RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) detection primer, probe and detection method for bacterial fruit blotch of cucurbit
A technology for the detection of fruit spot bacteria and detection methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity, expensive reagents and instruments, and time-consuming, etc., to achieve high sensitivity, Good specificity and results visible to the naked eye
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1 designs and screens specific primer pair
[0033] (1) Design primers:
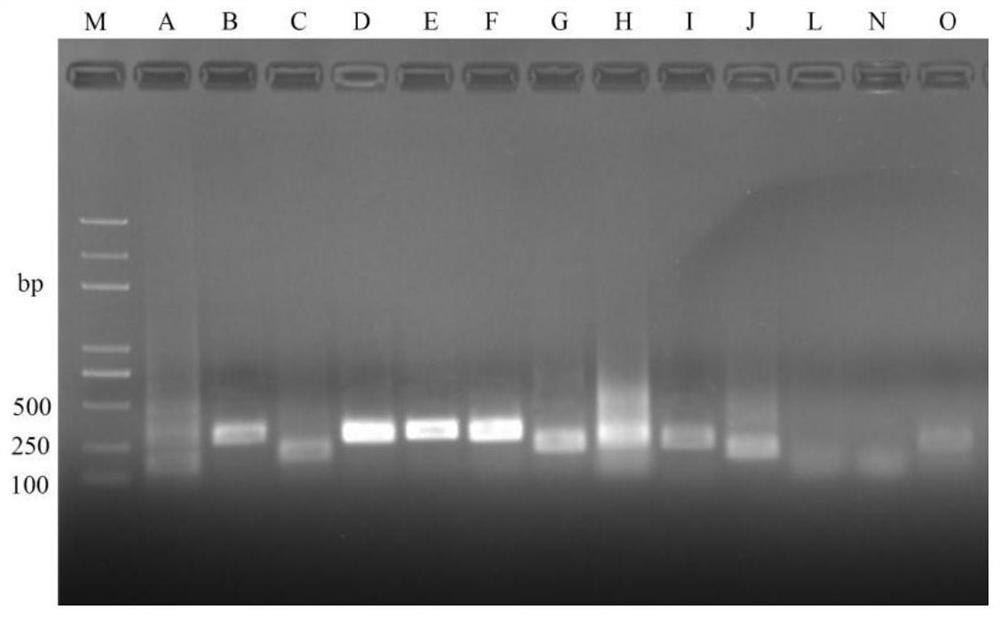
[0034] For the 651bp ORF specific sequence CP029373.1 (896040-896693) of cucurbit bacterial fruit spot bacterium, the specific nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and 12 pairs of different RPA primers were designed, wherein the primers Set the TM value between 65-75°C and the amplification length between 150-294bp, and configure the alternative RPA primer pairs into solutions with a concentration of 10μM.
[0035] The specific sequences of the designed 13 pairs of different RPA primer pairs are shown in Table 1, from 5' to 3'.
[0036] Table 1
[0037]
[0038]
[0039] (2) The screening process is as follows:
[0040]Isolate and purify the bacterial fruit spot disease of melons, extract DNA according to the conventional method, and use the extracted DNA as a template for PRA detection. The RPA reaction system is: complex solution 29.5 μL, sterile deionized water 13.0 ...
Embodiment 2
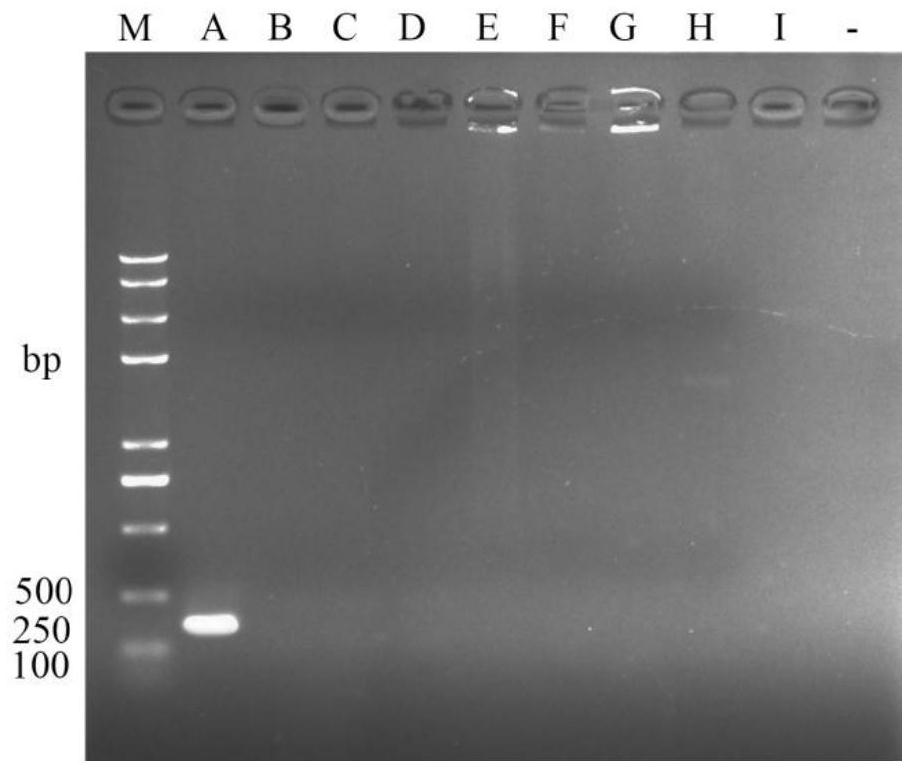
[0043] The specificity test of embodiment 2 melon bacterial fruit spot pathogen RPA detection primer
[0044] The DNA templates were from reference bacteria: Pseudomonas syringae (bacterial leaf spot of melon), Erwinia carotovora (soft rot of Chinese cabbage), E.chrysanthemi (bottom rot of rice), Xanthomonasoryzae (bacterial leaf spot of rice), Microbacterium arborescens (Microbacterium dendriticum), Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense (cucumber stem rot fungus), Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), Agrobacterium sp. (Agrobacterium).
[0045] Purify the melon bacterial fruit spot bacteria and each reference bacteria, configure the primer pair Ac-F1 and Ac-R1 respectively into a solution with a concentration of 10.0 μmol / L, extract the DNA according to the conventional method for use, and use the extracted DNA as a template for RPA Detection, wherein, the RPA reaction system is: complex solution 29.5 μL, sterile deionized water 13.0 μL, 10 μmol / L forward / reverse prime...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3 The sensitivity test of the detection primer of melon bacterial fruit spot pathogen RPA and the sensitivity test of test paper detection
[0050] 1) Purify the bacterial fruit spot pathogen of melons, and prepare 2.5 × 10 with sterile water after cultivation. 9 -2.5×10 1 cfu / mL bacterial suspension;
[0051] 2) According to the primer specificity results of examples 1 and 2, design and detect the probe in the amplified fragment of the primer pair Ac-F1 and Ac-R1, and modify it, name it Ac-nfo, and use the primer pair Ac-F1 and Ac-R1, probe Ac-nfo were respectively configured into a solution with a concentration of 10 μM;
[0052] 3) Use the bacterial suspension prepared in step 1) as a template for PRA detection. The RPA reaction system is: 29.5 μL of complex solution, 12.4 μL of sterile deionized water, 0.6 μL of 10 μmol / L Ac-nfo, 0.6 μL of 10 μmol / L Ac-F1 / Ac-R1 each 2.0 μL, 280 mmol / L magnesium acetate solution 2.5 μL, DNA template 1.0 μL, total volume...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com