Rice blast resistance gene RMg41 and applications thereof
A rice blast resistance gene and rice technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of tedious and time-consuming breeding process, and achieve the effects of broadening the resistance spectrum, enhancing resistance and shortening the breeding cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment one: Evolutionary Analysis of Rice Blast Resistance Gene RMg41
[0027] Based on the whole genome sequencing of rice varieties 93-11 and Nipponbare, all NBS-LRR type disease resistance genes in the genome were identified first, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed. On this basis, we selected 20 candidate blast resistance gene loci, one of which is RMg41. This locus has the following characteristics: (1) The gene mostly exists in the form of gene families and gene clusters, with 4 similar copies in the Nipponbare genome and only 1 copy in the 93-11 genome; (2) Its LRR region, especially the xxLxLxx region has a higher Ka / Ks value.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment two:Isolation and Cloning of Rice Blast Resistance Gene RMg41 (Os03g63150_GM)
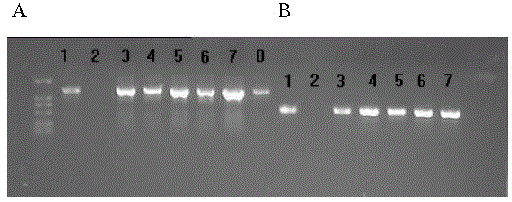
[0029] Using public database sequencing species Nipponbare (Nipponbare) and 93-11 as reference sequences, design primers (both ends of the primers have enzyme cutting sites AscI). Refer to the sequence listing for the primer sequence, the forward primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:4; the reverse primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:5.
[0030] Using disease-resistant rice varieties Tetep, Gumei 2 and Q2436 as templates, long-segment PCR (Long-PCR) was used to amplify candidate gene fragments. The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, renaturation at 60°C for 45 seconds, extension at 68°C for 7 minutes, a total of 35 cycles, followed by incubation at 72°C for 10 minutes, and finally constant temperature at 10°C. Subsequently, the PCR products were recovered by tapping rubber.
Embodiment 3
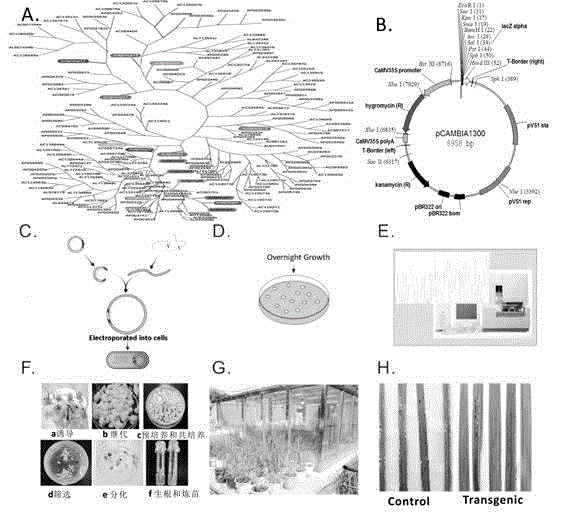
[0031] Embodiment three: Preparation of bifunctional base vectors
[0032] The rare restriction site AscI was introduced between the multiple cloning sites BamHI and SalI of the bifunctional vector pCAMBIA1300, and the restriction site XbaI was replaced to form the basic vector pCAMBIA1300-AscI with the rare restriction site AscI.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com