Application of amaranthus in plant disease prevention and treatment
A technology of plant diseases and plant pathogens, applied in the fields of application, plant growth regulators, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of pesticide residues, destruction of ecological balance, pollution of the environment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Preparation of Example 1 Amaranth Leaf Extract (illustrated with ethyl acetate as the extraction solvent)
[0021] Take amaranth leaves, wash them, dry them in the sun until the water content is 3%, and at room temperature, grind them into 100-120 mesh fine powder through a high-speed pulverizer at a speed of 8000-12000r / min to obtain amaranth leaf powder; take 10g of amaranth leaf powder , add analytically pure ethyl acetate 180mL, shake on a shaker at 90-120r / min at 20-25°C for 30h, filter, and collect the filtrate; Shake at -120r / min for 30h on a shaker, filter, and collect the filtrate; repeat this for the filter residue once, and combine the filtrate three times to obtain the extract; put the obtained filtrate into a rotary concentration evaporator, The temperature of the water bath is 40-43°C, the condensation temperature is 8-10°C, and the rotation speed is 80-120r / min, and concentrated to a paste to obtain the extract.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2 The inhibitory effect of amaranth leaf extract on watermelon bacterial fruit spot and citrus canker
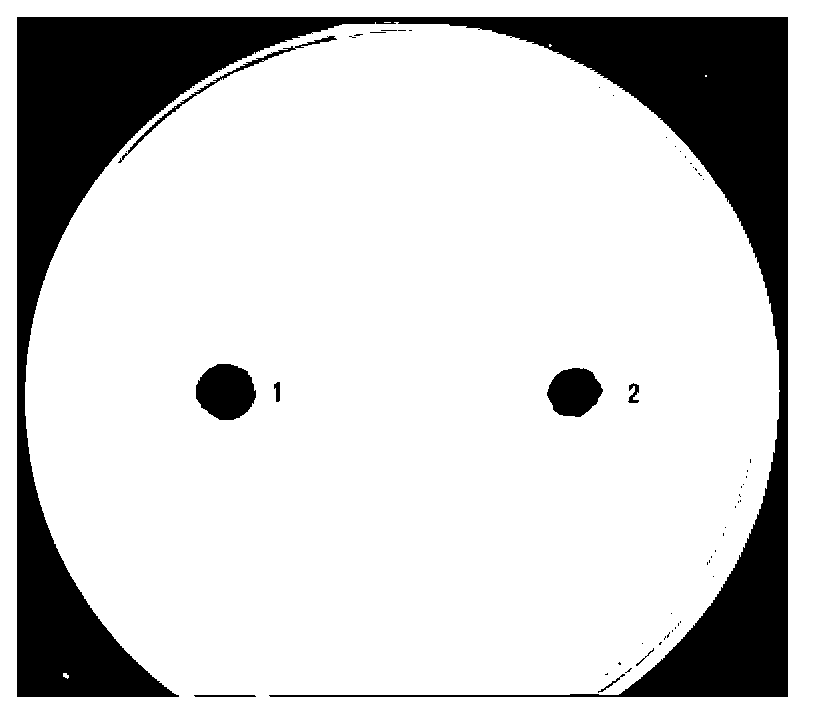
[0023] Take 1g of amaranth leaf extract and add 5-10mL of analytically pure ethyl acetate to dissolve to obtain the active substance to be tested. The antibacterial effect was detected by plate punching method. The watermelon bacterial fruit blotch suspension and the citrus canker sore suspension (1×10 8 cfu / mL) 60 μL was evenly spread on the NA plate, and then a hole was made on the central side of the plate (φ=5mm), and the active substance to be tested was injected, and ethyl acetate was injected symmetrically on the other side of the plate as a control. Incubate 50 μL of the well at 28°C for 24-48 hours, and observe the antibacterial situation. Each treatment was repeated 3 times. It can be seen by observation that the extract of amaranth leaves has inhibitory effects on watermelon bacterial fruit spot and citrus canker, see figure 1 and figure 2 , w...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 The inhibitory effect of amaranth leaf extract on rice sheath blight bacteria
[0025] Take 1g of amaranth leaf extract and add 5-10mL of analytically pure ethyl acetate to dissolve to obtain the active substance to be tested. The inhibitory activity of the extracts against rice sheath blight was detected by punching method. Put the rice sheath blight bacteria in the center of the PDA plate, punch holes at 1cm on both sides, inject the active substance to be tested on one side, and inject ethyl acetate on the other side as a control, repeat each treatment 3 times, and place at 25-28°C In the incubator, cultivate for 48 hours, and observe whether there is any antibacterial phenomenon. It can be known by observation that the extract of amaranth has inhibitory effect on rice sheath blight bacteria, see image 3 , while the control ethyl acetate had no inhibitory effect on sheath blight bacteria. It shows that there are antibacterial active substances in the le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com