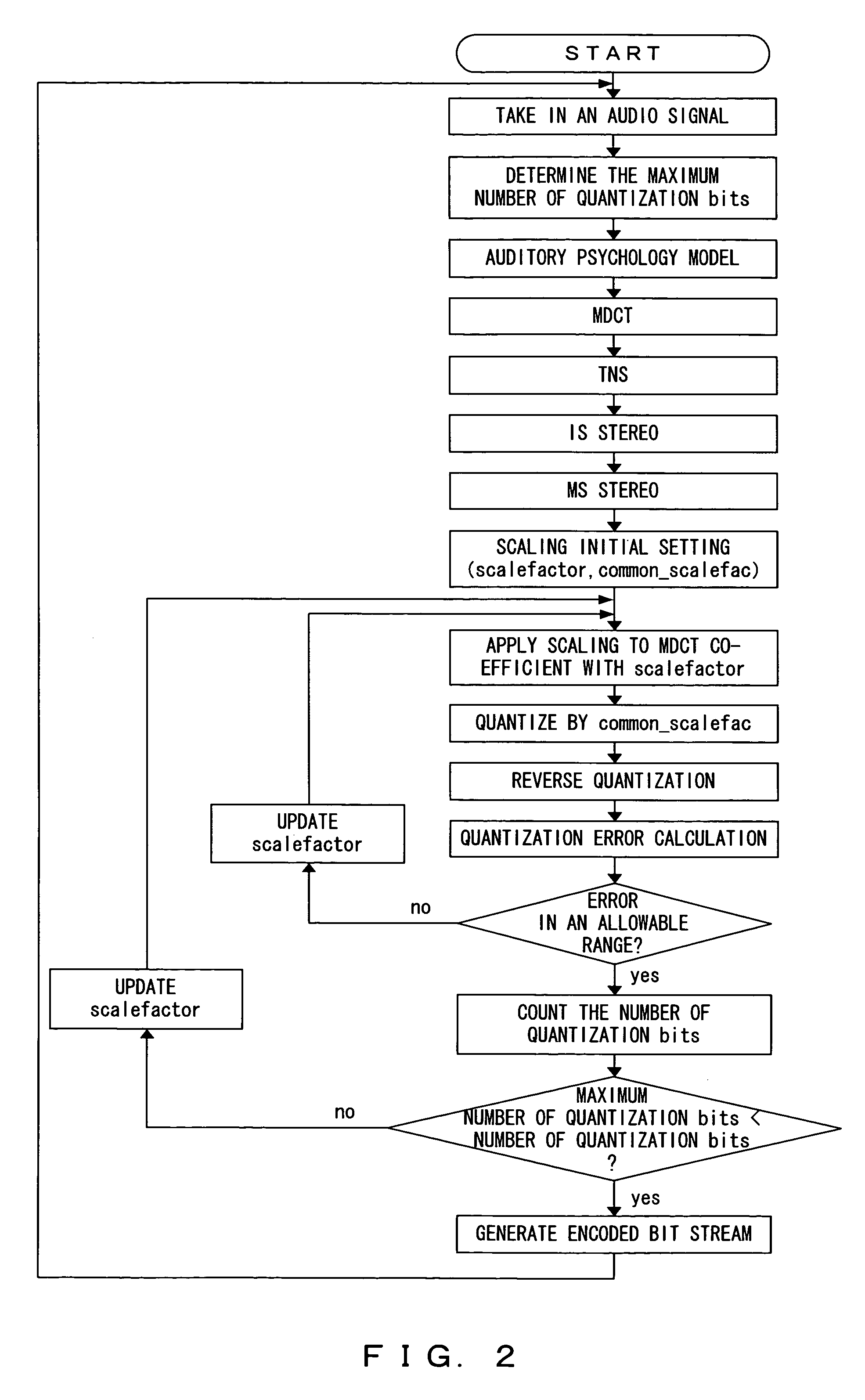
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Masking threshold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
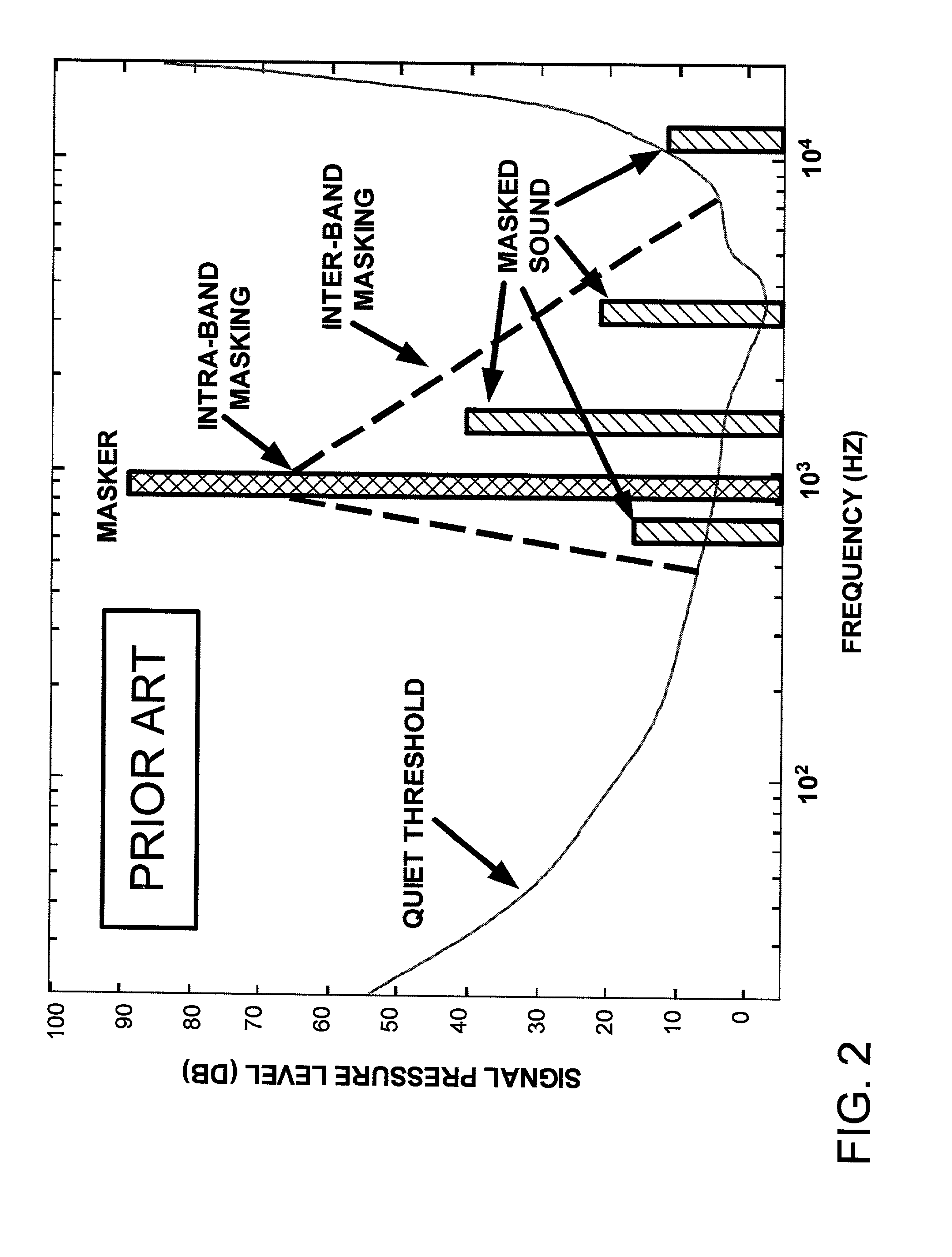
The masking threshold is the sound pressure level of a sound needed to make the sound audible in the presence of another noise called a "masker". This threshold depends upon the frequency, the type of masker, and the kind of sound being masked. The effect is strongest between two sounds close in frequency.
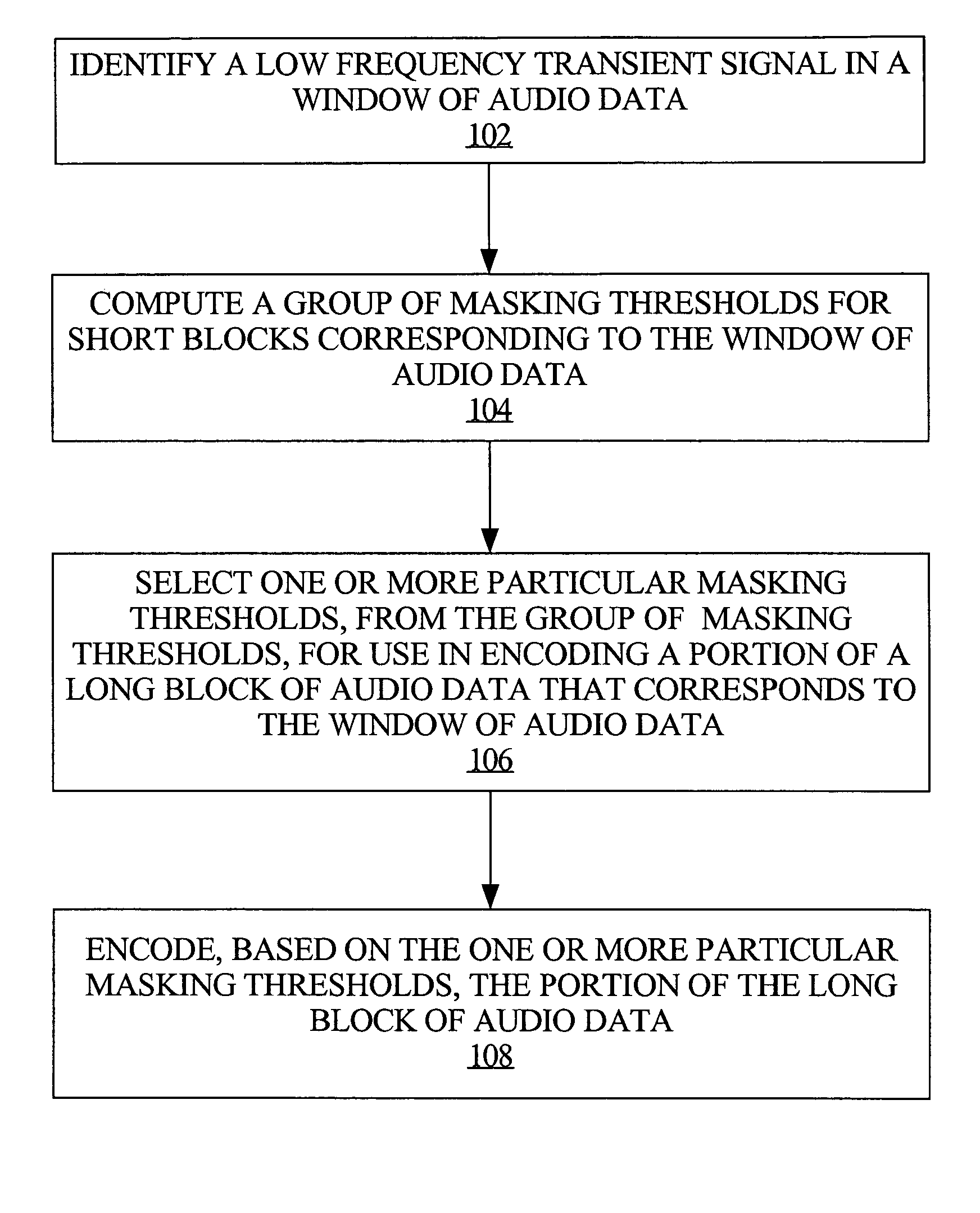
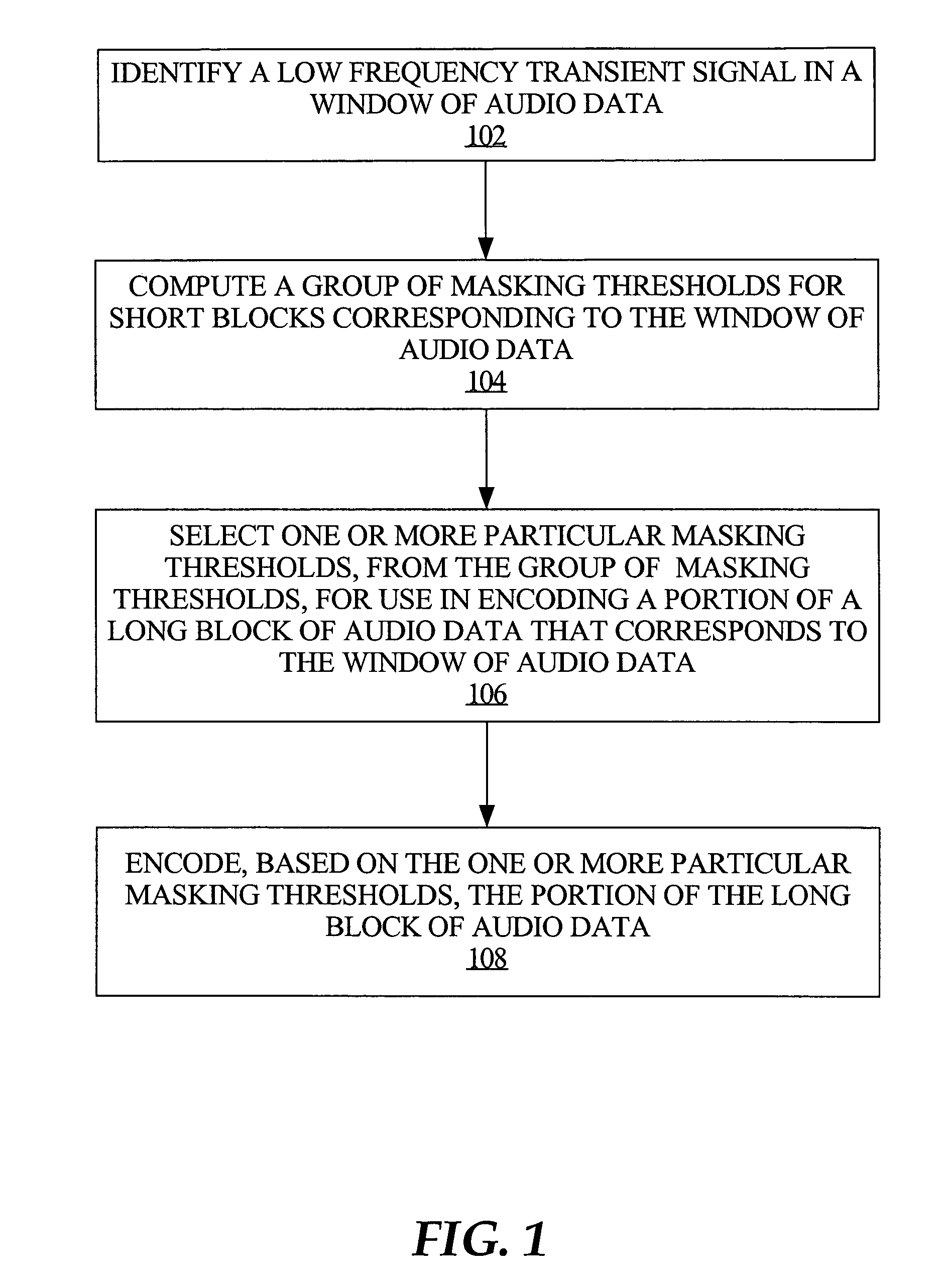
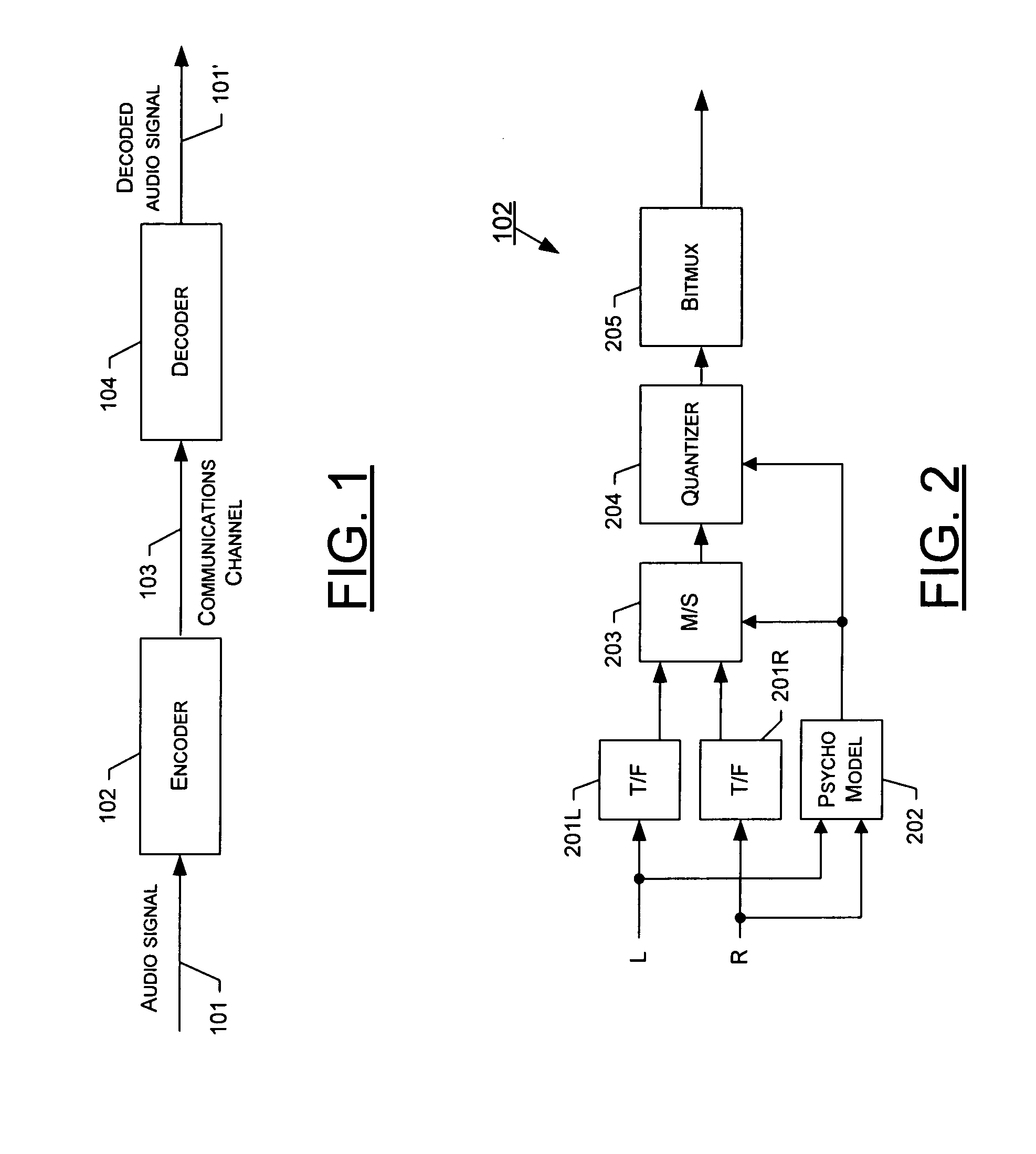
Adapting masking thresholds for encoding a low frequency transient signal in audio data
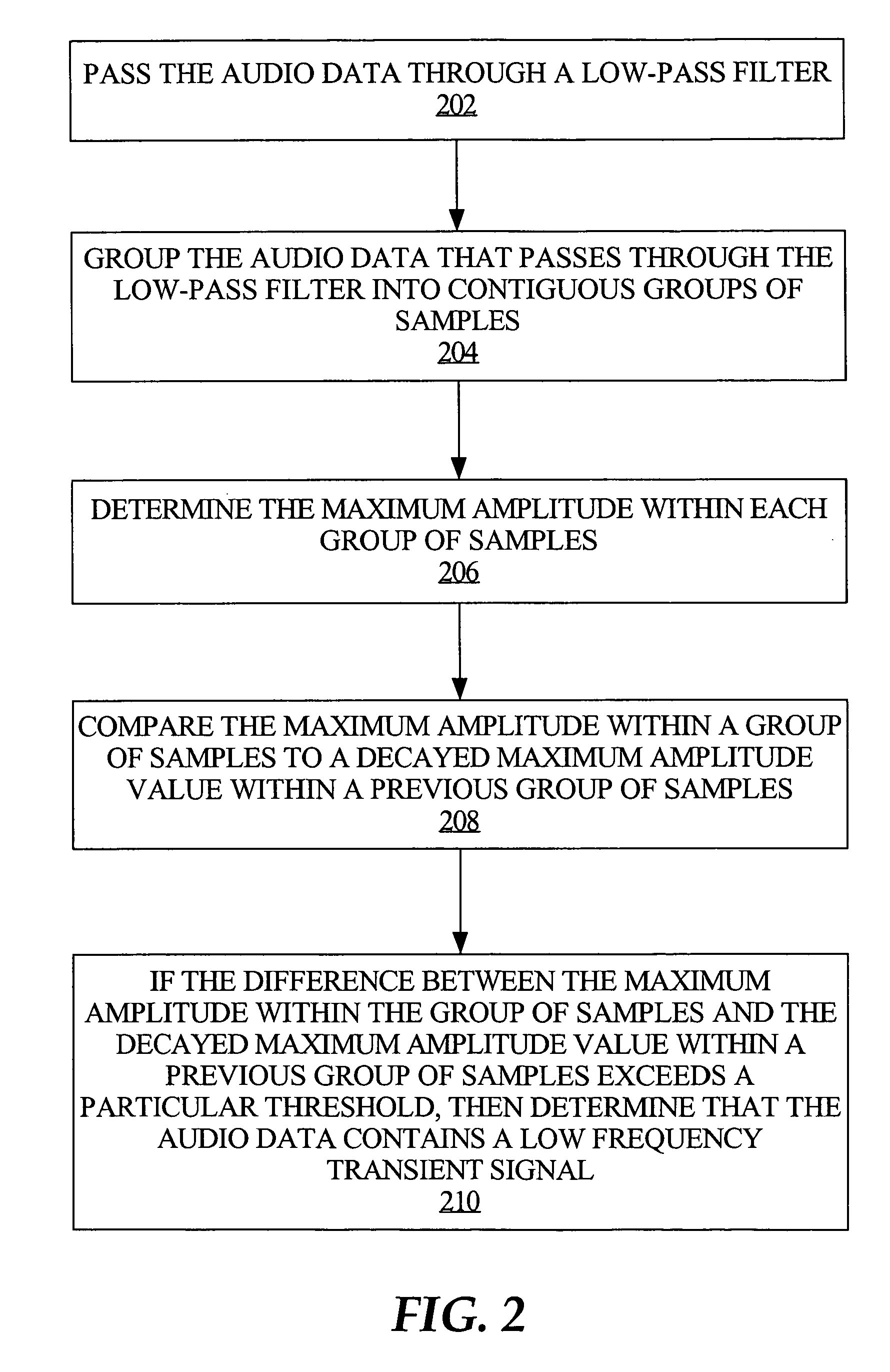
An improved audio coding technique encodes audio having a low frequency transient signal, using a long block, but with a set of adapted masking thresholds. Upon identifying an audio window that contains a low frequency transient signal, masking thresholds for the long block may be calculated as usual. A set of masking thresholds calculated for the 8 short blocks corresponding to the long block are calculated. The masking thresholds for low frequency critical bands are adapted based on the thresholds calculated for the short blocks, and the resulting adapted masking thresholds are used to encode the long block of audio data. The result is encoded audio with rich harmonic content and negligible coder noise resulting from the low frequency transient signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
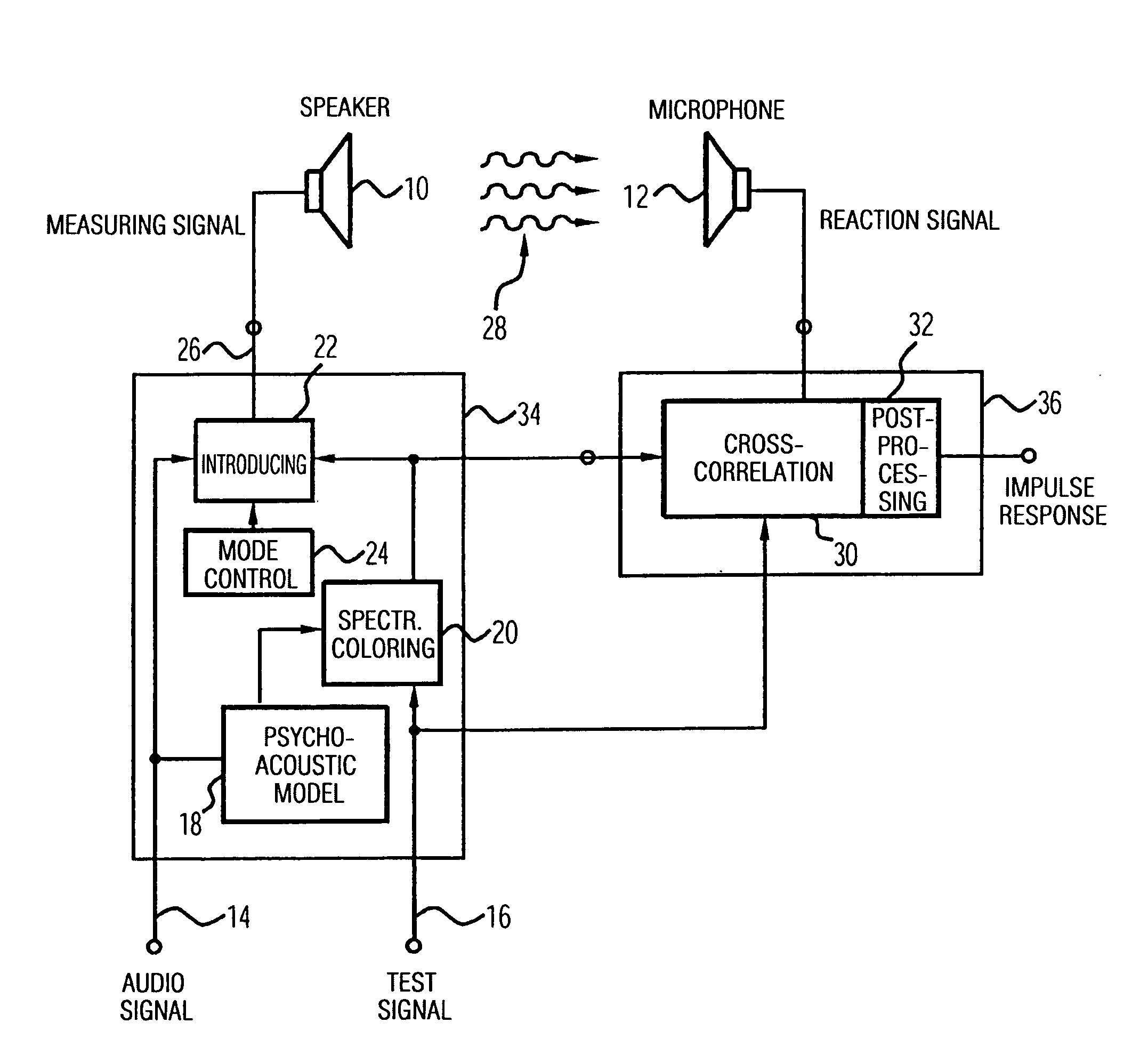
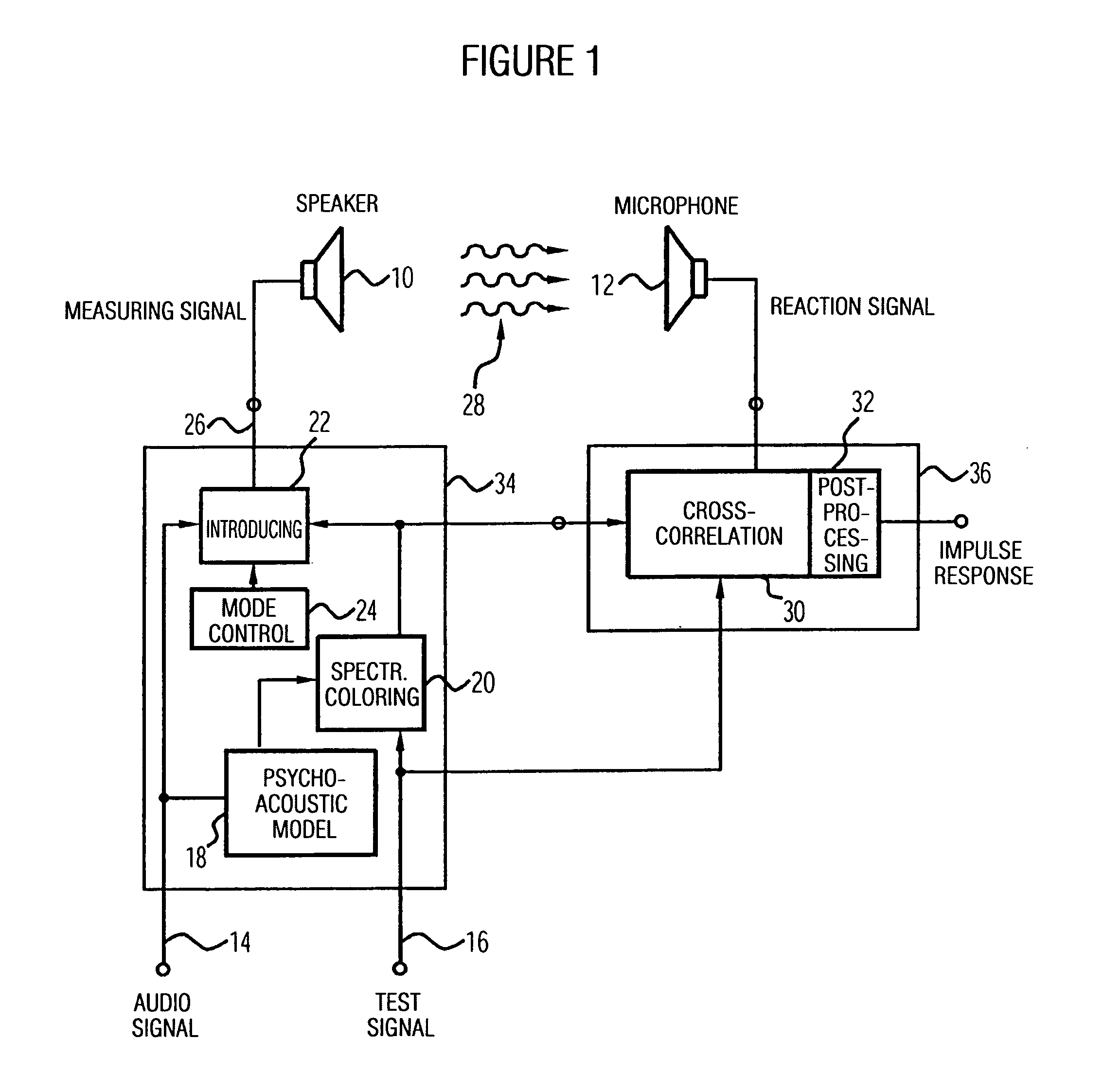
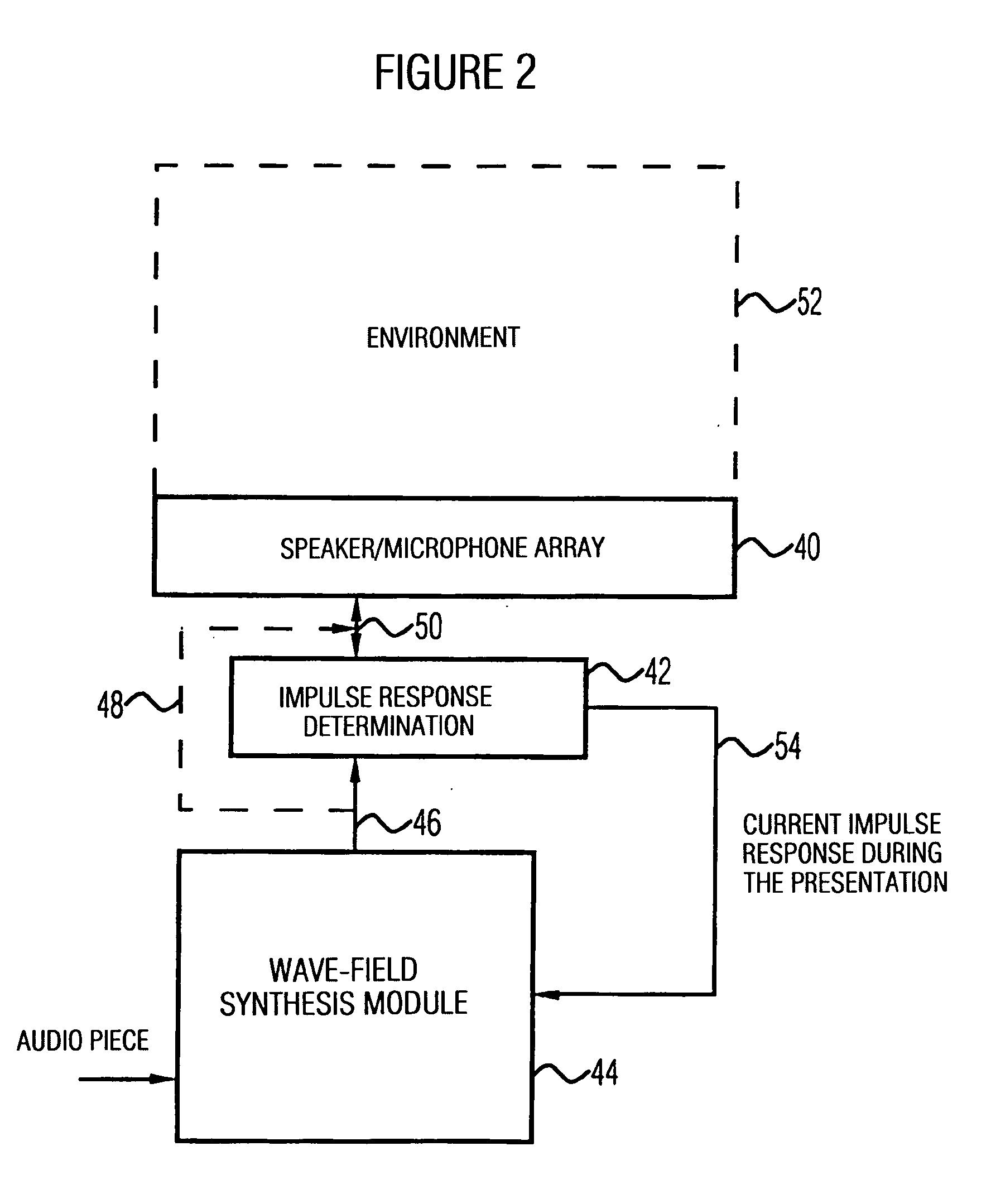
Apparatus and method of determining an impulse response and apparatus and method of presenting an audio piece
InactiveUS20050207592A1Accurate impulse responseImprove sound qualityTransmission noise suppressionStereophonic systemsFrequency spectrumWave field synthesis
The apparatus for determining an impulse response in an environment in which a speaker and a microphone are placed works using an audio signal. Means for spectrally coloring a test signal, which preferably is a pseudonoise signal, works using a psychoacoustic masking threshold of the audio signal to obtain a colored test signal, which is embedded in the audio signal to obtain a measuring signal, which can be fed to the speaker. Means for determining the impulse response preferably performs a cross-correlation of a reaction signal received via the microphone from the environment and the test signal or the colored test signal. With this, an impulse response of an environment may also be determined during the presentation of an audio piece to provide an optimal description of environment for a wave-field synthesis.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
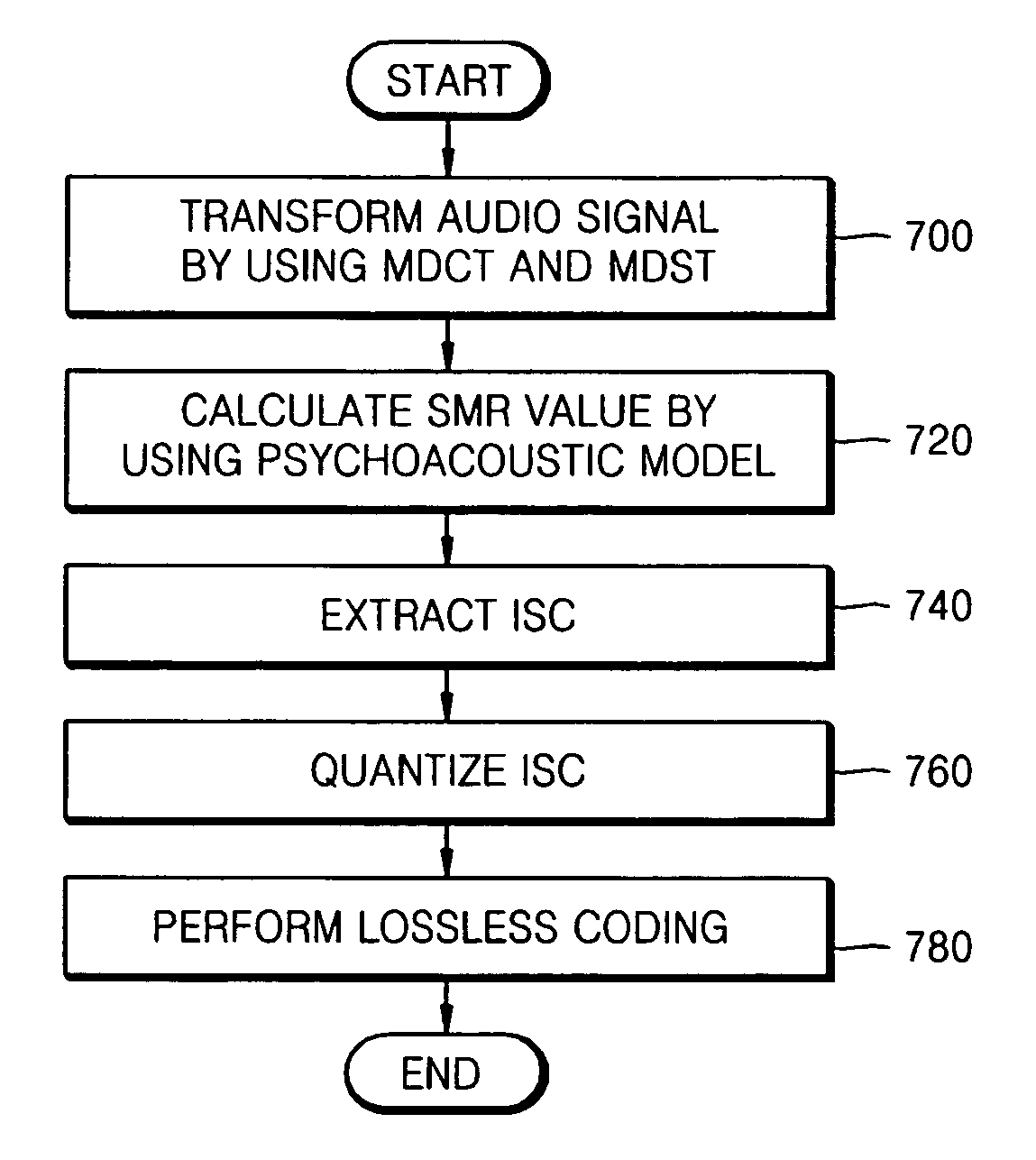
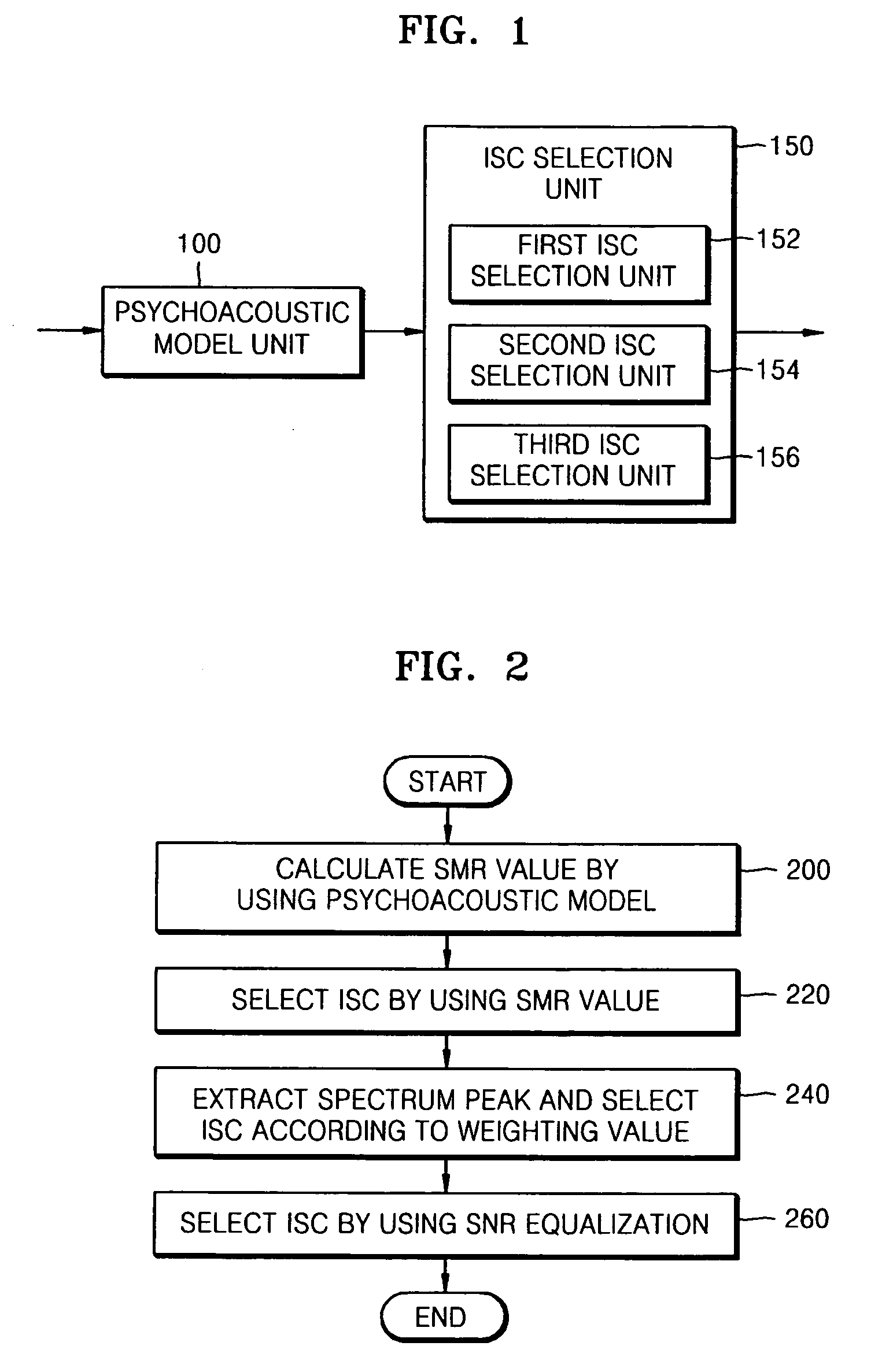
Method and apparatus to extract important spectral component from audio signal and low bit-rate audio signal coding and/or decoding method and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20070016404A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast circuit arrangementsDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
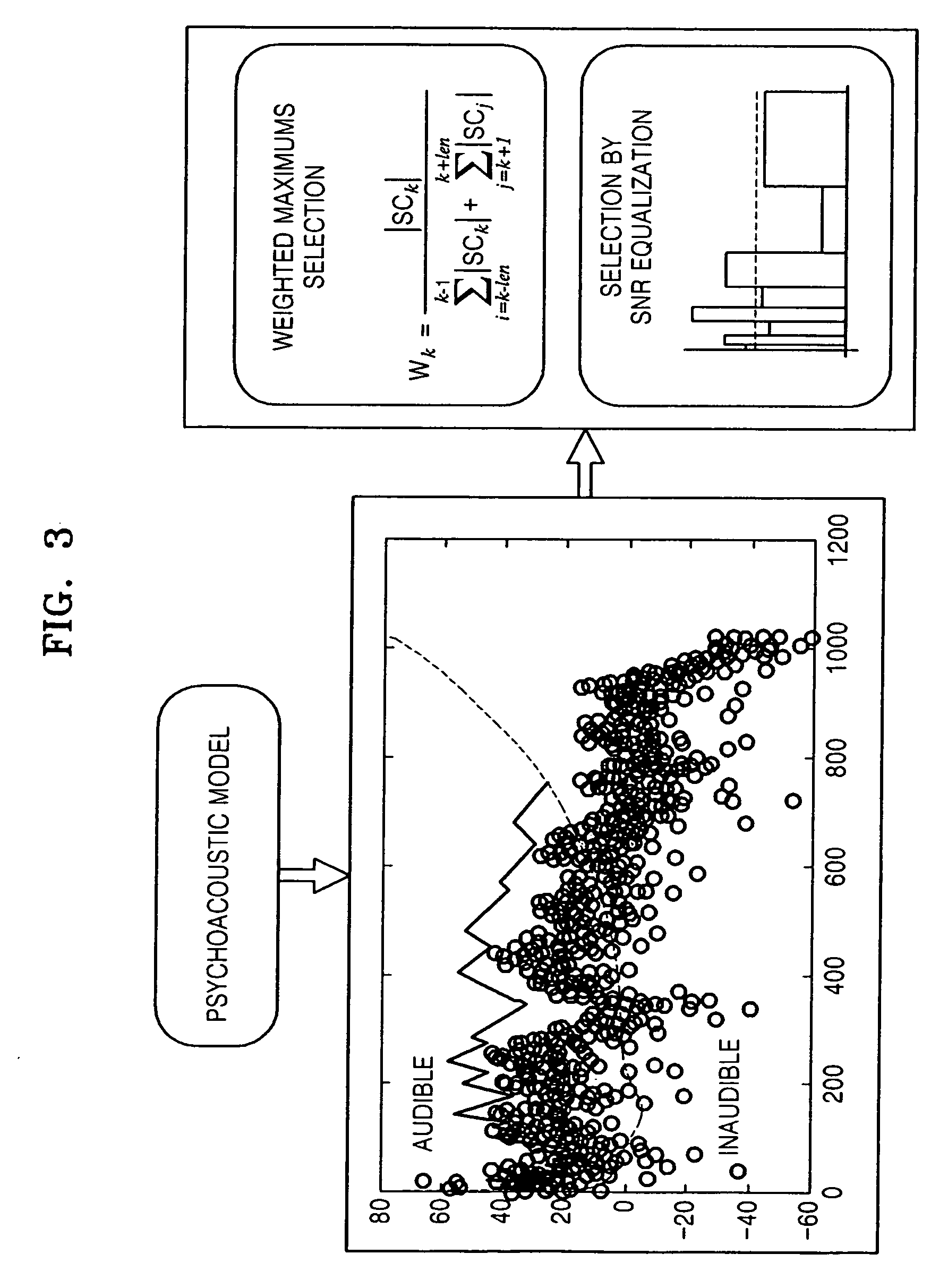
An method and apparatus to extract an audio signal having an important spectral component (ISC) and a low bit-rate audio signal coding / decoding method using the method and apparatus to extract the ISC. The method of extracting the ISC includes calculating perceptual importance including an SMR (signal-to-mark ratio) value of transformed spectral audio signals by using a psychoacoustic model, selecting spectral signals having a masking threshold value smaller than that of the spectral audio signals using the SMR value as first ISCs, and extracting a spectral peak from the audio signals selected as the ISCs according to a predetermined weighting factor to select second ISCs. Accordingly, the perceptual important spectral components can be efficiently coded so as to obtain high sound quality at a low bit-rate. In addition, it is possible to extract the perceptual important spectral component by using the psychoacoustic model, to perform coding without phase information, and to efficiently represent a spectral signal at a low bit-rate. In addition, the methods and apparatus can be employed in all the applications requiring a low bit-rate audio coding scheme and in a next generation audio scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for embedding a watermark in an audio signal
ActiveUS7346514B2Adequate watermark detectabilityEasy to detectFilamentary/web record carriersUser identity/authority verificationFrequency spectrumMasking threshold
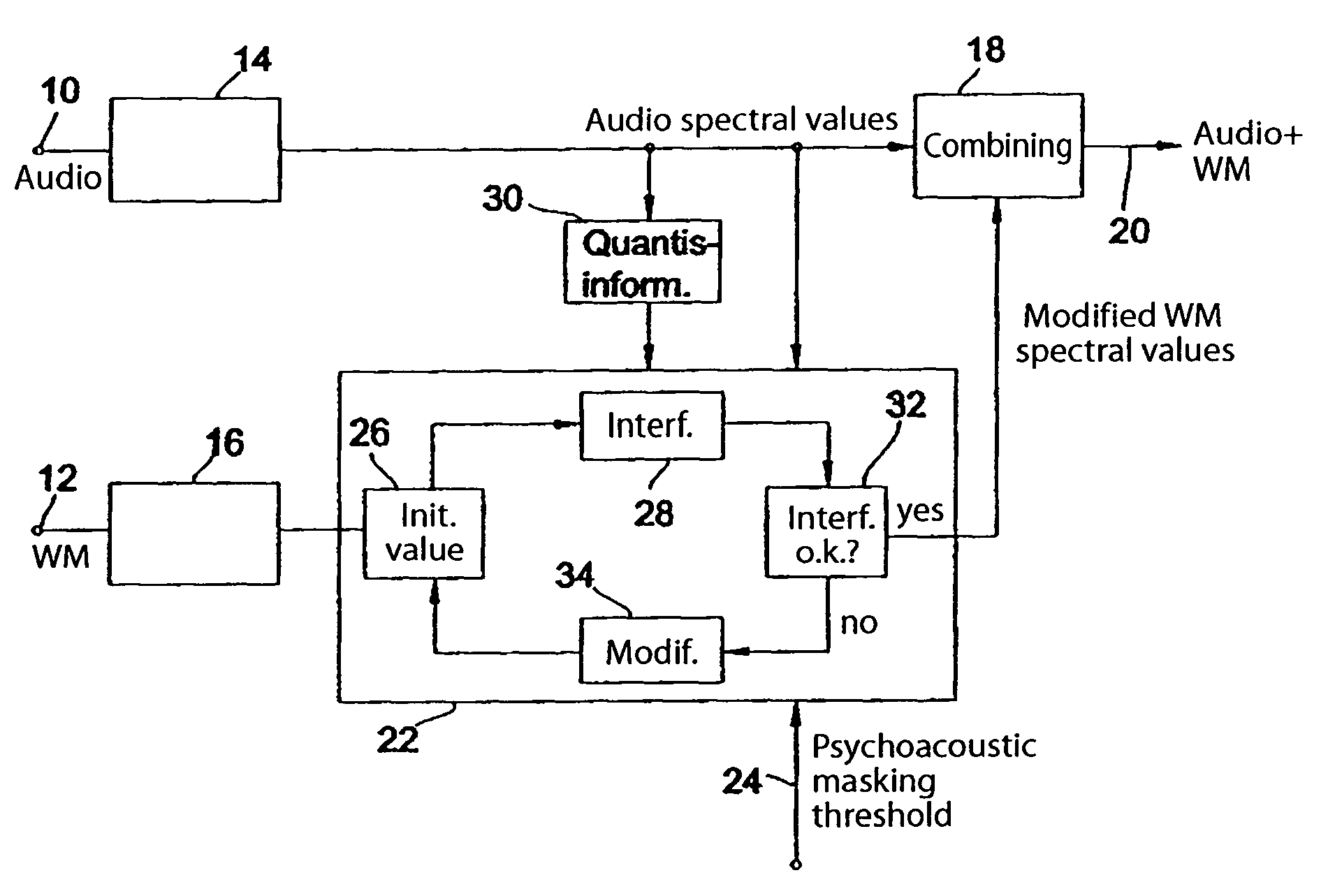
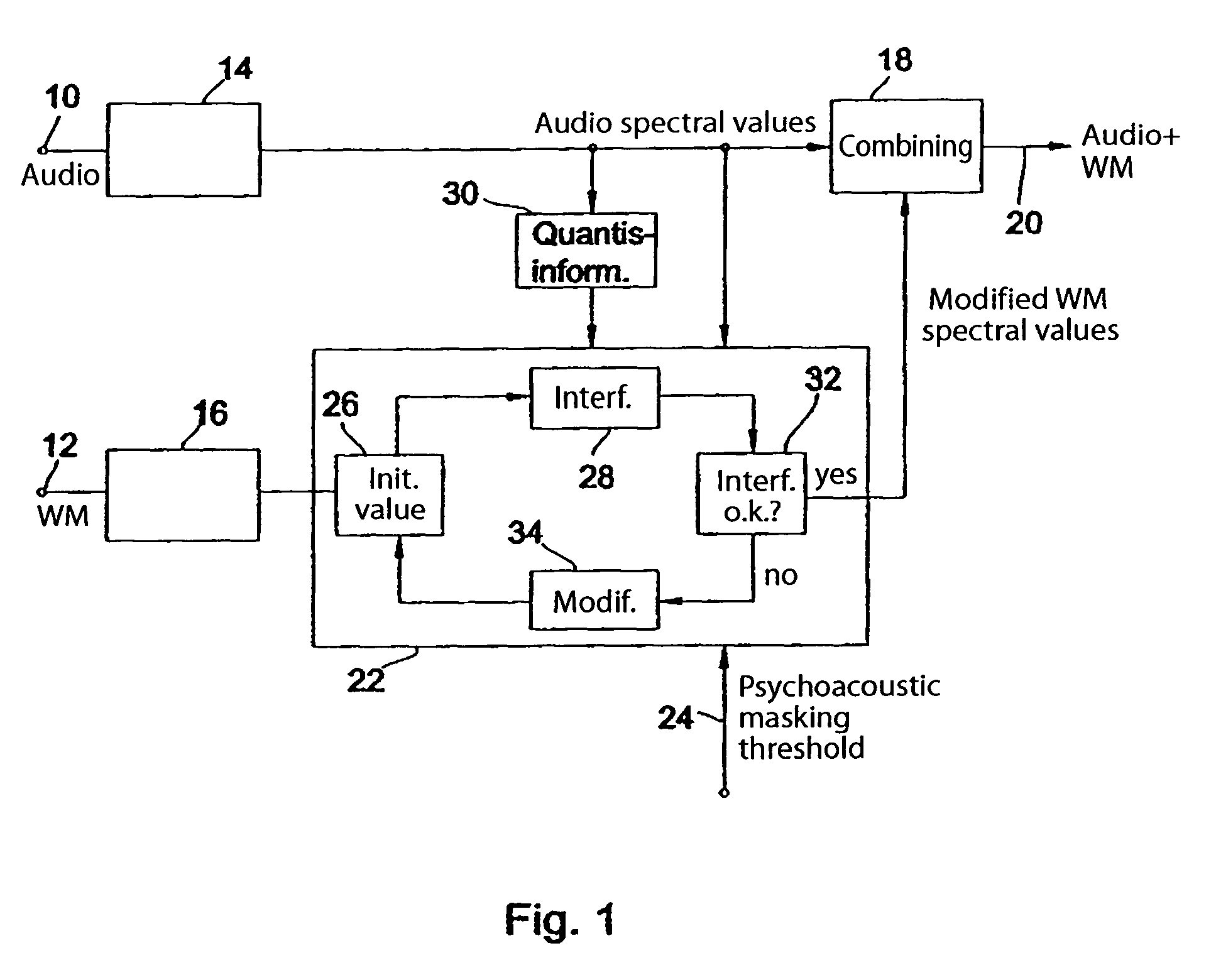
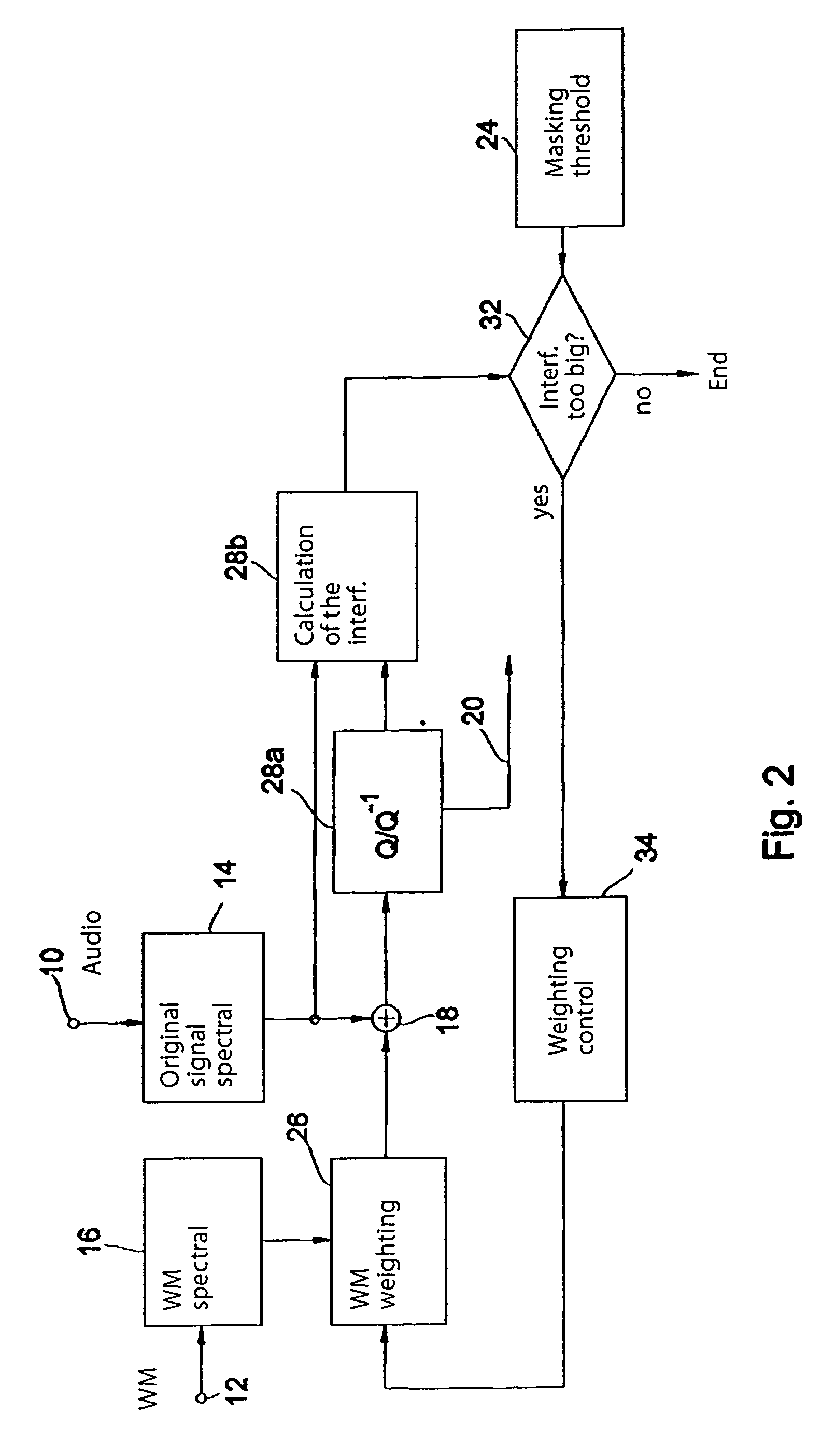
Prior to embedding a watermark in an audio signal, a spectral representation of the audio signal and a spectral representation of the watermark signal are determined. The spectral representation of the watermark signal is then processed on the basis of a psychoacoustic masking threshold of the audio signal. The processed watermark signal is combined with the audio signal to obtain an audio signal bearing a watermark. The spectral representation of the watermark signal is processed iteratively as follows: first a predetermined watermark initial value is selected, then the interference introduced into the spectral representation of the audio signal after a quantization of the spectral representation of the audio signal is determined and then, if the interference introduced by the watermark initial value exceeds the predetermined interference threshold, the watermark initial value is modified progressively until the resulting interference introduced into the spectral representation of the audio signal after quantization is less than or equal to the predetermined interference threshold. The modified watermark initial value at the end of the iteration is used as the processed watermark signal to be combined with the audio signal. As a result it is no longer possible for a watermark to be quantized out. Instead, full control over the energy of the watermark is achieved. A watermark can therefore be embedded in an audio signal to provide either the best possible degree of watermark detectability or the best possible audio quality.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
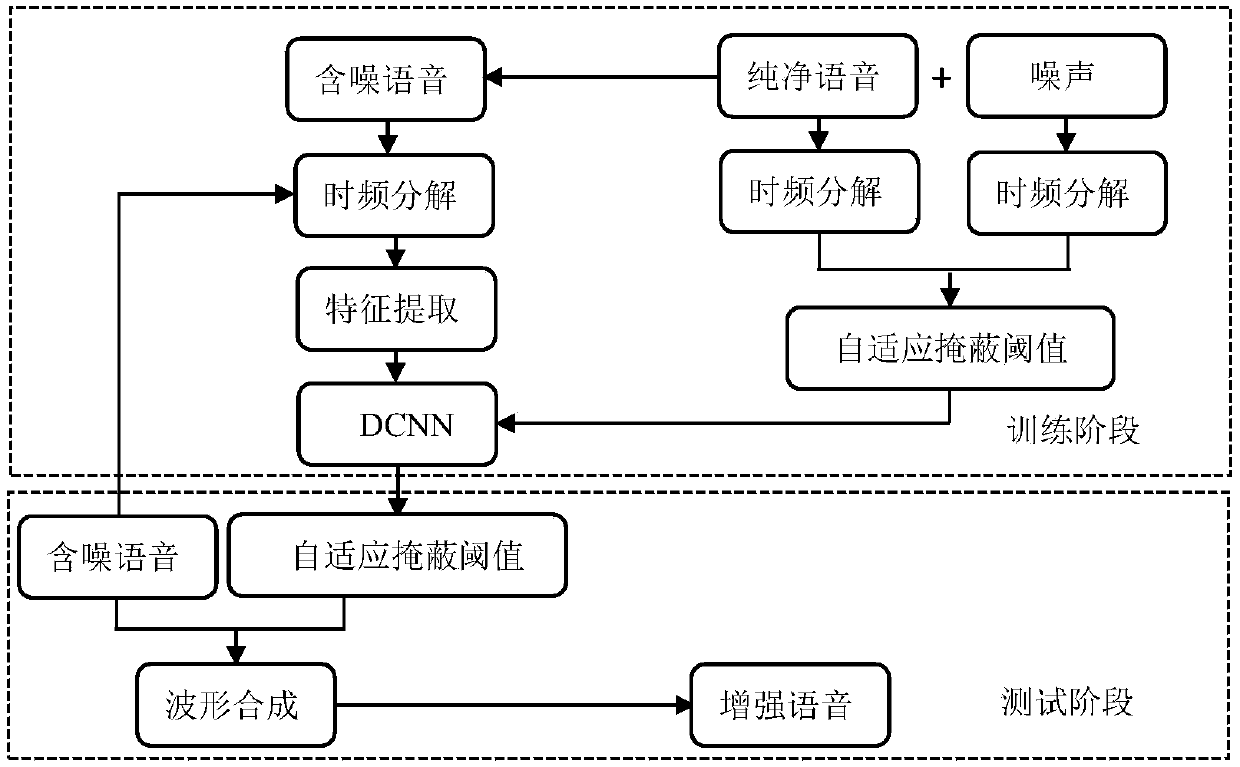
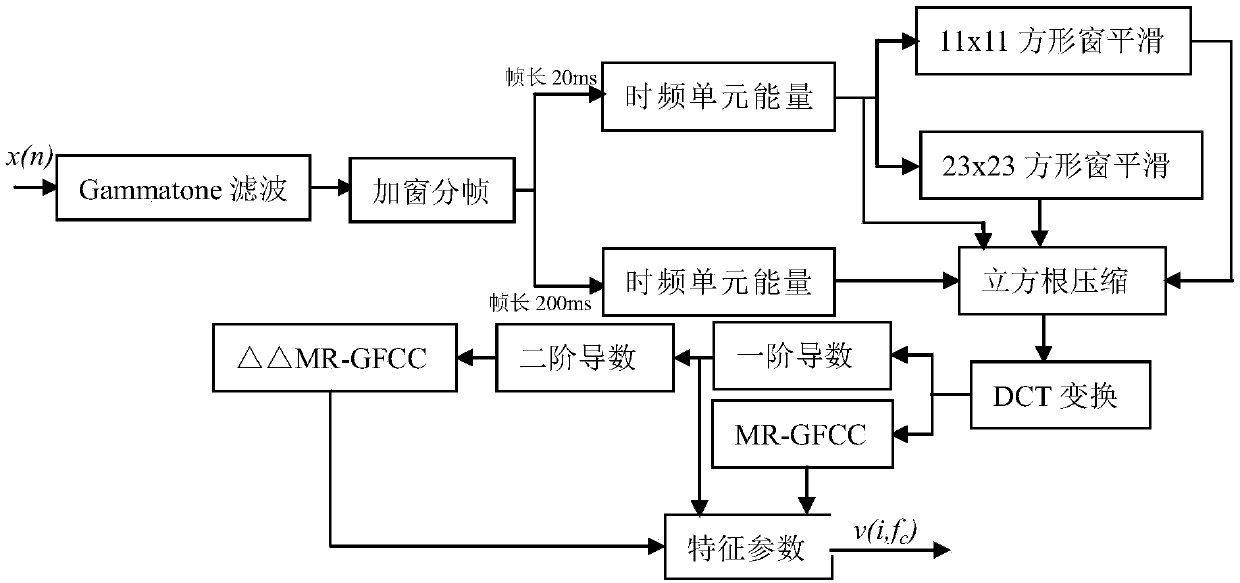
Voice enhancing method based on multiresolution auditory cepstrum coefficient and deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN107845389AReduce complexityCompatible with auditory perception characteristicsSpeech recognitionMasking thresholdHuman ear
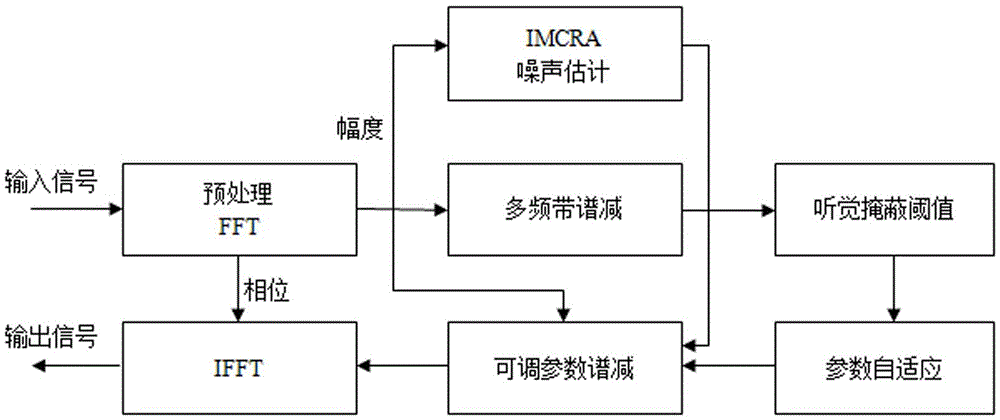
The invention discloses a voice enhancing method based on a multiresolution auditory cepstrum system and a deep convolutional neural network. The voice enhancing method comprises the following steps:firstly, establishing new characteristic parameters, namely multiresolution auditory cepstrum coefficient (MR-GFCC), capable of distinguishing voice from noise; secondly, establishing a self-adaptivemasking threshold on based on ideal soft masking (IRM) and ideal binary masking (IBM) according to noise variations; further training an established seven-layer neural network by using new extracted characteristic parameters and first / second derivatives thereof and the self-adaptive masking threshold as input and output of the deep convolutional neural network (DCNN); and finally enhancing noise-containing voice by using the self-adaptive masking threshold estimated by the DCNN. By adopting the method, the working mechanism of human ears is sufficiently utilized, voice characteristic parameters simulating a human ear auditory physiological model are disposed, and not only is a relatively great deal of voice information maintained, but also the extraction process is simple and feasible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
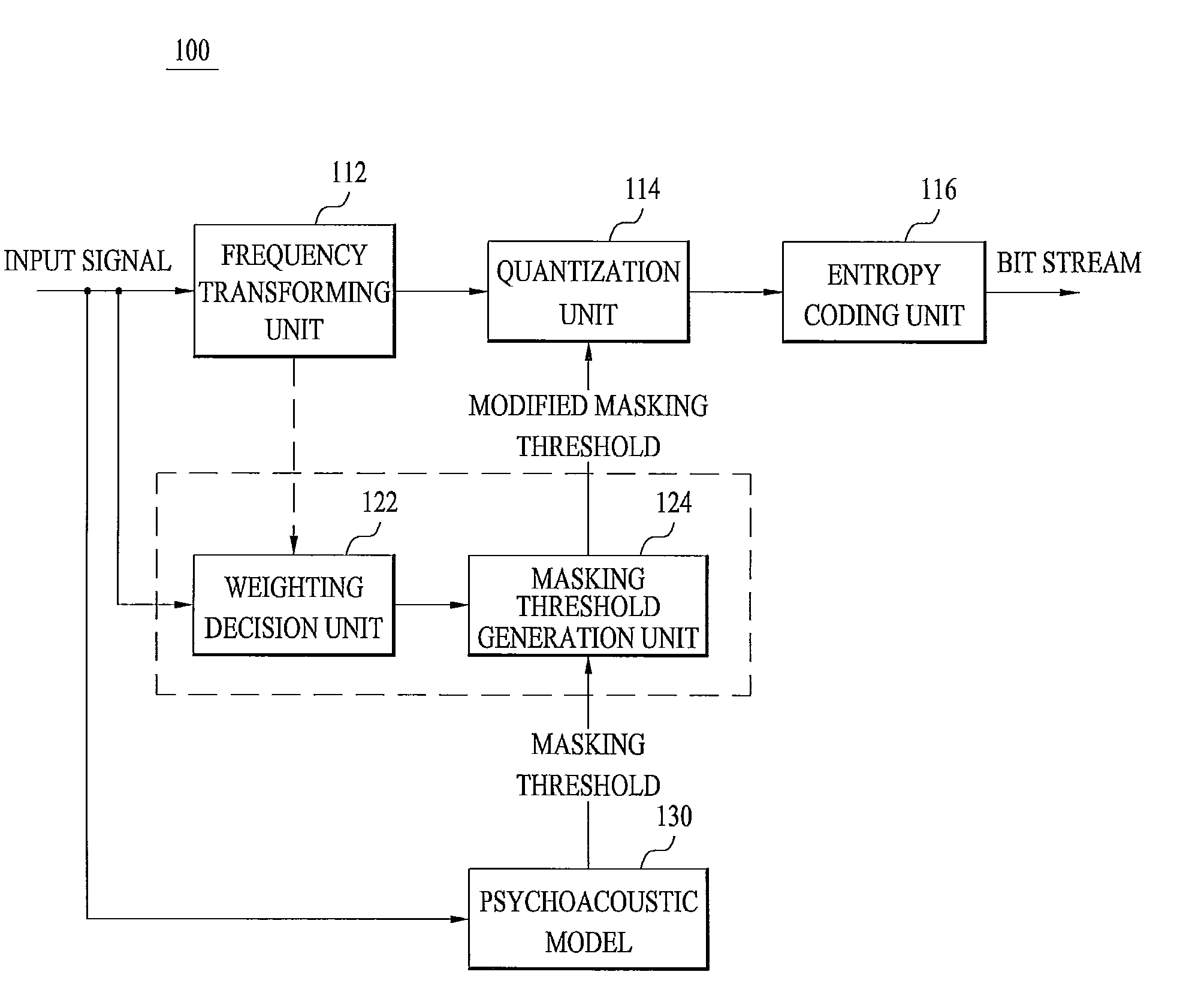
Method and apparatus for processing audio signals
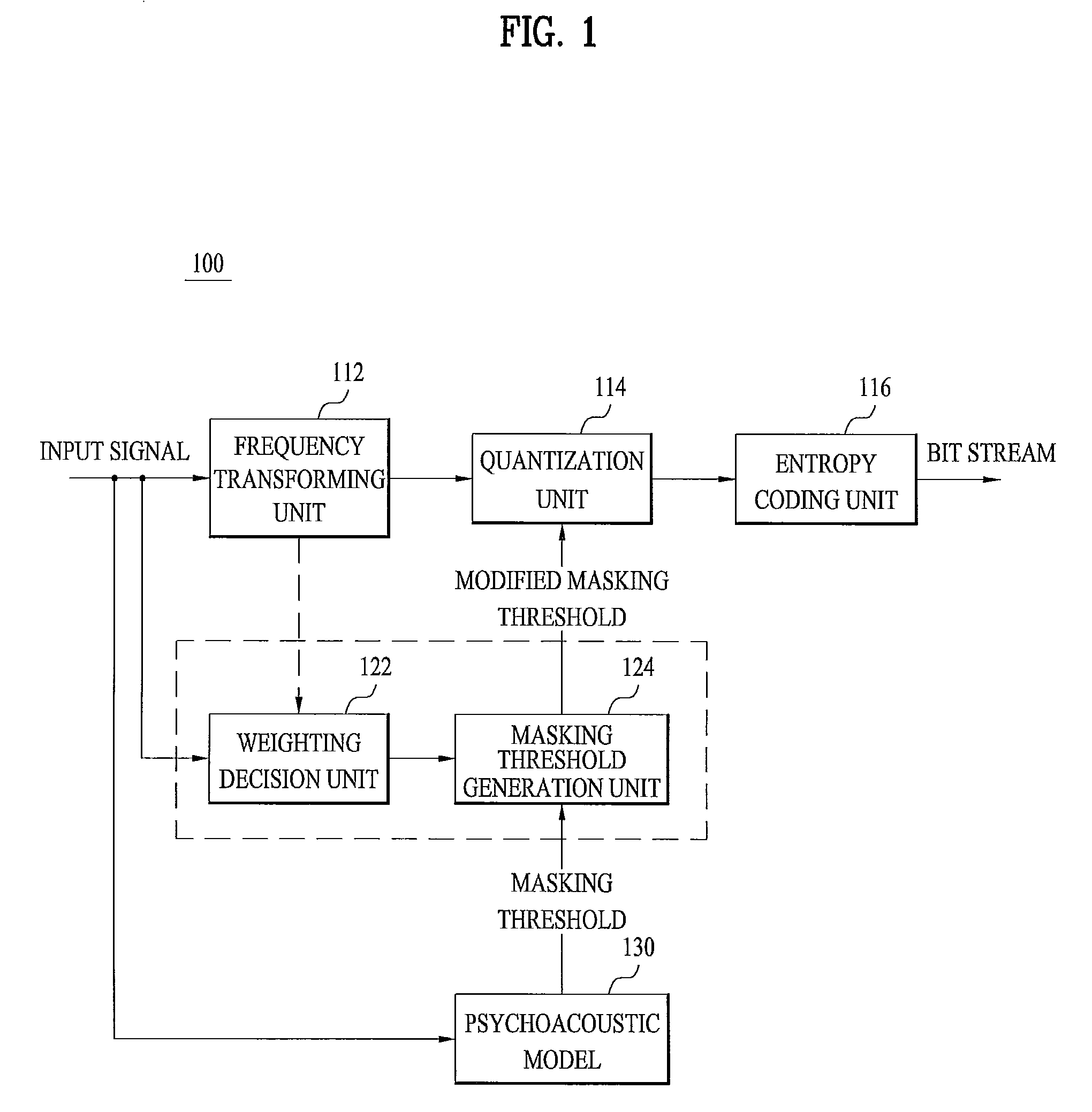
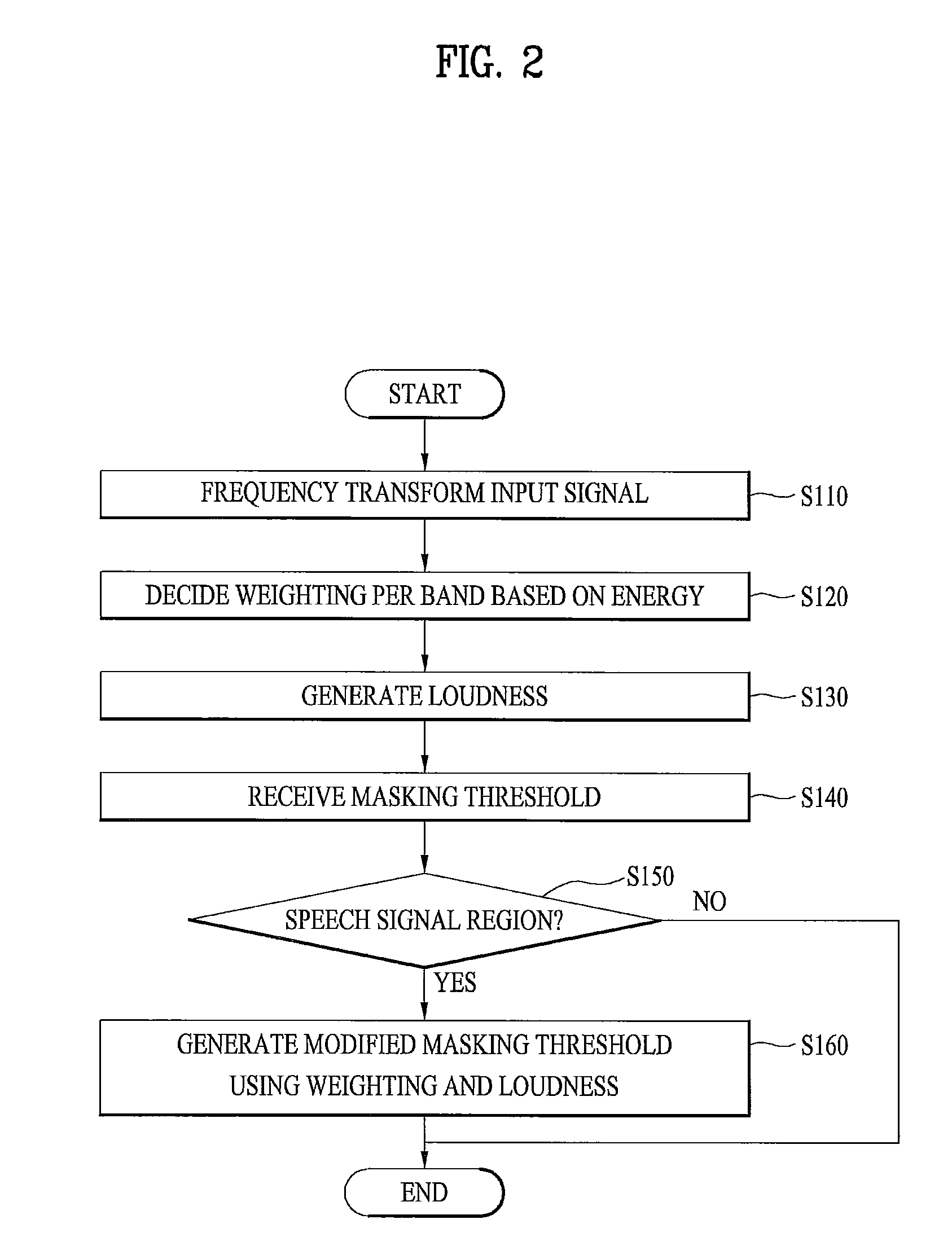
ActiveUS20110075855A1Minimizing perceived distortionMaintain sound qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumMasking threshold
A method for processing an audio signal is disclosed. The method for processing an audio signal includes frequency-transforming an audio signal to generate a frequency-spectrum, deciding a weighting per band corresponding to energy per band using the frequency spectrum, receiving a masking threshold based on a psychoacoustic model, applying the weighting to the masking threshold to generate a modified masking threshold, and quantizing the audio signal using the modified masking threshold.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Masking Based Gain Control
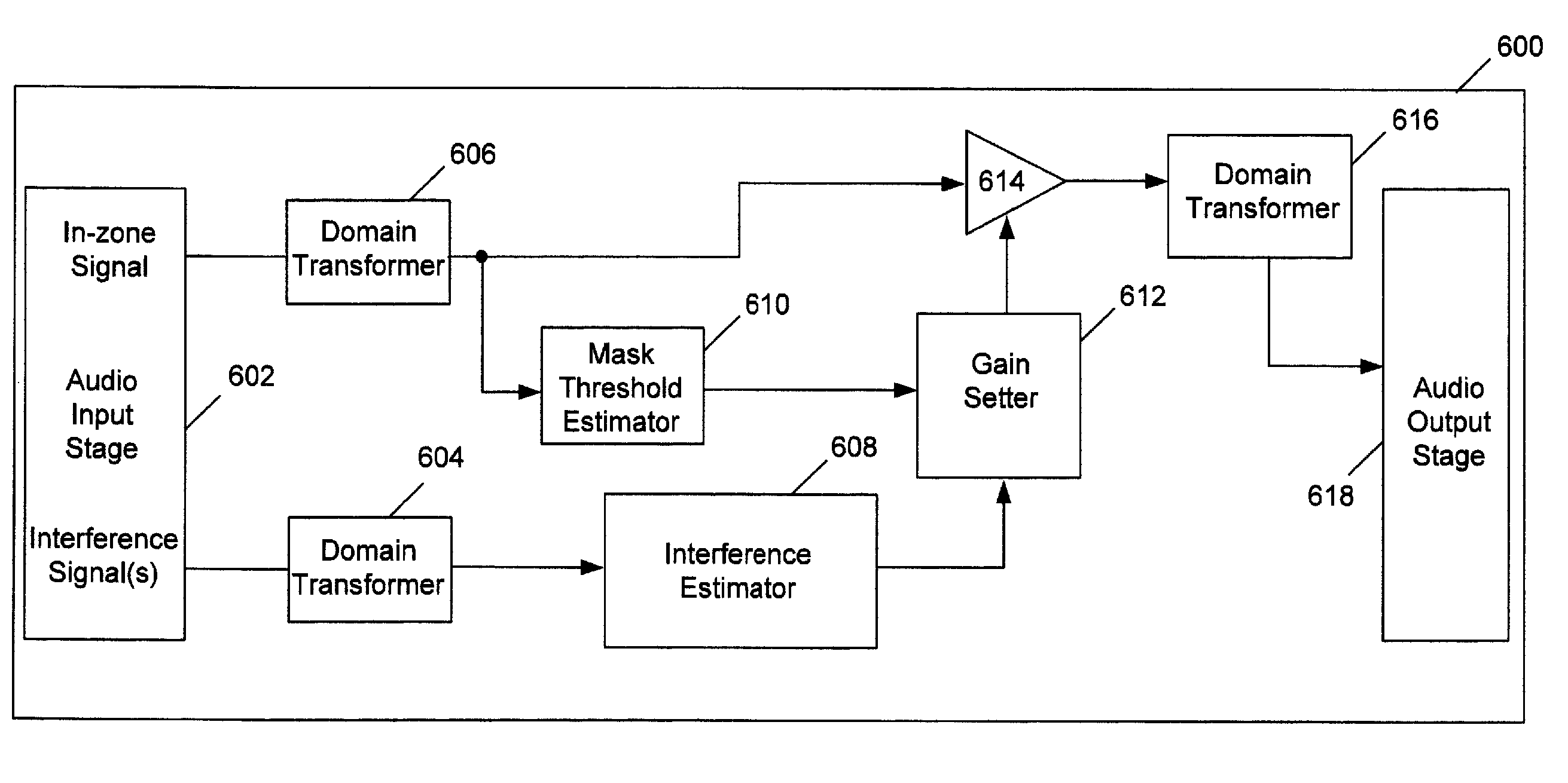
ActiveUS20100158263A1Reducing audibilityAttenuation of signal levelCommunication jammingTransducer acoustic reaction preventionMasking thresholdSignal correlation
Interfering signals that may be present in a listening environment are masked by reproducing a desired signal in a listening environment, determining a masking threshold associated with the desired signal, identifying an interfering signal that may be present in the environment, comparing the interfering signal to the masking threshold, and adjusting the desired signal over time to raise its masking threshold above the level of the interfering signal.
Owner:BOSE CORP
Information Signal Encoding
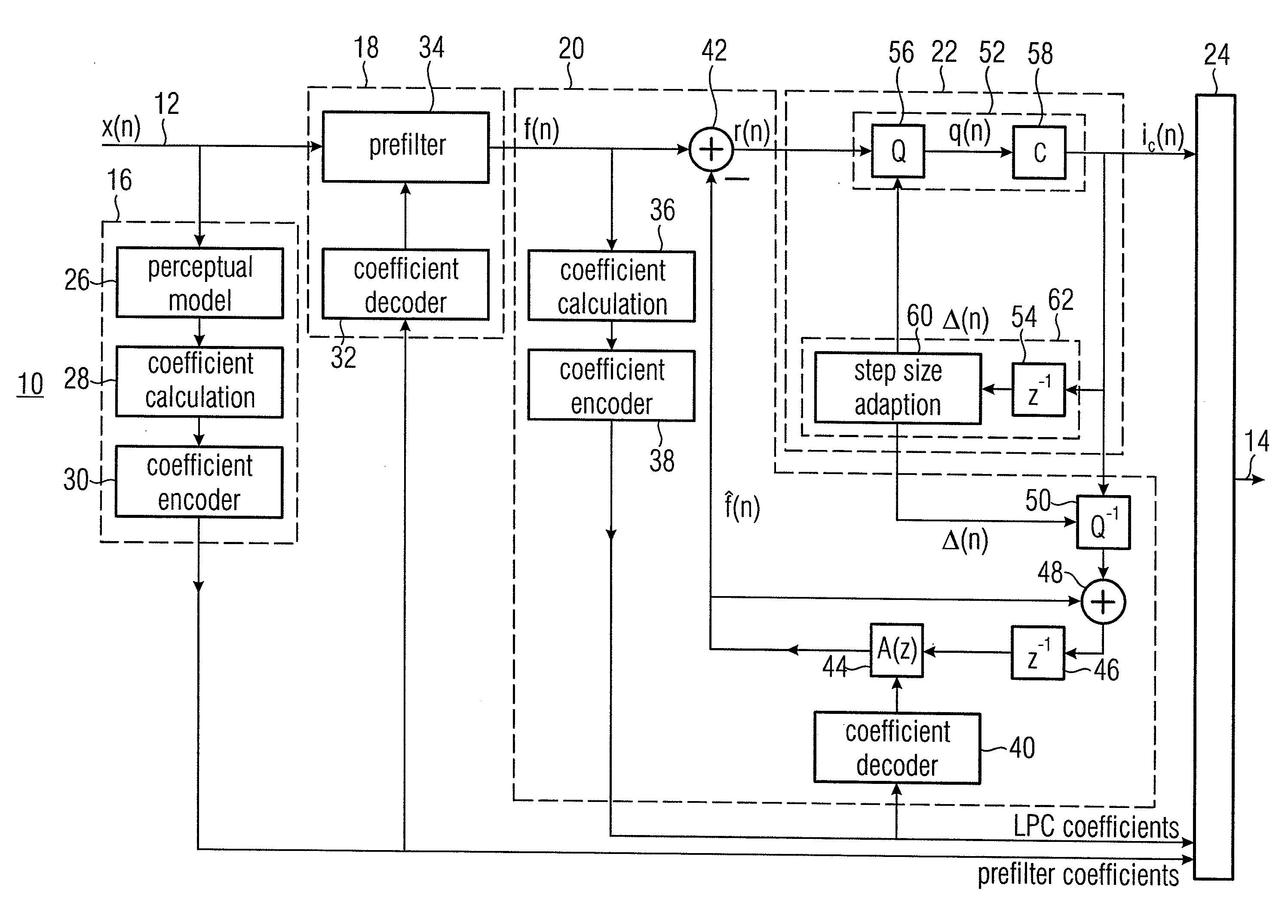
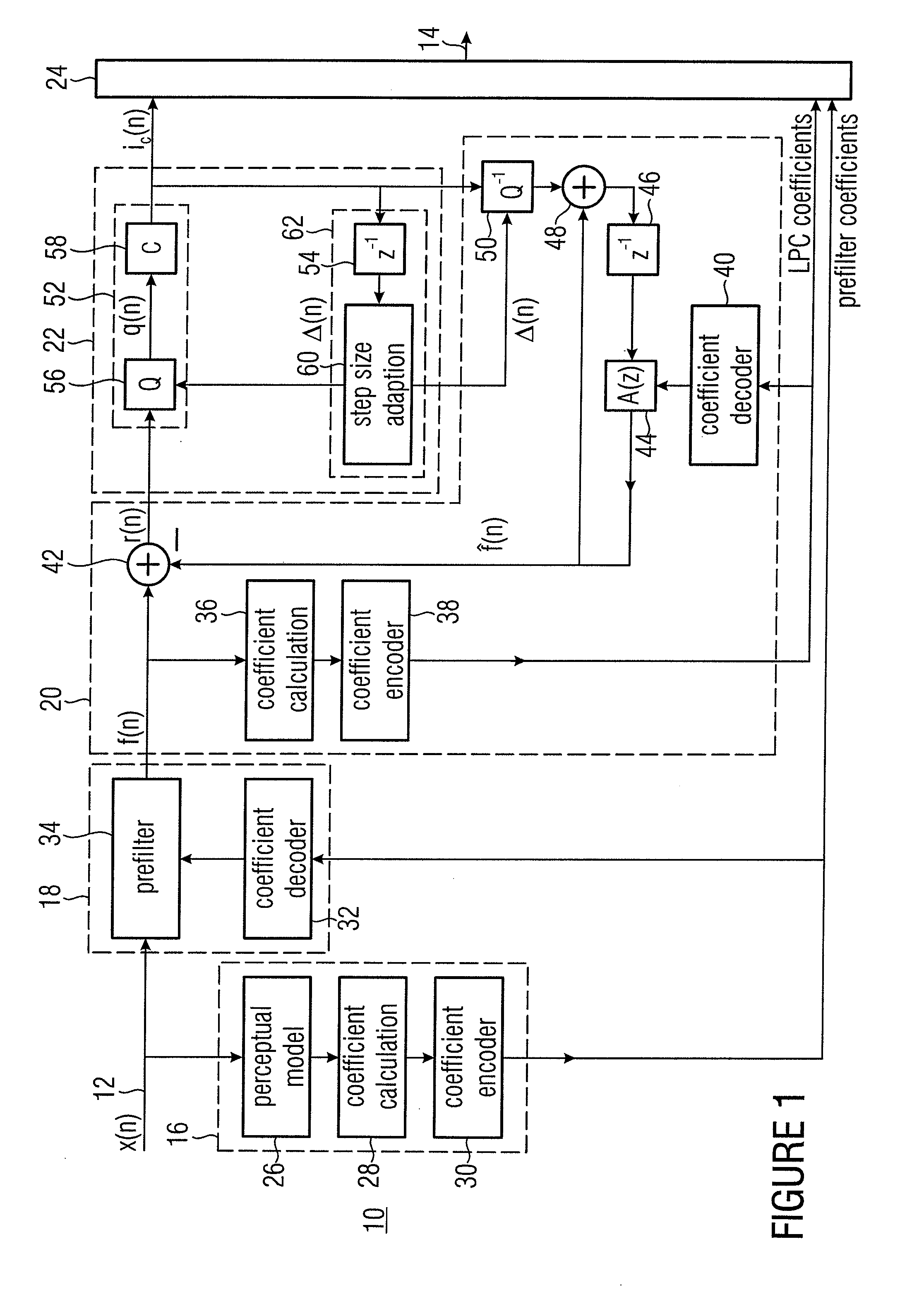
ActiveUS20090254783A1Improve listening qualityMaintain qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningAlgorithmEngineering
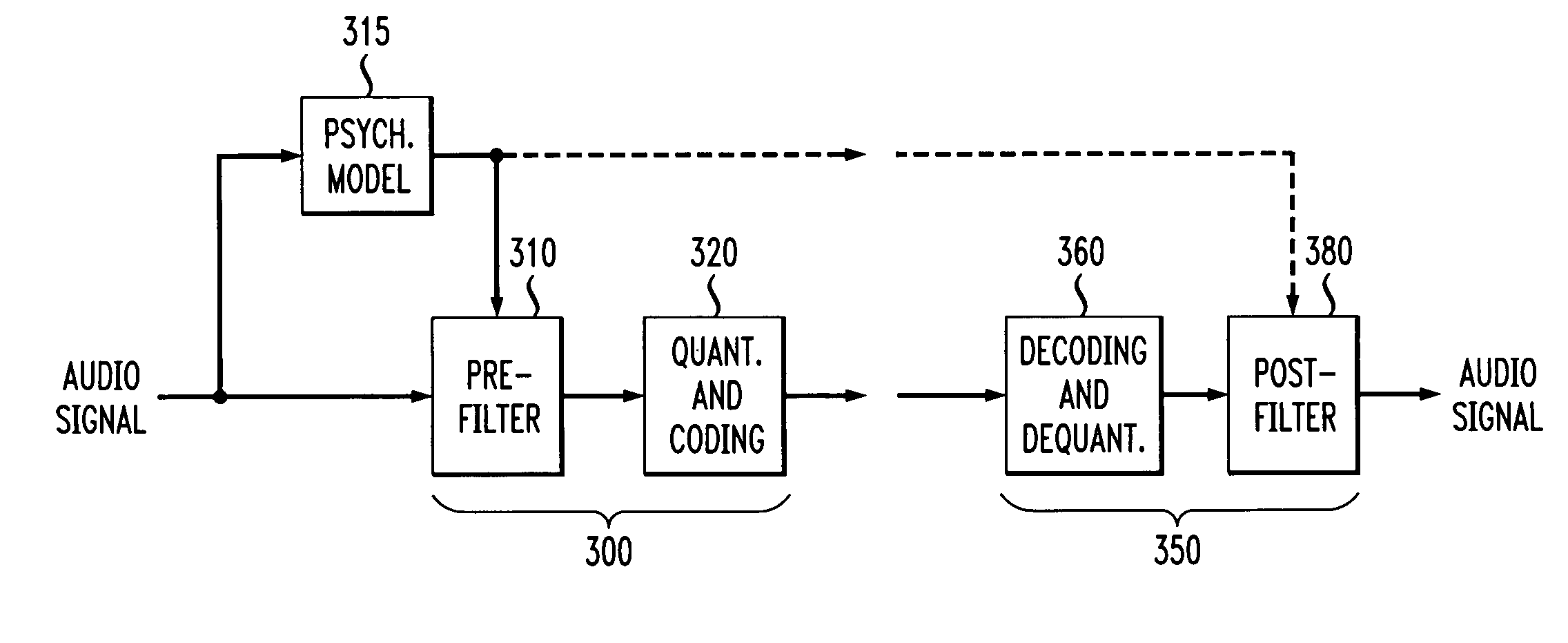
A very coarse quantization exceeding the measure determined by the masking threshold without or only very little quality losses is enabled by quantizing not immediately the prefiltered signal, but a prediction error obtained by forward-adaptive prediction of the prefiltered signal. Due to the forward adaptivity, the quantizing error has no negative effect on the prediction on the decoder side.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
System and method for embedded audio coding with implicit auditory masking
InactiveUS7110941B2Eliminate overheadImprove compression efficiencySpeech analysisMasking thresholdComputer science
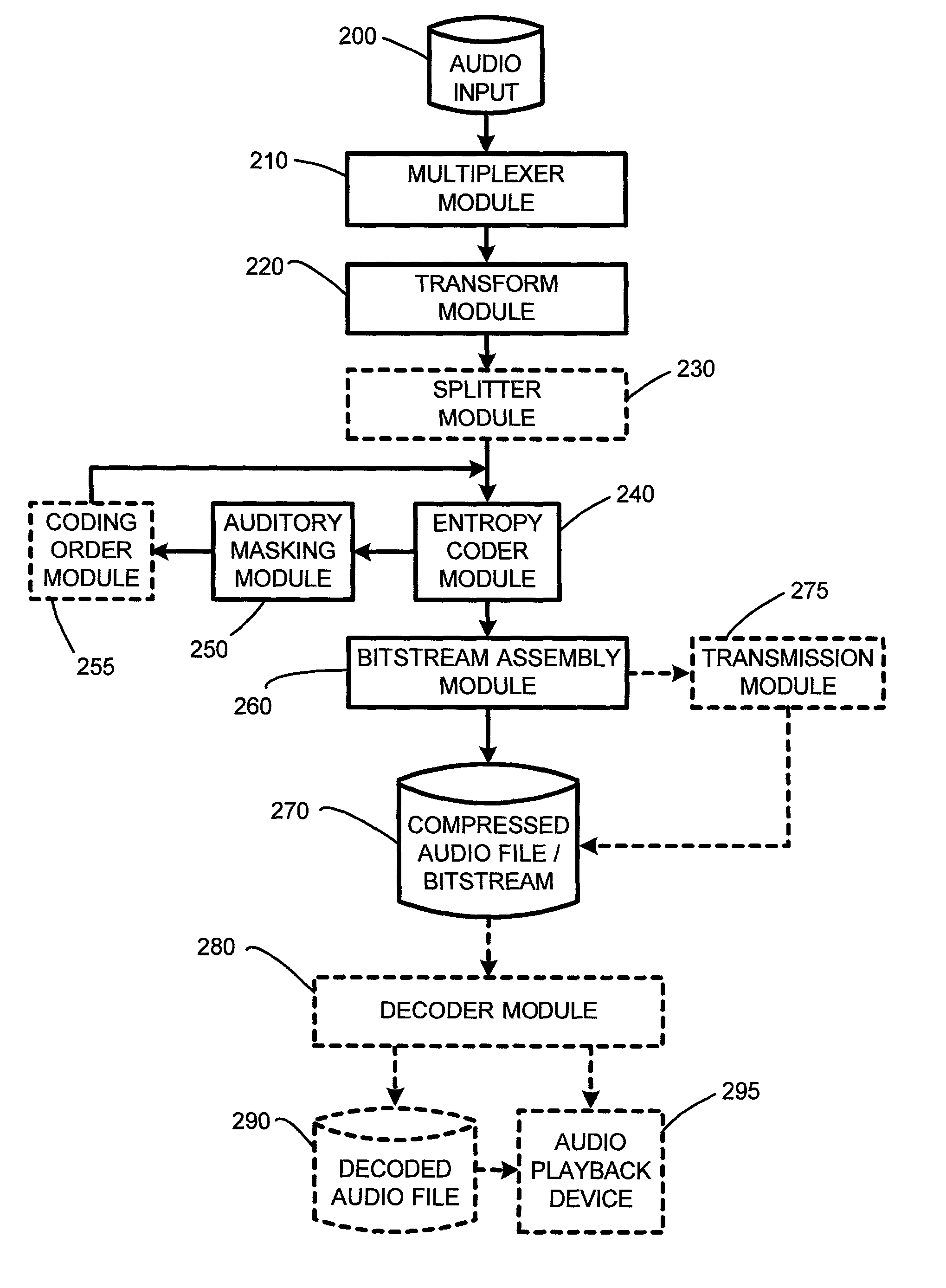
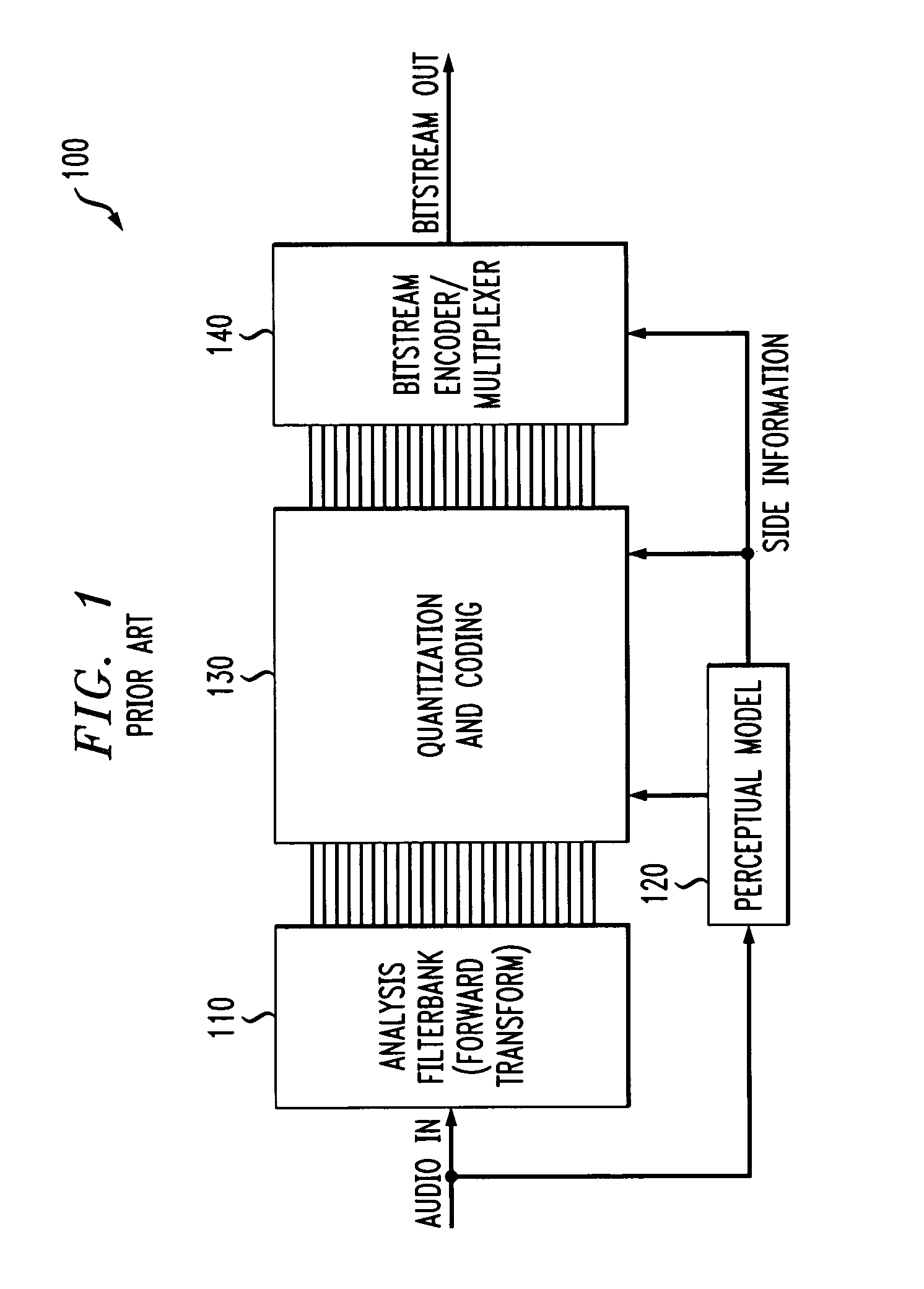
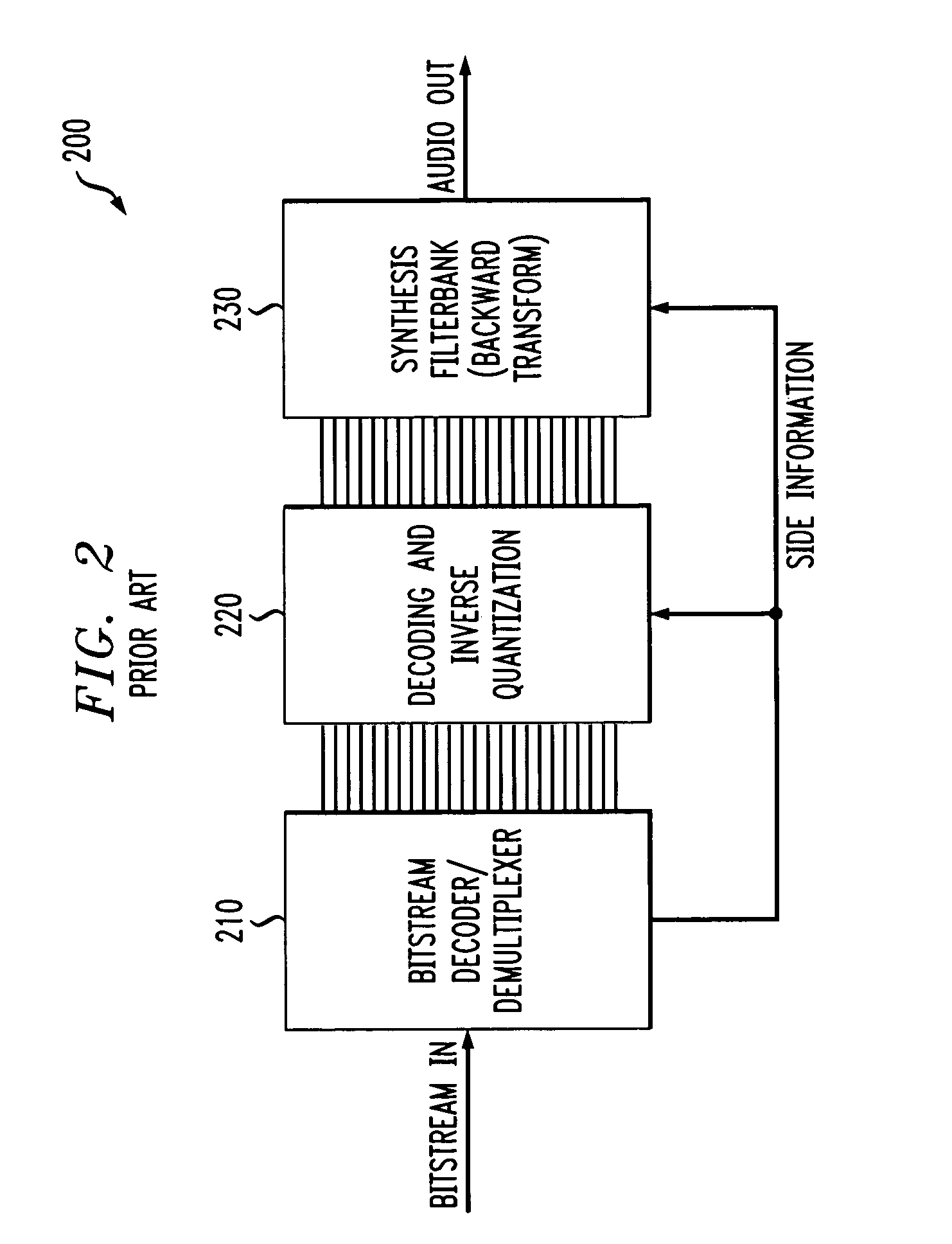
The embedded audio coder (EAC) is a fully scalable psychoacoustic audio coder which uses a novel perceptual audio coding approach termed “implicit auditory masking” which is intermixed with a scalable entropy coding process. When encoding and decoding an audio file using the EAC, auditory masking thresholds are not sent to a decoder. Instead, the masking thresholds are automatically derived from already coded coefficients. Furthermore, in one embodiment, rather than quantizing the audio coefficients according to the auditory masking thresholds, the masking thresholds are used to control the order that the coefficients are encoded. In particular, in this embodiment, during the scalable coding, larger audio coefficients are encoded first, as the larger components are the coefficients that contribute most to the audio energy level and lead to a higher auditory masking threshold.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
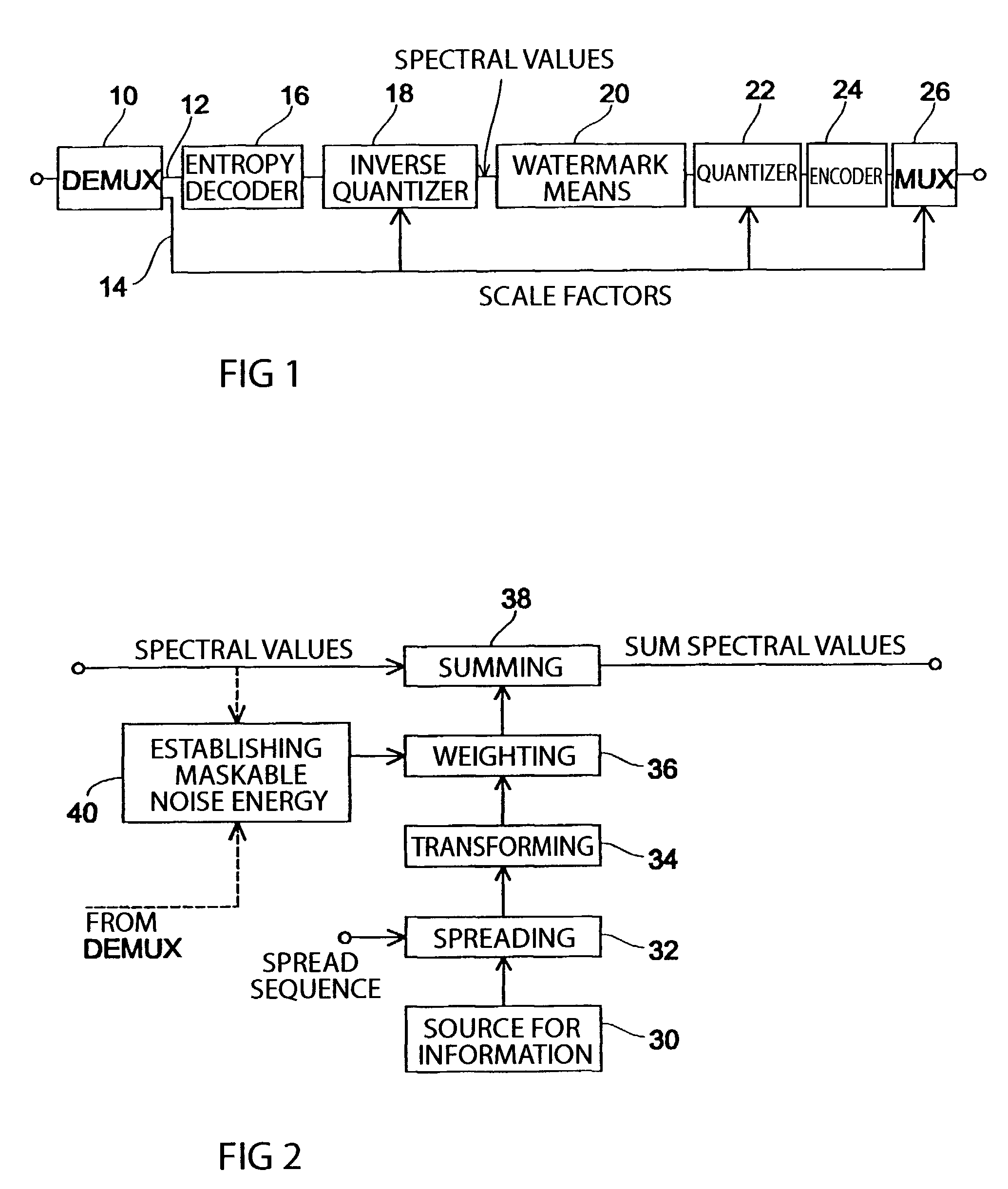
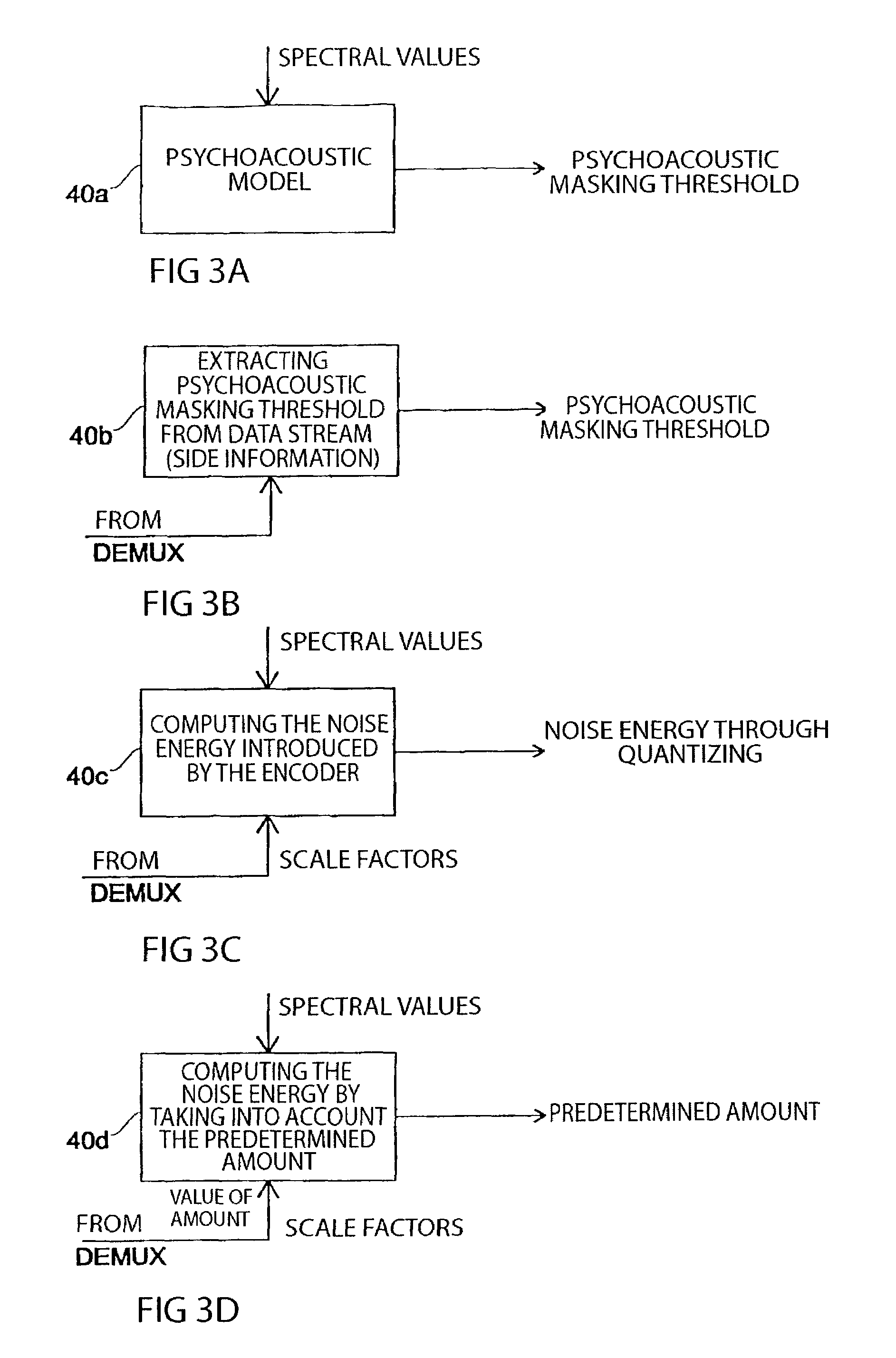
Method and apparatus for introducing information into a data stream and method and apparatus for encoding an audio signal
InactiveUS7454327B1Improve interoperabilityEasy to implementSpeech analysisPlural information simultaneous broadcastTime domainFrequency spectrum
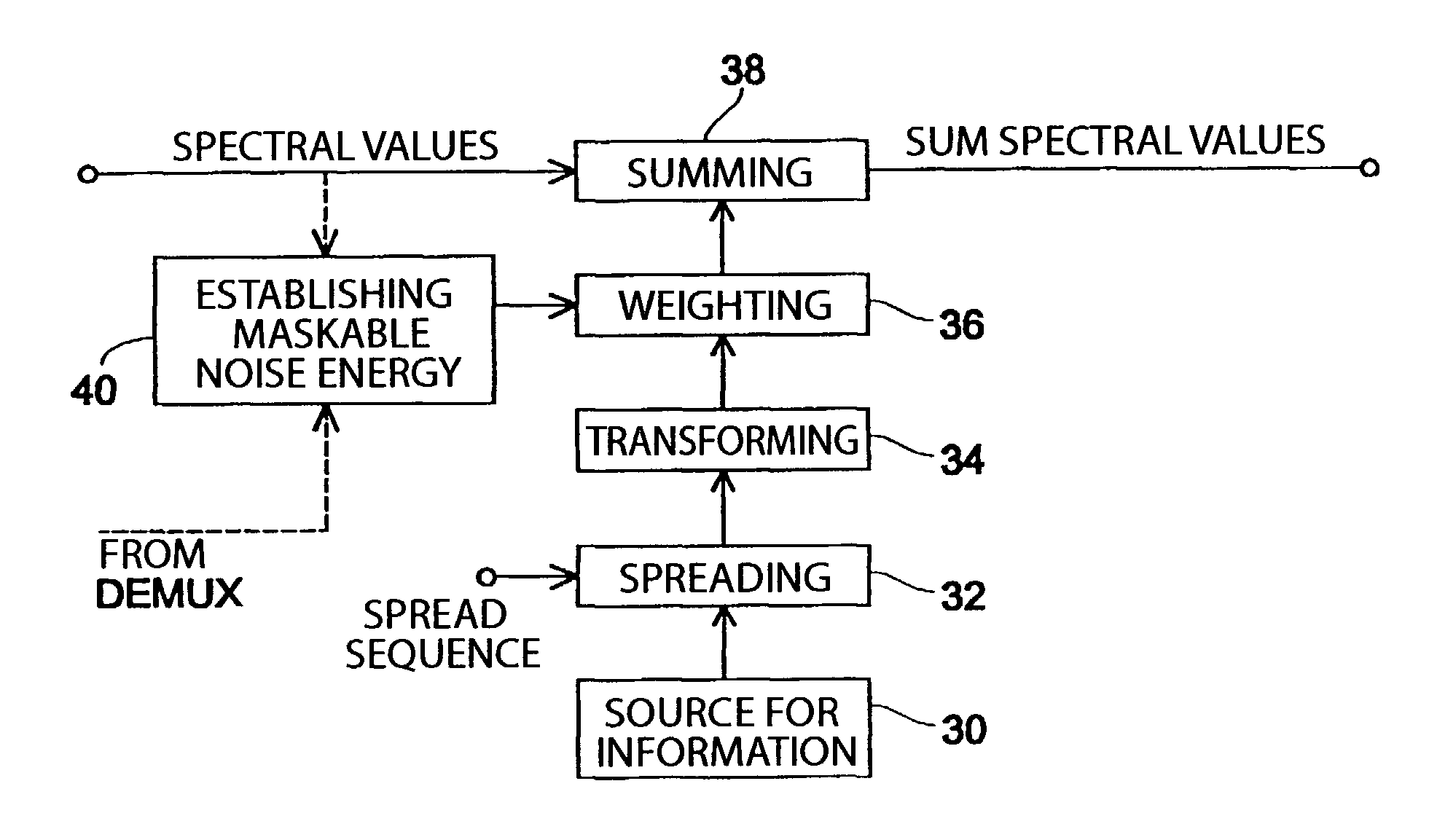
An inventive method for introducing information into a data stream including data about spectral values representing a short-term spectrum of an audio signal first performs a processing of the data stream to obtain the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal. Apart from that, the information to be introduced are combined with a spread sequence to obtain a spread information signal, whereupon a spectral representation of the spread information is generated which will then be weighted with an established psychoacoustic maskable noise energy to generate a weighted information signal, wherein the energy of the introduced information is substantially equal to or below the psychoacoustic masking threshold. The weighted information signal and the spectral values of the short-term spectrum of the audio signal will then be summed and afterwards processed again to obtain a processed data stream including both audio information and information to be introduced. By the fact that the information to be introduced are introduced into the data stream without changing to the time domain, the block rastering underlying the short-term spectrum will not be touched, so that introducing a watermark will not lead to tandem encoding effects.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
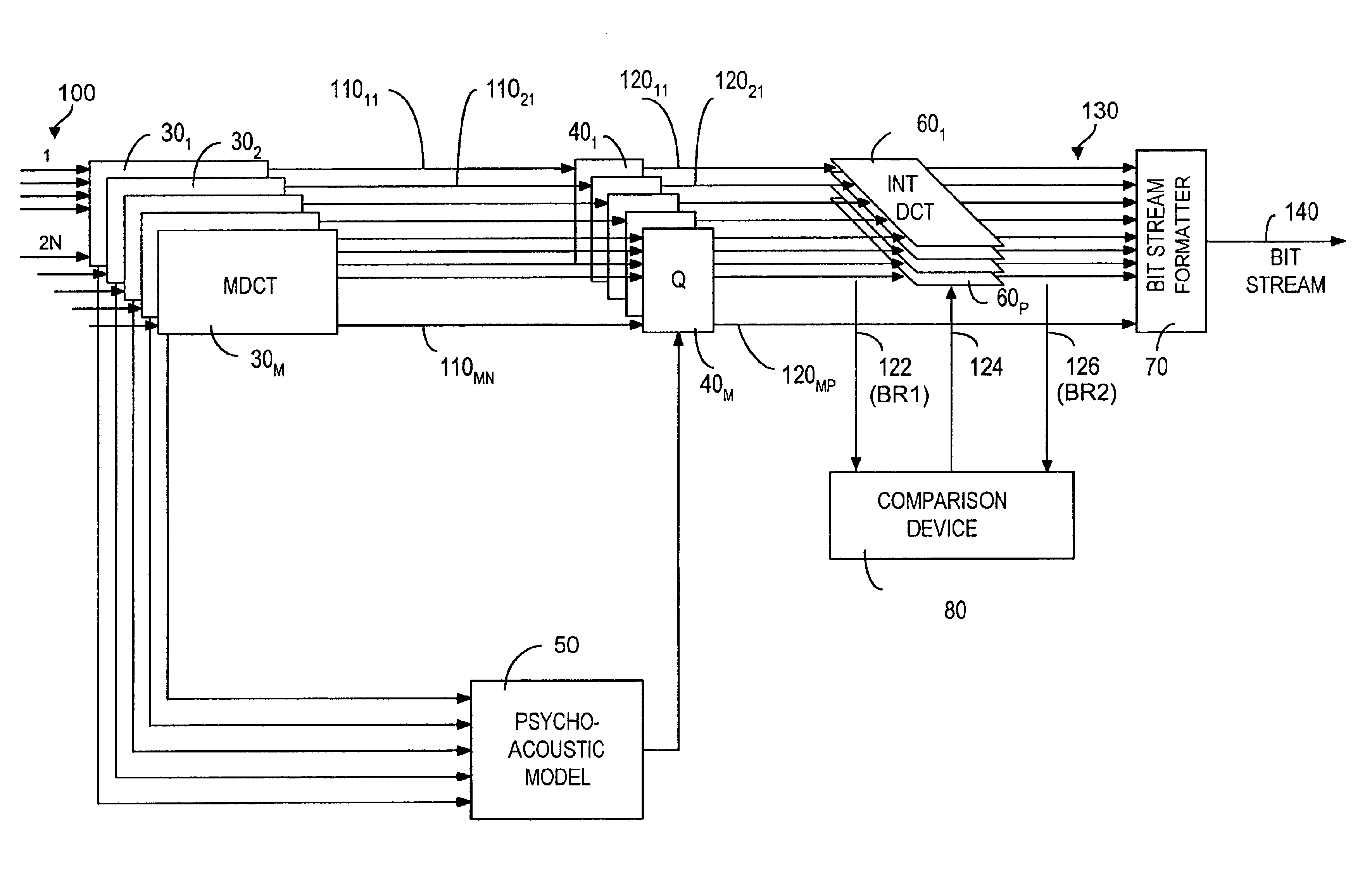
Method and system for inter-channel signal redundancy removal in perceptual audio coding
InactiveUS6934676B2Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisVocal tractMasking threshold
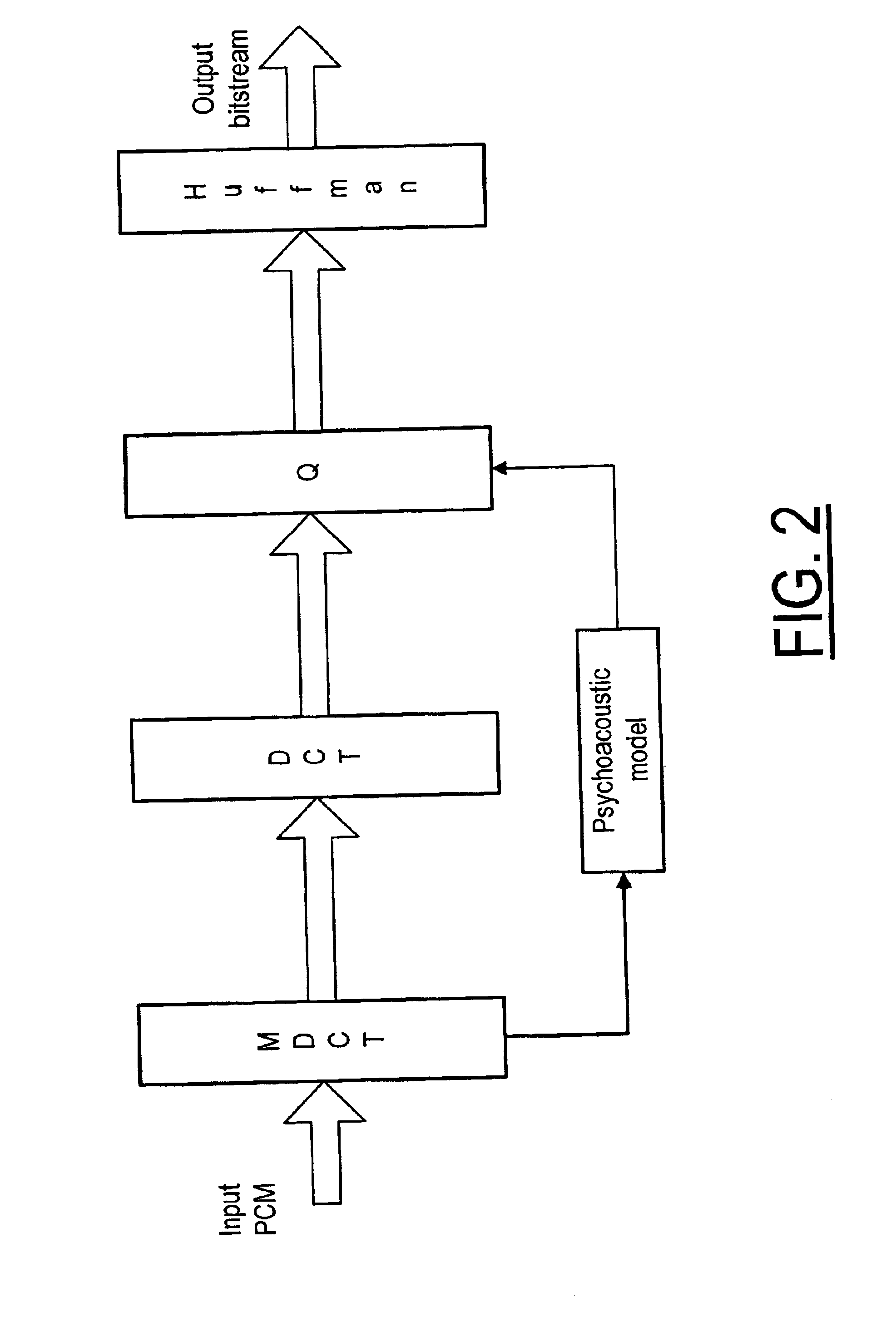
A method and system for coding audio signals in a multi-channel sound system, wherein a plurality of MDCT units are used to reduce the audio signals for providing a plurality of MDCT coefficients. The MDCT coefficients are quantized according to the masking threshold calculated from a psychoacoustic model and a plurality of INT (integer-to-integer) DCT modules are used to remove the cross-channel redundancy in the quantized MDCT coefficients. The output from the INT-DCT modules is Huffman coded and written to a bitstream for transmission or storage.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Audio coding
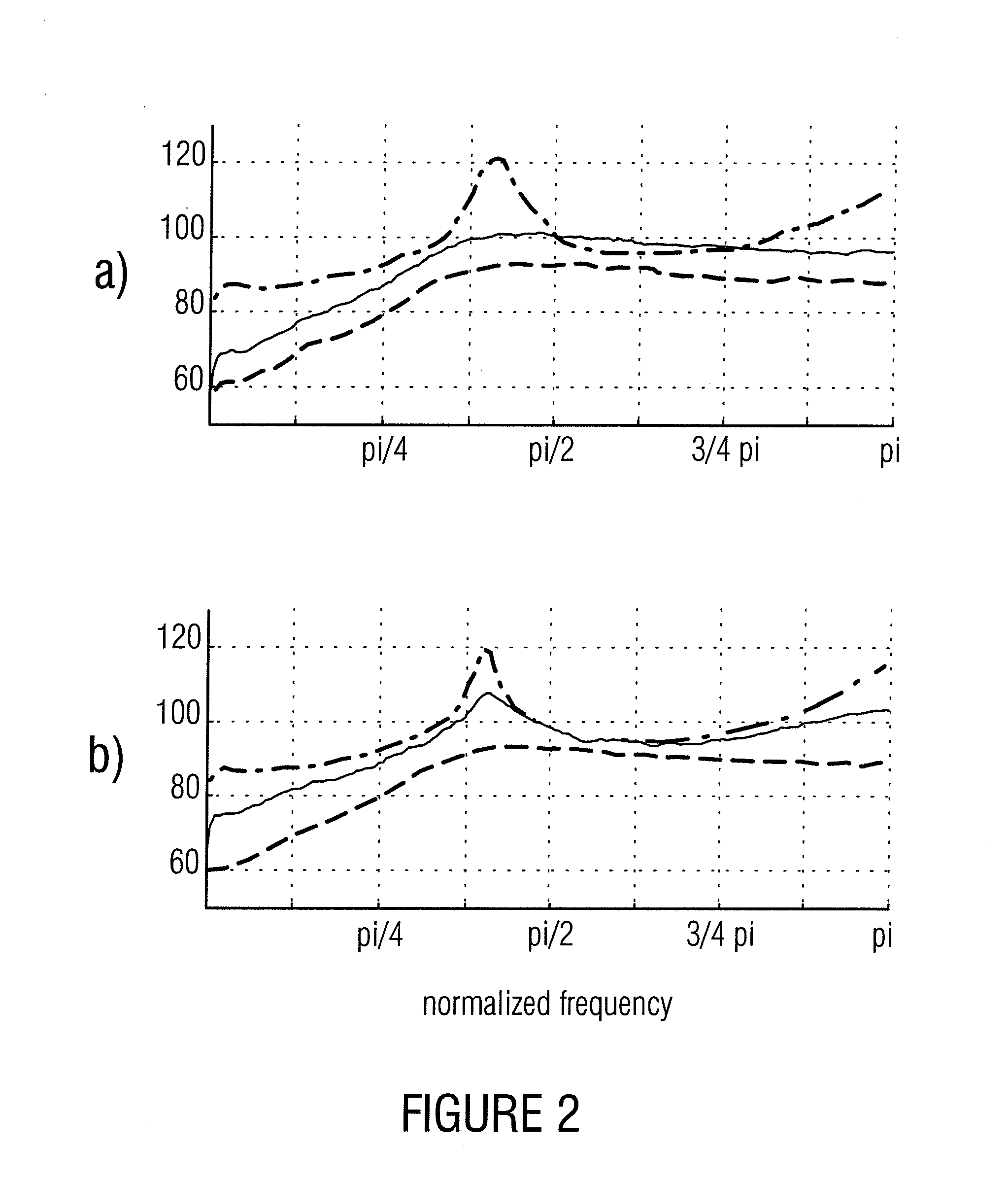
ActiveUS20070016403A1Many solutionsFew artifactSpeech analysisCode conversionConstant frequencyMasking threshold
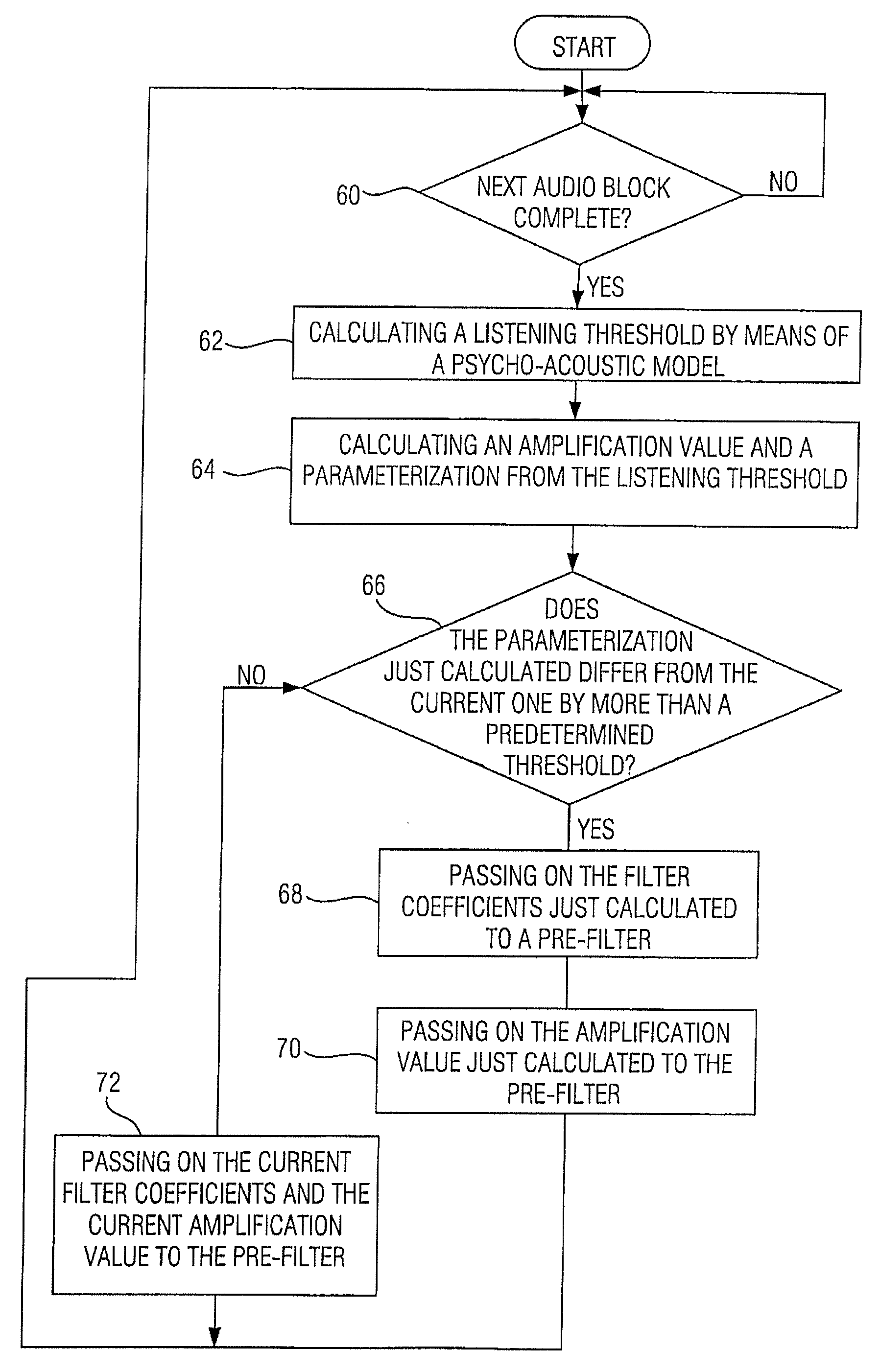
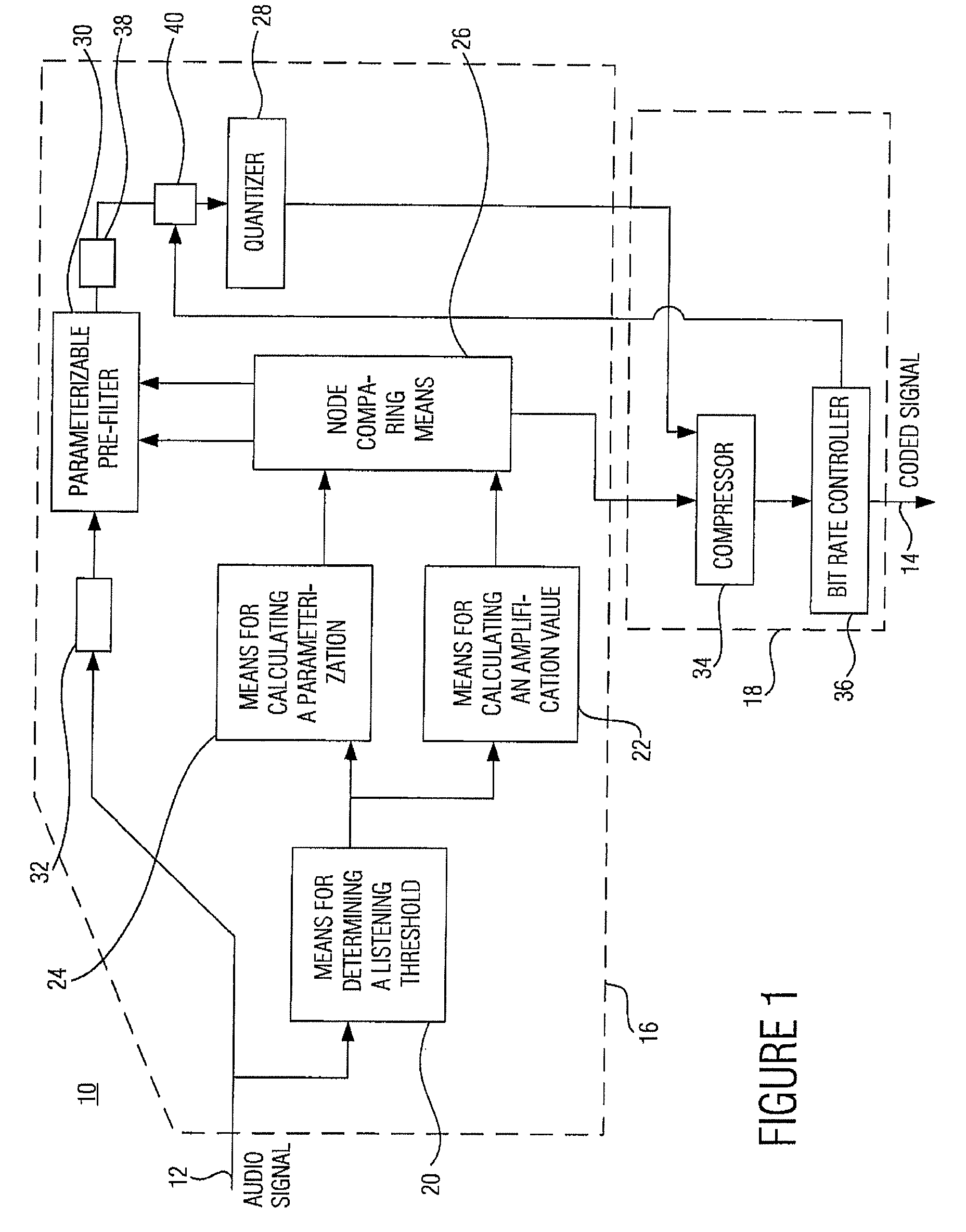
The central idea of the present invention is that the prior procedure, namely interpolation relative to the filter coefficients and the amplification value, for obtaining interpolated values for the intermediate audio values starting from the nodes has to be dismissed. Coding containing less audible artifacts can be obtained by not interpolating the amplification value, but rather taking the power limit derived from the masking threshold, preferably as the area below the square of the magnitude of the masking threshold, for each node, i.e. for each parameterization to be transferred, and then performing the interpolation between these power limits of neighboring nodes, such as, for example, a linear interpolation. On both the coder and the decoder side, an amplification value can then be calculated from the intermediate power limit determined such that the quantizing noise caused by quantization, which has a constant frequency before post-filtering on the decoder side, is below the power limit or corresponds thereto after post-filtering.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Perceptual coding of audio signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS7110953B1Conserving transmitted bitsGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Audio steganography method and apparatus using cepstrum modification
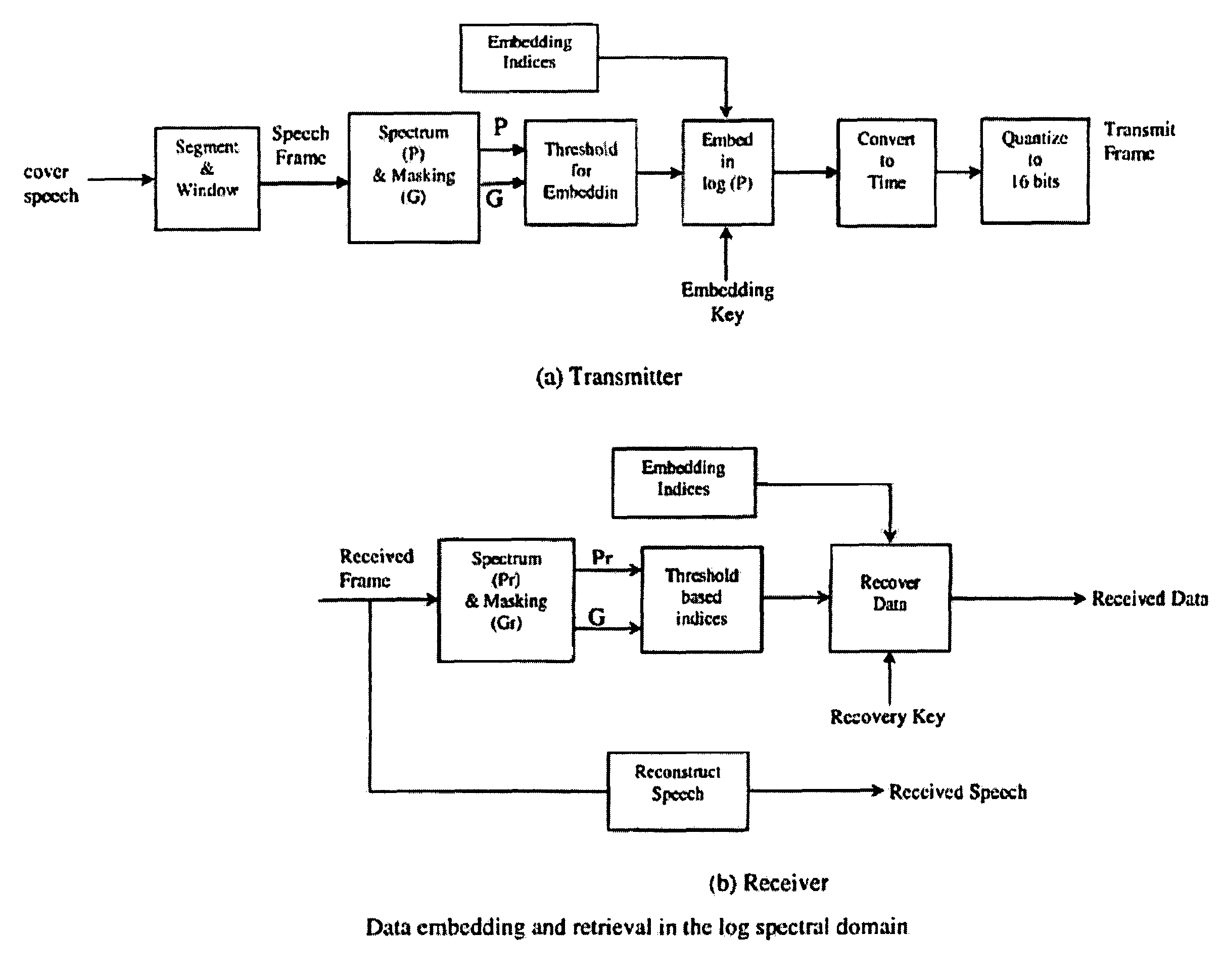
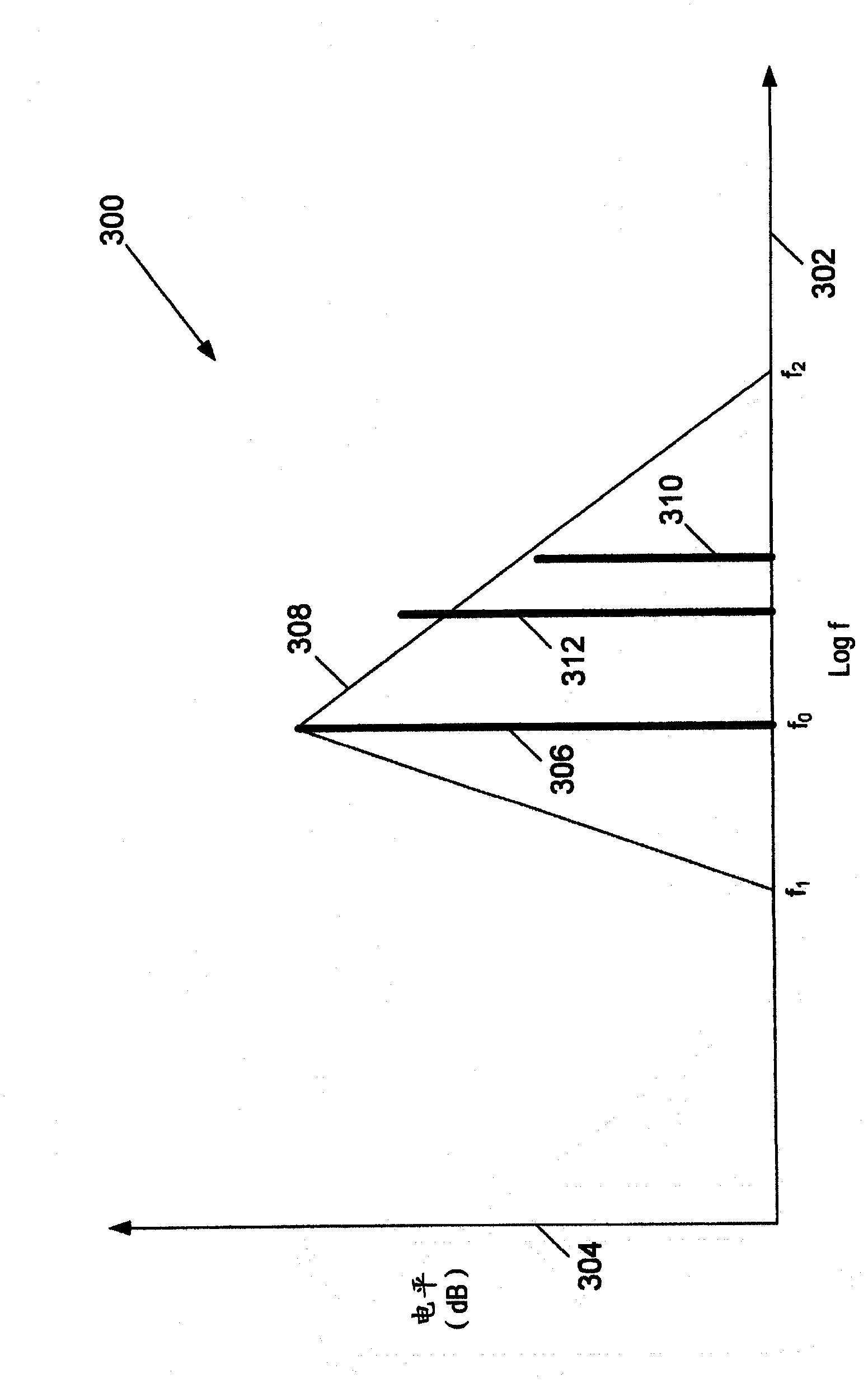
Audio steganography methods and apparatus using cepstral domain techniques to make embedded data in audio signals less perceivable. One approach defines a set of frames for a host audio signal, and, for each frame, determines a plurality of masked frequencies as spectral points with power level below a masking threshold for the frame. The two most commonly occurring masked frequencies f1 and f2 in the set of frames are selected, and a cepstrum of each frame is modified to produce complementary changes of the spectrum at f1 and f2 to correspond to a desired bit value. Another aspect of the invention involves determining a masking threshold for a frame, determining masked frequencies within the frame having a power level below threshold, obtaining a cepstrum of a sinusoid at a selected masked frequency, and modifying the frame by an offset to correspond to an embedded data value, the offset derived from the cepstrum.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Audio signal encoding device and storage medium for storing encoding program
InactiveUS20060004565A1Small sizeTone quality is improvedSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumMasking threshold
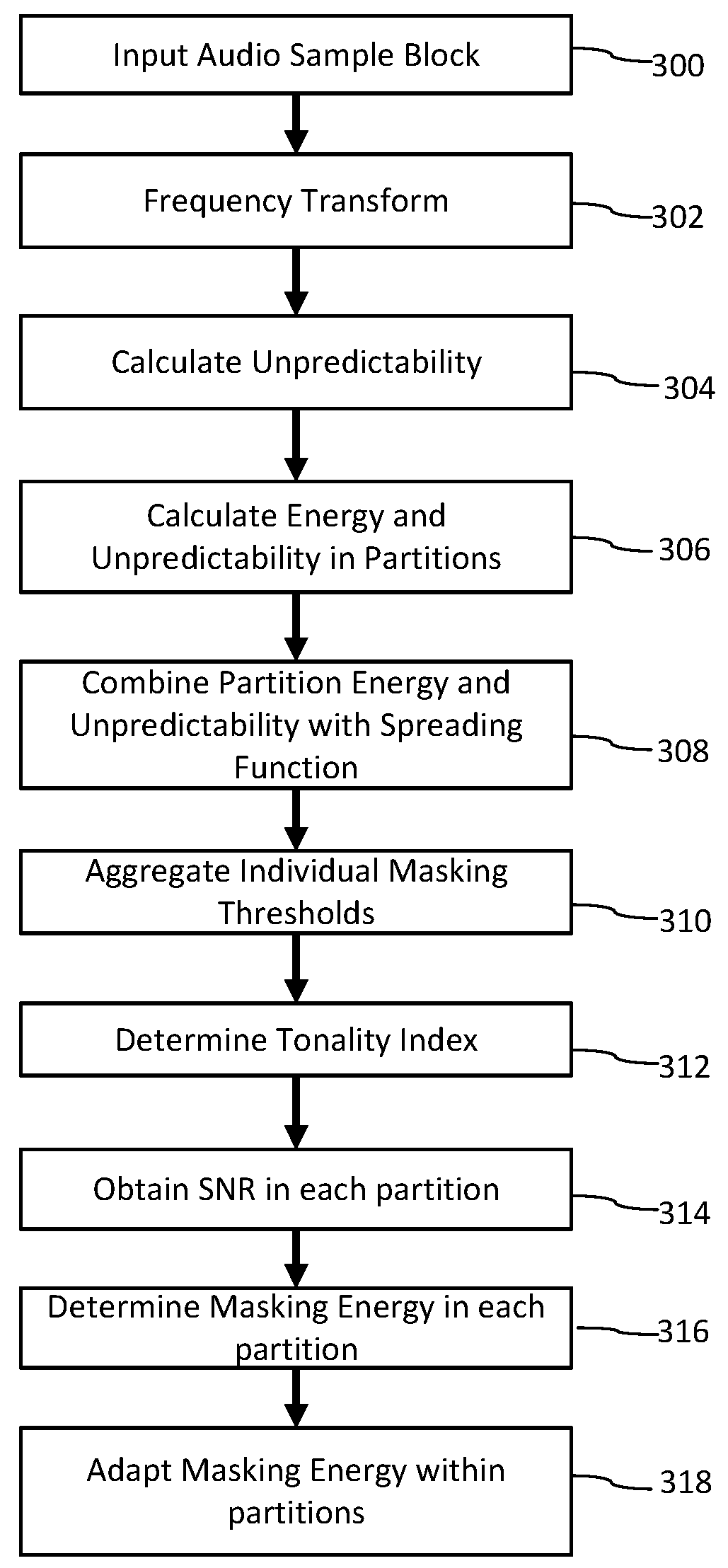
An encoding device which encodes audio signals comprises a spectrum power calculation unit for calculating the power of each spectrum obtained by analyzing the frequency of an input audio signal, a tonality parameter calculation unit for calculating a tonality parameter indicating the pure tone level of the input audio signal in each sub-band, using the result of the calculation when dividing the frequency range of the spectrum of the input audio signal into a plurality of sub-bands, and a dynamic masking threshold calculation unit for calculating a dynamic masking threshold value of the masking energy of the input audio signal, using the calculated tonality parameter.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Audio code rate control method and system
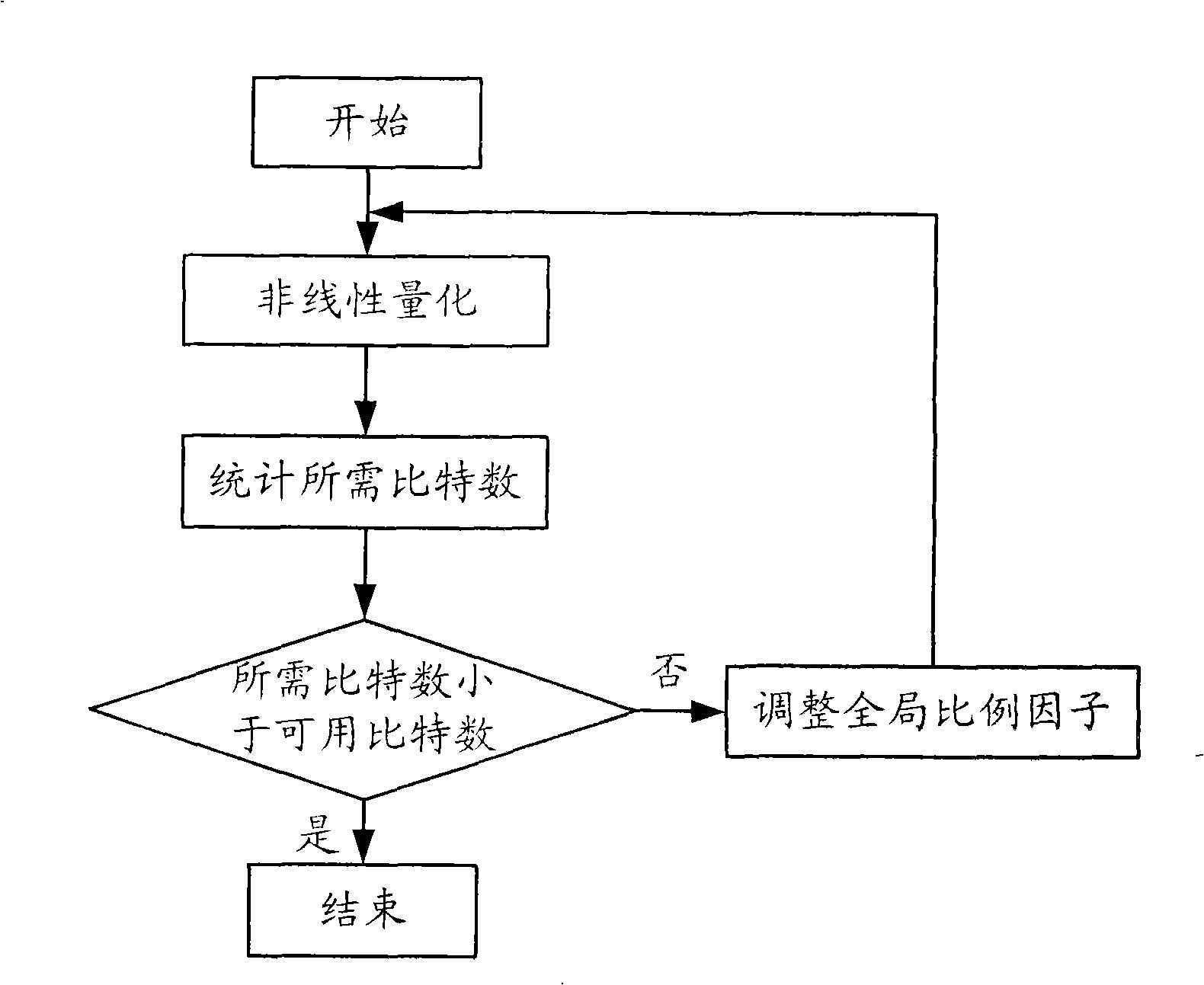
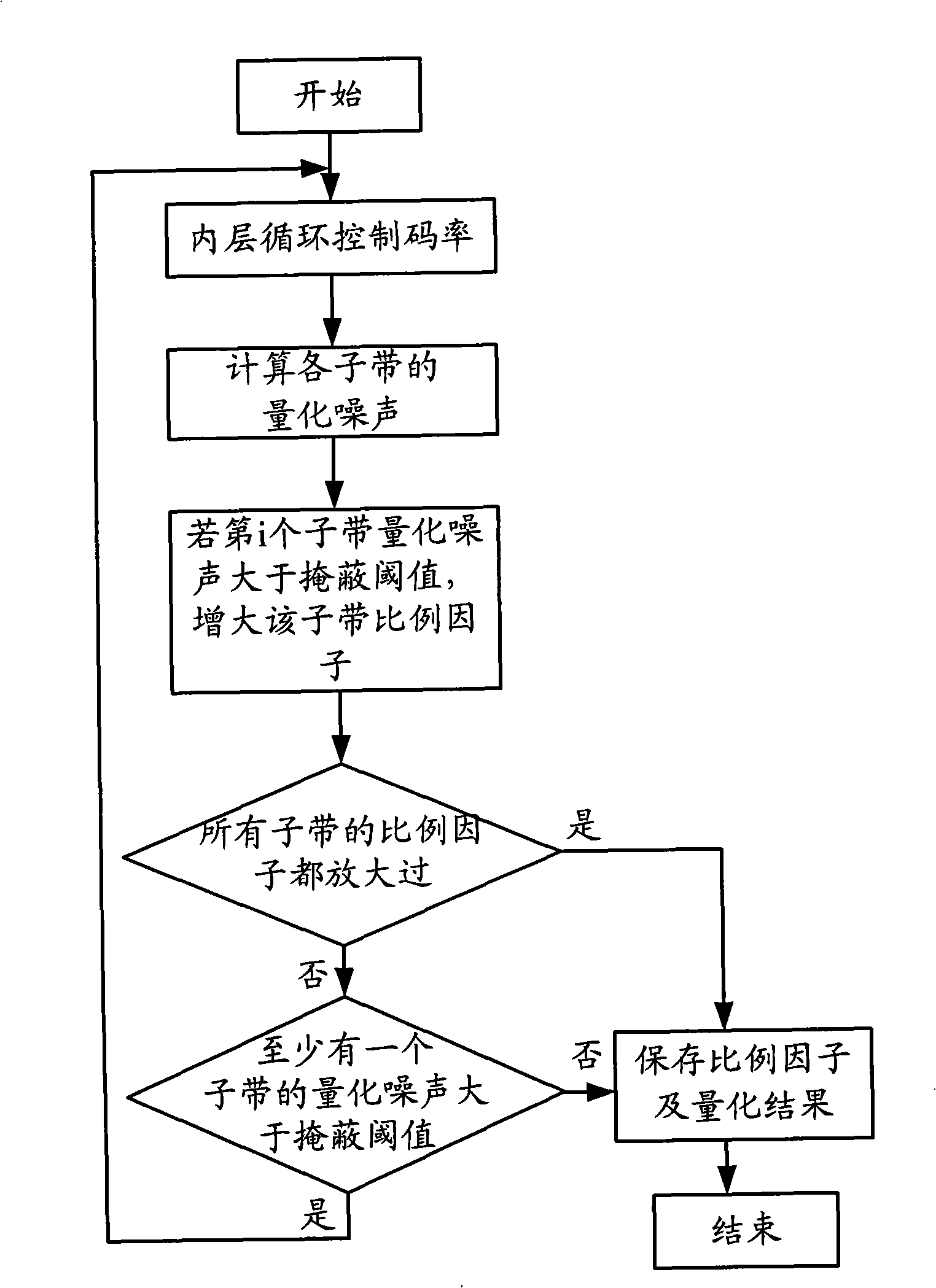
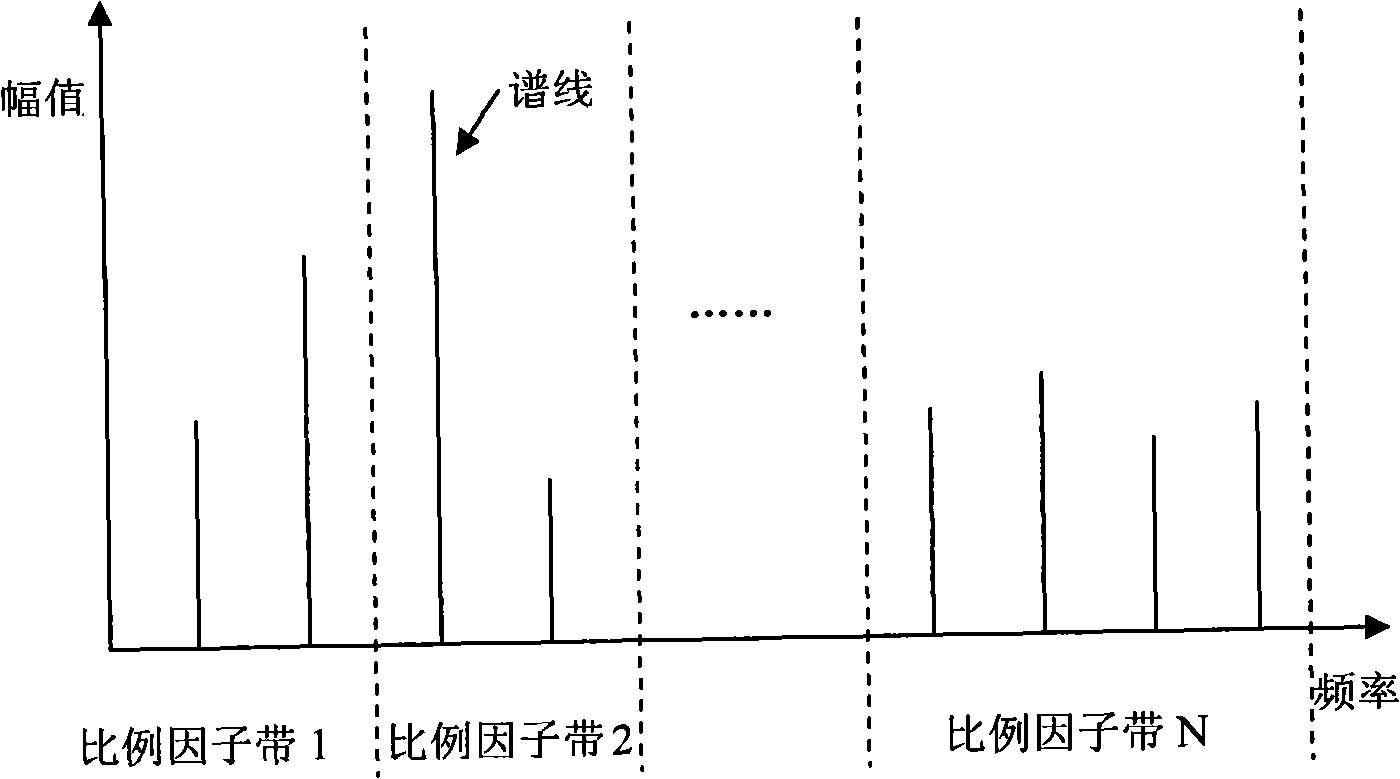
InactiveCN101494054AReduce computational complexityReduce the number of encoded bitsSpeech analysisSound qualityMasking threshold
The embodiment of the invention discloses an audio bit rate control method and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps as follows: a sub band for initial coding is determined according to an available bit number; an initial value of the active proportion factor of the sub band is calculated according to the masking threshold value of the sub band; the active proportion factor is adjusted according to the initial value of the active proportion factor of the sub band so as to cause the quantization noise of a sub band frequency-domain coefficient to be smaller than the masking threshold value; the sub band is quantized according to the active proportion factor; coding is conducted to the frequency-domain coefficient after quantization and the bit number needed by the coding is determined; when the bit number needed by the coding is larger than the available bit number, the bit number needed by the coding can be adjusted by adjusting the active proportion factor step by step so as to cause the bit number for coding to be smaller than the available bit number. The method and the system thereof can keep good sound quality on the basis of lowering the algorithm complexity.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Digital deaf-aid frequency response compensation method based on mask curve
InactiveCN1870135AResolve claritySolve the problem of decreased intelligibilitySpeech analysisDeaf-aid setsMasking thresholdFrequency response
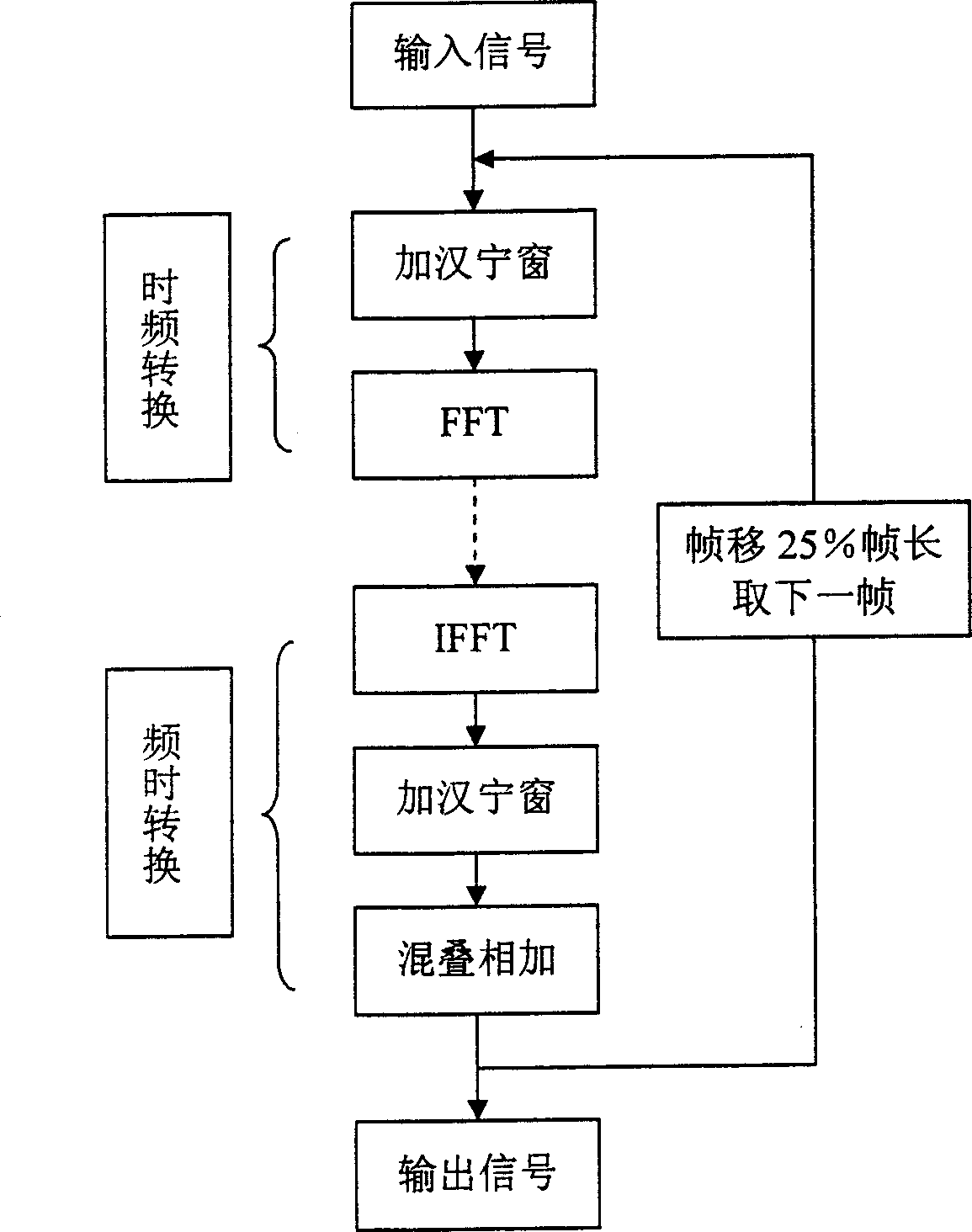
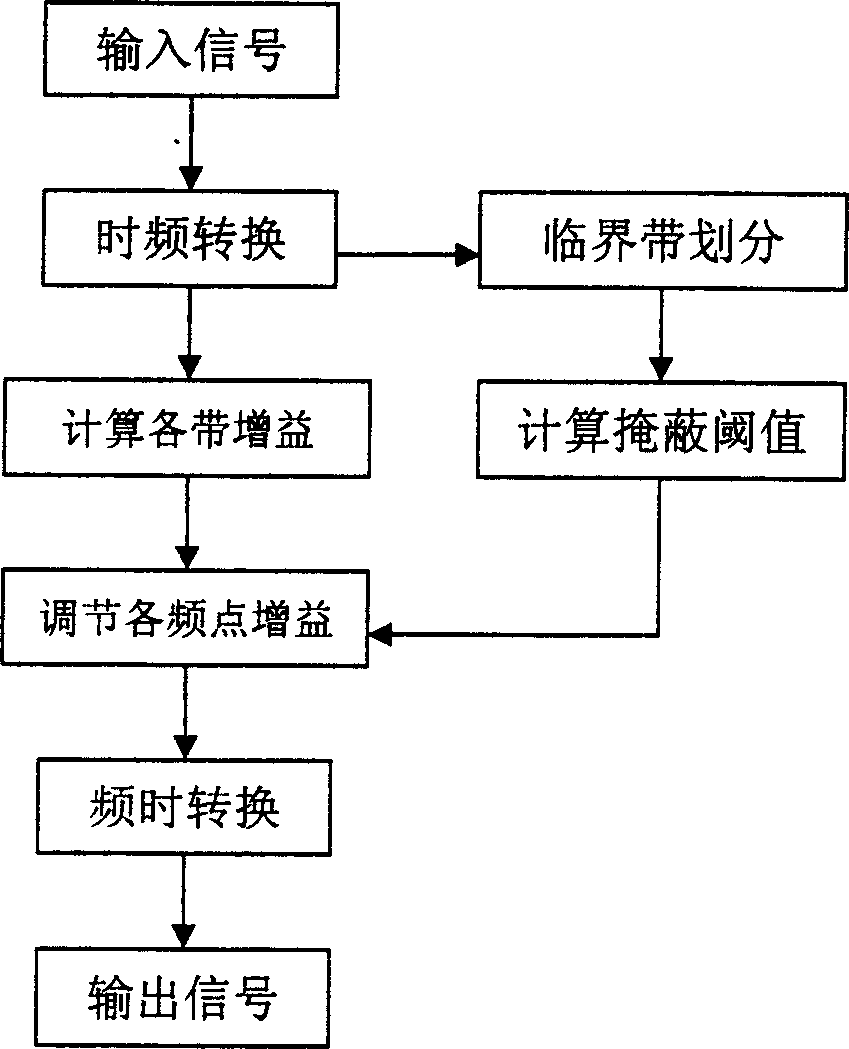
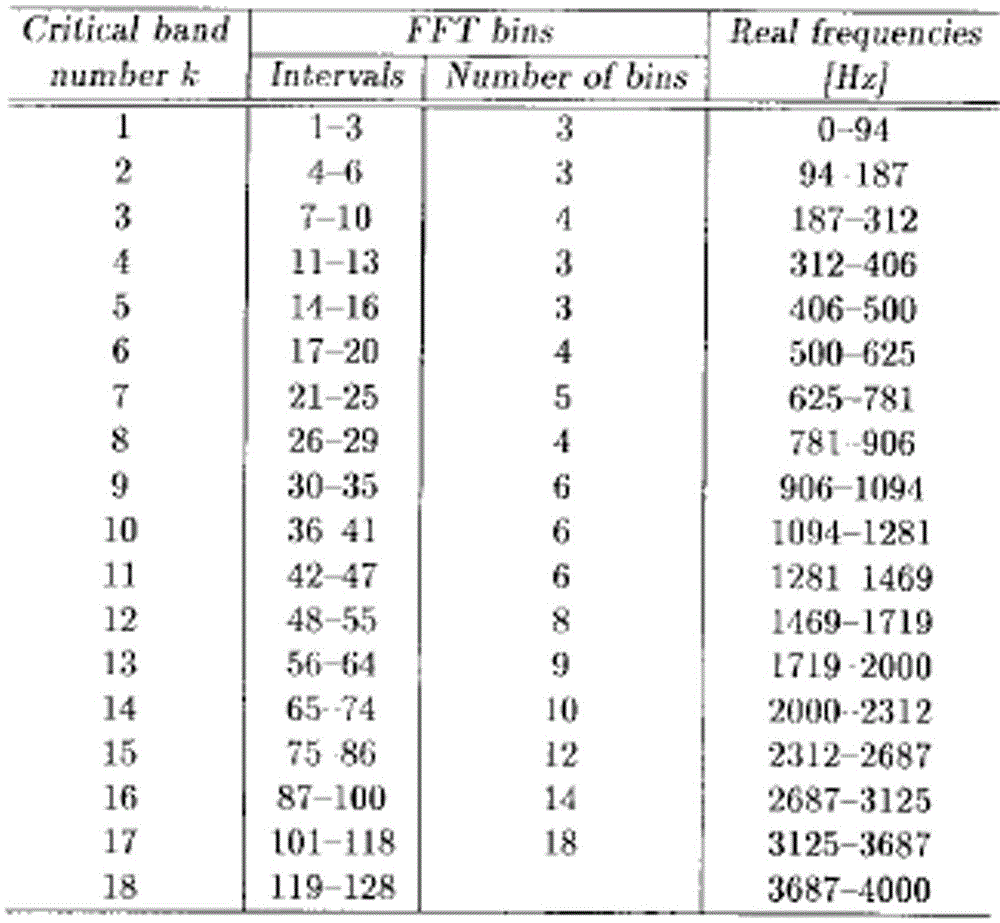
A method for compensating frequency response of digital deaf-aid based on masked curve includes techniques of time frequency domain switch-over, critical band division, masking threshold calculation and frequency response compensation to improve hearing threshold rising phenomenon caused by hearing-masking effect.
Owner:北达万坤(北京)科技发展有限公司
Microphone array postfiltering sound enhancement method based on multi-models and hearing characteristic
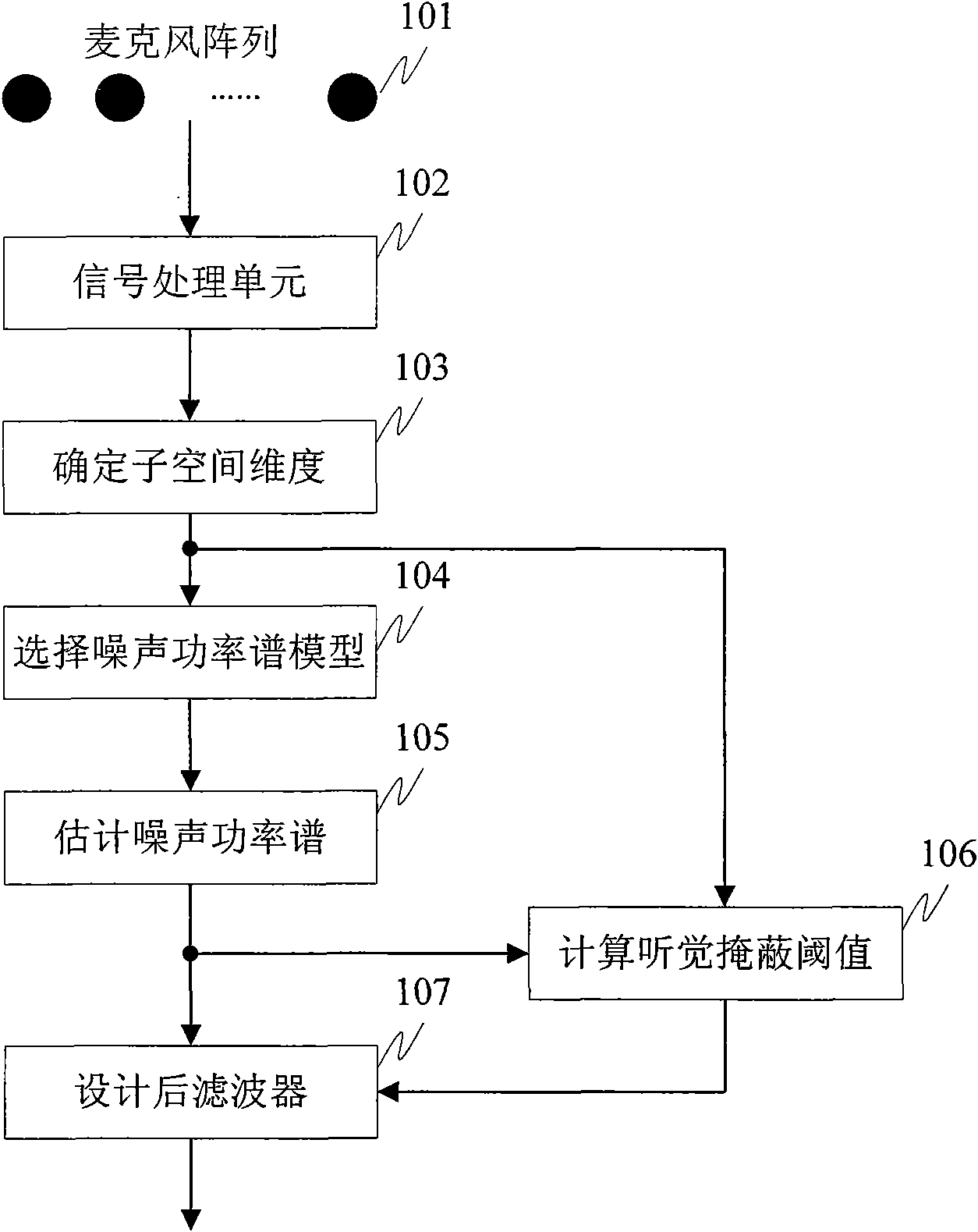
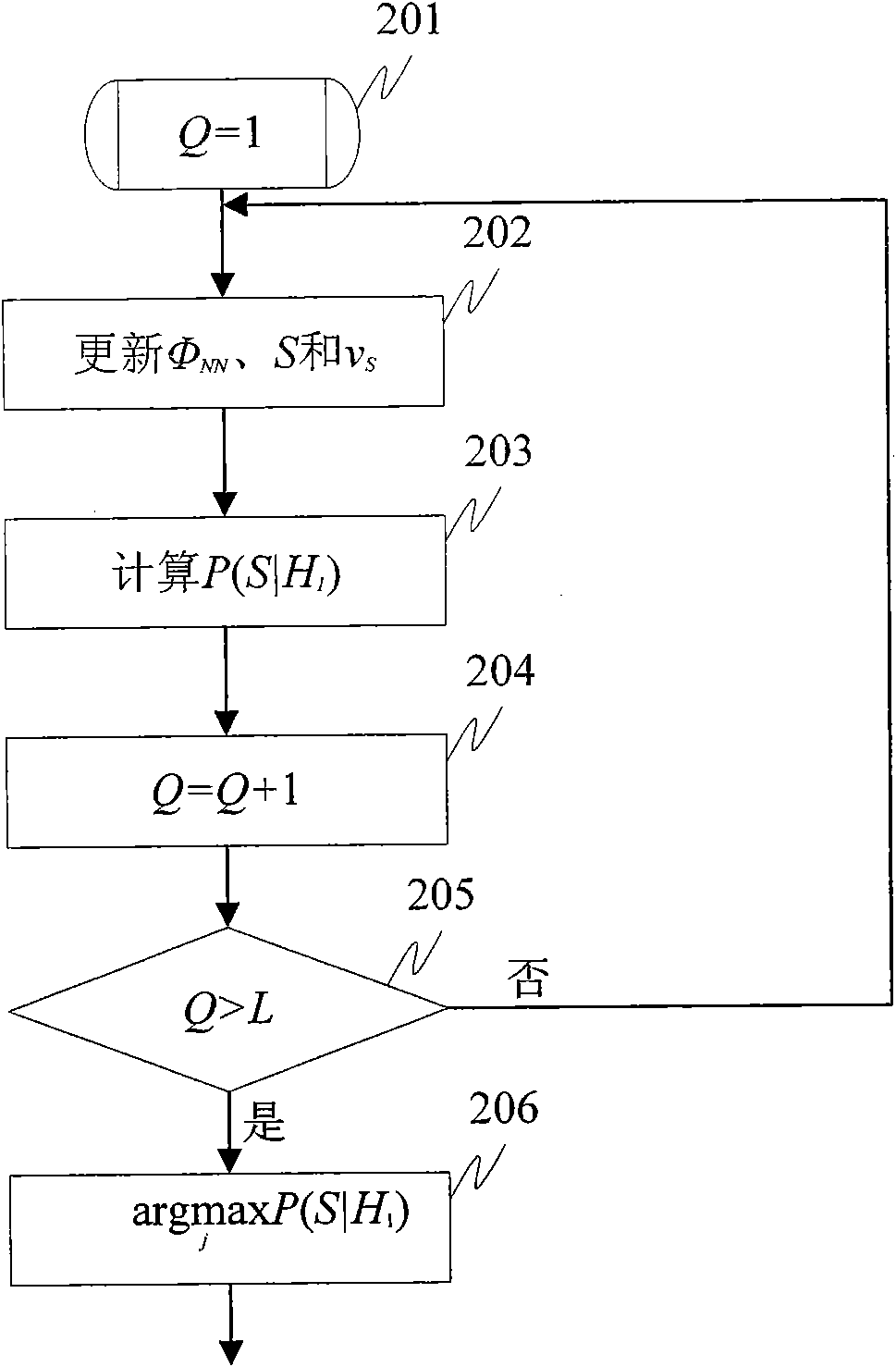
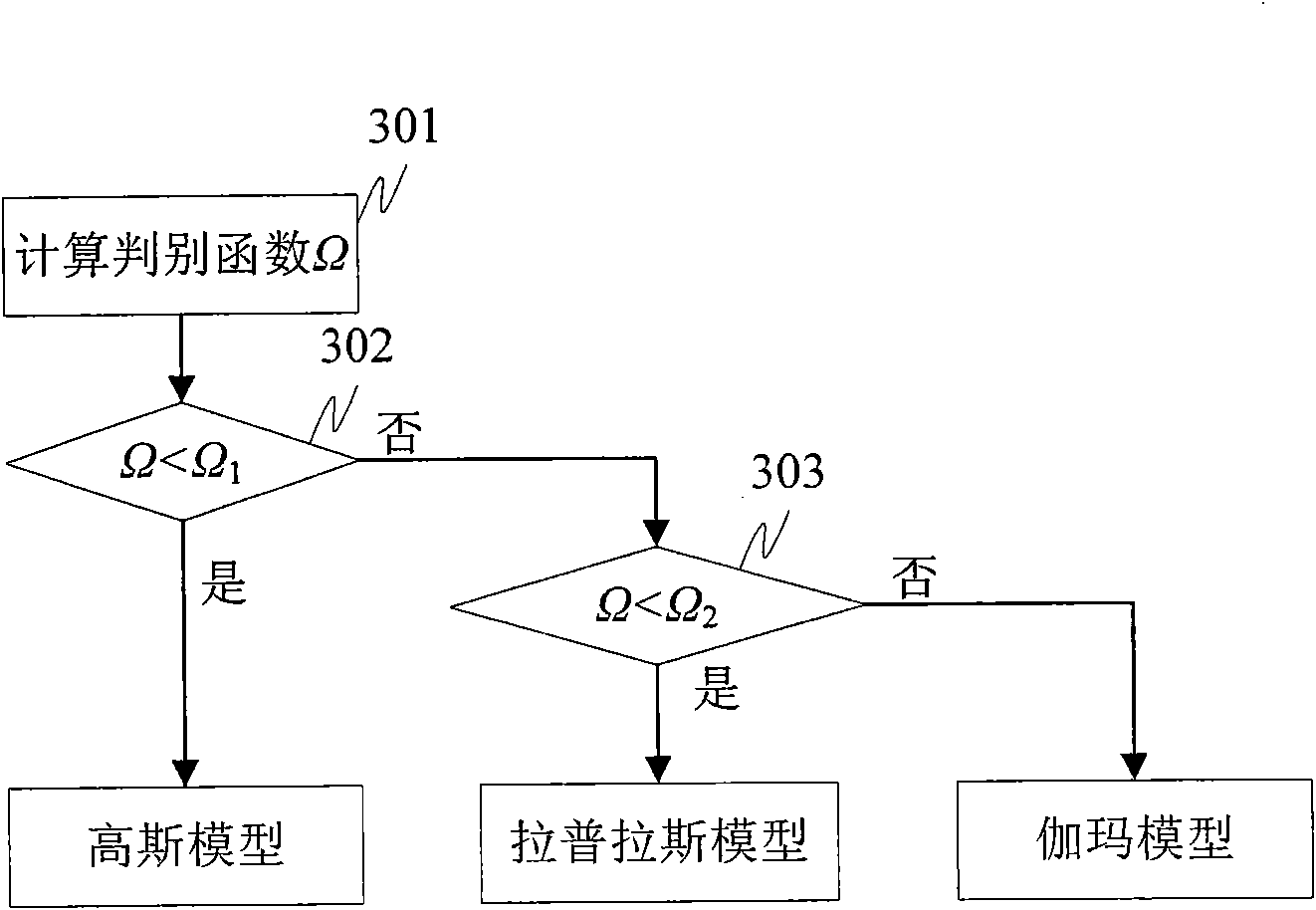
ActiveCN101778322ASmall distortionReduce estimation errorSpeech analysisFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsNoise power spectrumSignal subspace
The invention discloses a microphone array postfiltering sound enhancement method based on multi-models and hearing characteristic, aiming at two important factors influencing the postfiltering sound enhancement performance of a microphone array, i.e. accurate estimation for signal parameters and suitable compromise between increasing noise reduction performance and reducing voice distortion. Thescheme of the invention comprises the following steps of carrying out time domain alignment on signals collected by the microphone array, and carrying out short-time Fourier transform and characteristic value analysis based of power spectrum; determining the dimensionality of a signal subspace through the existence probability of target voice signal in maximation noise-carried voice signals; self-adaptively selecting a distribution model of a noise power spectrum in the noise-carried voice signals; estimating noise power spectrum by utilizing a conditional probability; estimating an auditory masking threshold value based on the signal subspace; and estimating a postfilter by combining Lagrange multipliers according to the auditory sensing characteristics.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
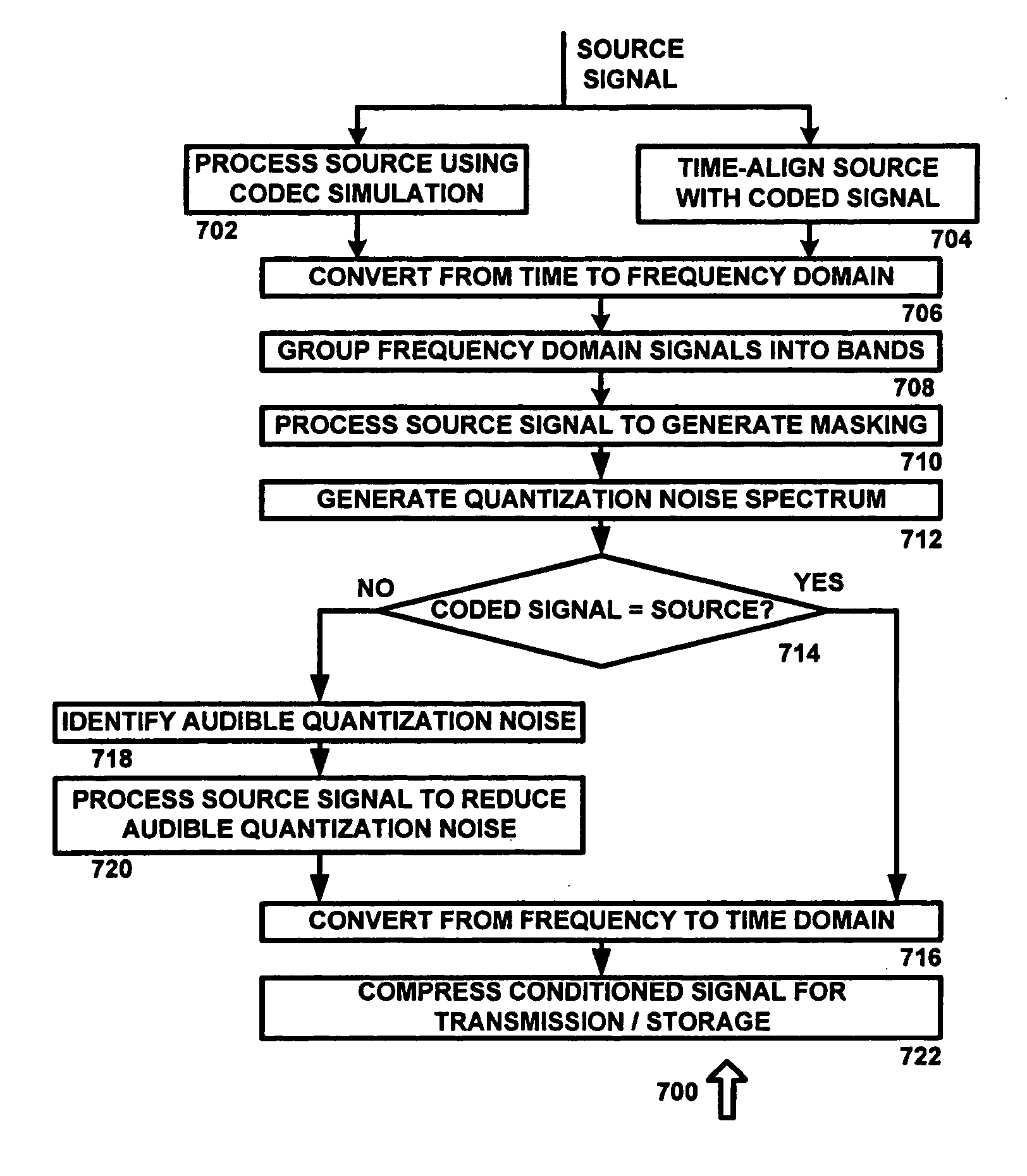
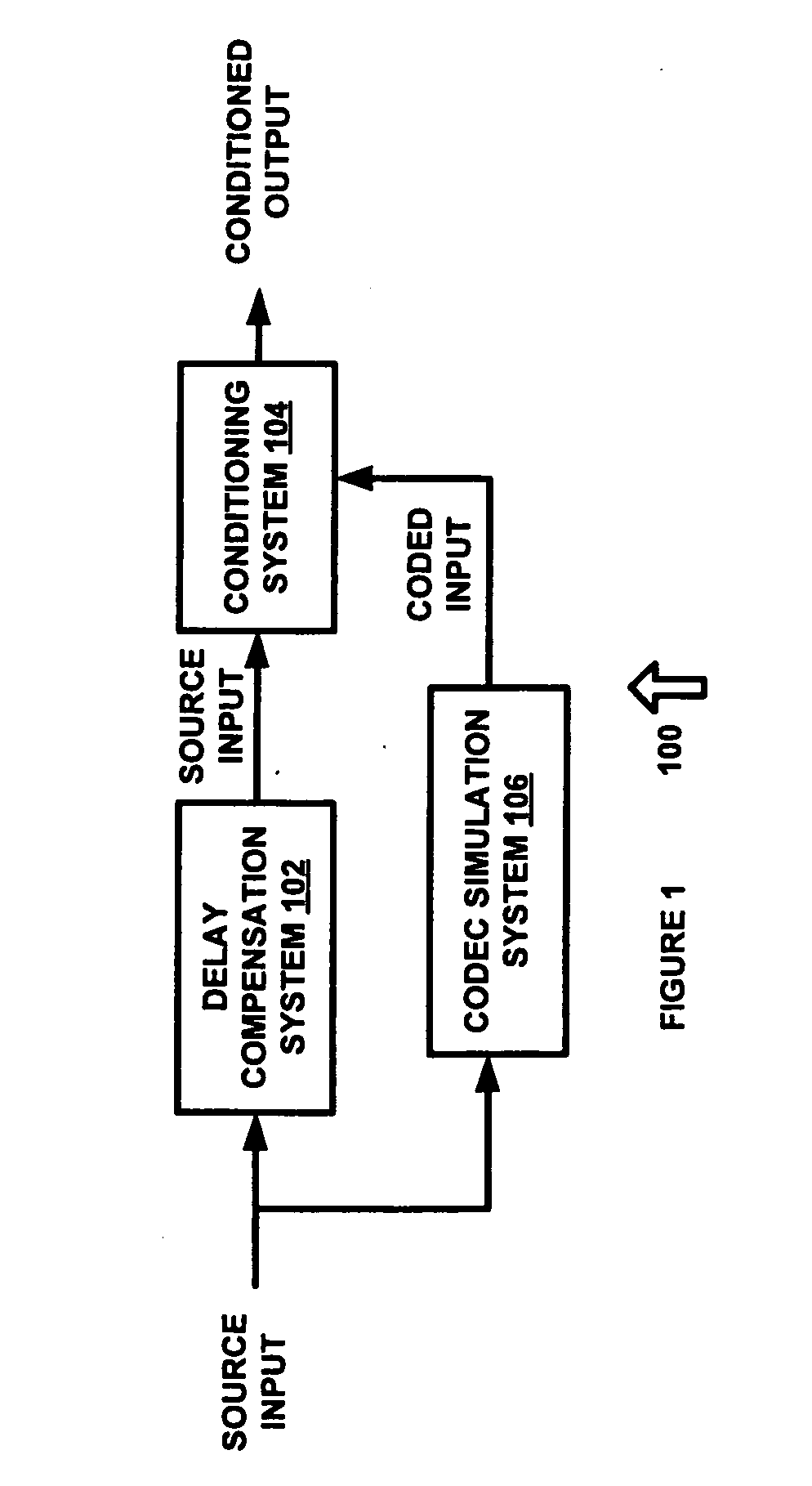
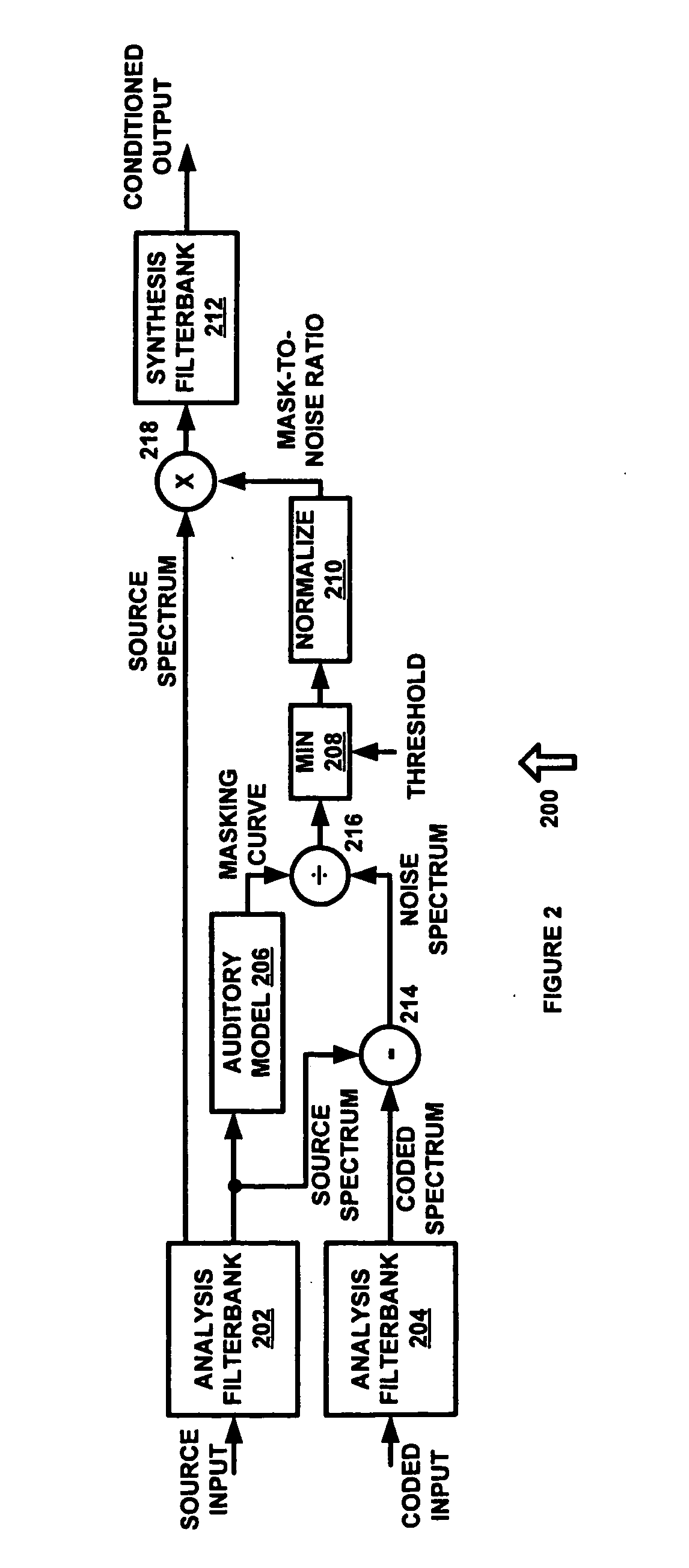
Codec conditioning system and method
An audio processing application is provided which utilizes an audio codec encode / decode simulation system and a psychoacoustic model to estimate audible quantization noise that may occur during lossy audio compression. Mask-to-noise ratio values are computed for a plurality of frequency bands and are used to intelligently process an audio signal specifically for a given audio codec. In one exemplary embodiment, the mask-to-noise ratio values are used to reduce the extent of perceived artifacts for lossy compression, such as by modifying the energy and / or coherence of frequency bands in which quantization noise is estimated to exceed the masking threshold.
Owner:DTS
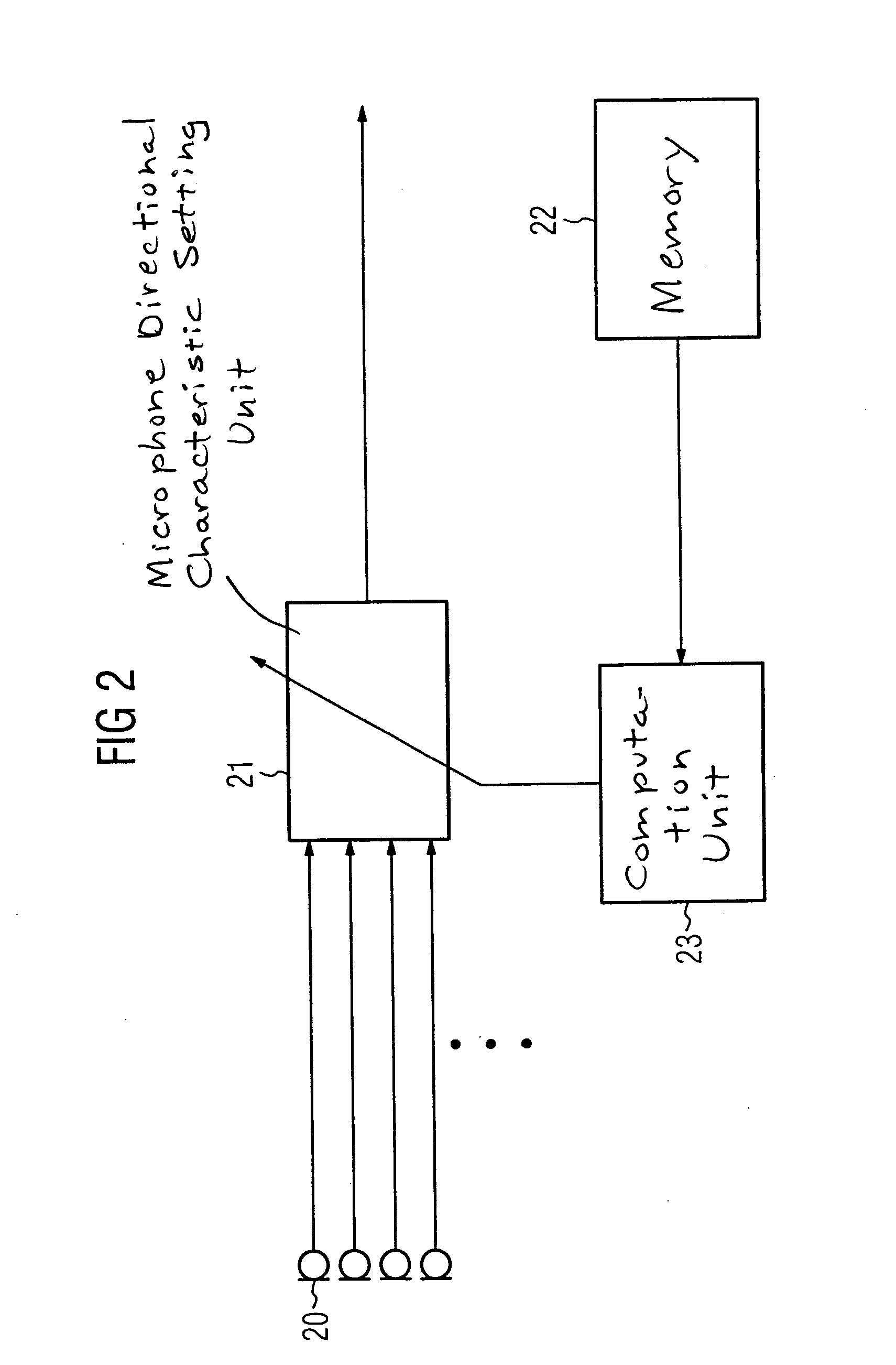
Hearing aid, method, and programmer for adjusting the directional characteristic dependent on the rest hearing threshold or masking threshold
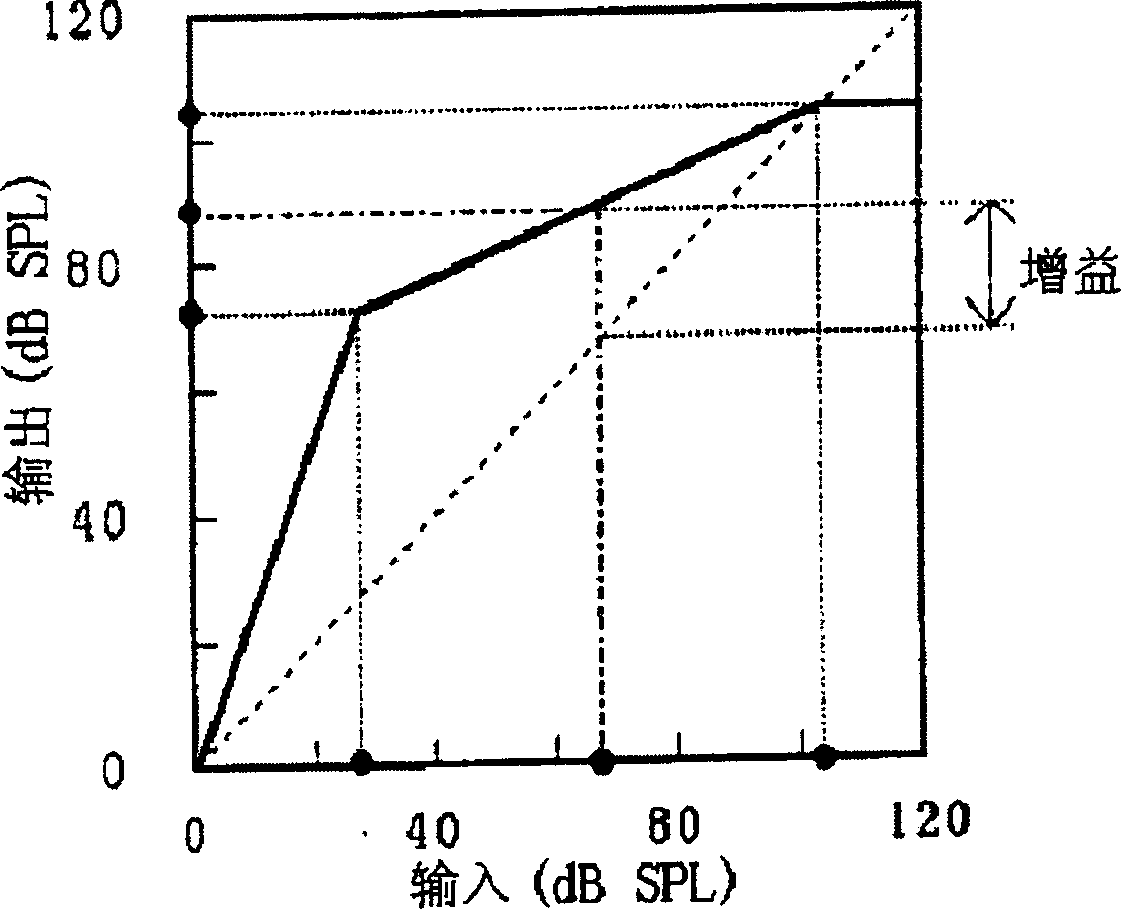
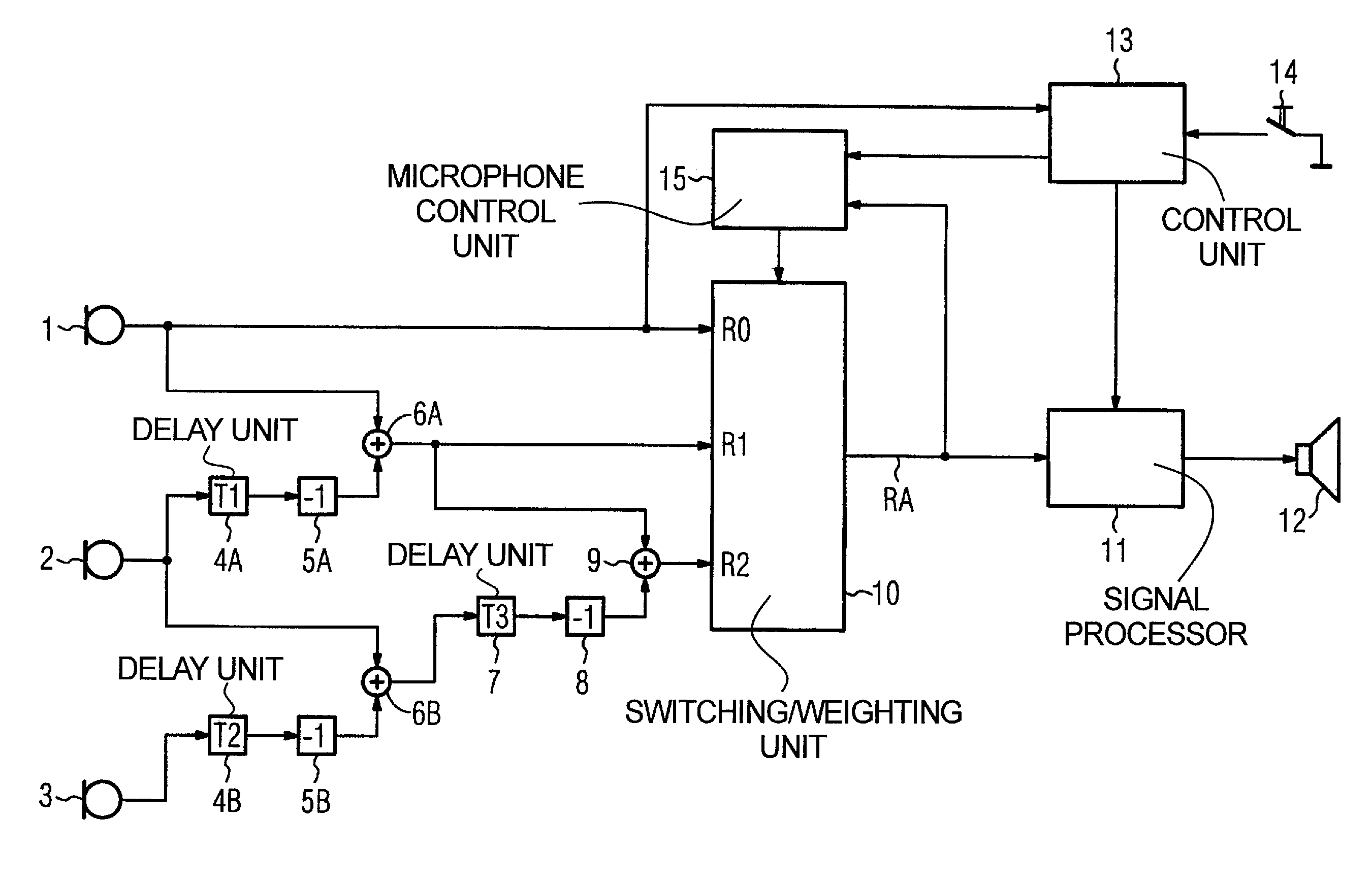
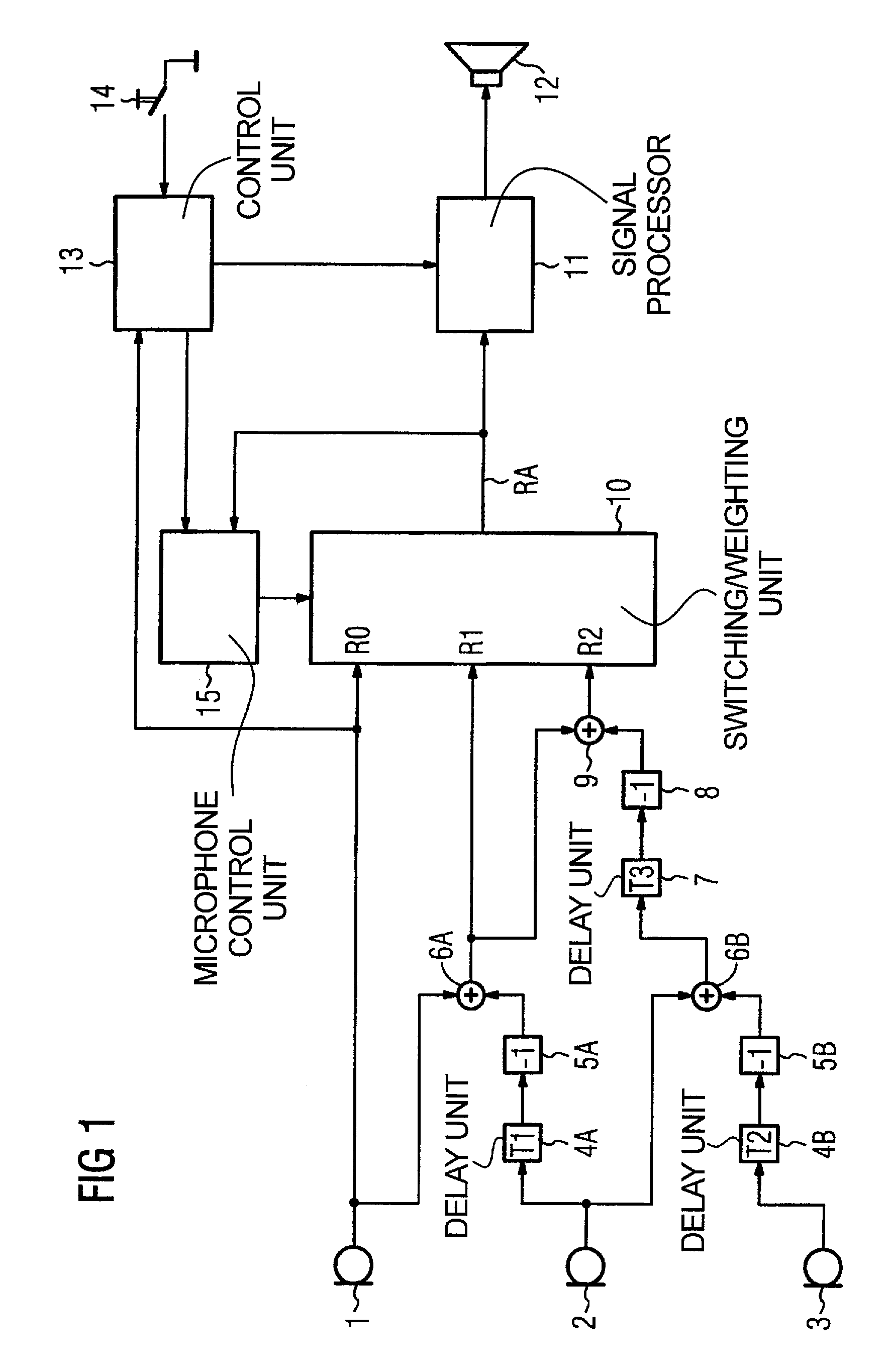
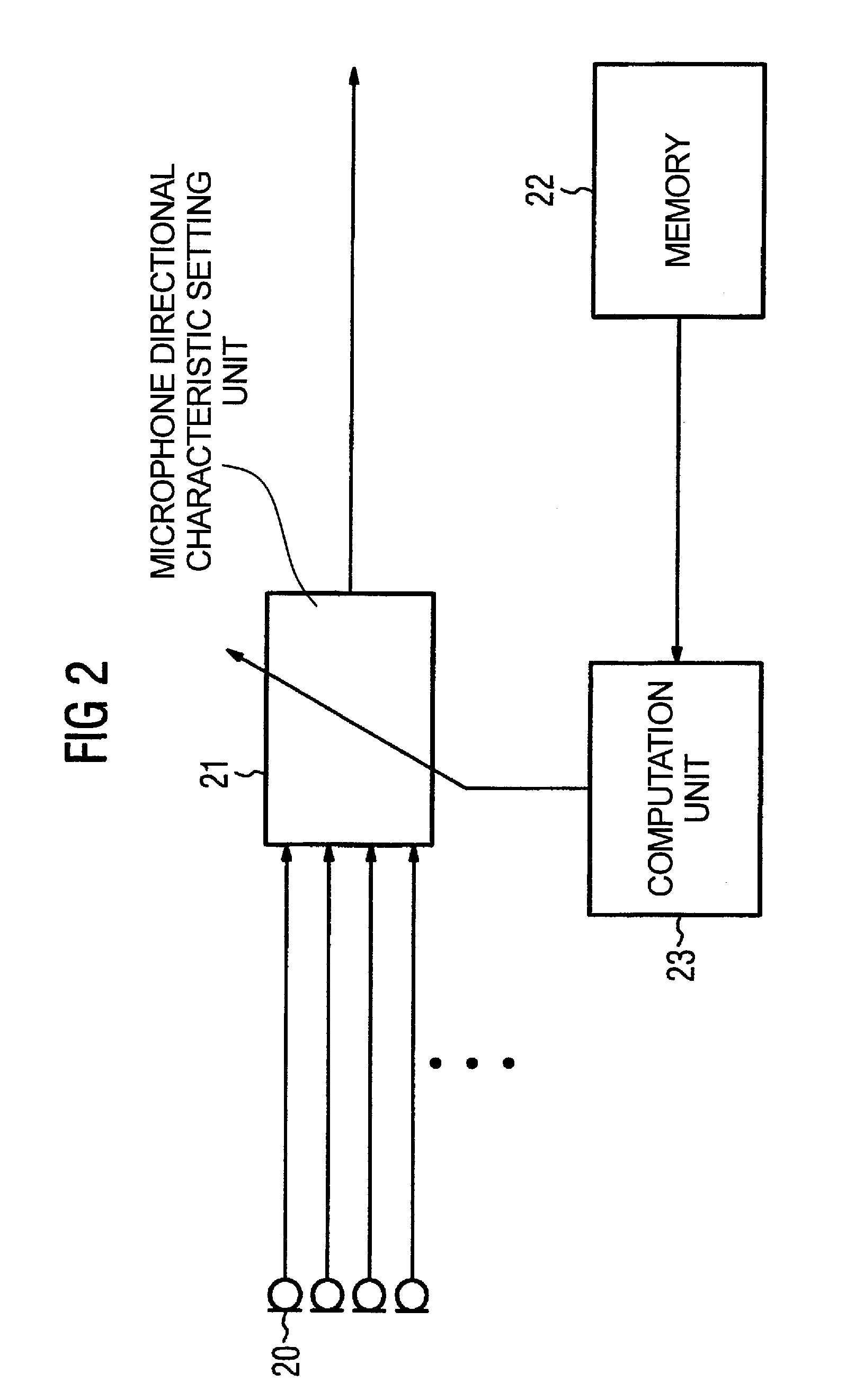
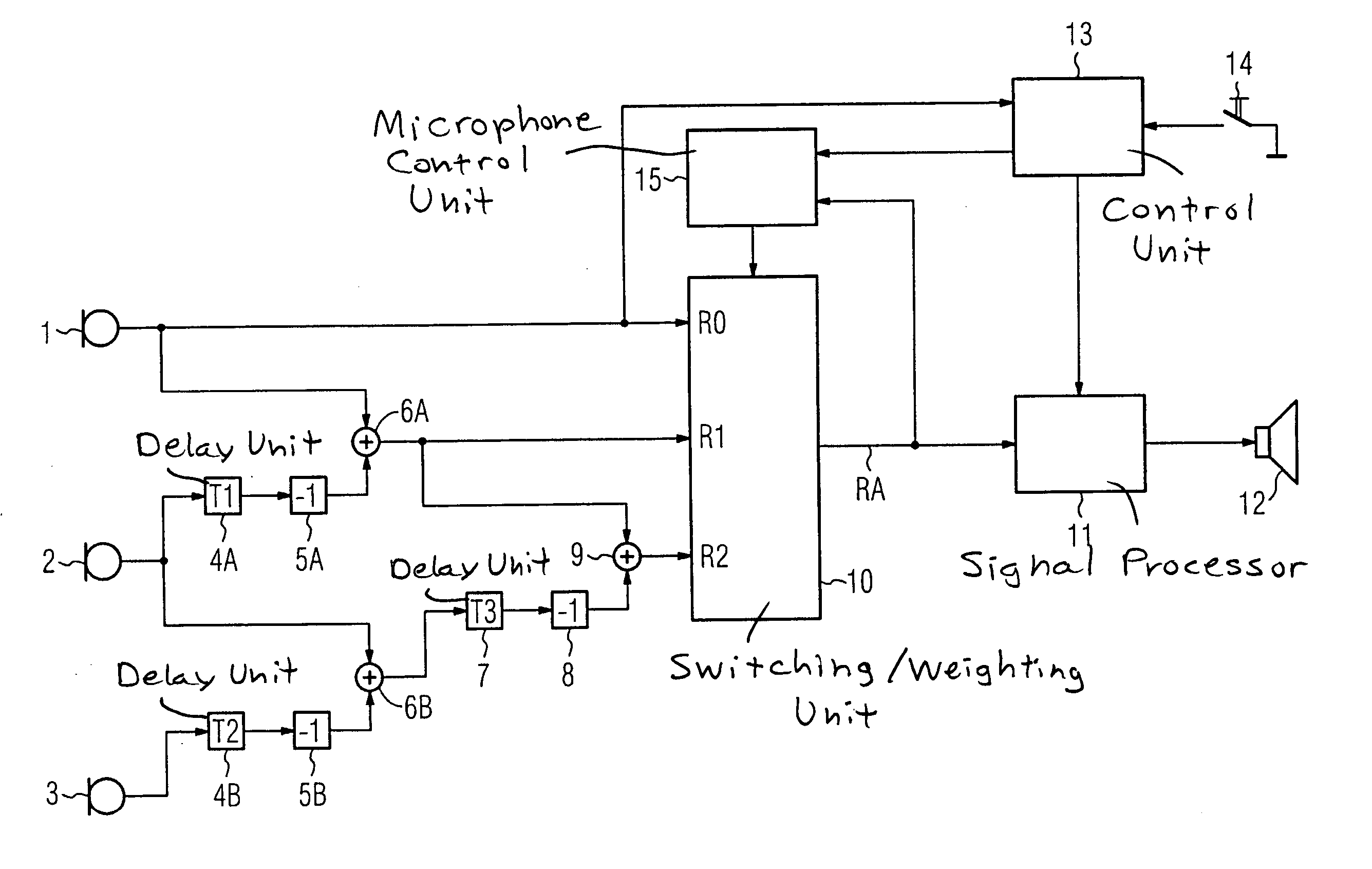
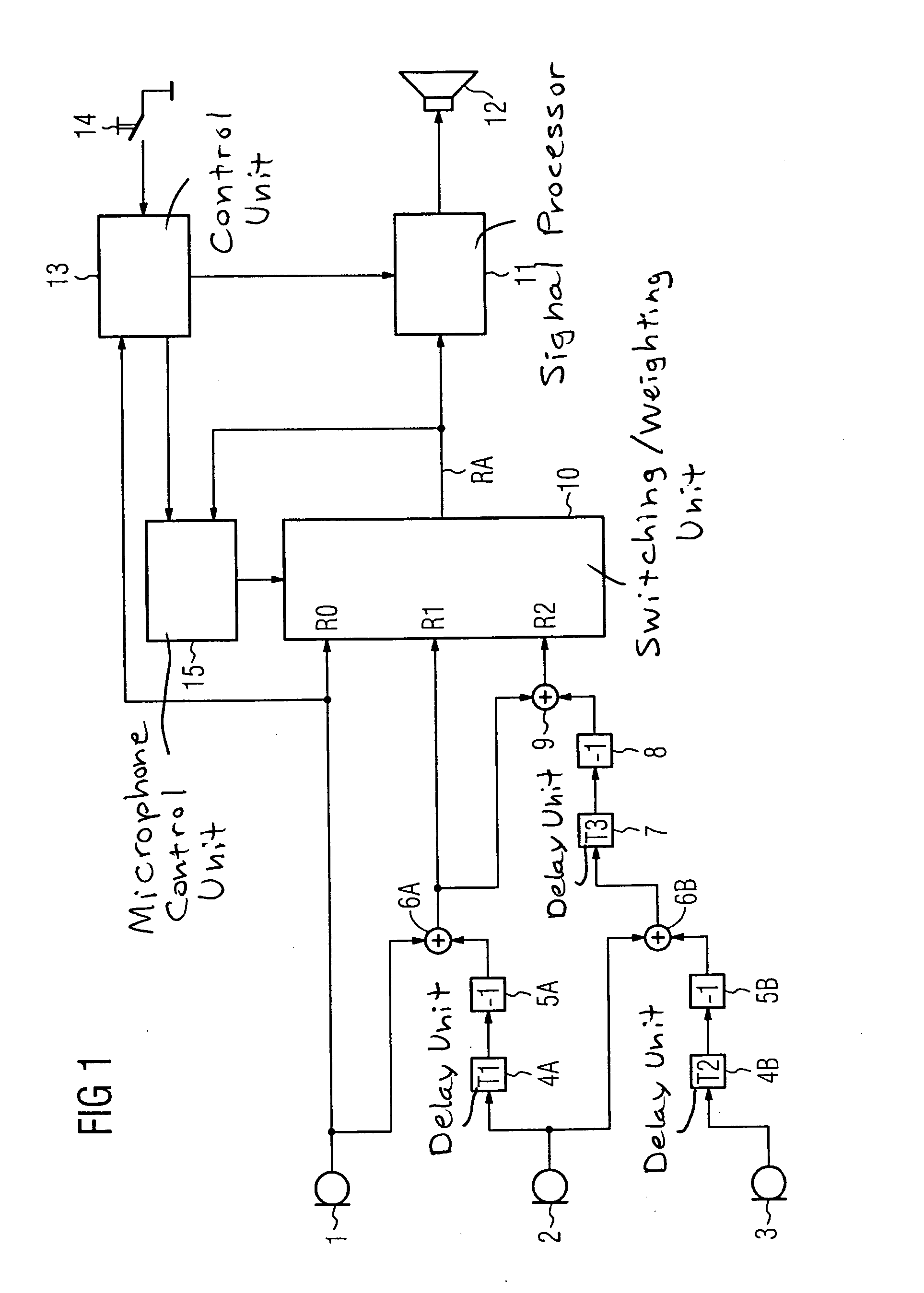
ActiveUS7330557B2Improve sound qualityPrecise positioningTransmission noise suppressionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsHearing aidMasking threshold
For improving the directionality of a hearing aid having a microphone system formed by two or more microphones without in the process creating an increase in the microphone noise that the hearing aid wearer finds to be disturbing, the microphone system is adjusted statically or adaptively taking into account the individual rest hearing threshold and / or taking into account the individual masking threshold for the microphone noise that is produced by the microphone system. The greatest possible extent of directionality thus can be allowed, without the hearing aid wearer in the process finding the microphone noise that is produced by the microphone system to be disturbing.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD +1
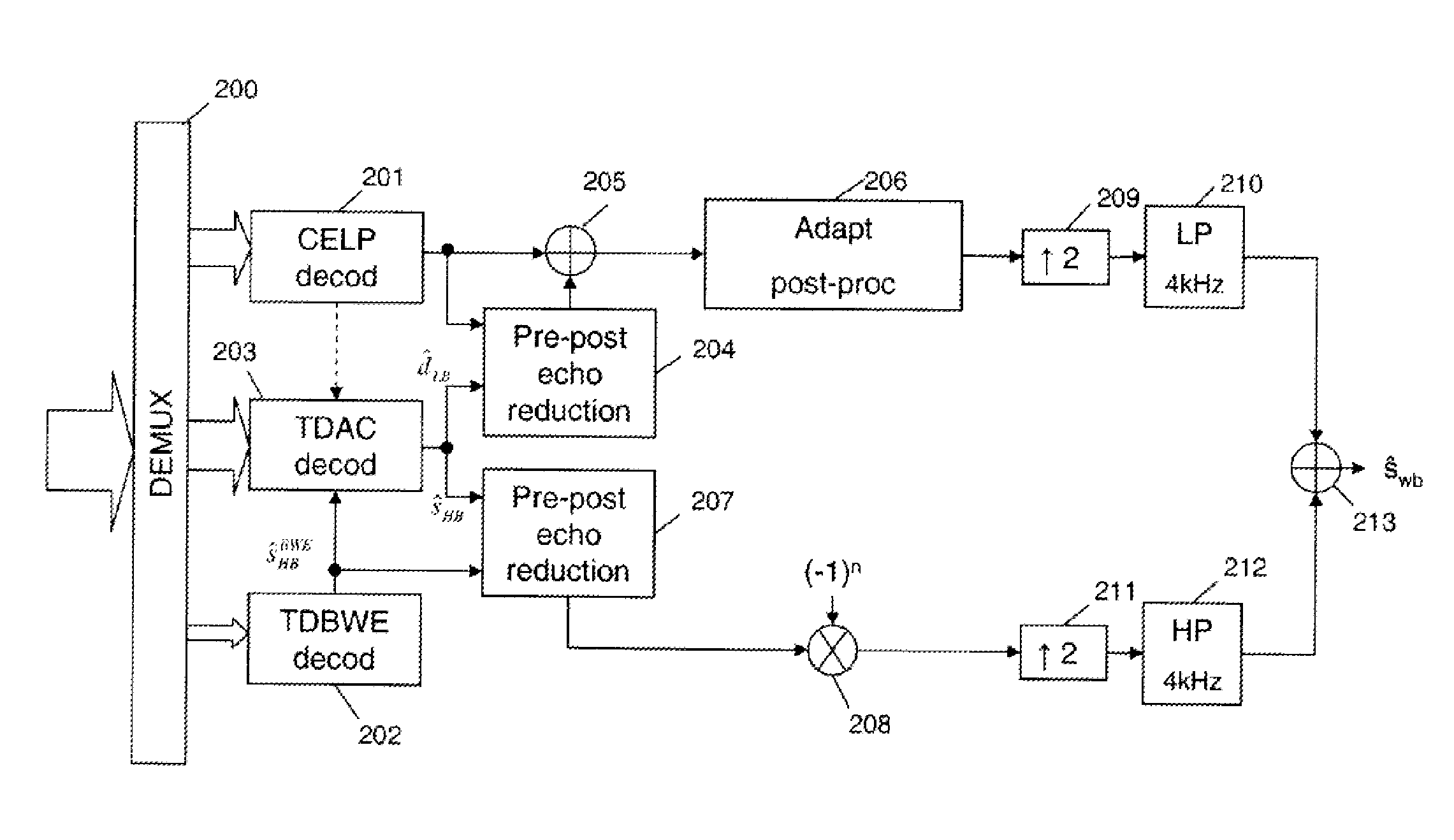
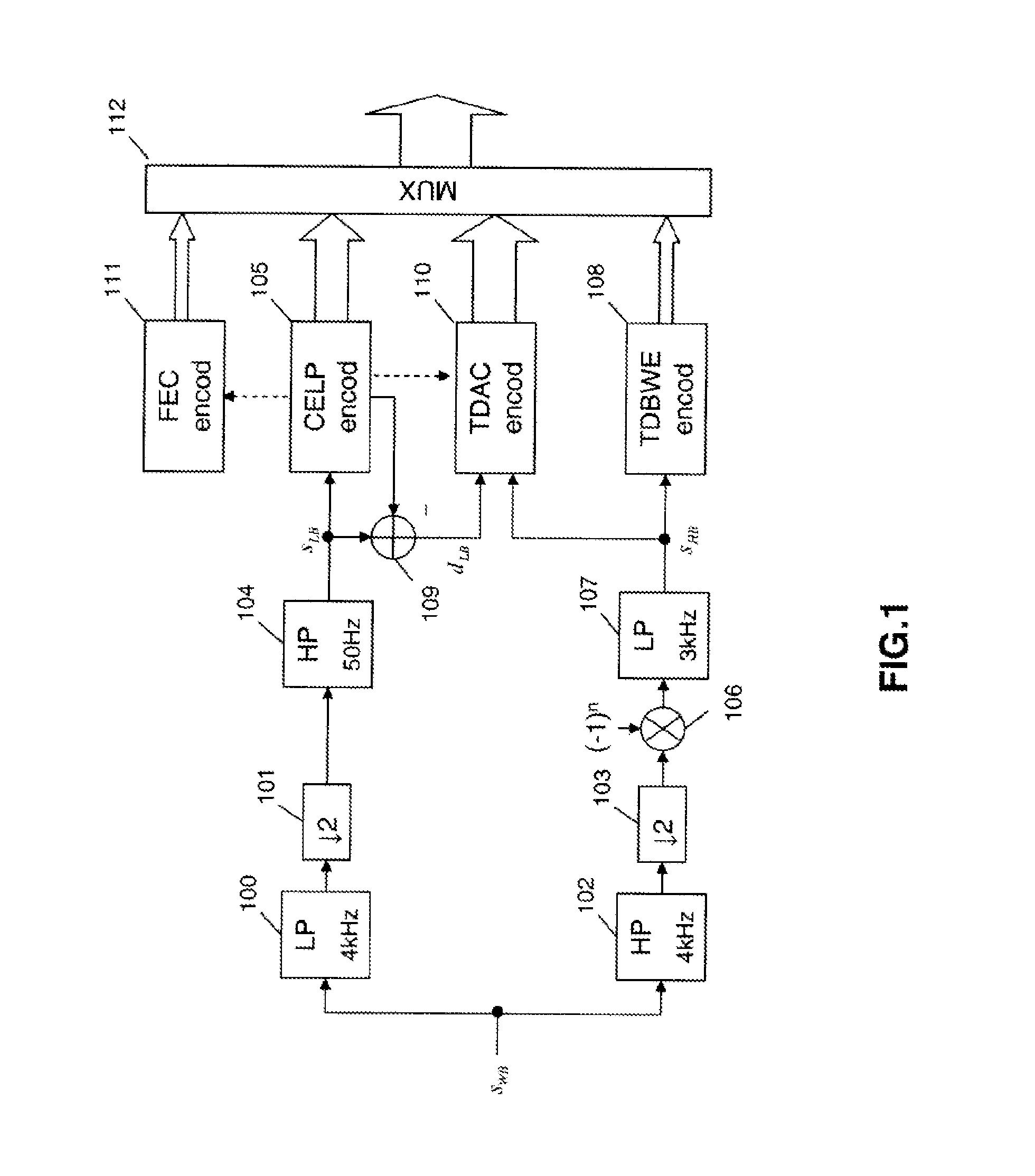
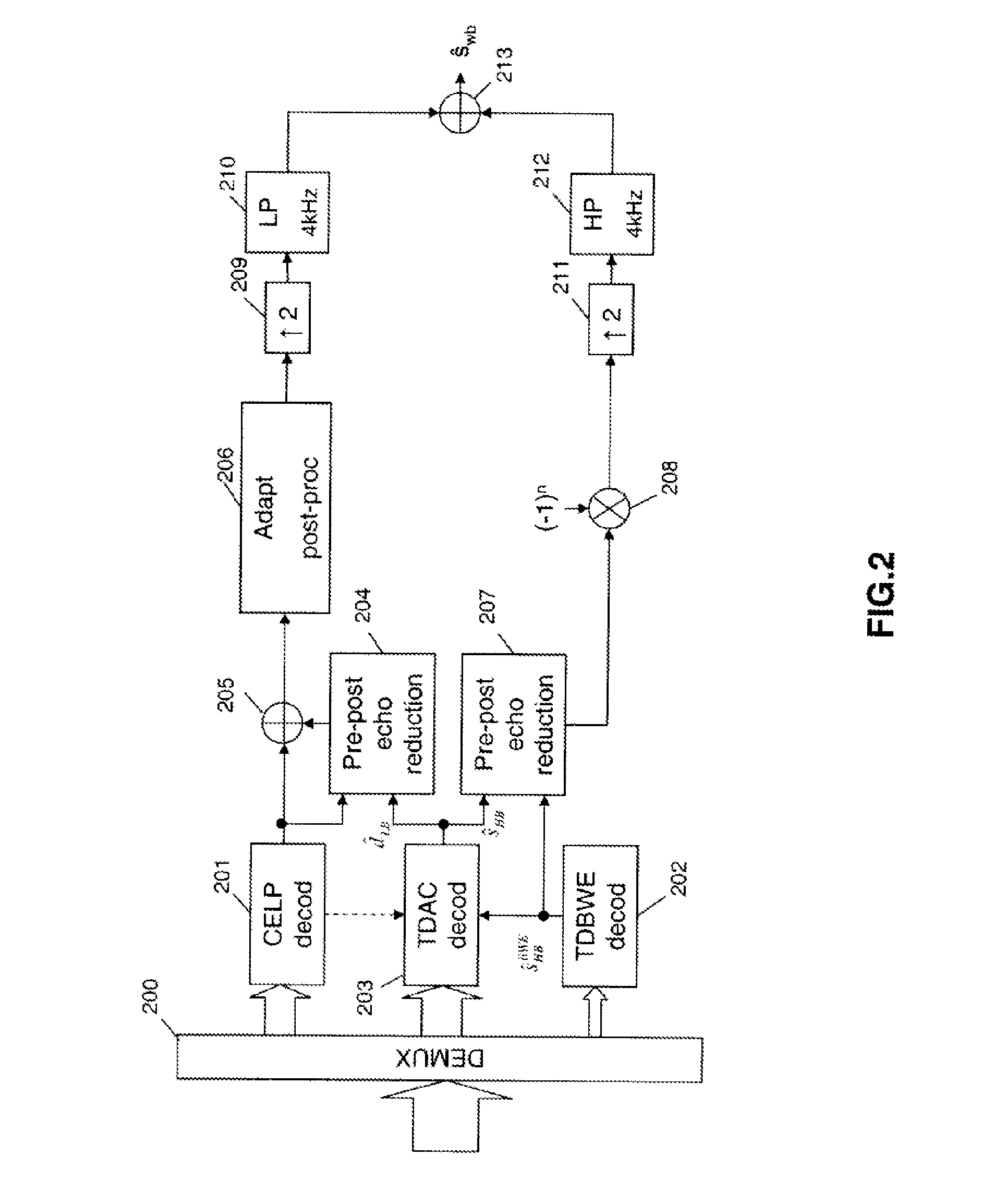
Coding/decoding of digital audio signals
ActiveUS8543389B2Good conditionImprove audio qualitySpeech analysisNatural language data processingMasking thresholdPerceptual weighting
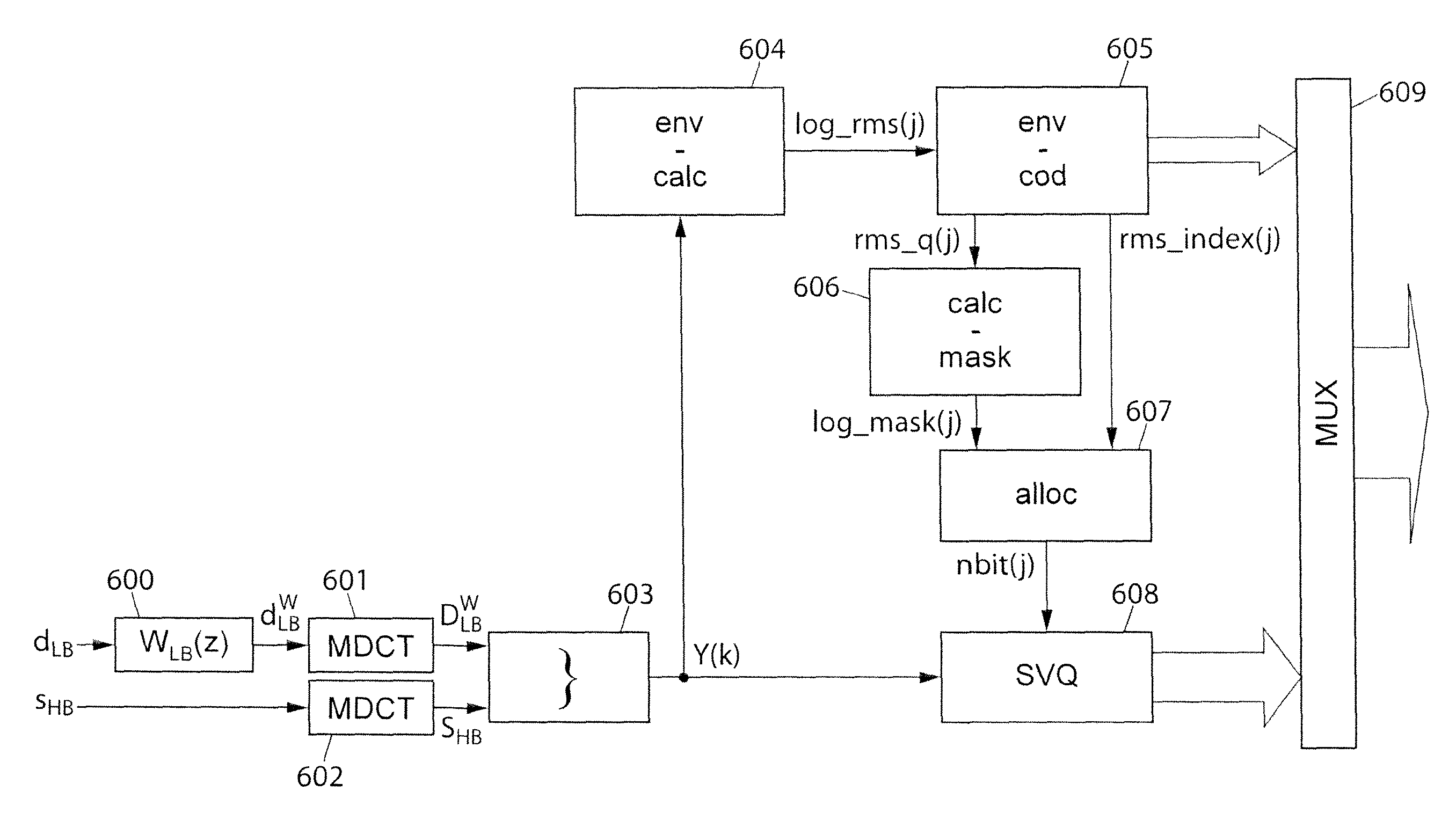
The invention relates to the coding / decoding of a signal into several sub-bands, in which at least a first and a second sub-bands which are adjacent are transform coded (601, 602). In particular, in order to apply a perceptual weighting, in the transformed domain, to at least the second sub-band, the method comprises:—determining at least one frequency masking threshold (606) to be applied on the second sub-band; and normalizing said masking threshold in order to provide a spectral continuity between the above-mentioned first and second sub-bands. An advantageous application of the invention involves a perceptual weighting of the high-frequency band in the TDAC transform coding of a hierarchical encoder according to standard G.729.1.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Human auditory system modeling with masking energy adaptation
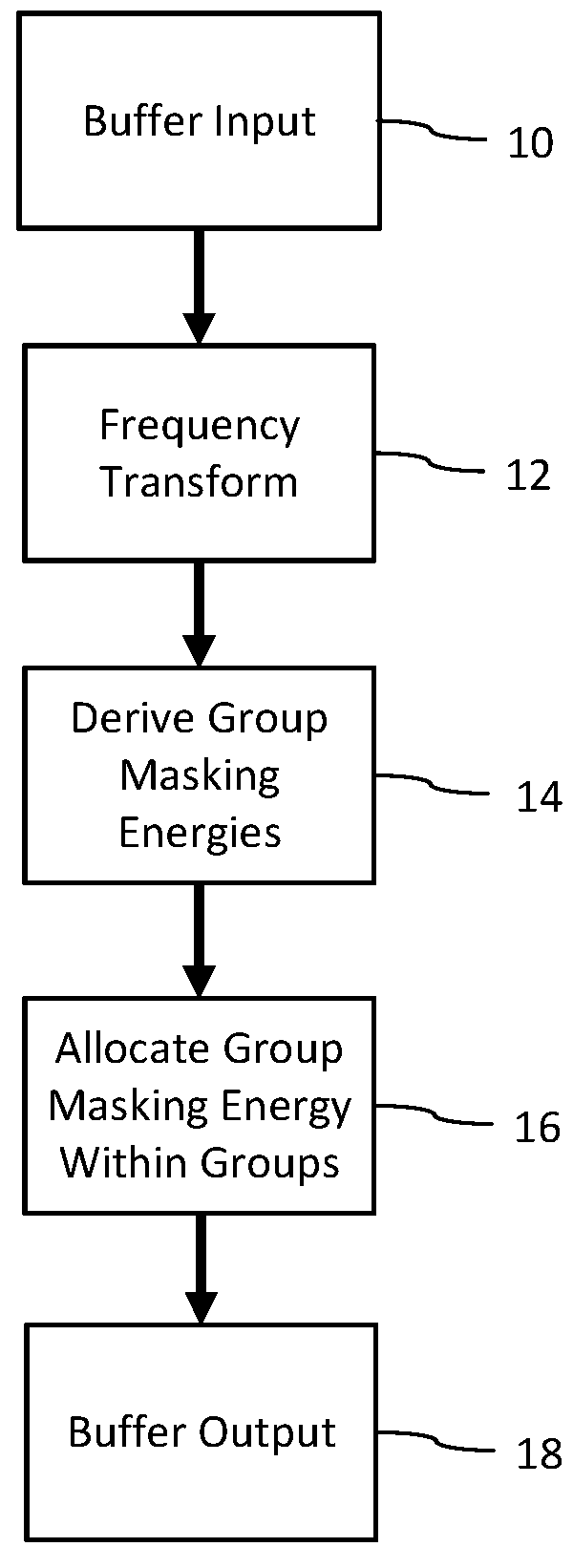
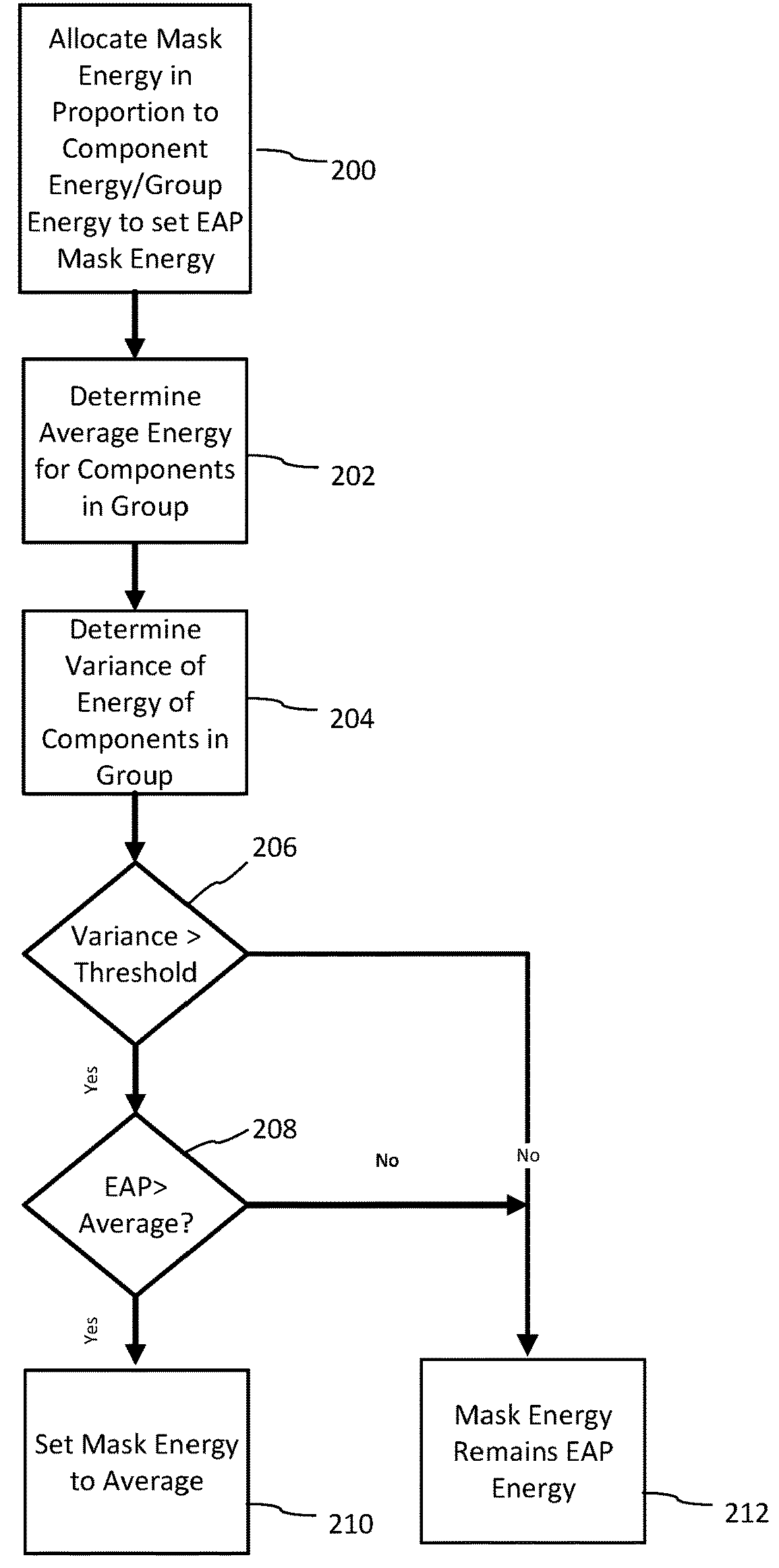
ActiveUS10043527B1Improve performanceEffective meanSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementFrequency spectrumHuman auditory system
A method for generating a psychoacoustic model from an audio signal transforms a block of samples of an audio signal into a frequency spectrum comprising frequency components. From this frequency spectrum, it derives group masking energies. These group masking energies each correspond to a group of neighboring frequency components in the frequency spectrum. For a group of frequency components, the method allocates the group masking energy to the frequency components in the group in proportion to energy of the frequency components within the group to provide adapted mask energies for the frequency components within the group, the adapted mask energies providing masking thresholds for the psychoacoustic model of the audio signal.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Hearing aid, method, and programmer for adjusting the directional characteristic dependent on the rest hearing threshold or masking threshold
ActiveUS20050008166A1Improve sound qualityPrecise positioningTransmission noise suppressionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringHearing aid
For improving the directionality of a hearing aid having a microphone system formed by two or more microphones without in the process creating an increase in the microphone noise that the hearing aid wearer finds to be disturbing, the microphone system is adjusted statically or adaptively taking into account the individual rest hearing threshold and / or taking into account the individual masking threshold for the microphone noise that is produced by the microphone system. The greatest possible extent of directionality thus can be allowed, without the hearing aid wearer in the process finding the microphone noise that is produced by the microphone system to be disturbing.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD +1
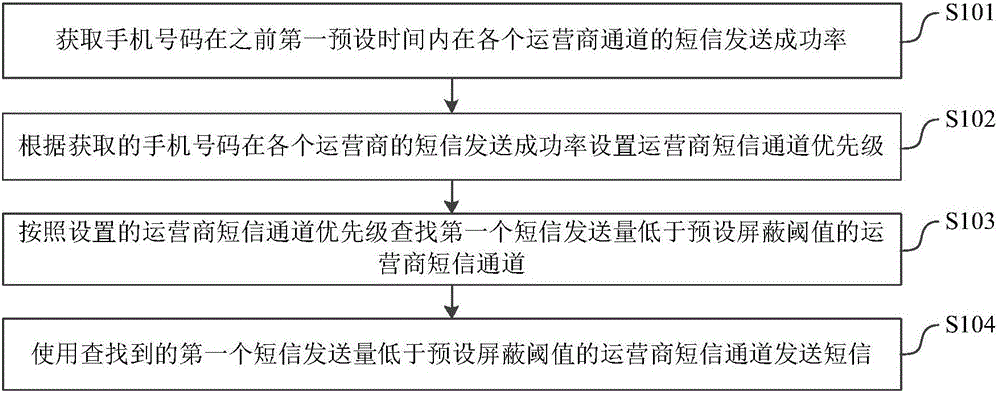
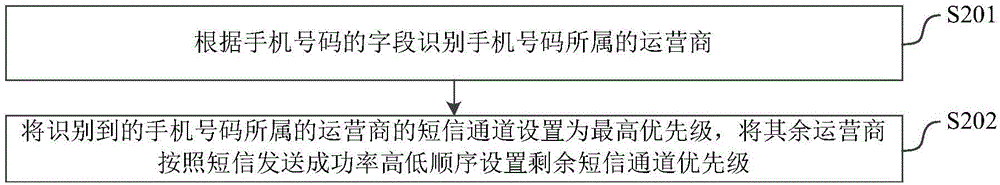
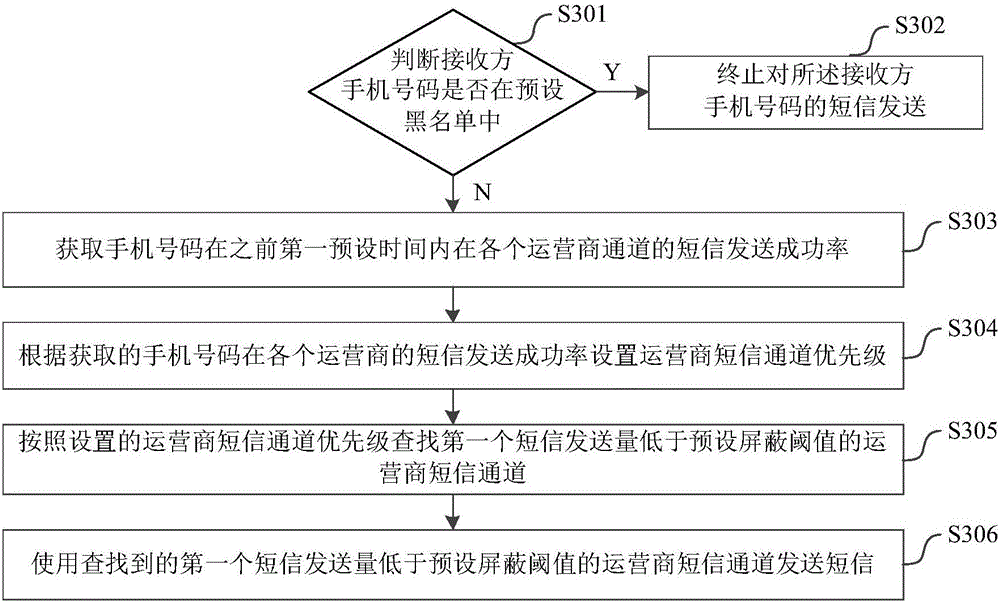
Short message sending method and system
InactiveCN106255080AIssues Affecting SendingLow failure rateMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsFailure rateMobile Telephone Number
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, and discloses a short message sending method and system. The short message sending method comprises the steps that the short message sending success rate of a mobile phone number in each operator channel in a first preset time before is acquired; the operator short message channel priority is set according to the short message sending success rate of the mobile phone number in each operator; according to the set operator short message channel priority, an operator short message channel whose first short message sending volume is lower than a preset mask threshold is found; and the found operator short message channel whose first short message sending volume is lower than the preset mask threshold is used to send a short message. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the failure rate of short message sending is reduced, and the success rate and the work efficiency of short message sending are improved.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Audio signal processing method, system and audio signal transmitting/receiving device
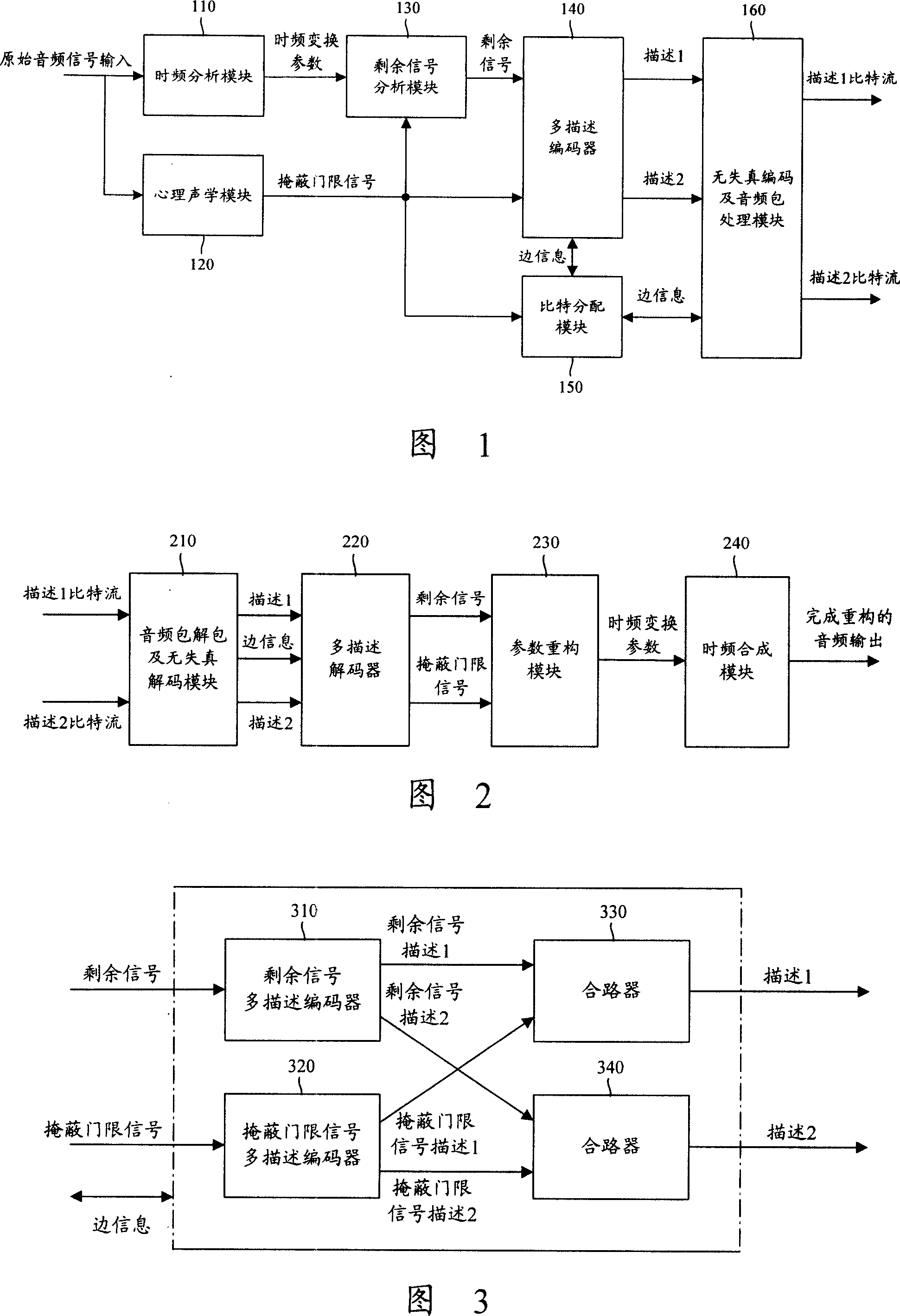
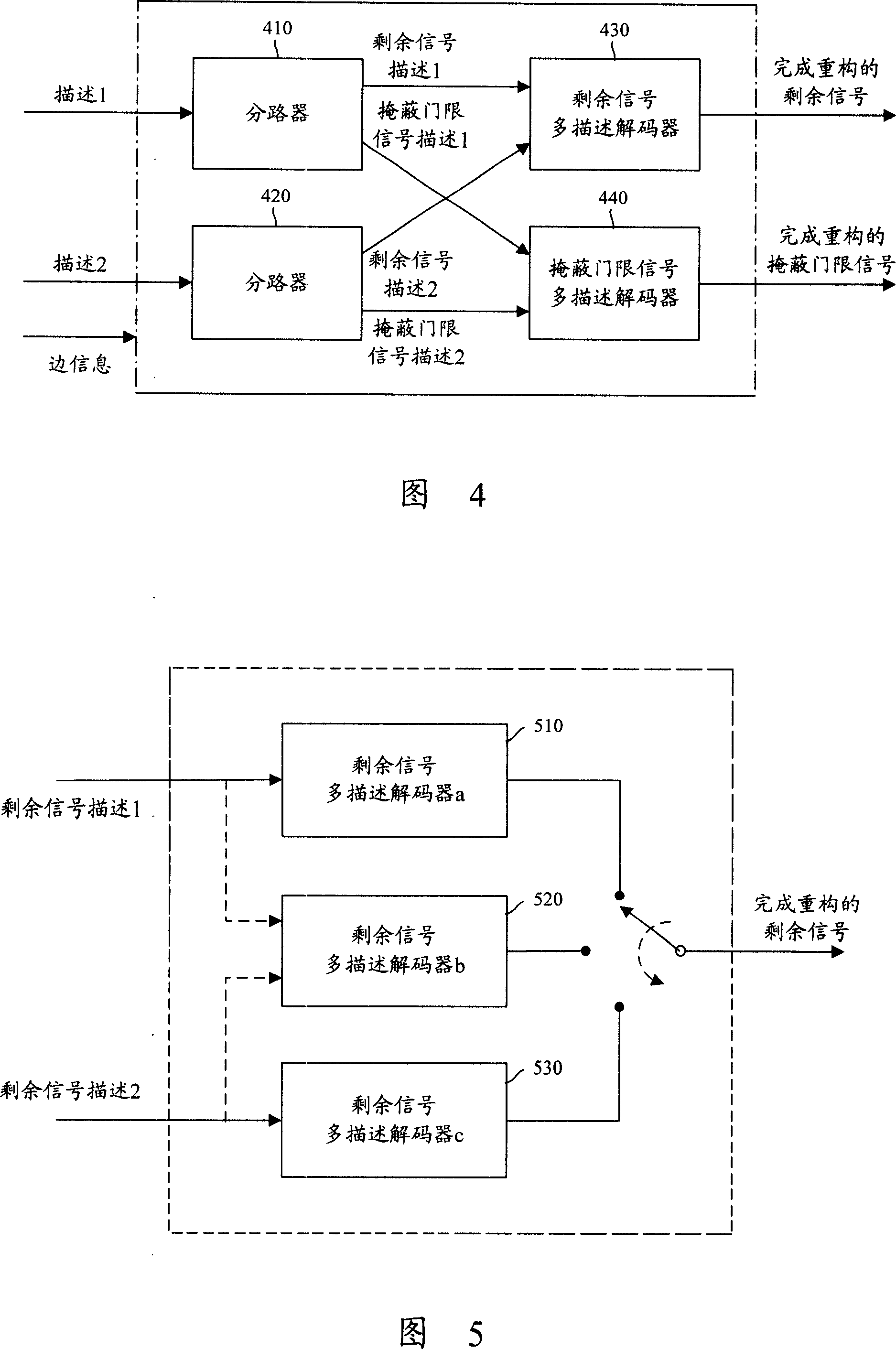
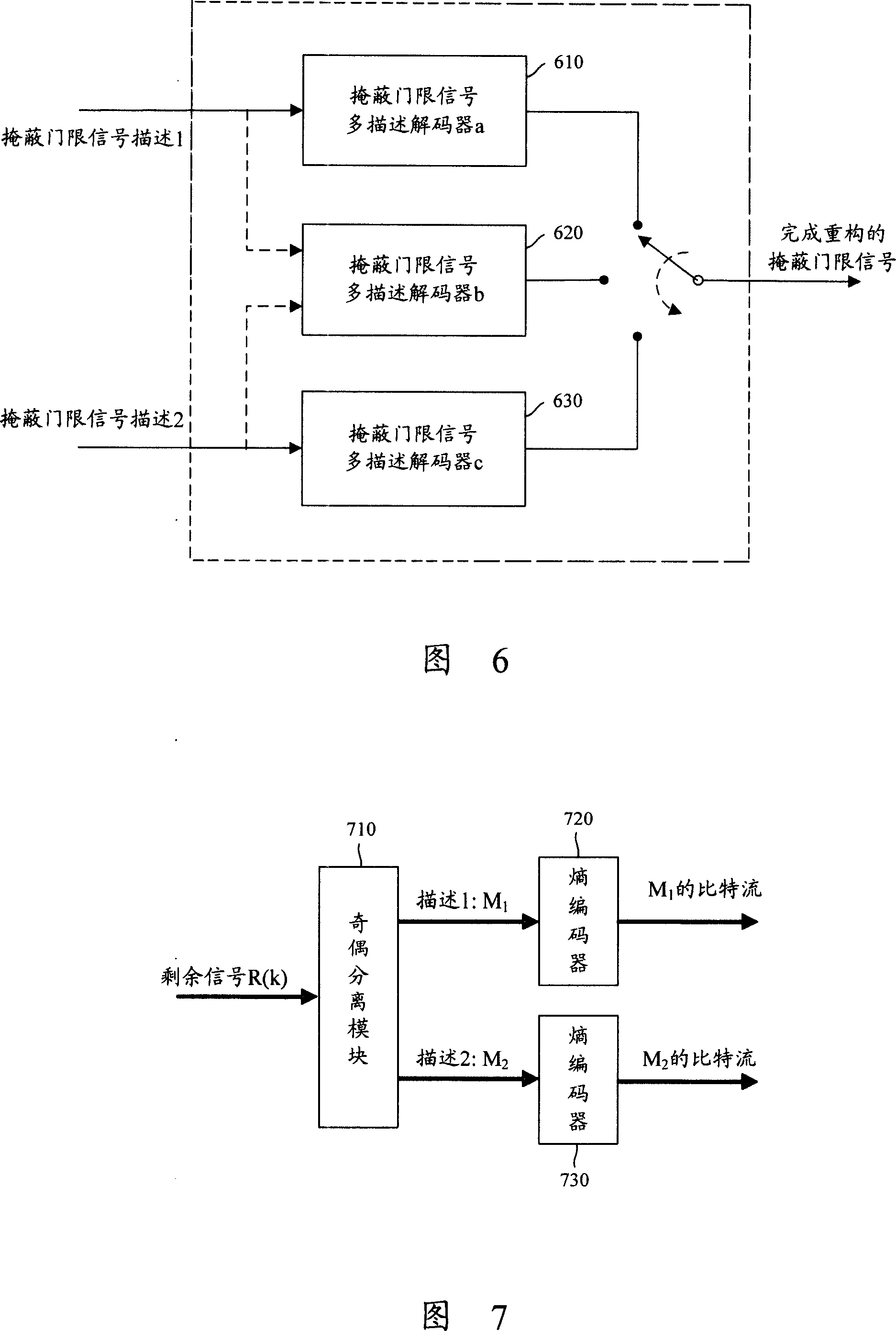
InactiveCN101115051AImprove satisfactionImprove audio qualitySpeech recognitionTransmissionTransceiverMultiple description
The invention discloses an audio signal processing method and system, and a transceiver device of audio signals. At the transmitting end of audio signals, the residue signals and mask threshold signals obtained by the processing of audio signals are respectively coded to residue signals multiple description and multiple description; and every residue signal description and one path of multiplex mask threshold signal description are combined to form a multiplex description that contains the residue signals and mask threshold signals. At the receiving end of the audio signals, the residue signal description and the mask threshold signal description contained in every one of the descriptions received are decommuted, all residue signal descriptions created after decommutation are decoded to one path of residue signals, and then all mask threshold signals created after decommutation are decoded to one path of mask threshold signals. The invention can effectively enhance audio quality in the process of communication and enhance user satisfaction degree.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method, system, apparatus and computer program product for stereo coding
ActiveUS20080130903A1High stereophonic qualityGreat amount of noiseBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisMasking thresholdSignal correlation
A method, system, apparatus and computer program product are provided for improved stereo coding. In particular, the method, system, apparatus and computer program product provide a technique for performing Mid-Side (M / S) stereo coding, in which an additional step is added to the coding process, whereby a parameter that is used in determining when the mid and side signals will be used instead of the left and right input signals is modified prior to making the selection between the signal pairs. In particular, the masking threshold associated with either the left or the right input signal may be modified based on a relationship between the energies of the two input signals. In addition, once the selection between the signal pairs has been made, the masking thresholds of the selected signals may be further modified, again based on a relationship between the energies of the left and right input signals.
Owner:RPX CORP
Masking based gain control
Interfering signals that may be present in a listening environment are masked by reproducing a desired signal in a listening environment, determining a masking threshold associated with the desired signal, identifying an interfering signal that may be present in the environment, comparing the interfering signal to the masking threshold, and adjusting the desired signal over time to raise its masking threshold above the level of the interfering signal.
Owner:BOSE CORP
Front voice enhancement method for identifying speaker
InactiveCN105427859AGuaranteed to minimize speech distortionEmbodies masking propertiesSpeech recognitionMasking thresholdNoise estimation
Owner:SHENZHEN YINJIAMI TECH CO LTD
Improved coding/decoding of digital audio signals
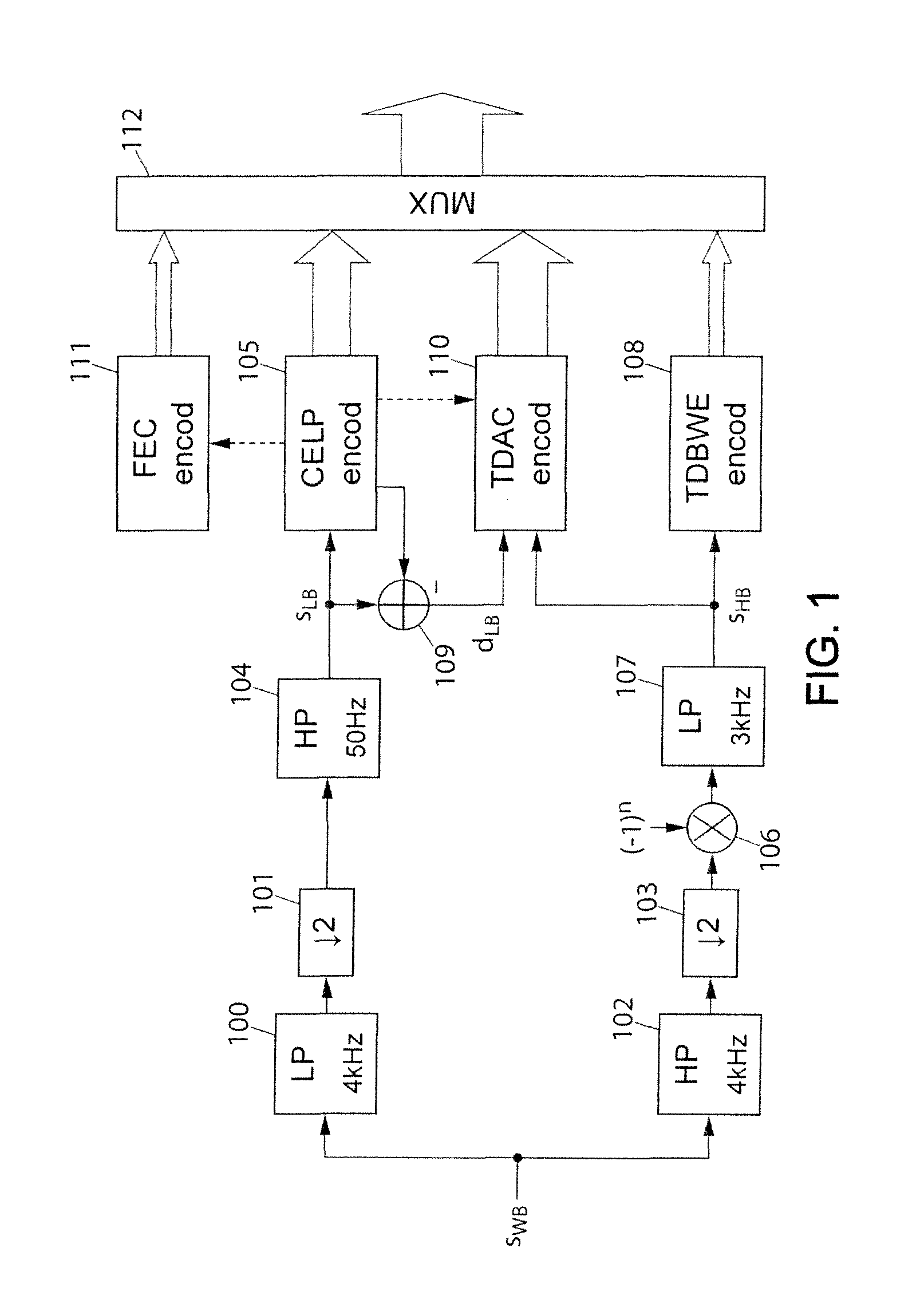
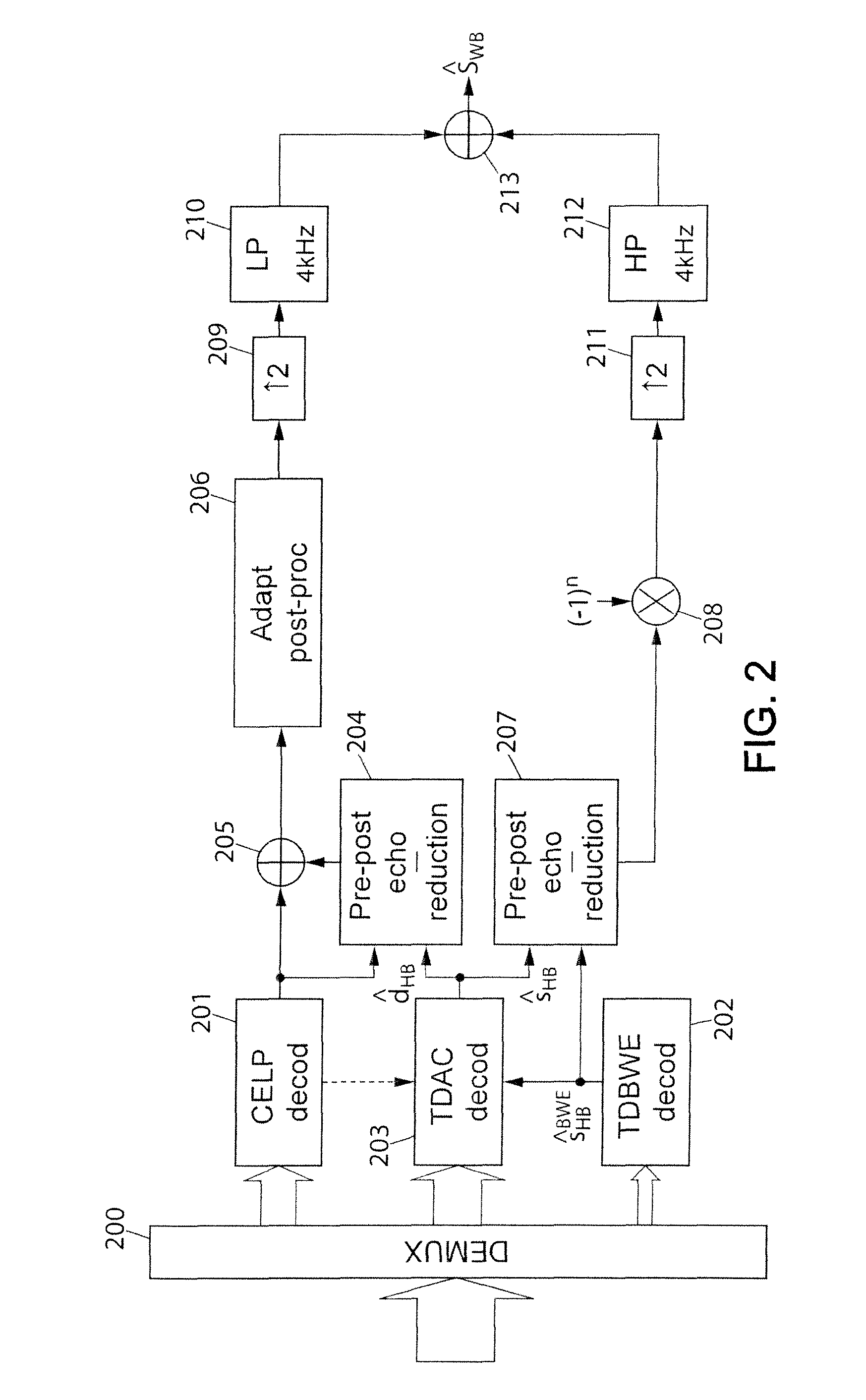
ActiveUS20120185255A1Quality improvementImprove encoding qualitySpeech analysisBit allocationMasking threshold
A method of hierarchical coding of a digital audio frequency input signal into several frequency sub-bands, including a core coding of the input signal according to a first throughput and at least one enhancement coding of higher throughput, of a residual signal. The core coding uses a binary allocation according to an energy criterion. The method includes for the enhancement coding: calculating a frequency-based masking threshold for at least part of the frequency bands processed by the enhancement coding; determining a perceptual importance per frequency sub-band as a function of the masking threshold and as a function of the number of bits allocated for the core coding; binary allocation of bits in the frequency sub-bands processed by the enhancement coding, as a function of the perceptual importance determined; and coding the residual signal according to the bit allocation. Also provided are a decoding method, a coder and a decoder.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
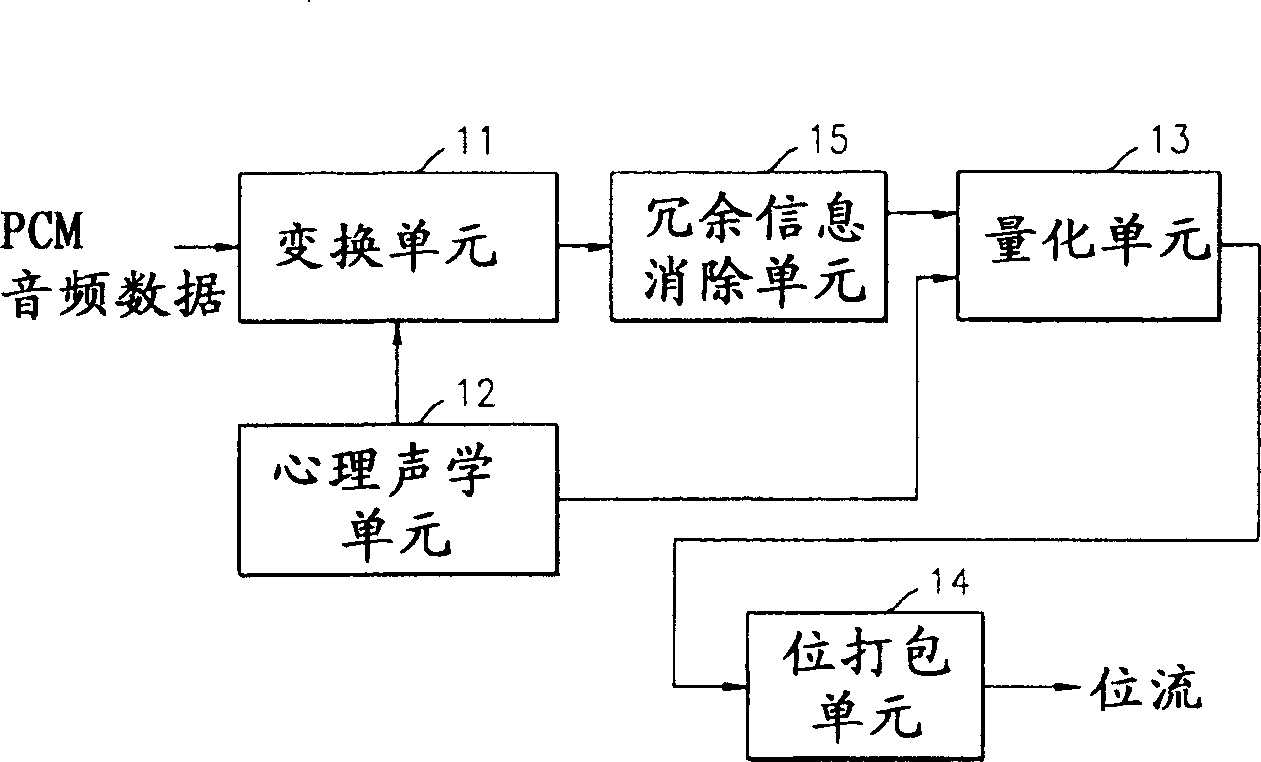
Stereo audio encoding method and device, audio stream decoding method and device
InactiveCN1525438ABroadcast information characterisationStereophonic circuit arrangementsLossless codingDecoding methods
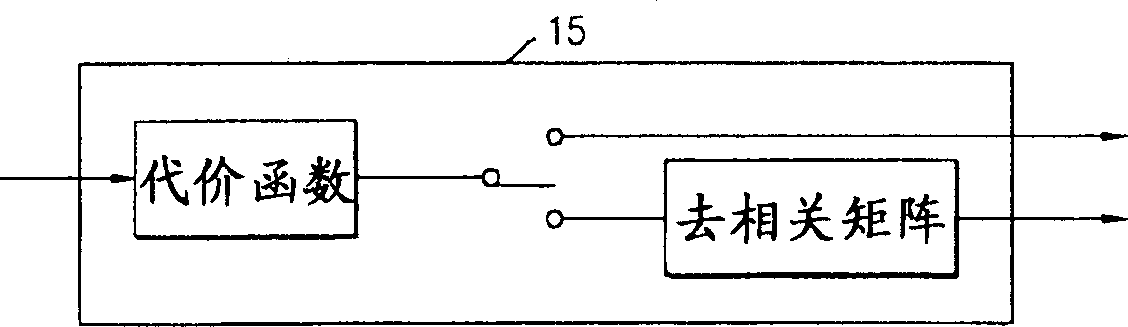
A stereo audio coding method, an apparatus thereof, a decoding method and an apparatus thereof are provided to supply more stable sound quality at a low frequency bandwidth and encode stereo audio into less bits. A conversion unit(11) converts audio samples obtained from a plurality of channels, respectively. A psychological sound unit(12) supplies attack sensing information to the conversion unit(11), ties the converted audio signal as proper subband signals, calculates a masking threshold in each subband by using the masking phenomenon due to the interaction of each signal and then supplies the calculated value to a quantizing unit(13). The quantizing unit(13) quantizes correlation cancellation samples of each band on the basis of corresponding scale factor information and supplies the quantized samples. A bit packing unit(14) codes the quantized samples without loss and packages the coded samples by the unit of frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com