Method for knocking out torulopsis glabrata mitochondrion gene
A technology of Togus glabrata and mitochondrial genes, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, to achieve the effect of simple knockout method, easy identification and protection, and keeping the original characteristics unchanged
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
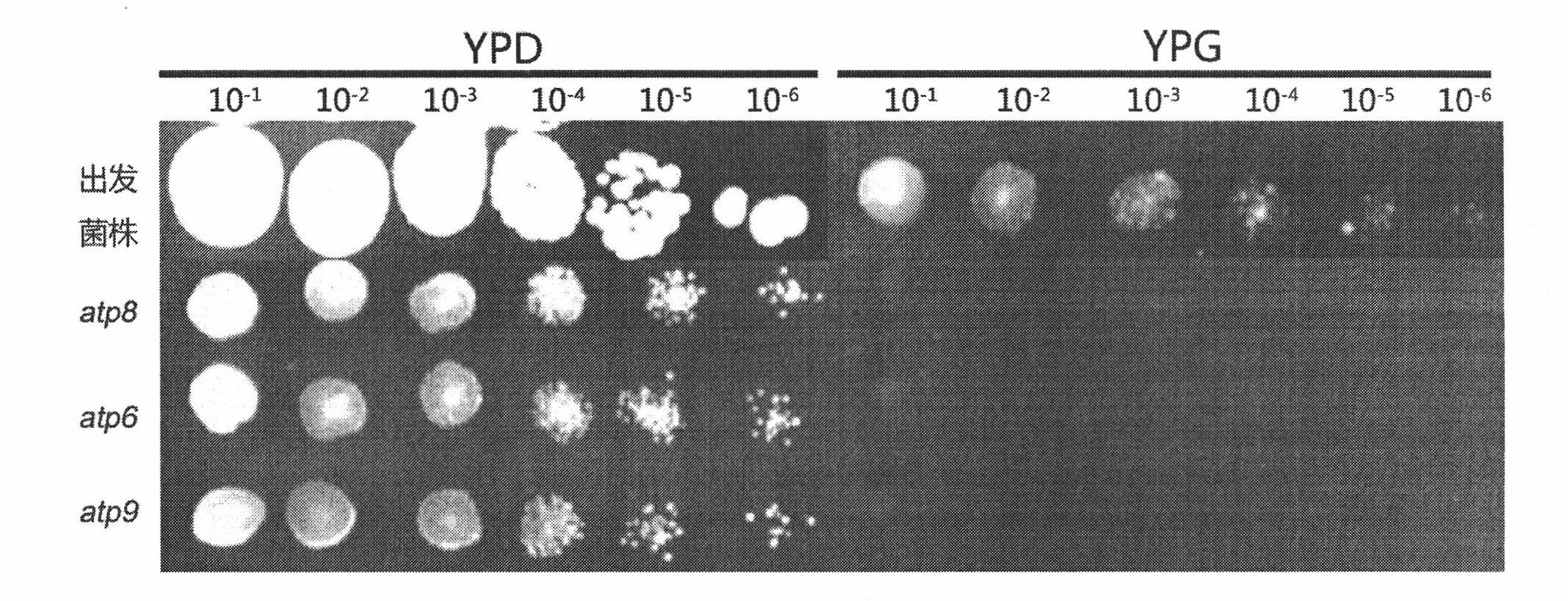
Embodiment 1
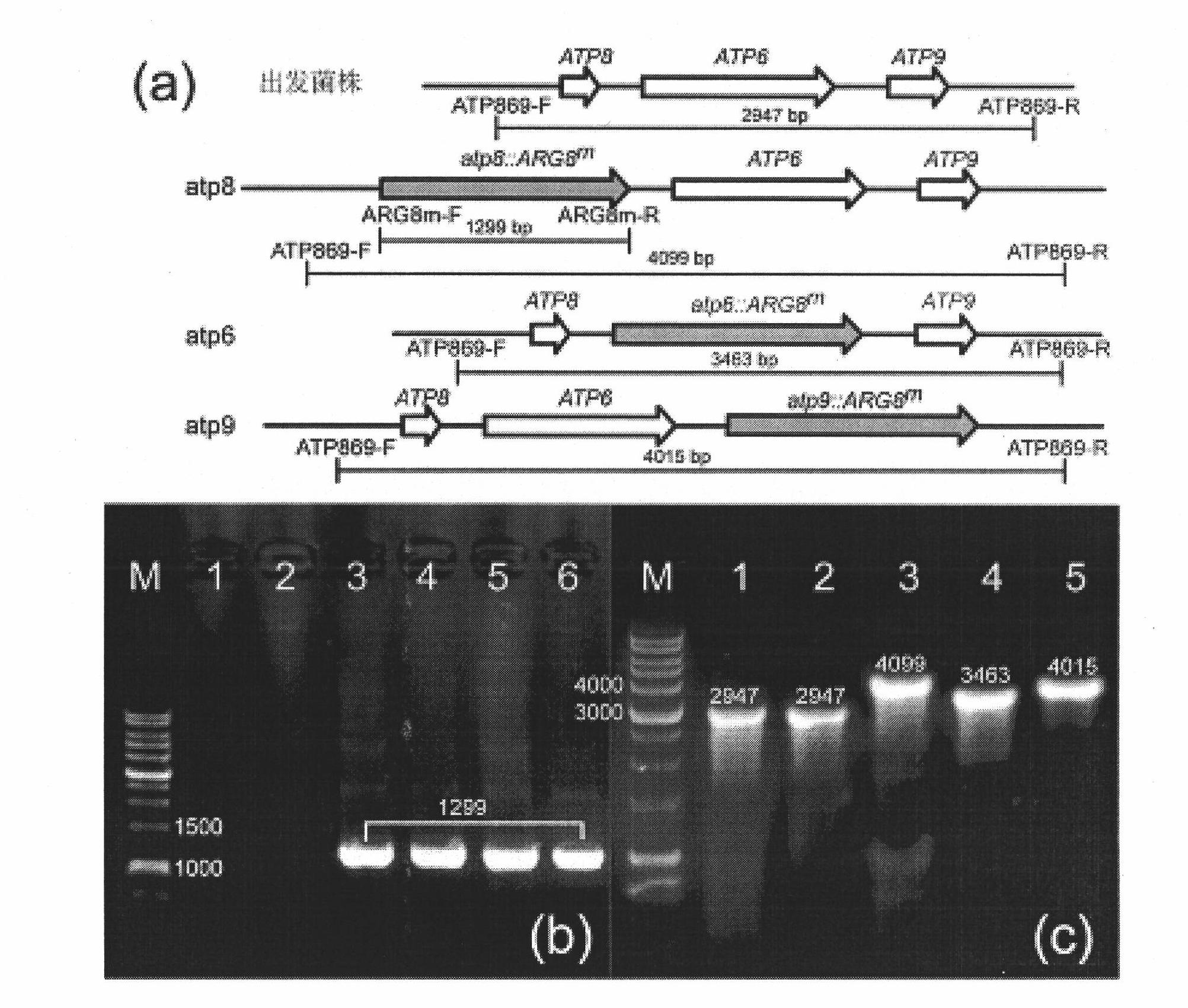
[0024] Example 1 The method for knocking out the chromosomal gene ATP6 of Torulopsis glabrata
[0025] 1. Obtaining the pUC-atp6::ARG8m plasmid containing the target fragment
[0026] Use primer pairs:
[0027] Con-ATP6-F:
[0028] 5'GCggatccAATATTATTTTATTATAATAATAATTTAAATTTTAATAAGTTATAATATATATTTAAAGT ATGACACATTTAGAAAGAAG 3'
[0029] Con-ATP6-R:
[0030] 5'GCGggatccTATTAATAATAATTAATTAAAGAATATTATAATATAATTAATTTATTTGTATTATATAAA TTAAGCATATACAGCTTCG 3'
[0031] The knockout box Δatp6::ARG8m for knocking out ATP6 was amplified from the plasmid pDS24 containing the ARG8m gene. Starting from the 5' end of the primers, they are the protected bases of the restriction site (capital letters), the BamHI restriction site (lower case letters), the fragment homologous to ATP6 (capital letters) and the homology of ARG8m (underlined) sequence.
[0032] PCR conditions are: 95°C, 3min; {95°C, 50s; 55°C, 60s; 72°C, 1min}, 30 cycles; 72°C, 15min; -20°C storage. After the PCR product wa...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 The method for knocking out the chromosomal gene ATP8 of Torulopsis glabrata
[0054] 1. Obtaining the pUC-atp8::ARG8m plasmid containing the target fragment
[0055] Use primer pairs:
[0056] Con-ATP8-F:
[0057] 5'GCggatccATAATAATTTATTTATTTATTAATGTTGTATTTATATTAAATATAAAAAATATATAAAT ATGACACATTTAGAAAGAAG 3'
[0058] Con-ATP8-R:
[0059] 5'GCGggatccATAATTATATATTATTAATTATATTATATTATAATTATATATTATTATTATTAATTATAT TTAAGCATATACAGCTTCG 3'
[0060] The knockout box Δatp6::ARG8m for knocking out ATP6 was amplified from the plasmid pDS24 containing the ARG8m gene. Starting from the 5' end, the primers are the protected bases of the restriction site (capital letters), the BamHI restriction site (small letters), the fragment homologous to ATP8 (capital letters) and the homology of ARG8m (underlined). source sequence.
[0061] PCR conditions are: 95°C, 3min; {95°C, 50s; 55°C, 60s; 72°C, 1min}, 30 cycles; 72°C, 15min; -20°C storage. After the PCR product was dige...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 The method for knocking out the chromosomal gene ATP9 of Torulopsis glabrata
[0083] 1. Obtaining the pUC-atp9::ARG8m plasmid containing the target fragment
[0084] Use primer pairs:
[0085] Con-ATP9-F:
[0086] 5’GCggatccATATATATATATATATTAATTATTTAAATATAATAAAGATTATAAAAAATATAATATT ATGACACATTTAGAAAGAAG 3'
[0087] Con-ATP9-R:
[0088] 5'GCGggatccAAATATTTTATTTATTAAGAATATTATAATATTACTATATTAATAGTAAACATTATTATTA TTAAGCATATACAGCTTCG 3'
[0089] The knockout box Δatp9::ARG8m for knocking out ATP6 was amplified from the plasmid pDS24 containing the ARG8m gene. Starting from the 5' end of the primers, they are the protected bases of the restriction site (capital letters), the BamHI restriction site (small letters), the fragment homologous to ATP9 (capital letters) and the homology of ARG8m (underlined). source sequence.
[0090] PCR conditions are: 95°C, 3min; {95°C, 50s; 55°C, 60s; 72°C, 1min}, 30 cycles; 72°C, 15min; -20°C storage. After the PCR product ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com