Patents
Literature
47 results about "Deficient mutant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
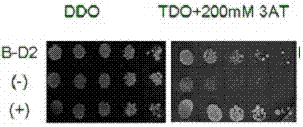
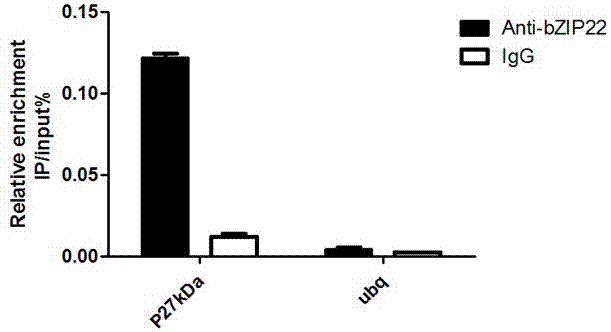
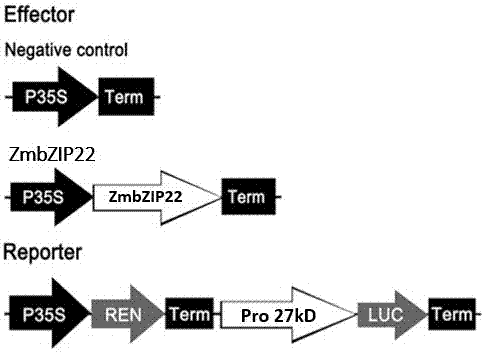
Zea mays transcription factor ZmbZIP22 and application thereof
ActiveCN107298701AReduce accumulationIncrease methionine contentPlant peptidesFermentationWild typeEssential amino acid
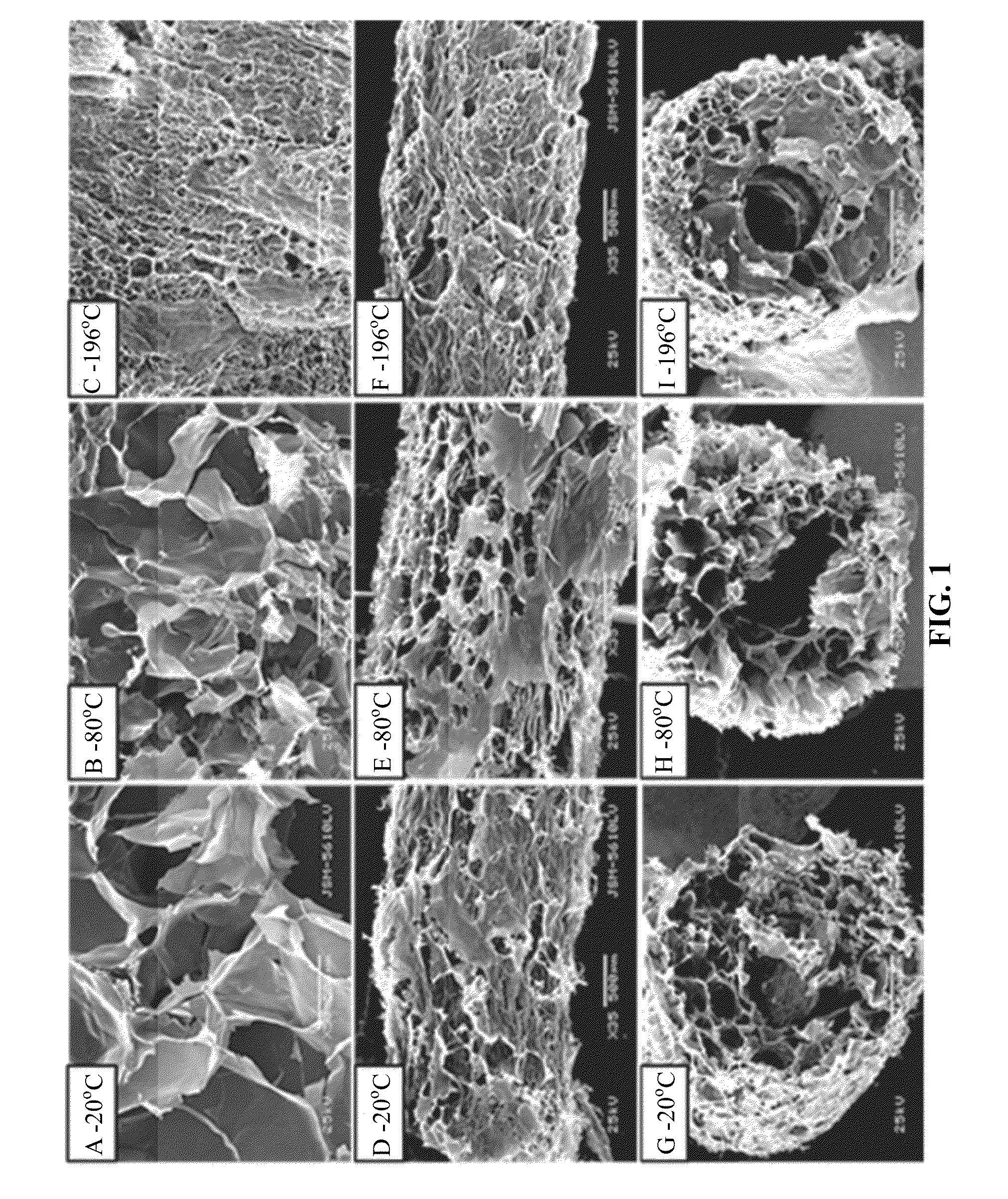
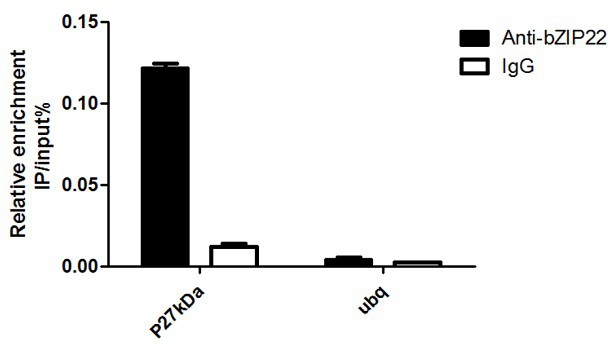
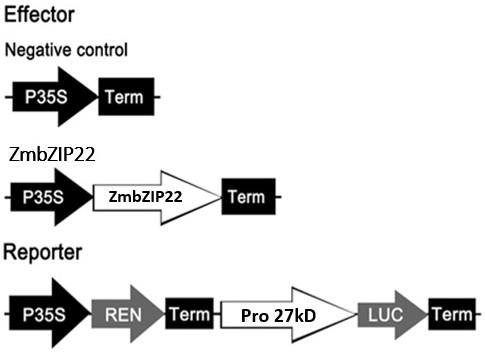
The invention relates to an application of a Zea mays grain transcription factor in the aspect of regulation and control of alcohal-soluble proteins. The factor comprises a base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The protein ZmbZIP22 encoded by the sequence can be directly bonded to a 27kDa gamma-gliadin promoter and activate the 27kDa gamma-gliadin promoter. Gene-deficient mutant plants are obtained through carrying out Zea mays immature-embryo conversion by taking a gene fragment, shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, of ZmbZIP22 as a guide RNA by using a CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Compared with wild type grains, transgenic mutants have Zea mays grains with irregular and relative-thin protein body shells, the content of alcohal-soluble proteins in mature grains is remarkably lowered, the content of essential amino acids such as lysine, which are deficient to the conventional Zea mays, in the mature grains is remarkably increased, and thus, the nutritional quality of Zea mays is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
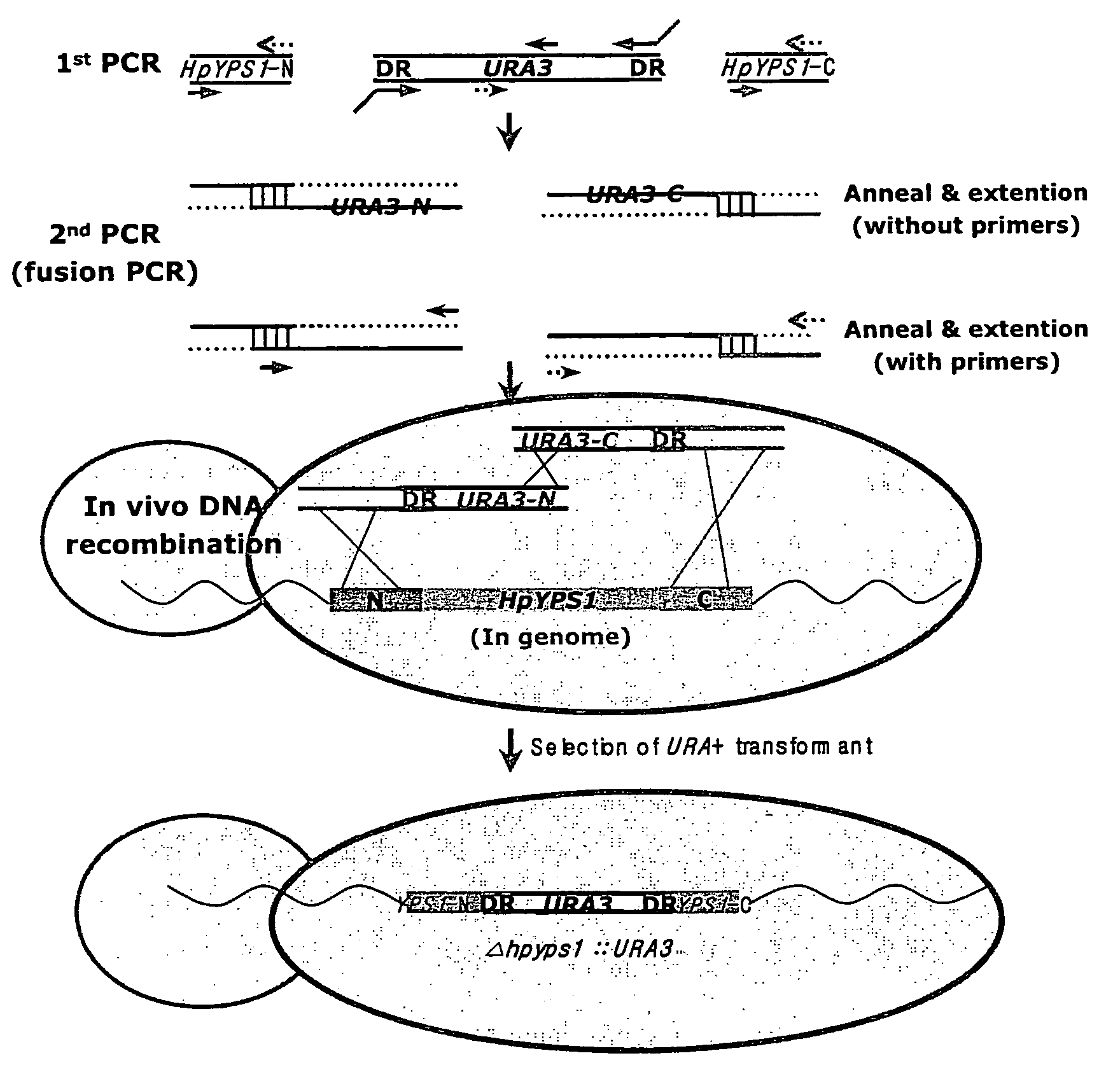
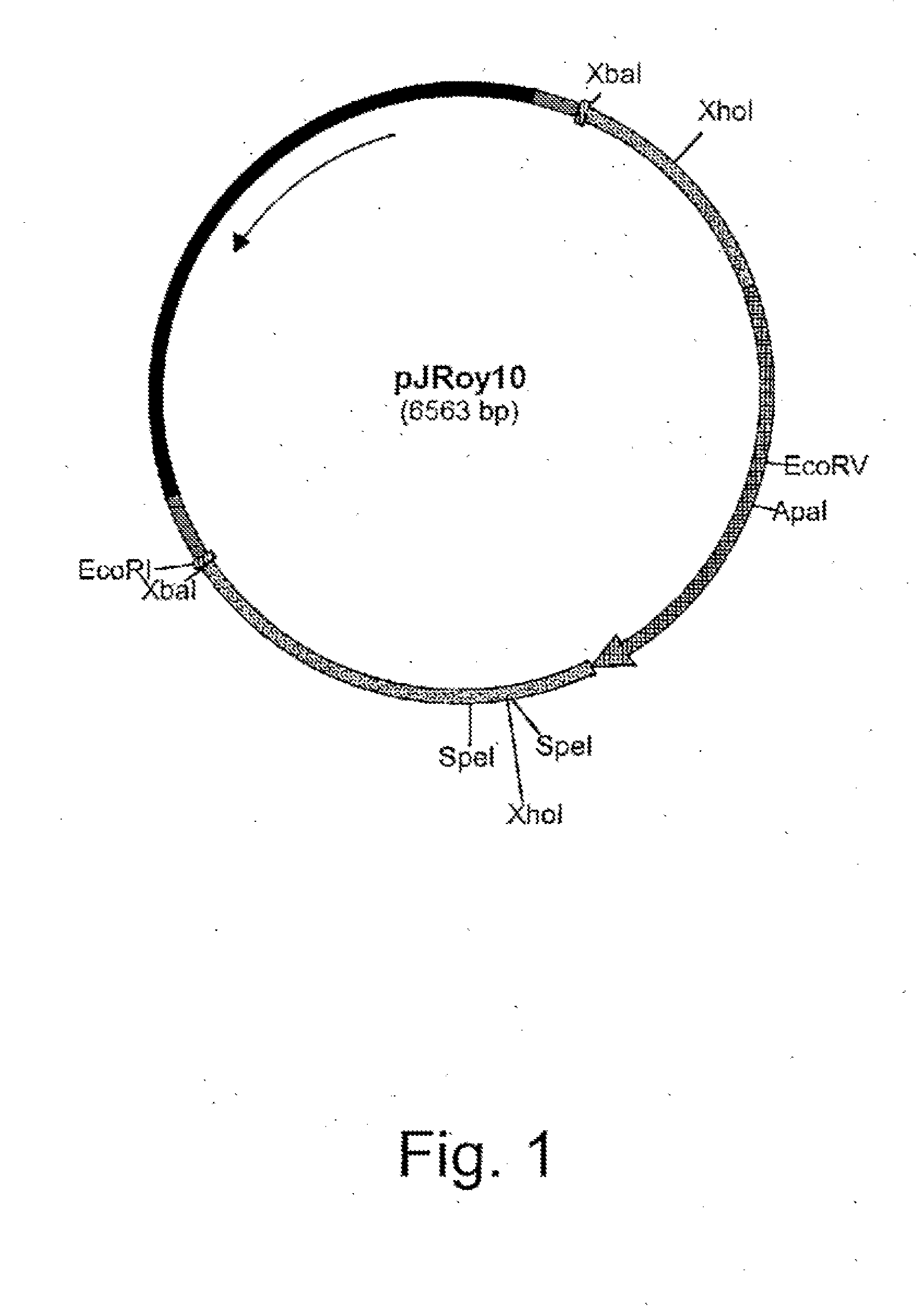
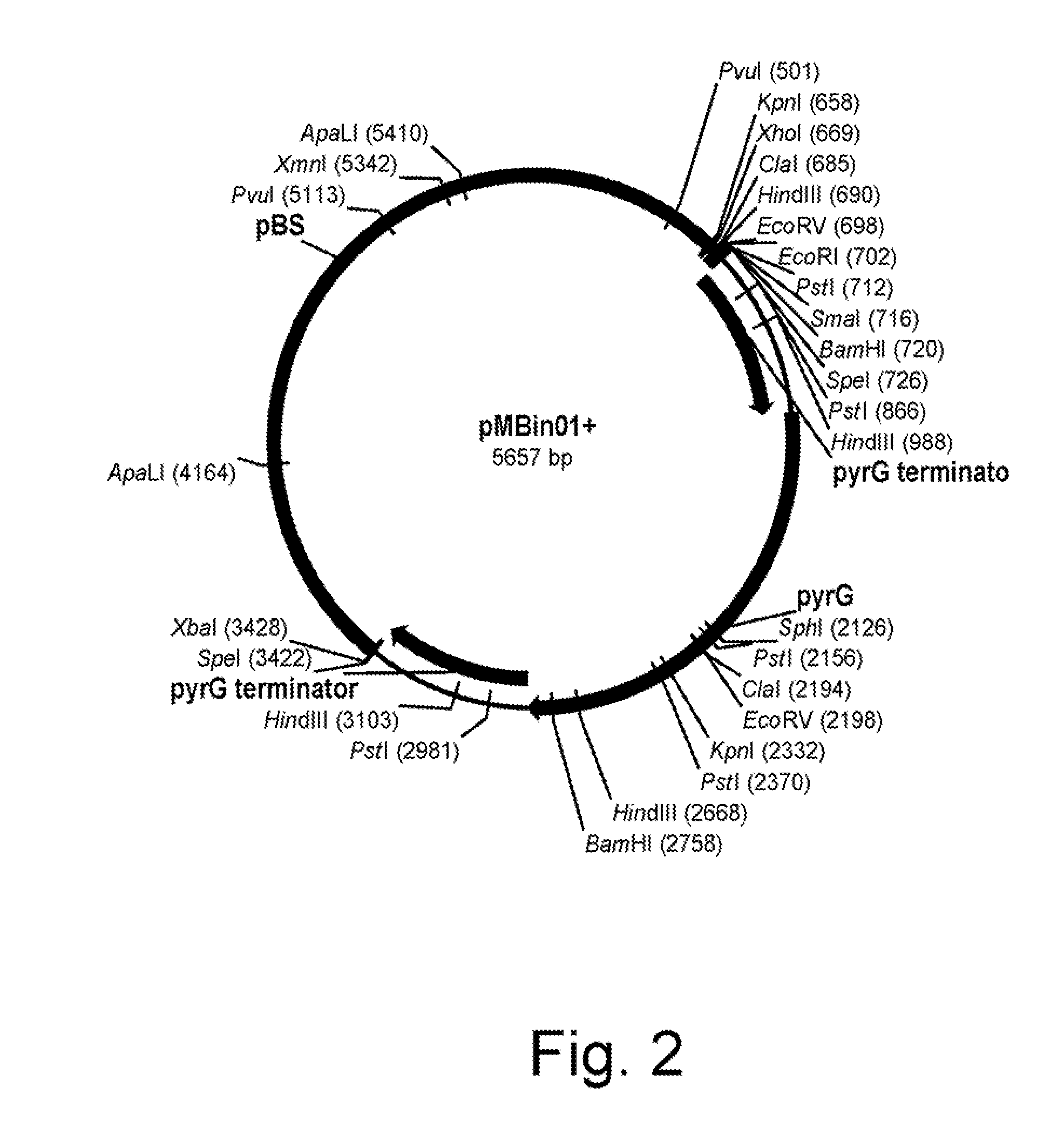
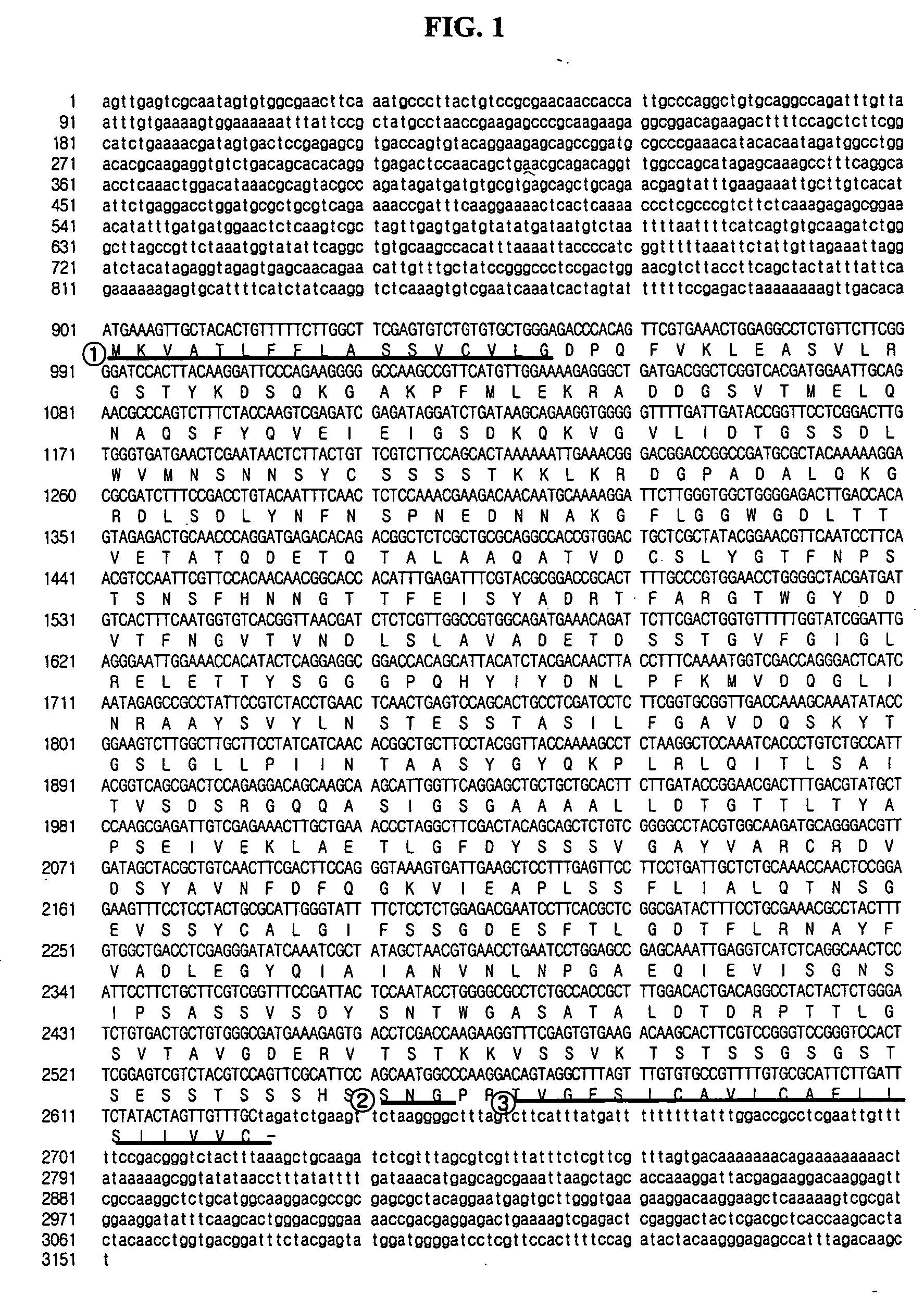
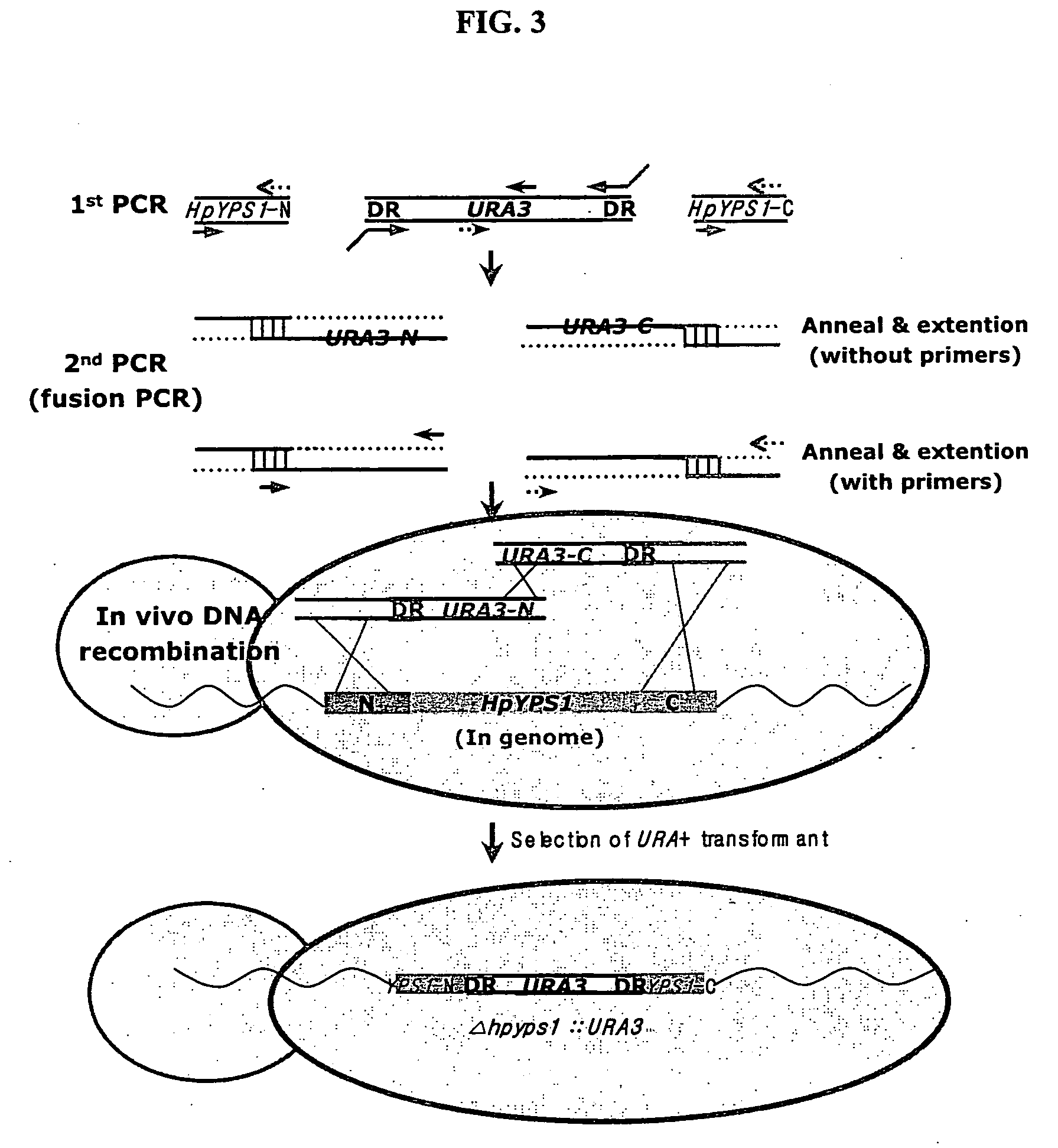
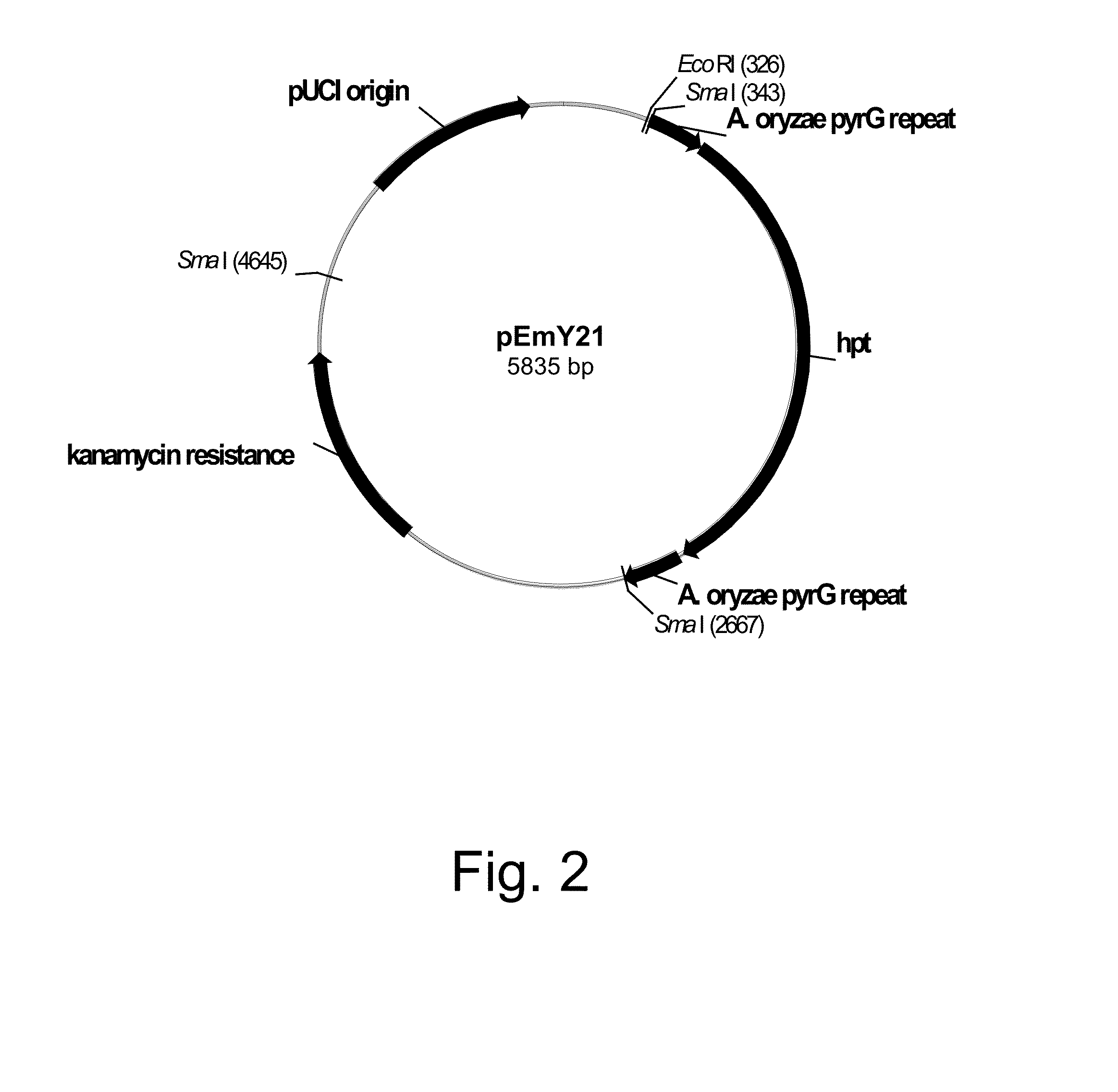
Hansenula polymorpha yapsin deficient mutant strain and process for the preparation of recombinant proteins using the same
InactiveUS7262287B2High-efficiency <i>Improve efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiBiotechnologyForeign protein
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule comprising the HpYPS1 gene encoding H. polymorpha yapsin1, a polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid molecule, a H. polymorpha mutant strain having reduced yapsin activity by mutation of the HpYPS gene encoding H. polymorpha yapsin1, a recombinant H. polymorpha strain expressing a foreign protein produced by introducing a gene encoding the foreign protein into the H. polymorpha mutant strain, and a process for preparing a foreign protein comprising culturing the recombinant H. polymorpha strain under conditions to express the foreign protein and isolating the foreign protein from the culture.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH +2
Methods for producing biological substances in enzyme-deficient mutants of Aspergillus
ActiveUS7303877B2Simplifies downstream processingSimple processMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousAlpha-amylase
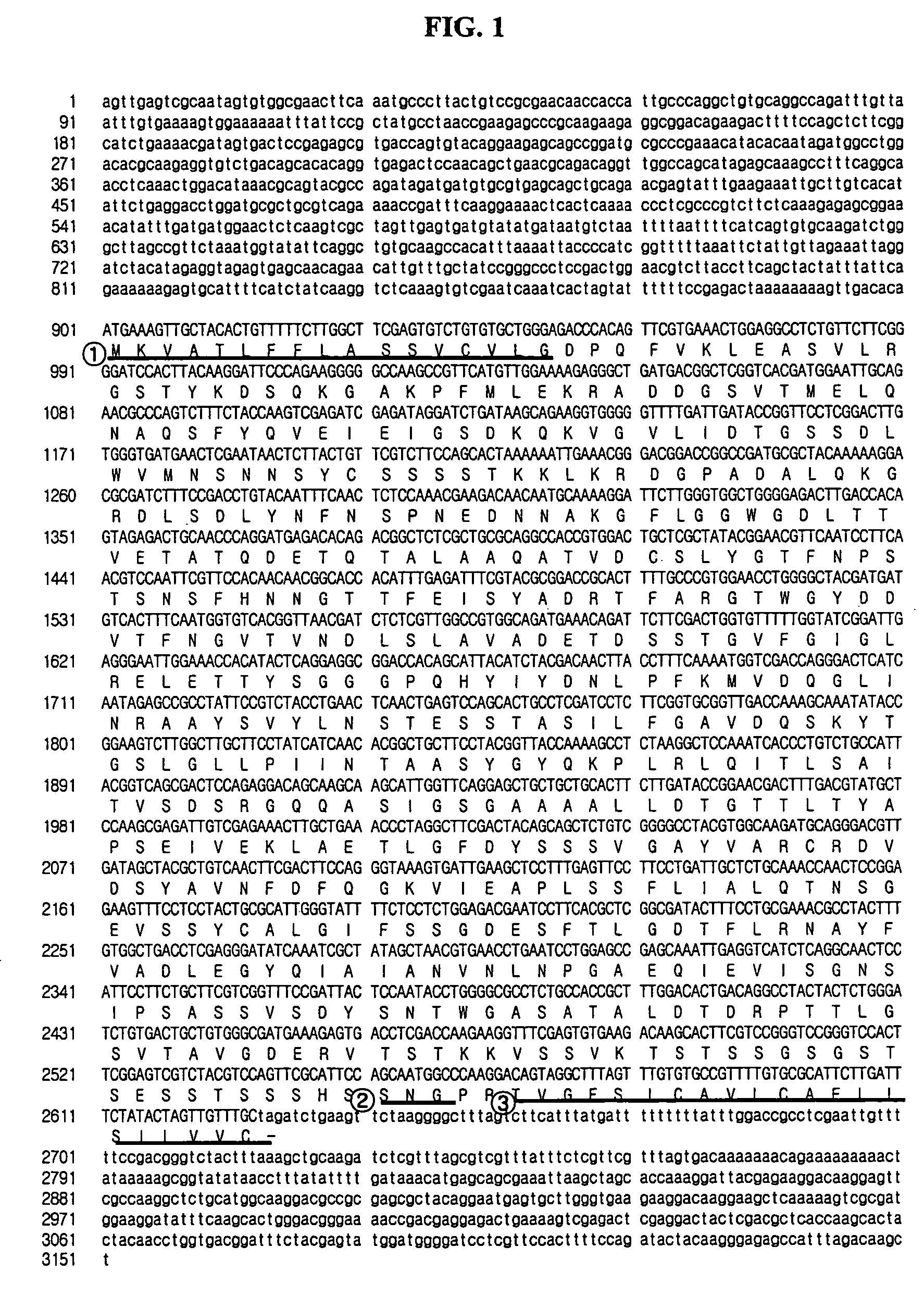
The present invention relates to methods of producing a heterologous biological substance, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Aspergillus niger strain in a medium suitable for the production of the heterologous biological substance, wherein (i) the mutant strain comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding the heterologous biological substance and one or more second nucleotide sequences comprising a modification of glaA and at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of asa, amyA, amyB, prtT, and oah, and (ii) the mutant strain is deficient in the production of glucoamylase and at least one enzyme selected from the group consisting of acid stable alpha-amylase, neutral alpha-amylase A, and neutral alpha-amylase B, protease, and oxalic acid hydrolase compared to the parent Aspergillus niger strain when cultivated under identical conditions; and (b) recovering the heterologous biological substance from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to enzyme-deficient mutants of Aspergillus niger strains and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
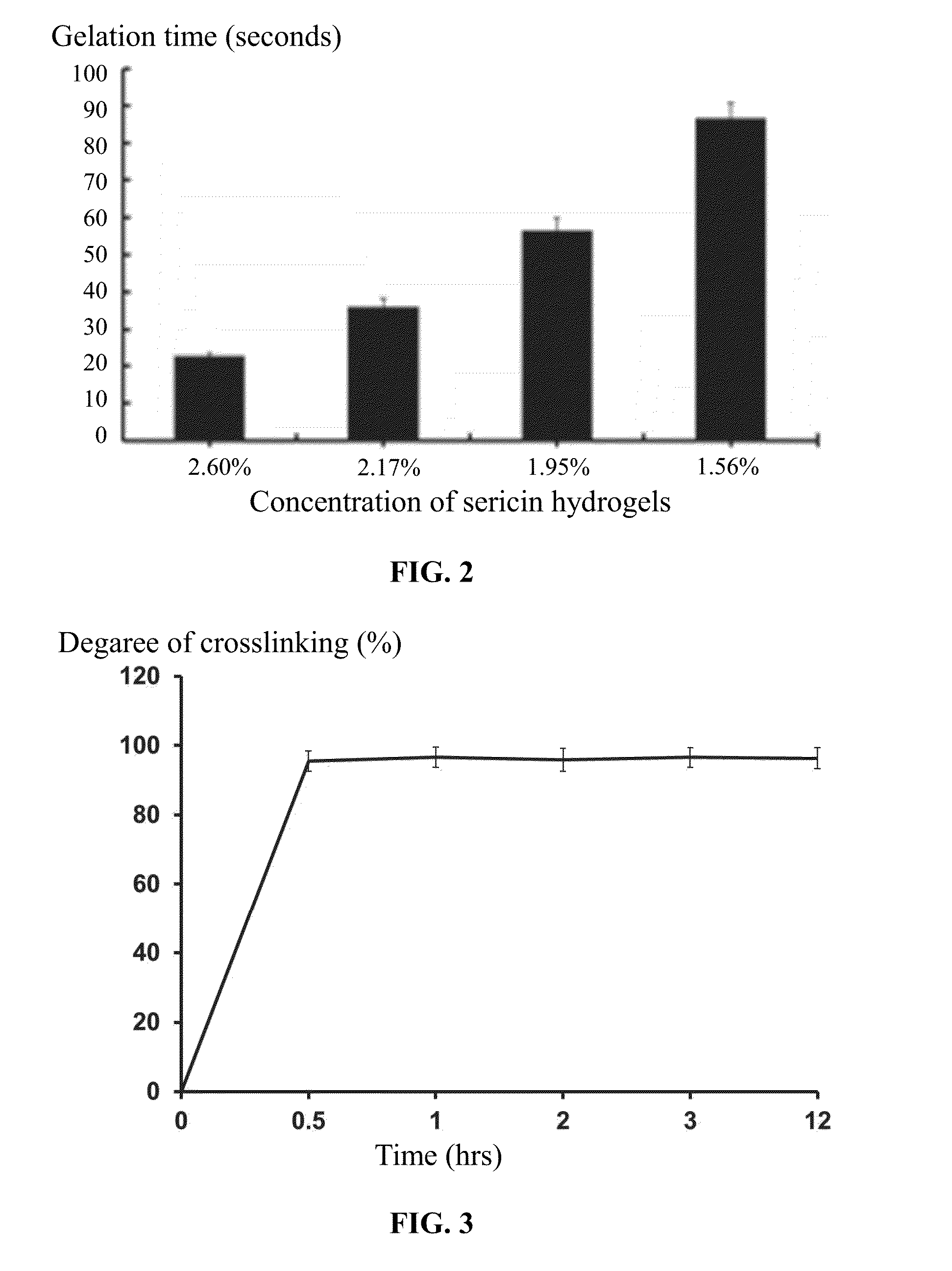
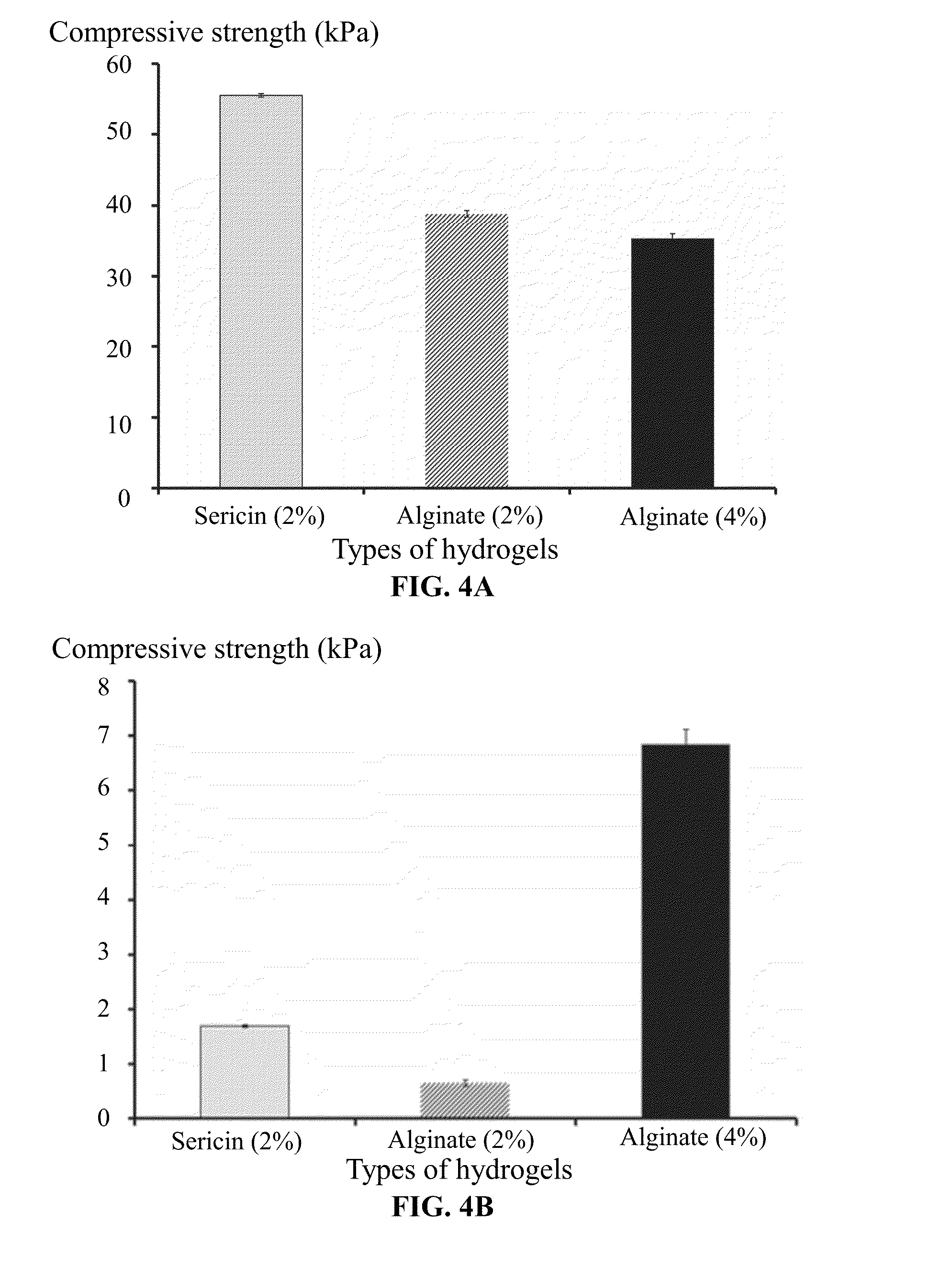
Methods of preparing and using sericin hydrogel
InactiveUS20160136241A1Good biocompatibilityPromote cell adhesionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsNervous disorderAqueous solutionSericin
A method for preparing a sericin hydrogel, the method including: 1) weighing a cocoon of a fibroin-deficient mutant silkworm, Bombyx mori, extracting the cocoon by an aqueous solution of LiBr or LiCl, dialyzing an extracted solution to yield a sericin solution having a concentration of a non-degraded sericin of between 0.1 and 4 wt. %; and 2) concentrating the sericin solution to a concentration of between 1.5 and 10 wt. %, adding a crosslinking agent to the concentrated sericin solution at a ratio of between 2 and 500 μL of the crosslinking agent per each milliliter of the sericin solution, fully blending the crosslinking agent with the concentrated sericin solution, and keeping a resulting mixture at the temperature of between 4 and 45° C. for between 5 s and 36 hrs to yield a hydrogel.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Methods for producing polypeptidies in protease-deficient mutants of trichoderma
The present invention relates to mutants of a parent Trichoderma strain, comprising a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide and one or more (several) genes selected from the group consisting of a first subtilisin-like serine protease gene, a first aspartic protease gene, a trypsin-like serine protease gene, a second subtilisin-like serine protease gene, and a second aspartic protease gene, wherein the one or more (several) genes are modified rendering the mutant strain deficient in the production of one or more (several) enzymes selected from the group consisting of a first subtilisin-like serine protease, a first aspartic protease, a trypsin-like serine protease, a second subtilisin-like serine protease, and a second aspartic protease, respectively, compared to the parent Trichoderma strain when cultivated under identical conditions. The present invention also relates to methods of producing a polypeptide in such mutants and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
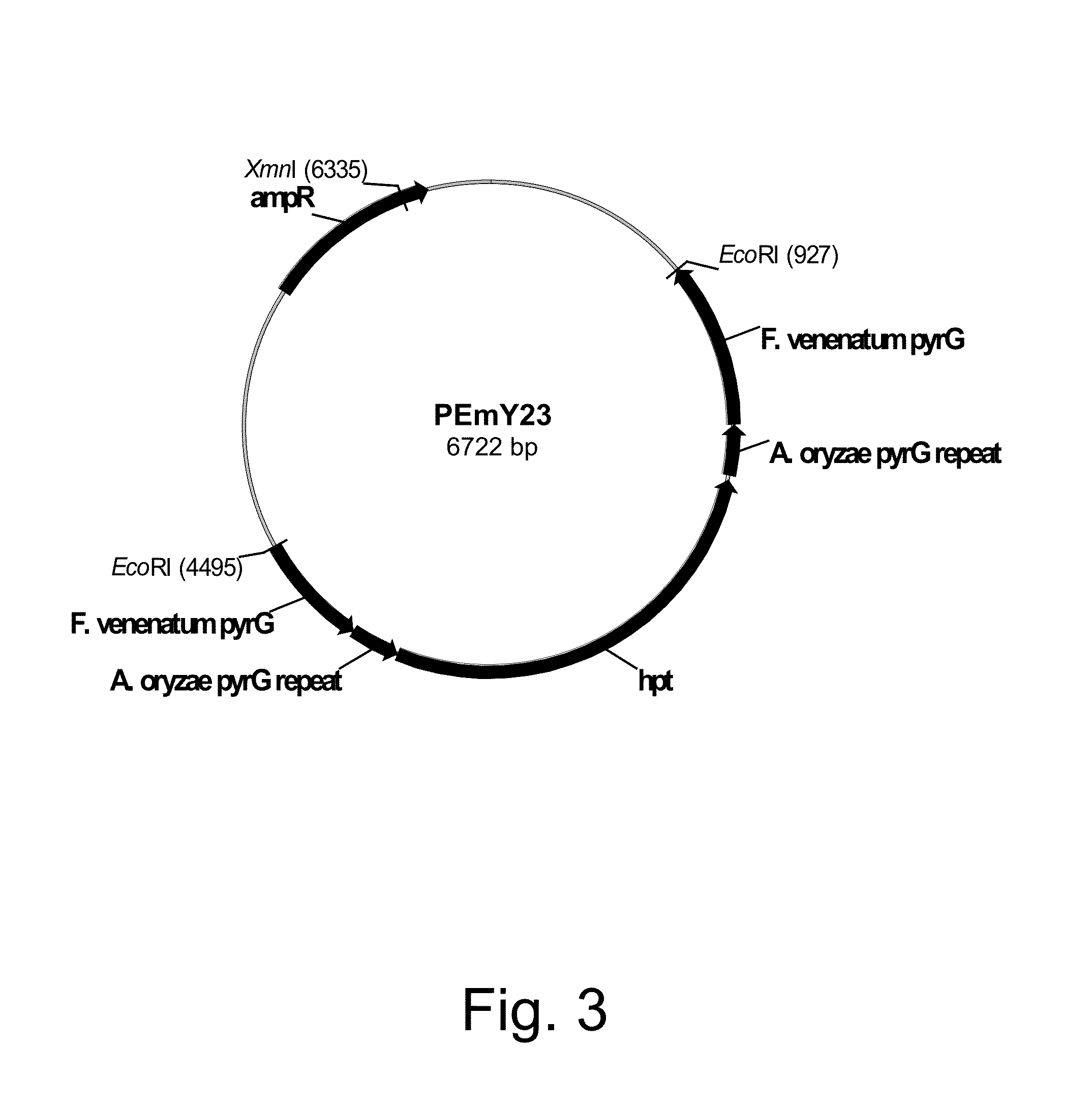
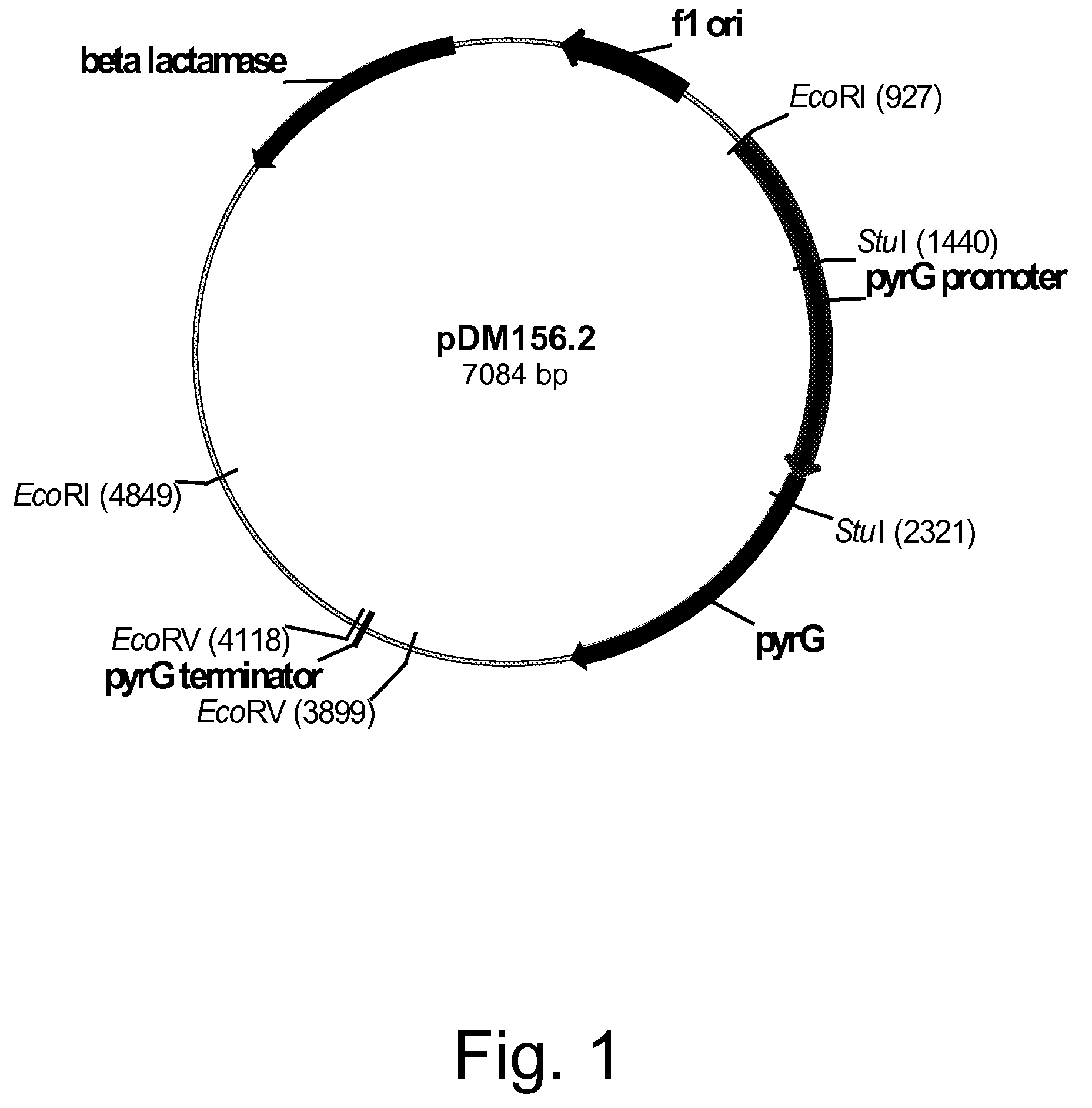
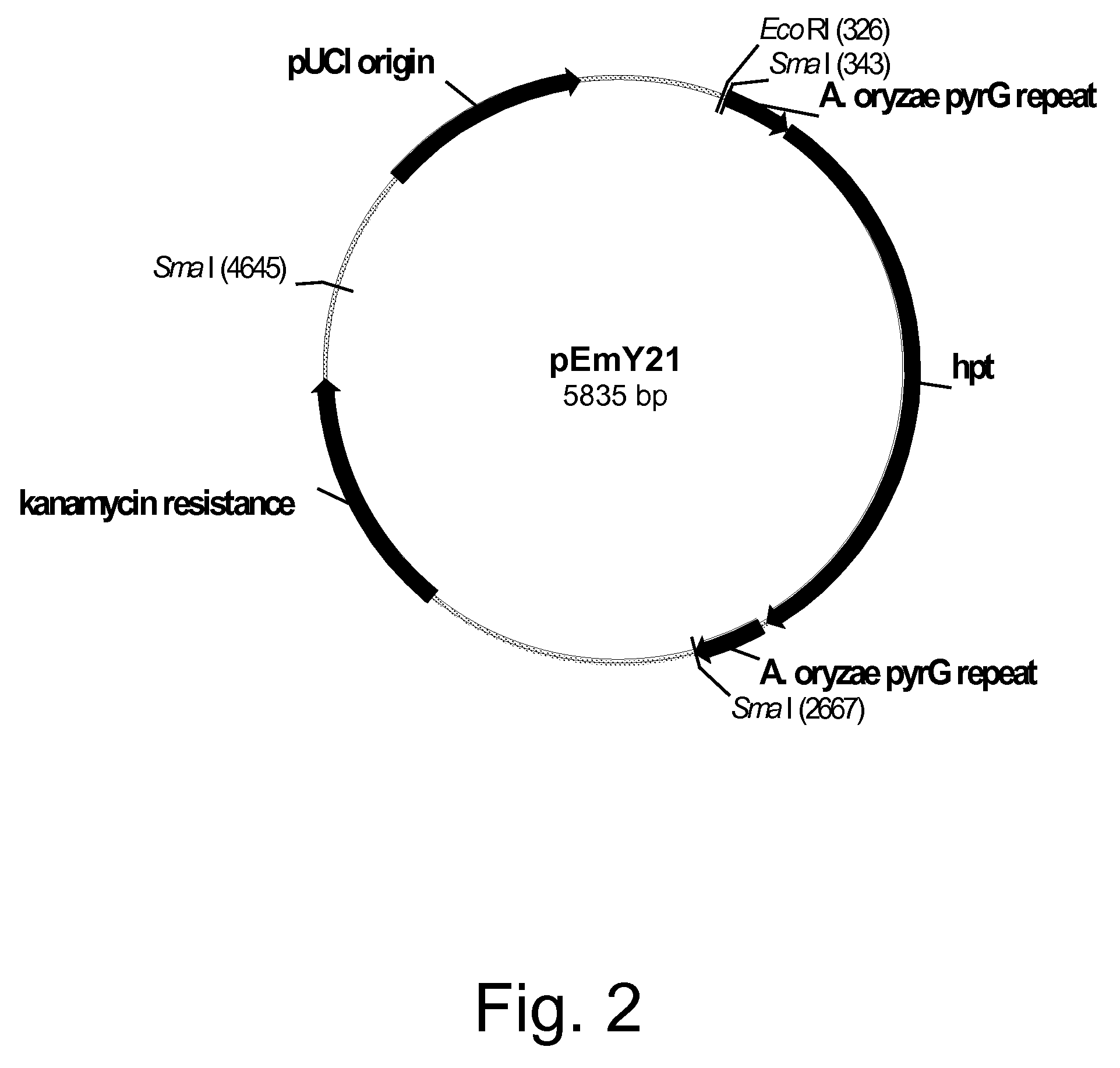
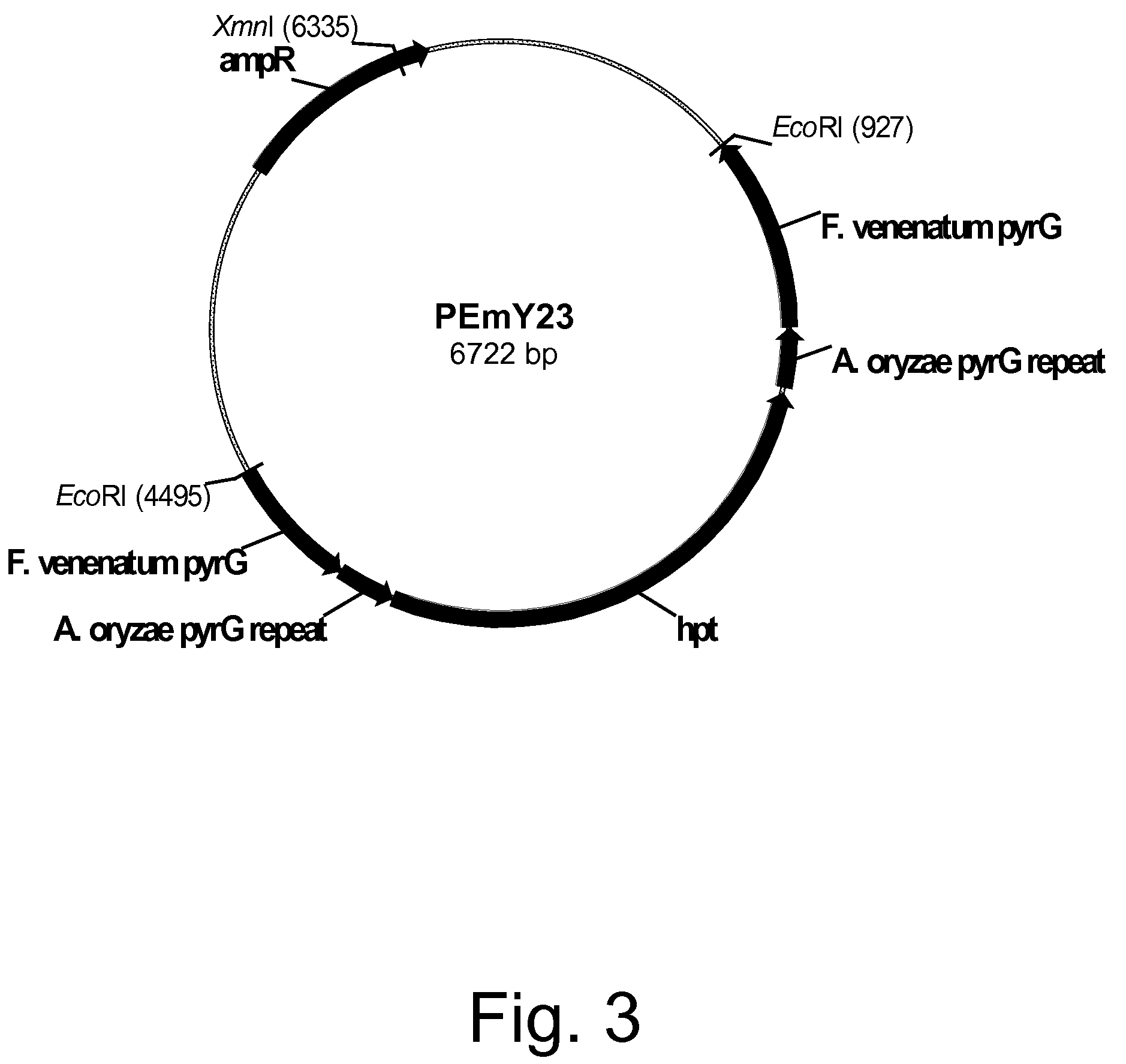
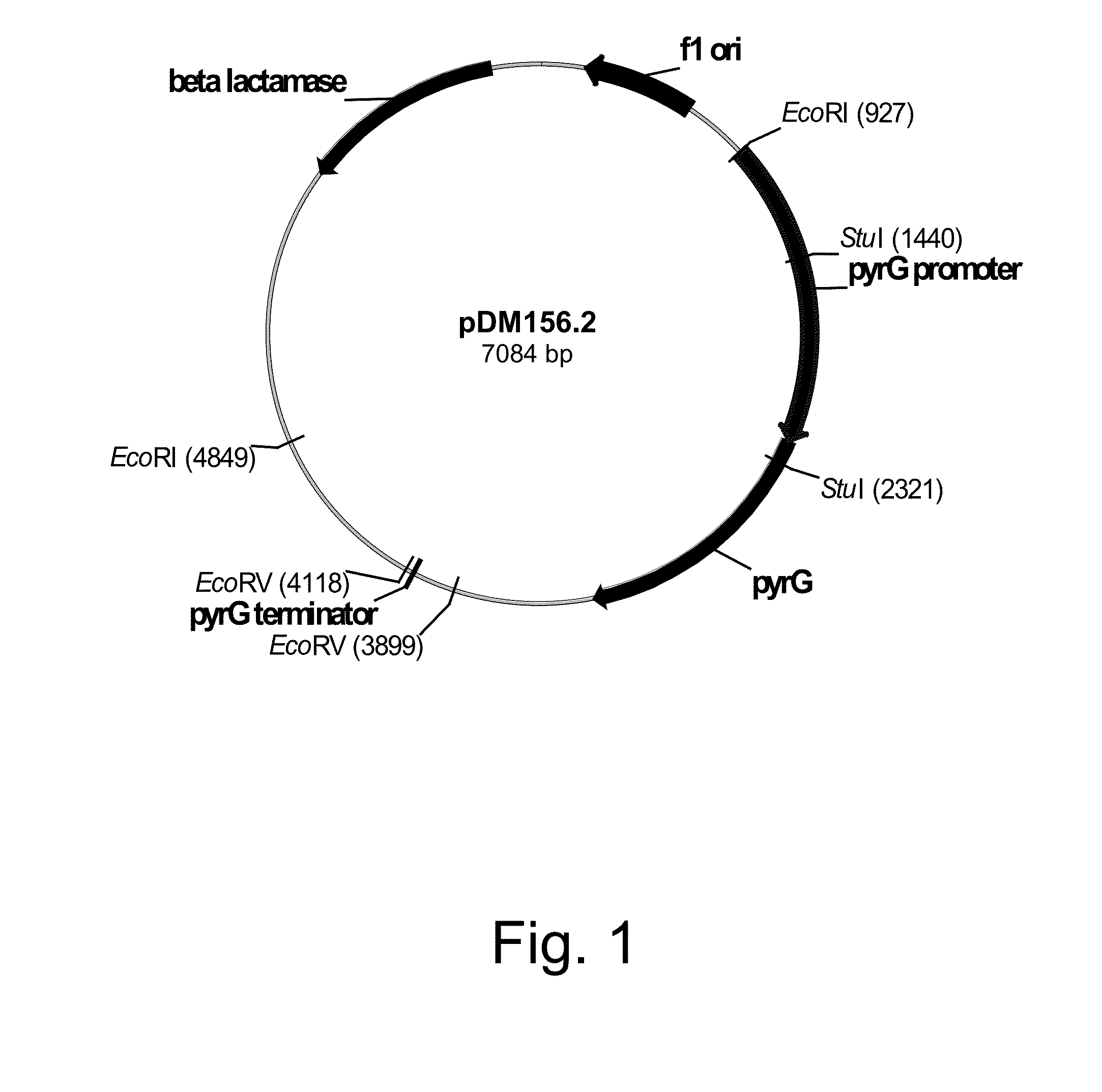
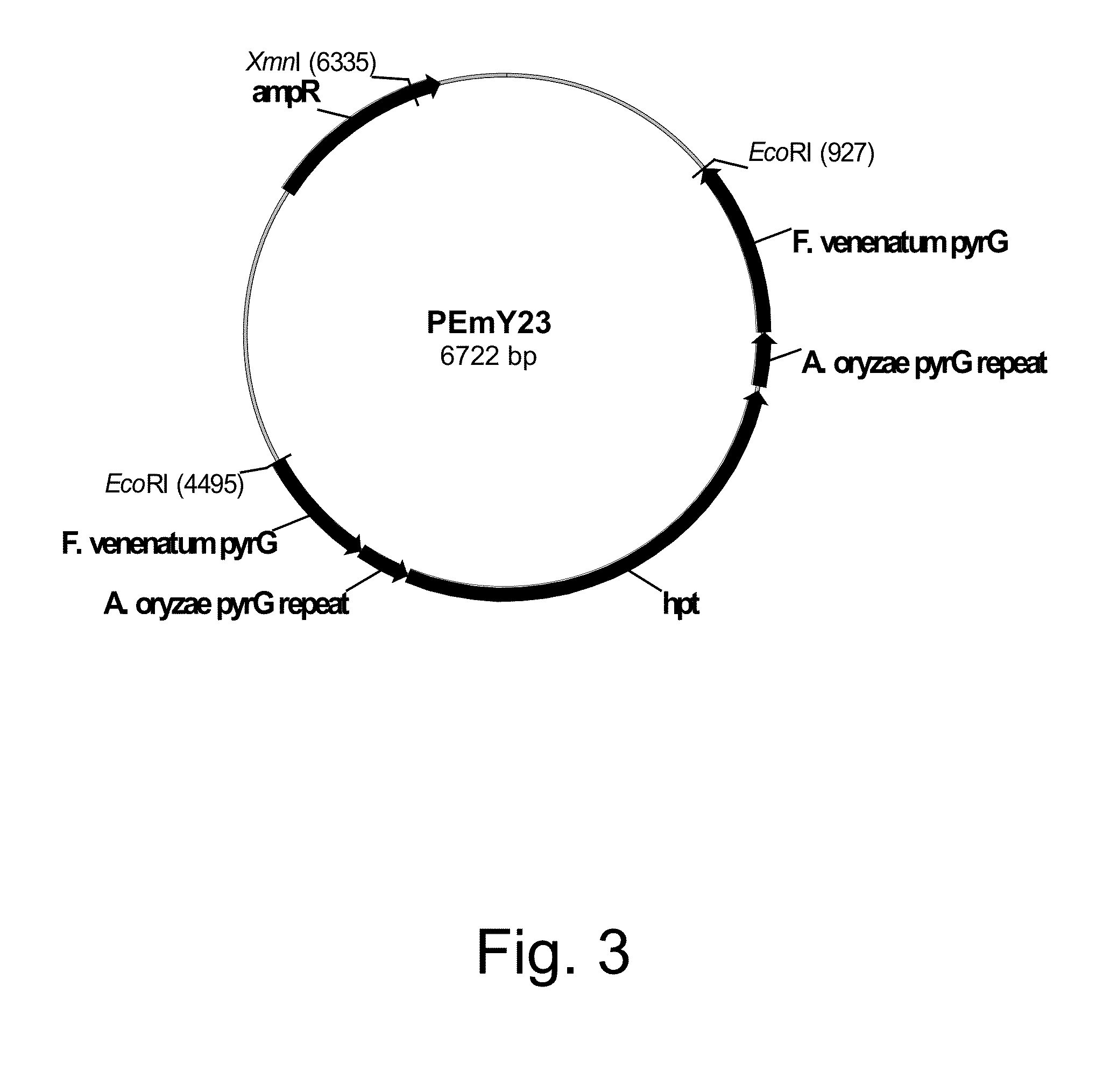
Methods for producing polypeptides in enzyme-deficient mutants of Fusarium venenatum
InactiveUS8647856B2Reduce expressionAffect expressionFungiFermentationBiotechnologyAlkaline protease
The present invention relates to methods of producing a polypeptide, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Fusarium venenatum strain in a medium for the production of the polypeptide, wherein the mutant strain comprises a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide and one or more (several) genes selected from the group consisting of pyrG, amyA, and alpA, wherein the one or more (several) genes are modified rendering the mutant strain deficient in the production of one or more (several) enzymes selected from the group consisting of orotidine-5′-monophosphate decarboxylase, alpha-amylase, and alkaline protease, respectively, compared to the parent Fusarium venenatum strain when cultivated under identical conditions; and (b) recovering the polypeptide from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to enzyme-deficient mutants of Fusarium venenatum strains and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Mutants of gram negative mucosal bacteria and application thereof in vaccines
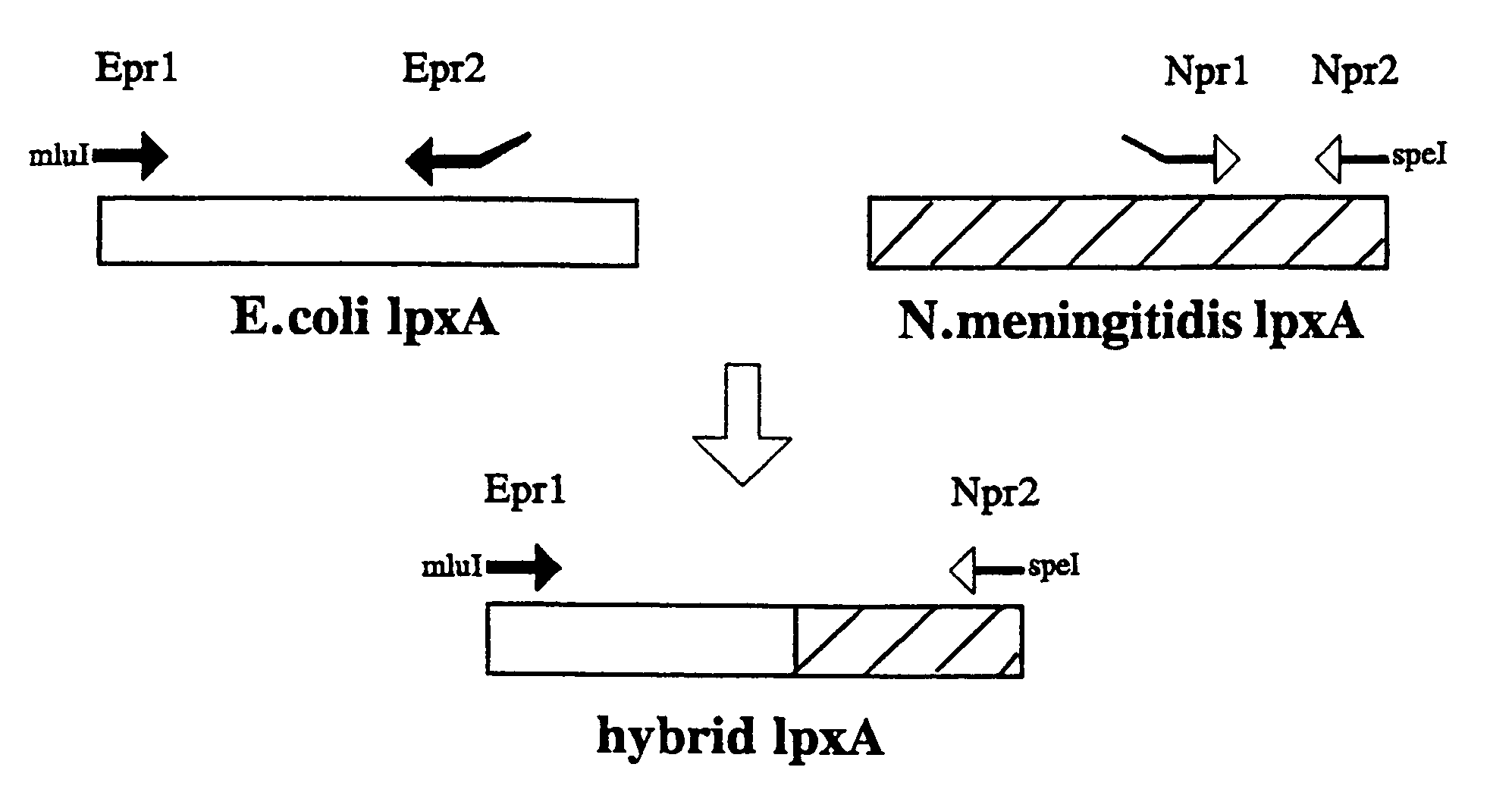
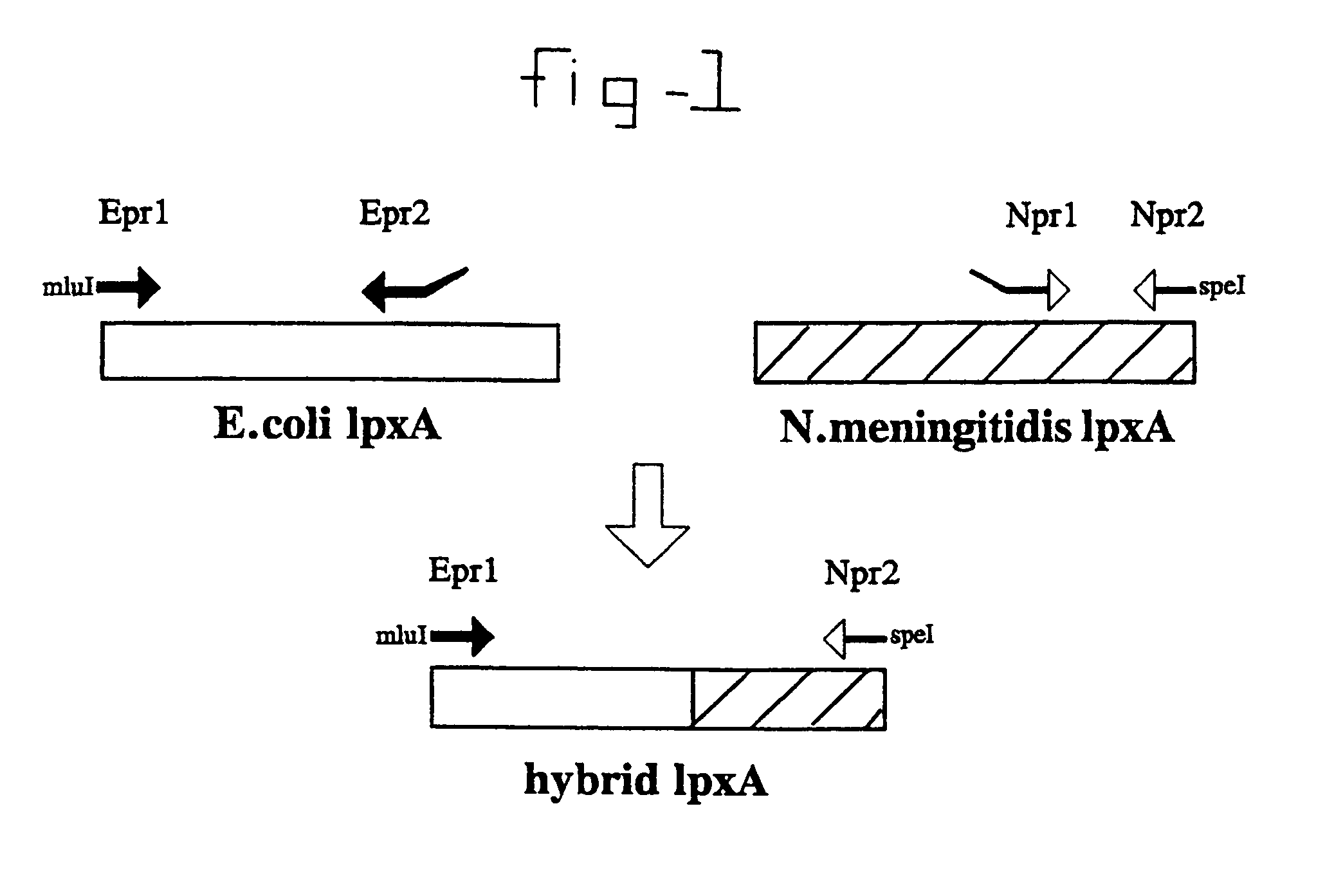
It is possible to inactivate the early stage of lipid A synthesis of mucosal gram negative bacteria without compromising cell viability. In particular the lpxA gene in N. meningitidis was mutated and resulting lpxA knockout mutants were found to be completely lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-deficient. The major outer membrane proteins (OMPs) were detected in normal amounts. The finding provides important implications for understanding of structure and biogenesis of the outer membrane. On a practical level, the availability of LPS-deficient mutants of pathogenic mucosal bacteria such as N. meningitidis opens up new avenues to vaccine development. It enables easy isolation of endotoxin-free purified proteins, outer membranes or even whole-cell preparations for use in immunisation.
Owner:INTRAVACC BV +1
Paddy rice gene of synthetase of coded beta - keto acyl coenzyme A
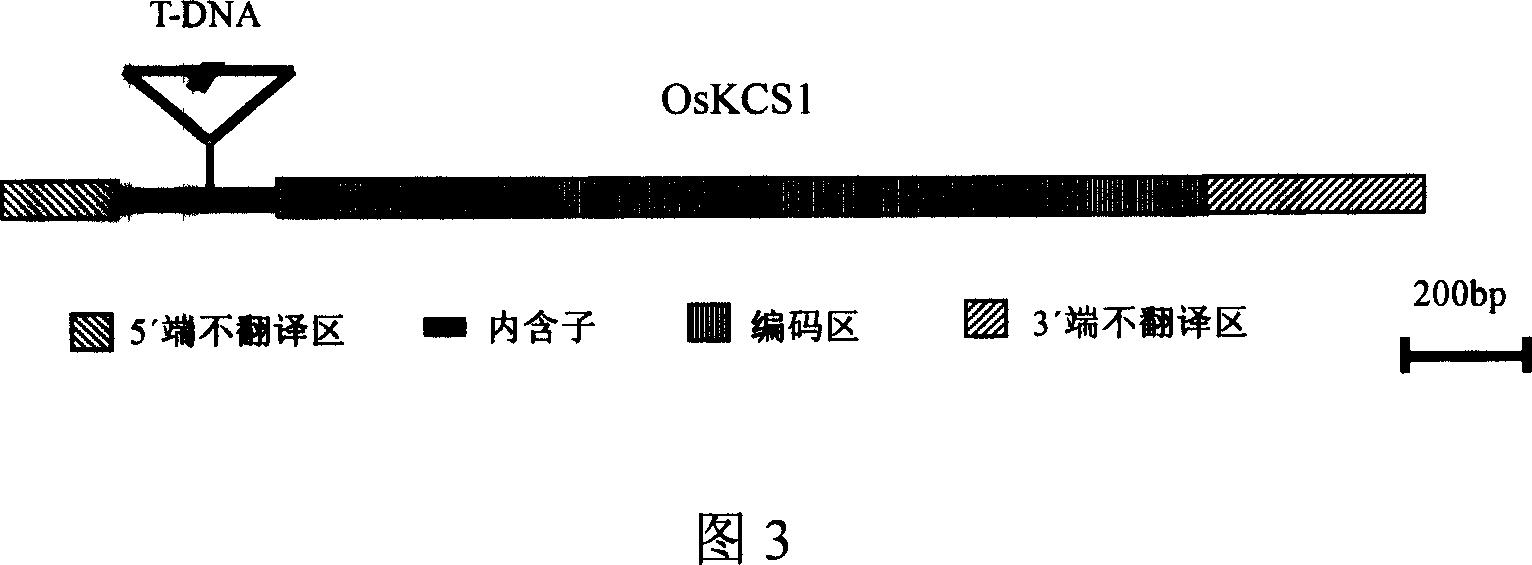
This invention provides a rice gene coding beta-keto co A synthetase, OsKCS1, which comprises 2186bp and 1560bp coding zones at the upstream of the start codon with promoter function, codes 519 amino acid, and contains typical FAE1 CUT1 RppA domain. The function-deficient mutant P1424 obtained by inserting T-DNA into rice OsKCS1 gene has short plants, occasionally curled leaves, and low fruiting rate. Further research shows that the wax at the surfaces of the mutant gas-generating organs is obviously reduced, and the draught resistance is seriously influenced. The expression of OsKCS1 gene in the mutant can recover its wild phenotype, thus can confirm the direction relationship between OsKCS1 gene and synthesis and growth of wax on rice surfaces. The identification of the gene is important to research on synthesis of wax on rice surfaces, and breeding of draught-resistant rice or other monocotyledon crops.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving microalgae growth rate and oil yield
InactiveCN104140929AIncrease growth rateHigh yieldUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiofuelBiology
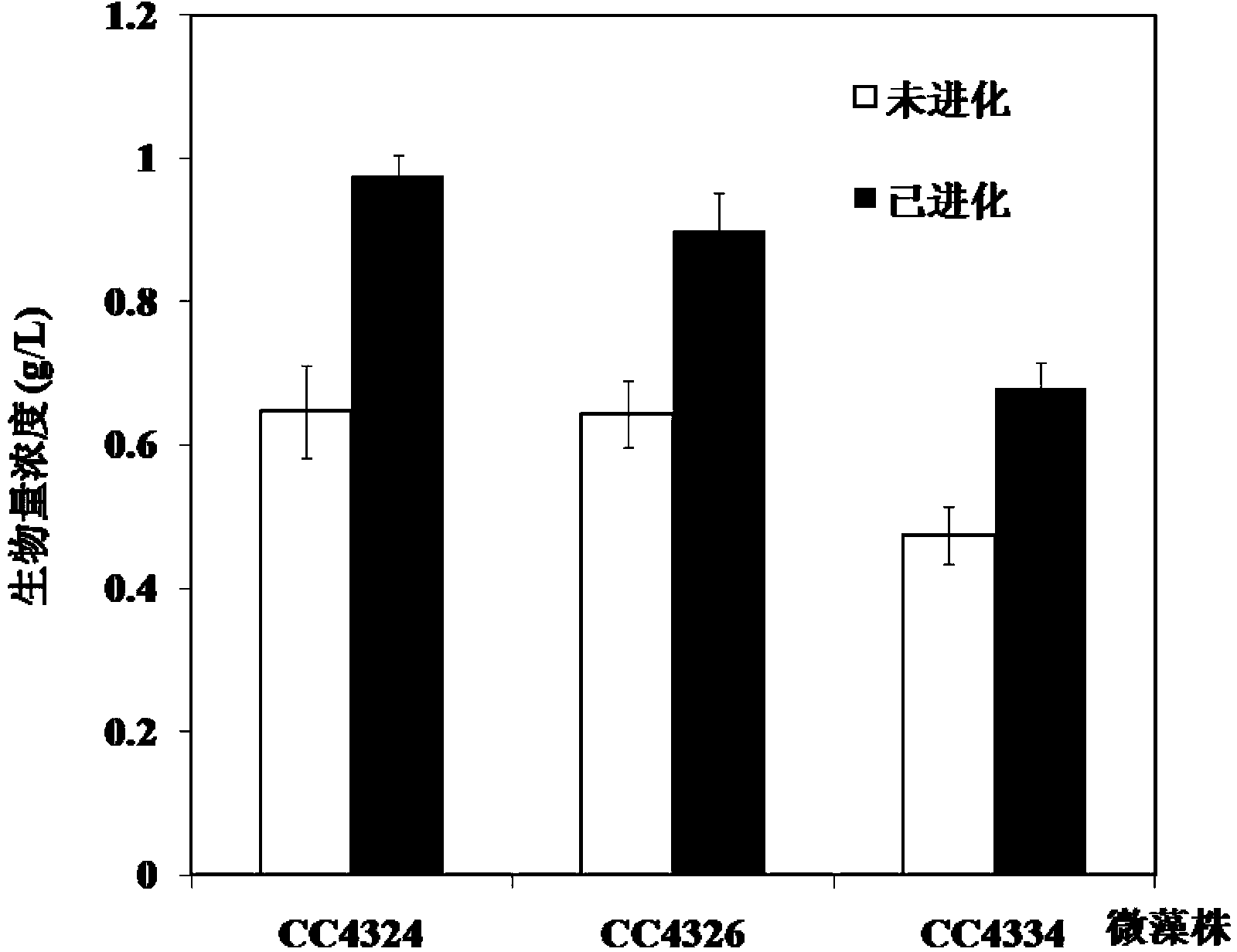
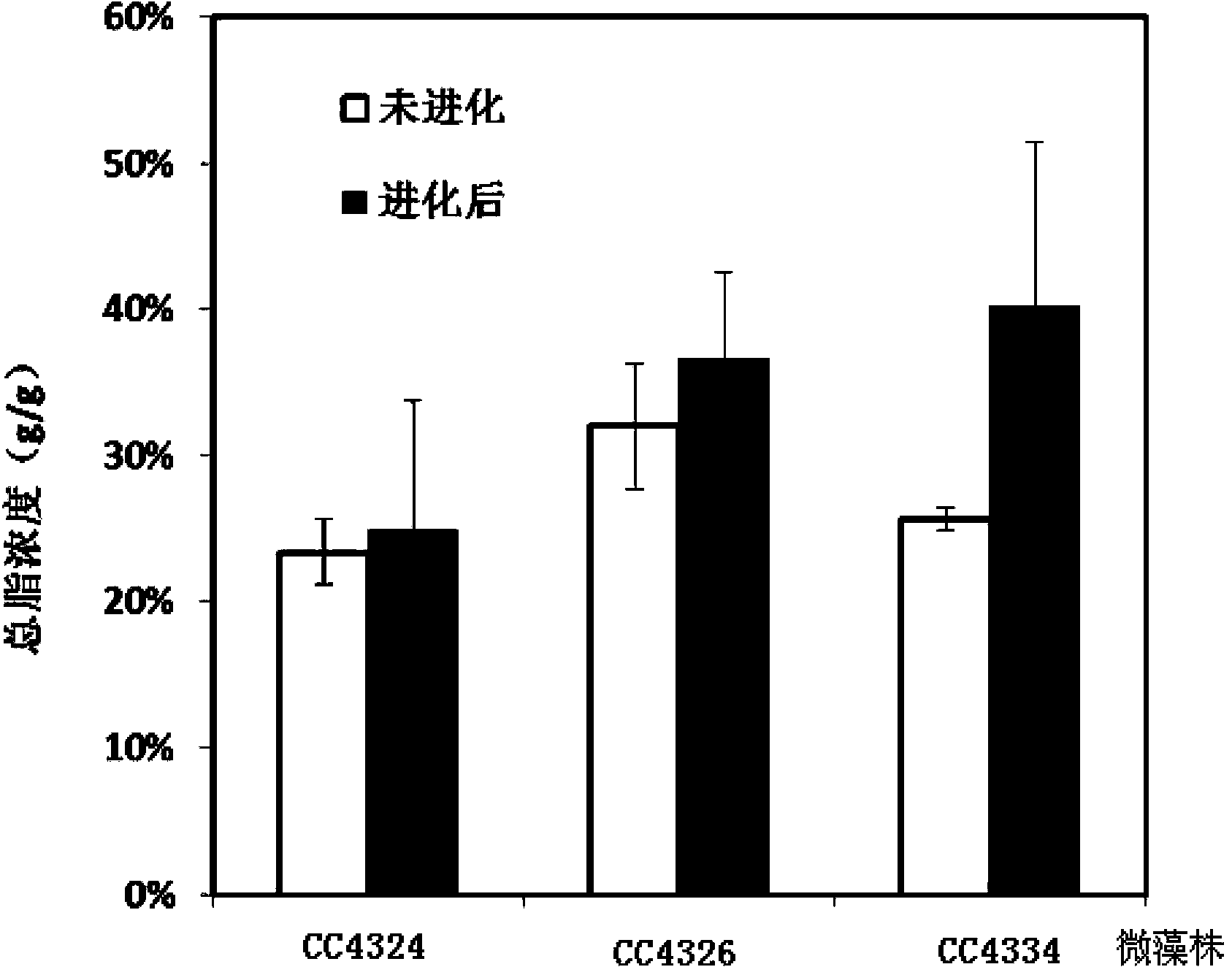
The invention discloses a method for improving microalgae growth rate and oil yield, and the method includes the following steps: 1), after inoculation of microalgae, the microalgae is cultured for 2-5 days by continuous illumination or cycled illumination in a certain light and dark conditions at 20-35 DEG C and in the conditions of 20-200 mu mol photon in m<-2>s<-1>; 2), the microalgae strain obtained by the step 1) is inoculated again, and then cultured; and 3), the microalgae strain is cultured by step 1) as a training cycle, and then cultured by step 2) as a next training cycle, and the microalgae strain with the growth rate and oil yield both increased can be obtained by the cycled training. According to the method, the growth rate and oil yield both of wild microalgae strains and microalgae gene deficient mutants are increased, and compared with the large-scale screening, the method is less in workload and high in efficiency, is a new strain selection method, and has broad application prospects in microalgae biofuel development.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Extractability and Bioavailability of the Natural Antioxidant Astaxanthin From a Green Alga, Haematococcus Pluvialis
InactiveUS20090214475A1Excellent extractabilityImprove bioavailabilityMilk preparationBiocideCystAntioxidant
As the richest source of astaxanthin, a natural antioxidant and coloring agent, the unicellular green alga, Haematococcus pluvialis, is being commercially exploited. A major constraint in the Haematococcus production system, however, is the thick, rigid cell walls associated with astaxanthin-rich cysts (or aplanospores). The thick walls prevent the extraction of cellular materials and consequently reduce the bioavailability of astaxanthin. Using a physical, chemical, or enzymatic method to disrupt the cell wall has proven to be very expensive and also introduce the risk of oxidation of astaxanthin by atmospheric oxygen The present invention provides a novel method for solving this problem by introducing two genetically modified Haematococcus pluvialis mutants. These two mutants, named as D 13-17 and N54-22, contain remarkably reduced amounts of cell wall materials, but retain the growth potential and ability to accumulate astaxanthin as high as the wild type strain. Organic solvent extraction efficiency assay has demonstrated that cellular astaxanthin can be more effectively and efficiently extracted from the cell wall-deficient mutants than from the wild type, suggesting that the mutants may provide better bioavailability of astaxanthin to humans and animals. The said mutants can be used for production of natural astaxanthin for human and animal consumption
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
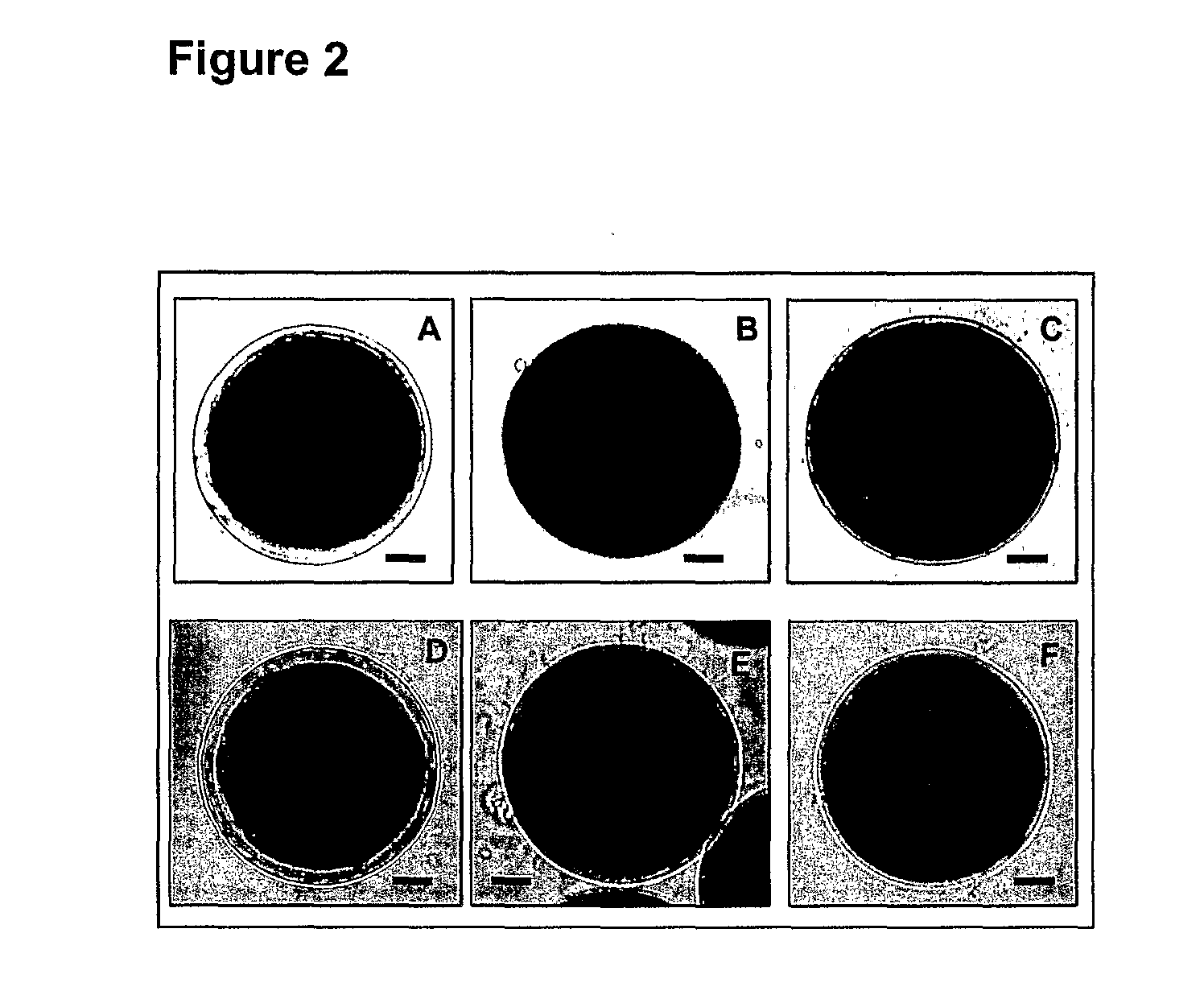
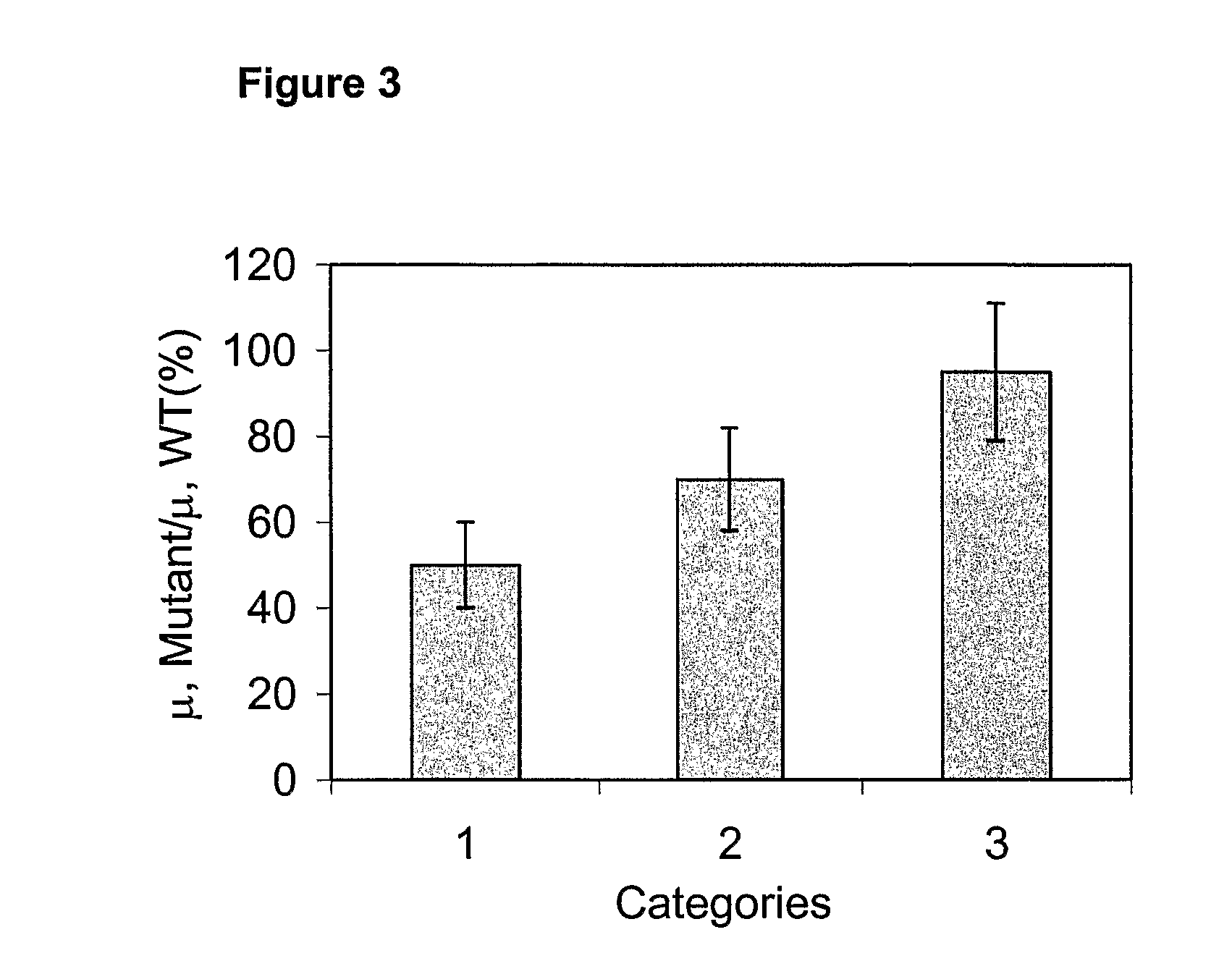
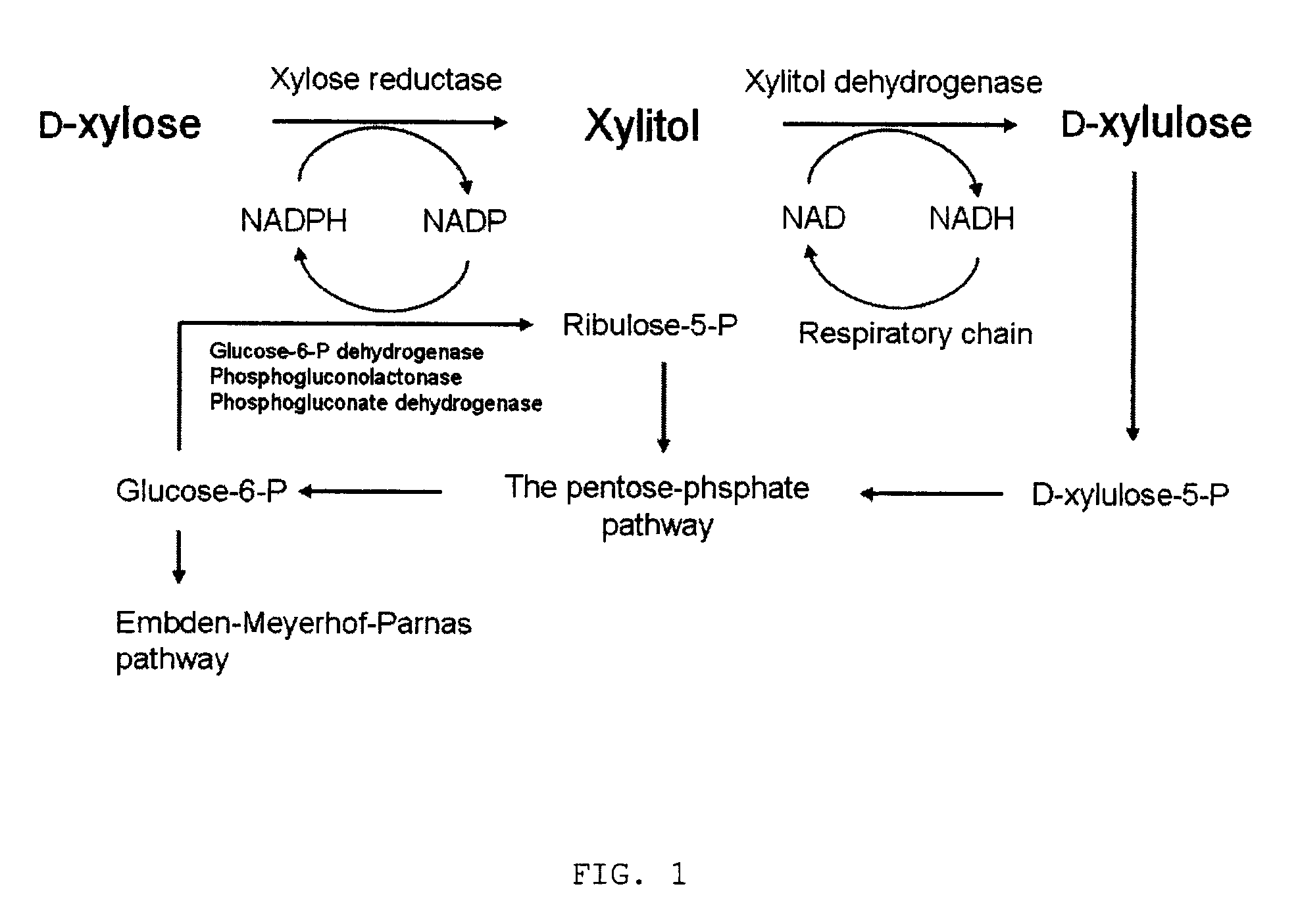
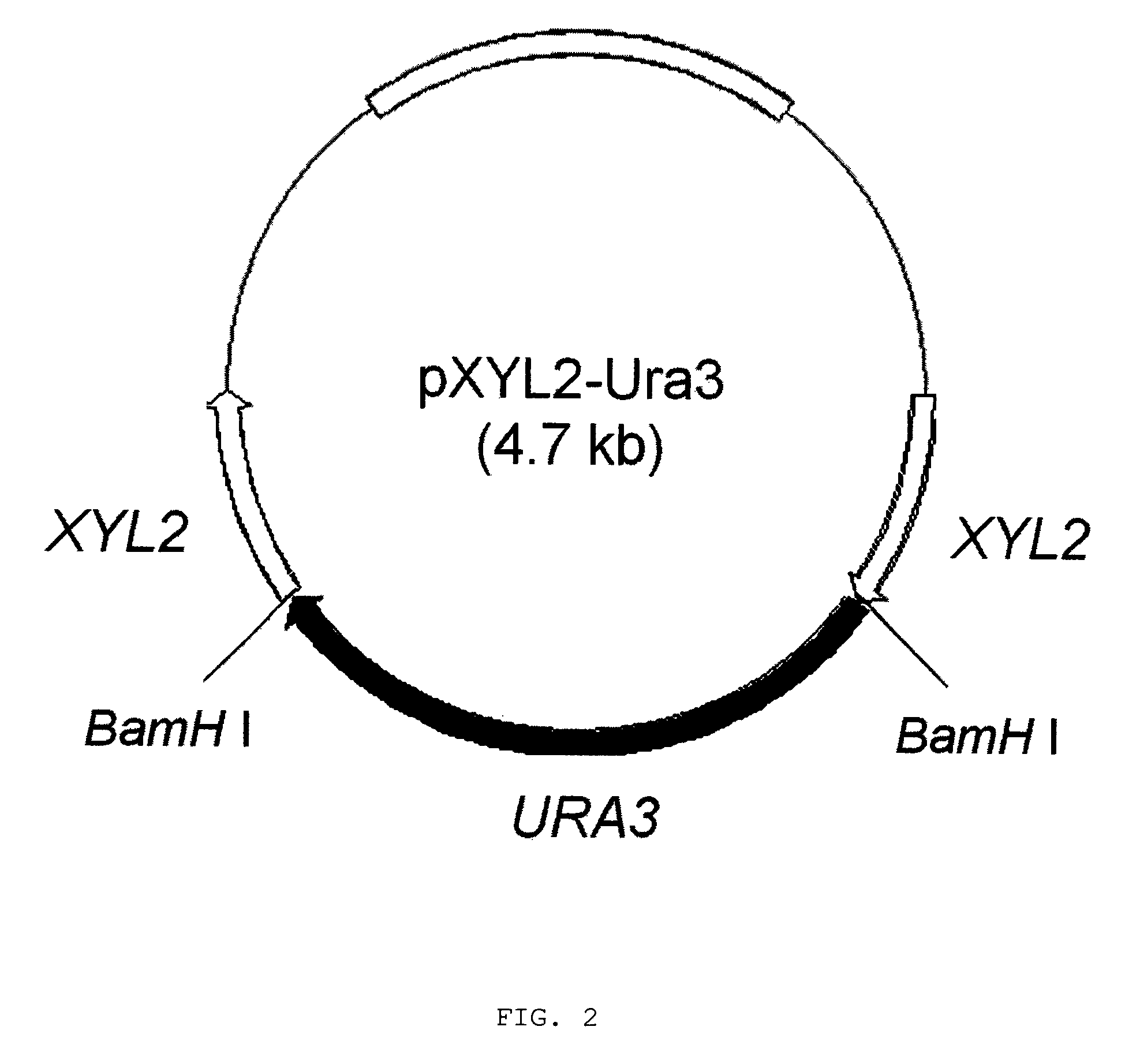
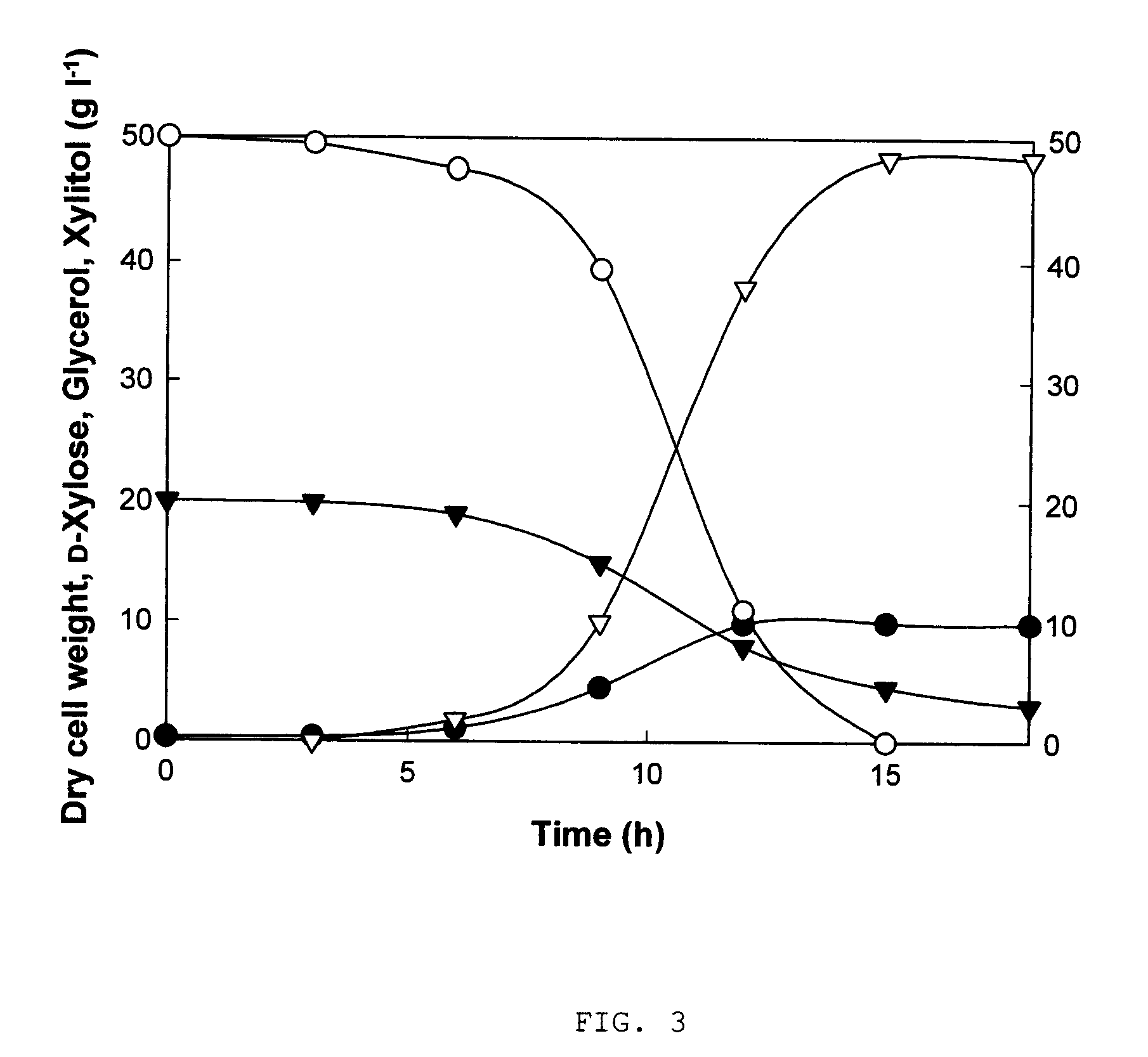
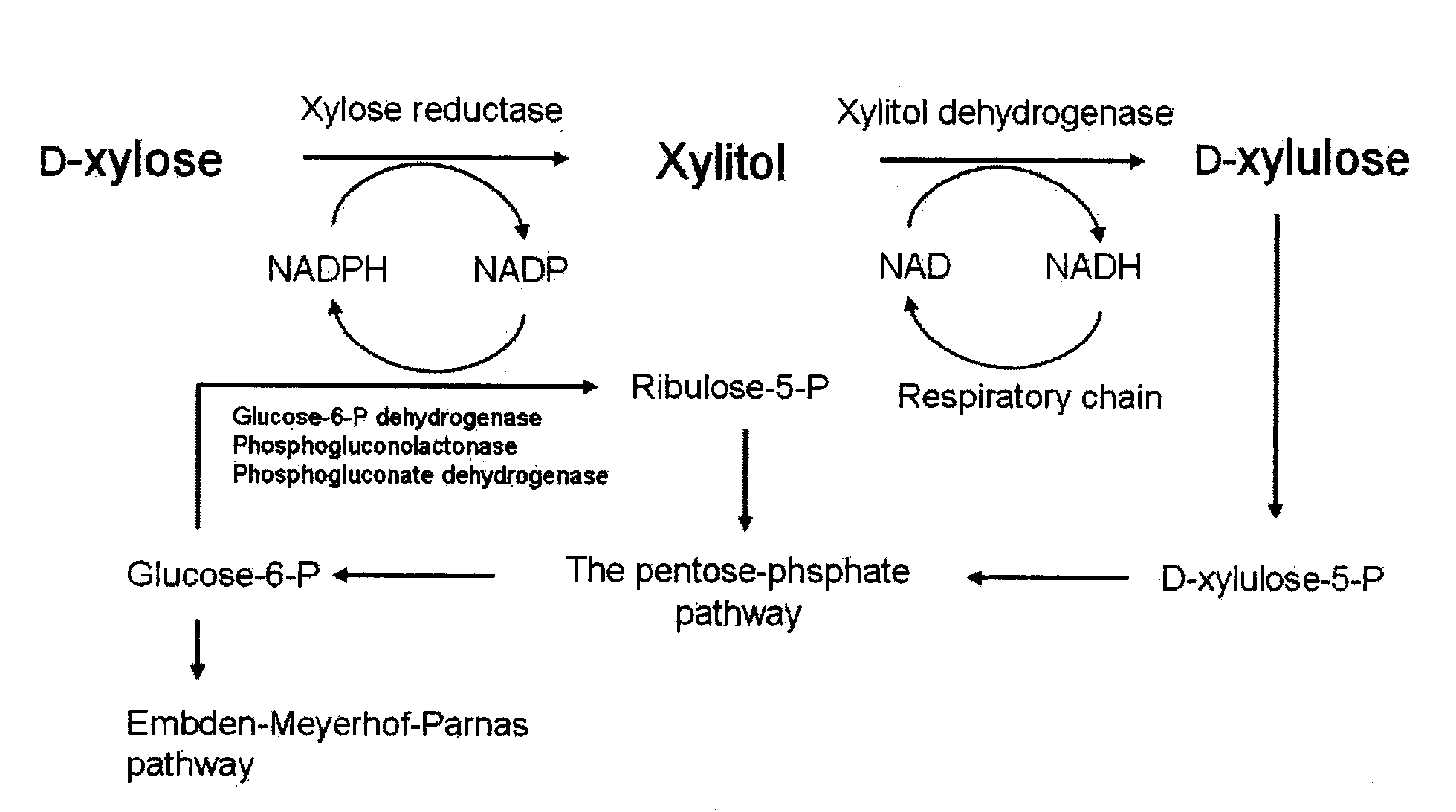
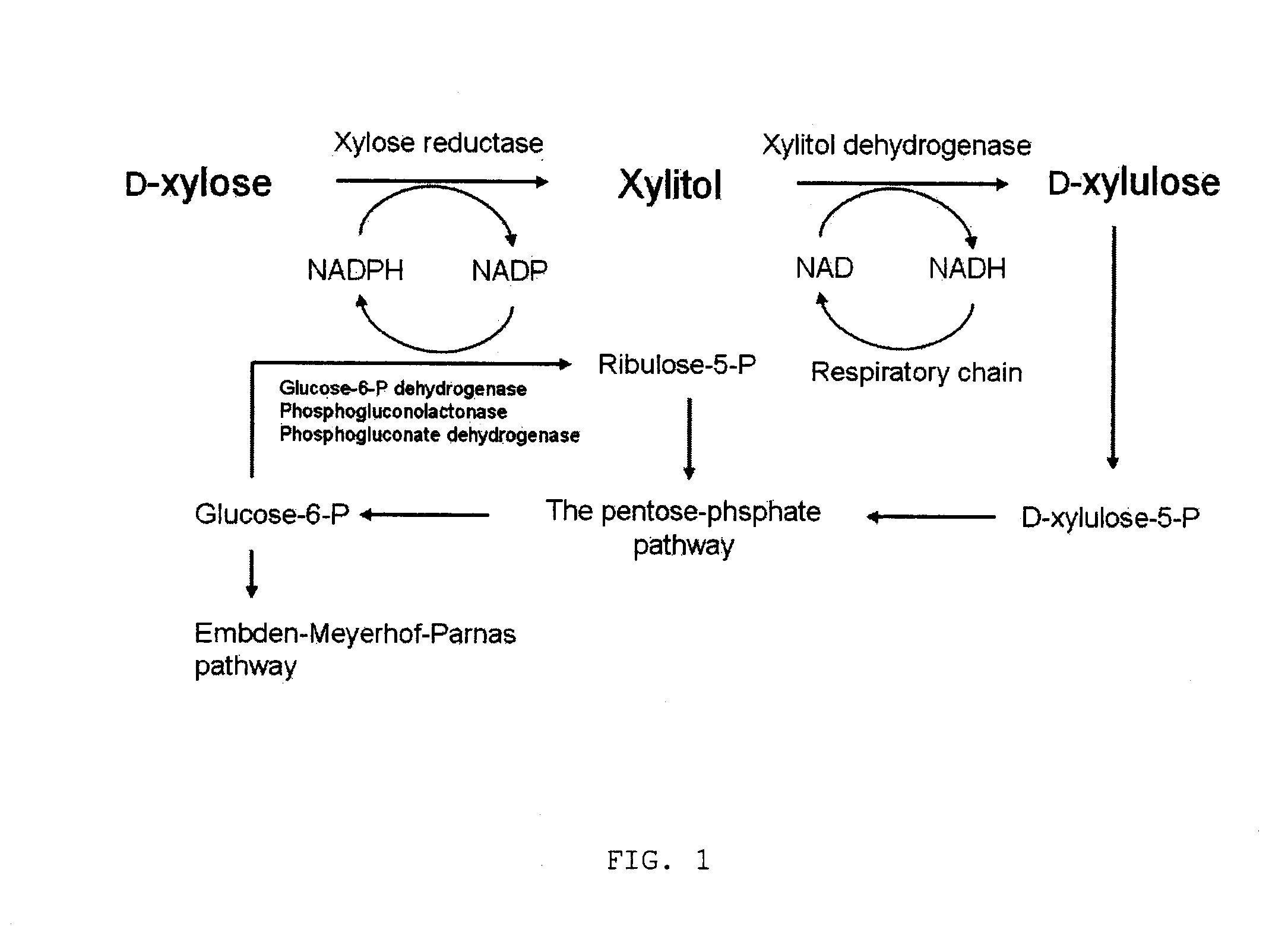
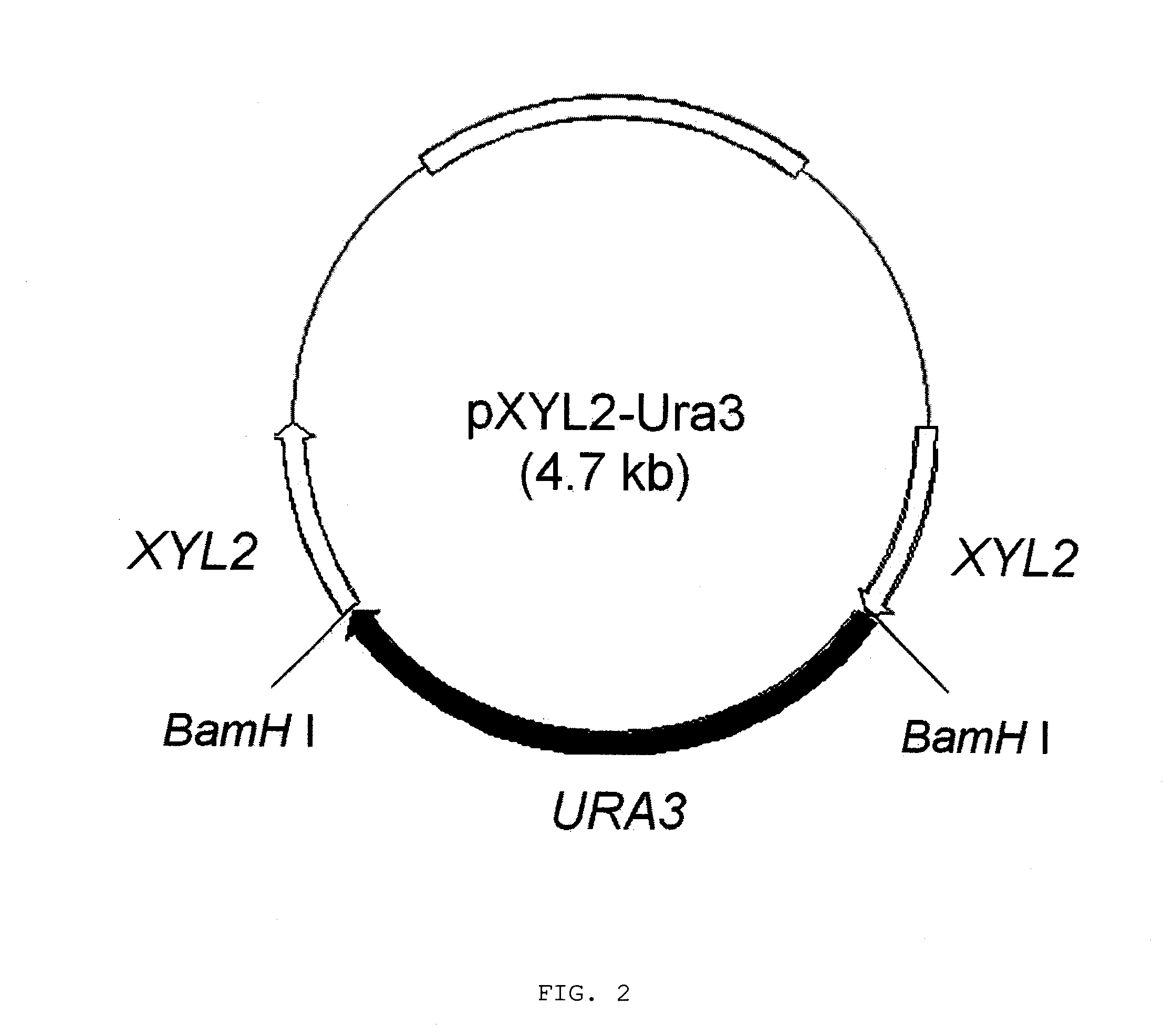
Method for manufacturing xylitol with high-yield and high-productivity
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing xylitol with high-yield and high-productivity by using a xylitol dehydrogenase-deficient mutant of xylitol producing microorganism. This goal is achieved through modification of the metabolic pathway of the xylitol producing microorganism, preferably a natural xylose-assimilating yeasts and fungi, by disrupting or inactivating the expression of desired genes.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
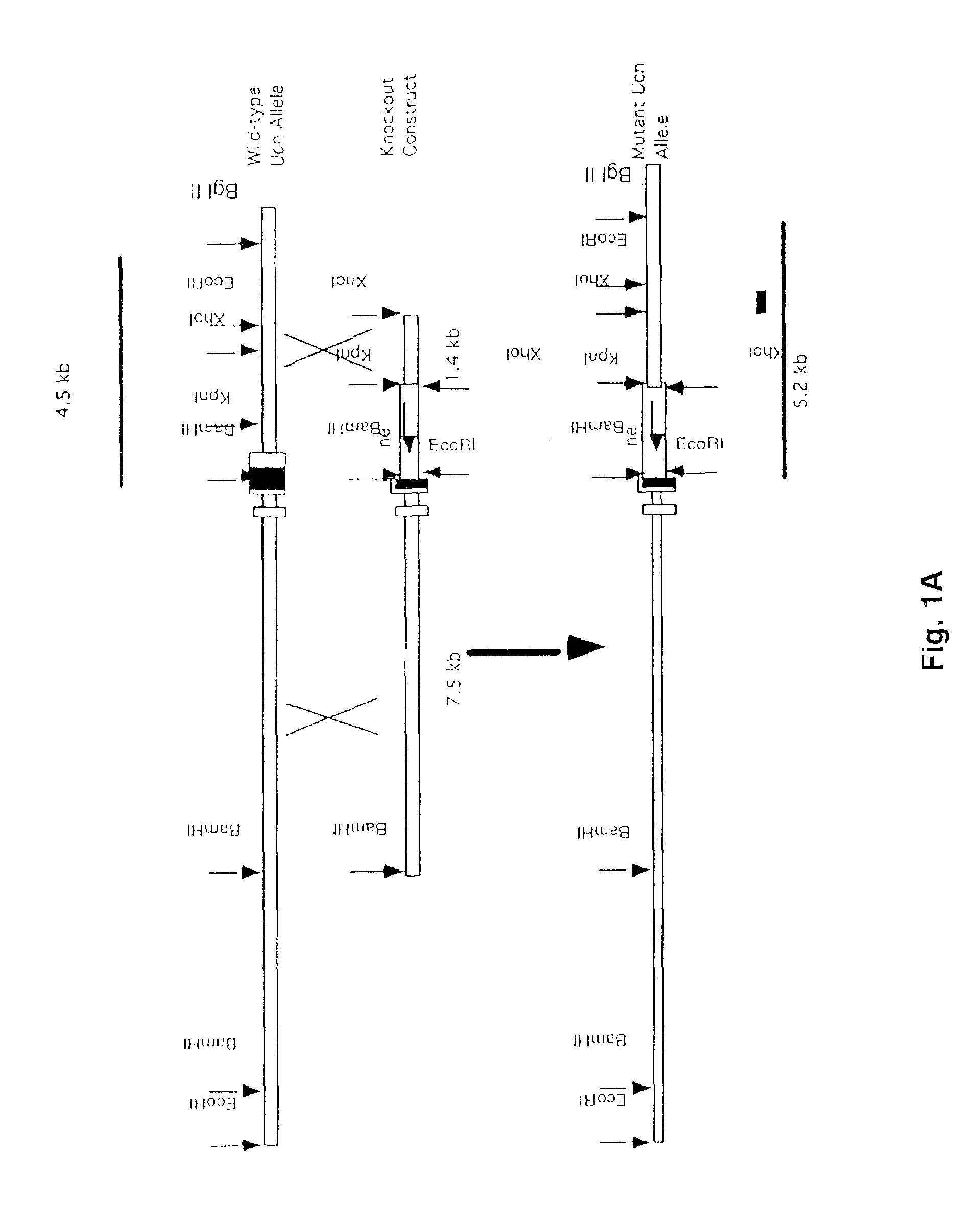
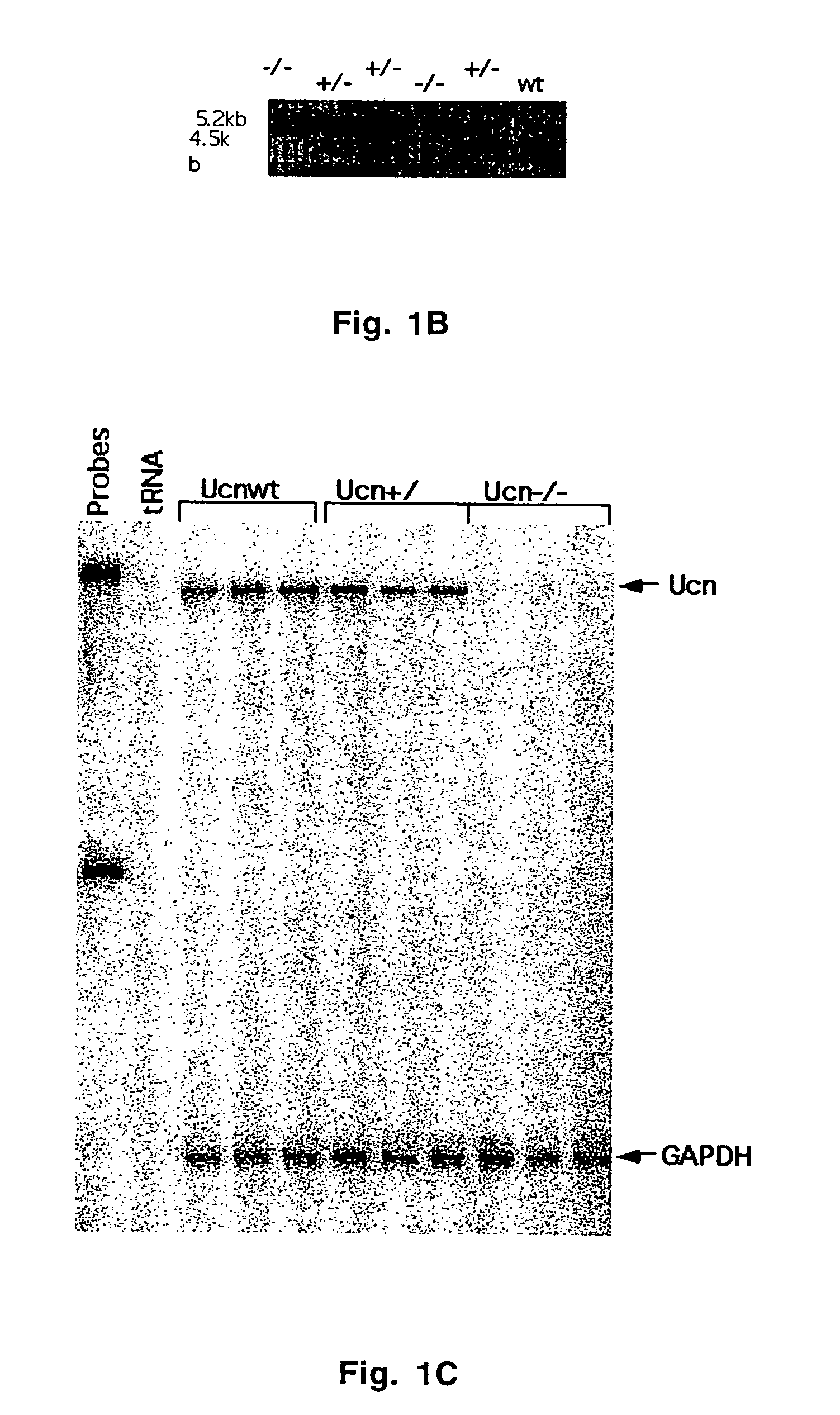
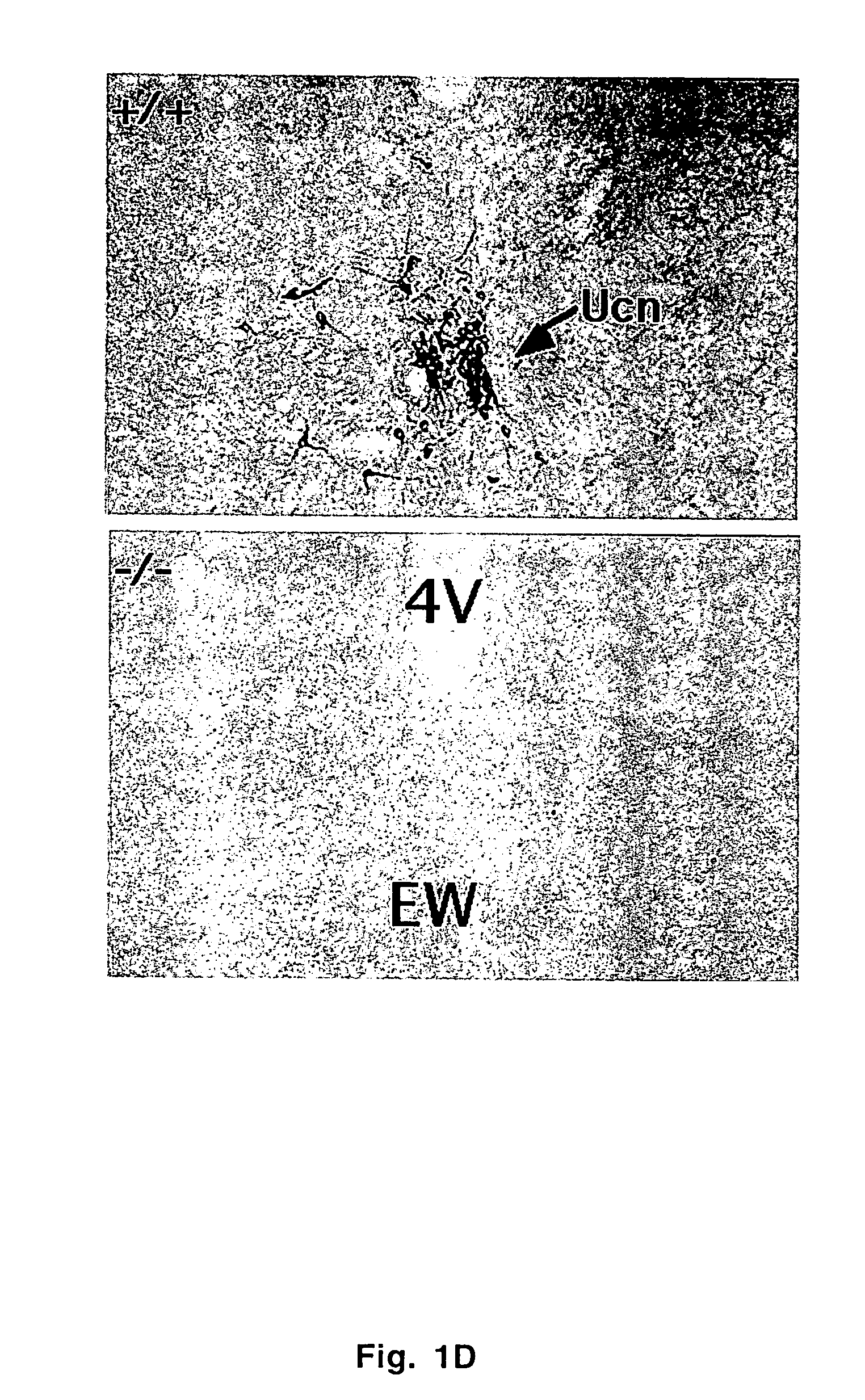
Urocortin-deficient mice and uses thereof
InactiveUS7488865B2Reduced food intakeHigh affinityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionAuditory thresholdsMolecular level
The present invention provides transgenic mice deficient in urocortin. Urocortin null mutant mice are hypersensitive to stress and display heightened anxiety-like behaviors in the elevated plus maze and open field tests. These mice also demonstrate physiological alterations in auditory thresholds and distortion product otoacoustic emissions. These results indicate that urocortin plays a modulatory role in anxiety-related behaviors and in contributing to the establishment of auditory thresholds. Such urocortin deficient mutant mice can provide useful models in the study of anxiety pathology and hearing physiology at the biochemical and molecular levels.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Polyketone compounds with antitumor activity, preparation method therefor and application of polyketone compounds
ActiveCN107698602AInterference analysis and judgmentInterfere with separabilityOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesFermentationTumor cells
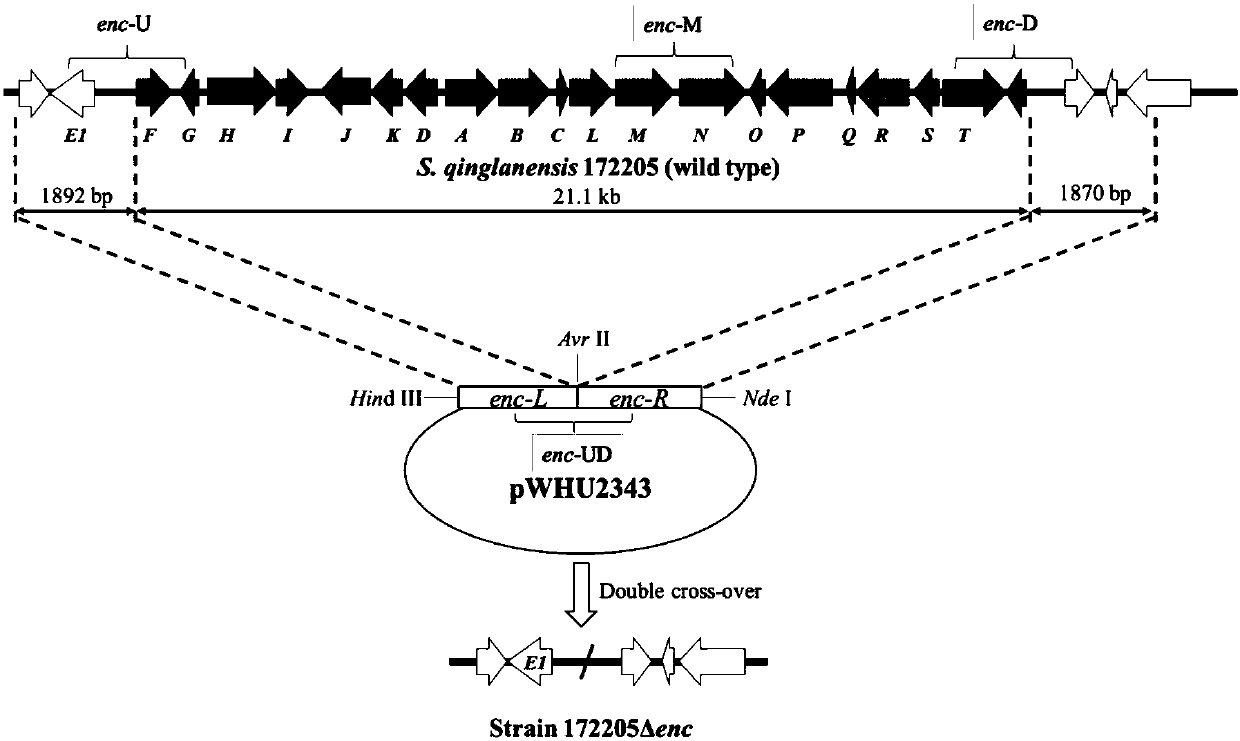
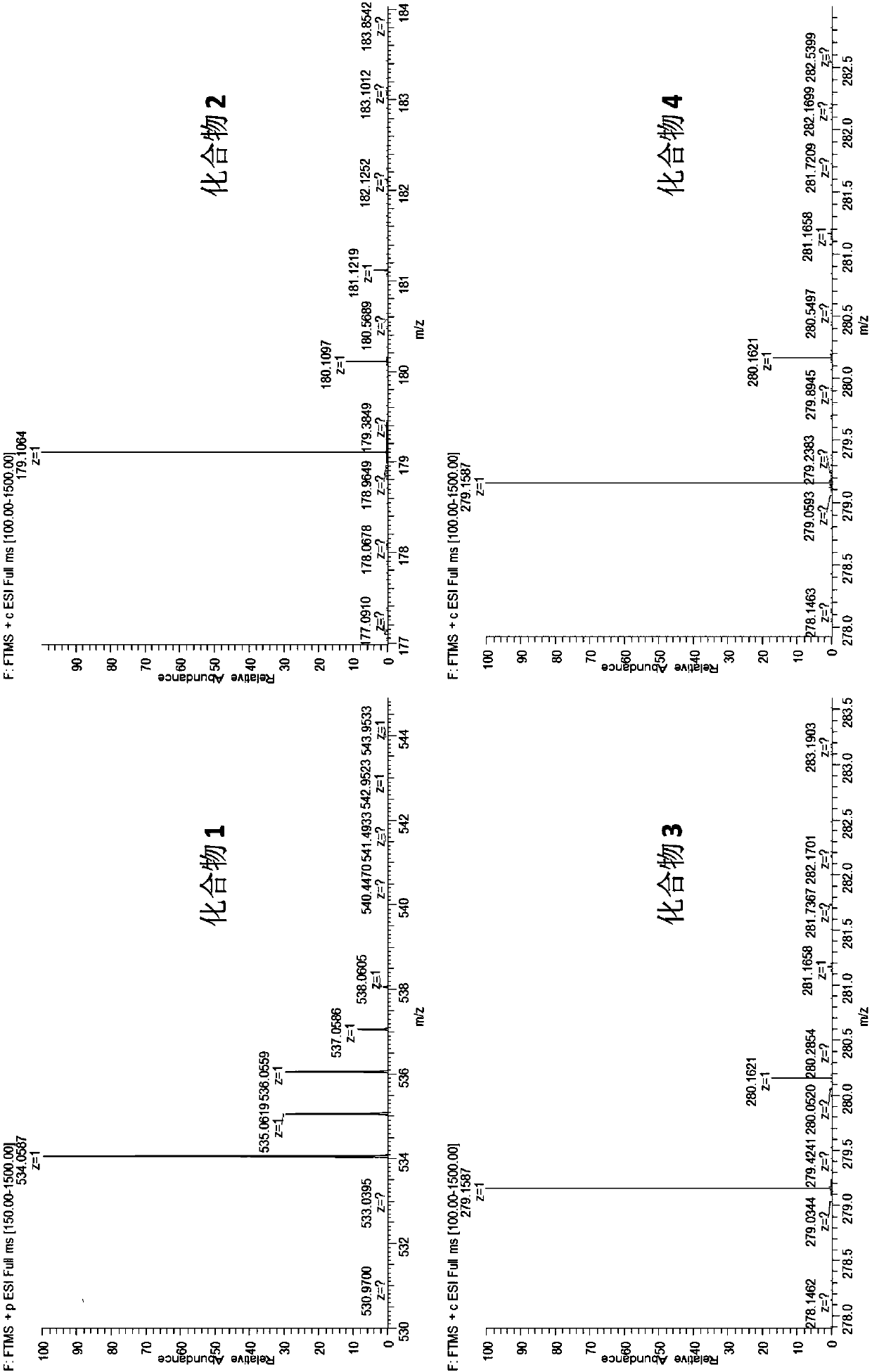
The invention discloses polyketone compounds with antitumor activity, a preparation method therefor and an application of the polyketone compounds. The polyketone compounds (1 to 4) with structures represented by a formula (I) shown in the description are prepared through subjecting an enterocin gene cluster deficient mutant of Steptomyces qinglanensis 1772205 to fermentation and carrying out separation. Proven by in-vitro cytotoxin activity tests, the compounds (1 to 4) disclosed by the invention show inhibition activity of different degrees to tumor cells (HeLa and MCF-7), and particularly,the compound 1 shows a remarkable inhibiting effect on the tumor cells. Ideal candidate compounds are provided for the development of efficient antitumor drugs.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
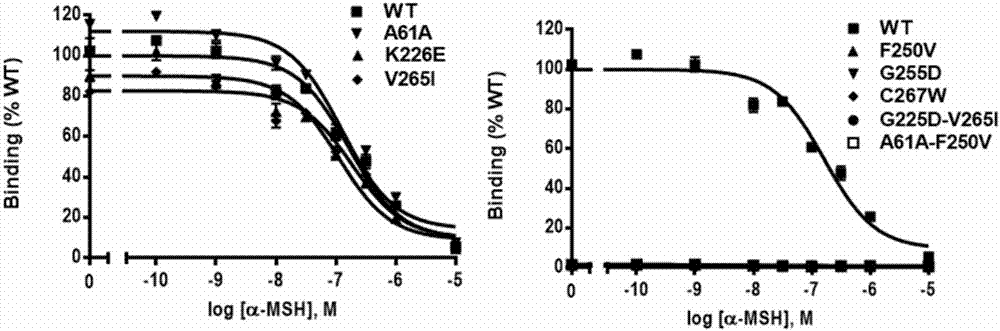
Three goat MC1R deficient mutants and application thereof
ActiveCN107022022AMicrobiological testing/measurementReceptors for hormonesMarker-assisted selectionTransmembrane domain
The invention belongs to the technical field of goat molecular marker preparation, and in particular relates to three goat MC1R deficient mutants and application thereof. Three deficient mutants are found in a goat MC1R and application thereof, two mutation sites F250V and G255D casing receptor defects both are located in a sixth transmembrane domain, and another mutation site C267W casing the receptor defects is located on a third external loop. The alpha-MSH ligand affinity of the three MC1R deficient mutants is lost, inducible and constitutive cAMP levels are significantly reduced, and inducible and constitutive p-ERK are significantly reduced. The goat MC1R deficient mutants can lead to the fact that a melanin production signal is blocked and the formation of black coat is affected. The molecular marker can be applied to assisted marker selection of goat wool color.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for Manufacturing Xylitol with High-Yield and High-Productivity
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing xylitol with high-yield and high-productivity by using a xylitol dehydrogenase-deficient mutant of xylitol producing microorganism. This goal is achieved through modification of the metabolic pathway of the xylitol producing microorganism, preferably a natural xylose-assimilating yeasts and fungi, by disrupting or inactivating the expression of desired genes.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
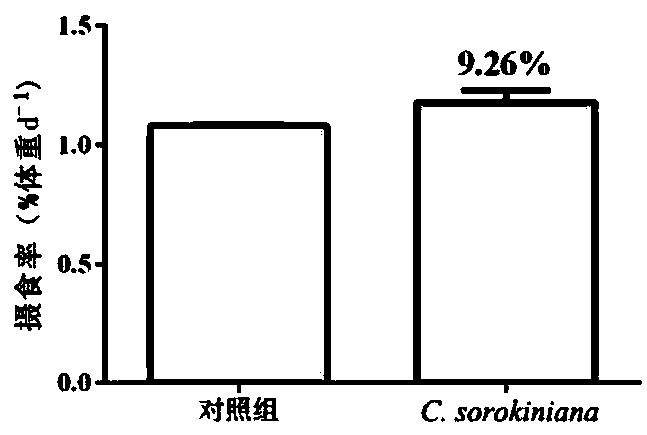
Application of chlorella sorokiniana in functional feed for improving health condition of fishes
InactiveCN110604234ATaking into account the costTaking into account the breeding effectClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyWeight gaining
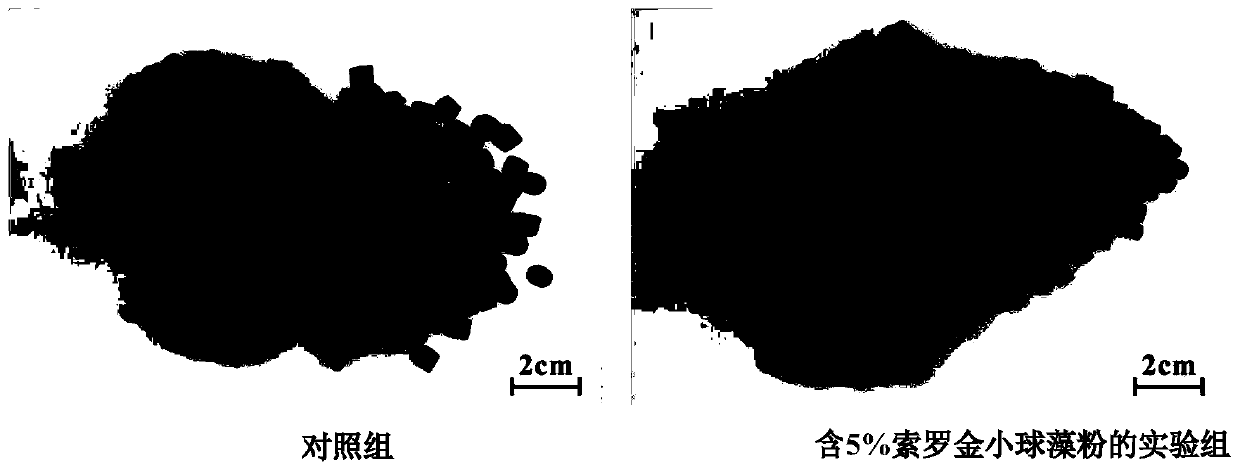
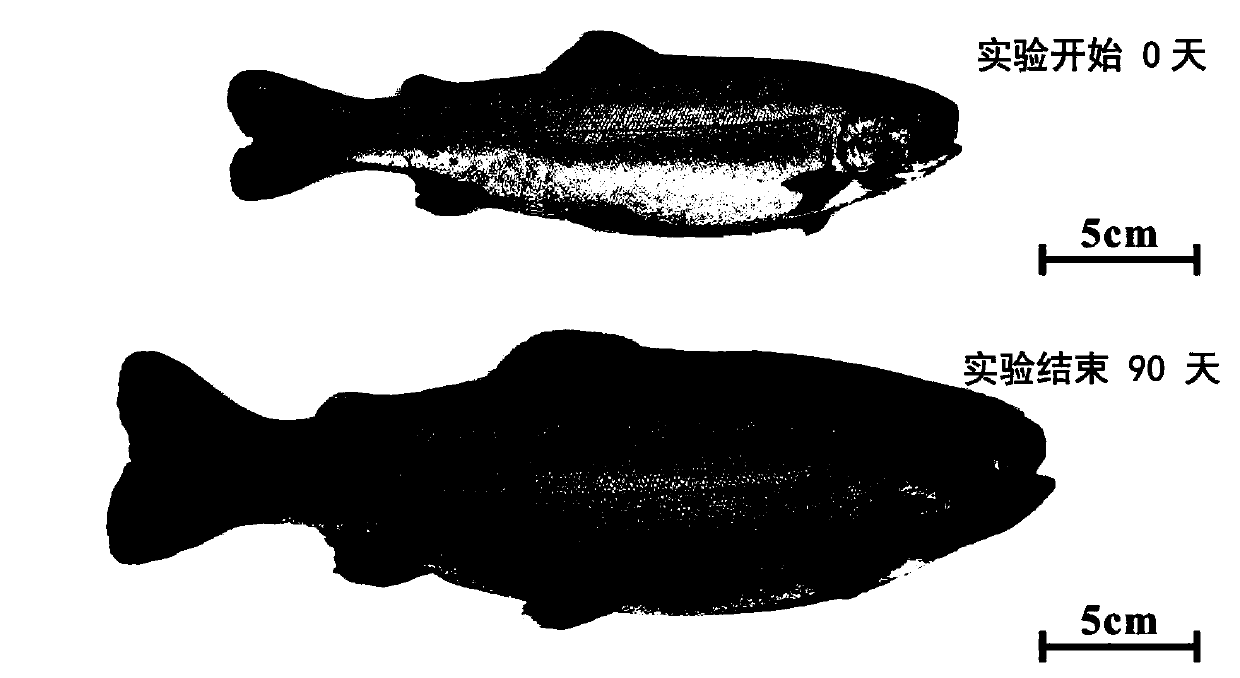
The invention relates to an application of chlorella sorokiniana in a functional feed for improving the health condition of fishes. The Chlorella sorokiniana disclosed by the invention is a starch defect type mutant strain GT-1-SLM2, and a preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.13862, and the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC, an address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing). According to the invention, chlorella sorokiniana is used as starch-deficient mutant strain algae powder and is added into the fish feed, which can replace part of fish meal, can significantly improve the food intake, growth weight gain speed, oxidation resistance and immunity of fishes, the product can replace traditional antibiotics, and avoids the problems of ecological environment damage and food safety caused by large-scale application of antibiotics in the feed. Therefore, the invention provides a brand-new, green and safe immunopotentiator, a phagostimulant or an antioxidant.
Owner:DEMETER BIOTECH (ZHUHAI) LTD
Sugarcane saccharose translocator ShSUT2 genes and application
The invention discloses two saccharose translocator ShSUT2 genes derived from sugarcane and application. According to the saccharose translocator genes ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B, amino acid sequences are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO 2 and 4, and base sequences of encoding genes ShSuT2A and ShSUT2B are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO 1 and 3. Absorbing function deficient mutant by yeast saccharose shows that the proteins encoded by ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B have saccharose transport activity. The ShSUT2A and ShSUT2B encoding genes are responsible for absorbing saccharose of apoplast in sugarcane plant and participate in transportation, distribution and accumulated physiological processes of sugarcane plant saccharose. The genes can provide new ways for improving transportation and distribution efficiency of sugarcane saccharose, promoting growth of the plant and improving sugarcane yields and sugar content.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Methods for producing biological substances in enzyme-deficient mutants of aspergillus niger
The present invention relates to methods of producing a heterologous biological substance, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Aspergillus niger strain in a medium suitable for the production of the heterologous biological substance, wherein (i) the mutant strain comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding the heterologous biological substance and one or more second nucleotide sequences comprising a modification of glaA and at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of asa, amyA, amyB, prtT, and oah, and (ii) the mutant strain is deficient in the production of glucoamylase and at least one enzyme selected from the group consisting of acid stable alpha-amylase, neutral alpha-amylase A, and neutral alpha-amylase B, protease, and oxalic acid hydrolase compared to the parent Aspergillus niger strain when cultivated under identical conditions: and (b) recovering the heterologous biological substance from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to enzyme-deficient mutants of Aspergillus niger strains and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Hansenula polymorpha yapsin deficient mutant strain and process for the preparation of recombinant proteins using the same
InactiveUS20050239074A1High-efficiency <i>Improve efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesForeign proteinProteinase activity
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule comprising the HpYPS1 gene encoding H. polymorpha yapsin1, a polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid molecule, a H. polymorpha mutant strain having reduced yapsin activity by mutation of the HpYPS gene encoding H. polymorpha yapsin1, a recombinant H. polymorpha strain expressing a foreign protein produced by introducing a gene encoding the foreign protein into the H. polymorpha mutant strain, and a process for preparing a foreign protein comprising culturing the recombinant H. polymorpha strain under conditions to express the foreign protein and isolating the foreign protein from the culture.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH +2
Method for screening chlamydomonas reinhardtii cycle adjustment and control defect mutants
ActiveCN111088289AAccurate and fast measurementEasy to operateUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
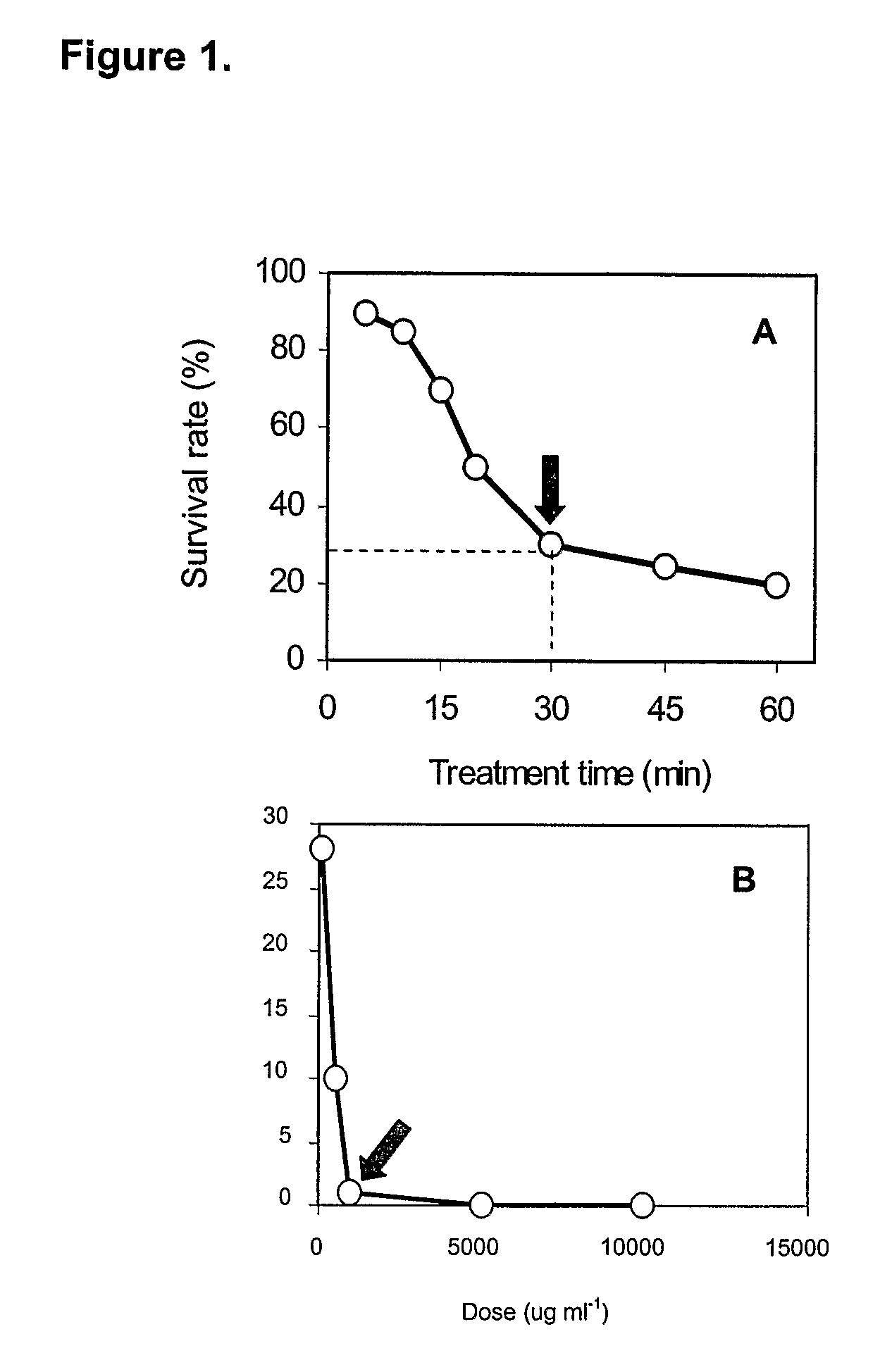
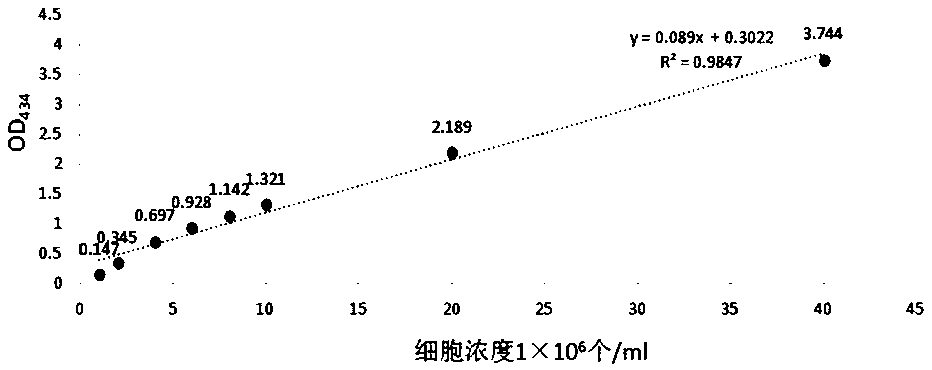
The invention discloses a method for screening chlamydomonas reinhardtii cycle adjustment and control defect mutants. The method comprises specific steps that after a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutantlibrary is established, cell cycle adjustment and control defect mutants are directly screened, wherein primary screening is performed according to the size of the diameter of a monoclone, and in re-screening, the concentration of cells is detected through a microplate reader OD434, so that the ratio of a 24h light absorption value to a 48h light absorption value is calculated, and chlamydomonas cell cycle adjustment and control defect mutants are screened and identified reference to a wild type reproduction ratio. According to the method disclosed by the invention, changes of the quantity ofchlamydomonas reinhardtii cells are detected through the microplate reader, so that the chlamydomonas cell cycle adjustment and control defect mutants are screened and identified. The method is simpleand convenient to operate and high in efficiency, cell cycle adjustment and control defect mutants can be quickly and stably obtained, and a base is established for subsequent experiments.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Natural deficient mutant strain of PhoP gene existing in clinical isolates of mycobacterium tuberculosis in Xinjiang areas
The invention relates to a natural mutant strain of mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoP of clinical isolates of mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum samples of patients with tuberculosis in Xinjiang areasin the field of study on microbes. By collecting sputum samples of patients with tuberculosis in the department of infectious diseases in multiple Xinjiang areas, 438 clinical isolates are obtained,and by total DNA extraction, ordinary PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and fluorescence quantitative PCR, the natural mutant strain of PhoP in the clinical isolates is discovered.
Owner:JINING MEDICAL UNIV
Methods for producing polypeptides in enzyme-deficient mutants of fusarium venentatum
InactiveUS20140147847A1Reduce expressionAffect expressionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAlkaline protease
The present invention relates to methods of producing a polypeptide, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Fusarium venenatum strain in a medium for the production of the polypeptide, wherein the mutant strain comprises a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide and one or more (several) genes selected from the group consisting of pyrG, amyA, and alpA, wherein the one or more (several) genes are modified rendering the mutant strain deficient in the production of one or more (several) enzymes selected from the group consisting of orotidine-5′-monophosphate decarboxylase, alpha-amylase, and alkaline protease, respectively, compared to the parent Fusarium venenatum strain when cultivated under identical conditions; and (b) recovering the polypeptide from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to enzyme-deficient mutants of Fusarium venenatum strains and methods for producing such mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Construction method for producing fumaric acid based on pichia stipitis synthetic strain fermented xylose
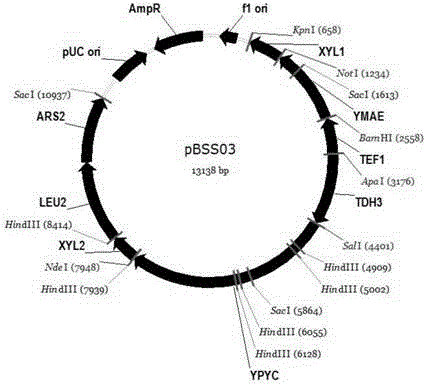
The invention provides a construction method for producing fumaric acid based on pichia stipitis synthetic strain fermented xylose. The method comprises the following steps: using pichia stipitis having a natural xylose metabolic capability as a host; deleting genes PSfum1 and PSfum2 that encode fumarase in tricarboxylic acid cycle of pichia stipitis, to acquire fumarase deficient mutants; heterologously expressing a modified fumaric reduction synthesis module on the basis of the acquired mutants, using xylose to ferment yeast synthesis strains of fumaric acid; on the basis of the yeast synthesis strains, expressing translocator YMAE that is modified with codons and originated from Chestnut wine fission yeasts, to acquire pichia stipitis synthesis strains for producing fumaric acid by fermented xylose; efficiently fermenting the acquired strains in a fully synthesized fermentation culture medium to produce fumaric acid by fermentation of xylose; cultivating by fermentation for 3-4 days at a temperature of 30 degrees centigrade with a stirring speed of 150-200rpm. The content of fumaric acid is greater than 4g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Methods for producing biological substances in pigment-deficient mutants of bacillus cells
InactiveUS20090098606A1Promote recoveryEasy to purifyBacteriaUnicellular algaeHeterologousBacillus e
The present invention relates to methods of producing a heterologous biological substance, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Bacillus cell under conditions conducive for the production of the heterologous biological substance, wherein (i) the mutant cell comprises a first nucleic acid sequence directing synthesis of the heterologous biological substance and a second nucleic acid sequence comprising a modification of at least one of the genes cypX and yvmC, which are involved in the production of a red pigment, and (ii) the mutant cell is deficient in the production of the red pigment compared to the parent Bacillus cell when cultivated under the same conditions; and (b) recovering the heterologous biological substance from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to mutants of Bacillus cells and methods for producing the mutants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Construction of a quadruple enterotoxin-deficient mutant of bacillus thuringiensis
Some HBL and NHE enterotoxins are known to cause food-borne diseases in humans. Enterotoxin-deficient mutants of member strains of the Bacillus cereus group that do not produce HBL, HBLa1, HBLa2, or NHE enterotoxins are disclosed. Enterotoxin-deficient mutants are suitable for use as biocontrol agents. Methods for making the mutants and for using the mutants are described.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Sericin nerve conduit and its preparation method and application
The invention provides a sericin nerve guide, its preparation method and application. The sericin nerve conduit component provided by the present invention is sericin, and its preparation method comprises: using silkworm cocoons of a silk fibroin-deficient mutant variety Bombyx mori as raw material, pulverizing it and sterilizing it with ultraviolet light or ethanol, and then using LiBr or LiCl aqueous solution Carry out the extraction of sericin protein, and make the sericin protein aqueous solution with the concentration of 0.5~20wt% from the extract; For semi-finished catheters, the amount of covalent cross-linking agent used is to add 2-500 μL of covalent cross-linking agent with a concentration of 0.1-50 wt% per 1 ml of sericin aqueous solution; freeze-dry the semi-finished sericin nerve catheter to obtain sericin nerve guide. The sericin nerve conduit provided by the invention has good biological activity and biocompatibility, can be naturally degraded in vivo and can promote regeneration of long-distance injured peripheral nerves.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Maize transcription factor zmbzip22 and its application
ActiveCN107298701BReduce accumulationIncrease methionine contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyBase J
The invention relates to an application of a Zea mays grain transcription factor in the aspect of regulation and control of alcohal-soluble proteins. The factor comprises a base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The protein ZmbZIP22 encoded by the sequence can be directly bonded to a 27kDa gamma-gliadin promoter and activate the 27kDa gamma-gliadin promoter. Gene-deficient mutant plants are obtained through carrying out Zea mays immature-embryo conversion by taking a gene fragment, shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, of ZmbZIP22 as a guide RNA by using a CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Compared with wild type grains, transgenic mutants have Zea mays grains with irregular and relative-thin protein body shells, the content of alcohal-soluble proteins in mature grains is remarkably lowered, the content of essential amino acids such as lysine, which are deficient to the conventional Zea mays, in the mature grains is remarkably increased, and thus, the nutritional quality of Zea mays is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
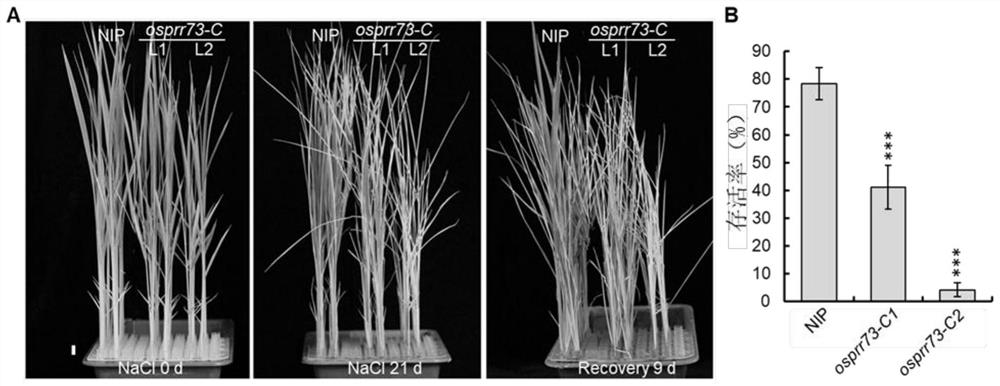
Method for regulating plant salt tolerance and salt tolerance related protein
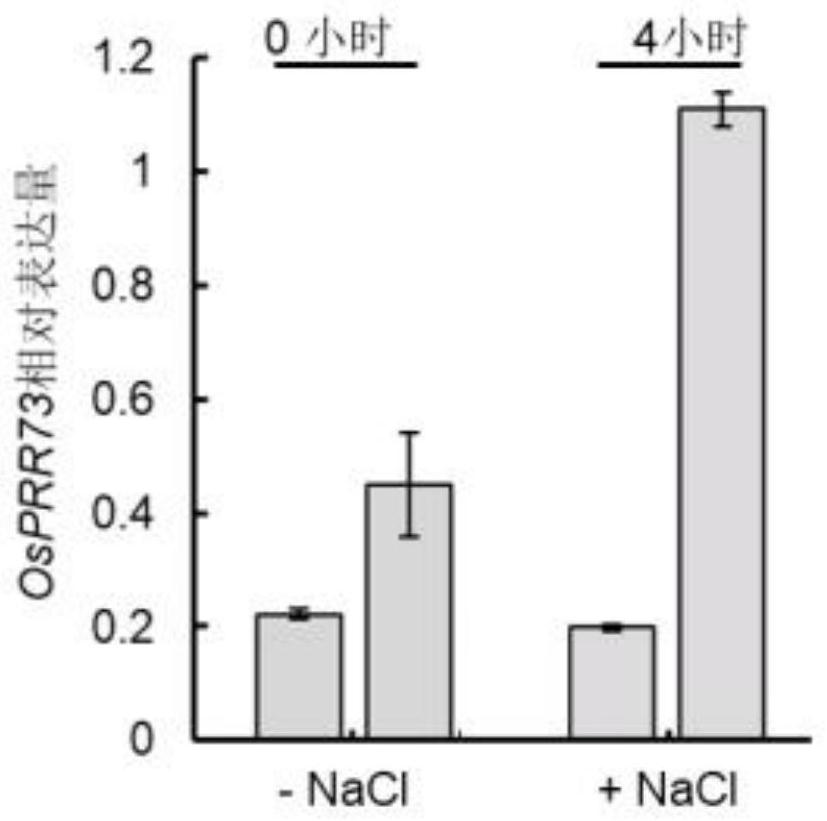
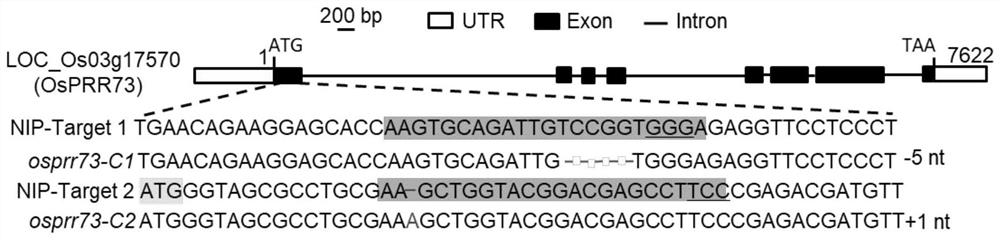
The invention discloses a method for regulating the salt tolerance of plants and salt-tolerance-related proteins. The invention provides a method for cultivating and regulating the salt-tolerance of plants, which includes regulating the expression of genes encoding salt-tolerance-related proteins in target plants, wherein , the salt-tolerance-related protein is a salt-tolerance-related protein from rice, the name is OsPRR73, and it is from rice Nipponbare. The present invention uses CRISPR / Cas9 technology to obtain OsPRR73 function-deficient mutants, performs 180mM NaCl simulated salt stress treatment, observes the phenotype and counts the survival rate after recovery treatment, and finally confirms that OsPRR73 plays a positive role in the process of responding to rice salt stress effect. The OsPRR73 of the present invention can be used as a salt tolerance gene and play an important role in rice salt resistance.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lipid a deficient mutants of neisseria meningitidis
InactiveUS20100003283A1Reduced lipooligosaccharideReduced LOSAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesBiochemistryNeisseria meningitidis
The invention provides lipid A deficient mutant Neisseria meningitidis cells, pharmaceutical compositions incorporating such cells, and methods of using such cells.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Methods for producing biological substances in pigment-deficient mutants of Bacillus cells
ActiveUS7476516B2Elimination and reduction of red pigmentPromote recoveryBacteriaUnicellular algaeHeterologousBacillus e
The present invention relates to methods of producing a heterologous biological substance, comprising: (a) cultivating a mutant of a parent Bacillus cell under conditions conducive for the production of the heterologous biological substance, wherein (i) the mutant cell comprises a first nucleic acid sequence directing synthesis of the heterologous biological substance and a second nucleic acid sequence comprising a modification of at least one of the genes cypX and yvmC, which are involved in the production of a red pigment, and (ii) the mutant cell is deficient in the production of the red pigment compared to the parent Bacillus cell when cultivated under the same conditions; and (b) recovering the heterologous biological substance from the cultivation medium. The present invention also relates to mutants of Bacillus cells and methods for producing the mutants.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com