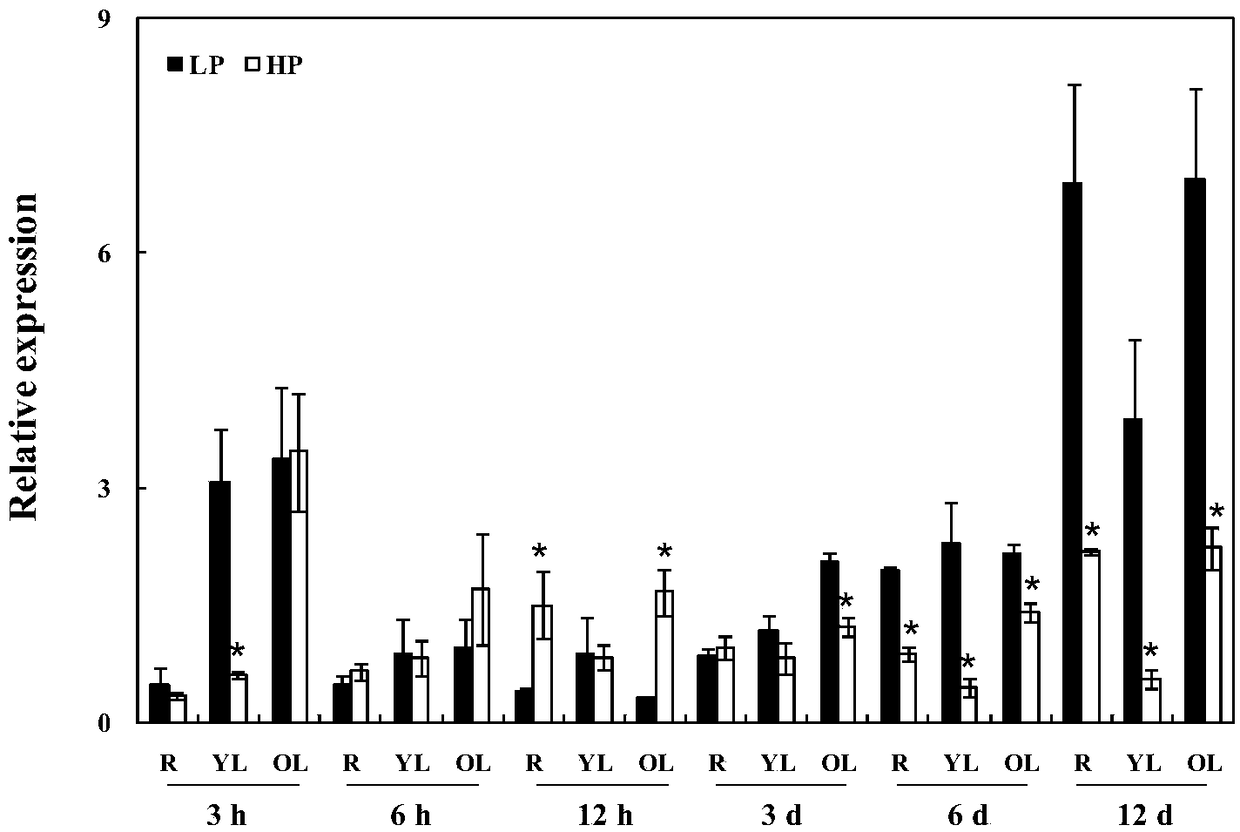
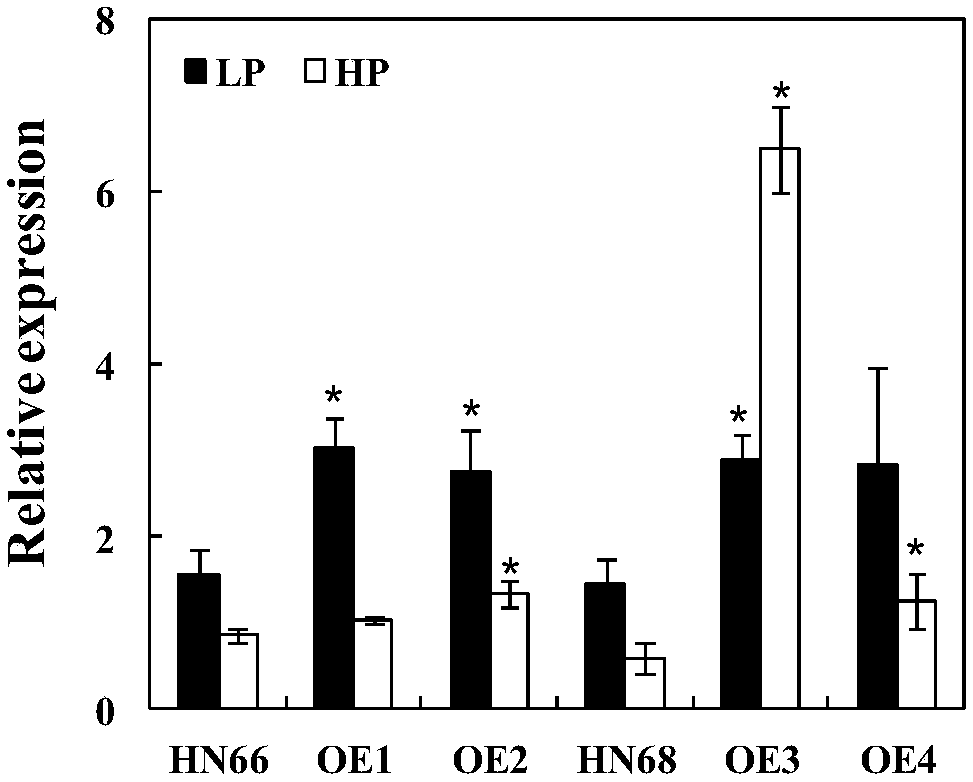
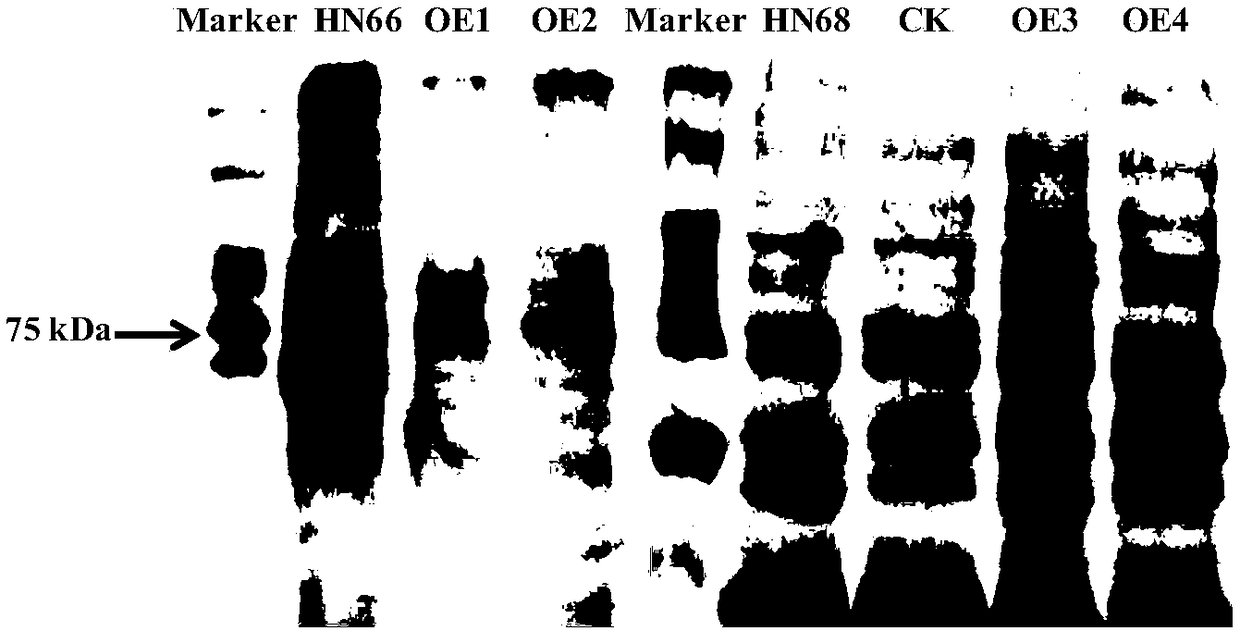
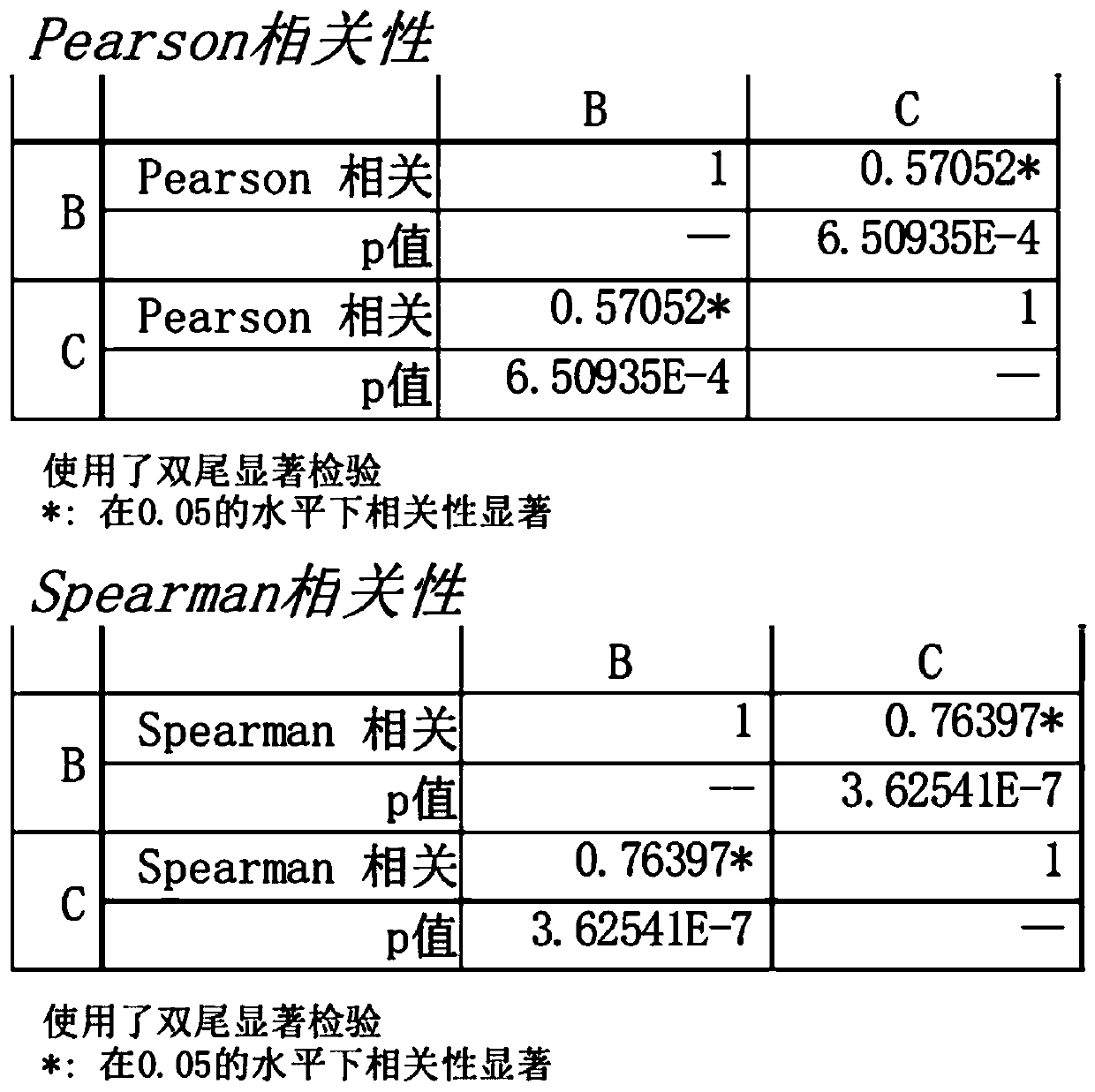
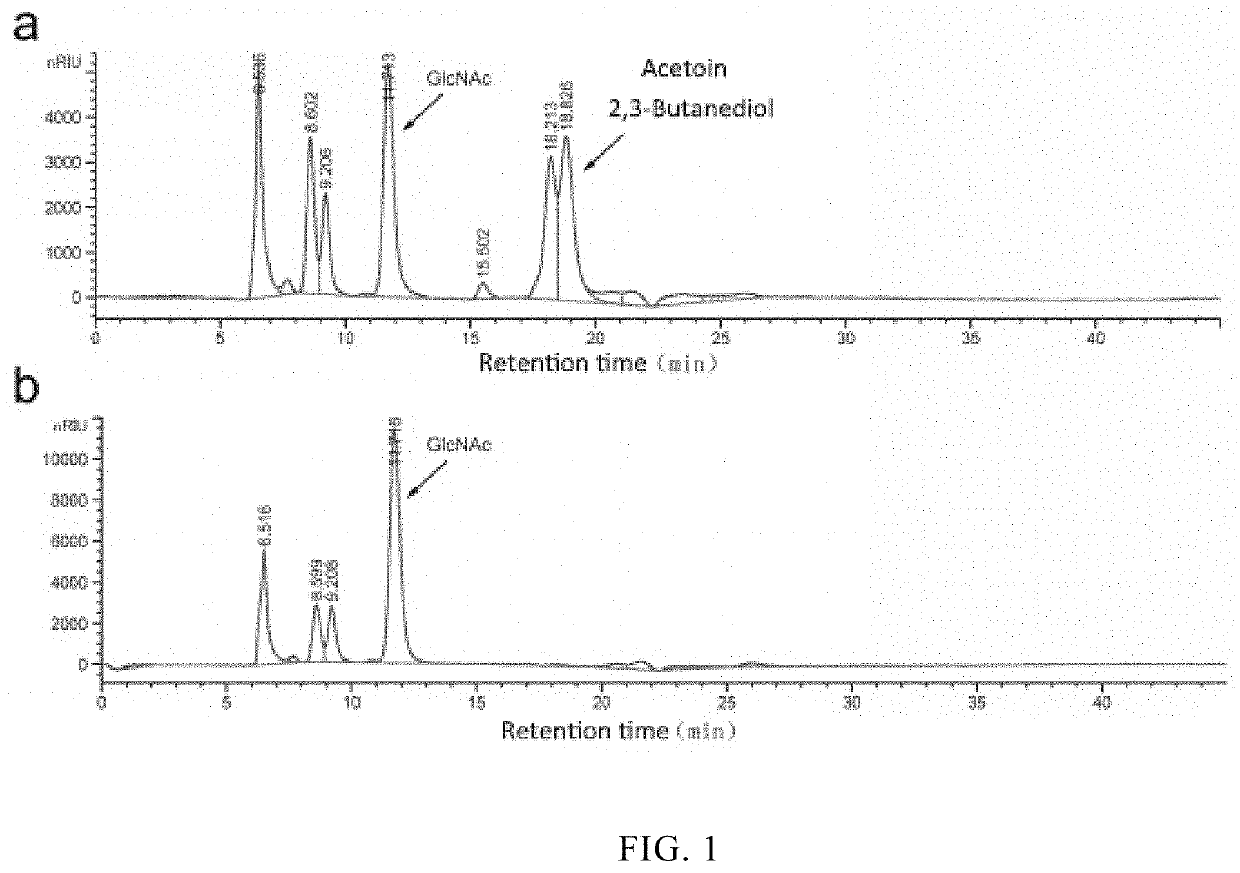
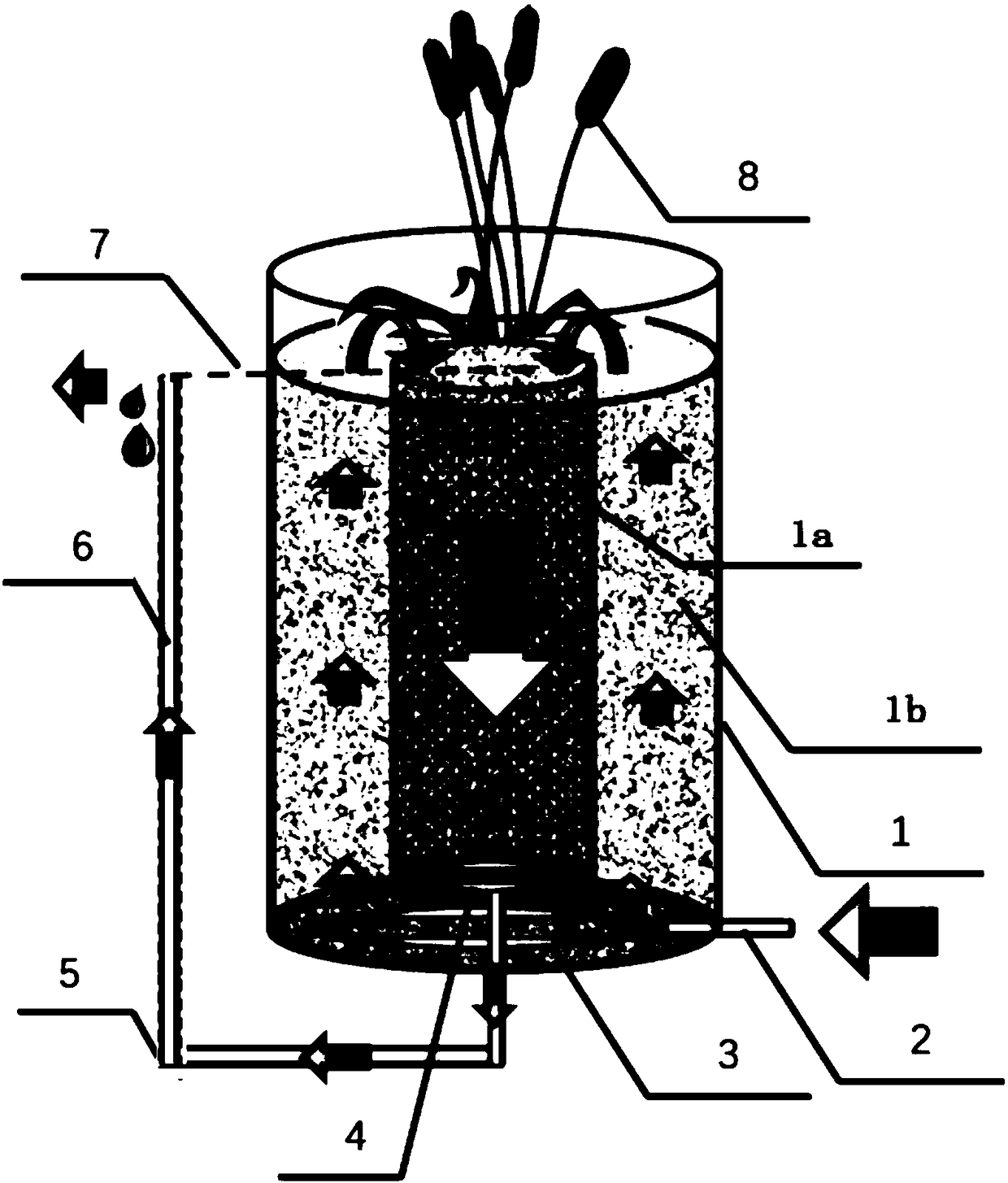
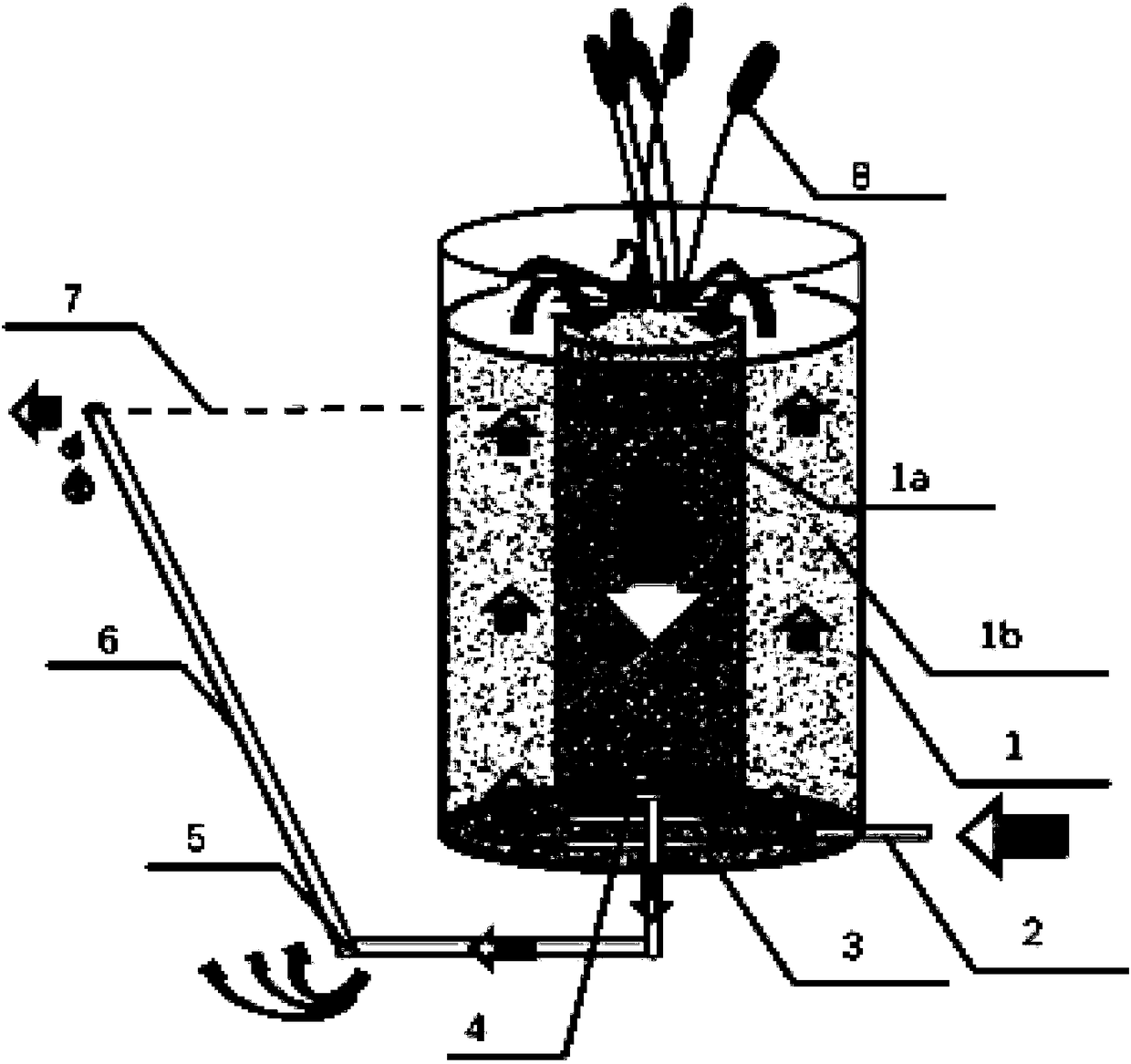
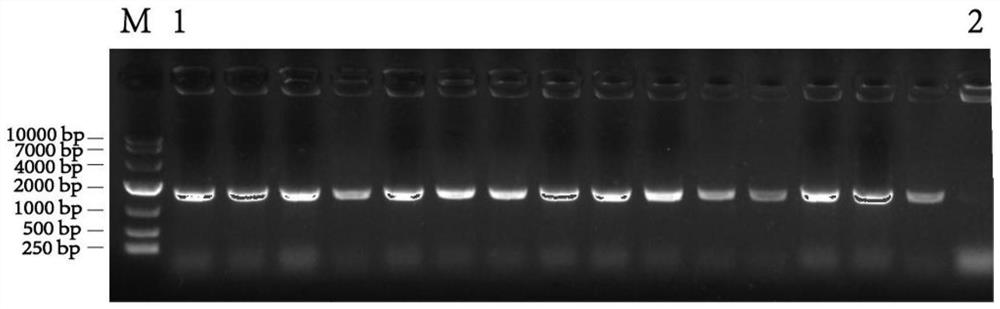
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Carbon metabolism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The metabolism of carbon atoms through one carbon metabolism is linked with changes in redox status. These changes largely occur through the reduction of NADPH and oxidation of NADP +. Tetrahydrofolate reductase reduces THF and this reaction consumes one molecule of NADPH for each turn of the folate cycle.
Methods and materials for identifying polymorphic variants, diagnosing susceptibilities, and treating disease
InactiveUS20080213775A1Increased susceptibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCarbon metabolism
The invention is directed to materials and methods associated with polymorphic variants in two enzymes involved in folate-dependent and one-carbon metabolic pathways: MTHFD1 (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase, 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase) and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+dependent) 1-like (MTHFD1L). Diagnostic and therapeutic methods are provided involving the correlation of polymorphic variants in MTBFD1, MTHFD1, and other genes with relative susceptibility for various pregnancy-related and other complications.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +2
Leaf fertilizer special for tobacco
The invention discloses a leaf fertilizer special for tobacco, which comprises monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, zinc sulfate, borax, ammonium molybdate, L-malic acid, glutamic acid, brassinolide and solvent water. Inorganic and organic nutrient substances are provided for the growth of tobacco to meet the basic growth requirement of tobacco; for example, magnesium, boron and zinc are medium trace nutrient elements deficient at the tobacco zone in Hubei; the glutamic acid and the malic acid can be directly involved in certain important metabolic activities during the growth of tobacco, in particular tricarboxylic acid cycle, and promote the growth of tobacco in the later stage to timely switch from nitrogen metabolism into carbon metabolism, so as to improve maturity and quality; and the plant growth modifier, brassinolide, can induce to strengthen the immunity of tobacco and improve the virus and fungal disease resisting capability of tobacco.
Owner:XIANGYANG COMPANY OF HUBEI TOBACCO
Method for improving poly-malic acid yield
ActiveCN103789363AIncrease productionRealize the flowMicroorganism based processesFermentationPullulanCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a method for improving the poly-malic acid yield in aureobasidium pullulans through surface active agent tween or span. The method particularly comprises the steps that after the aureobasidium pullulans is activated, the aureobasidium pullulans is fermented under the condition containing 0.1 g / L to 0.5 g / L tween or span. The method is simple, the tween or the span can be directly added into a fermentation medium, the carbon metabolism flow direction of synthesis of the poly-malic acid and Pulullan can be adjusted, the poly-malic acid yield can be improved to a large extent, and the method has the advantages of being low in fermentation cost, high in yield, strong in technical economical efficiency, capable of being applied to poly-malic acid industrial production and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as construction method and application of genetic engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104388371AIncrease productionImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaPeptidesCarbon metabolismCarbon storage
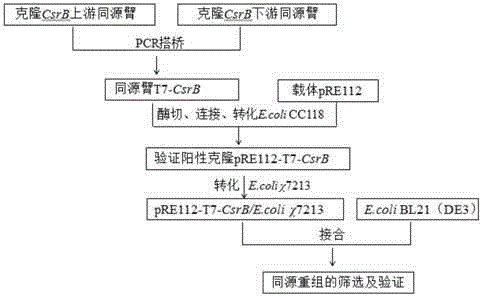
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for high-yield phloroglucinol as well as a construction method and an application of the genetic engineering bacterium and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium over-expresses carbon storage and regulation factor gene CsrB shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and co-expresses a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor gene marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase. The invention also provides the construction method and the application of the genetic engineering bacterium for the high-yield phloroglucinol. With the adoption of the genetic engineering bacterium, the yield of the phloroglucinol is firstly increased by 115.6 percent by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level of the genetic engineering bacterium, and the genetic engineering bacterium has a high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
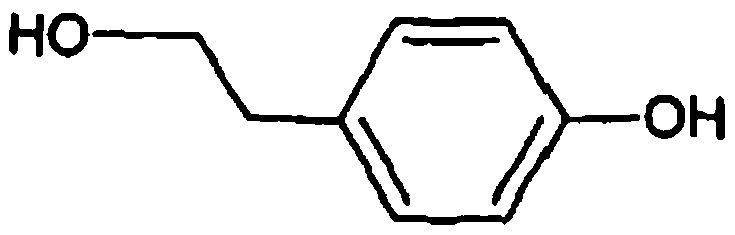
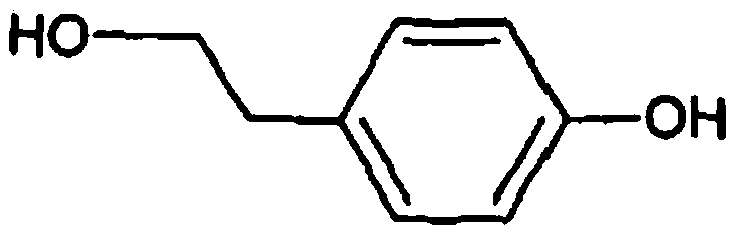
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof for producing tyrosol and derivative
InactiveCN109929883AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
Owner:YANTAI HUAKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
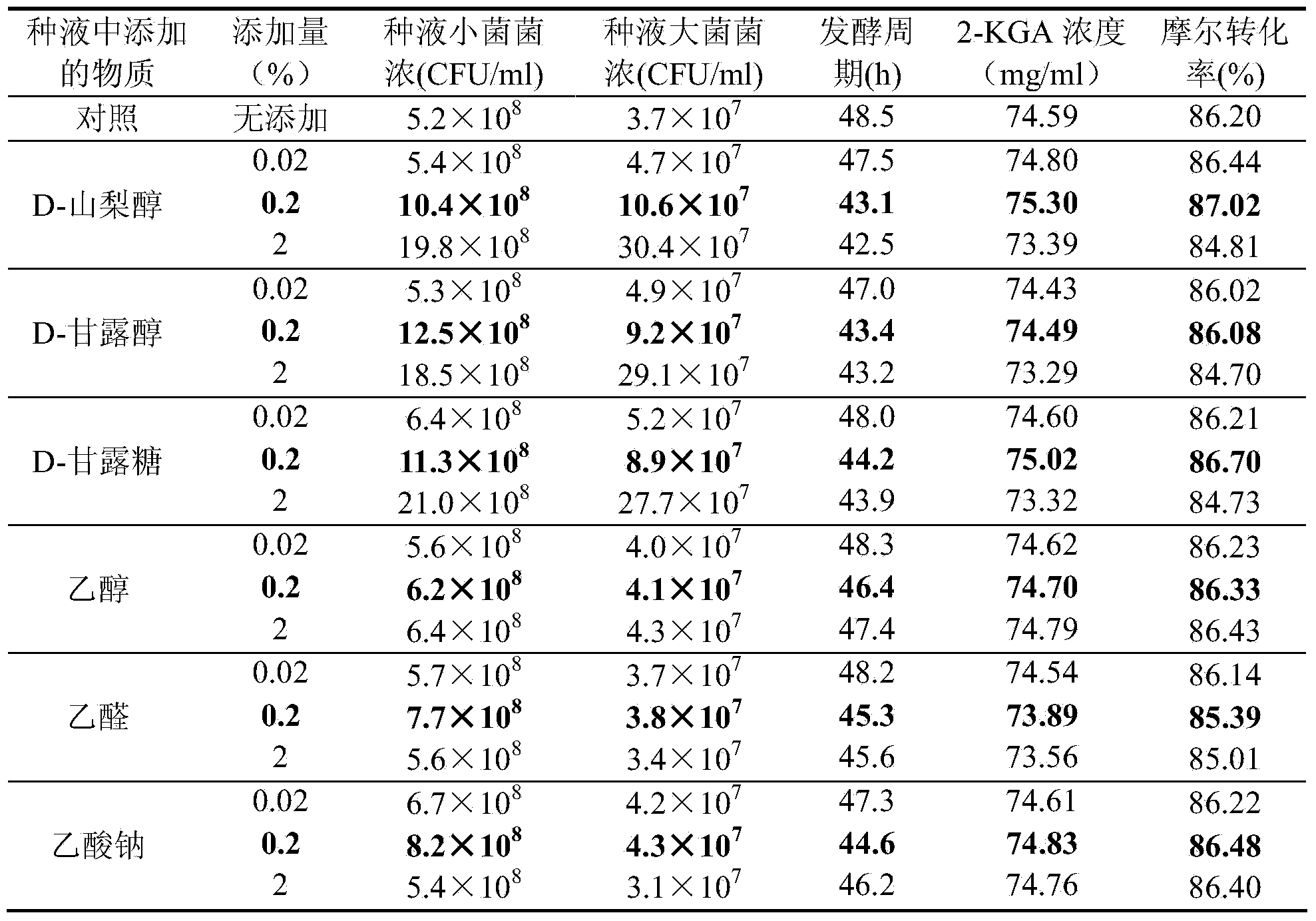
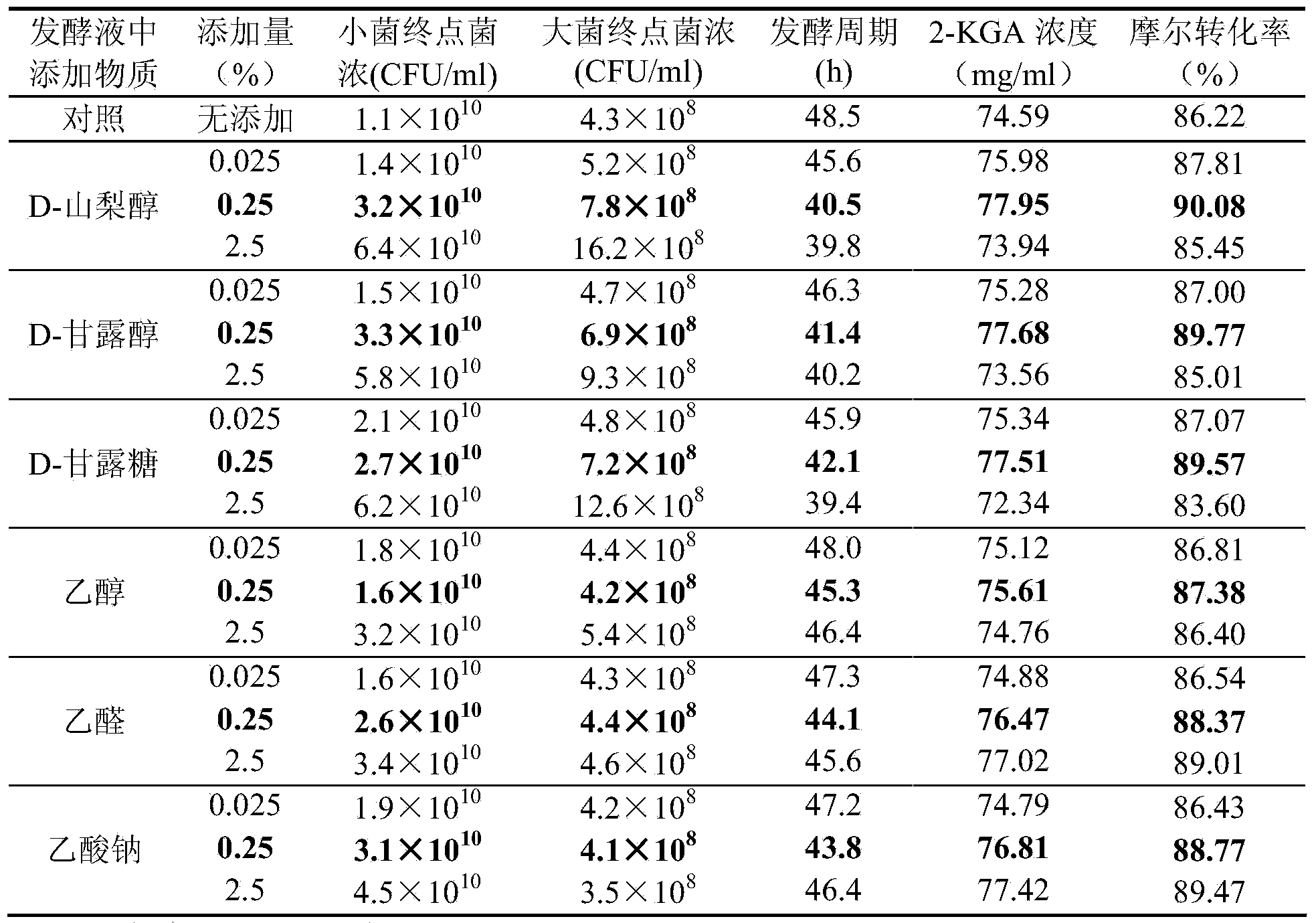
Method for improving production capacity of 2-KGA (2-keto-L-gulonic acid) through enhancement of Ketogulonogeniumvulgarum carbon metabolism level
InactiveCN104357529AIncrease profitPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationCarbon metabolismVITAMIN C PREPARATIONS
The invention discloses a method which enhances glycometabolism efficiency of Ketogulonogeniumvulgarum, increases the number of bacteria, greatly shortens the incubation period of 2-KGA (2-keto-L-gulonic acid) and improves the production efficiency by adding carbon sources including two-carbon units such as ethyl alcohol, acetaldehyde and acetic acid as well as six-carbon units such as D-sorbitol, D-mannitol and D-mannose which facilitates utilization of Ketogulonogeniumvulgarum in a mixed fermentation process of a vitamin C two-step fermentation method according to research results of Ketogulonogeniumvulgarum metabolic network analysis. In a 5L fermentation tank, the period can be shortened by 14.04%, and the yield is increased by 3.40 %. According to another application, L-sorbose is taken as a carbon source by reducing Ketogulonogeniumvulgarum, so that the efficiency for converting L-sorbose into 2-KGA is also improved. According to the method, the production process is advanced, the raw material cost is low, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production and is improvement and promotion of vitamin C preparation technology with a biological fermentation method in about forty years of China; and besides, harmful substance emission in a production process is prevented, pollution and public hazard to the ambient environment are avoided, and environment protection requirements are met.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
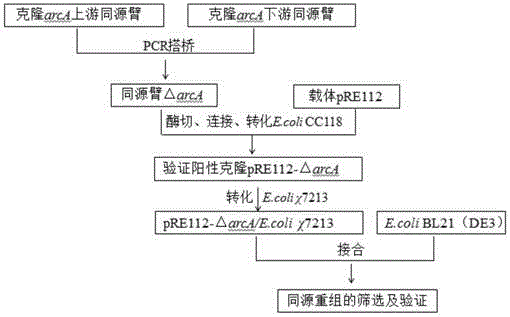
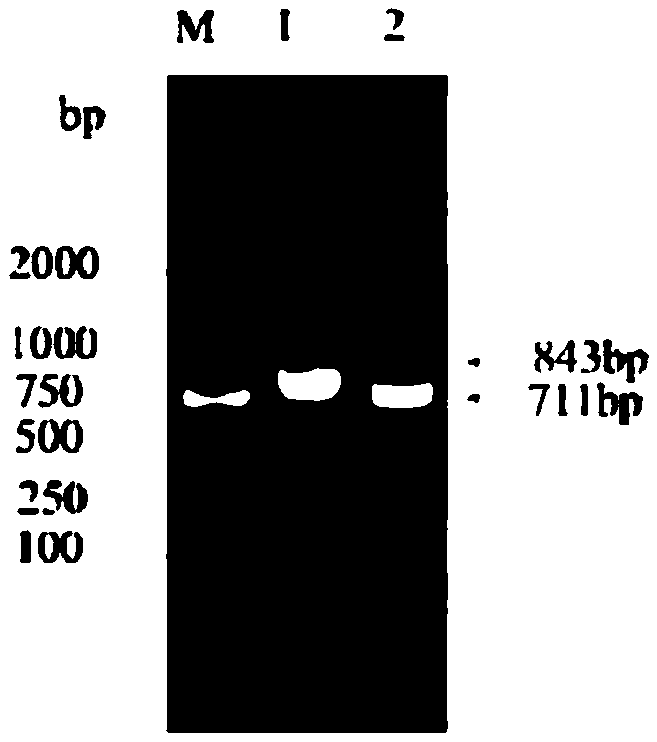
Gene modification method for increasing yield of phloroglucinol and application of same
InactiveCN104388457AIncrease productionHigh industrial application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a gene modification method for increasing the yield of phloroglucinol and application of the same, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The gene modification method comprises the following steps: obtaining a mutant strain by virtue of a mode of knocking out or inserting a global regulating factor arcA gene of an original strain, converting the state of the mutant strain to a competent state, introducing recombinant plasmids containing a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activating factor marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase, and obtaining a recombinant cell. The invention also provides a method of producing the phloroglucinol by utilizing the recombinant cell. According to the gene modification method and application disclosed by the invention, the yield of the phloroglucinol after fermentation is firstly increased by 2.06 times by adopting a mode of globally regulating carbon metabolism after post-transcriptional level, and the gene modification method and application have high industrial application value.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
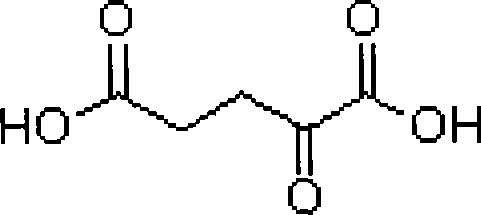
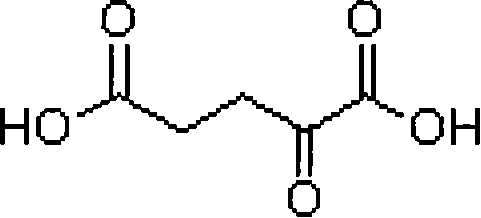
Method for realizing excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate acid by adding alpha-ketoglutarate acid dehydrogenase inhibitor
InactiveCN101250563AImproved compared to the controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a method for adding alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor to realize excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutaric acid, which belongs to the technical field of the metabolic regulation optimized fermentation process of the protein level. The method of the invention comprises following steps: utilizing multi - vitamin - auxotrophic yeast of Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019 as producing strains, regulating the activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through adding the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor: hydrogen peroxide, methotrexate, sodium hypochlorite or hydroxyamino in culture medium, purposively lowing the activity of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, reducing the degradation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid in the metabolic process, and achieving the aim of the excessive accumulation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid. The method of the invention cuts off carbon metabolism flow on a node of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid through regulating the stream distribution of carbon metabolism and the carbon metabolism flow, wherein the maximum output of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid reaches 23.2g / L, which is increased by 12.2% compared with the control. The invention provides a new thought for the fermentation research of TCA cycle intermediate metabolite.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
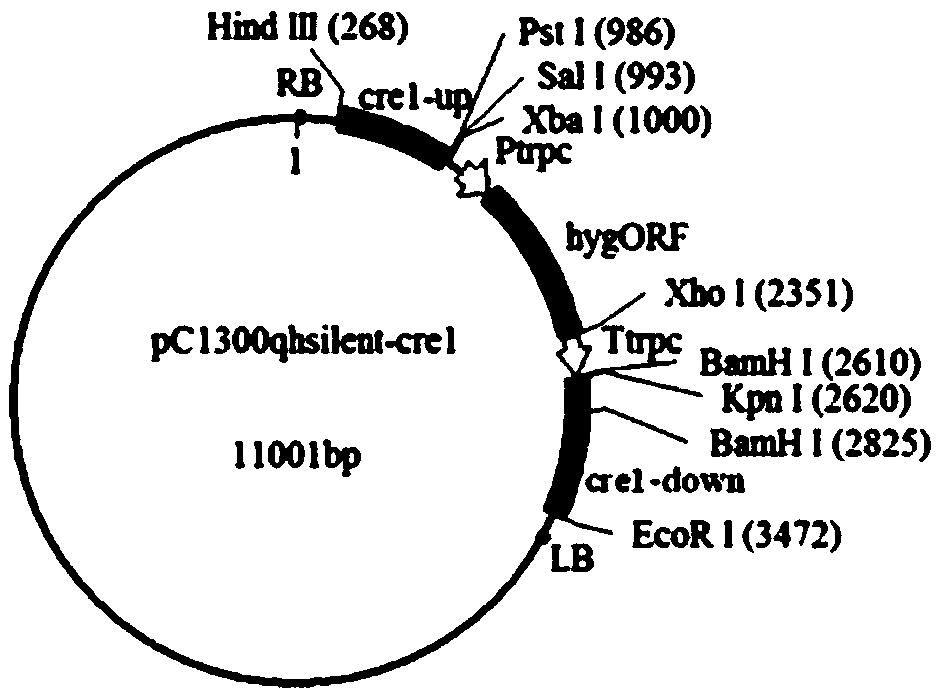
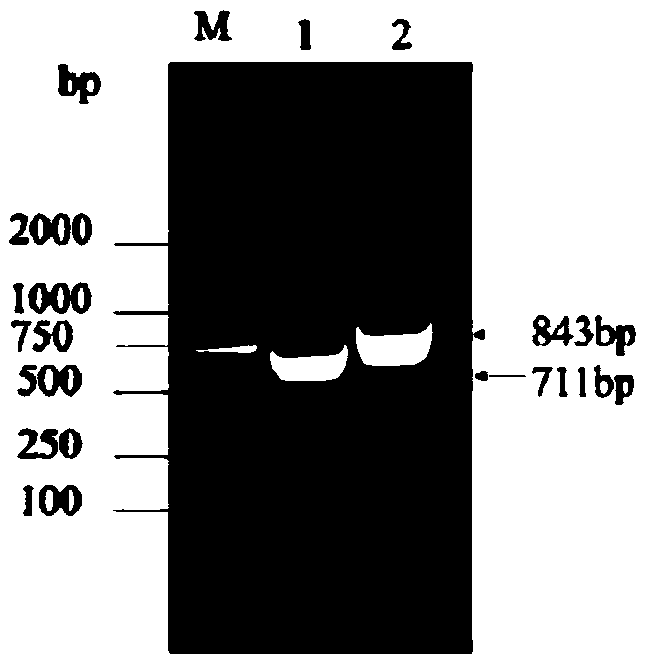
Application of improved ATMT (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation) to construction of trichoderma atroviride T23 deltaCrel
ActiveCN105368866ARepress transcriptionInhibition of secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses an application of improved ATMT (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation) to construction of trichoderma atroviride T23 deltaCrel. The application is characterized in that the genomic DNA of trichoderma atroviride T23 is taken as a template, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is carried out on the Crel gene sequence, and thus upstream and downstream flanking sequences of the Crel gene are obtained; then leading in respectively to knock out upstream and downstream of plasmid pC1300qh, so as to form recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel; converting escherichia coli competence of the recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, performing verification, screening positive clone, extracting recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, leading in agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1, and carrying out improved ATMT. By using the improved ATMT technique, a trichoderma atroviride carbon metabolism inhibiting factor CRE1-knocked-out mutant strain is successfully constructed; the T23 deltaCrel bacterial strain has the functions of promoting secretion and activity of degrading enzyme of cell walls of trichoderma spp., and indirectly improving the function of trichoderma spp. to antagonize pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
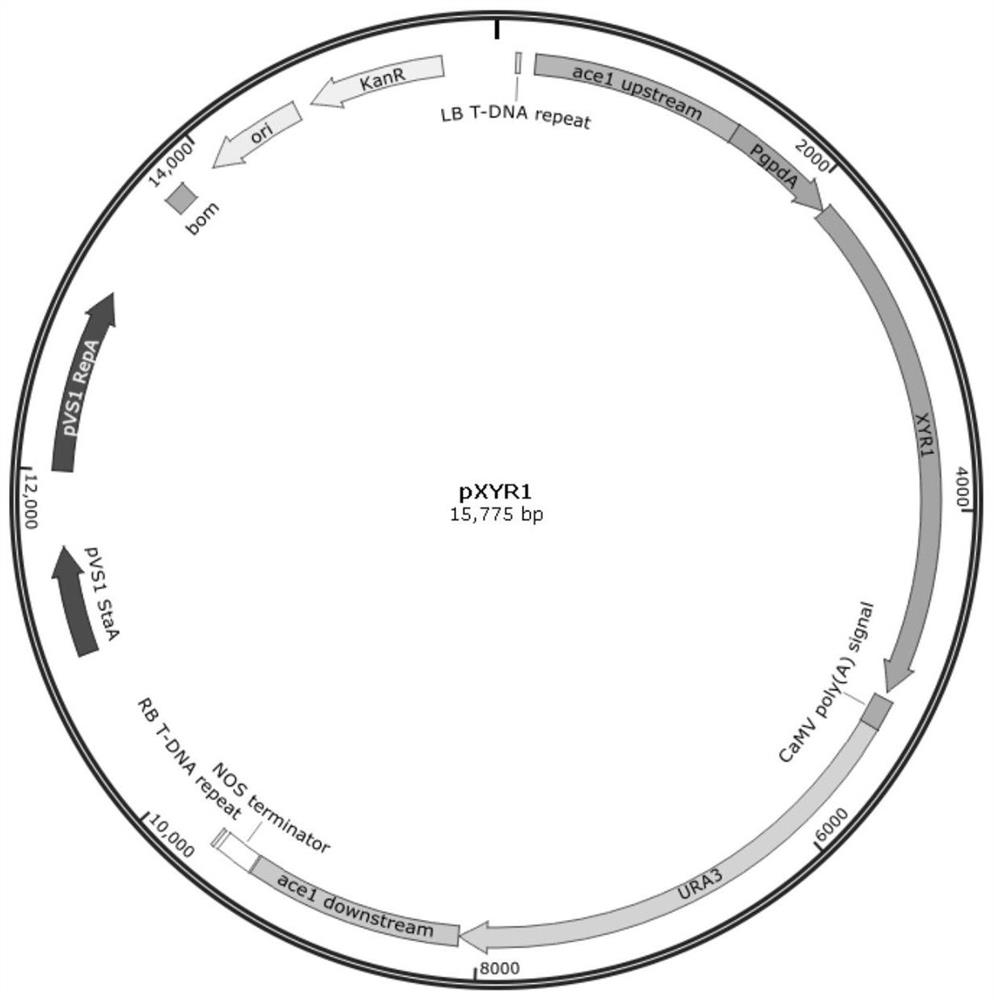
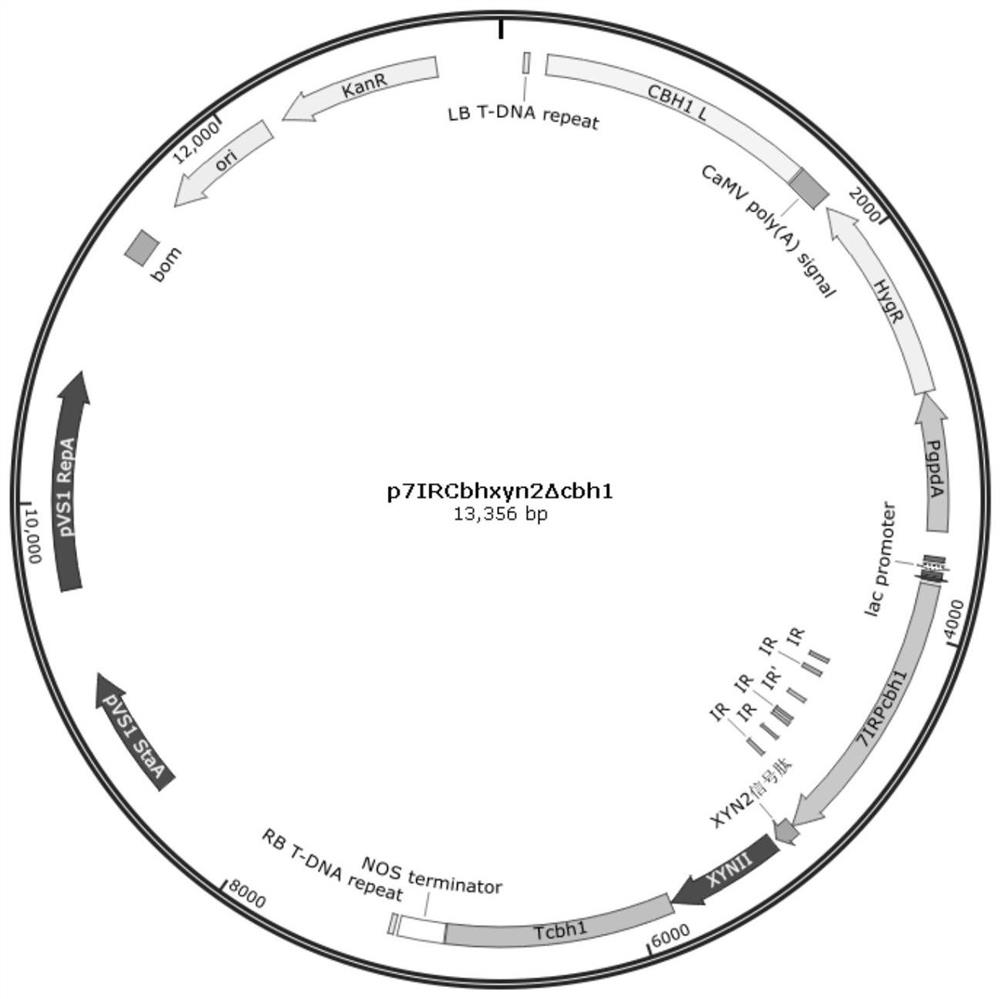
Method for producing xylanase at high yield from trichoderma reesei and application of xylanase
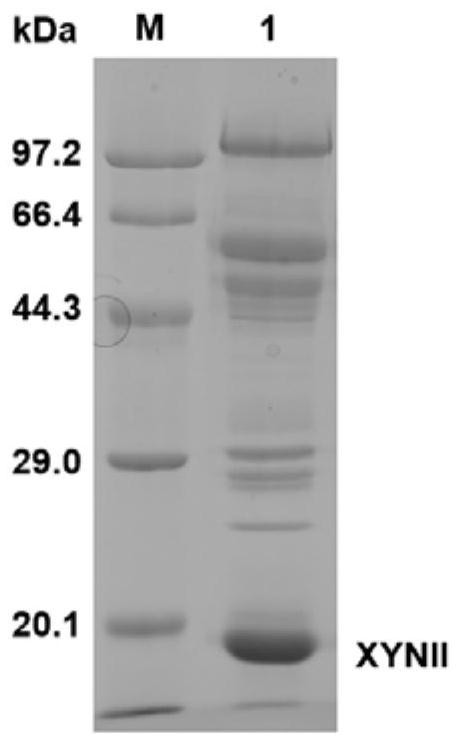
The invention discloses a method for producing xylanase at high yield from trichoderma reesei and application of the xylanase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a transcription activator XYR1 is expressed to enhance the xylan degrading enzyme expression ability, and a transcription factor binding site on a promoter Pcbh1 is designed, so that XYR1 of constitutive expression can further activate the artificial promoter Pcbh1, and the artificial promoter Pcbh1 is used for expressing homologous xylanase XYNII to obtain recombinant trichoderma reesei. Under the cellulose induction condition, the expression quantity of the recombinant strain xylanase reaches 6410U / mL, which is 9.28 times higher than that of a parent; meanwhile, the activity of xylosidase is improved by 1.93 times and reaches 9.08 U / mL; and the recombinant strain can relieve carbon metabolism repression, soluble cheap carbon sources glucose and lactose are used as fermentation carbon sources, the activity of the extracellular xylanase of 2514 U / mL and the activity of the extracellular xylanase of 3446 U / mL can also be obtained, and meanwhile, the yield of the xylosidase is increased by 9.3 times and 2.3 times compared with that of the parent. Meanwhile, the xylanase produced with the method cooperates with commercial cellulose to perform straw saccharification, so that the saccharification efficiency can be improved by 35%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving acid production rate of L-phenylalanine genetic engineering bacterial
InactiveCN102041284AImproves ability to ferment L-phenylalaninePromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon metabolismGenetic engineering
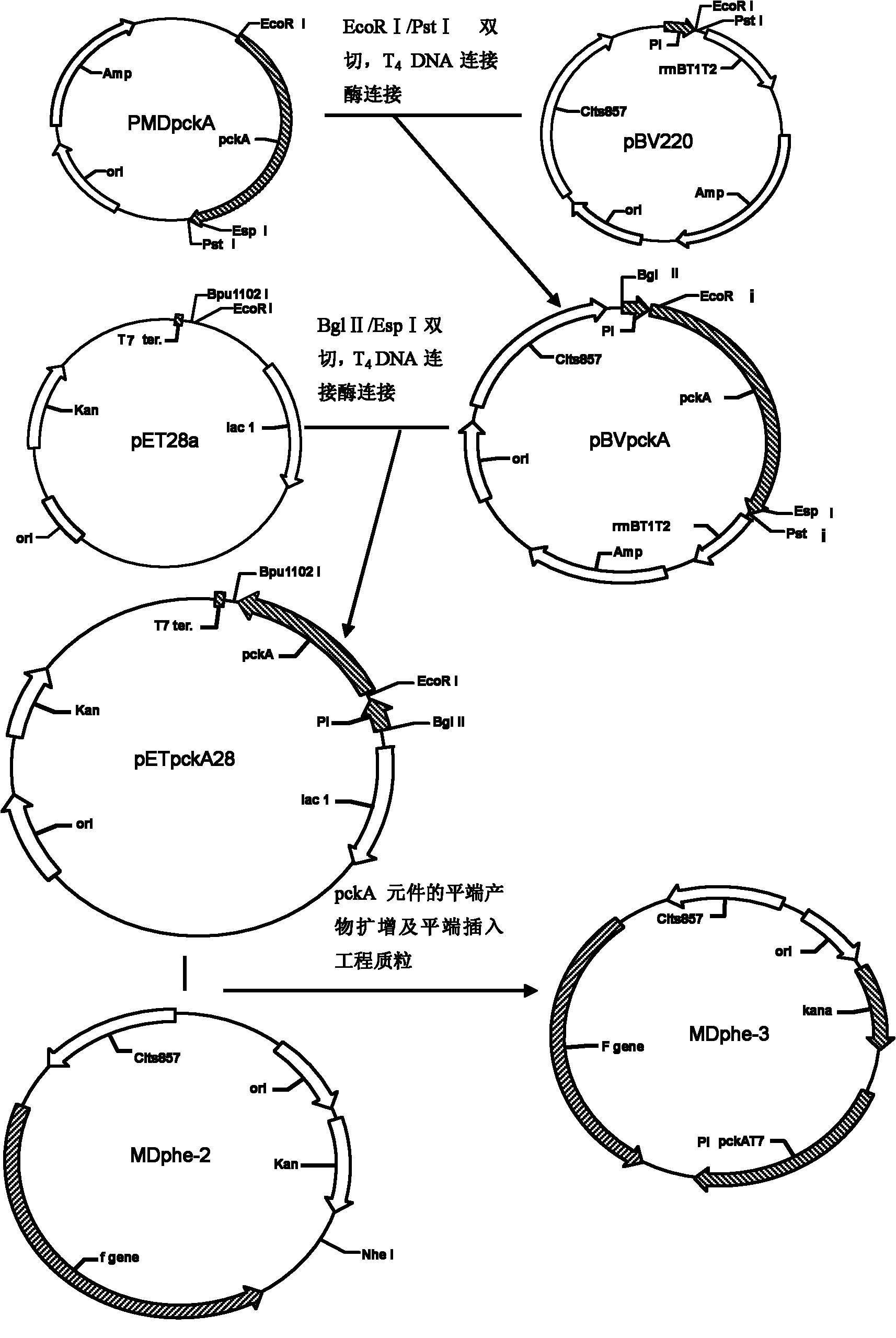
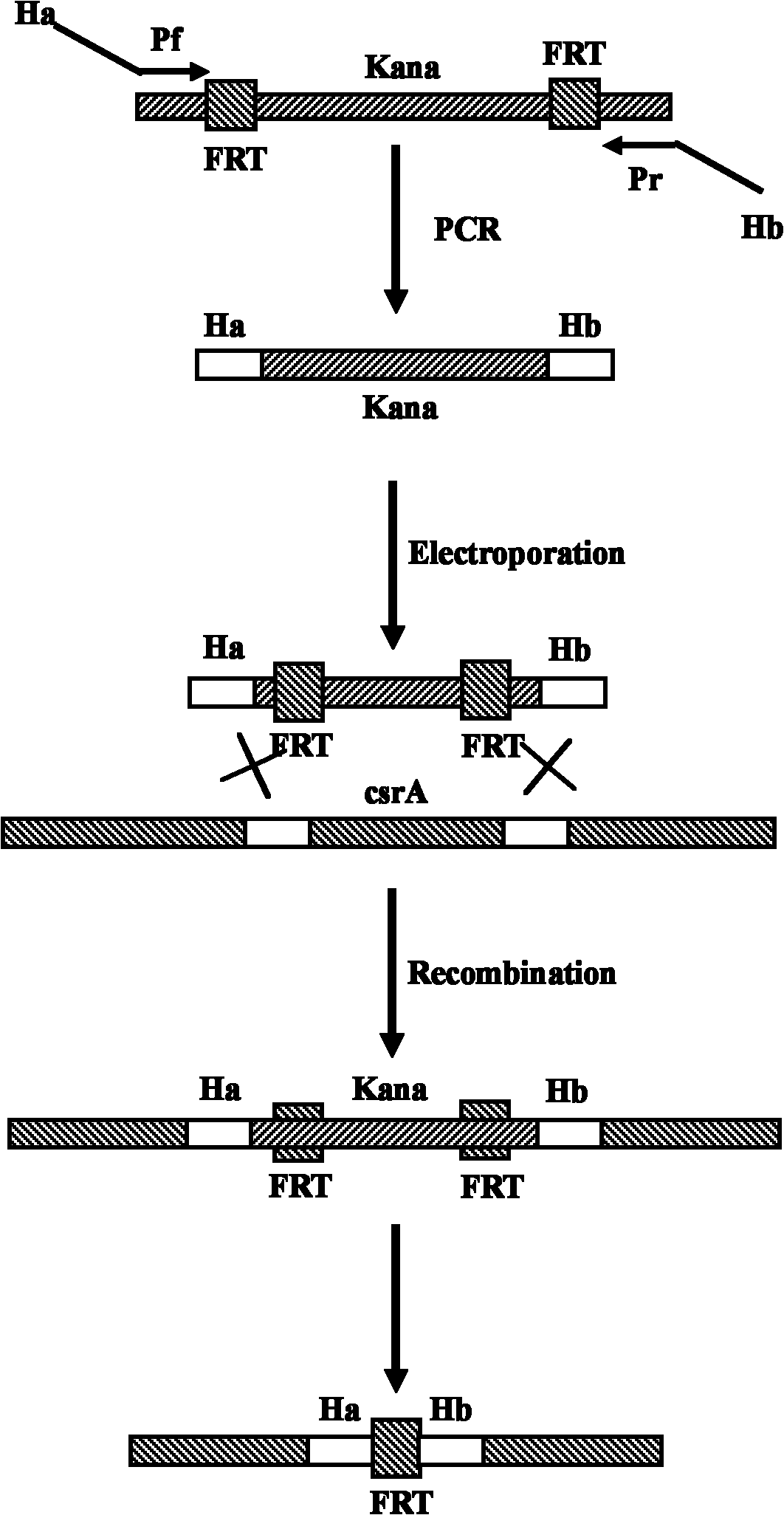
The invention relates to a method for improving acid production rate of L-phenylalanine genetic engineering bacterial. The method comprises the steps of: constructing the original engineering plasmid MDphe-2 of L-phenylalanine into a new generation of engineering plasmid MDphe-3 by adopting a PCR (polymerase chain reaction)technology; carrying out deletion constructing on a whole metabolism network regulatory gene csrA of the engineering host bacterial of the engineering plasmid MDphe-3 through a Red system; then implanting the engineering plasmid MDphe-3 in the engineering host bacterial which is in deletion of the whole metabolism network regulatory gene csrA to construct a new L-phenylalanine genetic engineering bacterial; and finally verifying and reserving the L-phenylalanine gene engineering bacterial with high hereditary stability and high acid production rate. The method has the advantages that the PEP accumulation of one of precursors of aromatic amino acid is strengthened, simultaneously the carbon metabolism flux can be converted heavily to a shikimic acid way, the large flowing of the metabolism flux of the aromatic amino acid to the synthesis of the L-phenylalanine is ensured, and the ability of the engineering bacterial to ferment the L- phenylalanine is further improved.
Owner:MAIDAN BIOLOGICAL GROUP FUJIAN
Method for improving yield of fumaric acid
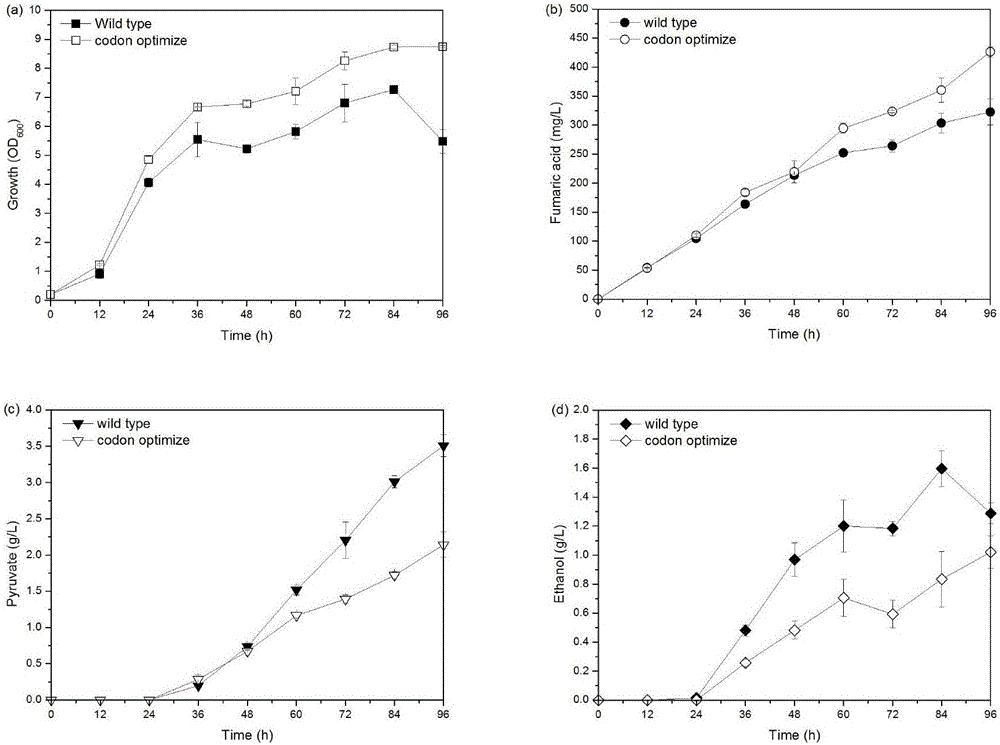
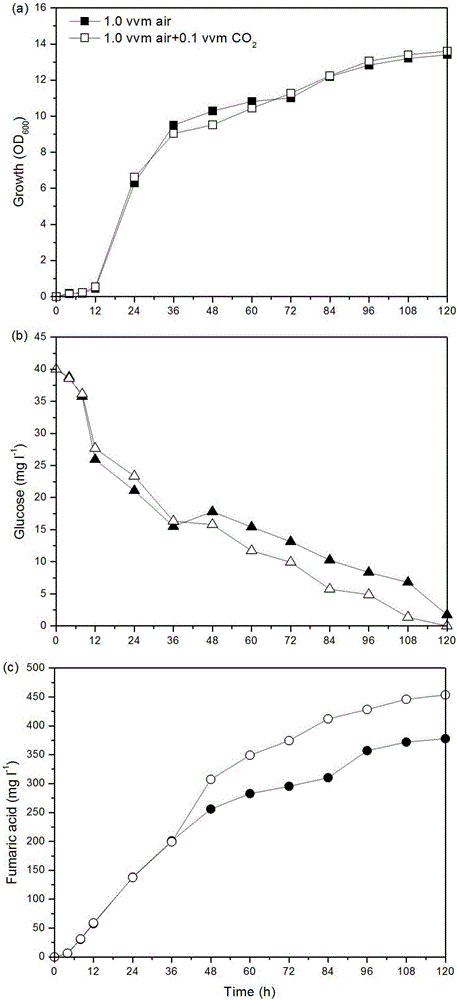
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of fumaric acid and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. The method comprises the following steps: performing codon optimization on a pyruvate carboxylase gene RoPYC of rhizopus oryzae to obtain a gene RoPYC* and then mutating a R485 site of the gene RoPYC* into proline. In comparison with the yield after the expression of a wild type pyruvate carboxylase before codon optimization, the yield is improved by 24.6 percent; 10 percent of carbon dioxide is additionally introduced when genetically-engineered bacteria of an expression mutant is fermented for 36 hours in a fermentation tank of 7L, so that the yield of the fumaric acid reaches 453.6 mg / Lm and is improved by 20 percent through comparison. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a synthetic route through which a carbon metabolic flow enters the fumaric acid from pyruvic acid is effectively enhanced, so that conditions are created for the construction of engineering yeasts to efficiently produce the fumaric acid and other dicarboxylic acid, therefore, the industrial application value and the prospect are good.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genes coding carbon metabolism and energy-producing proteins
InactiveUS7141664B2Efficient producerImprove efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to novel nucleic acid molecules, to the use thereof for constructing genetically improved microorganisms and to methods for preparing fine chemicals, in particular amino acids, with the aid of said genetically improved microorganisms.
Owner:DAESANG CORP
Optimized mutant of maltose promoter and application of mutant
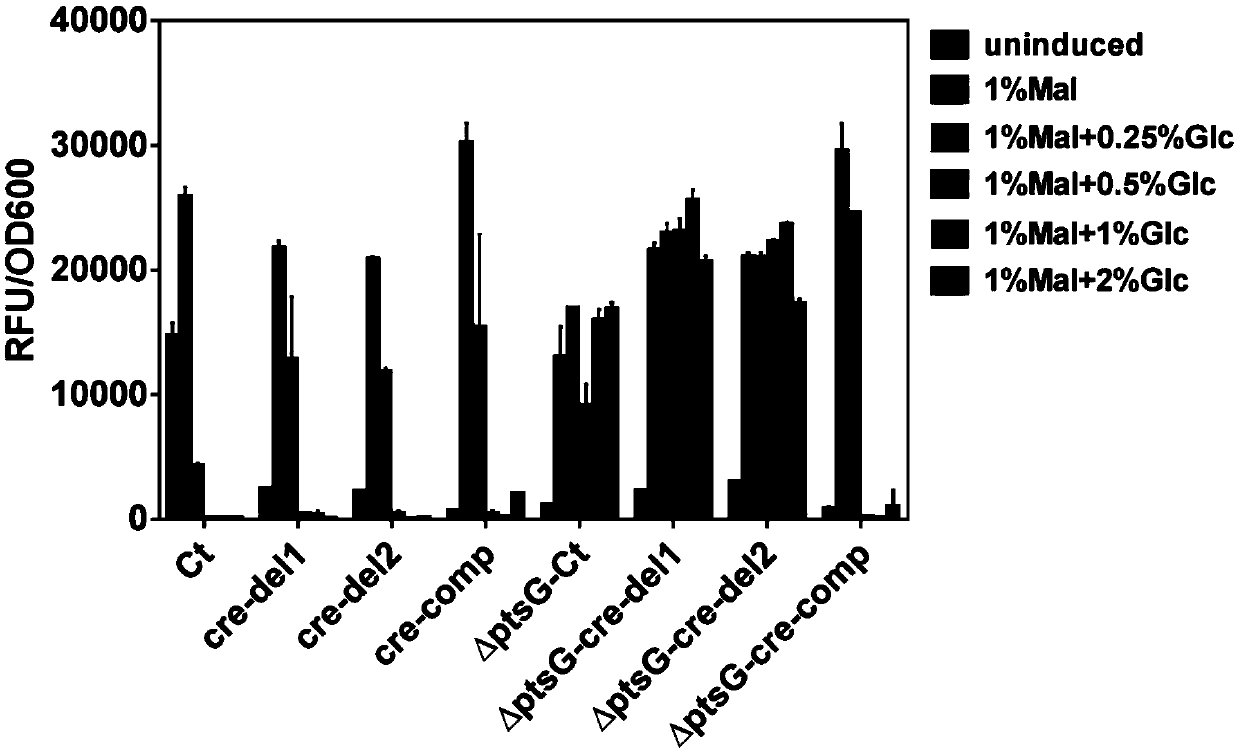
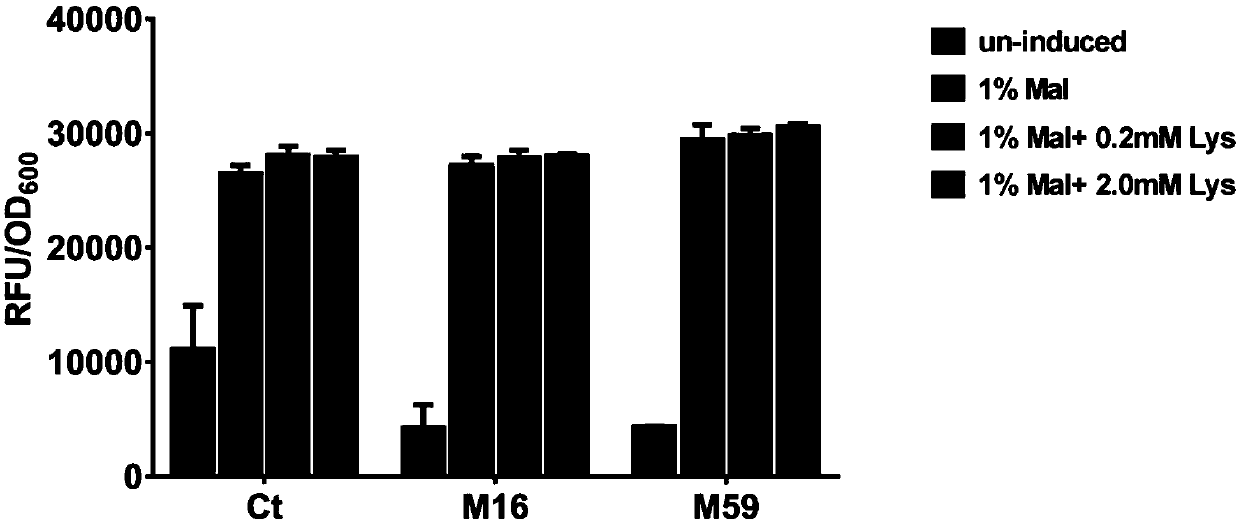
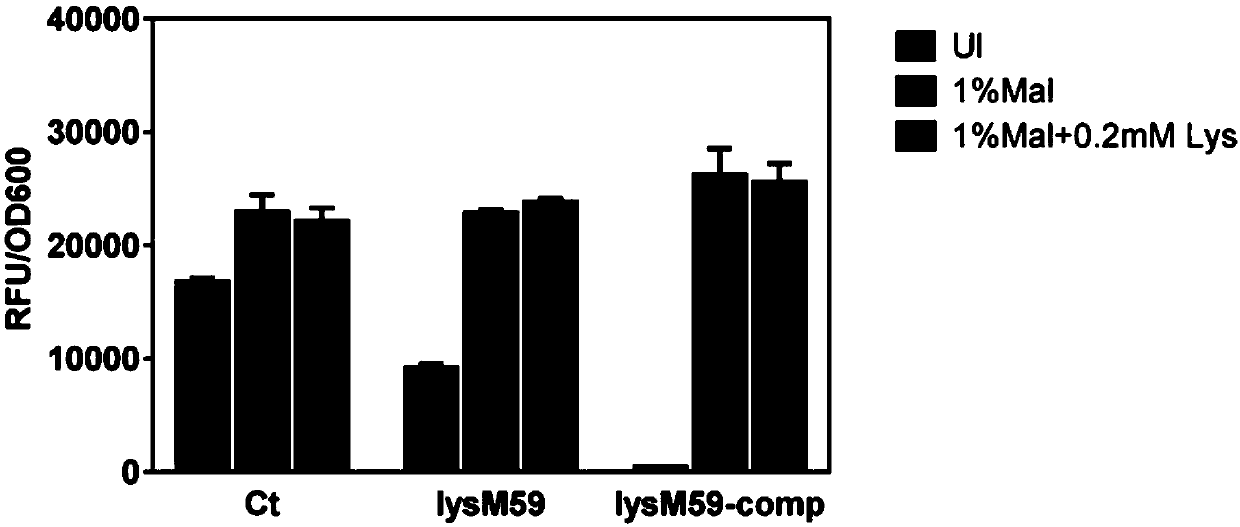
ActiveCN110592080AReduced leaky expressionIncrease the intensity of induced expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon metabolismMutant
The invention uses Bacillus as a starting strain, uses a carbon metabolism response element cre in a maltose promoter to transform a target, a lysine ribose switch is fused at the same time, a mutantof the maltose promoter is constructed, the mutant that can reduce the leaky expression of the maltose promoter and improve the induced expression strength of the maltose promoter is obtained, and anexpression vector and host cell which contain the mutant of the promoter are constructed, so as to be conducive to the application of the maltose promoter in protein expression.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for implementing excessive accumulation of alpha-oxoglutarate by regulation and control of carbon metabolism flow with assist factor
A method with adjuvant factor to regulate the carbon metabolism to accomplish the overdose accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate (alpha-KG) is provided, which belongs to the technical field of fermentation process optimized by the strategy of adjuvant factor regulation. The invention adopts the method of adjuvant factors including vitamins and metal ions, etc. which are added into the fermentation process with the sub-proper amount, and then the pathway flux of PDH and PC are increased selectively to accomplish the overdose accumulation of alpha-KG. During the process of the production of alpha-KG through fermentation of T.glabrata, the concentration of vitamin B1 is raised to increase the accumulated alpha-KG to 10.3g / L; then the biotin concentration is raised to increase the accumulated alpha-KG to 43.7g / L, and the concentration of pyruvic acid is decreased to 21.8g / L. The strategy also has the significance to guide the production of the other fermented products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
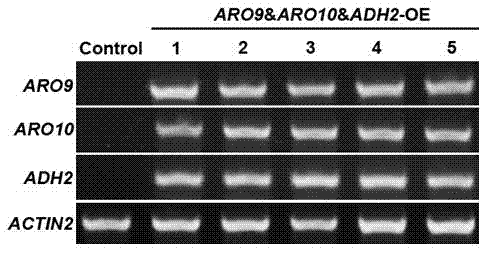
Metabolic pathway reconstruction method for reducing lignin content and use thereof
InactiveCN104212731ALow lignin contentNormal growth is not affectedFungiVector-based foreign material introductionFiberEthanol dehydrogenase
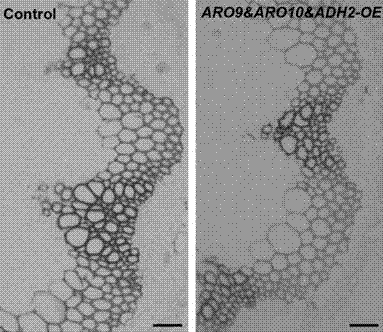
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and discloses a metabolic pathway reconstruction method for reducing lignin content and a use thereof. The metabolic pathway reconstruction method can construct a 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway in the plant so that lignin synthesis is reduced and thus fiber biomass conversion efficiency is improved. The 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway is from yeast and comprises three key genes of amino acid transaminase gene ARO9, pyruvate decarboxylase gene ARO10 and ethanol dehydrogenase gene ADH2. The 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway is constructed in arabidopsis thaliana, and through competition between 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis and lignin synthesis in initial substrate phenylalanine use, carbon metabolism shunting is caused and synthesis of lignin in the transgenic plant is reduced. The method provided by the invention can reduce fiber biomass pretreatment difficulty by reducing plant lignin synthesis. At present, the method can reduce lignin synthesis in arabidopsis thaliana and can improve glucose release efficiency of stem cell wall extract enzymolysis.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-yield cultivation method based on corn carbon and nitrogen metabolism difference
InactiveCN105613014AGood coordination of carbon and nitrogen metabolismIncrease productionFertilising methodsPlant cultivationCarbon metabolismCoordination type
The invention relates to a high-yield cultivation method based on a corn carbon and nitrogen metabolism difference. The method comprises the following steps: 1, determining a carbon and nitrogen metabolism type from a nitrogen sensitive type, a carbon and nitrogen coordination type, a vigorous nitrogen metabolism type and a weak carbon metabolism type based on a genotype difference presented by coordination of corn variety carbon and nitrogen metabolism; 2, specific to different carbon and nitrogen metabolism types, adopting different fertilizer applying measures: (1) for the nitrogen sensitive type, dressing urea at a nutrient growth and reproduction growth stage of corn, wherein the total amount of applied pure nitrogen is less than or equal to 360kg / ha; (2) for the carbon and nitrogen coordination type, controlling the total amount of applied pure nitrogen at 200-240kg / ha; (3) for the vigorous nitrogen metabolism type, applying a pure fertilizer in an amount of 240-320kg / ha; (4) for the weak carbon metabolism type, dressing urea at the nutrient growth and reproduction growth stage, wherein the using amount of pure nitrogen needs to be controlled at 240-320kg / ha. By adopting the high-yield cultivation method, seeds are selected scientifically, fertilization is optimized, and corn physiological metabolism is coordinated in order to increase the nutrient utilization rate, lower environmental pollution and improve the yield and quality of the corn.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of purple acid phosphatase gene GmPAP35 of soybean
ActiveCN108588116AIdentify the functions involved in carbon metabolismWith fertilizer saving and high yieldVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsCarbon metabolismGenetically modified crops
The invention discloses the application of a purple acid phosphatase gene GmPAP35 of a soybean, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. Through functional analysis of the GmPAP35 in a whole conversion material of the soybean, a function of the GmPAP35 participating in carbon metabolism in a plant is specified. Overexpression of the GmPAP35 can increase the height of a soybean plant and the contents of glucose and fructose in the plant body, so that the soybean biomass and the phosphorus uptake are increased, and the soybean phosphorus efficiency is improved; a theoretical basis is laid for culturing a new variety of phosphorus efficient-transgenic crops. The purple acid phosphatase gene GmPAP35 has the capacity of promoting the carbon metabolism of the crops through a transgenic technology, so that the plant phosphorus efficiency is improved, and new purposes of fertilizer use amount reduction and high yield are achieved. The purple acid phosphatase gene GmPAP35 has an importanttheoretical and practical significance on developing environmentally-friendly sustainable agriculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
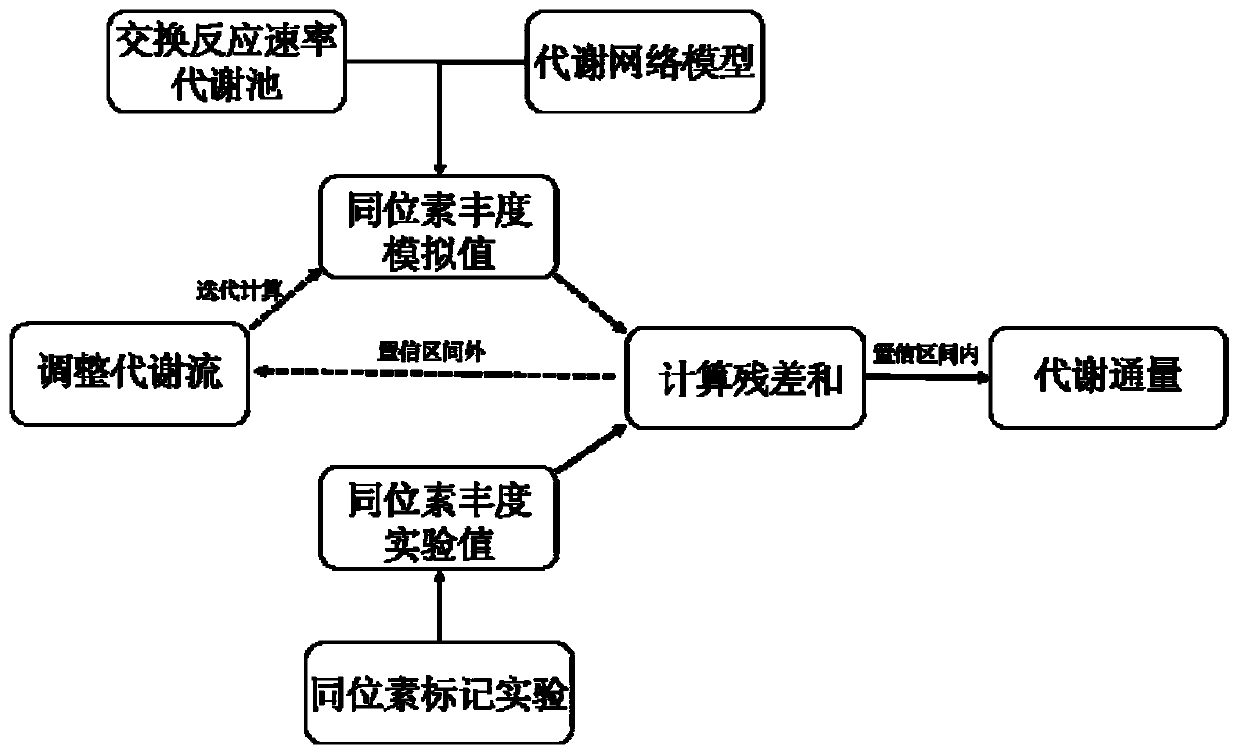
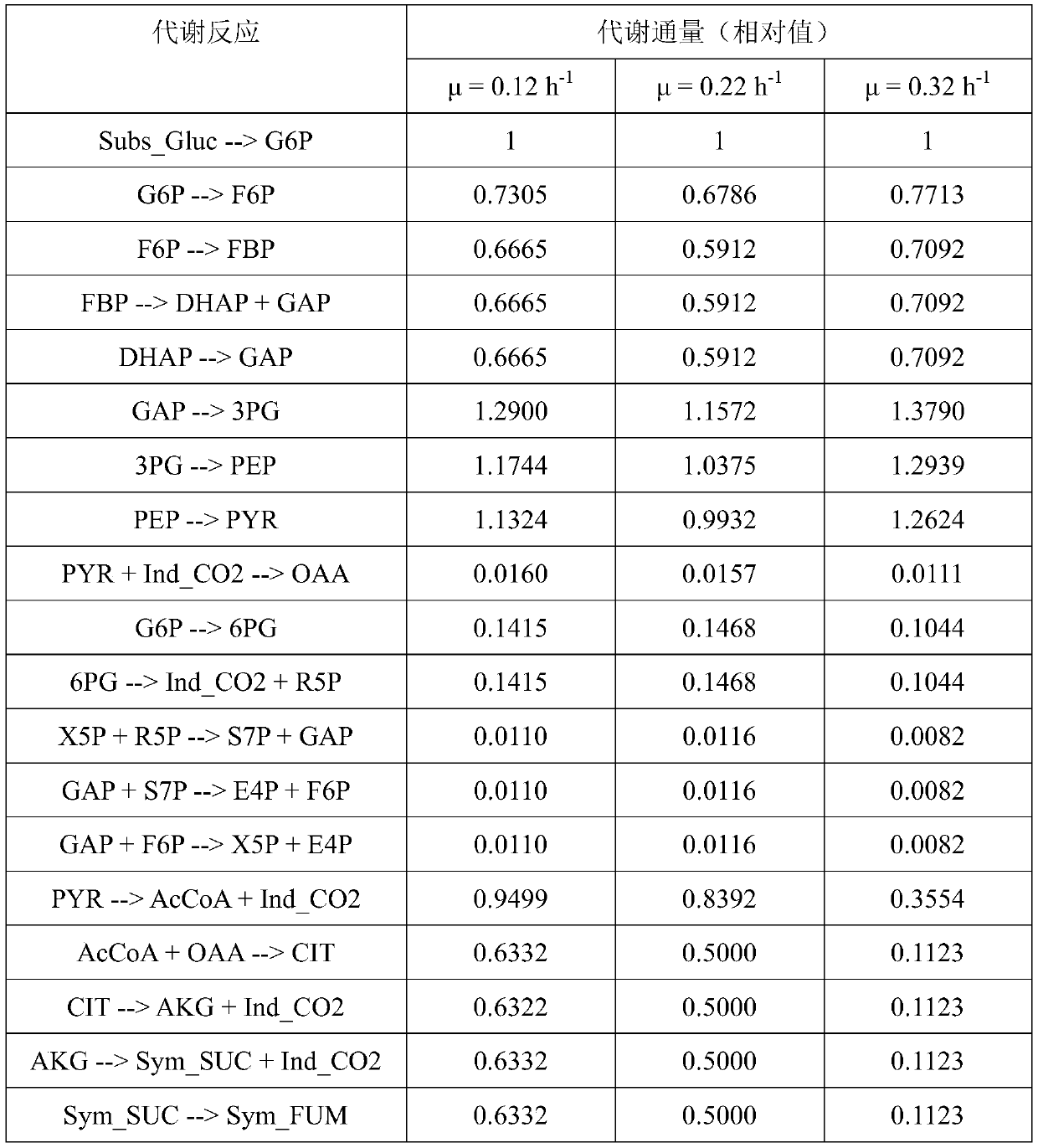
Method for obtaining metabolic flux of intracellular central carbon metabolic pathway in unsteady state of metabolic steady-state isotopes
PendingCN111575336AAccurate Abundance DataAccurate speedComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotopic labelingCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a method for obtaining metabolic flux of an intracellular central carbon metabolic pathway in an unsteady state of metabolic steady-state isotopes. The method adopts a batch culture module, a constant culture module, a sampling module and a sample processing and analyzing module. When the OUR and the CER in the batch culture module decline at the same time, culture is performed in the constant culture module. The constant culture module specifically adopts a process of feeding a nutrient solution containing no isotope labeling substrate, starting waste discharge at thesame time, carrying out constant culture, until the microbial cells are in a metabolic steady state, feeding a nutrient solution containing the isotope labeling substrate, and keeping culture conditions unchanged; and when the isotope labeling substrate flows into a reactor, starting rapid and continuous sampling, and entering the sampling module at the same time. According to the method, a seriesof fermentation liquor samples are obtained in a short time, and then the samples are processed and analyzed to obtain accurate intracellular metabolite isotope abundance data; and the method plays acrucial role in calculating the metabolic flux.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application of recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives
ActiveCN111139194AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
The invention relates to a recombinant yeast, a construction method thereof and an application of the recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives. The recombinant yeast is obtained by introducing an exogenous fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase expression gene into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway of synthesizing tyrosol through 4-erythrose phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The invention first discloses the fact that in a process of expressing fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in yeast, fructose-6-phosphoric acid iscatalyzed into erythrose-4-phosphoric acid and acetyl phosphoric acid while 1,6-fructose diphosphate is synthesized, and xylulose-5-phosphoric acid is catalyzed into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphoric acidand acetyl phosphoric acid, so that distribution of the carbon metabolism flow in yeast is changed, synthesis of an important intermediate substance erythrose-4-phosphoric acid in tyrosol biosynthesisis enhanced, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol is optimized, and the yield of tyrosol and derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol and the like is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
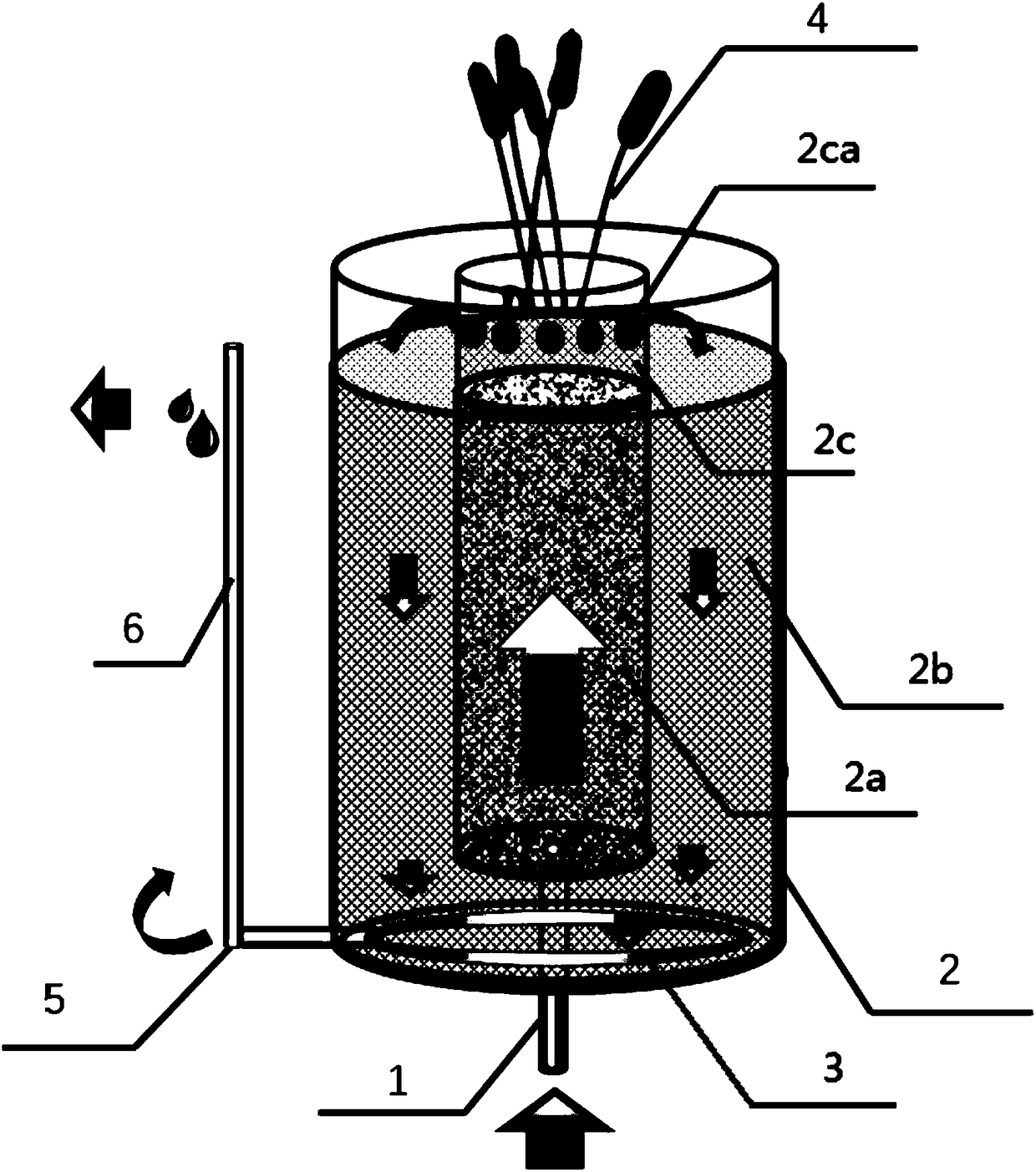
Internal guide type bacterium-alga integrated microbial fuel cell ecological water purification system
ActiveCN108163982AImprove reoxygenationEfficient metabolismTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsCarbon metabolismFiltration
The invention discloses an internal guide type bacterium-alga integrated microbial fuel cell ecological water purification system. The system includes a water inlet pipe, a double-layer pool body, a porous water-collecting pipe, aquatic plants, a rotatable angle fitting and a U-shaped water-discharging pipe; the double-layer pool body includes an electricity-generating inner layer, a no-electricity generation outer layer and a free water layer; aquatic algae are grown in the free water layer; sewage enters the bottom of the electricity-generating inner layer, and organic pollutants in the sewage are degraded by electricity-generating microorganisms; a water flow flows upwards, and nitrification and denitrification occur; the water flow enters the no-electricity generation outer layer fromwater passing holes in the upper part of the free water layer, and reaeration is accelerated; and the no-electricity generation outer layer intercepts the aquatic algae in the free water layer throughthe filtration effect of a filler, and pollutants in the water are further removed. According to the system provided by the invention, a microbial fuel cell technology and a traditional ecological water purification technology are integrated, the electricity-generating microorganisms and the purification function of the algae are coupled, and high-efficiency organic carbon metabolism and removalof nitrogen and phosphorus are compactly controlled in the same ecological water purification system.
Owner:恒晟水环境治理股份有限公司
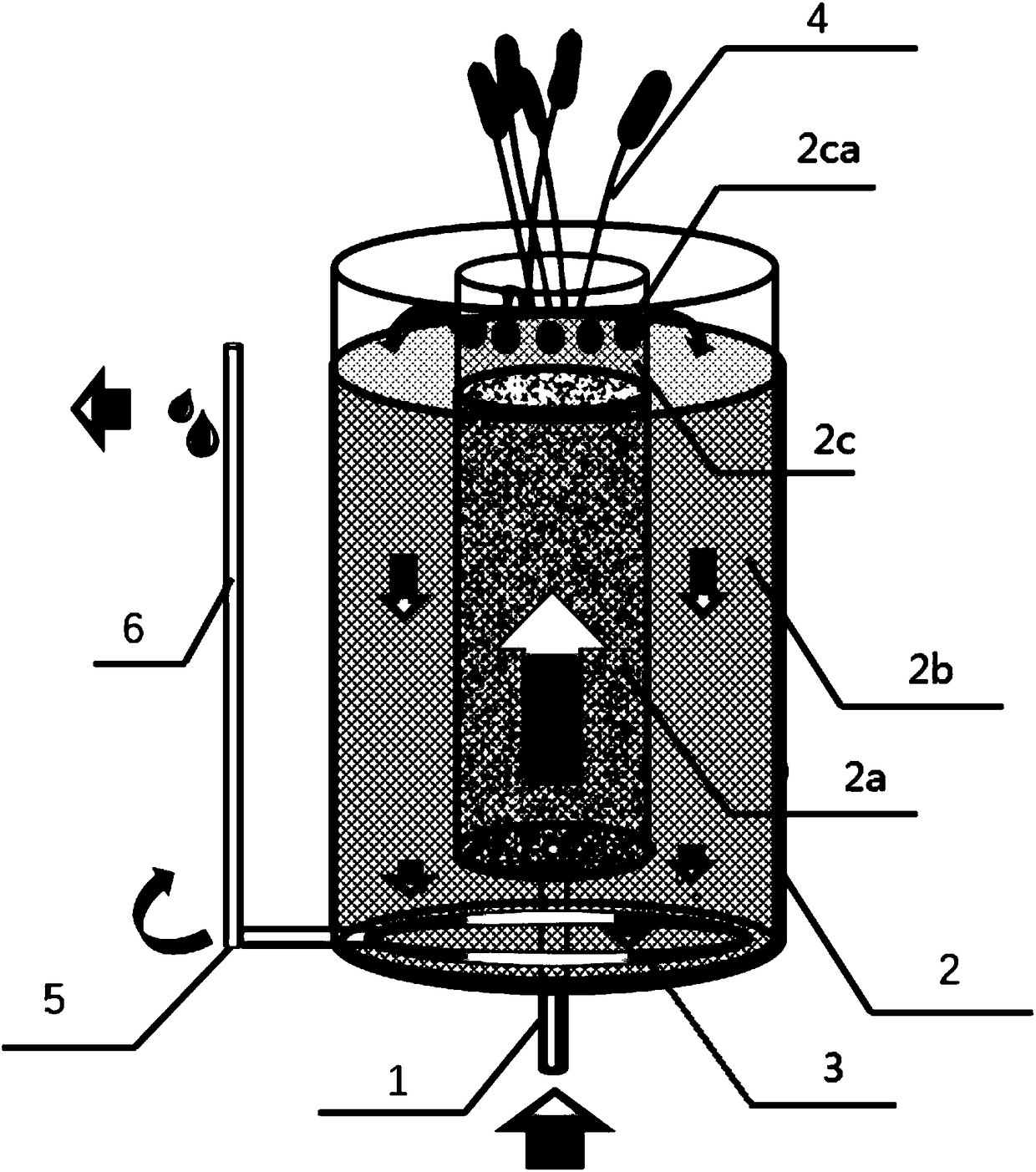
Internal conductive bacteria and algae integrated microbial fuel cell ecological water body purification method
ActiveCN108059248AEfficient degradationImprove reoxygenationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsCarbon metabolismPurification methods
The invention discloses an internal conductive bacteria and algae integrated microbial fuel cell ecological water body purification method. An ecological water body purification system is establishedand comprises a water inlet pipe, a double-layer pool body, a porous water collection pipe, aquatic plants, a rotatable elbow and a U-shaped drain pipe; the double-layer pool body comprises an electricity generation inner layer, a non-electricity-production outer layer and a free water layer; hydrobiontic algae grows in the free water layer; sewage enters the bottom of the electricity generation inner layer, and organic pollutants in the sewage are degraded by electricity production microorganisms. Water flow flows upwards and nitrification and denitrification nitrogen removal occurs. The water flow enters the non-electricity-production outer layer from a water through hole above the free water layer, and reoxygenation is accelerated; the non-electricity-production outer layer intercepts the hydrobiontic algae in the free water layer by filtering of a filler so as to further remove pollutants in water. According to the invention, a microbial fuel cell technology and a conventional ecological water body purification technology are integrated, purification functions of the electricity production microorganisms and the algae are coupled, and high-efficiency organic carbon metabolism and removal of nitrogen and phosphorus are compactly controlled in the same ecological water body purification system.
Owner:恒晟水环境治理股份有限公司
Post-emergence composite herbicide for corn and application thereof
ActiveCN102976860AEasy to synthesizeEnhanced synthesisBiocideAnimal repellantsCarbon metabolismPhytotoxicity
The invention relates to a post-emergence composite herbicide for corn and an application of the post-emergence composite herbicide, which belongs to the technical field of herbicide production. The post-emergence composite herbicide for corn consists of herbicide and zinc fertilizers according to the weight ratio of 1:1.5. The use method of the post-emergence composite herbicide for corn comprises the following steps: dissolving the post-emergence composite herbicide for corn in water which is 200 times of zinc sulfate in weight; and taking an aqueous solution to spray the stem leaves of corn seedlings in the seedling stage of corn. The post-emergence composite herbicide for corn provided by the invention has the advantages of promoting seedling to premature, strengthening the plant, enhancing the disease resistance and phytotoxicity resistance, improving the carbon metabolism, synthesis of amino acids and activity of enzymes, and promoting nitrogen absorption and transfer as the zinc fertilizers are added into conventional herbicide, a proper amount of zinc element in the use process of post-emergence composite herbicide for corn is added, and zinc is added into the post-emergence herbicide sprayed.
Owner:李成国
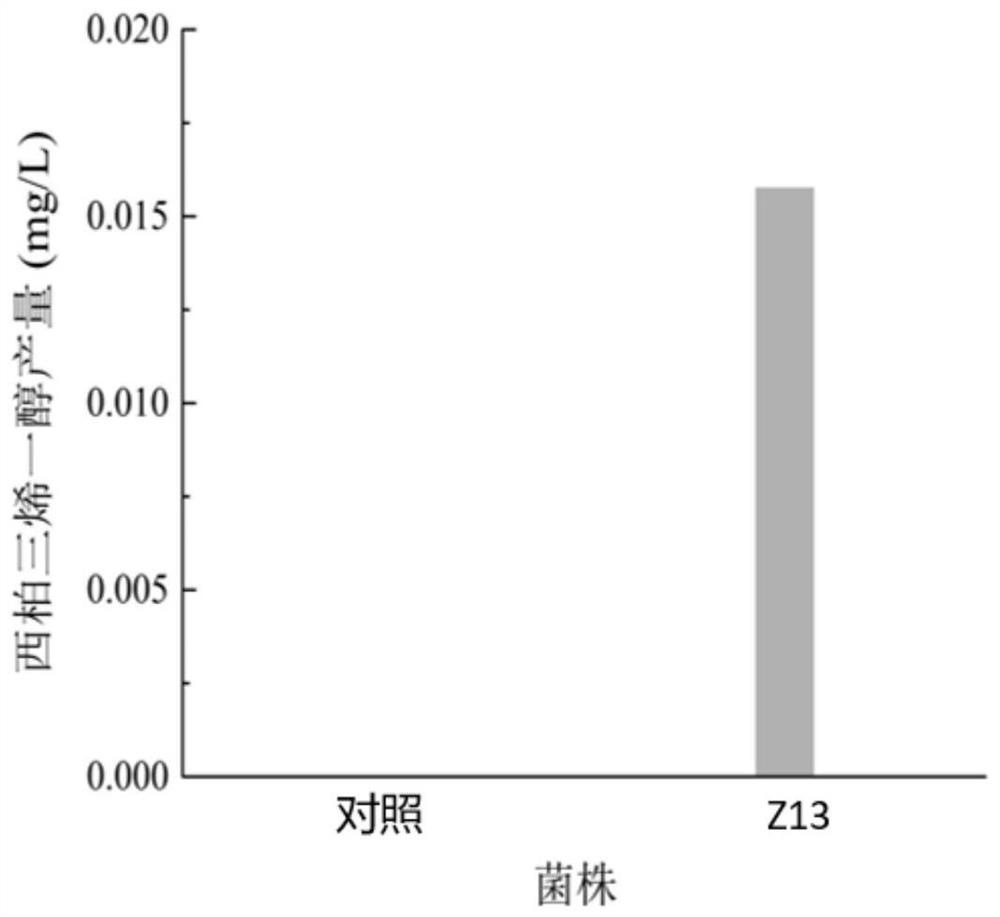
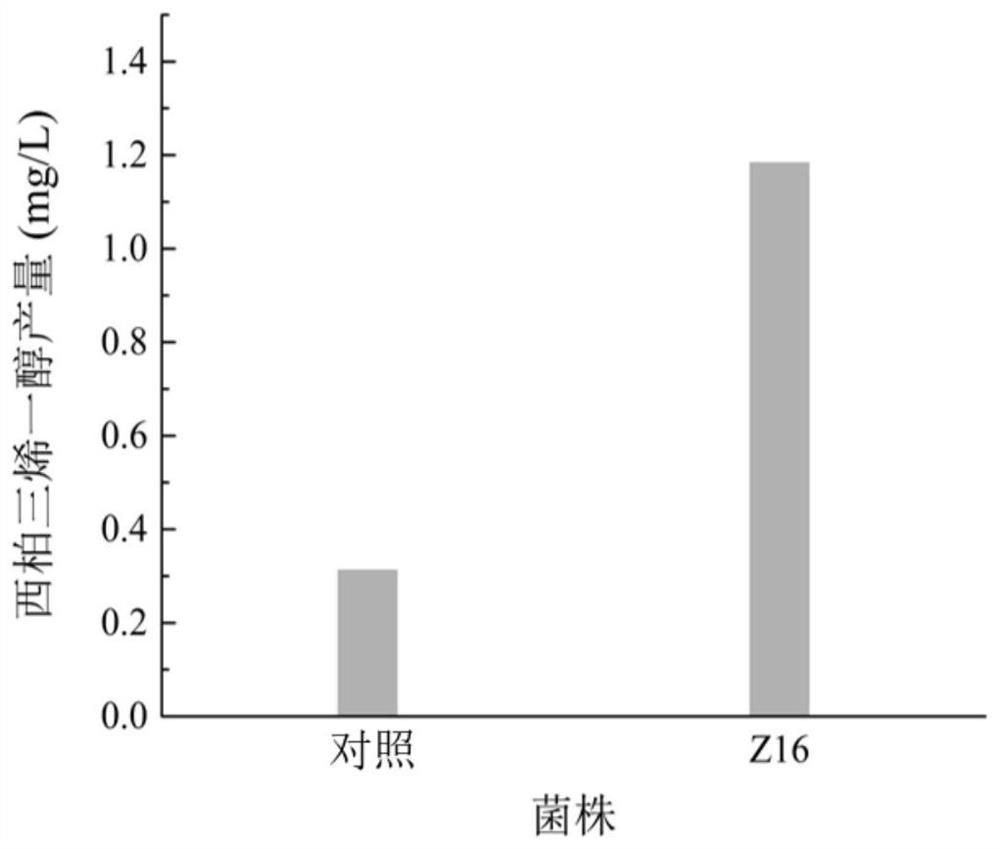
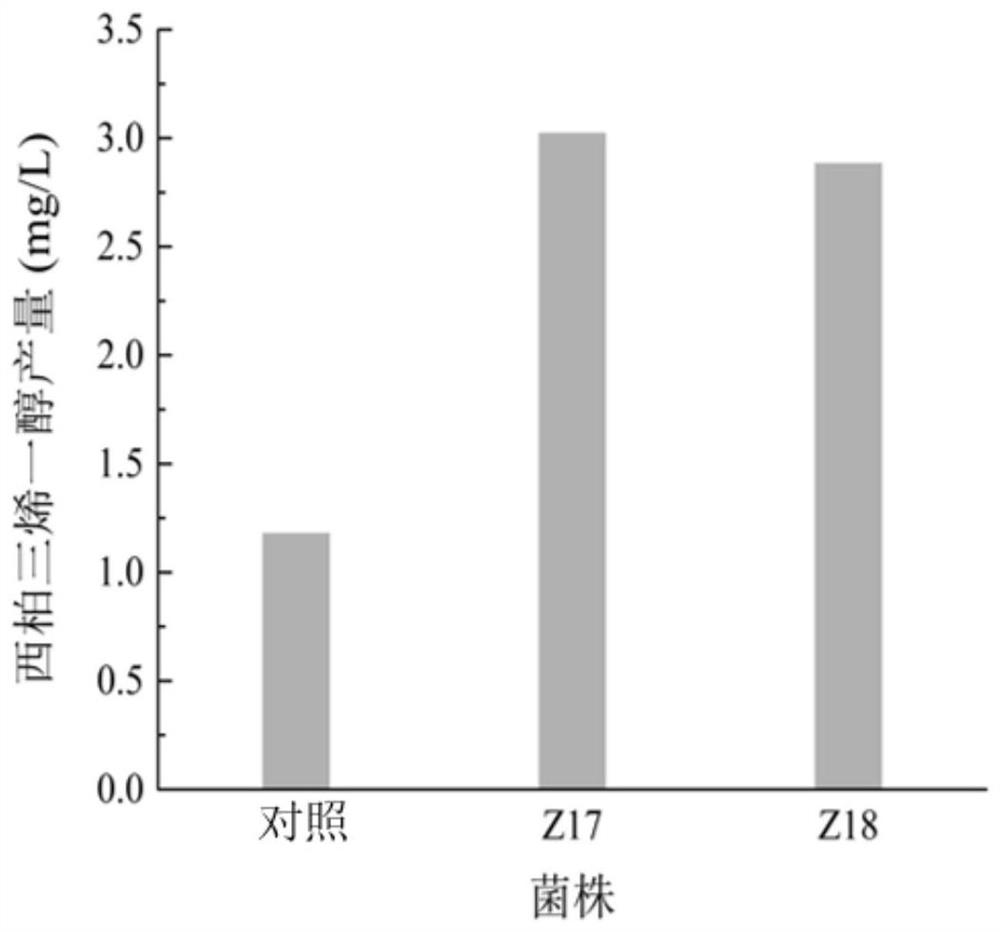
Recombinant bacterium for producing Cembrenediol and application thereof
PendingCN112852699AEfficient productionIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a recombinant strain for producing Cembrenediol and application of the recombinant strain, wherein the recombinant strain capable of producing Cembrenediol from plants is constructed by heterologous expression of a GGPP synthase gene gpps and a Cembrenediol synthase gene cbts. The yield of Cembrenediol is improved by overexpressing key genes of carbon metabolism flux in a DXP (Dixanthone) pathway, namely a 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene dxs and an isoprene pyrophosphate isomerase gene idi. The expression plasmid is further optimized to excessively express dxs and idi, and the yield of Cembrenediol is increased to 2.60 times of that of a control group. By adopting the high-yield Cembrenediol strain and the method disclosed by the invention, the Cembrenediol can be efficiently produced, and the application of the strain in the fields of agriculture, tobaccos and the like can be promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
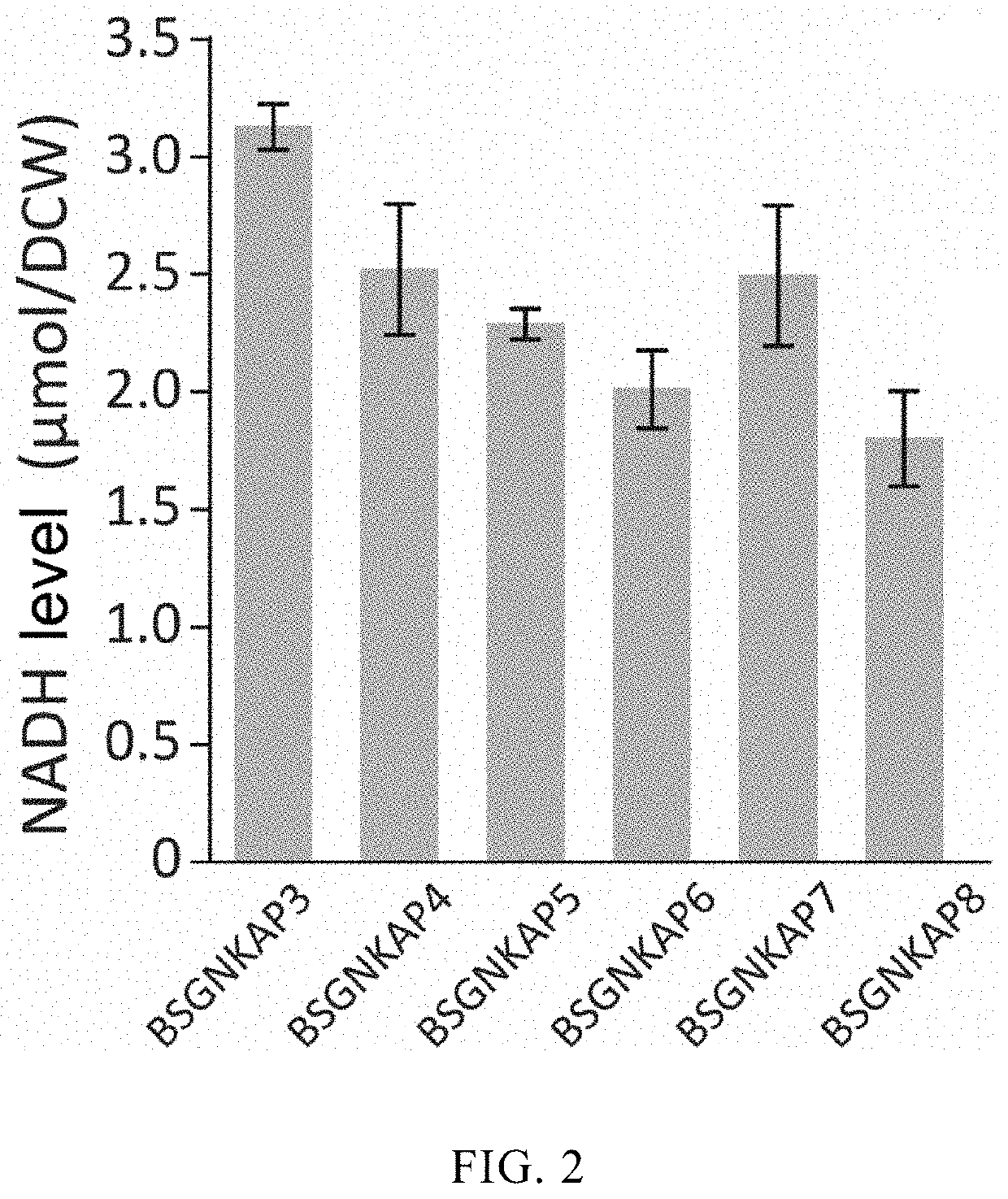
Recombinant strain of bacillus subtilis
ActiveUS20200032237A1Promoting acetylglucosamine synthesisEasy to useOxidoreductasesLigasesQuinoneCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a recombinant strain of Bacillus subtilis, wherein pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin dehydrogenase gor, isocitrate NAD+ dehydrogenase icd, malate quinone dehydrogenase mqo, pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase porAB and nitrogenase ferritin cyh are integrated and expressed in the recombinant strain. The invention also discloses use of the recombinant strain in fermentation production of acetylglucosamine. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis of the invention eliminates the central carbon metabolism overflow of the Bacillus subtilis and balances the intracellular reducing force, and the fermentation yield of acetylglucosamine is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Constructed wetland sewage purification system based on external electricity production and internal confluence water flow
ActiveCN108217941ATreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesFinal product manufactureConstructed wetlandCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a constructed wetland sewage purification system based on external electricity production and internal confluence water flow. The system comprises a double-layer pool, a waterinlet pipe, a porous water distribution pipe, a porous water collection pipe, a rotatable elbow, a U-shaped drain pipe and aquatic plants, wherein the double-layer pool comprises an electricity non-production inner layer and an electricity production outer layer. Sewage enters the bottom of the electricity production outer layer firstly, and organic pollutants in the sewage are degraded by electricigens and release electrons; water flows upwards to the top of the electricity production outer layer, and nitrification and denitrification for nitrogen removal are performed. Water flow converges to the center and enters the inner layer area, the inclination degree of the U-shaped drain pipe is changed by adjusting the rotatable elbow, reoxygenation is accelerated, and pollutants such as phosphorus and the like in water are further removed under actions of filtration, adsorption, coprecipitation and the like. The microbial fuel cell technology is tightly combined with traditional constructed wetlands, and efficient organic carbon metabolism, microbial denitrogenation and adsorption coprecipitation based phosphorus removal are compactly controlled in one constructed wetland.
Owner:恒晟水环境治理股份有限公司
Pyruvate response biosensor as well as construction method and application thereof
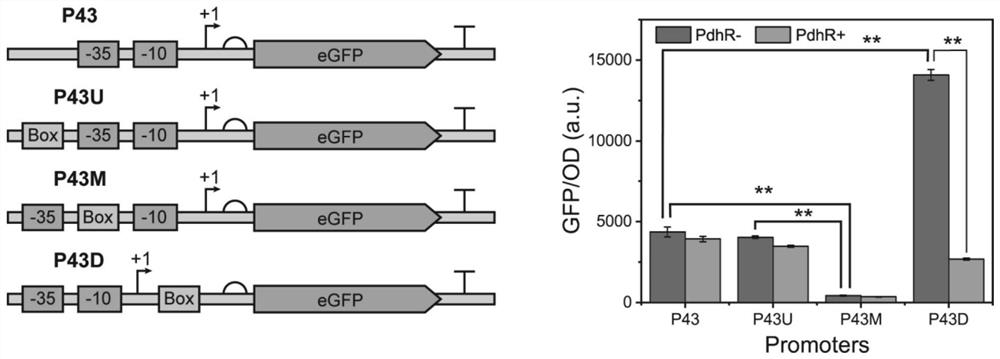
ActiveCN111690647AStrong specificityAvoid harmful effectsVectorsMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteCarbon metabolism
The invention discloses a pyruvate response biosensor as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pyruvate response biosensor with different dynamic ranges is successfully constructed in the invention by optimizing a PdhR binding sequence inserted into a P43 promoter and optimizing an insertion site, wherein the minimum dynamic range is increased by 0.6 times, and the maximum dynamic range is increased by 30.7 times. The biosensor can be used for finely controlling the expression quantity of each gene in cells. Pyruvic acid is a key central carbon metabolite in cells, so thatthe biosensors can dynamically regulate and control the expression levels of intracellular genes according to the change of the content of pyruvic acid in the cells, thereby realizing dynamic controlof intracellular metabolic flux. The pyruvate biosensor obtained by the invention has good specificity, and in addition, the response range of the pyruvate biosensor to pyruvic acid is 10-35nmol / g DCW.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
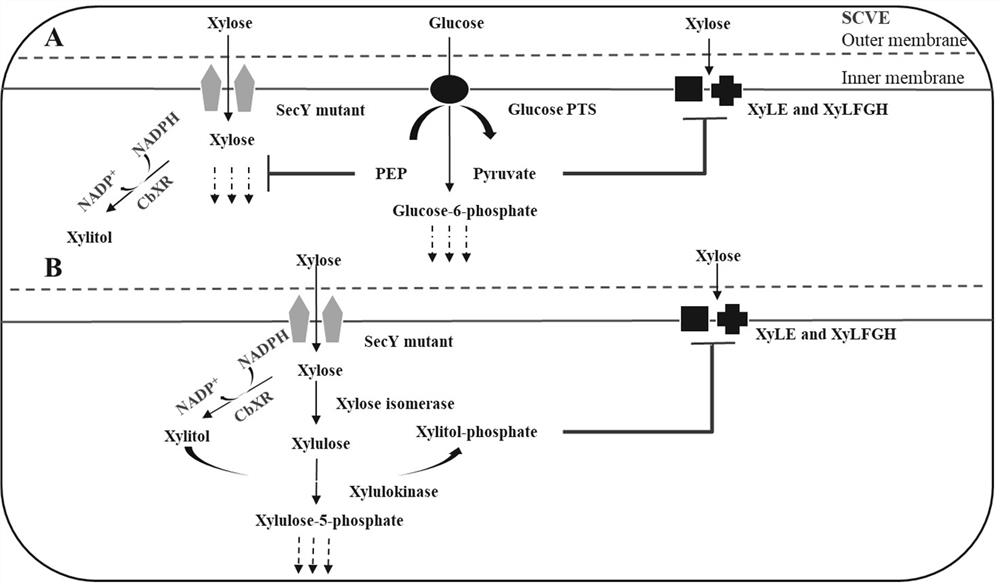
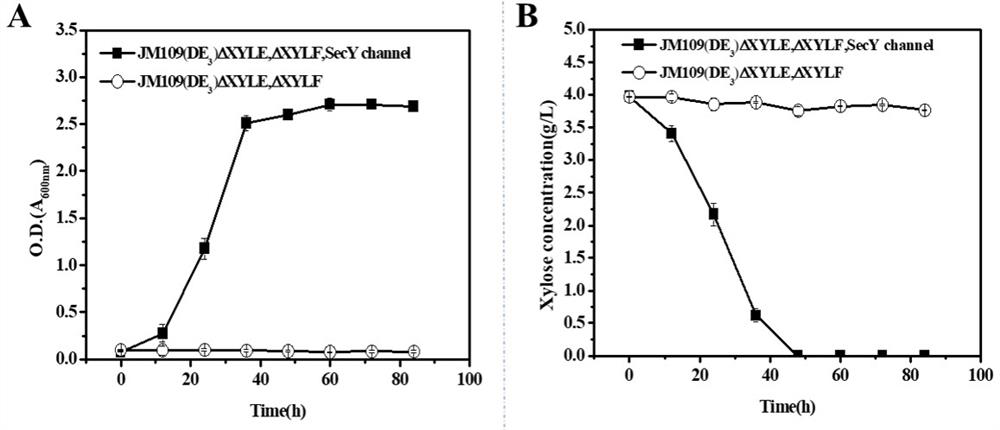
Intelligent regulation and control method for carbon metabolism flow of xylitol produced by escherichia coli
ActiveCN113293121ADisinhibition effectProduction constraintsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention provides an intelligent regulation and control method for carbon metabolism flow of xylitol produced by escherichia coli, and aims to realize efficient synthesis of xylitol in a process of preparing xylitol by utilizing a cell factory. According to the invention, a strain of SecY engineered Escherichia coli is successfully constructed by introducing a SecY non-specific sugar transport channel and simultaneously overexpressing heterologous xylose reductase (CbXR). The strain can overcome the CCR effect through self-regulation and relieve the inhibition effect of the 5-phosphate xylitol on xylose transported by the strain. By taking the change of an external carbon source as a response signal, the CCR effect and the inhibition effect of the xylitol 5-phosphate are converted into two important regulating switches in a carbon metabolism network, and the metabolic capability of cells on glucose and xylose is regulated. The method can completely metabolize glucose and xylose in any proportion in a substrate, ensures the maximum conversion efficiency of energy to a target product, and better meets the requirements of green biological manufacturing.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
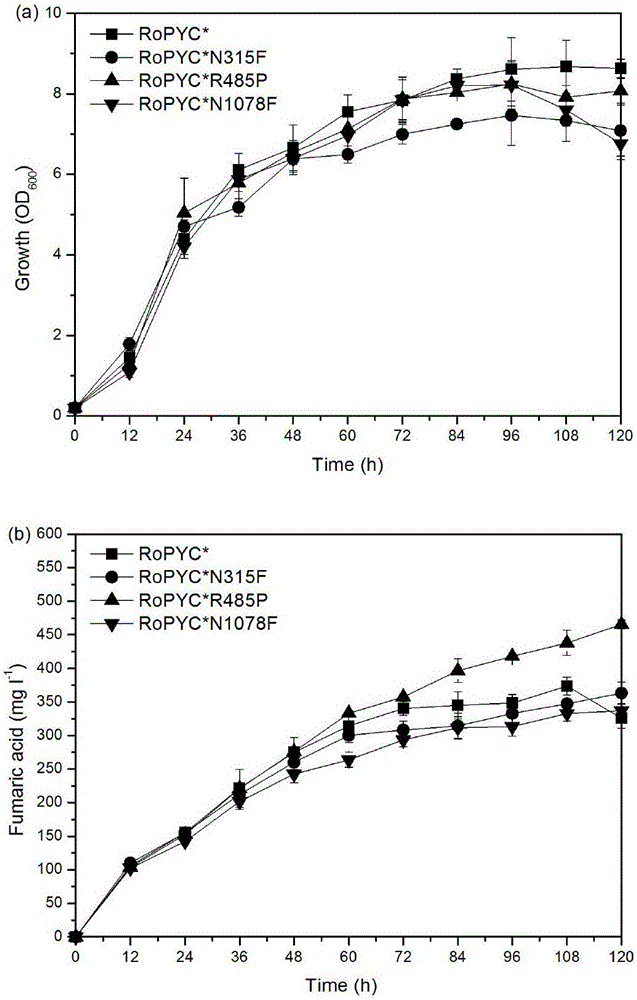
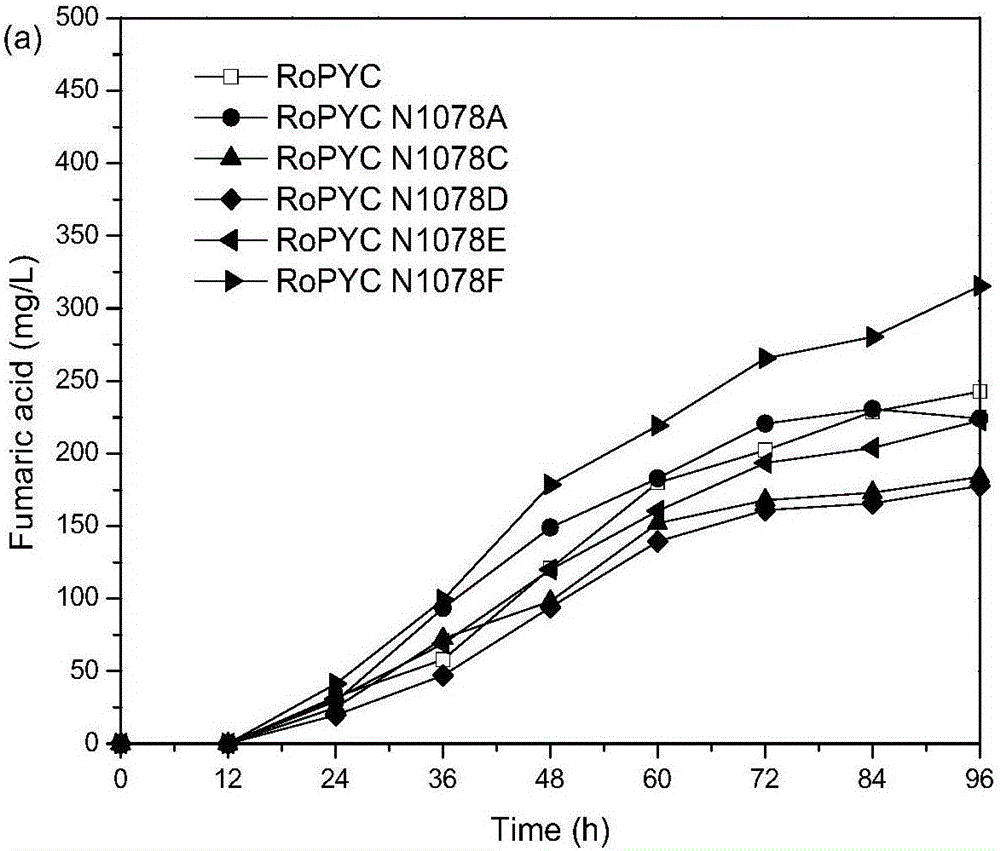
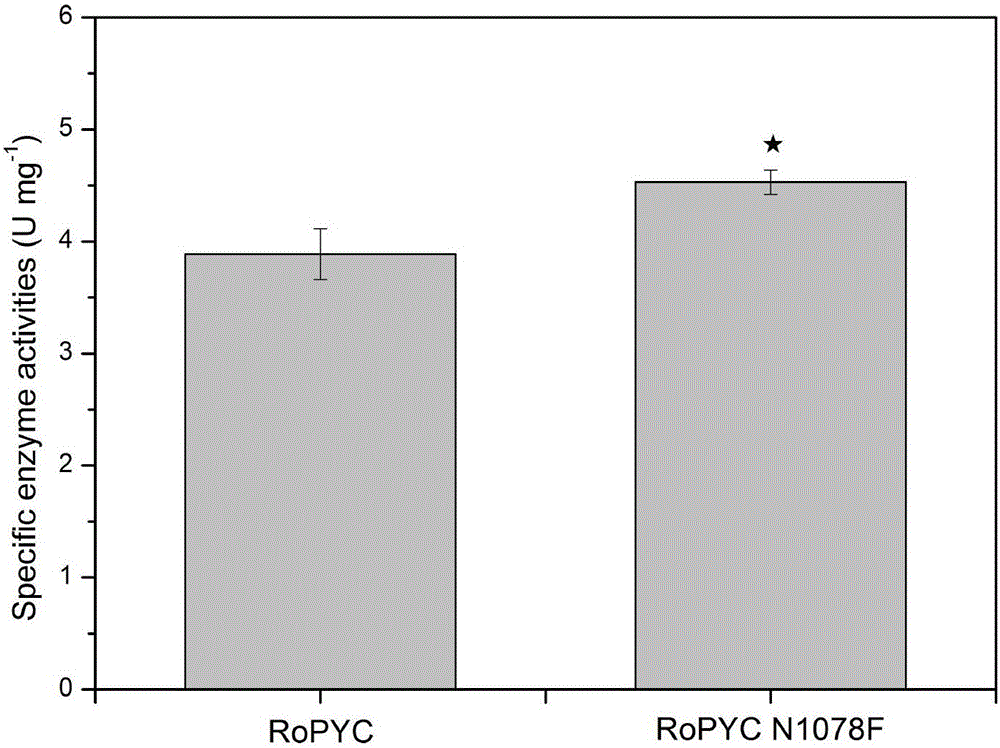
Enzymatic activity improved pyruvate carboxylase mutant N1078F and application thereof
The invention discloses an enzymatic activity improved pyruvate carboxylase mutant N1078F and an application thereof and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and fermentative engineering. According to the mutant N1078F and the application thereof, a locus N1078 of pyruvate carboxylase of Rhizopus oryzae is mutated into phenylalanine, so that the enzymatic activity of the obtained mutant is improved by 16.5%. A gene FUM1 is knocked out on the basis of knocking out PDC1 and ADH1, and meanwhile, the pyruvate carboxylase mutant N1078F is excessive, so that the yield of fumaric acid is increased by 20.5%. According to the mutant N1078F and the application thereof, a way of synthesis of carbon metabolic flux into fumaric acid from pyruvic acid is effectively strengthened, and conditions for constructing engineering yeasts and efficiently producing fumaric acid and other dicarboxylic acids are created, so that the mutant N1078F has very good industrial application values and prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
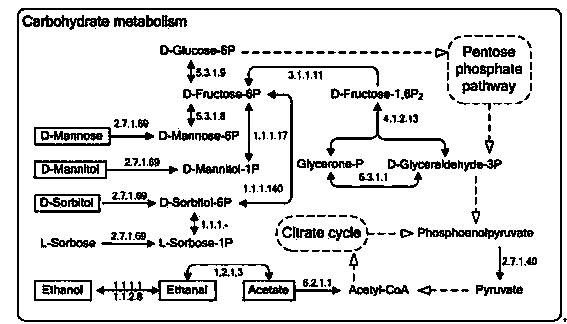
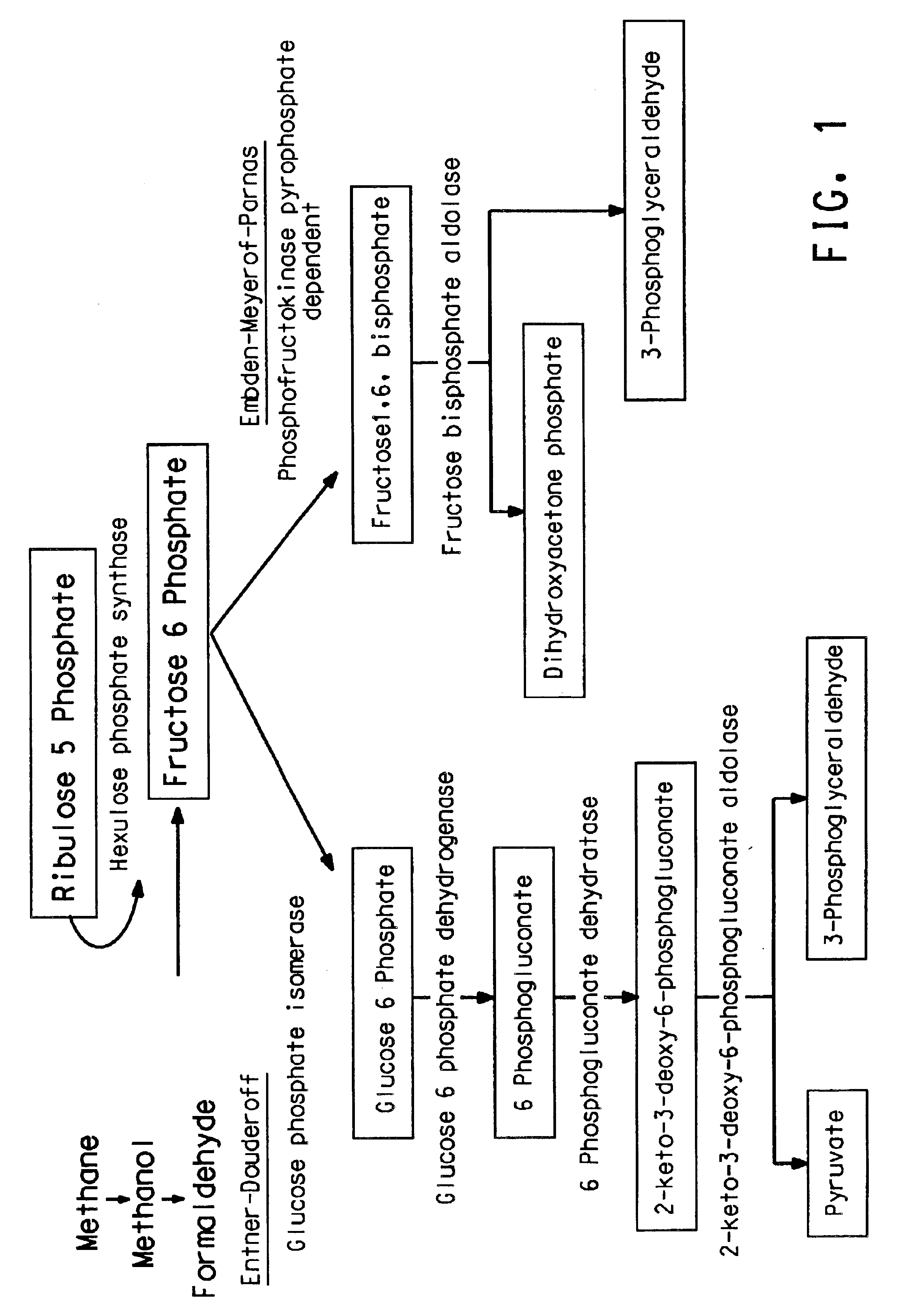
Methanotrophic carbon metabolism pathway genes and enzymes
Genes have been isolated from a Methylomonas sp encoding enzymes in the carbon flux pathway. The genes encode a 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPGA) and a fructose bisphosphate aldolase (FFBPA), as well as numerous other genes. The genes will be useful in C1 metabolizing microorganisms for the manipulation of the carbon flux pathway.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com