Method for improving yield of fumaric acid
A technology of arginine and proline, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve problems such as carbon flow loss, and achieve the effects of increasing production, good industrial application value and prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
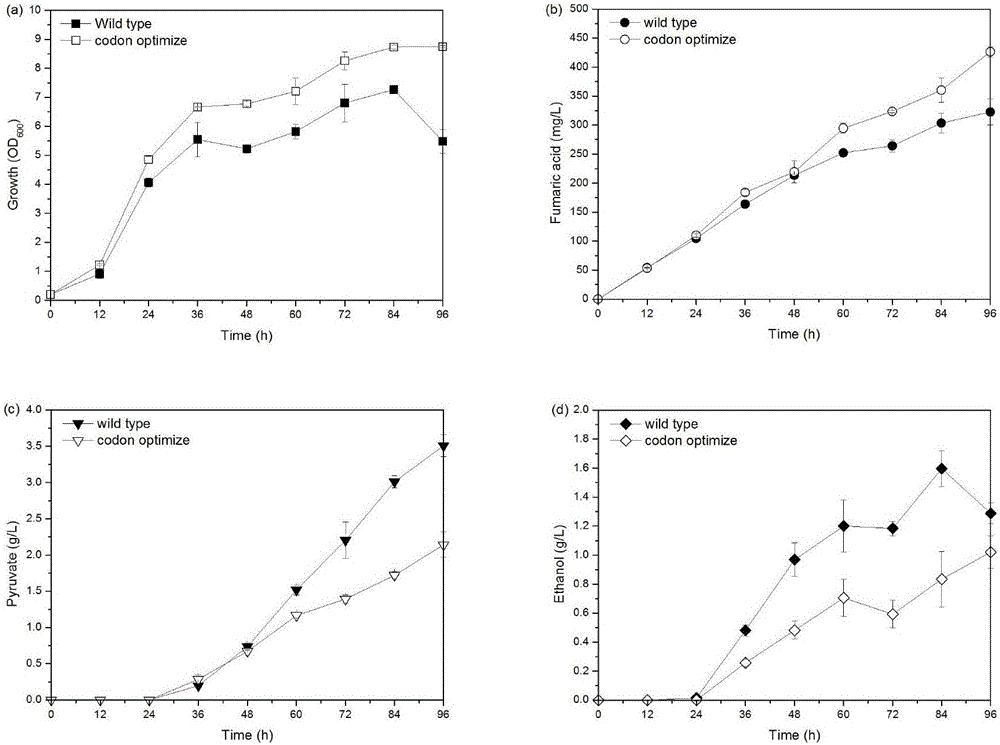
[0030] Codon optimization of embodiment 1 RoPYC (pyruvate carboxylase from Rhizopus oryzae) gene and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0031] 1. Gene acquisition after RoPYC codon optimization
[0032] Submit the RoPYC nucleotide sequence derived from Rhizopus oryzae to the sequence box of the codon optimization website (http: / / www.jcat.de / ), and then select the expression host as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the codon can be obtained after submission For the optimized gene sequence, the gene corresponding to this sequence is named RoPYC*.
[0033] The sequence of RoPYC* was sent to Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. for gene synthesis, and the synthesized gene was connected to the T vector. On this basis, we carried out PCR amplification using RoPYC*+T carrier as a template, and the primers used are shown in Table 1.
[0034] Table 1 Amplifies the primers of RoPYC* gene
[0035]
[0036]The obtained PCR product was double-digested with SpeI and SalI, and then lig...
Embodiment 2
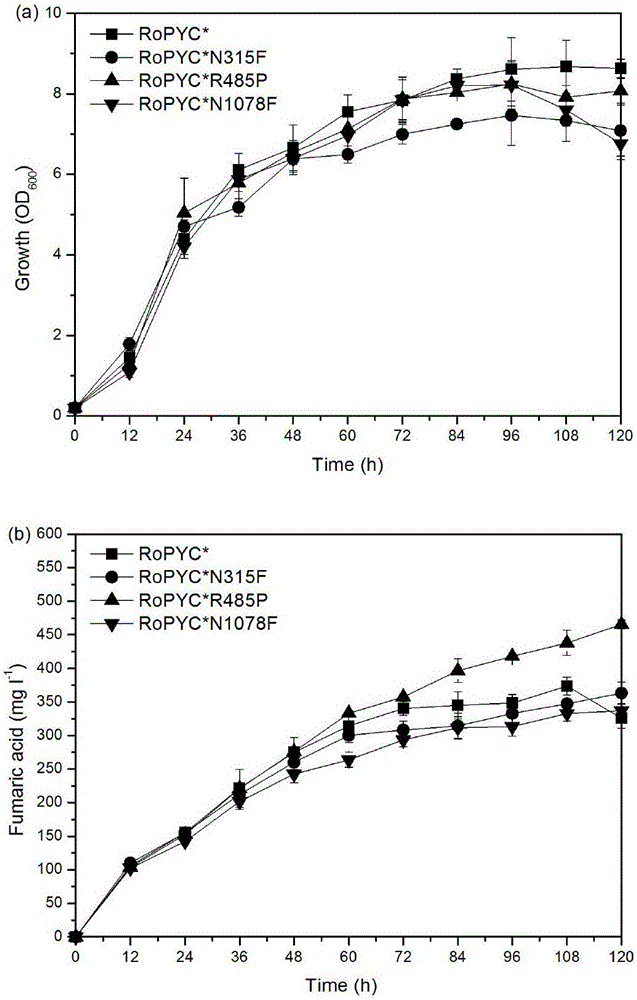
[0039] Example 2 RoPYC* site-directed mutation and expression
[0040] Site-directed mutation was performed by PCR method, and the N315F, R485P, and N1078F sites of RoPYC* were subjected to site-directed mutation. The pY15TEF1-RoPYC plasmid was used as a template, F and R containing mutation sites were used as primers, and Takara's high-fidelity enzyme PrimeSTARGXL was used for PCR amplification. Entire plasmids are amplified. The enzyme digestion system contains 1 μL of PCR product and 1 μL of DpnI enzyme, with a total volume of 20 μL, digested overnight at 37°C. Fragment purification of digested products. Take 5 μL of the purified product and transform it into 30 μL of competent cells Trans1-T1, smear the LA plate, inoculate the grown transformant in the LA medium, extract the plasmid and send it to Shanghai Sangon for sequencing.
[0041] The primers F(Pro) and R(Pro) (sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6 respectively) used for RoPYC*R485P mutation are shown in ...
Embodiment 3
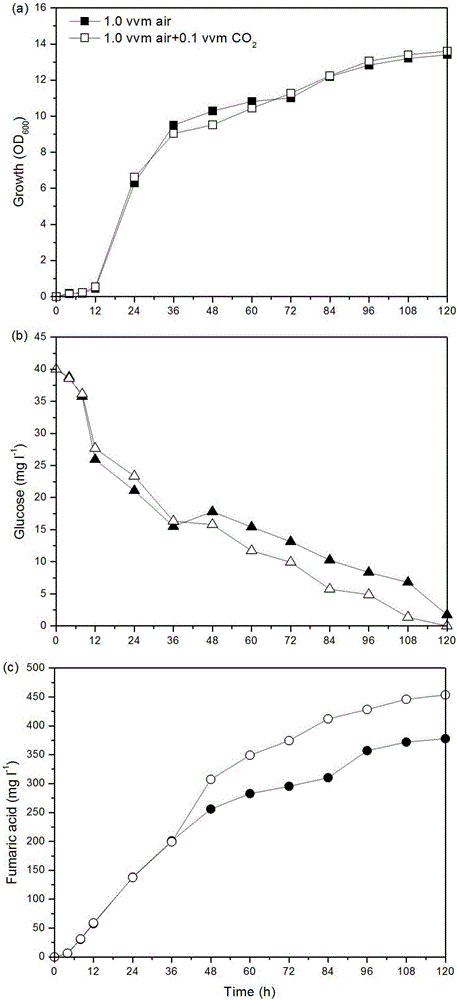
[0046] The feeding of embodiment 3 carbon dioxide is to the influence of fumaric acid fermentation
[0047] On the level of 7L fermenter, the influence of the introduction of carbon dioxide on the fermentation of fumaric acid was investigated, and the results are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0048] Culture conditions: Transfer the seeds of genetically engineered bacteria cultured at 30°C and 220rpm for 24 hours into the fermentation medium to make the initial OD 600 = 0.2, and cultured at 30°C for 96 hours, the aeration rate was 1vvm, the stirring speed was 300rpm, and when the fermentation was carried out for 36 hours, 0.1vvm of carbon dioxide was introduced.
[0049] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that after the fermentation was carried out for 36 hours, after the carbon dioxide of 0.1vvm was introduced, compared with the control (no carbon dioxide was introduced during the whole fermentation process), the output of fumaric acid gradually increased, and when the fermen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com