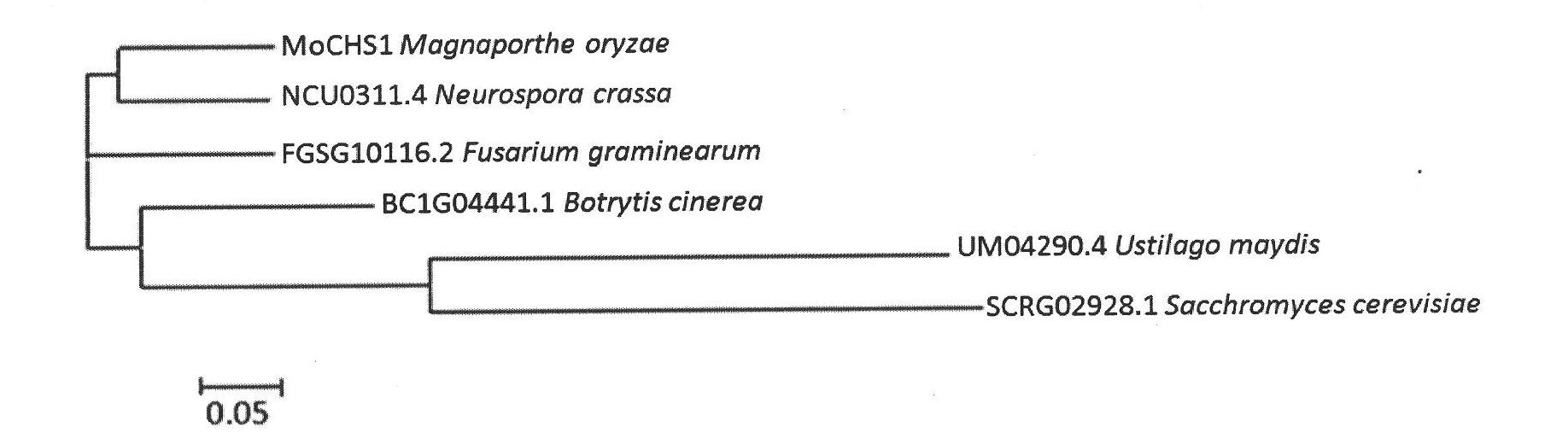
[0035] Example 1, Cluster analysis of homologous proteins in MoChs1 and other fungi
[0036] Using the amino acid sequence of the rice blast fungus MoChs1 protein in NCBI ( http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to perform a blastp search on different species to obtain its homologous analogues among different species: NCU0311.4 (Neurosporacrassa, XP_961338), FGSG10116.2 (Fusarium graminearum, XP_390292), BC1G04441.1 (Botrytis cinerea, XP_001557191), UM04290.1 (Ustilago maydis, XP_760437), SCRG (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, NP_009594). Wherein, the amino acid sequence of the MoChs1 homologous protein in Fusarium graminearum is shown in SEQ ID No: 4, the amino acid sequence of the MoChs1 homologous protein in Botrytis cinerea is shown in SEQ ID No: 5, and the amino acid sequence of the MoChs1 homologous protein in Ustilago maydis is shown in Shown in SEQ ID No:6. Use clustalx1.83 software to compare and analyze the above amino acid sequences, and construct a phylogenetic tree between Mo...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2, the effect of MoCHS1 gene in blast fungus conidia morphogenesis and conidia production
[0038] 1) Construction of knockout vector
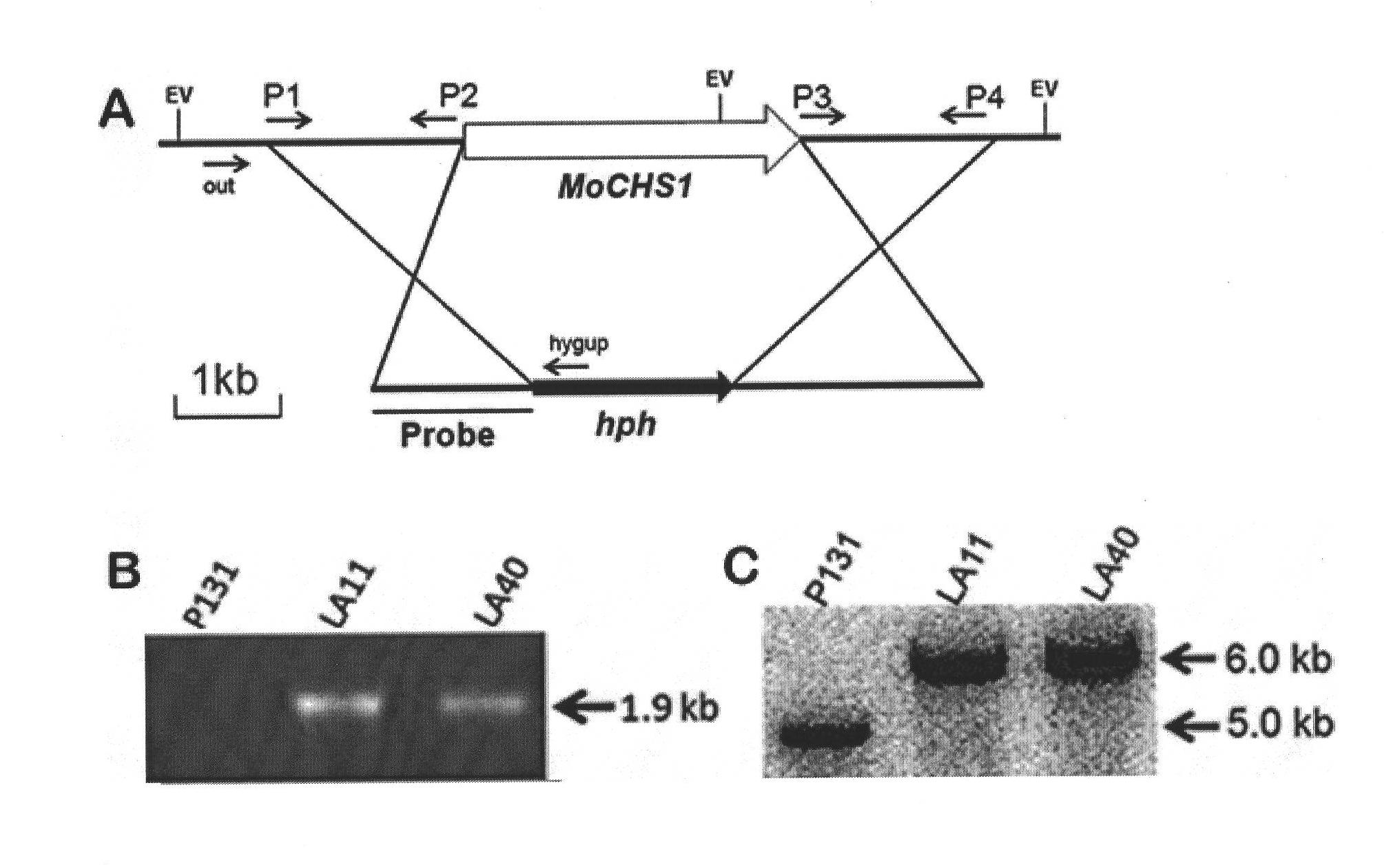
[0039] Gene knockout adopts the method of homologous recombination, and replaces the coding region of the MoCHS1 gene in the wild-type P131 with the hygromycin phosphotransferase gene. The specific strategy is shown in the appendix figure 2 a. Using the genomic DNA of wild-type P131 as a template, primer P1 (5'-TACTAGTCGATGTCCGTCAGCG-3', containing a SpeI restriction site at the 5' end) and primer P2 (5'-AGAATTCCTGAGTGAGATGGCG-3', containing an EcoRI enzyme at the 5' end cleavage site) as the left arm; use primer P3 (5'-AGTCGACGACTAAGGCTTGGTG-3, 5' end containing SalI restriction site) and primer P4 (5'-TGGTACCAGGACACCTTCTTCG-3', 5' end containing KpnI restriction site) amplified fragment was used as the right arm. The left arm was double-digested with SpeI and EcoRI, and the right arm was double-digested with SalI and Kp...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3, the effect of MoCHS1 gene in the formation of rice blast fungus appressorium
[0053] 1) Formation of appresses after conidia attach
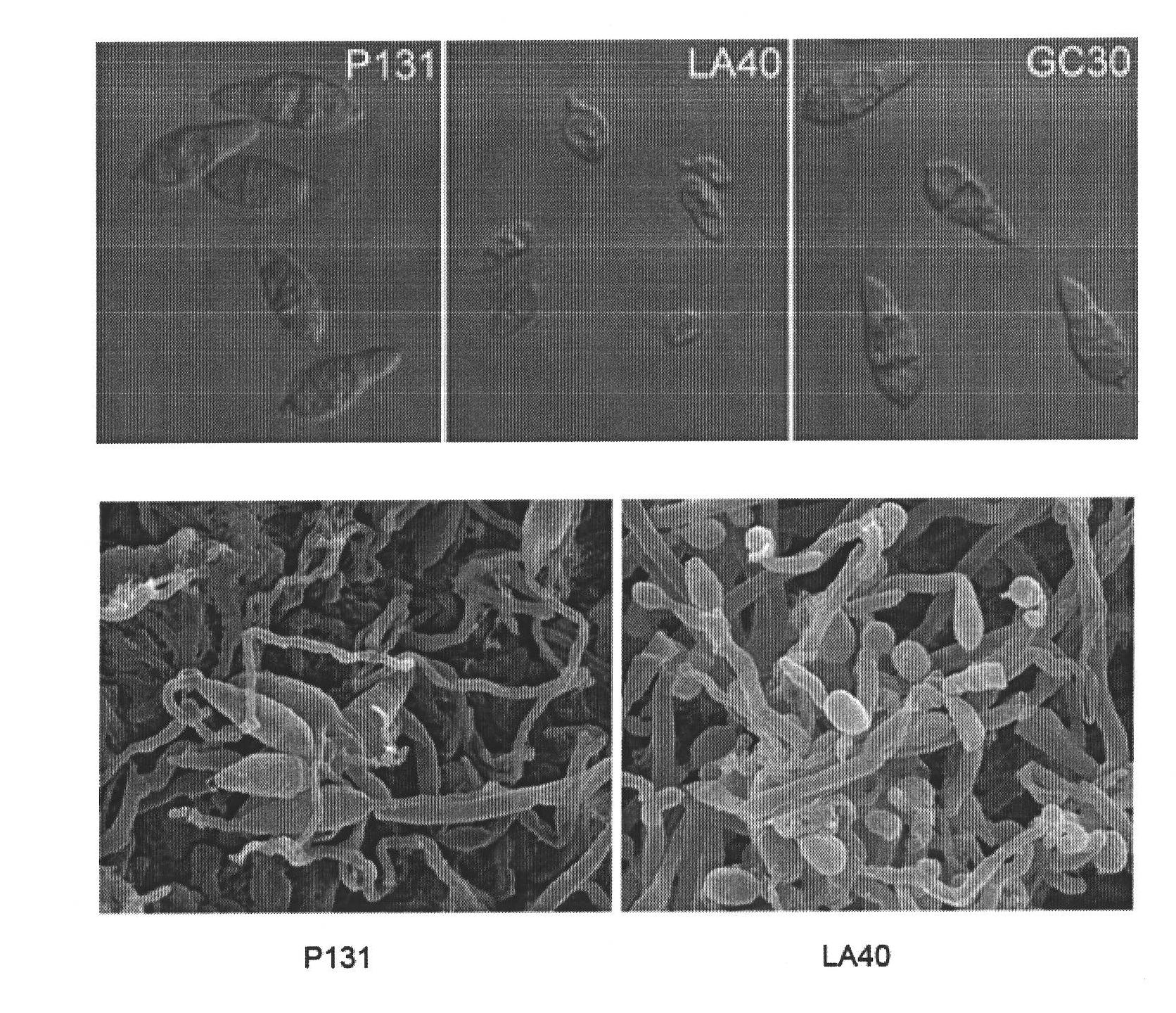
[0054] Pipette 20ul of wild-type P131, knockout LA40, and complement GC30 spore suspensions (concentration: 50,000 spores / ml) and drop them on hydrophobic coverslips. After cultivating in the dark at 25°C for 24 hours, observe under a microscope and The formation rate of appressoria was counted. According to the statistics of appressoria formation rate = number of conidia that germinated to form appressoria / number of germinated spores, it was found that the appressoria formation rates of wild-type P131, knockout LA40 and complement were 96%, 61% and 95%, respectively. % (attached Figure 5 ), the appressorial formation rate of the knockout body was significantly lower than that of the wild type, while the appressorial formation rate of the complement could be restored to the wild type level.
[0055] 2) Formation of appr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com