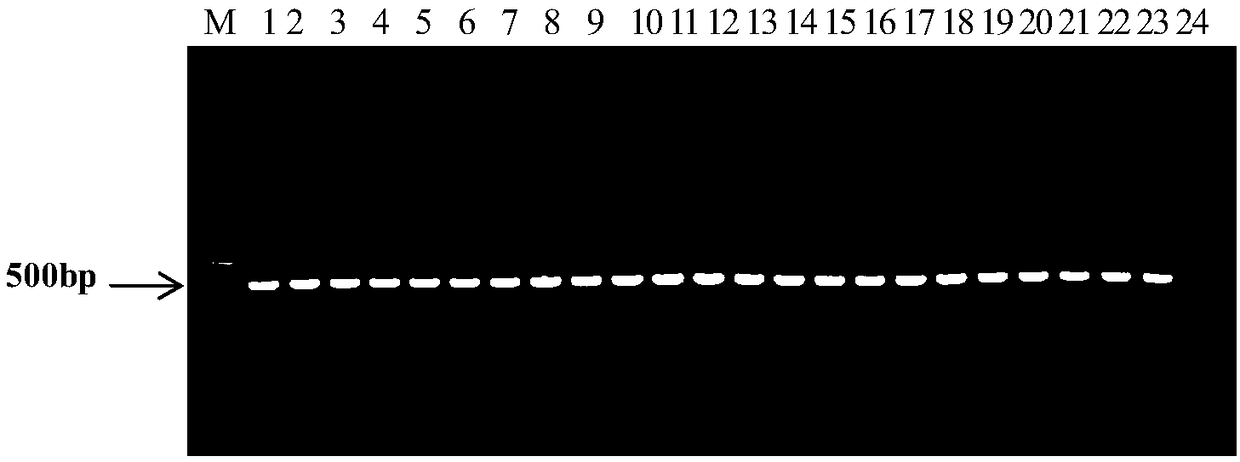
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Bacterial fruit blotch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial fruit blotch (BFB) affects cucurbit plants around the world and can be a serious threat to farmers because it spreads through contaminated seed. BFB is the result of an infection by Gram-negative Acidovorax citrulli bacteria, which has only been recently studied in detail. Members of A. citrulli are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria with the dimensions 0.5× 1.7 μm. They move via polar flagella. No known reliable sources of BFB resistance exist today, so seed hygiene and thorough testing of breeding facilities are the best way to control spreading. No known control methods, however, are extremely reliable for reducing BFB infection.
Bio-control strain for preventing and controlling bacterial fruit blotch of watermelon
InactiveCN102174431AConducive to pollution-free productionConducive to export tradeBiocideBacteriaGrowth promotingMicrobiology
The invention relates to a bio-control strain JC65 for preventing and controlling bacterial fruit blotch of watermelon, and belongs to the technical field of crop disease prevention and control. The bacteria are Bacillus sp.; and the bacteria are subjected to shaking culture for 20 to 24 hours in load balance (LB) culture solution at the temperature of 30 DEG C and at the revolution speed of 180rpm, then the solution is centrifuged for 10 minutes at the revolution speed of 6,000rpm, the wet bacteria and the bacteria preservation solution are prepared into bactericide in a ratio of 1:40 (g / ml), and the total concentration of living bacteria in the finished product is 1*10<9> to 1*10<12>cfu / ml. The bactericide is diluted to the concentration of 1*10<8>cfu / ml in use, the prevention effect on the bacterial fruit blotch of watermelon is 50 to 90 percent, and the yield increasing effect on a sick field is 10 to 200 percent. The growth promoting effect on the disease-free plants can reach 10to 200 percent, and the yield increasing effect on the disease-free field is 5 to 20 percent. The bactericide can be blended with water for spraying or made into compost for use, and can also be diluted for irrigating roots during transplanting.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
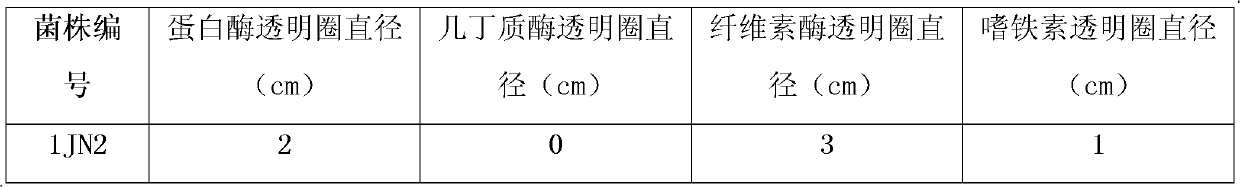
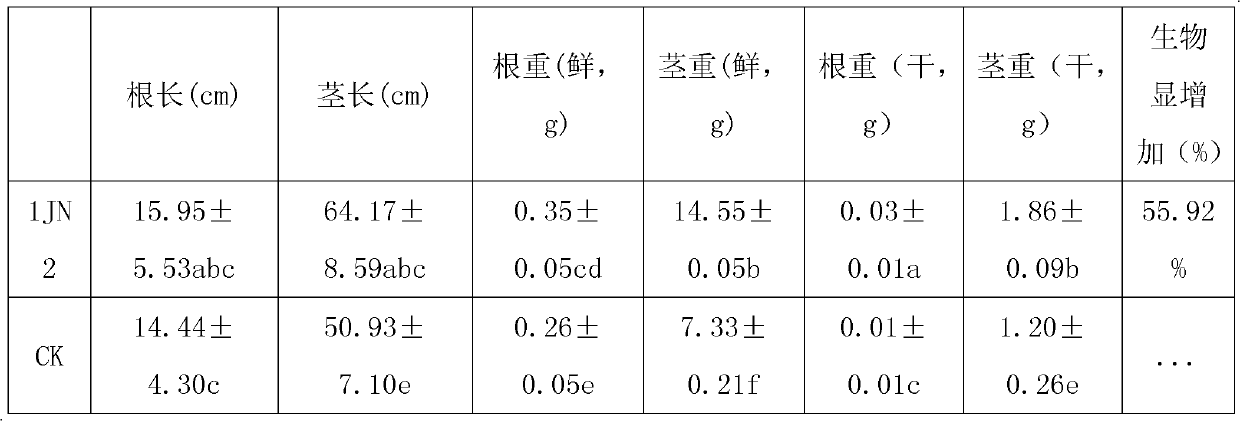
Bio-control bacteria strain 1JN2 for preventing and treating bacterial fruit blotches of watermelons and application thereof
ActiveCN102604869AConducive to pollution-free productionConducive to export tradeBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop disease prevention and treatment and discloses a bio-control bacteria strain 1JN2 for preventing and treating bacterial fruit blotches of watermelons and application thereof. The bio-control bacteria strain 1JN2 is named as Bacillus axarquiensis in classification, and is filed at General Microbiological Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Committee with CGMCC No.5731 on January 16, 2012. The bio-control bacteria strain 1JN2 is cultured in LB (luria-bertani) broth at the temperature of 28 DEG C by vibration of 180rpm for 12-16 hours, centrifuged by 6000rpm for 10 minutes, diluted by sterilization water to prepare bactericide, and total concentration of viable bacteria in the finished bactericide is 1X10<9>-1X10<10>CFU / ml. The experiment results in a greenhouse indicates that the bio-control bactericide with the 1JN2 has evident growth acceleration effect to watermelons, biomass live weight is increased to 55.92% and evident prevention effect to disease of fruit blotches of the watermelons, disease incidence can be reduced by 50.13%.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip for watermelon bacterial fruit blotches as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102128832AAccurate detectionMeet the needs of residue detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAptamer
The invention discloses a colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip for watermelon bacterial fruit blotches as well as preparation and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of colloidal gold detection. A detected substance is firstly bound with colloidal gold coupled Aptamers (1) in a competitive way under the action of a capillary siphoning effect formed by an absorbent pad, and residual aptamers drift to a detection zone to be bound with streptavidin-Aptamers (2) and realize color development in the presence of excessive coupled Aptamers (1); and the V region binding sites of the colloidal gold coupled Aptamers (1) bound with the detecting substance are occupied by the detected substance, so that the Aptamers can only cross the detection zone and drift to a reference zone to be unspecifically bound with streptavidin-Aptamers (3) at binding sites in a C region and carry out color comparison with the detection zone to semi-quantitatively detect the residual quantity of watermelon bacterial fruit blotches in the sample. The test strip can meet the requirement of food safety on the residual quantity of watermelon bacterial fruit blotches, is suitable for feeds, meat producing plants and government detection mechanisms, and has the characteristics of convenience for using, economical efficiency, rapidness, easiness in manufacturing and low cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fruit blotch immune colloidal gold detection test strip, and monoclonal antibody and hybridoma cell strain thereof
ActiveCN104991069AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisCelluloseColloid
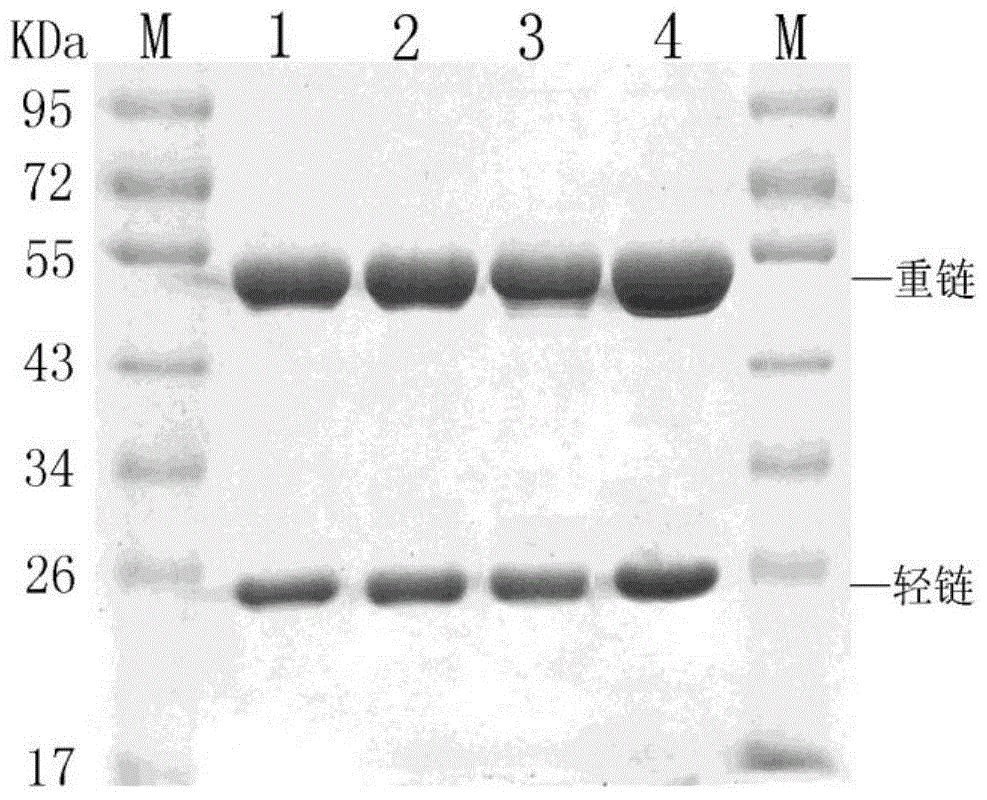
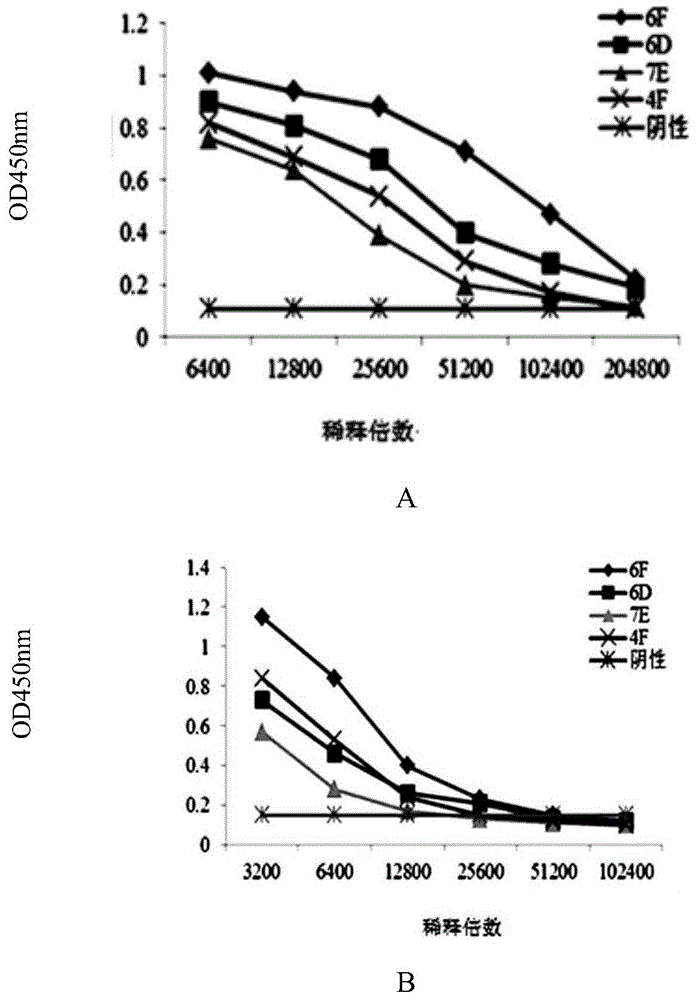
The invention relates to a melon bacterial fruit blotch immune colloidal gold rapid detection test strip. The test strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal gold sample closely connected with the sample pad, a cellulose membrane arranged on the colloidal gold pad and closely connected with the colloidal gold pad, and a water absorption pad closely connected with the other end of the cellulose membrane, one end of the cellulose membrane away from the colloidal gold pad is provided with a quality control line, and the cellulose membrane between the quality control line and the colloidal gold pad is provided with a detection line, wherein the colloidal gold pad is provided with a monoclonal antibody coupling with colloidal gold, the monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.10413, and the detection line is formed by the monoclonal antibody. The fruit blotch immune colloidal gold rapid detection test strip adopts the colloidal gold pad and the detection lime to be respectively sprayed with the new screened monoclonal antibody and has high detection specificity and sensitivity on fruit blotch. The invention also relates to monoclonal antibody for the test strip, and the hybridoma cell strain thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch biocontrol bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104894008AGood antibacterial effectStrong plant growthBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention provides a cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch biocontrol bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and the application thereof. The biological preservation number of the obtained cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch biocontrol bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain JD001 is CGMCC No.10421. The strain JD001 is separated from a soil sample of a watermelon producing area and is preserved, has good bacteriostasis on a plurality of kinds of phytopathogen bacteria and can be used for biological control over cucurbit bacterial fruit blotches. New microbial resources are provided for prevention and cure of the cucurbit bacterial fruit blotches, and the good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Extraction method of essential oil of artemisia argyi and application thereof in inhibiting pathogenic bacteria of plants
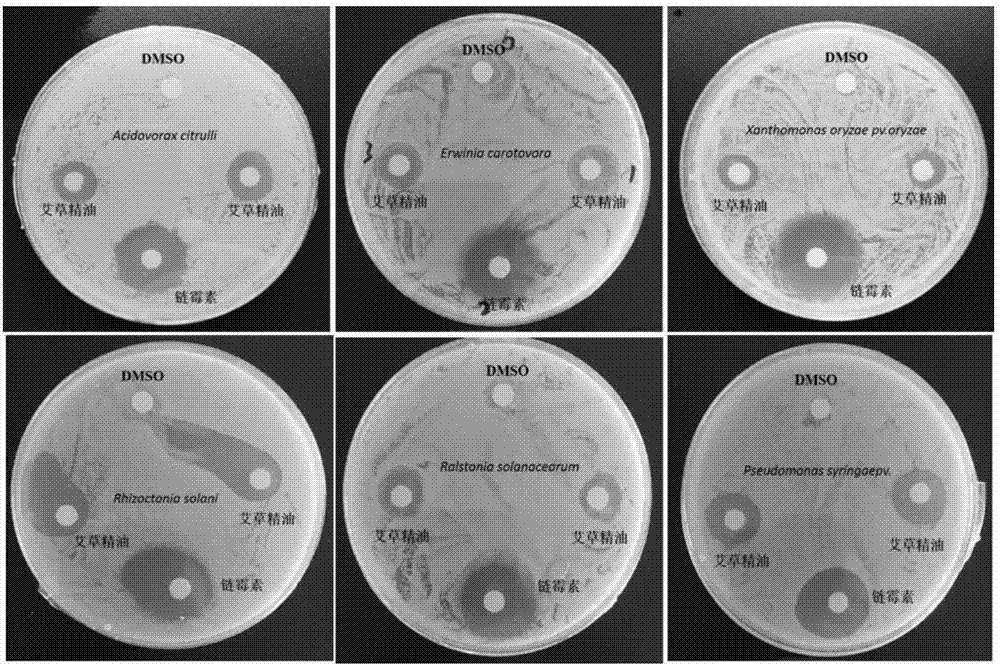
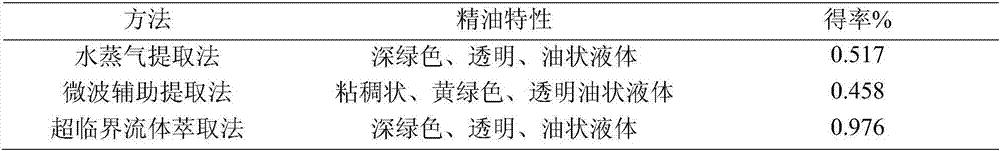
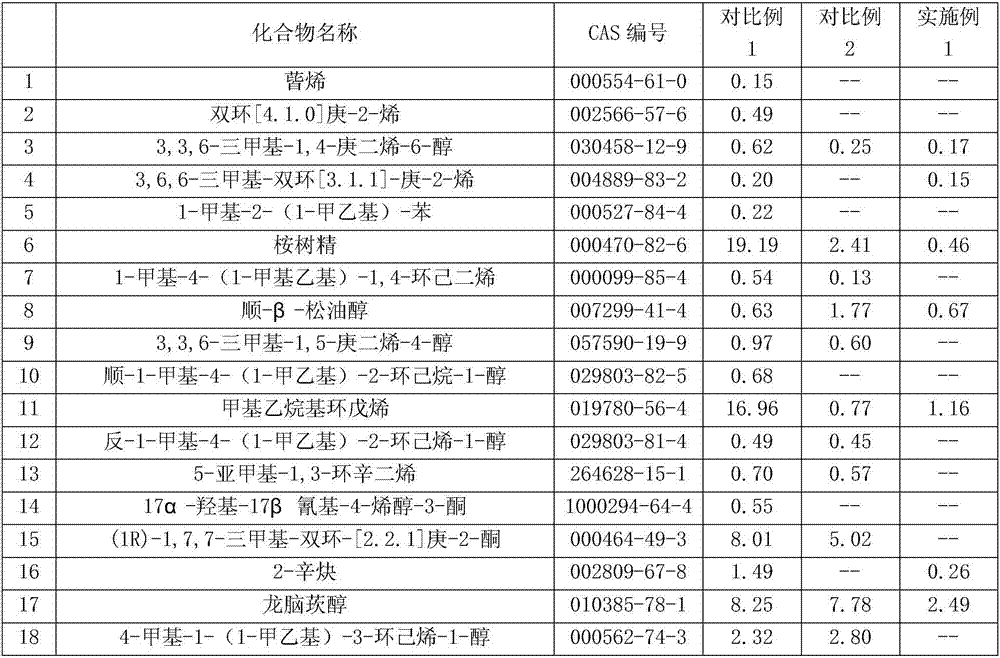
The invention relates to an extraction method of essential oil of artemisia argyi. The extraction method comprises the following steps: obtaining plants of artemisia argyi from saline land, drying plants of artemisia argyi at a temperature of 40 DEG C until the weight is constant, grinding and sieving the plants to obtain artemisia argyi powder; adding an artemisia argyi powder sample into a supercritical CO2 extraction apparatus, starting a water bath until the extraction temperature reaches 35 DEG C, carrying out extraction for 90 minutes under following conditions: extraction pressure: 20 MPa, CO2 flowing speed: 20 g / min, and temperature of separation kettle: 30 DEG C; after extraction, washing out the extract by anhydrous ethanol, carrying out centrifugation to remove wax, removing water by anhydrous sodium sulfate; and subjecting filtrate to reduced pressure distillation at a temperature of 30 DEG C to recover ethanol and obtain wax free volatile oil of artemisia argyi. The provided method can quickly and efficiently extract essential oil of artemisia argyi. The essential oil comprises many components. The aromatic components of essential oil of artemisia argyi can be well maintained. The essential oil of artemisia argyi has a good effect on inhibiting xanthomonas oryzae, ralstonia solanacearum, pathogenic bacteria that causes cucumber bacterial angular leaf spot, pathogenic bacteria that causes bacterial fruit blotch of cucurbit, potato rhizoctonia solani, soft-rot fungi of cabbage, and the like.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and method for identifying different subgroups of bacterial fruit blotch of melons
ActiveCN108179207AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerNucleotide
The invention relates to inspection and quarantine of bacterial fruit blotch of melons, and particularly relates to a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and a method for identifying different subgroups of bacterial fruit blotch of melons. A PCR primer group for identifying different subgroups of bacterial fruit blotch of melons, which is provided by the invention, comprises a forward primer BFB and reverse primers BFB1 and BFB2, and nucleotide sequences of the primers are as follows: BFB: 5'ATGAAGCGTACTGTTCAG-3'; BFB1: 5'ACCATCGATATTAGCATC-3'; BFB2: 5'-TTAAGGAGCAAACGTGC-3'.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
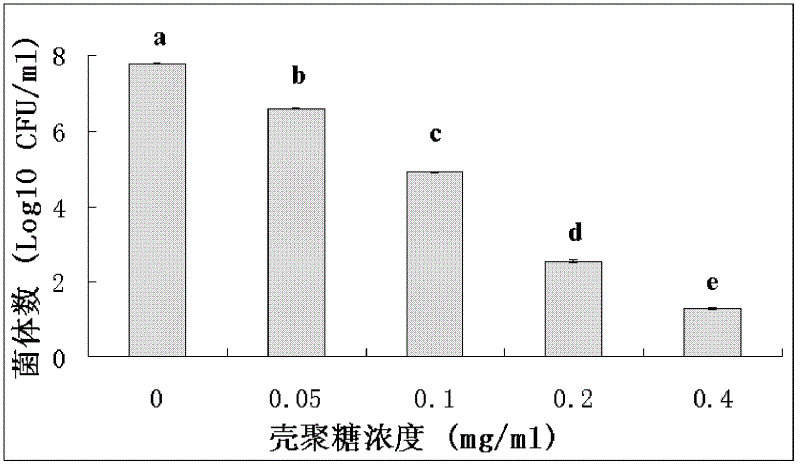
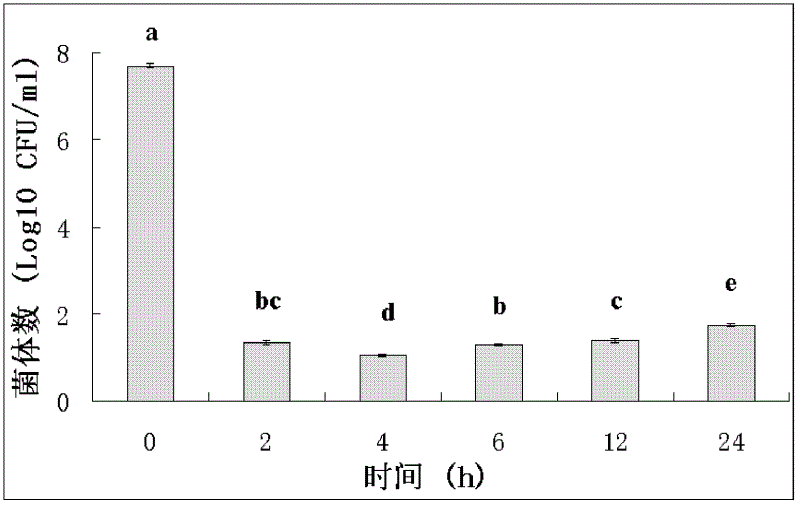
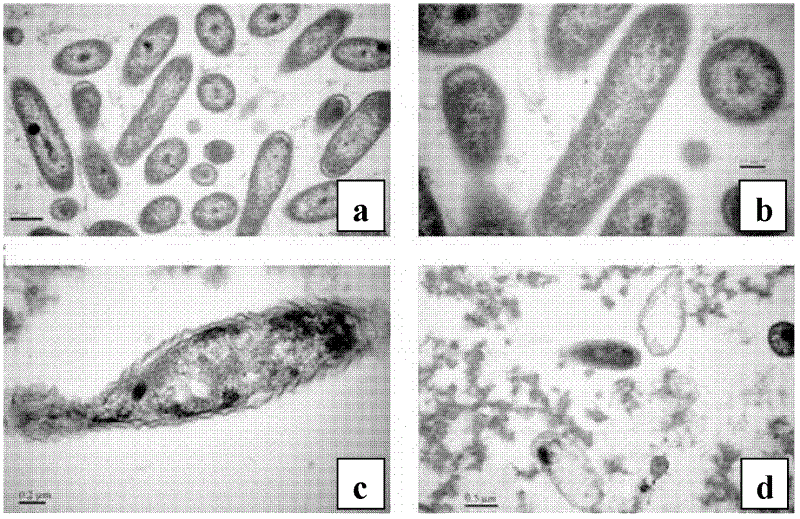
Application of chitosan in prevention and control of bacterial fruit blotch of plants
InactiveCN102613186APromote seedling growthRaw materials are easy to getBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlanting seedCitrullus
The invention discloses application of chitosan in prevention and control of bacterial fruit blotch of plants, wherein the deacetylation degree of the chitosan is more than 85%. The plants are melon plants. The application comprises the steps of placing plant seeds in a chitosan solution to be soaked for 3-5 hours or using the chitosan solution to perform spraying treatment to leaves of the plants at a trefoil stage. The chitosan uses as a main raw material, the prepared and obtained chitosan solution can effectively inhibit the activity of the bacterial fruit blotch and prevent and control the bacterial fruit blotch of the plants. The chitosan solution with certain concentration further can effectively promote growth of watermelon seedlings. The raw material is easily obtained, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, and the chitosan is low in toxicity and harm and good in preventing and controlling effect on the bacterial fruit blotch of melon plants. In addition, the chitosan can further promote the growth of plant seedlings to some extent and is suitable for actual production and easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Immunochromatographic assay test strip for bacterial fruit blotch of melons
InactiveCN104777302ASimple resultIntuitive and accurate result judgmentMaterial analysisBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention specifically relates to an immunochromatographic assay test strip for bacterial fruit blotch of melons. The immunochromatographic assay test strip for the bacterial fruit blotch of melons comprises a support bottom plate arranged on the lowest layer, as well as a sample buffer layer, a bearing layer loading labelled proteins, a coating adsorption layer and a liquid absorption layer, which are sequentially connected and arranged on the support bottom plate, and at least one test line and quality control line is formed on the coating adsorption layer. The immunochromatographic assay test strip for the bacterial fruit blotch of melons is high in specificity, rapid, simple and convenient, wide in application range, convenient to popularize and apply, and capable of being widely used in basic areas.
Owner:河南省农业科学院园艺研究所
Protein chip for rapid quantitative determination of bacterial fruit blotch of watermelon and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102207503AStrong specificityRapid Quantitative DetectionMaterial analysisPositive controlQuantitative determination
Owner:上海慧耘生物科技有限公司
Bacillus velezensis HP-24 and application thereof in preparation of liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch
ActiveCN113755393AOpen up new ways of biological controlEffective controlBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacilli
The invention relates to bacillus velezensis HP-24 and application thereof in preparation of liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch, which can effectively solve the problem of bacterial liquid for preventing and treating fruit blotch caused by melon pathogenic bacteria Acidovorax citrulli and can realize biological prevention and treatment of fruit blotch. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 is classified and named as bacillus velezensis and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation number is CGMCC NO.22973, the preservation date is July 28, 2021, and the preservation address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 has the function of apoptosis of melon pathogenic bacteria watermelon acidophilus, is effectively used for preparing liquid for preventing and treating melon bacterial fruit blotch, and realizes prevention and treatment of fruit blotch. The bacillus velezensis HP-24 and the application thereof can effectively prevent and treat melon bacterial fruit blotch caused by watermelon acidophilic bacteria, develop a new way for biological prevention and treatment of fruit blotch, and have remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY +1
Bacterial fruit blotch seed disinfectant and application thereof
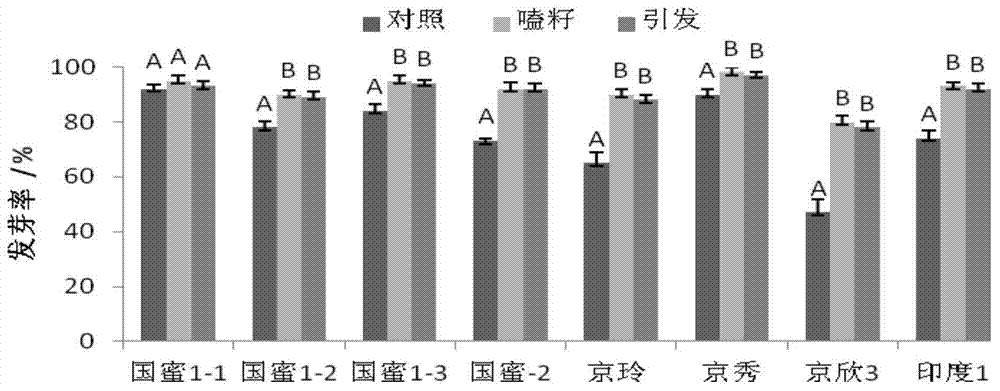
ActiveCN105660694AGerminate fastPromote germinationBiocideSeed and root treatmentChlorine dioxideDisinfectant
The invention belongs to the field of disinfection and control of plant seed-borne diseases, particularly relates to disinfection, prevention and treatment of watermelon bacterial fruit blotch, and discloses a novel compound disinfectant.The disinfectant comprises chlorine dioxide (ClO2) mainly having a disinfection effect, sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) mainly having a germination promoting effect, and potassium iodate (KIO3) mainly having an effect of stabilizer By means of the disinfectant, detected watermelon seeds with bacterial fruit blotch bacteria and artificial simulating watermelon seeds with bacterial fruit blotch bacteria are processed, the germination rate and germination potential of seeds are promoted, and the disinfection effect is remarkable and is obviously better than that of a reported existing bacterial fruit blotch disinfectant and a reported existing disinfecting method.The disinfection method can easily, rapidly and thoroughly kill bacterial fruit blotch bacteria carried by watermelon seeds, is easy to operate, free of toxin and pollution and has huge actual application value.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Melon bacterial fruit blotch germs immunofluorescent quick detection test paper and application thereof
InactiveCN106872696AHigh detection specificityImprove accuracyBiological testingNitrocelluloseMicrobiology
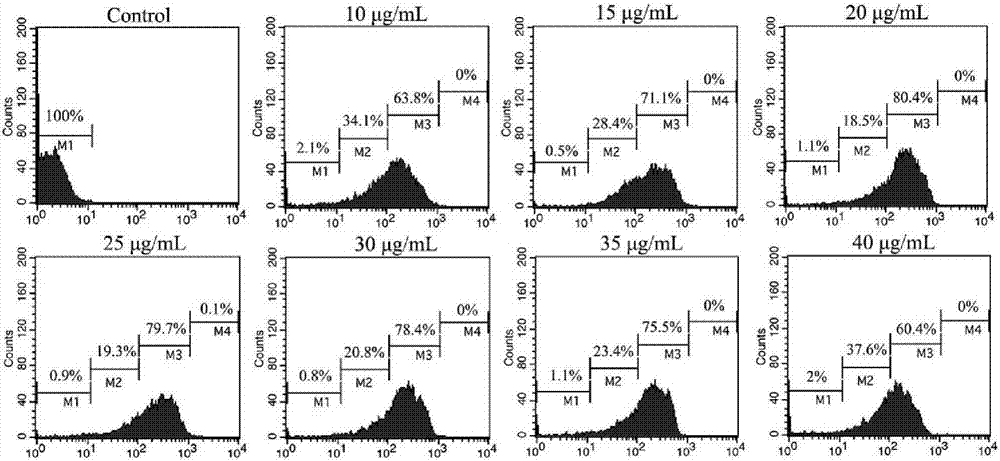
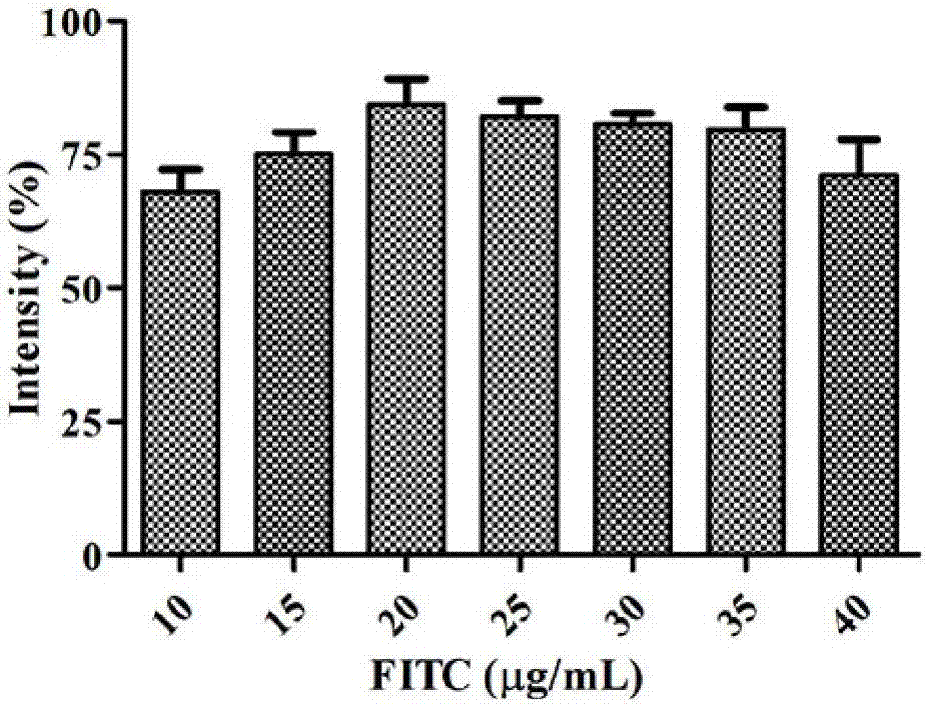
The invention provides a melon bacterial fruit blotch germs immunofluorescent quick detection test paper. The test paper comprises a supporting layer, wherein a sample pad and a water absorption pad are arranged on the supporting layer; a nitrocellulose (NC) membrane is arranged between the sample pad and the water absorption pad; a detection line is arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane and consists of monoclonal antibodies secreted by hybridoma cell strains with the preservation number of No. 10413. The invention also provides a method for detecting melon bacterial fruit blotch germs by using the test paper. A brain-heart infusion culture medium added with FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate) is adopted to culture bacteria, and the cultured bacteria can emit yellow and green fluorescence, so that the bacteria are fluorescent probes; the monoclonal antibodies generated by the hybridoma cell strains with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 10413 are taken as detection antibodies and are sprayed onto the NC membrane to form the detection line. The immunofluorescent quick detection test paper is a mark-free single-line immunofluorescent test paper. In the whole preparation process, the antibodies do not require mark, so that the influence of a mark effect to a detection result is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Seed processing agent for preventing cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch
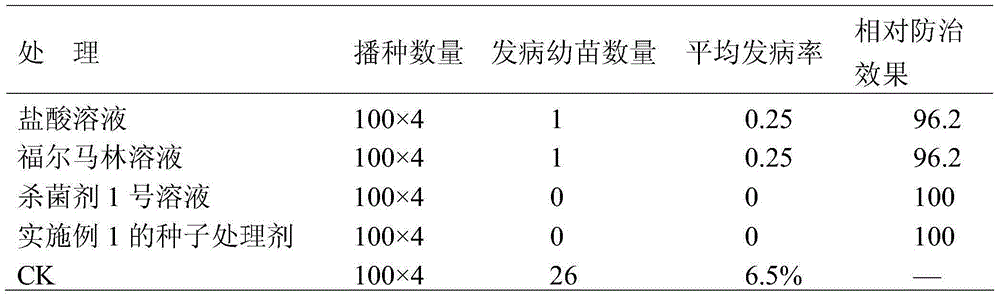
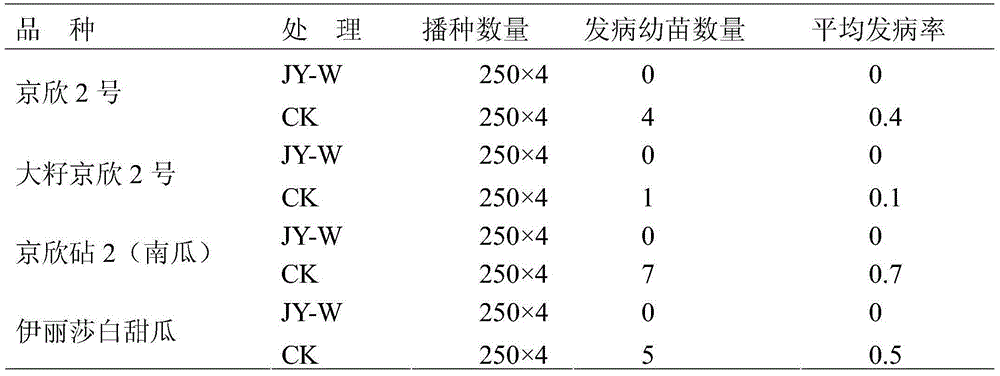
ActiveCN105028478AReduce the carrier rateHigh sterilization rateBiocideDisinfectantsAcetic acidCitrullus
The invention belongs to the field of crop breeding, and specially relates to a seed processing agent for preventing cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch. The processing agent comprises the following raw materials, the mass to volume to volume ratio of which is 1-5 of copper oxychloride to 0.2-2 of acetic acid to 500-3000 of water. Copper oxychloride comes from wettable powder of copper oxychloride, preferably the wettable powder of 50% of copper oxychloride. The acetic acid comes from vinegar, preferably white vinegar. According to the seed processing agent, copper oxychloride and acetic acid are taken as effective components and have a synergistic effect, so that the bactericidal rate is improved. The seed processing agent is suitable for dry seeds and wet seeds, and the bacteria carrying rate of cucurbit seeds is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Watermelon seed disinfection technology for controlling occurrence of bacterial fruit blotch and application of watermelon seed disinfection technology
The invention discloses a watermelon seed disinfection technology for controlling the occurrence of bacterial fruit blotch. The technology comprises the step of disinfecting seeds with a CuSO4 water solution. A result shows that the treated seeds can effectively kill bacterial fruit blotch bacteria carried by the seeds so that the occurrence of field fruit blotch can be reduced after the seeds are planted. Meanwhile, the treatment is triggered by a solid base material so that the germination speed and the uniformity of diploid watermelon seeds can be effectively improved; and the germination obstacle of triploid watermelon seeds can be alleviated and the final germination rate is improved.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Compound for preventing and treating plant pathogenic bacteria and application thereof
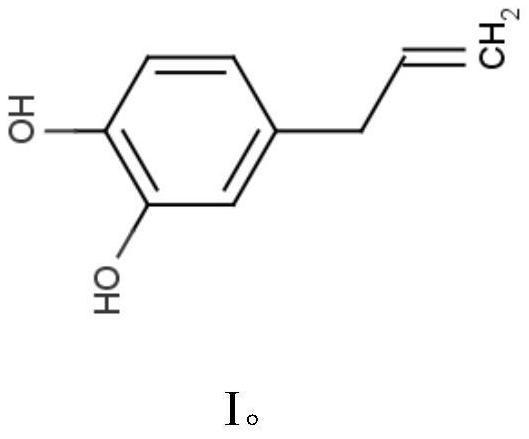
ActiveCN112079692AGood antibacterial effectGood inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
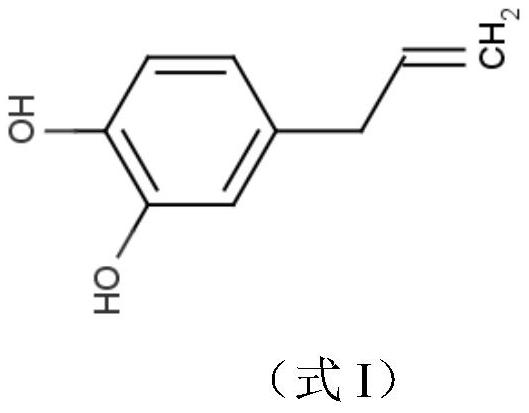
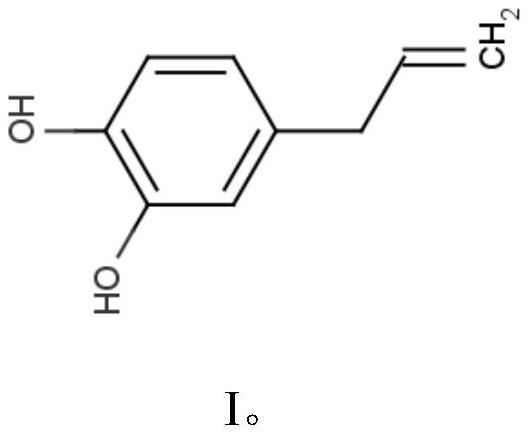
The invention discloses a compound for preventing and treating plant pathogenic bacteria and application thereof. The compound is 4-allyl catechol, tests prove that the 4-allyl catechol has antibacterial activity, and when the test concentration of the compound is 1000 [mu] mol / L, the compound has a good antibacterial effect on xanthomonas campestris pv, xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, xanthomonas citri, bacterial fruit blotch of muskmelon, bacterial wilt of tomato, bacterial angular leaf spot of strawberry, bacterial angular leaf spot of mango, black rot of cabbage and soft rot of potato, and the inhibition rate is 90% or above; meanwhile, in-vivo test results show that the compound has a good inhibition effect on pathogenicity of potato soft rot fungi, and also has a good prevention and treatment effect on mango bacterial angular leaf spot bacteria and melon bacterial fruit blotch bacteria. The results show that the 4-allyl catechol has a broad-spectrum bactericidal effect on plantpathogenic bacteria. Therefore, a foundation is laid for further creating a novel pollution-free botanical pesticide by utilizing a unique plant, namely South China pepper, in China.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Application of 1% isothiazolinone.2% methylene bisthiocyanate missible oil in prevention and treatment of bacterial fruit blotch, and 1% isothiazolinone.2% methylene bisthiocyanate missible oil
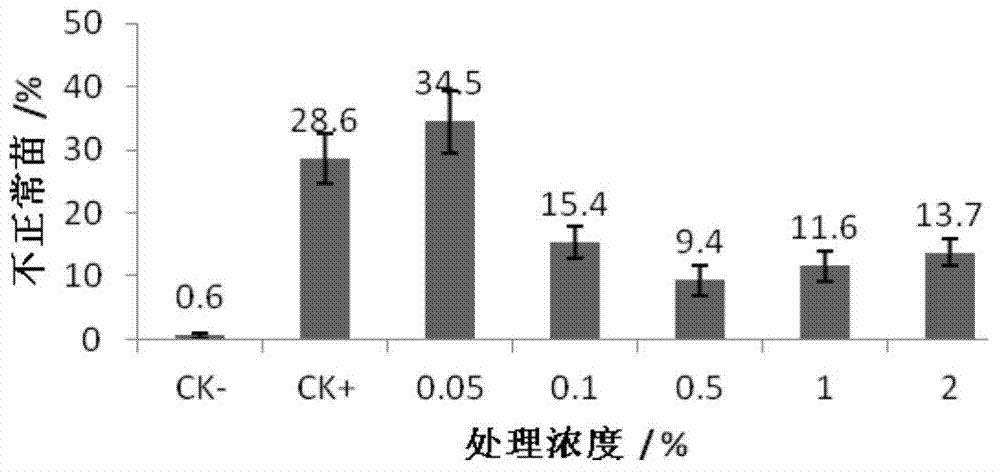
The invention provides an application of 1% isothiazolinone.2% methylene bisthiocyanate missible oil in the prevention and treatment of bacterial fruit blotch, and 1% isothiazolinone.2% methylene bisthiocyanate missible oil, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The optimum use concentration of the 1% isothiazolinone.2% methylene bisthiocyanate missible oil in the field spray prevention and treatment and the optimum soup concentration, the optimum processing time and the like used for processing infected seeds are obtained through the indoor toxicity test, seed processing and the field prevention and treatment in the invention, so the germination percentage of seeds can be improved, the growth of roots can be promoted, a technical support is provided for the scientific and safe use of the missible oil, and a theoretical basis is provided for the prevention and treatment of the fruit blotch.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel method for preventing and treating muskmelon bacterial fruit blotch
InactiveCN106550708AControl bacterial fruit spotIncrease productionBiocideAnimal repellantsChemical controlMusk melon
The invention discloses a novel method for preventing and treating muskmelon bacterial fruit blotch. The novel method is characterized in that the purpose of preventing and treating muskmelon bacterial fruit blotch can be realized through processes such as seed sterilization, soil sterilization, crop rotation, ridge culture, reasonable watering, timely control of injurious insects in a shed room, bagging treatment of plastic bags and chemical control. This way is convenient to operate, can effectively increase the yield of muskmelons and can effectively improve the quality of the muskmelons, and is suitable for preventing and treating muskmelon bacterial fruit blotch.
Owner:于辉
Novel method for prevention and treatment of muskmelon bacterial fruit blotch
InactiveCN107950259AControl bacterial fruit spotIncrease productionPlant protectionGreenhouseChemical control
A new method for preventing and treating bacterial fruit spot of melon, which is characterized in that through the process of seed disinfection, soil disinfection, crop rotation, ridge cultivation, rational watering, timely prevention and control of greenhouse pests, plastic bag bagging treatment, chemical control, etc., The purpose of preventing and controlling the bacterial fruit spot disease of the melon can be realized. This method is not only easy to operate, but also can effectively improve the yield and quality of the melon, and is suitable for the prevention and treatment of the bacterial fruit spot disease of the melon.
Owner:张瑞芹
Immune colloidal gold test strips for detection of fruit spot fungus and its monoclonal antibody and hybridoma cell line
ActiveCN104991069BImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisCelluloseBacterial fruit blotch
The invention relates to a melon bacterial fruit blotch immune colloidal gold rapid detection test strip. The test strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal gold sample closely connected with the sample pad, a cellulose membrane arranged on the colloidal gold pad and closely connected with the colloidal gold pad, and a water absorption pad closely connected with the other end of the cellulose membrane, one end of the cellulose membrane away from the colloidal gold pad is provided with a quality control line, and the cellulose membrane between the quality control line and the colloidal gold pad is provided with a detection line, wherein the colloidal gold pad is provided with a monoclonal antibody coupling with colloidal gold, the monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.10413, and the detection line is formed by the monoclonal antibody. The fruit blotch immune colloidal gold rapid detection test strip adopts the colloidal gold pad and the detection lime to be respectively sprayed with the new screened monoclonal antibody and has high detection specificity and sensitivity on fruit blotch. The invention also relates to monoclonal antibody for the test strip, and the hybridoma cell strain thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Watermelon bacterial fruit blotch controlling novel technology
InactiveCN105557398AQuality improvementIncrease productionFertilising methodsPlant protectionBiotechnologyDiseased plant
The invention relates to a watermelon bacterial fruit blotch controlling novel technology. According to the invention, a purpose of controlling watermelon bacterial fruit blotch can be realized through the processes of cleaning diseased plant residues in the field, adopting crop rotation, selecting disease-resistant or disease-tolerant varieties, reasonably fertilizing, adopting chemical agent control, and the like. The technology has good effect in improving watermelon quality and yield, and is suitable to be used in controlling watermelon bacterial fruit blotch.
Owner:韩浩良
Method for detecting bacterial fruit blotch and xanthomonas malvacearum of melons simultaneously and special kit thereof
ActiveCN108220462AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDisease monitoringFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting bacterial fruit blotch and xanthomonas malvacearum of melons simultaneously and a special kit thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adoptinga sample to be detected as a template, adopting the kit to carry out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and obtaining reaction products; reading fluorescence signals of the reaction products, then judging whether the sample to be detected contains the bacterial fruit blotch and / or the xanthomonas malvacearum of the melons. The kit comprises a primer pair combination. The nucleotide sequences of 4 primers forming the primer pair combination are shown as a sequence 3 to a sequence 6 in a sequence table. Proved by experiments, on an LGC molecular detection platform, by adoption of thekit provided by the invention, whether the bacterial fruit blotch and / or the xanthomonas malvacearum of the melons are / is carried on melon seeds can be detected rapidly by high flux, so that the method and the kit can be used as a prevention technology for preventing and controlling circulation of infected seeds, also can be used as a disease monitoring and early-warning technology for the fieldplanting stage and provide a fast and accurate detection method for agricultural production and port quarantine.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method and special seed fungicide for preventing and controlling bacterial fruit blotch of melons
ActiveCN109497067AEfficient removalInhibition of emergence morbidityBiocideDisinfectantsXanthomonas campestrisSodium Pyrithione
The invention discloses a method and a special seed fungicide for preventing and controlling bacterial fruit blotch of melons. The method comprises the step of soaking seeds with zinc pyrithione. Experiments show that zinc pyrithione can effectively remove acidovorax citrulli from the outside and inside of the seeds of cucurbitaceae crops (such as watermelons and muskmelons), and can be absorbed by seedlings during seed germination, so that the acidovorax citrulli spread between the seeds and the seedlings is reduced, the emergence incidence rate of the seeds carrying the acidovorax citrulli is effectively inhibited, and the purpose of preventing and controlling the bacterial fruit blotch of the melons is achieved; furthermore, the zinc pyrithione does not affect seed germination and seedling growth; the zinc pyrithione has no significant effect on the growth of plant growth promoting rhizosphere bacteria (such as pseudomonas fluorescens and bacillus subtilis) while inhibiting the growth of pathogens (such as bacterial canker of tomato and xanthomonas campestris pv.campertris). The zinc pyrithione can be used as a seed bactericide for production and promotion. The method and the special seed fungicide have an important application value.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
A watermelon seed disinfection technology and its application to control the occurrence of bacterial fruit spot
The invention discloses a watermelon seed disinfection technology for controlling the occurrence of bacterial fruit spot disease. The technique involves using CuSO 4 The aqueous solution sterilizes the seeds. The results show that the treated seeds can effectively kill the bacterial fruit spot disease bacteria carried by the seeds, and reduce the occurrence of field fruit spot disease after planting. At the same time, the initiation treatment of the solid substrate can effectively improve the germination speed and uniformity of the diploid watermelon seeds, reduce the germination obstacles of the triploid watermelon seeds, and increase the final germination rate of the seeds.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for preventing and curing bacterial fruit blotch disease of melon in solar greenhouse
InactiveCN109744010APrevents Bacterial Fruit SpotIncrease productionHorticulture methodsBacterial diseaseSugar melon
The present invention discloses a method for preventing and curing bacterial fruit blotch of melon in a solar greenhouse. Preventing and curing of bacterial diseases are strengthened after the melon is planted, when freshly born melon grows to 3 to 5 cm, the melon is dipped with 150 to 200 mg / kg of a potassium phosphite aqueous solution for the first time, and within 8 to 10 days after melon dipping for the first time, the melon is dipped with 350 to 450 times of an aqueous solution of 3% of ZhongShengmycin wettable powder for the second time. According to the method for preventing and curingbacterial fruit blotch of the melon in the solar greenhouse, bacterial fruit blotch on melon fruits in the solar greenhouse can be effectively prevented.
Owner:巨野县恒蔬无疆蔬菜产业有限公司
A kind of bacterial fruit spot disease seed fungicide and its application
ActiveCN105660694BGerminate fastPromote germinationBiocideSeed and root treatmentDiseaseChlorine dioxide
The invention belongs to the field of disinfection and control of plant seed-borne diseases, particularly relates to disinfection, prevention and treatment of watermelon bacterial fruit blotch, and discloses a novel compound disinfectant.The disinfectant comprises chlorine dioxide (ClO2) mainly having a disinfection effect, sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) mainly having a germination promoting effect, and potassium iodate (KIO3) mainly having an effect of stabilizer By means of the disinfectant, detected watermelon seeds with bacterial fruit blotch bacteria and artificial simulating watermelon seeds with bacterial fruit blotch bacteria are processed, the germination rate and germination potential of seeds are promoted, and the disinfection effect is remarkable and is obviously better than that of a reported existing bacterial fruit blotch disinfectant and a reported existing disinfecting method.The disinfection method can easily, rapidly and thoroughly kill bacterial fruit blotch bacteria carried by watermelon seeds, is easy to operate, free of toxin and pollution and has huge actual application value.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for preventing and treating bacterial fruit blotch of watermelons
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating bacterial fruit blotch of watermelons, and relates to the technical field of watermelon disease prevention and treatment. The method comprises the following steps that (1), first treatment is carried out, specifically, a botanical pesticide composition and a bactericide are sprayed on leaf surfaces after the disease blotch is found in the watermelon seedling stage or in the middle and later periods of watermelon expansion; (2) secondary treatment is carried out, specifically, a botanical pesticide composition is sprayed on the leaf surfaces after 2-3 days of the first treatment. The botanical pesticide composition is prepared from thymol, carvacrol and menthol, and the mass ratio of the thymol to the carvacrol to the menthol is (8-20) to (4-12) to (1-2). The method for preventing and treating the bacterial fruit blotch of the watermelons has the beneficial effects that the botanical pesticide composition is used as a core and is mixed or combined with the bactericide, the disease blotch is dried up in the seedling stage or middle and later periods of watermelon expansion within 24 hours after the composition is used, the microenvironment humidity of the leaf surfaces and fruit surfaces is reduced, and the propagation of pathogenic bacteria and the prevalence of diseases are quickly blocked.
Owner:安徽金敦福农业科技有限公司
RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) detection primer, probe and detection method for bacterial fruit blotch of cucurbit
ActiveCN114277166AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrobiologyRecombinase Polymerase Amplification
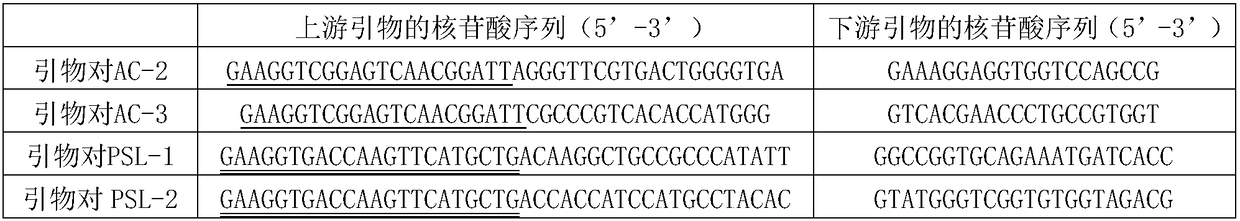
The invention relates to an RPA detection primer, a probe and a detection method of cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch, the RPA detection primer comprises an RPA primer pair Ac-F1 and Ac-R1 of cucurbit bacterial fruit blotch and a detection probe Ac-nfo, the amplification product size of the RPA primer pair Ac-F1 and Ac-R1 is 342bp, the 5'terminal of the primer Ac-R1 is labeled with biotin, the 5 'terminal of the primer Ac-R1 is labeled with biotin, and the 5' terminal of the detection probe Ac-nfo is labeled with biotin. The 5'tail end of the detection probe Ac-nfo is marked with FAM, the 3 'tail end of the detection probe Ac-nfo is marked with C3Spacer, and the position, 32 bp away from the 5' tail end, of the probe is modified with dSpacer; the RPA primer group is high in detection sensitivity, and the detection limit reaches 2.5 * 10 < 4 > cfu / mL; the invention provides a detection method for detecting the melon bacterial fruit blotch based on RPA combined with lateral flow test paper, establishes a rapid isothermal visual detection method for the melon bacterial fruit blotch, can complete sample detection within 15-20 min, realizes rapid diagnosis, identification and detection of the melon bacterial fruit blotch in a constant-temperature environment, and has a wide application prospect. The kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity and the like, and provides technical support for quarantine, detection, prevention and control of the disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primers for detection of melon bacterial fruit spot pathogen lamp
InactiveCN103866029BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAcidovorax speciesBiology
The invention relates to a bacterial fruit acidovorax citrulli LAMP detection primer, belonging to the field of biotechnology. According to the whole genome sequence information of the bacterial fruit blotch strain AAC00-1, a set of specific primer for fruit blotch LAMP detection can be designed on Aave-4063 and Aave-4064 gene sequences. An LAMP detection method established on the basis of the primer has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity, low cost and the like, and is fast and easy to operate.
Owner:上海市农业技术推广服务中心
Novel watermelon sugar transporter as well as coding gene ClVST1 and application thereof
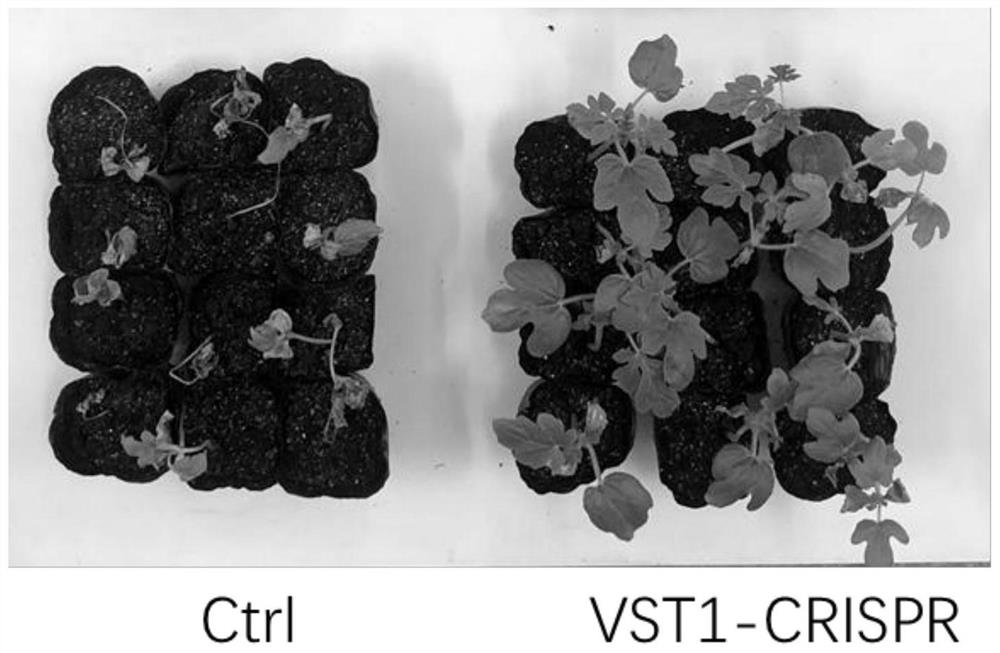
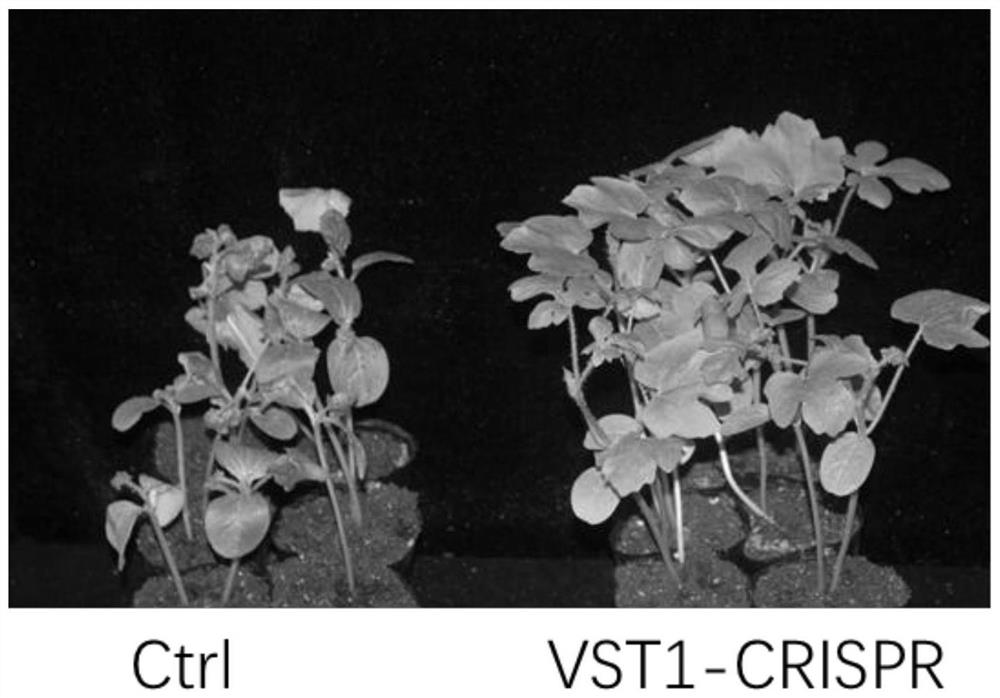
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and relates to a novel watermelon sugar transporter and a coding gene ClVST1 and application thereof. The novel watermelon sugar transport protein has a sequence composition shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and the coding gene ClVST1 has a sequence composition shown in a sequence 2 in the sequence table. The invention also relates to application of the novel watermelon sugar transporter protein and the novel watermelon sugar transporter coding nucleic acid sequence in watermelon disease and insect pest resistance. The invention further provides an obtaining method of the watermelon plant disease and insect pest resistant strain. The watermelon novel sugar transporter and the coding gene ClVST1 provided by the invention are closely related to disease and insect pest resistance, and the higher the expression quantity is, the stronger the disease and insect pest resistance is; therefore, a stable watermelon strain resistant to bacterial fruit blotch and aphid can be obtained by knocking out novel sugar transport of watermelons in watermelon plants, and a quick and efficient way is provided for breeding of watermelons resistant to diseases and insect pests.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com