Patents
Literature
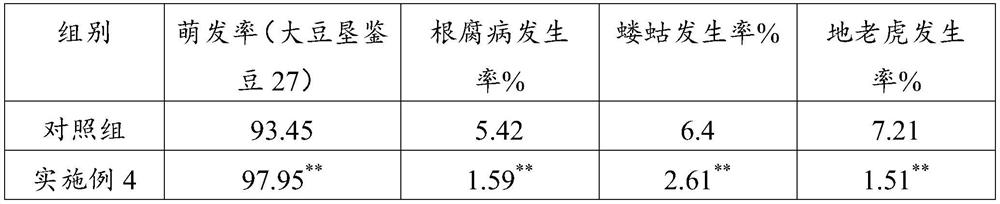
51 results about "Acidovorax" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acidovorax is a genus of Proteobacteria. All species are facultative. A. avenae causes bacterial fruit blotch on cucurbit crops.
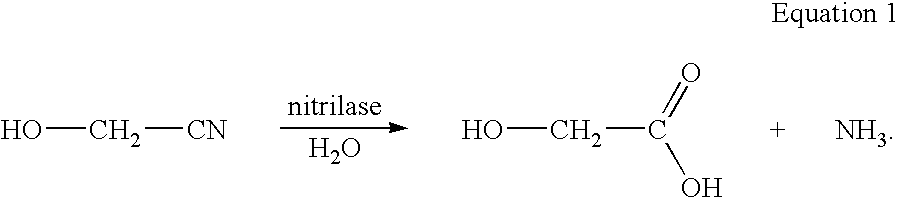
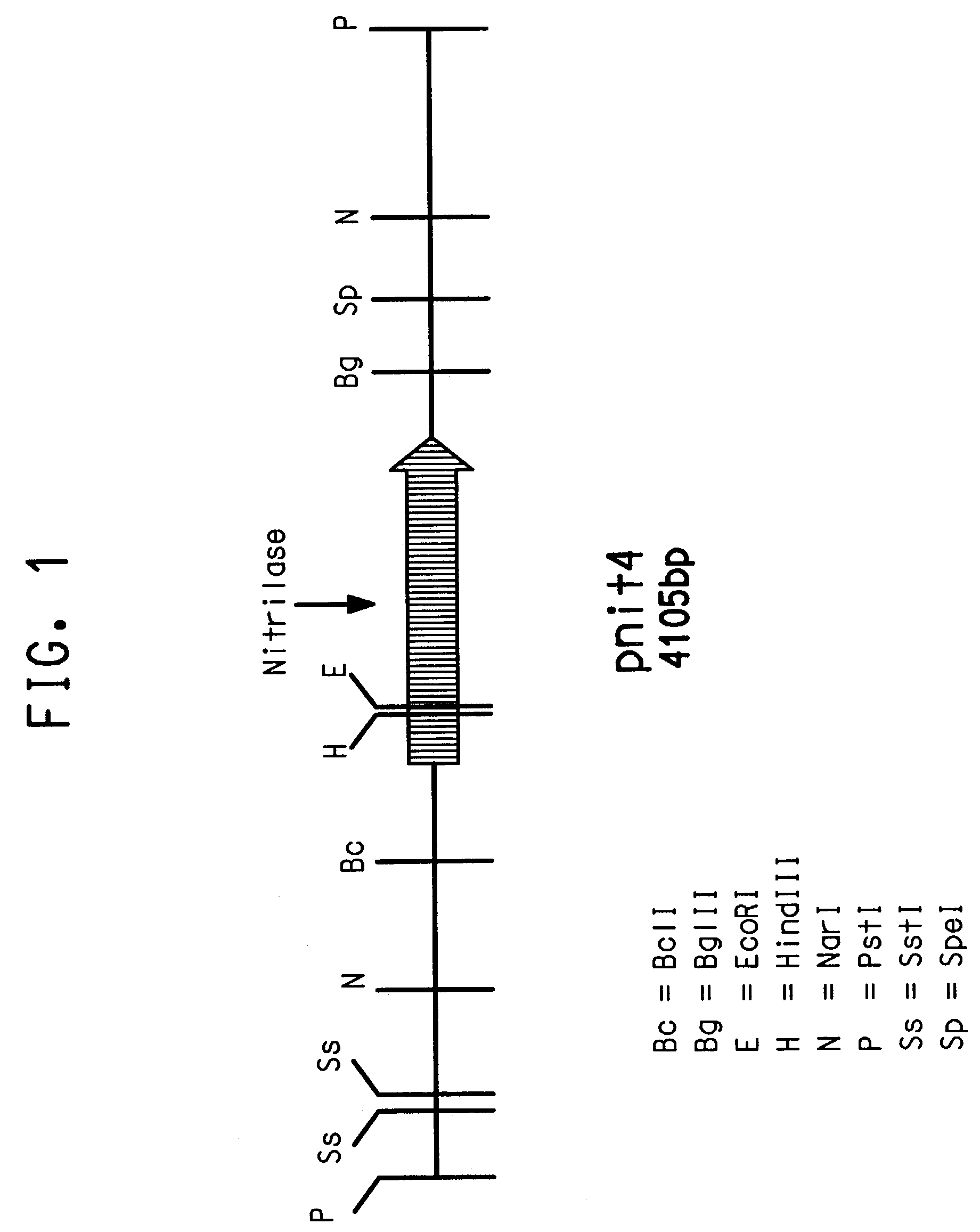
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
ActiveUS20060160199A1Facilitate recombinant expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaPtru catalystNitrilase activity
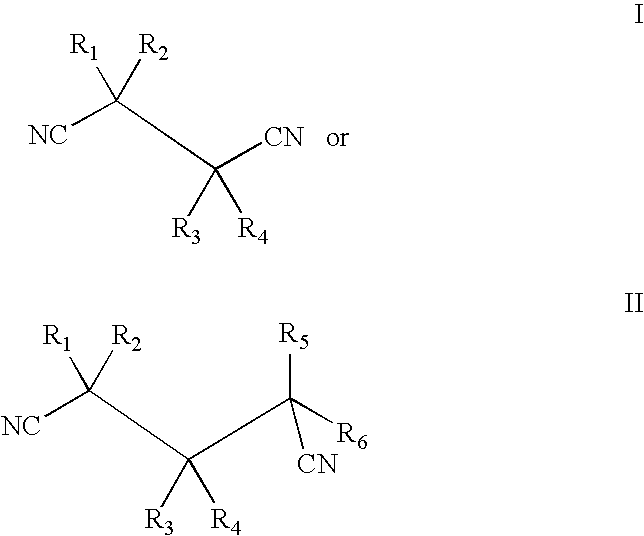
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Application of amaranthus in plant disease prevention and treatment
ActiveCN103238634AHas inhibitory effectHas a preventive effectBiocideFungicidesXanthomonas axonopodisTherapeutic effect
The invention provides an application of amaranthus in plant disease prevention and treatment, wherein amaranthus leaves are taken as the raw material and extracted by an organic solvent to obtain an extract, acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani are selected as sites of action, and research on indoor bacteriostasis effect and in-vitro and pot culture control effects is performed to find that the amaranthus leaf extract has an inhibition effect on acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani; and the in-vitro and pot culture tests also indicate that the amaranthus leaf extract has certain prevention and treatment effects on acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani; and all the facts show that the amaranthus has prevention and treatment effects on the plant diseases in addition to edible and medical values. The research discovers and expands the functions of the vegetable, and simultaneously provides a new train of thought and a new way for studying and developing biopesticide for preventing and treating the plant diseases.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
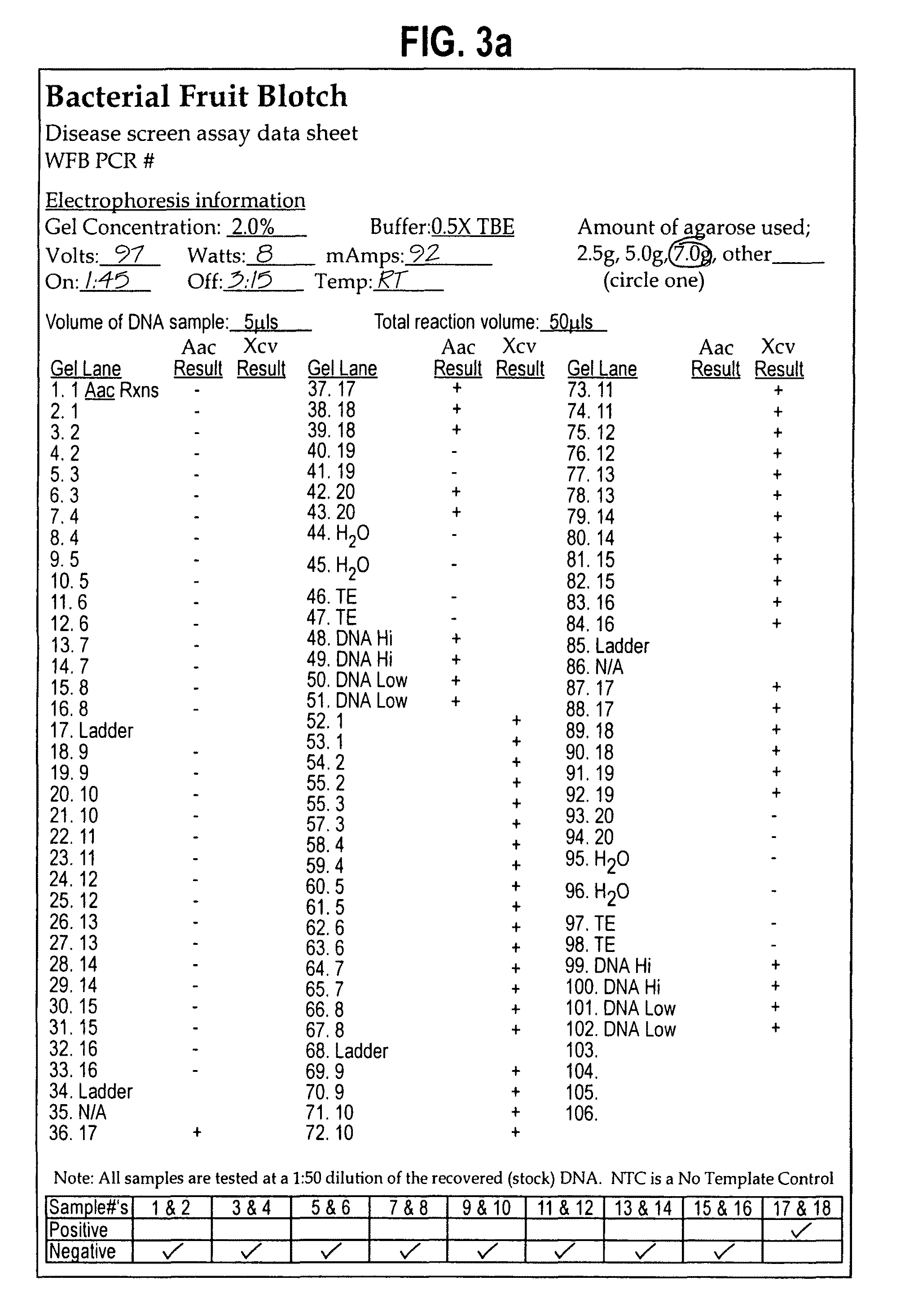
Molecular detection primer of acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli and application thereof
InactiveCN101899508AMethod results are reliableEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDiseased plant
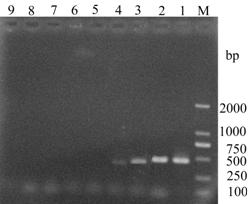
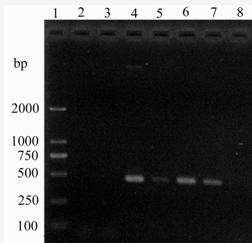
The invention provides a molecular detection primer of acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli and application thereof. The special primer comprises an upstream primer AIT1F: 5'-GCTGGATCACCTCCTTTCTG-3' and a downstream primer AIT2R: 5'-TGACGCAATCAAATTTTTGTCA-3'. Through PCG (Polymerase Chain Reation) amplification and agarose gel electrophoresis, a special amplification product with a fragment length of 462bp can be amplified in pure DNA of the acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli, a bacteria carrying disease plant tissue and a seed to rapidly detect the acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli. The special detection primer and the application thereof can be used for rapidly, sensitively and specially detecting the acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli in bacteria carrying watermelon seeds and plant seeds infected the acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli in production practice, can also be used for early diagnosis of field diseases and monitoring and identification of germs and provide a reliable technology and theoretical basis to control diseases caused by the acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli.
Owner:CROP RES INST OF FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
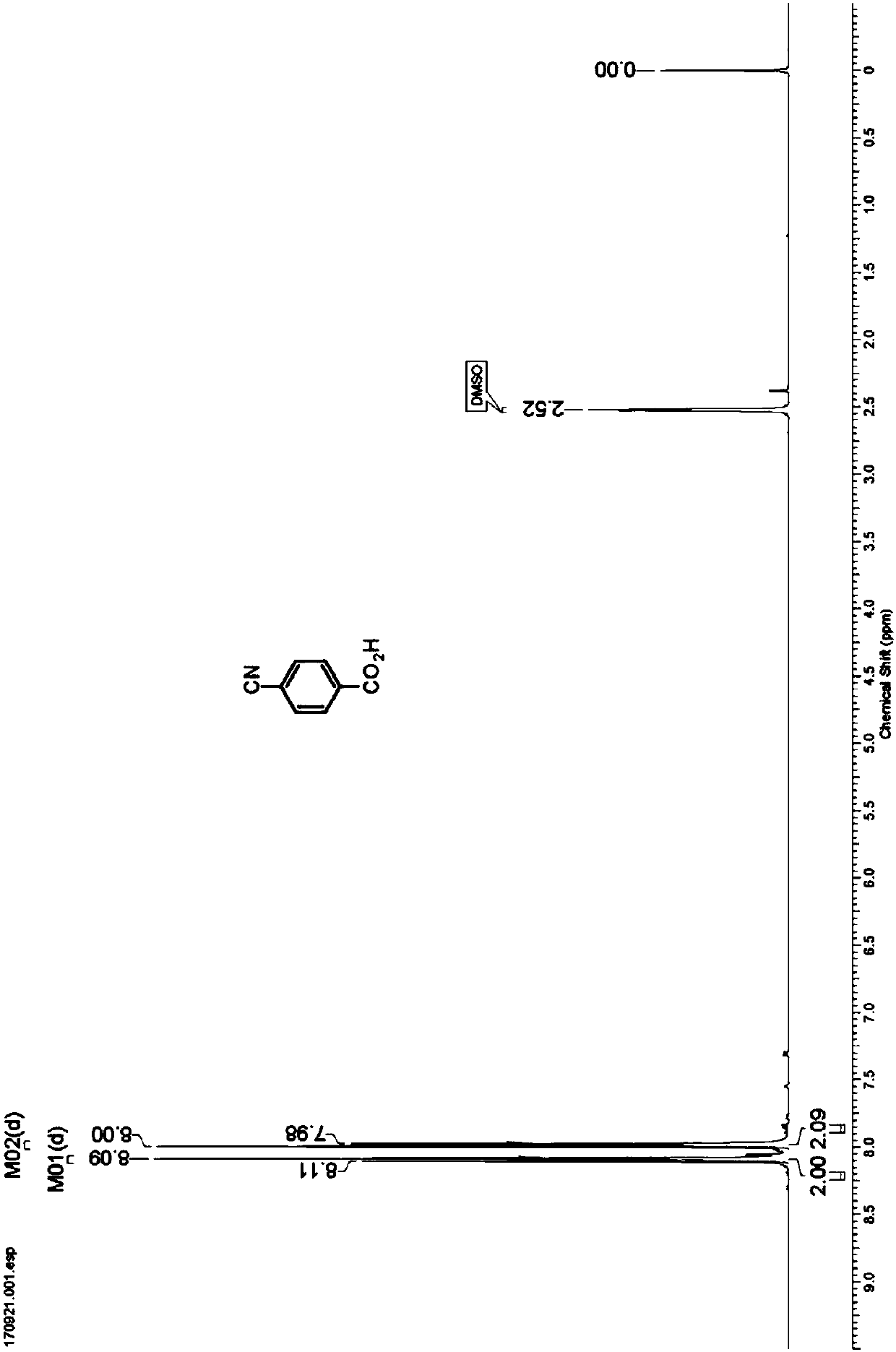
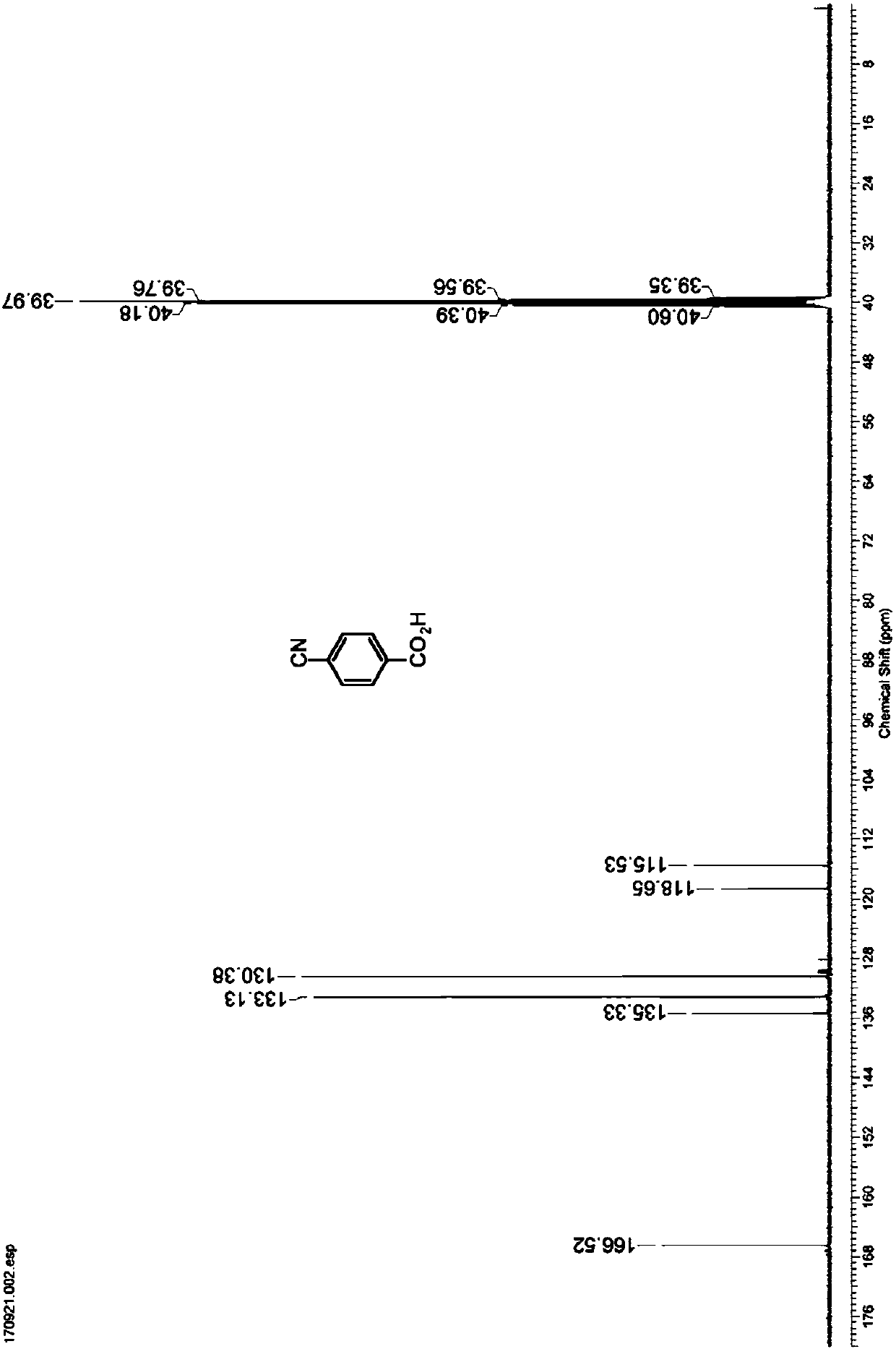
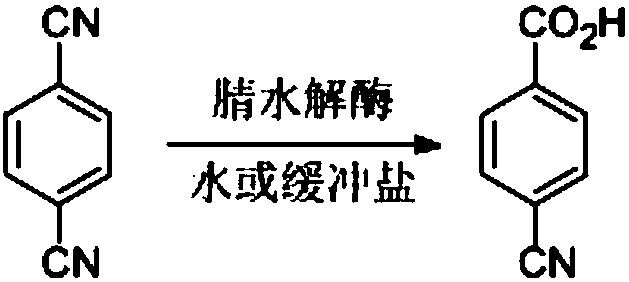
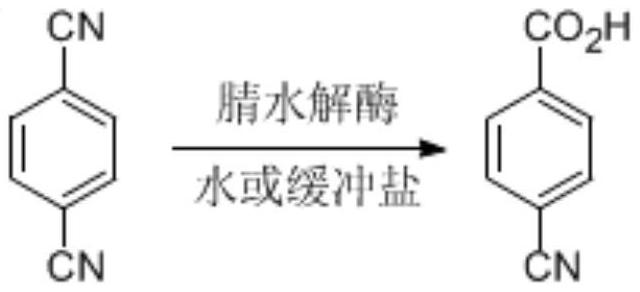
Nitrilase capable of preparing paracyanobenzoic acid by hydrolyzing p-benzenedicarbonitrile
ActiveCN107641622AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseHydrolasesFermentationArabidopsis thalianaPollution
The invention discloses a nitrilase N1 derived from pantoea sp.AS-PWVM4 and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N2 derived from arabidopsis thaliana and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N3 derived from acidovoraxfacilis 72W and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N4 derived from leptolyngbya sp. and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N5 derived from brassica oleracea var.oleracea and a gene thereof and a nitrilase N6 derived from camelina sativa and a gene thereof, and a method for preparing paracyanobenzoic acid as p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate by using the nitrilase as a biological catalyst; resting cells ofthe corresponding nitrilases can be used for catalyzing 100g / L of substrate; the conversion rate is greater than 99%; the method has the obvious characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution and simple process route, and has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Goffer pseudomonas P94 and application thereof
InactiveCN101012443AIncrease productionGood preventive effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPhospholipase
The invention discloses a new Pseudomonas corrugate strain (P94 GMCC No.1895), which is characterized by the following: manufacturing relative HCN to prevent bacteria, proteinase and phospholipase and IAA; inhibiting partial plant pathogenic fungus (Botrytis cinerea, Ceratocystis fimbriata, Monilinia laxa, Magnaporthe grisea, Pythium aphanidermatum and Phytophthora capsici) and partial pathogenic bacteria (Pseudomonas syringae, Acidovorax avenae and Ralstonia solanacearum); accelerating the growth of tomato and cucumber to improve production by 22%-28%.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Symbiotic bacterium system for increasing biomasses of scenedesmus obliquus and improving quality of grease and application of symbiotic bacterium system
ActiveCN105296376APromote growthPromote material exchangeBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiomassCarbon dioxide
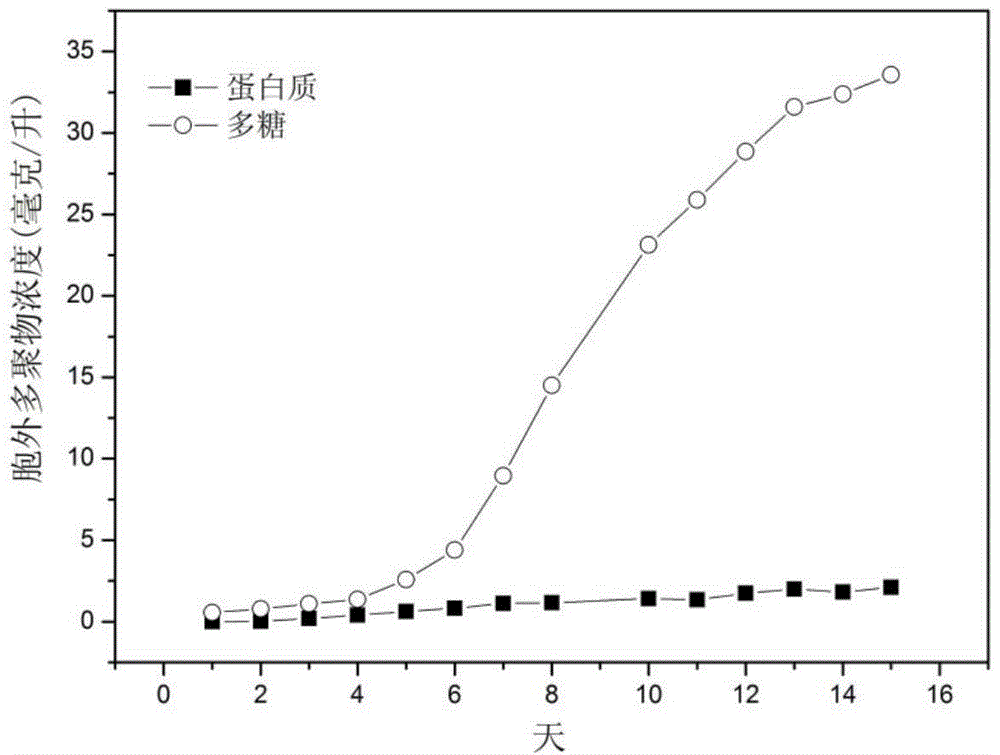
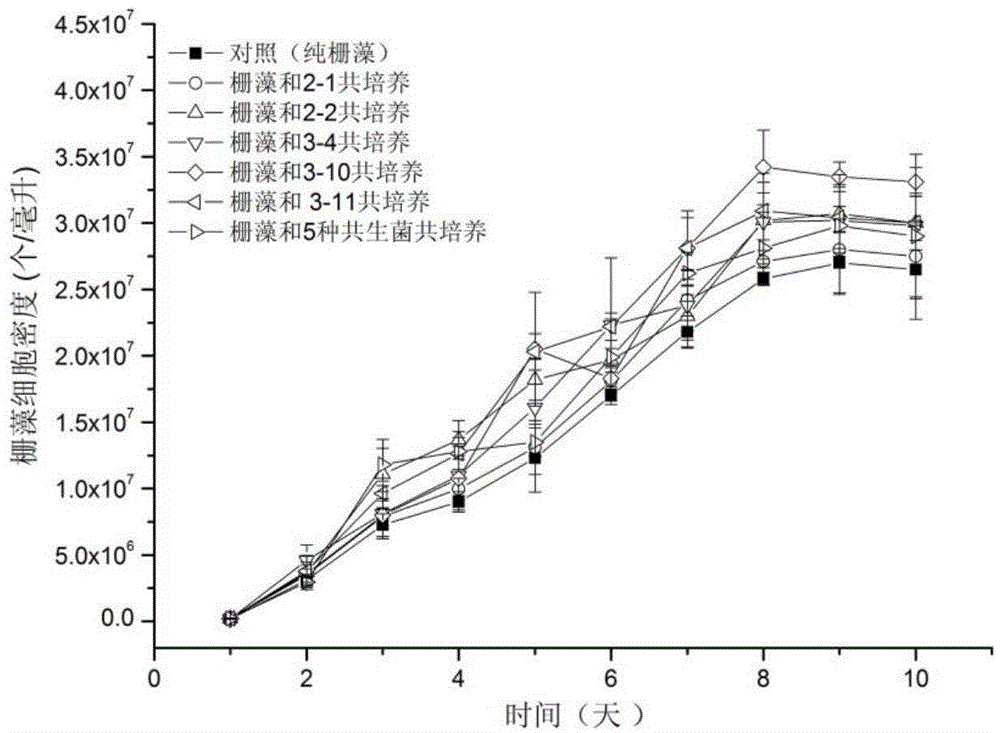
The invention relates to the field of micro-alga biotechnologies, in particular to a symbiotic bacterium system for increasing biomasses of scenedesmus obliquus and improving the quality of grease and the stability of culture systems and application of the symbiotic bacterium system. The symbiotic bacterium system comprises the scenedesmus obliquus and symbiotic bacteria. The symbiotic bacteria include one type or a plurality of types of brevunmdimonas sp., rhizobium sp., pseudomonas sp. and acidovorax sp. The symbiotic bacterium system and the application have the advantages that the symbiotic bacteria and mixed floras of the symbiotic bacteria are applied to scenedesmus obliquus culture procedures, extracellular substances and oxygen which are generated by the scenedesmus obliquus can be consumed by each single type of symbiotic bacteria and the mixed floras, carbon dioxides can be generated to be utilized by the scenedesmus obliquus, micro-environments favorable for growth of the scenedesmus obliquus can be created, and accordingly substance exchange and metabolism of the scenedesmus obliquus, the symbiotic bacteria and the mixed floras can be promoted.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
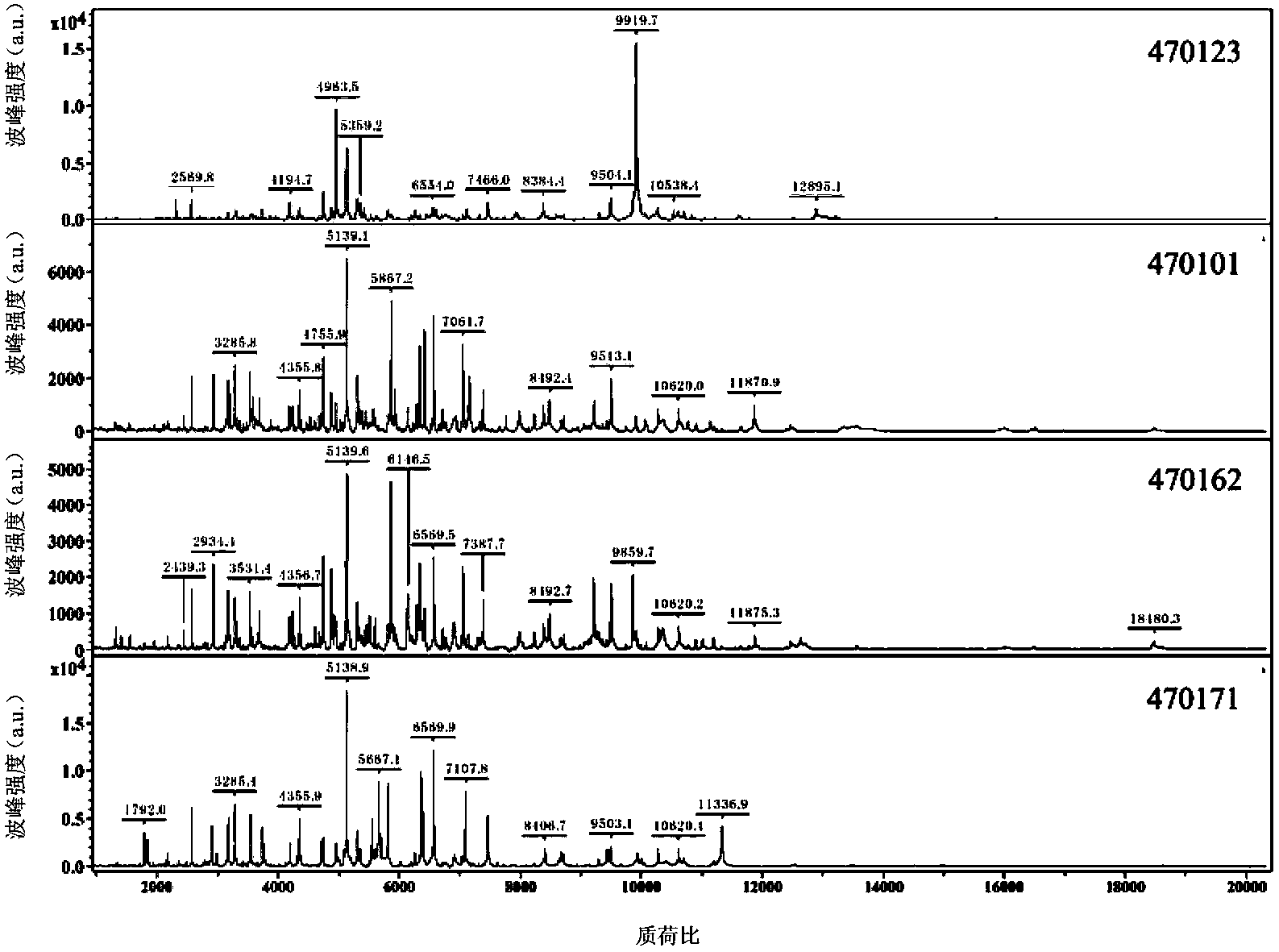
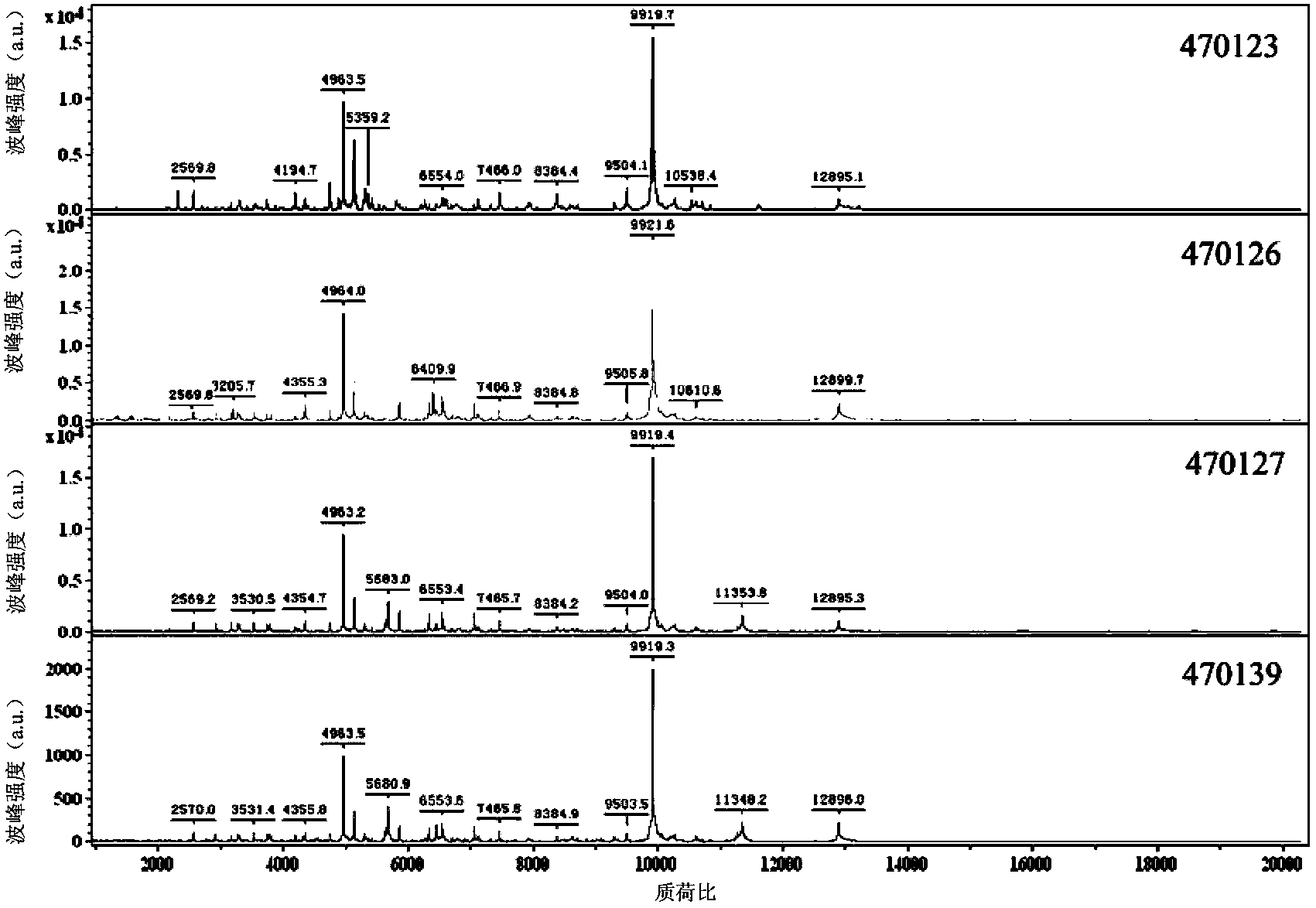
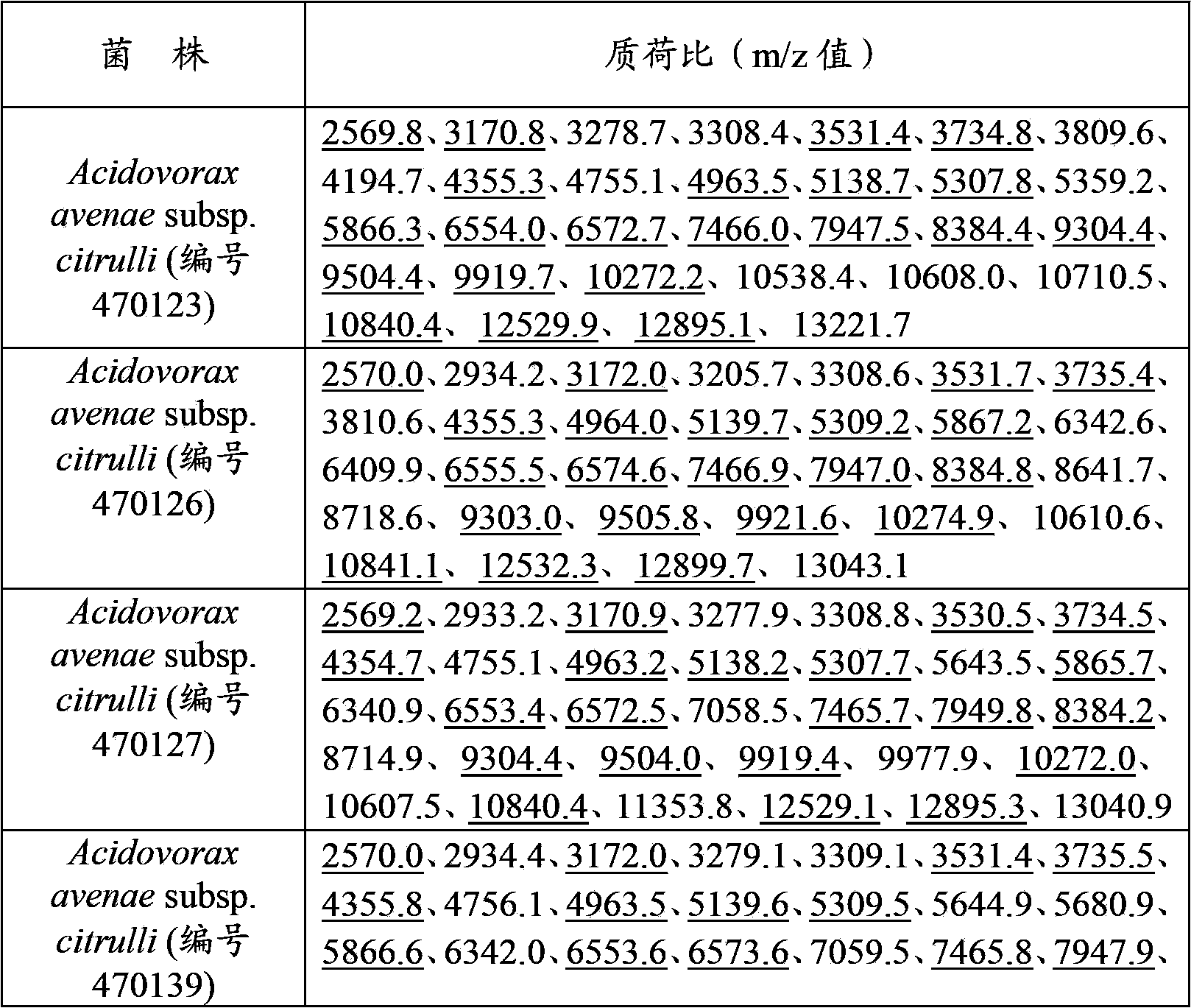
Protein fingerprint atlas-spectrum model of acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli and applications thereof
InactiveCN103424463AHas a specific recognition functionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMatrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flightMicrobiology
The invention disclose a protein fingerprint atlas-spectrum model of acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli, the model is drawn according to the mass-to-charge ratios of acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli protein and wave crest strength coefficients thereof, wherein the mass-to-charge ratios comprises: 3171.4, 3735.0, 4963.5, 5139.0, 5866.4, 6554.1, 7466.1, 7948.0, 8384.5, 9304.2, 9504.3, 9920.0, 10272.8, 10840.7, 12530.5, and 12896.5. The invention also discloses a matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization flying time mass spectrum detection method based on the model. The method can qualitatively detect whether a sample contains acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli. The model has a function of specific recognition, is capable of being applied to commercial detection of acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli, and is especially suitable for rapid and high throughout detection for departments such as port inspection and quarantine.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH +1
Monoclonal antibody for resisting acidovorax citrulli and application thereof
InactiveCN103881980AStrong specificityHigh potencyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismHybridoma cell
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody for resisting acidovorax citrulli and application thereof. The monoclonal antibody for resisting the acidovorax citrulli provided by the invention is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain 4C6 for secreting the monoclonal antibody of acidovorax citrulli; the mouse hybridoma cell strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the collection number of CGMCC No.8960. The monoclonal antibody for resisting acidovorax citrulli provided by the invention is good in specificity and high in valence, reacts with different separators of the acidovorax citrulli, and has good broad-spectrum performance. The monoclonal antibody is applied to an acidovorax citrulliserological diagnosis reagent, good in specificity, and avoids cross reaction. The monoclonal antibody for resisting acidovorax citrulli developed by the invention can be used for developing immunological diagnostic reagents such as an ELISA diagnosis reagent, a colloidal gold immune test paper strip, an antibody chip, a biological sensor, and the like, of the acidovorax citrulli.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
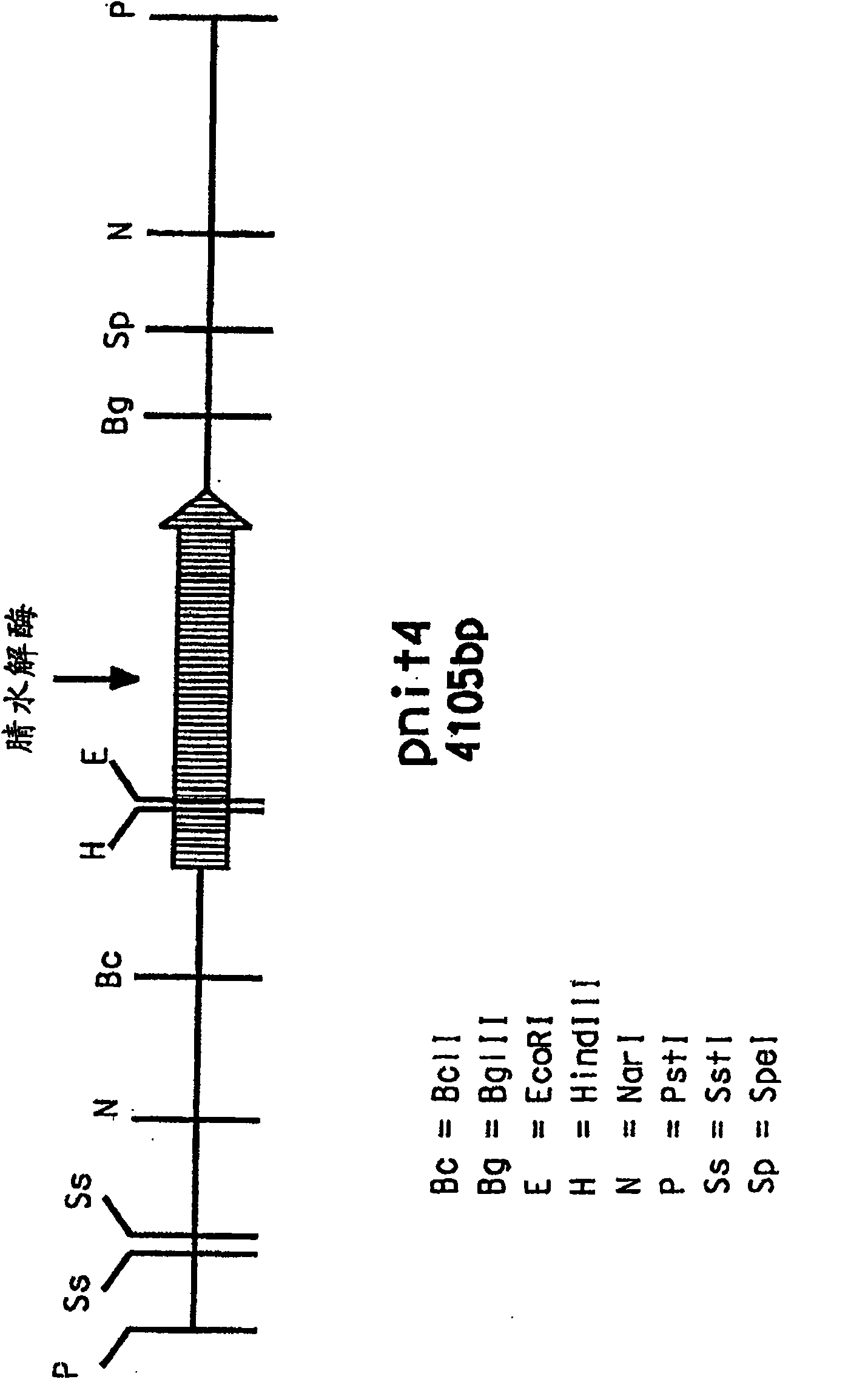
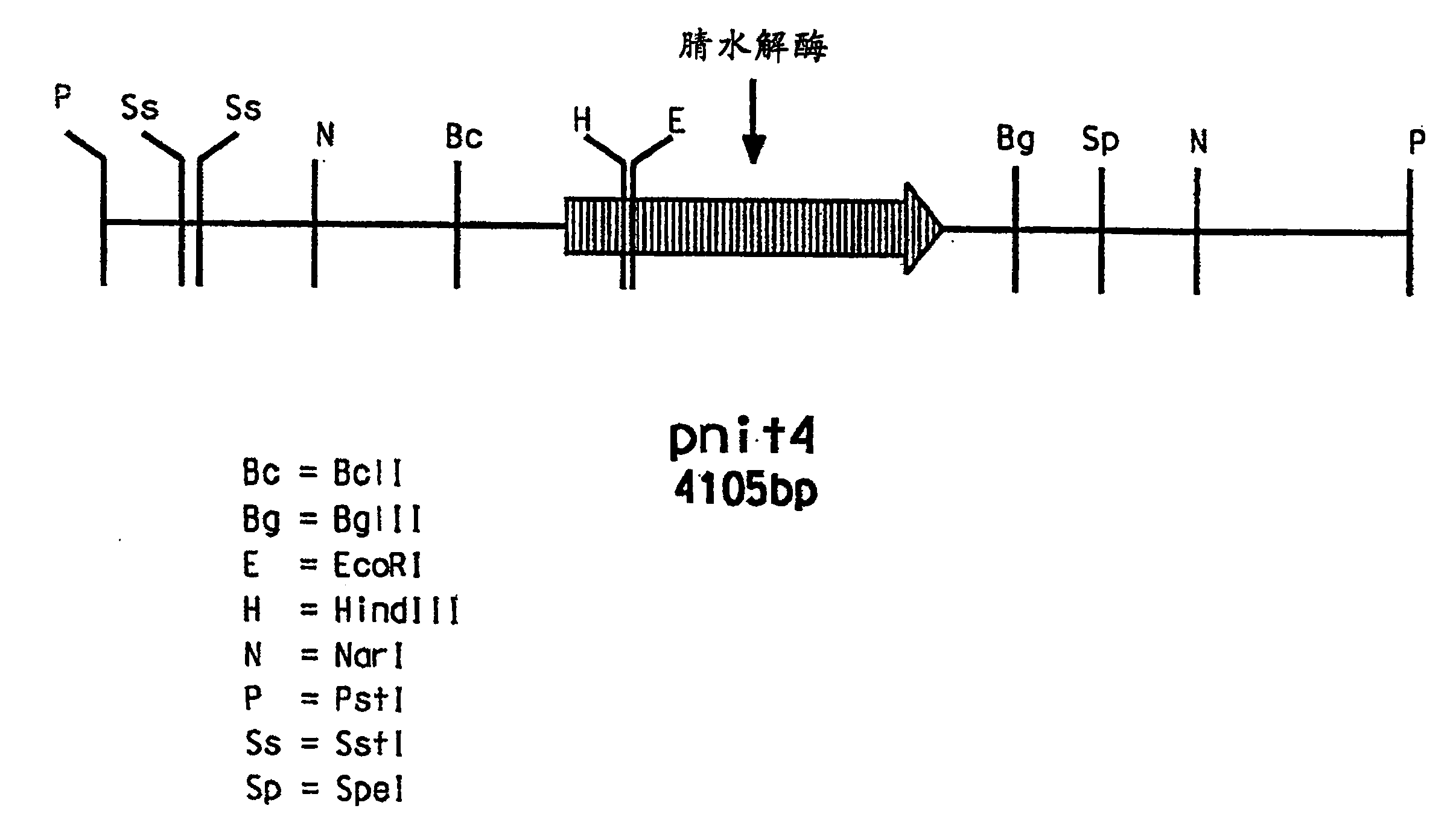
Isolation and expression of a gene for a nitrilase from Acidovorax faclilis 72W
Recombinant microbial strains are provided that express nitrilase enzyme and are useful as biocatalysts for the hydrolysis of nitrile-containing substrates. The recombinant cells are transformed with a foreign gene isolated from Acidovorax facilis 72W encoding a thermostable nitrilase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of nitrile-containing substrates to carboxylic acids under mild reaction conditions. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrilase gene and the deduced amino acid sequence encoded by the nitrilase gene are provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Microbiological degradation method for nitrobenzene industrial wastewater
InactiveCN102515366AImproved shock load capabilityImprove biological activityWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyIndustrial waste water
The invention aims to provide a microbiological degradation method for nitrobenzene industrial wastewater. According to experimental selection, composite bacteria liquid of Pseudomonas, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Acinetobacter baumannii, Aquaspirillum, Acidovorax avenae, Alcaligenes faecalis and Bacillus is provided. Domestication culture and three-stage amplification culture are carried out on the composite bacteria liquid so as to obtain a high efficiency composite microbial inoculum suitable for industrial production. When used to treat nitrobenzene wastewater, the microbial inoculum provided in the invention has the advantages of strong biological activity, long survival time, high capability in resisting impact load of influent quality and thorough treatment.
Owner:CHONGQING WENTAI ENERGY CONSERVATION & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Application method for bactericide controlling vegetable bacterial diseases
InactiveCN103371143AGood control effectImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideDisinfectantsBiotechnologyBacterial disease
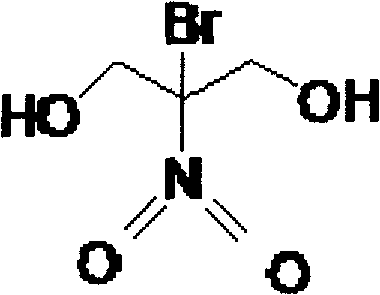
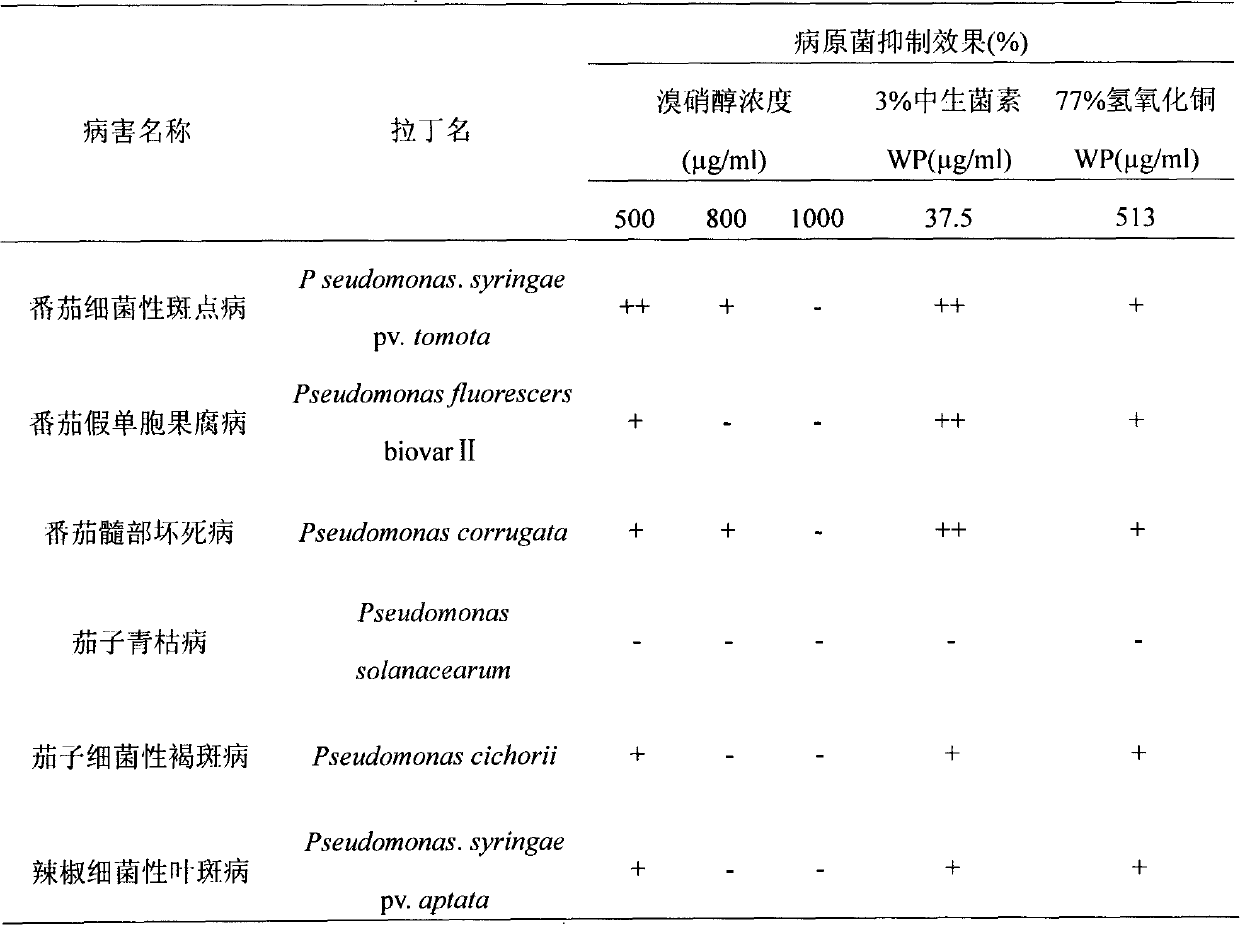
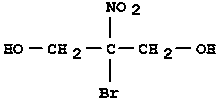
The invention discloses an application method for an agent used to control vegetable bacterial diseases, and belongs to the field of chemical protection of plants. The agent is characterized in that the active ingredient is 2-Br-2-nitro-1, 3-propylene glycol, and by the way that the agent with an effective concentration of 1000 micrograms / ml is sprayed over whole plants, vegetable bacterial diseases can be controlled effectively. The agent has obvious effects of prevention and treatment on vegetable bacterial diseases caused by Pseudomonas Acidovorax, Xanthomonas, Erwinia, Clavibacter, and provides new technical supports for controlling the occurrence and development of vegetable bacterial diseases during production.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Anthraquinone compounds, preparation method and application
ActiveCN107473952AHigh bactericidal activityGood effectBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyPlant disease
The invention provides anthraquinone compounds, a preparation method and an application, and belongs to the field of compounds. The anthraquinone compounds have the activity of resisting pathogenic bacteria of plants, and can be used for preventing and treating plant diseases caused by the pathogenic bacteria of the plants when applied as bactericides. The anthraquinone compounds are extracted from marine fungus Fusarium equiseti GLY27 with the collection number being CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 14348. The anthraquinone compounds are used for preventing and treating the plant diseases caused by the pathogenic bacteria of the plants, wherein the pathogenic bacteria of the plants comprise P.syringae, A.avenae and E.carotovora.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
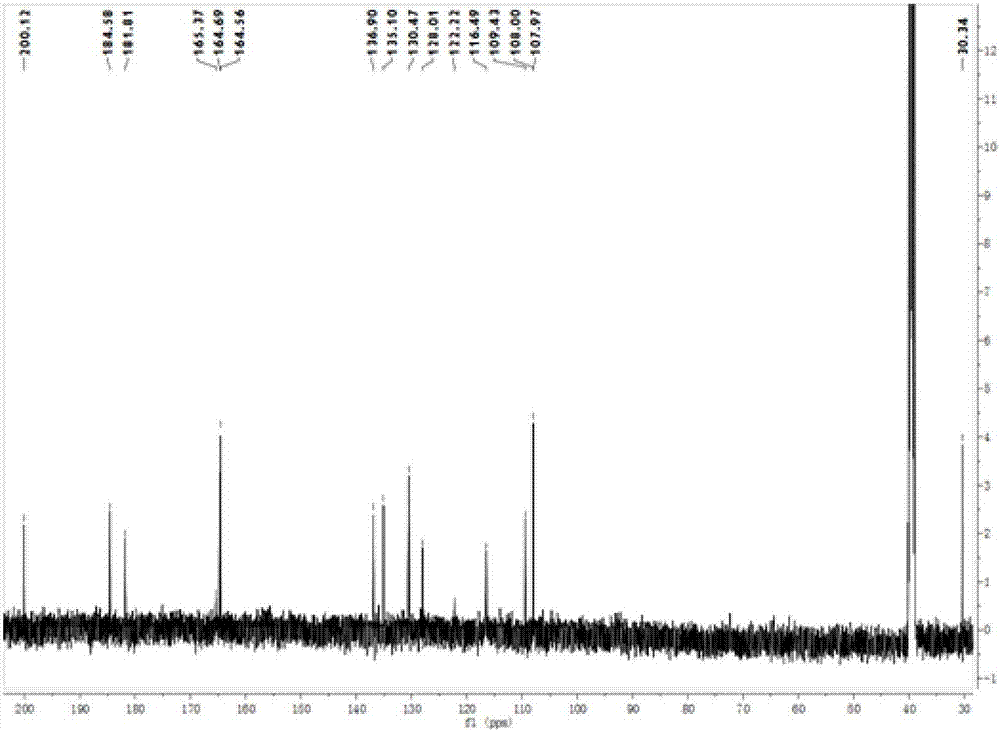
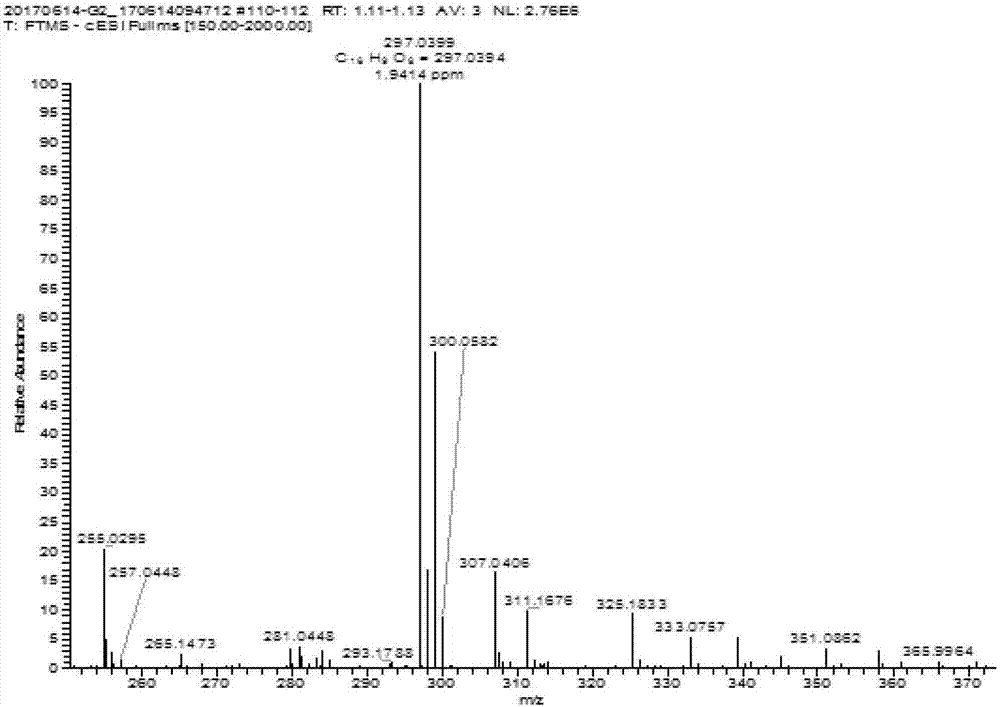
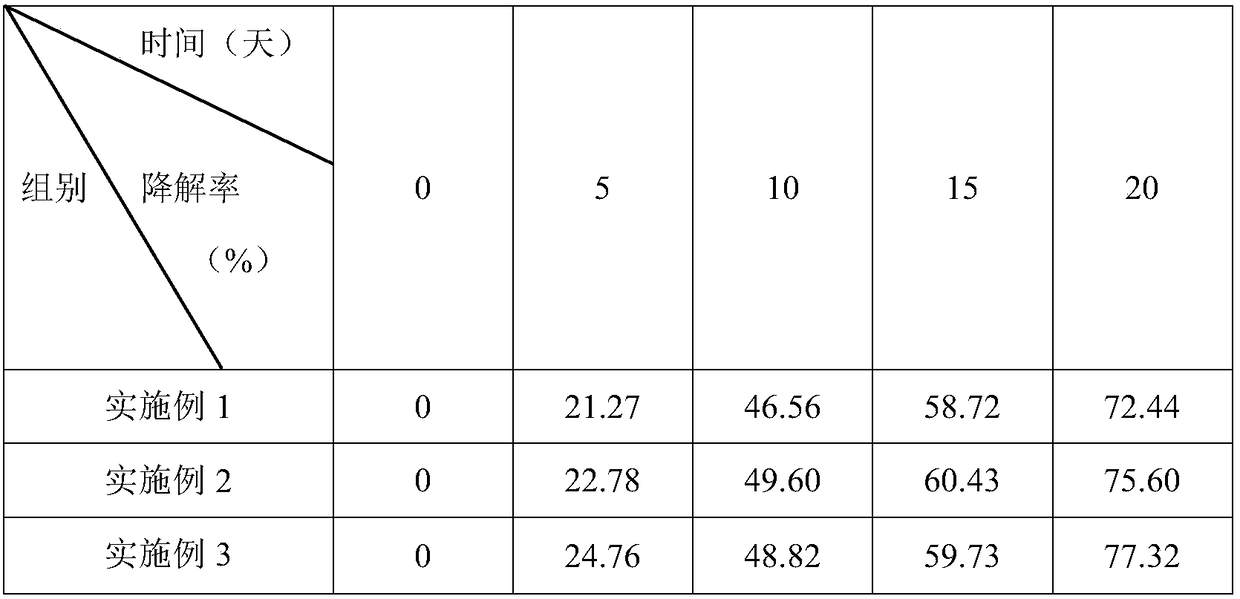
Acidovorax wautersii TCP2011036 and application thereof
ActiveCN108130303AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDiseaseEcological environment
The invention discloses Acidovorax wautersii TCP2011036. The classification name of the Acidovorax wautersii TCP2011036 is Acidovorax wautersii TCP2011036, the 16S rDNA gene sequence list of the strain is SEQ ID NO.1 as shown in the specification, the preservation institute is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is June 19, 2017, and the preservationnumber is CGMCC No.14252. The strain disclosed by the invention has a remarkable promotion function on growth of sugarcane seedlings, and the strain can be applied to production of microbial agents and biological organic fertilizers for promoting growth of plants and inhibiting insects and diseases of plants, has great significances for reducing chemical pesticides and protecting ecological environments, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compound microbial agent for treating soil pollution and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108251330AEfficient degradationSimple manufacturing methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentMicrobiology
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent comprises the following raw material components: a pseudomonas japonica culture, a comamonas testosteroni culture, a microbacillus culture and an acidovorax delafieldii culture; according to the invention, multiple bacterial cultures are subjected to mixed fermentation to prepare the compound microbial agent; and thecompound microbial agent has an effective degradation effect on organic residues such as nitrobenzene compounds formed by insecticides or pesticides in soil, and furthermore, special strains are subjected to mixed cultivation and multiple strains are subjected to mixed fermentation to provide a simple and easy preparation method.
Owner:江苏世邦生物工程科技有限公司
Method for stabilizing nitrilase activity and preserving microbial cells
A method for preserving immobilized or unimmobilized microbial cells having nitrilase activity and for stabilizing the nitrilase activity of unimmobilized or immobilized microbial cells has been developed. The unimmobilized or immobilized microbial cells are stored in an aqueous solution containing from about 0.10 M to the saturation concentration of an inorganic salt of bicarbonate or carbonate, including ammonium, sodium and potassium salts of bicarbonate or carbonate. Aqueous suspensions containing at least 100 mM bicarbonate or carbonate limit microbial contamination of the stored enzyme catalyst, as well as stabilize the desired nitrilase activity of the unimmobilized or immobilized cells. Microorganisms which are characterized by a nitrilase activity and are stabilized and preserved by this method include Acidovorax facilis 72-PF-15 (ATCC55747), Acidovorax facilis 72-PF-17 (ATCC55745), Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC55746), and transformed microbial cells having nitrilase activity, preferably Escherichia coli SS1001 (ATTCCPTA-1177) which is transformed with Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
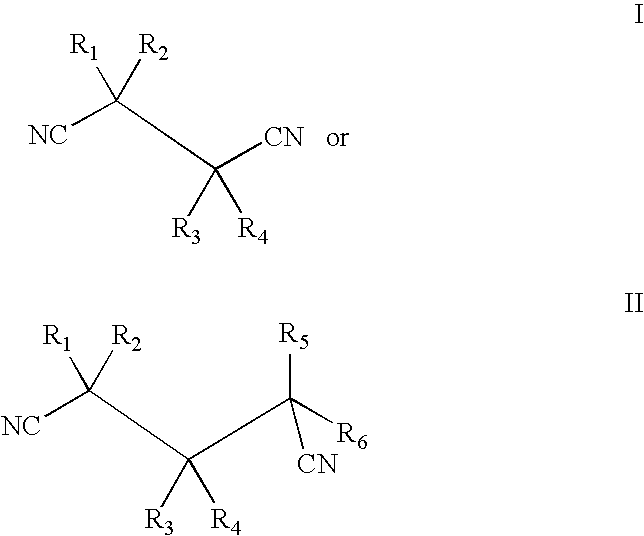
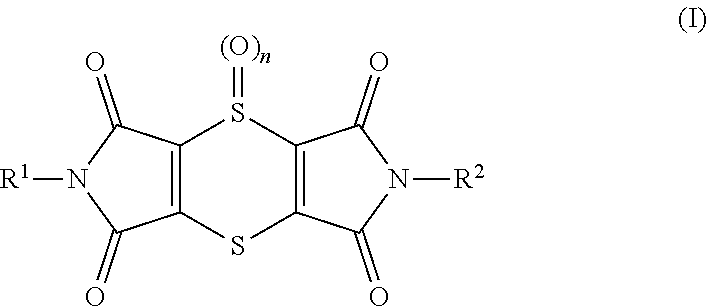
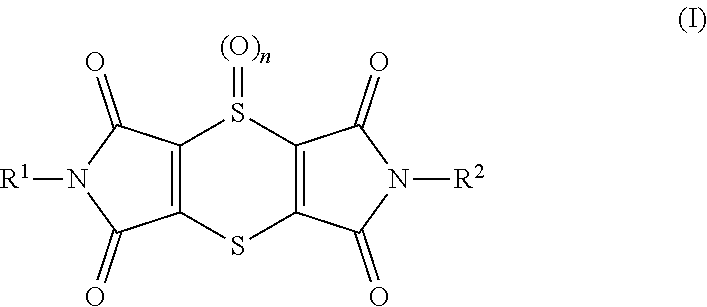
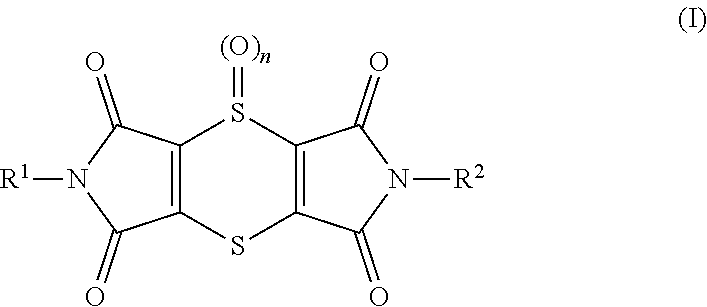
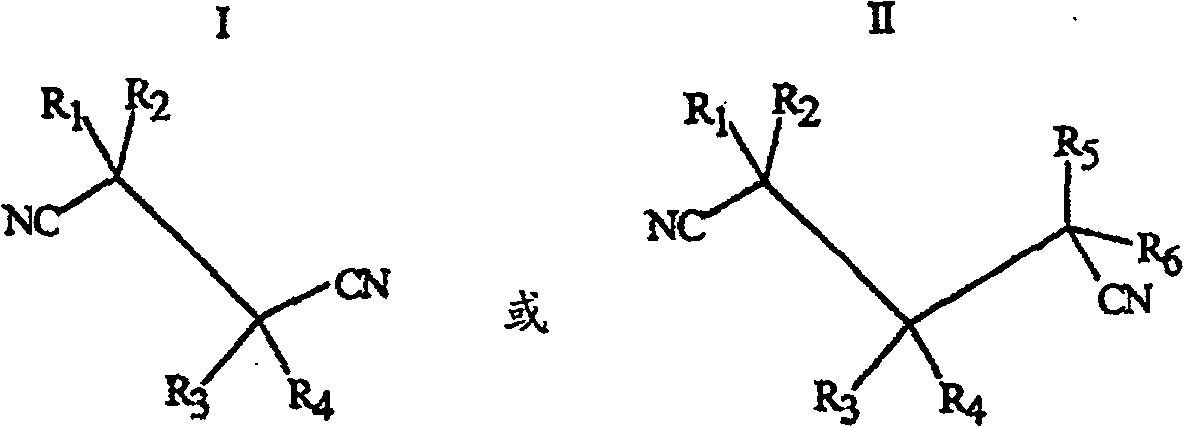
Use of dithiine-tetracarboximides for controlling bacterial harmful organisms in useful plants
The present invention relates to the use of dithiine-tetracarboximides of formula (I) for controlling selected bacterial harmful organisms in useful plants, wherein the bacterial harmful organisms are selected from the group consisting of Acidovorax avenae, Burkholderia spec., Burkholderia glumae, Candidatus Liberibacter spec., Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, Corynebacterium, Erwinia spec. (Dickeya, Pectobacterium carotovorum, Erwinia amylovora), Pseudomonas syringae, Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidae, Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans, Pseudomonas tumefaciens (=Agrobacterium tumefaciens), Streptomyces spp., Xanthomonas spp., Xanthomonas ampelina, Xanthomonas axonopodis, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines, Xanthomonas campestris, Xanthomonas campestris pv. musacearum, Xanthomonas campestris pv. pruni, Xanthomonas campestris pv. Viticola, Xanthomonas fragariae and Xanthomonas transluscens or Xylella fastidiosa. The present invention also relates to a method for controlling the selected bacterial harmful organisms in useful plants by treatment with a dithiine-tetracarboximides of formula (I).
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Novel microbial agent and soybean planting method
PendingCN112940969AImprove germination rateImprove seedling survival rateBacteriaSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a novel microbial agent and a soybean planting method. The novel microbial agent disclosed by the invention comprises the following strains: 1) one or more of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, Herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthomonas, flavobacterium and wautersia; and 2) azospirillum and azotobacter. The novel microbial agent can improve the emergence rate and the survival rate of soybeans, improve the growth of soybean seedlings, promote the accumulation of organic matter, improve the disease resistance of the soybeans to harmful bacteria and improve the nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate of the soybeans.
Owner:兴安盟莱绅生物农业有限公司
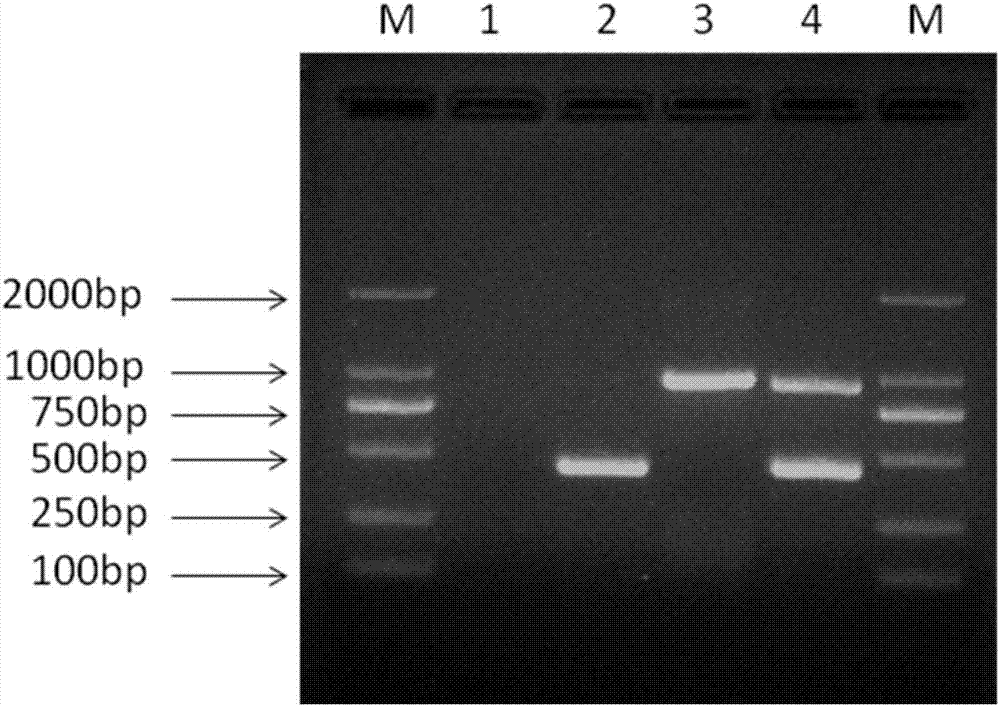
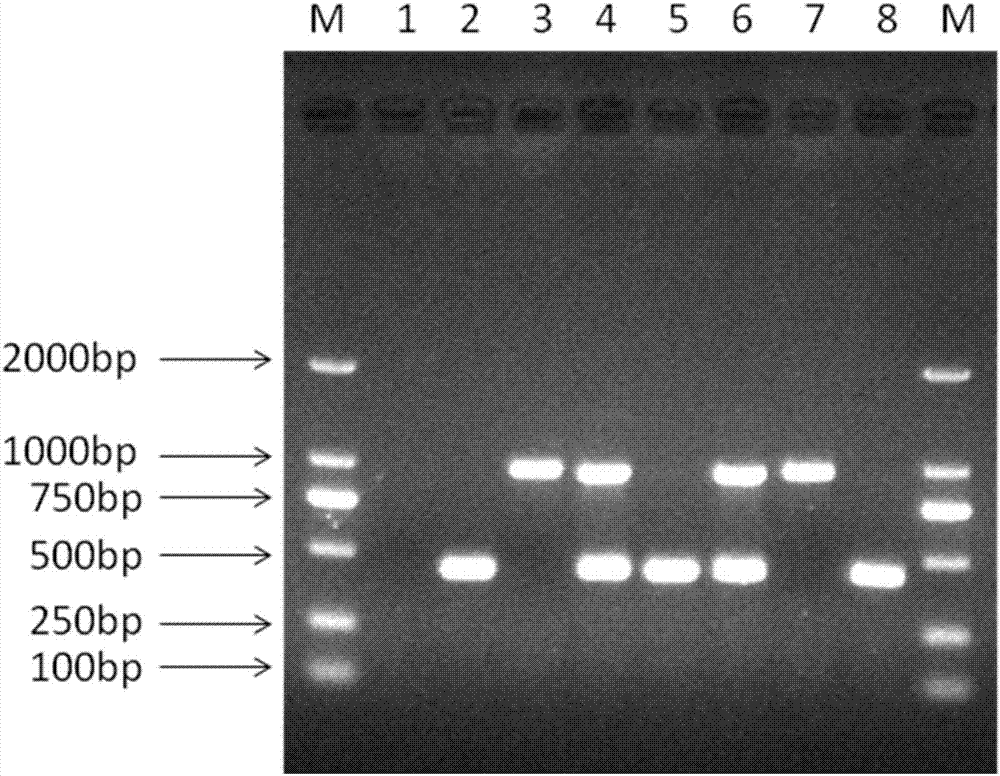
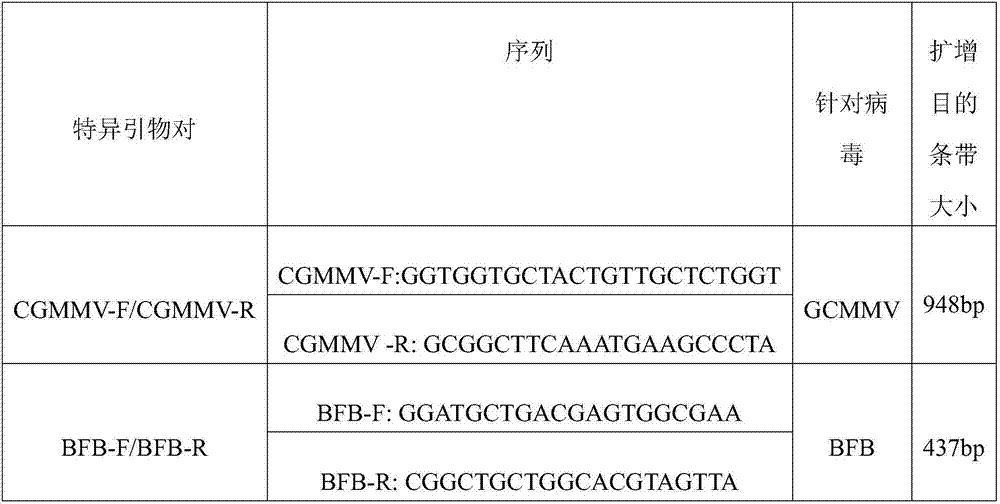
Method capable of synchronously detecting RT-PCR detection primer group of two melon quarantine diseases, kit and application of method
InactiveCN106947837ASimple methodThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseTrue positive rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection on melon quarantine diseases, especially relates to a method capable of synchronously and quickly detecting RT-PCR detection primer group of two melon quarantine diseases, i,e., cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV) and acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli (Aac), a kit and application of the method. According to the method provided by the invention, specific primers CGMMV-F / CGMMV-R, BFB-F / BFB-R are designed specifically for cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease and acidovorax avenae subsp. Citrulli disease, and a RT-PCR detection technique is combined, synchronous detection and identification of the two diseases can be realized. The method provided by the invention is a specific, sensitive, convenient and cost-effective detection method which can synchronously and quickly detect CGMMV and Aac, can ensure the sensitivity and specificity of the detection, meanwhile, detection cost is reduced, time is saved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
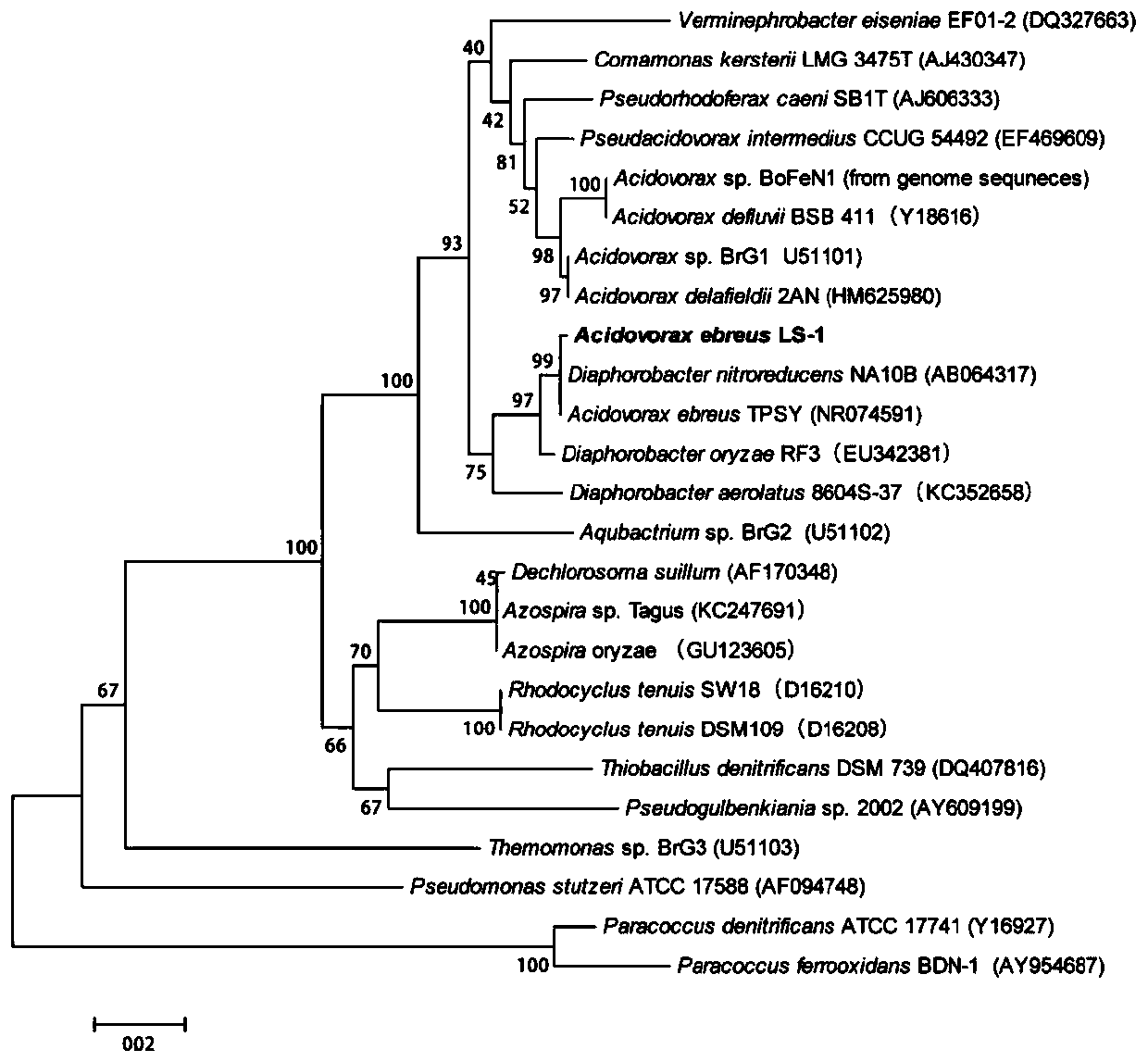
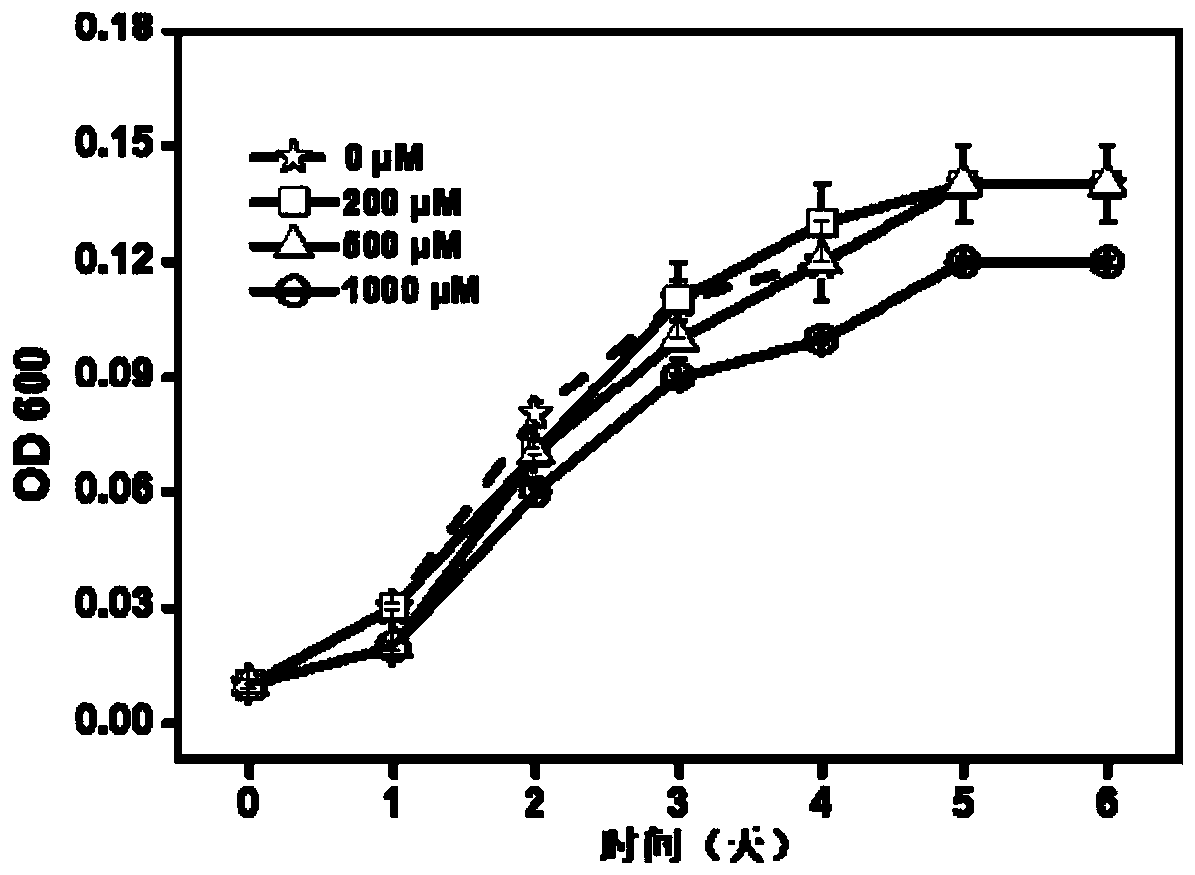
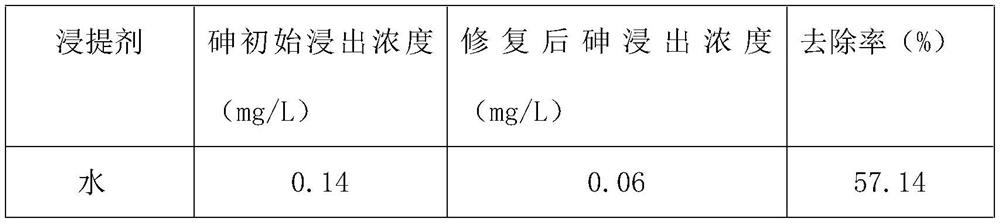
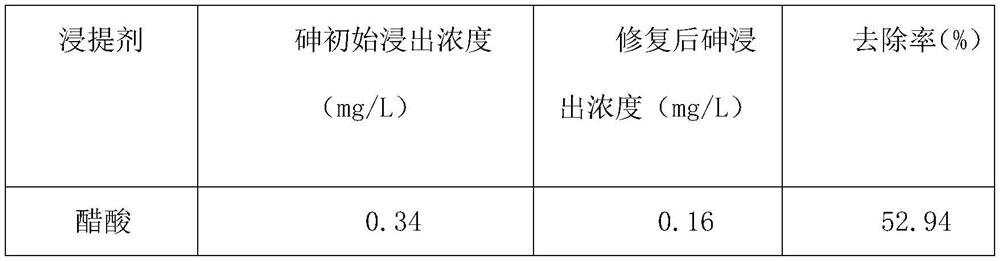
New application of Acidovorax LS-1, and kit for repairing arsenic pollution, and applications thereof
ActiveCN110467274AEasy to enrich and absorbImprove bioavailabilityWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentArsenic pollutionBioavailability
The invention relates to a new application of Acidovorax LS-1, and a kit for repairing arsenic pollution, and applications thereof. The new application is the application of the Acidovorax LS-1 in repairing of arsenic pollution, wherein the Acidovorax LS-1 is added to an arsenic pollutant under anaerobic conditions to reduce pentavalent arsenic into trivalent arsenic, and the Acidovorax LS-1 has apreservation number of CGMCC NO: 11555. According to the present invention, the research results show that the Acidovorax LS-1 can reduce pentavalent arsenic into trivalent arsenic under anaerobic conditions, wherein the bioavailability and the mobility of the trivalent arsenic are much higher than the bioavailability and the mobility of the pentavalent arsenic, such that the activity of arsenicin the environment can be improved through the treatment so as to easily clear or reutilize the trivalent arsenic in the subsequent process; and with the application of the Acidovorax LS-1 in treatment of arsenic pollution, the pentavalent arsenic can be reduced into trivalent arsenic so as to be easily absorbed and enriched, such that the application has good application prospect in the repairingof arsenic pollution.
Owner:广东省科学院南繁种业研究所
Compound bactericide containing bronopol and amino-oligosaccharin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110250178AImprove the effect of prevention and controlGood antibacterial effectBiocideDisinfectantsBacteroidesBronopol
The invention provides a compound bactericide containing bronopol and amino-oligosaccharin and a preparation method thereof, the mass ratio of bronopol to amino-oligosaccharin is 25-60: 0.4-0.8. The bromonol and the aminooligosaccharide have synergistic effect within a certain compound proportion range, have chemical protection effect on crops in the actual use process, and obviously improve the prevention and control effect of the crops on bacterial diseases compared with single dose alone, the compound bactericide has wide sterilization range, is used for prevention and control of melon bacterial gummy stem blight, field melon bacterial angular leaf spot and most bacteria and fungi on vegetables, and has obvious prevention and treatment effects on pseudomonas, acidovorax, xanthomonas, erwinia and coryneform bacteria.
Owner:山东亿嘉农化有限公司
Microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and oilseed rape planting method thereof
ActiveCN112980732AIncrease productionIncrease harvestPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and an oilseed rape planting method thereof. The microbial agent provided by the invention comprises the following bacteria: a) at least one of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthobacter, flavobacterium and wautersia; B) acetobacter, and c) azospirillum. The microbial agent provided by the invention improves the yield of oilseed rape, and is matched with a specific oilseed rape planting method to increase the yield of oilseed rape per mu, reduce the nitrogen fertilizer demand, reduce harmful germs, restore the number of microorganisms in soil and increase the diversity of the microorganisms.
Owner:GUANGDONG RICHHOLD BIOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
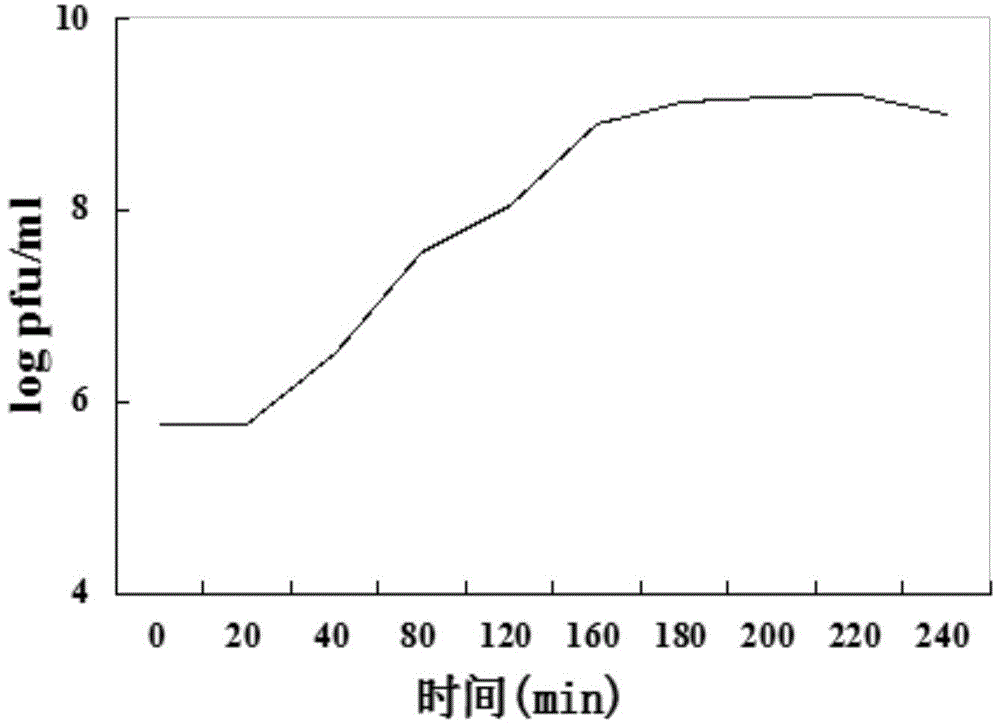
Rice bacterial brown streak germ phage and application thereof
ActiveCN104630154AStrong cracking abilityBiocideMicroorganism based processesInfected cellAnaplasma phagocytophilum
The invention discloses a rice bacterial brown streak germ phage and an application thereof. The classification term of the phage is rice bacterial brown streak germ phage AP1 (Acidovorax avenae subsp.Avenae phage AP1), and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2014599. The application comprises an application of the rice bacterial brown streak germ phage in preparation of a phage preparation used for inhibiting rice bacterial brown streak germs, an application for inhibiting the rice bacterial brown streak germs and an application of preventing and treating the rice bacterial brown streak germs. The rice bacterial brown streak germ phage disclosed by the invention can specifically crack the rice bacterial brown streak germ, the burst size is about 160PFU / infected cells, and the cracking performance is stronger, so that the rice bacterial brown streak germ phage can be used for preventing and treating rice bacterial brown streak caused by the rice bacterial brown streak germs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
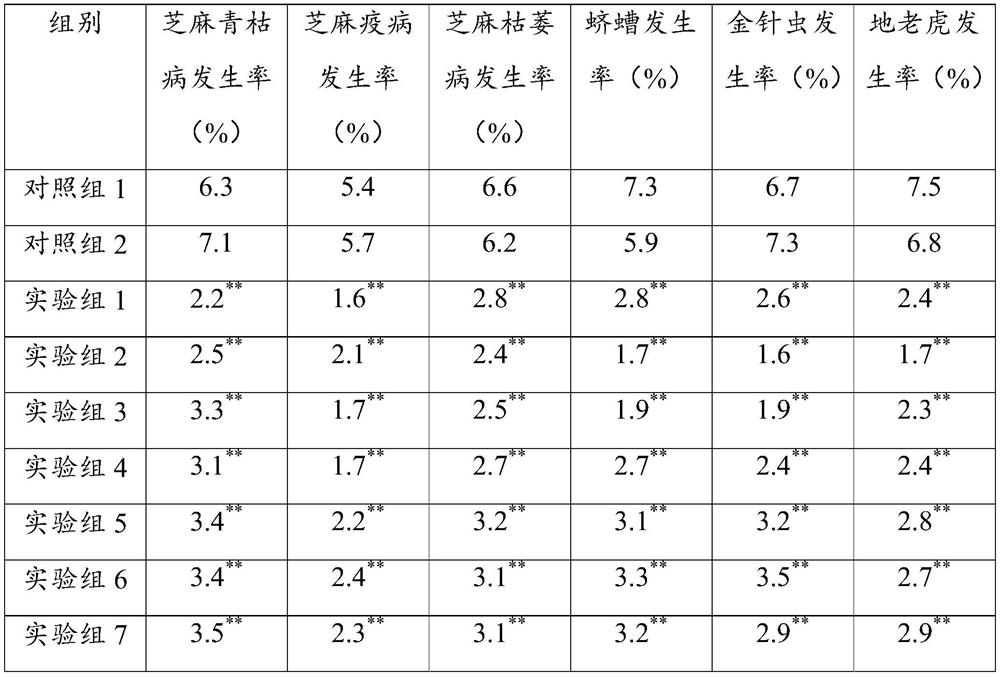
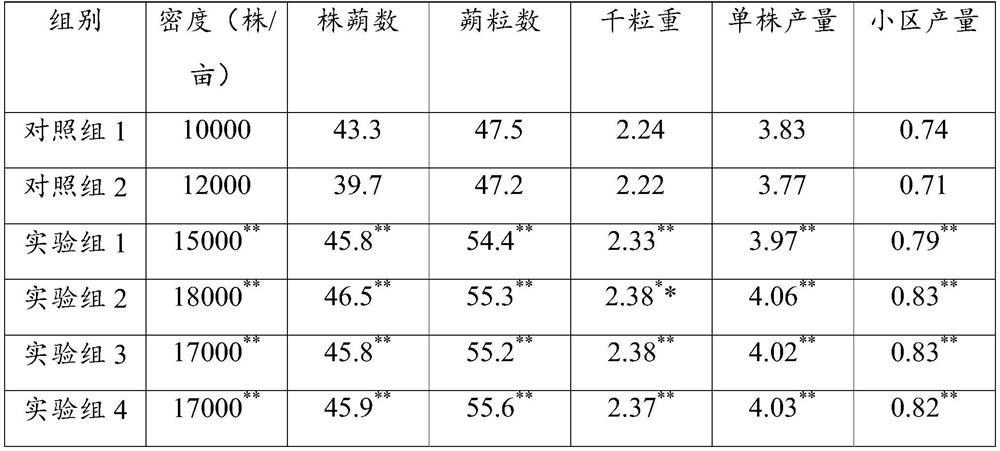
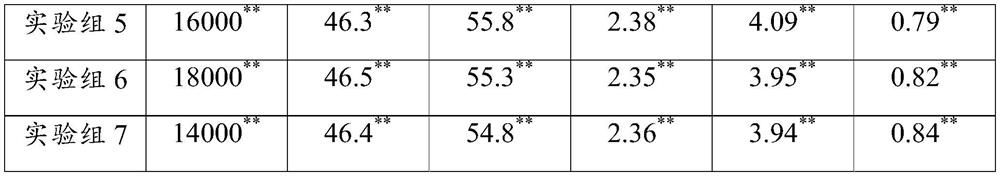
Microbial agent and planting method for promoting sesamum indicum growth
PendingCN113215041AIncrease vitalityIncrease planting densityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses a microbial agent and a planting method for promoting sesamum indicum growth. The microbial agent comprises the following bacteria of a) at least one of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidothiobacter, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthobacter, flavobacterium and wautersia; and b) Frankia, and c) xanthobacter. The microbial agent provided by the invention can improve the vitality of sesamum indicum root systems, increase the mass production of sesamum indicum and improve the disease resistance of sesamum indicum; and the planting method can improve the planting density of the sesamum indicum and reduce the dependence of excessive fertilizer application.
Owner:GUANGDONG RICHHOLD BIOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
Isolation and expression of a gene for a nitrilase from acidovorax facilis 72W
Recombinant microbial strains expressing nitrilase enzymes and useful as biocatalysts for hydrolyzing nitrile-containing substrates are provided. The recombinant cells were transformed with an exogenous gene isolated from Acidovorax facilis 72W encoding a thermostable nitrilase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of nitrile-containing substrates to carboxylic acids under mild reaction conditions. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrilase gene and the putative amino acid sequence encoded by the nitrilase gene are provided.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Primers and primer sets for use in methods to detect the presence of Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli
The present invention relates to oligonucleotide primers and primer sets that can be used to identify the bacterial pathogen Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli in a test sample.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
Bacillus acidovorax capable of producing cream fruity flavor and application of bacillus acidovorax
PendingCN114181848ABoosts Fermented FlavorLow total acidBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyKetone
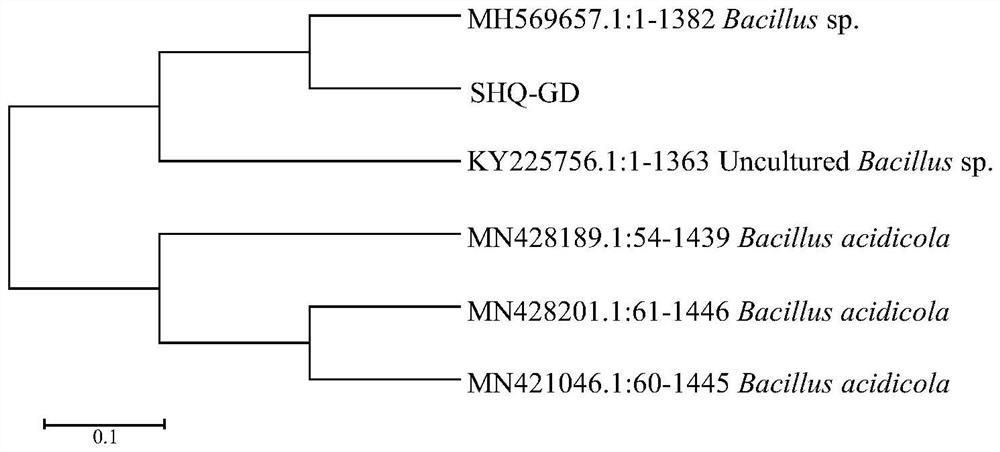
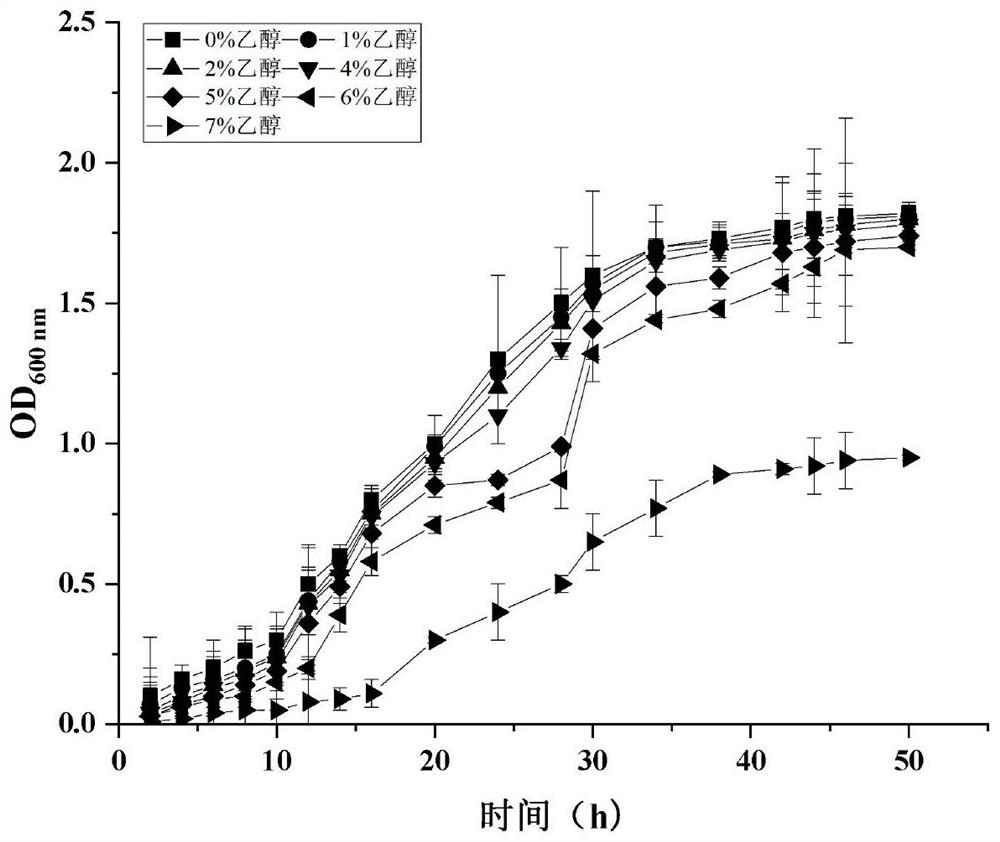
The invention discloses bacillus acidophilus capable of producing cream fruity flavor, the name of the bacillus acidophilus is SHQ-GD, the classification name of the bacillus acidophilus is bacillus acidophilus, the preservation number of the bacillus acidophilus is CGMCC No.23421, the preservation date of the bacillus acidophilus is September 15, 2021, the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number of the bacillus acidophilus is CGMCC No.23421, the preservation number of the bacillus acidophilus is CGMCC No.23421, the preservation number of the bacillus acidophilus is CGMCC No.23421, and the preservation number of the bacillus acidophilus is CGMCC No.23421. And Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No.1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The table vinegar obtained by fermenting the acid bacillus SHQ-GD can generate esters with fruit fragrance, ketones with butter fragrance, aldehydes with green grass fragrance and acids with cheese fragrance, so that the flavor of liquid fermented vinegar is greatly enriched.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for repairing arsenic and antibiotic polluted soil through cooperation of bacteria and magnetic diatomite
PendingCN114789193AAchieve the purpose of repairReach the adsorption functionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAcidovorax sp.Bacterial strain
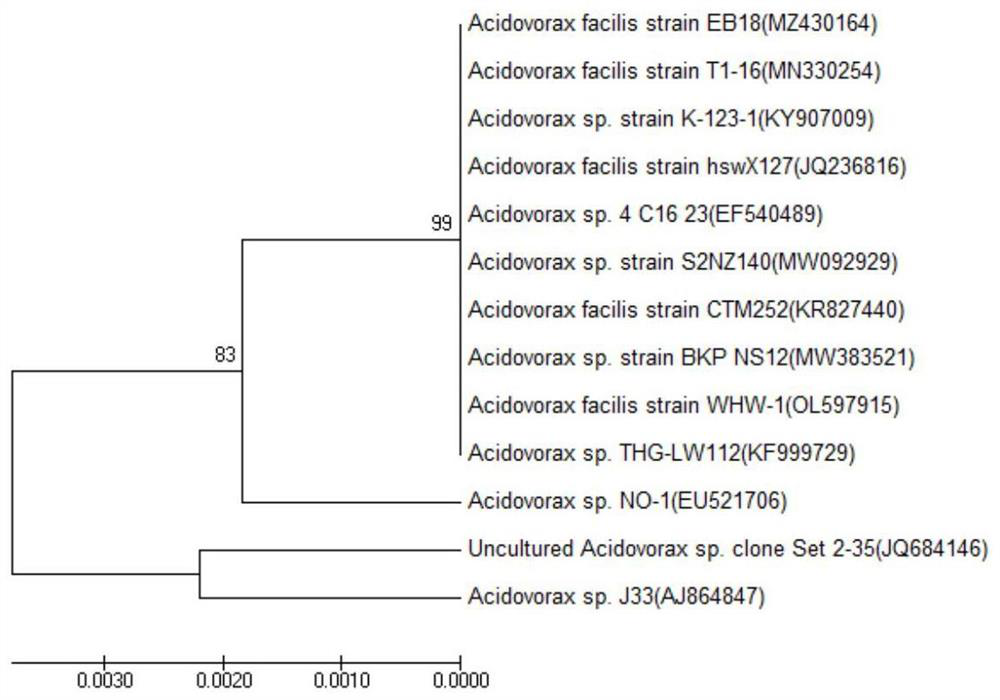
The invention discloses a method for repairing soil polluted by arsenic and antibiotics through cooperation of bacteria and magnetic diatomite. The method comprises the following steps of bacterial strain separation, strain enrichment culture, magnetic diatomite material preparation and soil repairing. The method comprises the following steps: selecting acidovorax agilis WHW-1, and carrying out enrichment culture on the acidovorax agilis WHW-1 in an enrichment culture medium; then, the strain, divalent manganese, a carbon source and the like are added into the composite polluted soil together and stirred uniformly, microorganisms are induced to generate biological manganese oxides, the biological manganese oxides, trivalent arsenic and antibiotics in the soil are subjected to a series of physical-chemical-biochemical reactions, water-soluble arsenic in the soil is converted into a stable state, and the soil is polluted by the microorganisms. The bio-availability of arsenic in the soil is reduced, so that the aim of repairing the arsenic is achieved, and meanwhile, the bacteria and the biological manganese oxide induced by the bacteria convert antibiotics into carbon dioxide and water through intracellular metabolism, oxygenolysis and the like. The process is simple to operate, low in treatment cost and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
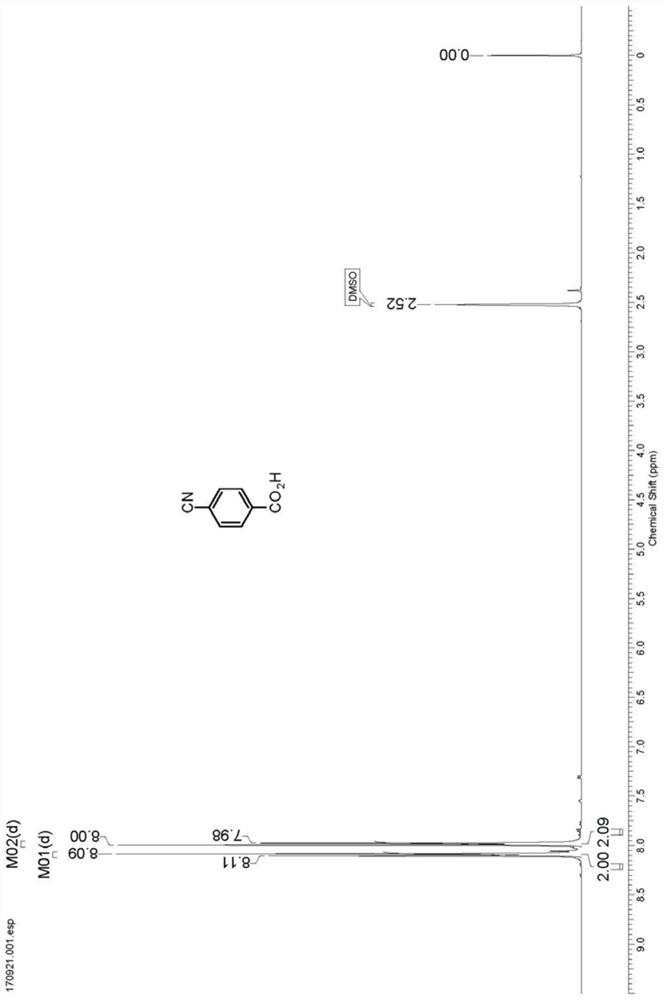
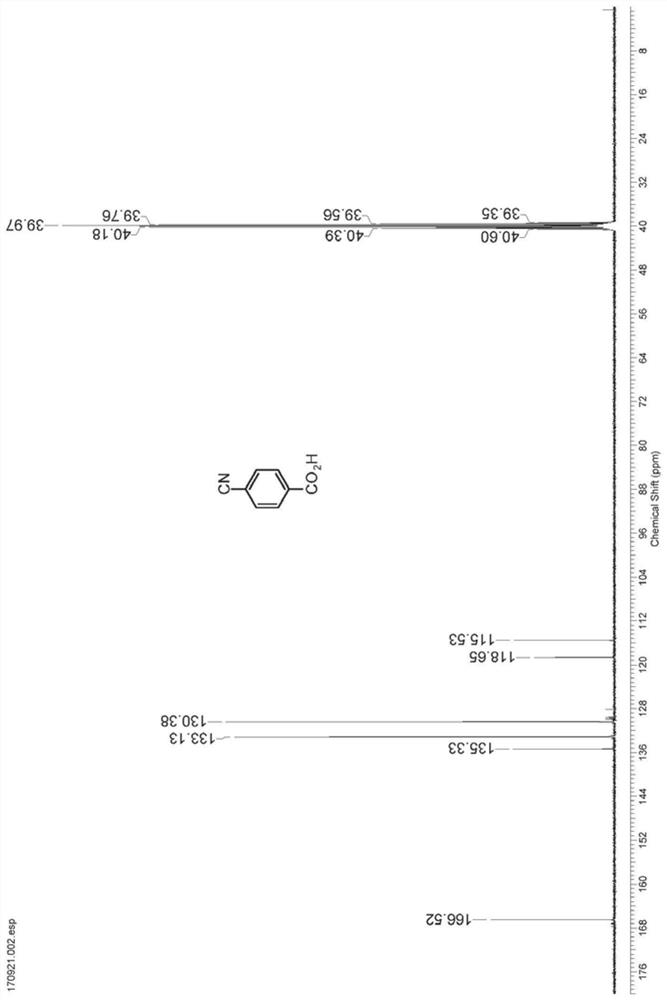
A nitrilase that can hydrolyze terephthalonitrile to p-cyanobenzoic acid
The invention discloses nitrilase N1 and its gene derived from Pantoea sp. ) nitrilase N3 and its gene, Leptolyngbya sp. nitrilase N4 and its gene, Brassica oleracea var. oleracea nitrilase N5 and its gene and Camelina sativa nitrilase N6 and its gene, and using the nitrilase as a biocatalyst to prepare p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate p-cyanobenzoic acid. The resting cells of the corresponding nitrilase can catalyze 100g / L of the substrate, and the conversion rate is greater than 99%. The method has the remarkable characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution, simple process route, etc., and has great industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Composite microbial bacterial agent for treating soil pollution and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108251330BEfficient degradationSimple manufacturing methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent comprises the following raw material components: a pseudomonas japonica culture, a comamonas testosteroni culture, a microbacillus culture and an acidovorax delafieldii culture; according to the invention, multiple bacterial cultures are subjected to mixed fermentation to prepare the compound microbial agent; and thecompound microbial agent has an effective degradation effect on organic residues such as nitrobenzene compounds formed by insecticides or pesticides in soil, and furthermore, special strains are subjected to mixed cultivation and multiple strains are subjected to mixed fermentation to provide a simple and easy preparation method.
Owner:江苏世邦生物工程科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com