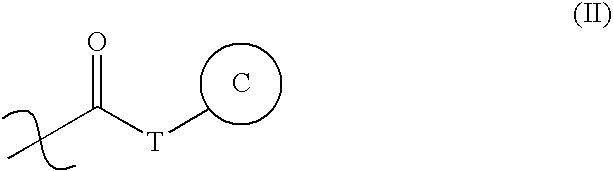
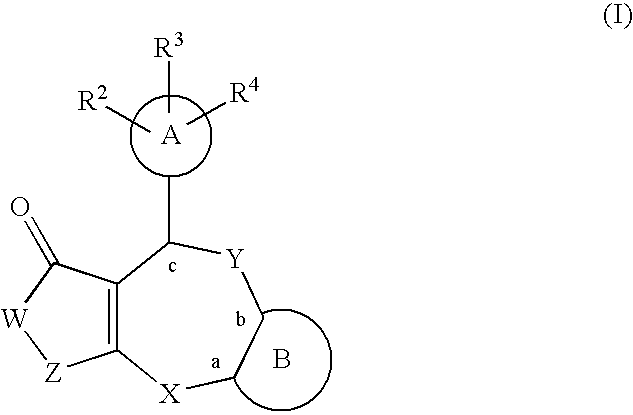
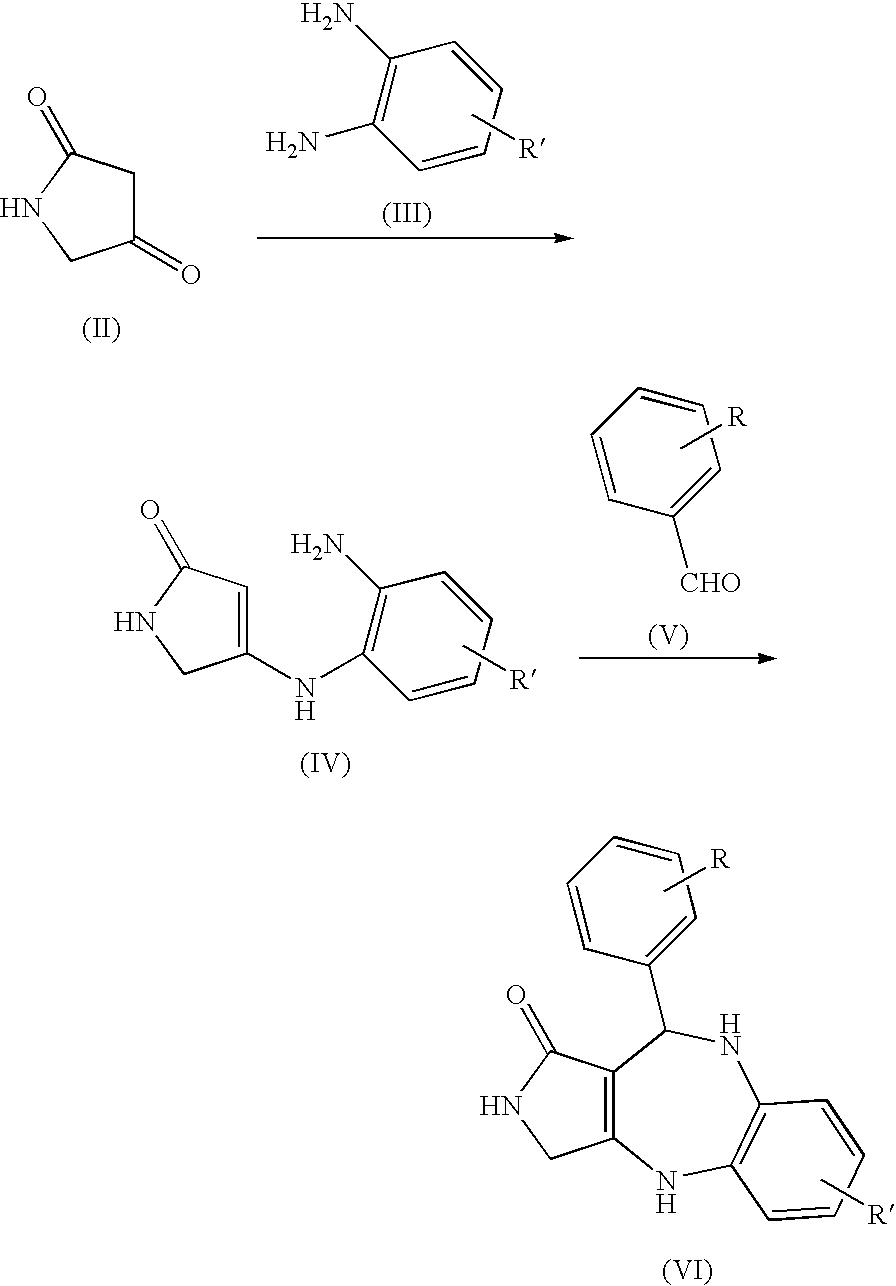
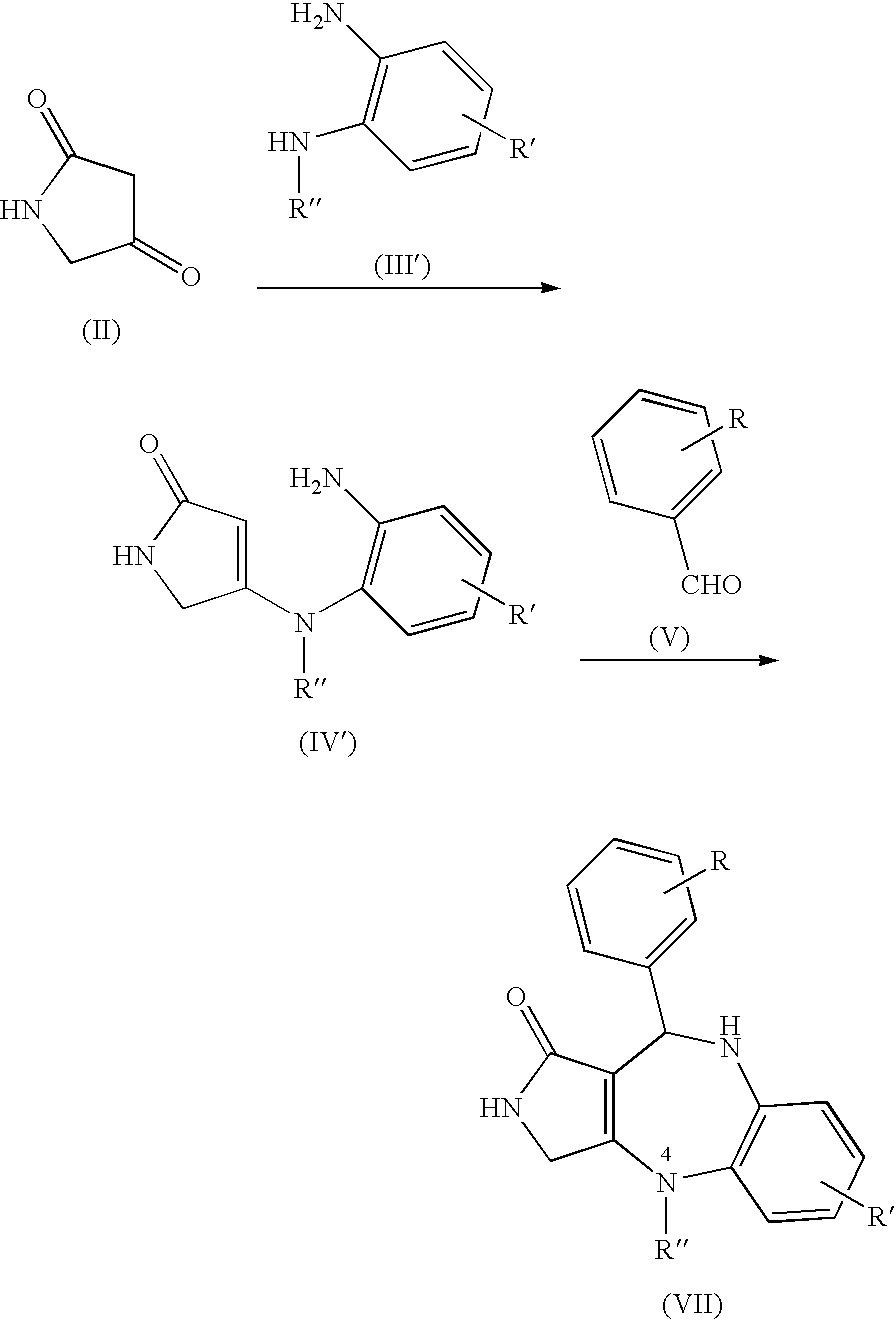
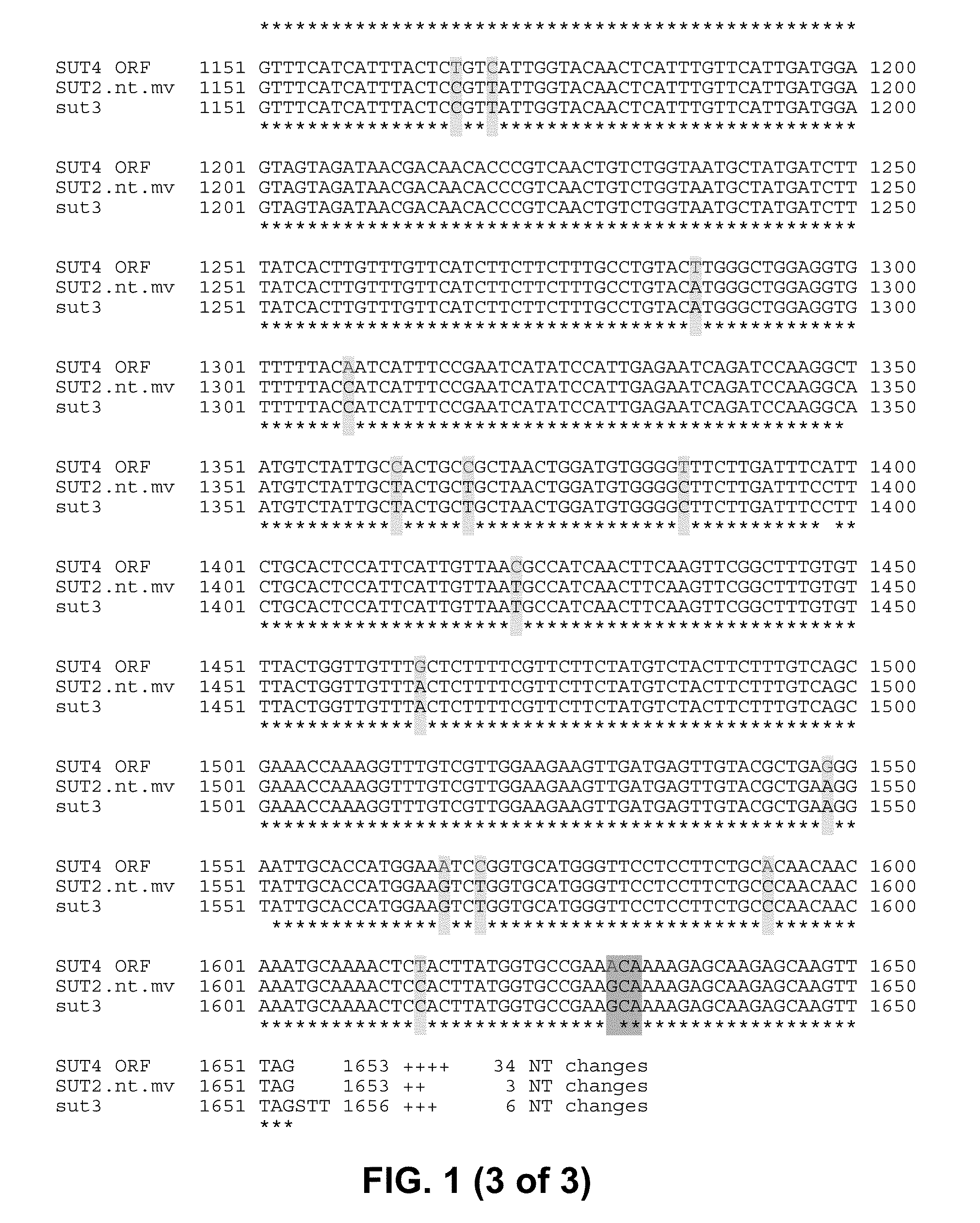
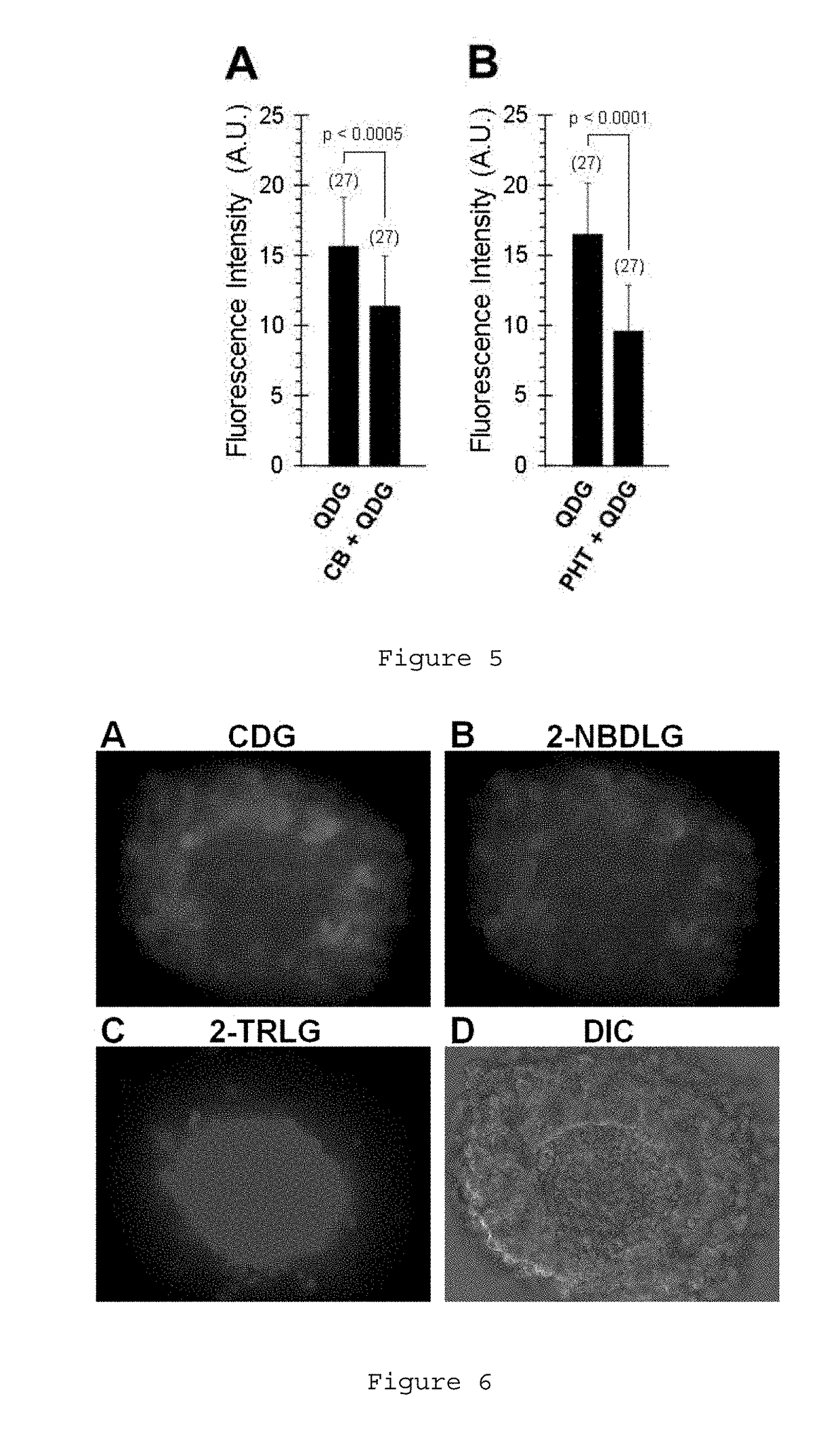
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Sugar transport" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sugar Transport. <<. >>. Sugars, which are formed by the plant during photosynthesis, are an essential component of plant nutrition. Like water, sugar (usually in the form of sucrose, though glucose is the original photosynthetic product) is carried throughout the parts of the plant by the vascular system.
Methods and compositions for improving sugar transport, mixed sugar fermentation, and production of biofuels
InactiveUS8431360B2Easy to transportPromote cell growthFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiofuelPolynucleotide
The present disclosure relates to host cells containing a recombinant polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide where the polypeptide transports cellodextrin into the cell. The present disclosure further relates to methods of increasing transport of cellodextrin into a cell, methods of increasing growth of a cell on a medium containing cellodextrin, methods of co-fermenting cellulose-derived and hemicellulose-derived sugars, and methods of making hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon derivatives by providing a host cell containing a recombinant polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide where the polypeptide transports cellodextrin into the cell. The present disclosure relates to host cells containing a recombinant polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide where the polypeptide transports a pentose into the cell, methods of increasing transport of a pentose into a cell, methods of increasing growth of a cell on a medium containing pentose sugars, and methods of making hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon derivatives by providing a host cell containing a recombinant polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide where the polypeptide transports a pentose into the cell.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +2
Fused polycyclic compounds
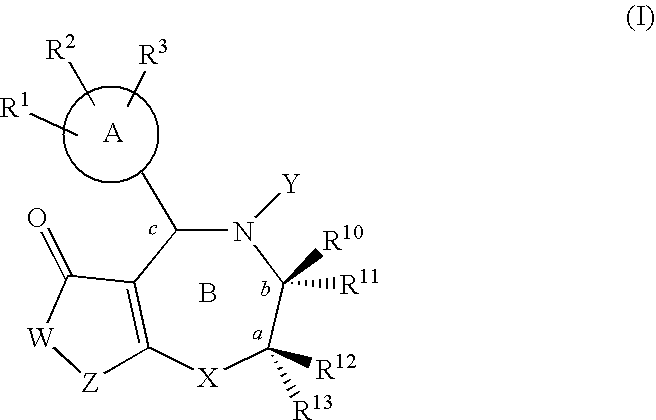
InactiveUS20060258637A1High medicinal valueFew side-effectsBiocideSenses disorderPolycyclic compoundDiabetes mellitus
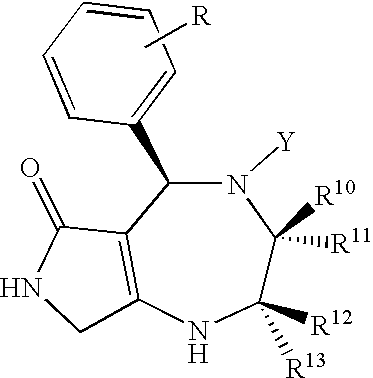
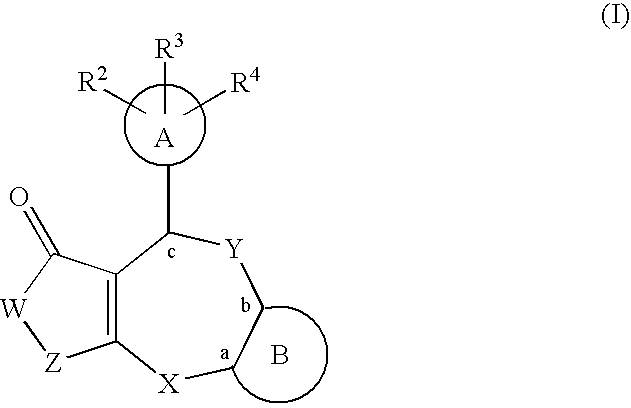
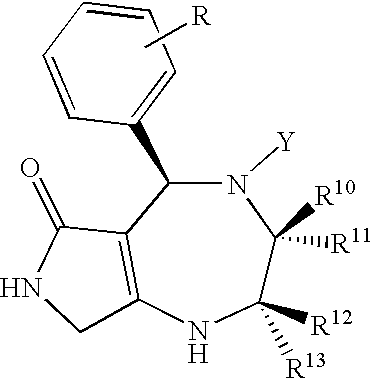
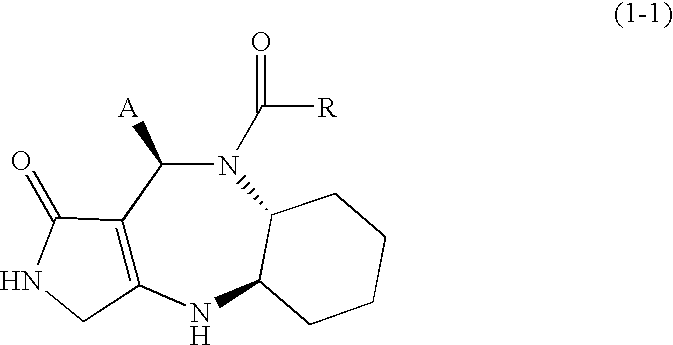
The following fused polycyclic compound, analogues thereof or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof have an effect of increasing the sugar-transporting capacity and an effect of lowering the blood glucose level and, therefore, they are useful for preventing and / or treating diabetes and the like. wherein R is a methoxy group, Y is a (2-thiazolyl)-2-ethylcarbonyl group, R10 and R13 are hydrogen atoms, and R11 and R12 are methyl groups.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Lactam compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof
InactiveUS20060189597A1High medicinal effectLittle side effectsBiocideSenses disorderDiabetic retinopathyBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
An agent for increasing the sugar-transporting capacity and an agent for preventing and / or treating diabetes, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macroangiopathy, impaired glucose tolerance or adiposis, which contains a lactam compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as the active ingredient.
Owner:EA PHARMA CO LTD
Lactam compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof
InactiveUS7153850B2High medicinal effectLittle side effectsBiocideSenses disorderDiabetic retinopathyIGT - Impaired glucose tolerance
An agent for increasing the sugar-transporting capacity and an agent for preventing and / or treating diabetes, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macroangiopathy, impaired glucose tolerance or adiposis, which contains a lactam compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as the active ingredient.
Owner:EA PHARMA CO LTD
Fused polycyclic compounds
The following fused polycyclic compound, analogues thereof or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof have an effect of increasing the sugar-transporting capacity and an effect of lowering the blood glucose level and, therefore, they are useful for preventing and / or treating diabetes and the like.wherein R is a methoxy group, Y is a (2-thiazolyl)-2-ethylcarbonyl group, R10 and R13 are hydrogen atoms, and R11 and R12 are methyl groups.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Lactam compound, a method for producing the same, and a diabetic therapy by administering the same
InactiveUS7951799B2Little side effectsGood physical propertiesBiocideSenses disorderDiabetic retinopathyMacrovascular disease
The present invention provides a lactam compound, a sugar transport enhancement agent containing this compound as an active ingredient, an agent for the prevention and / or treatment of diabetes mellitus, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macrovascular disease, glucose tolerance anomaly, obesity and the like. In addition, the present invention also provides a preparation method for the novel lactam compound, and a preparation intermediate thereof.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemiclas using facilitated diffusion for sugar import
InactiveUS20160160245A1Facilitated DiffusionImprove filtering effectBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyGlucose utilization
This invention relates to the production of succinic acid and other chemicals derived from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) by fermentation with a microorganism in which the fermentation medium contains one or more sugars, and in which one or more of the sugars is imported into the cell by facilitated diffusion. As a specific example, succinic acid is produced from a glucose-containing renewable feedstock through fermentation using a biocatalyst. Examples of such a biocatalyst include microorganisms that have been enhanced in their ability to utilize glucose as a carbon and energy source. The biocatalysts of the present invention are derived from the genetic manipulation of parental strains that were originally constructed with the goal to produce one or more chemicals (for example succinic acid and / or a salt of succinic acid) at a commercial scale using feedstocks that include, for example, glucose, fructose, or sucrose. The genetic manipulations of the present invention involve the introduction of exogenous genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose into the parental strains. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose can also be introduced into a microorganism prior to developing the organism to produce a particular chemical. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be used to augment or improve the efficiency of sugar transport and metabolism by strains already known to have some ability for glucose utilization in biological fermentations.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
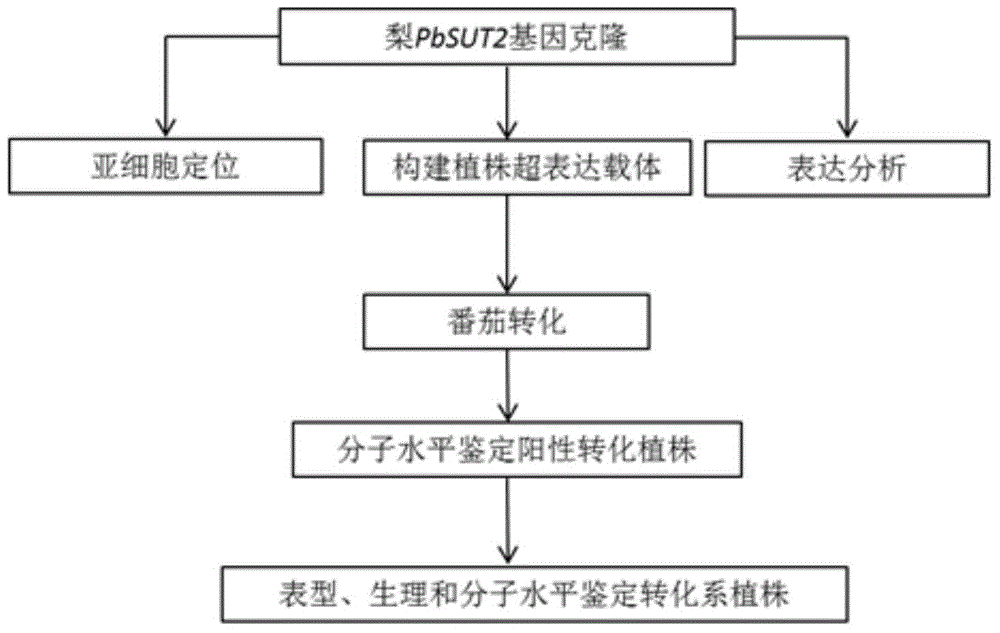
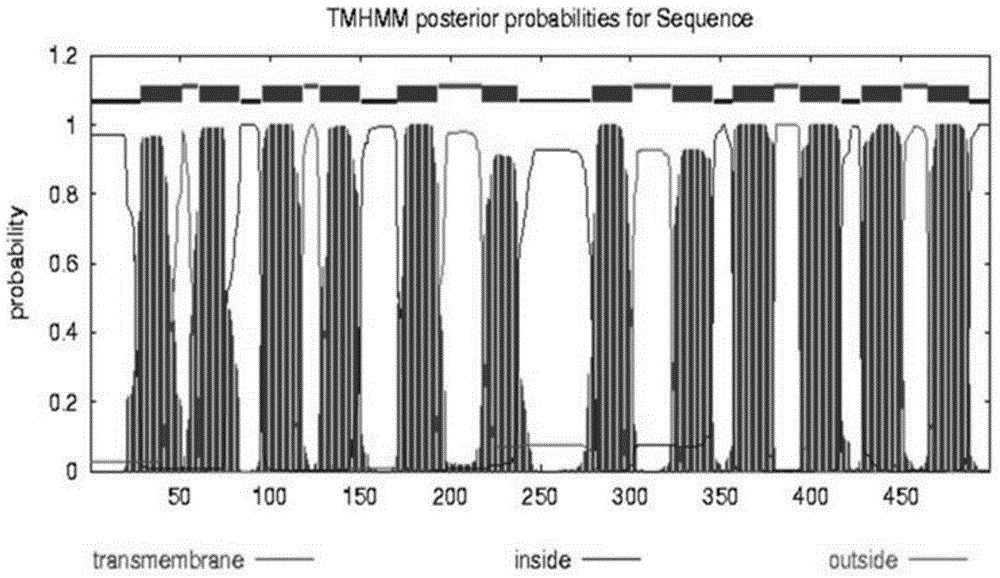
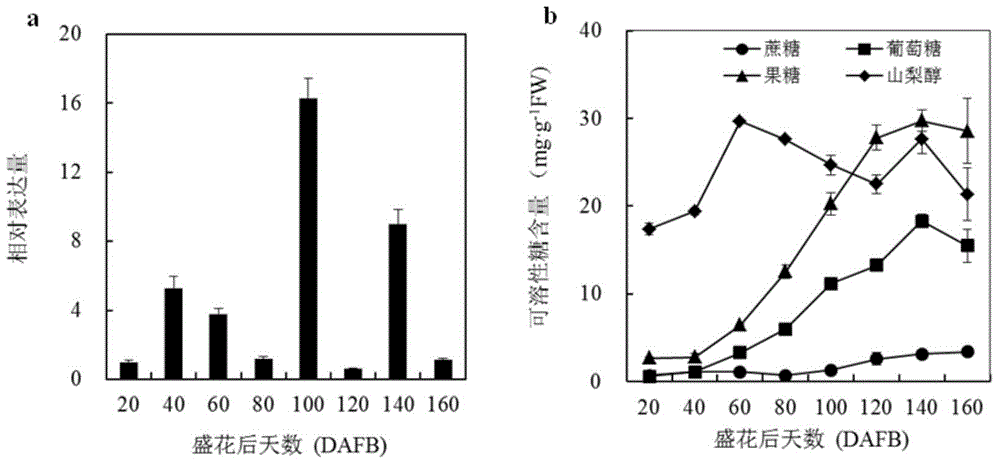
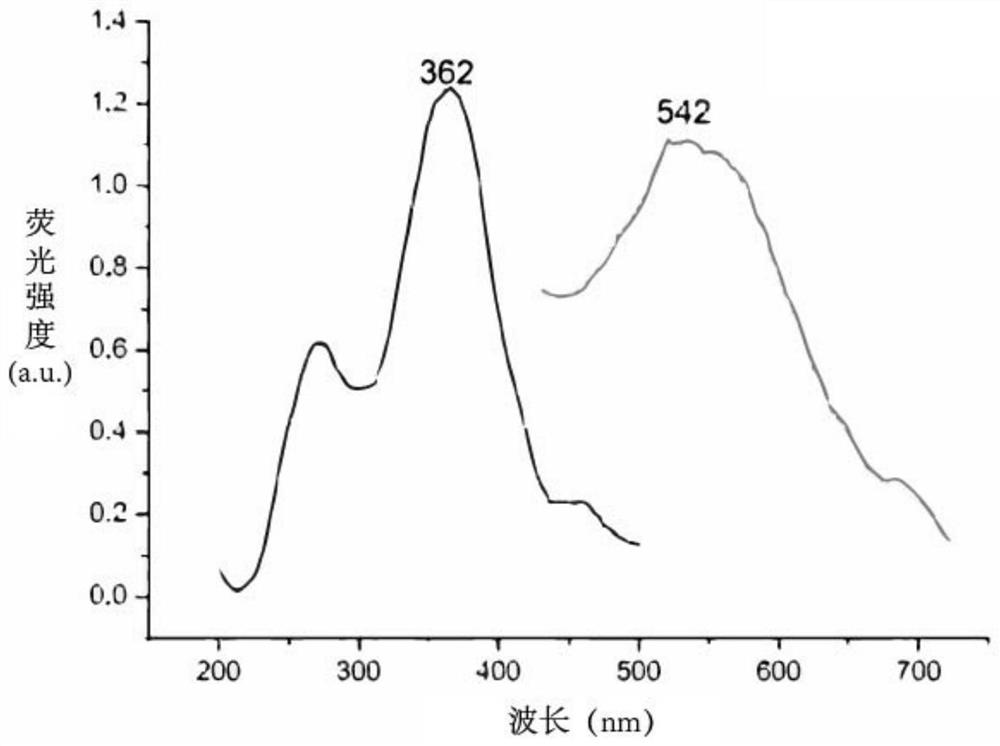
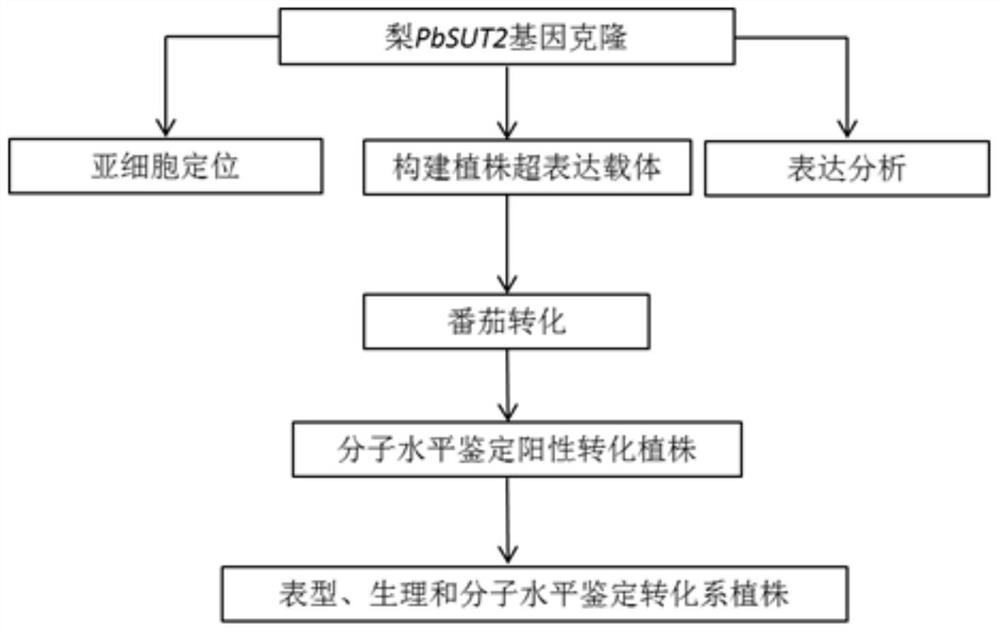
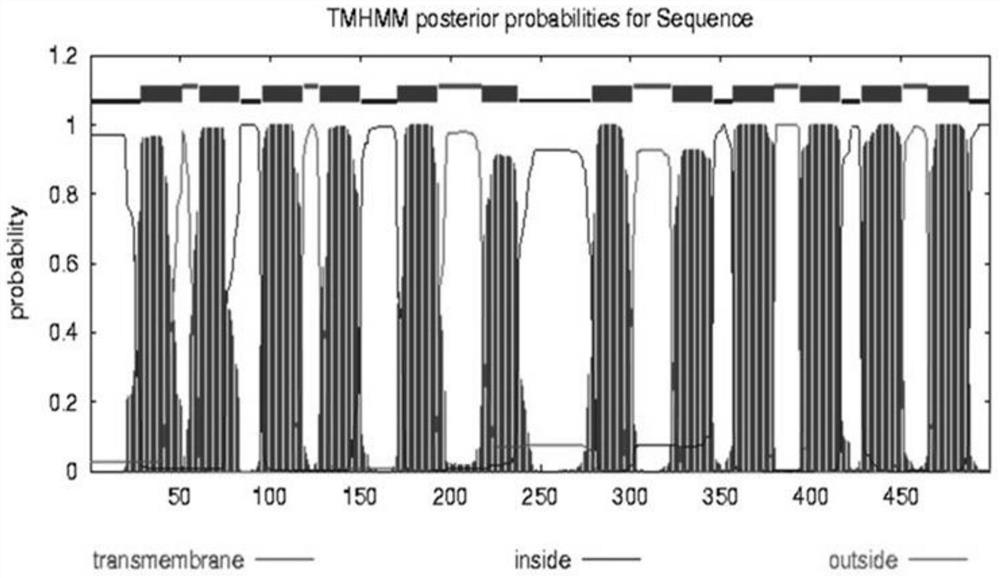
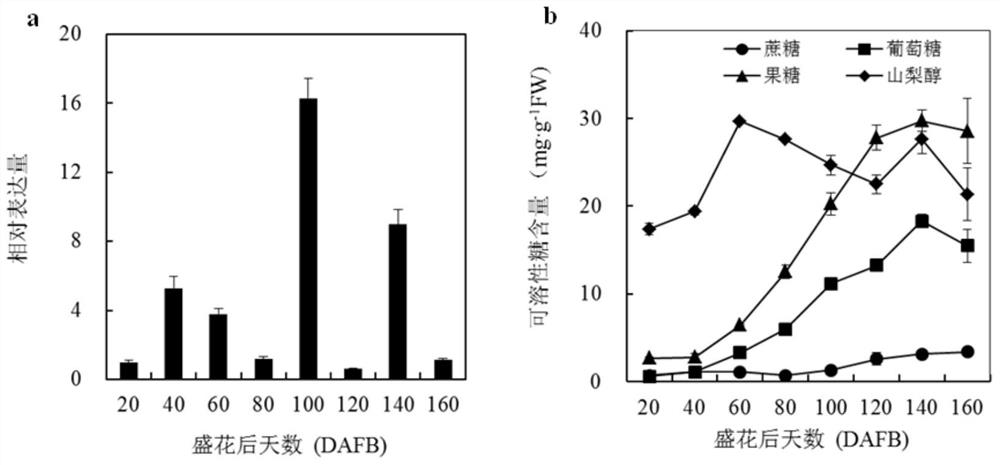
Pear sugar transport protein gene PbSUT2 and application thereof
ActiveCN105624171ABreak through the barriers of traditional breeding methodsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologySucrose
The invention discloses a pear sugar transport protein gene PbSUT2 and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the pear sugar transport protein gene separated from a pear fruit is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and a coded amino acid sequence of the pear sugar transport protein gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. The gene PbSUT2 is transformed into a tomato through an agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation method; the biological function verification of an obtained transgenic plant indicates that the cloned gene PbSUT2 has the functions of promoting plant early flowering and increasing the content of sucrose in the fruit. The discovery of the gene PbSUT2 provides new genetic resources for promoting the molecular breeding of plant fruit quality.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Glucose derivative, and cell imaging method and imaging agent using said derivative
ActiveUS10001487B2Improve accuracySugar derivativesGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsQuinoloneCancer cell
Owner:ORBIO CORP
Sugar transport sequences, yeast strains having improved sugar uptake, and methods of use
Disclosed are nucleic acid constructs comprising coding sequences operably linked to a promoter not natively associated with the coding sequence. The coding sequences encode Pichia stipitis proteins that allow recombinant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the protein to grow on xylose, and allow or increase uptake of xylose by Pichia stipitis or Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the coding sequences. Expression of the coding sequences enhances uptake of xylose and / or glucose, allowing increased ethanol or xylitol production.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Intelligent regulation and control method for carbon metabolism flow of xylitol produced by escherichia coli
ActiveCN113293121ADisinhibition effectProduction constraintsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
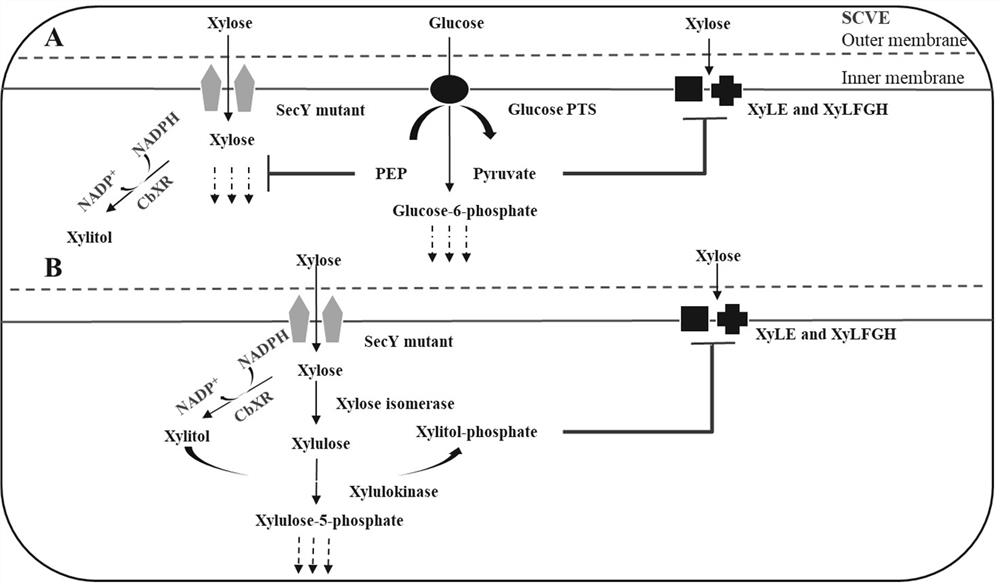
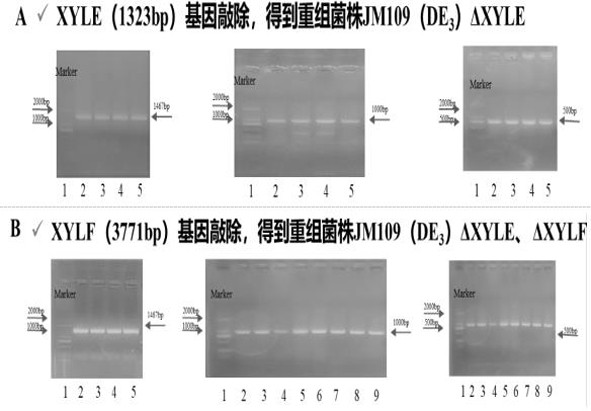
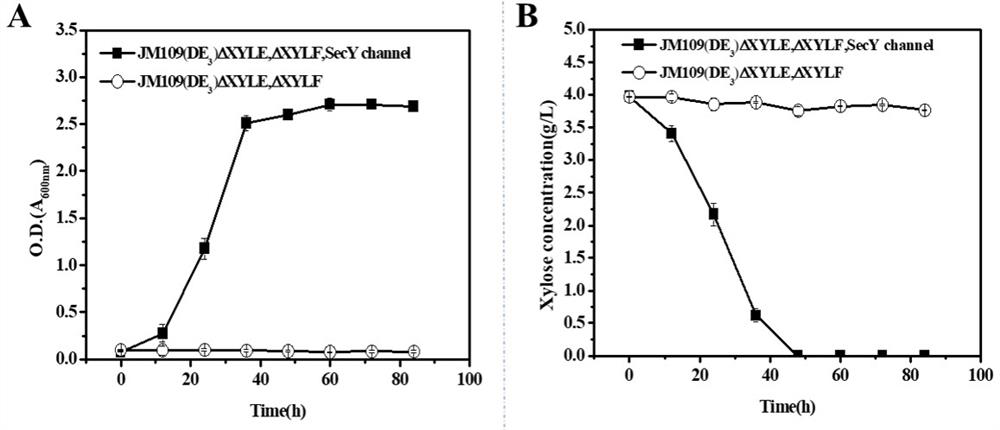
The invention provides an intelligent regulation and control method for carbon metabolism flow of xylitol produced by escherichia coli, and aims to realize efficient synthesis of xylitol in a process of preparing xylitol by utilizing a cell factory. According to the invention, a strain of SecY engineered Escherichia coli is successfully constructed by introducing a SecY non-specific sugar transport channel and simultaneously overexpressing heterologous xylose reductase (CbXR). The strain can overcome the CCR effect through self-regulation and relieve the inhibition effect of the 5-phosphate xylitol on xylose transported by the strain. By taking the change of an external carbon source as a response signal, the CCR effect and the inhibition effect of the xylitol 5-phosphate are converted into two important regulating switches in a carbon metabolism network, and the metabolic capability of cells on glucose and xylose is regulated. The method can completely metabolize glucose and xylose in any proportion in a substrate, ensures the maximum conversion efficiency of energy to a target product, and better meets the requirements of green biological manufacturing.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Sugarcane saccharose translocator ShSUT2 genes and application
The invention discloses two saccharose translocator ShSUT2 genes derived from sugarcane and application. According to the saccharose translocator genes ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B, amino acid sequences are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO 2 and 4, and base sequences of encoding genes ShSuT2A and ShSUT2B are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO 1 and 3. Absorbing function deficient mutant by yeast saccharose shows that the proteins encoded by ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B have saccharose transport activity. The ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B encoding genes are responsible for absorbing saccharose of apoplast in sugarcane plant and participate in transportation, distribution and accumulated physiological processes of sugarcane plant saccharose. The genes can provide new ways for improving transportation and distribution efficiency of sugarcane saccharose, promoting growth of the plant and improving sugarcane yields and sugar content.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Novel glucose derivative, and cell imaging method and imaging agent using said derivative
ActiveUS20170122955A1Increase contrastImprove accuracyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesQuinoloneCancer cell
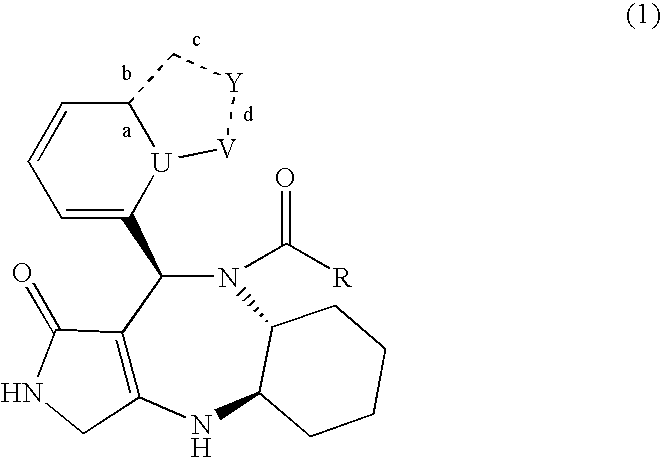
Provided is a glucose derivative, which is taken into cells via a membrane sugar transport system and is represented by formula (1). Also provided are an imaging agent and an imaging method for a cell or intracellular molecule using said glucose derivative. Further provided are a method for detecting cancer cells with good accuracy using said glucose derivative and an imaging agent to be used in said method. More specifically provided are D-glucose derivatives and L-glucose derivatives in which glucose is bound to the 7-position of a fluorescent molecular group with a coumarin backbone or a quinolone backbone. Also provided are a cell imaging agent and imaging method using the derivative. A cancer cell imaging agent and imaging method using the L-glucose derivative is also provided. G is a group selected from formulas (G1)-(G4) below.
Owner:ORBIO CORP
Novel antidiabetic medicine
InactiveCN103468680AEasy to synthesizeLow costMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsEfficacyPharmaceutical Substances
The invention provides a novel antidiabetic medicine. The novel antidiabetic medicine is obtained by the steps of finding a lead compound acting on sodium-sugar transport synergistic protein with an 'antisense chemical medicine design' method and performing targeted chemical modification (for example: methylated modification of the two ends of the lead compound, synergistic design of an unmodified compound and a modified compound, and development of MgCl2 serving as a medicine efficacy enhancer). Therefore, the novel antidiabetic medicine provided by the invention can inhibited integrated sodium-sugar transport synergistic protein efficiently and specifically, has low side effects and achieves an effect which is more excellent than that of the existing sodium-sugar transport protein II inhibitor, so as to achieve an effect of effectively treating type II diabetes and fill the gap in the chemical design of antisense medicines in China.
Owner:KINDEESU ZHOUMEDICAL TECH
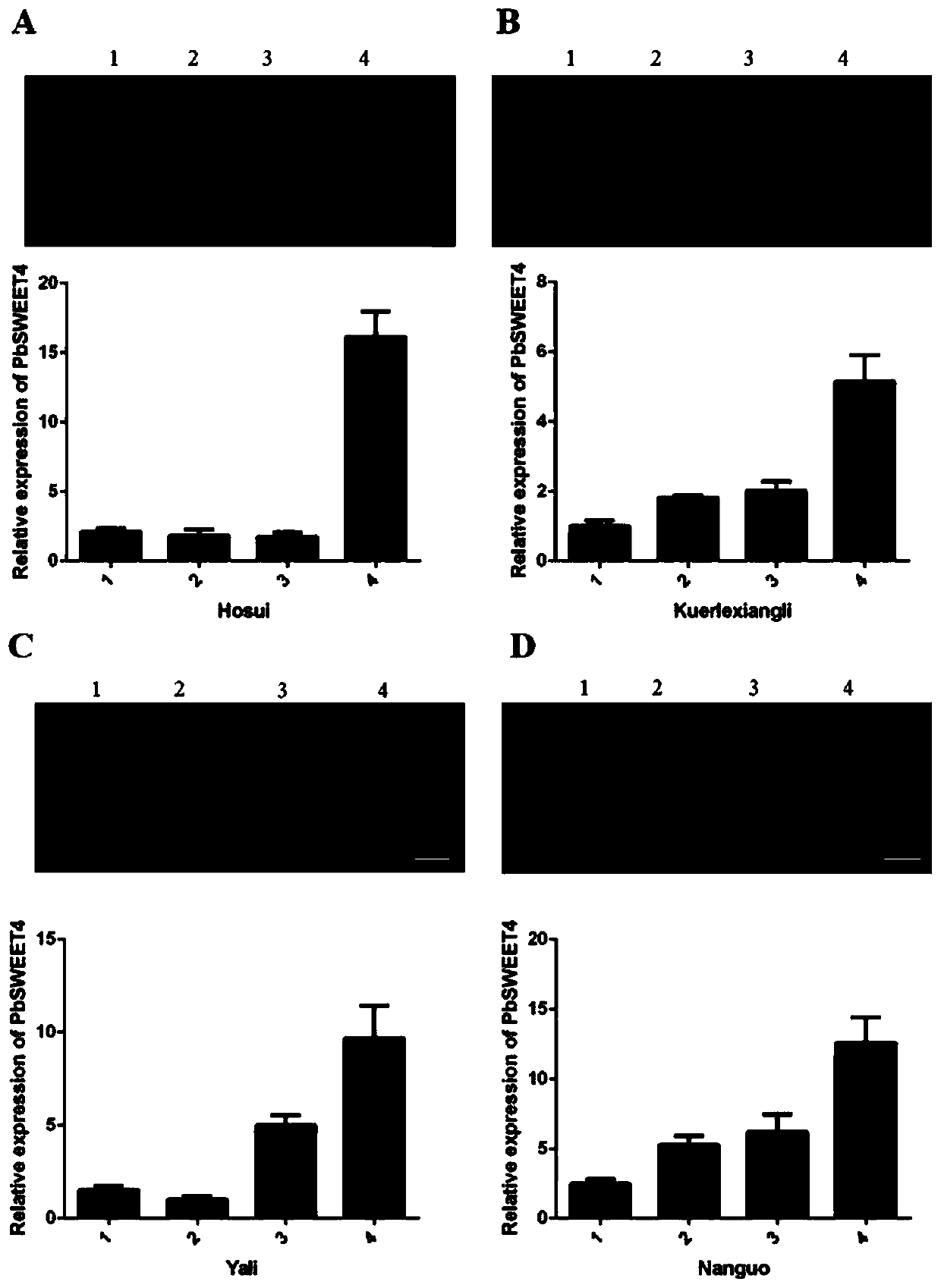
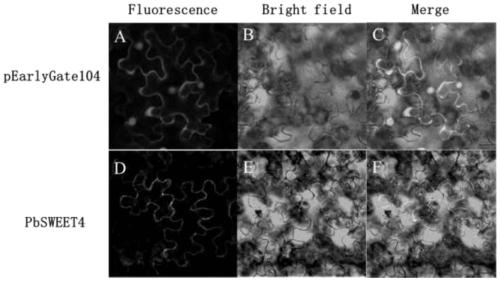
Pyrus sugar transport gene PbSWEET4 and applications thereof
ActiveCN111154772ASpeed up effluxAccelerated agingPlant peptidesFermentationFragariaPremature aging
The invention discloses a pyrus sugar transport gene PbSWEET4 and applications of a recombinant expression vector of the gene. The nucleotide sequence of the structural gene PbSWEET4 separated from Dangshan pears and having sugar efflux functions is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. The gene PbSWEET4 is converted into diploid forest strawberries to perform function verification; wild strawberries are taken as reference, the sucrose content of the obtained transgenic strawberry leaves can be significantly reduced, and the leaves show the phenomenon ofpremature aging; and therefore, the cloned PbSWEET4 gene is the functional structure gene encoding sugar transporters and has the functions of the efflux of soluble sugar, so that negative regulationeffects in leaf sugar accumulation can be achieved, and the gene also takes part in the aging process of the leaves.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
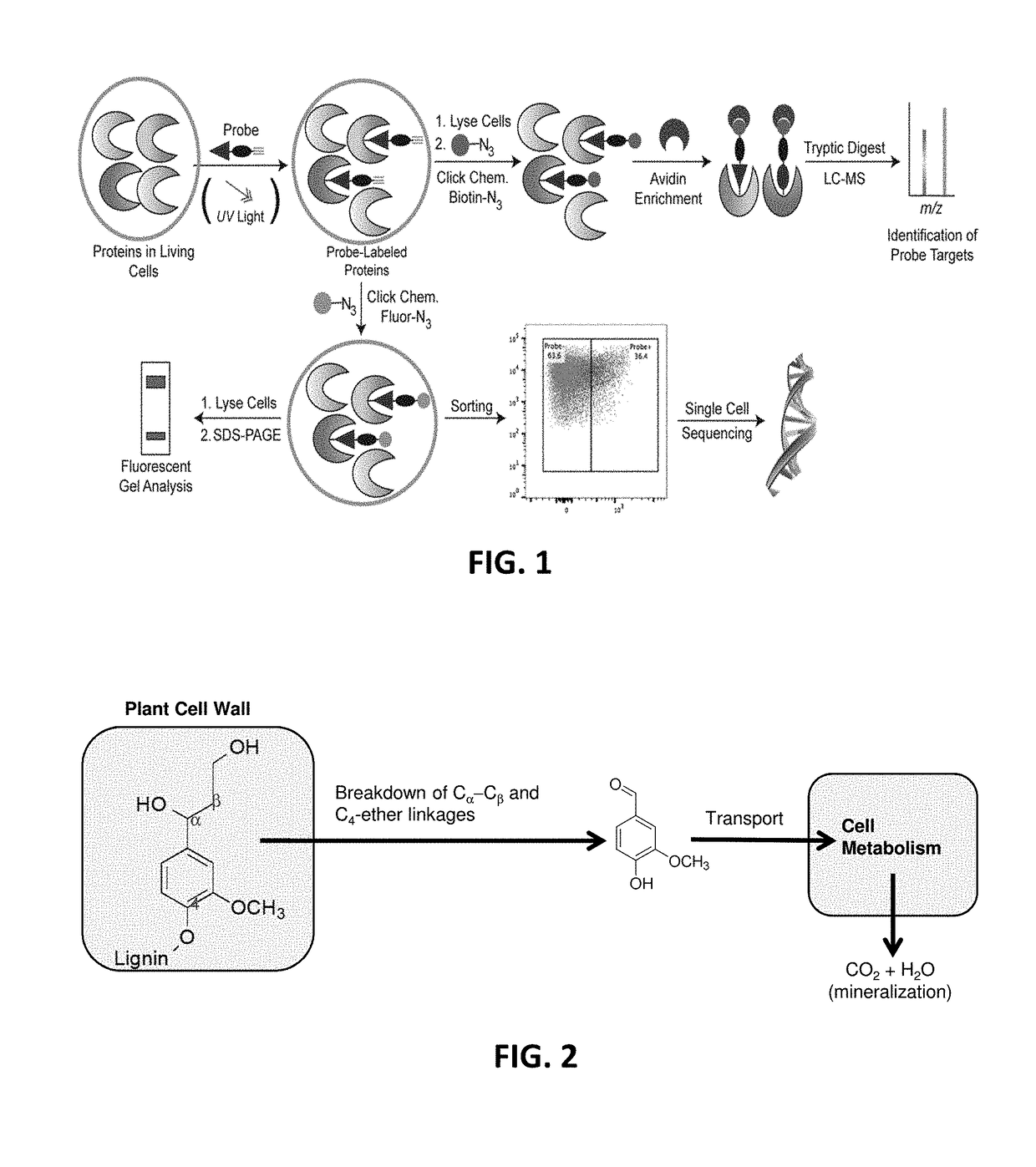
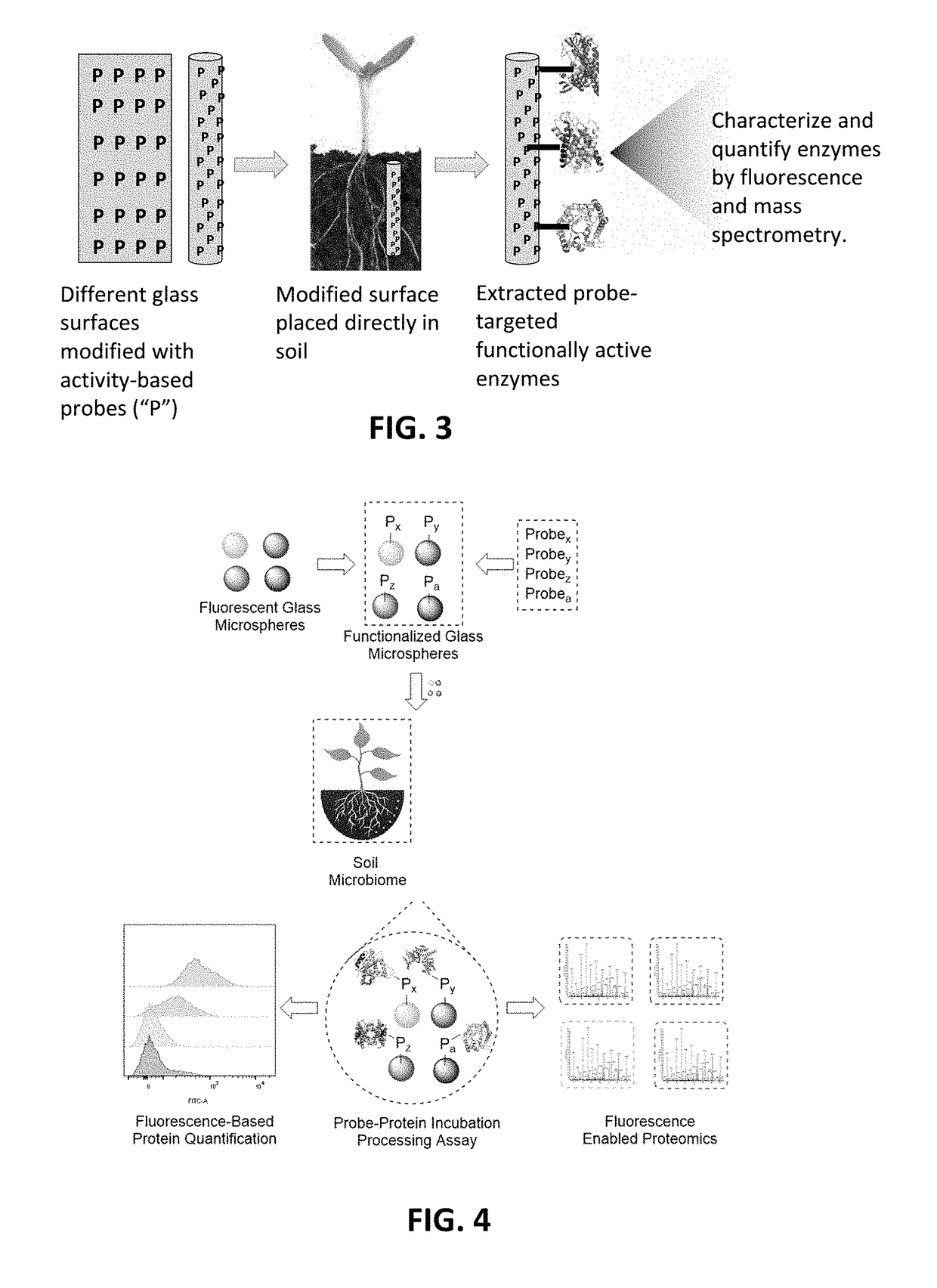
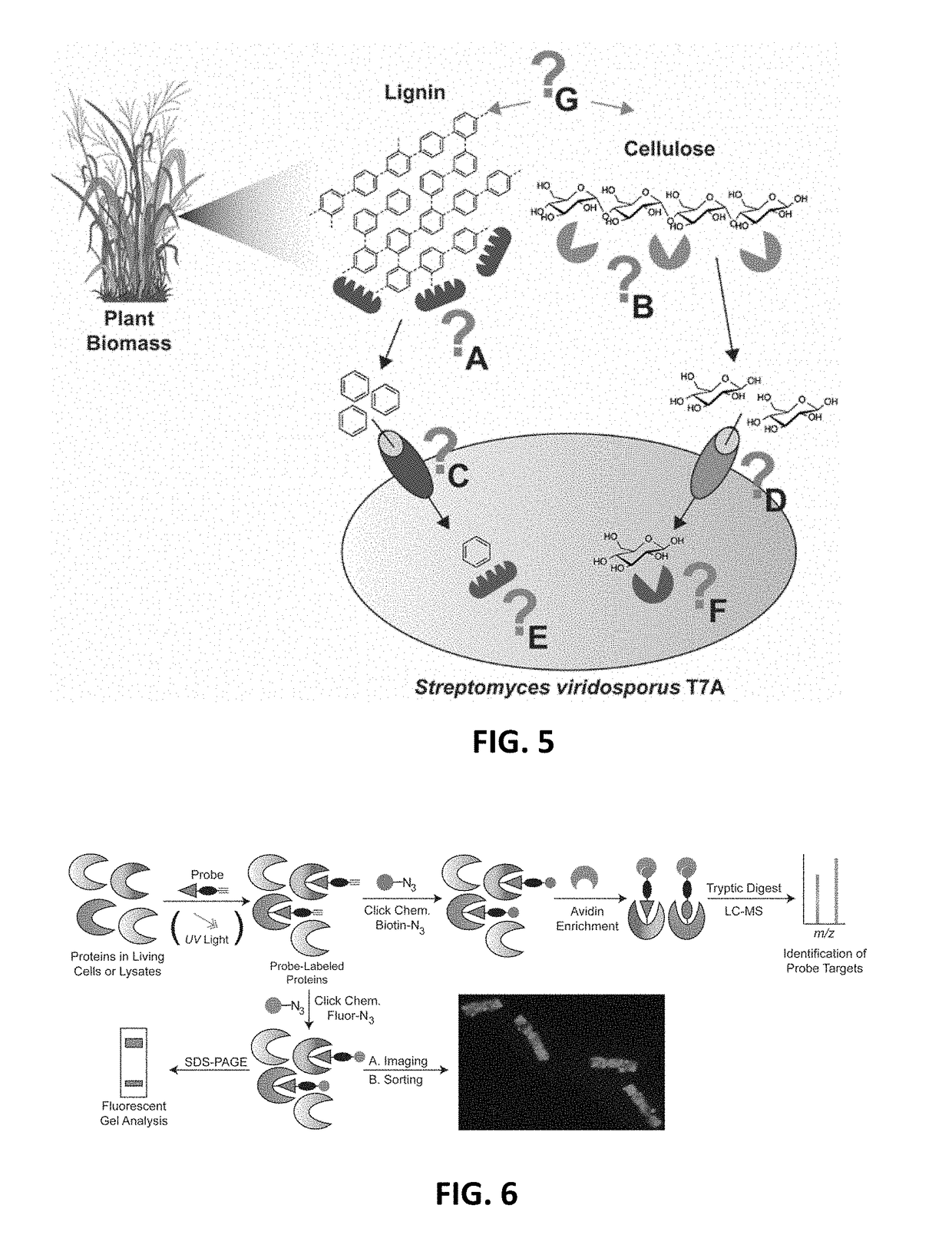
Function-based probes for environmental microbiome analysis and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20190086410A1Promote formationAlter metabolismSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiomeBioremediation
Probe embodiments for identifying analytes involved in biofuel or bioenergy production, bioremediation, or nutrient cycling as well as methods of making and use are described herein. In some embodiments, probes identifying cellulose degradation and / or sugar transport, lignin or chitin degradation, or peptide or toxin metabolism are included. In some embodiments, probes for identifying analytes in a soil sample are included in the compositions and methods disclosed herein.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
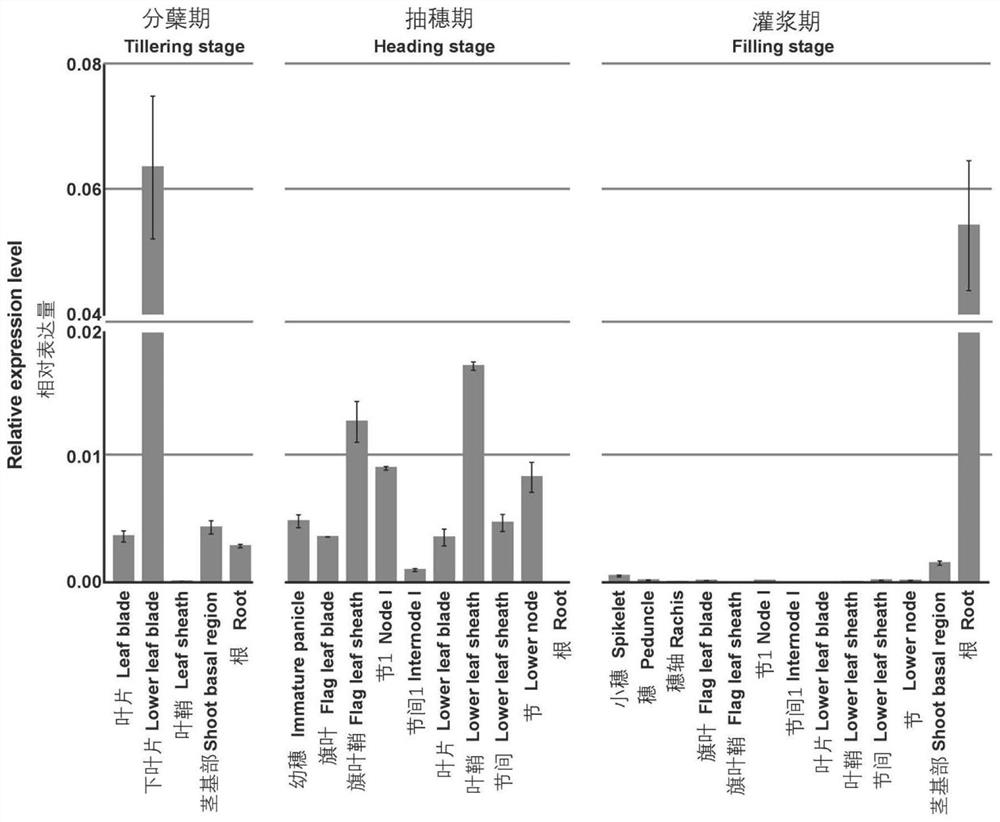
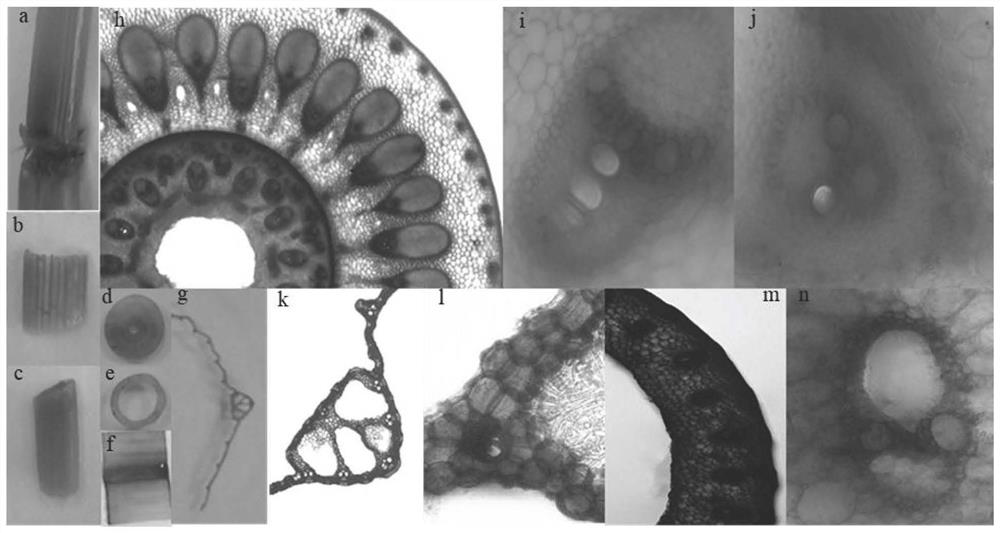
Rice sugar transport gene osvgt2 and its sugar transporter, application and amplification primers
ActiveCN112341531BReduce outputIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologySugar transport
The invention discloses a rice sugar transport gene OsVGT2 and a sugar transporter encoded by the rice sugar transport gene OsVGT2. The overexpression of the rice sugar transport gene OsVGT2 in rice can significantly increase the rice yield per plant, and the yield of a plot can be increased by 10-11 %, the seed setting rate and yield of rice can be significantly reduced after the mutation / knockout, and the yield of the plot can be reduced by 15‑18%; by affecting the transportation and distribution of photosynthetic products, it can affect the yield of rice, but has no effect on fertility; for Enhance the transport and distribution capacity of photosynthetic products through genetic improvement of varieties, and provide a realistic basis for continuous improvement of rice yield. The invention also discloses the application of the rice sugar transport gene OsVGT2 and its sugar transporter in cultivating high-yield crops, which can rapidly and effectively increase the yield of crops. The invention also discloses several PCR amplification primers of the rice sugar transport gene OsVGT2, which can effectively and quickly amplify the gene OsVGT2 from the rice cDNA.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemicals using facilitated diffusion for sugar import
ActiveUS10934565B2Augment or improve an already existing capacity of the biocatalystsImprove filtering effectMutant preparationBiofuelsGlucose utilizationSucrose
This invention relates to the production of succinic acid and other chemicals derived from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) by fermentation with a microorganism in which the fermentation medium contains one or more sugars, and in which one or more of the sugars is imported into the cell by facilitated diffusion. As a specific example, succinic acid is produced from a glucose-containing renewable feedstock through fermentation using a biocatalyst. Examples of such a biocatalyst include microorganisms that have been enhanced in their ability to utilize glucose as a carbon and energy source. The biocatalysts of the present invention are derived from the genetic manipulation of parental strains that were originally constructed with the goal to produce one or more chemicals (for example succinic acid and / or a salt of succinic acid) at a commercial scale using feedstocks that include, for example, glucose, fructose, or sucrose. The genetic manipulations of the present invention involve the introduction of exogenous genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose into the parental strains. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of glucose or fructose can also be introduced into a microorganism prior to developing the organism to produce a particular chemical. The genes involved in the transport and metabolism of sucrose can also be used to augment or improve the efficiency of sugar transport and metabolism by strains already known to have some ability for glucose utilization in biological fermentations.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
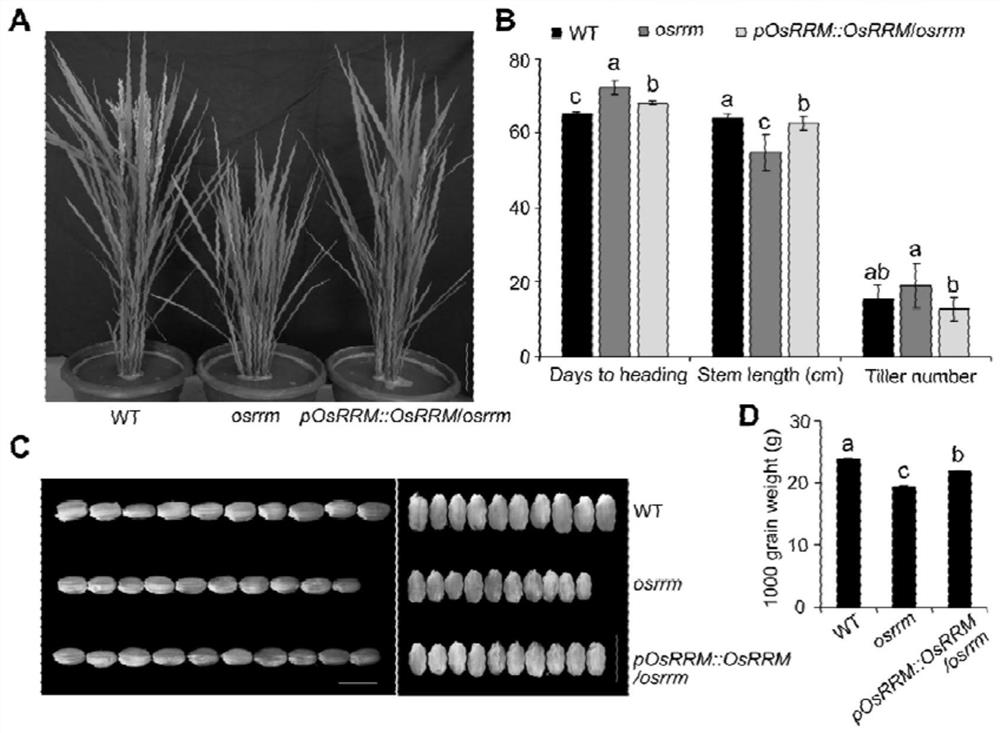
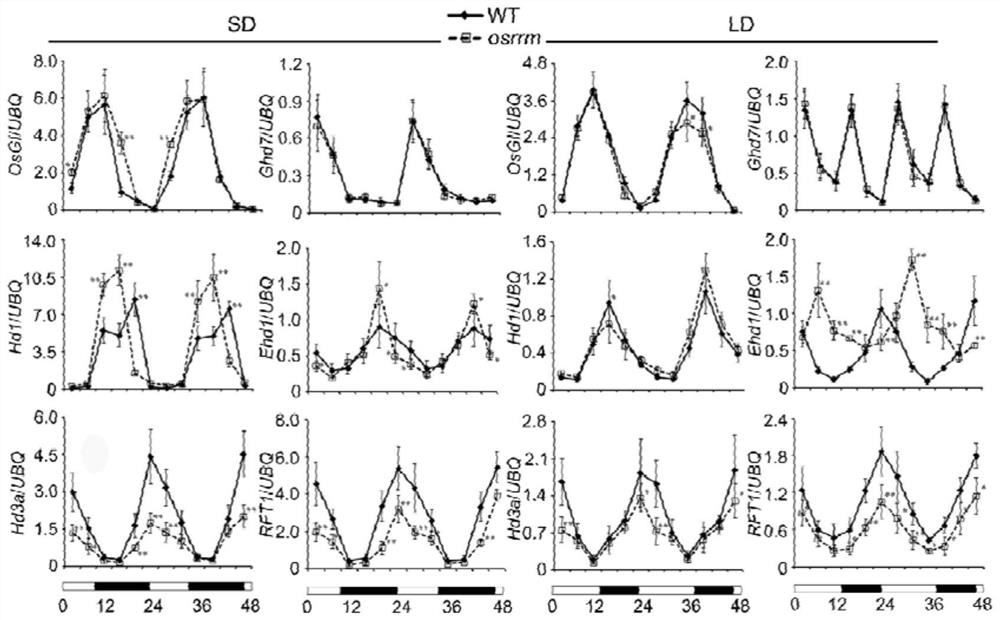
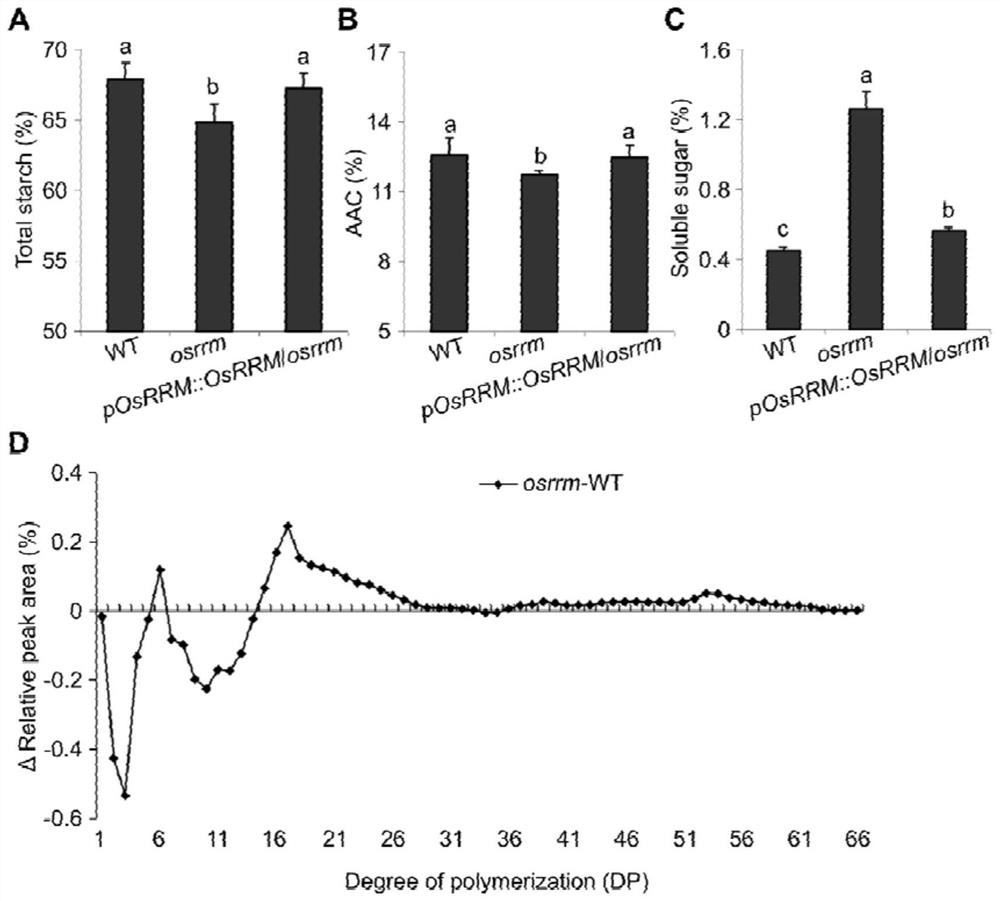
RNA binding protein OsRRM and application of RNA binding protein OsRRM in regulation and control of sugar transport in rice
ActiveCN112375128AReveal Physiological FunctionImprove stabilityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an RNA binding protein OsRRM and application of the RNA binding protein OsRRM in regulation and control of sugar transport in rice. The RNA binding protein OsRRM is one of thefollowing nucleotide sequences: (1) a DNA sequence shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and (2) a DNA sequence which has more than 90% of homology with the DNA sequence limited by the sequence 1in the sequence table and encodes the same functional protein. On the other hand, the invention discloses application of the RNA binding protein OsRRM in regulation and control of sugar transport inrice. The RNA binding protein OsRRM has the beneficial effect that an encoding gene of a sugar transporter is regulated and controlled by the new RNA-binding protein OsRRM. OsRRM directly and specifically binds to mRNA of a plurality of the multiple sugar transporter encoding genes, and may increase their stability. As the distribution of sugar is crucial to the growth, development and yield of plants, the research provides a new guidance direction for the increase of the crop yield.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV +1
Method of producing succinic acid and other chemicals using facilitated diffusion for sugar import
ActiveUS20200032301A1Augment or improve an already existing capacity of the biocatalystsImprove filtering effectMutant preparationBiofuelsGlucose utilizationSucrose
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Sugarcane cane sugar transport protein ShSUT2 type genes and application thereof
InactiveCN103204916BIncrease productionImprove qualityFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastSucrose
The invention discloses two cane sugar transport protein ShSUT2 type genes from sugarcanes and application thereof. The cane sugar transport protein genes ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B are that: the amino acid sequences are respectively as shown by SEQ ID NO: 2 and 4; and the base sequences of coding genes ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B are as shown by SEQ ID NO: 1 and 3. The absorption of a deletion function mutant through yeast cane sugar shows that both the ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B coding proteins have the cane sugar transport activity. The cane sugar transport protein ShSUT2 type genes are responsible for absorbing cane sugar in the apoplast of a sugarcane plant and participating in the physiological process of cane sugar transportation, distribution and accumulation of the sugarcane plant. The sugarcane cane sugar transport protein ShSUT2 type genes can provide a new path for improving cane sugar transportation and distribution efficiency of the sugarcane, promoting growth and development of plants and improving yield of the sugarcane and the sugar content.
Owner:GUANGXI KANGTIAN AGRI TECH CO LTD
Novel glucose derivative, and cell imaging method and imaging agent using said derivative
ActiveUS20180238899A1Improve accuracySugar derivativesGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCancer cellIntracellular
Provided is a glucose derivative, which is taken into cells via a membrane sugar transport system and is represented by formula (1). Also provided are an imaging agent and an imaging method for a cell or intracellular molecule using said glucose derivative. Further provided is a method for detecting cancer cells with good accuracy using said glucose derivative and an imaging agent to be used in said method. More specifically provided are D-glucose derivatives and L-glucose derivatives in which glucose is bound to the 7-position of a fluorescent molecular group with a coumarin backbone or a quinolone backbone. Also provided are a cell imaging agent and imaging method using the derivative. A cancer cell imaging agent and imaging method using the L-glucose derivative is also provided. G is a group selected from formulas (G1)-(G4) below.
Owner:ORBIO CORP
Sugarcane monosaccharide transport protein ShHXT2 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107043777APromote growthImprove cold stress resistancePlant peptidesFermentationMonosaccharide Transport ProteinsSaccharum
The invention provides a sugarcane monosaccharide transport protein ShHXT2 gene of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also provides a protein coded by the ShHXT2 gene and application of the ShHXT2 gene. According to the invention, the ShHXT2 gene is cloned from sugarcane for the first time, and the gene has a transport function of a sugar transport protein and can be positioned in the cell membrane of a cell; thus, the capability of the plant resistance against cold stress can be enhanced, the growth of a plant such as sugarcane is facilitated in an inverse condition, and a genetic basis is provided for revealing the regulation function of a sucrose transport mechanism on the growth development and quality improvement of the plant and a gene engineering research for increasing crop yield and improving quality.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Transformed plant, method for producing sugar-containing exudate using transformed plant
ActiveCN105848471BHigh in sugarRecombinant DNA-technologyPlant peptidesHigh concentrationTranslocator protein
Exudates containing high concentrations of sugars are produced from plants. A nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transport having a defined consensus sequence derived from the amino acid sequence of a SWEET protein classified as clade III is introduced and / or expression of the protein is enhanced.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
Cell sugar transport channel inhibitor
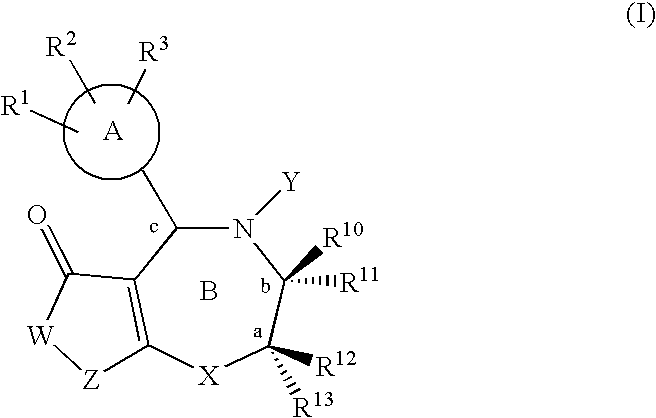
ActiveCN113149930APrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugBiochemistry
The invention discloses a cell sugar transport channel inhibitor of which the structure is shown as a formula (I). The cell sugar transport channel inhibitor disclosed by the invention can target a cell sugar transport channel, and inhibit tumor cell proliferation by directly blocking a GLUT channel and intake of sugar nutrients by tumors; the invention also relates to an application in preparation of antitumor drugs or a reagent for inhibiting a cell sugar transport channel GLUT.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pear Sucrose Transporter Gene pbsut2 and Its Application
ActiveCN105624171BBreak through the barriers of traditional breeding methodsPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologySucrose
The invention discloses a pear sugar transport protein gene PbSUT2 and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the pear sugar transport protein gene separated from a pear fruit is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and a coded amino acid sequence of the pear sugar transport protein gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. The gene PbSUT2 is transformed into a tomato through an agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation method; the biological function verification of an obtained transgenic plant indicates that the cloned gene PbSUT2 has the functions of promoting plant early flowering and increasing the content of sucrose in the fruit. The discovery of the gene PbSUT2 provides new genetic resources for promoting the molecular breeding of plant fruit quality.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
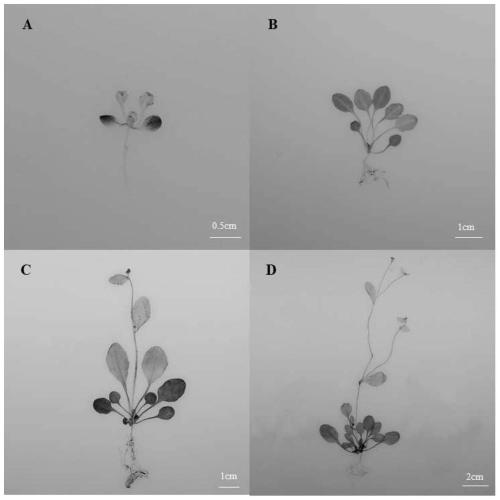
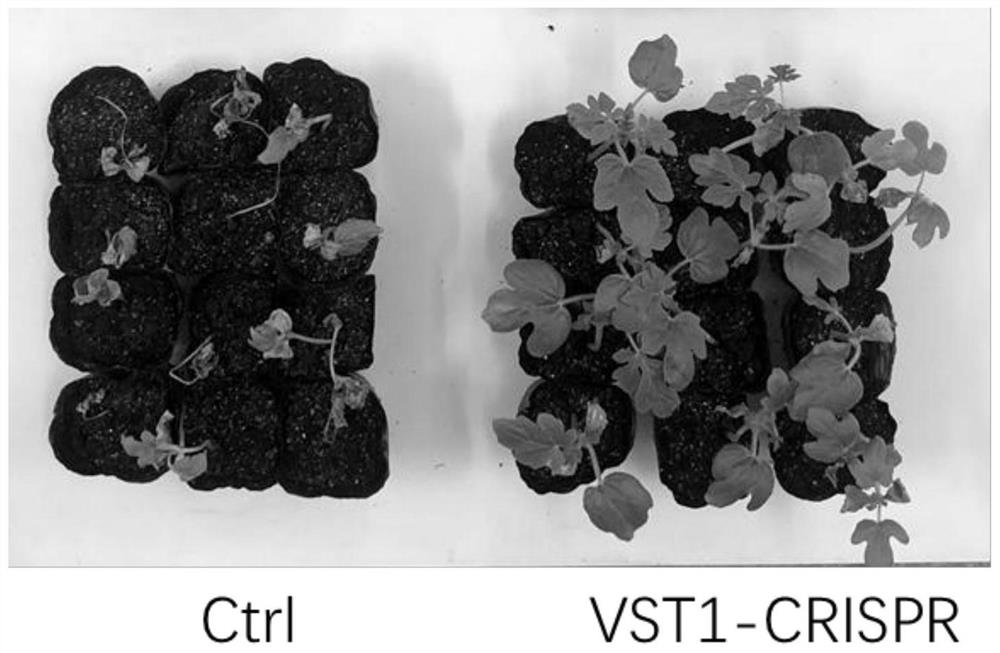
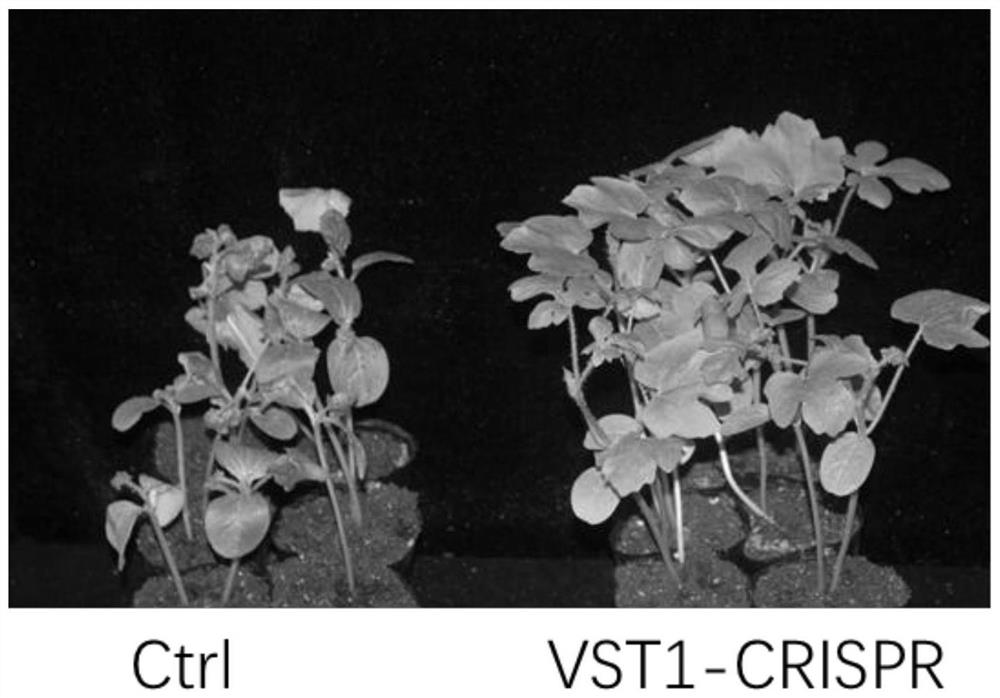
Novel watermelon sugar transporter as well as coding gene ClVST1 and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and relates to a novel watermelon sugar transporter and a coding gene ClVST1 and application thereof. The novel watermelon sugar transport protein has a sequence composition shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and the coding gene ClVST1 has a sequence composition shown in a sequence 2 in the sequence table. The invention also relates to application of the novel watermelon sugar transporter protein and the novel watermelon sugar transporter coding nucleic acid sequence in watermelon disease and insect pest resistance. The invention further provides an obtaining method of the watermelon plant disease and insect pest resistant strain. The watermelon novel sugar transporter and the coding gene ClVST1 provided by the invention are closely related to disease and insect pest resistance, and the higher the expression quantity is, the stronger the disease and insect pest resistance is; therefore, a stable watermelon strain resistant to bacterial fruit blotch and aphid can be obtained by knocking out novel sugar transport of watermelons in watermelon plants, and a quick and efficient way is provided for breeding of watermelons resistant to diseases and insect pests.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
A block candy folding packaging machine
ActiveCN104192357BAvoid stickingAvoid accumulationWrapper folding/bending apparatusPackaging automatic controlTemperature controlTransmission belt
The invention discloses a block candy folding packaging machine, which comprises a frame, a sugar conveying mechanism, a sugar sorting mechanism, a sugar wrapping mechanism and a paper feeding device. The sugar conveying mechanism, the sugar sorting mechanism, the wrapping Sugar mechanism, sugar conveying mechanism includes sugar conveying motor and conveyor belt, sugar sorting mechanism includes sugar sorting motor, sugar dividing rod and temperature controller, sugar wrapping mechanism includes electrical control system, sugar pressing rod, packing table, first bag sugar rod, The second pack of sugar rods, the third pack of sugar rods, and the fourth pack of sugar rods; a paper feeding device is installed on the frame, and the paper feeding device corresponds to the bottom of the sugar wrapping mechanism, and the paper feeding device is connected with the paper storage box; the machine A control box is also installed in the frame, the control box is located below the paper storage box, and the control box is connected with the paper feeding device and the sugar wrapping mechanism. The present invention realizes the hexahedron folding packaging of block candies through the sugar conveying mechanism, the sugar sorting mechanism and the sugar wrapping mechanism, has a reasonable structure, avoids the sticking and accumulation of sugar blocks, and has high production efficiency.
Owner:衡阳周福记食品有限公司
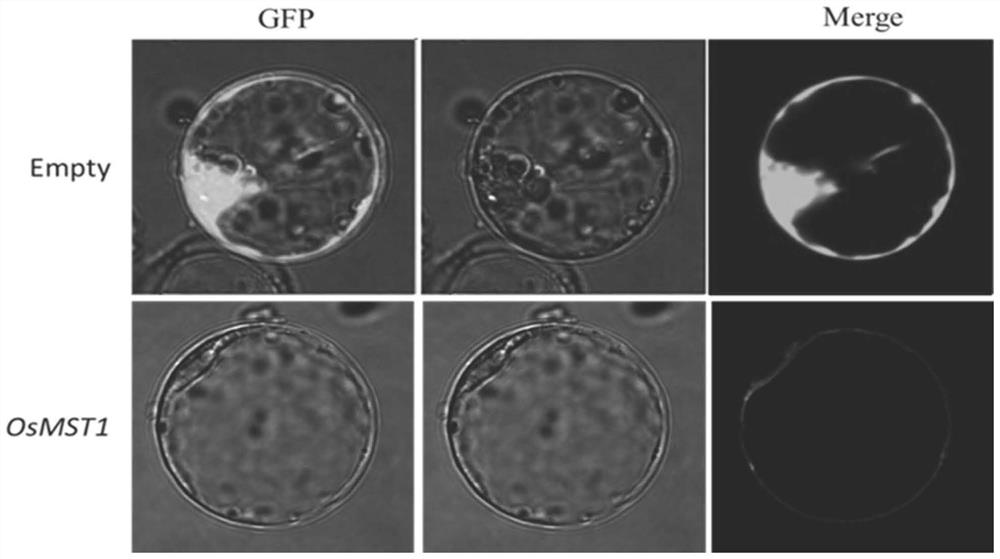
Rice sugar transport gene osmst1 and its sugar transporter, application and amplification primers
ActiveCN112342220BReduce outputIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologySugar transport
The invention discloses a rice sugar transport gene OsMST1 and a sugar transporter encoded by the rice sugar transport gene OsMST1. Overexpression of the rice sugar transport gene OsMST1 in rice can significantly increase the yield of rice per plant, and the yield of a plot can be increased by 15-16 %, the seed setting rate and yield of rice can be significantly reduced after the mutation / knockout, and the yield of the plot can be reduced by 20‑22%; by affecting the transportation and distribution of photosynthetic products, it can affect the yield of rice, but has no effect on fertility; for Enhance the transport and distribution capacity of photosynthetic products through genetic improvement of varieties, and provide a realistic basis for continuous improvement of rice yield. The invention also discloses the application of the rice sugar transport gene OsMST1 and its sugar transporter in cultivating high-yield crops, which can rapidly and effectively increase the yield of crops. The invention also discloses several PCR amplification primers of rice sugar transport gene OsMST1, which can effectively and quickly amplify the gene OsMST1 from rice cDNA.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
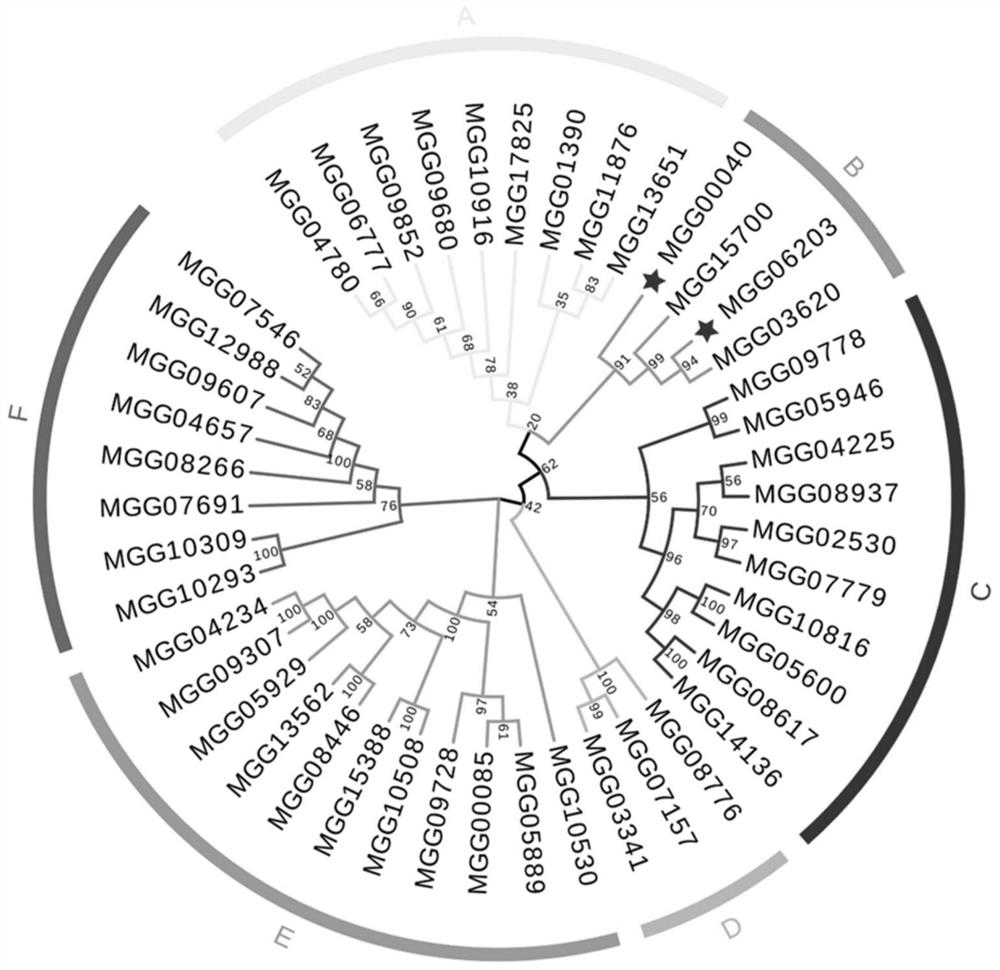
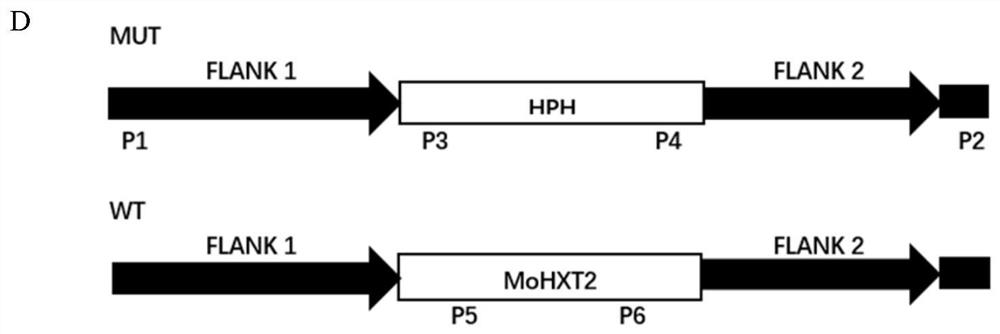
Application of the rice blast fungus gene mohxt2 in the regulation of sugar transport in plants
ActiveCN111411122BEffective controlReduce melanin contentPeptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDrug target
The invention discloses the application of the rice blast fungus gene MoHXT2 in regulating the plant sugar transport function. The present invention finds that the transporter encoded by MoHXT2 accepts a variety of sugars as substrates, that is, the MoHXT2 gene is a hexose transporter of Magnaporthe grisea. After knocking out MoHXT2 using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout system, the melanin content of the mutant hyphae is found The pathogenicity was significantly reduced, and phlorizin could inhibit the transport of hexose by MoHXT2, thereby inhibiting the growth of Magnaporthe oryzae. Therefore, the MoHXT2 gene can be used to regulate plant sugar transport function, regulate the pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea and regulate the growth and development of Magnaporthe grisea, and it can also be used as a drug target for new pesticides, providing a more reliable direction for the synthesis of targeted fungicides .
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com