Patents
Literature
92results about How to "Excellent extractability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
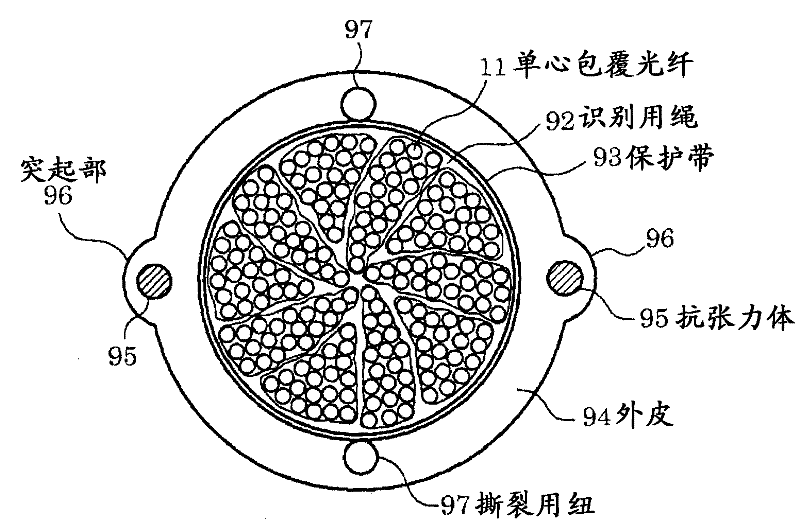
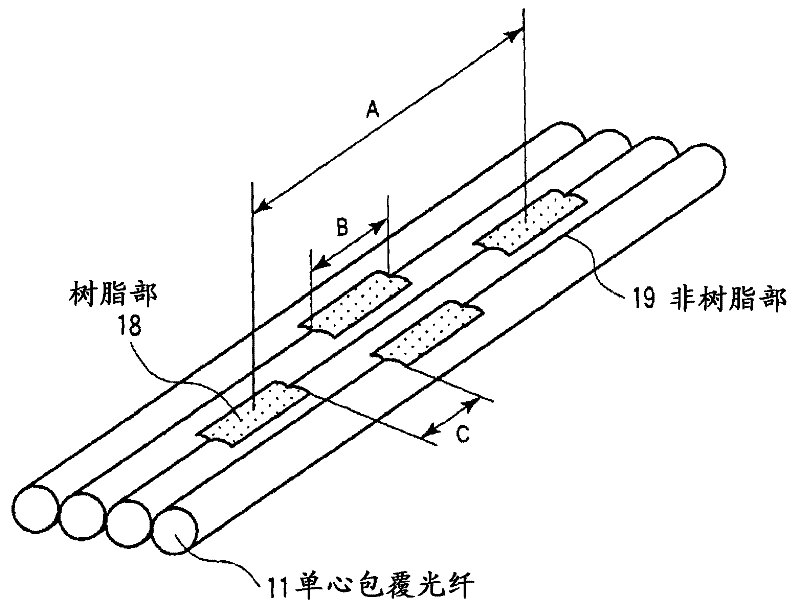
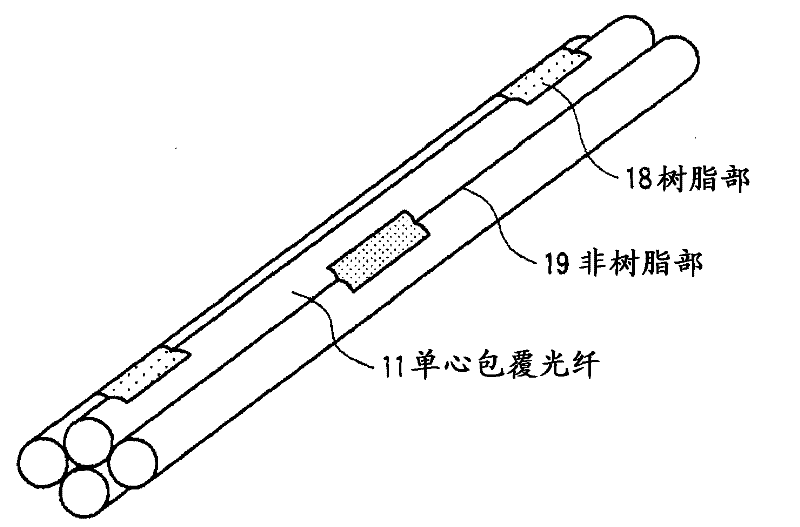
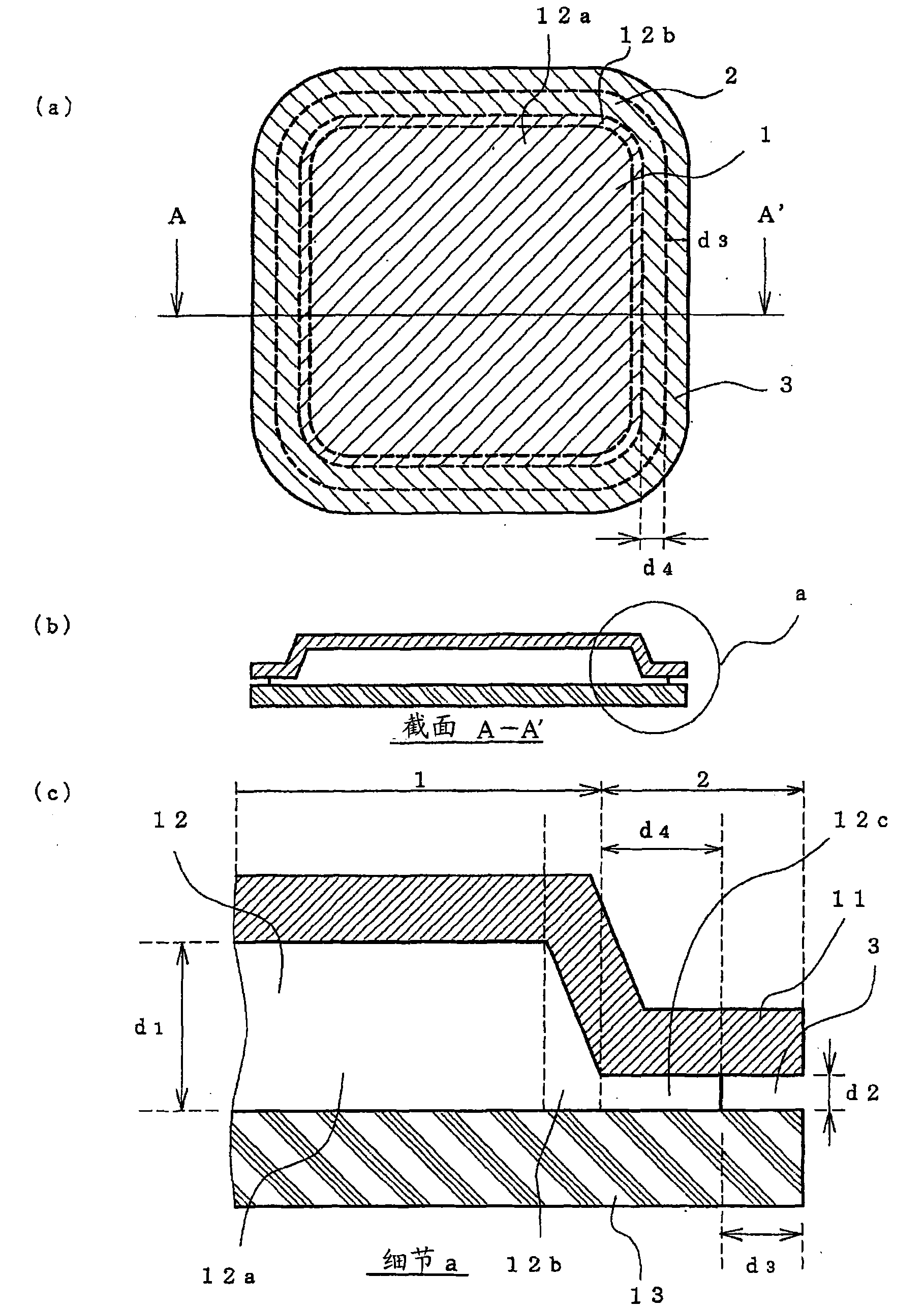
Optical fiber cable and optical fiber tape
ActiveCN102057309ARecognizableExcellent extractabilityFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringBend radius
Provided is a single-core coated optical fiber (11) having such a curve loss characteristic that an optical loss increase at a bending radius 13 mm is 0.2 dB / 10 turn or below. An optical fiber tape conductor includes two-dimensionally arranged resin portions (18) for bonding each two adjacent single-core coated optical fibers (11). The resin portions (18) are arranged apart from one another in the longitudinal direction of the optical fiber tape conductor. An optical fiber cable includes a cable core unit for containing a plurality of sets of the single-core coated optical fibers (11) constituting the optical fiber tape conductor which are twisted together.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
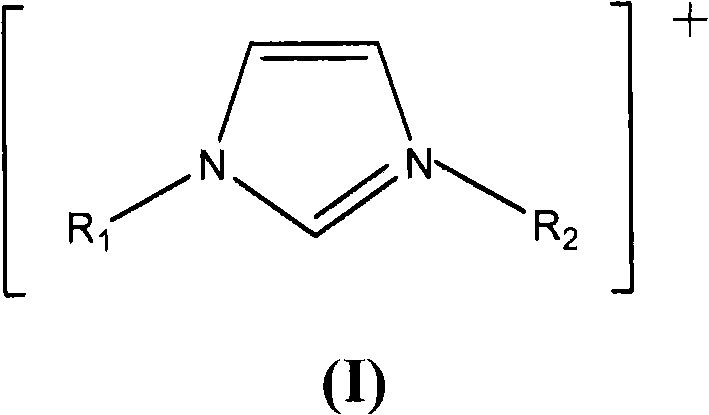
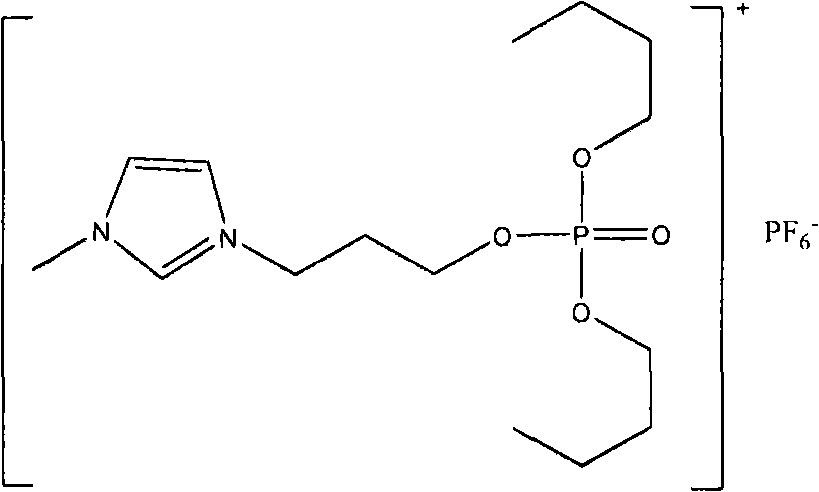
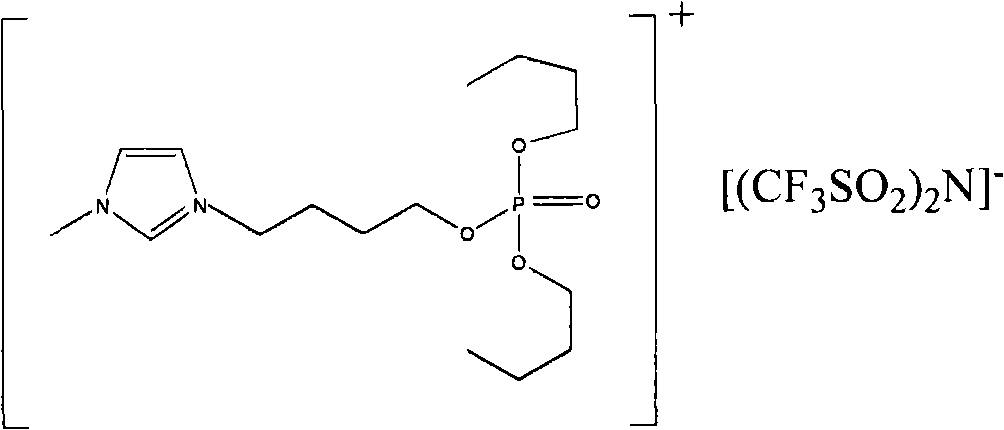
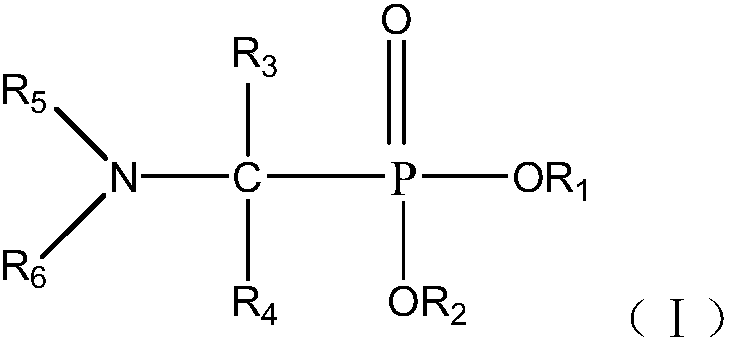
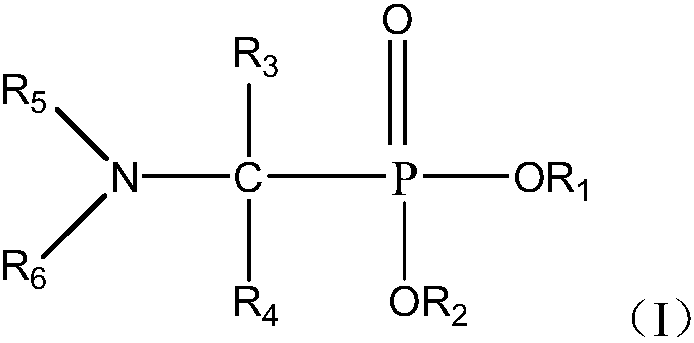
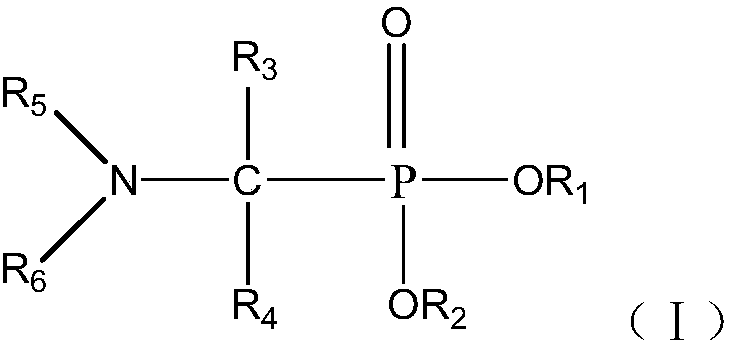
Functionalized ionic liquid containing a phosphorus and oxygen structure, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to functionalized ionic liquid containing a phosphorus and oxygen structure with a general formula of A+ B-, which is characterized in that A+ is shown in a formula (I), and R 1 and R 2 are defined in the specification; and B- is Cl-, Br-, I -, BF4-, PF6-, NO3-, CF3SO3-, [(CF3SO2) 2N] - or CH3CO2-. The invention also relates to a method for preparing ionic liquid with the formula of A + B-, which comprises the following steps: a compound in a formula (III) is reacted with a compound in a formula (II ') to obtain a compound in a formula (II'') , and then a compound in a formula (II'') is reacted with a compound in a formula (IV) to obtain a halide ionic liquid A + B-, wherein B- is Cl-, Br-or I-, and ionic liquids with the other anions can be obtained by carrying out the ion exchange of the halide ionic liquid. The invention also relates to application of the ionic liquids in extraction of uranium from uranium-containing water systems. HO-(CH2) nCH2-X (III).
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF CHEM ENG & METALLURGY
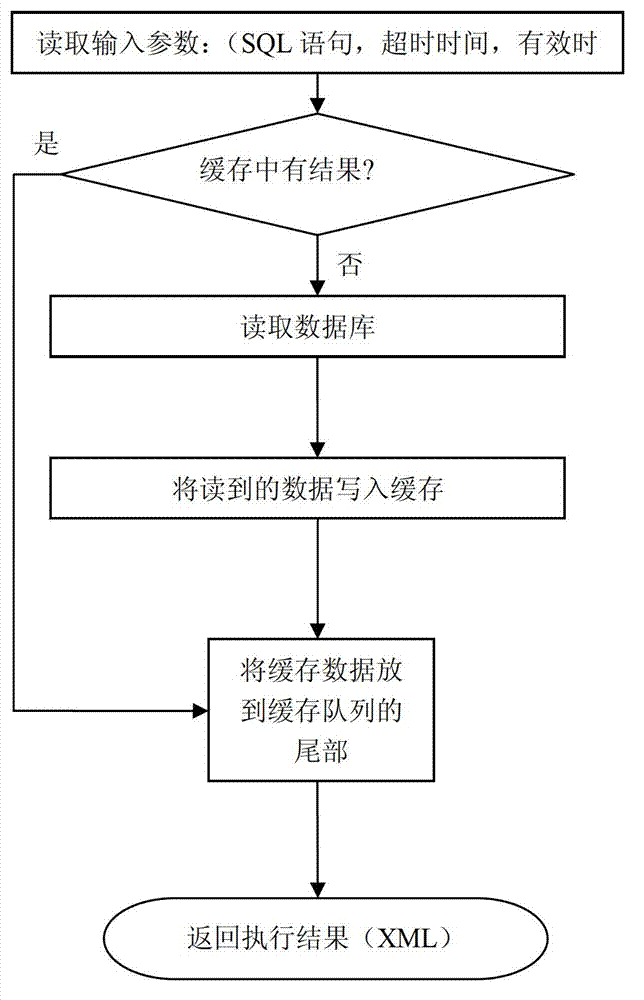
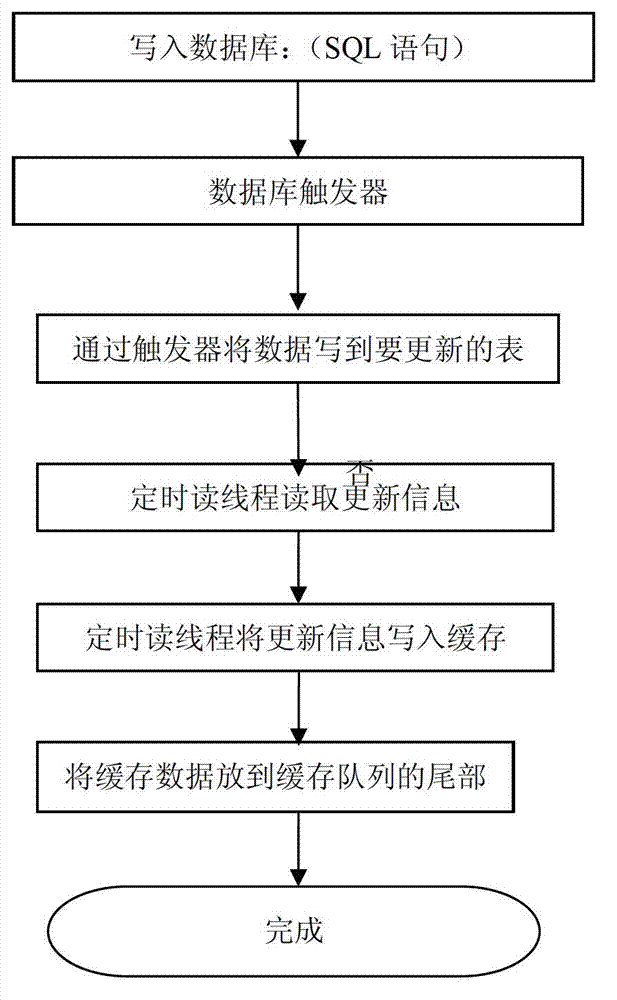
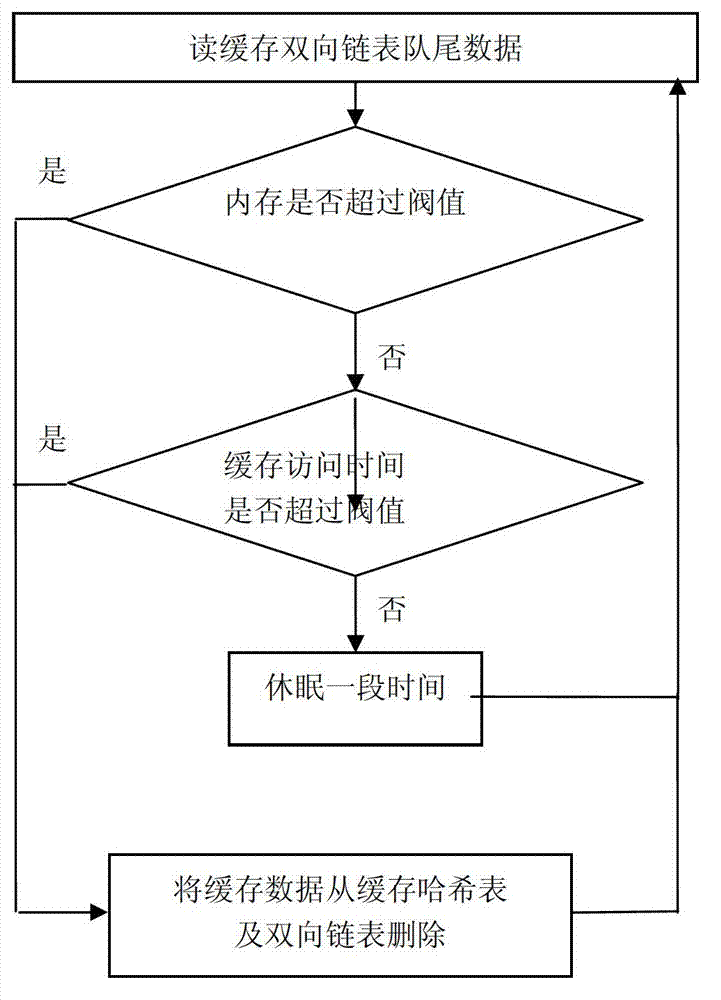
High-concurrency database access method and method applied to multi-server system
InactiveCN103246696AGuaranteed uptimeImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsAccess methodData access
The invention discloses a high-concurrency database access method. The high-concurrency database access method is characterized in that a trigger is installed in a database; a cache is installed outside the database; when the database is read, the cache is read firstly; and when the database is written, updating data are written into an updating data table and the cache through the trigger. The high-concurrency database access method has the advantages that a caching technology is applied to access and processing procedures of the database, and recently accessed data blocks are stored in the cache generally by the caching technology by the aid of an LRU (least recently used) algorithm; and since core operations of database applications are data access and data processing, if most of the data blocks which are accessed by an application system are already stored in the cache, namely data are hit in the cache, disk I / O (input / output) waiting and bottlenecks applied to data access can be eliminated, and disk data access efficiency and database access efficiency can be optimized maximumly to close to speed of memory access.
Owner:宁波公众信息产业有限公司
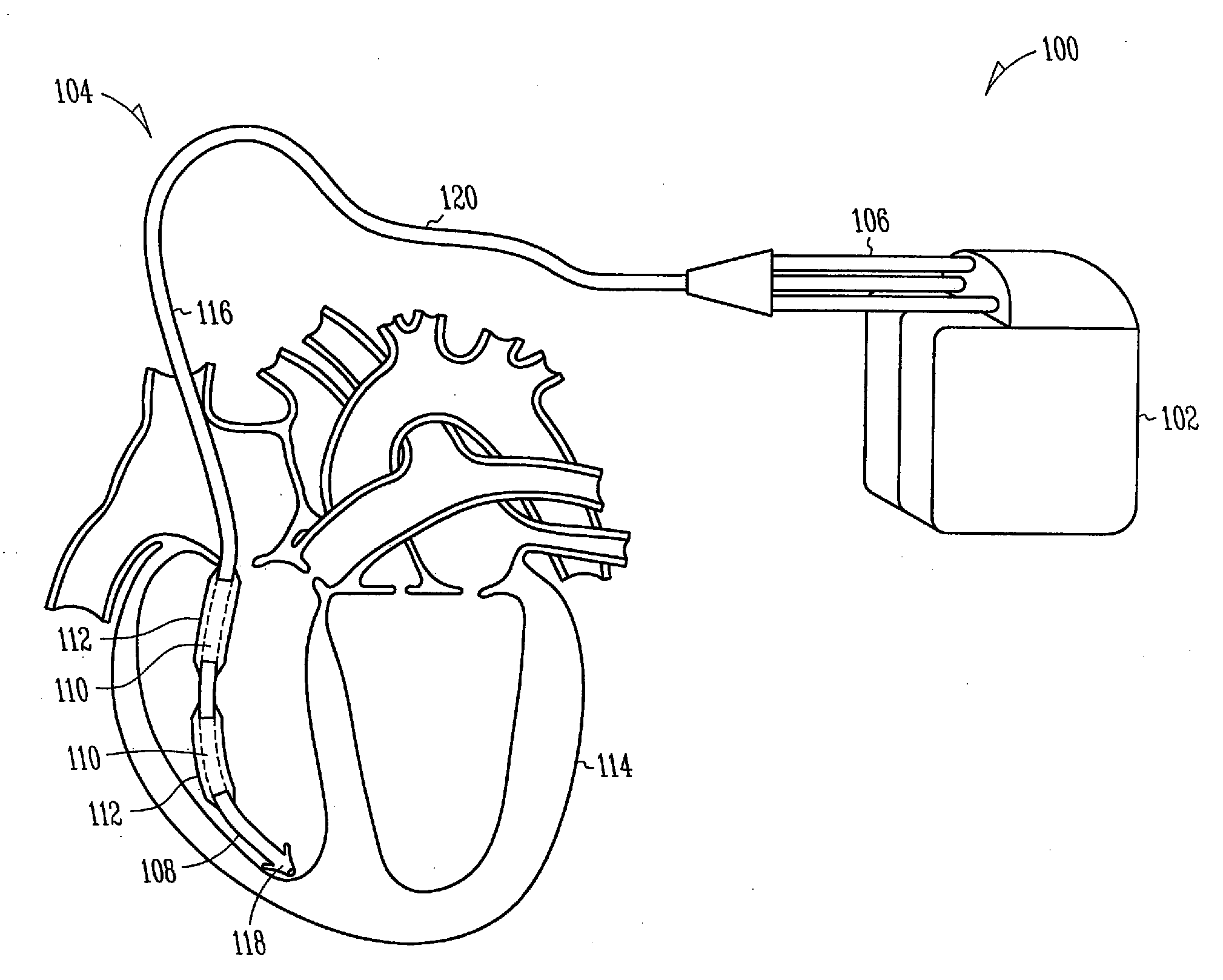
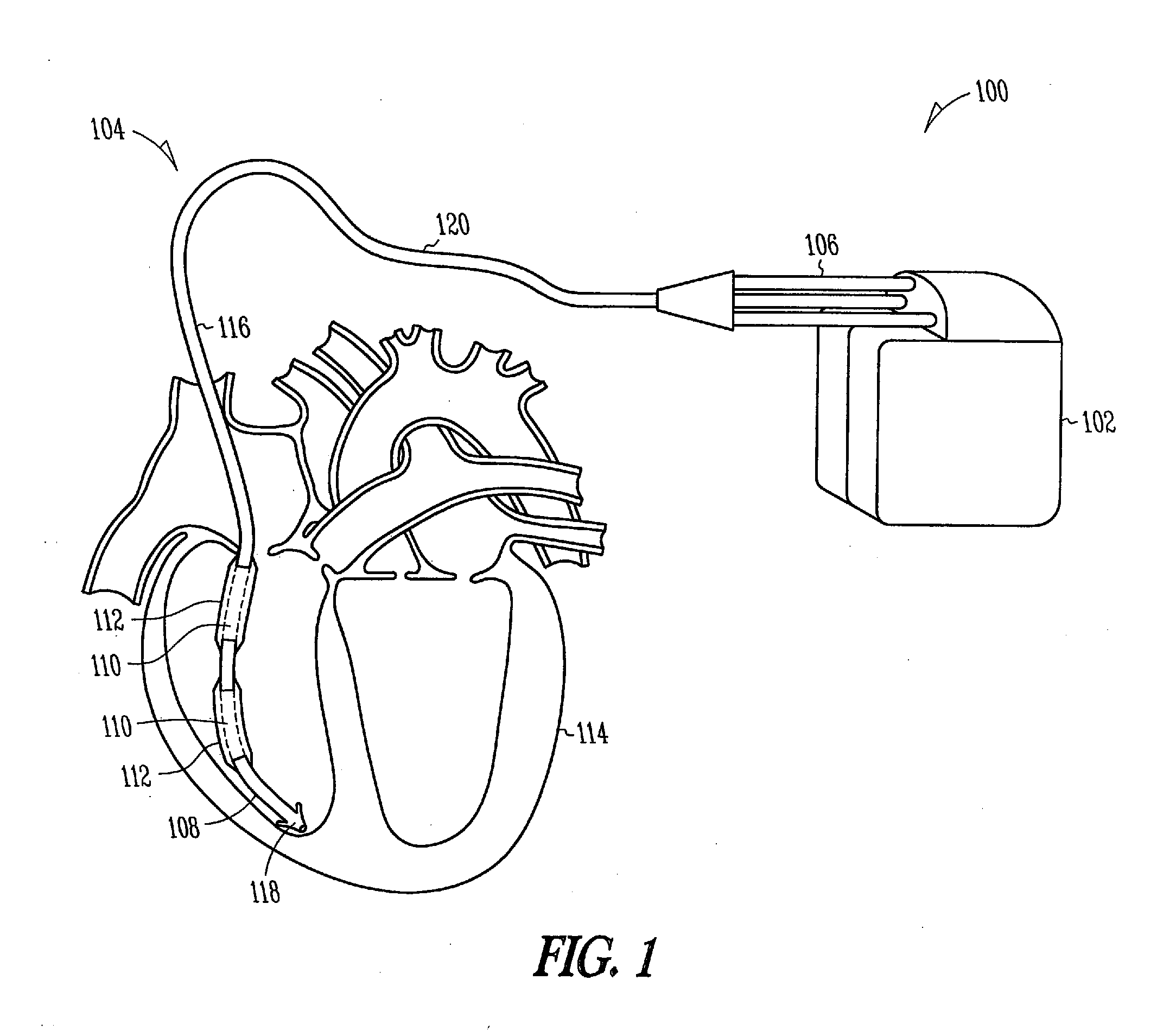
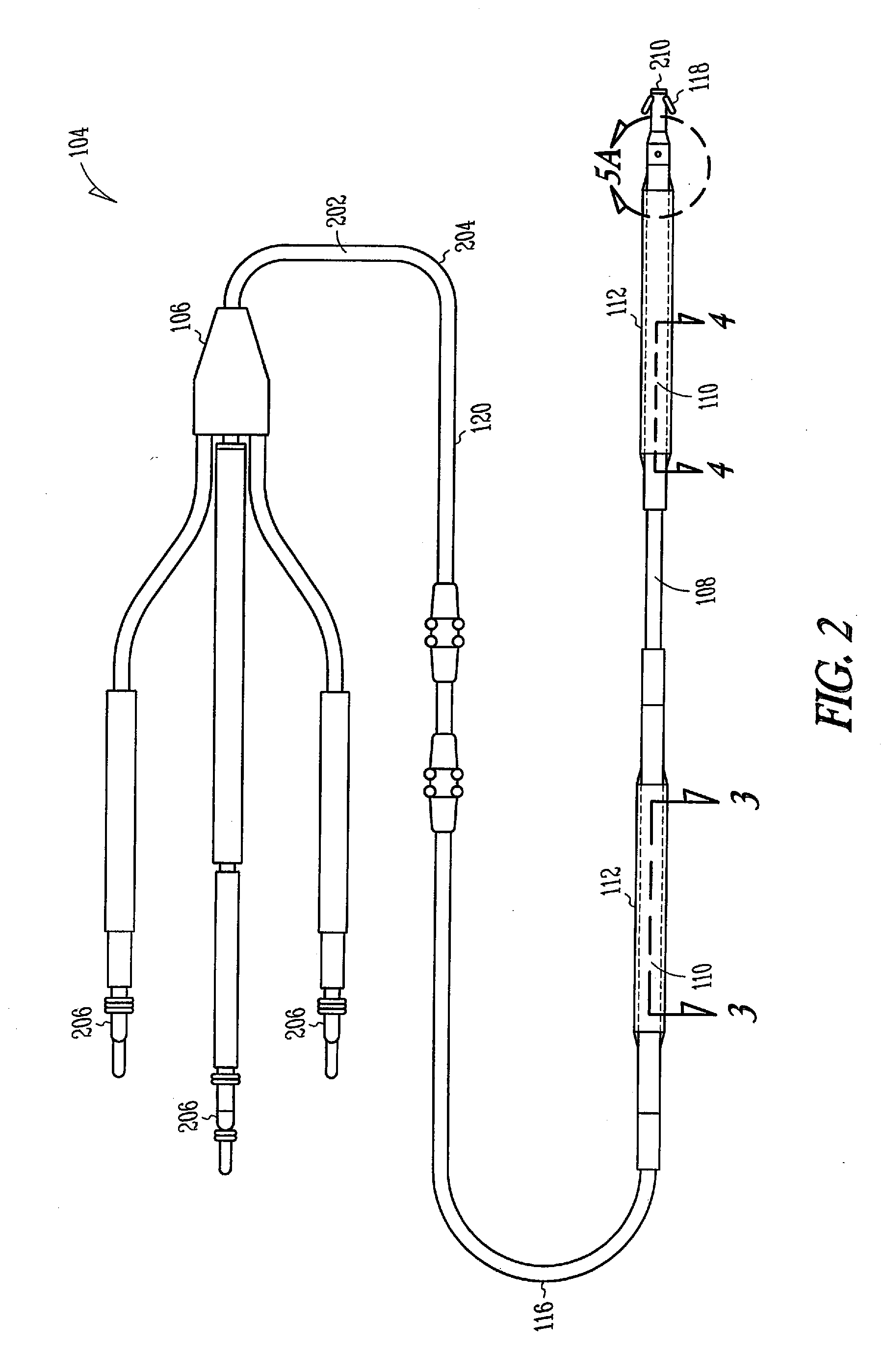
Fibrosis-limiting material attachment
InactiveUS20080183261A1Reduce the possibilityImprove usabilityElectrotherapyFibrosisSacroiliac joint
Defibrillator lead designs and methods for improved attachment strength between a fibrosis-limiting material covering, a shocking coil electrode, and an implantable lead body are disclosed herein. In certain examples, a portion of the fibrosis-limiting material extends proximal or distal to a shocking coil end and is disposed between a first and a second lead component. In certain examples, a length of compression tubing is utilized. A chronically implanted lead is often encapsulated by a body's fibrotic reaction, which in turn causes future lead explantation to be exceedingly difficult. To reduce fibrotic entanglement, the fibrosis-limiting material covering surrounds strategic portions of the lead. Improving the attachment between the fibrosis-limiting material covering, the shocking coil electrode, and the lead body will allow for improved performance, durability, and extractability of the lead. This disclosure describes several defibrillator lead designs and methods to create these improved joints.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
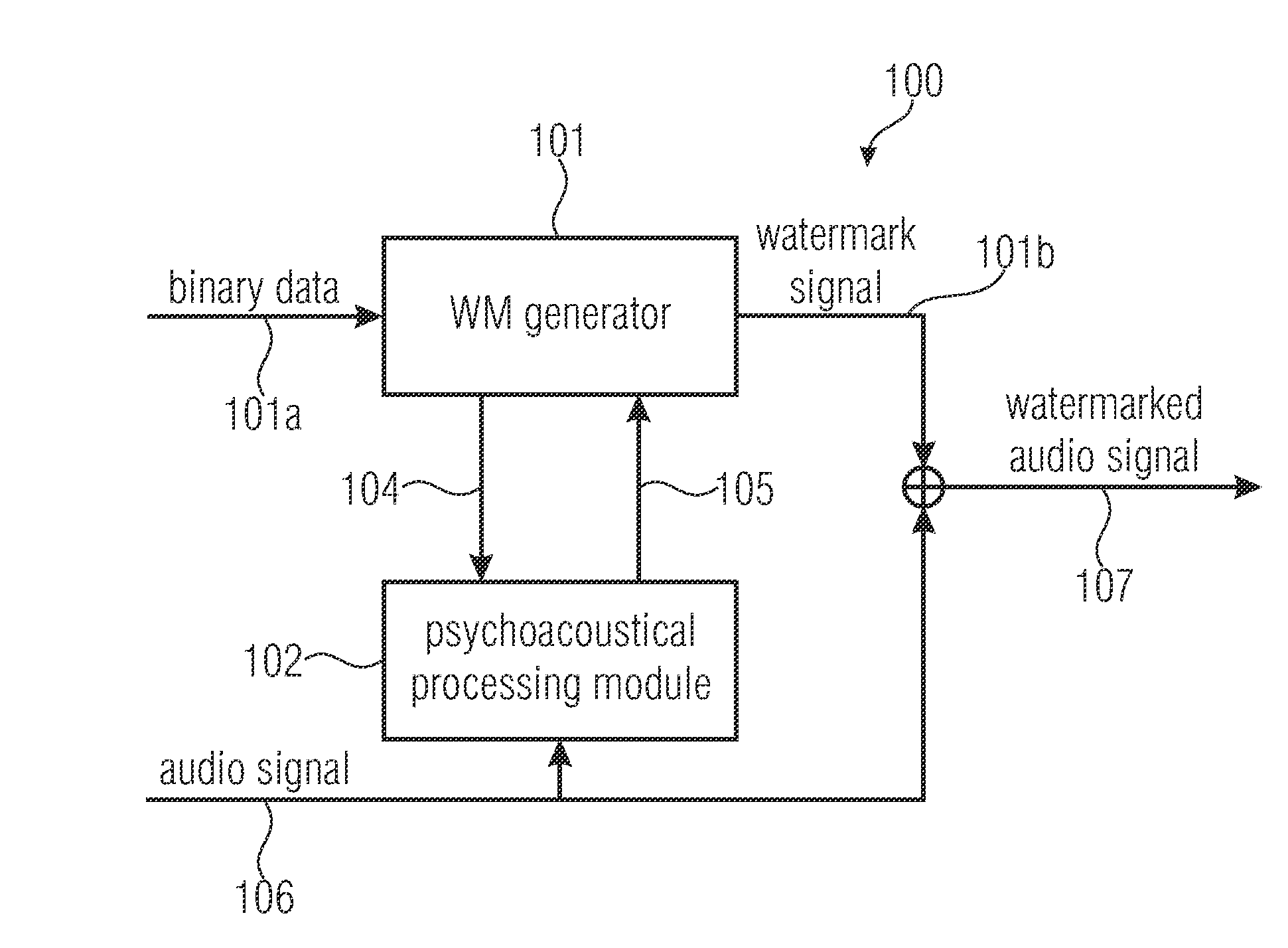
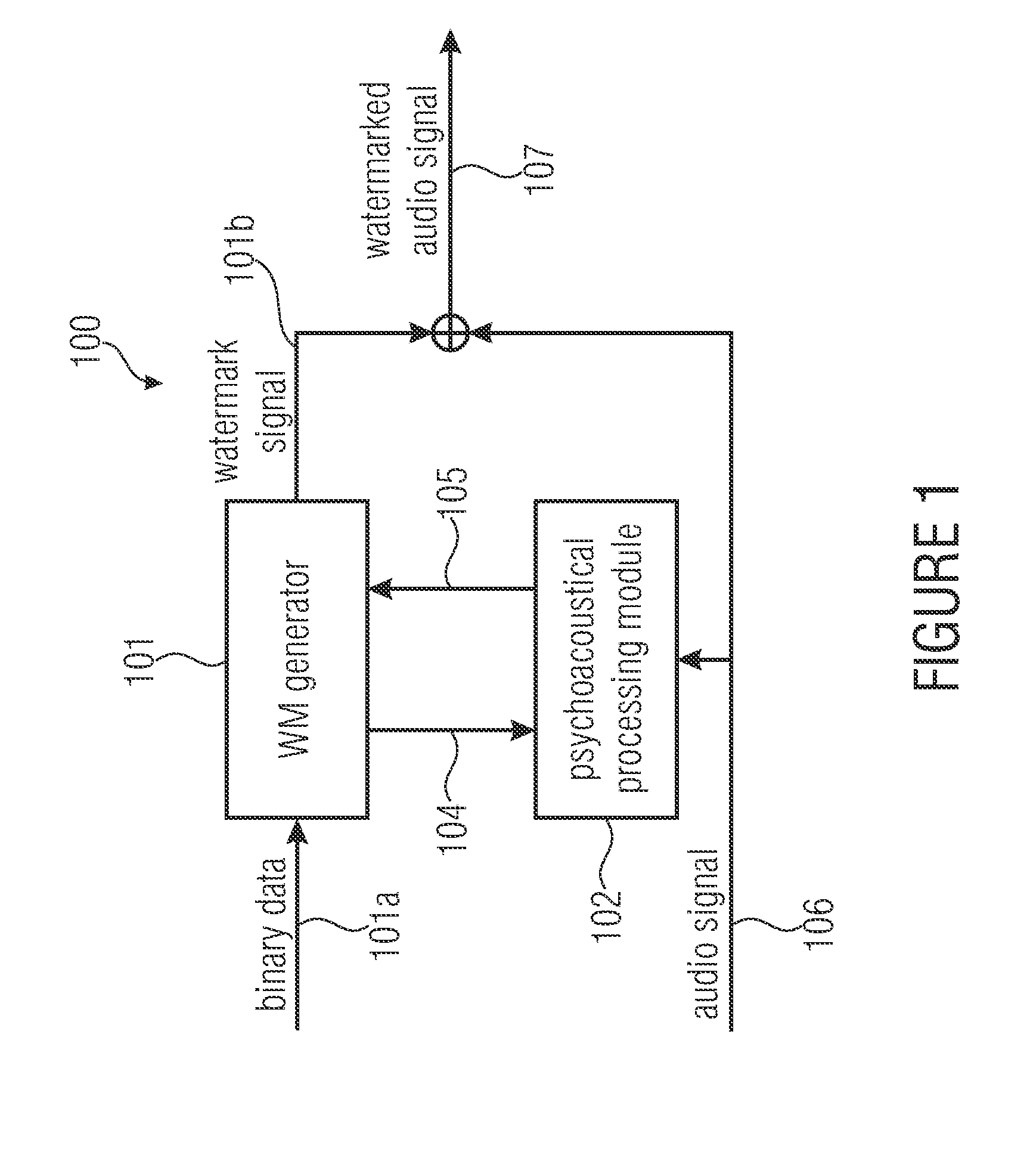
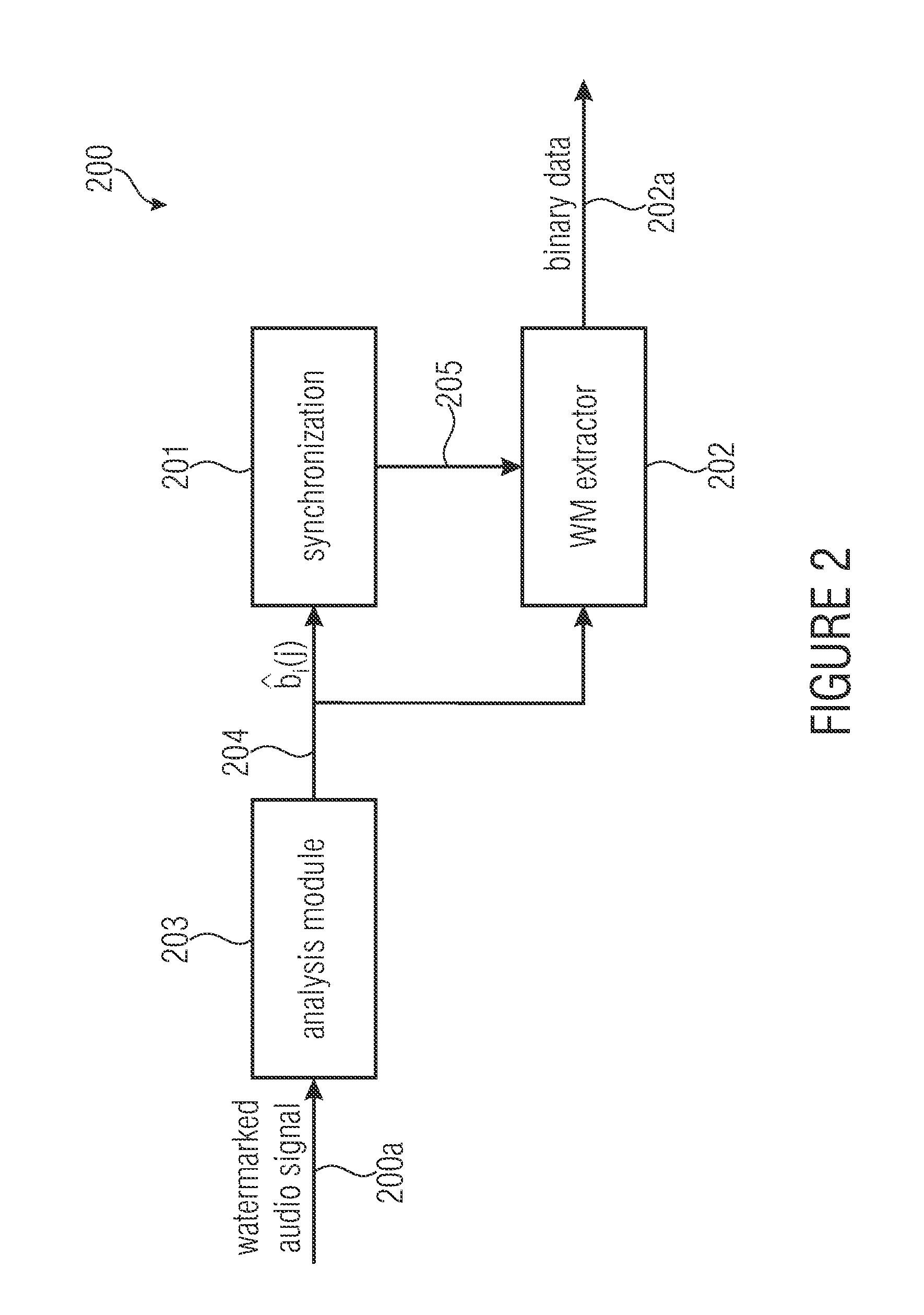
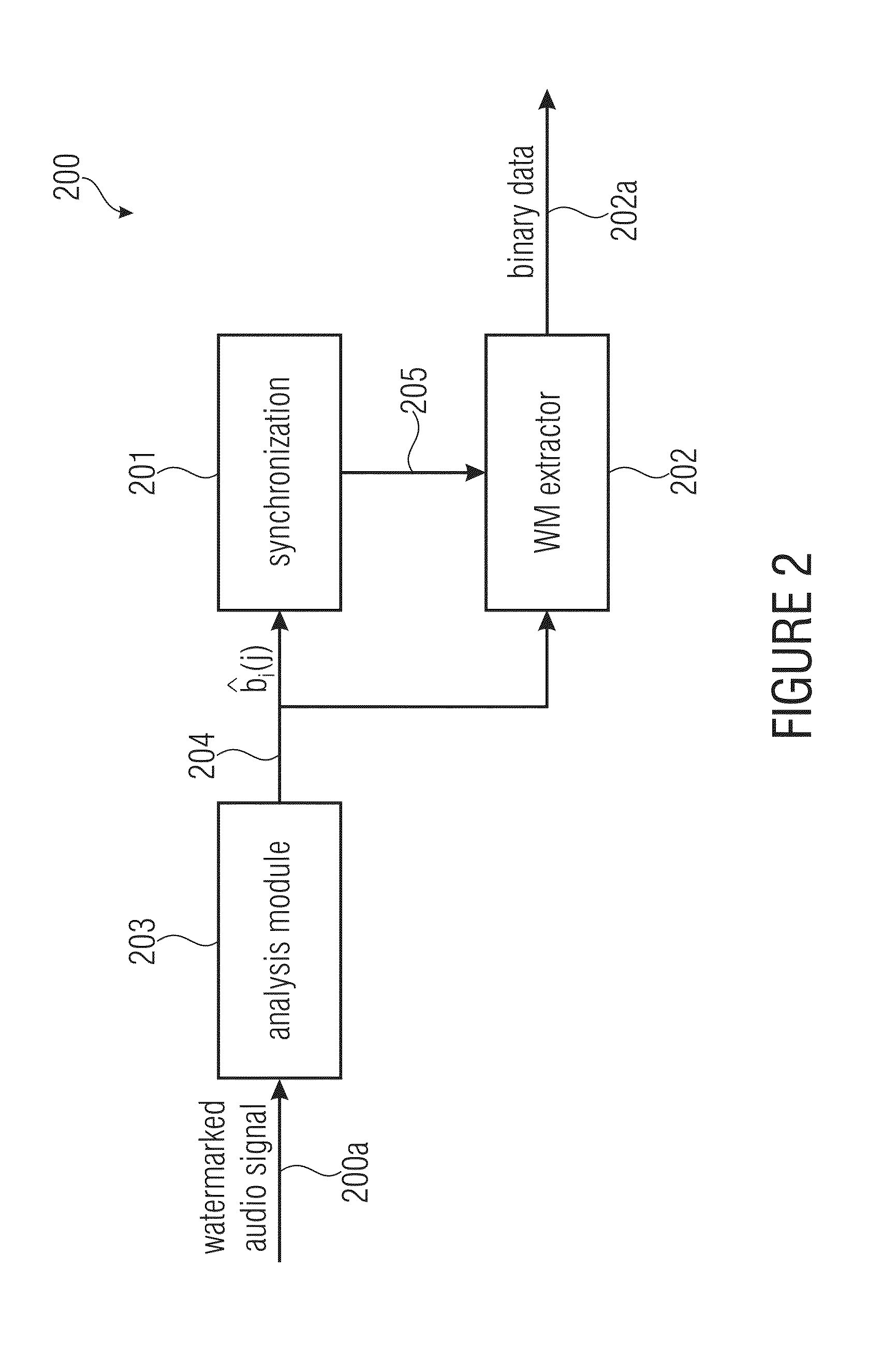
Watermark signal provision and watermark embedding
ActiveUS20130218314A1Good trade-offBetter trade-offSpeech analysisBroadcast information monitoringAudio signalWatermark embedding
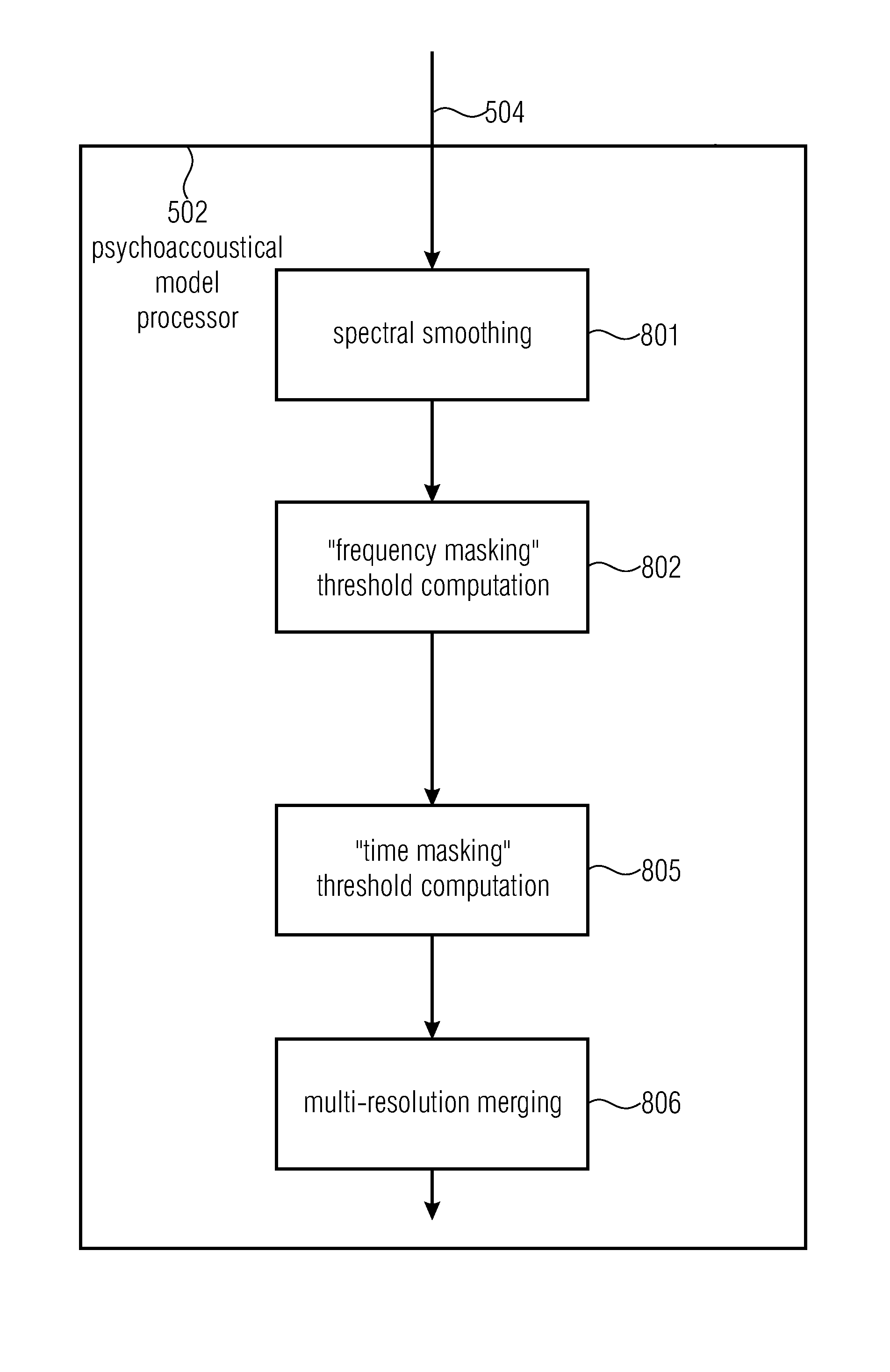
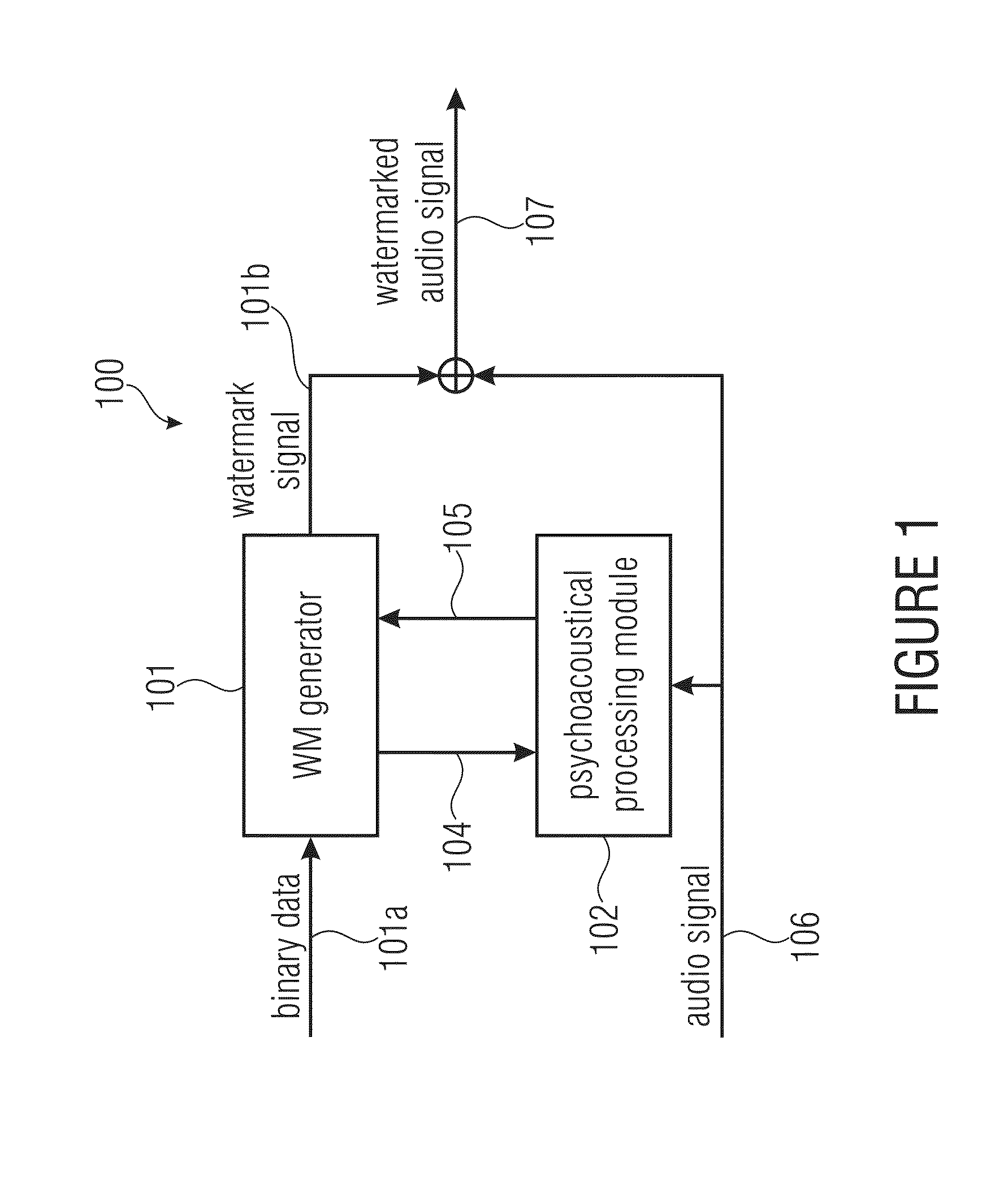
A watermark signal provider provides a watermark signal suitable for being hidden in an audio signal when the watermark signal is added to the audio signal, such that the watermark signal represents watermark data. The watermark signal provider includes a psychoacoustical processor for determining a masking threshold of the audio signal; and a modulator for generating the watermark signal from a superposition of sample-shaping functions spaced apart from each other at a sample time interval of a time-discrete representation of the watermark data, each sample-shaping function being amplitude-weighted with a respective sample of the time-discrete representation, multiplied by a respective amplitude weight depending on the masking threshold, the modulator being configured such that the sample time interval is shorter than a time extension of the sample-shaping functions; and the respective amplitude weight also depends on samples of the time-discrete representation neighboring the respective sample in time.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
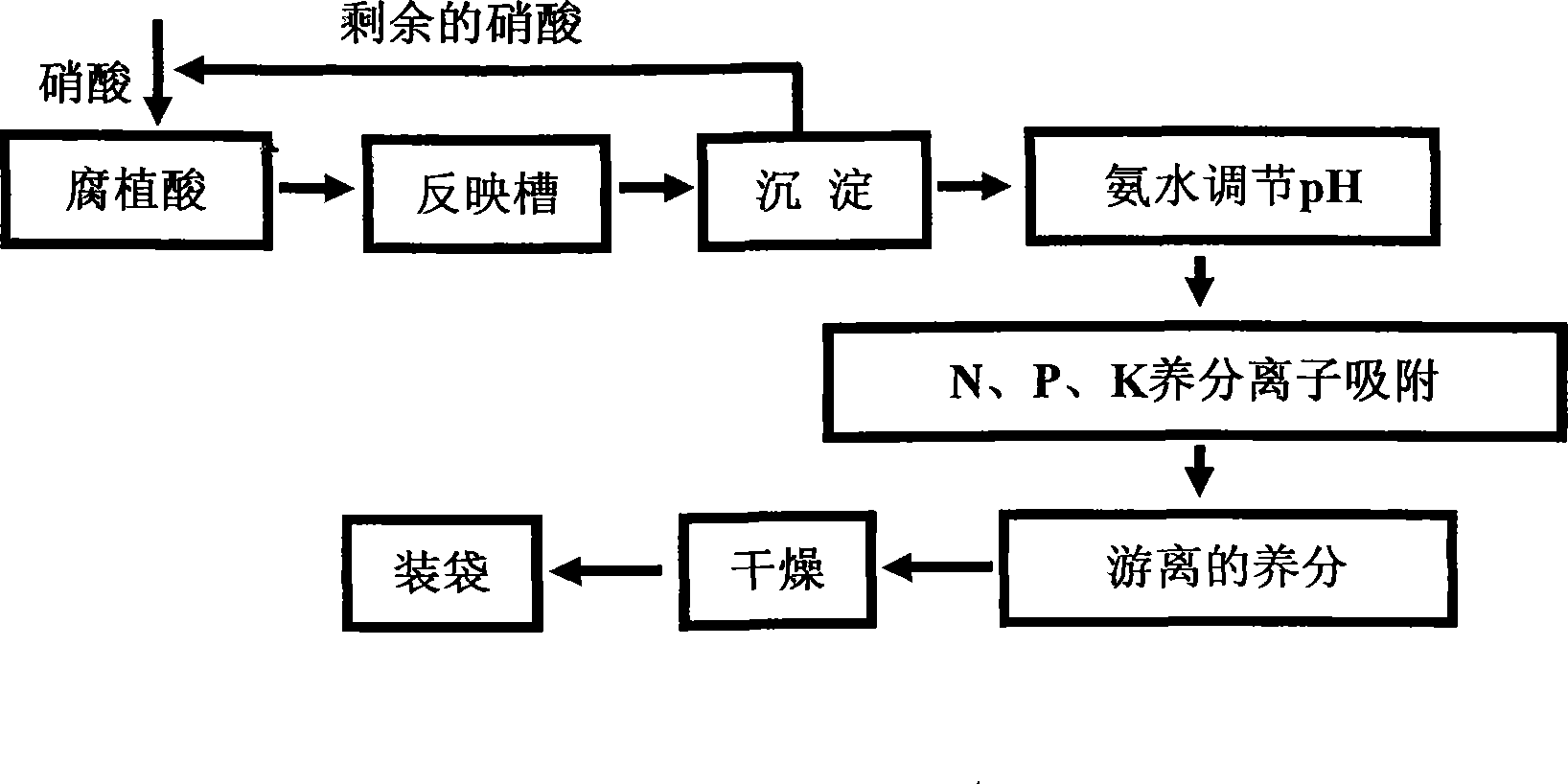
Humic acid slowly available fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101225005AExcellent extractabilityImprove ion adsorption performanceOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesPotassiumOrganic compound
The invention discloses a humic acid slow release fertilizer and the preparation method, which uses the lignite as raw material, the preparation method is as follows: first adding the lignite and the nitric acid first to the reactor, agitate, enabling to react, and filtrate after stirring for 20 to 40 minutes; then adding strong ammonia into the filtered materials; adjusting the pH to 7 to 9, finally adding nitrogenous fertilizer, the phosphate fertilizer and the potassium fertilizer into the humic acid after the adjustment of pH value and stirring for 30 to 45 minutes. The humic acid slow release fertilizer has nitrogen of different morphas, and the ions have both the absorption state and ionized state, thus can satisfy the short-term and the long-term demand of the crops to the nutrients. The raw material is the cheap humic acid which is an inexpensive non-pollution high polymer organic compound with no side effects to the soil and no residues after the application of the fertilizer. The humic acid slow release fertilizer has the advantages of simple preparation method, needing no large-scale equipment, and low cost.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
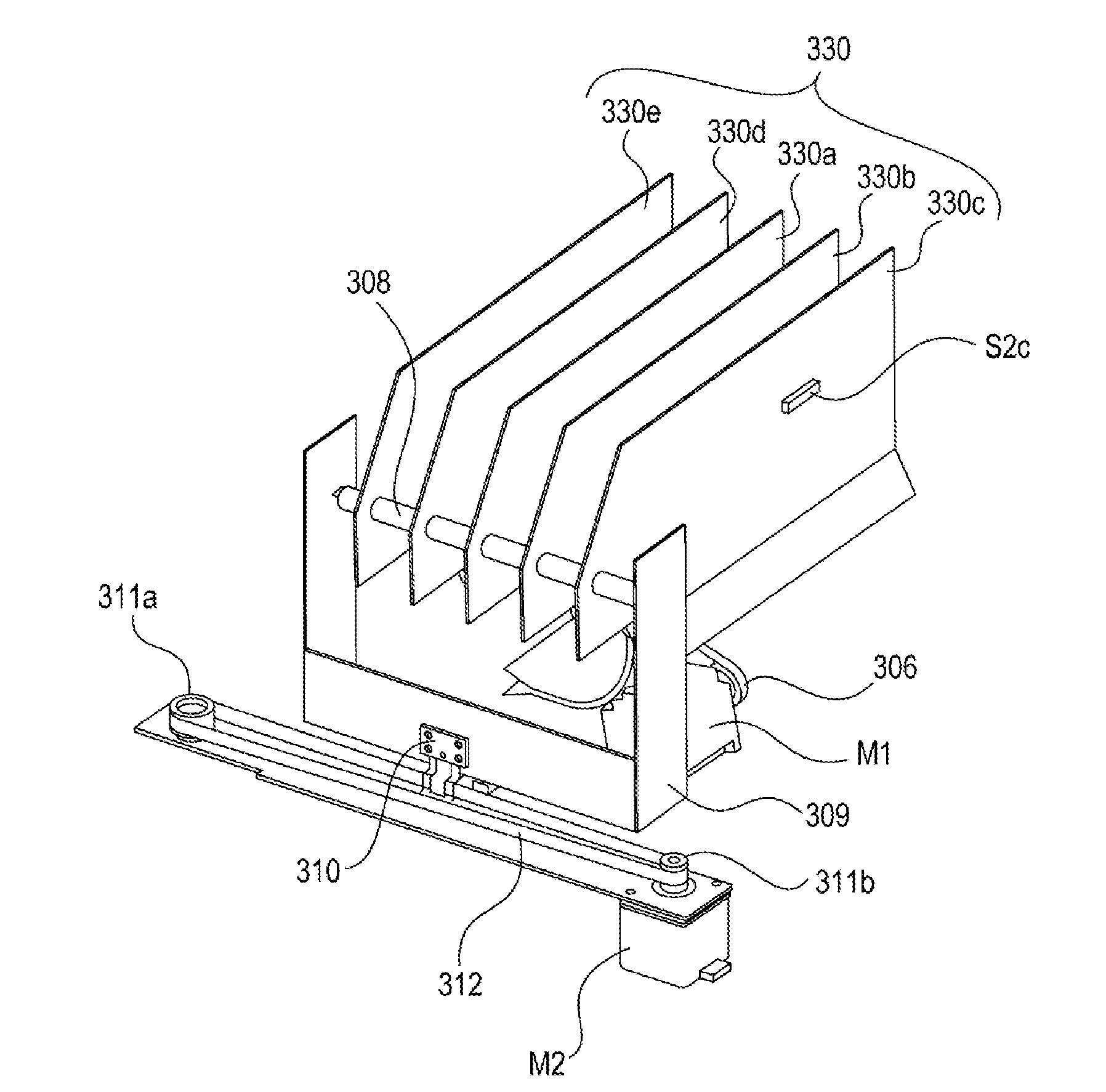
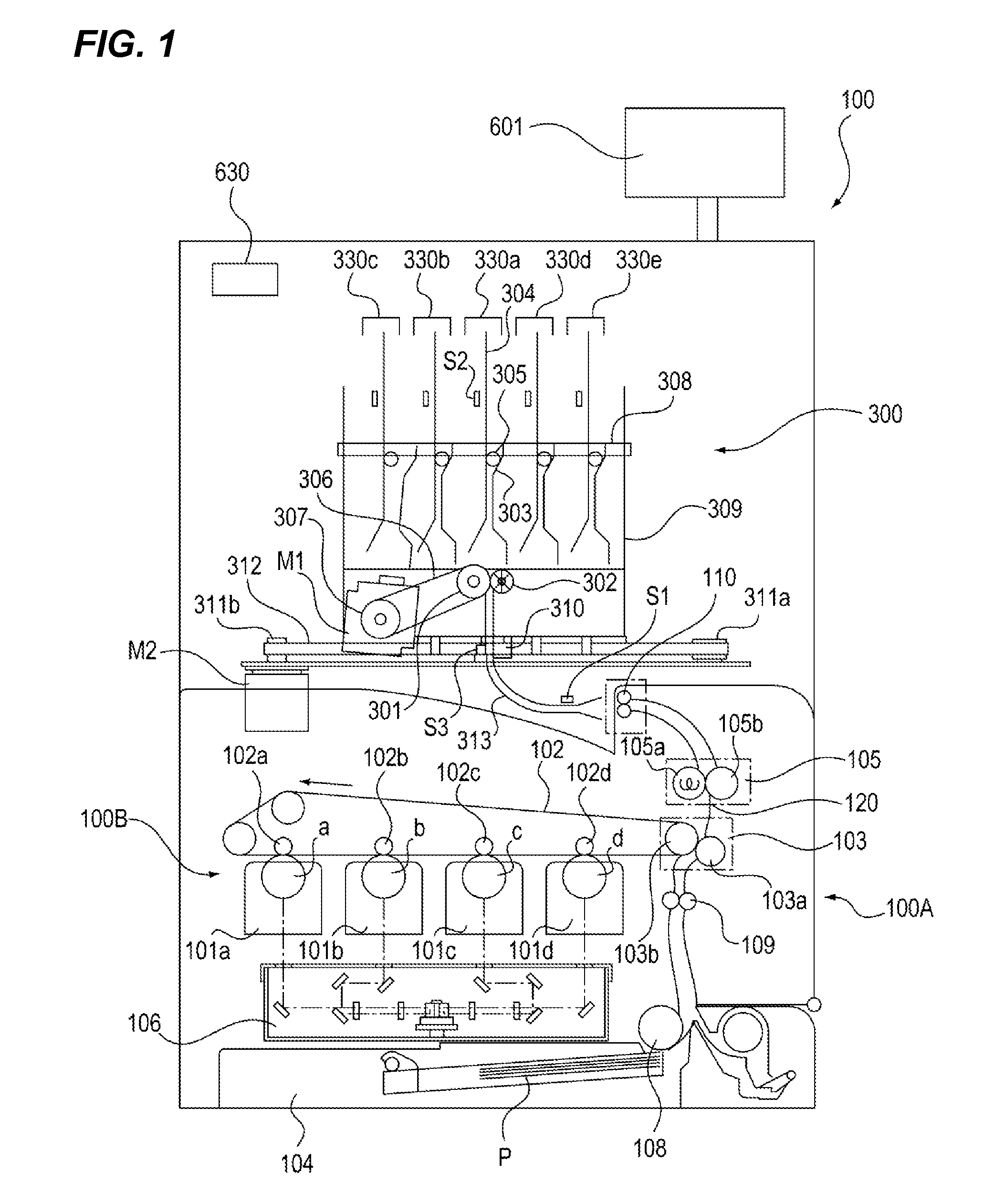
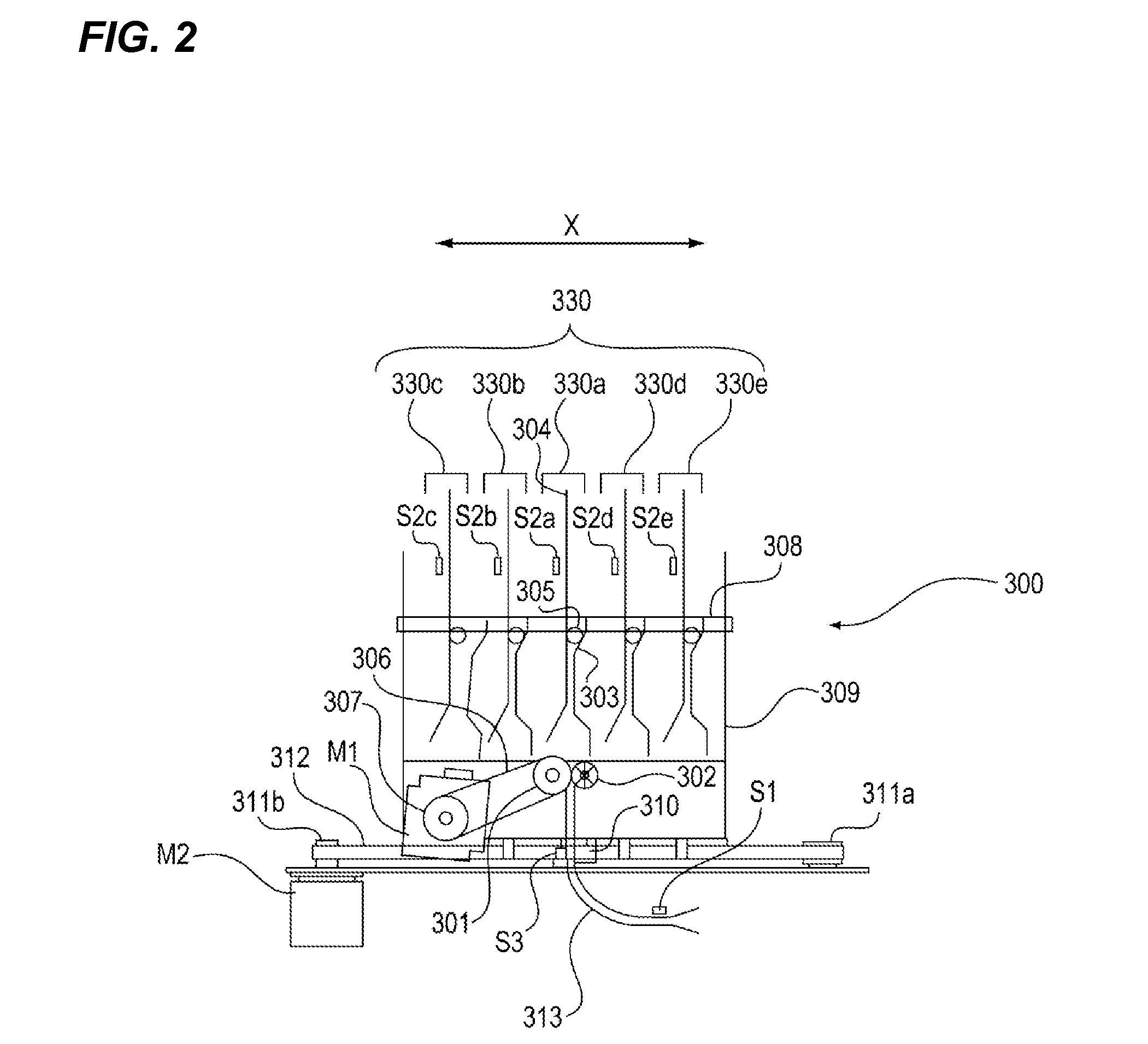
Sheet storage device and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20120275839A1Excellent extractabilityImprove visibilityElectrographic process apparatusPile receiversVisibilityEngineering
A sheet storage device and an image forming apparatus capable of increasing extractability and visibility are provided. A plurality of trays 330 (330a to 330e) receives sheets sequentially conveyed from an image forming apparatus main body 100A from a lower part thereof and stores the sheets in a standing condition. The plurality of trays 330 (330a to 330e) is configured such that a downstream end in a sheet conveying direction and a front end in a direction perpendicular to a sheet conveying direction of the stored sheets protrude from the trays 330 (330a to 330e).
Owner:CANON KK
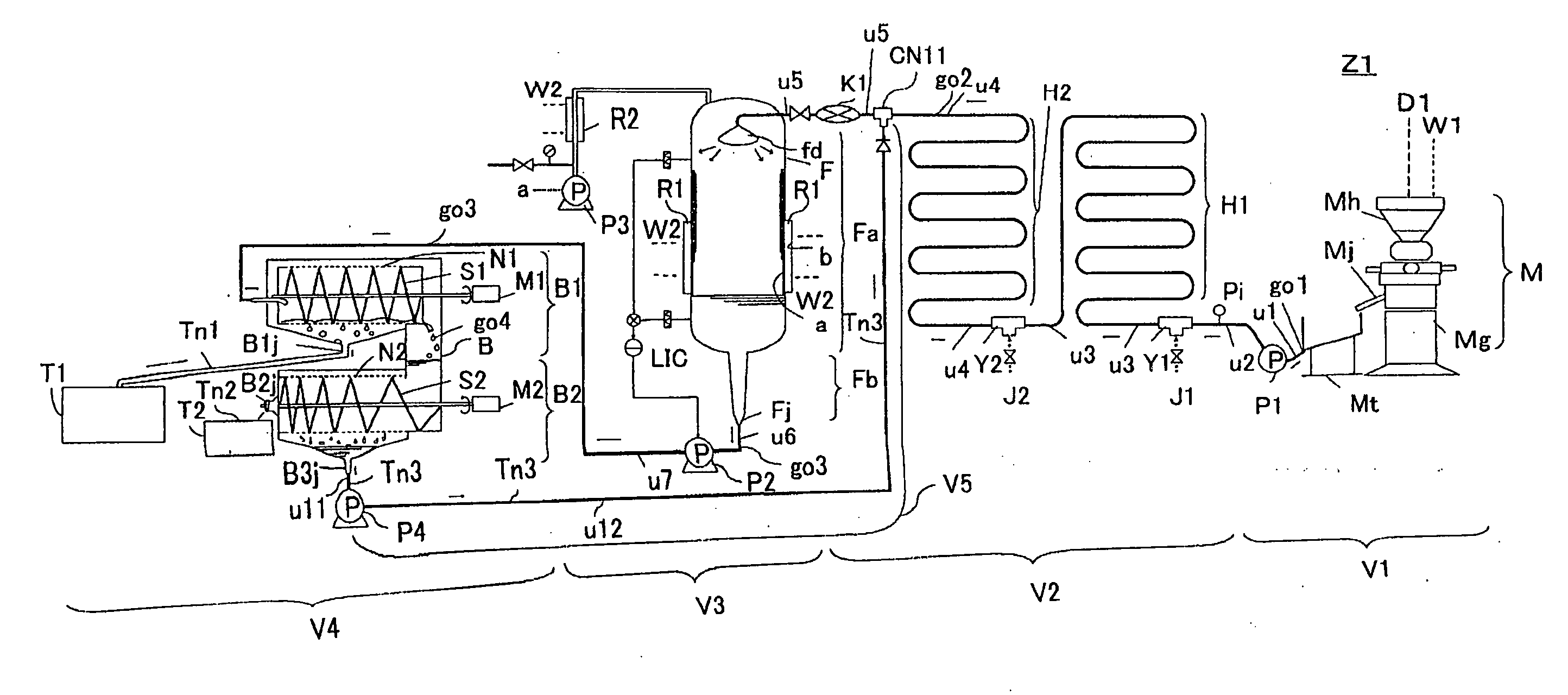
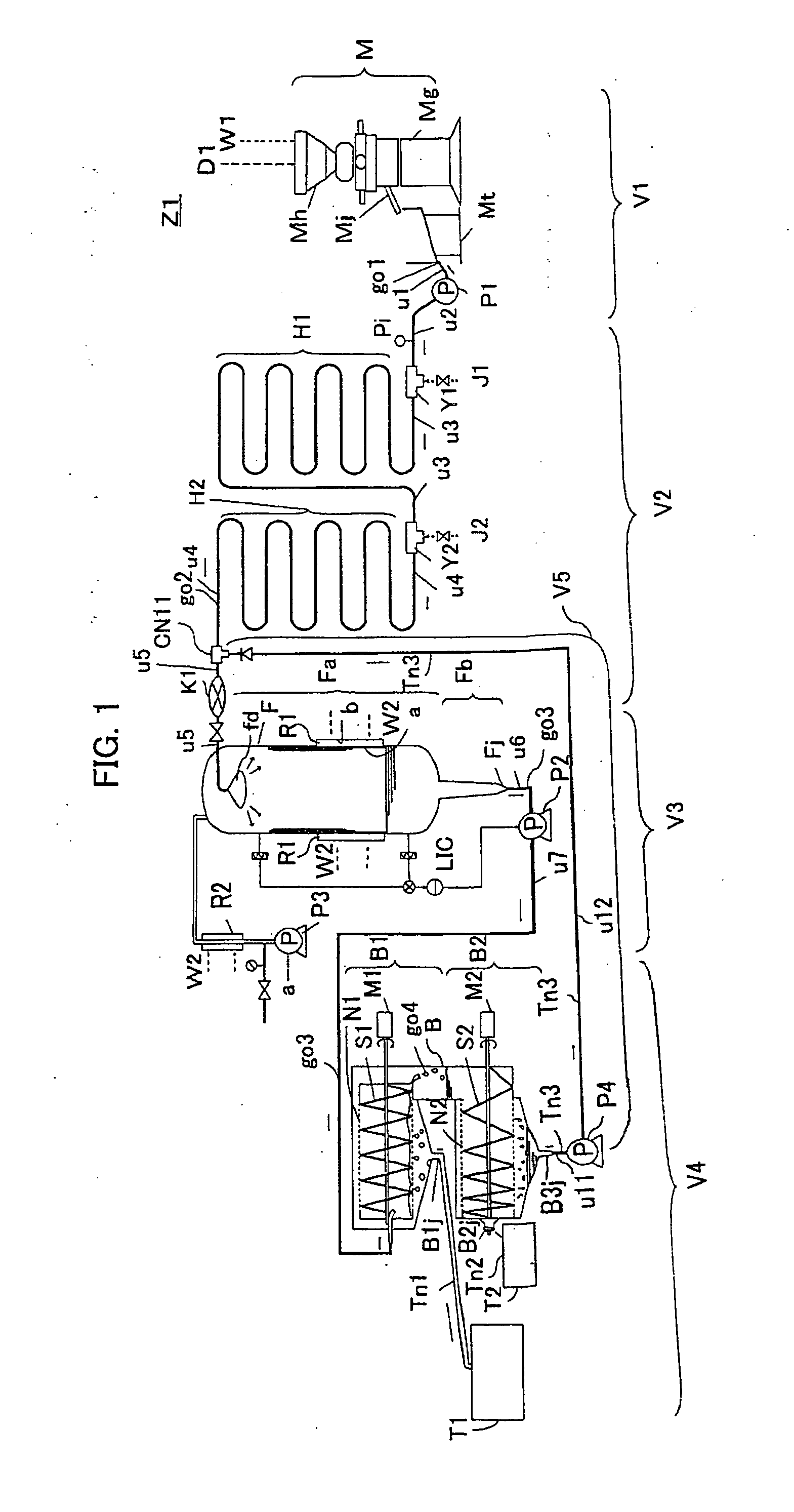
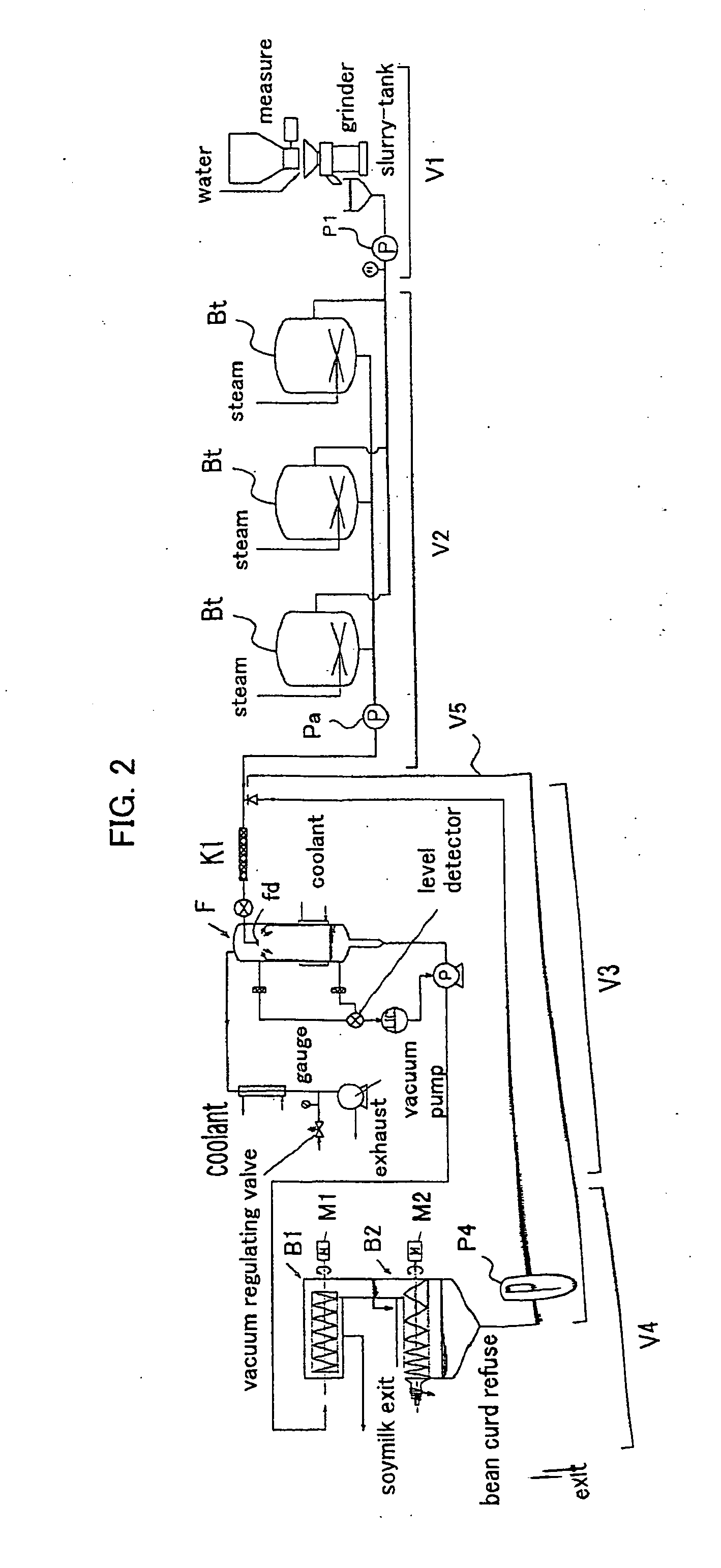
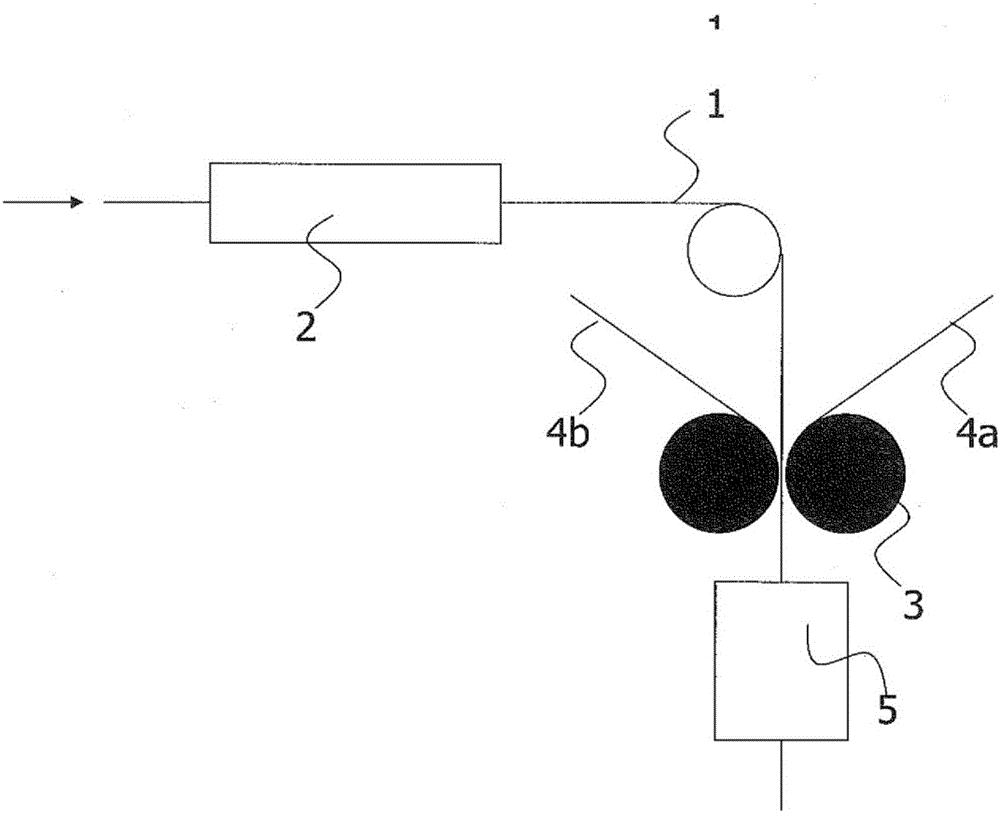
Process for producing soymilk and apparatus for producing soymilk
ActiveUS20100323075A1Excellent extractabilityQuality improvementWort preparationWine preparationChemistry
[Task] High-quality soymilk is produced, with overflow of foam or bubbles avoided in an extracting step, and the extractability (extraction ratio) of the soymilk is simultaneously heightened.[Solving Means] An apparatus for producing soymilk includes heating units H1 and H2 for heating a soybean soup go1; a defoaming unit F for defoaming a heated soybean soup go2; an extracting unit B for separating a defoamed soybean soup go3 into soymilk Tn1, bean curd refuse Tn2 and a liquid residue Tn3; and pipe lines u11 and u12 for returning the separated liquid residue Tn3 to a position before the defoamng unit F or behind the heating unit H2 (H1) and feeding it again to the defoaming unit F, wherein the pipe lines u11 and u12 for feeding the separated liquid residue to the defoaming unit F are connected to a liquid residue discharge port B3j of the extracting unit B from which the liquid residue Tn3 having been separated is taken out. The liquid residue Tn3 is then fed forcibly to the defoaming unit F again with a transfer pump P4.
Owner:TAKAI TOFU & SOYMILK EQUIP
Solid phase micro-extraction fiber, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN105268414AHigh porosityEasy extractionOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationFiberOrganic solvent
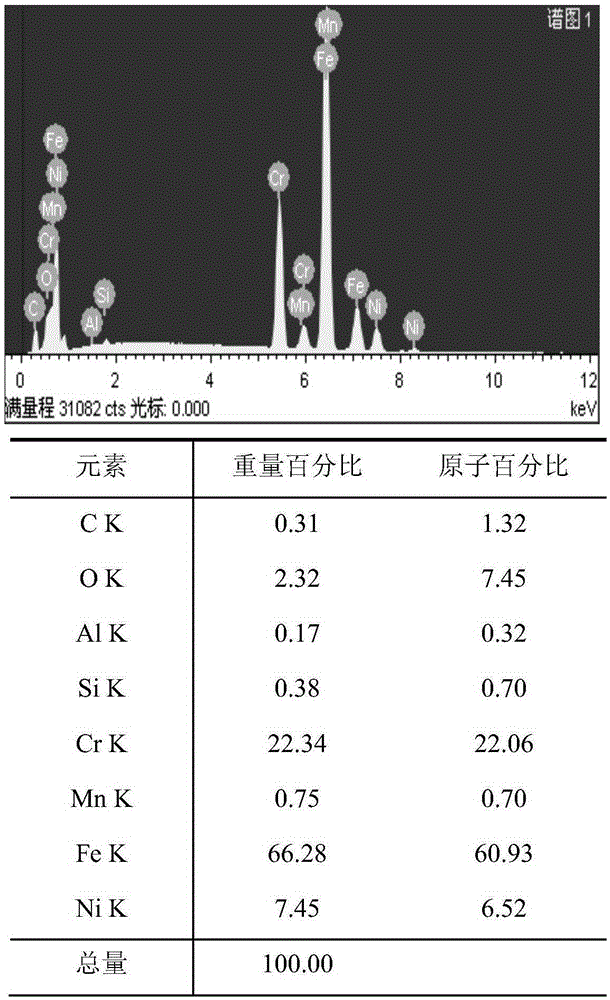
The invention discloses a solid phase micro-extraction fiber. The solid phase micro-extraction fiber comprises a stainless steel wire and a coating, and the oxygen atom percentage of elements on the surface of the stainless steel wire is not smaller than 30%. The invention also provides a preparation method of the solid phase micro-extraction fiber, and an application of the solid phase micro-extraction fiber in manufacturing of solid phase micro-extraction products. The solid phase micro-extraction fiber has the advantages of firm combination between the coating and the stainless steel wire, difficult shedding, long service life, good temperature resistance, good organic solvent resistance, good acid and alkali resistance, and also combines the respective advantages of solid phase micro-extraction fibers with fused quartz as a matrix material and solid phase micro-extraction fibers with stainless steel wires as a matrix material;, the solid phase micro-extraction fiber has better extraction performance and higher detection sensitivity than commercial extract fibers; and the fiber prepared in the invention has good reappearance and repeatability, and is very suitable for industrial practical application.
Owner:段忆翔 +1
Mixed solvent low-pressure fluid critical extract method
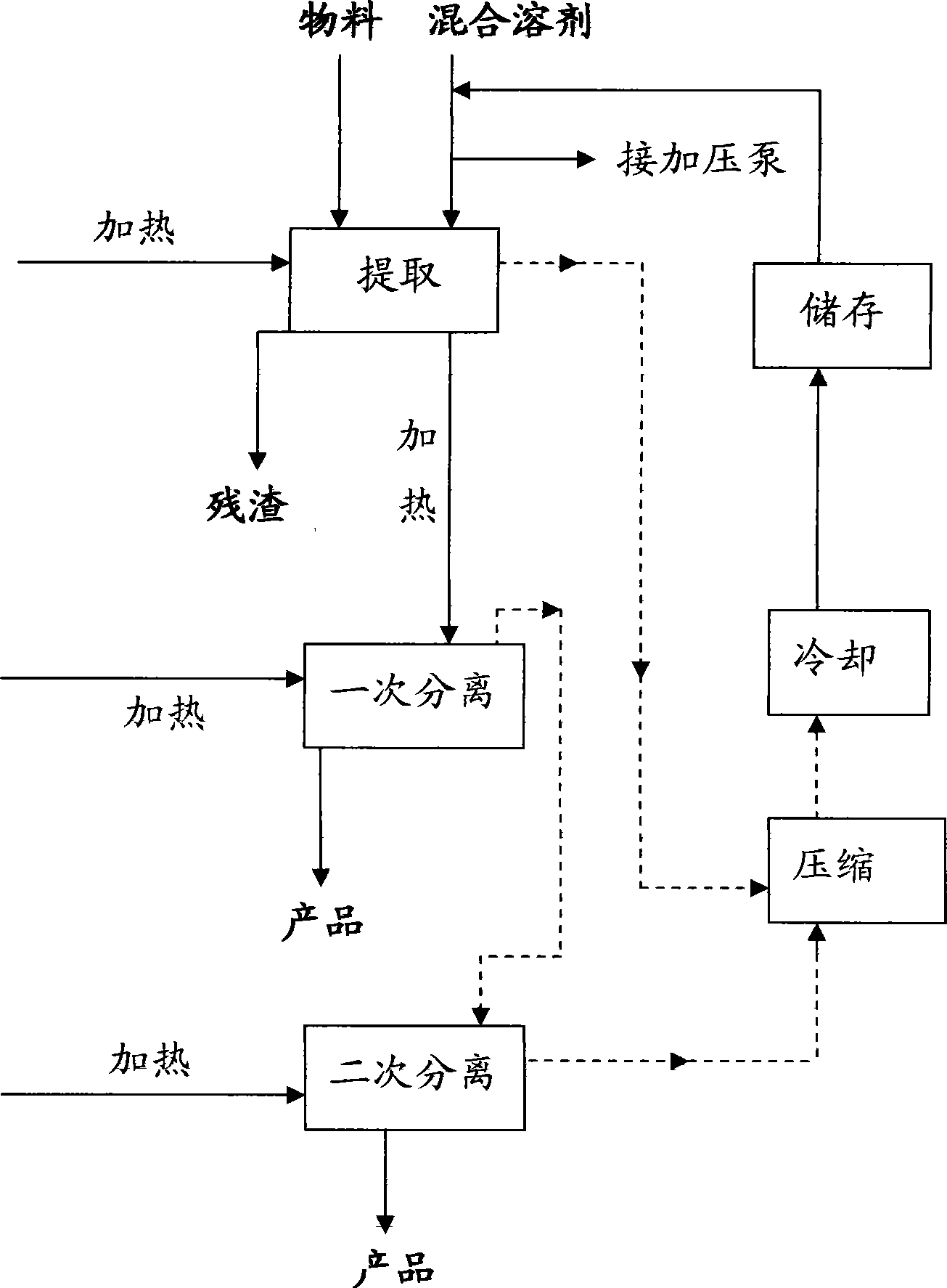
The invention relates to a method for critically extracting component solvent low pressure fluid, which comprises extraction, separation and solvent recovery. The method is characterized in that 75-95 wt% of 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrafluoroethane and 5-25 wt% of normal butane are taken as component solvent; in the extracting process, the component solvent is controlled to be in a liquid to be contacted with materials to lead the active ingredients of the materials to be dissolved in the liquid component solvent; in the separating process, the component solvent is controlled to be in a gas state and separated from the extracted liquid active ingredients; the separated component solvent is compressed and cooled to become liquid in a mixed state, and then is recovered for cyclic utilization; and the steps of extraction, separation and solvent recovery are carried out in a sealing state at the same time. The operating pressure and the manufacturing cost of the equipment are both lower than those of a carbon dioxide supercritical extraction method; the GWP of the component solvent is lower than that of the 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrafluoroethane, so that the method of the invention is in accordance with environmental requirements, is low in price and has high extraction efficiency.
Owner:符文飙
Watermark signal provision and watermark embedding
ActiveUS8965547B2Better trade-offExcellent extractabilitySpeech analysisBroadcast information monitoringTime extensionComputer hardware
A watermark signal provider provides a watermark signal suitable for being hidden in an audio signal when the watermark signal is added to the audio signal, such that the watermark signal represents watermark data. The watermark signal provider includes a psychoacoustical processor for determining a masking threshold of the audio signal; and a modulator for generating the watermark signal from a superposition of sample-shaping functions spaced apart from each other at a sample time interval of a time-discrete representation of the watermark data, each sample-shaping function being amplitude-weighted with a respective sample of the time-discrete representation, multiplied by a respective amplitude weight depending on the masking threshold, the modulator being configured such that the sample time interval is shorter than a time extension of the sample-shaping functions; and the respective amplitude weight also depends on samples of the time-discrete representation neighboring the respective sample in time.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Inbred corn line SMM11BM
ActiveUS9554526B1High yieldBetter stalkPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred corn line, designated SMM11BM, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line SMM11BM, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line SMM11BM with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line SMM11BM with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SMM11BM, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SMM11BM and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Increasing starch extraction rate in cereals
InactiveUS20080009615A1Enhanced grain production and storage and digestibility and palatabilityPromote weight gainSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBiotechnologyHardness
The present invention provides for control of seed grain hardness resulting in improved cereals for both agricultural feed and commercial food products for human consumption.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
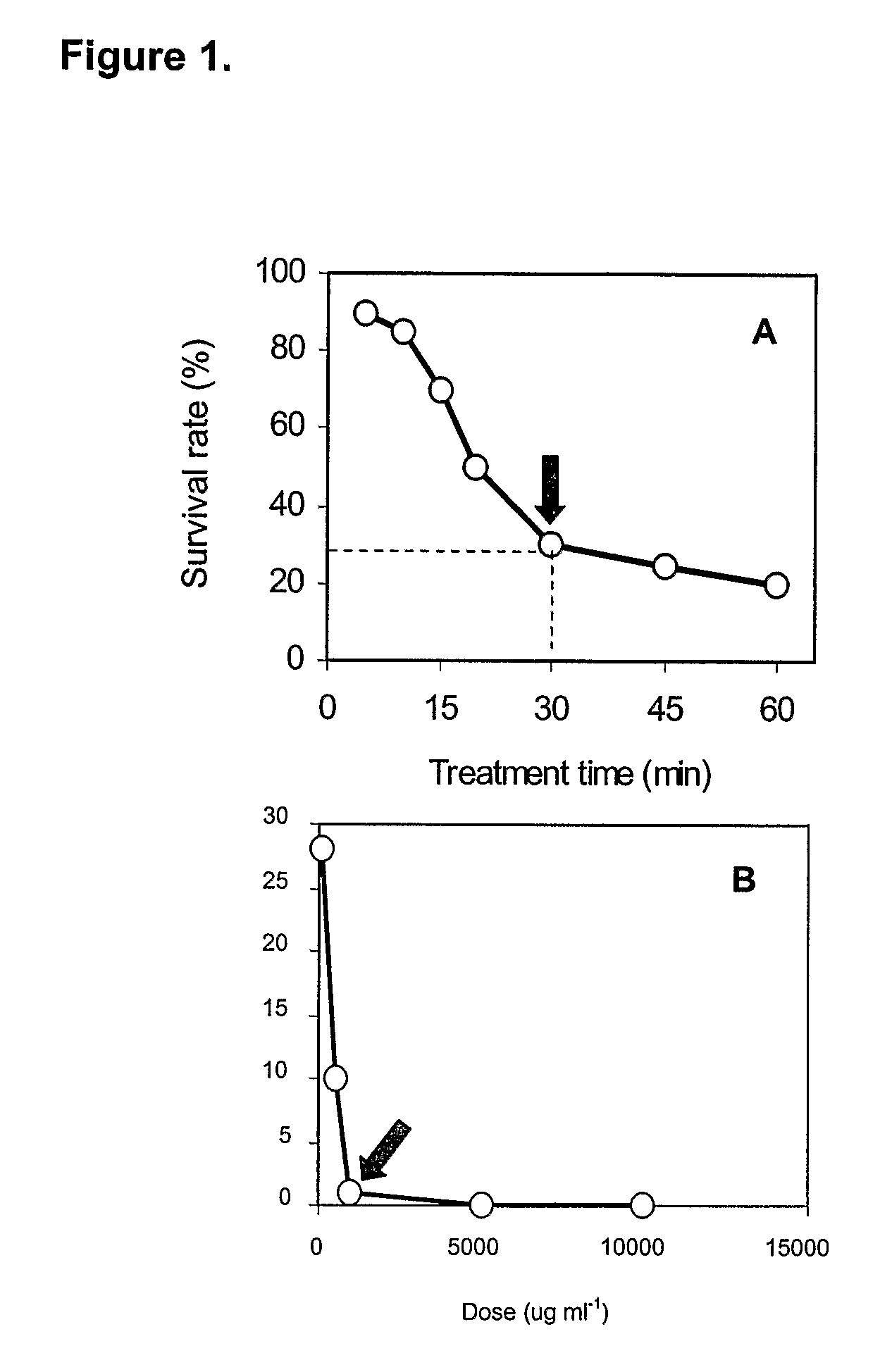
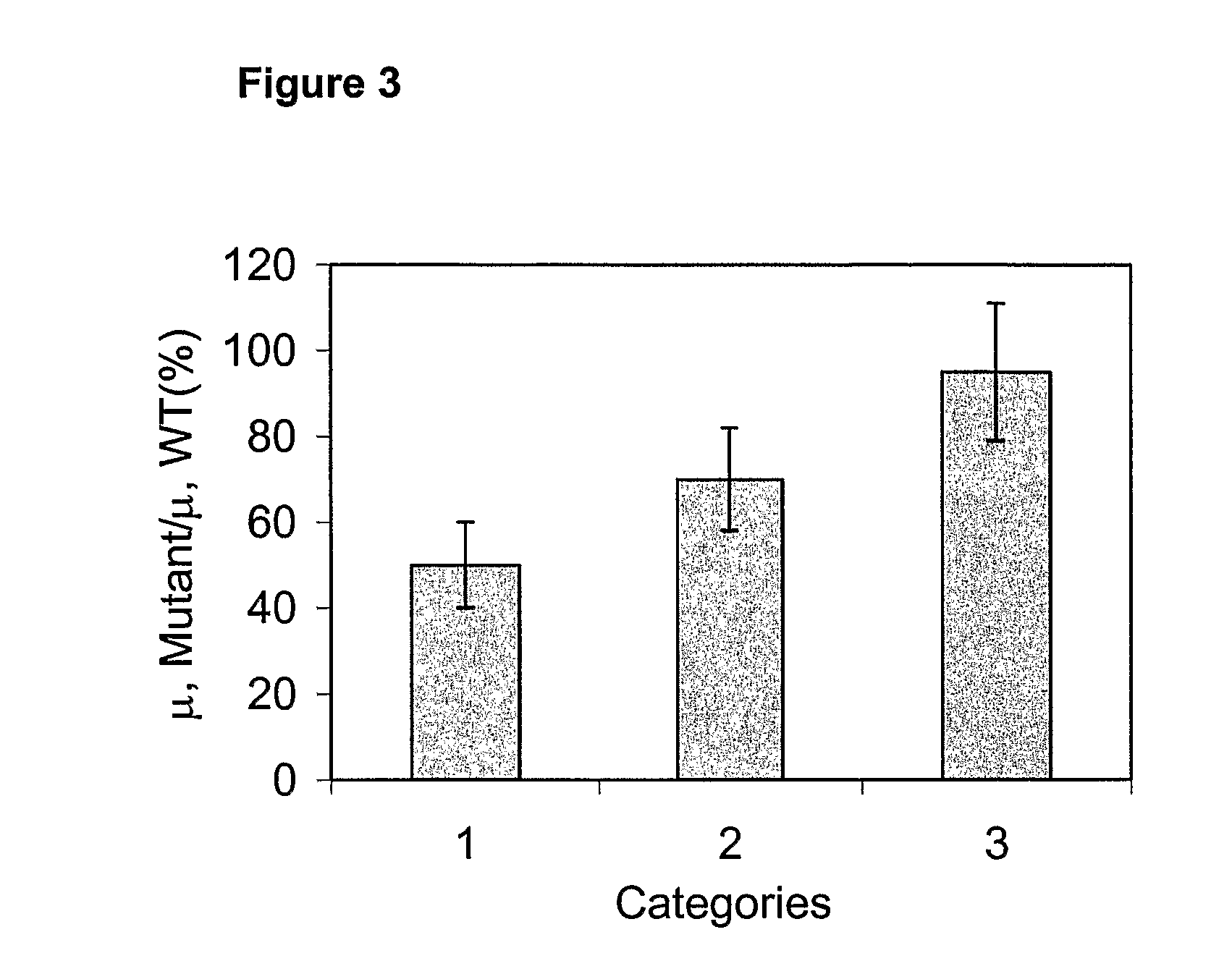
Extractability and Bioavailability of the Natural Antioxidant Astaxanthin From a Green Alga, Haematococcus Pluvialis
InactiveUS20090214475A1Excellent extractabilityImprove bioavailabilityMilk preparationBiocideCystAntioxidant
As the richest source of astaxanthin, a natural antioxidant and coloring agent, the unicellular green alga, Haematococcus pluvialis, is being commercially exploited. A major constraint in the Haematococcus production system, however, is the thick, rigid cell walls associated with astaxanthin-rich cysts (or aplanospores). The thick walls prevent the extraction of cellular materials and consequently reduce the bioavailability of astaxanthin. Using a physical, chemical, or enzymatic method to disrupt the cell wall has proven to be very expensive and also introduce the risk of oxidation of astaxanthin by atmospheric oxygen The present invention provides a novel method for solving this problem by introducing two genetically modified Haematococcus pluvialis mutants. These two mutants, named as D 13-17 and N54-22, contain remarkably reduced amounts of cell wall materials, but retain the growth potential and ability to accumulate astaxanthin as high as the wild type strain. Organic solvent extraction efficiency assay has demonstrated that cellular astaxanthin can be more effectively and efficiently extracted from the cell wall-deficient mutants than from the wild type, suggesting that the mutants may provide better bioavailability of astaxanthin to humans and animals. The said mutants can be used for production of natural astaxanthin for human and animal consumption
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
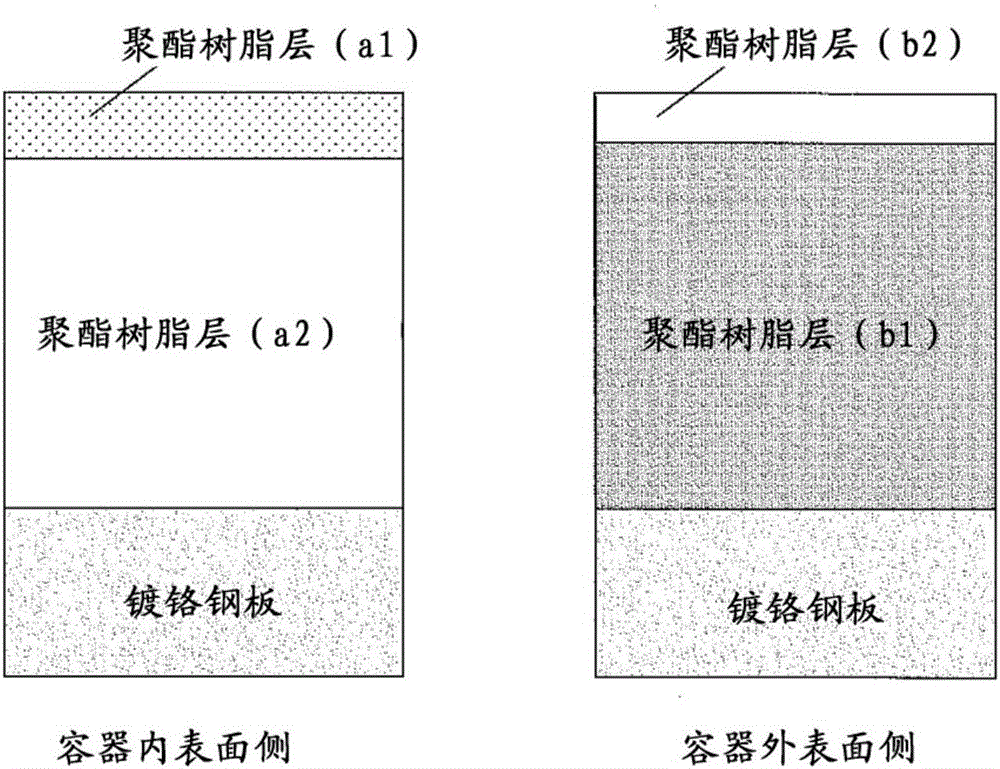
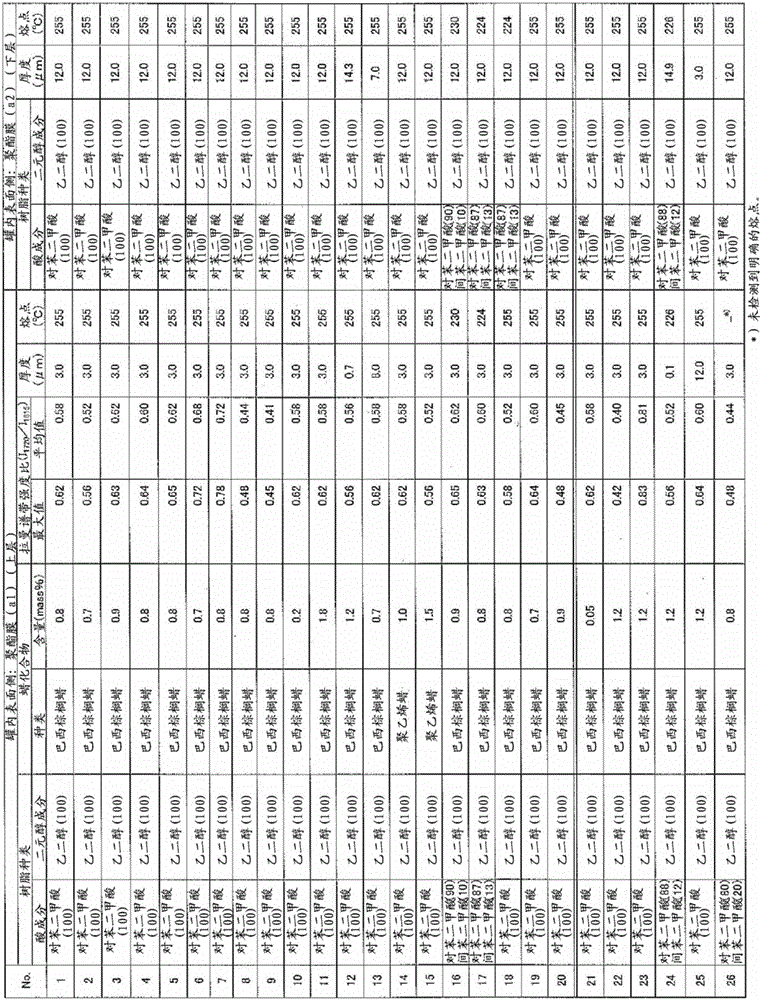
Resin-coated metal plate for container and production method therefor
ActiveCN106029511AExcellent extractabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsWaxTerephthalic acid
Provided is a resin-coated metal plate that is for a container, that maintains excellent extraction properties, and that stably satisfies various characteristics. The resin-coated metal plate for a container comprises a resin layer (A) that has a multilayer structure and that comprises a polyester as a main component thereof on a side that serves as a container inner surface when forming the metal plate on a container. 1) The resin layer (A) contains 85 mol% or more of terephthalic acid. 2) The resin layer (A) is configured from at least two layers, and the uppermost resin layer (a1) that comes into contact with the container contents contains 0.10-2.0 mass% of a wax compound with respect to the uppermost resin layer (a1). 3) The maximum value of the Raman band intensity ratio (I1720 / I1615) when a cross-section of the uppermost resin layer (a1) is measured using a laser polarization plane that is parallel to the surface of the resin layer (a1) is in the range of 0.45-0.80. 4) The thickness of the uppermost resin layer (a1) is 0.5-10 mu m. 5) The thickness of the resin layer (A) excluding the thickness of the uppermost resin layer (a1) is 5-20 mum.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
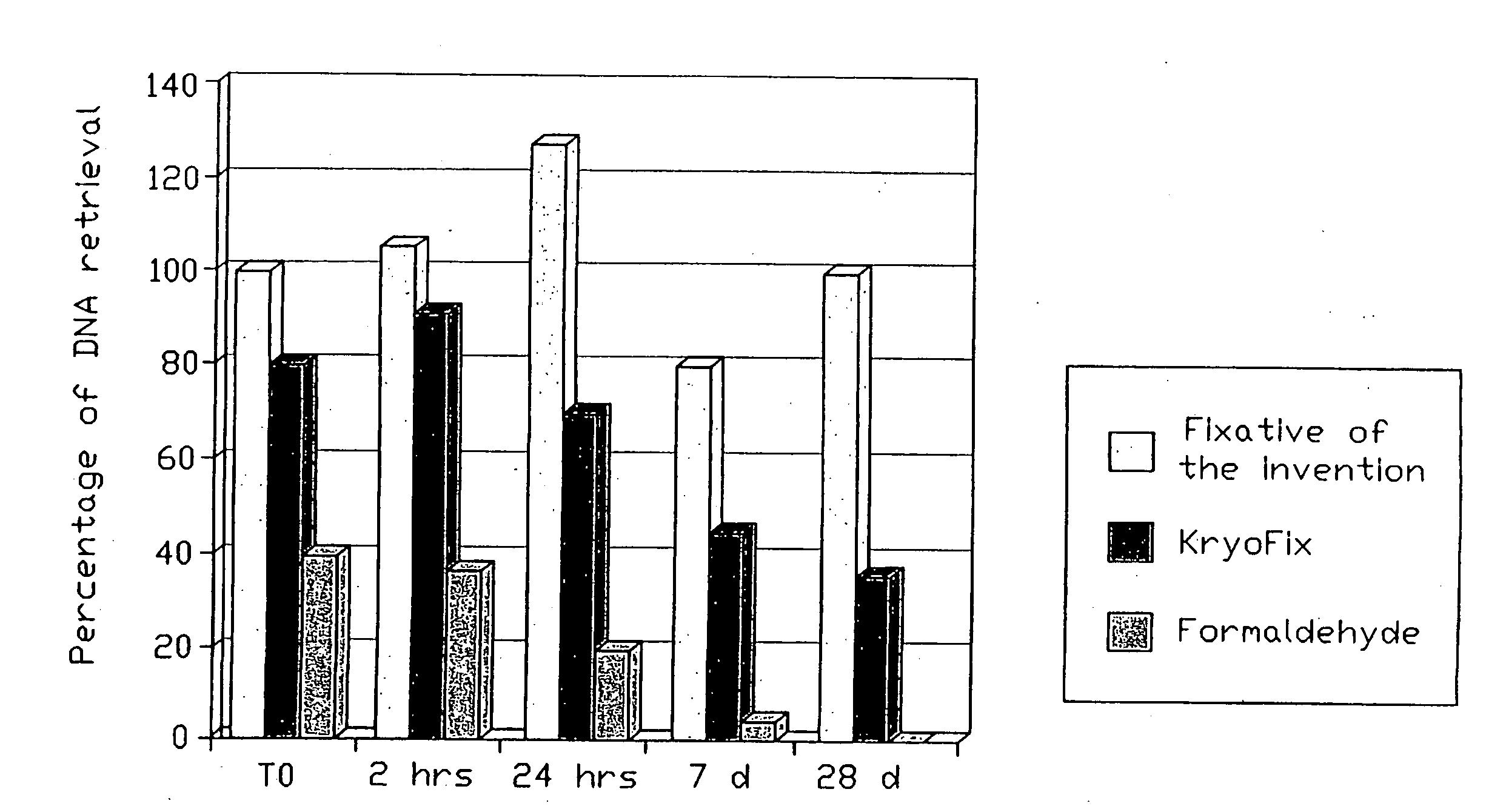
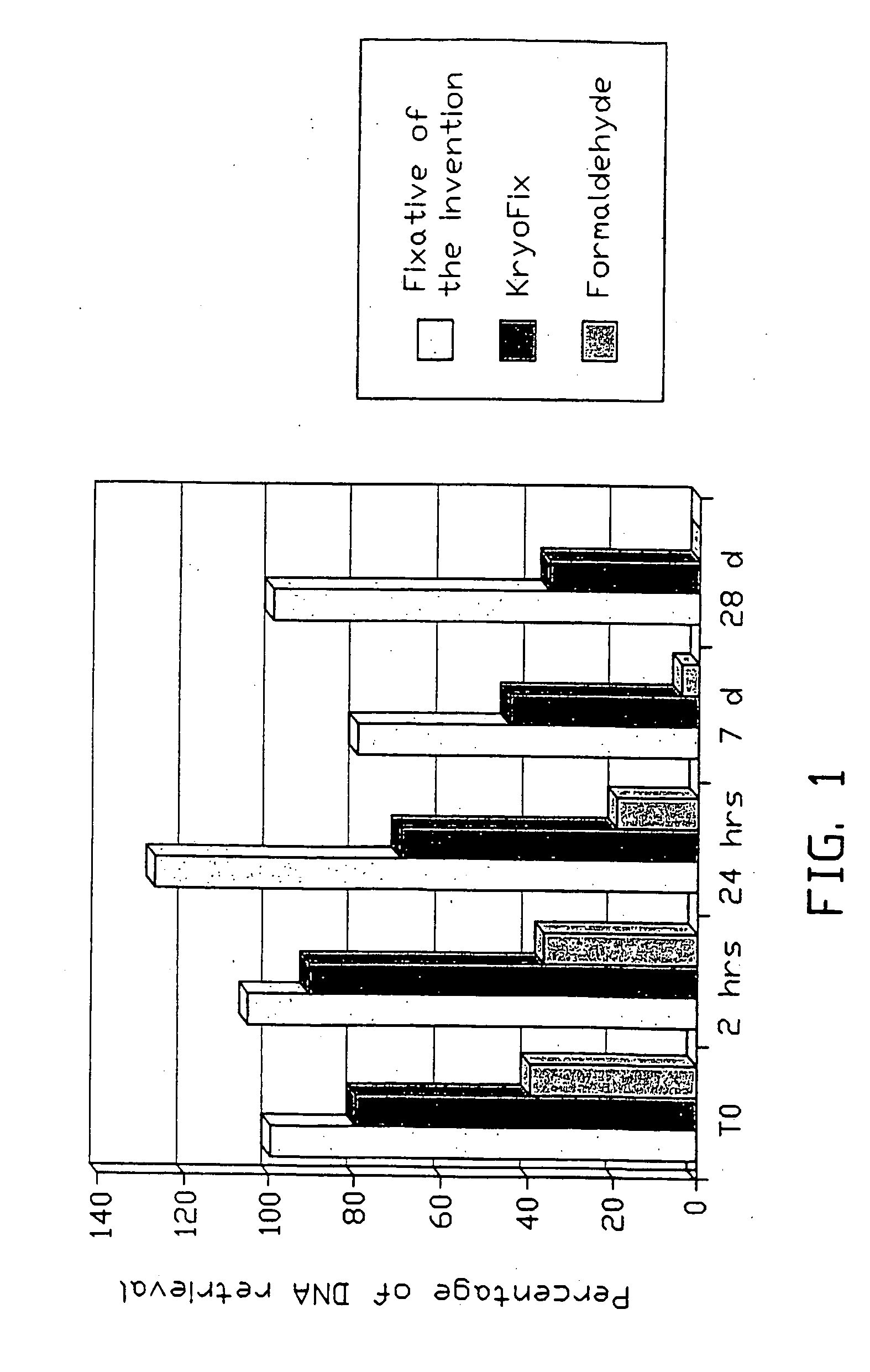
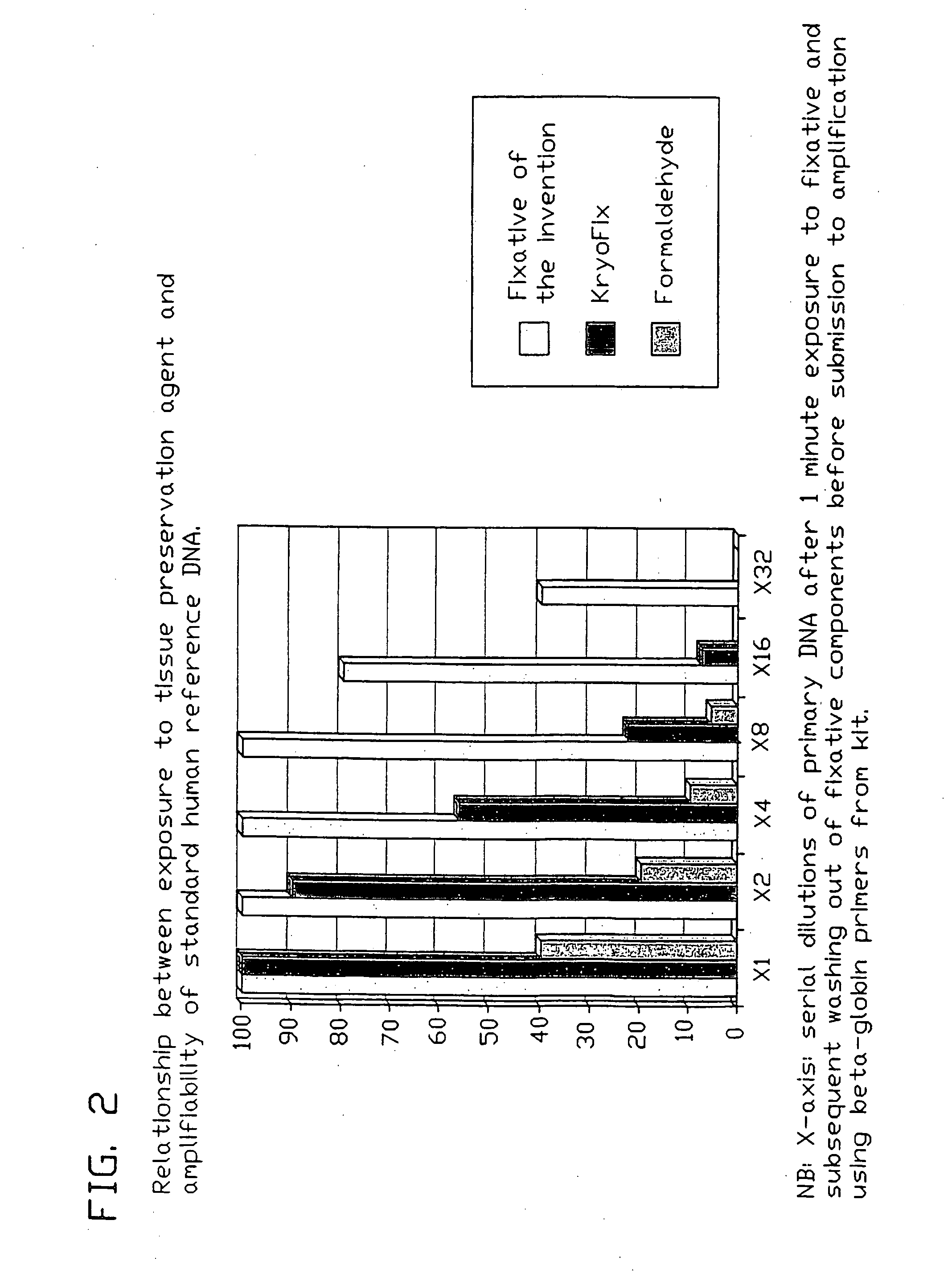
Fixative composition
InactiveUS20090017437A1Reduce compoundingImprove stabilityPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationCross-linkOrganic acid
The invention relates to a fixative composition for preservation of tissue and biological samples. Current fixative compositions have the drawback that they do not sufficiently protect against DNA / RNA degeneration. In addition their use impairs extractability and compromises amplifiability of extracted DNA. The invention solves the combined but related problems and provides a fixative composition comprising one or more alkanols, polyethylene glycol having a molecular weight of 200-600, one or more weak organic acids in a combined concentration of 0.01 to 0.10 mole per liter of the fixative composition, and water. The fixative composition is essentially free of any cross-linking agents such as formaldehyde.
Owner:MATHILDE E BOON +1
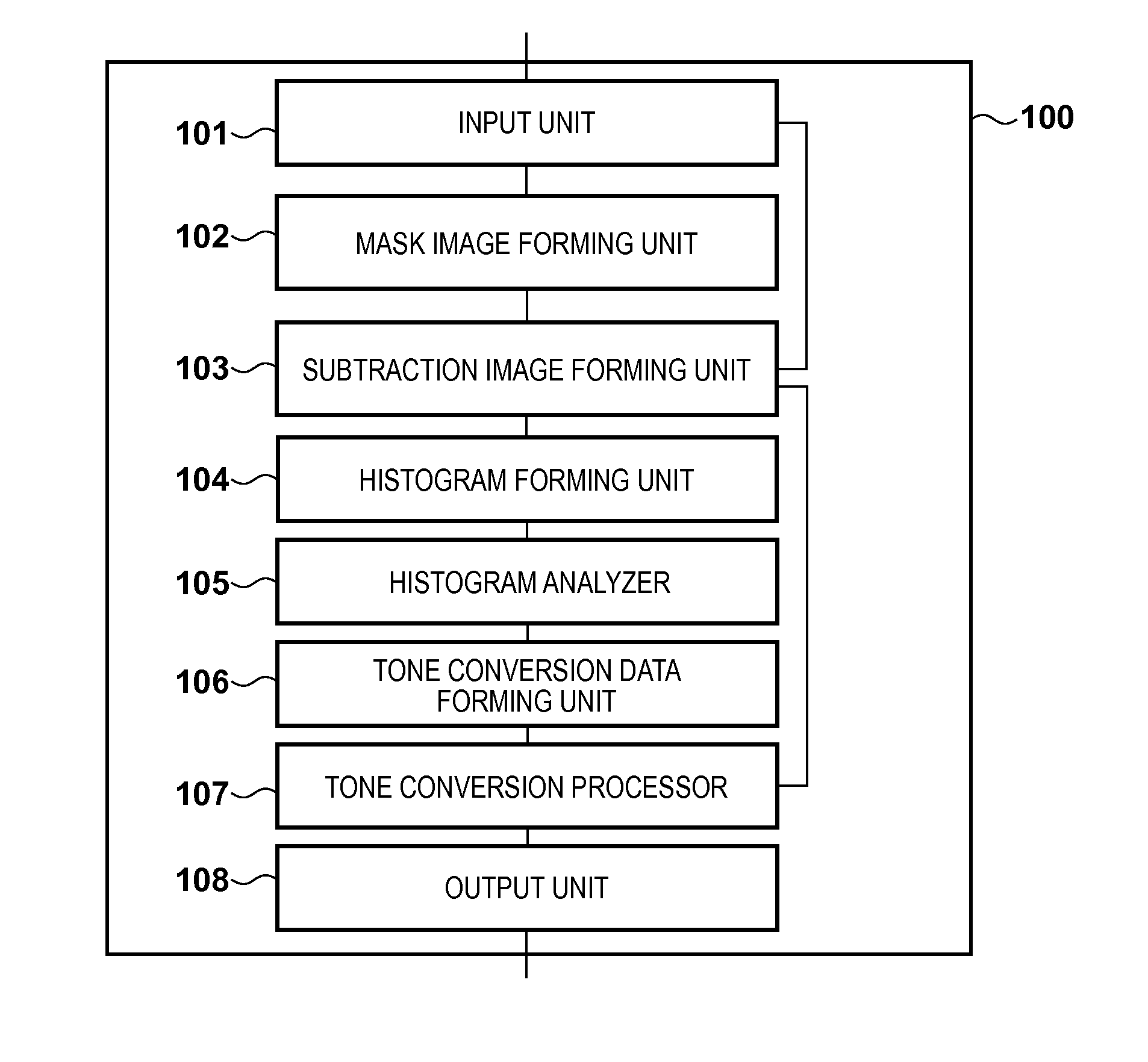
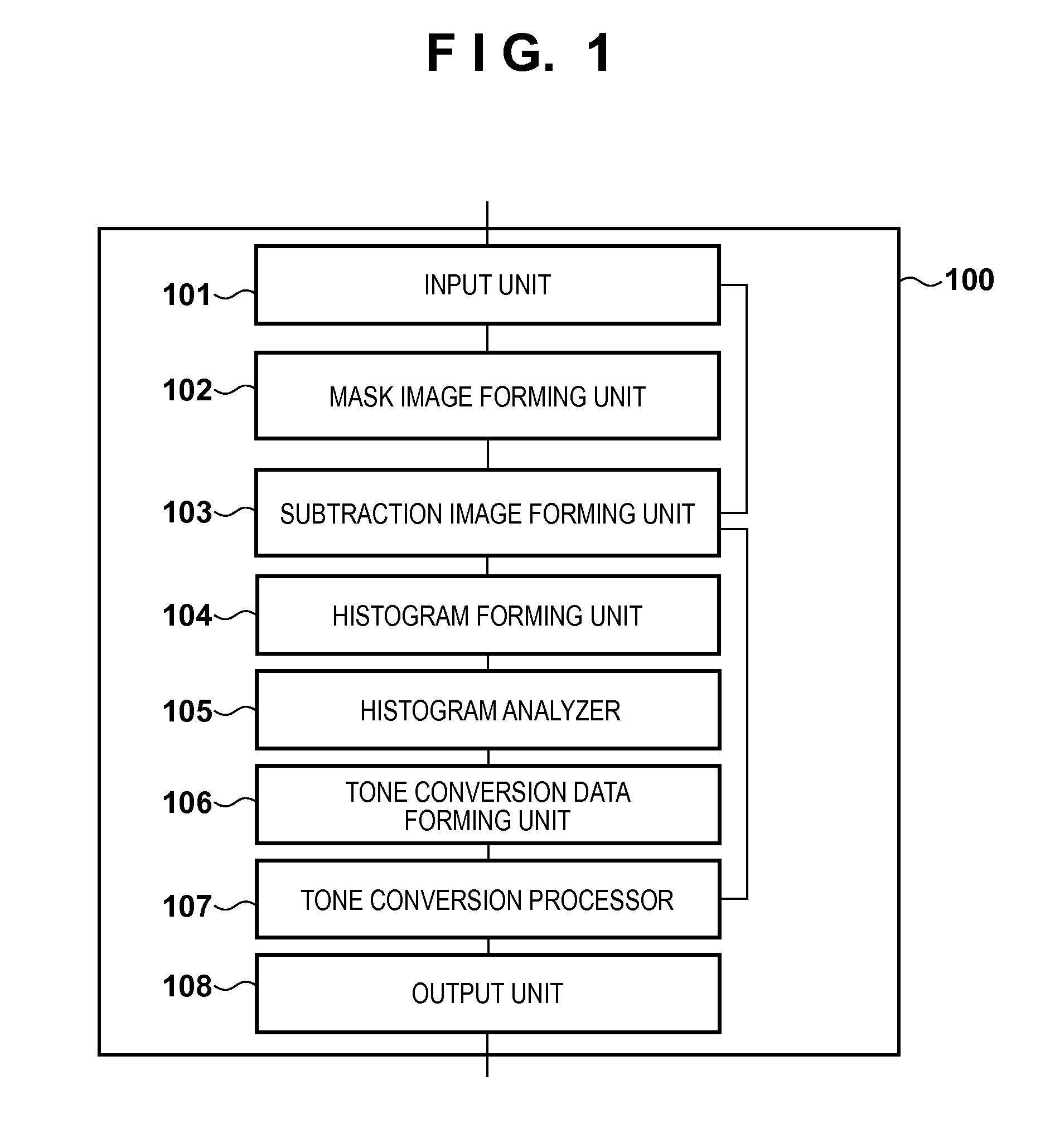
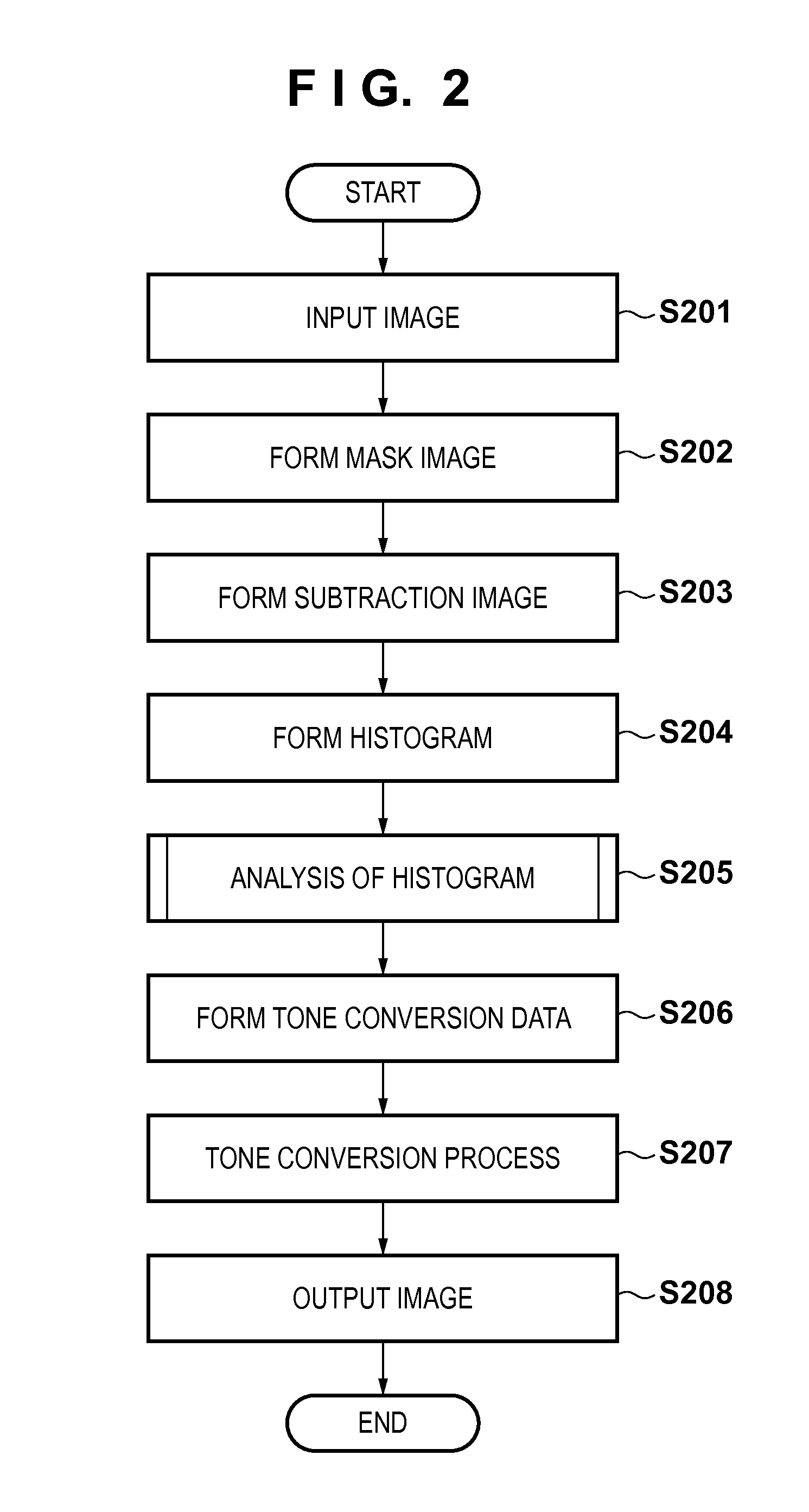
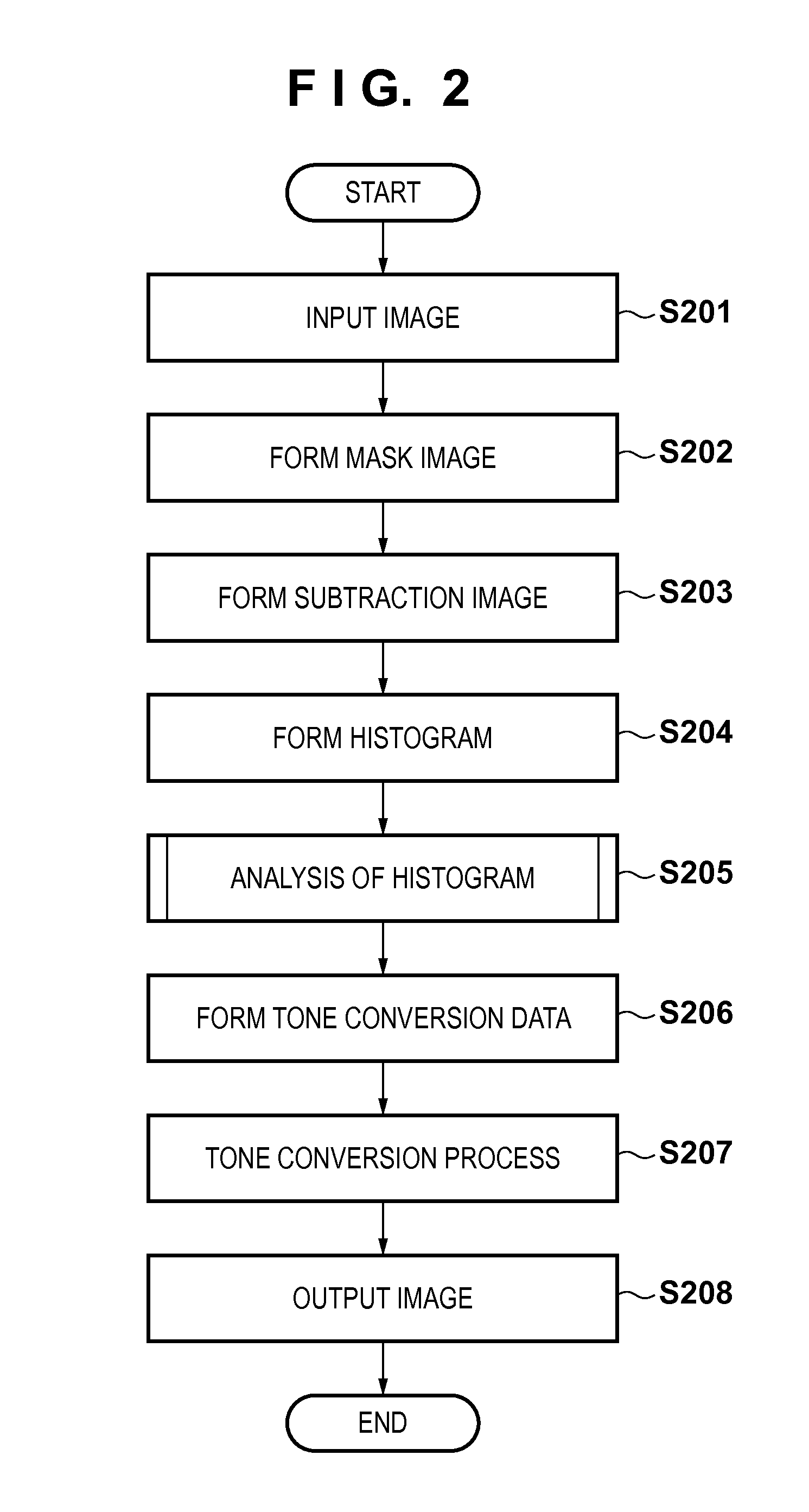
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
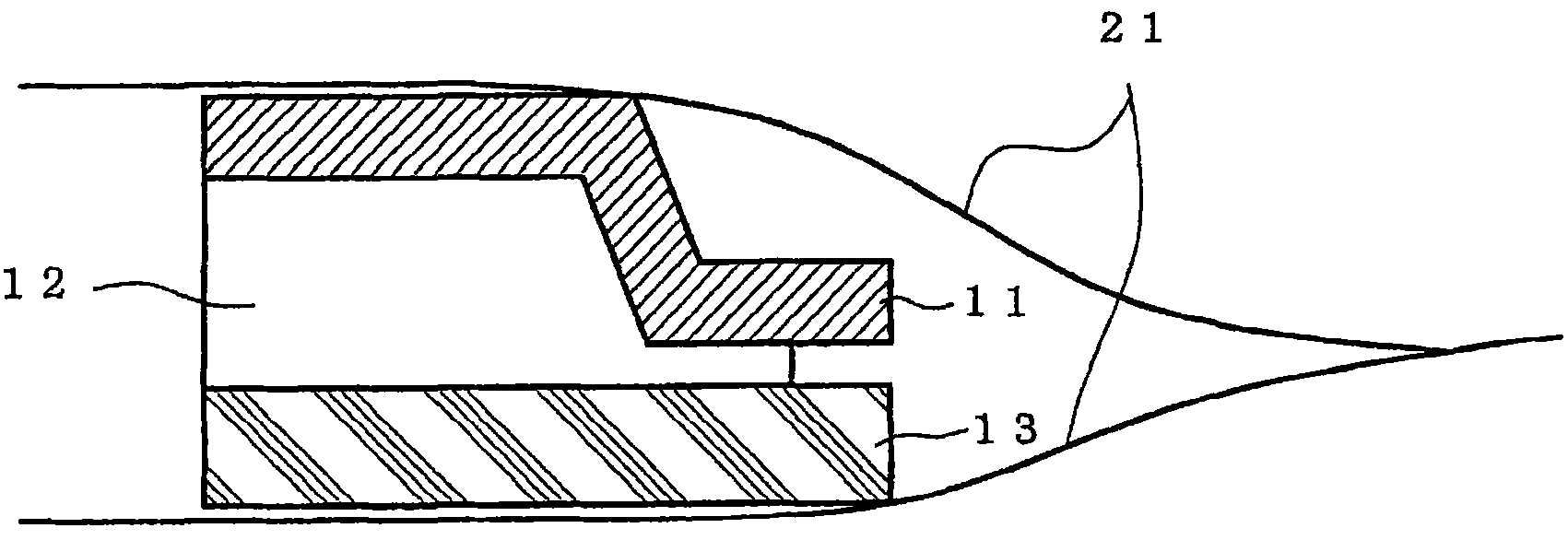
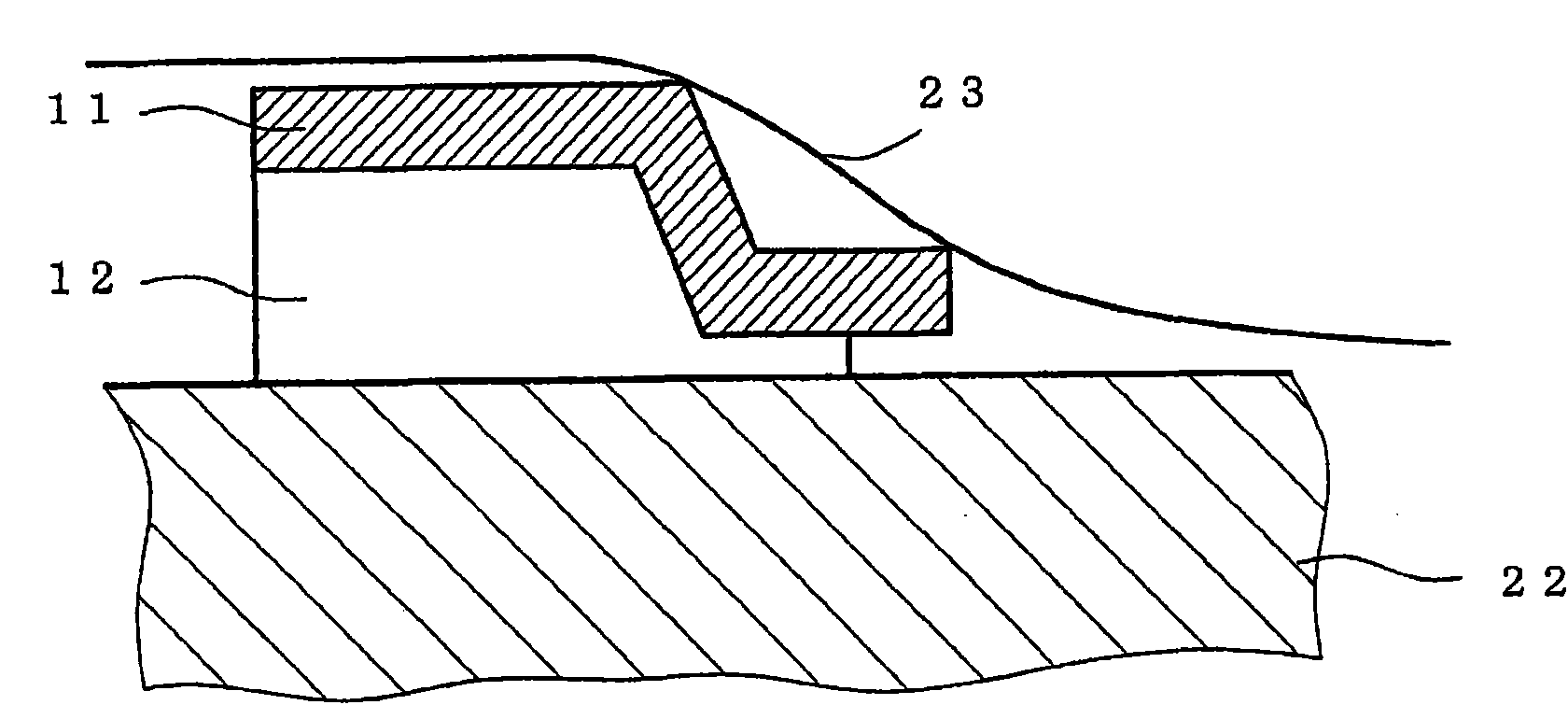
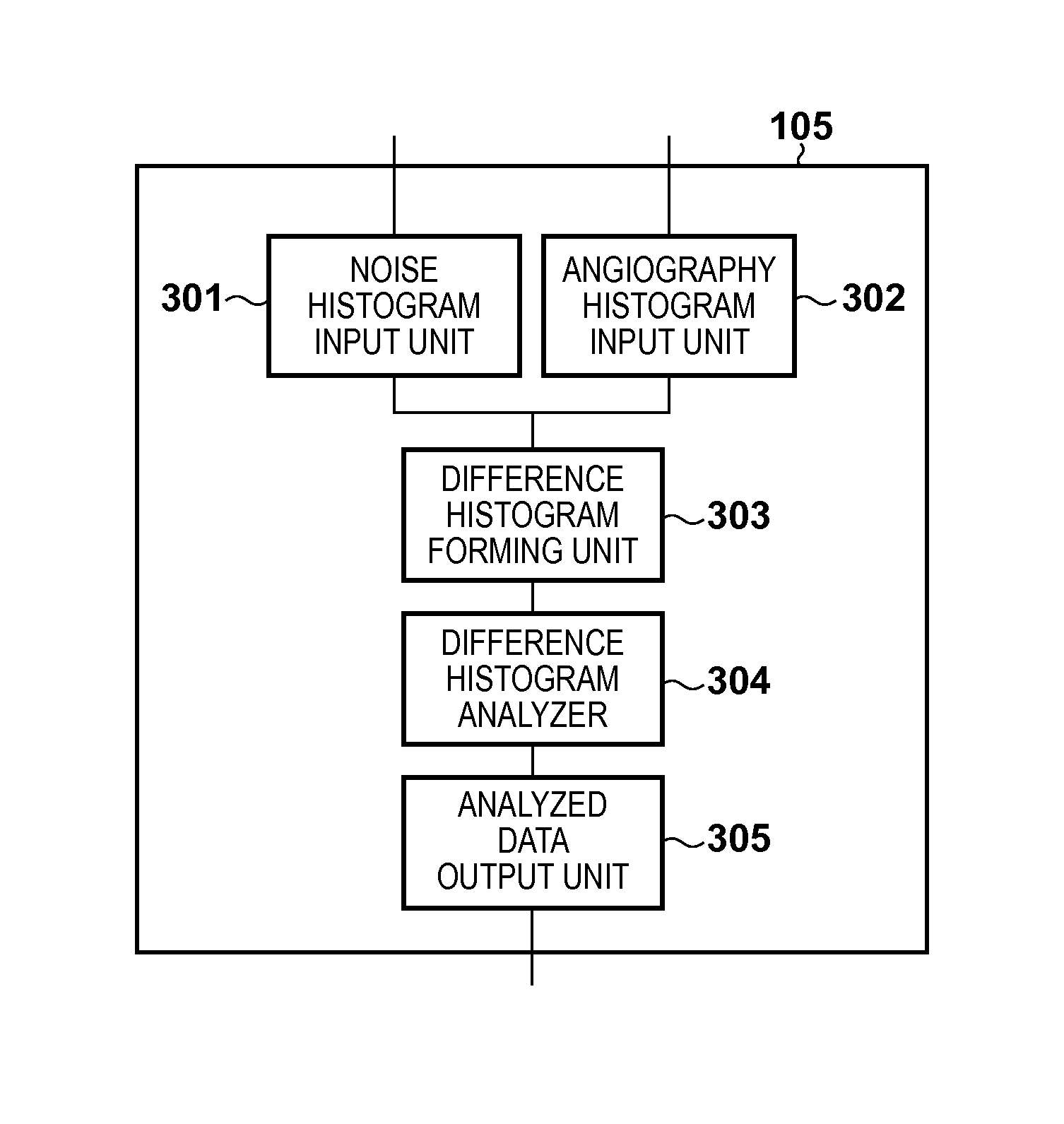
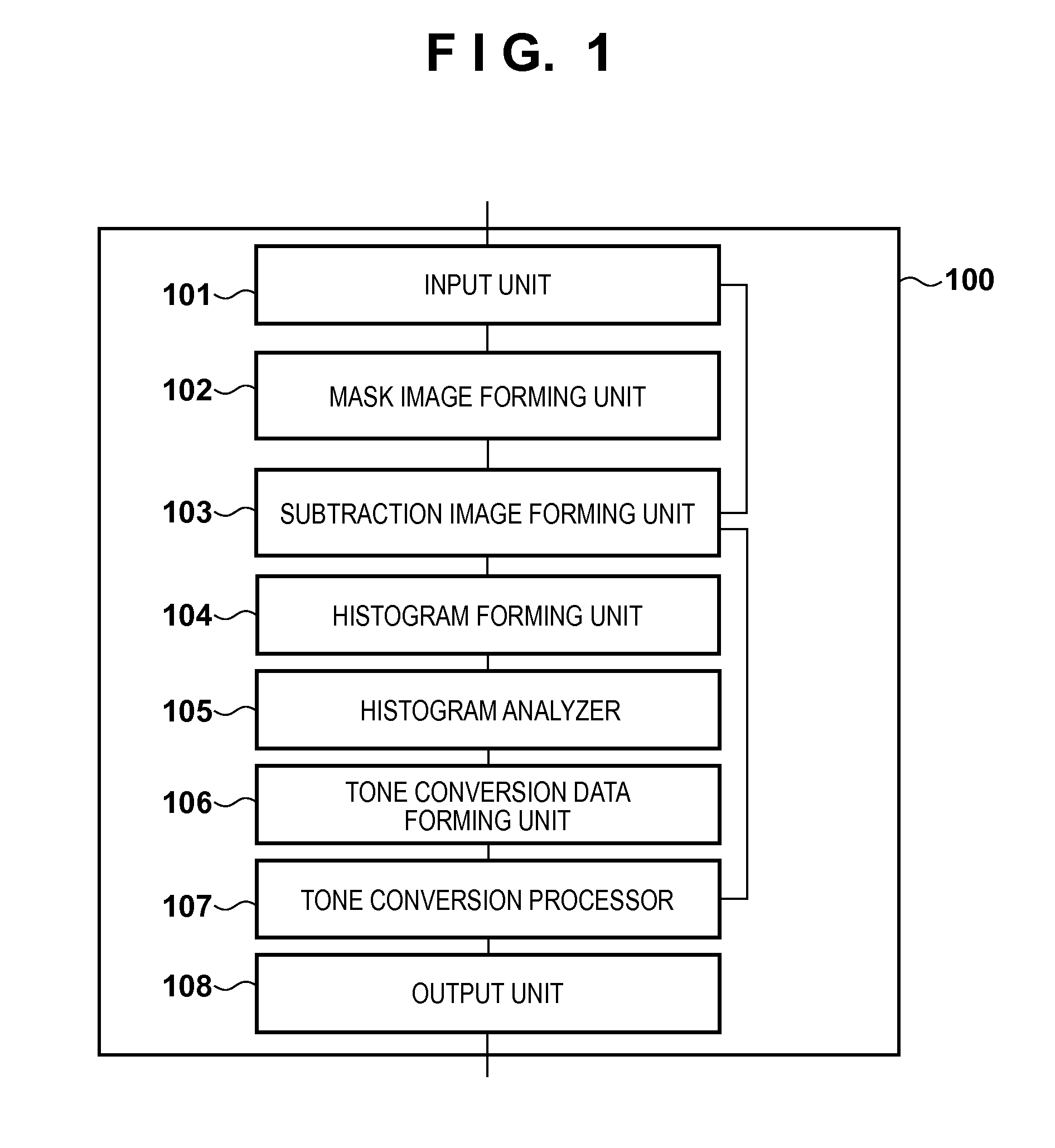
ActiveUS20130261443A1Reduce noiseIncrease extractabilityAngiographyRadiation diagnosticsPost injectionX ray image
A histogram of pixel values in a difference image between a post-injection X-ray image and composite image is generated. A histogram of pixel values in a difference image between a pre-injection X-ray image and the composite image is generated. From the difference between the histograms, information on pixel values in a region where a radiopaque dye is imaged in the difference image between the post-injection X-ray image and composite image is collected. Pixel values in the difference image between the post-injection X-ray image and composite image are converted by using the collected information, and the converted difference image is output.
Owner:CANON KK
Application and method for extracting and recovering copper by amino-contained neutral phosphine extracting agent
ActiveCN107674974AExcellent extractabilityLow water solubilityProcess efficiency improvementSolubilityWater soluble
The invention relates to application and a method for extracting and recovering copper by a amino-contained neutral phosphine extracting agent expressed by the formula I. The method comprises a step of extracting and recovering copper by using the amino-contained neutral phosphine extracting agent expressed by the formula I. The amino-contained neutral phosphine extracting agent is excellent in copper extracting capacity, low in water solubility, simple in synthesis, low in cost, low in loss in recycling, capable of effectively reducing the copper recovery cost and higher in industrial application value. FORMULA.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveCN105810841ASolve total reflection light lossNo special material requiredSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMirror reflectionOptoelectronics
The invention discloses an organic electroluminescent device, comprising a substrate and an organic electroluminescent unit arranged on the substrate, wherein the organic electroluminescent unit comprises a first electrode layer, an organic functional layer and a second electrode layer stacked in sequence, and the first electrode layer is arranged close to the substrate; the organic electroluminescent device further comprises a second light extraction layer arranged between the substrate and the second electrode layer, a plurality of different interface regions for changing the flatness of a second electrode reflecting interface are formed in the second light extraction layer, and the different interface regions occupy 0.1-30% of the area of the second light extraction layer. The device has high definition while keeping mirror reflection.
Owner:GUAN YEOLIGHT TECH CO LTD
Method of producing fermentation-based products from corn
InactiveUS20060246558A1Reduce the number of stepsReduce the amount requiredProtein composition from vegetable seedsClimate change adaptationCorn mealFermentation
Corn oil and corn meal obtained from corn are included in useful products. A method for producing fermentation-based products comprises combining corn meal with water and an enzyme, and mixing the combination with a micro-organism capable of fermenting a carbon source to produce a fermentation-based product. The corn meal is produced by cracking whole corn, conditioning the whole corn and extracting the whole corn to produce corn meal without flaking the corn during processing. The corn grain process generally includes the steps of cracking corn grain having a total oil content of from about 3% by weight to about 30% by weight and extracting a corn oil from the cracked corn grain.
Owner:RENESSEN
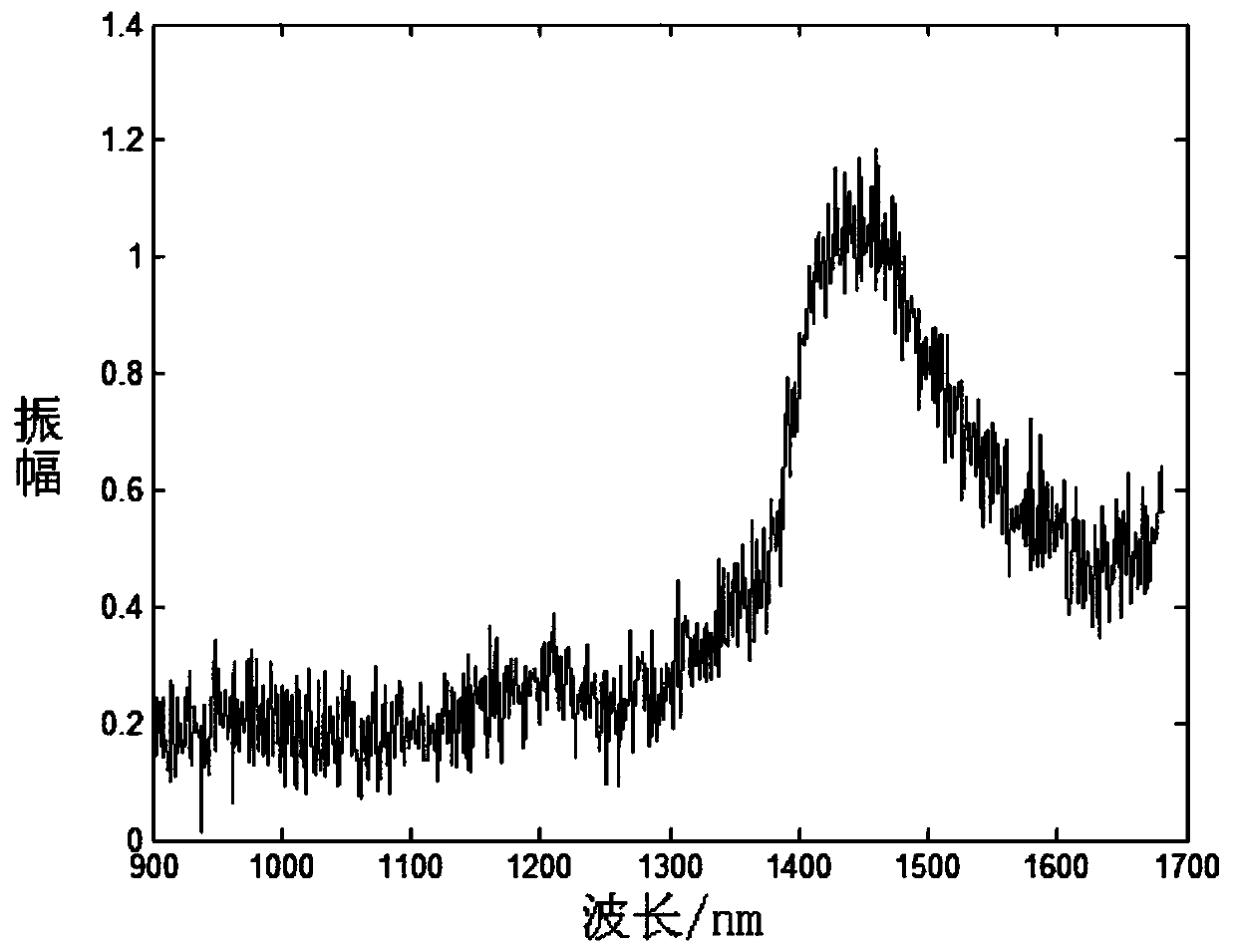
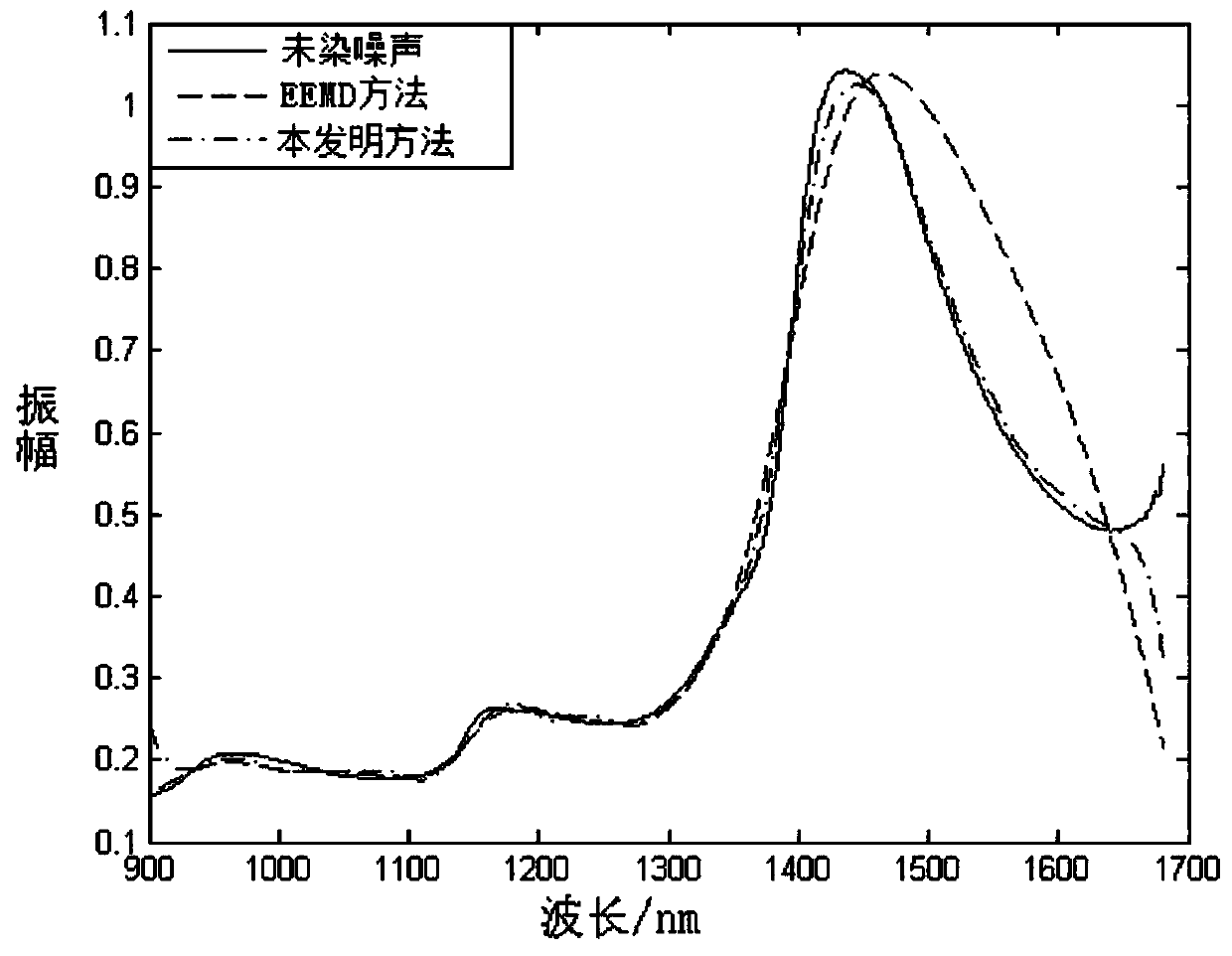
Near-infrared spectroscopy noise reduction method for pesticide residue detection
ActiveCN110208211ASolve the noiseSolve the problem of white noise introduced by EEMDMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a near-infrared spectroscopy noise reduction method for pesticide residue detection. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a near-infrared spectrum of a target is acquired; 2, an EEMD method is used to decompose signals of the near-infrared spectrum, and a plurality of IMF components are obtained; 3, a threshold is adaptively acquired based on the IMF components, andthe IMF components containing noise are selected; 4, an improved L2 regularization method is used to perform noise reduction processing on the selected noise-containing IMF components; and 5, the components after noise reduction and effective information components are reconstructed to acquire noise reduction signals. The problems that the near-infrared spectrum itself contains noise and white noise is introduced by the EEMD are solved, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the near-infrared spectrum and the recognition accuracy of the classification in the pesticide residue detection are improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
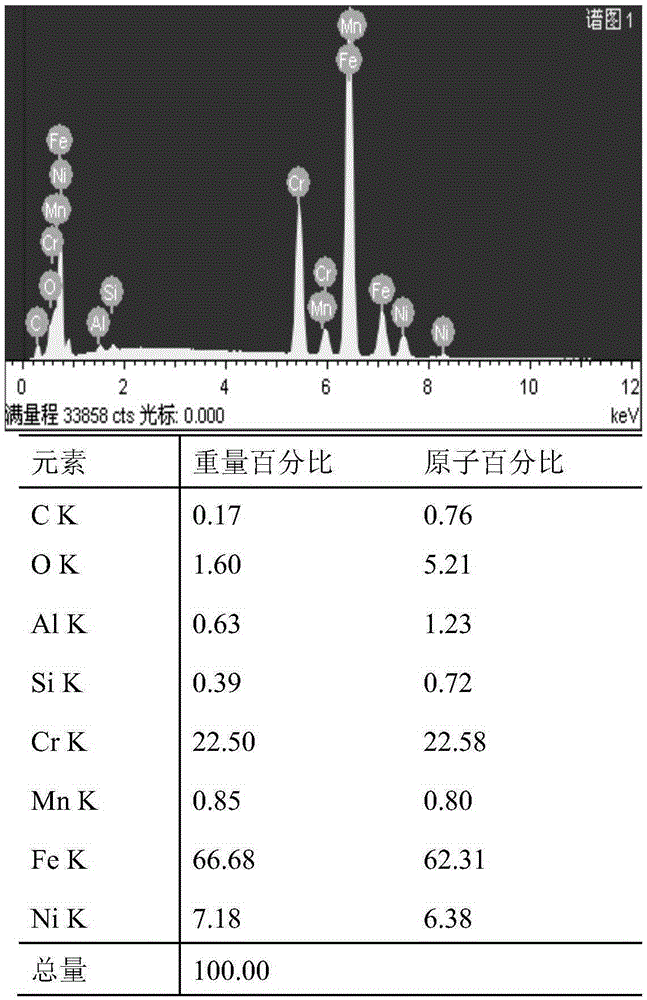
High-toughness corrosion-resistant wear-resistant ball and production process thereof
InactiveCN107739973AHigh strengthImprove plasticityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesWear resistantToughness
The invention provides a high-toughness corrosion-resistant wear-resistant ball and a production process thereof. The high-toughness corrosion-resistant wear-resistant ball comprises the following components of, by weight, .3-2.9% of C, 1.1-1.7% of Si, 1.2-1.9% of Mn, 2.5-3.8% of Ni, 4.5-8% of Cr, 0.4-1.1% of Mo, 0.2-0.7% of V, 0.1-0.3% of Cu, 0.05-0.2% of Y, 0.02-0.04% of P, 0.01-0.02% of S and the baclance Fe and inevitable impurities. The production process thereof mainly comprises the three following steps of smelting raw materials, spheroidizing and inoculation treatment and heat treatment. According to the high-toughness corrosion-resistant wear-resistant ball and the production process thereof, the components of the elements are reasonably configured, the optimized production process is coordinated, so that the prepared wear-resistant ball is high in strength, high in hardness, excellent in toughness and good in corrosion resistance.
Owner:NINGGUO ZHENGXING WEAR RESISTANT MATERIALS
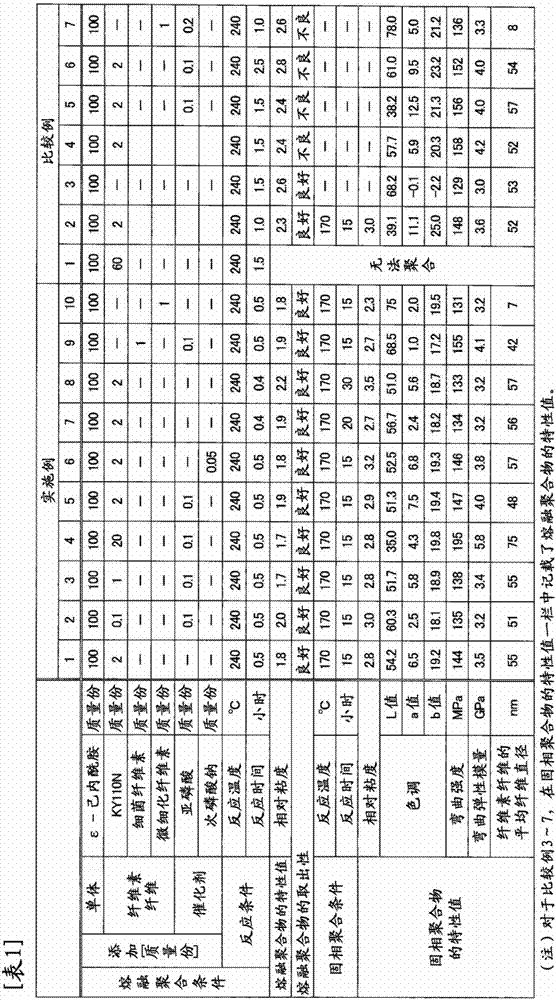
Polyamide resin composition
The invention provides a polyamide resin composition. This polyamide resin composition contains 0.01-50 parts by mass of cellulose fibers for every 100 parts by mass of a polyamide resin, has a relative viscosity of 2.3 or greater, and, in a Lab color space, has an 'L' value of 20 or greater, an 'a' value of 10 or less and a 'b' value of 20 or less. This polyamide resin composition is obtained by solid-phase polymerization of a polyamide resin composition that has a relative viscosity of 2.2 or less.
Owner:UNITIKA LTD
Inbred corn line SLD04
ActiveUS9992947B1High yieldBetter stalkPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred corn line, designated SLD04, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line SLD04, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line SLD04 with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line SLD04 with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLD04, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLD04 and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Inbred corn line SLM16
ActiveUS9258958B1High yieldBetter stalkHorticulture methodsAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred corn line, designated SLM16, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line SLM16, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line SLM16 with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line SLM16 with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLM16, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLM16 and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Water resistant patch preparation
ActiveCN102008458AExcellent extractabilityInhibit elutionPlastersAdhesive dressingsWater resistantBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a water resistant patch preparation having a central part and a peripheral part, which preparation is comprised of a support and an adhesive layer comprising a drug, which is formed on one surface of the support, wherein at least a part of a lateral end of the adhesive layer in the peripheral part is located inside a lateral end of the support, and the adhesive layer in the peripheral part has a thickness smaller than that of the adhesive layer in the central part.
Owner:安柏士有限公司
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
ActiveUS9265474B2Reduce noiseExcellent extractabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionAngiographyImaging processingX ray image
Owner:CANON KK
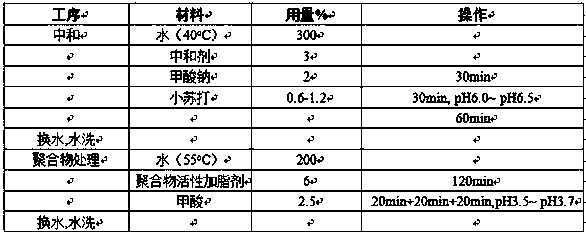
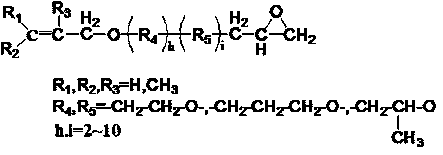
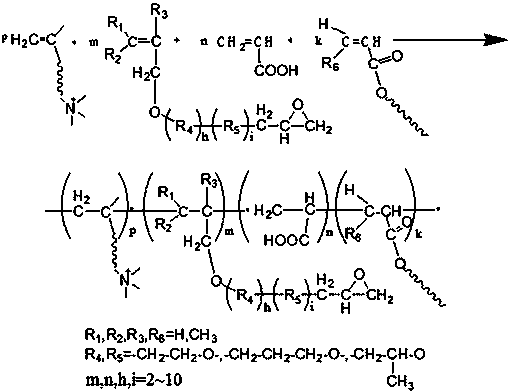
Preparation and application of polyoxyalkyl epoxy acrylate-containing polymer active fatting agent
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a reactive polymer leather fatting agent. According to the method, a vinyl monomer with a polyoxyalkyl epoxy group structure, acrylic acid long-chain ester, acrylic acid and a cationic vinyl monomer are adopted and subjected to emulsion copolymerization to obtain the multi-element amphiphilic copolymer fatting agent. Epoxy groups in the molecular structure of the fatting agent have high reaction activity and can be covalently combined with skin collagen fibers; the polyoxyalkyl structure endows the copolymer with hydrophilicity and is beneficial toimproving the stability of an emulsion system; the long-chain alkyl structure plays a role in lubricating the leather fibers; and the cationic monomer can improve the bonding and fixing performance of the cationic monomer and the leather fiber. A solvent-free emulsion polymerization method is adopted for preparing the fatting agent, the requirement of the ecological fatting agent can be met, andthe fatting agent is particularly suitable for fatting non-chrome tanned leather. Because of the saturability of the molecular structure of the polymer and a reactive group contained in the molecularstructure, the defects that a traditional natural fatting agent is prone to oxidation and yellowing, poor in migration resistance and the like can be overcome.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Inbred corn line LLM06BM
ActiveUS9615520B1High yieldBetter stalkPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred corn line, designated LLM06BM, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line LLM06BM, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line LLM06BM with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line LLM06BM with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line LLM06BM, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line LLM06BM and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Inbred corn line SLD34BM
ActiveUS10154639B1High yieldBetter stalkPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred corn line, designated SLD34BM, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line SLD34BM, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line SLD34BM with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line SLD34BM with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLD34BM, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line SLD34BM and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com