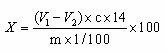Patents
Literature
178 results about "Gamma irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
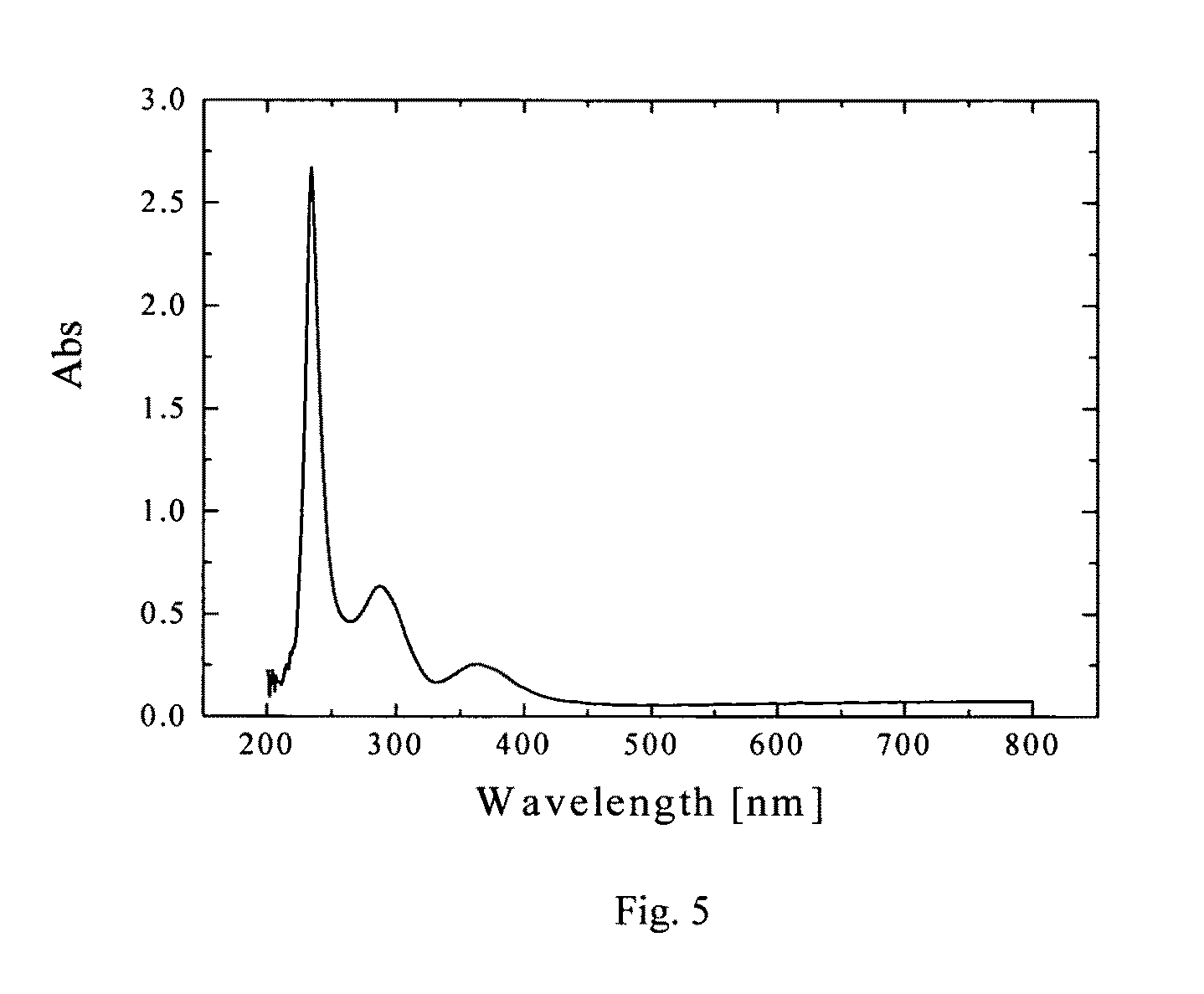
Gamma Irradiation. A form of electromagnetic energy characterized by its deep penetration and low-dose rates, Gamma irradiators are powered by Cobalt-60, effectively killing microorganisms throughout the product and its packaging with very little temperature effect and no residues. The amount of radiation received depends on the type...
Sterilization of dispersions of nanoparticulate active agents with gamma radiation
The present invention relates to methods for sterilization of dispersions of one or more nanoparticulate active agents via gamma irradiation.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
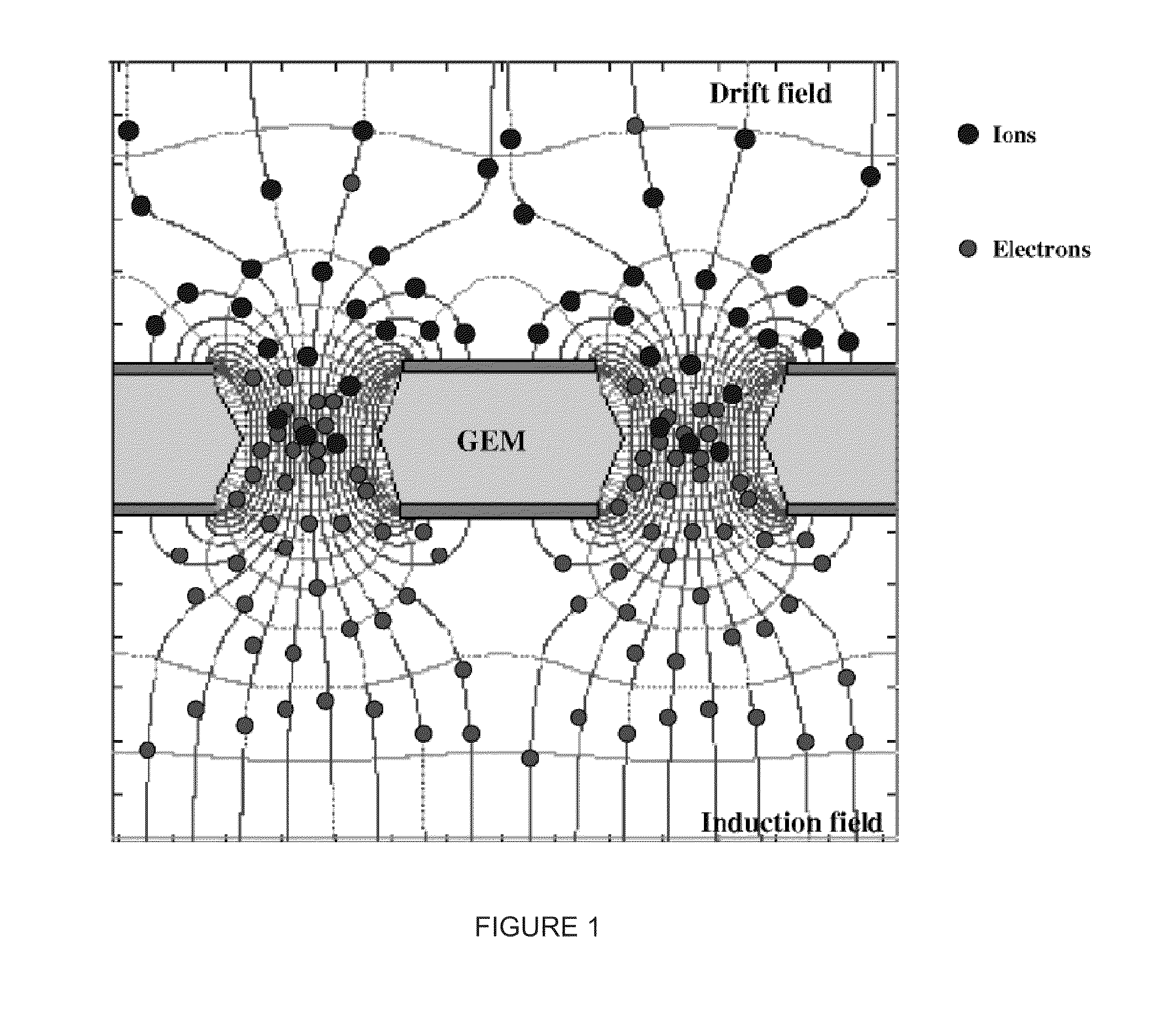
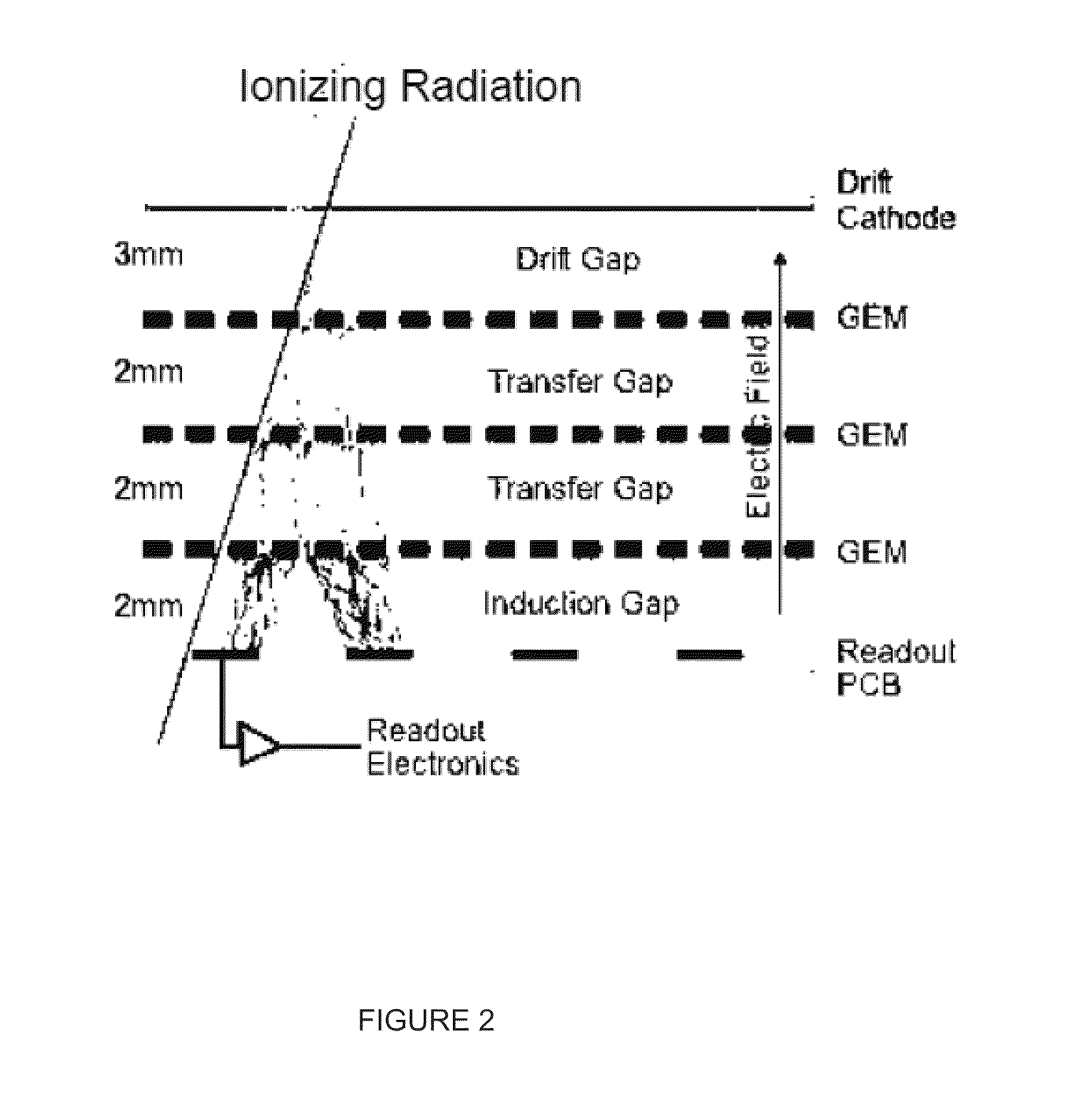
Apparatus, method and system for measuring prompt gamma and other beam-induced radiation during hadron therapy treatments for dose and range verification purposes using ionization radiation detection
InactiveUS20110284757A1Easy to detectElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansCritical structureGamma irradiation
An apparatus, method and system for measurement of radiation during or directly following hadron therapy treatment for dose and range verification purposes accomplished through measurement of prompt gamma and other beam-induced radiation. One example includes the measurement of secondary prompt gamma radiation during proton and carbon ion beam irradiation. The measurement can also be made of other beam-induced radiation results. The measurement of gamma radiation or other beam-induced radiation allows for optimization of radiation dose disposition to the target tissue, with improved sparing of surrounding critical structures and normal tissue. Adjustments to a radiation treatment may be made as needed based on actual and measured applied dosages.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
Cancer treatments
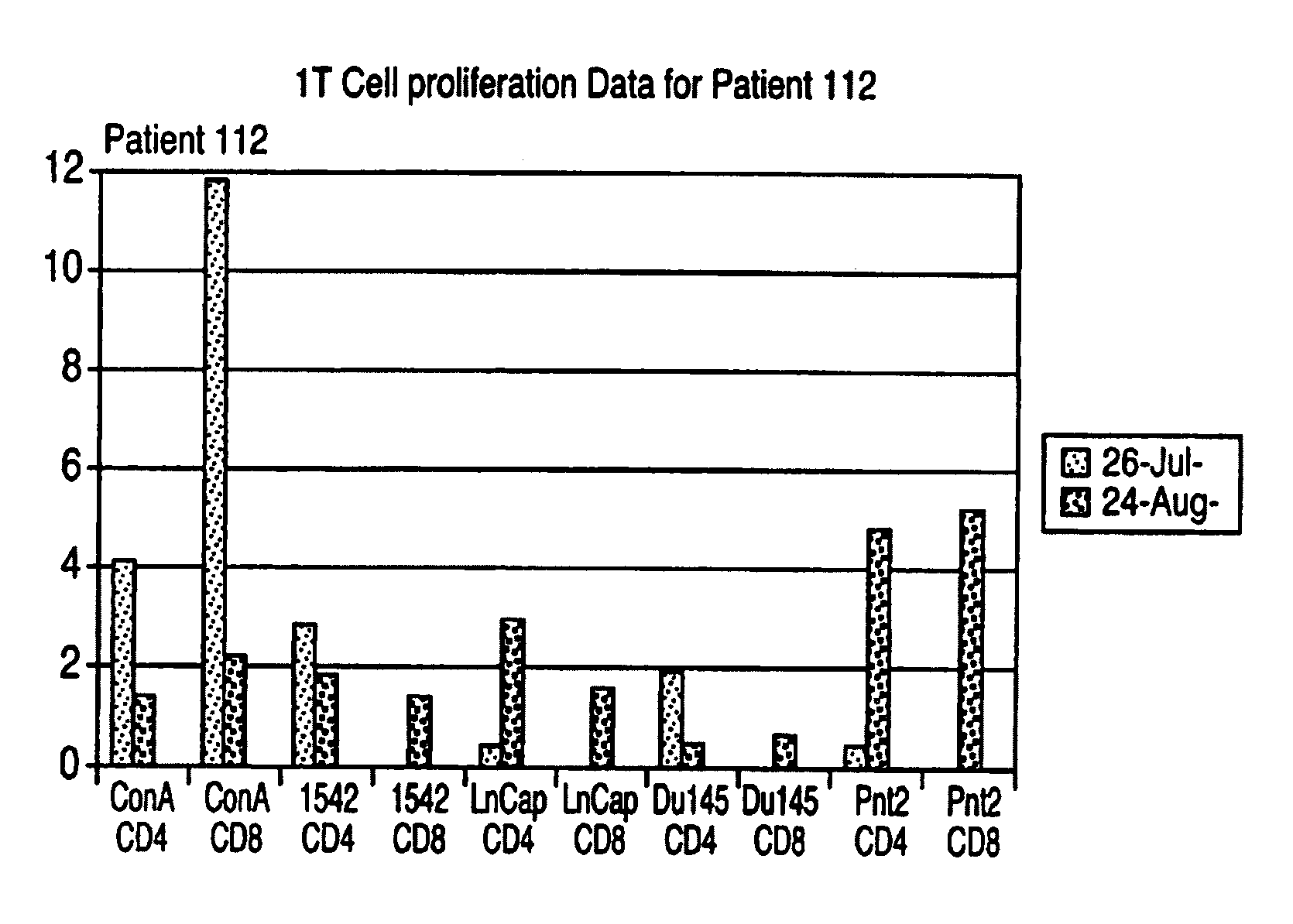
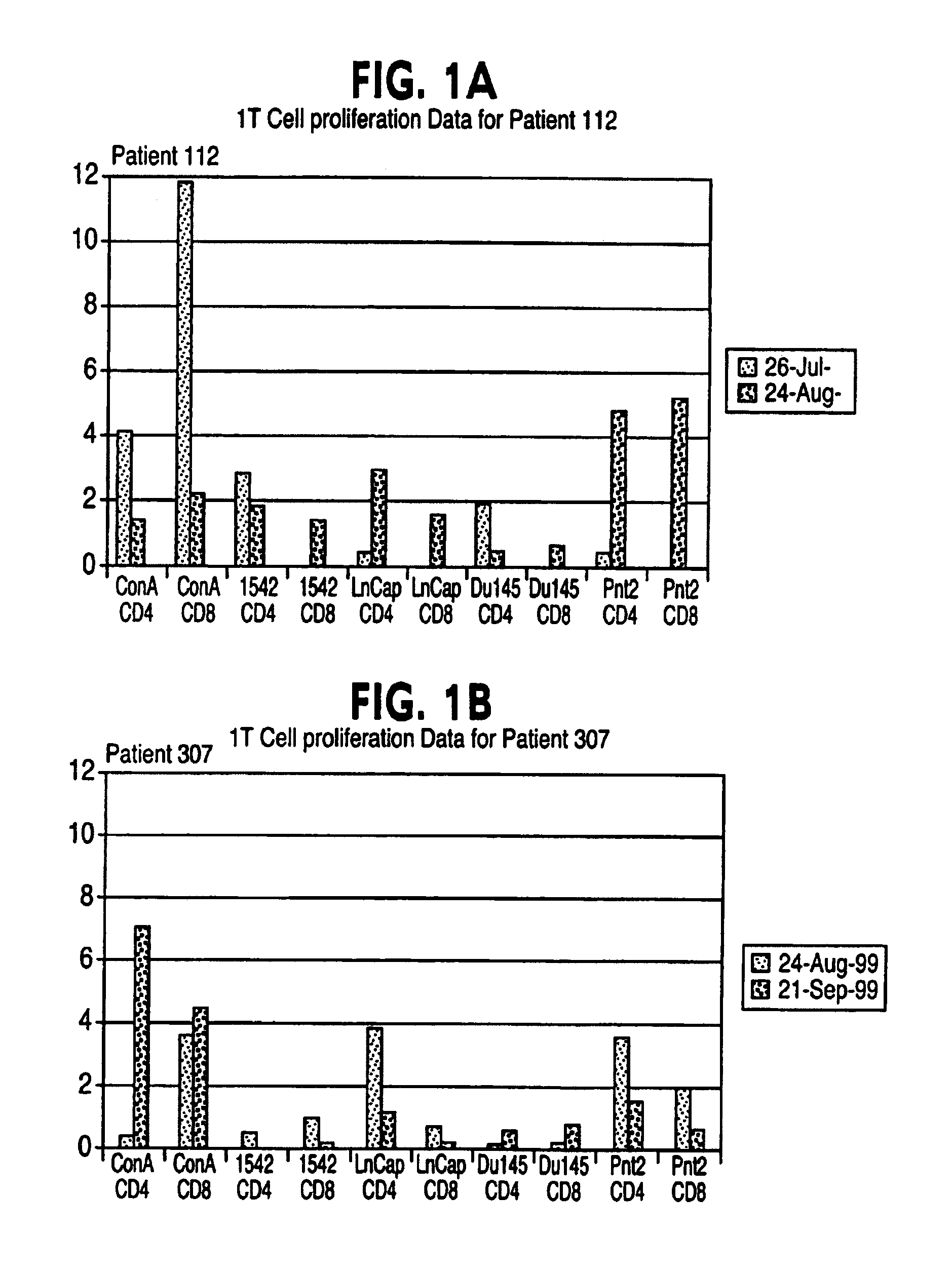
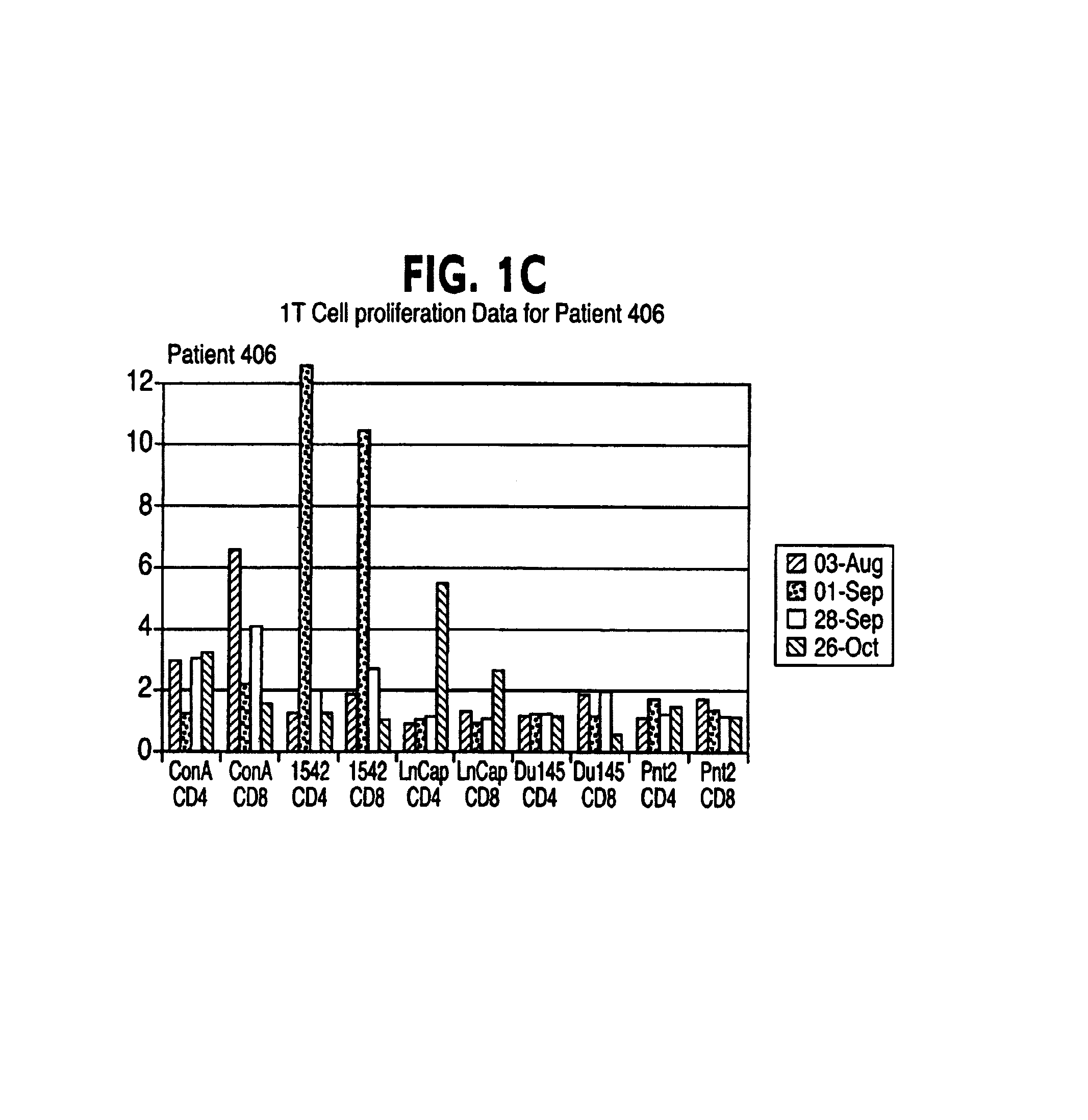
The invention relates to a product comprised of specific combinations of cell lines intended for use as an allogeneic immunotherapy agent for the treatment of prostate cancer in humans. The heterogeneity of the immunotherapeutic matches the heterogeneity of the antigenic profile in the target prostate cancer and immunises the recipients with many of the potential TAA and TSA which are expressed at various stages of the disease. The invention discloses a vaccine comprising a combination of three different cell lines prepared from primary or metastatic prostate cancer biopsy material. The cell lines are lethally irradiated utilising gamma irradiation at 50-300 Gy to ensure that they are replication incompetent.
Owner:ONYVAX
Halide-based scintillator nanomaterial
ActiveUS20100001209A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduced dosLuminescent dosimetersGlass/slag layered productsAlkaline earth metalGamma irradiation
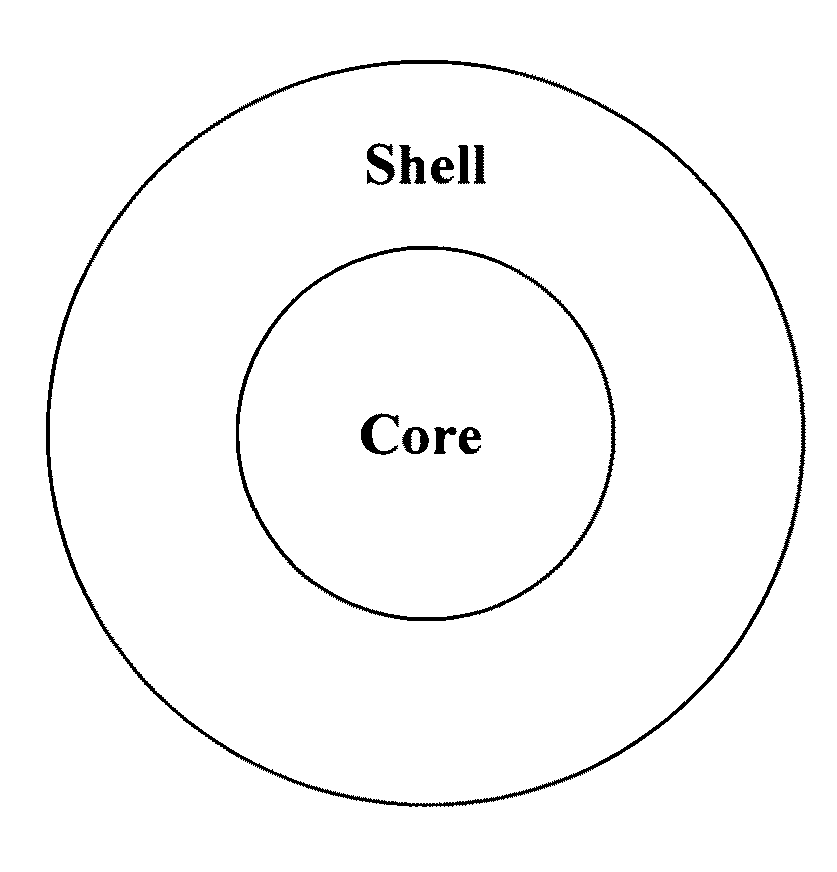
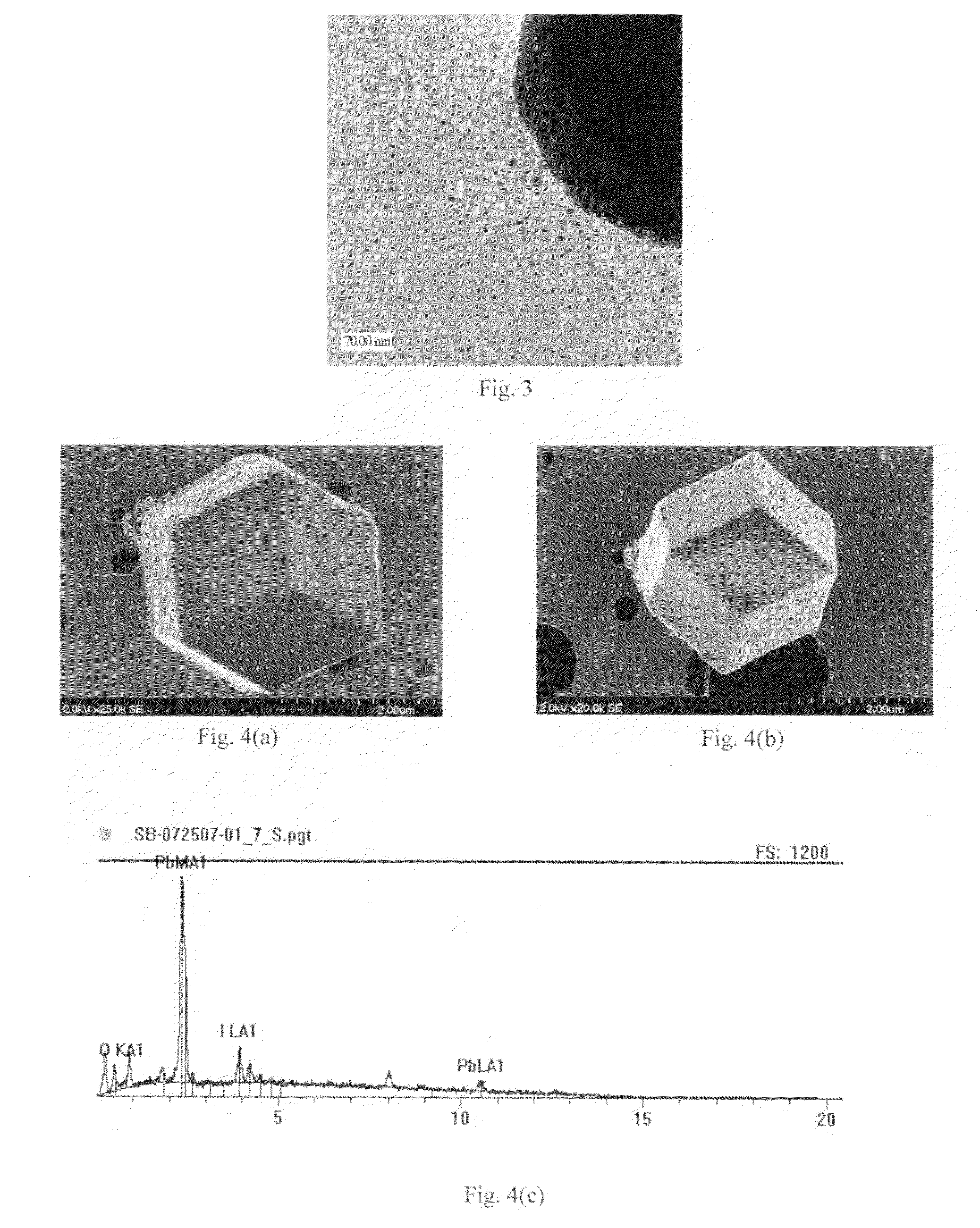
Scintillator material comprising nanoparticles (nanocrystals) comprising lead (Pb), iodine (I), and optionally one or both of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) wherein the nanoparticles exhibit room-temperature scintillation under gamma irradiation. The scintillator nanoparticles can comprise Pb3O2I2. The scintillator nanoparticles can comprise PbIOH in generally equiatomic proportions or non-equiatomic variants thereof that exhibit scintillation under gamma irradiation. The scintillator nanoparticles have a particle dimension in the range of about 5 to about 100 nm. Microparticles (microcrystals) also are provided comprising lead (Pb), iodine (I), and optionally one or both of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) grown in a nanoparticle colloidal solution over time to a particle dimension greater than 0.1 μm, such as about 2 microns. A heterogeneous scintillator material is provided comprising core / shell nanoparticles having a highly hygroscopic or deliquescent halide-based core activated with trivalent Ln3+ or divalent Ln2+ lanthanide ions (Ln=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) and a stable non-hygroscopic shell thereon. The heterogeneous nanoparticles can comprise highly hygroscopic lanthanide halide (LaBr3, LuI3) cores protected with stable non-hygroscopic LaF3 shells. The heterogeneous nanoparticles can comprise deliquescent alkaline earth halide (SrI2, BaI2) cores protected with stable non-hygroscopic (SrF2, BaF2) shells.
Owner:STC UNM
Method to reduce damage caused by irradiation of halogenated polymers
InactiveUS20050279054A1Not easy to deteriorateSynthetic resin layered productsPackage sterilisationScavengerGamma irradiation
A method for producing a polymeric film resistant to degradation during sterilization such as gamma irradiation is presented. The method includes the steps of minimizing the number of free radicals formed during sterilization through use of an inert gas and a reactant scavenger within a sterilization pouch, which reactant scavenger may be acid adsorbents which scavenge the acid by-products formed during irradiation. The films retain physical and mechanical properties with long-term storage. The films are particularly amenable for use as packaging laminates in pharmaceutical, food, semiconductor and medical device industries.
Owner:ARADIGM
Method to reduce damage caused by irradiation of halogenated polymers
InactiveUS6933026B2Deteriorate with timeNot easy to deteriorateSynthetic resin layered productsPackage sterilisationScavengerGamma irradiation
A method for producing a polymeric film resistant to degradation during sterilization such as gamma irradiation is presented. The method includes the steps of minimizing the number of free radicals formed during sterilization through use of an inert gas and a reactant scavenger within a sterilization pouch, which reactant scavenger may be acid adsorbents which scavenge the acid by-products formed during irradiation. The films retain physical and mechanical properties with long-term storage. The films are particularly amenable for use as packaging laminates in pharmaceutical, food, semiconductor and medical device industries.
Owner:ARADIGM
Gamma-stable high pressure stopcock
InactiveUS6880808B2Improve fitDifferent melting pointPlug valvesThin material handlingGamma irradiationStopcock
A medical stopcock is provided that is constructed and arranged to withstand high pressures and gamma irradiation. The stopcock generally includes a housing and a valve member. The valve member is trapped within the housing so that, when subjected to relatively high pressures, the valve member is unlikely to become separated from the housing. A handle member is attached to the valve member and allows the valve member to be rotated from open to closed positions. In some preferred embodiments, the handle member locks the valve member within the housing, when attached. All of the components are constructed of gamma-stable materials so that the stopcock may be sterilized, in its package, using gamma irradiation.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Methods of sterilizing elastomeric sealing articles
ActiveUS20070053788A1Maintaining percentage strainAvoid timeLavatory sanitoryIntravenous devicesPolymer scienceGamma irradiation
The present invention provides a method sterilizing butyl rubber / styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) articles used in syringes or medical containers, comprising irradiating the butyl rubber / SBR elastomeric copolymer rubber article with gamma irradiation, wherein the SBR elastomeric copolymer comprises about 5% to about 50% of the rubber composition on a basis of total weight of the composition; and then exposing the irradiated rubber composition to a sterilizing gas for a time period sufficient to sterilize the rubber composition. The irradiated, sterilized rubber composition of the present invention is capable of maintaining superior performance standards with respect to sealability, recoverability from stress and elasticity.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
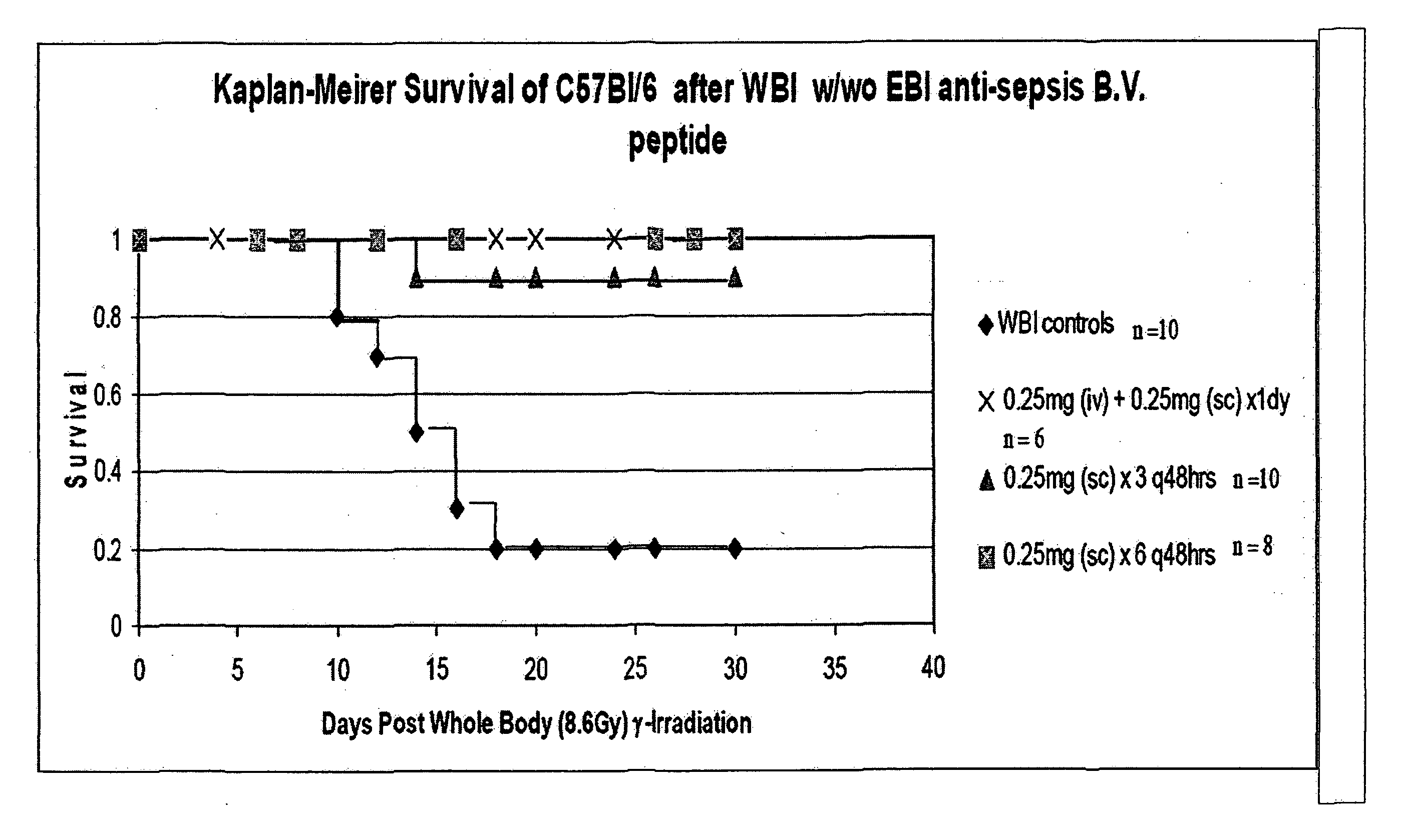
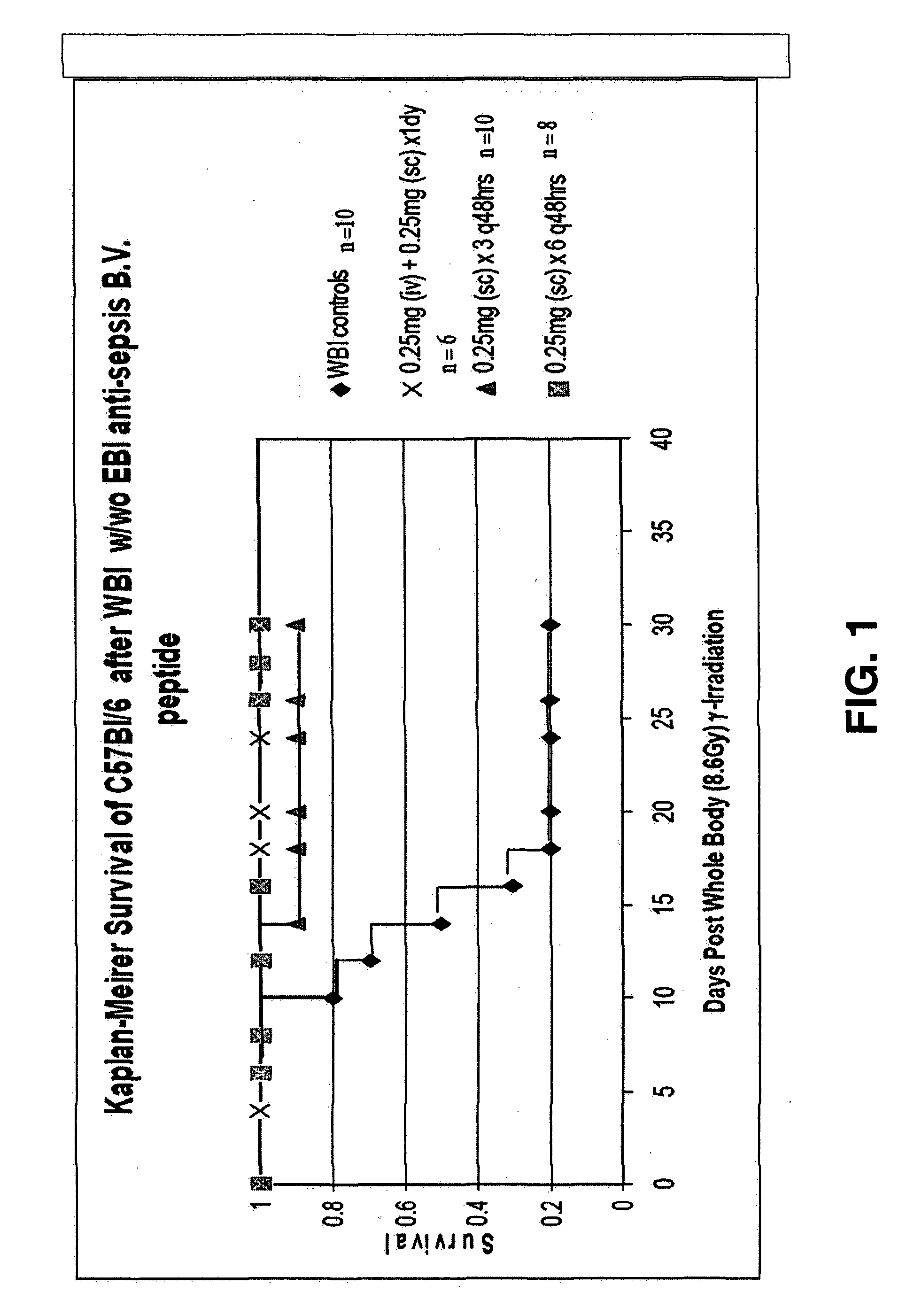
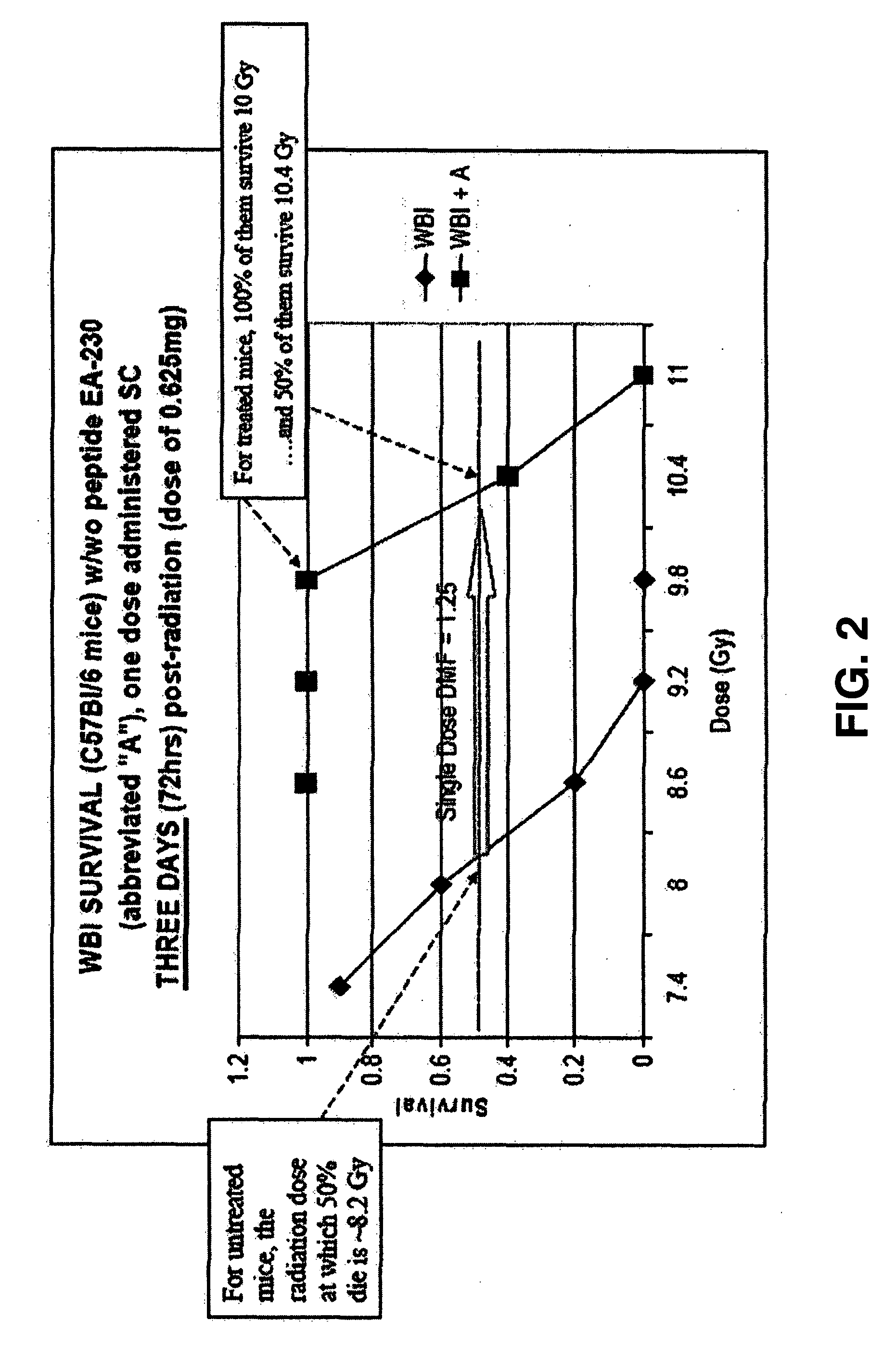
Control of radiation injury
ActiveUS20080027007A1Shorten the counting processBad radiation exposureDigestive systemTetrapeptide ingredientsWhole bodyGamma irradiation
The invention relates to the field of drug development against acute radiation injury caused by exposure to high-energy electromagnetic waves (X-rays, gamma rays) or particles (alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons). To date, there is no effective drug to ameliorate radiation injury after accidental exposure to ionizing irradiation. The invention provides a method of treating radiation injury of a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids. Furthermore, the invention provides use of a peptide, or functional analogue or derivative thereof, of smaller than 30 amino acids for the production of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of a subject suffering from or believed to be suffering from radiation injury. In particular, the invention provides anti-radiation peptides having a dose reduction factor (DRF) against acute gamma irradiation of at least 1.10, said DRF determinable by testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a test group of mice treated with said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and, testing which dose of radiation results in 50% mortality at 30 days (LD50 / 30) after whole body radiation (WBI) in a control group of mice treated only with the vehicle of said peptide at 72 hours after WBI and wherein the DRF is calculated by dividing the LD50 / 30 of the peptide-treated animals by the LD50 / 30 of the vehicle-treated animals.
Owner:BIOTEMPT
Terminal sterilization of prefilled containers
InactiveUS20050129569A1Effective sterilizationAvoid adverse reactionsLavatory sanitoryRadiationPolyolefinGamma irradiation
A method for inhibiting adverse reaction of the contents of a prefilled container during a radiation sterilization procedure is disclosed. In the method, a container which is made of a material including a radiation stable polyolefin is prefilled with a medium prior to being subjected to a gamma irradiation sterilization treatment. By using a radiation stable polyolefin material as the container, such as a polyolefin with a radiation stabilizer additive, and by prefilling the container prior to the gamma irradiation treatment, the container can be effectively sterilized without adversely affecting its contents.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Methods of sterilizing elastomeric sealing articles
ActiveUS7758806B2Maintaining percentage strainAvoid timeLavatory sanitoryIntravenous devicesSufficient timePolymer science
The present invention provides a method sterilizing butyl rubber / styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) articles used in syringes or medical containers, comprising irradiating the butyl rubber / SBR elastomeric copolymer rubber article with gamma irradiation, wherein the SBR elastomeric copolymer comprises about 5% to about 50% of the rubber composition on a basis of total weight of the composition; and then exposing the irradiated rubber composition to a sterilizing gas for a time period sufficient to sterilize the rubber composition. The irradiated, sterilized rubber composition of the present invention is capable of maintaining superior performance standards with respect to sealability, recoverability from stress and elasticity.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method for preserving white fish
InactiveCN102578204APlay a health roleInhibition of health benefitsMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsMeat/fish preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentCobalt-60Gamma irradiation
The invention relates to a method for preserving white fish by removing the scales and the internal organs of the white fish, cleaning the whiter fish, cutting into sections, pretreating, preserving and storing at low temperature. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pickling the pretreated white fish with salt and garlic powder for 5-15min, cleaning the white fish, and soaking into a preservative for 20-40min; (2) subjecting the white fished treated in the step (1) to modified atmosphere packaging by using a modified atmosphere packaging machine; and (3) subjecting the packaged white fish to direct gamma irradiation by using a cobalt 60 irradiation source. The method is easy to operate and practical. Due to the adoption of the method, the freshness and the color of the meat of the white fish can be better kept, and the shelf life of the meat of the white fish can be prolonged. The preservative is convenient to use and is safe and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
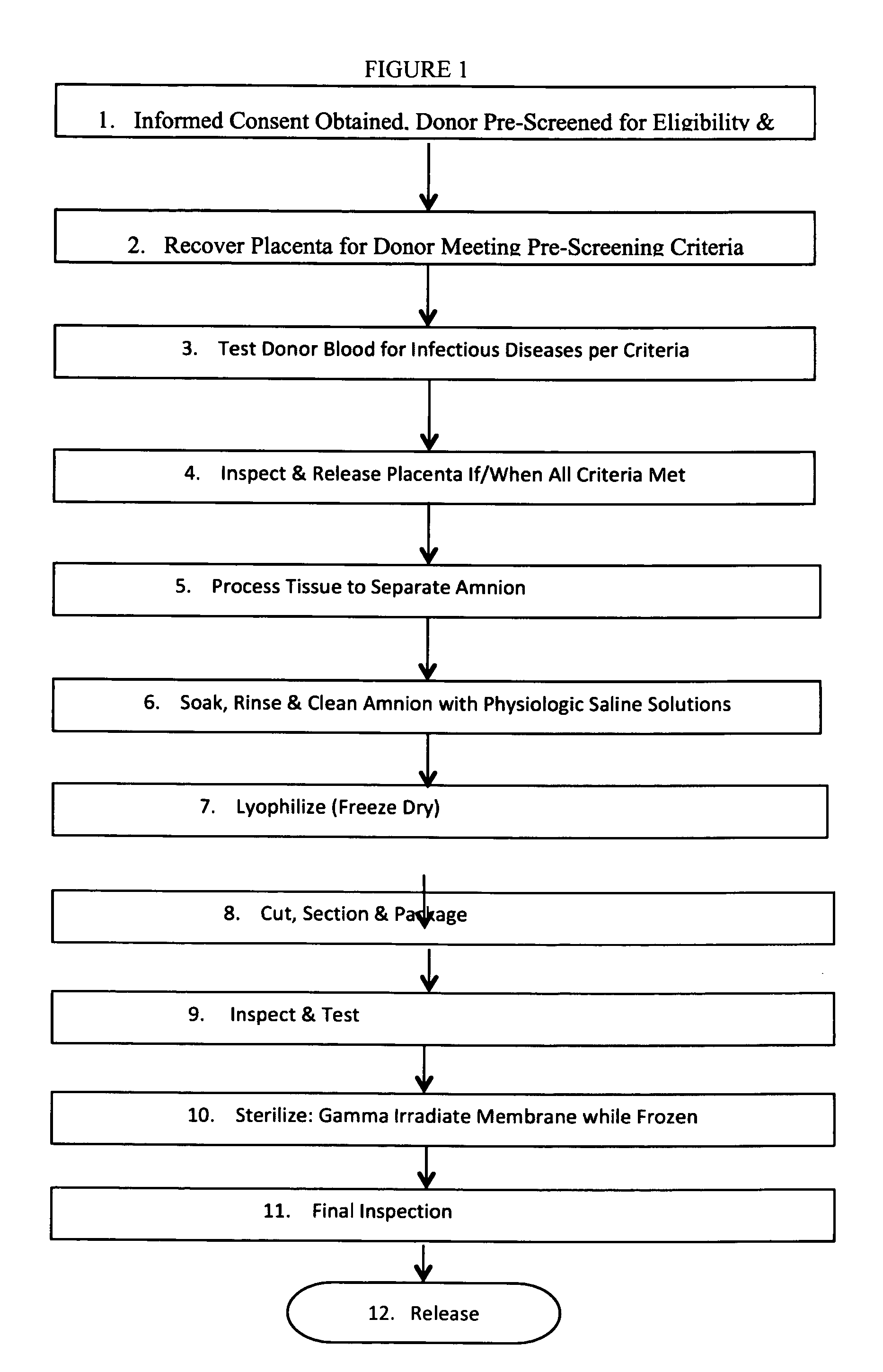
Human Amniotic Membrane Lyophilized Grafts
InactiveUS20140186461A1Retain biological propertiesNeed for refrigerationMammal material medical ingredientsEmbryonic cellsBiological propertyGamma irradiation
Described herein are human amniotic membrane tissue grafts derived from the placenta. The grafts are composed of three layers as seen in the amniotic membrane in utero. These grafts are processed using physiologic solutions, lyophilized and terminal sterilized (via gamma irradiation in a frozen state) that thereby preserves the graft in such a manner as to retain the naturally occurring biological properties of the amniotic membrane and offer a sterile graft for transplantation. By dehydration via lyophilization and terminal sterilization, the graft has the advantage of storage at ambient temperatures for prolonged periods of time prior to transplantation.
Owner:ALPHA TISSUE
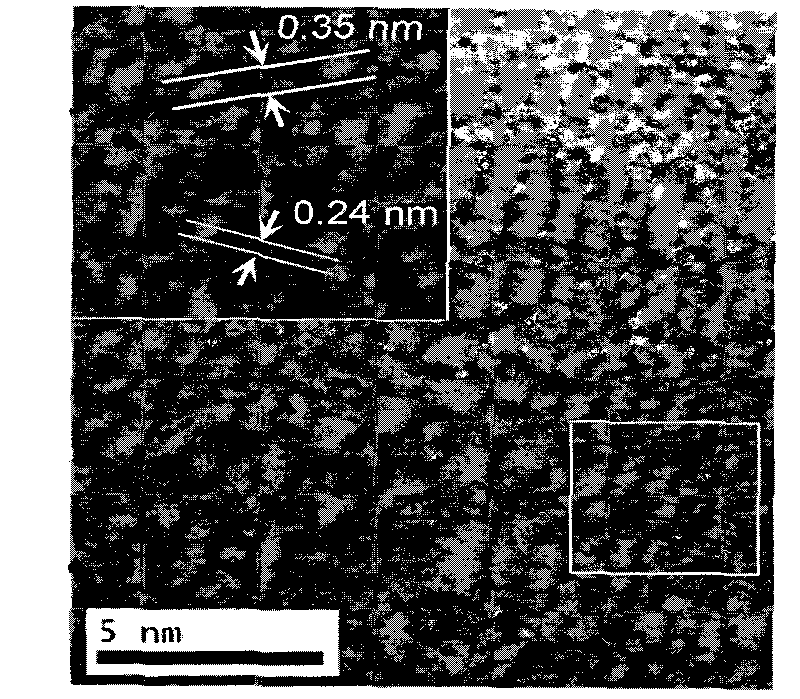
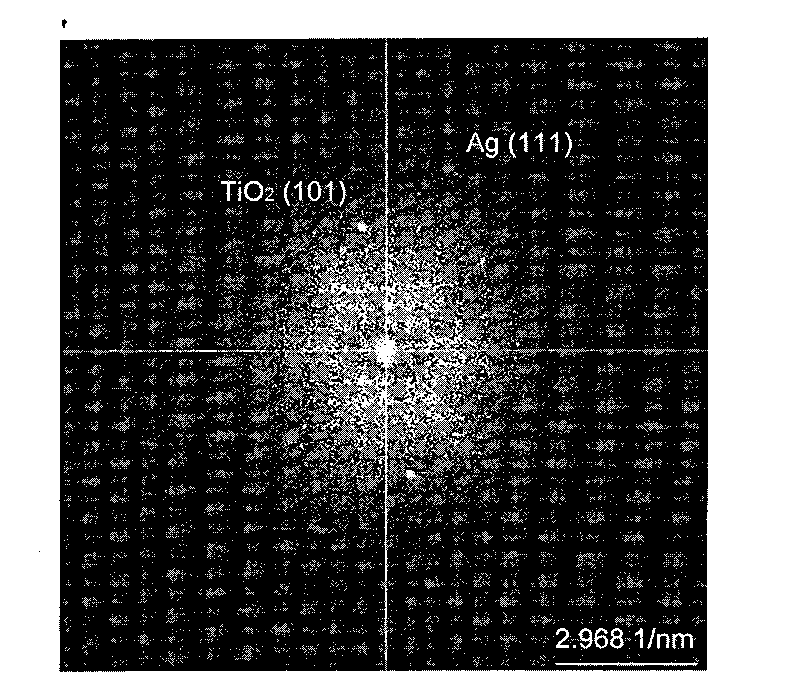
Method for preparing metal/titanium dioxide composite nano material at low temperature by gamma-irradiation
InactiveCN101734615AImprove photocatalytic activityHigh temperature and high photocatalytic activityNanostructure manufactureMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGamma irradiationGamma ray
The invention provides a method for preparing a metal / titanium dioxide composite nano material at low temperature by gamma-irradiation, which relates to a method for preparing a metal / titanium dioxide composite nano material. The invention solves the problems that the preparation of the metal / titanium dioxide composite material in the prior art needs a high-temperature reaction and needs to be introduced with a large amount of reducers or organic stabilizers, the obtained product has poor dispersivity and low photocatalytic activity, and the size and the pattern of metal particles generated by reduction are still difficult to control even if a gamma-irradiation reduction method is adopted. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a precursor solution of titanium; (2) preparing pulpous liquid; (3) preparing TiO2 transparent sol; (4) adding a metal precursor solution and isopropanol into the transparent sol to obtain mixed reaction liquid, introducing nitrogen gas and carrying out gamma-ray radiation reduction by a 60Co source after sealing to obtain metal / titanium dioxide composite sol; and (5) drying or coating to obtain the metal / titanium dioxide composite nano material. In the invention, the size and the distribution of the metal particles are controllable, a template agent does not need to be added, the high-temperature reaction is not needed, and the product has good dispersivity and high photocatalytic activity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
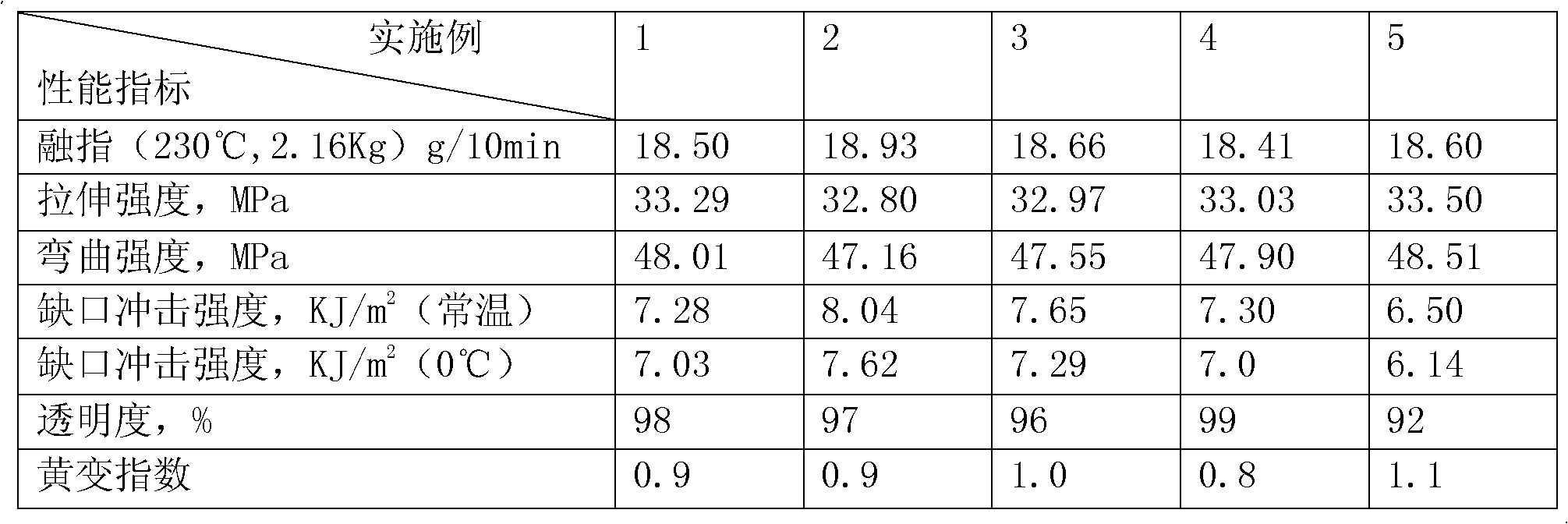
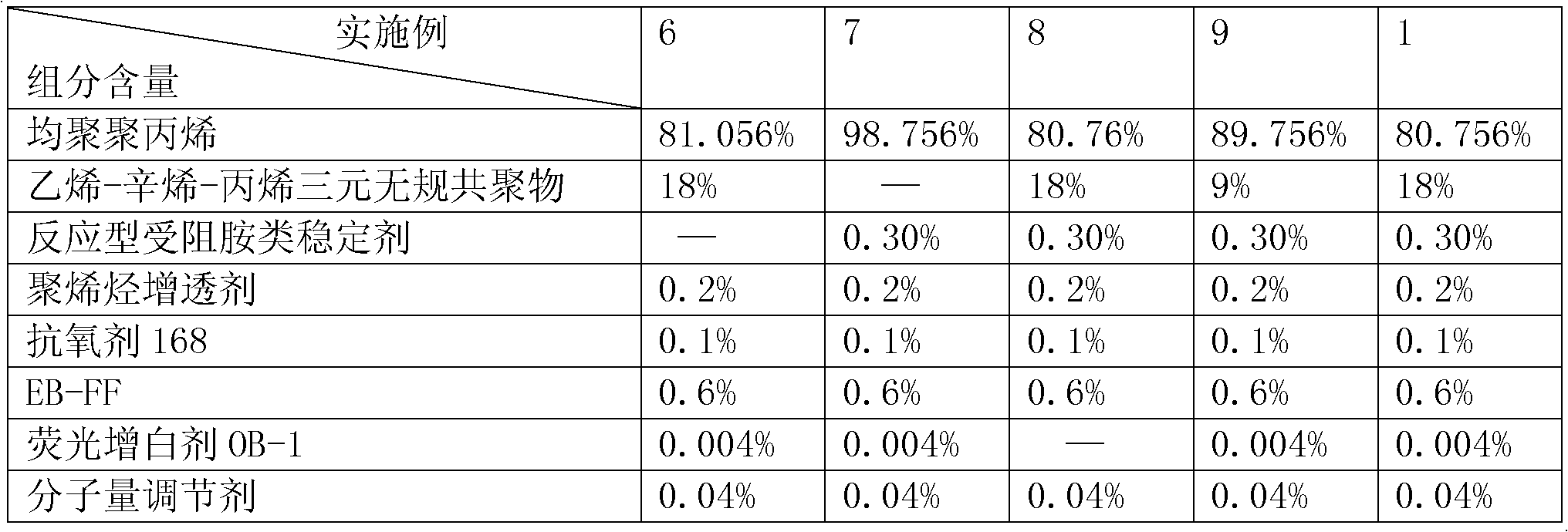
Medicinal low-temperature-resistant toughening anti-gamma ray impact-resistant transparent polypropylene material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a medicinal low-temperature-resistant toughening anti-gamma ray impact-resistant transparent polypropylene material and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal low-temperature-resistant toughening anti-gamma ray impact-resistant transparent polypropylene material is prepared by completely mixing a base material, a flexibilizer, a gamma shielding auxiliary agent, a transparent nucleating agent, an antioxidant, a lubricant, a brightening agent and a molecular weight regulator according to the proportion, wherein homopolymerized polypropylene serves as the base material. An ethylene-octylene-propylene ternary random copolymer is adopted, so the medicinal low-temperature-resistant toughening anti-gamma ray impact-resistant transparent polypropylene material has excellent toughness and impact resistance and low-temperature resistance, is transparent, and fundamentally solves the problem that a medicinal polypropylene material is not transparent. A reactive type hindered amine stabilizing agent is grafted on a polypropylene molecular chain by a reaction extrusion method, so the gamma ray resistance is improved. After the medicinal polypropylene material prepared by the method is subjected to 25-kilojoule gamma irradiation, the yellowing index is less than 1; and then a moulding part is placed in a 70-DEG C baking oven for 8 weeks, the yellowing index is 3, the comprehensive mechanical property is reduced by 5 percent, and the transparency maintains over 90 percent.
Owner:苏州晋圣博高分子材料科技有限公司
A kind of mushroom cordyceps militaris essence seasoning and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102266036AImprove absorption rateHigh nutritional valueFood preparationFluidized bed dryingMonosodium glutamate
A mushroom and cordyceps militaris extract flavoring and a preparation method thereof. The mushroom and cordyceps militaris extract flavoring comprises monosodium glutamate, mushroom submicron powder, maltodextrin, yeast extract, disodium 5'-ribonucleotide, hydrolyzed vegetable protein, disodium succinate, powdered oil and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps of cleaningmushrooms and cordyceps militaris extract, drying them by an oven, sieving the dried mushrooms and the cordyceps militaris extract, crushing the sieved mushrooms and the cordyceps militaris extract into superfine powder having the size less than 10 micrometers, mixing well the superfine powder and other crushed materials with stirring, granulating by rotation, drying by a fluidized bed, grading by vibration, packaging automatically, and carrying out sterilization by gamma irradiation at a dose of 3KGy. The preparation method adopts ultra-microprocessing of mushrooms and cordyceps militaris extract to realize that taste-producing substances and nutrient components are released fully, and thus a delicate flavor is increased and an absorption rate of nutrients is improved. Through reasonableproportions and interaction of superfine powder and powdered oil, a unique delicious taste is obtained. Through a fluidized bed drying technology, materials are heated uniformly; heating time is short; temperature-sensitive components in a condiment are retained; energy consumption is low; and product quality is stable. Through irradiation sterilization, a shelf-life of two years can be realized.
Owner:武汉鲜师令农产品加工有限公司
Use of a Biologically Active Blood Serum for the Treatment of a Disorder Characterized in a Reduced Function of a GABA Receptor
InactiveUS20090252786A1Counteracts reduced GABA receptor functionEasy dischargeNervous disorderAntipyreticHuman animalDisease
The present invention relates to a method of preventing or treating in a subject a disorder characterized in a reduced GABA receptor function by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmacologically active blood serum product obtainable by a method comprising electrostimulation of a non-human animal, withdrawal of blood from said animal isolation of serum from said blood, and gamma irradiation of said serum.
Owner:OWEN HLDG
Use of human prostrate cell lines in prostate cancer treatment
InactiveUS6972128B1Promote growthSufficient characteristicBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGamma irradiationProstate cancer
The invention here relates to a product comprised of a cell line or lines intended for use as an allogeneic immunotherapy agent for the treatment of cancer in mammals and humans. All of the studies of cell-based cancer vaccines to date have one feature in common, namely the intention to use cells that contain at least some TSAs and / or TAAs that are shared with the antigens present in patients' tumour. In each case, tumour cells are utilised as the starting point on the premise that only tumour cells will contain TSAs or TAAs of relevance, and the tissue origins of the cells are matched to the tumour site in patients. A primary aspect of the invention is the use of immortalised normal, non-malignant cells as the basis of an allogeneic cell cancer vaccine. Normal cells do not possess TSAs or relevant concentrations of TAAs and hence it is surprising that normal cells are effective as anti-cancer vaccines. For prostate cancer, for example, a vaccine may be based on one or a combination of different immortalised normal cell lines derived from the prostate. The cell lines are lethally irradiated utilising gamma irradiation at 50–300 Gy to ensure that they are replication incompetent prior to use in the mammal or human.
Owner:ONYVAX
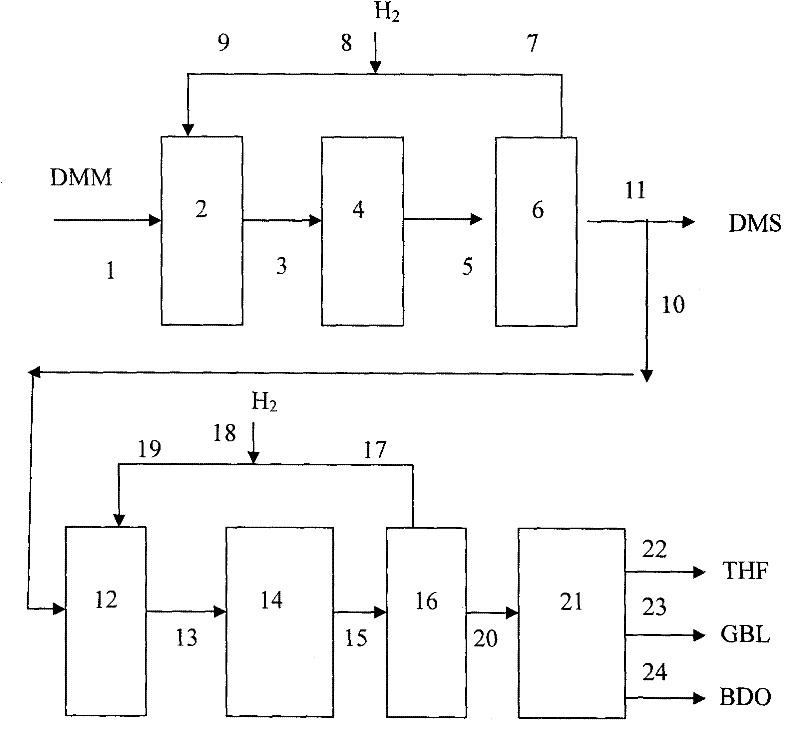
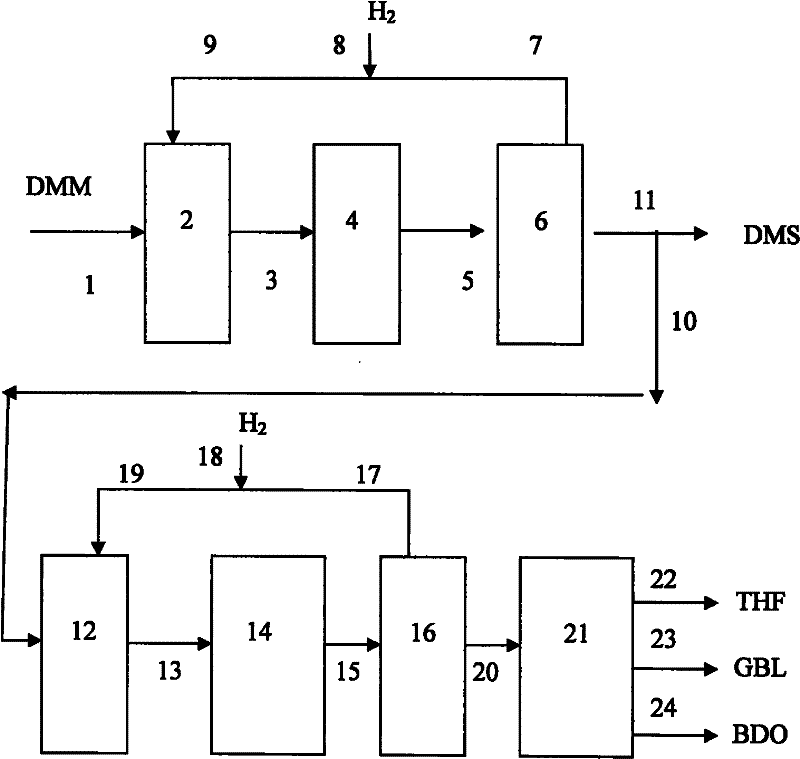
Method of simultaneously producing dimethyl succinate and 1,4-butyl glycol
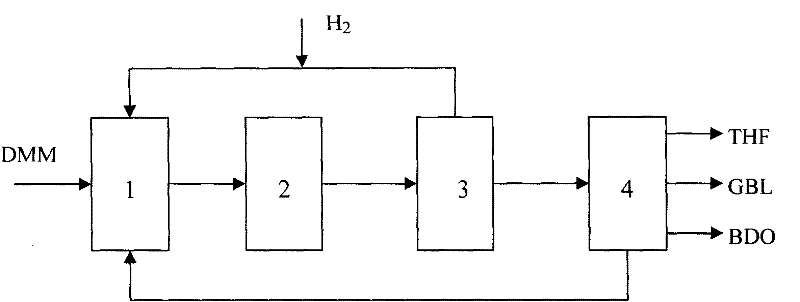
ActiveCN102190582AFlexible productionOvercome defectsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFuranGas phase
The invention relates to a method of simultaneously producing dimethyl succinate (DMS) and 1, 4-butyl glycol. The method can also be used to simultaneously produce at least one of Tetrahydro furan (THF) and gamma-irradiation butyl lactone (GBL). In the invention, dimethyl maleate (DMM) is used as raw materials and contacts with hydrogen under the condition of gas phase in a low pressure reaction district and a middle pressure reaction district respectively. A low-pressure reactor and a middle-pressure reactor are equipped with a catalyst. DMS products are produced in the low pressure reaction district and 1, 4-butyl glycol products are produced in the middle pressure reaction district. Simultaneously, at least one of the GBL and THF can be produced in the middle pressure reaction district. Purity of DMS can reach over 99.5% without refining through using a gas-liquid separator. In the invention, the method is used in mild condition; heavier component does not need to be circulated; operation is simple; transesterification type polymerization and other side reactions are greatly reduced in a system.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI ENERGY CHEM
GelMA hydrogel human acellular amniotic membrane three-dimensional two-layer dressing preparation method
InactiveCN109125799APromote growthHigh mechanical strengthBandagesGamma irradiationBiological dressing
The invention relates to the field of medical biological dressings, in particular to a GelMA hydrogel human acellular amniotic membrane three-dimensional two-layer dressing preparation method which isa method for preparing a GelMA hydrogel / human acellular amniotic membrane three-dimensional two-layer dressing through integration of electrostatic spinning and photo-crosslinking. The method includes: subjecting gelatin to MA (methylacrylic acid) graft modification to form GelMA, covering D-HAM (decellularized human amniotic membrane) with GelMA in a porous fiber form through electrostatic spinning to obtain the three-dimensional two-layer bioactive dressing, and subjecting the dressing to photo-crosslinnking with a photoinitiator Irgacure2959; lyophilizing the dressing subjected to photo-crosslinnking, performing gamma irradiation sterilization, and packaging under sterile conditions. Great anti-inflammation and anti-infection effects and high biocompatibility are achieved, and quick healing of oral mucous wounds can be promoted.
Owner:张强
Broad spectrum disinfectant
A broad spectrum disinfectant includes a quaternary ammonium halogen, an alkaline agent, a chelating agent, a nonionic surfactant coupler, at least one alkoxylated nonionic surfactant, and water or any aliphatic alcohol. The disinfectant composition is phenol-free, is effective in eradicating microorganisms such as various fungi, and is stable to gamma-irradiation.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene for bearing surfaces
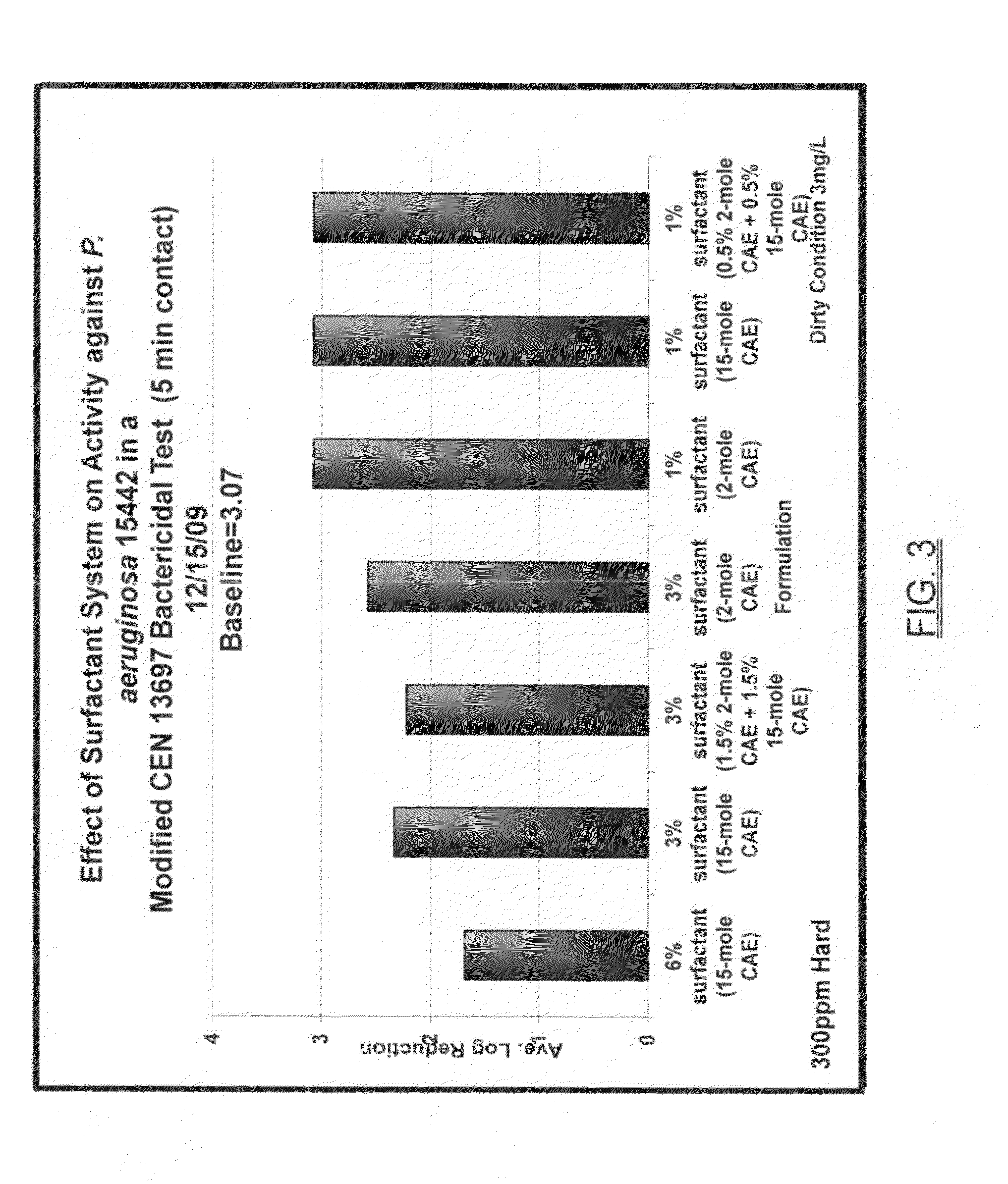
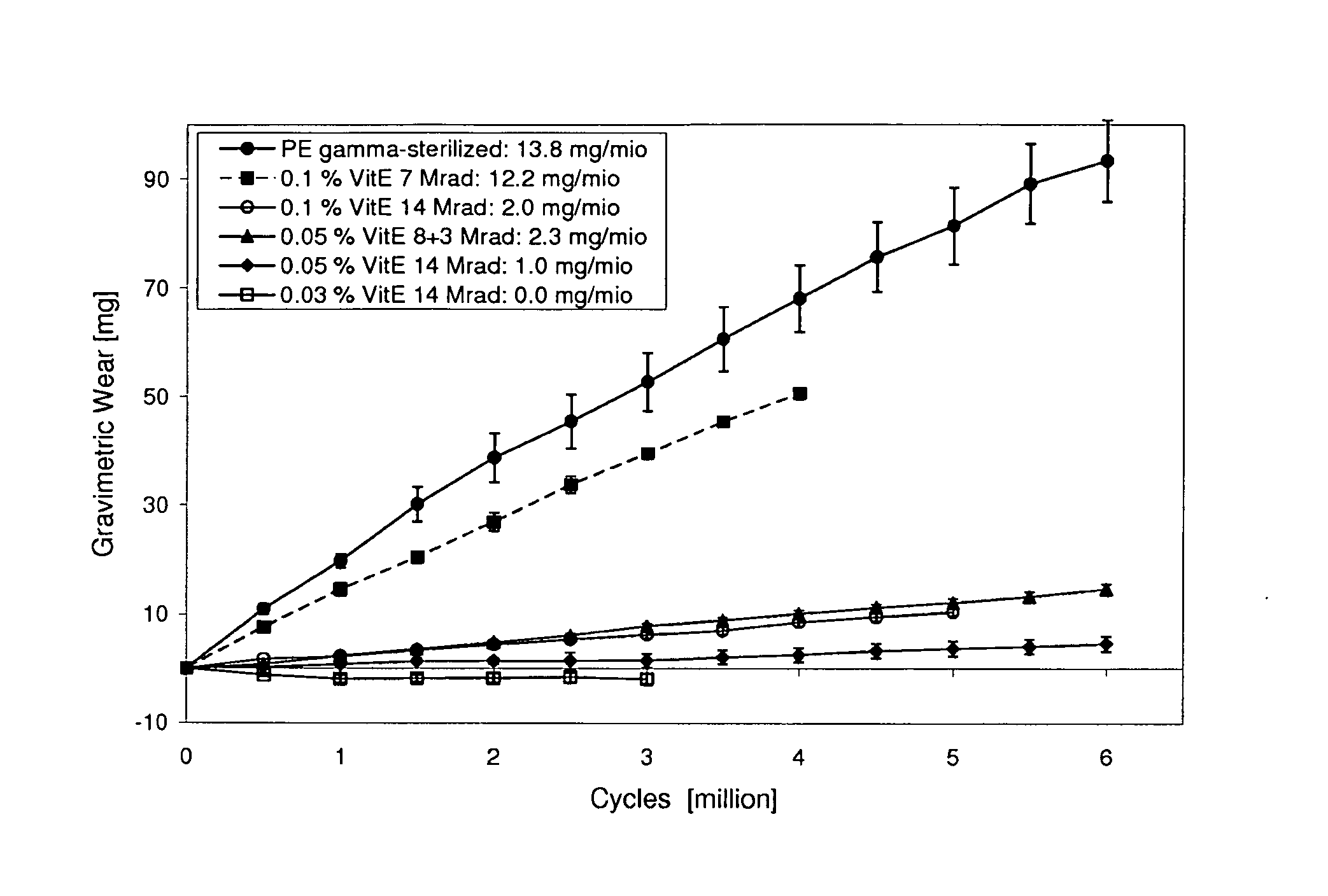
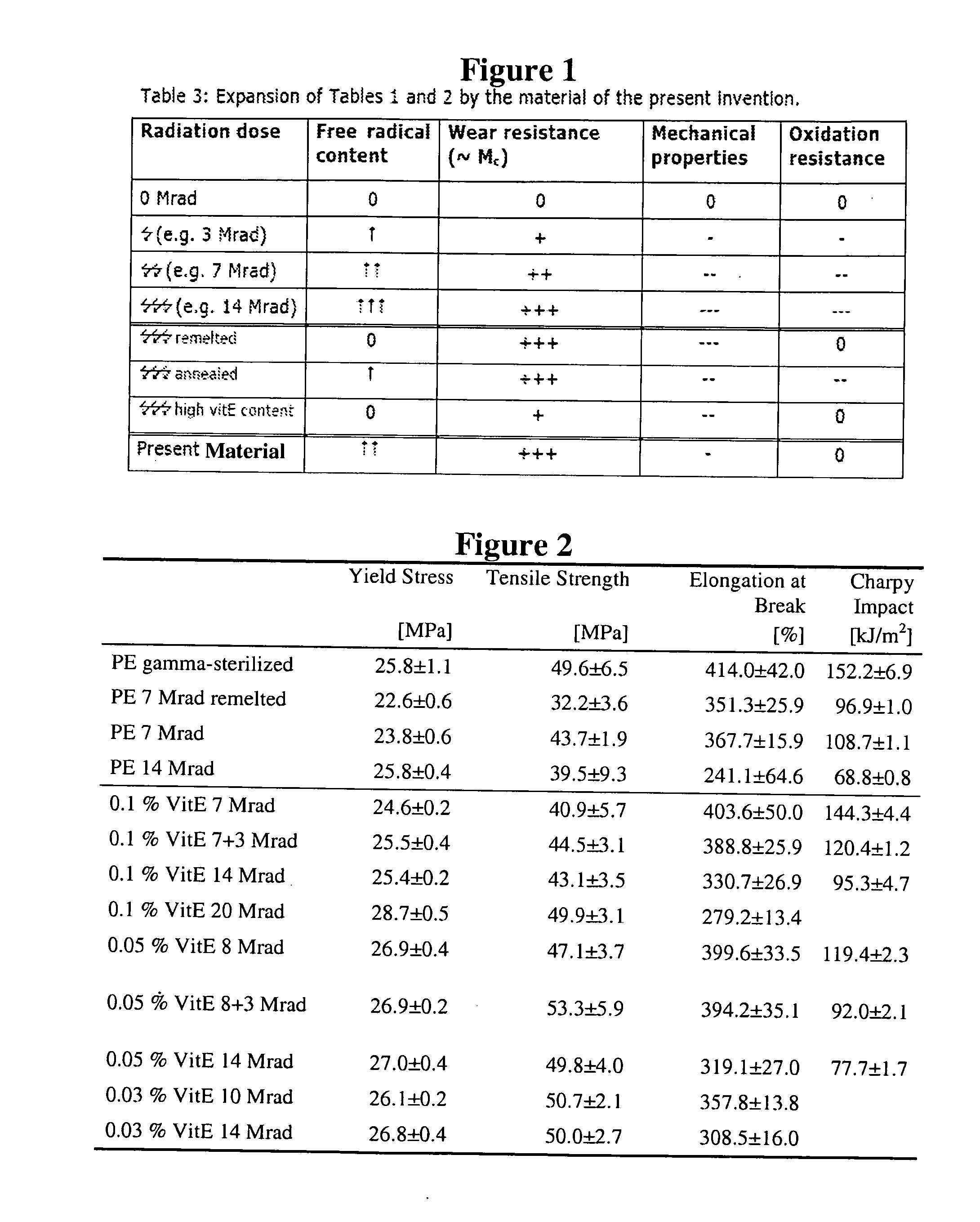
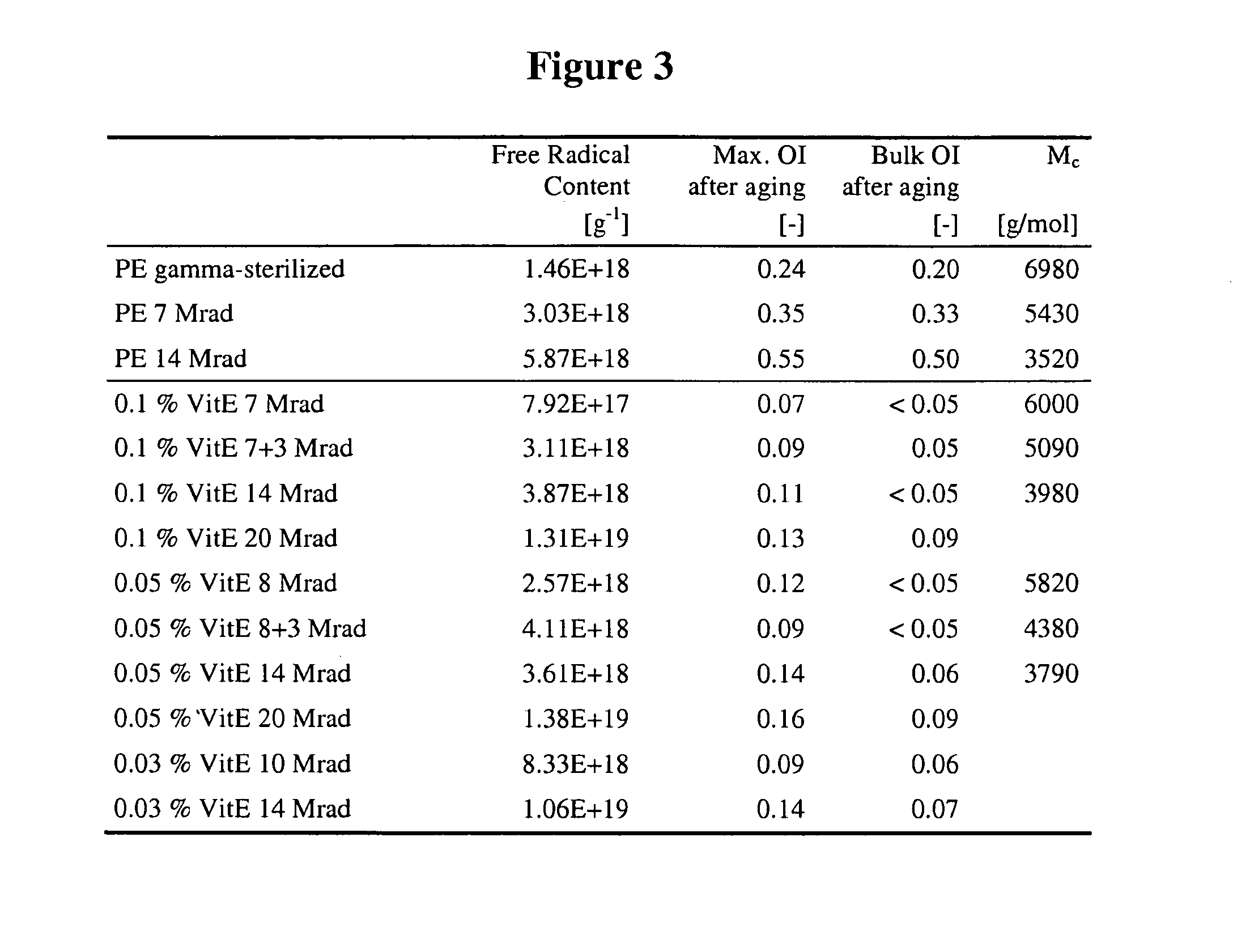
A prosthetic device may comprise an insert having a first surface configured to contact a first prosthetic component and a bearing surface configured to articulate against a second prosthetic component. The insert comprises an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and vitamin E. The vitamin E may have a concentration in the range of 0.02 to 0.12 wt % first mixed with the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and then molded with the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene at a temperature greater than the melting point of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. The ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and vitamin E may be gamma irradiated with a dosage of radiation between 5 and 20 Mrad. The insert may be machined prior to gamma irradiating the insert in air such that the gamma irradiation, at suitably high dosages, may also sterilize the insert.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
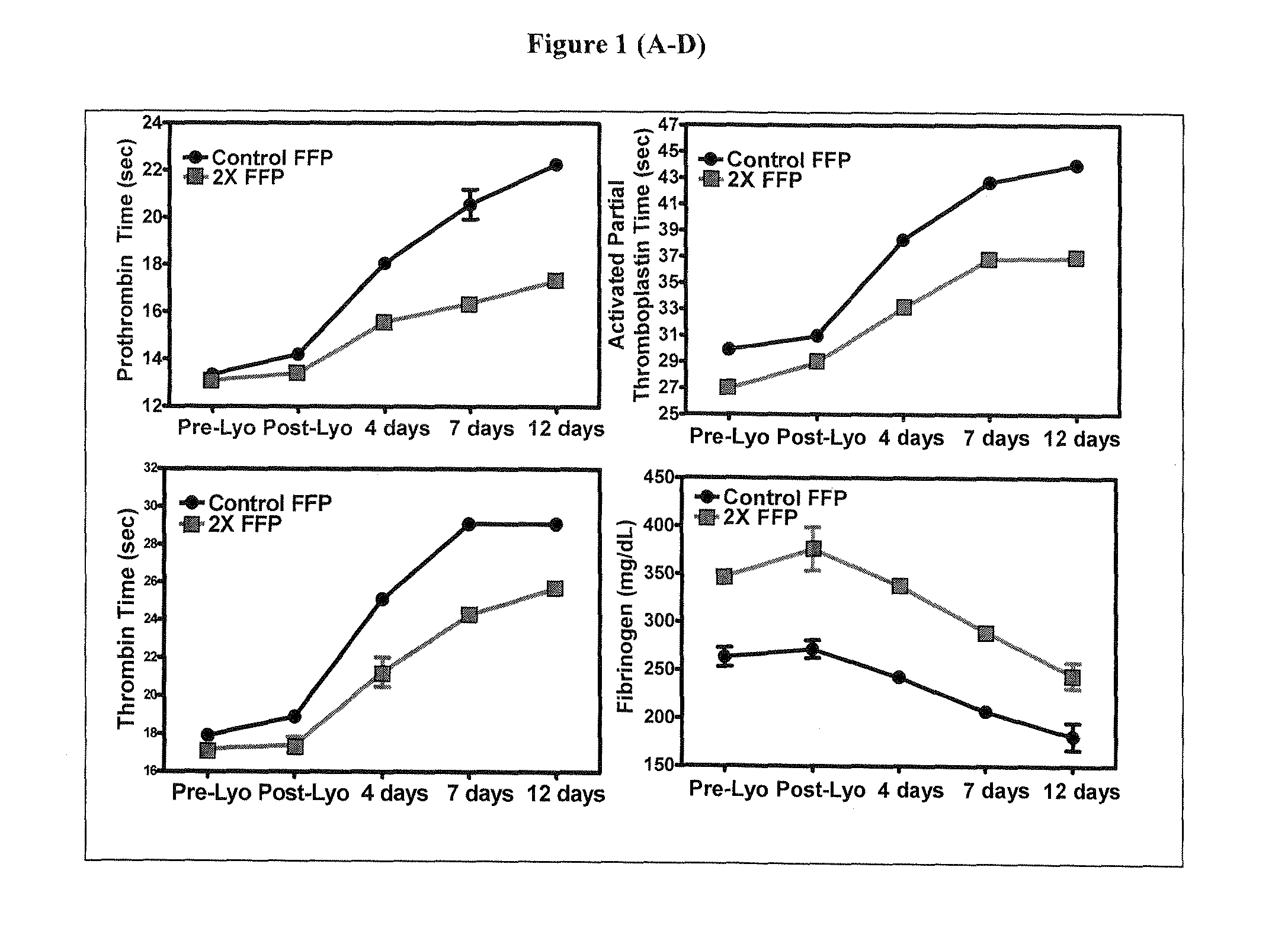
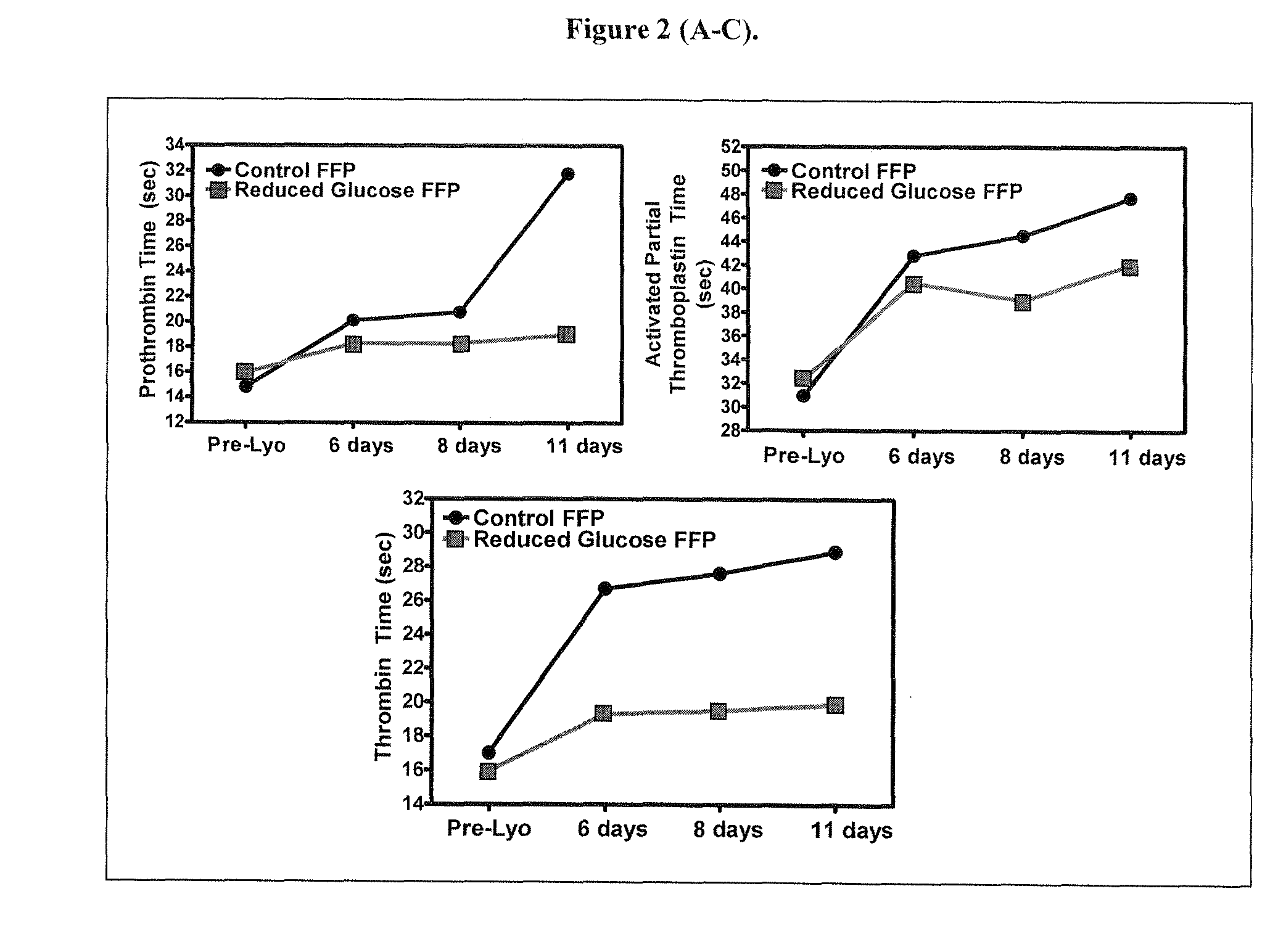
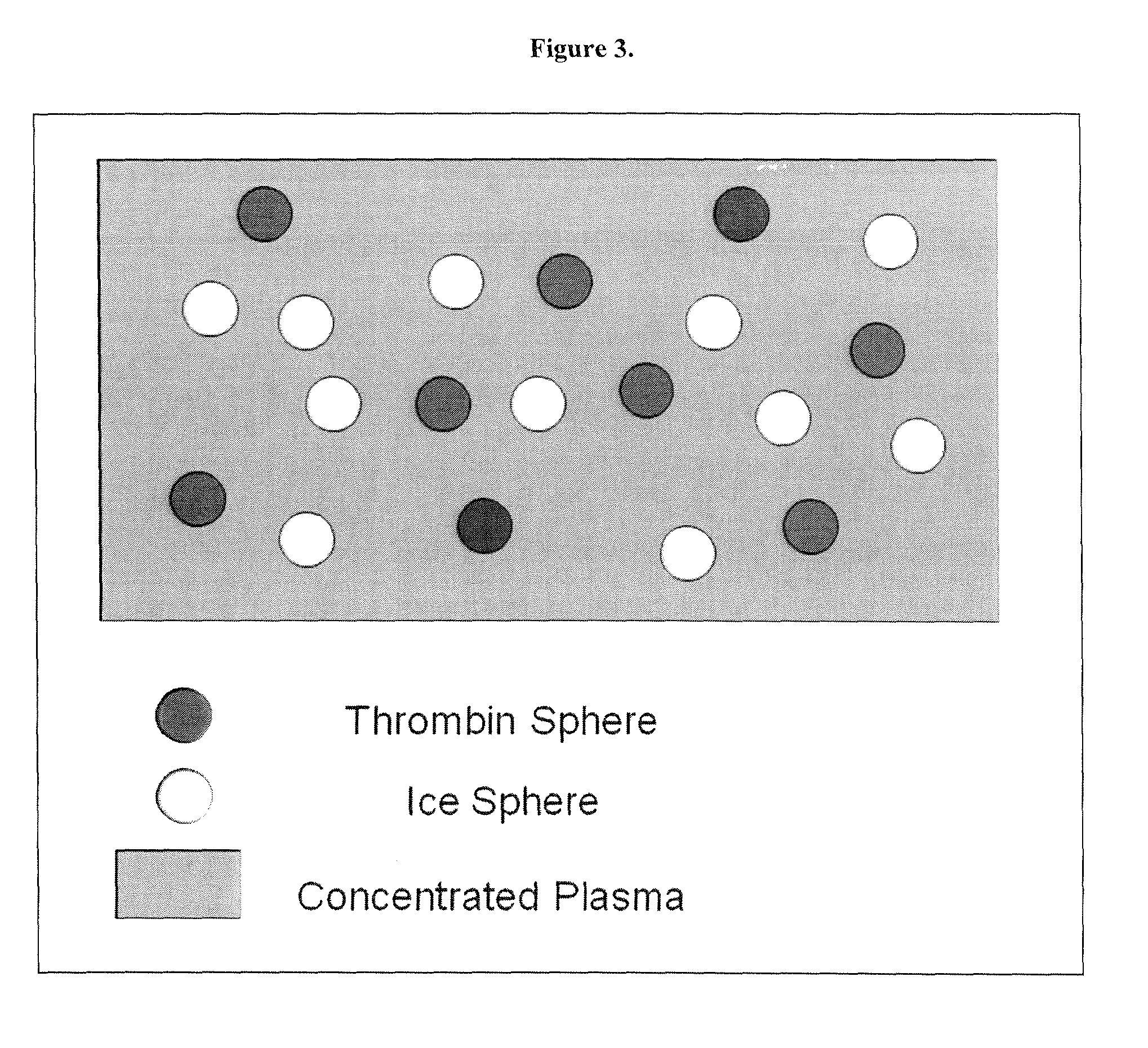
Freeze-dried plasma formats for the trauma care field
InactiveUS20100233671A1Increasing coagulation factor stabilityHigh protein concentrationDipeptide ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsDipeptideFreeze-drying
Disclosed are freeze-dried plasma formats specifically designed for the trauma care field. Blood plasma is subjected to a glucose removal step, a protein fraction up-concentration step and addition of stabilizers prior to freeze-drying. Preferable stabilizers are glutamine dipeptides, glutamine and glycine. The glutamine based formulation is added direct to plasma and serves three main purposes: 1) Increases stability of plasma proteins and stabilizes pH in freeze-dried state; 2) Increases stability of plasma proteins against Gamma Irradiation and thus allows for the application of a terminal sterilization step; 3) Introduces supplements beneficial to the trauma patient.
Owner:BAKALTCHEVA IRINA B
Methods for packaging and sterilizing elastomeric articles, and packaged elastomeric articles produced thereby
ActiveUS20110203227A1Reduced ozone attackReduce degradationFlexible coversWrappersGamma irradiationEngineering
The present invention relates generally to methods of sterilizing elastomeric articles in a manner that prevents and / or reduces degradation to the articles, particularly degradation that may be caused and / or accelerated by sterilization techniques such as gamma irradiation, x-ray irradiation, and electron-beam processing. The methods include packaging the elastomeric articles in order to improve their resistance to degradation. In certain aspects of the invention, packaged elastomeric articles, optionally containing one or more antidegradants, such as antioxidant and / or antiozonant compounds, are also provided. The methods of providing degradation-resistant elastomeric articles in accordance with the present invention may also be used to reduce the occurrence of cracking and discoloration in elastomeric articles, regardless of whether they are subjected to sterilization.
Owner:ALLEGIANCE CORP
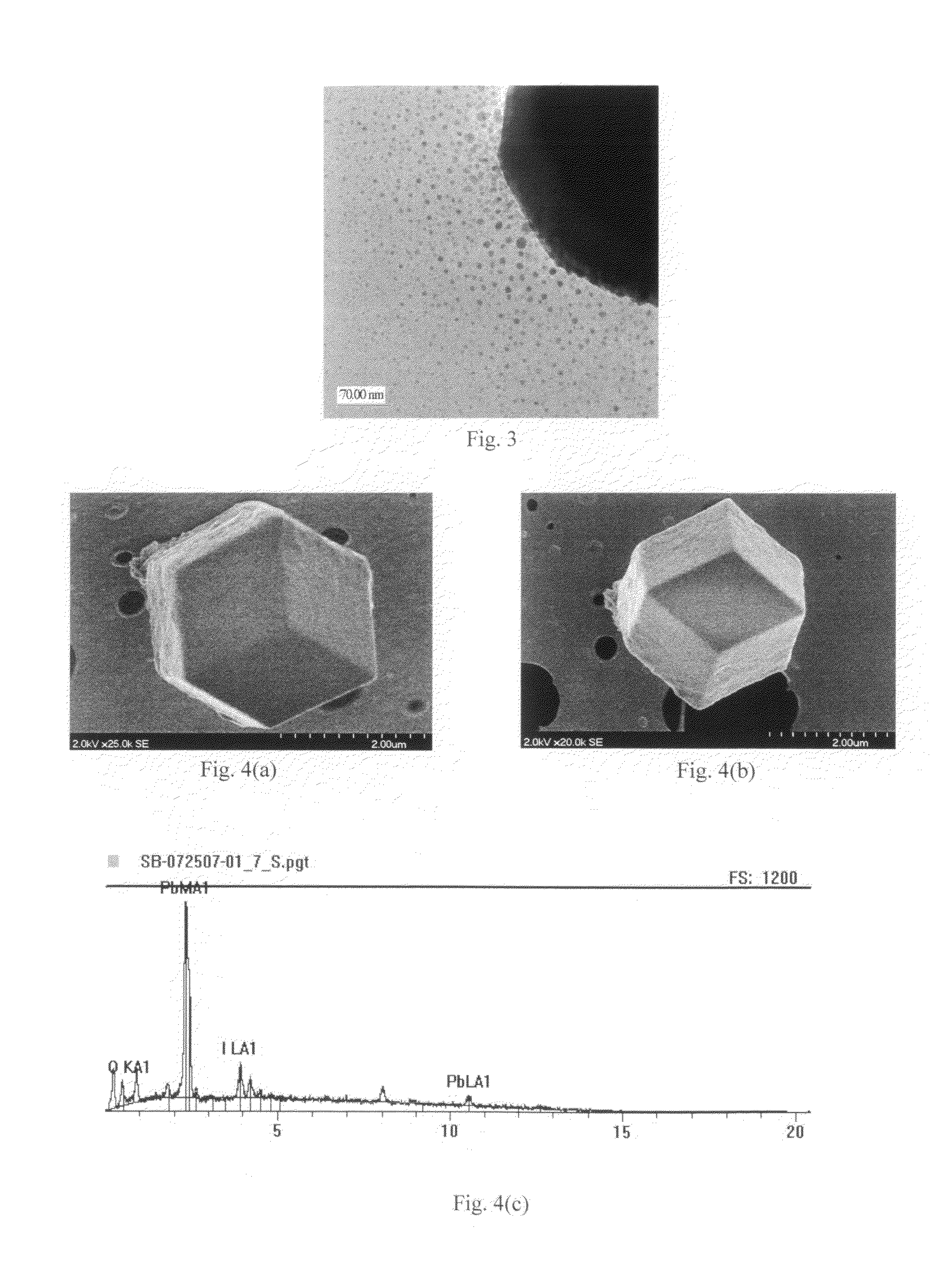
Lead-iodide-based scintillator materials
InactiveUS20100072374A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduced dosIodide preparationMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma irradiationMicroparticle
Scintillator material comprising nanoparticles (nanocrystals) comprising lead (Pb), iodine (I), and optionally one or both of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) wherein the nanoparticles exhibit room-temperature scintillation under gamma irradiation. The scintillator nanoparticles can comprise Pb3O2I2. The scintillator nanoparticles can comprise PbIOH in generally equiatomic proportions or non-equiatomic variants thereof that exhibit scintillation under gamma irradiation. The scintillator nanoparticles have a particle dimension in the range of about 5 to about 100 nm. Microparticles (microcrystals) also are provided comprising lead (Pb), iodine (I), and optionally one or both of oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) grown in a nanoparticle colloidal solution over time to a particle dimension greater than 0.1 μm, such as about 2 microns.
Owner:STC UNM
Epoxy pouring sealant as well as preparation method and application thereof to nuclear power equipment
InactiveCN108165220ASolve the problem of easy crackingImprove thermal stabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyGamma irradiation
The invention relates to an epoxy pouring sealant as well as a preparation method and application thereof to nuclear power equipment. The epoxy pouring sealant comprises a main agent and a curing agent with a weight ratio of 1:(0.5-2); the main agent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-100 parts of poly-functional epoxy resin, 10-35 parts of phenolic epoxy resin, 10-50 parts of toughened and modified epoxy resin, 10-30 parts of an active diluent, 5-25 parts of an active toughening agent, 60-100 parts of functional inorganic pigments and fillers and 1-10 parts of an auxiliary; the curing agent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100-200 parts by weight of an anhydride curing agent, 0.1-3 parts of a promoting agent, 100-200 parts of functional inorganic fillers, 5-40 parts of a flame retardant and 1-10 parts by of an auxiliary. The epoxy pouring sealant provided by the invention has the advantages of gamma irradiation resistance, high and low temperature impact resistance, good air tightness, insulation properties and mechanical properties, low shrinkage rate, long service life and the like. The epoxy pouring sealant can meet a special application environment in a nuclear power plant.
Owner:BEIJING GUANGKEBOYE SCI & TECH
Method for efficiently preparing graphene/metal oxide composite material
The present invention provides a method for efficiently preparing a graphene / metal oxide composite material based on gamma irradiation. The method comprises the following steps: irradiating a mixed solution of graphene oxide and metal salts through gamma rays, and inducing oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of graphene oxide to react with metal ions so as to synchronously achieve reduction of graphene oxide and oxidation of the metal ions and prepare the graphene / metal oxide composite material through one step. The method provided by the invention has beneficial effects as follows: the method is low in cost and simple in process, has high controllability, does not need to add high-risk reducing agents, is environment-friendly, and is beneficial for batch preparation of the material; under the oxidation-reduction action between rich oxygen-containing groups on the surface of graphene oxide and the metal ions, uniform dispersion and firm anchoring of metal oxide nano-particles on the surface of graphene can be effectively achieved, and uniform and stable material structures can be ensured; and additionally, as a cathode of a lithium battery, the material has relatively high theoretical specific capacity as well as excellent cycling performance and rate performance.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Tuberculosis vaccine and method of using same
InactiveUS20100112007A1Reduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryGamma irradiationMycobacterium
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition that includes one or more inactivated Mycobacterium spp., which are preferably inactivated using gamma irradiation, and which is than formulated for mucosal or pulmonary delivery to a subject. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for preventing or treating mycobacterium-associated infections in a subject, including a human subject.
Owner:MICO BIO
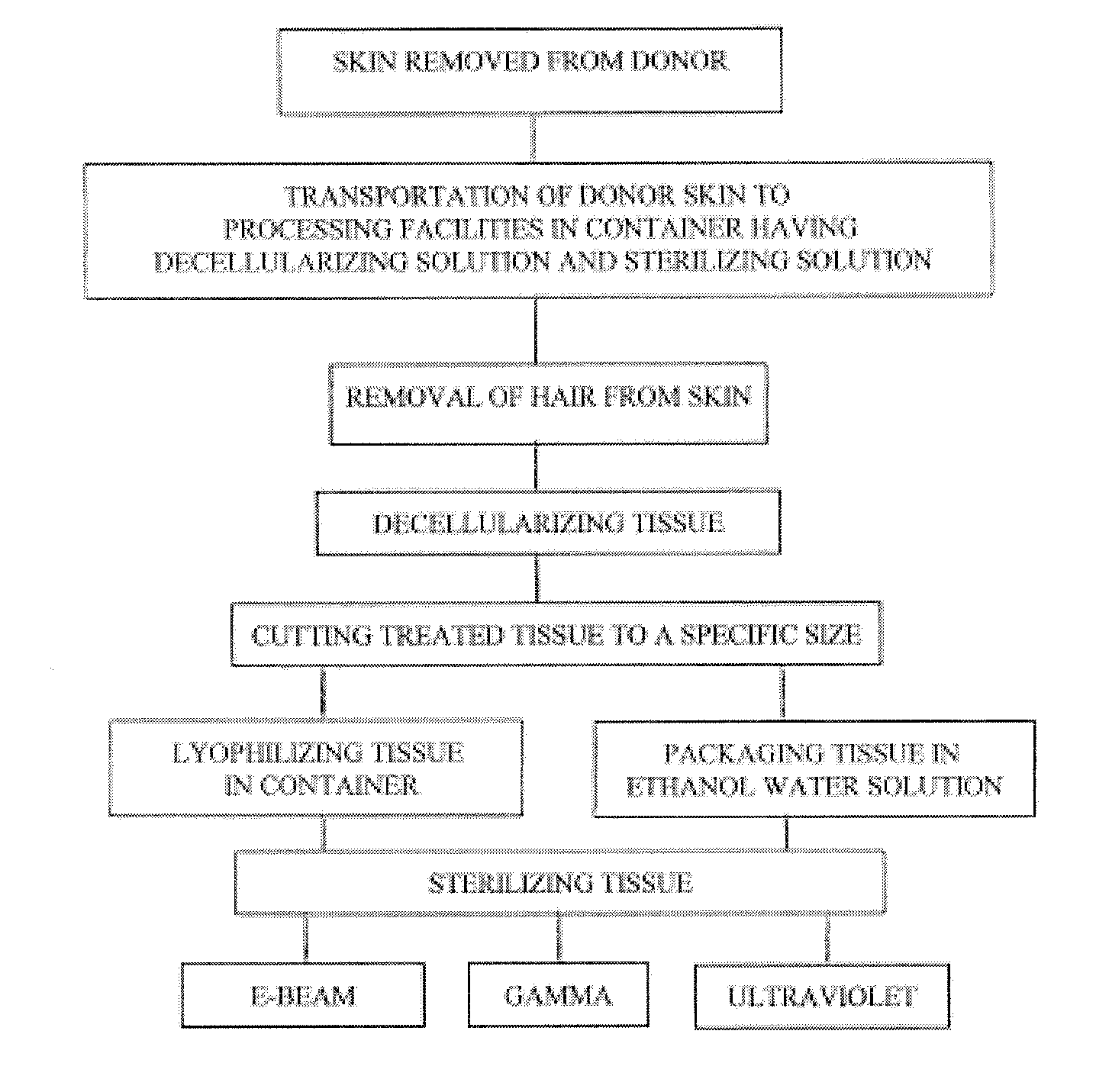
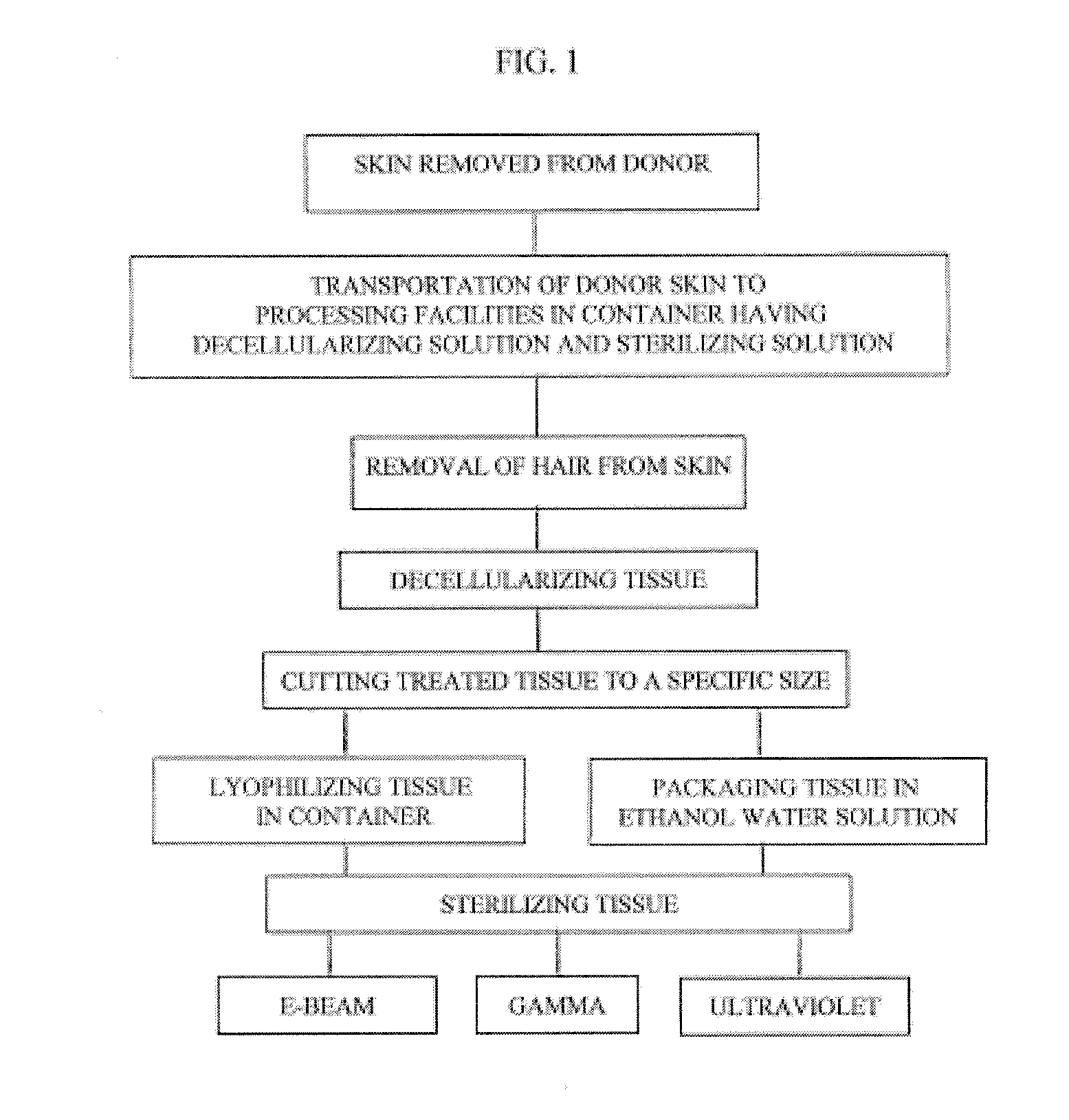
Process for sterilizing acellular soft tissue with irradiation
InactiveUS20120297550A1Pre-tanning chemical treatmentLavatory sanitoryCellular componentGamma irradiation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing skin removed from a human donor, removal of cellular components and sterilizing the decellularized skin. The process comprises the following steps:(1) decellularizing the skin including soaking the tissue in a detergent and rinsing same with sterile water;(2) sterilizing the skin with electronic beam irradiation, gamma irradiation or ultraviolet light for a time period to achieve a concentration to maximize sterilization; and(3) processing the tissue by cutting the tissue to a designated size.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
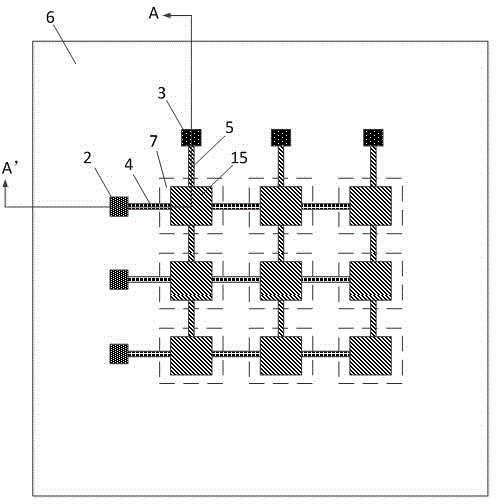
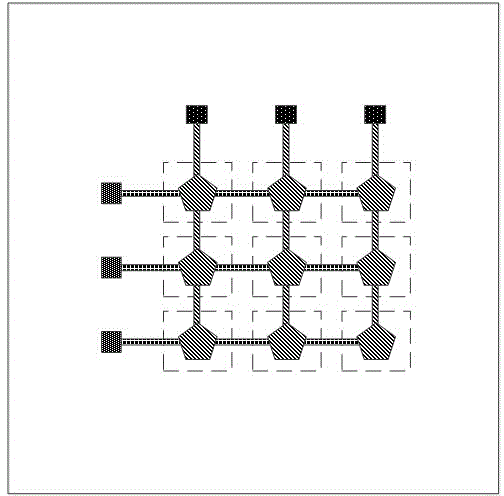
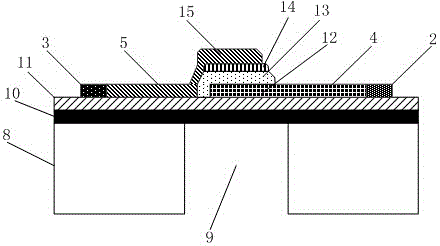
Array-type gamma irradiation dosimeter of FBAR structure on diaphragm
The invention discloses an array-type gamma irradiation dosimeter of a FBAR structure on a diaphragm. The array-type gamma irradiation dosimeter comprises a detection element, a composite thin film, and a Si substrate. The detection element is disposed on the upper part of the composite thin film, and the composite thin film is used to support the detection element, and the Si substrate is disposed on the lower part of the composite thin film. The detection element comprises a plurality of FBAR, which are in an array-type arrangement, and are disposed on the composite thin film. Each of the FBAR comprises, from bottom to top, a bottom electrode, a piezoelectric layer, and a top electrode sequentially. An irradiation sensitive layer is disposed between each of the piezoelectric layers and each of the bottom electrodes, or is disposed between each of the piezoelectric layers and each of the top electrodes, and the bottom electrodes are tightly attached to the upper surface of the composite thin film. The Si substrate is provided with a plurality cavities, which are respectively corresponding to the irradiation sensitive layers in a vertical direction. The cavities are used to form the volume acoustic wave reflection interfaces, and the composite thin film areas corresponding to the cavities are the composite thin film suspension areas. The array-type gamma irradiation dosimeter has advantages of small size, high sensitivity, good temperature stability, good manufacturability, and ability of detecting irradiation dose distribution.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com