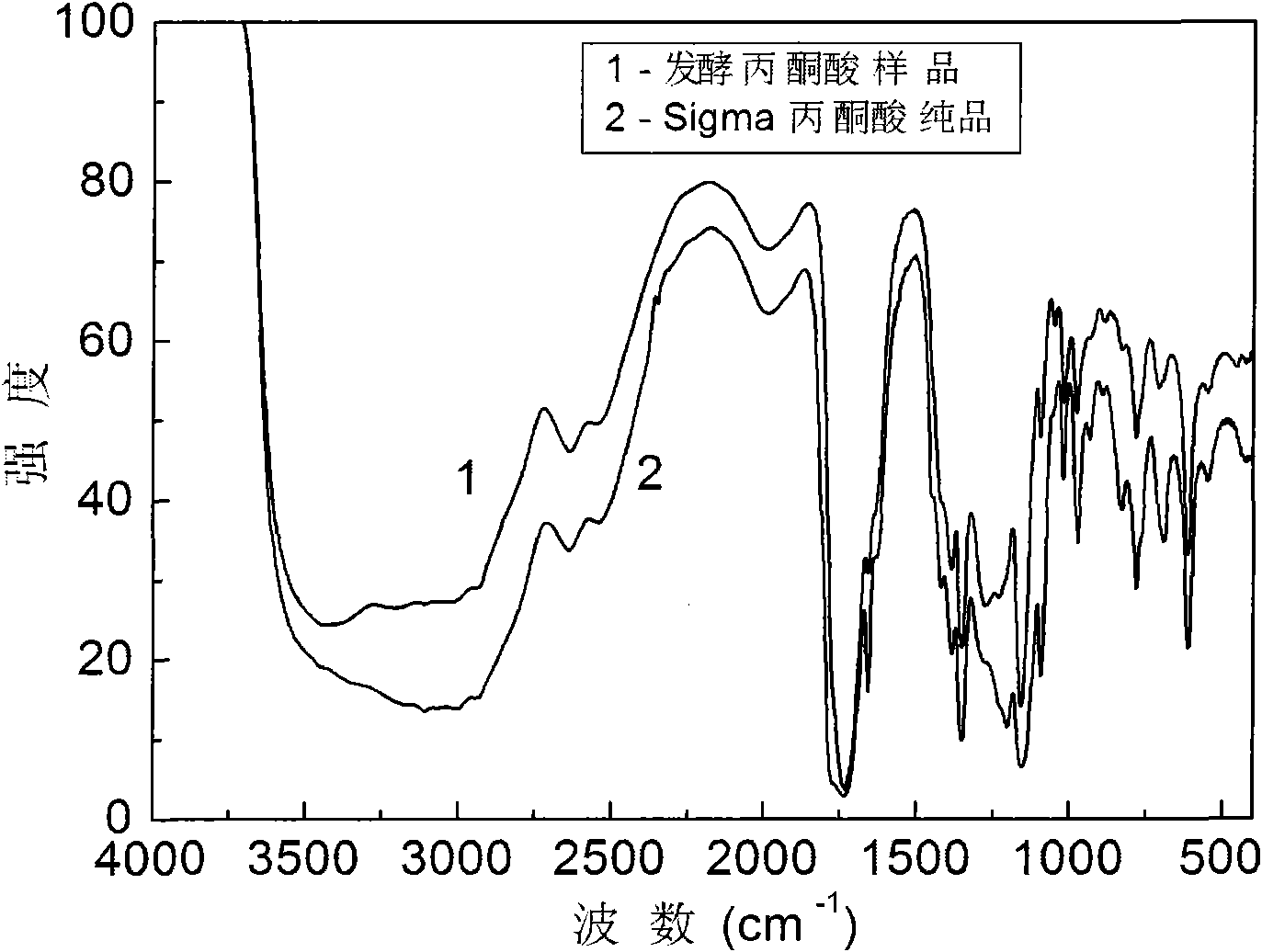
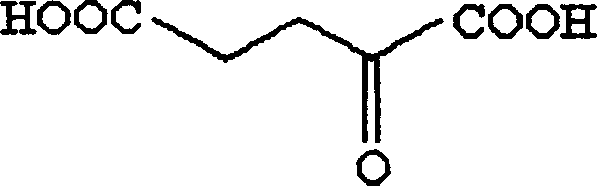
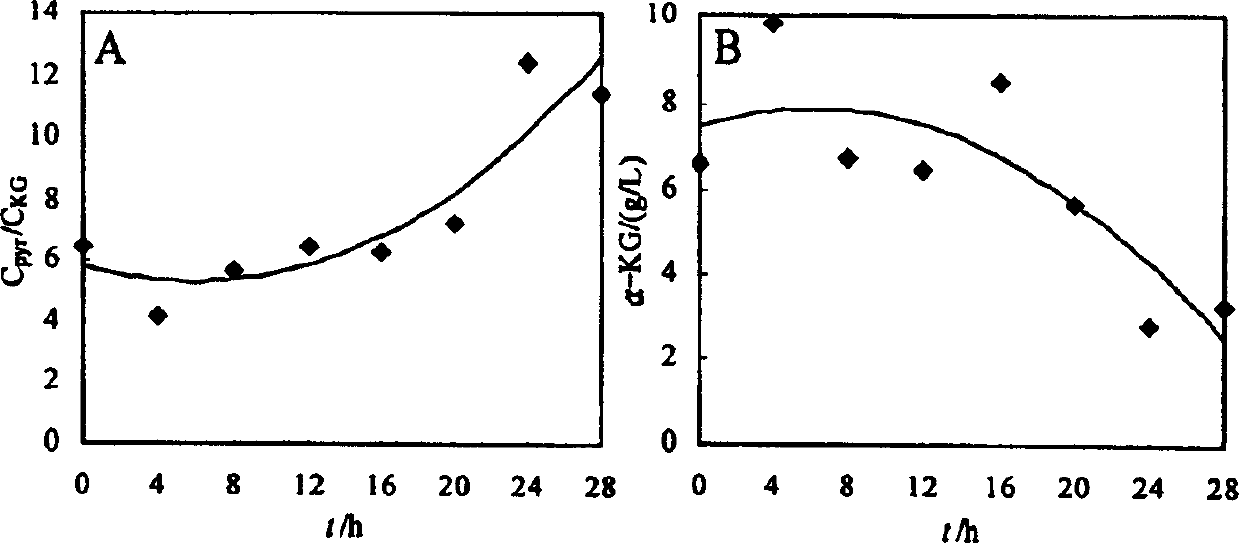
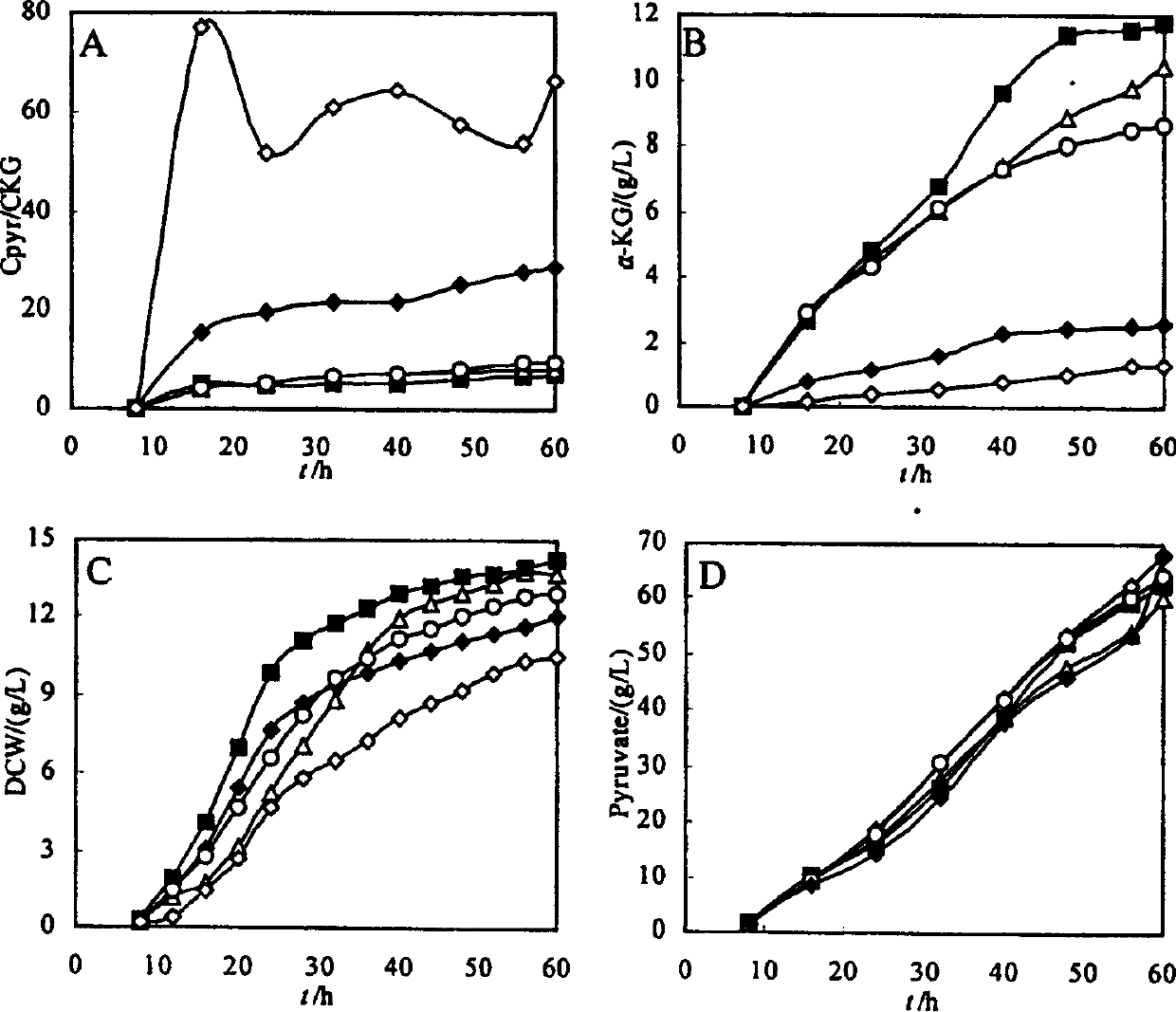
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Torulopsis glabrata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for realizing excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate acid by adding alpha-ketoglutarate acid dehydrogenase inhibitor
InactiveCN101250563AImproved compared to the controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataCarbon metabolism
The invention relates to a method for adding alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor to realize excessive accumulation of alpha-ketoglutaric acid, which belongs to the technical field of the metabolic regulation optimized fermentation process of the protein level. The method of the invention comprises following steps: utilizing multi - vitamin - auxotrophic yeast of Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019 as producing strains, regulating the activity of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through adding the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibitor: hydrogen peroxide, methotrexate, sodium hypochlorite or hydroxyamino in culture medium, purposively lowing the activity of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, reducing the degradation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid in the metabolic process, and achieving the aim of the excessive accumulation of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid. The method of the invention cuts off carbon metabolism flow on a node of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid through regulating the stream distribution of carbon metabolism and the carbon metabolism flow, wherein the maximum output of the alpha-ketoglutaric acid reaches 23.2g / L, which is increased by 12.2% compared with the control. The invention provides a new thought for the fermentation research of TCA cycle intermediate metabolite.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
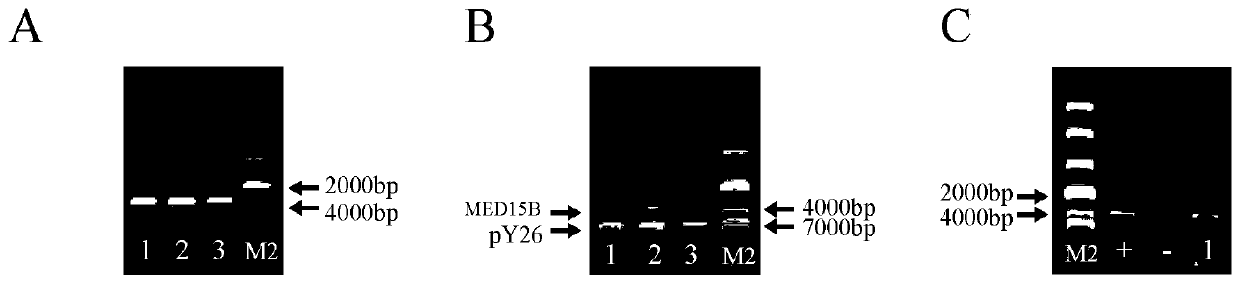
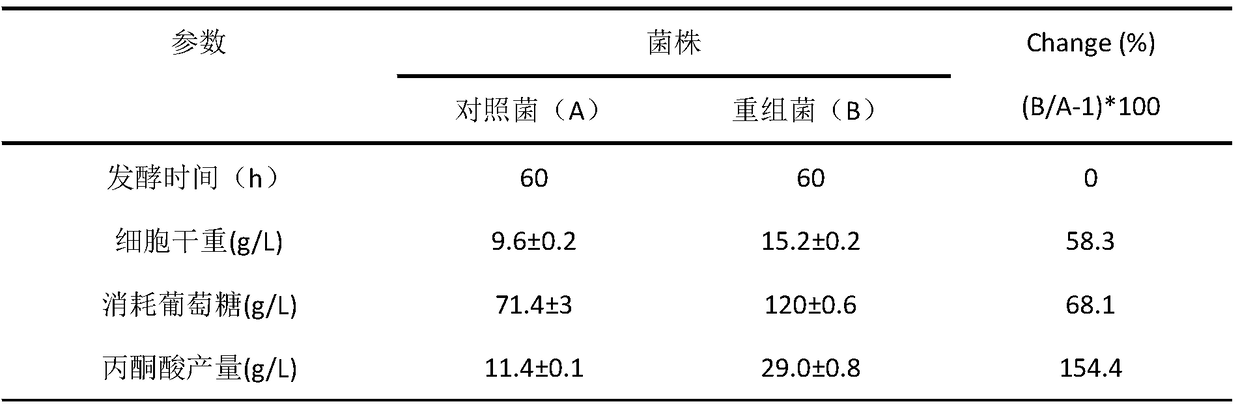
Recombinant bacterium with function of pyruvate production intensity improvement and application of recombinant bacterium with function of pyruvate production intensity improvement
ActiveCN105368884AIncrease productionIncrease production intensityFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataCell membrane
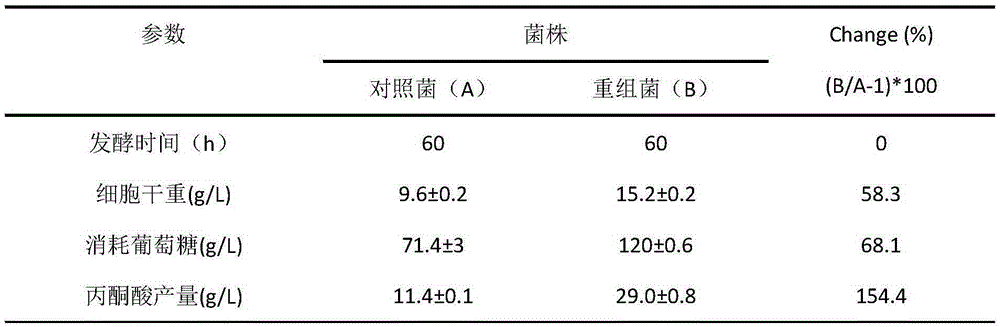
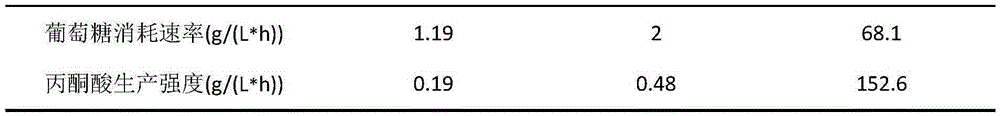
The invention belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering and discloses a recombinant bacterium with a function of pyruvate production intensity improvement and application of the recombinant bacterium with the function of pyruvate production intensity improvement. By targeting expression of a mitochondrion pyruvate carrier protein to a cell membrane in a torulopsis glabrata strain, cell outgoing rate of pyruvate is increased while a feedback inhibition effect of the pyruvate on glycolytic pathway key enzymes is weakened, and consequently pyruvate yield is increased, and production intensity is improved. By means of genetic engineering technology, a signal peptide sequence Shrew1p and MPC1 derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae are positioned and integrated to a pY26 expression vector to construct a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant expression plasmid pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1 which is electrophoretically transferred into a recipient bacterium TgU to obtain an engineering strain TgU-(pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1) high in pyruvate yield. Compared with a reference strain TgU-(pY26), the engineering strain TgU-(pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1) has the advantage that dry cell weight, glucose consumption rate, pyruvate yield and pyruvate production intensity are increased by 58.3%, 68.1%, 154.4% and 152.6% respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for constructing non-resistance mark auxotroph torulopsis glabrata
InactiveCN101240250AHomologous recombination avoidanceAvoid back mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataLarge fragment
A constructing method for non-resistance badge auxotrophy smoothing ball false yeast belongs to biological engineering technology field. The invention is a system method for breeding large fragment deletion non-resistance badge auxotrophy smoothing ball false yeast comprising obtaining large fragment deletion consanguinity recombination fragments by blending PCR method, preparing high efficient sprout fungi electric conversion competence, concentrating candio-hermal and screening restrictive culture medium. Goal auxotrophy bacterial strain can be obtained quickly within 3 to 5 days by a suit system method. The deletion of large fragments avoids efficiently reversion and consanguinity recombination of exogenous plasmid. Furthermore, the method can be used many times in a same leaving strain so that multiplex auxotrophy for following genetic engineering study can be obtained because any resistance badge is not used in entire process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction method and use of fumaric acid producing candida glabrata engineering strain
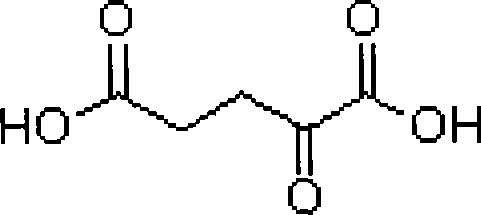
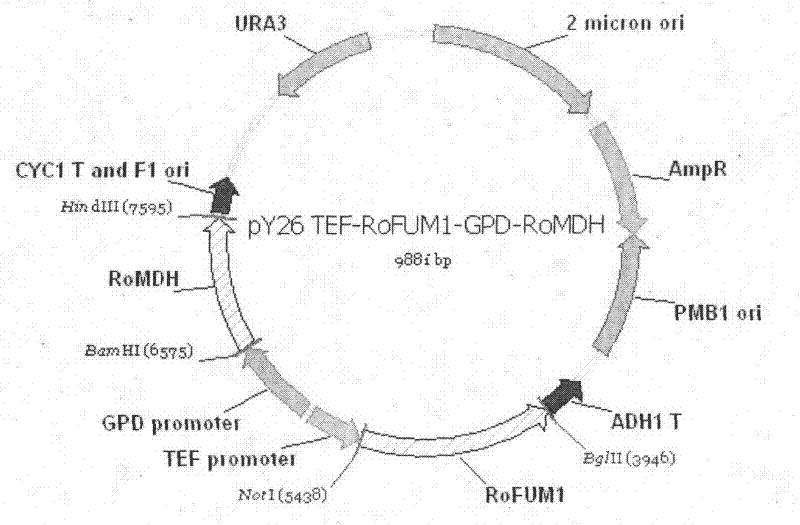
The invention discloses a construction method and use of a fumaric acid producing T.glabrata candida glabrata engineering strain and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the invention, a recombinant T.glabrata FMME045 strain is obtained by overexpression of a malic dehydrogenase (RoMDH) gene and a fumarase (RoFUM1) gene from rhizopus oryzae in a uracil deficient (Ura) T.glabratadeltaura3 strain of a pyruvic acid producing strain T.glabrata in a free expression mode. When the strain is used for fermentation production of fumaric acid, the fumaric acid yield after the fermentation is performed for 60 hours is increased by 6 times to 35mg / L compared with that of a starting strain. Thus, a new approach is provided for producing fumaric acid by a microbial fermentation process. The method has a bright application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High temperature-resistant yeast strain for producing pyruvic acid and use thereof
The invention discloses a high temperature-resistant yeast strain for producing pyruvic acid and a use thereof. Pyruvic acid is an important organic acid in metabolism. The high temperature-resistant yeast strain for producing pyruvic acid has wide purposes. The high temperature-resistant yeast strain is high temperature-resistant Torulopsis glabrata TIB-G90 CGMCC No. 5434 and is screened by a high-temperature adaptive evolution method. The high temperature-resistant Torulopsis glabrata TIB-G90 CGMCC No. 5434 can grow well at a temperature of 40-45 DEG C and does not influence an accumulation amount of pyruvic acid in a fermentation broth. The high temperature-resistant yeast strain can reduce a temperature reduction cost in production and has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
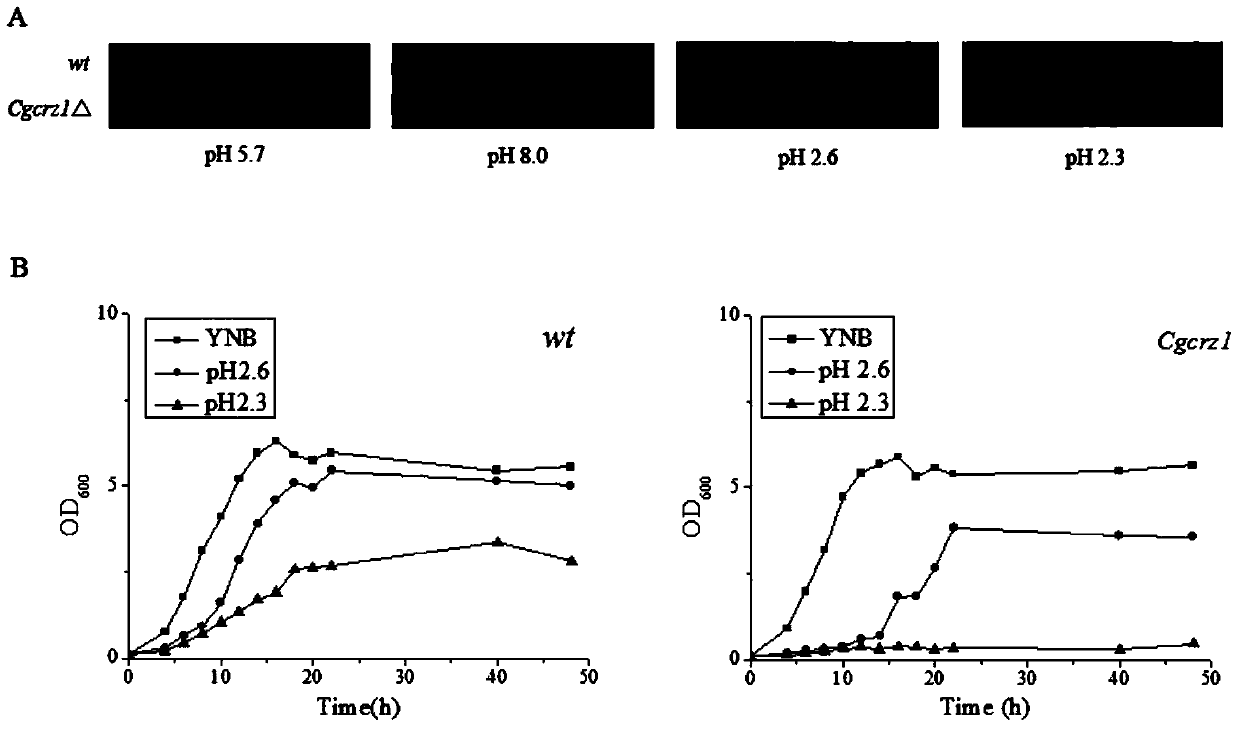
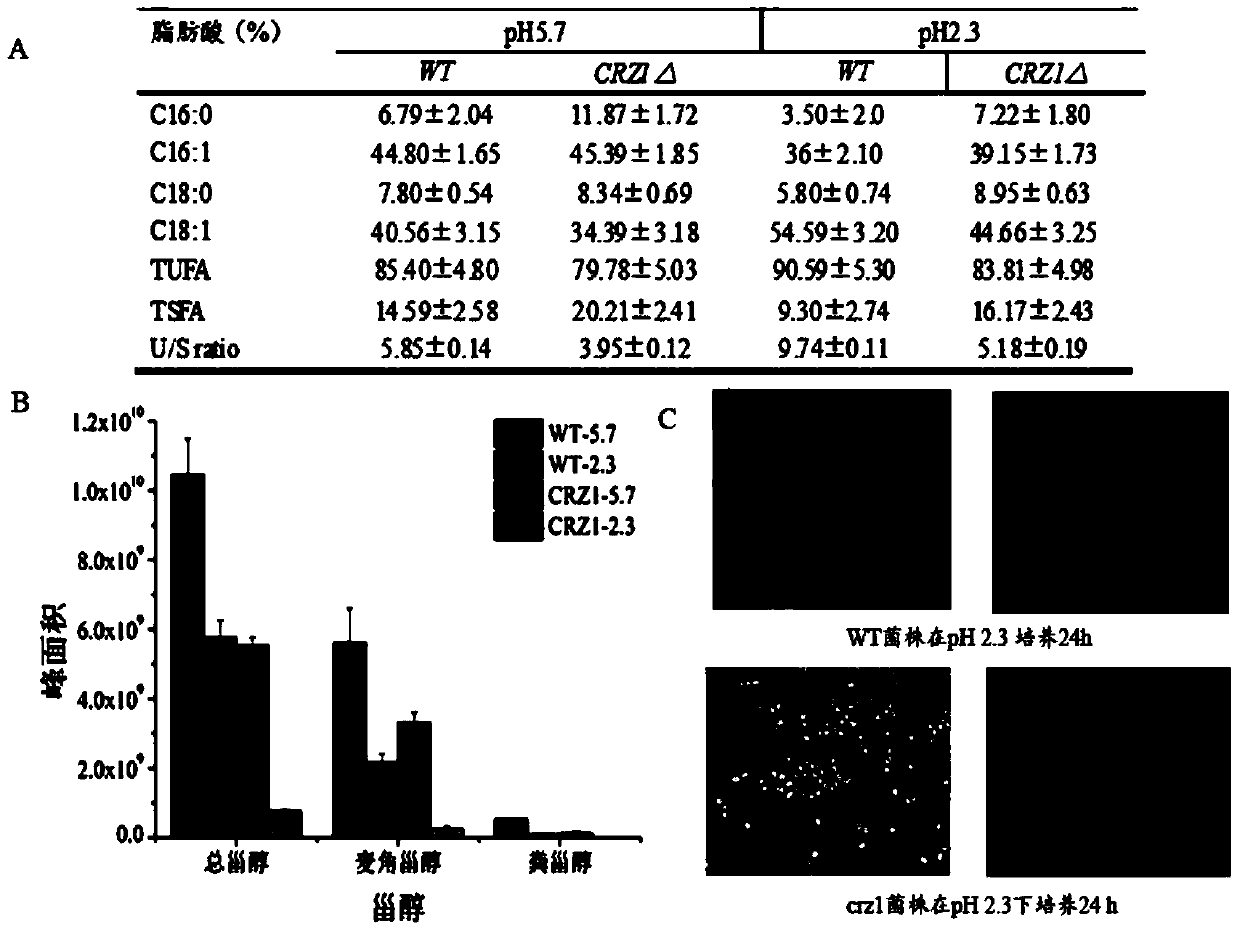
Method for regulating acid stress resistance of torulopsis glabrata by utilizing transcription factor Crz1p
ActiveCN105400770AReduced acid stress resistanceImprove acid stress resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataCell membrane
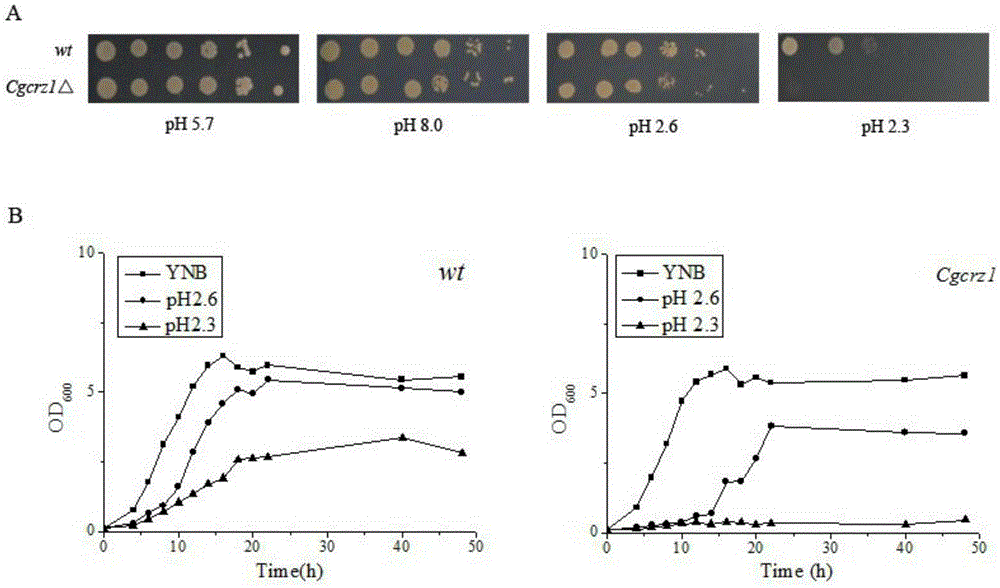
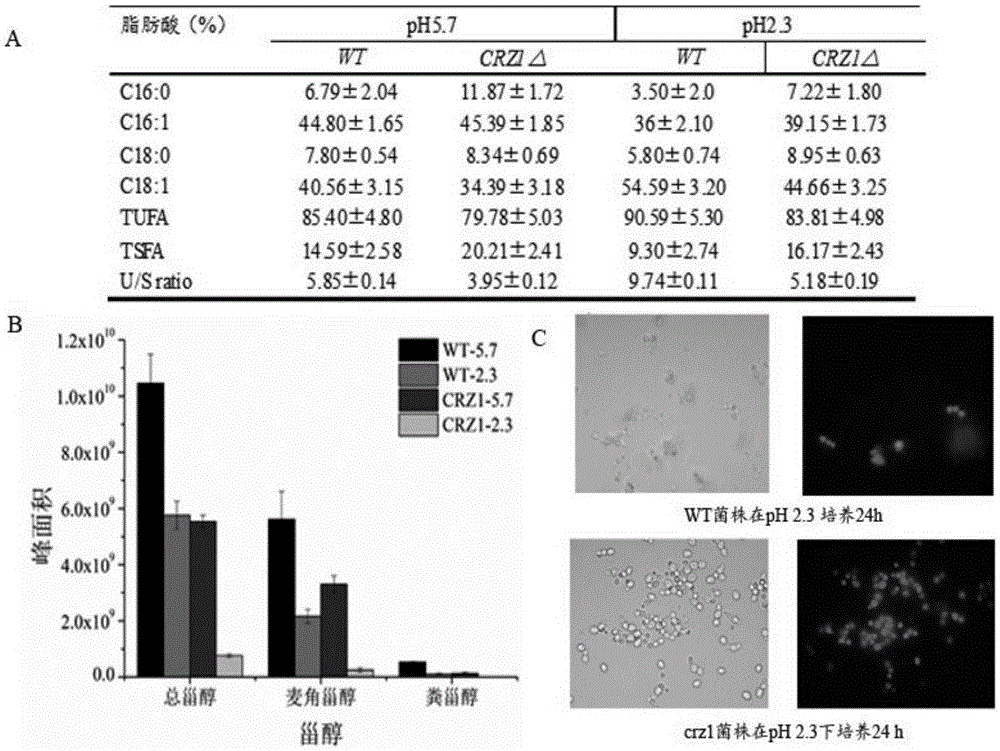
The invention discloses a method for regulating acid stress resistance of torulopsis glabrata by utilizing a transcription factor Crz1p and belongs to the field of bioengineering. By deletion or overexpression of Cgcrz1 genes of torulopsis glabrata, the acid stress resistance of strains is reduced or improved correspondingly. The cell membrane fatty acid and sterol ingredients and proportion and permeability of deletion mutant strains Cgcrz1 delta under acid stress are compared, it is found that Crz1p is an essential transcription factor for torulopsis glabrata to resist the acid stress, and by the overexpression of Crz1p, the acid stress resistance of torulopsis glabrata can be improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for increasing yield of pyruvic acid
InactiveCN102121035APromote growthImprove acid resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataPyruvic acid
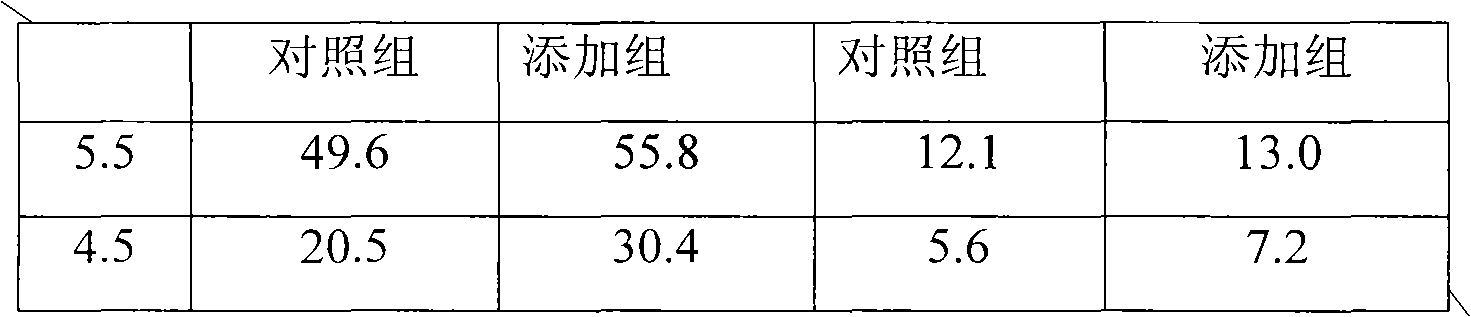
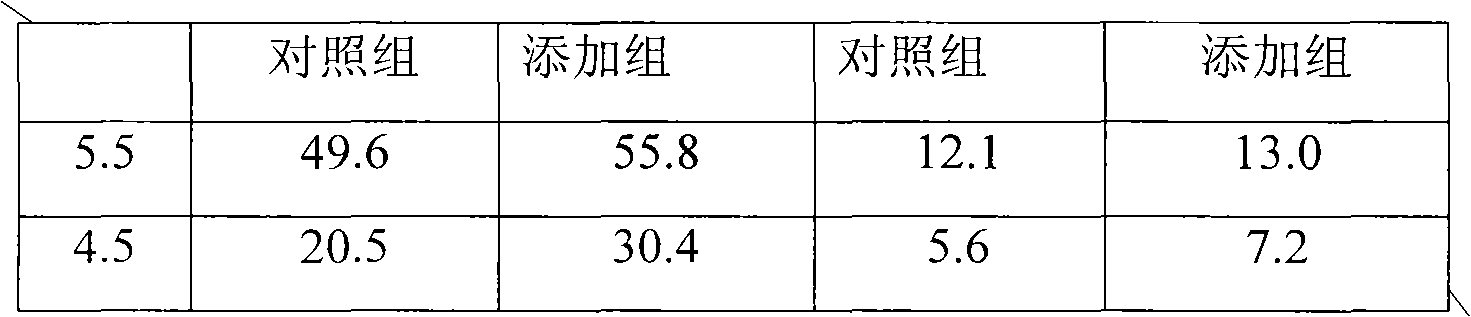
The invention discloses a method for increasing yield of pyruvic acid, belonging to the fermentation engineering field. The method is as follows: when Torulopsis glabrata (CCTCC NO: M202019) is used to ferment and produce pyruvic acid, aspartic acid is added to increase the acid stress resistance of Torulopsis glabrata. When the pH values are 5.5 and 4.5, the yields of pyruvic acid are separately55.8g / L and 30.4g / L which are separately increased by 12.4% (49.6g / L) and 48.4% (20.5g / L) than the control groups without aspartic acid; and the method has better technical effect and wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for increasing yield of pyruvic acid
InactiveCN102121035BPromote growthImprove acid resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataPyruvic acid
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
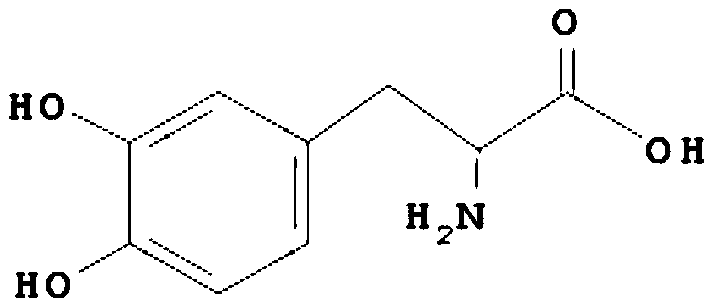
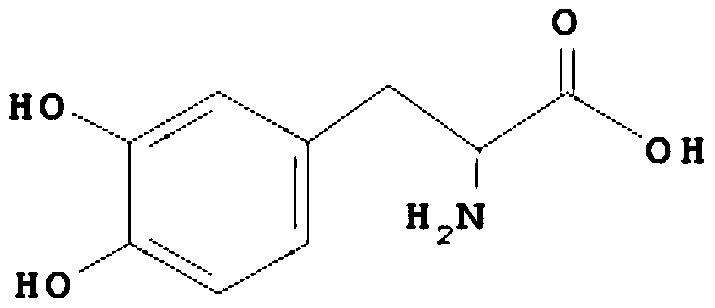
Pyruvic acid and L-dopa co-production process and application
ActiveCN110055292ALow costThree wastes lessMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a pyruvic acid and L-dopa co-production process and application. The process comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a pyruvic acid feed liquid by fermentation with torulopsis glabrata, sterilizing the feed liquid by a ceramic membrane, and removing proteins, nucleic acids, pigments and other macromolecules by an ultrafiltration membrane; (2) adding a certain amount of catechol, ammonium acetate, EDTA, sodium sulfite and other compounds to a pyruvic acid concentrate according to the molar amount of pyruvic acid, adjusting the pH to 7.0-9.0, and preparing an enzyme-catalyzed substrate solution; (3) fermenting with tyrosine-phenol lyase genetic engineering bacteria to obtain a tyrosine-phenol lyase bacterial solution, centrifuging to collect thalli, breaking cells by a high-pressure homogenizer, centrifuging, and collecting an enzyme solution; and (4) adding a certain amount of substrate solution to the enzyme solution, stirring evenly, and at the temperature of 25 DEG C, carrying out seal shock reaction. The substrate solution is prepared from the pyruvic acid concentrate, and the concentration of catechol is controlled at 0-10 g / L by fed-batching the substrate solution, the product reaches 120 g / L or more, and fed-batch of the substrate solution is stopped; when the content of catechol in the reaction solution is less than 0.2 g / L, and the reactionis stopped.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
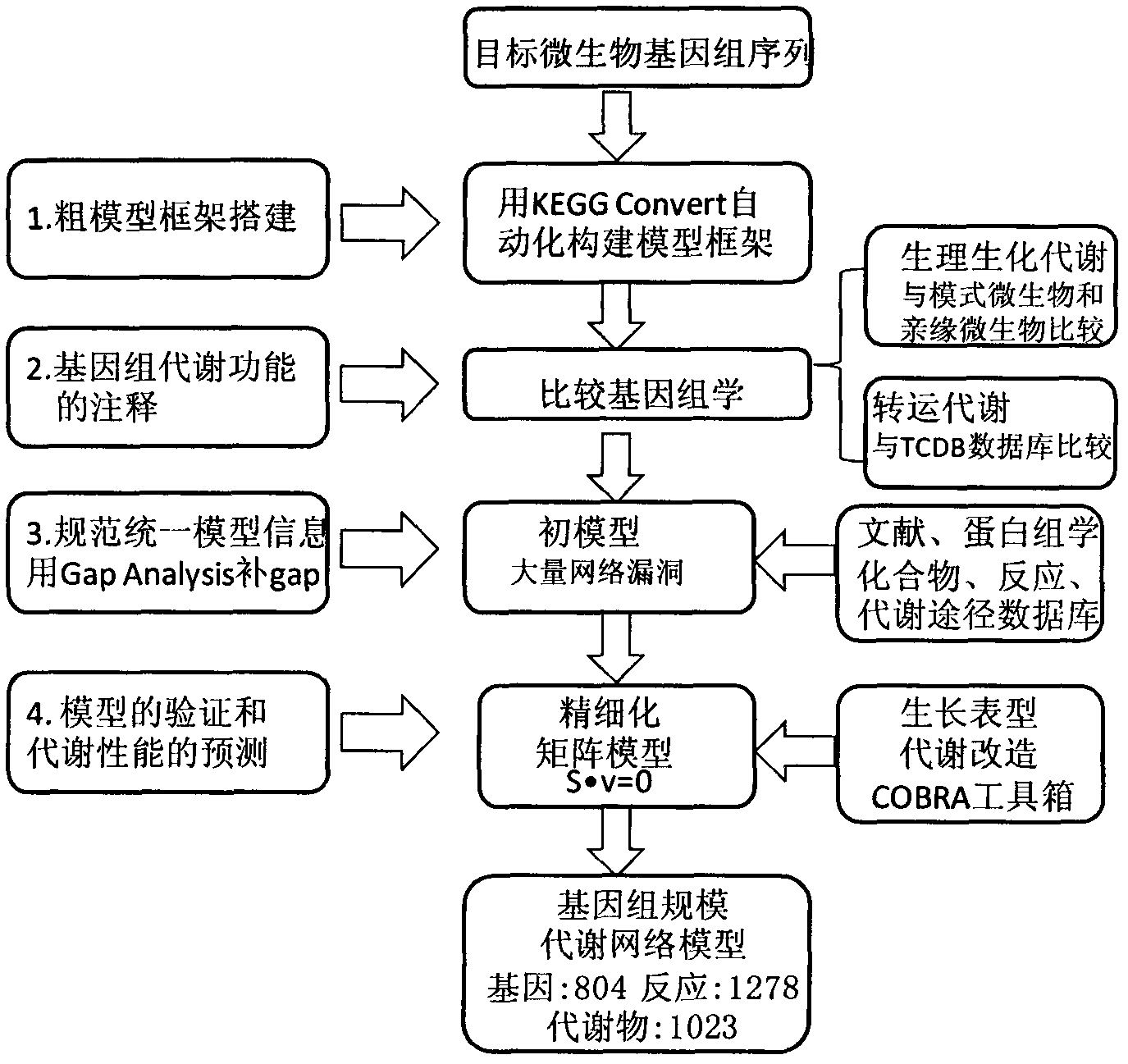
Construction and application technology of Torulopsis glabrata genome metabolism model
InactiveCN102622533AIncrease productionSpecial data processing applicationsTorulopsis glabrataEthanol dehydrogenase
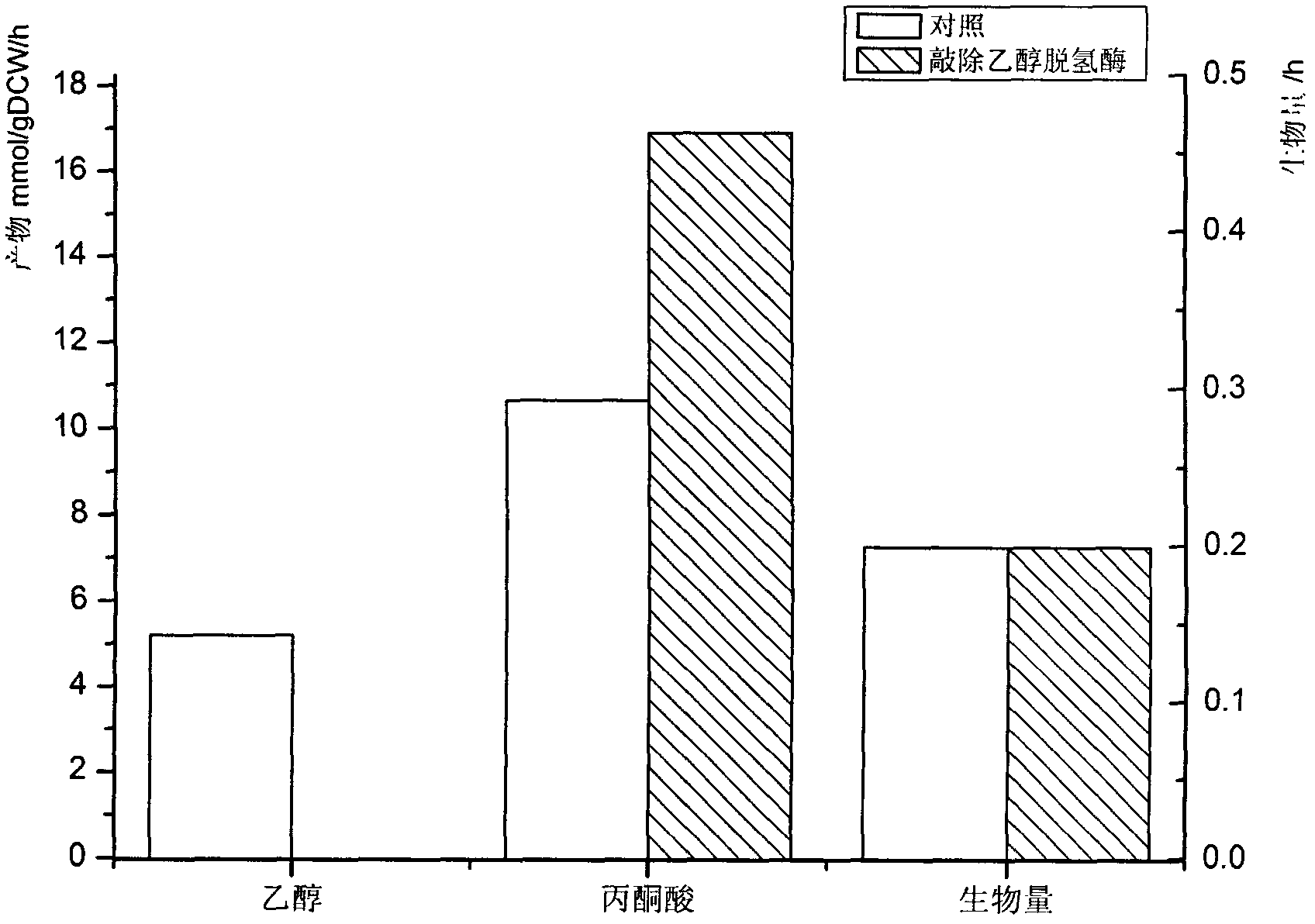
The invention discloses a construction method and an application technology of a Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model, belonging to the field of systems biology. The construction method of the model is an all-round semi-automatic construction method of combining comparative genomics annotation and bacteria-specific information of Torulopsis glabrata protein homology based on an automatic model. The invention provides a method for characterizing auxotroph characteristics in a Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network by adding necessary nutrient substances, lacked in bacteria, to a biomass equation. Alcohol dehydrogenase is knocked out by using single genes in the Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network model, and flow equilibrium analysis is applied, so that the output of pyruvic acid is increased. The construction method and the application technology of the Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model provide a high-efficient platform for fully understanding and reforming physiological and biochemical metabolisms of the Torulopsis glabrata.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Torulopsis glabrata mutant strain and application thereof in fermentation and production of pyruvic acid
InactiveCN101659925ASimple extraction processLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySaccharic acid
The invention relates to a torulopsis glabrata mutant strain and an application thereof in producing pyruvic acid through fermentation and provides a method for producing pyruvic acid through fermentation and culture of the strain, and the strain is the torulopsis glabrata mutant strain (CGMCC N0. 3077). The strain is a mutant strain that takes torulopsis glabrata NBRC 0005 as an original strain and is finally determined after going through ultraviolet mutation, preliminary screening of mutant strains and repeated screening by fermentation of a triangular flask. Under optimized medium component and fermentation conditions, the mutant strain takes glucose as the raw material to be fermented in a fermenter and produce over 0.5M of pyruvic acid. Counted by pyruvic acid sodium, the pyruvic acid reaches more than 5.5 percent, the conversion rate of saccharic acid is more than 30 percent and the fermentation period ranges from 45-55h. The technology is characterized by low content of competitive byproducts of pyruvic acid during downstream extraction process and simplified extraction process.
Owner:SHENZHOUSPACEBIOTECHGRP
Method for microbial fermentation synthesis of ª‡-ketoglutaric acid
InactiveCN1259425CInhibitionIncrease carbon molar ratioMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataPyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a method for microbial fermentative synthesis of α-ketoglutaric acid, in which calcium carbonate is added to a culture medium and the concentration of biotin is increased to promote the generation of a large amount of α-ketoglutarate during pyruvate fermentation. During the fermentative production of pyruvate by Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019, delaying the addition of calcium carbonate inhibited the formation of α-KG and increased the carbon molar ratio of pyruvate to α-KG (C PYR / C KG ), and increasing the concentration of calcium carbonate in the medium will promote the accumulation of a large amount of α-KG, and when the concentration of calcium carbonate is 40g / L, it is most conducive to the formation of α-KG. Keep the concentration of calcium carbonate in the medium constant, increase the concentration of biotin in the medium, promote the concentration of α-KG to rise continuously and C PYR / C KG The value decreased continuously, and the accumulation of α-KG was 23.5g / L when the biotin concentration was 60μg / L. When there is Ca 2+ When present, the activity of intracellular pyruvate carboxylase can be increased by 40%, while the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase system does not change significantly. Ca in medium 2+ The increase of the concentration of biotin and biotin can significantly increase the activity of pyruvate carboxylase, so that T. glabrata shifts from fermentative production of pyruvate to synthesis of high-concentration α-KG.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Torulopsis and method for producing acetonic acid by fermenting the same
InactiveCN101440351ALower metabolismImprove conversion rateFungiMutant preparationTorulopsis glabrataPyruvic acid
The invention discloses Torulopsis glabrata and a method for fermenting to produce pyruvic acid by adopting a strain. The Torulopsis glabrata is an aspartic acid and lactamine defective pyruvate high yield strain, can reduce the metabolism of the pyruvic acid, and increase the conversion rate of sugar acid. In addition, in the Torulopsis glabrata, a transamination reaction from the pyruvic acid to lactamine exists, and a decarboxylic reaction from aspartic acid to the lactamine also exists. Compared with the prior art, when the strain is adopted to ferment for producing the pyruvic acid, the acid yield can be improved by 38 percent in the same production period, and the conversion rate can be improved by between 2 and 3 percent, so the strain has better prospect of industrialized production.
Owner:上海新立工业微生物科技有限公司
Method for constructing non-resistance mark auxotroph torulopsis glabrata
InactiveCN101240250BHomologous recombination avoidanceAvoid back mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataLarge fragment
A constructing method for non-resistance badge auxotrophy smoothing ball false yeast belongs to biological engineering technology field. The invention is a system method for breeding large fragment deletion non-resistance badge auxotrophy smoothing ball false yeast comprising obtaining large fragment deletion consanguinity recombination fragments by blending PCR method, preparing high efficient sprout fungi electric conversion competence, concentrating candio-hermal and screening restrictive culture medium. Goal auxotrophy bacterial strain can be obtained quickly within 3 to 5 days by a suit system method. The deletion of large fragments avoids efficiently reversion and consanguinity recombination of exogenous plasmid. Furthermore, the method can be used many times in a same leaving strain so that multiplex auxotrophy for following genetic engineering study can be obtained because any resistance badge is not used in entire process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method for regulating acid stress resistance of T. glabrata using the transcription factor crz1p
ActiveCN105400770BReduced acid stress resistanceImprove acid stress resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataSterol
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for promoting acetonic acid excess accumulation by adding proline
InactiveCN101225410APromote growthReduce outputMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataFermentation
The invention relates to a method of boosting excessive accumulation of pyruvate by adding praline, belonging to directionally changing and optimizing microorganism metabolic function and optimizing fermentation process technical field, which is characterized in that: the torulopsis glabrata strain (T.glabrata) CCTCC M202019 of multiplex vitamin drawback is used as the starting strain, when the concentration of the sodium pyruvate is 0.4mol / L, praline is added into the culture medium and the concentration of the praline in the culture medium is 1g / L, the praline protects the torulopsis glabrata strain cells as compatible material and boosts the CCTCC M202019 to synthesize pyruvate. The method of boosting excessive accumulation of pyruvate by adding praline has the advantages that: the pyruvate fermentation cycle is shortened for 8 hours by adding 1g / L praline into the culture medium, and the pyruvate yield and production intensity is respectively enhanced for 5.4 percent and 18.6 percent; the research result can be applied to the organic acid fermentation and other typical industrial biological process, and provides new technique to industrial biotechnique, in particular the optimization of the fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
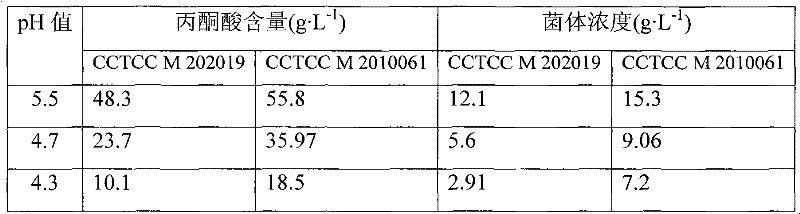
Yeast capable of enduring high-concentration pyruvic acid and low pH and breeding method thereof
InactiveCN102051334ALow professional quality requirementsImprove growth performanceFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTorulopsis glabrata
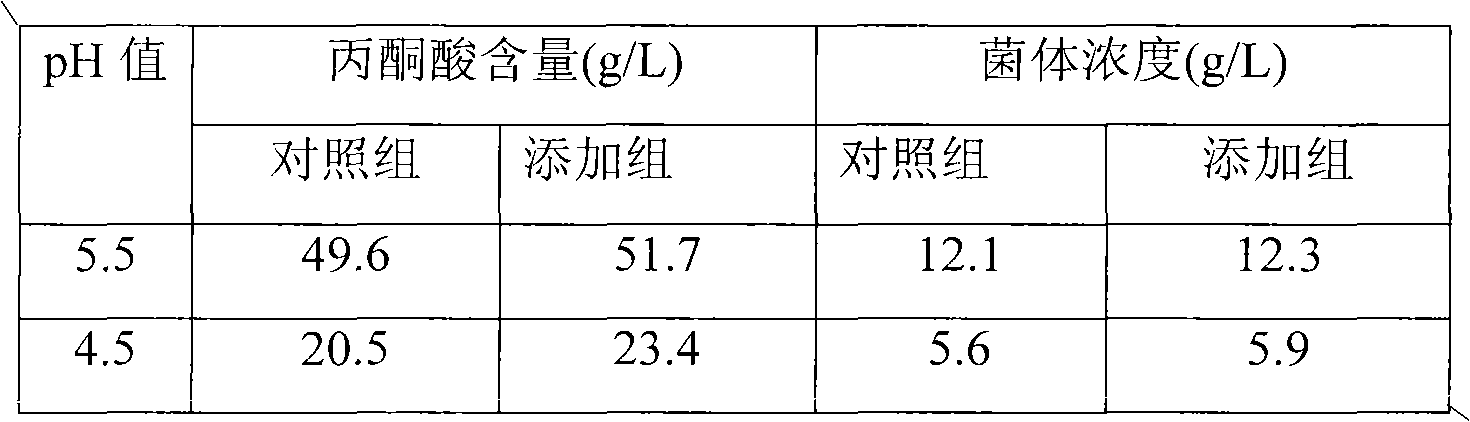
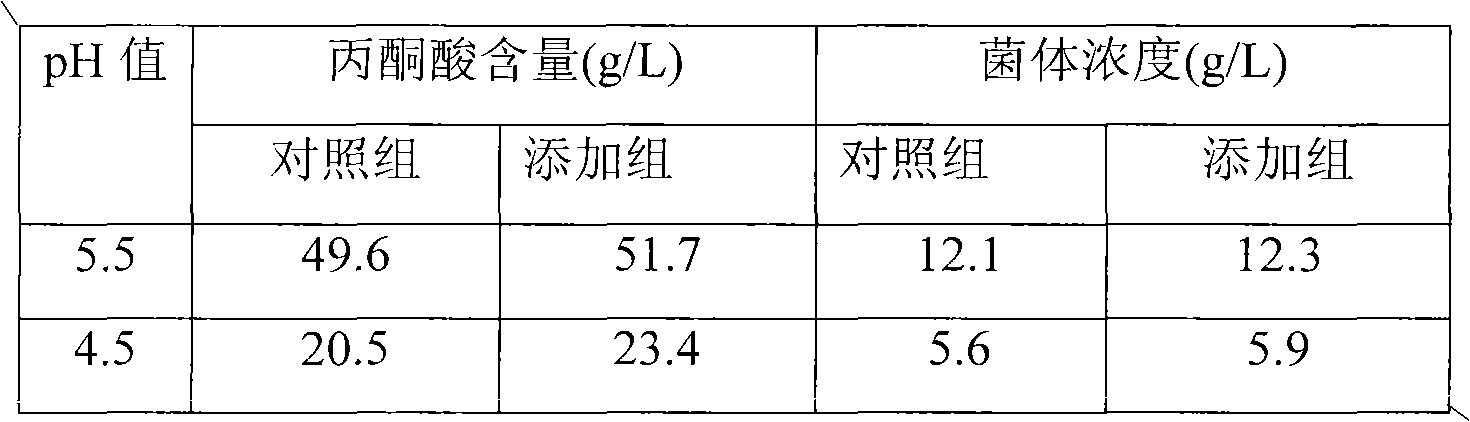
The invention discloses yeast capable of enduring high-concentration pyruvic acid and low pH and a breeding method thereof, and belongs to the field of strain breeding. In the invention, adaptive evolution technology is adopted, Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019 is subjected to progressive increase of stress intensity of high-concentration sodium pyruvate by a chemostat culture system under the condition of low pH of 4.5, and an evolved strain capable of enduring high-concentration pyruvic acid and low pH stress is obtained. Under the condition that the pH is 5.5, 4.7 and 4.3 respectively, the pyruvic acid yield is 55.8g.l<-1>, 35.97g.l<-1> and 18.5g.l<-1> respectively, which is improved by 15.5 percent (48.3g.l<-1>), 51.8 percent (23.7g.l<-1>) and 83.2 percent (10.1g.l<-1>) respectively compared with that of a starting strain. The invention overcomes the sensitivity of the yeast to the low pH value and the high-concentration pyruvic acid, and has important significance for producing pyruvic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving production volume of pyruvic acid preparation of zymotechnics with additive gluconic acid sodium salt
InactiveCN101319235AIncrease productionIncrease production intensityMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataOrganic acid
The invention discloses a method for improving the output of pyruvic acid by a fermentation method through adding gluconic acid sodium salt, which belongs to the fermentation preparation of pyruvic acid technical field. The method adopts a strategy that during the aerobic fermentation process of Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019 with glucose as a substrate, 10 to 15g / L of the gluconic acid sodium salt is added as a mixed carbon source when the fermentation is performed for 12 to 16h, which ensures that the output of the pyruvic acid is improved by 11.16 percent and the production period is also reduced to 44h from 48h. The research thought has universal application significance to the production of various important fermented products in industry such as organic acid, amino acid and so on.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Industrial production and fermentation technology of pyruvic acid
InactiveCN106834364AShorten the fermentation cycleQuality improvementFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataMicrobiology
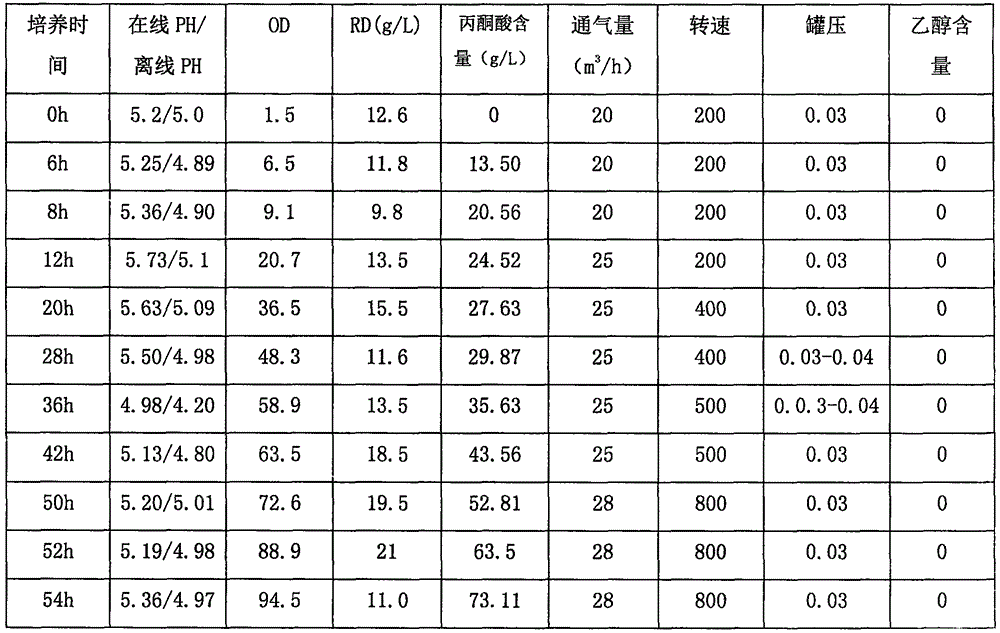
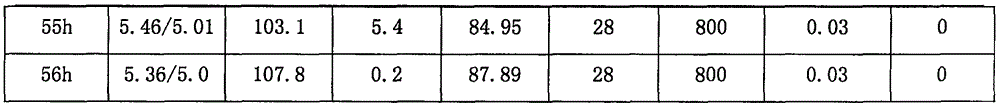
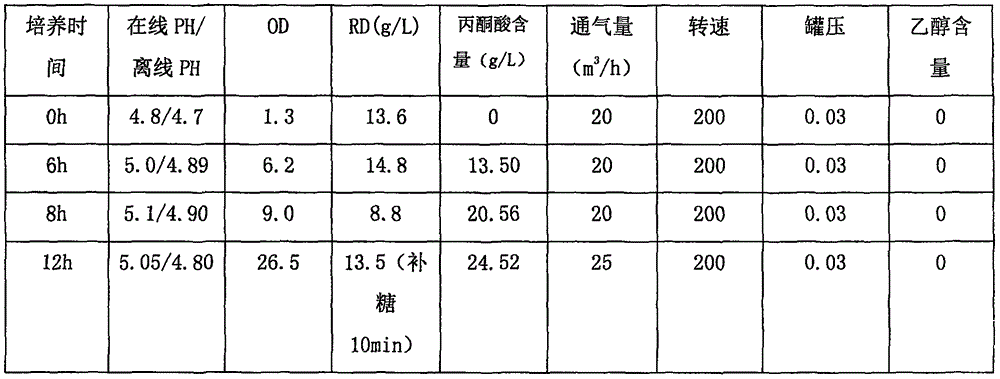
The invention discloses an industrial production and fermentation technology of pyruvic acid. The technology comprises plate cultivation of torulopsis glabrata, tomato bottle cultivation, shake-flask cultivation and first-level seed tank cultivation for industrial production and fermentation technology of a fermentation tank of 150 cubic meters, and determination of specific components and ratios of a culture medium. The process blank of industrial production and fermentation of the pyruvic acid, especially fermentation and production suitable for the large fermentation tank of 150 ic metes is filled; the fermentation period is shortened to 56h; relatively high yield is also obtained; internal friction and conversion of a strain on saturated pyruvic acid of a fermentation liquid are effectively solved; and the yield and quality of a product are ensured.
Owner:TONGLIAO HUANGHELONG BIOENG
Acetic acid leakage type high-yield pyruvate bacterium and its breeding method and producing pyruvic acid by said bacterium via fermentation process
InactiveCN1176205CImprove conversion rateHas industrial practical valueFungiFermentationTorulopsis glabrataBio engineering
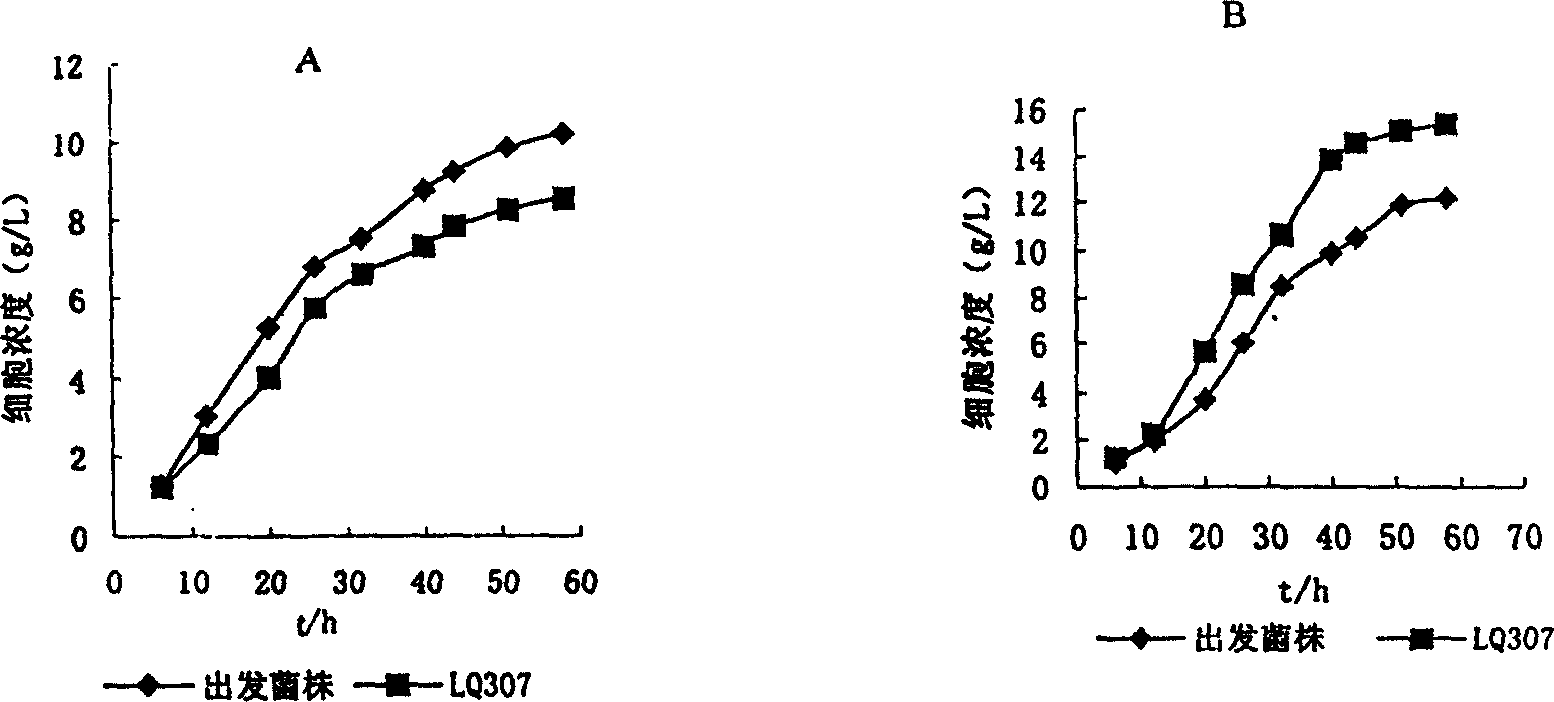
The present invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. The bacterium of the present invention is a kind of Torulopsis glabrata, WSH-, obtained with WSH-IP303 as starting strain and through NTG mutagenesis and breeding selection in culture medium with added acetic acid as replenishing carbon source. Compared with the starting strain, LQ307 has mush reduced pyruvate decarboxylase, and strong and stable pyruvate producing capacity. The yield of pyruvate reaches 46.2 g / L, 21% higher than that of starting strain when using acetic acid as replenishing carbon source and through shaking bottle culture for 48 hr; the yield of pyruvate may reach 68.7 g / L the glucose converting rate may reach 0.651 g / g through fermentation in a 5 L fermenting tank for 64 hr.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
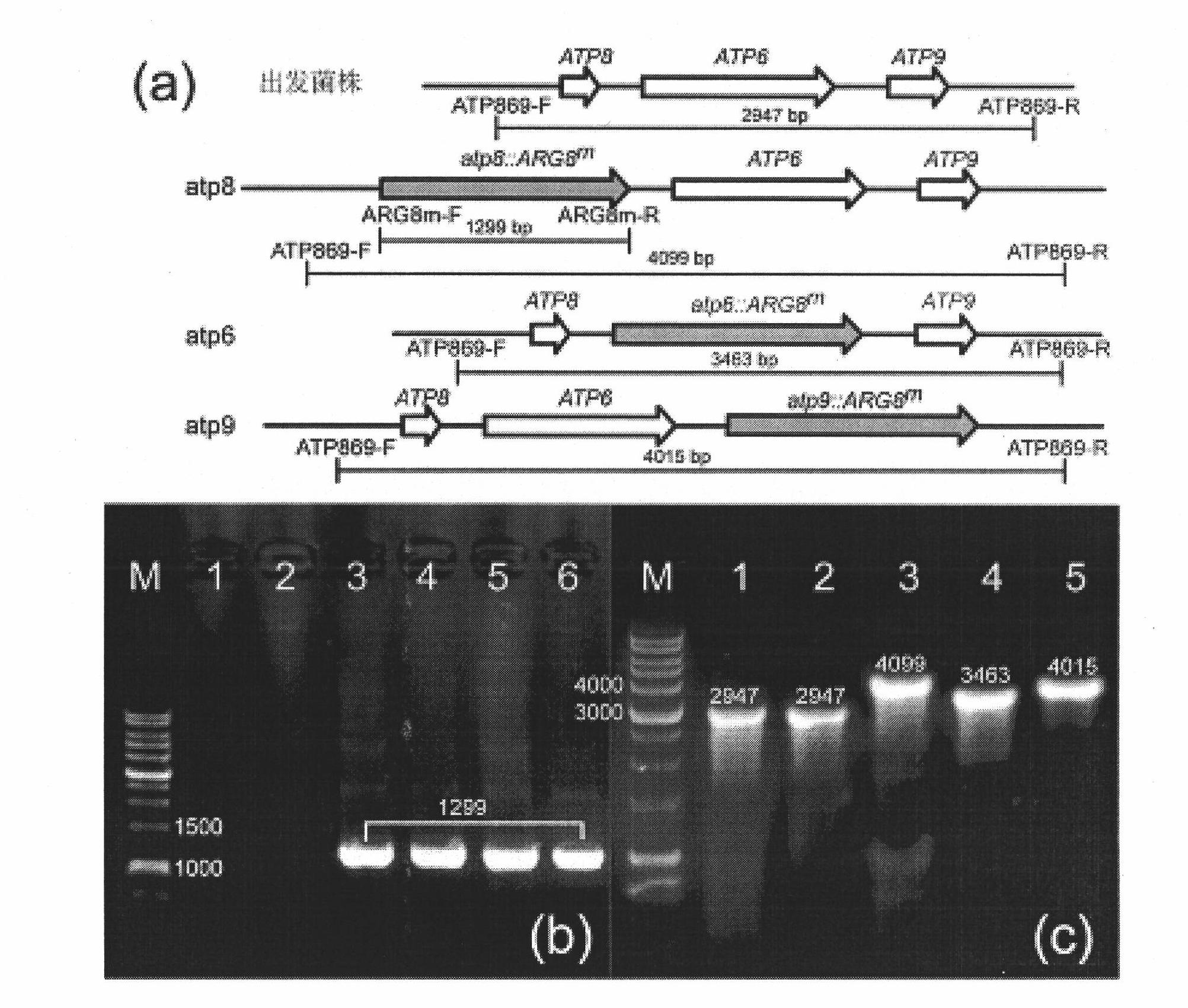
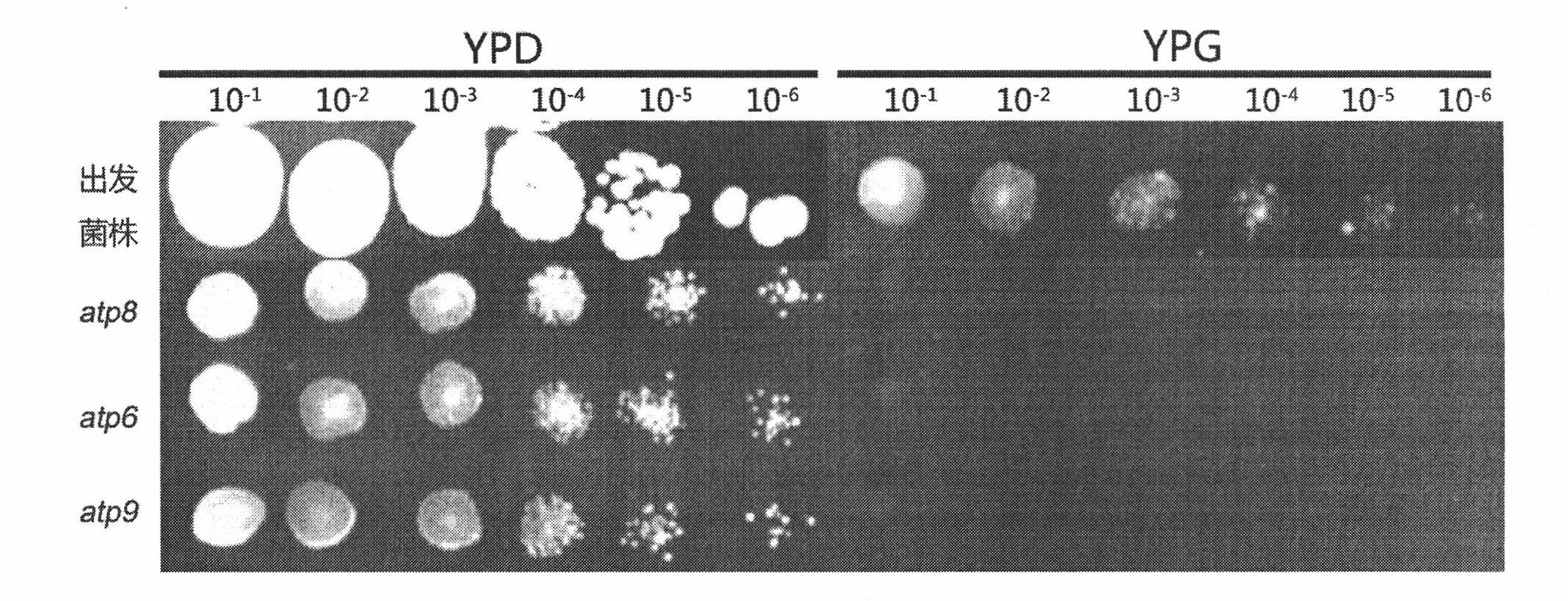
Method for knocking out torulopsis glabrata mitochondrion gene
InactiveCN101831449AKeep features unchangedSolving the problem of heterogeneous mitochondriaFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataMitophagy
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a torulopsis glabrata mitochondrion gene and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the invention, a homologous recombination fragment having the flanking sequences of an acetyl-ornithine transaminase gene (ARG 8m) and a mitochondrion gene to be knocked out is obtained by mainly using a long terminal primer, a torulopsis glabrata mitochondrion is transferred by a gene gun, and heterogeneity of the mitochondrion is eliminated by anaerobic culture to obtain a transformant which only has the gene on the modified mitochondrion. The torulopsis glabrata obtained by the invention is easy to identify and protect; the knocking method represents a novel approach and method for the genetic engineering modification of diploid of polyploidy yeasts; and the knocking method is simple and efficient, can retain the original characteristics of the yeasts, and can knock out the mitochondrion gene within 5 to 7 days.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
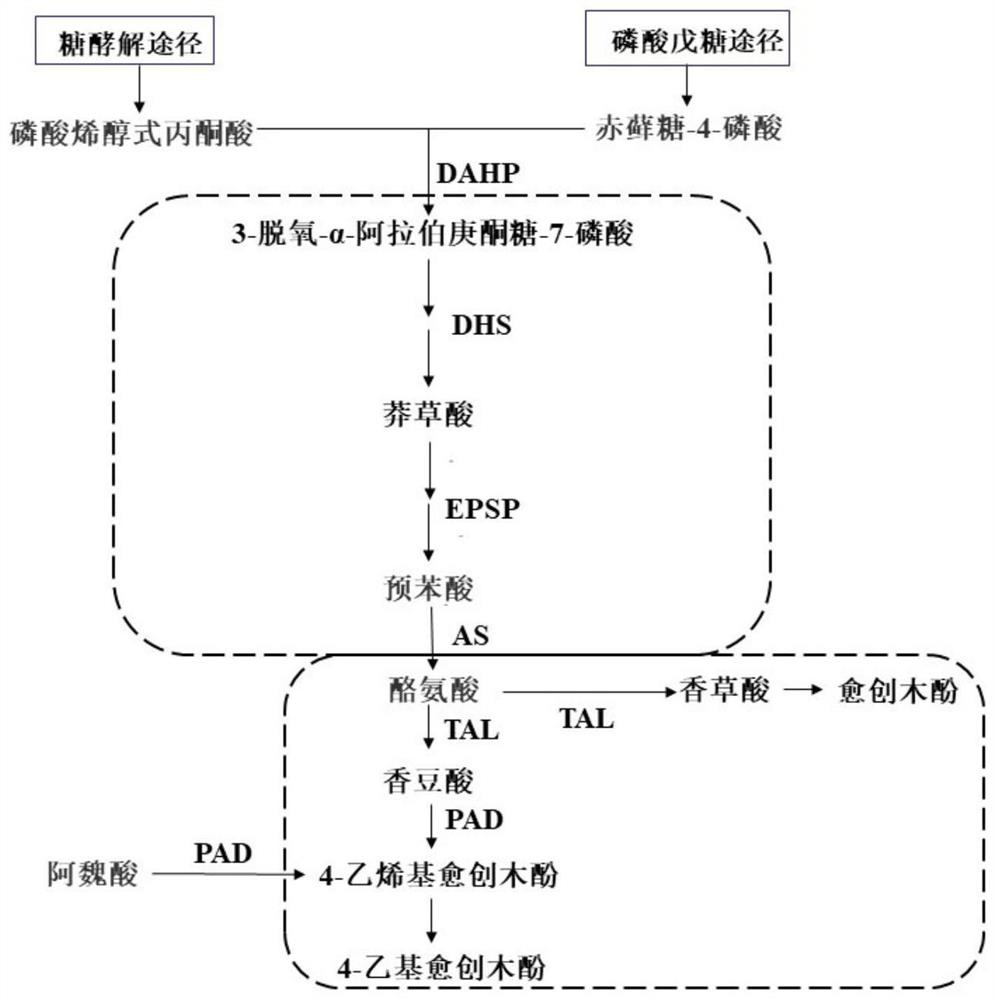
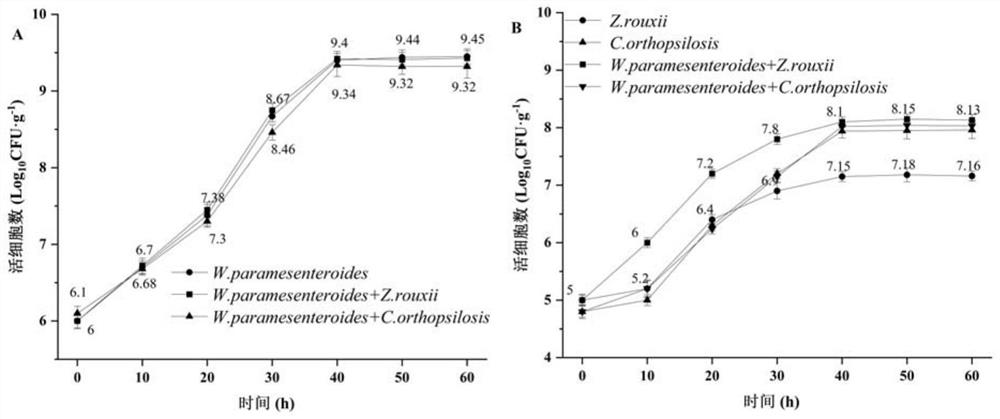
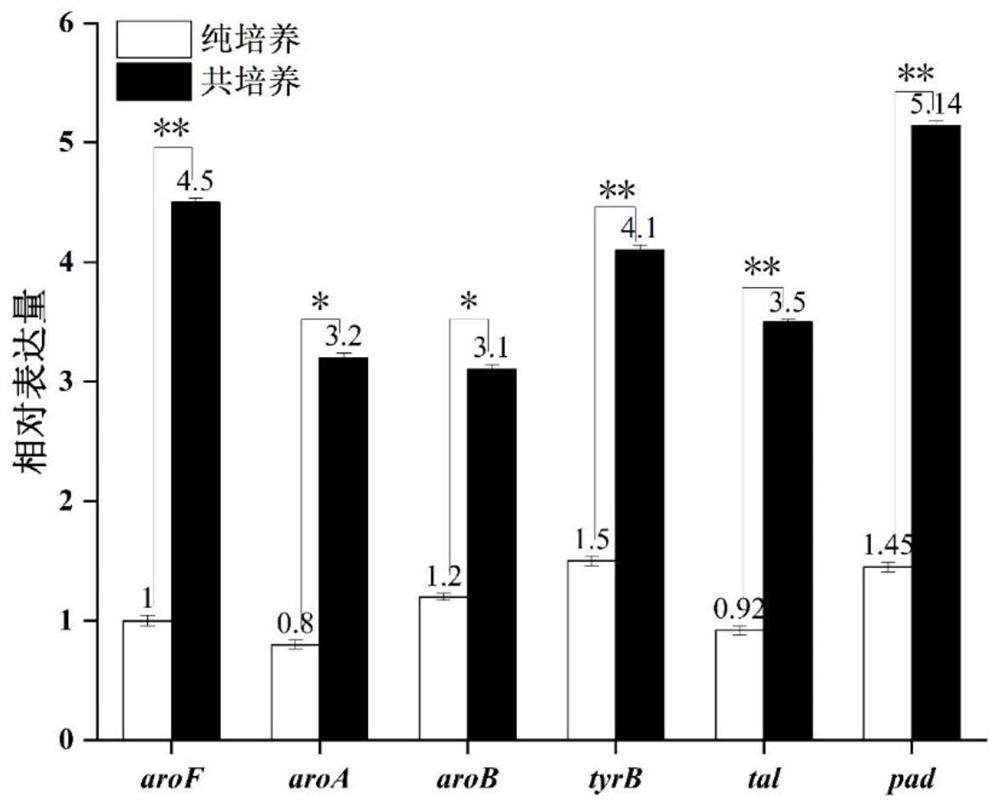
Weissella for promoting zygosaccharomyces rouxii to produce guaiacol substances
The invention discloses Weissella for promoting zygosaccharomyces rouxii to produce guaiacol substances, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. By co-culturing Weissella paramesenteroides LCW-28 and zygosaccharomyces rouxii ZQ-01 in a culture medium, the yield of guaiacol substances is effectively increased; the total yield of the guaiacol substances is the highest; the total yield of the guaiacol substances is increased by 3.87 times compared with the total yield of the guaiacol substances cultured independently, is increased by 15.71 times compared with candida, and is increased by 17.28 times compared with torulopsis glabrata, wherein the yield of 4-ethyl guaiacol is 2.12 mg / L, and is 8.8 times of that of the single culture of the zygosaccharomyces rouxii.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method for increasing the concentration of aroma components in liquid fermentation of fen-flavor liquor
InactiveCN105219594BSimple interfacePromote formationMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationTorulopsis glabrataChinese liquor
The invention discloses a method for increasing the concentration of flavor liquid fermentation components of a fen-favor liquor. The method comprises the following steps of adding a fen-favor high-temperature yeast into cooked and spread-cooled sorghum to stack; adding a liquefying enzyme and a saccharifying enzyme into a fermentation tank filled with sorghum flour paste, and adding the stacked sorghum to ferment for 2-4 days after liquefying and saccharifying; adding loofah sponge to ferment for 1.5-2.5 days; adding torulopsis glabrata to ferment for 1.5-2.5 days; connecting the fermentation tank and an overflow tower, and carrying out backflow fermentation on a fermentation mash between the fermentation tank and the overflow tower filled with carbon dioxide for 4-6 days; and stopping backflow, enabling all the fermentation mash to enter the fermentation tank, and then, adding the fen-favor high-temperature yeast to ferment for 2-4 days. A liquid-solid interface is increased by utilizing the loofah sponge, so that the formation quality of an ester substance is increased, and the flavor increasing aim is achieved; and meanwhile a gas-liquid interface is increased through the overflow of a fermentation liquid in the large overflow tower filled with carbon dioxide, and the formed flavor components are increased.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
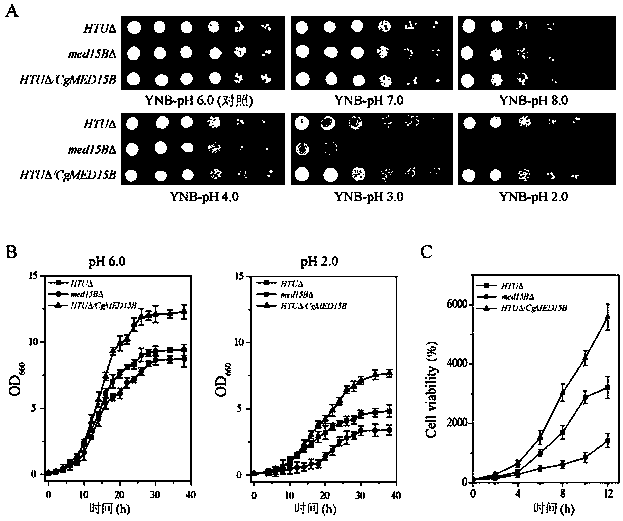
A Method of Improving Acid Tolerance Ability of Togumin glabrata
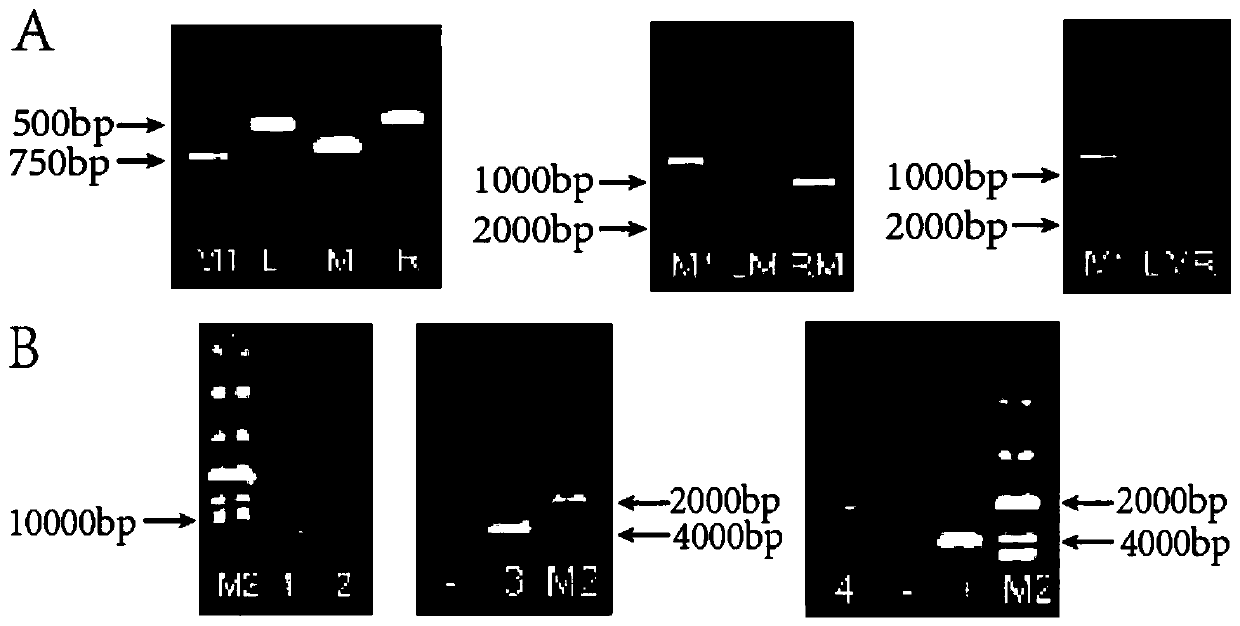
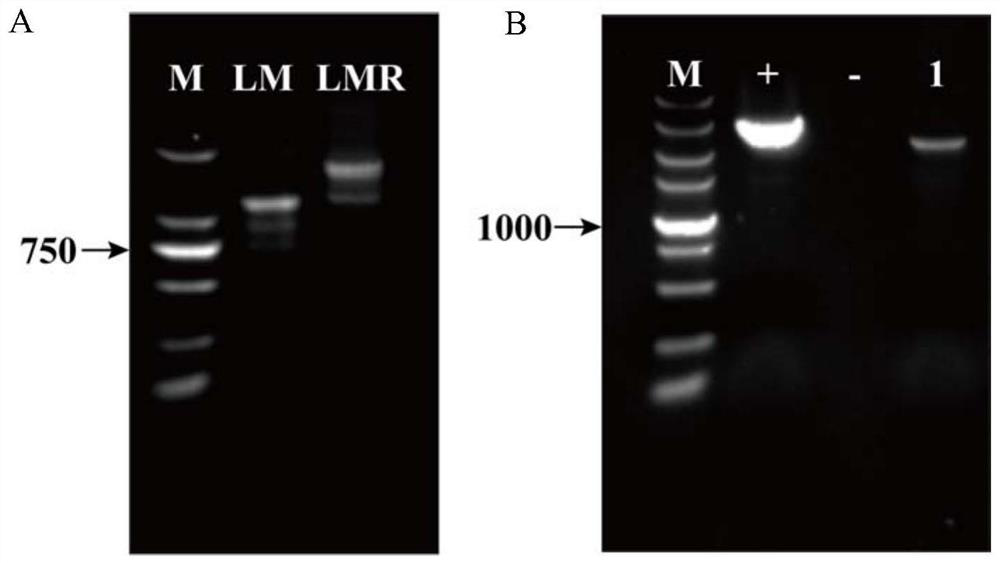
ActiveCN107267405BIncrease biomassIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for improving acid tolerance of torulopsis glabrata, and belongs to the field of biological engineering. The final biomass of the torulopsis glabrata is increased by 59.2% under the condition of pH2.0 by Med15B overexpression, under the condition of pH2.0, the 12h cell product of the torulopsis glabrata is increased by 73.8% compared with that of original strain, the content of cryptosterol, the content of coprosterol and the content of ergosterol of cell membranes are respectively increased by 970%, 16.6% and 94.5%, the integrity and the liquidity of the cell membrane are enhanced, low pH cell tolerance is increased, growth ability is enhanced, and pyruvic acid fermentation ability is increased by 100% compared with that of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A recombinant bacterium with improved pyruvate production intensity and its application
ActiveCN105368884BIncrease productionIncrease production intensityFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataCell membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering and discloses a recombinant bacterium with a function of pyruvate production intensity improvement and application of the recombinant bacterium with the function of pyruvate production intensity improvement. By targeting expression of a mitochondrion pyruvate carrier protein to a cell membrane in a torulopsis glabrata strain, cell outgoing rate of pyruvate is increased while a feedback inhibition effect of the pyruvate on glycolytic pathway key enzymes is weakened, and consequently pyruvate yield is increased, and production intensity is improved. By means of genetic engineering technology, a signal peptide sequence Shrew1p and MPC1 derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae are positioned and integrated to a pY26 expression vector to construct a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant expression plasmid pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1 which is electrophoretically transferred into a recipient bacterium TgU to obtain an engineering strain TgU-(pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1) high in pyruvate yield. Compared with a reference strain TgU-(pY26), the engineering strain TgU-(pY26-Shrew1p-MPC1) has the advantage that dry cell weight, glucose consumption rate, pyruvate yield and pyruvate production intensity are increased by 58.3%, 68.1%, 154.4% and 152.6% respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving production volume of pyruvic acid preparation of zymotechnics with additive gluconic acid sodium salt
InactiveCN101319235BIncrease productionIncrease production intensityMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataOrganic acid
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
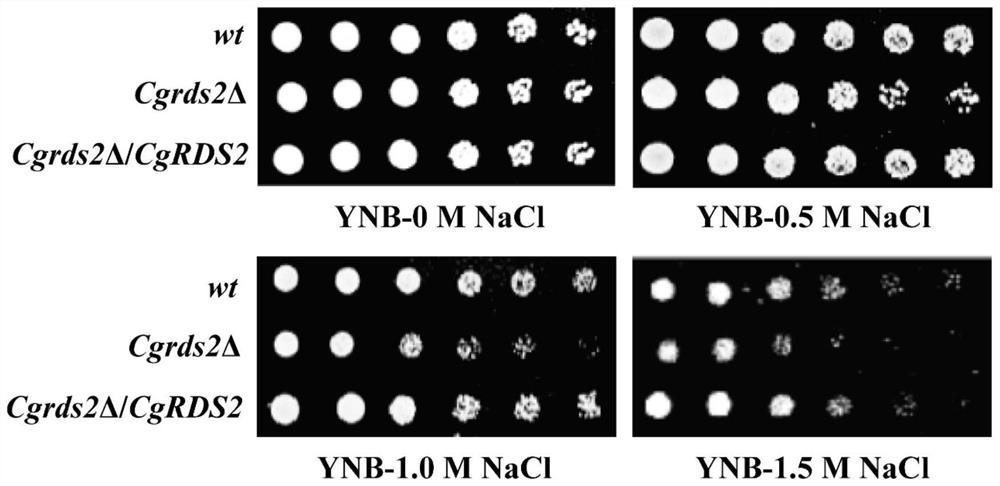
A method for regulating osmotic stress in Torulopsis glabrata
ActiveCN109266566BReduced integrityImprove integrityFungiMicroorganism based processesTorulopsis glabrataCell activity
The invention discloses a method for regulating the osmotic stress of Torulopsis glabrata, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The invention regulates the ability of resisting osmotic pressure stress of Torulopsis glabrata by overexpressing or deleting the coding gene CgRDS2 of the native transcription factor. The results showed that the deletion of CgRDS2 gene in Torulopsis glabrata, compared with the wild-type strain, could reduce the biomass by 23%, cell viability by 46%, and cell membrane integrity by 47.6% under osmotic stress conditions; after overexpressing the CgRDS2 gene , under the stress condition of 1.5M NaCl, the biomass of the strain increased by 10%, the cell activity increased by 39%, and the cell membrane integrity increased by 12.1%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of co-production process and application of pyruvic acid and levodopa
ActiveCN110055292BLow costThree wastes lessMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a pyruvic acid and L-dopa co-production process and application. The process comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a pyruvic acid feed liquid by fermentation with torulopsis glabrata, sterilizing the feed liquid by a ceramic membrane, and removing proteins, nucleic acids, pigments and other macromolecules by an ultrafiltration membrane; (2) adding a certain amount of catechol, ammonium acetate, EDTA, sodium sulfite and other compounds to a pyruvic acid concentrate according to the molar amount of pyruvic acid, adjusting the pH to 7.0-9.0, and preparing an enzyme-catalyzed substrate solution; (3) fermenting with tyrosine-phenol lyase genetic engineering bacteria to obtain a tyrosine-phenol lyase bacterial solution, centrifuging to collect thalli, breaking cells by a high-pressure homogenizer, centrifuging, and collecting an enzyme solution; and (4) adding a certain amount of substrate solution to the enzyme solution, stirring evenly, and at the temperature of 25 DEG C, carrying out seal shock reaction. The substrate solution is prepared from the pyruvic acid concentrate, and the concentration of catechol is controlled at 0-10 g / L by fed-batching the substrate solution, the product reaches 120 g / L or more, and fed-batch of the substrate solution is stopped; when the content of catechol in the reaction solution is less than 0.2 g / L, and the reactionis stopped.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for improving pyruvic acid yield via fermentation process by using urea as nitrogen source and application
InactiveCN102286550AIncrease productionIncrease production intensityMicroorganism based processesFermentationTorulopsis glabrataGram
The invention discloses a method for improving pyruvic acid yield via a fermentation process by using urea as a nitrogen source and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. In the invention, multi-vitamin auxotrophic torulopsis glabrata CCTCCM202019 is used as a producing strain, urea is used in place of ammonium chloride as a unique nitrogen source, the initial added amount per liter is 7 grams, and batch fermentation culture is performed in a laboratory 7-liter fermentation tank. The method can effectively improve pyruvic acid yield (11.9 percent) and production strength (30.9 percent) and greatly reduce a fermentation period (20.6 percent); the achievements are successfully tested in a 30-liter fermentation tank; and the method has a bright industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically Engineered Torulopsis glabrata with Enhanced Extracellular Secretion of Pyruvic Acid
ActiveUS20150176036A1Improve the level ofImprove temperature resistanceFungiBacteria peptidesTorulopsis glabrataBiotechnology
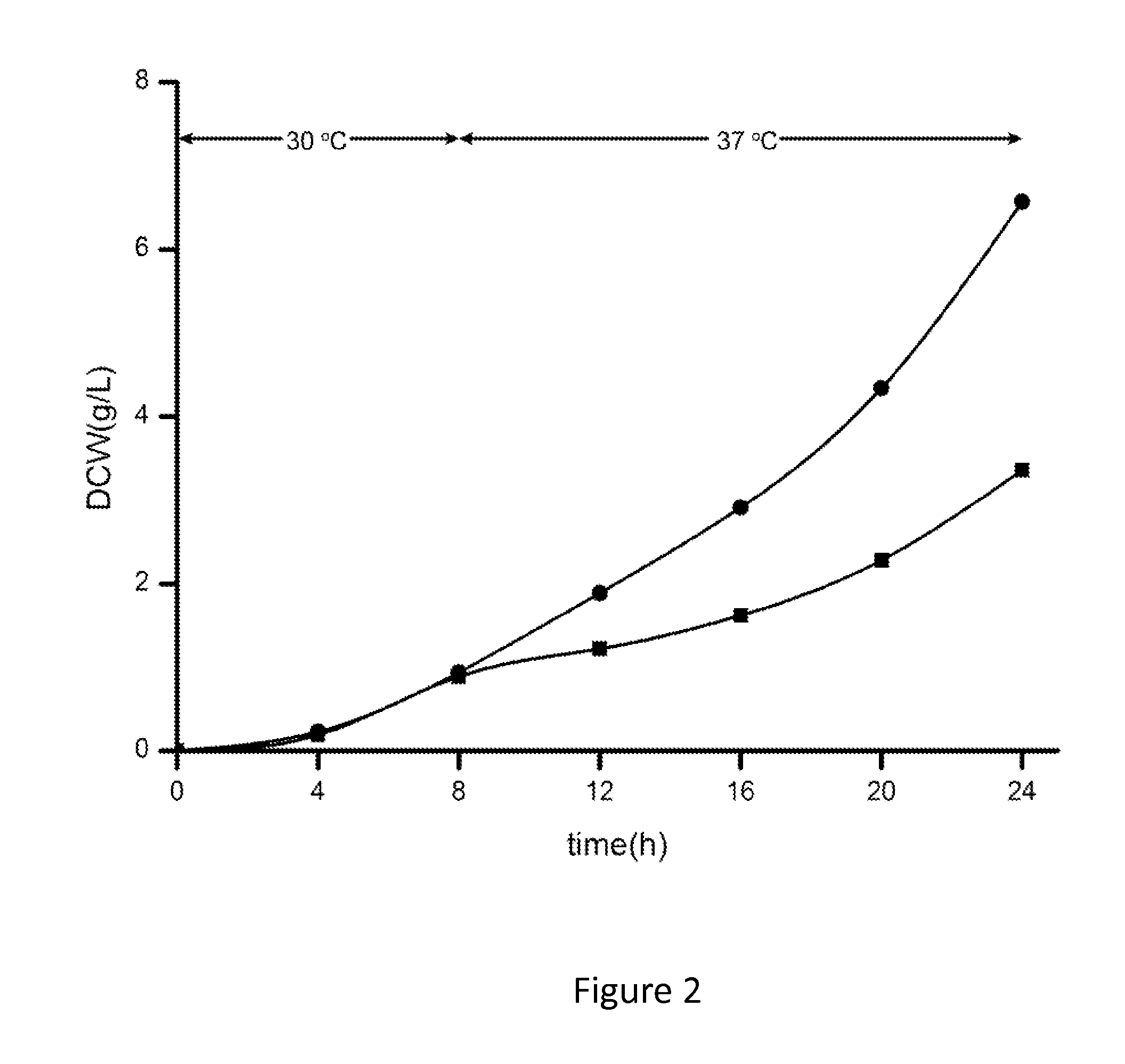
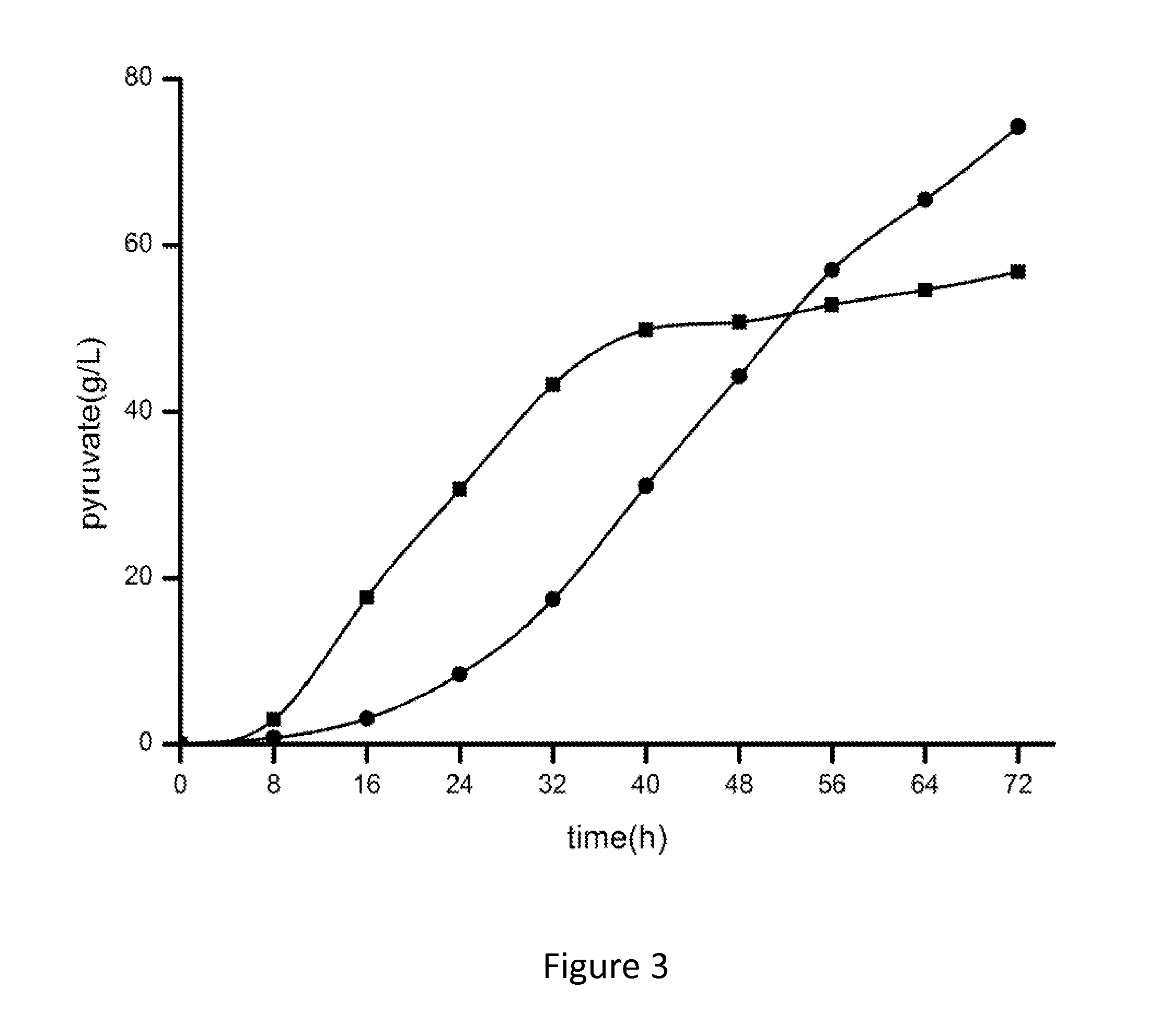
The present invention provides a genetically engineered Torulopsis glabrata with enhanced extracellular secretion of pyruvic acid. T. glabrata strain was obtained from China Center for Type Culture Collection with CCTCC No: M202019 and over-expressed the optimized CutA (SEQ ID NO:2) encoding stress protein. Both of the temperature tolerance of T. glabrata and extracellular concentration of pyruvate were improved by overexpressing the optimized CutA. The optimum growth temperature of genetically engineered T. glabrata was increased too. The present invention can be widely used to increase extracellular levels of pyruvate during the fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com