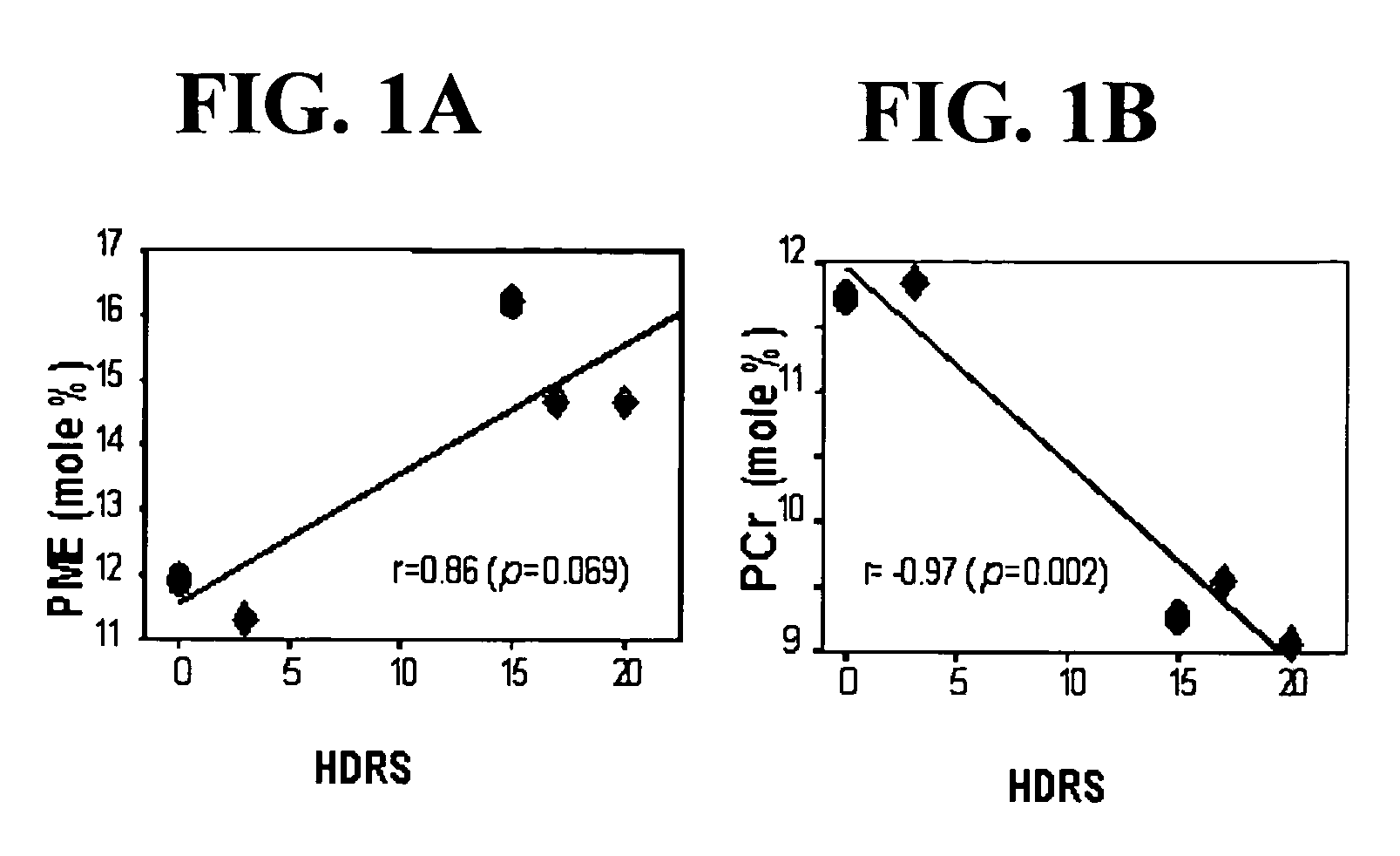
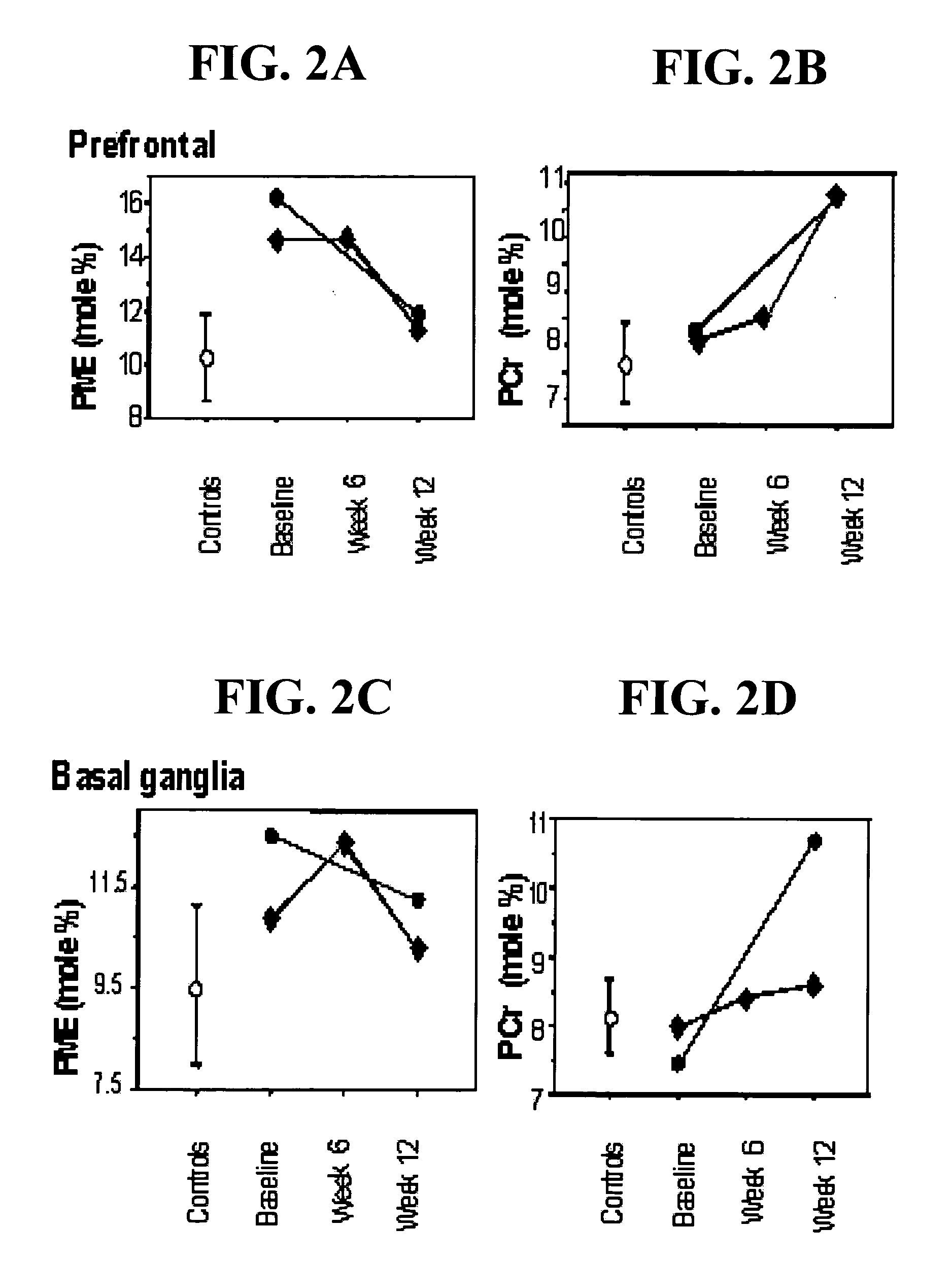
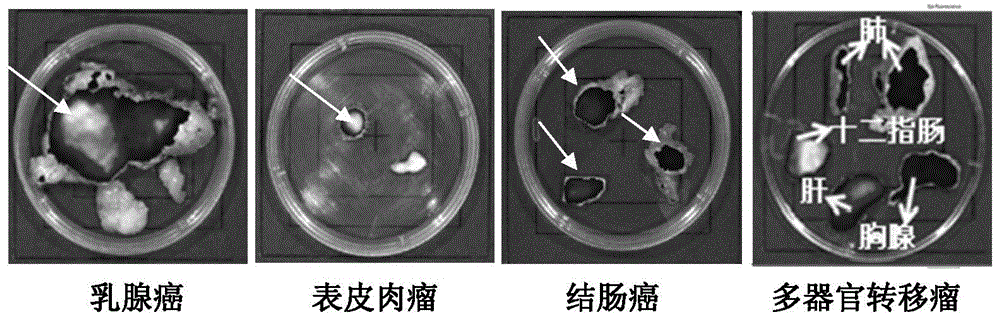
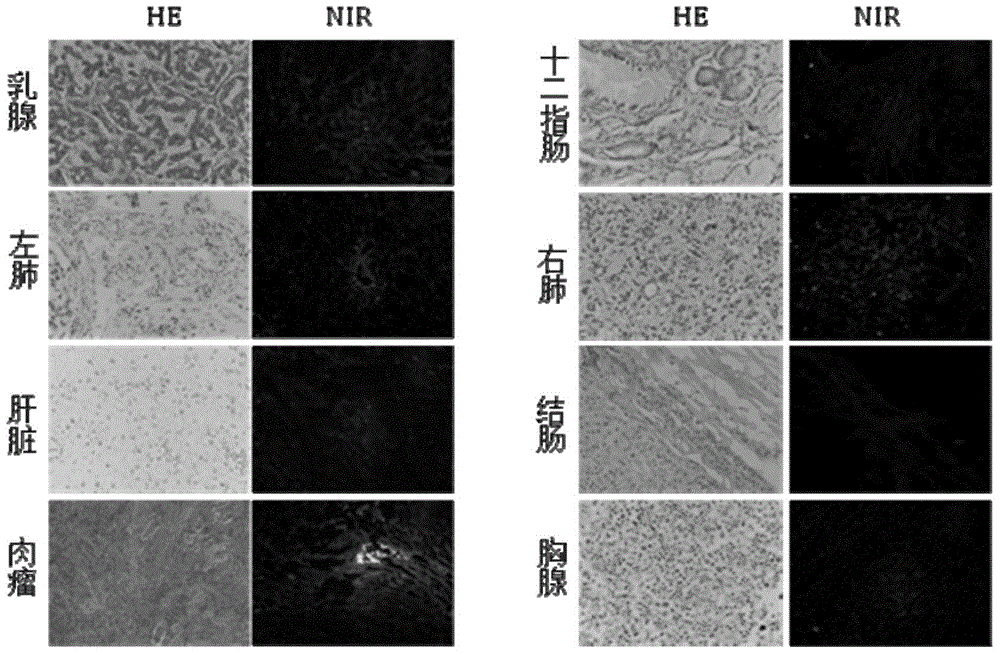
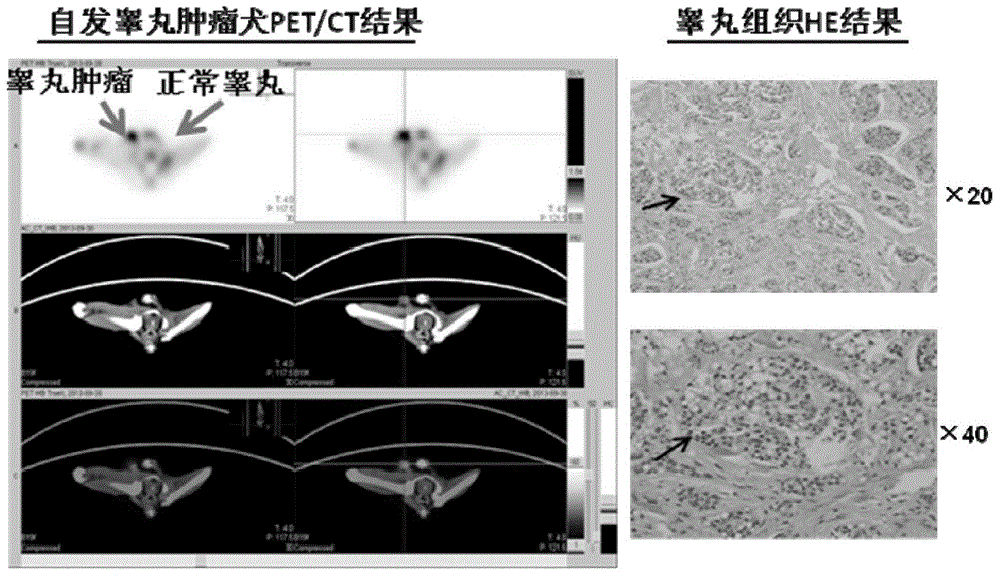
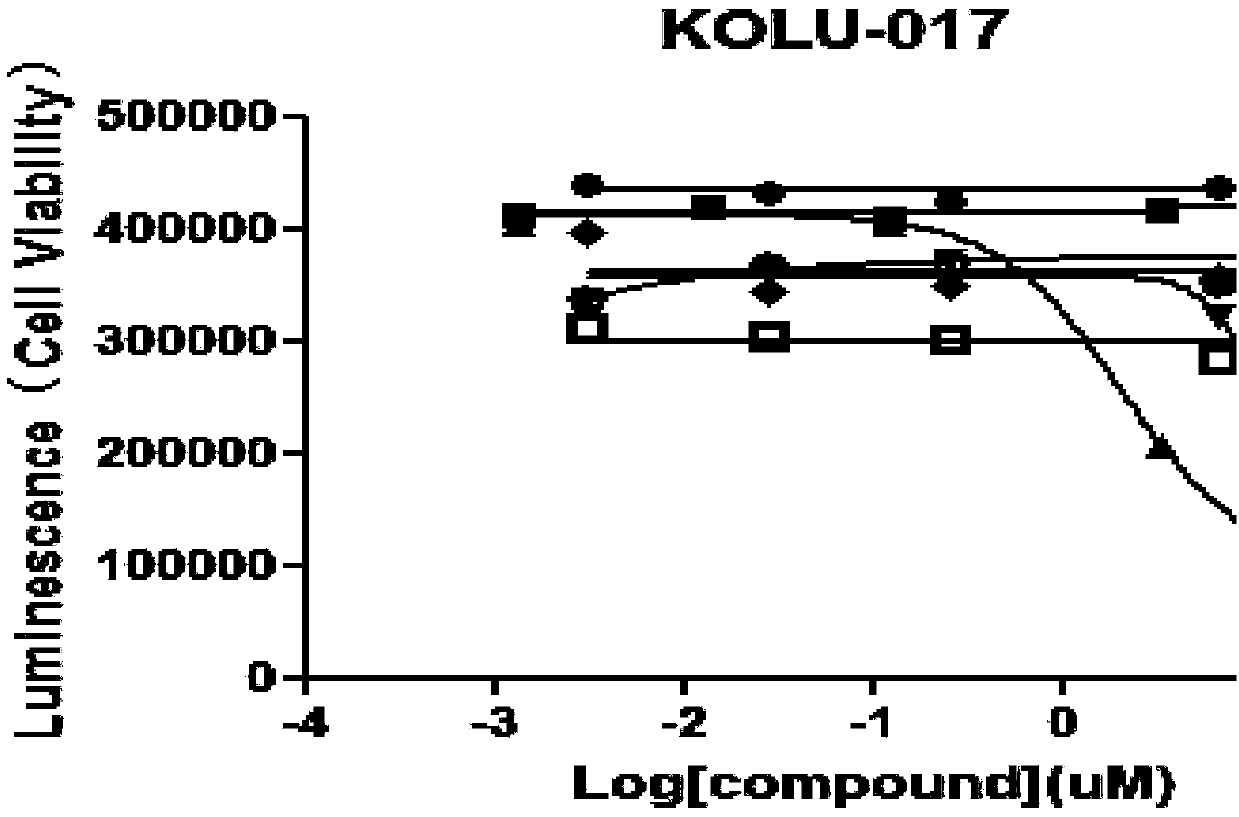
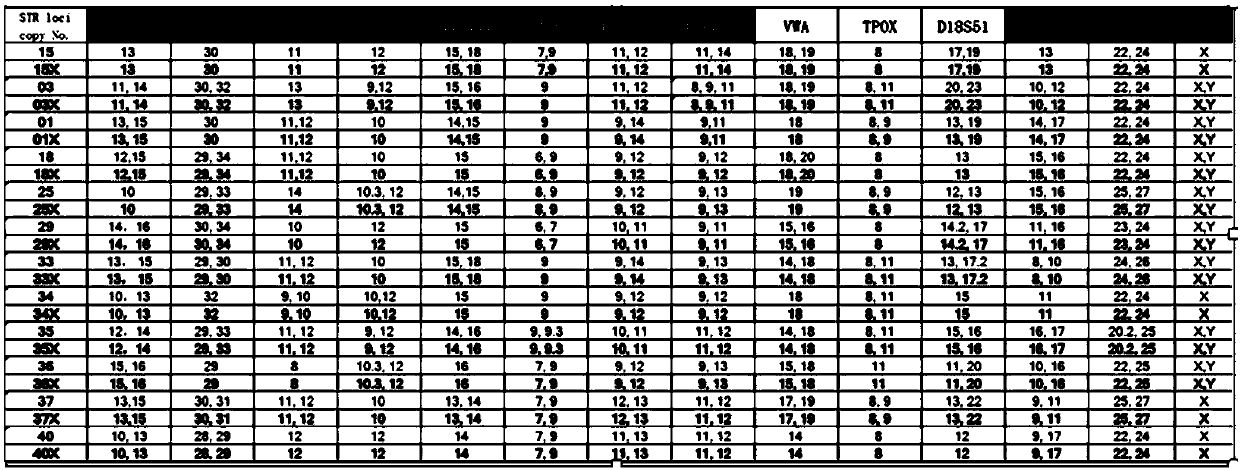
Patents
Literature
170 results about "Heteroplasmy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heteroplasmy is the presence of more than one type of organellar genome (mitochondrial DNA or plastid DNA) within a cell or individual. It is an important factor in considering the severity of mitochondrial diseases. Because most eukaryotic cells contain many hundreds of mitochondria with hundreds of copies of mitochondrial DNA, it is common for mutations to affect only some mitochondria, leaving most unaffected.
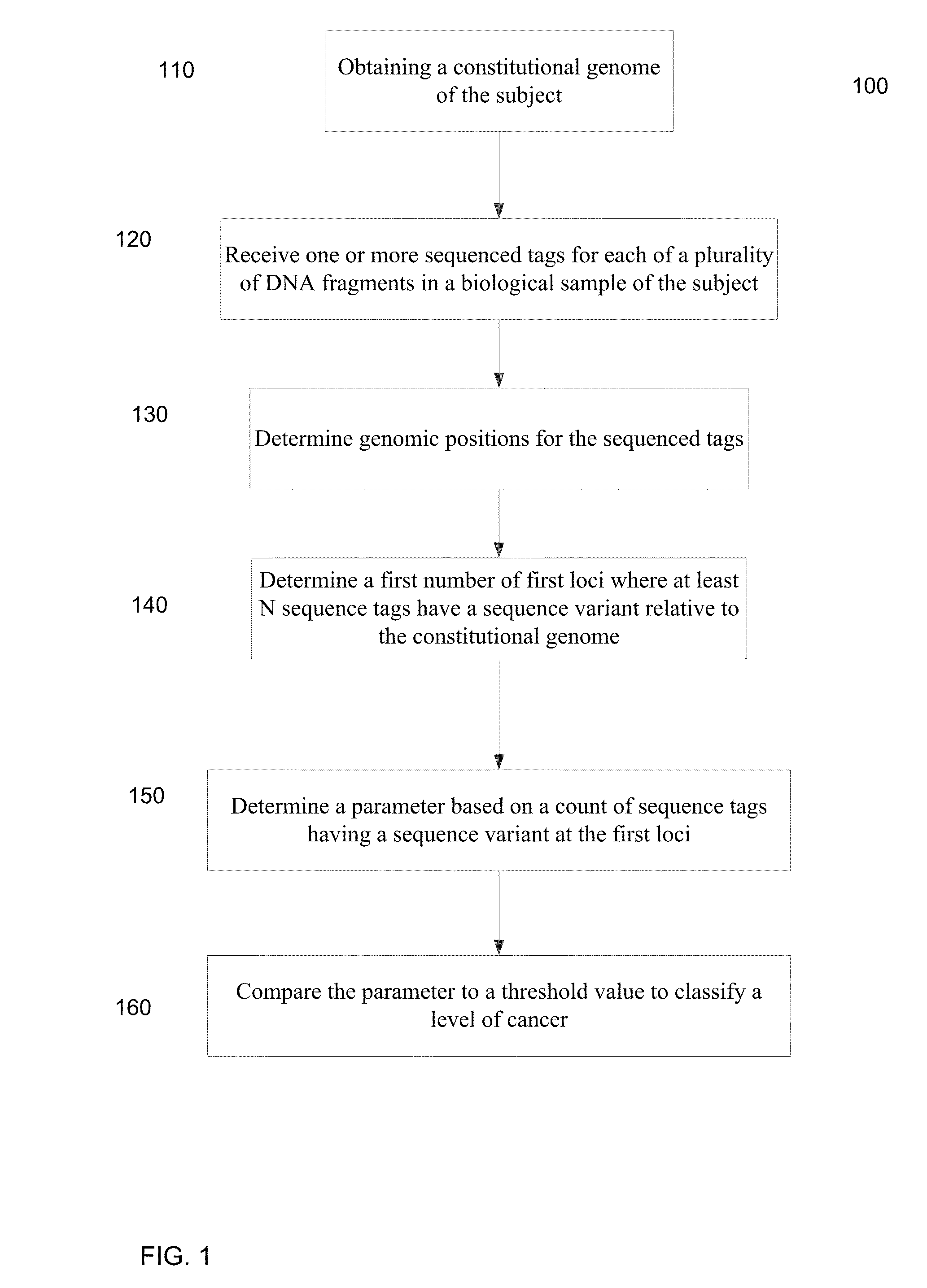
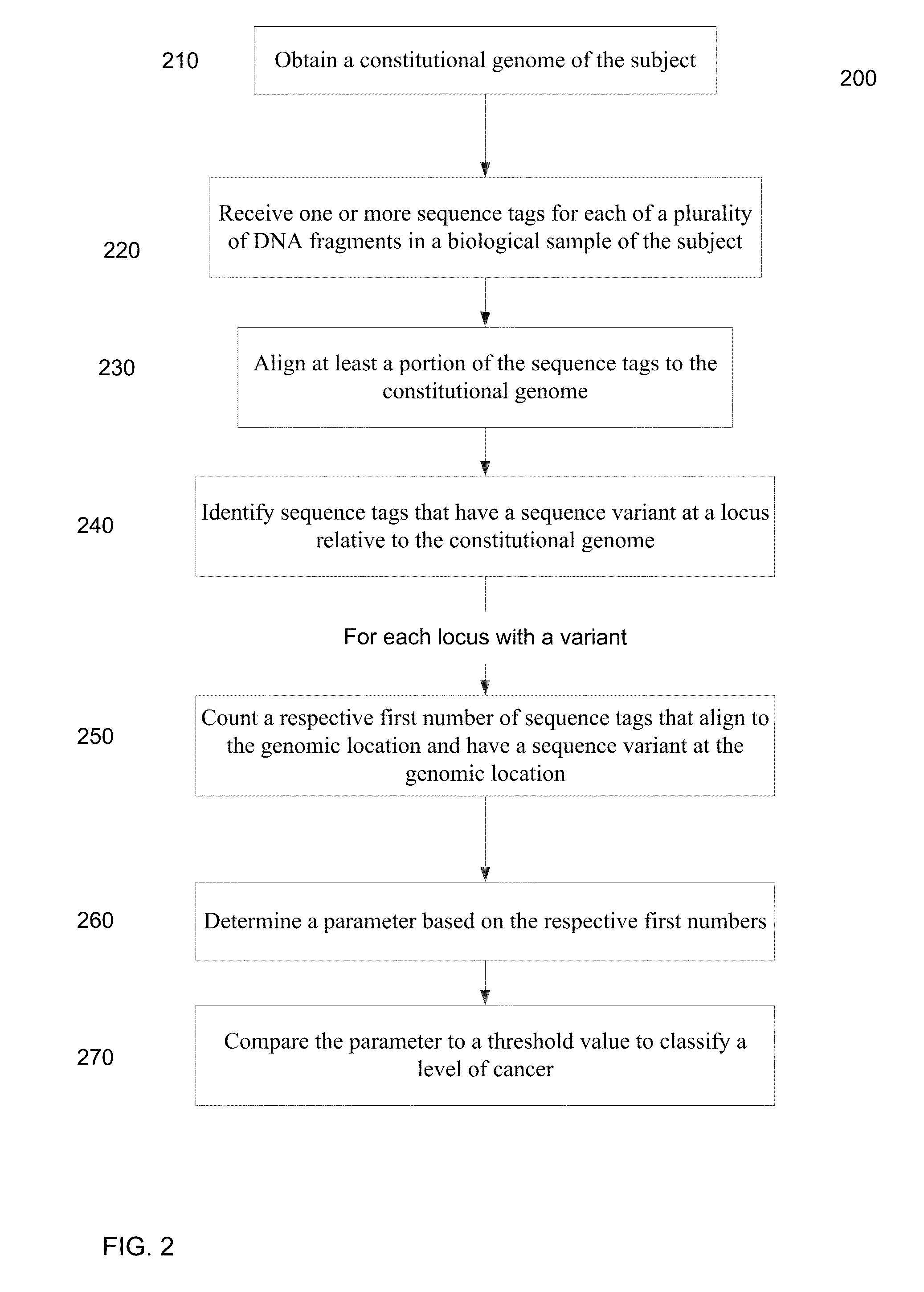
Mutational analysis of plasma DNA for cancer detection
ActiveUS20140100121A1Accurate parameterLevel of heterogeneity of tumorsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation frequencyBlood plasma
A frequency of somatic mutations in a biological sample (e.g., plasma or serum) of a subject undergoing screening or monitoring for cancer, can be compared with that in the constitutional DNA of the same subject. A parameter can derived from these frequencies and used to determine a classification of a level of cancer. False positives can be filtered out by requiring any variant locus to have at least a specified number of variant sequence reads (tags), thereby providing a more accurate parameter. The relative frequencies for different variant loci can be analyzed to determine a level of heterogeneity of tumors in a patient.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS6984522B2Improved anti-cancer drug discoveryPromote resultsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthCancer therapy
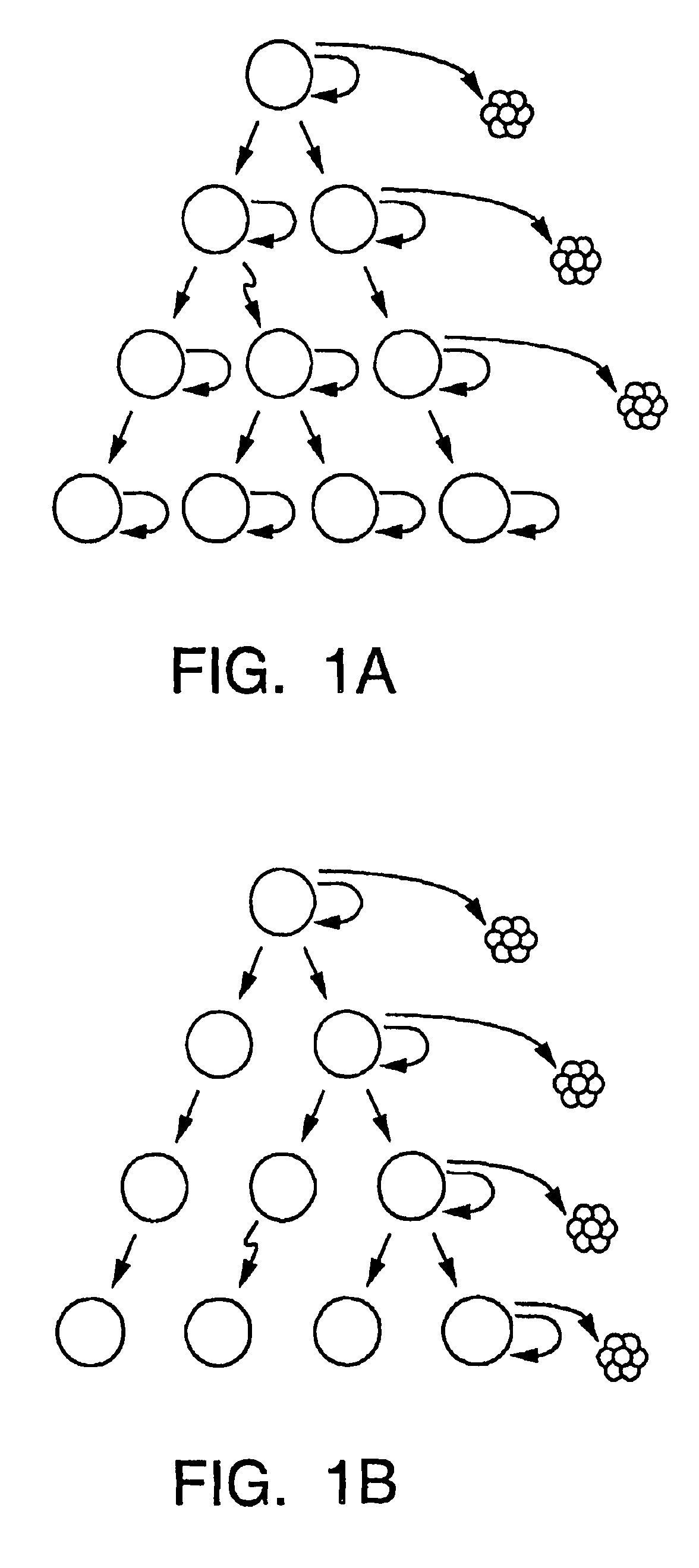
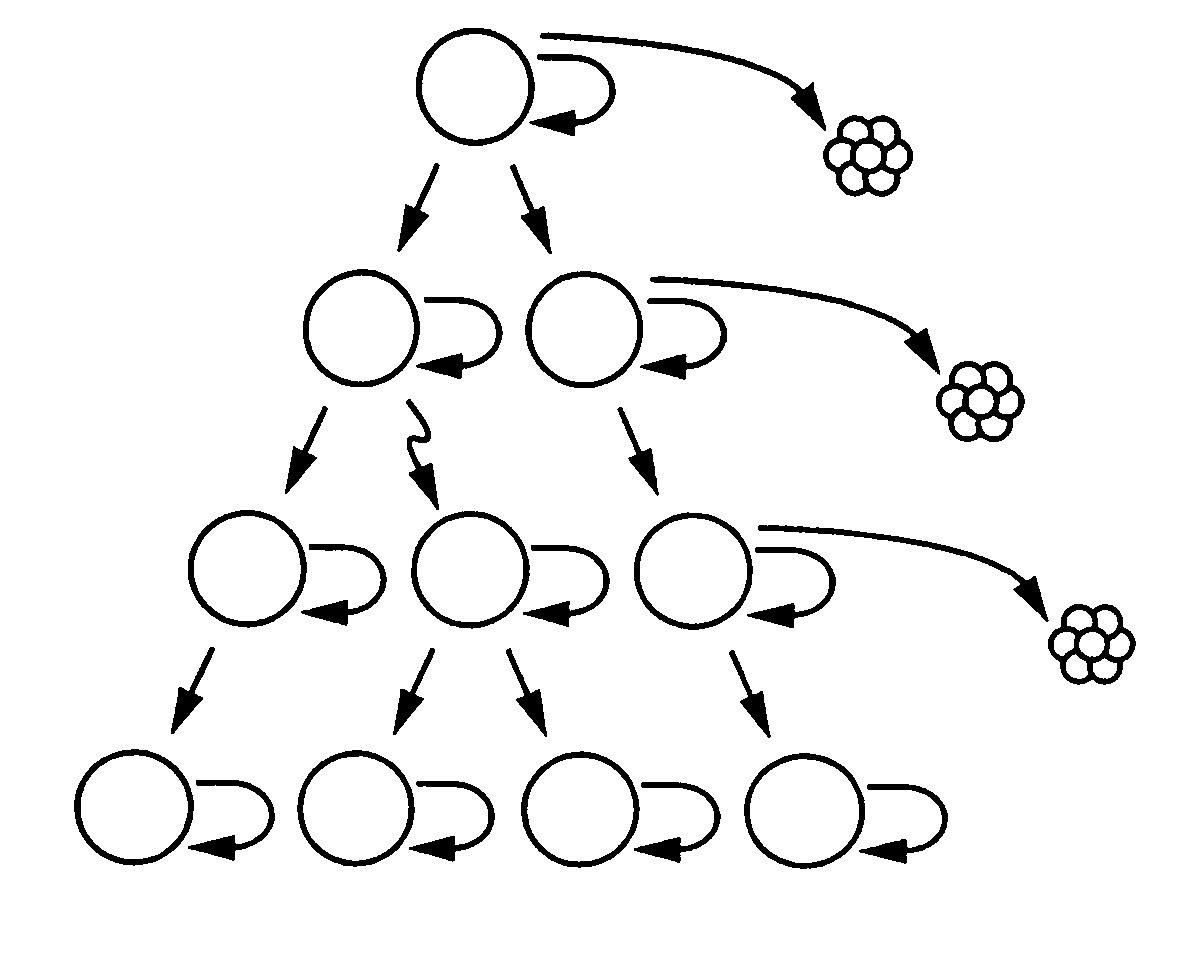
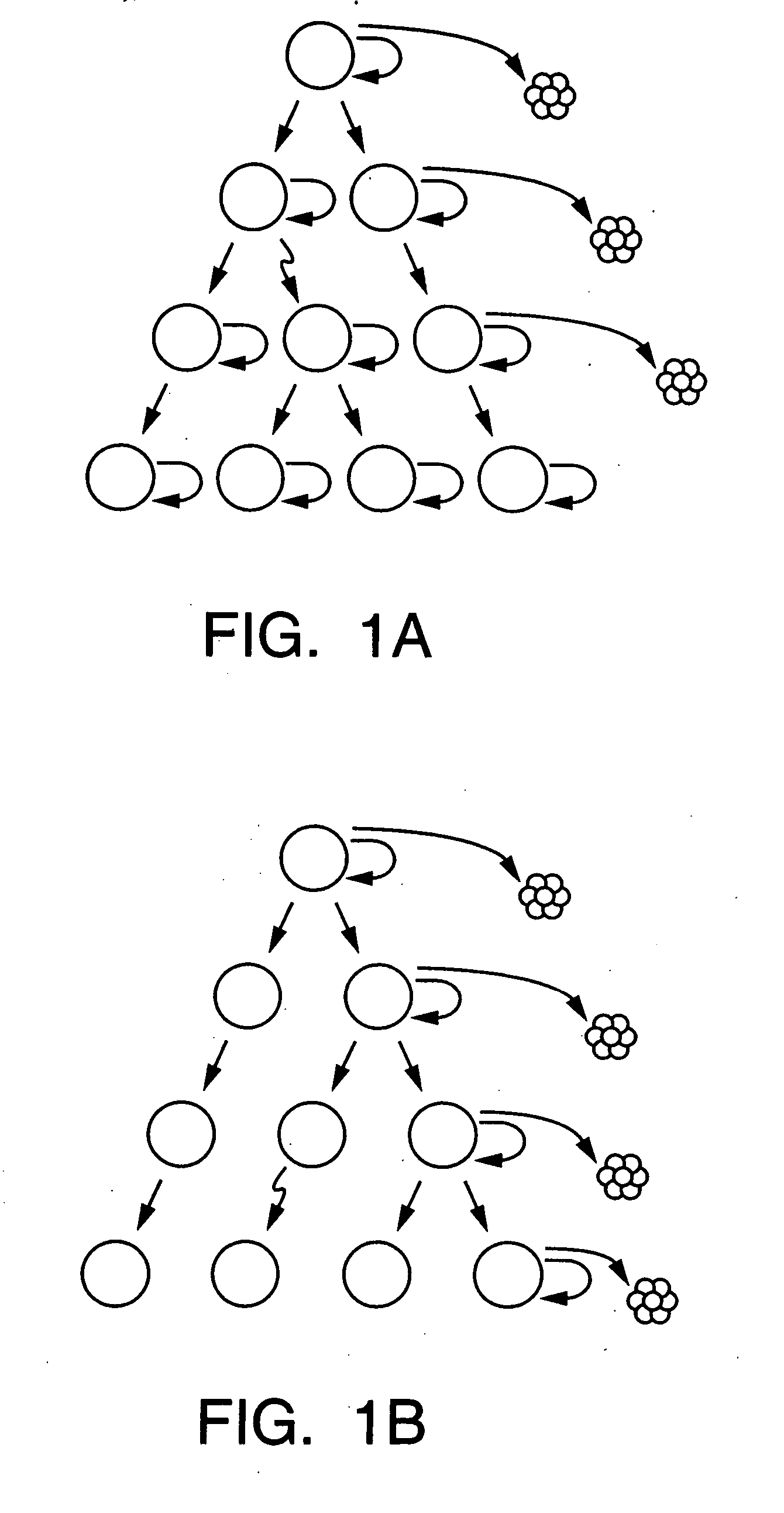
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. The solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell. This discovery is the basis for solid tumor stem cell compositions, methods for distinguishing functionally different populations of tumor cells, methods for using these tumor cell populations for studying the effects of therapeutic agents on tumor growth, and methods for identifying and testing novel anti-cancer therapies directed to solid tumor stem cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods for diagnosis, prognosis and methods of treatment
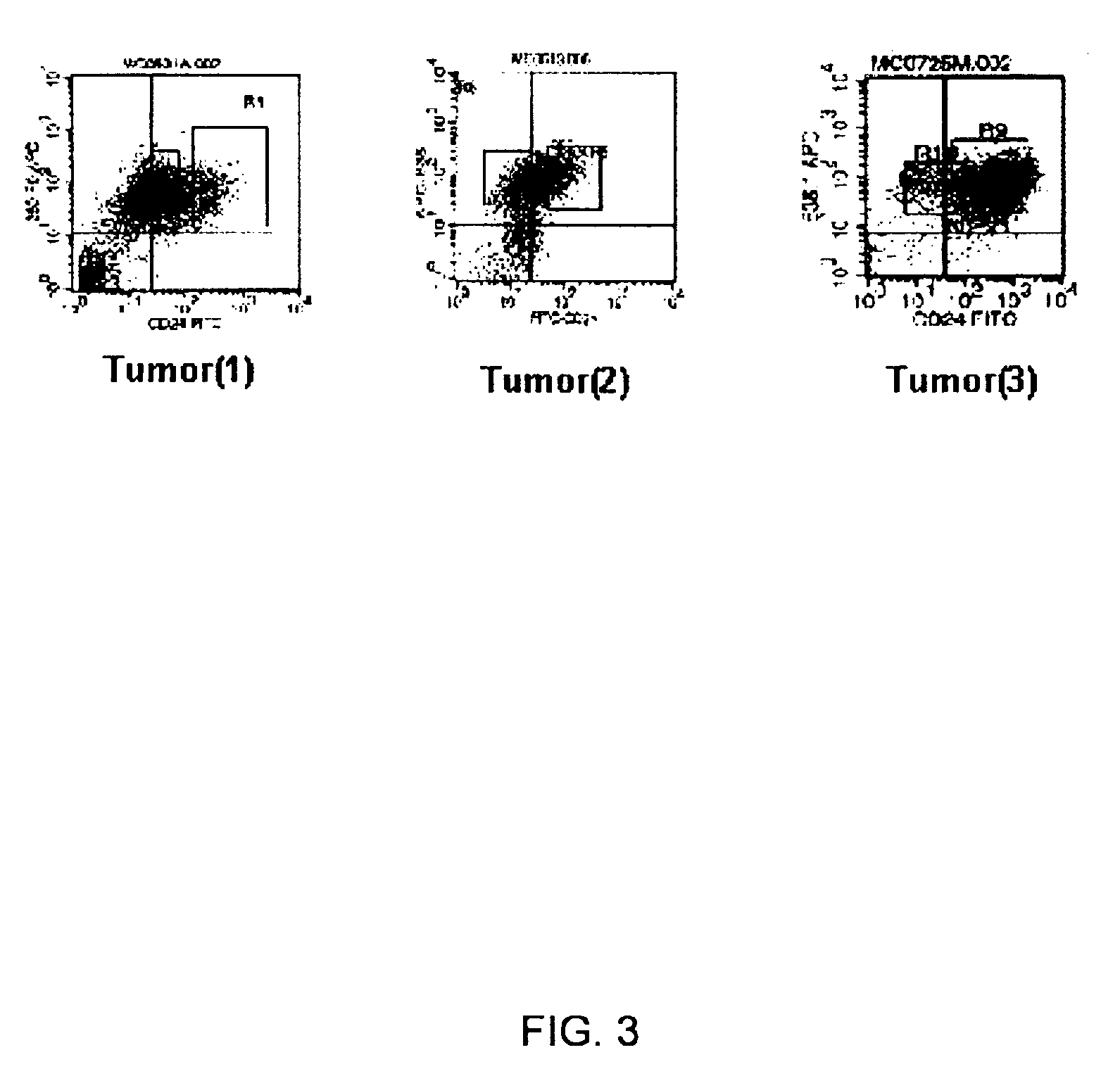
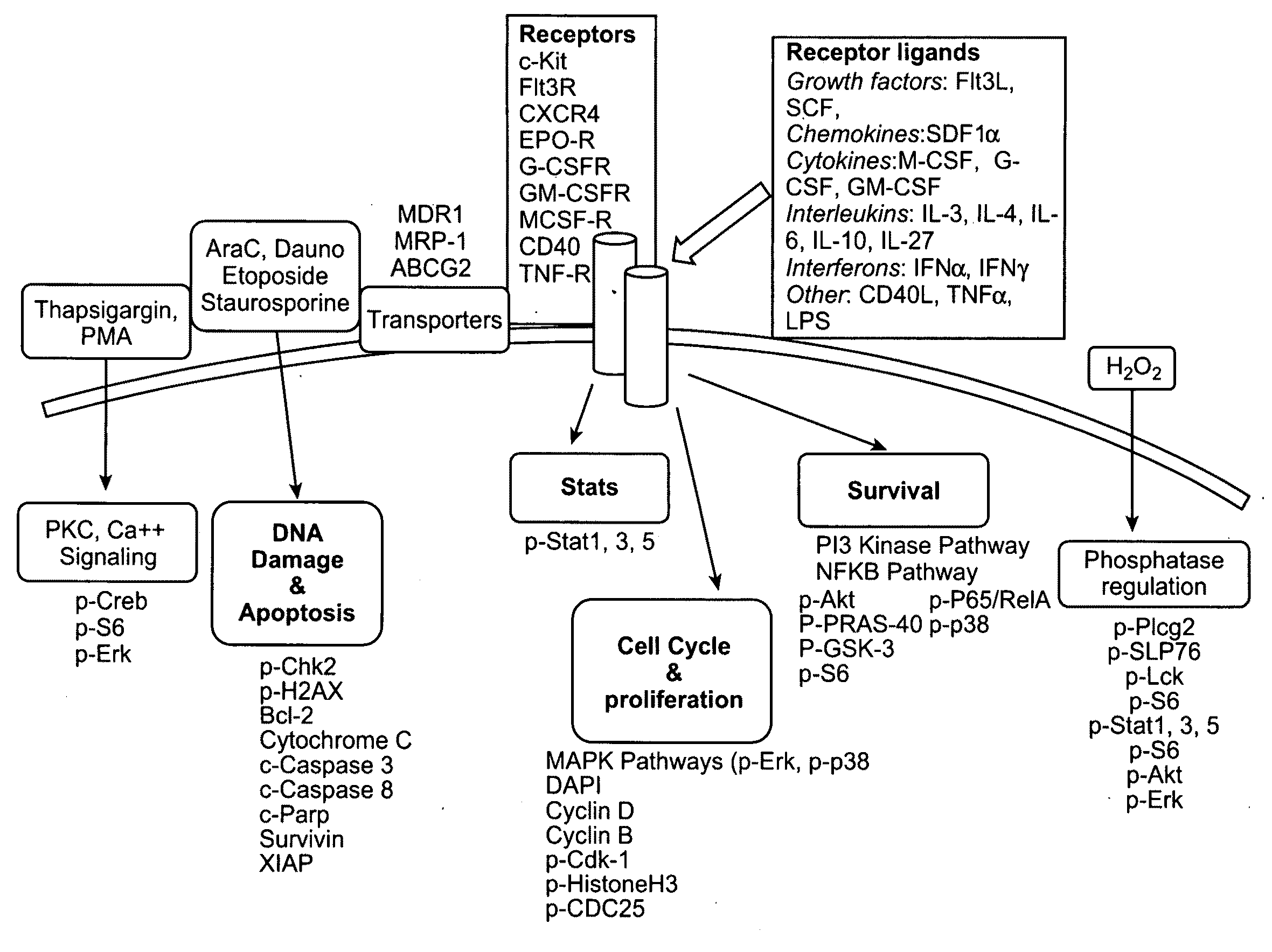
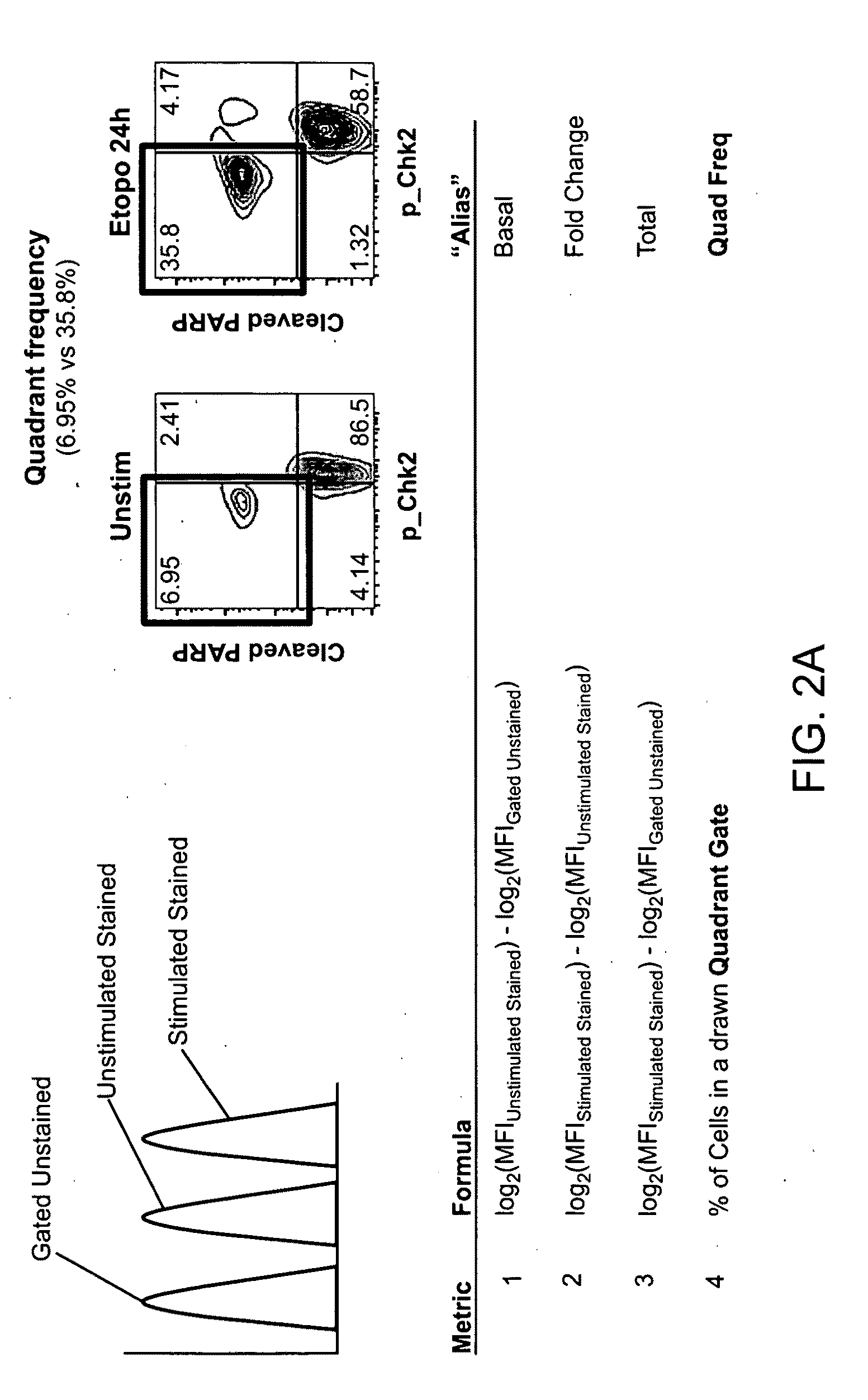
InactiveUS20100009364A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBiological activationHeteroplasmy
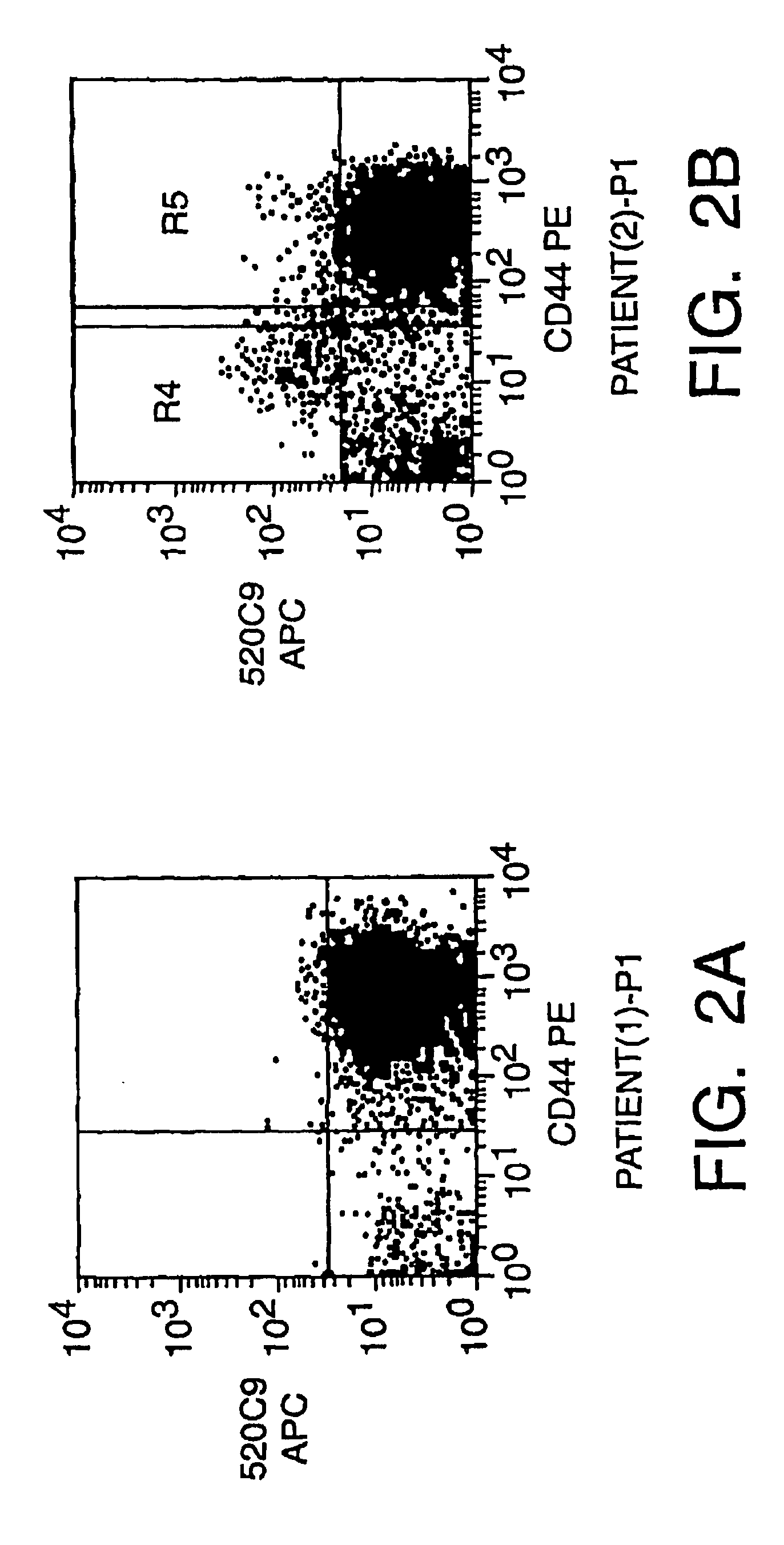
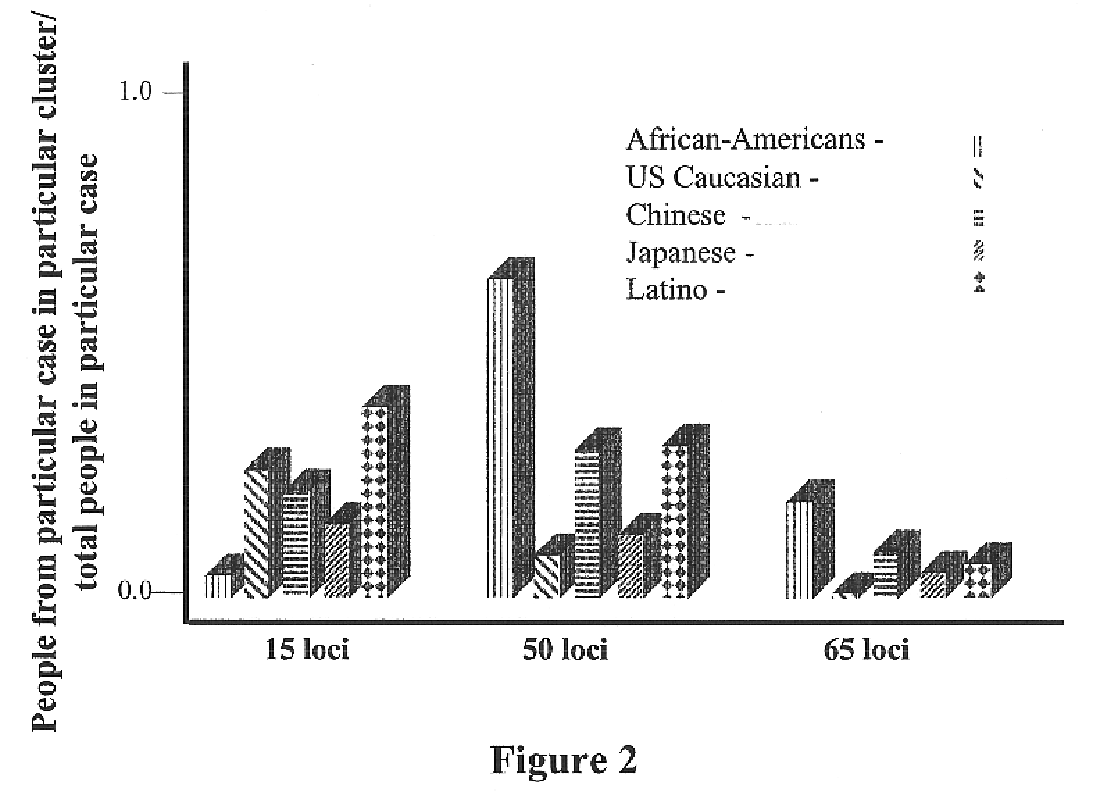
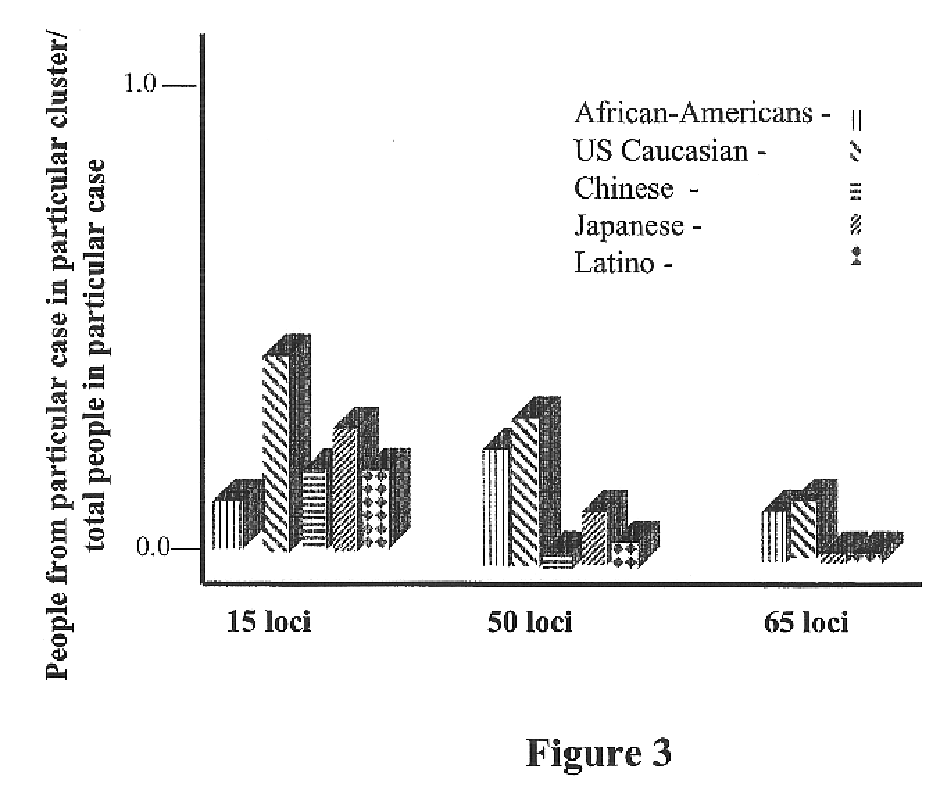
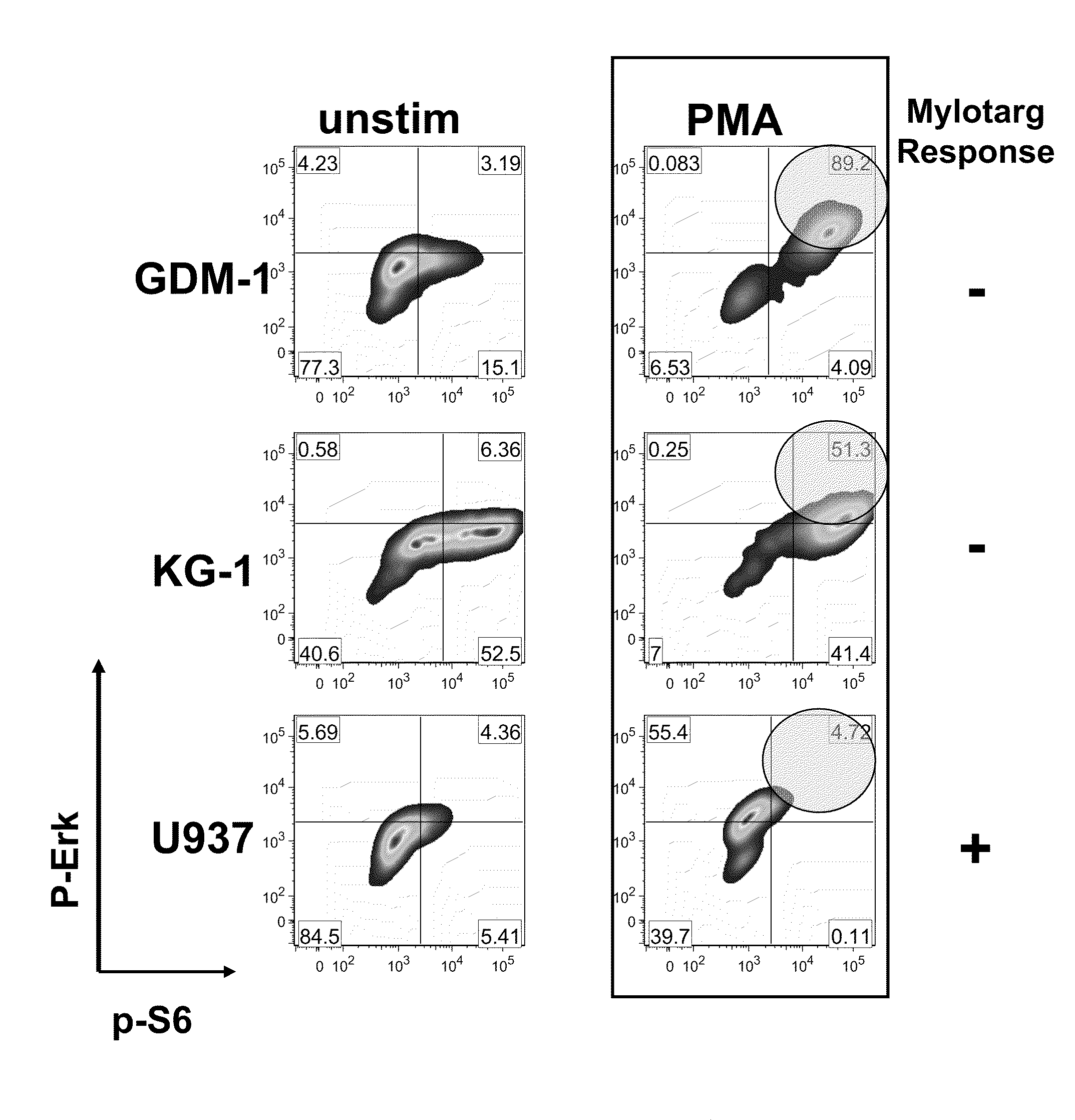
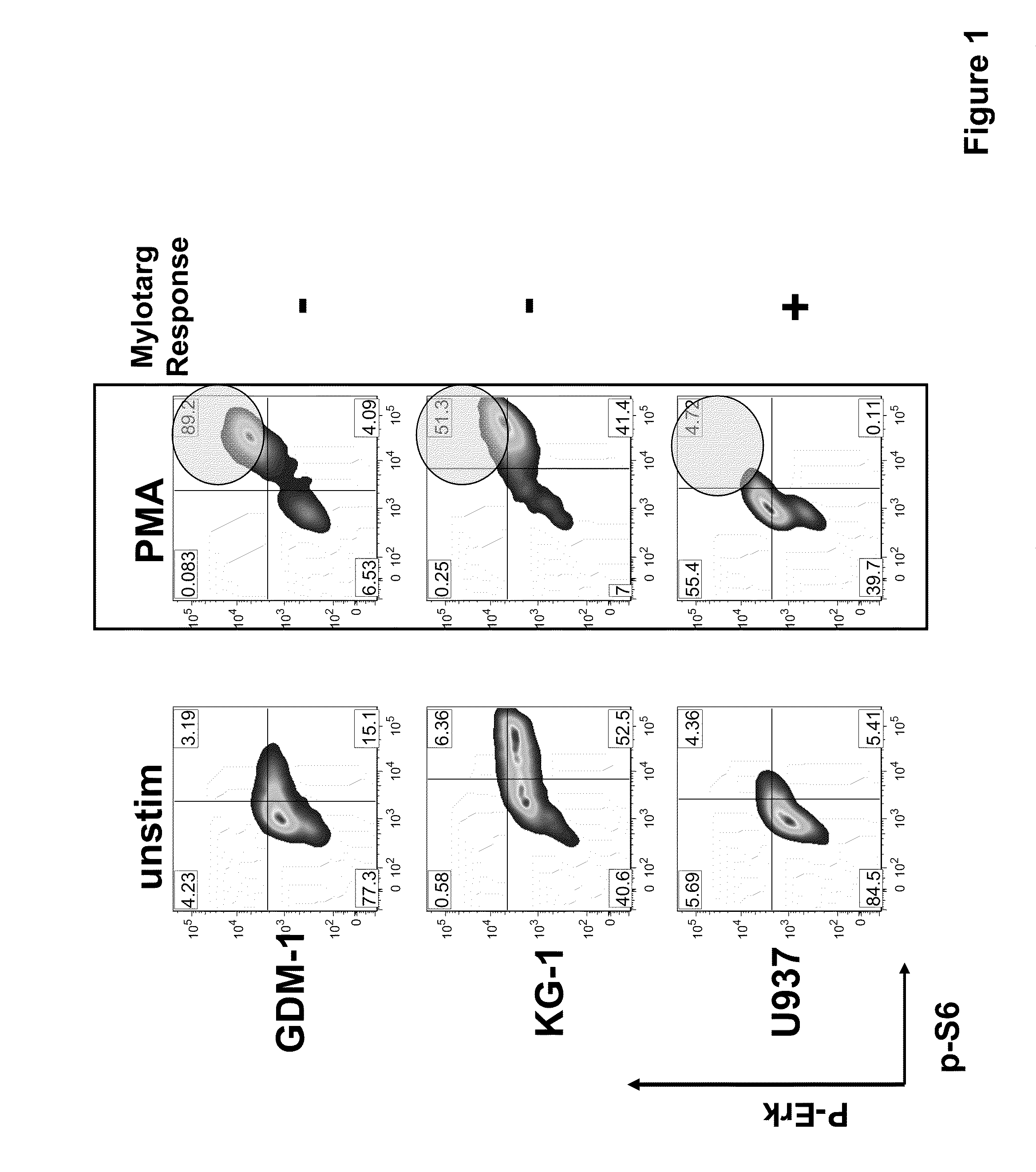
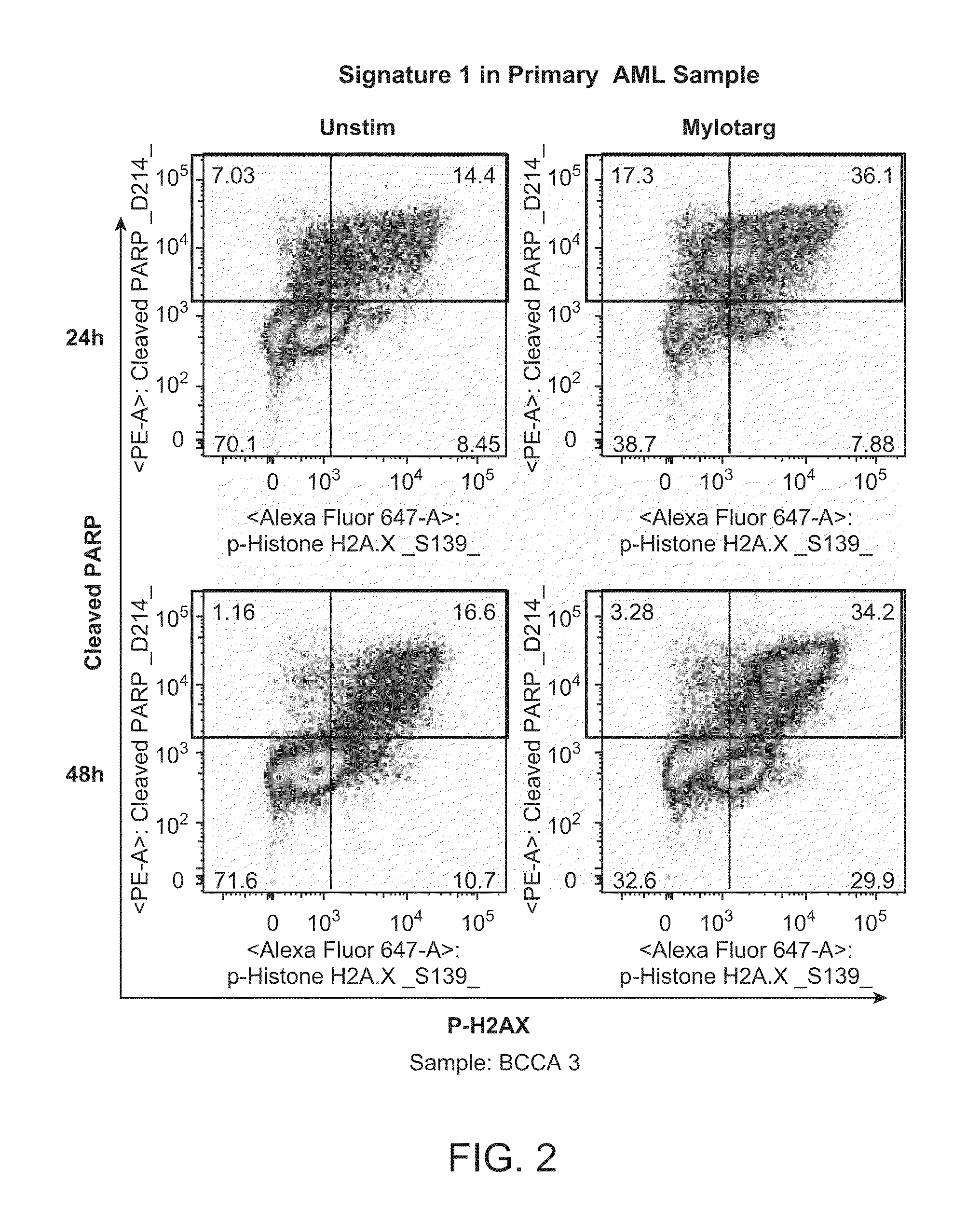
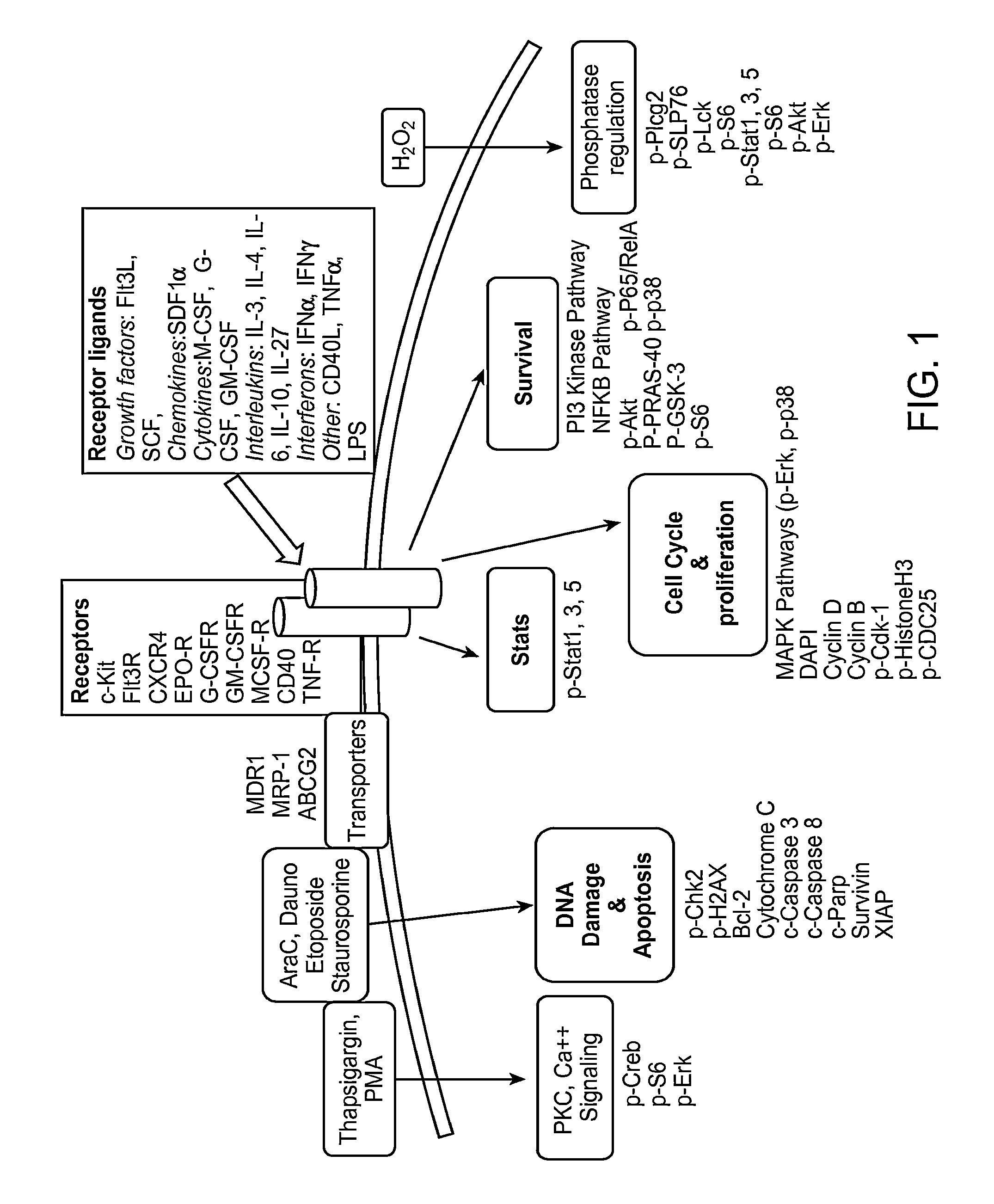
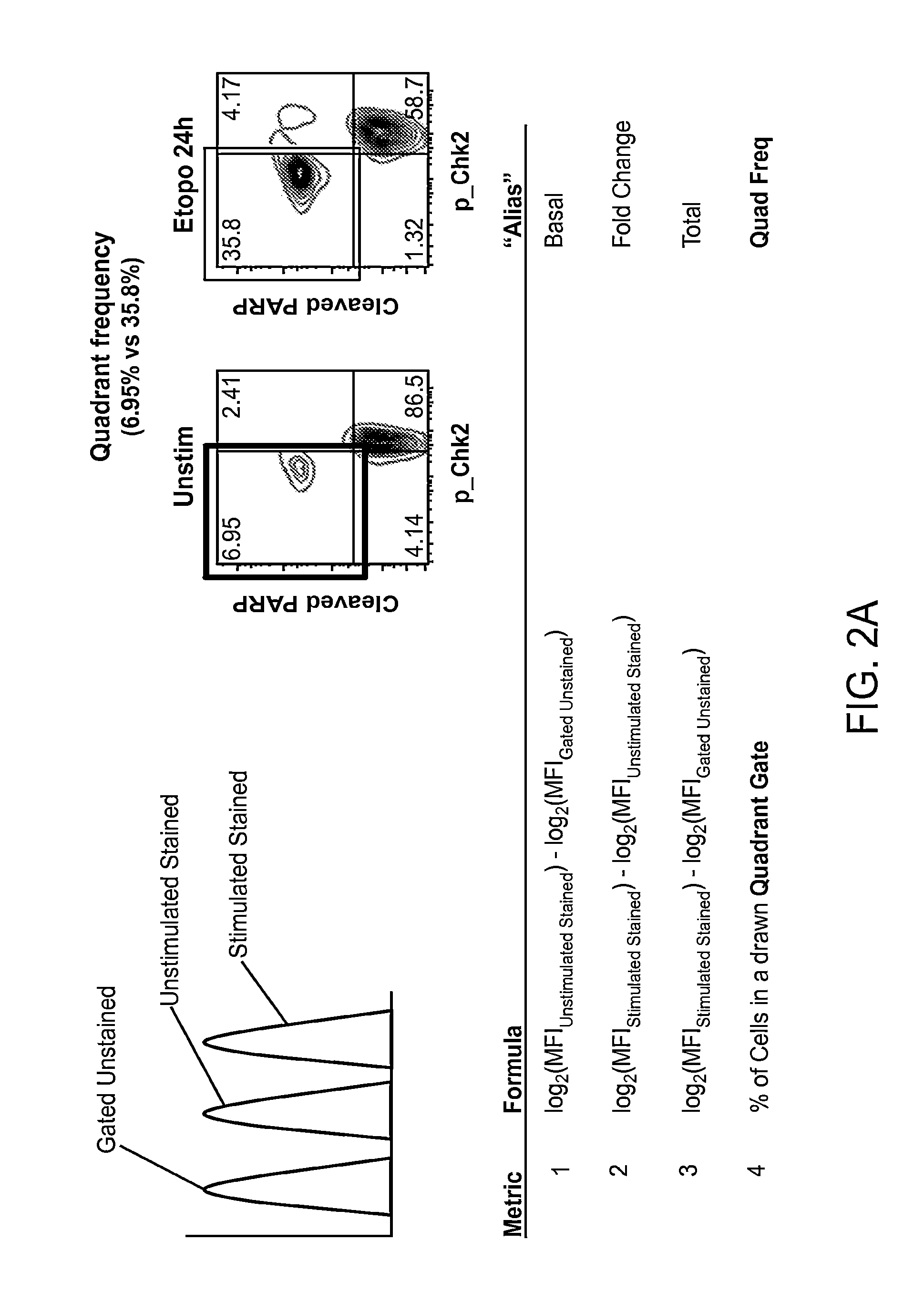
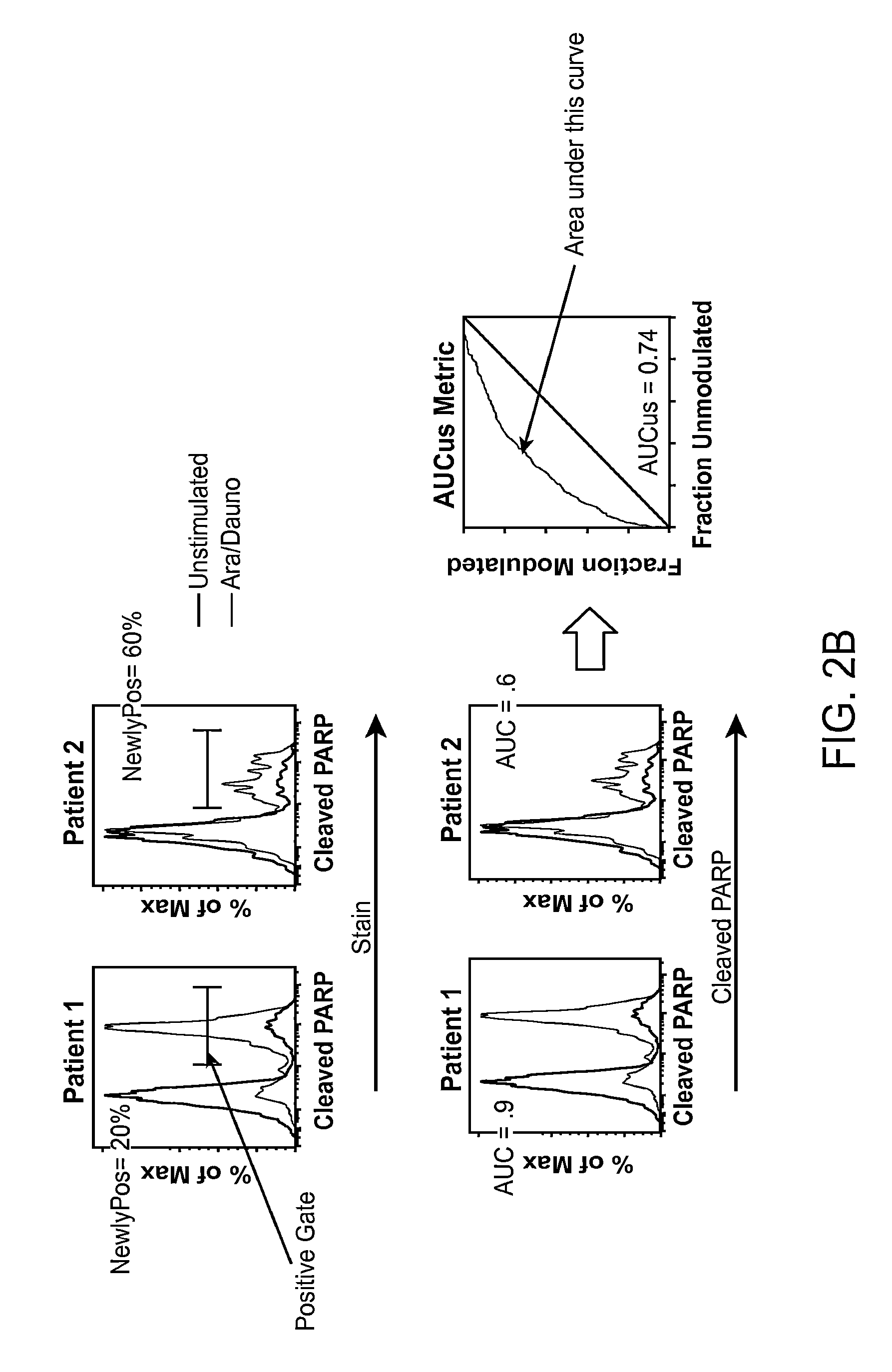
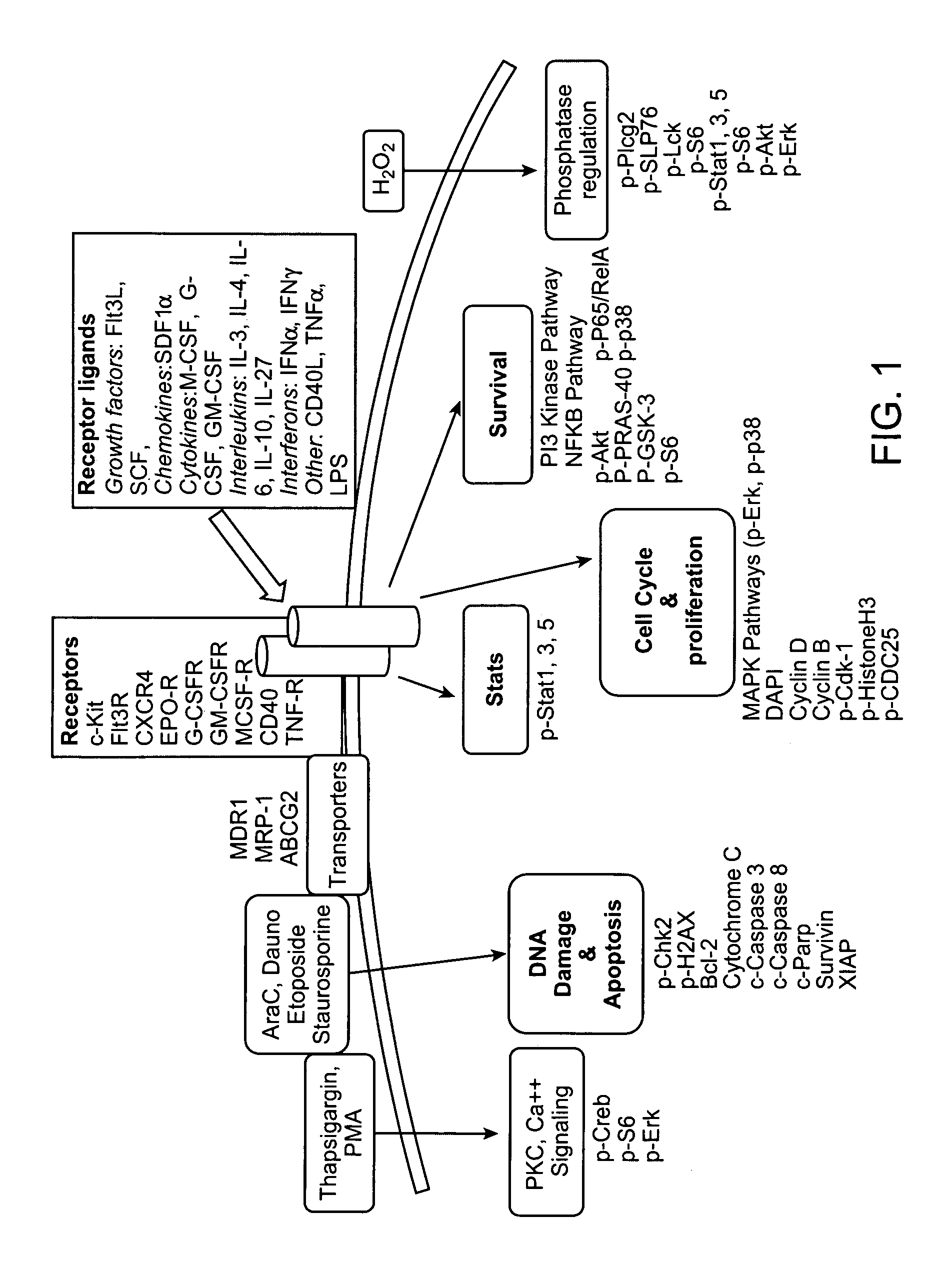
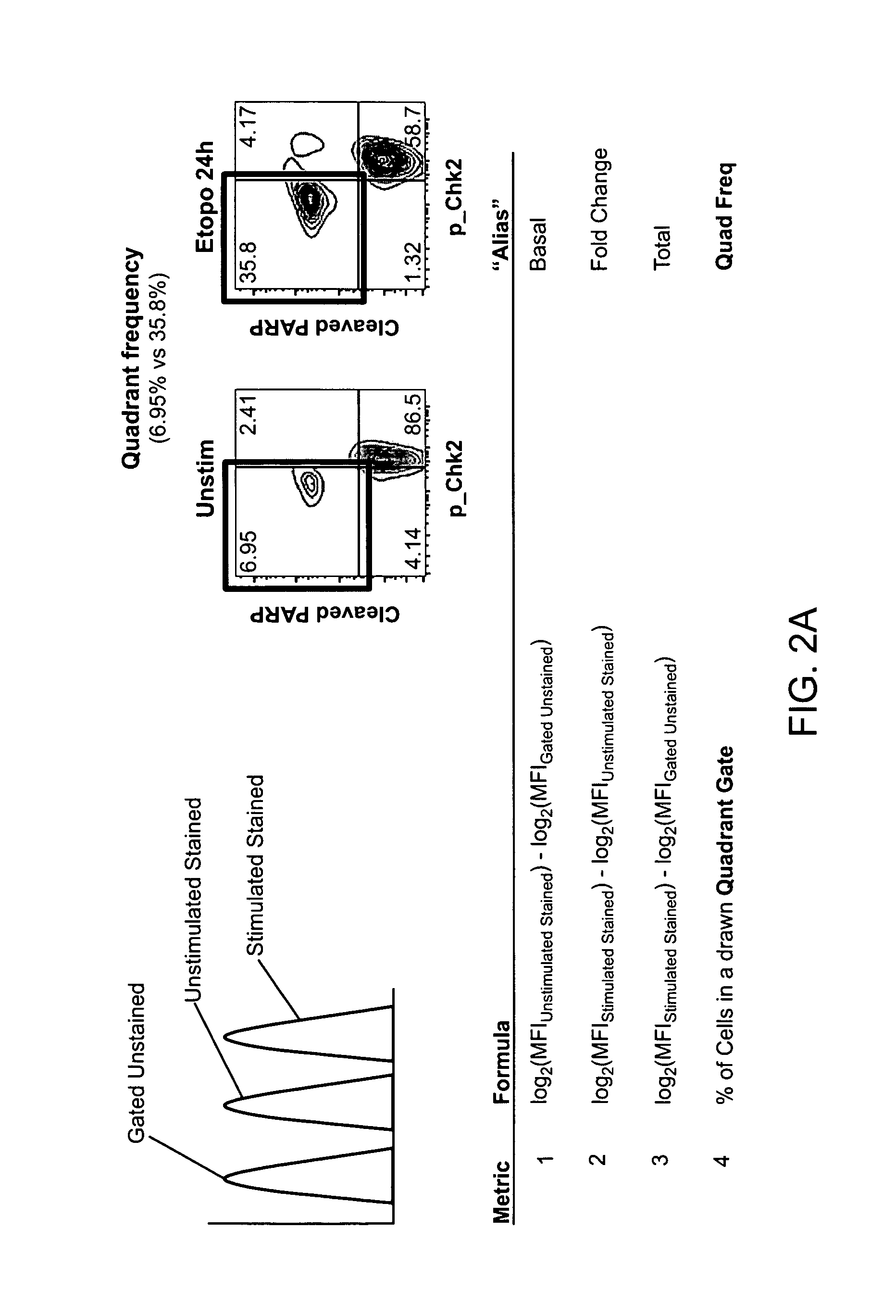
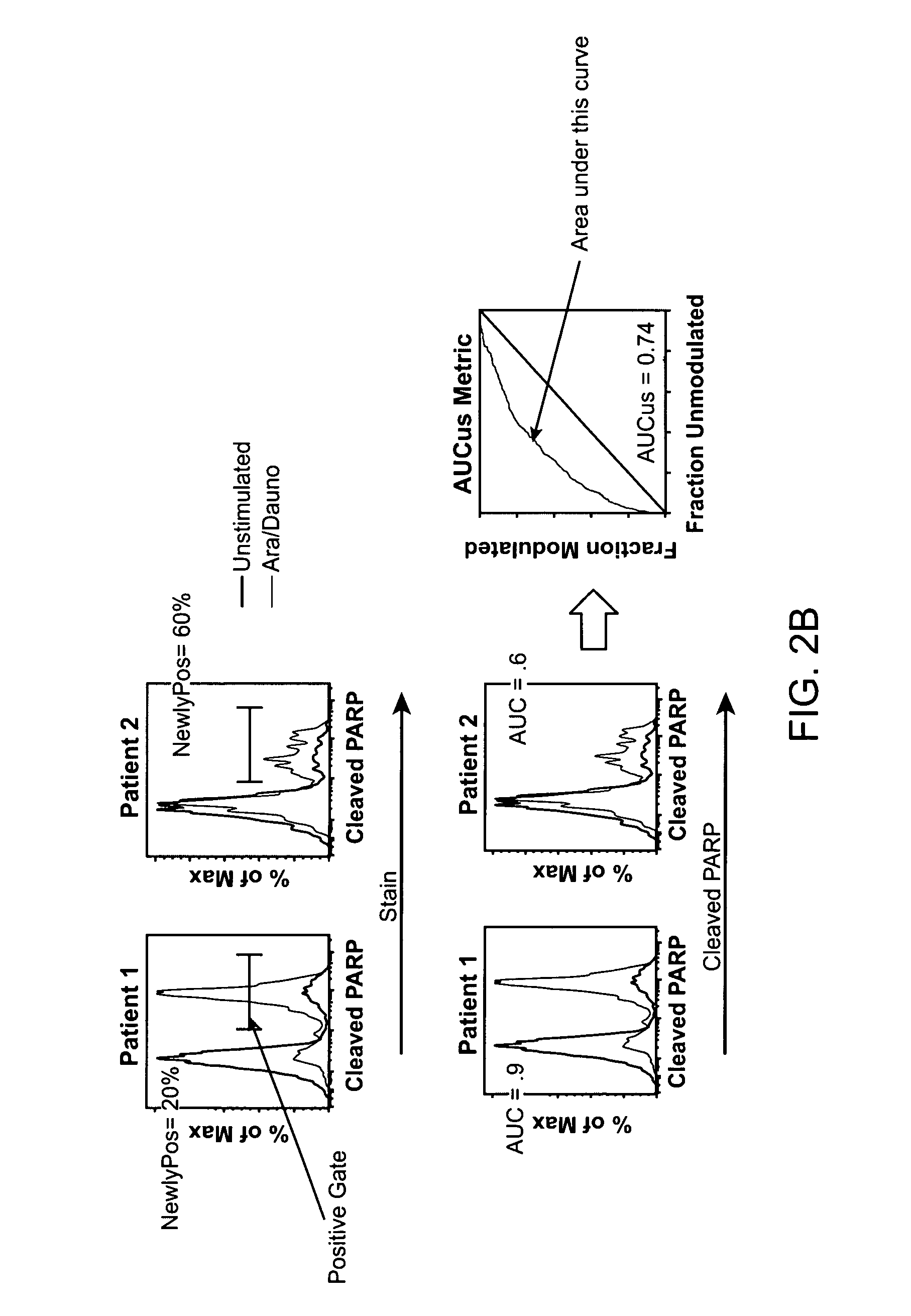
The present invention provides an approach for the determination of the activation states of a plurality of proteins in single cells. This approach permits the rapid detection of heterogeneity in a complex cell population based on activation states, expression markers and other criteria, and the identification of cellular subsets that exhibit correlated changes in activation within the cell population. Moreover, this approach allows the correlation of cellular activities or properties. In addition, the use of modulators of cellular activation allows for characterization of pathways and cell populations. Several exemplary diseases that can be analyzed using the invention include AML, MDS, and MPN.
Owner:NODALITY
Isolation And Use Of Solid Tumor Stem Cells
InactiveUS20080178305A1Reduce spreadIncreased proliferationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthMammary gland structure
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell. We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumor cells in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells. We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA +1
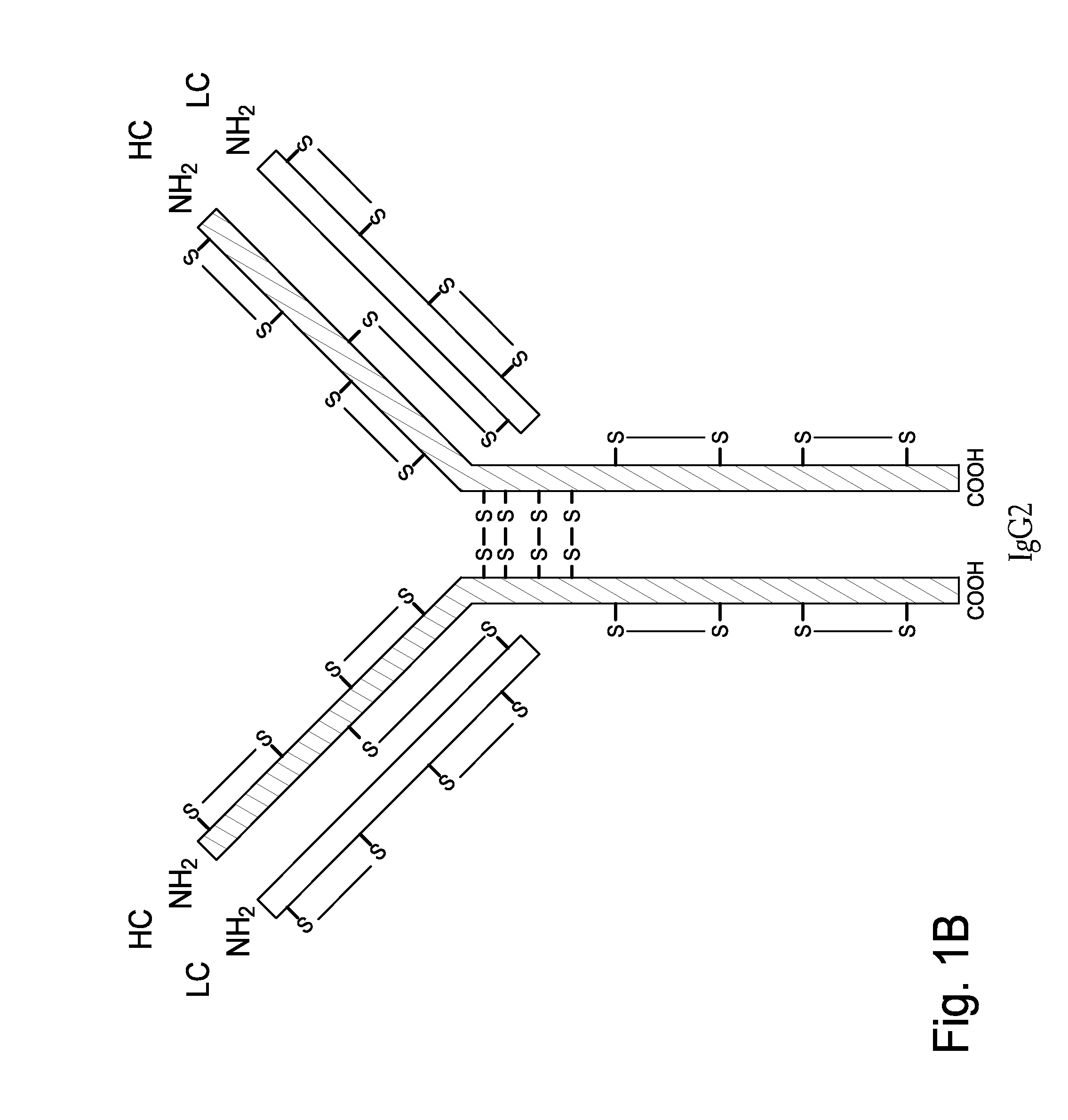
Homogeneous Antibody Populations
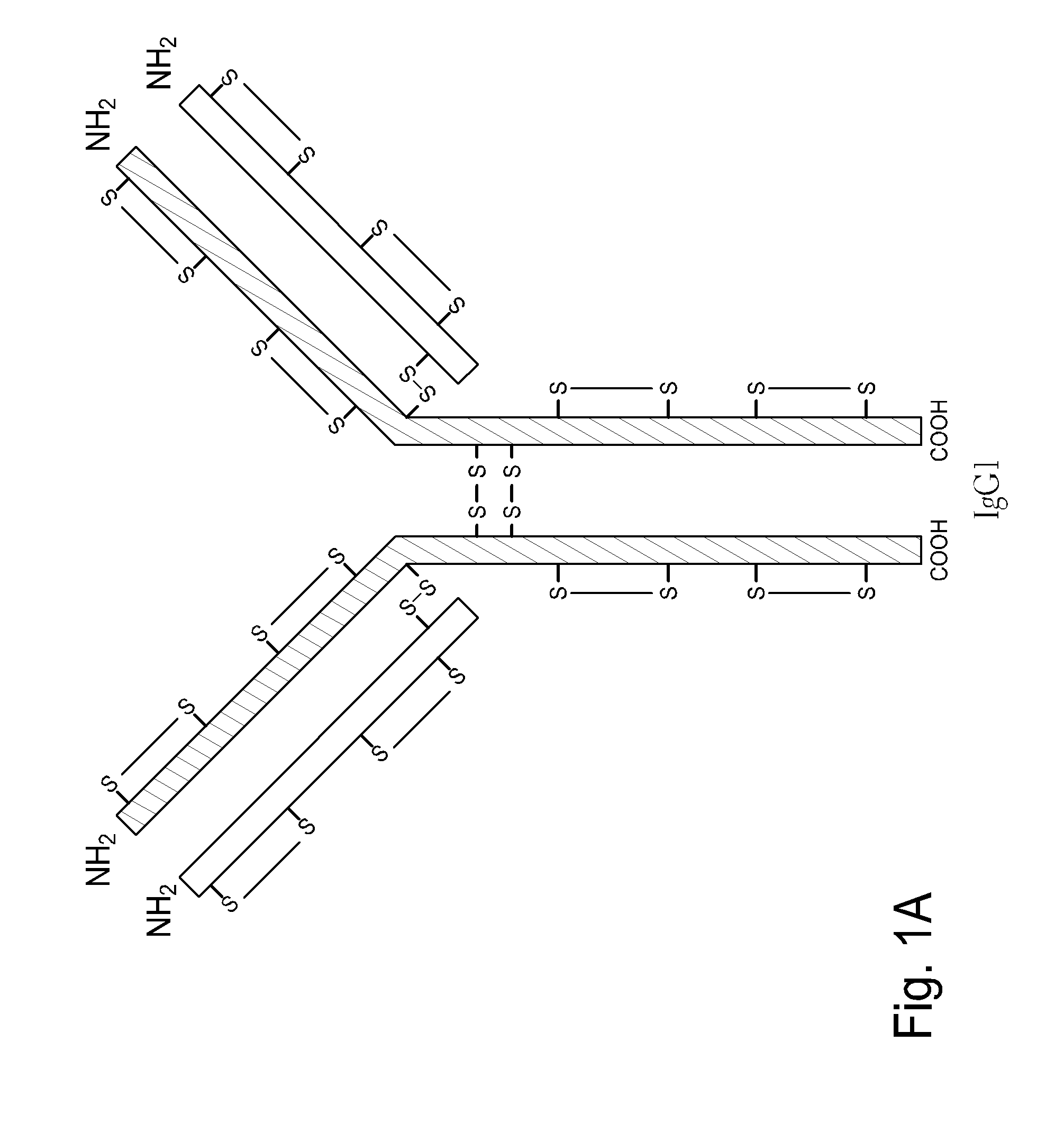
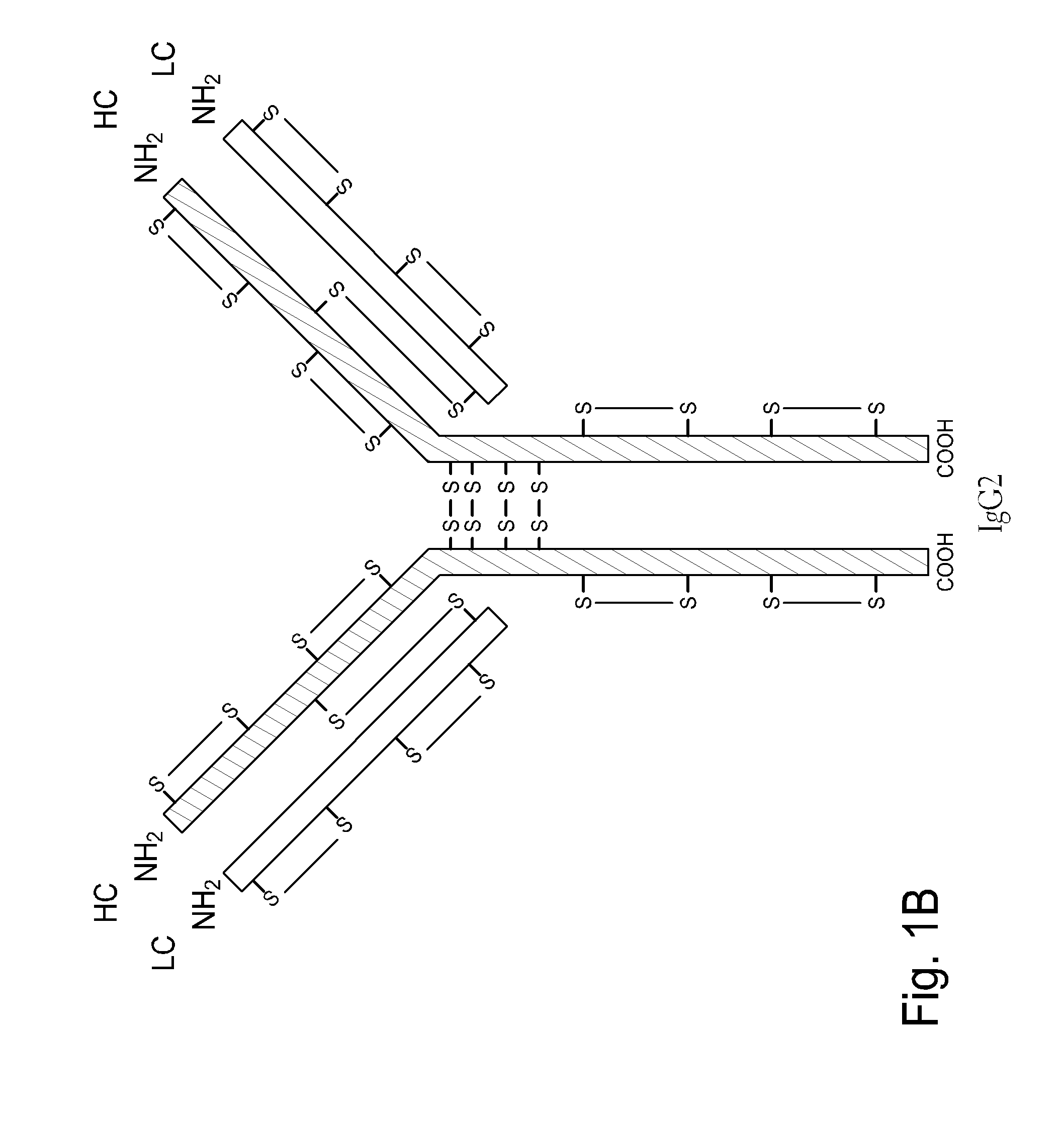
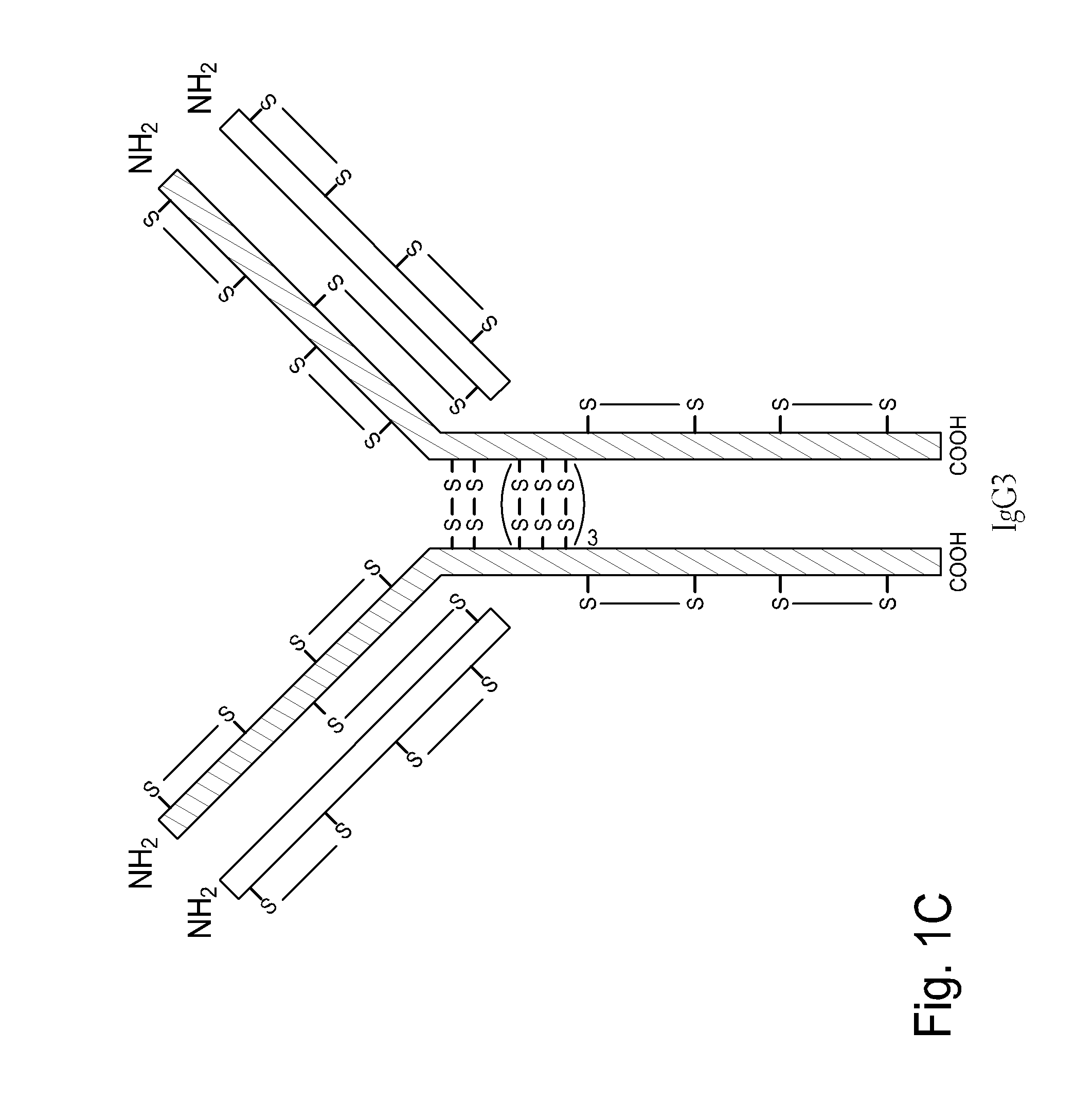
InactiveUS20100226925A1Efficient and economic productionImprove propertiesNervous disorderAntipyreticMonoclonal antibodyHinge region
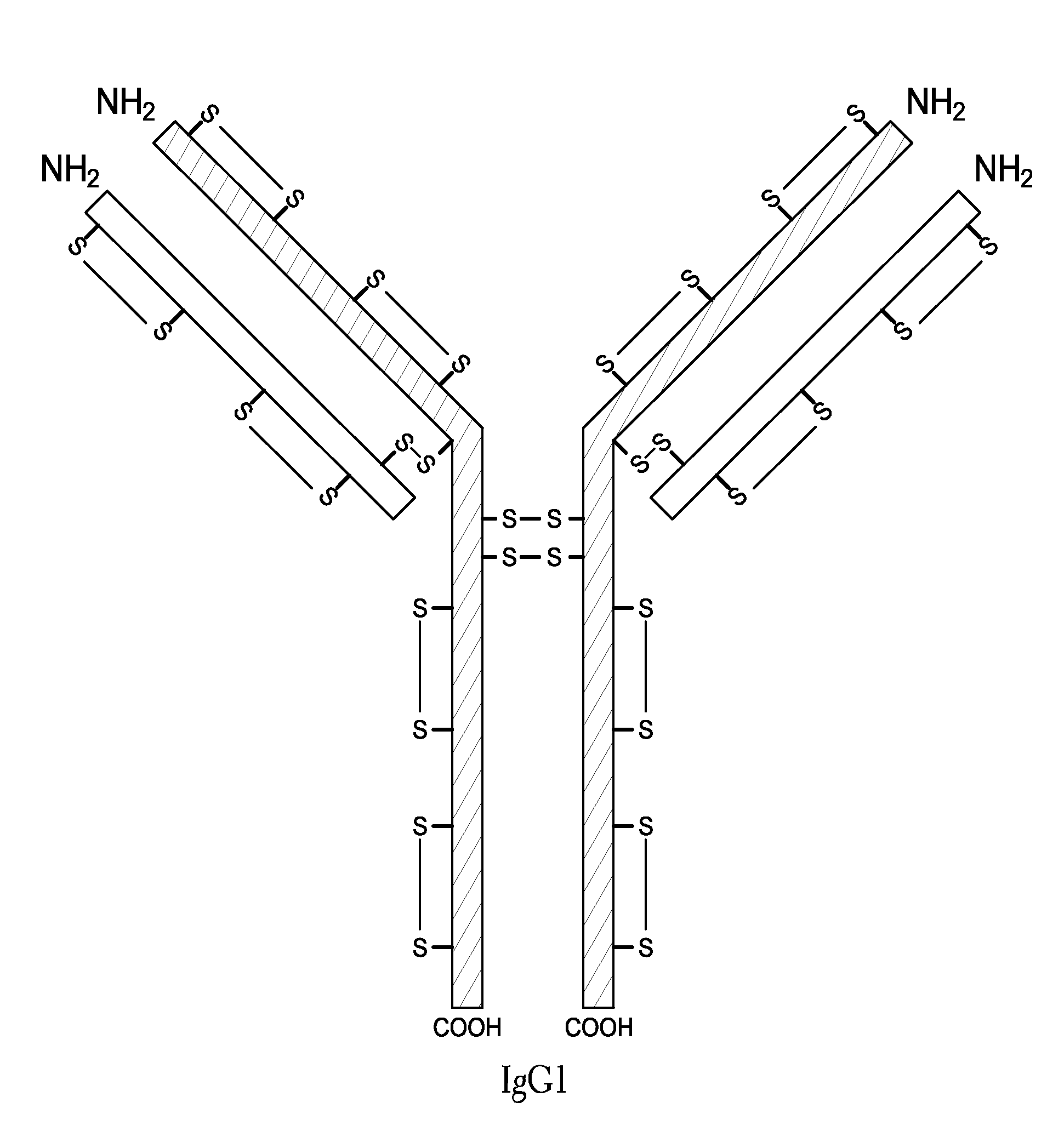
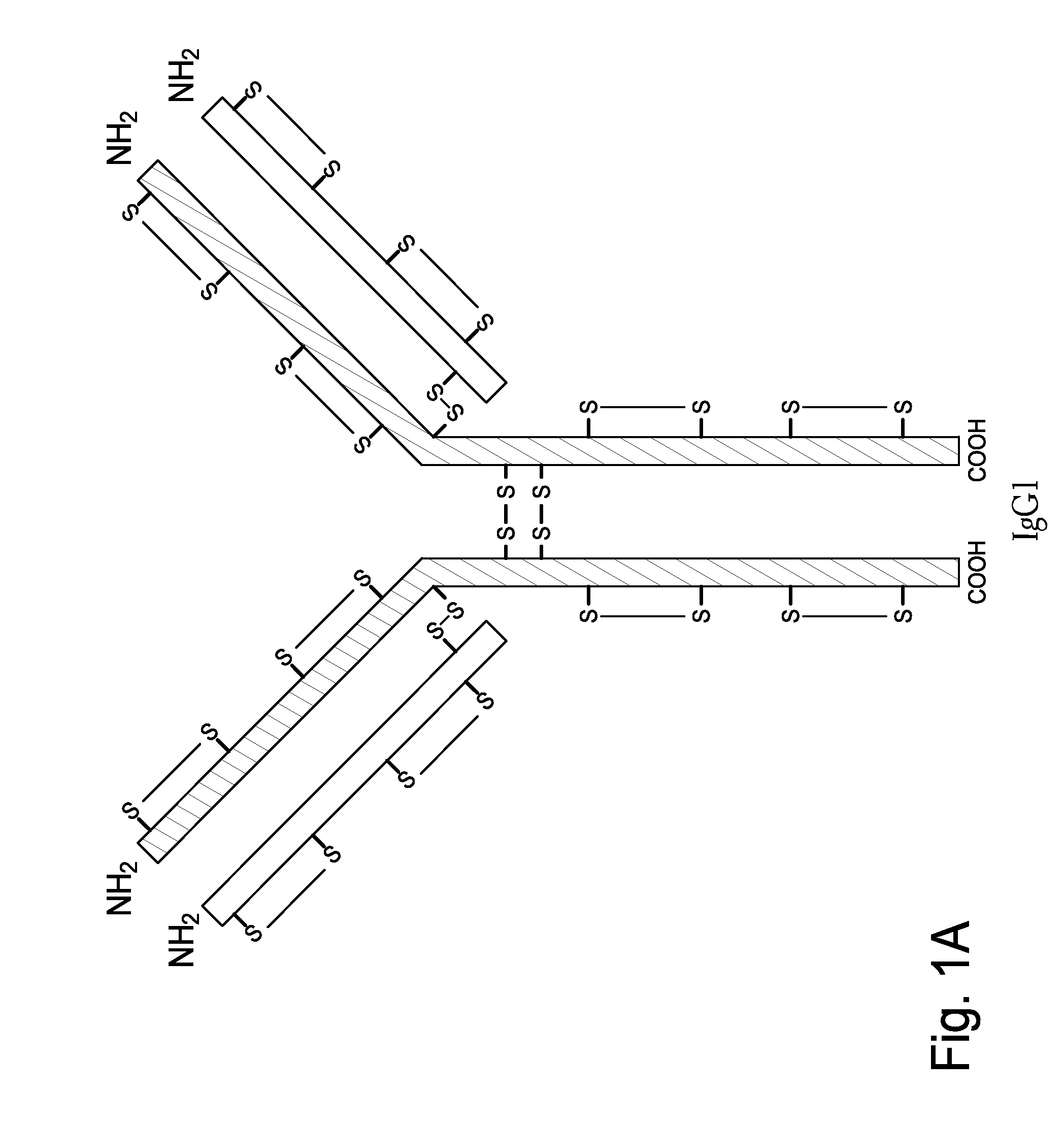
The present invention is generally directed to methods of producing an increase in the enrichment and / or recovery of preferred forms of monoclonal antibodies. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for eliminating disulfide heterogeneity in the hinge region of recombinant IgG2 antibody proteins.
Owner:AMGEN INC
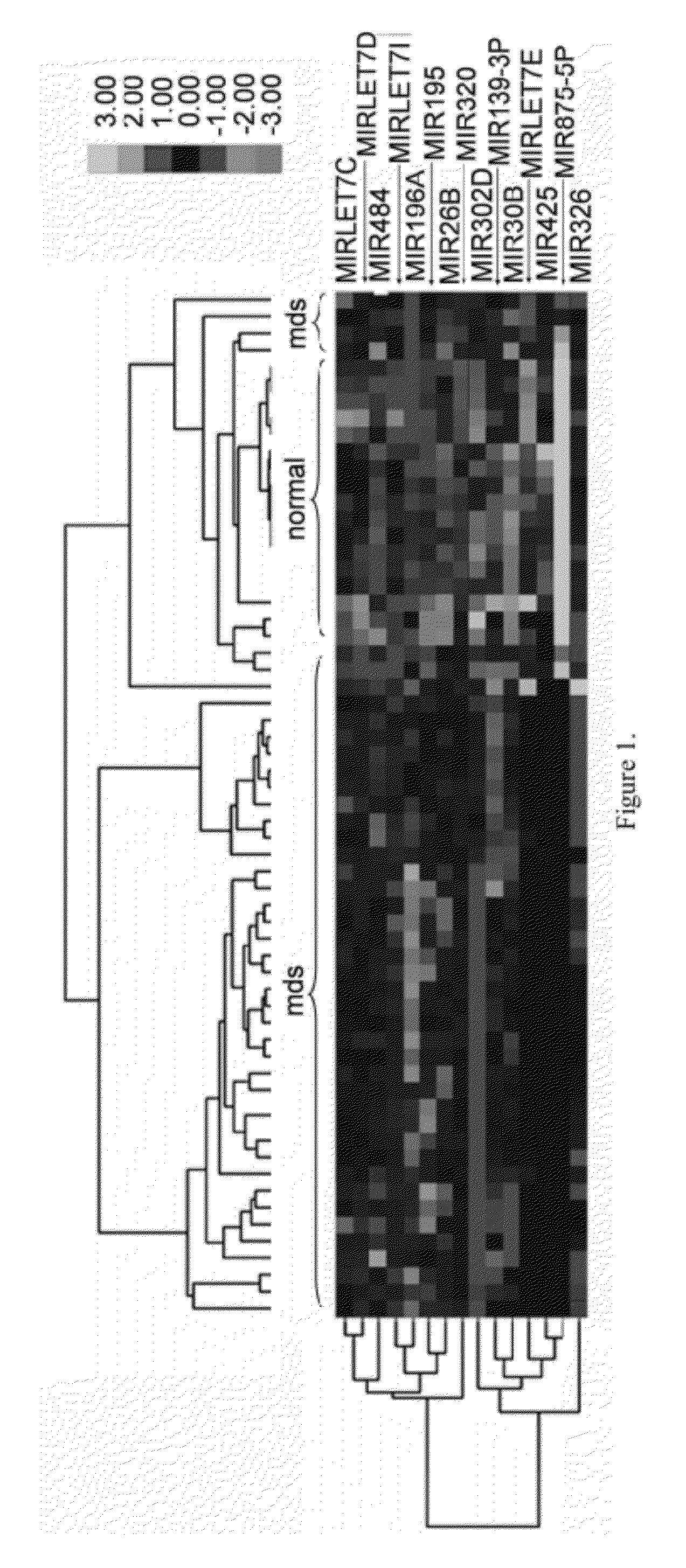
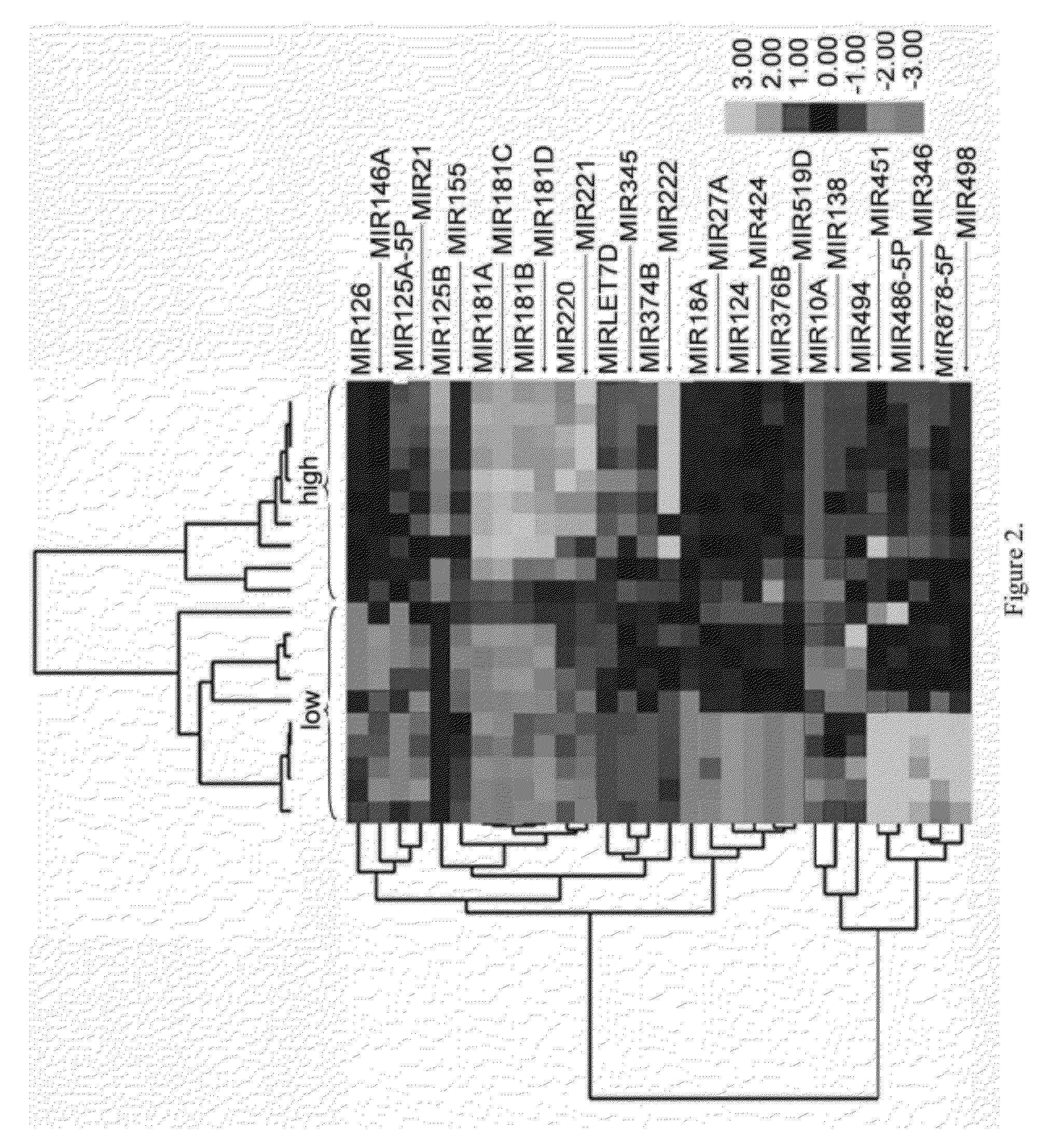
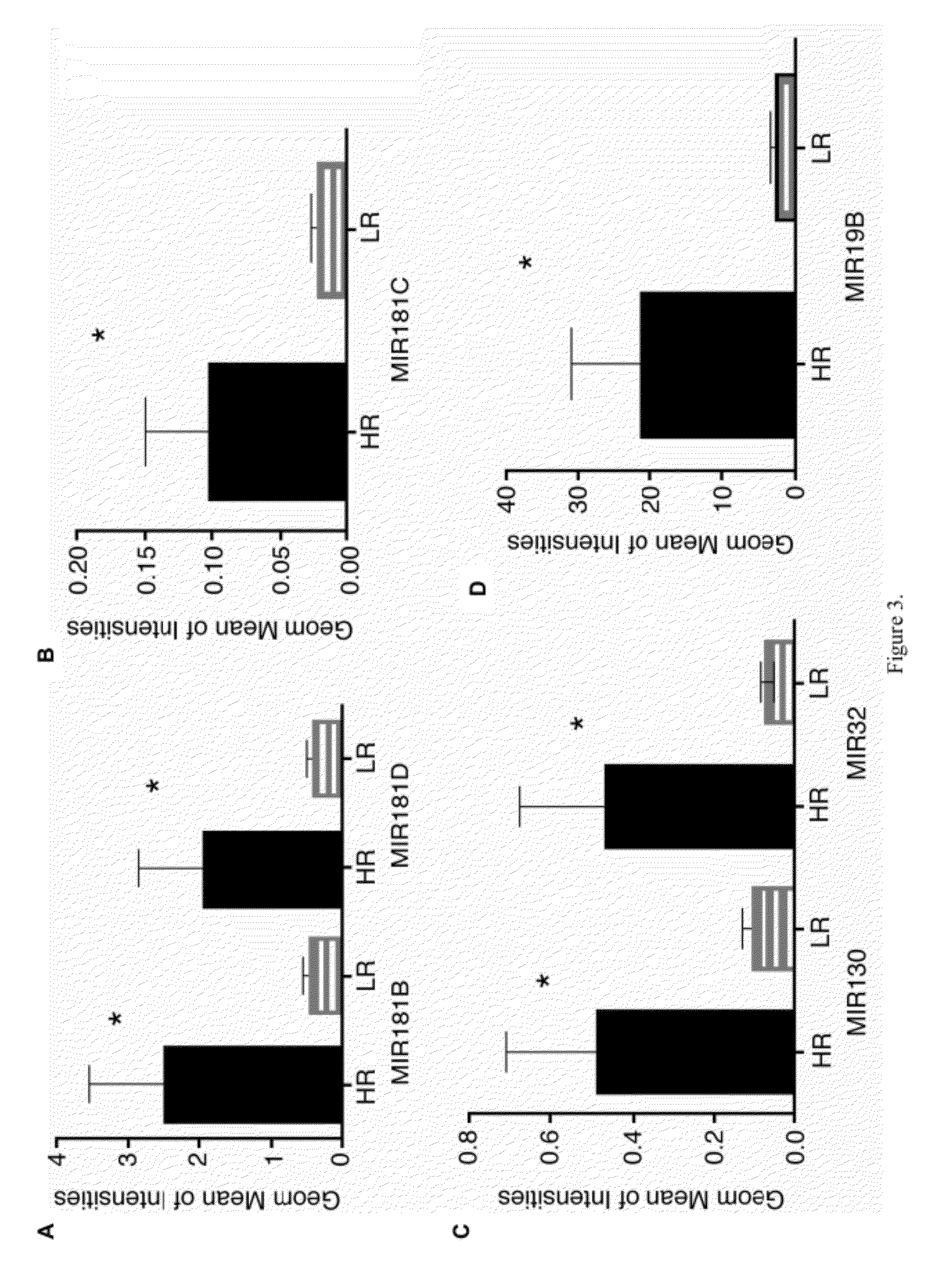
Method of Identifying Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Myelodysplastic syndromes display both hematological and biological heterogeneity with variable leukemia potential. To determine whether microRNAs expression offers diagnostic discrimination or influences malignant potential in MDS, bone marrow miRNA expression was investigated from prognostically distinct MDS subsets using a microarray platform. After background subtraction and normalization, data were analyzed indicating thirteen miRNA signature with statistically significant differential expression, including down-regulation of members of a leukemia associated miRNA family. A unique signature consisting of 10 miRNAs was closely associated with International Prognostic Scoring System risk category permitting discrimination between lower and higher risk disease. Selective overexpression of miRNA-181 family members was detected in higher risk MDS, indicating pathogenetic overlap with acute myeloid leukemia. Analysis of miRNA expression profile offers diagnostic utility, and provides pathogenetic and prognostic discimination in MDS.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Methods for identifying bioagents
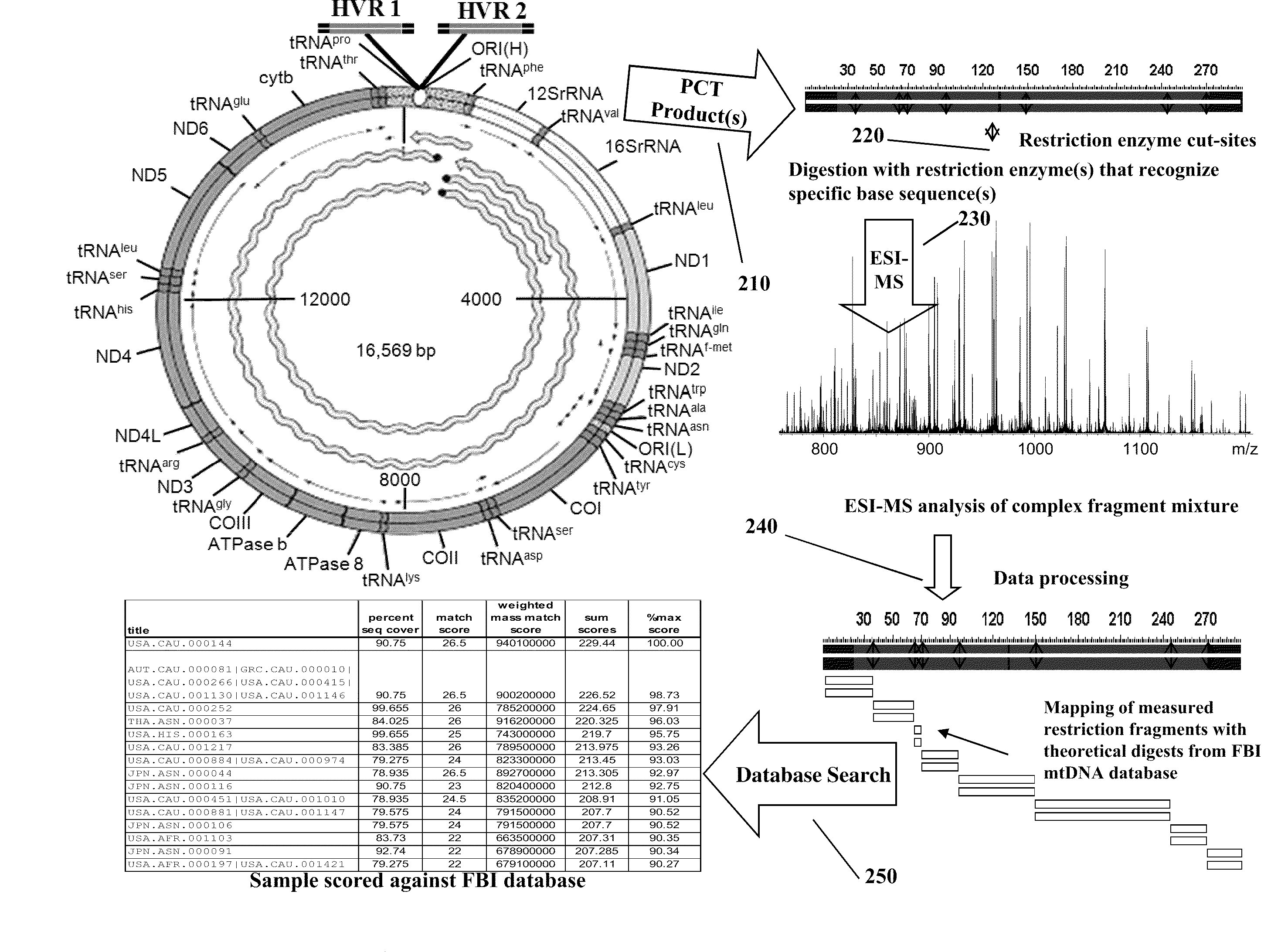
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA and methods for characterizing heteroplasmy of mitochondrial DNA, which can be used to assess the progression of mitochondrial diseases.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modifi-cation of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and inser-tion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA pro-duction system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also de-scribed. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intes-tine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
Methods of genetic cluster analysis and uses thereof
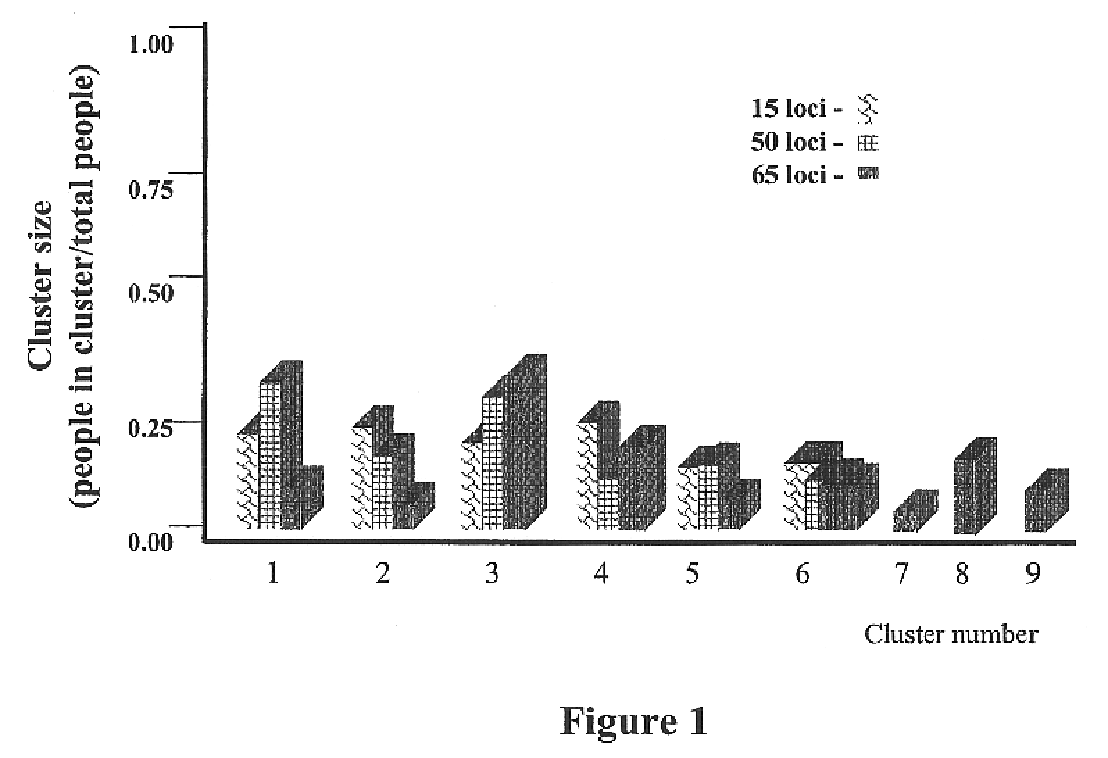
The present invention is primarily directed to methods of genetic cluster analysis for use in determining the homogeneity and / or heterogeneity of a population or sub-population. Determination of the heterogeneity or homogeneity of a population sample is important in many areas including DNA fingerprinting in forensics and population-based studies such as clinical trials, case-control studies of risk factors, and gene mapping studies.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
Methods for Analyzing Drug Response
InactiveUS20100099109A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingPhosphorylationOxidation-Reduction Agent
The present invention provides methods, instruments, reagents, kits and the biology involved in analyzing drug response. An embodiment of the present invention provides an approach for the characterization a plurality of pathways in single cells. This approach permits the rapid detection of heterogeneity in a complex cell population based on activation states of cellular molecules such as proteins, expression markers and other criteria, and the identification of cellular subsets that exhibit correlated changes in activation within the cell population. Some of these categories include redox potential, ITIM phosphorylation, intracellular pH and other categories allows for characterization of such pathways and cell populations. Also, the present analysis is useful for the analysis of the effect of compounds on potential target cells.
Owner:NODALITY
Cancer treatments
The invention relates to a product comprised of specific combinations of cell lines intended for use as an allogeneic immunotherapy agent for the treatment of prostate cancer in humans. The heterogeneity of the immunotherapeutic matches the heterogeneity of the antigenic profile in the target prostate cancer and immunises the recipients with many of the potential TAA and TSA which are expressed at various stages of the disease. The invention discloses a vaccine comprising a combination of three different cell lines prepared from primary or metastatic prostate cancer biopsy material. The cell lines are lethally irradiated utilising gamma irradiation at 50-300 Gy to ensure that they are replication incompetent.
Owner:ONYVAX
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modification of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and insertion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA production system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also described. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intestine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
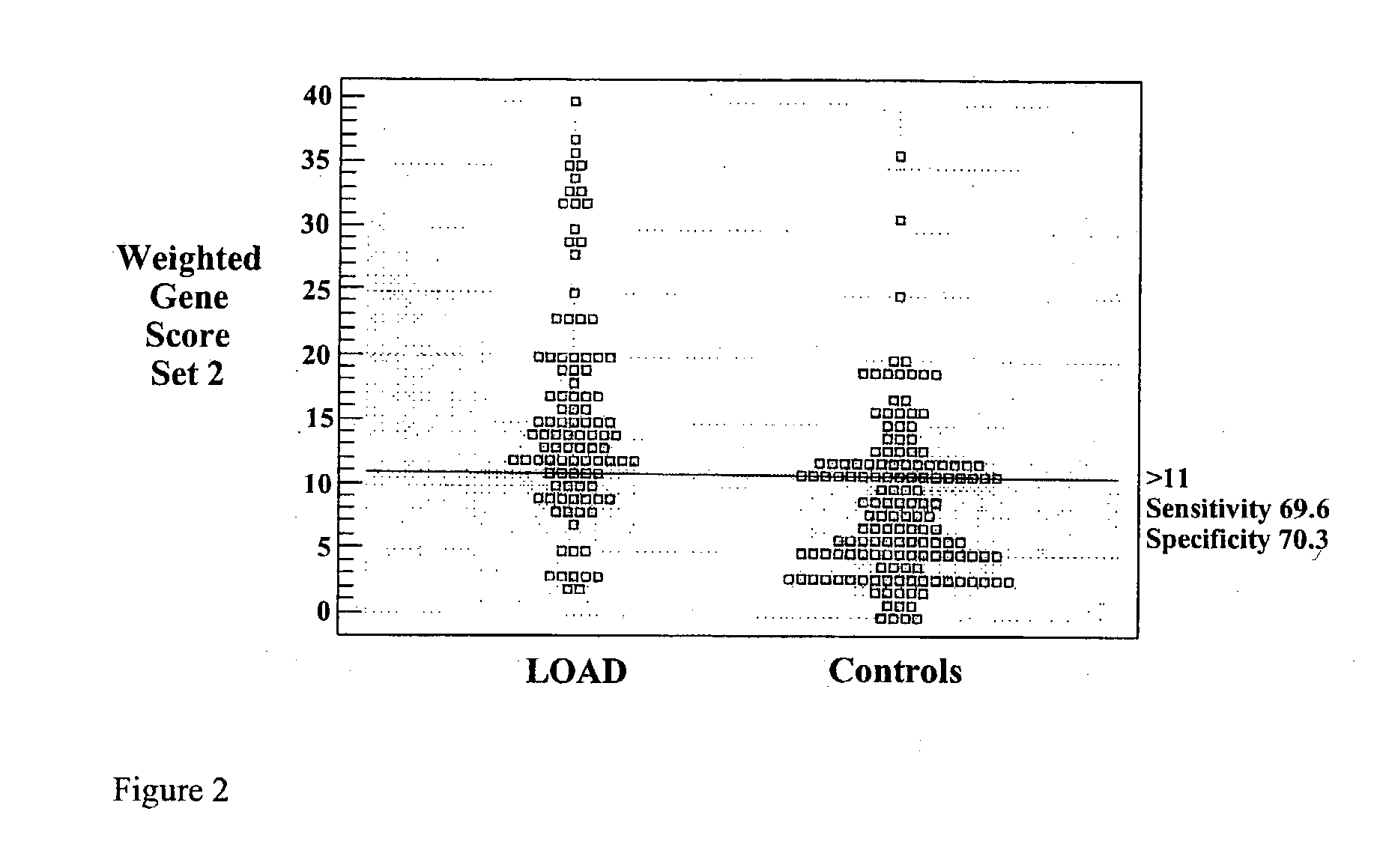
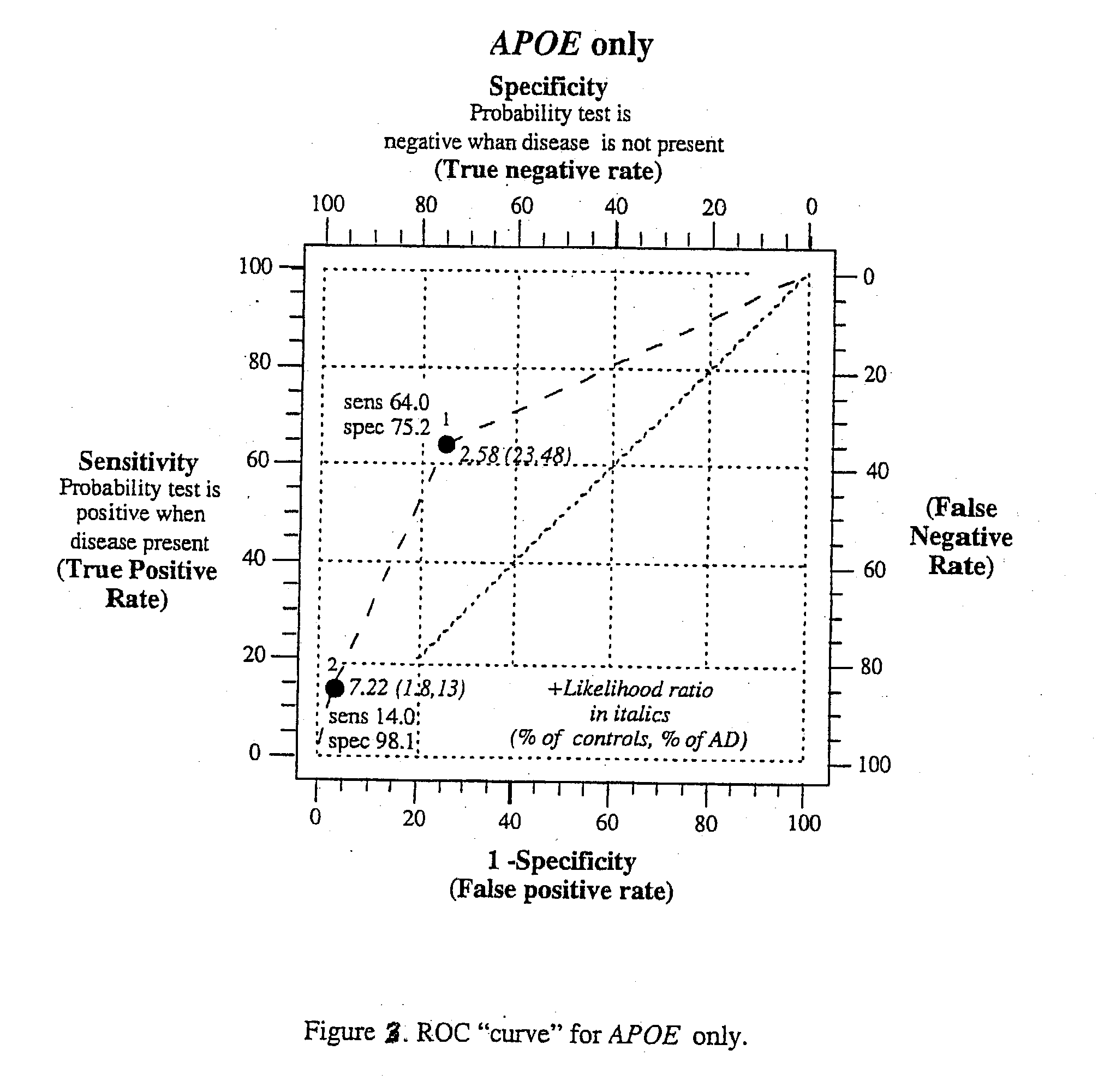
Multi-gene tests with ROC plots for the assessment of risk for polygenic disorders
InactiveUS20030162207A1Microbiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnostic testPolygenic disease
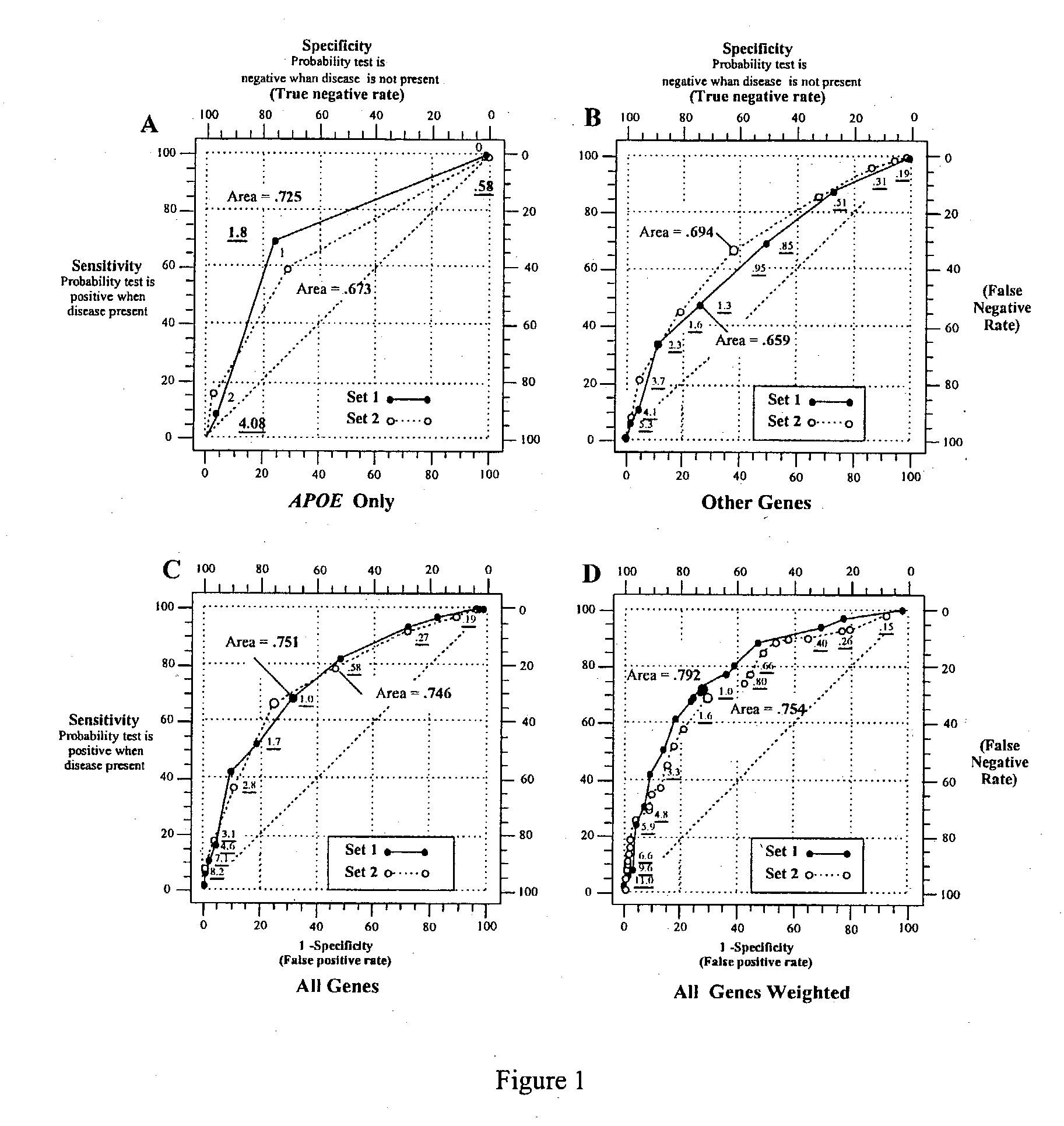
Polygenic disorders are due to the additive effect of multiple genes interacting with the environment. Because of the small effect size of each gene and considerable genetic heterogeneity, when single genes are examined, the outcome of association and linkage analyses are variable from study to study. Techniques are needed that take these unique characteristics of polygenic disorders into consideration. The present invention discloses that the formation of a polygenic score, consisting of the additive effect of multiple candidate genes, and its assessment using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plots, provides such a technique. Six genes previously shown to be associated with Alzheimer's disease were examined, APOE, ACE, ACP1, ESR1, PNMT and SLC6A4. The total fraction of the variance, the area under the ROC plots, and the range of risks were similar for both groups indicating that despite genetic heterogeneity and the small effect size of most genes, consistent risk analyses could be obtained by examining the additive effect of these multiple genes. The present invention also discloses diagnostic tests for determining a subject's risk of developing Alzheimer's Disease or specifically Late Onset Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
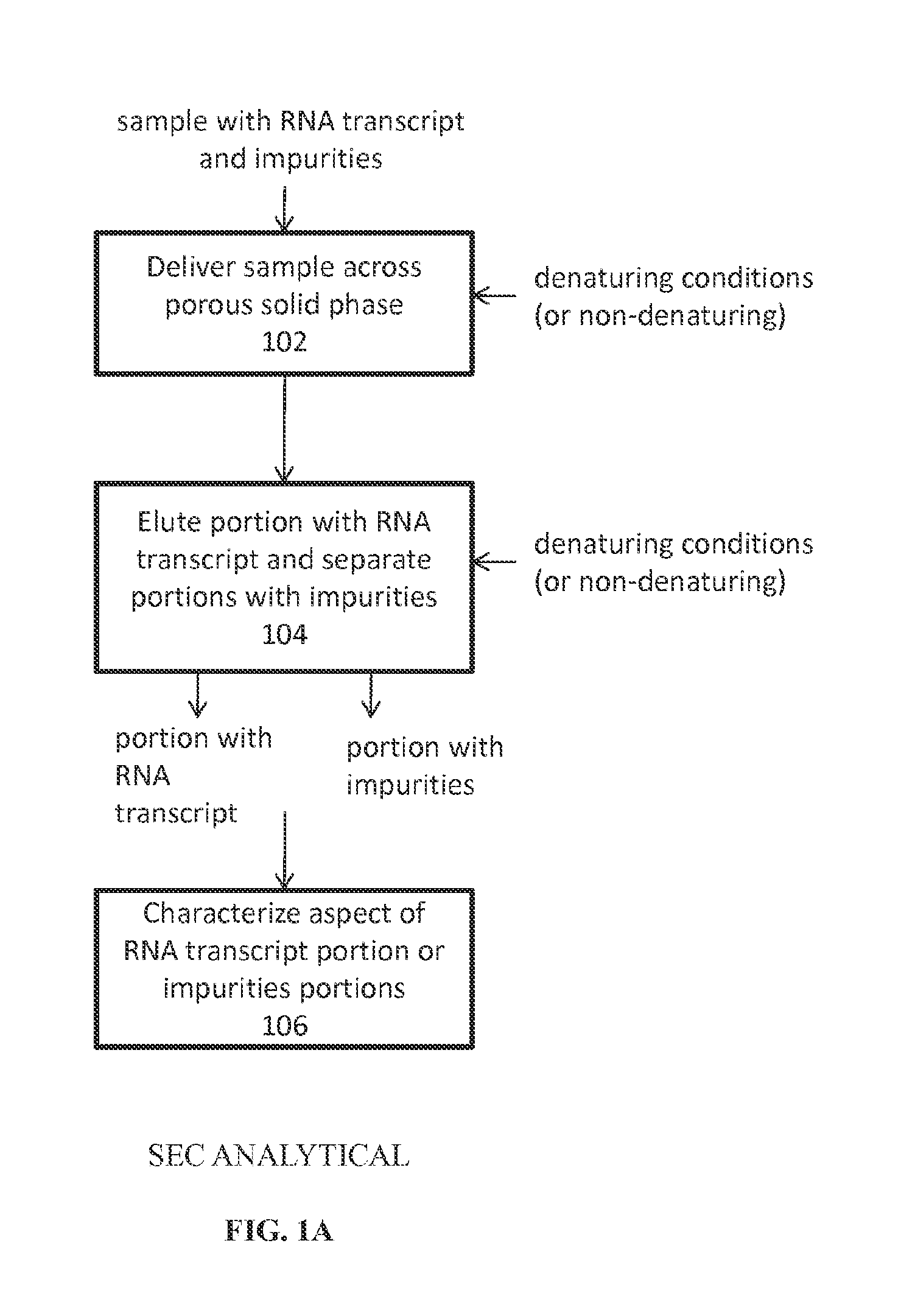
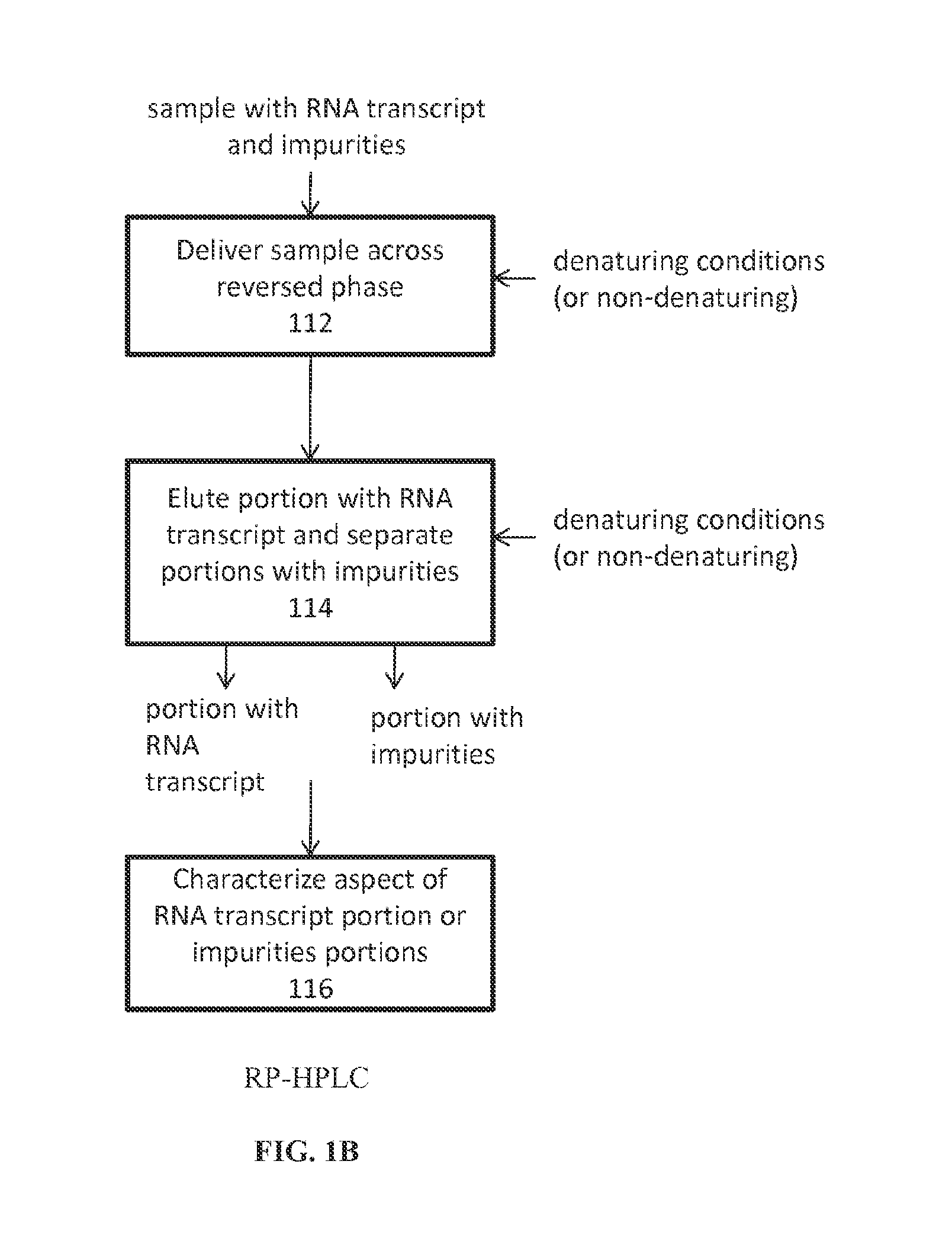
Analysis of mRNA heterogeneity and stability
InactiveUS20160017313A1Simple preparation processDemonstrate success of the manufacturing processElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotideQualitative analysis
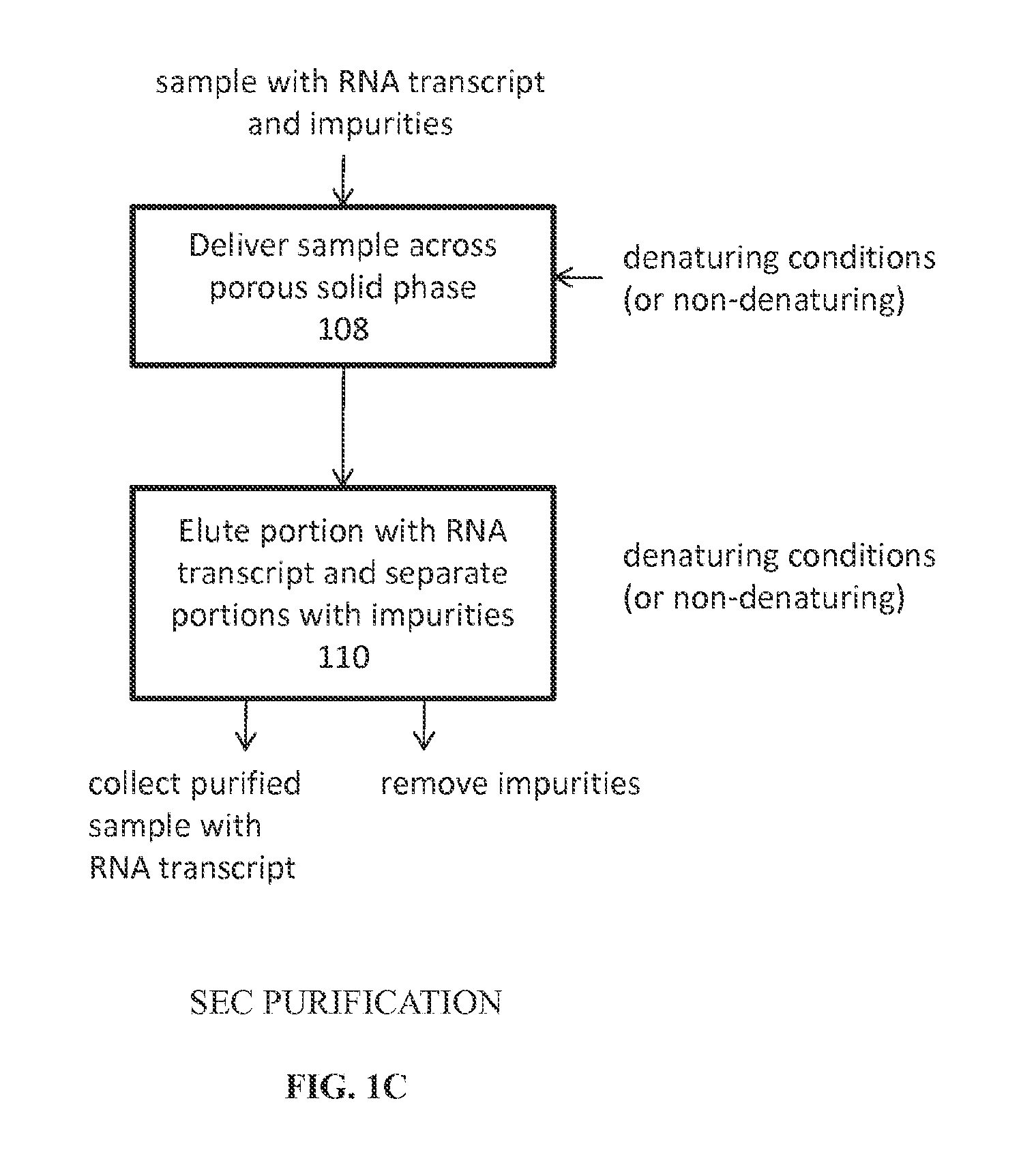
Reversed phase-High Performance (High Pressure) Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) and Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) methods have been developed for monitoring structural and size heterogeneity as well as stability of large RNA transcripts, including lengths of up to at least 10,000 nucleotides. The methods are designed for significantly larger mRNAs that could be monitored in the past, including lengths of up to at least 10,000 nucleotides, and including chemically modified RNA transcripts. SEC techniques are also used in the preparative purification of large RNA transcripts to remove impurities, including hybridized nucleic acid impurities and multimeric RNA species. All of these techniques are also beneficial in that they can be used for large scale manufacturing of therapeutics.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20110092378A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise to both more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
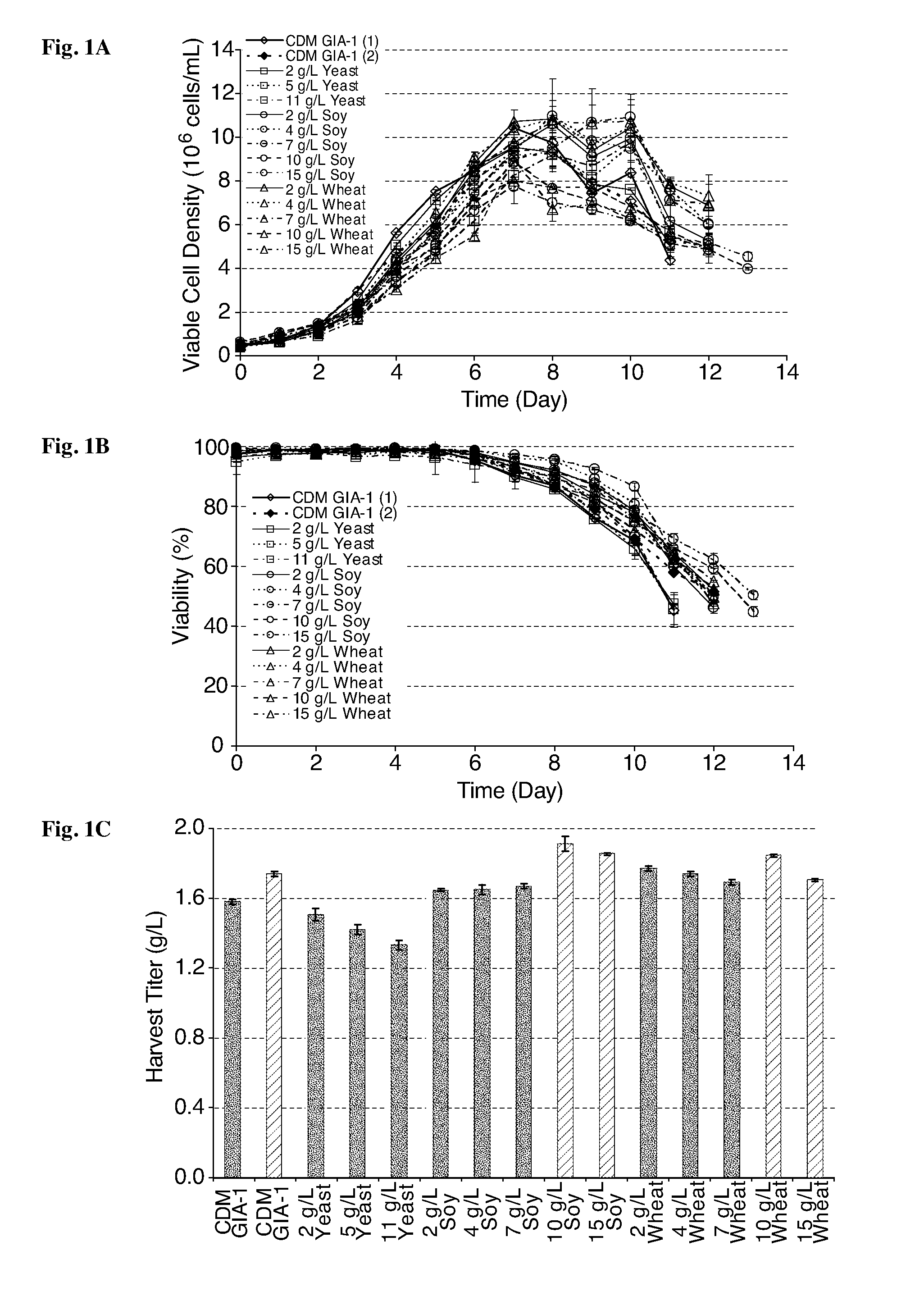
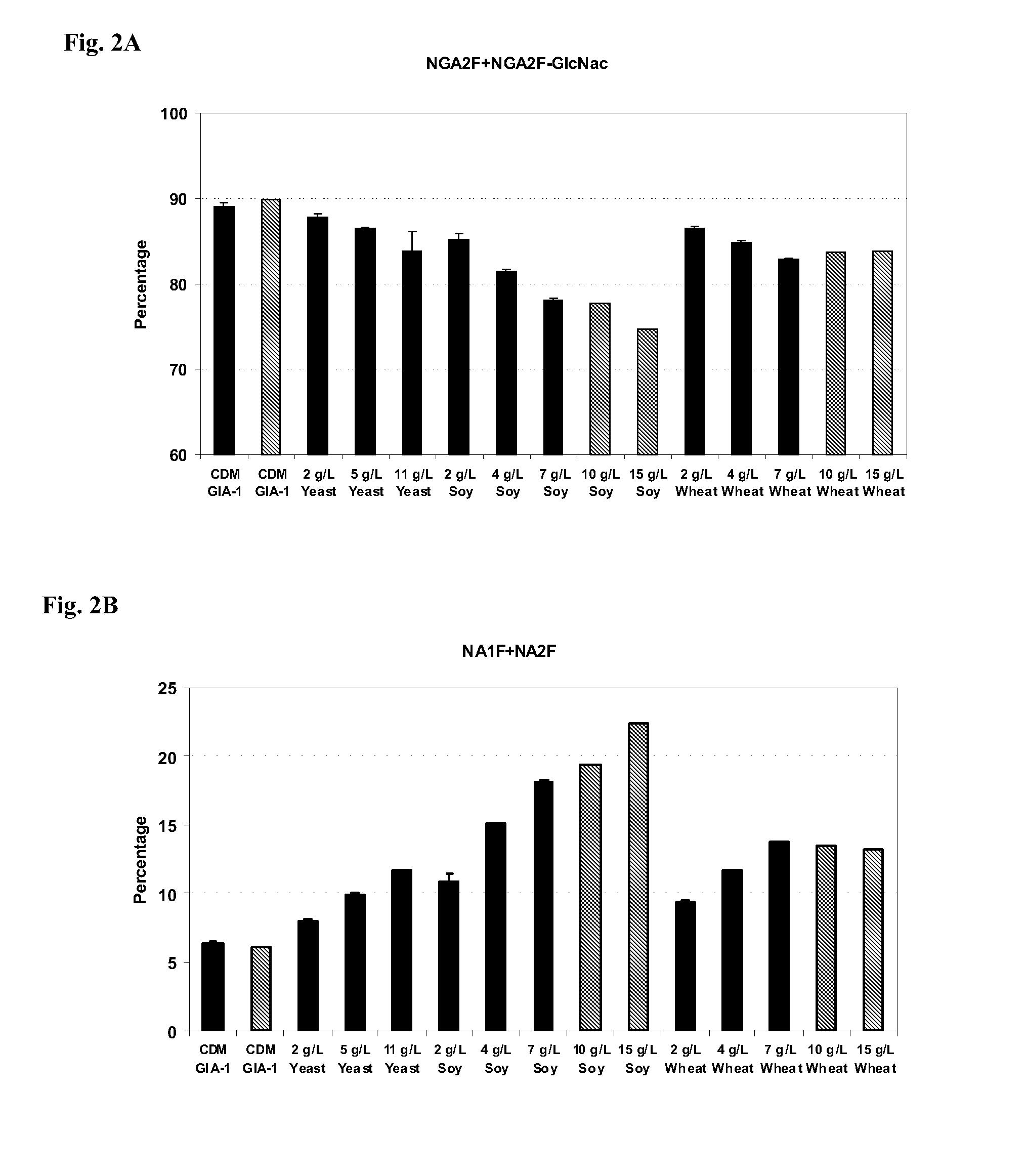
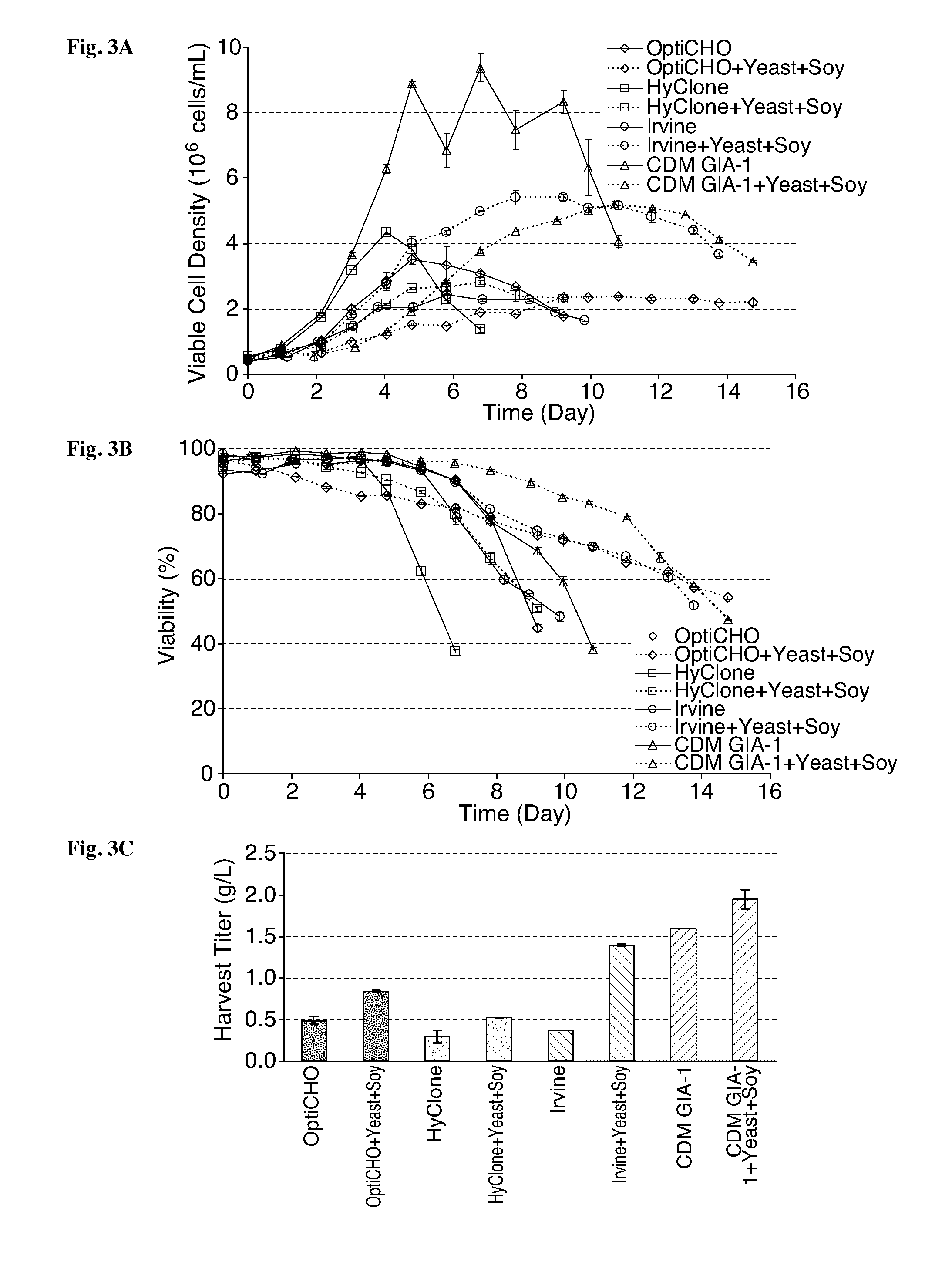
Methods to control protein heterogeneity
ActiveUS20150183866A1Genetically modified cellsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsHeteroplasmyProtein formation
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Methods for diagnosis, prognosis and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20140199273A1Easy to separateClear separationBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological activationHeteroplasmy
The present invention provides an approach for the determination of the activation states of a plurality of proteins in single cells. This approach permits the rapid detection of heterogeneity in a complex cell population based on activation states, expression markers and other criteria, and the identification of cellular subsets that exhibit correlated changes in activation within the cell population. Moreover, this approach allows the correlation of cellular activities or properties. In addition, the use of modulators of cellular activation allows for characterization of pathways and cell population.
Owner:NODALITY
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20060051325A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthCancer therapy
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20080194022A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsBiological testingPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Modified antibody constant region
ActiveUS9688762B2Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesAntipyreticAnalgesicsHigh concentrationHinge region
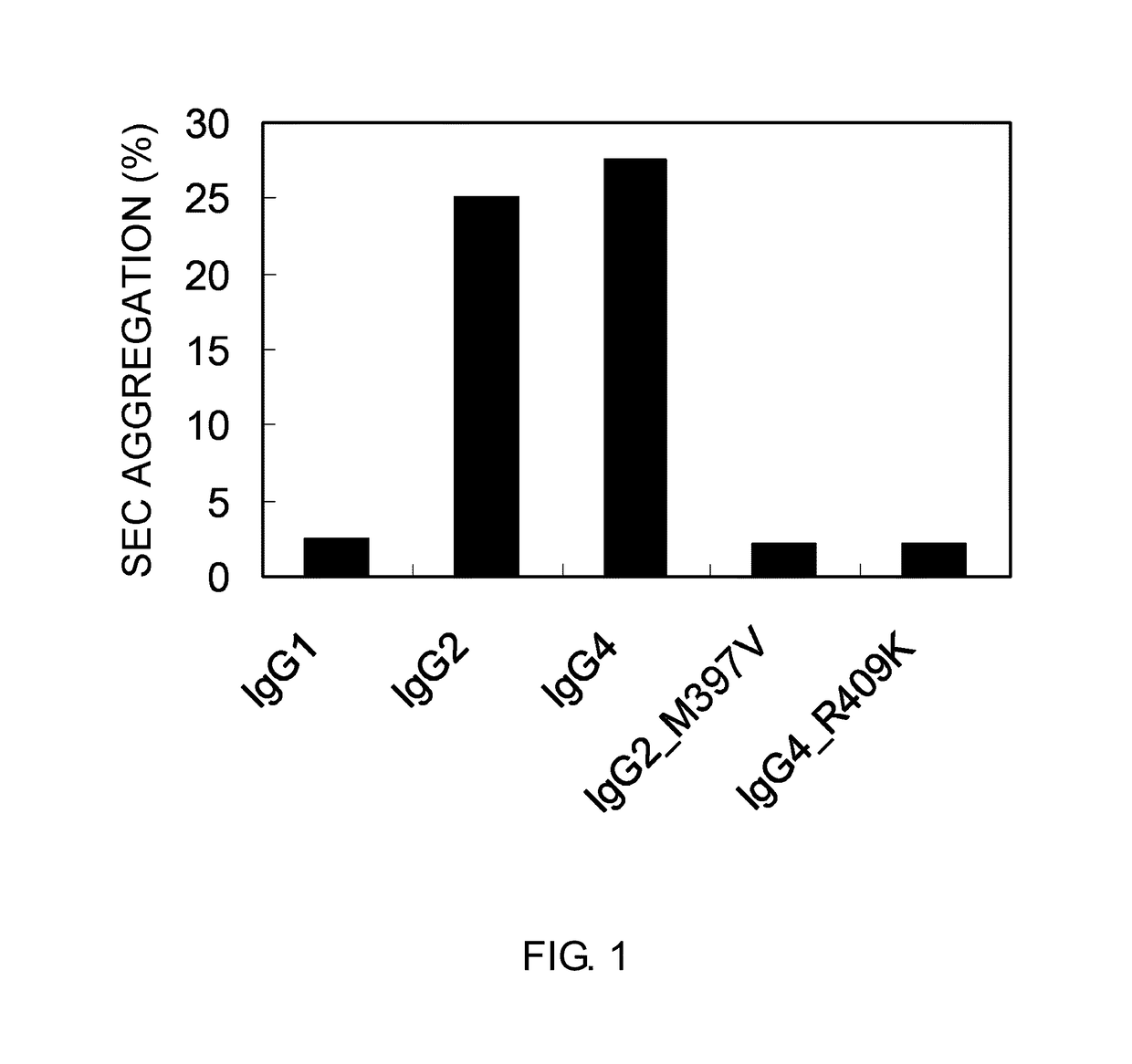
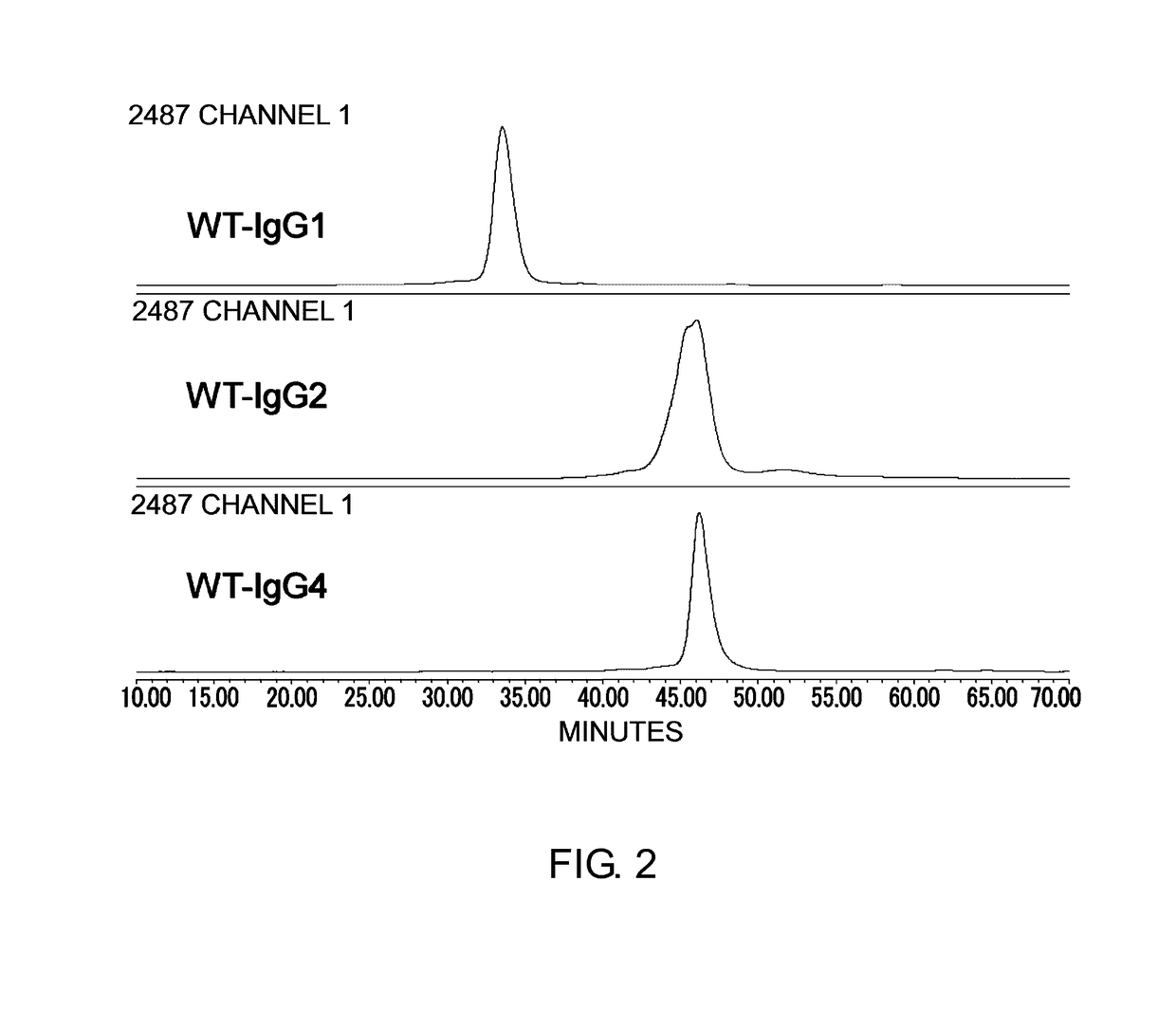
The present inventors succeeded in improving the antibody constant region to have increased stability under acid conditions, reduced heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, reduced heterogeneity originated from the H chain C terminus, and increased stability at high concentrations as well as in discovering novel constant region sequences having reduced Fcγ receptor-binding, while minimizing the generation of novel T-cell epitope peptides. As a result, the present inventors successfully discovered antibody constant regions with improved physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity), immunogenicity, safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
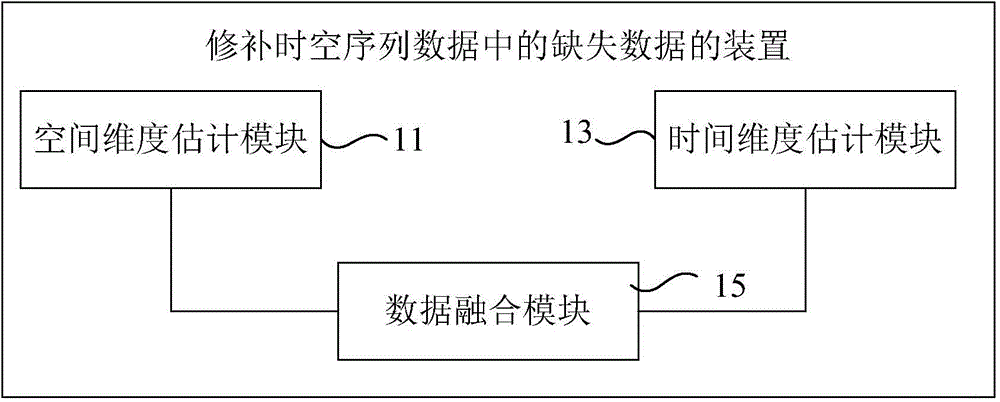
Missing data repairing method and device in time-space sequence data
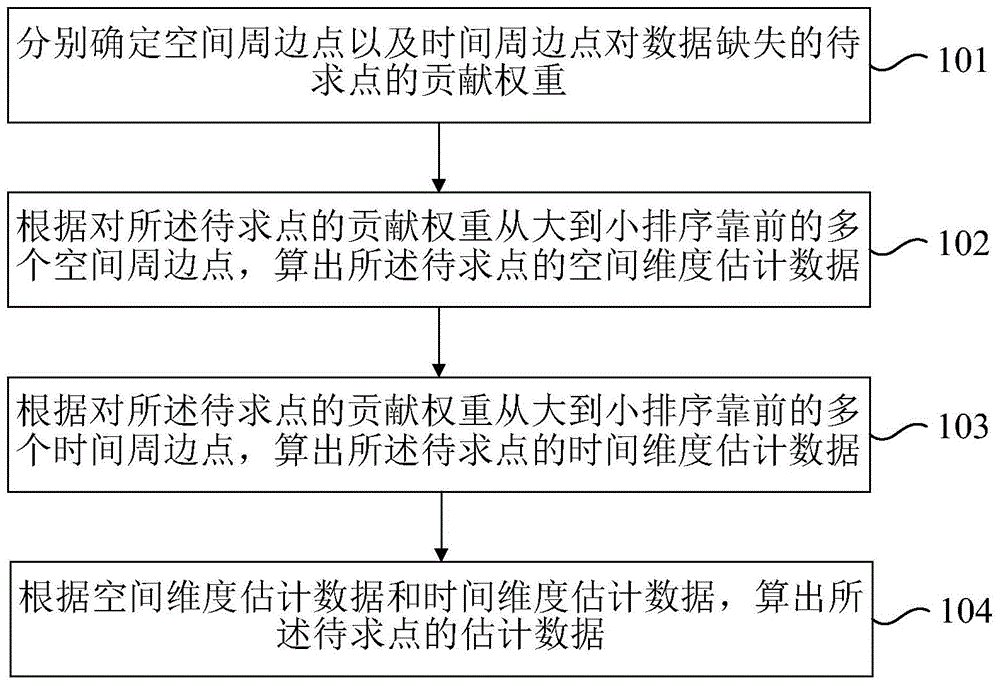
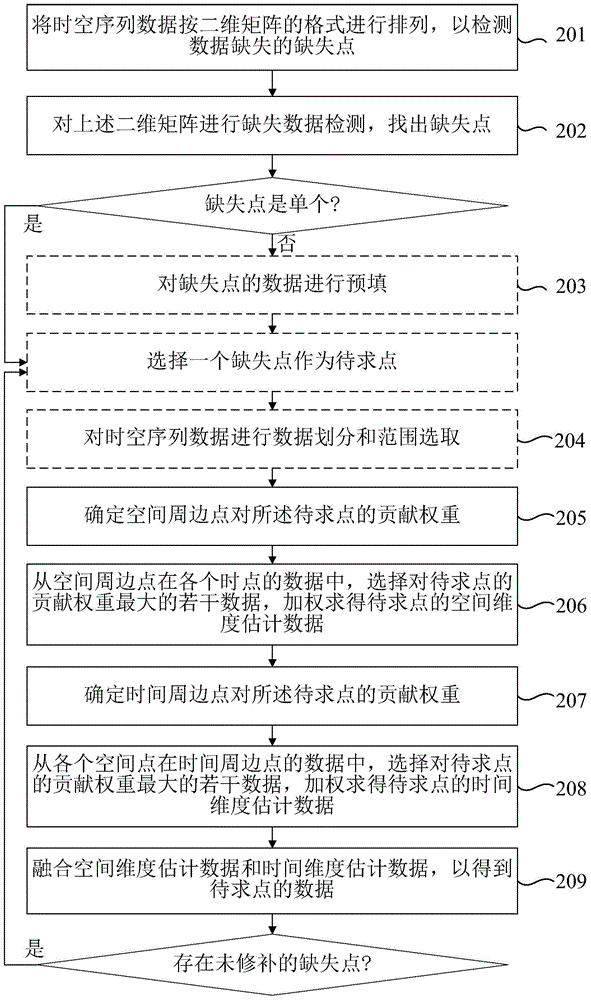
The present invention relates to a method and device for repairing missing data in time-space sequence data, wherein the method includes: separately determining the contribution weights of space peripheral points and time peripheral points to the missing data points; The contribution weights of the points are sorted from large to small, and the spatial dimension estimation data of the points to be obtained are calculated; according to the contribution weights of the points to be obtained, the first multiple points are sorted from large to small Calculate the estimated data of the time dimension of the point to be sought for the surrounding points in time; calculate the data of the point to be sought based on the estimated data of the spatial dimension and the estimated data of the time dimension. The invention makes full use of the time-space correlation and heterogeneity of the time-space sequence data, and the obtained data of the point to be sought has high precision.
Owner:NEC CORP
Specific culture medium for lung tumor organ and stentless 3D culturing method
ActiveCN110592022AStrong cell stemnessRetain heterogeneityCulture processCell culture active agentsY-27632HEPES
The invention discloses a specific culture medium for a lung tumor organ and a stentless 3D culturing method. The specific culture medium is prepared from the following components: FBS, double antibody, N-2, Noggin, B-27, EGF, FGF-10, Y-27632, A 83-01, SB202190, N-acetylcysteine, HEPES, Glutamax, IGF-1, hydrocortisone and Advanced DMEM / F12. The culturing method comprises the following steps: adding a tumor cell into a low serum culture medium, re-suspending the tumor cell, inoculating the tumor cell into a culture vessel, adding the specific culture medium into the culture vessel, changing thespecific culture medium once a day, and performing culturing until an organoid is formed. According to the culture medium and culturing method, a tumor organoid can quickly generate, can be stably cultured for a long time, is regular in spheroid form and has uniform and controllable size, and the heterogeneity of a tumor tissue of a patient can be well maintained in vitro.
Owner:浙江弘瑞医疗科技有限公司
Methods for diagnosis, prognosis and methods of treatment
The present invention provides an approach for the determination of the activation states of a plurality of proteins in single cells. This approach permits the rapid detection of heterogeneity in a complex cell population based on activation states, expression markers and other criteria, and the identification of cellular subsets that exhibit correlated changes in activation within the cell population. Moreover, this approach allows the correlation of cellular activities or properties. In addition, the use of modulators of cellular activation allows for characterization of pathways and cell populations. Several exemplary diseases that can be analyzed using the invention include AML, MDS, and MPN.
Owner:NODALITY
Method and system for diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders including chronic alcoholism
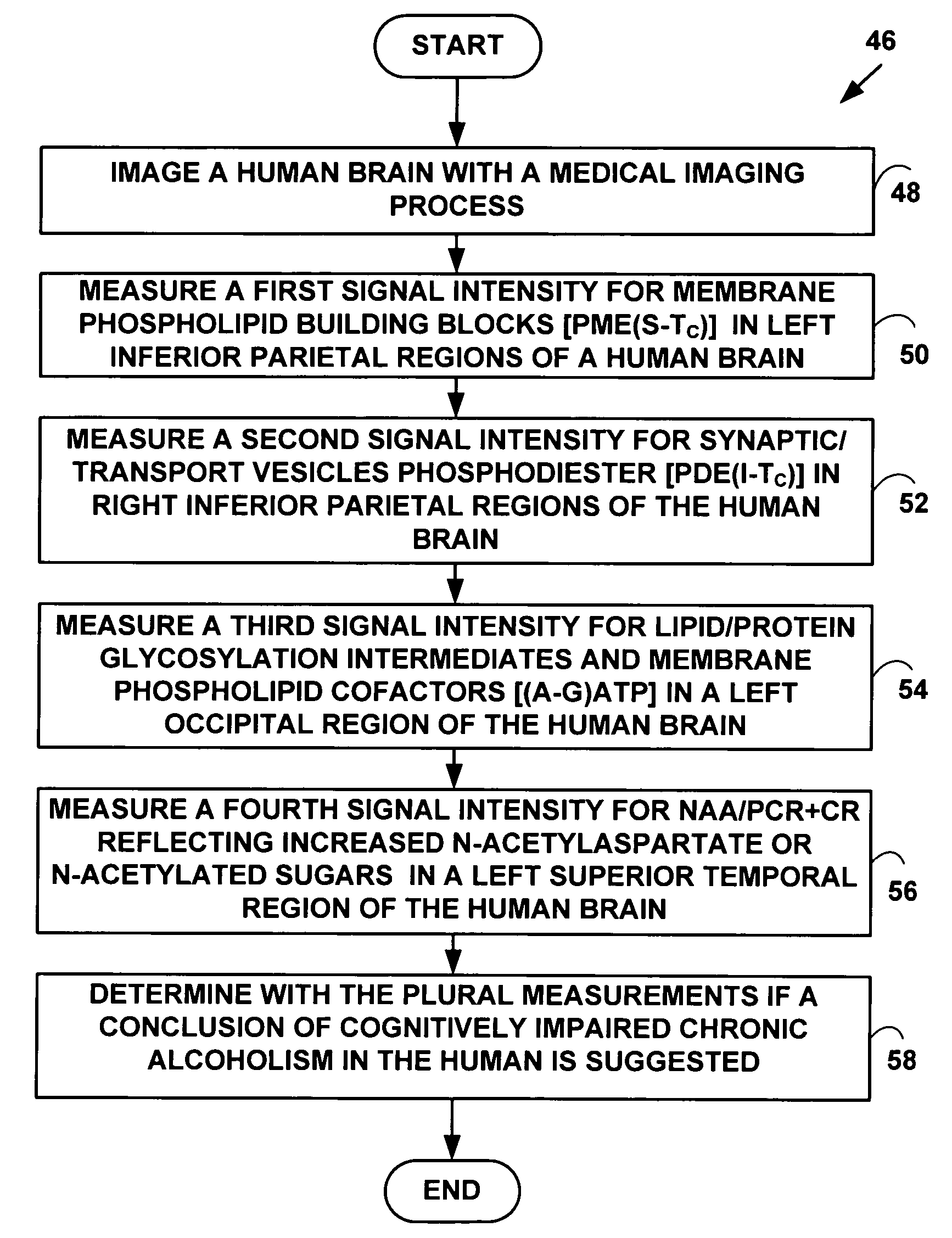
InactiveUS20060292547A1Neurological deficit scoreNavigation performance in was impairedBiocideMagnetic measurementsDiseaseLipid formation
Chronic alcoholism is a diverse and heterogeneous disorder that can be dichotomized into cognitively intact and cognitively impaired subgroups. At a molecular level, ethanol has been shown to have both acute and chronic effects on: Membrane biophysical properties, Membrane composition and metabolism, Protein phosphorylation, Lipid metabolic signaling, Lipoprotein transport of cholesterol. Actual molecular underpinnings are determined for cognitive impairment seen in some chronic alcoholism subjects including molecular / metabolic alterations of phospholipid and ganglioside metabolisms.
Owner:PETTEGREW JAY W +1
Near infrared fluorescent dye with tumor specificity targeting performance and applications thereof
InactiveCN104312194AWith imagingFunctionalMethine/polymethine dyesIn-vivo testing preparationsFluorescenceMolecular imaging
The invention provides a near infrared fluorescent dye with a tumor specificity targeting performance and applications thereof. The near infrared fluorescent dye is NIR dye PC-002, and can be automatically absorbed and accumulated by canine tumor cells; and the dye can be specifically accumulated in the tumor parts, and will not absorbed by the normal cells, so the dye can be used for tumor specificity target molecule imaging. The NIR specific combining between the near infrared fluorescent dye and the tumor cell is achieved by activating a HIF1[alpha] / OATPs signal molecule and oxygen deficiency. Heterogeneity of tumor cells is overcome, specific target molecule conjugate with common characters can be designed according to the characteristics of oxygen deficiency and OATP high expression of tumor cells, and through the observation on specific combining between the NIR dye and other tumor cells, the near infrared imaging technology can be applied to early warning and rapid diagnosis of more tumors.
Owner:师长宏 +3
Lung cancer organ model and application thereof in tumor research
PendingCN109554346AFast and efficient buildPreserve genetic informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningAbnormal tissue growthCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a lung cancer organ model and an application thereof in tumor research. An establishment method of the lung cancer organ model comprises the steps as follows: (1) lung cancer tumor cells are added to a three-dimensional culture medium for culture, and the lung cancer tumor cells are added to a culture medium to be continuously cultured after a tumor layer is formed, whereinthe culture medium contains growth factors and extracellular matrix suitable for growth lung cancer tumor cells; (2) a system obtained through culture in step (1) forms single cell after protease enzymolysis, resuspension is performed by the culture medium after separation, and then, the lung cancer organ model is obtained. By use of the method, a specimen library containing a large number of lung cancer organ models can be established, heterogeneity and diversity of lung cancer are greatly covered, the defect of insufficient representativeness of traditional lung cancer cell lines is effectively overcome, and the lung cancer organ model becomes an efficient platform for research of occurrence and development mechanisms of lung cancer.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Homogeneous antibody populations
InactiveUS20130144041A1Efficient and economic productionEasy to eliminateNervous disorderAntipyreticMonoclonal antibodyHinge region
The present invention is generally directed to methods of producing an increase in the enrichment and / or recovery of preferred forms of monoclonal antibodies. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for eliminating disulfide heterogeneity in the hinge region of recombinant IgG2 antibody proteins.
Owner:AMGEN INC
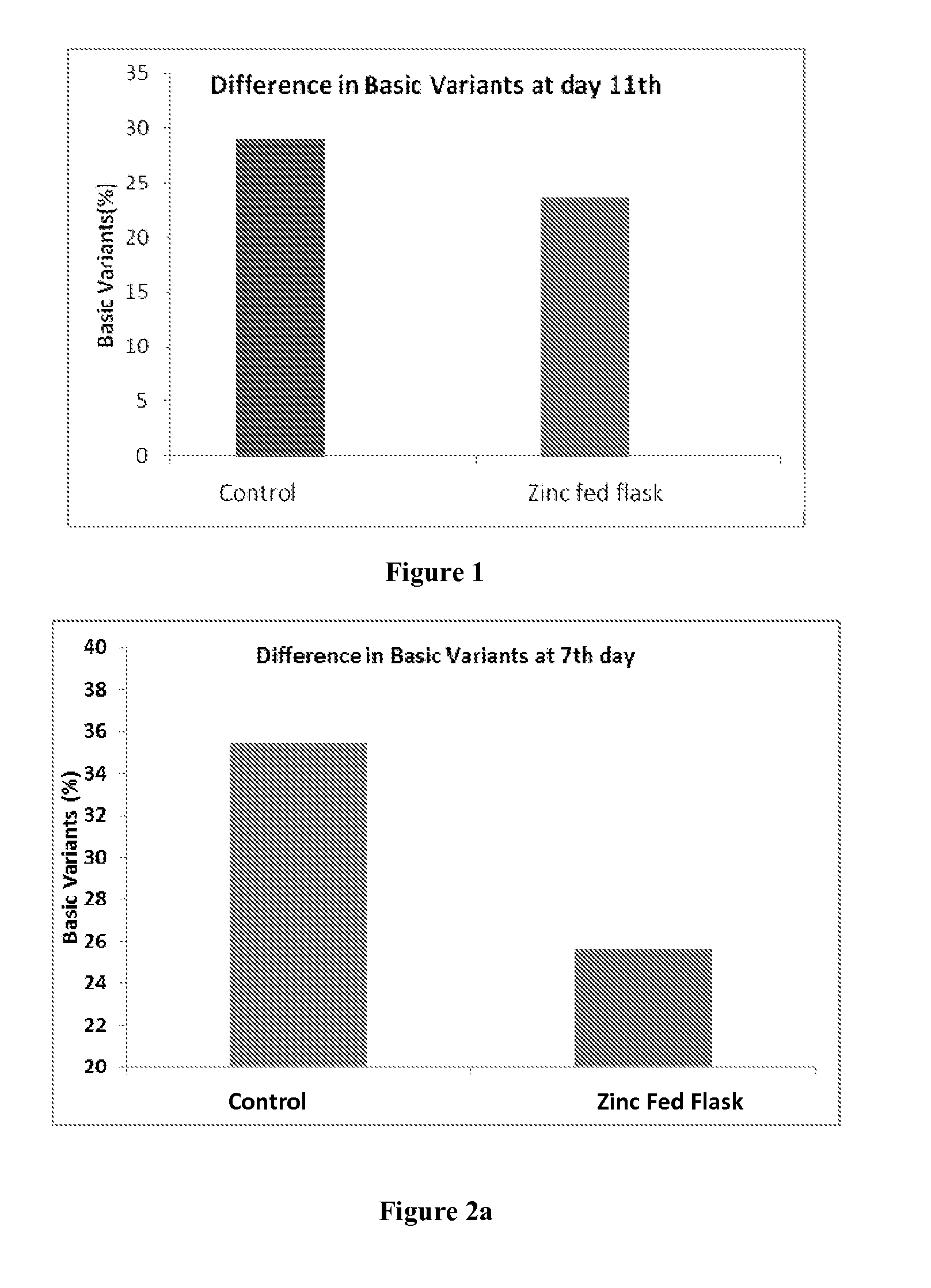
Method for Reducing Heterogeneity of Antibodies and a Process of Producing the Antibodies Thereof
ActiveUS20140199729A1Low heterogeneityAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCulture cellCell culture media
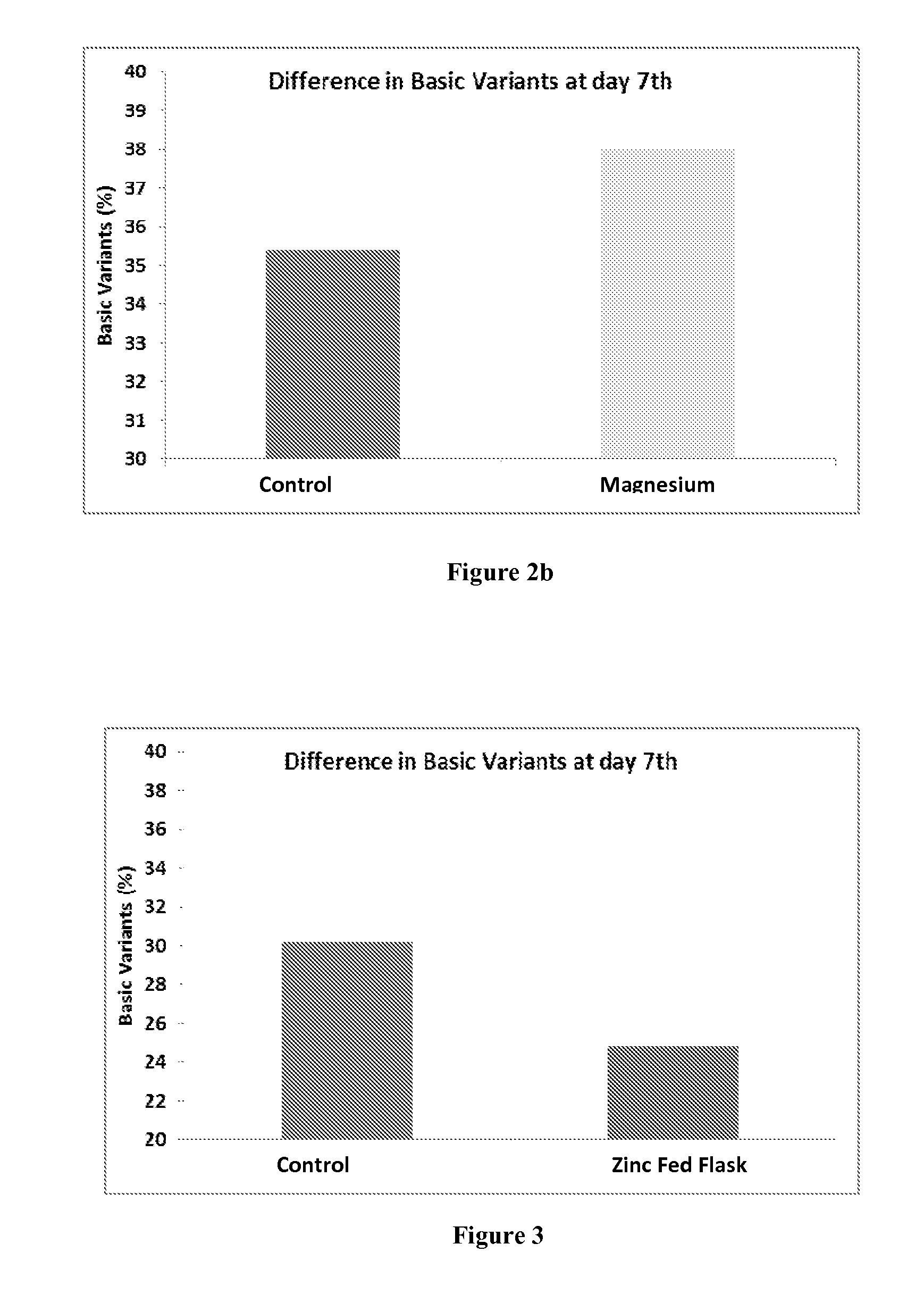
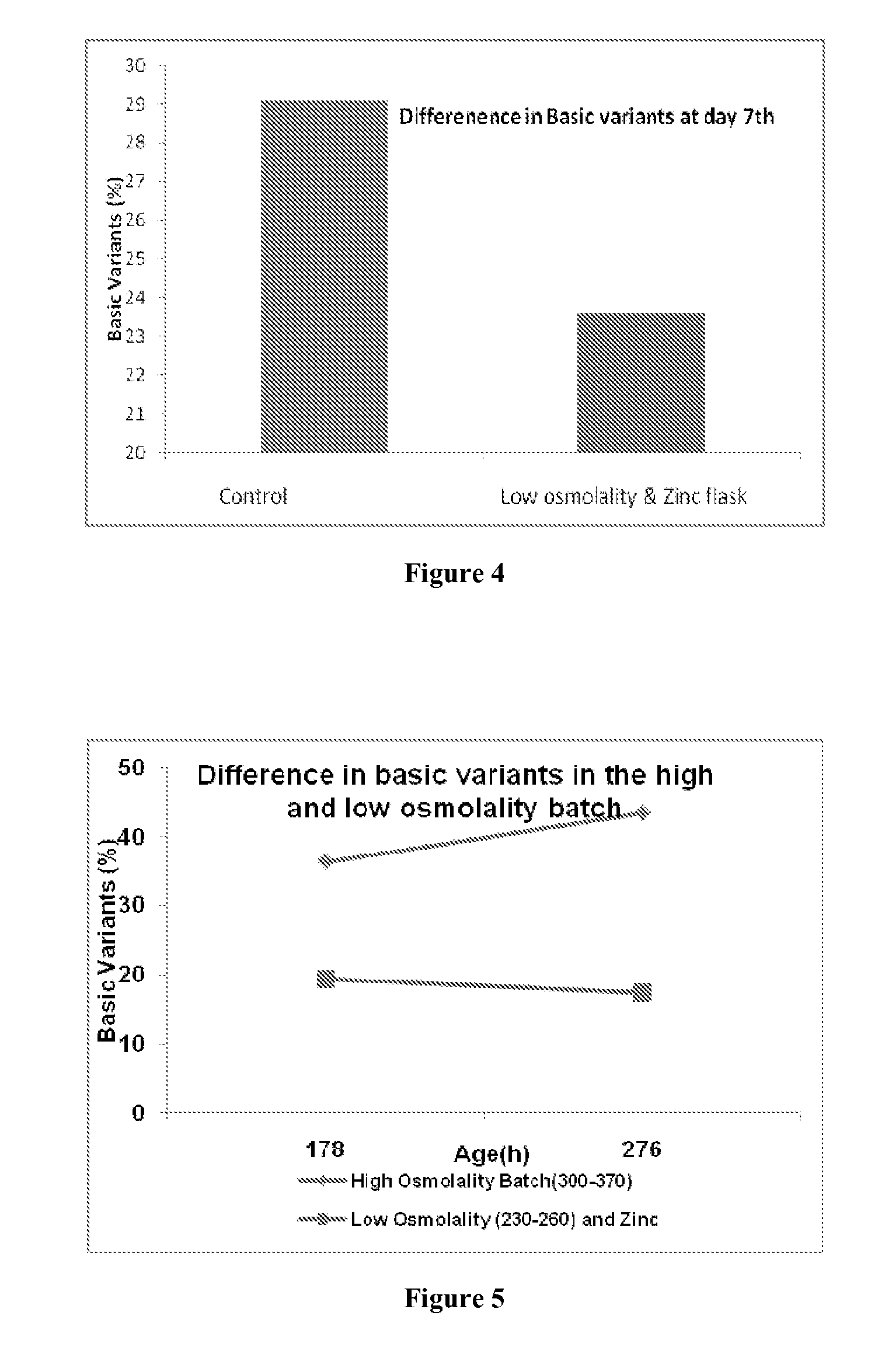
The present disclosure relates to a method of reducing heterogeneity in antibodies during culturing, wherein the heterogeneity is due to proportion of charge variant of the antibody. The disclosure also comprises a process of growing cells in a cell culture system that results in antibodies with the reduced heterogeneity. In one embodiment antibody heterogeneity is reduced by the addition of divalent transitional metal ions such as zinc (Zn2+) to the cell culture medium. In another embodiment antibody heterogeneity is reduced by decreasing the osmolality of the cell culture medium.
Owner:BIOCON BIOLOGICS INDIA LTD
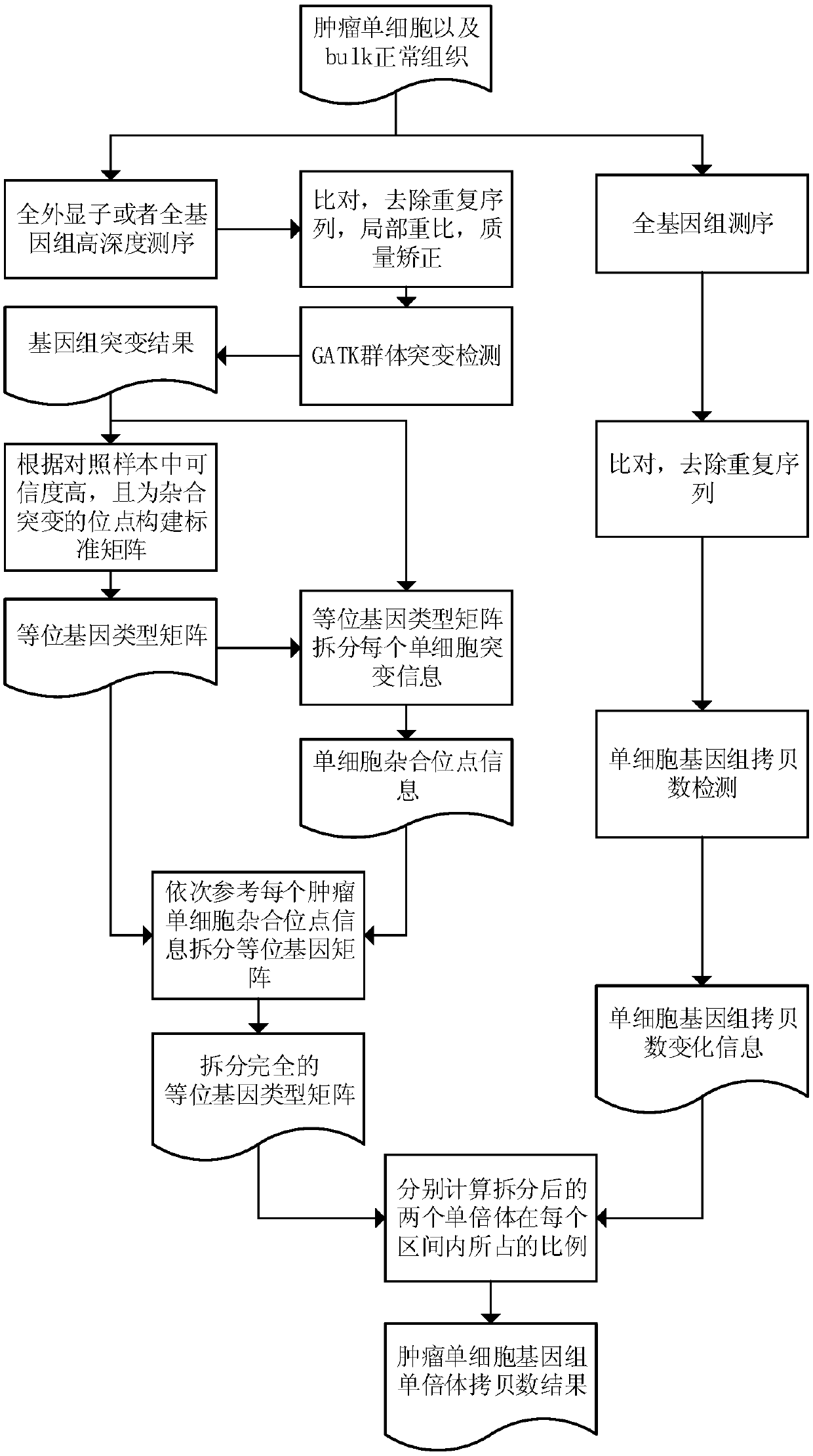
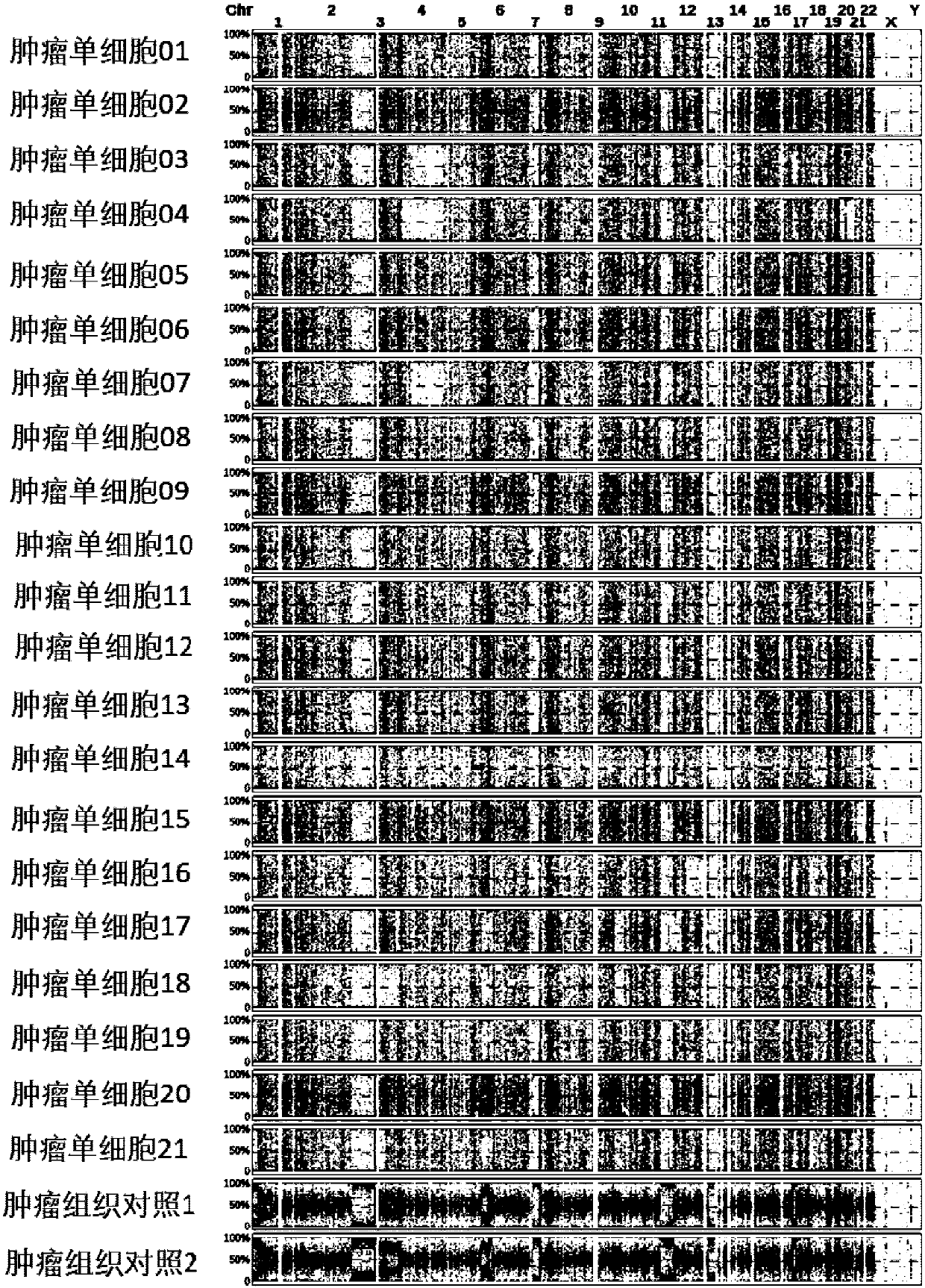
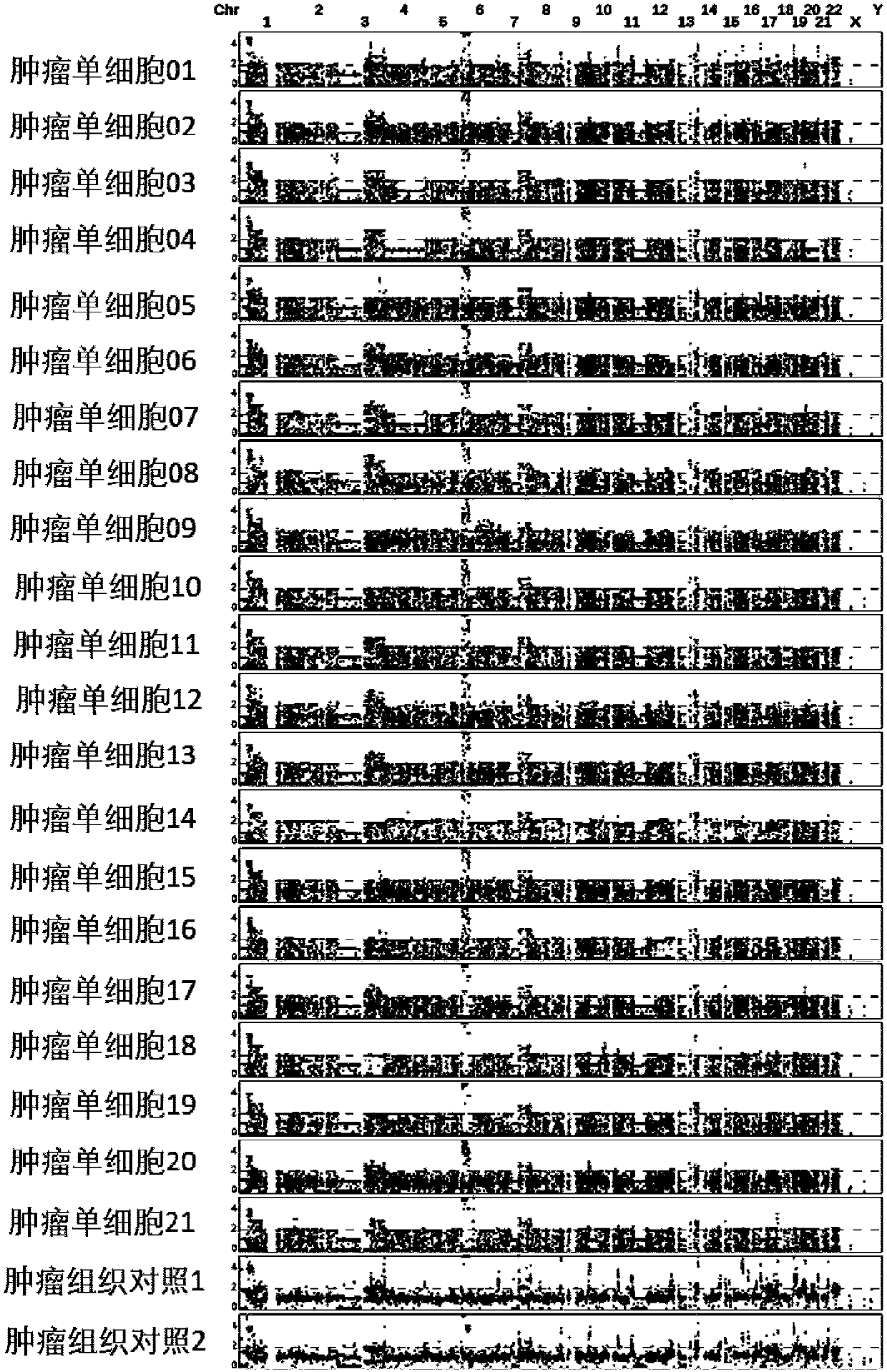
Method for detecting haploid copy number variation of tumor unicell genome
The invention discloses a method for detecting haploid copy number variation of tumor unicell genome. The method combines the population polymorphism site information of the tumor unicell and the change information of the genome copy number to analyze an abnormal region of the tumor unicell genome allele copy number, Compared with simple genome copy number changes or somatic mutations, one more dimension is increased, different unicell alleles can be effectively distinguished to from a zone with proportion abnormity, which has important significance for describe the heterogeneity of tumor genome and tumor genome evolution information.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Quantitation of RNA transcripts using genomic DNA as the internal amplification competitor
InactiveUS6063568ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid amplification techniqueIntein
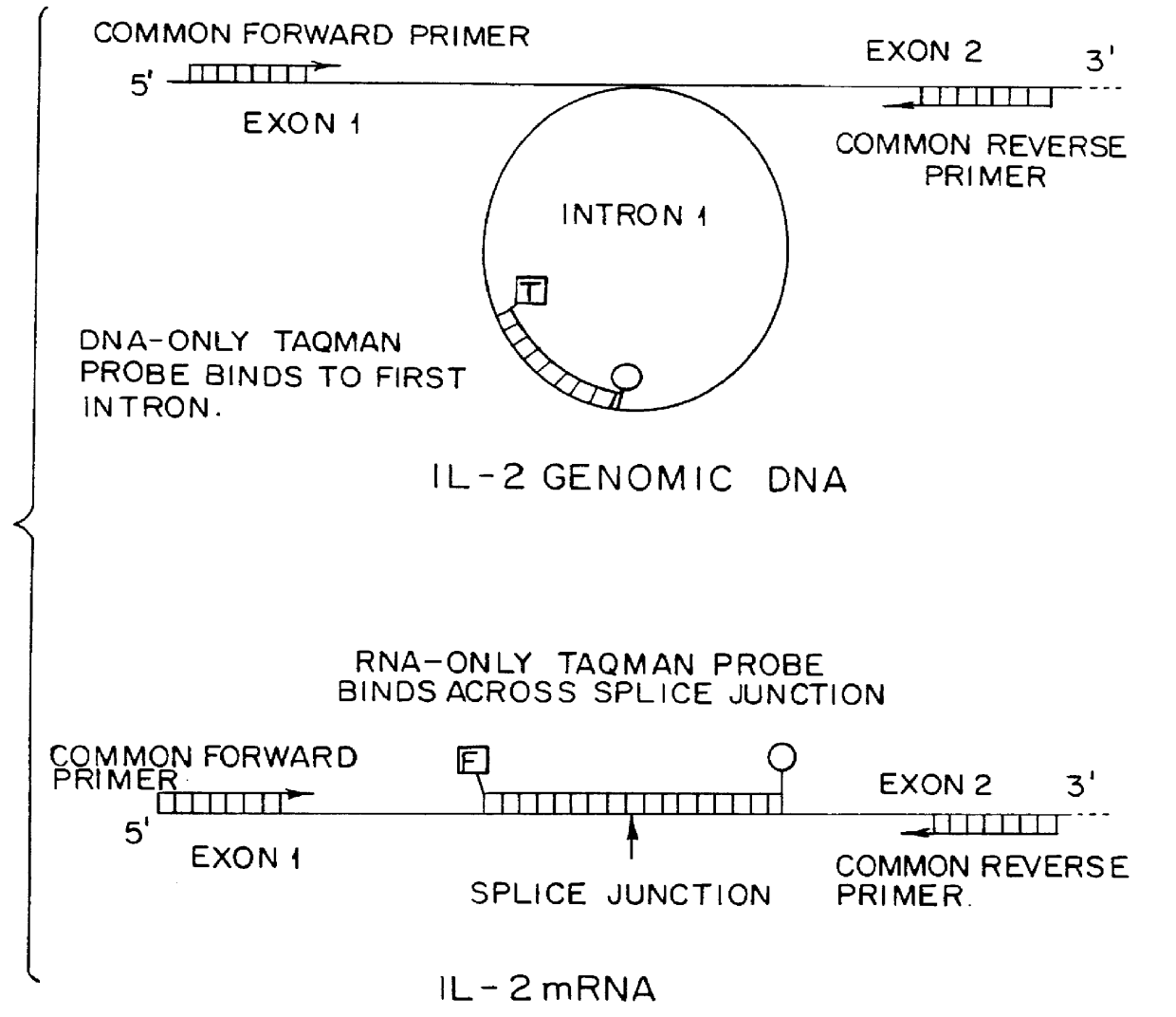
A method for the quantitative monitoring of gene expression without either co-amplification of an added template or use of an endogenous constitutive transcript is provided. The process involves a duplex amplification reaction in which a single set of primers is used to amplify both genomic DNA and expressed mRNA from the same gene sequence. These primers are targeted for sequences flanking the splice junction / intron sequences for the mRNA / DNA respectively. By their use, any suitable nucleic acid amplification technology yields mRNA and DNA amplimers which are distinguishable by length and sequence heterogeneity. These amplimers are present in the final amplification reaction in ratios which are dependent upon the ratios of the expressed mRNA to the DNA in the sample, allowing the quantitation of mRNA in a sample which is normalized to the number of copies of genomic DNA since the genomic DNA acts as the internal quantitation standard, and in effect yields the amount of mRNA per cell. Any detection methodology which can detect amplimers of different lengths or sequences can be used for post amplification quantitation. This strategy may be employed for any gene system in which the mRNA sequence differs from the original genomic DNA sequence. The invention may be used, for example, in the determination of gene expression in both research and commercial applications.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com