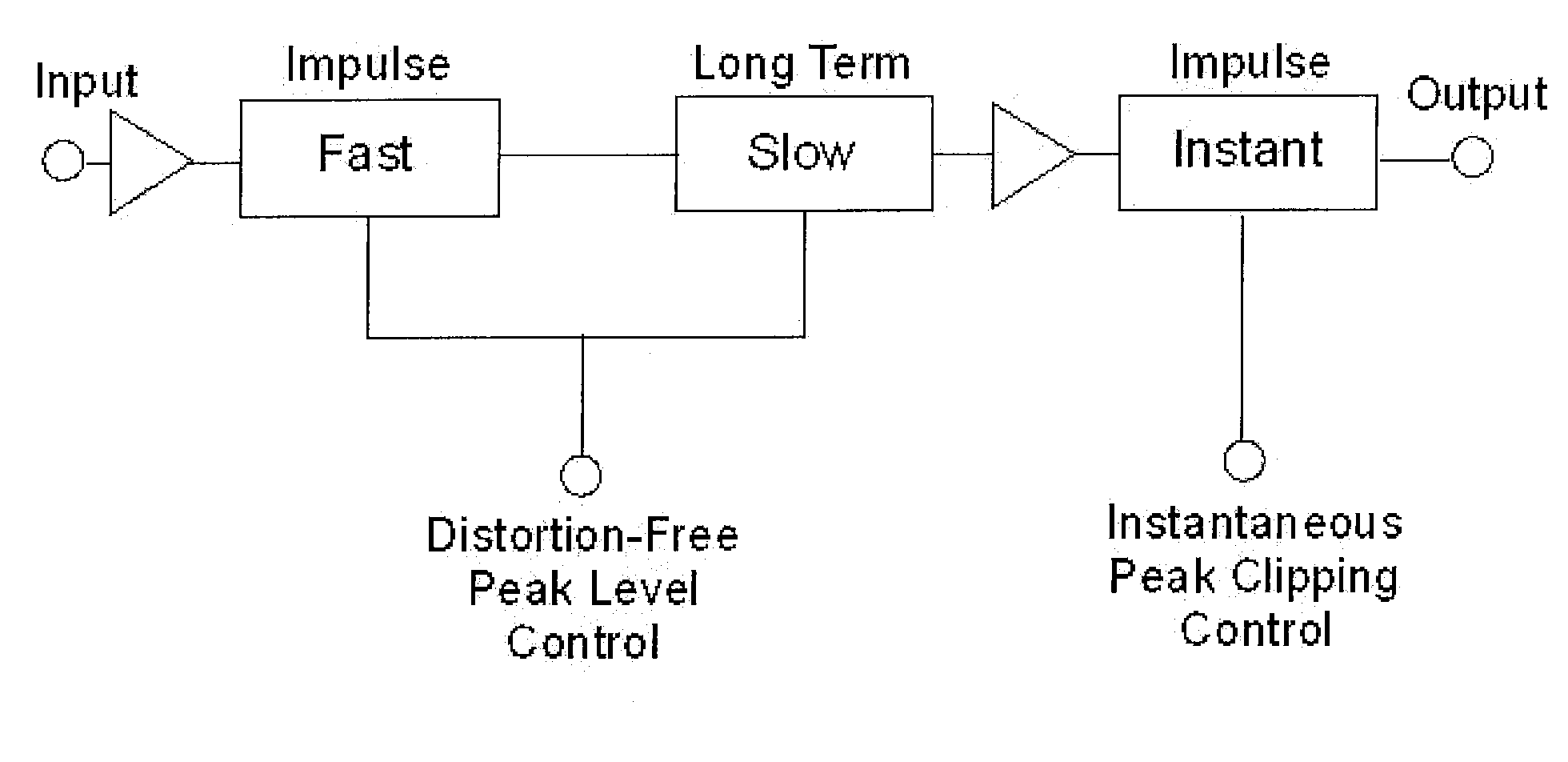
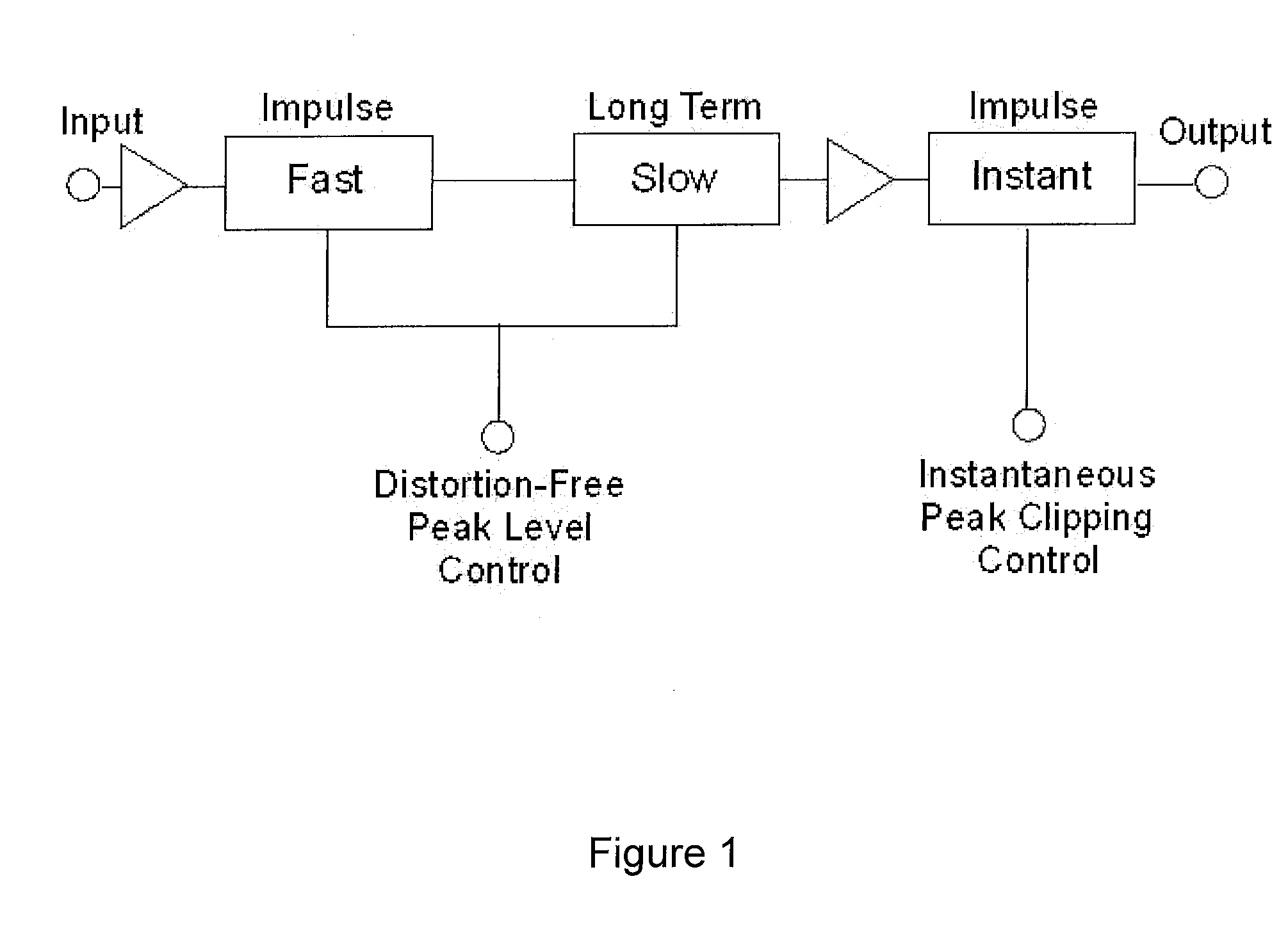
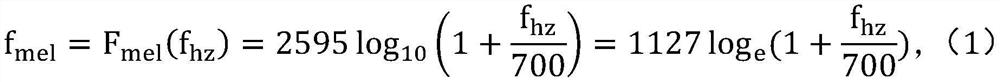Patents
Literature
40 results about "Human auditory system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
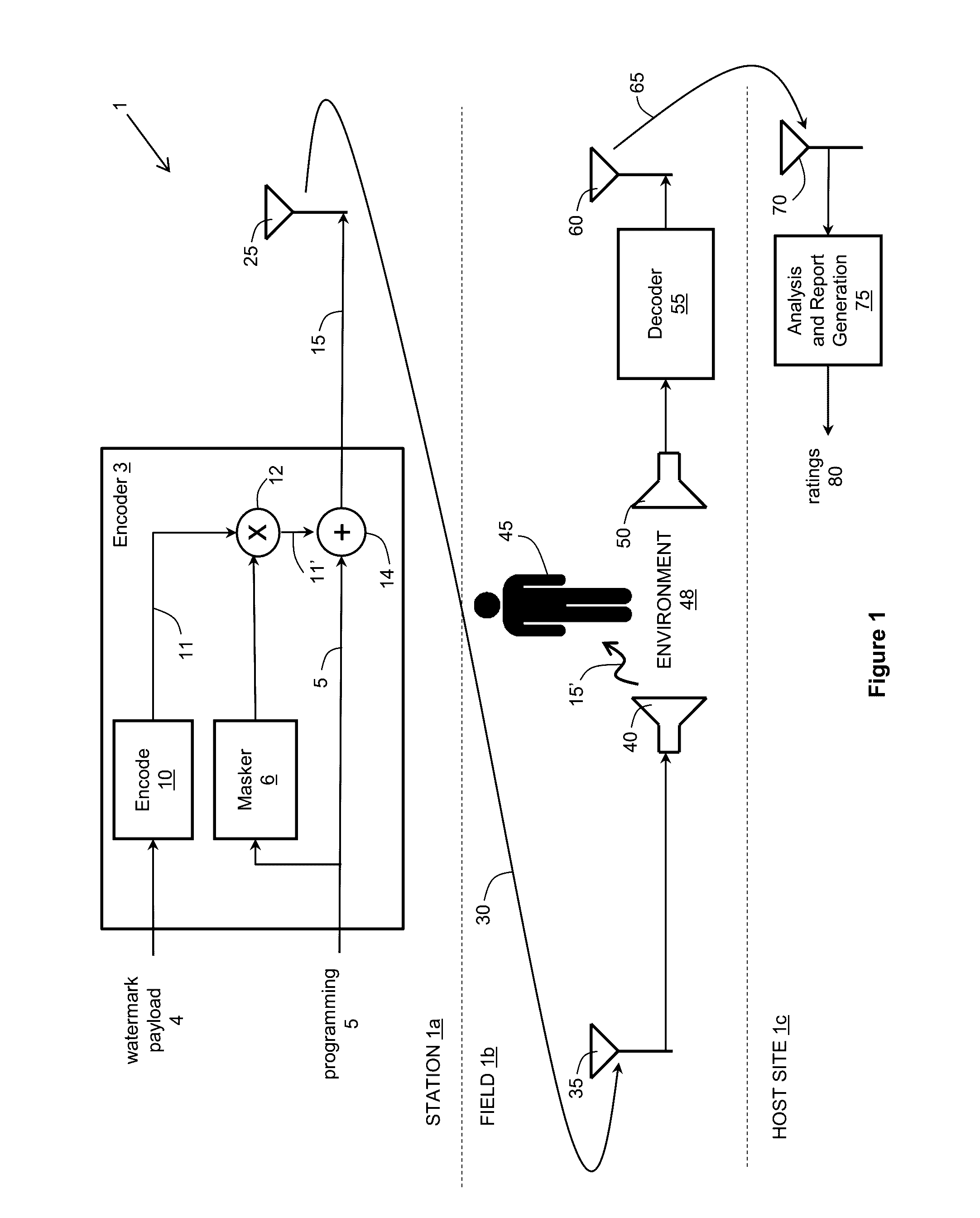
The human auditory system is composed of three parts. The outer ear , the middle ear and the inner ear. Let's see how it works. The sound waves are picked up by the ear pavilion of the outer ear . They are, then amplified and transmitted to the middle ear through the external ear canal .
Voice intelligibility enhancement system
InactiveUS6993480B1Improve intelligibilityImprove speech clarityPublic address systemsSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseHearing acuity
Intelligibility of a human voice projected by a loudspeaker in an environment of high ambient noise is enhanced by processing a voice signal in accordance with the frequency response characteristics of the human hearing system. Intelligibility of the human voice is derived largely from the pattern of frequency distribution of voice sounds, such as formants, as perceived by the human hearing system. Intelligibility of speech in a voice signal is enhanced by filtering and expanding the voice signal with a transfer function that approximates an inverse of equal loudness contours for tones in a frontal sound field for humans of average hearing acuity.
Owner:DTS
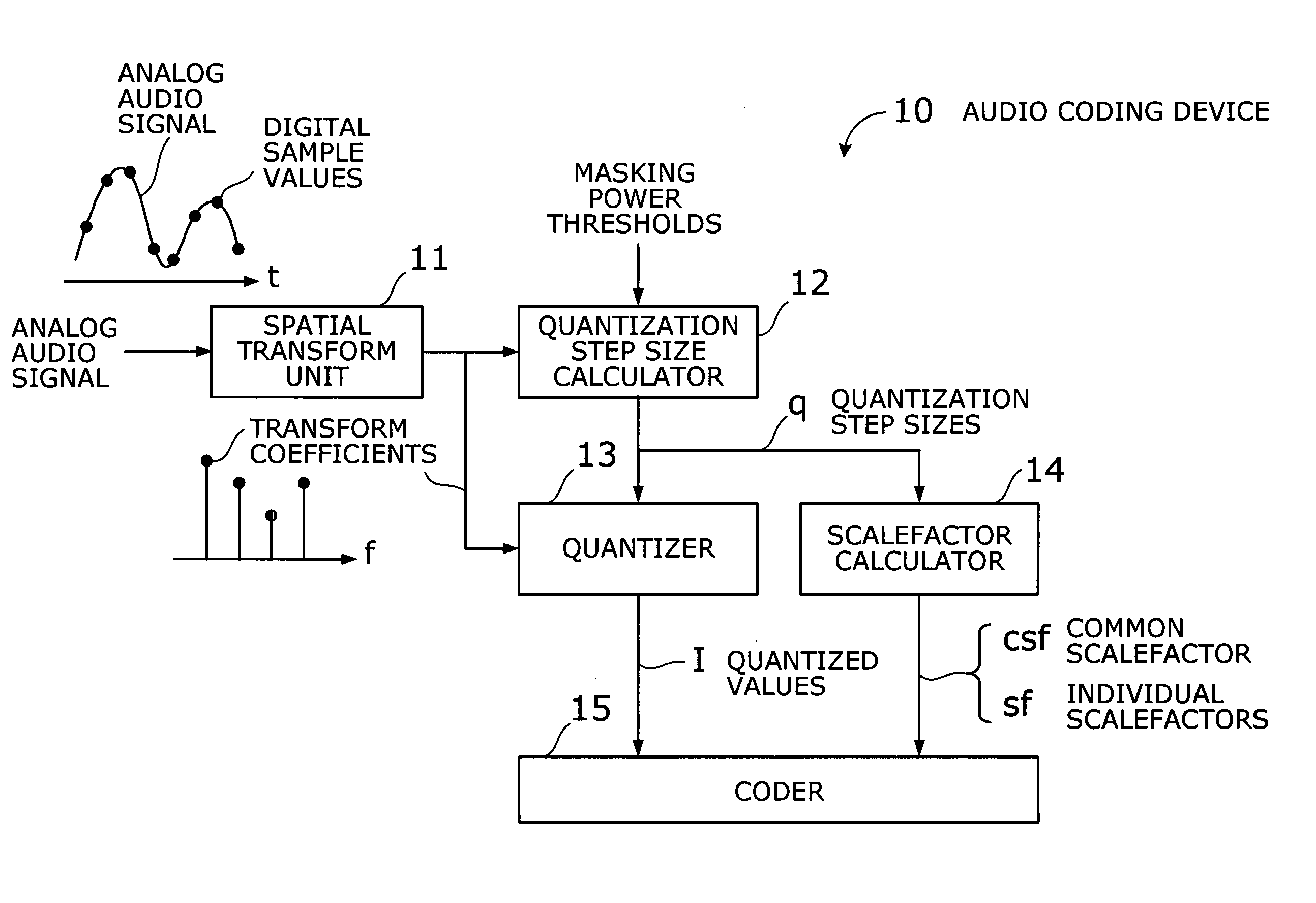
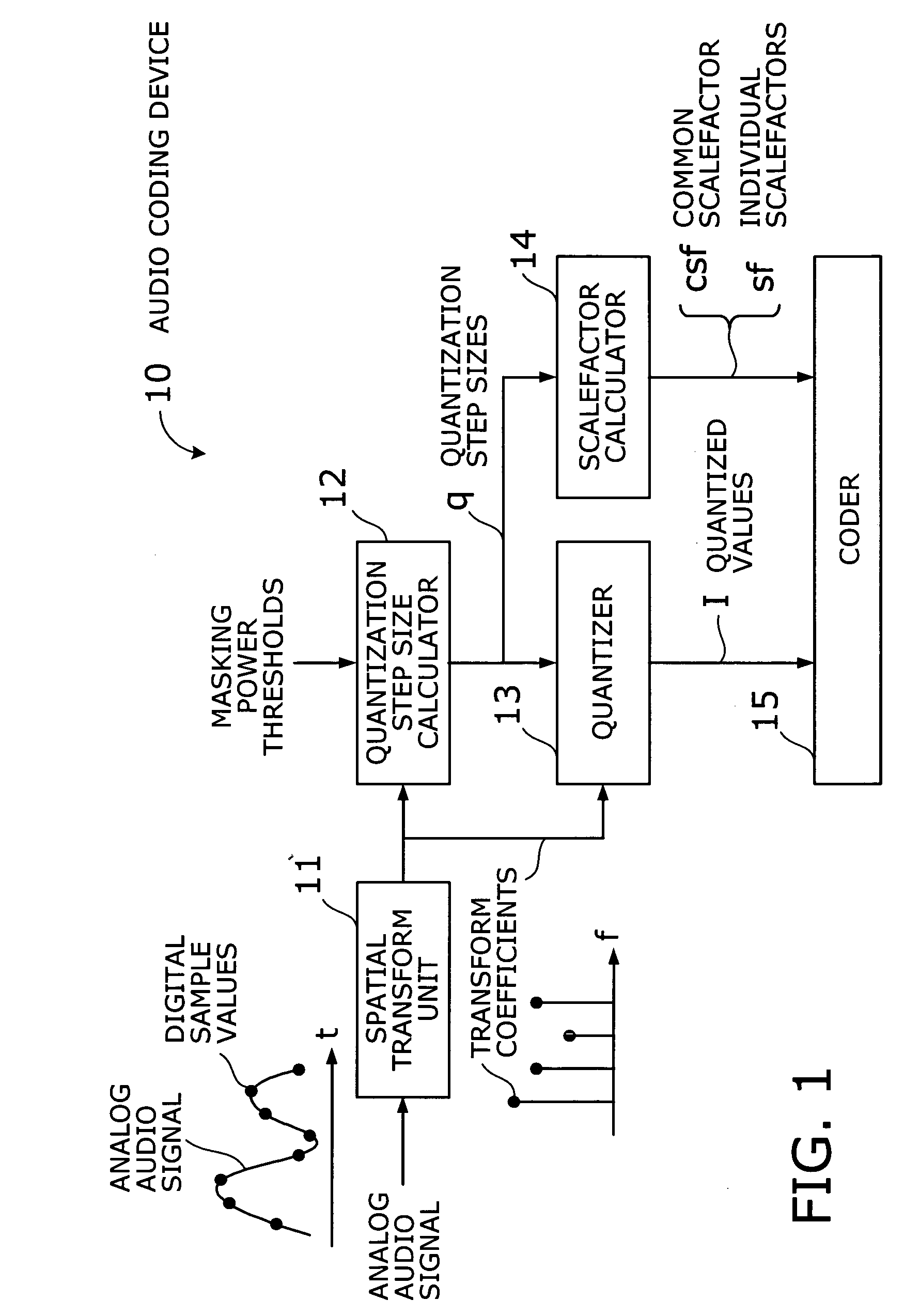
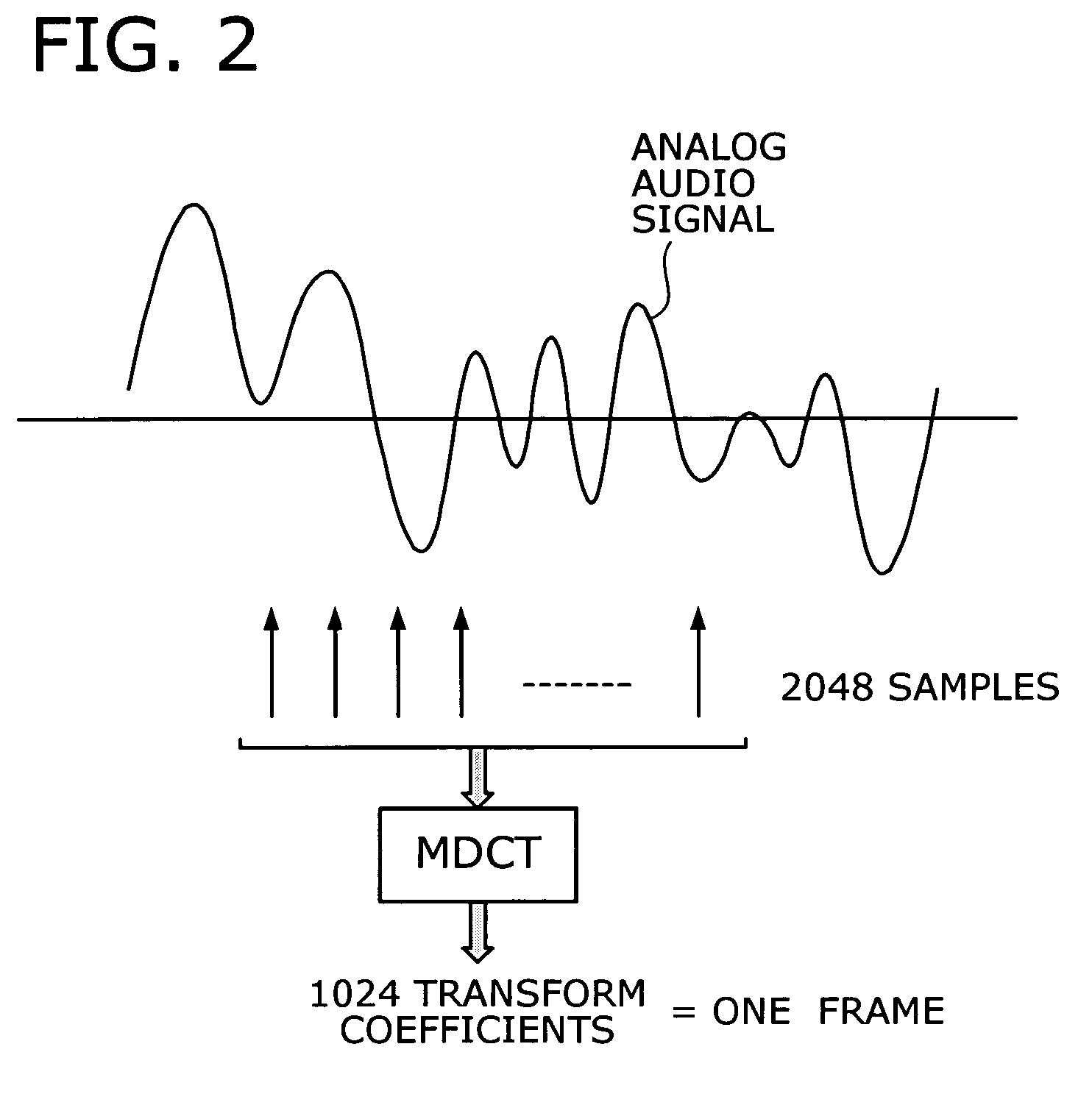
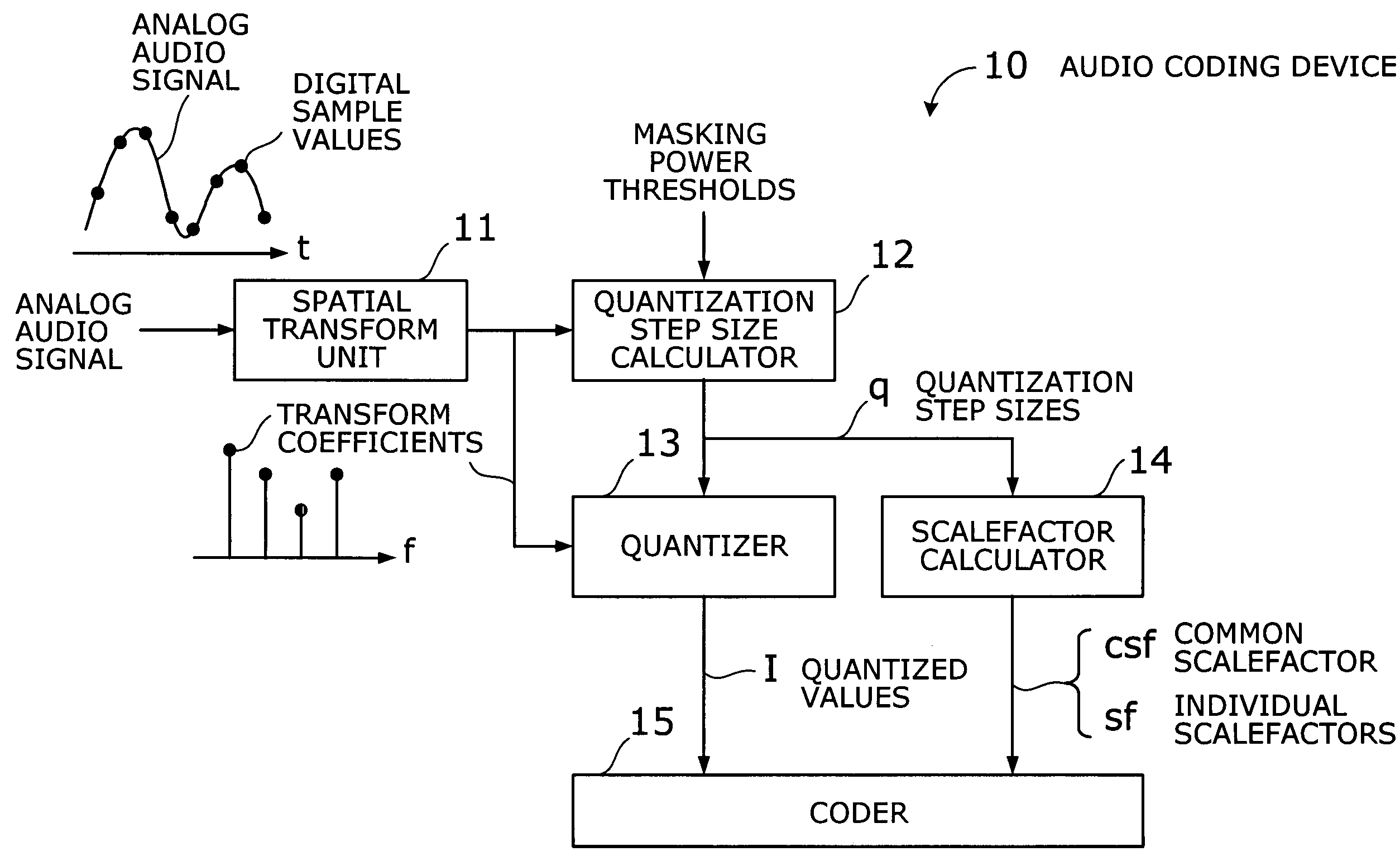
Audio coding device with fast algorithm for determining quantization step sizes based on psycho-acoustic model
ActiveUS20060074693A1Reduce the amount of calculationSpeech analysisFast algorithmHuman auditory system
An efficient audio coding device that quantizes and encodes digital audio signals with a reduced amount of computation. A spatial transform unit subjects samples of a given audio signal to a spatial transform, thus obtaining transform coefficients of the signal. With a representative value selected out of the transform coefficients of each subband, a quantization step size calculator estimates quantization noise and calculates, in an approximative way, a quantization step size of each subband from the estimated quantization noise, as well as from a masking power threshold determined from a psycho-acoustic model of the human auditory system. A quantizer then quantizes the transform coefficients, based on the calculated quantization step sizes, thereby producing quantized values of those coefficients. The quantization step sizes are also used by a scalefactor calculator to calculate common and individual scalefactors. A coder encodes at least one of the quantized values, common scalefactor, and individual scalefactors.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
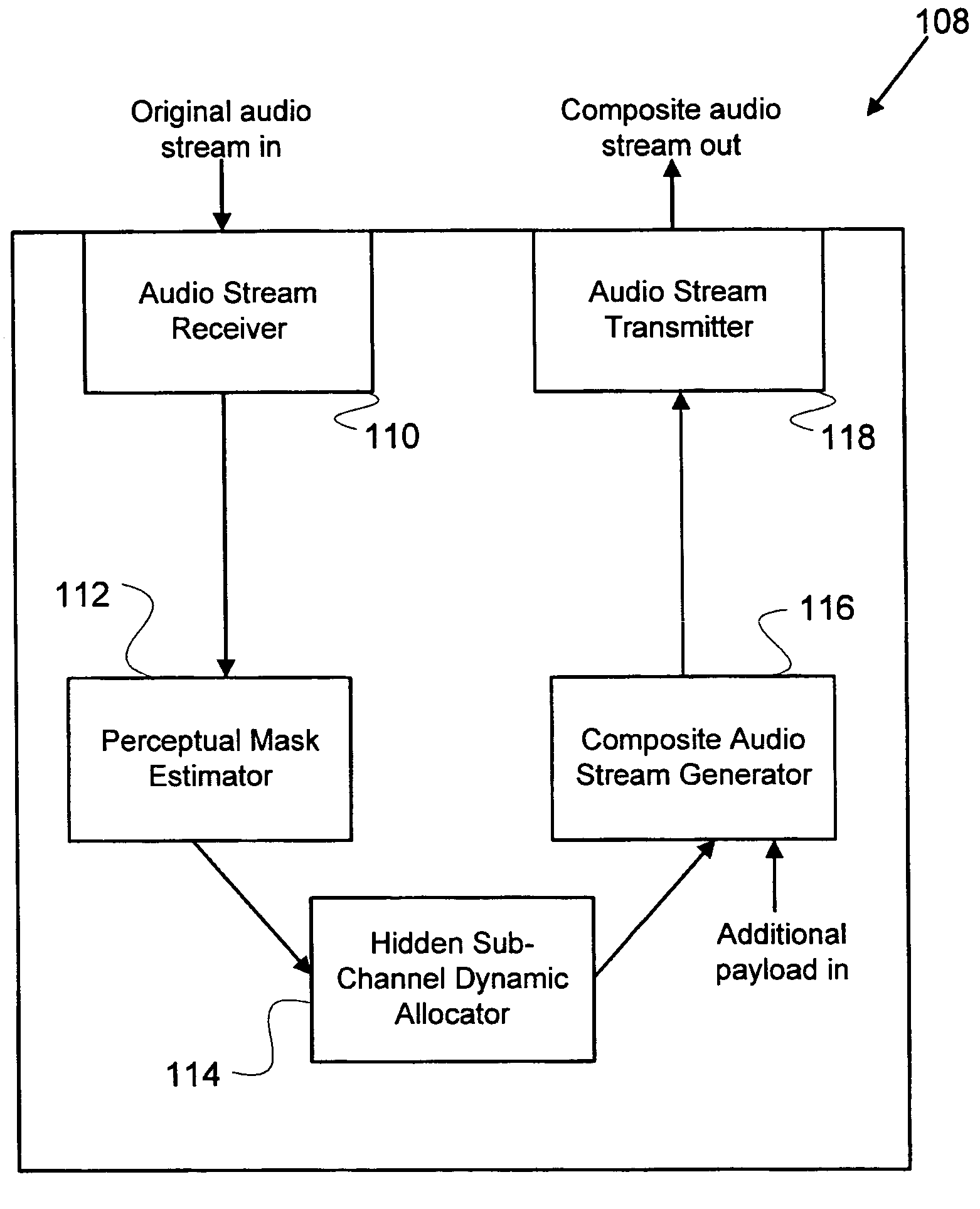
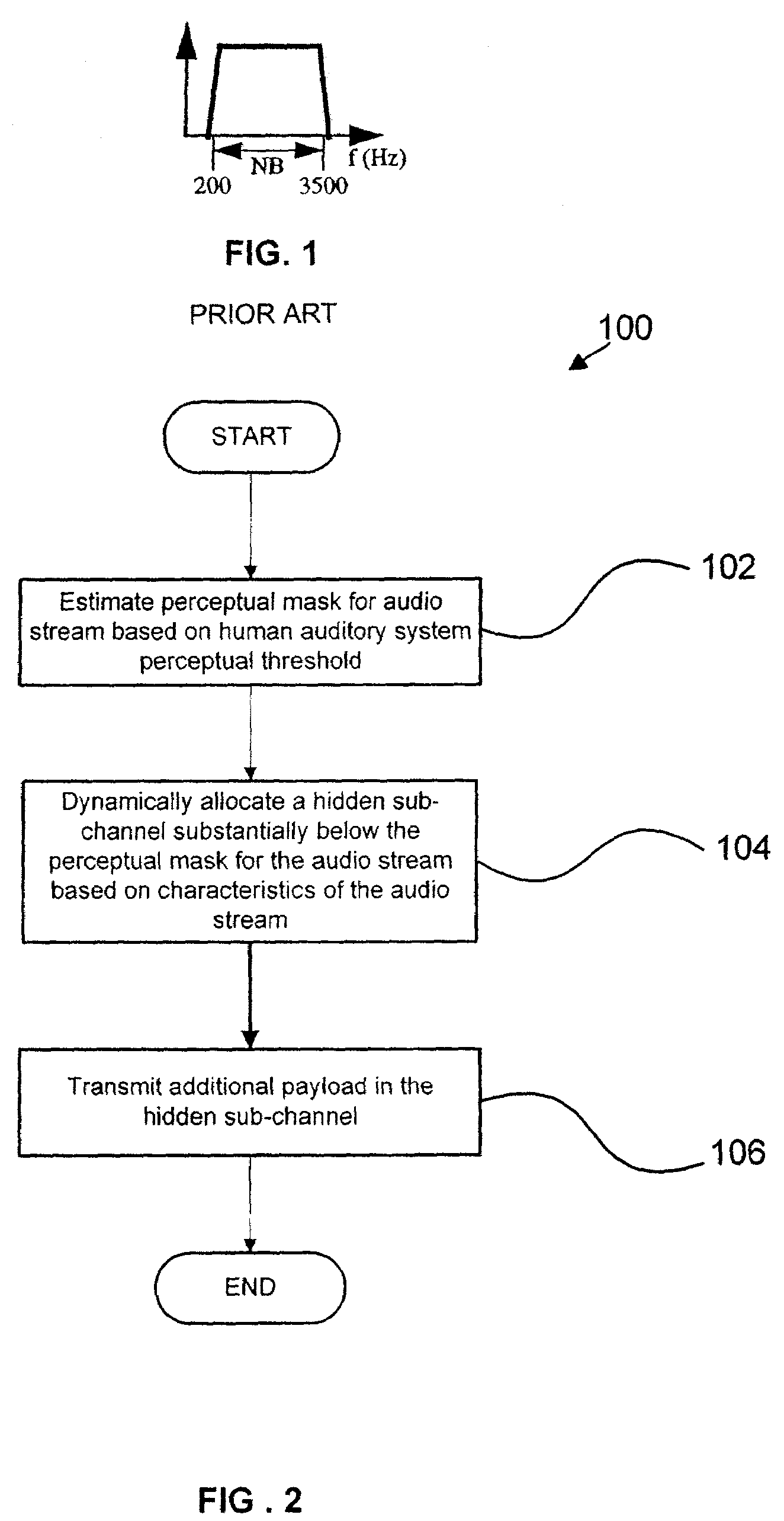
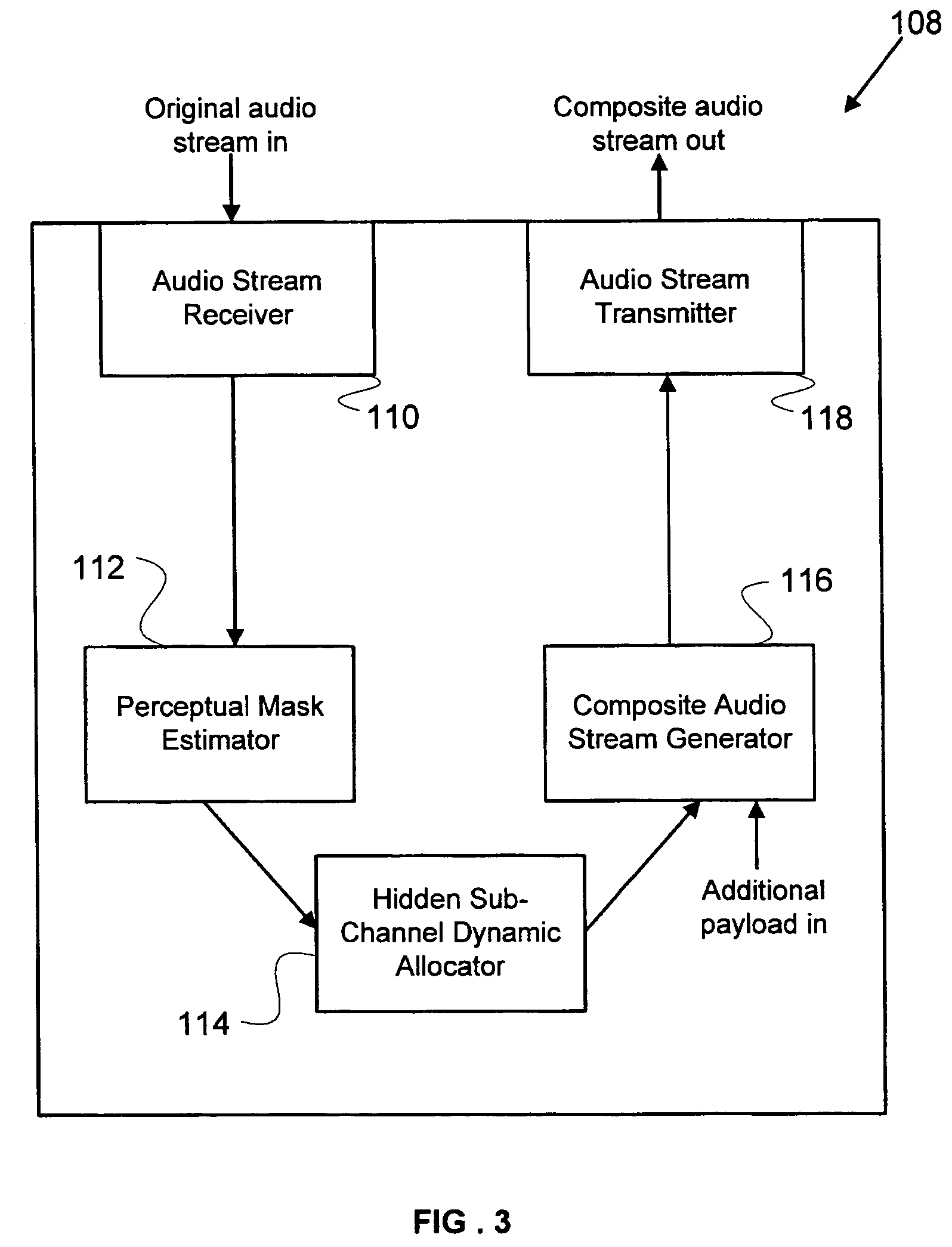
Method and apparatus for transmitting an audio stream having additional payload in a hidden sub-channel
InactiveUS7330812B2Speech analysisData switching by path configurationHuman auditory systemAudio frequency
Methods and apparatus are provided for communicating an audio stream. A perceptual mask is estimated for an audio stream, based on the perceptual threshold of the human auditory system. A hidden sub-channel is dynamically allocated substantially below the estimated perceptual mask based on the characteristics of the audio stream, in which additional payload is transmitted. The additional payload can be related to components of the audio stream that would not otherwise be transmitted in a narrowband signal, or to concurrent services that can be accessed while the audio stream is being transmitted. A suitable receiver can recover the additional payload, whereas the audio stream will be virtually unaffected from a human auditory standpoint when received by a traditional receiver. A coding scheme is also provided in which a portion of a codec is used to code an upper-band portion of an audio stream, while the narrowband portion is left uncoded.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
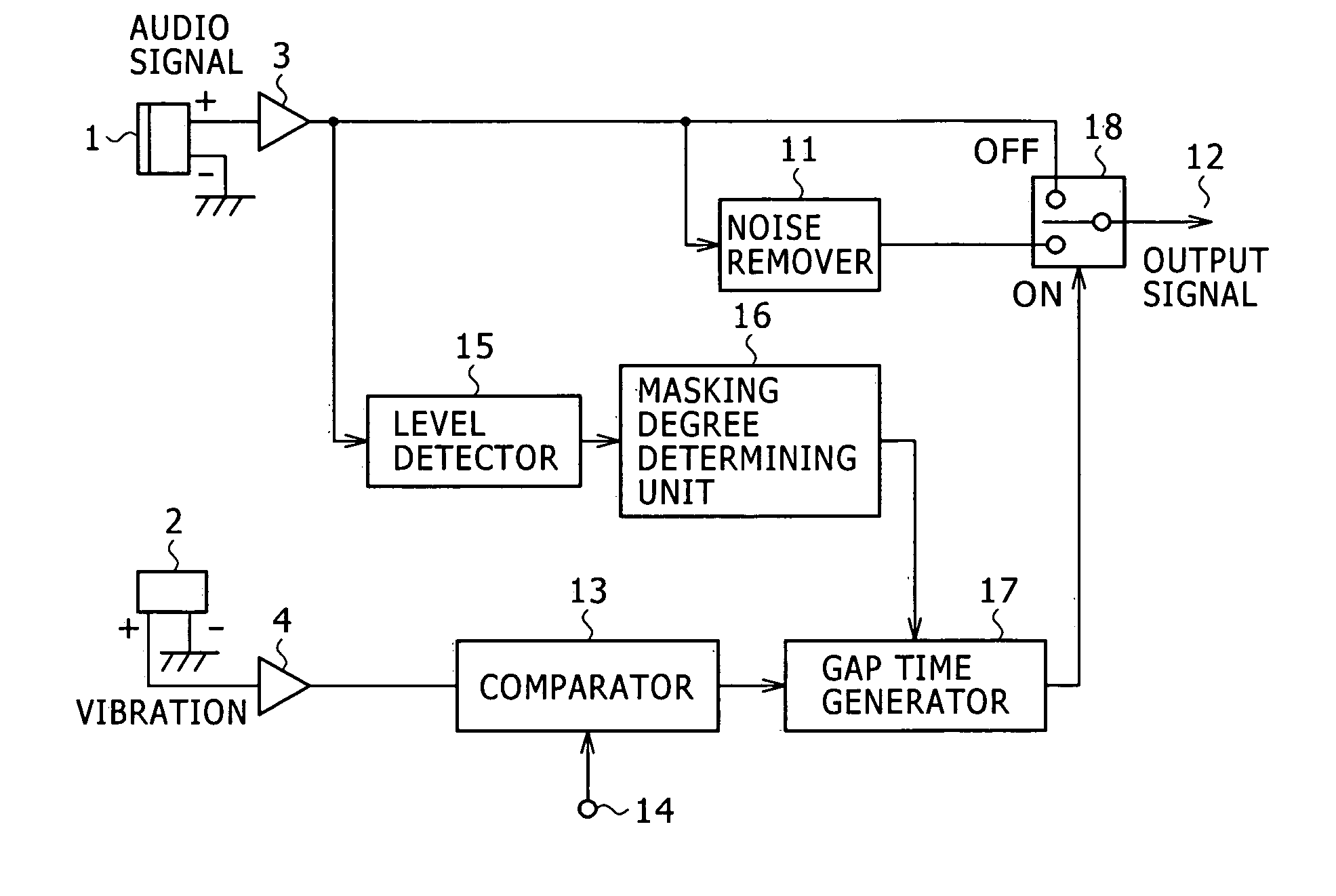
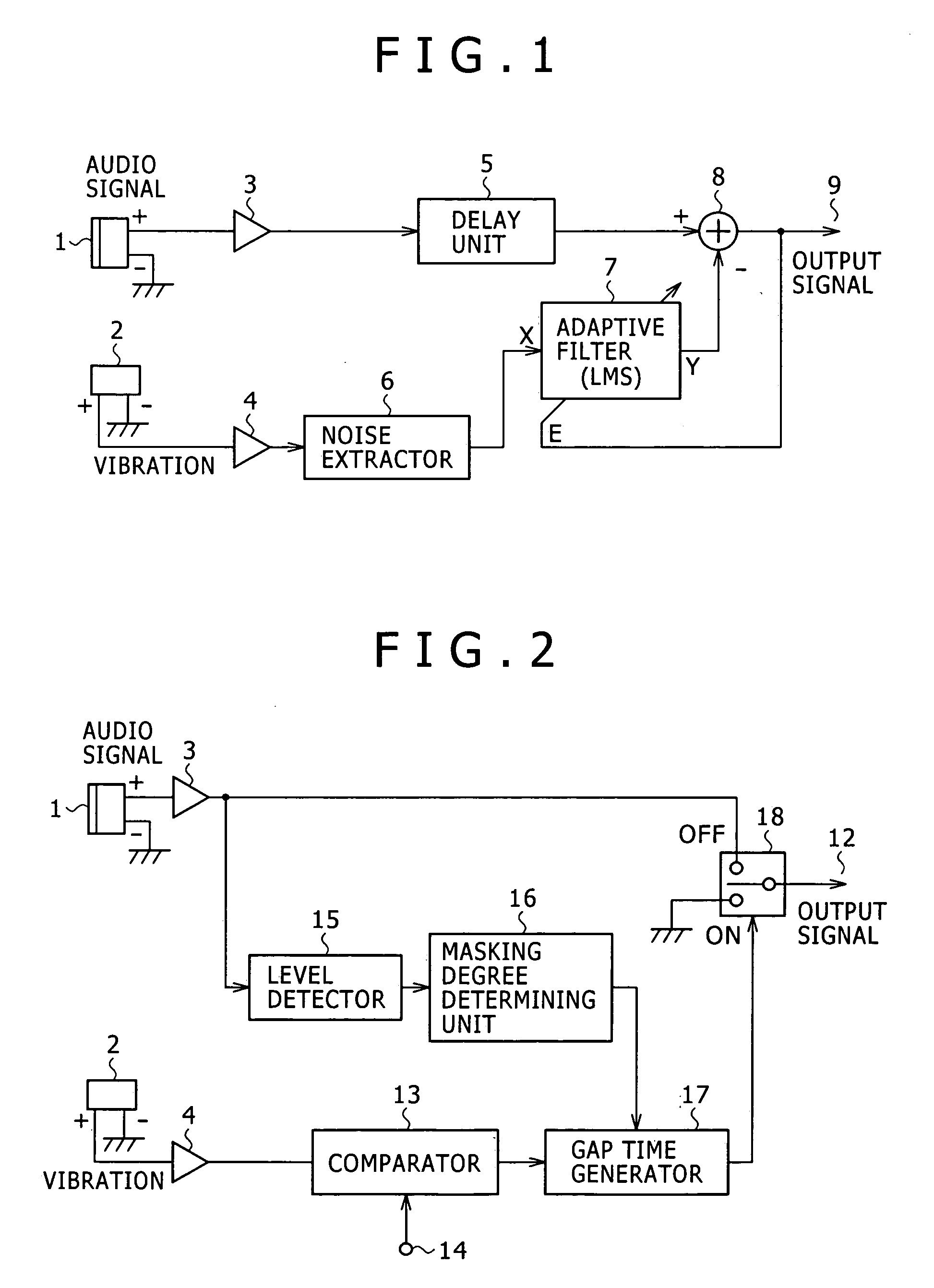
Method of and apparatus for reducing noise
InactiveUS20050234715A1Easily maskedImprove efficiencySubstation/switching arrangement detailsSpeech analysisHuman auditory systemEngineering
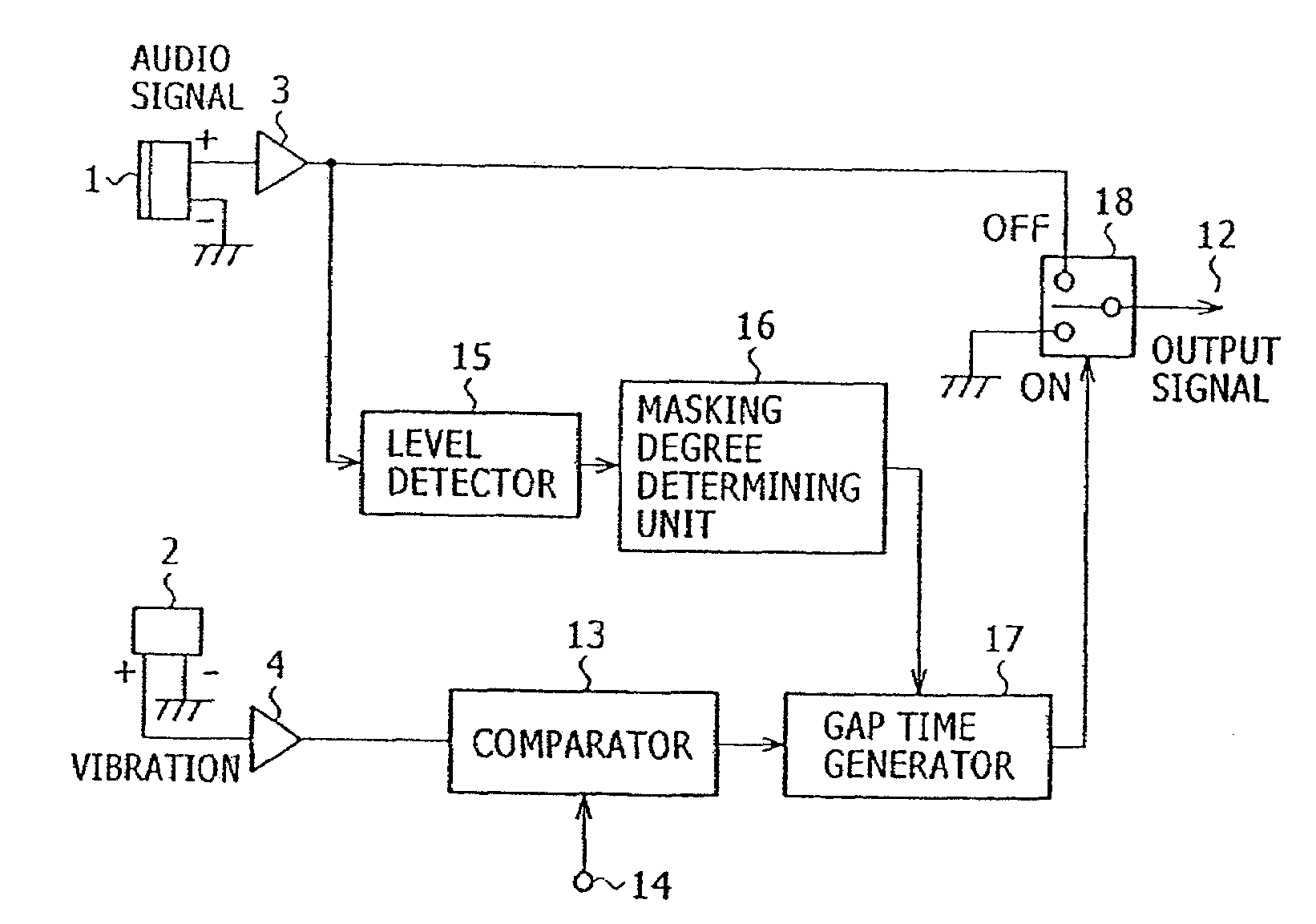
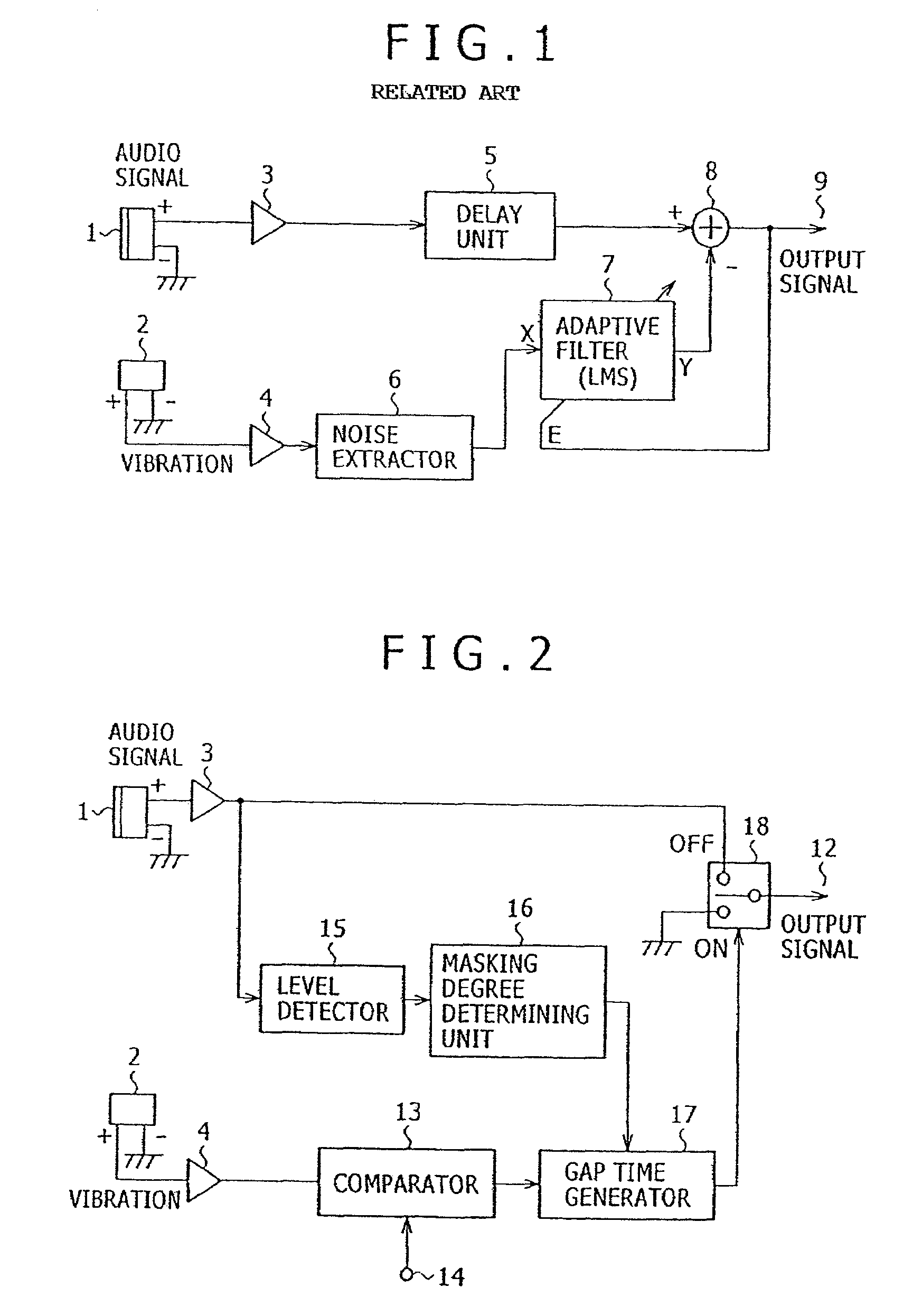
An apparatus for reducing noise includes a comparator for generating a noise timing signal corresponding to a noise producing period of noise introduced from a noise source and contained in an audio signal, a gap time generator for generating a gap period in which to remove noise from the audio signal, a selector switch for selectively outputting the audio signal and a noise-removed signal, a level detector for detecting a signal level of the audio signal, and a masking degree determining unit for determining from the signal level detected by the level detector a gap period for which the audio signal is masked by the human auditory system. The selector switch outputs the noise-removed signal in a period corresponding to the gap period within the noise producing period of the noise timing signal, and outputs the audio signal in other than the gap period.
Owner:SONY CORP
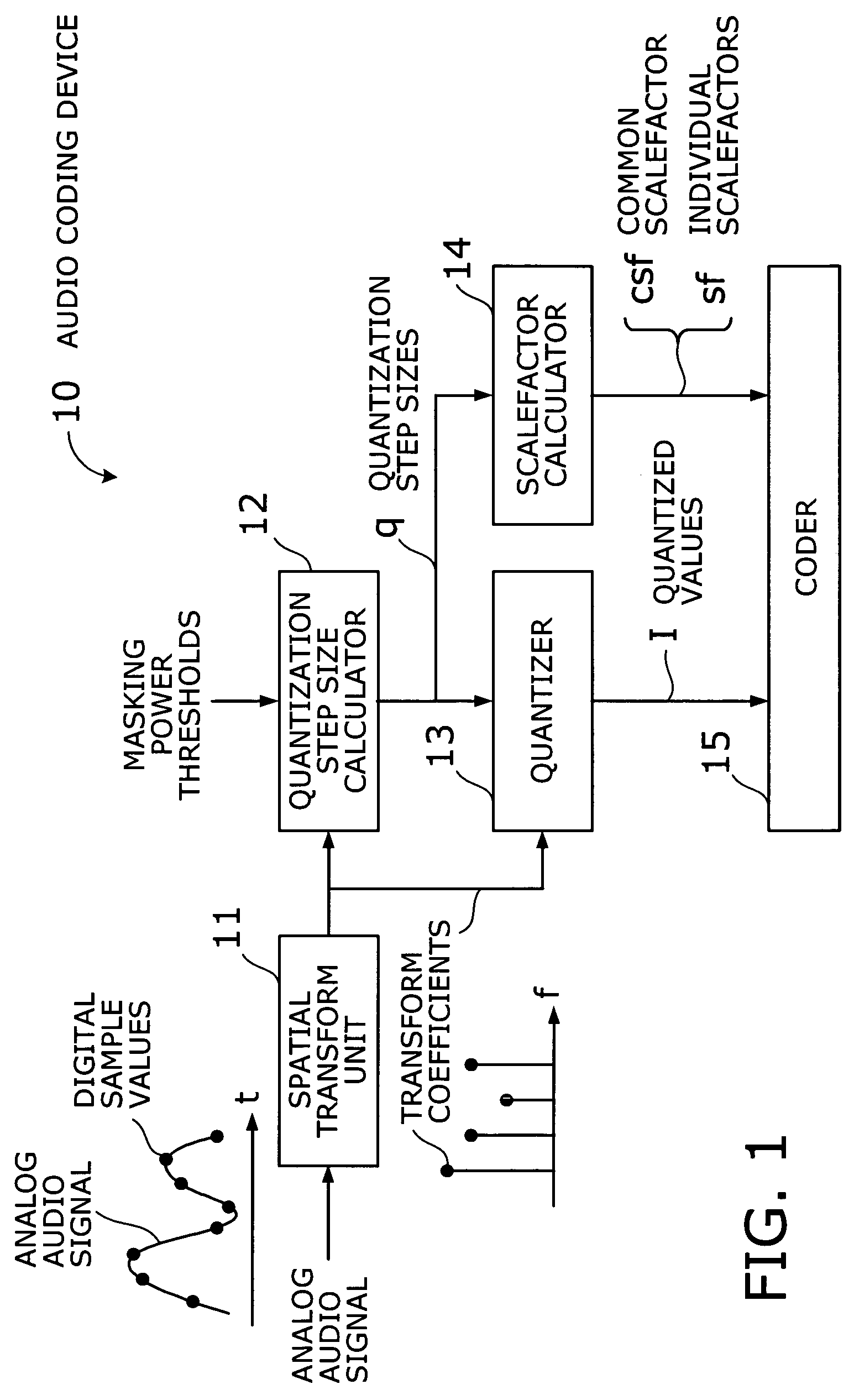
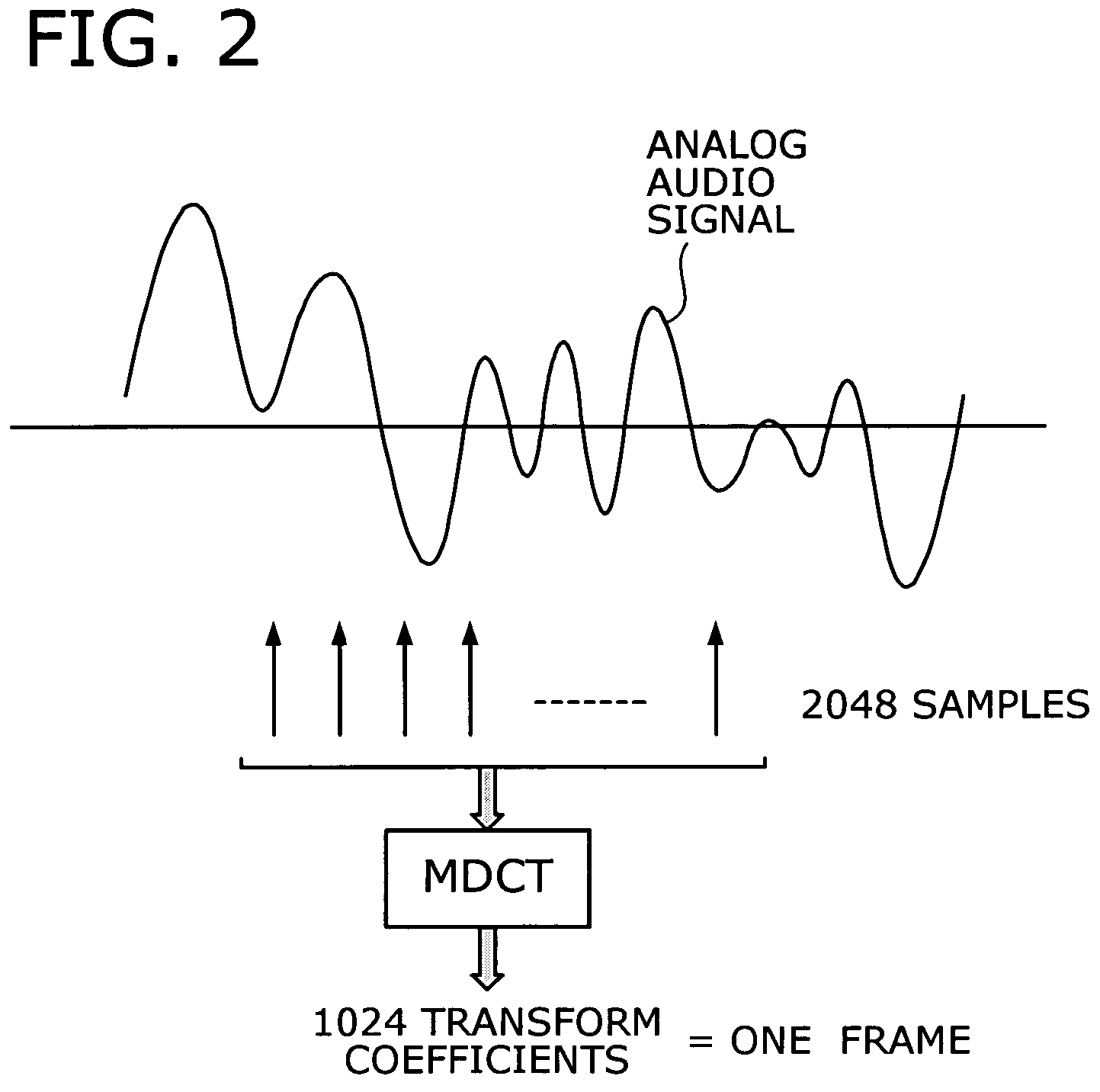
Audio coding device with fast algorithm for determining quantization step sizes based on psycho-acoustic model
An efficient audio coding device that quantizes and encodes digital audio signals with a reduced amount of computation. A spatial transform unit subjects samples of a given audio signal to a spatial transform, thus obtaining transform coefficients of the signal. With a representative value selected out of the transform coefficients of each subband, a quantization step size calculator estimates quantization noise and calculates, in an approximative way, a quantization step size of each subband from the estimated quantization noise, as well as from a masking power threshold determined from a psycho-acoustic model of the human auditory system. A quantizer then quantizes the transform coefficients, based on the calculated quantization step sizes, thereby producing quantized values of those coefficients. The quantization step sizes are also used by a scalefactor calculator to calculate common and individual scalefactors. A coder encodes at least one of the quantized values, common scalefactor, and individual scalefactors.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Vocal print feature recognition method and system
InactiveCN106782565ASolve the problem of lower voiceprint recognition rateImprove accuracySpeech analysisMixed noiseHuman auditory system
The embodiment of the invention provides a vocal print feature recognition method and a vocal print feature recognition system. The method comprises the following specific steps: after speech separation treatment based on hearing characteristics on pretreated noise-containing mixed noise, extracting a frequency cepstrum coefficient and a perceptual linear prediction coefficient of a signal, by utilizing the background distinction degree of the noise, analyzing the frequency cepstrum coefficient and the perceptual linear prediction coefficient under different noise environments so that the feature fusion is completed, and finally, in a pre-established vocal print feature template library, carrying out mode matching on the features after fusion by adopting a gaussian mixture model-universal background model (GMM-UBM). According to the vocal print feature recognition method, the human auditory system features and the traditional vocal print recognition method are combined, the problem that the vocal print recognition ratio under noise is low is solved from the point of bionics, and the vocal print feature recognition accuracy and system robustness under the noise environment are effectively promoted.
Owner:重庆重智机器人研究院有限公司
Noise reduction in a stereo receiver
InactiveUS7110549B2Improve noiseReduce audible noiseBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisHuman auditory systemControl signal
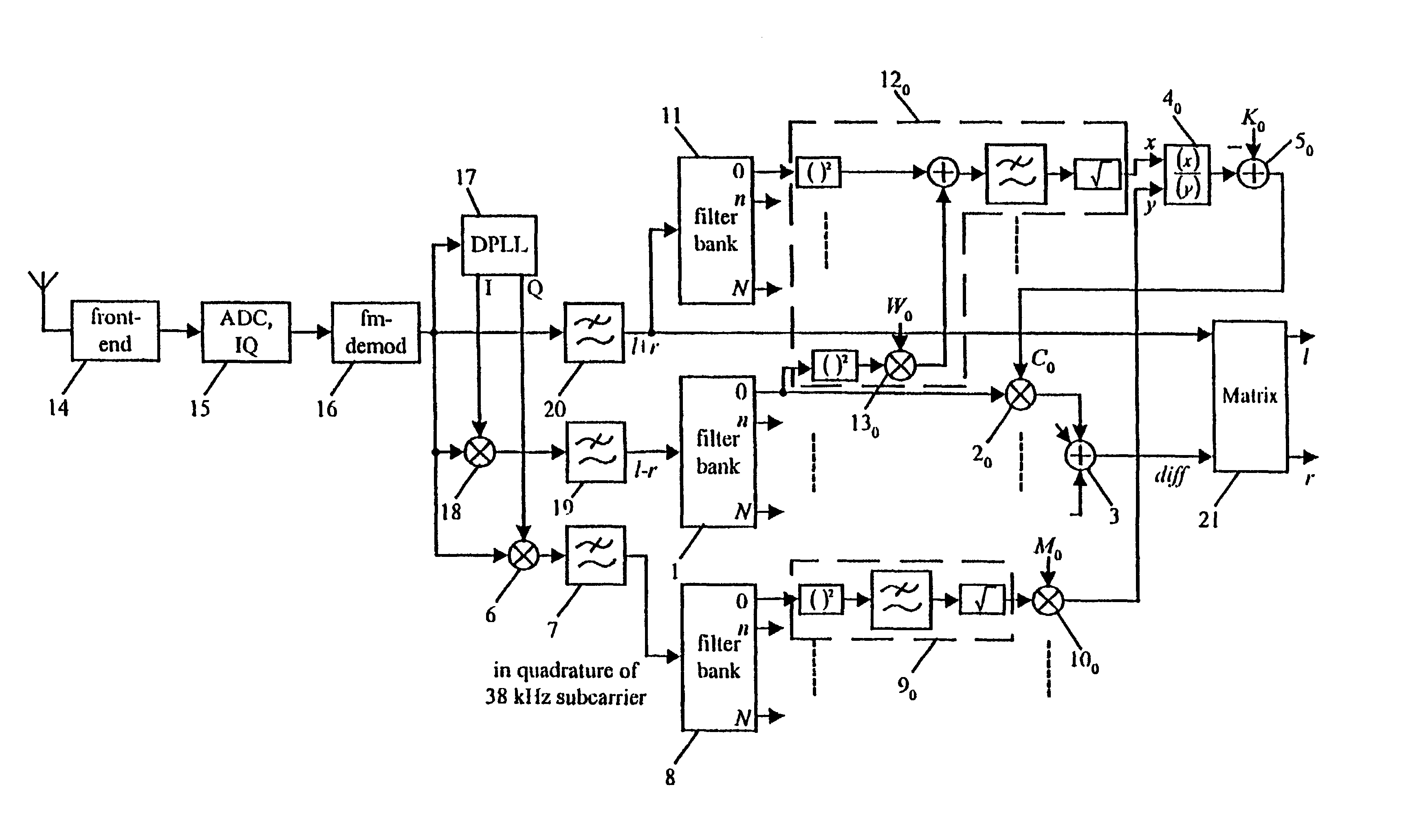
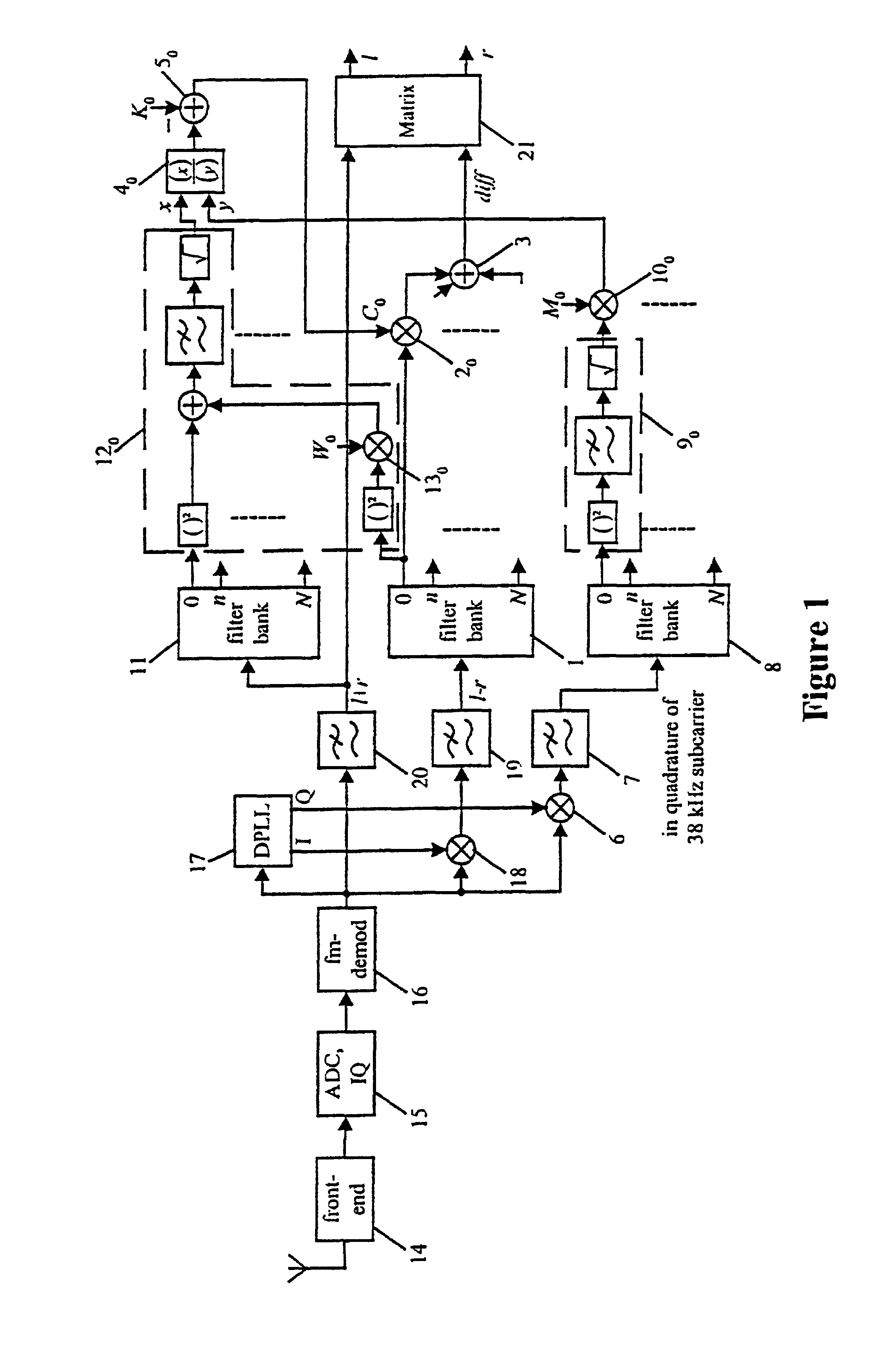
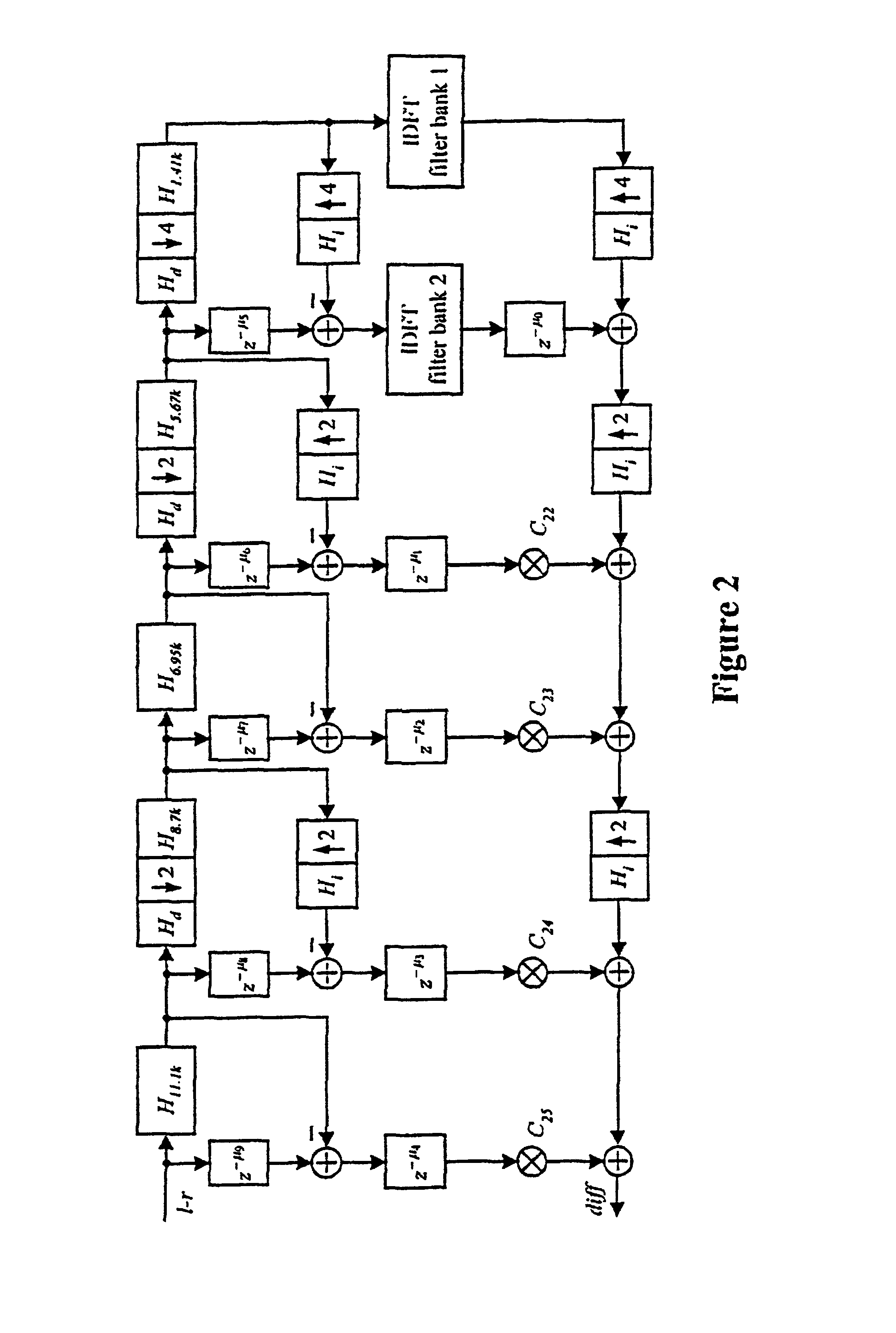
A method to denoise a stereo signal comprising a stereo sum signal and a stereo difference signal, performs a frequency selective stereo to mono blending based on the masking effect of the human auditory system. Therefore, a stereo signal noise reducer, comprising a first filter bank (1) to split the stereo difference signal (1−r) into a plurality of subbands, respective first multipliers (20, . . . , 2N) to weight each of the subbands of the stereo difference signal with a respective corresponding control signal (C0, . . . , CN), and a first adder (3) to sum all weighted subbands of the stereo difference signal (1−r) to build a frequency selective weighted stereo difference signal (diff), within which a number and width of the subbands obtained via the first filter bank (1) are choosen according to the properties of the human auditory system, further comprises a weighting factor determination unit which determines a respective control signal (C0, . . . , CN) frequency selective based on the masking effect of the human auditory system.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Signal processing utilizing a tree-structured array
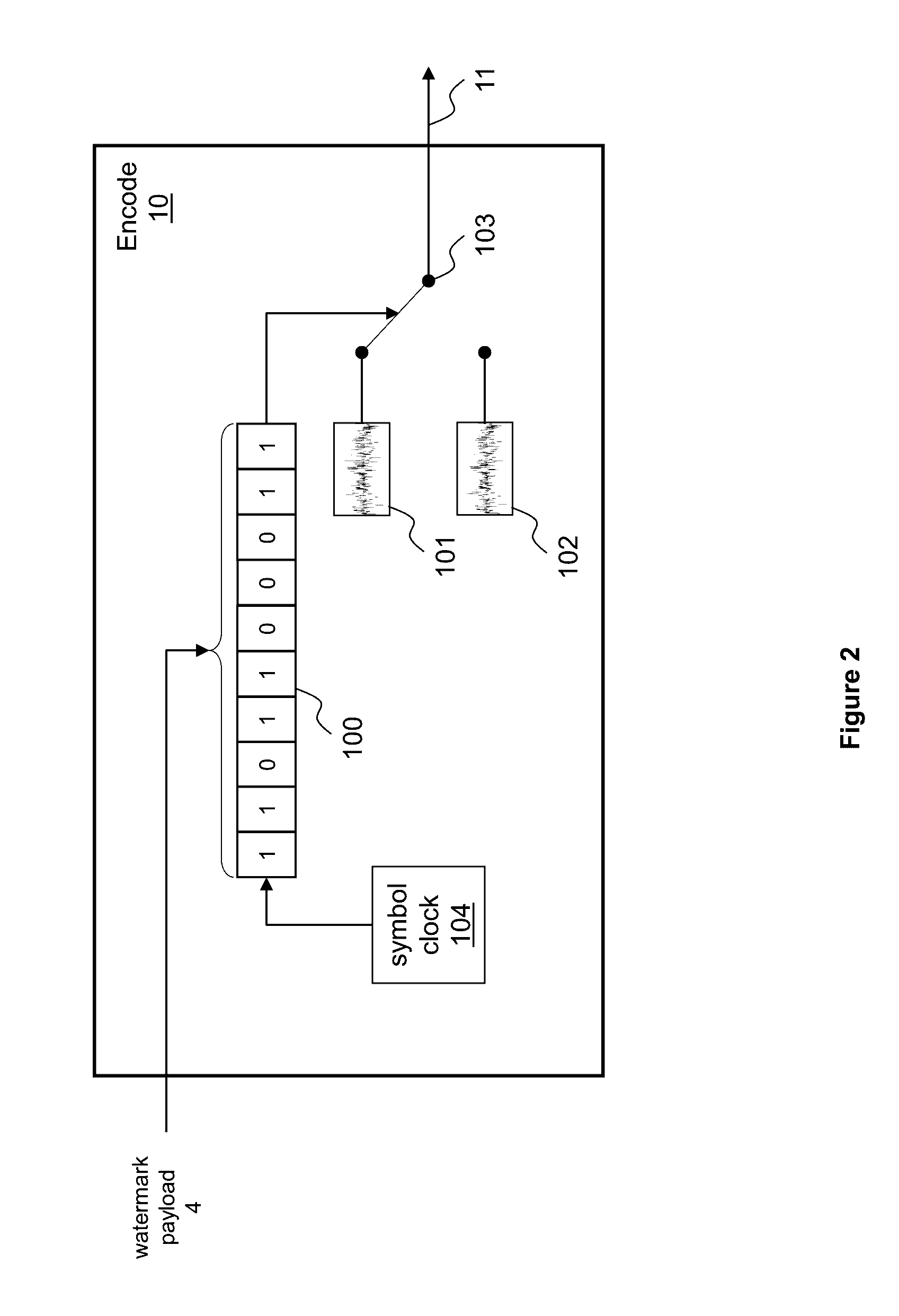
InactiveUSRE40281E1Computational workloadAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsSpeech analysisTelecommunications linkHuman auditory system
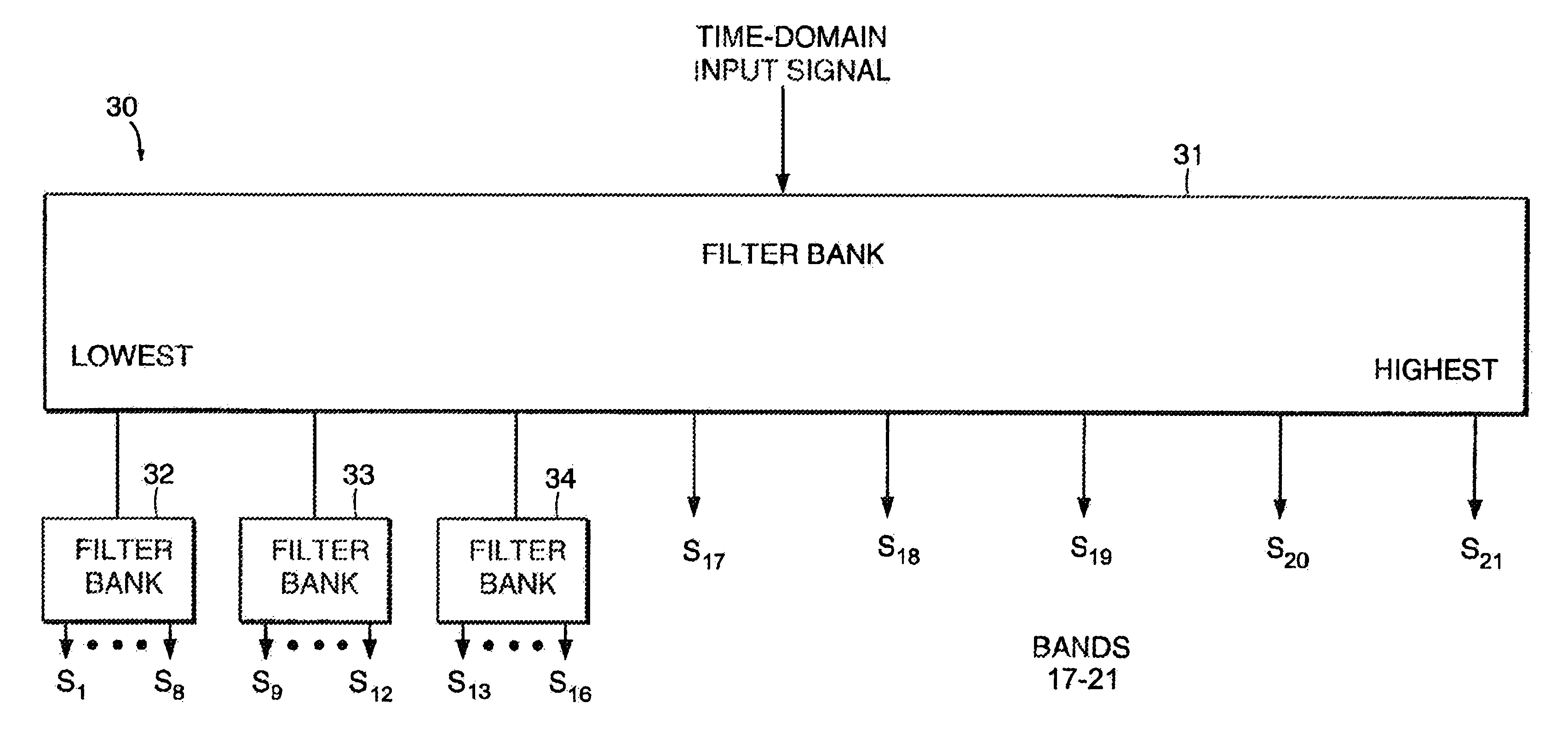
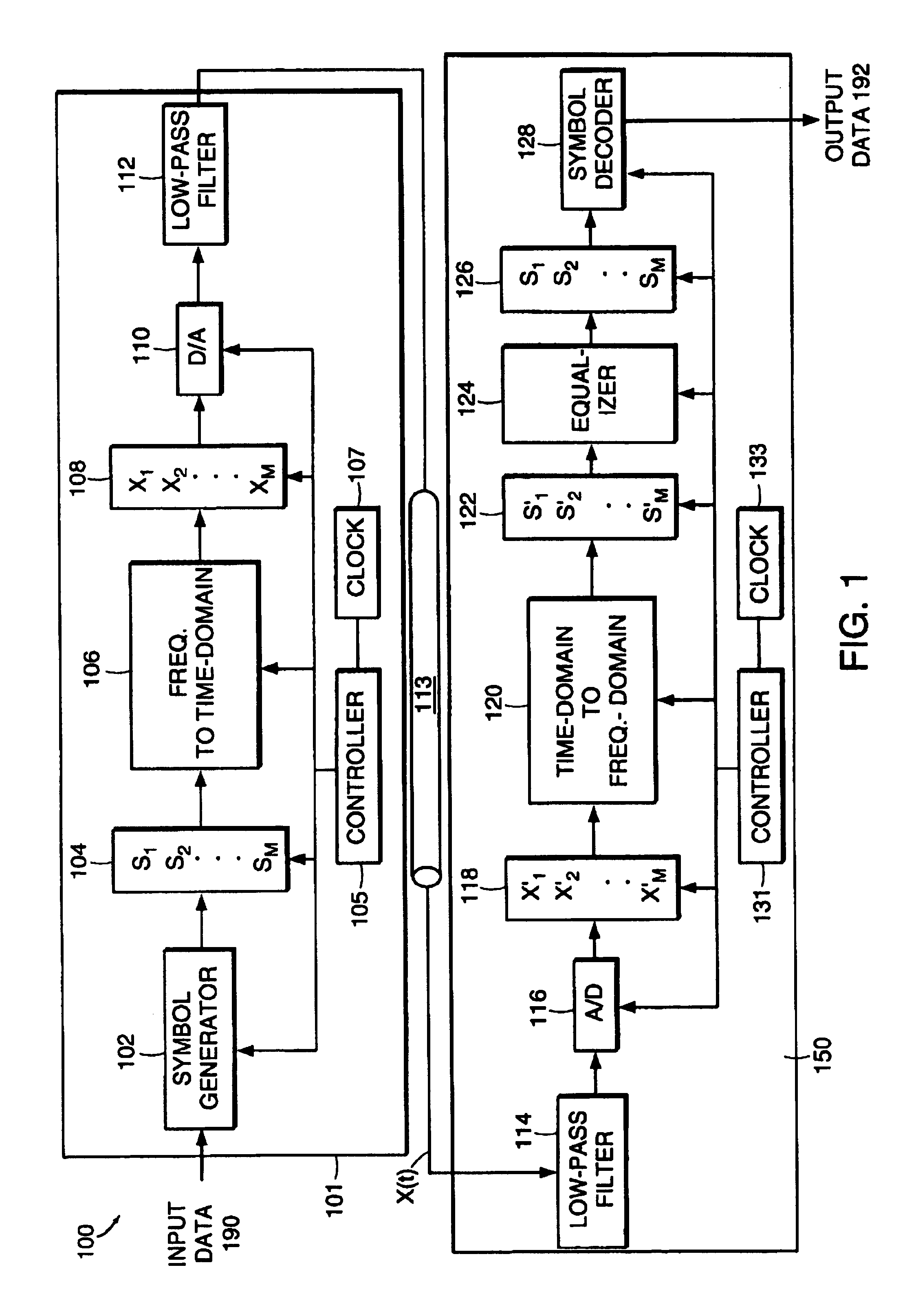
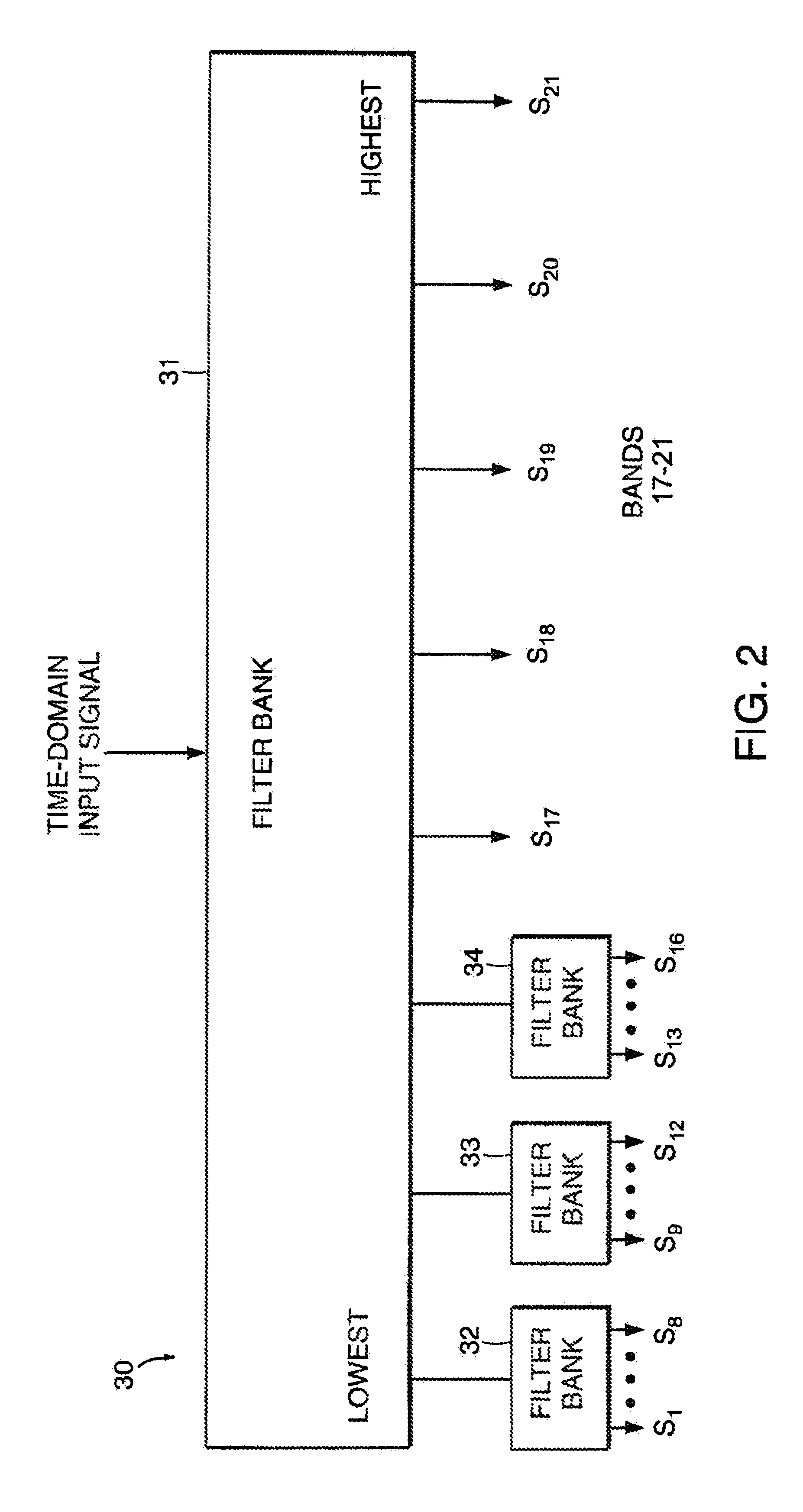
A communication system for sending a sequence of symbols on a communication link. The system includes a transmitter for placing information indicative of the sequence of symbols on the communication link and a receiver for receiving the information placed on the communication link by the transmitter. The transmitter includes a clock for defining successive frames, each of the frames including M time intervals, where M is an integer greater than 1. A modulator modulates each of M carrier signals with a signal related to the value of one of the symbols thereby generating a modulated carrier signal corresponding to each of the carrier signals. The modulated carriers are combined into a sum signal which is transmitted on the communication link. The carrier signals include first and second carriers, the first carrier having a different bandwidth than the second carrier. In one embodiment, the modulator includes a tree-structured array of filter banks having M leaf nodes, each of the values related to the symbols forming an input to a corresponding one of the leaf nodes. Each of the nodes includes one of the filter banks. Similarly, the receiver can be constructed of a tree-structured array of sub-band filter banks for converting M time-domain samples received on the communication link to M symbol values.Signal processing is performed by splitting a signal into subbands using a plurality of filter banks connected to form a tree-structured array. The filter banks are connected so that the signal is split into subbands of different size. The subbands can be designed to approximate the bands of the human auditory system for audio signal processing applications. Reconstruction of signals using a plurality of synthesis filter banks connected to form a tree-structured array is also performed.
Owner:HYBRID AUDIO
Method for individually fitting a hearing instrument
ActiveUS20070223752A1Reduce in quantityAccurate interpolationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman auditory systemHearing perception
A method for individually fitting a hearing instrument to a user, comprising at least one microphone for generating an input audio signal from ambient sound, an audio signal processing unit for processing the input audio signal into a processed output audio signal, and a transducer for stimulation of the human auditory system according to the processed output audio signal as input to said transducer is described, the method comprising: providing the user with the hearing instrument and starting operation of the hearing instrument; pre-defining a desired target loudness function, wherein loudness perception of a stimulus by the user when using the hearing instrument is defined as function of frequency and input sound pressure level at the microphone; measuring for a given measurement parameter set of perceived loudness levels and frequencies or frequency bands the respective transducer input audio signal level to be applied to the transducer input in order to achieve the respective perceived loudness level at the respective frequency or frequency band, said measurement parameter set comprising at least a low loudness level, an intermediate loudness level and a high loudness level, and said intermediate loudness level being measured for a larger number of frequencies or frequency bands and with a finer frequency resolution than said low and high loudness levels; calculating an individual gain function to be implemented in the audio signal processing unit in order to achieve the pre-defined target loudness function by taking into account the measured transducer input audio signal levels; and operating the hearing instrument with the individual gain function.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Binaural compression system
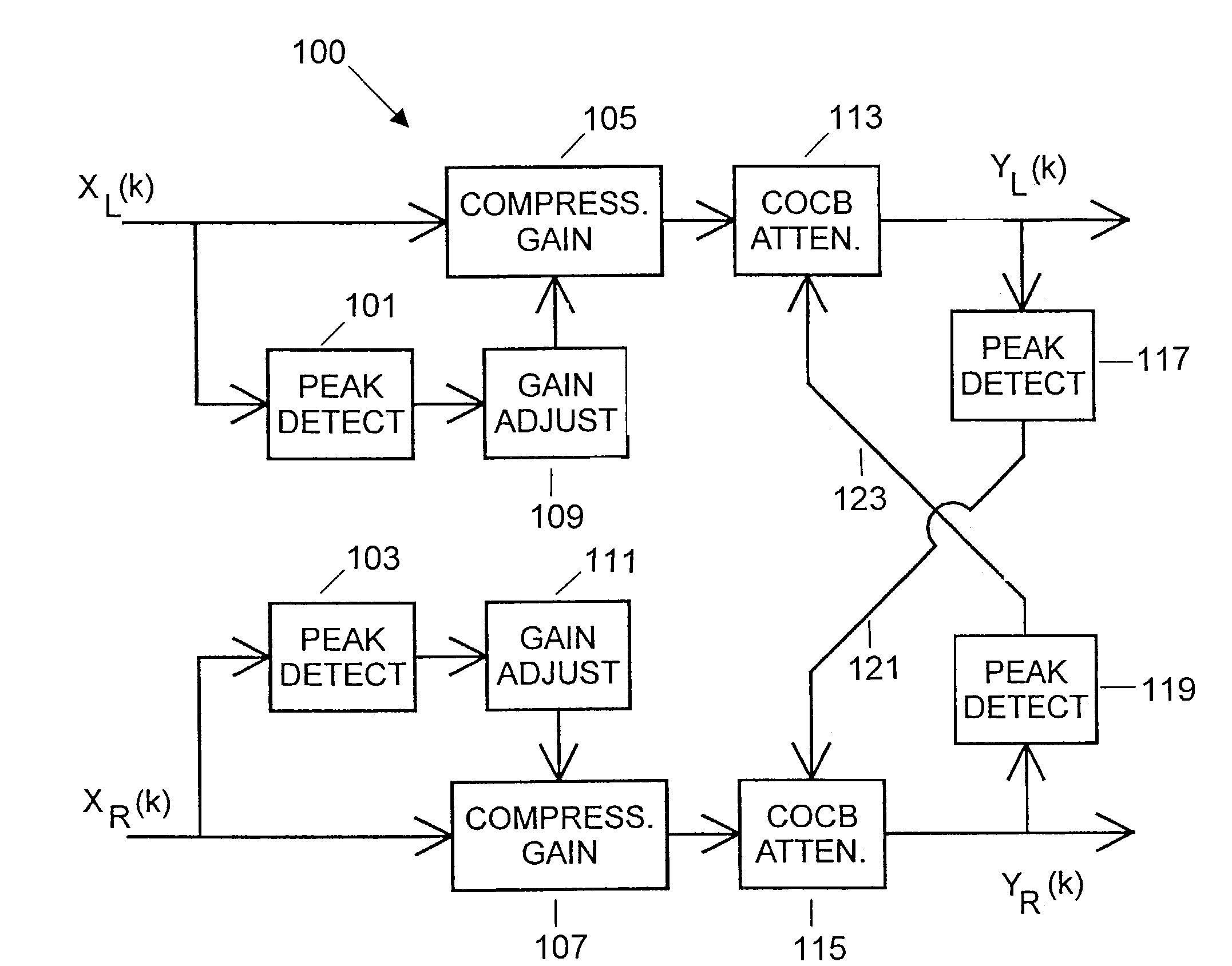
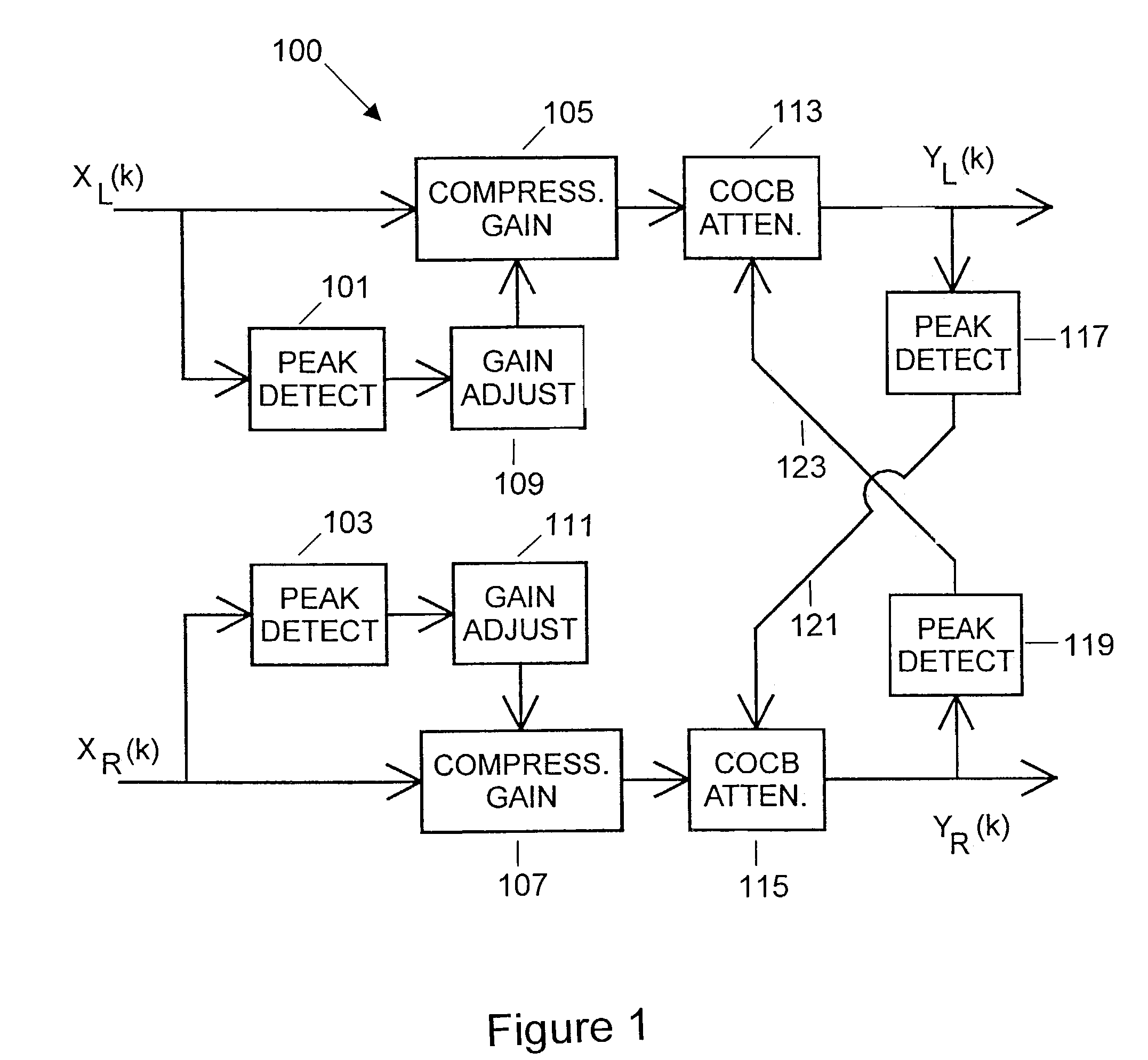
ActiveUS7630507B2Volume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesTransmissionControl signalHuman auditory system
A multi-channel signal processing system adapted to provide binaural compressing of tonal inputs is provided. Such a system can be used, for example, in a binaural hearing aid system to provide the dynamic-range binaural compression of the tonal inputs. The multi-channel signal processing system is essentially a system with two signal channels connected by a control link between the two signal channels, thereby allowing the binaural hearing aid system to model behaviors, such as crossed olivocochlear bundle (COCB) effects, of the human auditory system that includes a neural link between the left and right ears. The multi-channel signal processing system comprises first and second channel compressing units respectively located in first and second signal channels of the multi-channel signal processing system. The first and second channel compressing units receive first and second channel input signals, respectively, to generate first and second channel compressed outputs. The multi-channel signal processing system further includes peak detecting means detecting signal peaks of the first and second channel input signals for generating first and second channel control signals. Thereafter, gain adjusting means adjusts signal gains of the first and second channel control signals. The first and second channel compressing units then respectively compress the first and second channel input signals to produce the first and second channel compressed outputs in accordance with the adjusted first and second channel control signals, respectively.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Spectro-temporal varying approach for speech enhancement
ActiveUS20080167866A1Fine frequency resolutionLess frequency resolutionEar treatmentDigital computer detailsTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
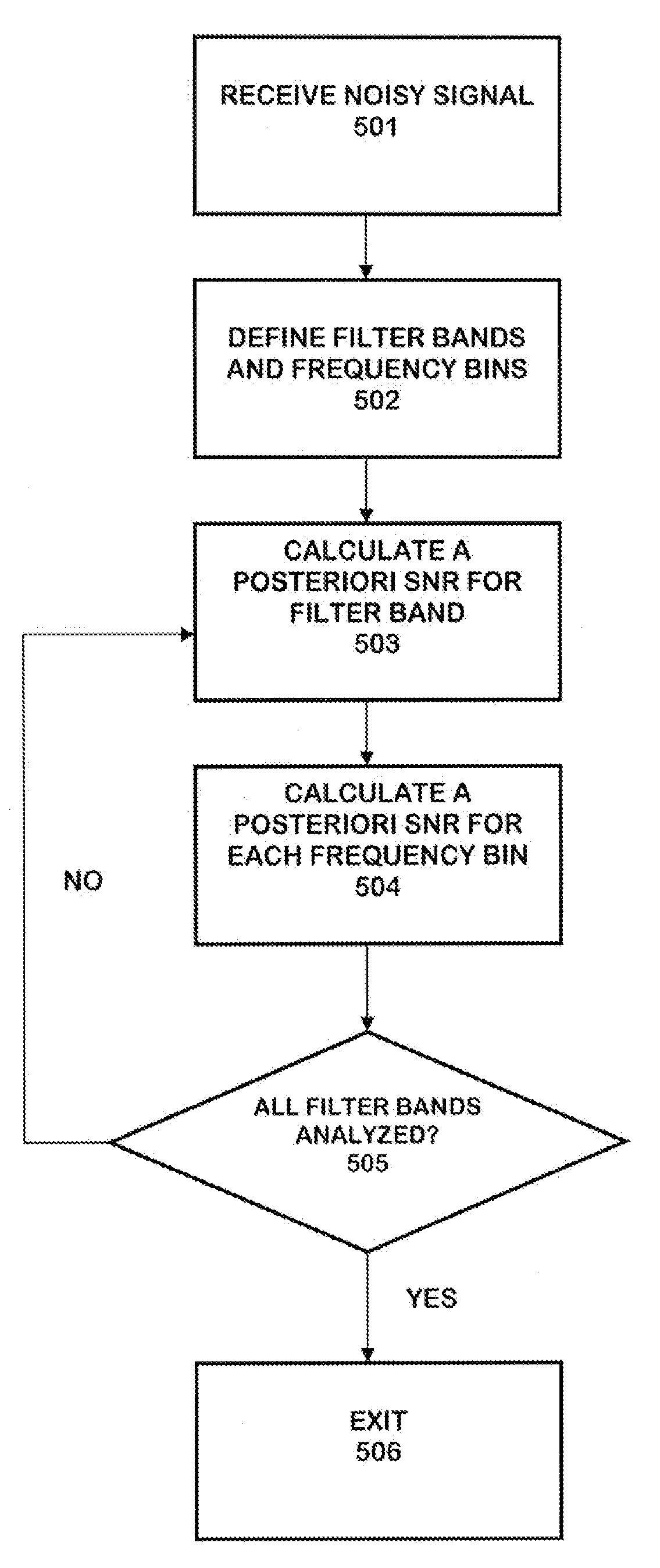
The present system proposes a technique called the spectro-temporal varying technique, to compute the suppression gain. This method is motivated by the perceptual properties of human auditory system; specifically, that the human ear has higher frequency resolution in the lower frequencies band and less frequency resolution in the higher frequencies, and also that the important speech information in the high frequencies are consonants which usually have random noise spectral shape. A second property of the human auditory system is that the human ear has lower temporal resolution in the lower frequencies and higher temporal resolution in the higher frequencies. Based on that, the system uses a spectro-temporal varying method which introduces the concept of frequency-smoothing by modifying the estimation of the a posteriori SNR. In addition, the system also makes the a priori SNR time-smoothing factor depend on frequency. As a result, the present method has better performance in reducing the amount of musical noise and preserves the naturalness of speech especially in very noisy conditions than do conventional methods.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
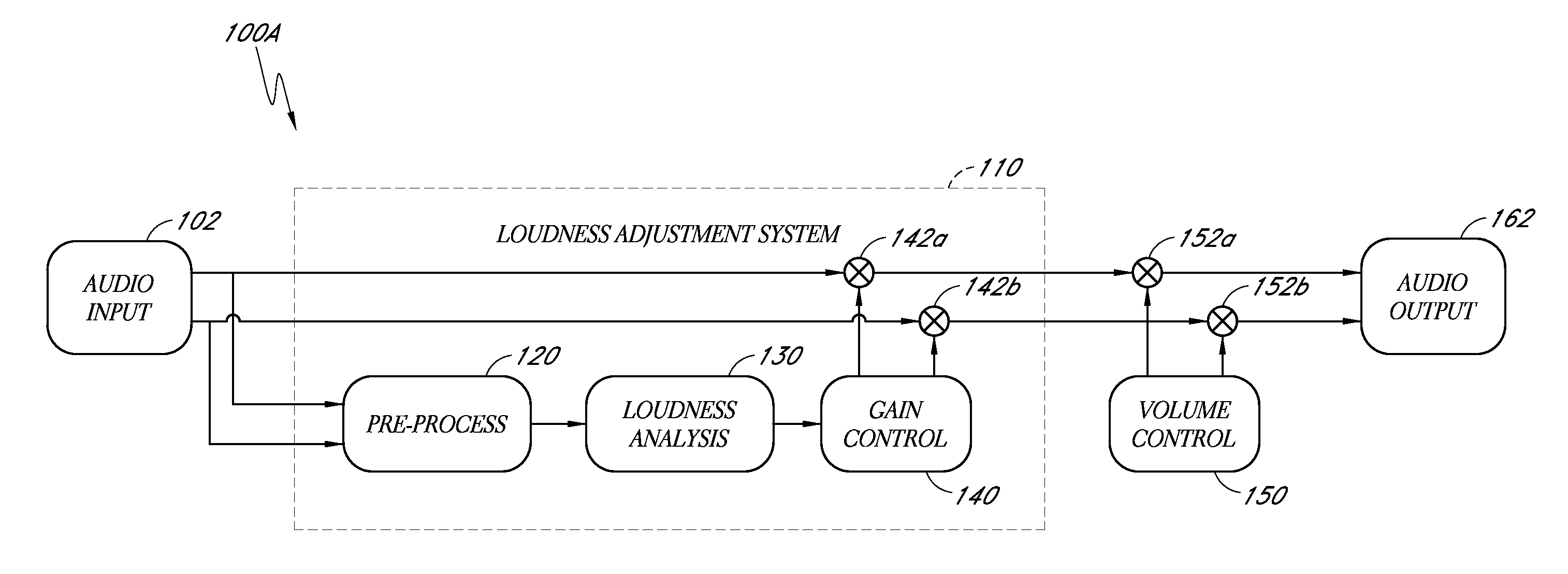
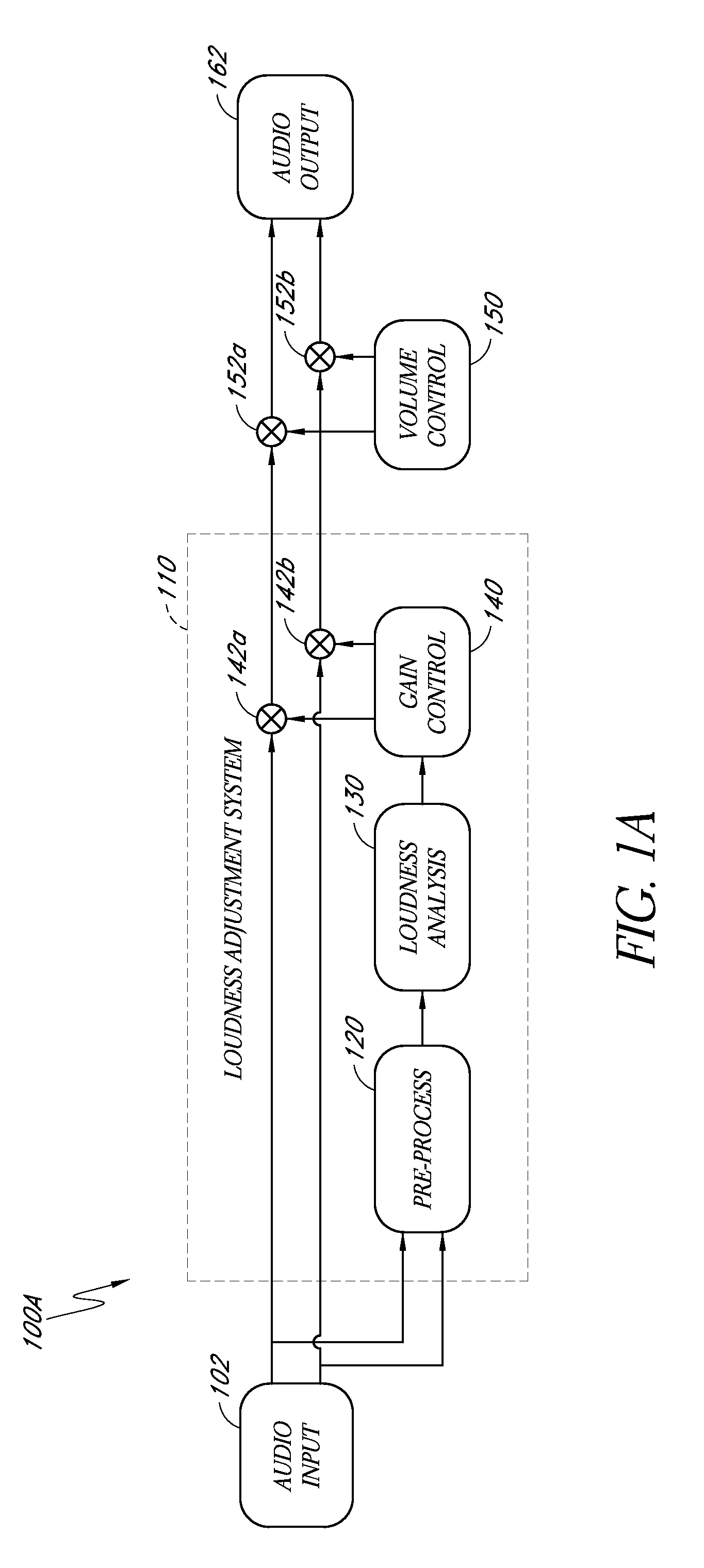
System for adjusting perceived loudness of audio signals
A method of adjusting a loudness of an audio signal may include receiving an electronic audio signal and using one or more processors to process at least one channel of the audio signal to determine a loudness of a portion of the audio signal. This processing may include processing the channel with a plurality of approximation filters that can approximate a plurality of auditory filters that further approximate a human hearing system. In addition, the method may include computing at least one gain based at least in part on the determined loudness to cause a loudness of the audio signal to remain substantially constant for a period of time. Moreover, the method may include applying the gain to the electronic audio signal.
Owner:DTS
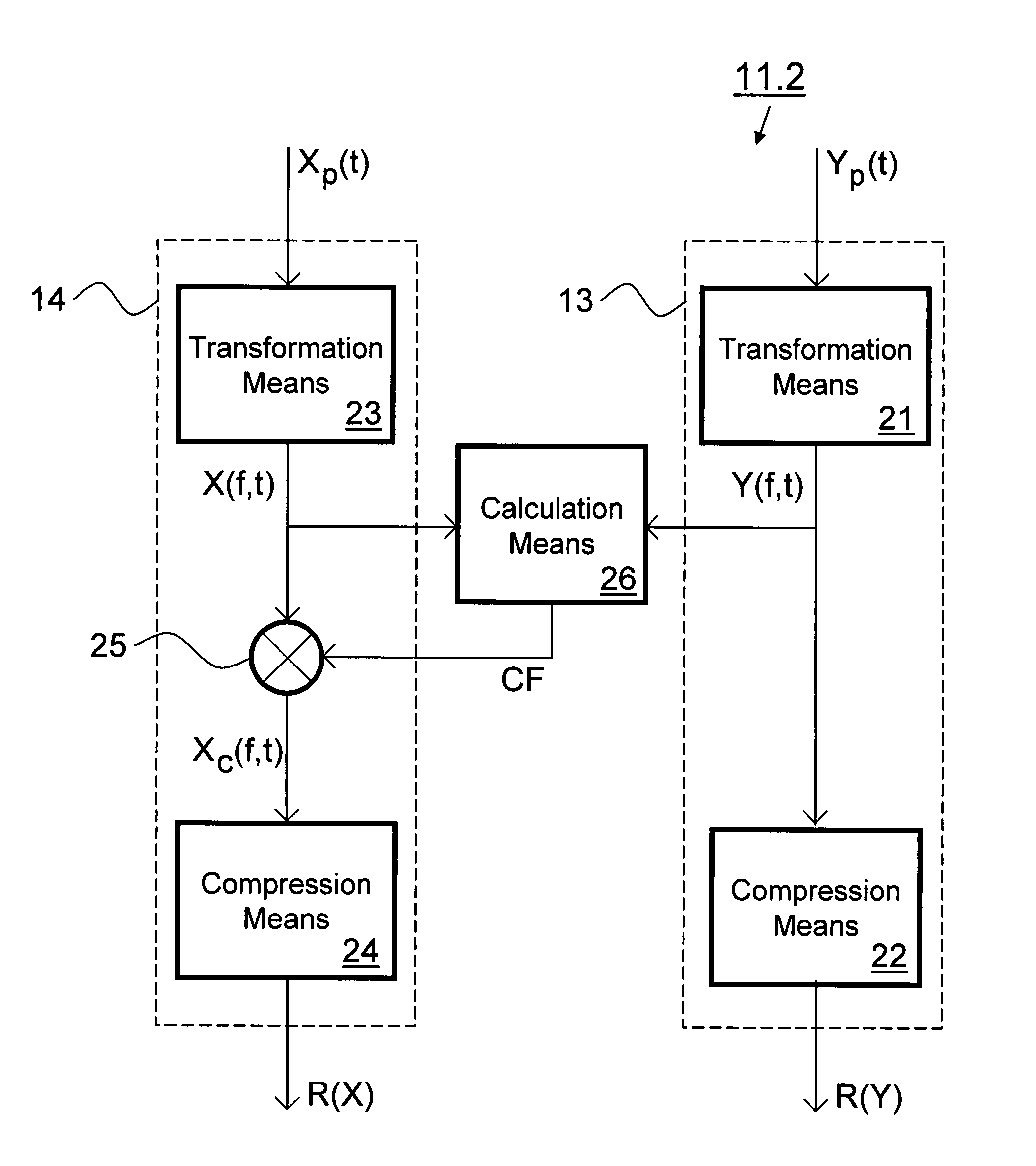
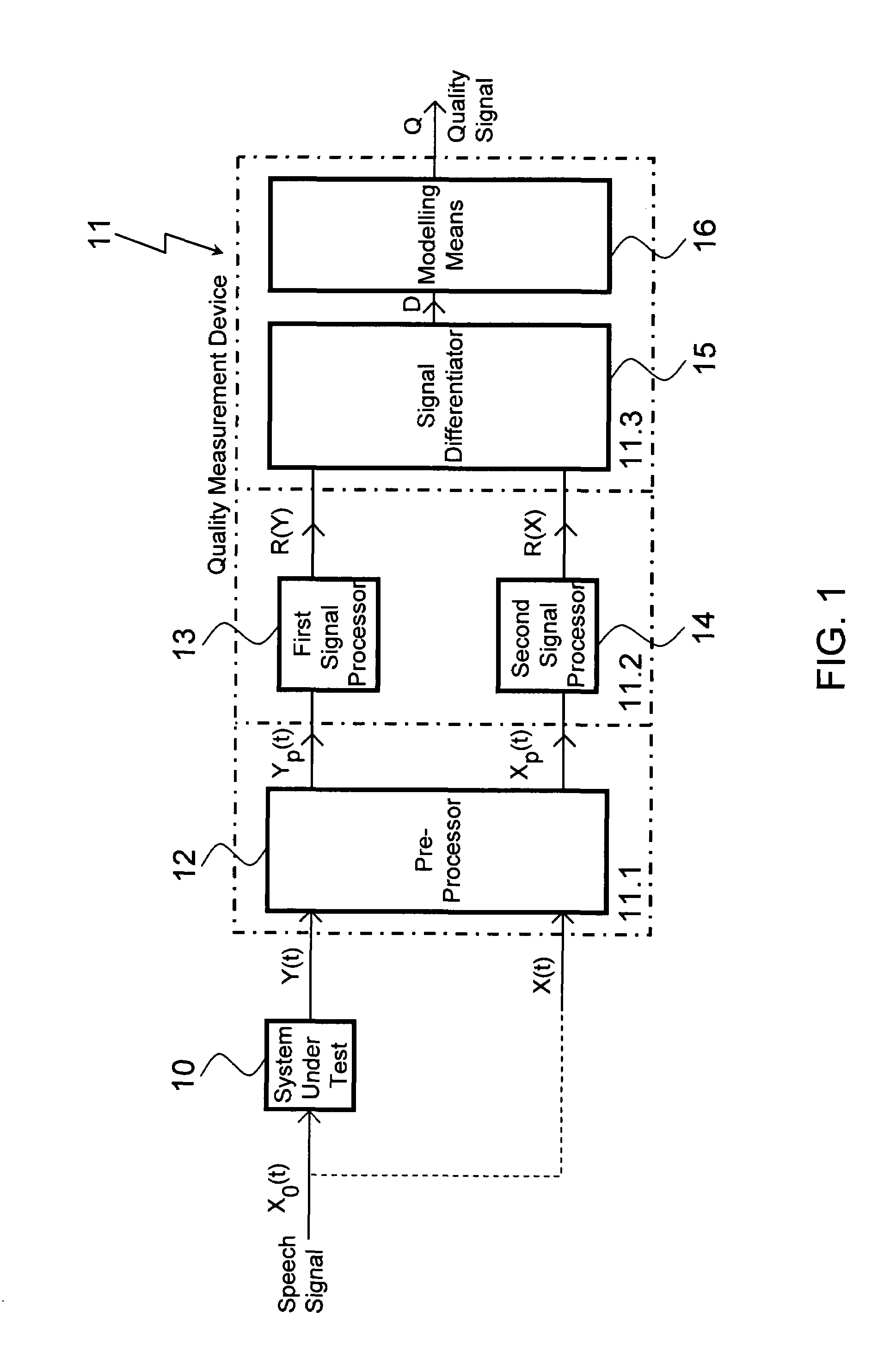
Method for determining the quality of a speech signal
Objective measurement methods and devices for predicting perceptual quality of speech signals degraded in speech processing / transporting systems have unreliable prediction results in cases where the degraded and reference signals show in between severe timbre differences. Improvement is achieved by applying a partial compensation step within in a signal processing stage using a frequency dependently clipped compensation factor for compensating power differences between the degraded and reference signals in the frequency domain. Preferably clipping values for clipping the compensation factor have larger frequency-dependency in a range of low frequencies with respect to a centre frequency of the human auditory system, than in a range of high frequencies.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
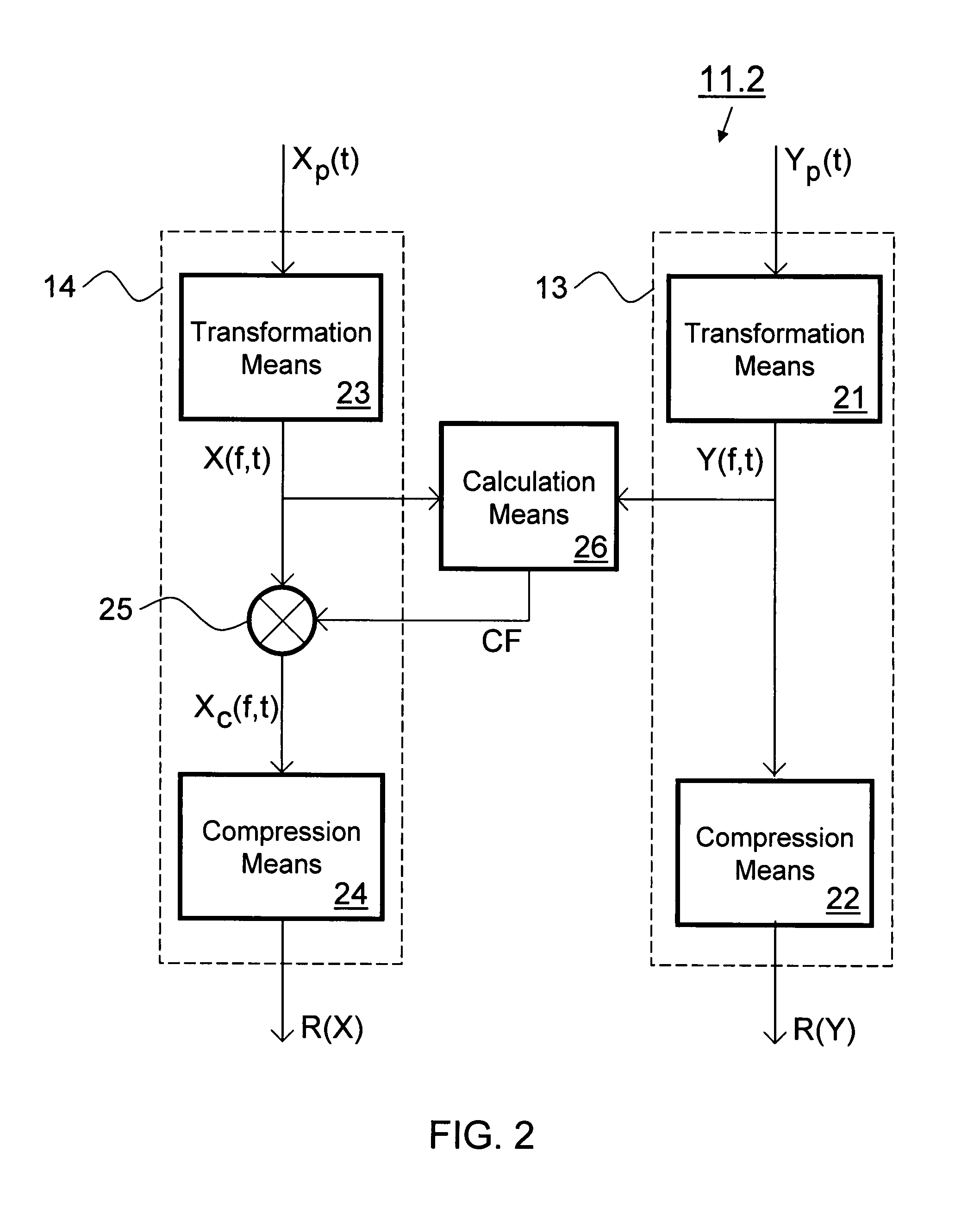
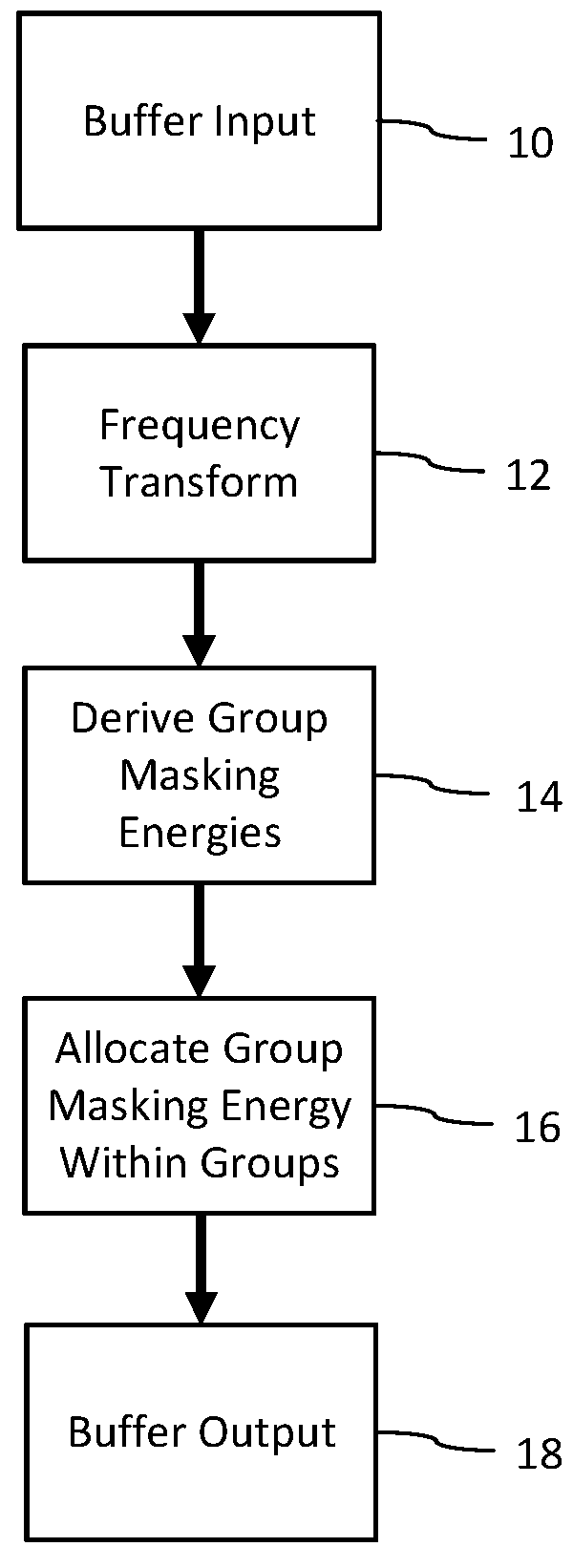
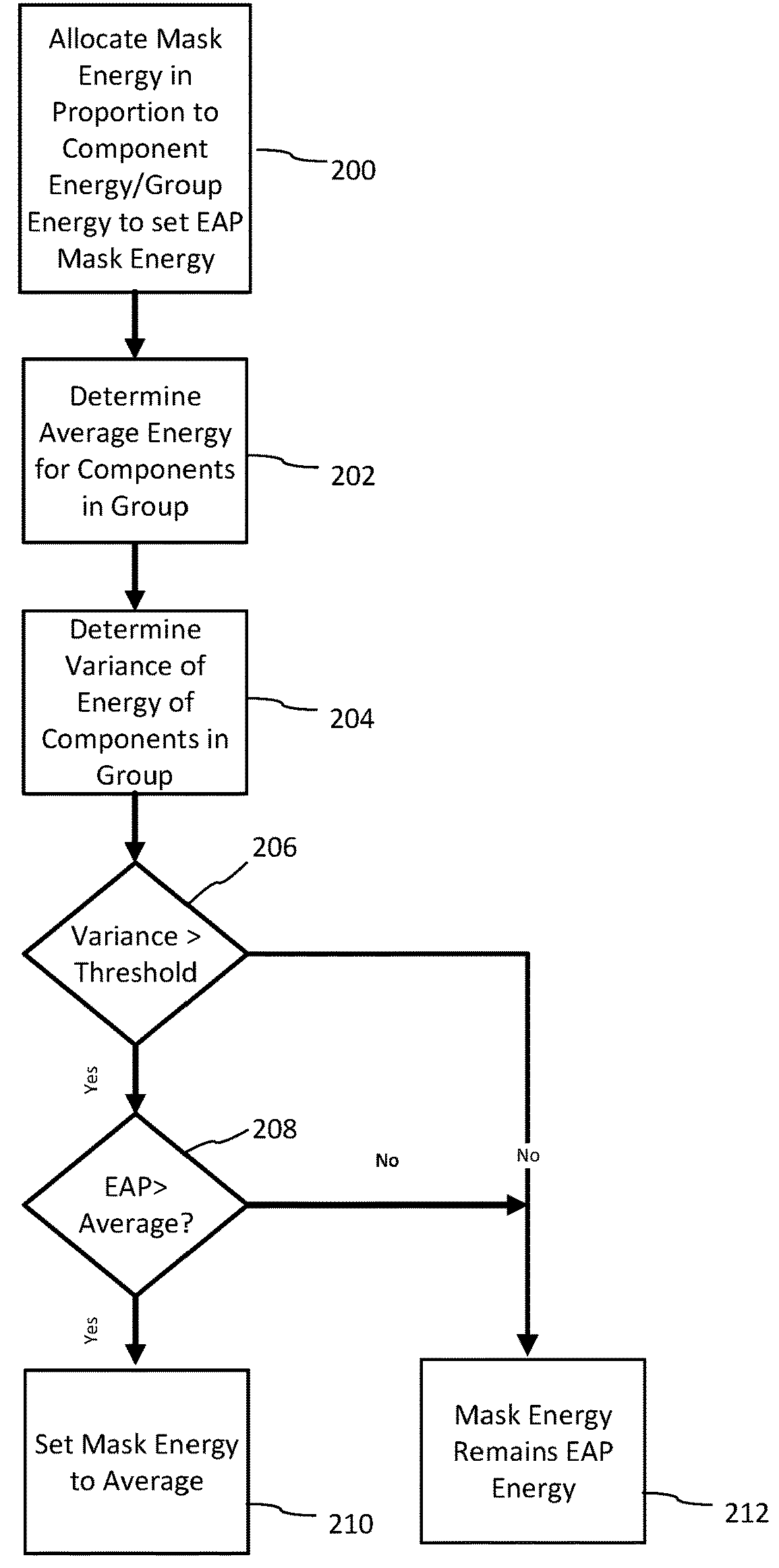
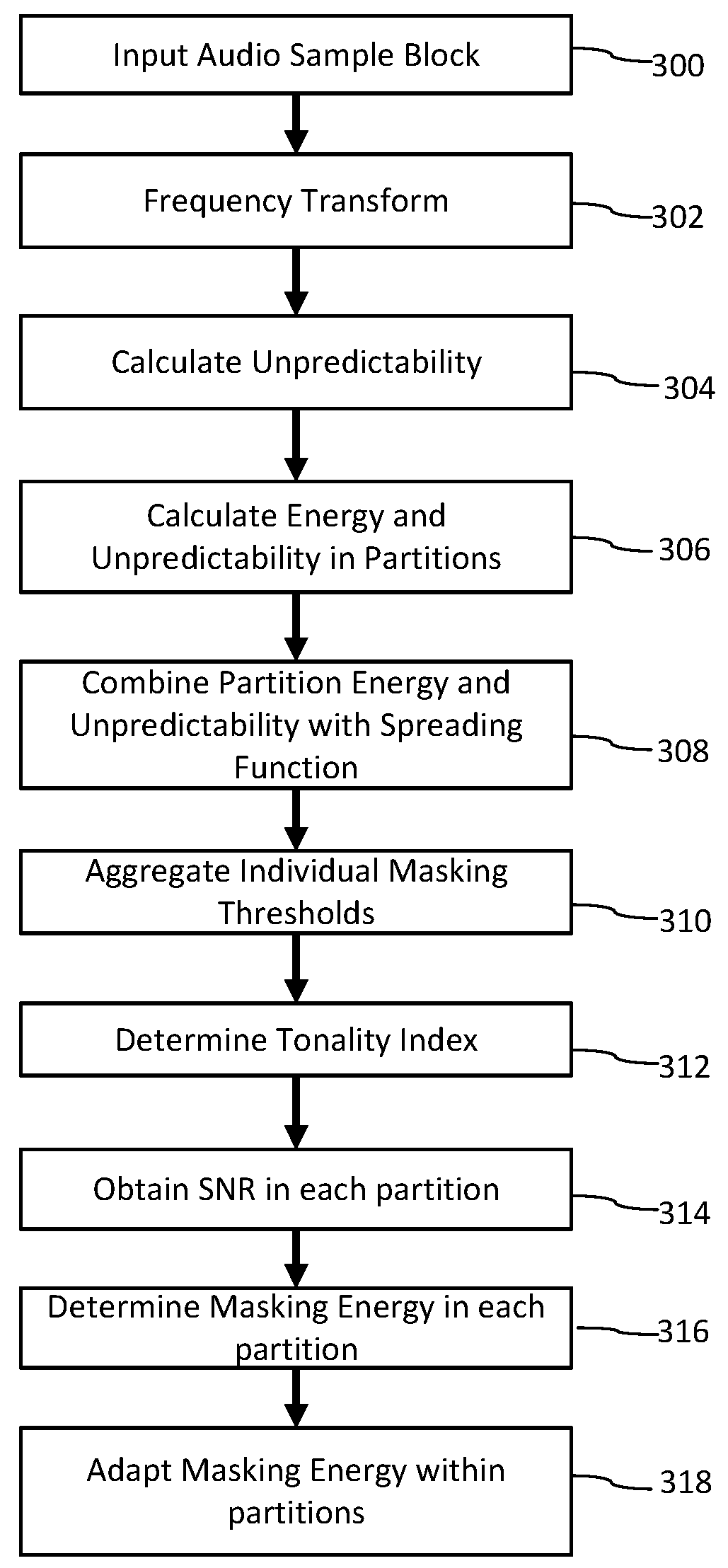
Human auditory system modeling with masking energy adaptation
ActiveUS10043527B1Improve performanceEffective meanSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementFrequency spectrumHuman auditory system
A method for generating a psychoacoustic model from an audio signal transforms a block of samples of an audio signal into a frequency spectrum comprising frequency components. From this frequency spectrum, it derives group masking energies. These group masking energies each correspond to a group of neighboring frequency components in the frequency spectrum. For a group of frequency components, the method allocates the group masking energy to the frequency components in the group in proportion to energy of the frequency components within the group to provide adapted mask energies for the frequency components within the group, the adapted mask energies providing masking thresholds for the psychoacoustic model of the audio signal.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
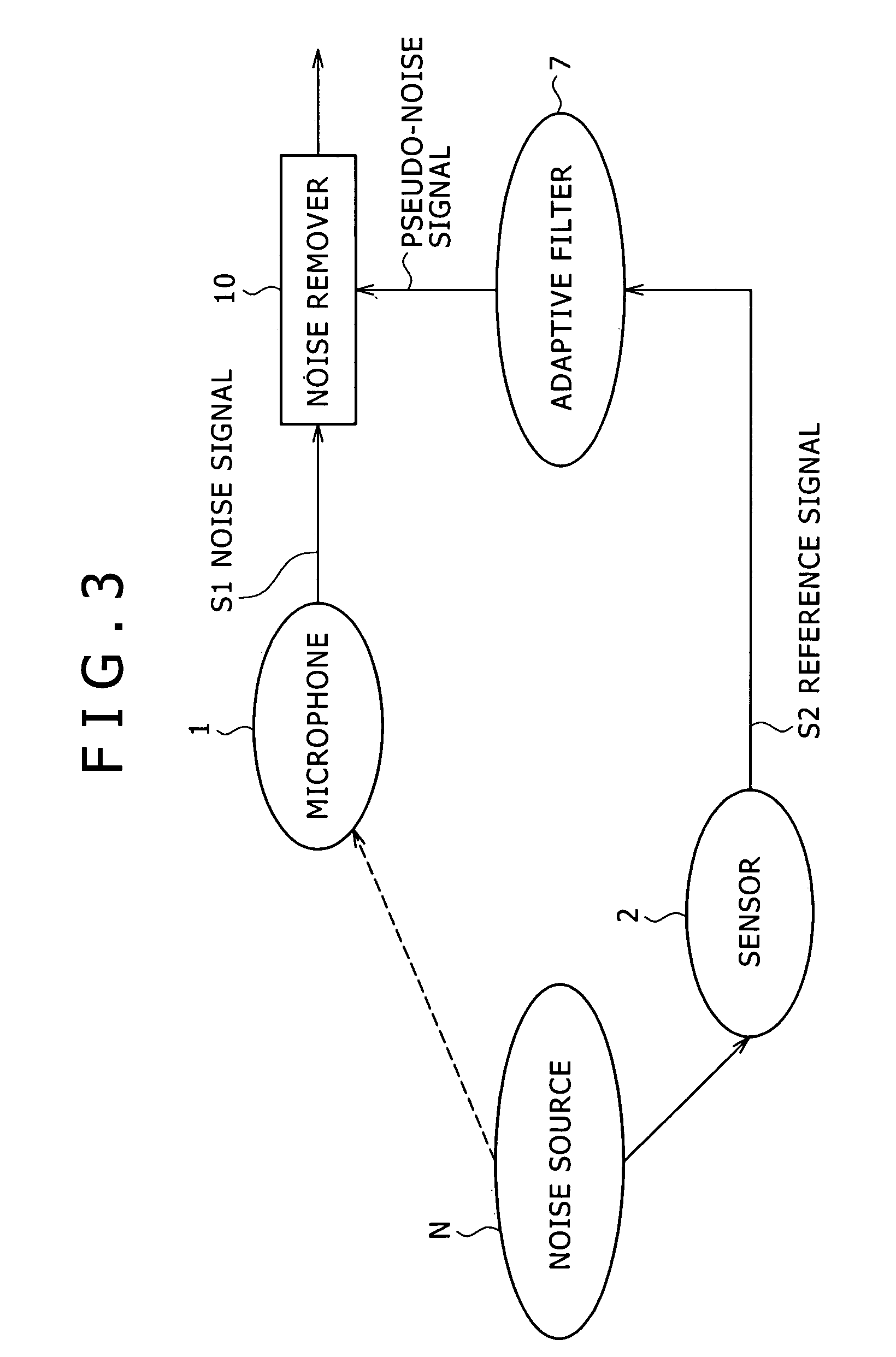
Method of and apparatus for reducing noise
InactiveUS7697699B2Reduce noiseCancel noiseSubstation/switching arrangement detailsSpeech analysisHuman auditory systemEngineering
An apparatus for reducing noise includes a comparator for generating a noise timing signal corresponding to a noise producing period of noise introduced from a noise source and contained in an audio signal, a gap time generator for generating a gap period in which to remove noise from the audio signal, a selector switch for selectively outputting the audio signal and a noise-removed signal, a level detector for detecting a signal level of the audio signal, and a masking degree determining unit for determining from the signal level detected by the level detector a gap period for which the audio signal is masked by the human auditory system. The selector switch outputs the noise-removed signal in a period corresponding to the gap period within the noise producing period of the noise timing signal, and outputs the audio signal in other than the gap period.
Owner:SONY CORP
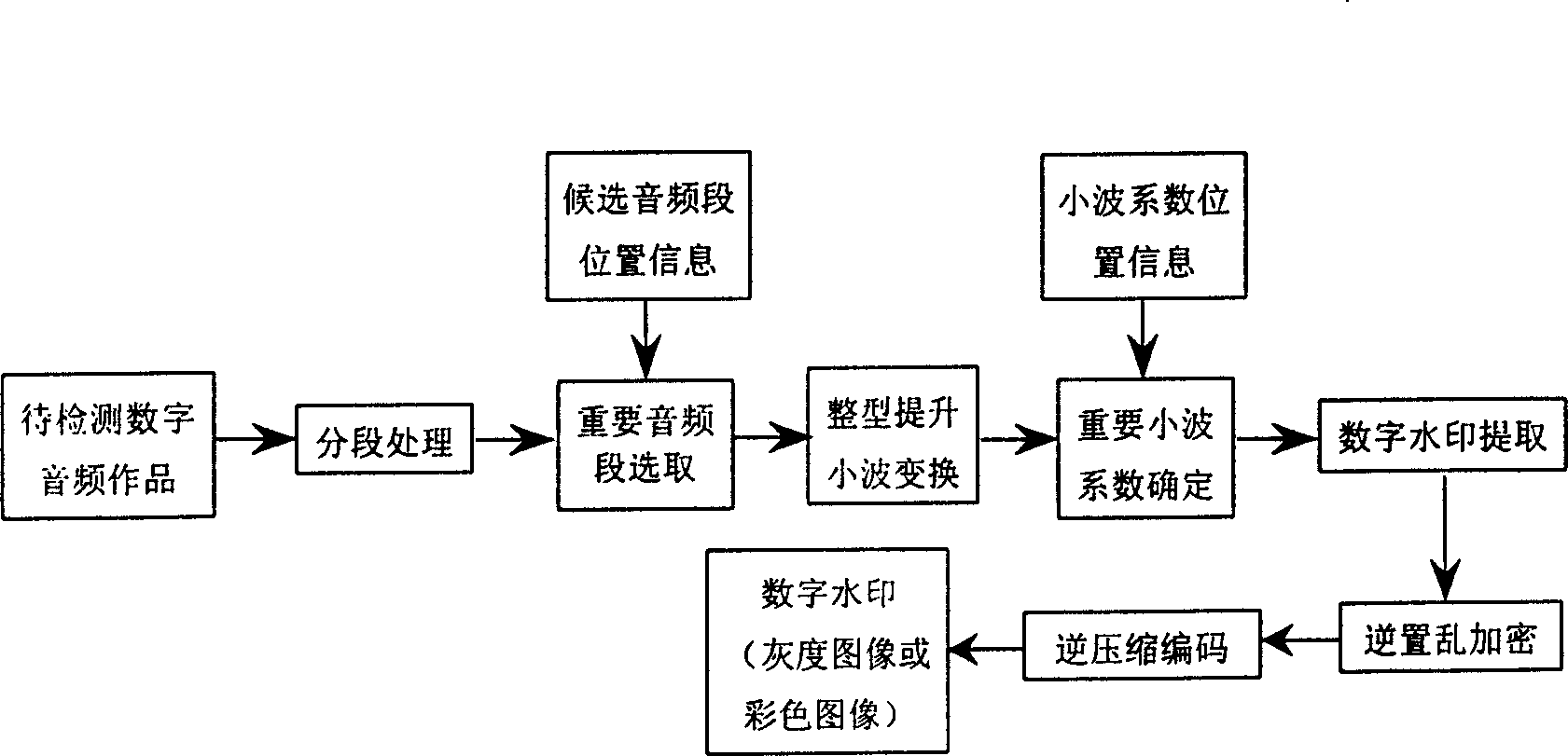
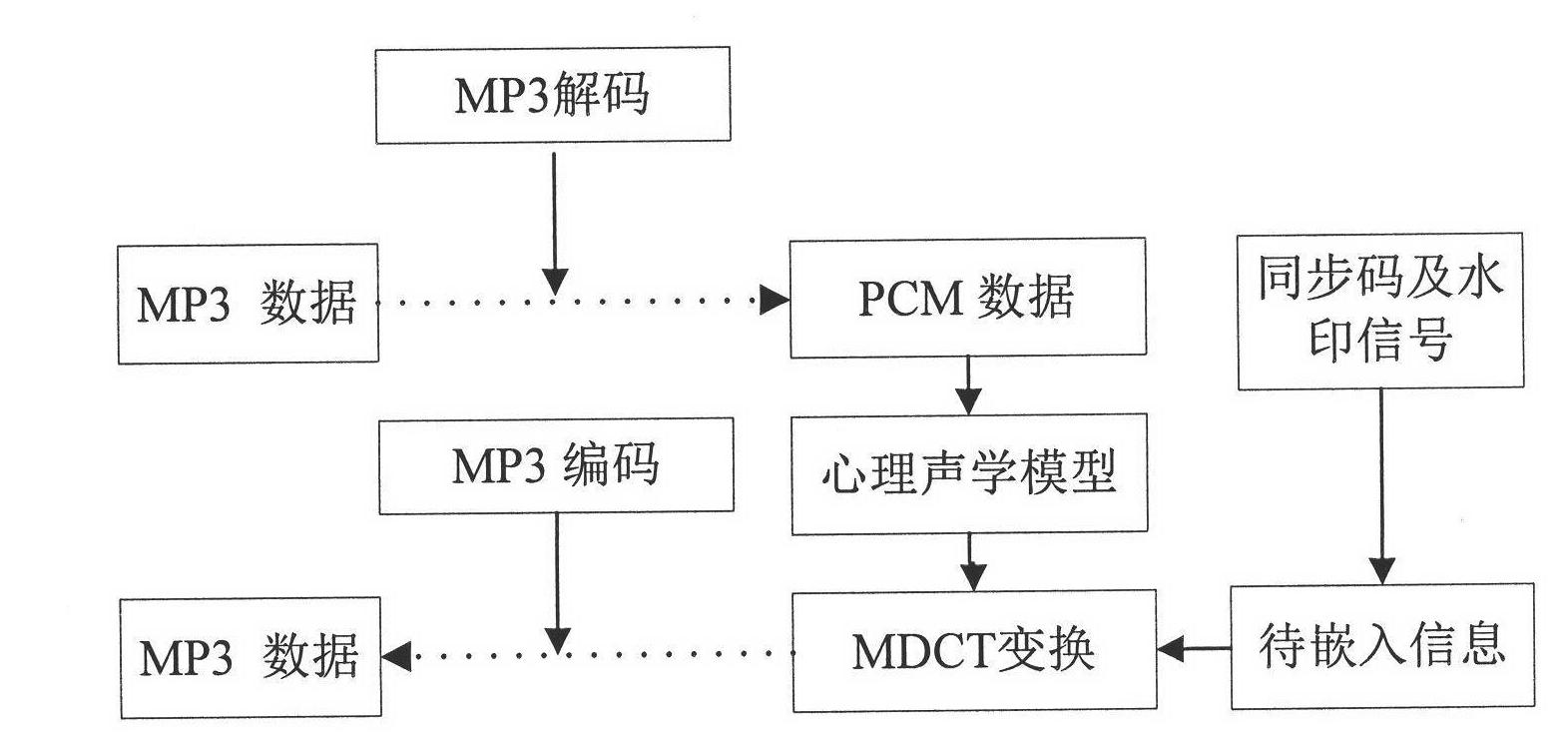
Digital audio-frequency water-print inlaying and detecting method based on auditory characteristic and integer lift ripple
InactiveCN1529246AImplementation of digital audio watermark embedding methodAchieving Adaptive DeterminationTelevision system detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionColor imageData segment
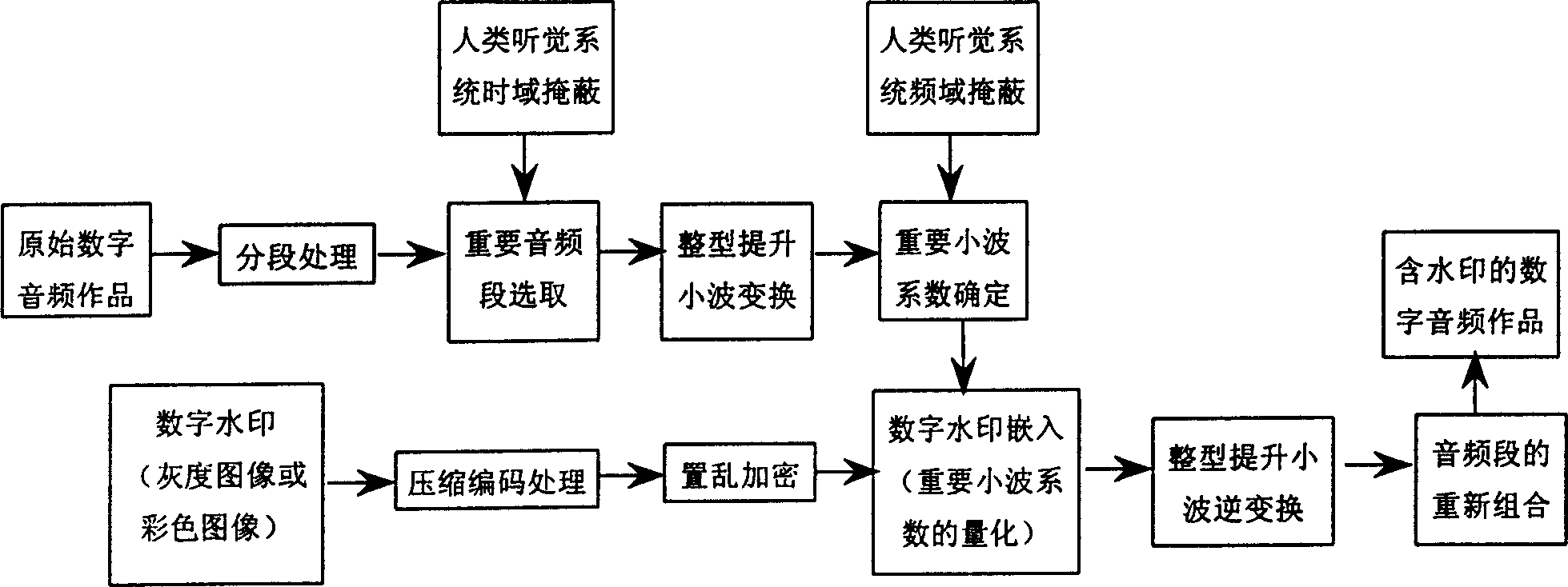
The invented method is a new digital watermark method for embedding gray image (or color image) into original digital audio production, belonging to area of information safety and multimedia information processing. first, watermark image is encoded as one dimension binary sequence, and scrambling encryption is added. Next, sectionalized treating is carried out for digital audio signal. Based on features of time domain shelter of human auditory system, integer type upgraded wavelet transform is carried out for sect of audio frequency selected in selfadaptation. Then, based on features of frequency domain, wavelet coefficient is determined in selfadaptation. Watermark information is embedded into hearing important coefficients with wavelet transformed by using quantization treating procedure. Finally, digital audio production with embedded watermark information is obtained by inversed wavelet transform and recombination of audio data sects. Inversed process can test digital watermark.
Owner:王向阳
Method and apparatus for removing signal noise
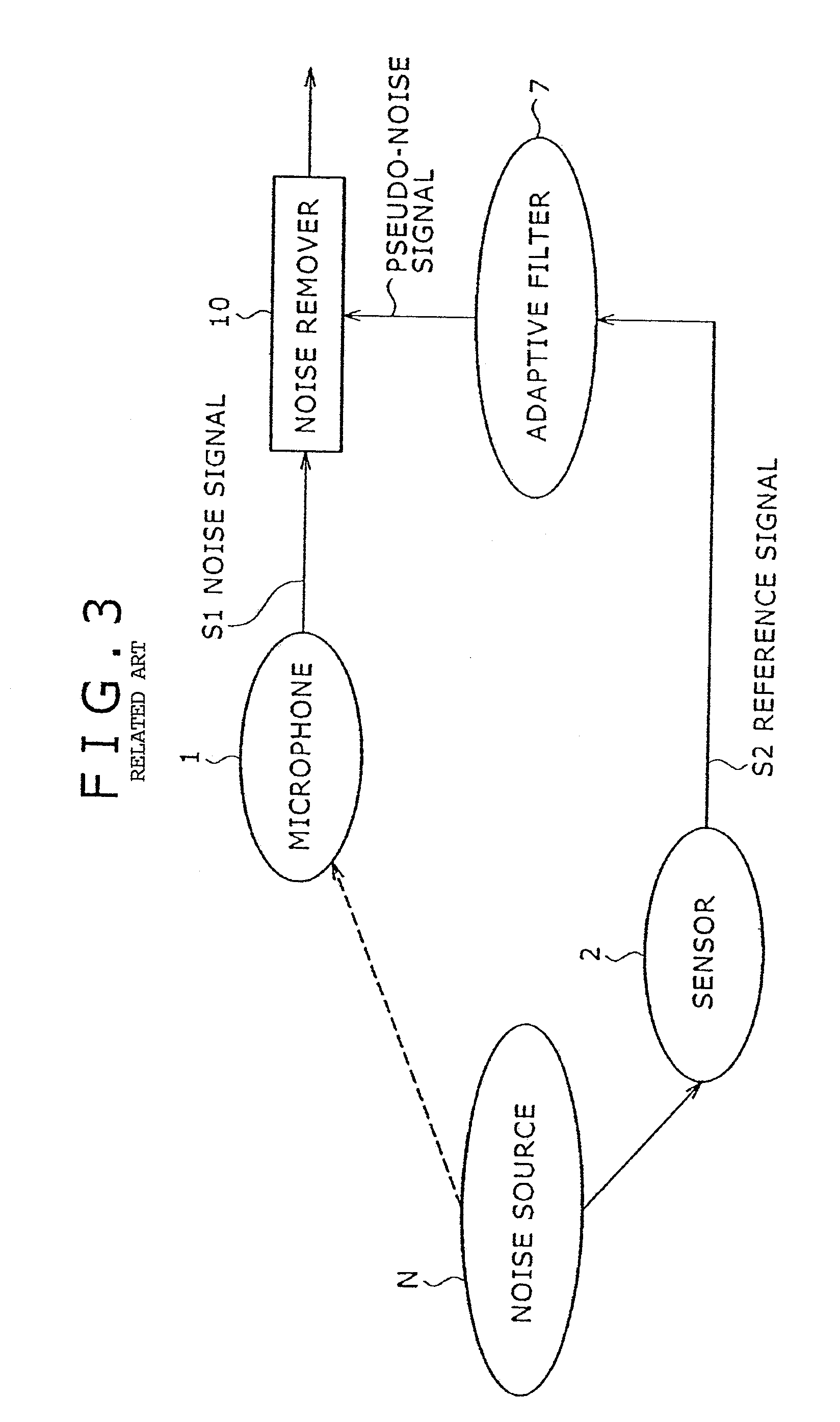
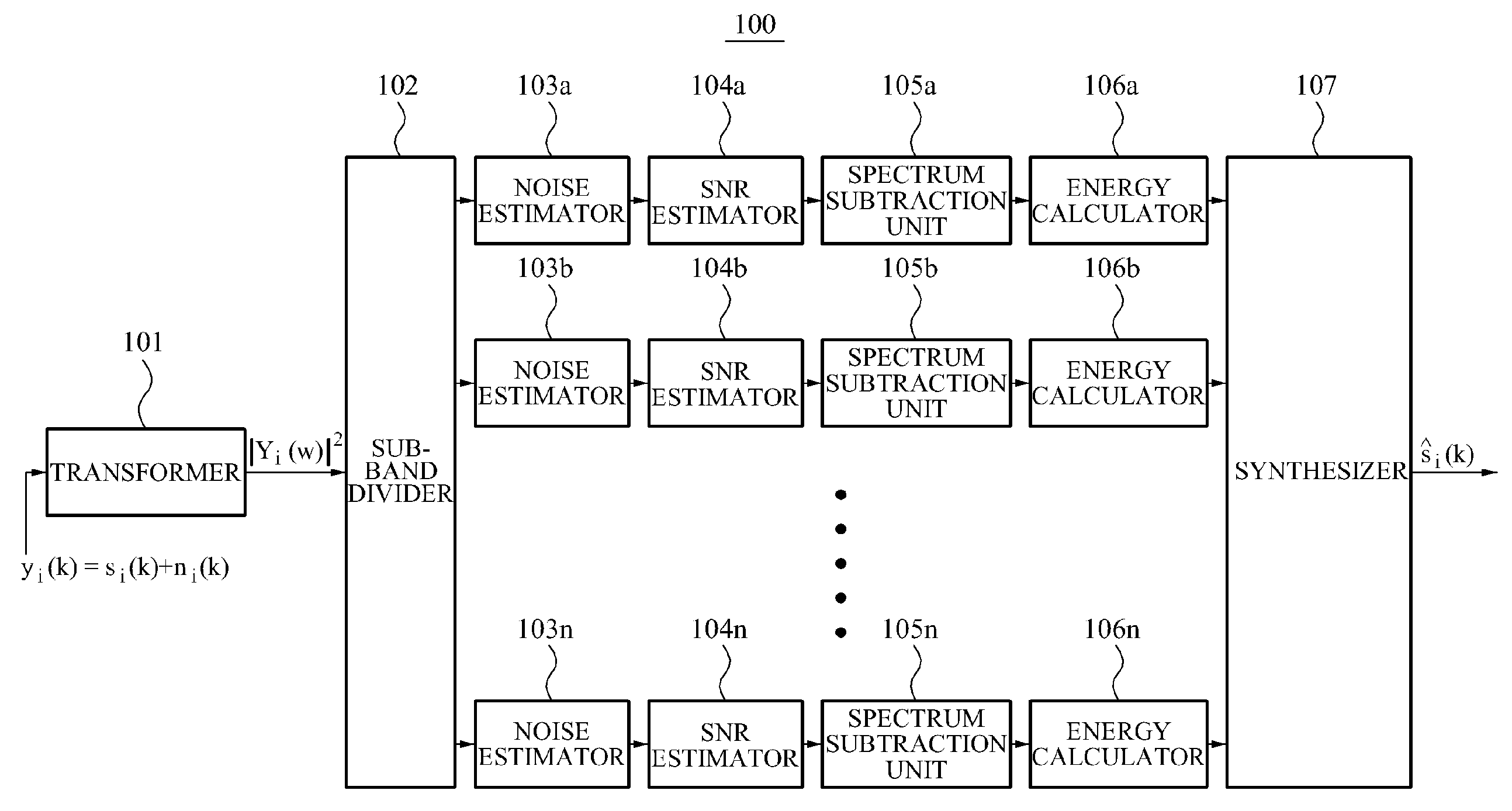
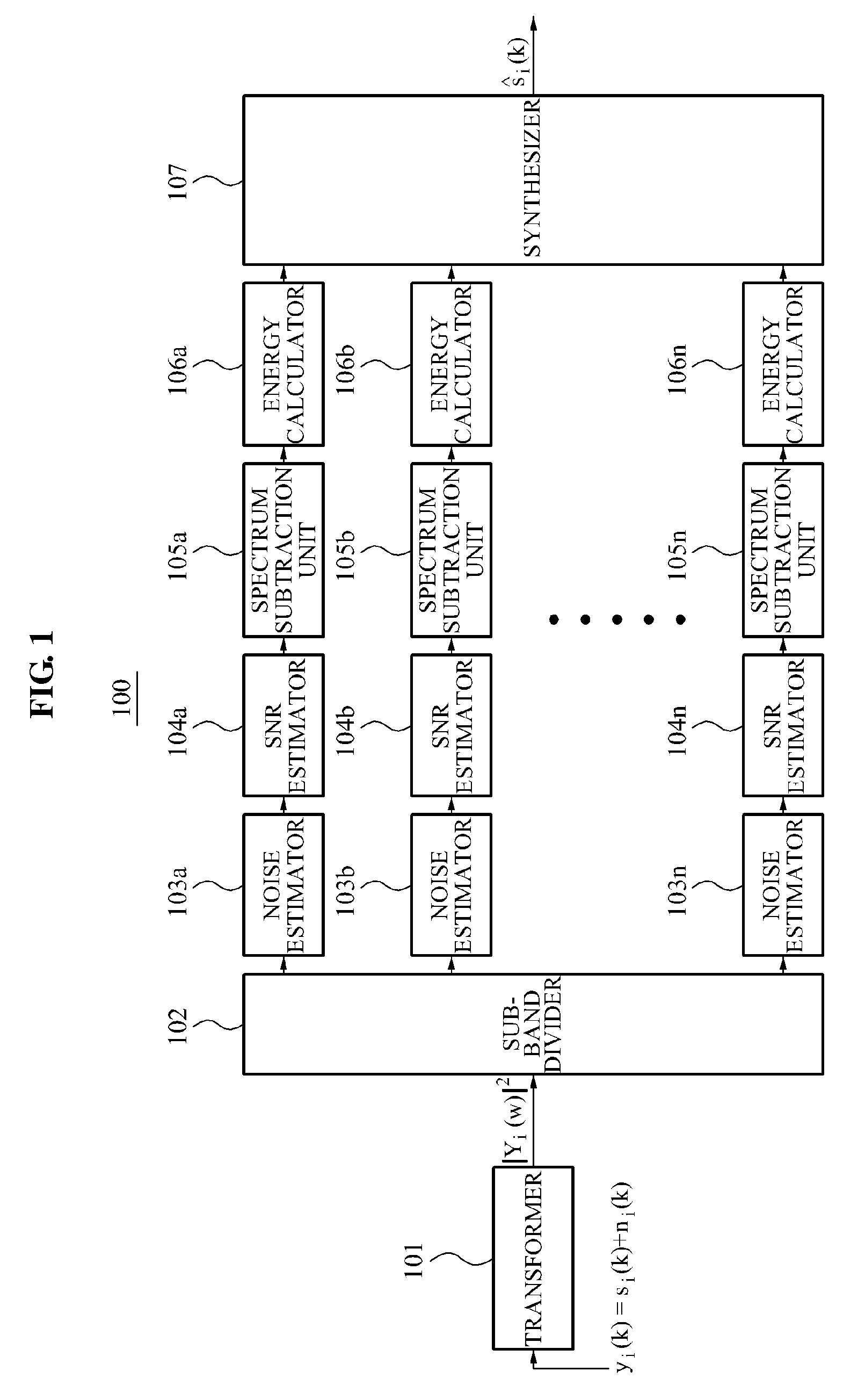
A method and apparatus for removing signal noise using multiple bands are provided. The noise removal apparatus may divide the entire frequency band into a plurality of sub-bands using a multiband filter that has characteristics similar to an auditory system of a human being and may effectively remove noise in each of the sub-bands according to a frequency subtraction scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
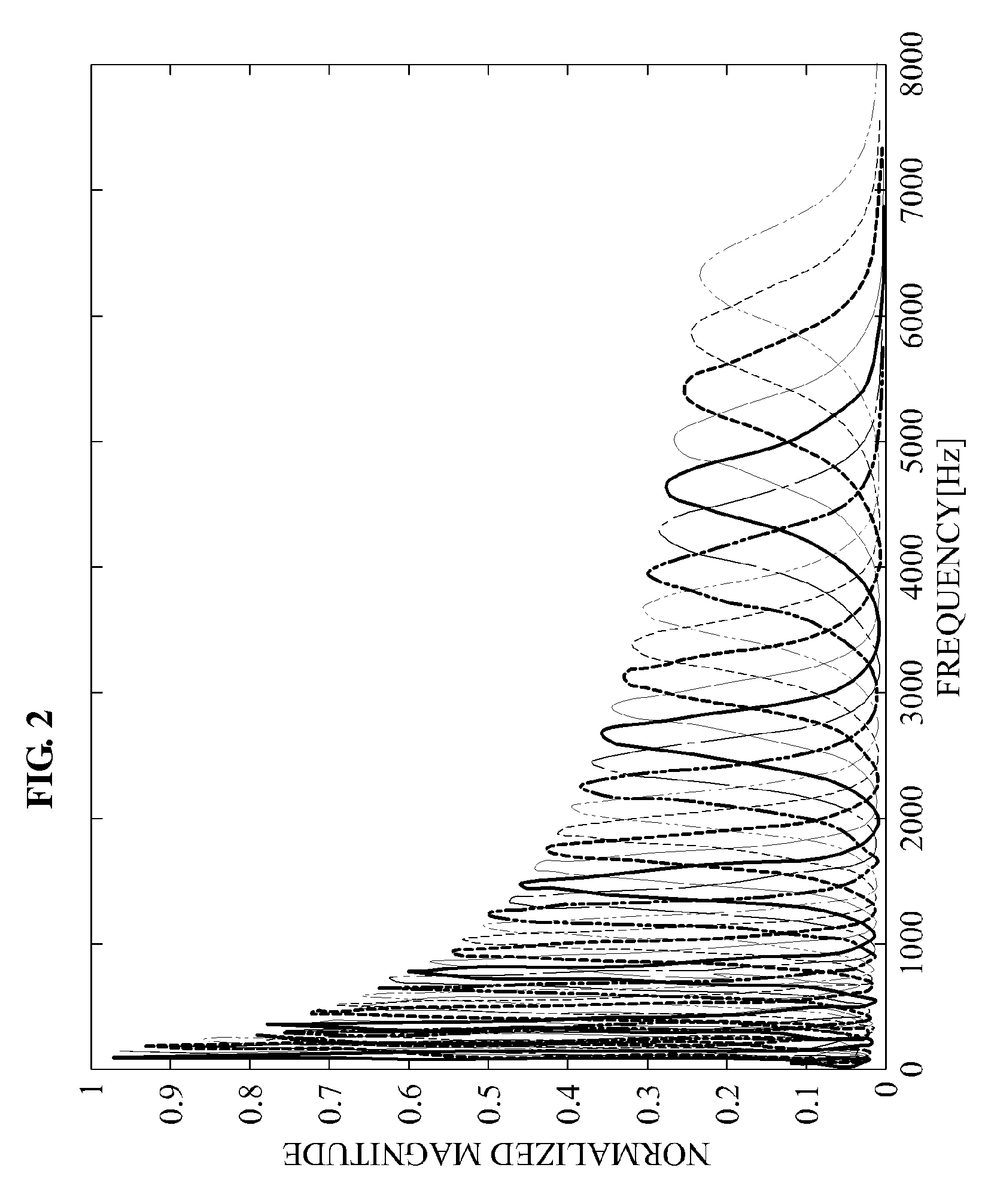
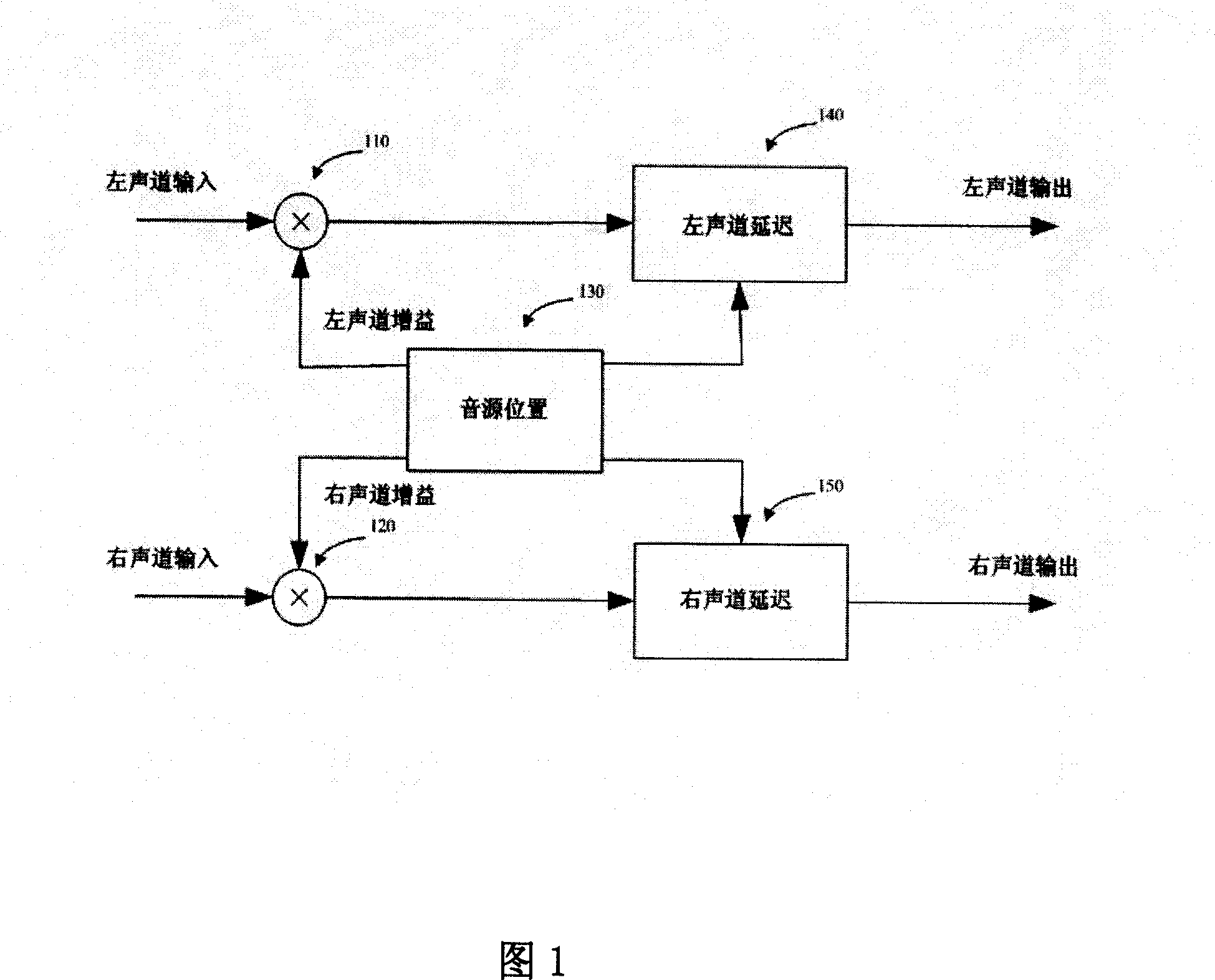
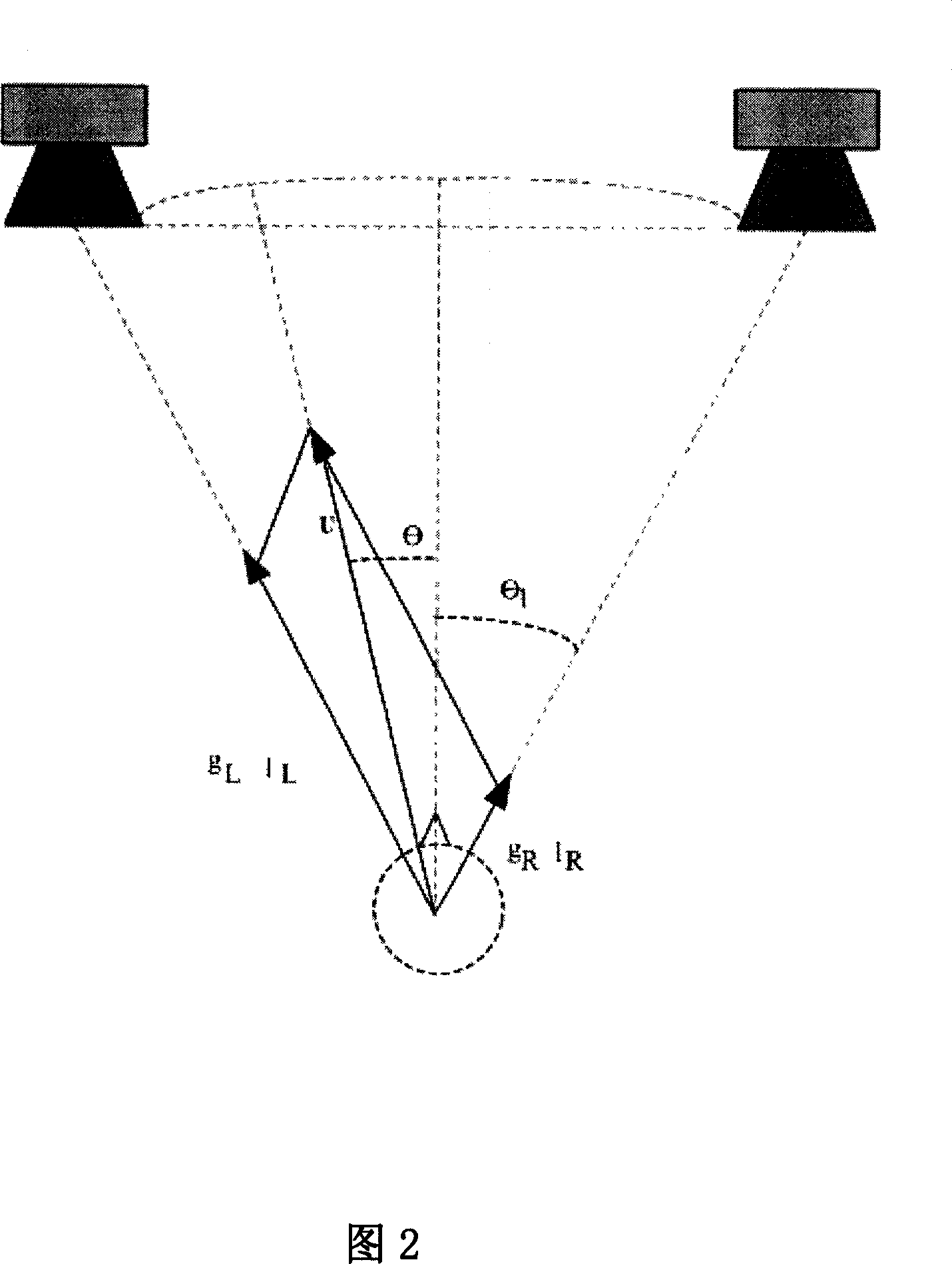
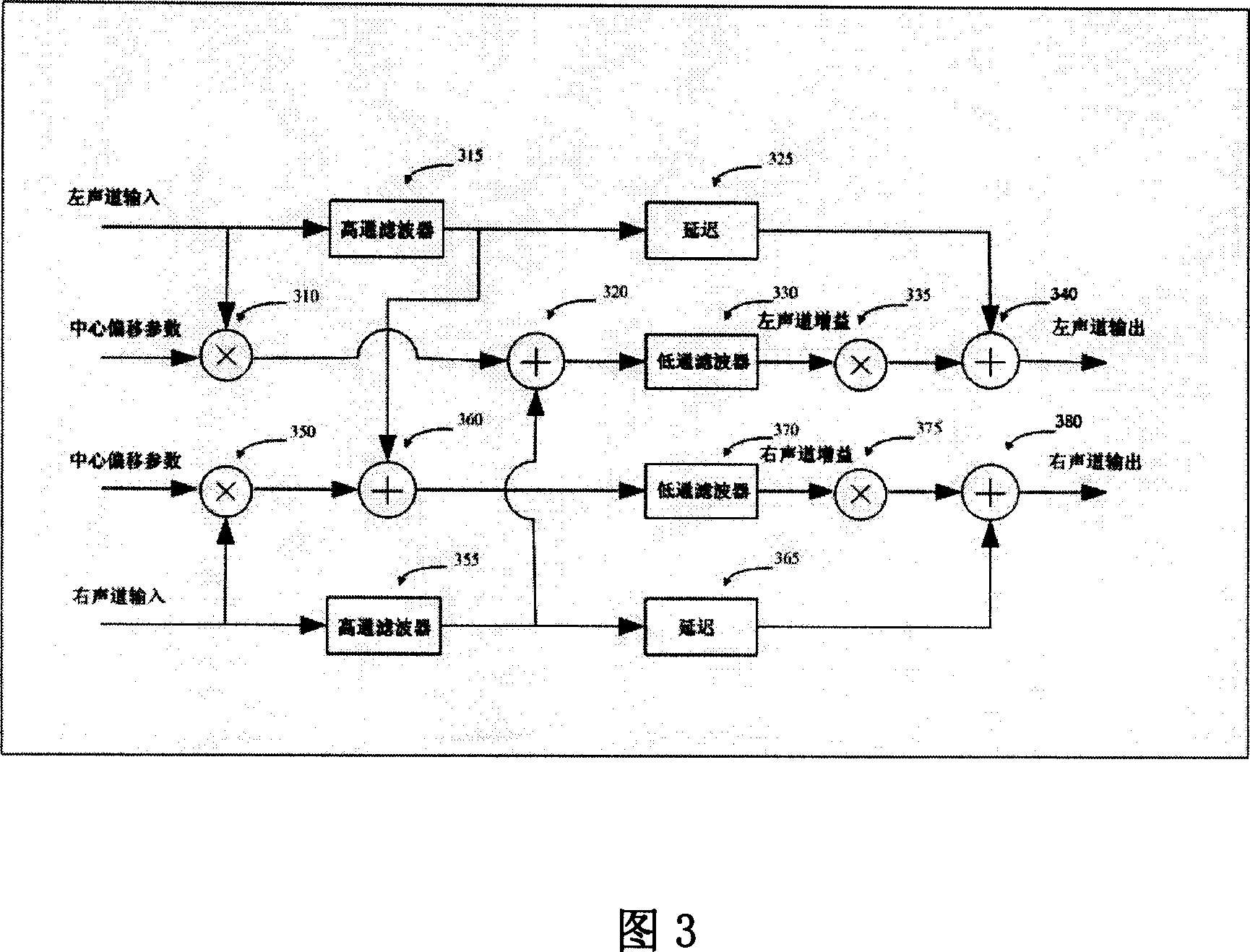
Three-dimensional around sound effect technology aiming at double-track audio signal
InactiveCN101155440AStereophonic circuit arrangementsTwo-channel systemsSound sourcesHuman auditory system
The present invention relates to a three-dimension surrounding sound effect method and equipment capable of leading double track audio signal to extend to multi-track three-dimension surrounding audio signal. The present invention establishes a novel model according to the subjective impression principle of human auditory. The hearer relative location between the two speakers can be reflected by the following three parameters: (1) center offset parameter: the hearer relative location between two speakers; (2) swing parameter: mapping the virtual direction of the hearer impression low frequency sound signal; (3) delay parameter: mapping the virtual direction of the hearer impression high frequency sound signal. The auditory system has different subjective impressions of sound directions of low frequency and high frequency, before the present invention using three-dimension surrounding sound effect method, dividing the input sound signals into high frequency sound signals and low frequency sound signals firstly, and mixing sound signals according to human auditory system subjective impression of different frequency band sound signals. The three-dimension surrounding sound effect method designed by the present invention can be easily applied and highly-effectively rebuilt double track sound three-dimension surrounding effect.
Owner:昊迪移通(北京)技术有限公司 +1
Audio watermarking method based on MP3 encoding principle
InactiveCN102324234AImprove robustnessMeet real-time requirementsSpeech analysisHuman auditory systemAudio watermark
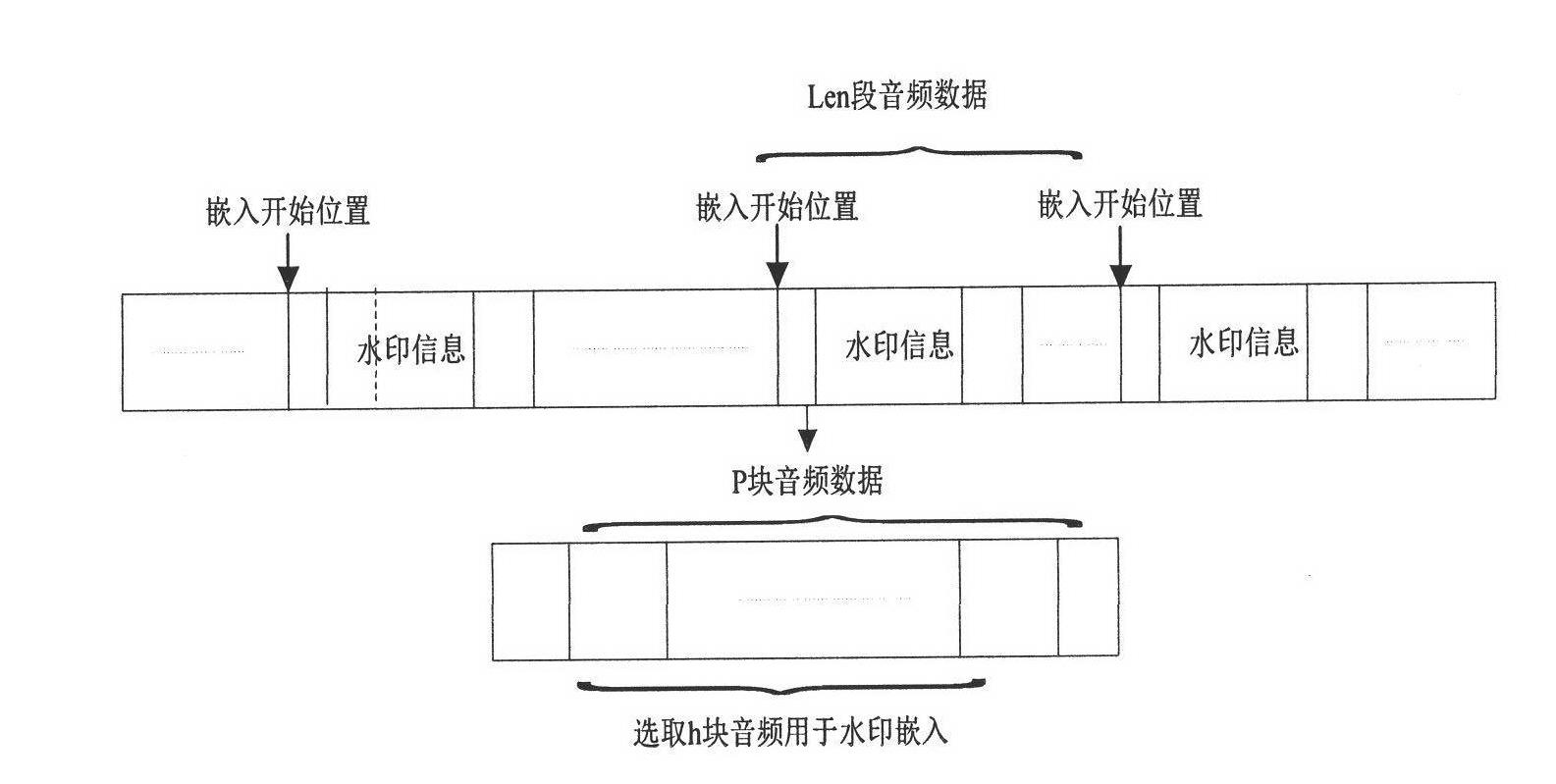
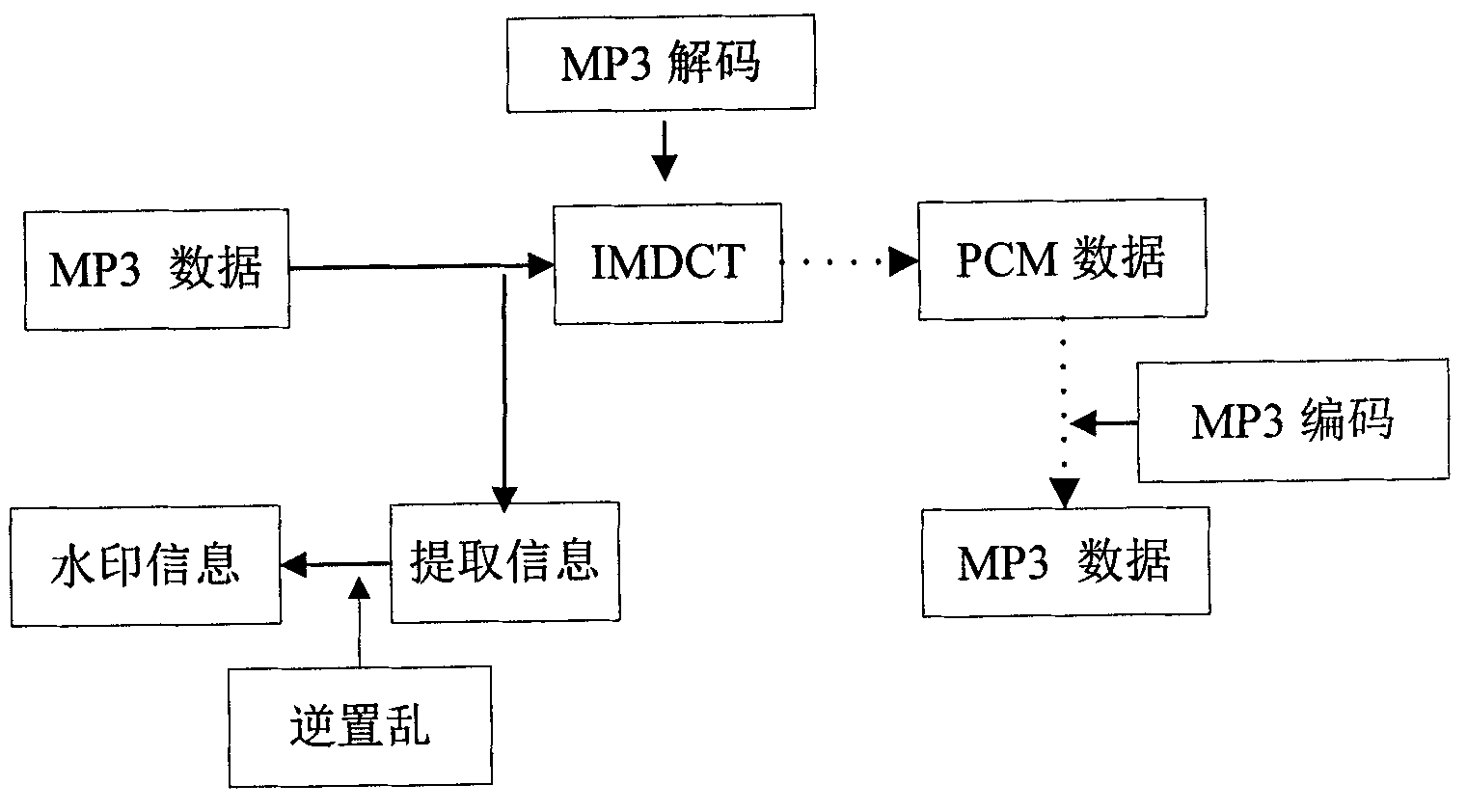
The invention discloses an audio watermarking method based on the MP3 encoding principle, which belongs to the technical field of multimedia digital watermarks. The method includes two processes, i.e. watermark embedment and watermark extraction; a watermark is embedded into a low-frequency MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficient as an encoding process is carried out synchronously; in order to enhance the robustness of the watermark, an appropriate audio segment is chosen in combination with the frequency domain masking effect in a human auditory system to be embedded; and in order to resist desynchronization attacks, a synchronization mechanism is introduced. By processing the encoding process, the method fulfills the injection of the watermark, and the method can effectively resist common audio attacks, and also has good robustness on desynchronization attacks (such as shearing attacks, time scaling and the like). While taking audio watermark robustness into consideration, the method guarantees the auditory invisibility of audio contents, the computational complexity of the algorithm is low, and the method is easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Inserting watermarks into audio signals that have speech-like properties
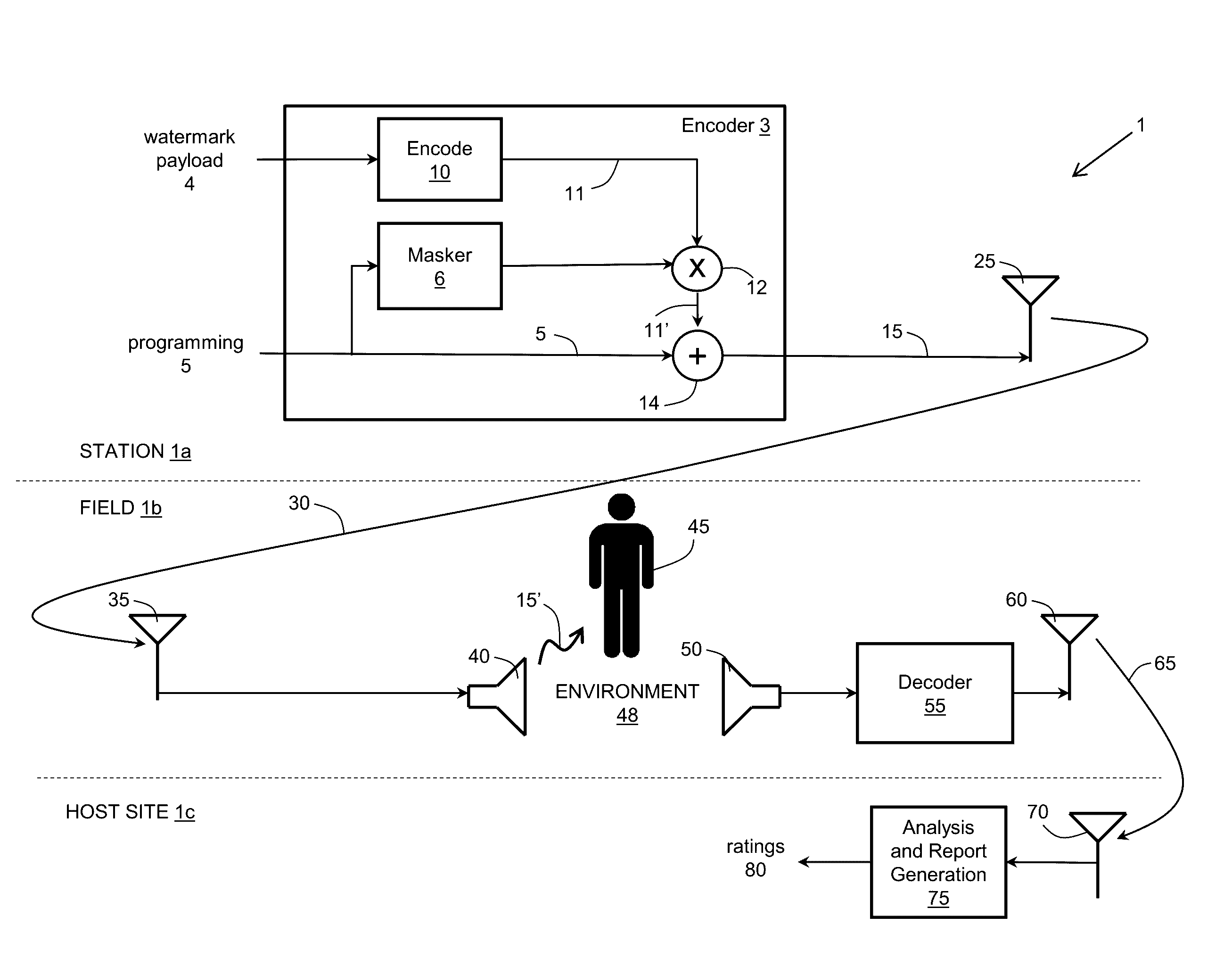
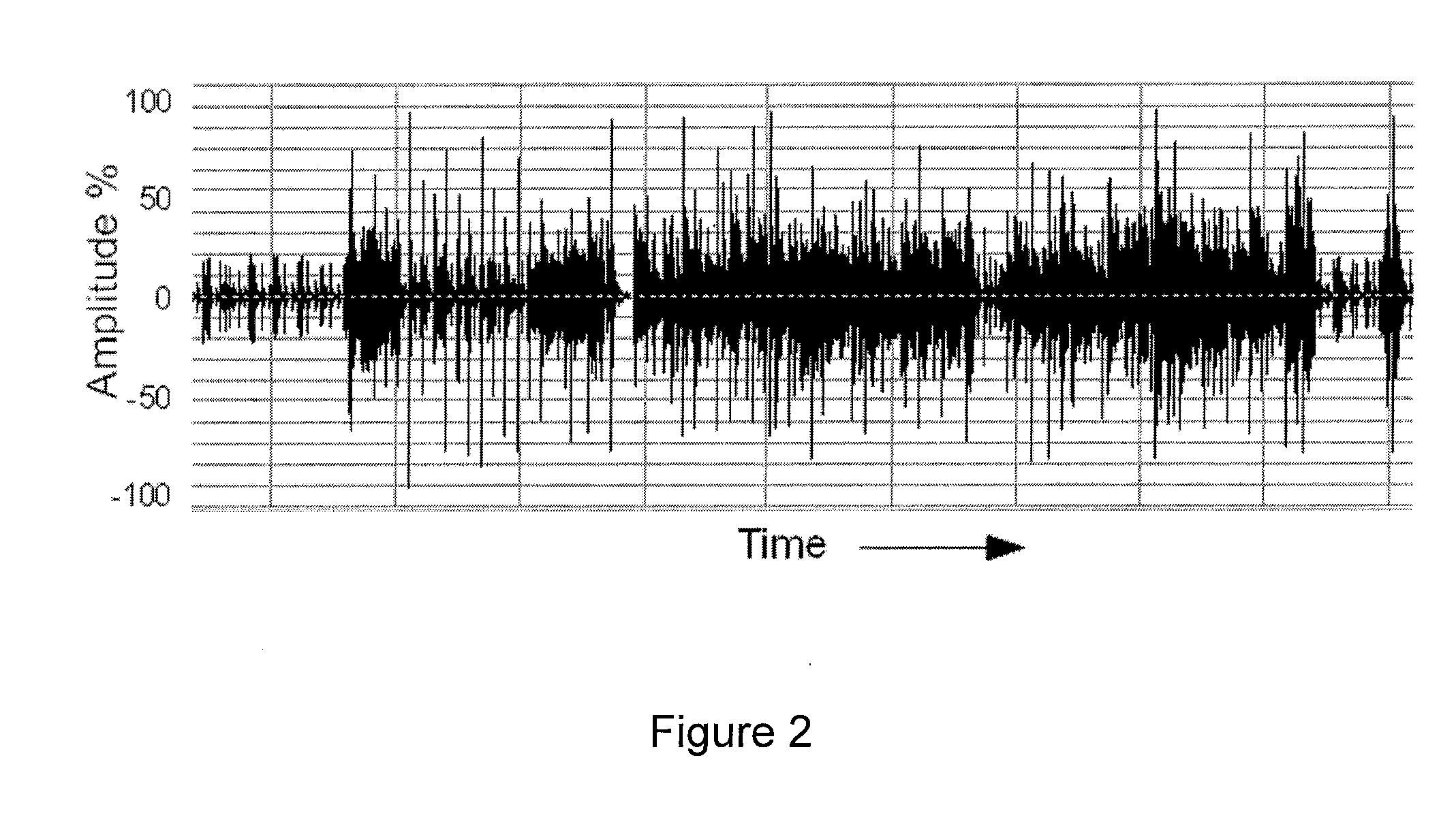
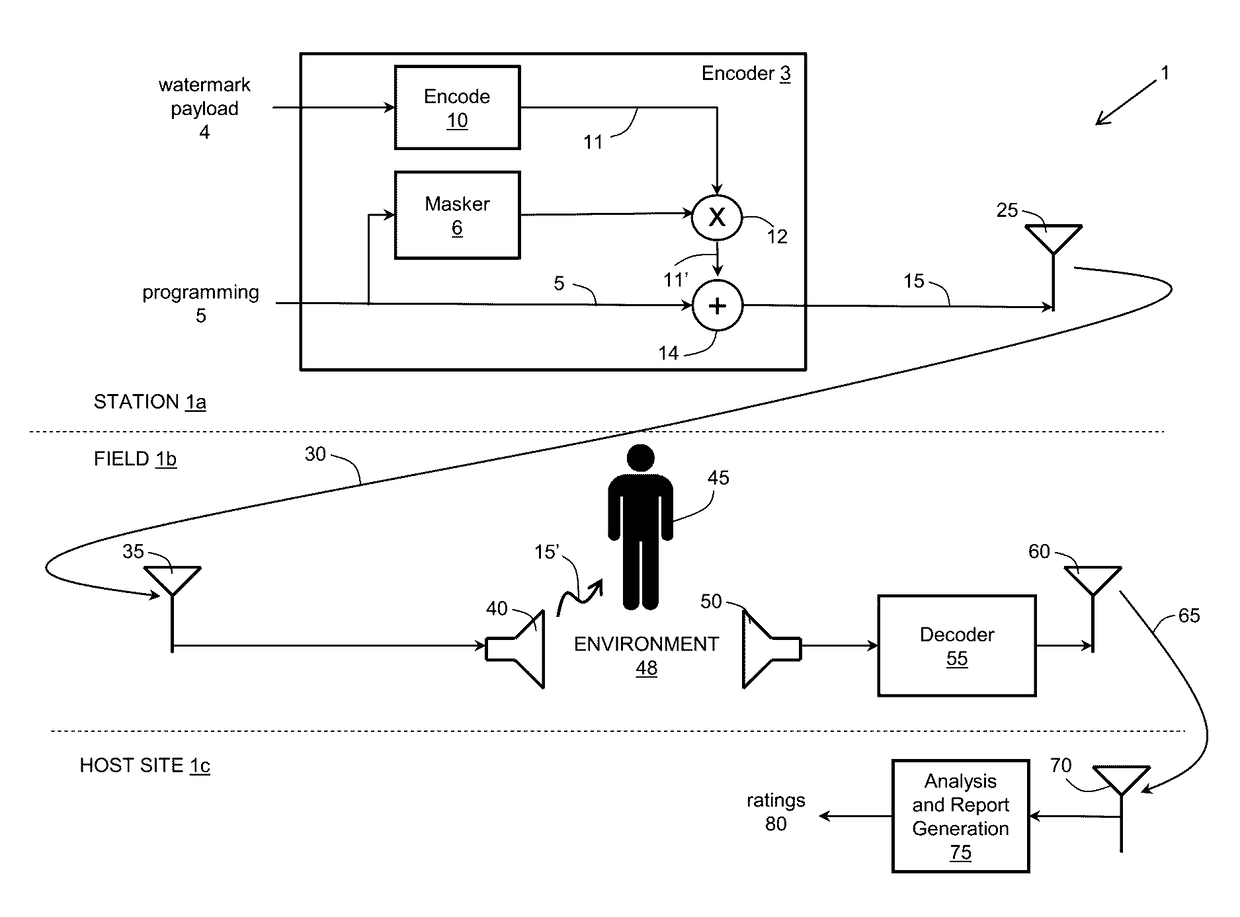
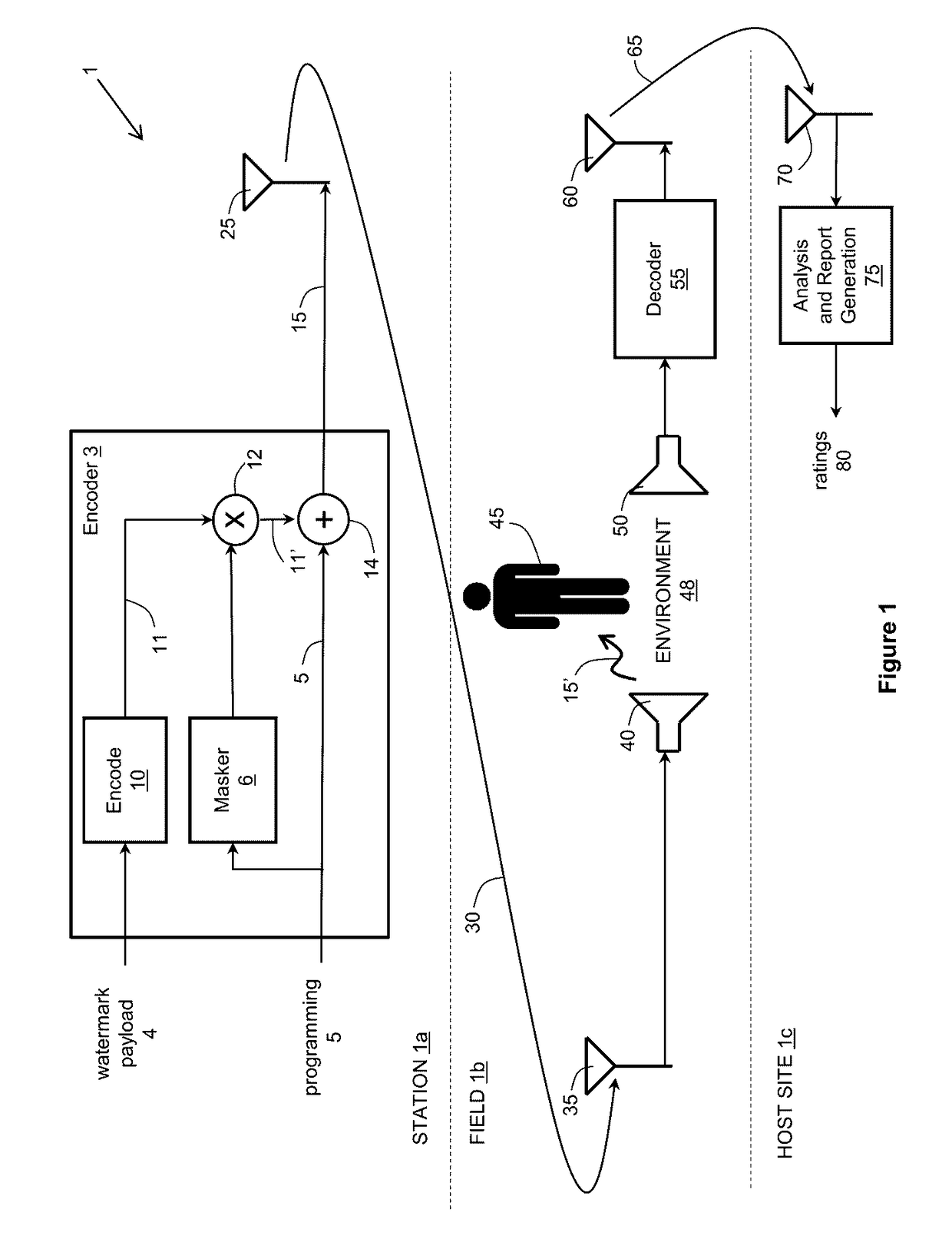
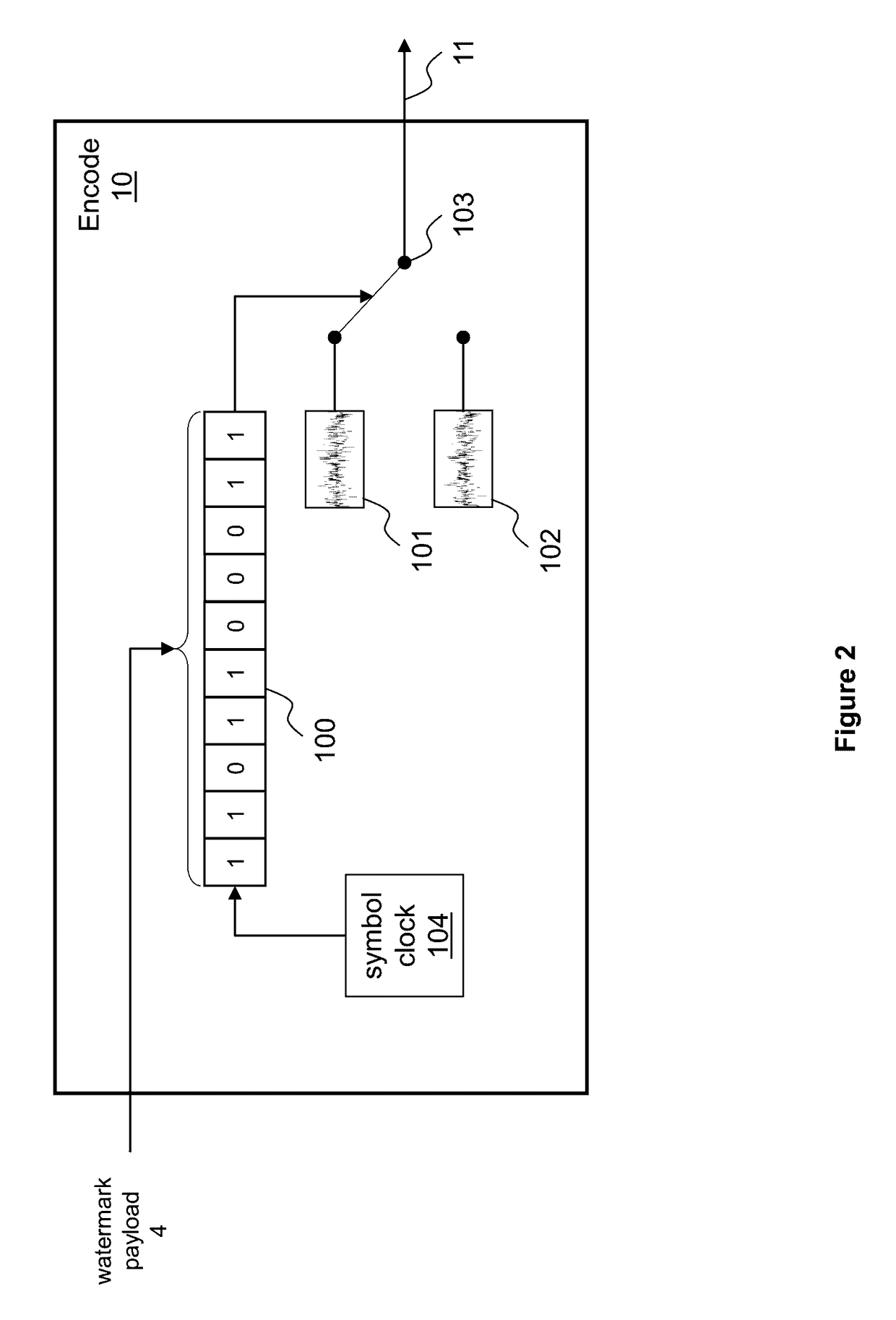
A method for a machine or group of machines to watermark an audio signal includes receiving an audio signal and a watermark signal including multiple symbols, and inserting at least some of the multiple symbols in multiple spectral channels of the audio signal, each spectral channel corresponding to a different frequency range. Optimization of the design incorporates minimizing the human auditory system perceiving the watermark channels by taking into account perceptual time-frequency masking, pattern detection of watermarking messages, the statistics of worst case program content such as speech, and speech-like programs.
Owner:TLS CORP
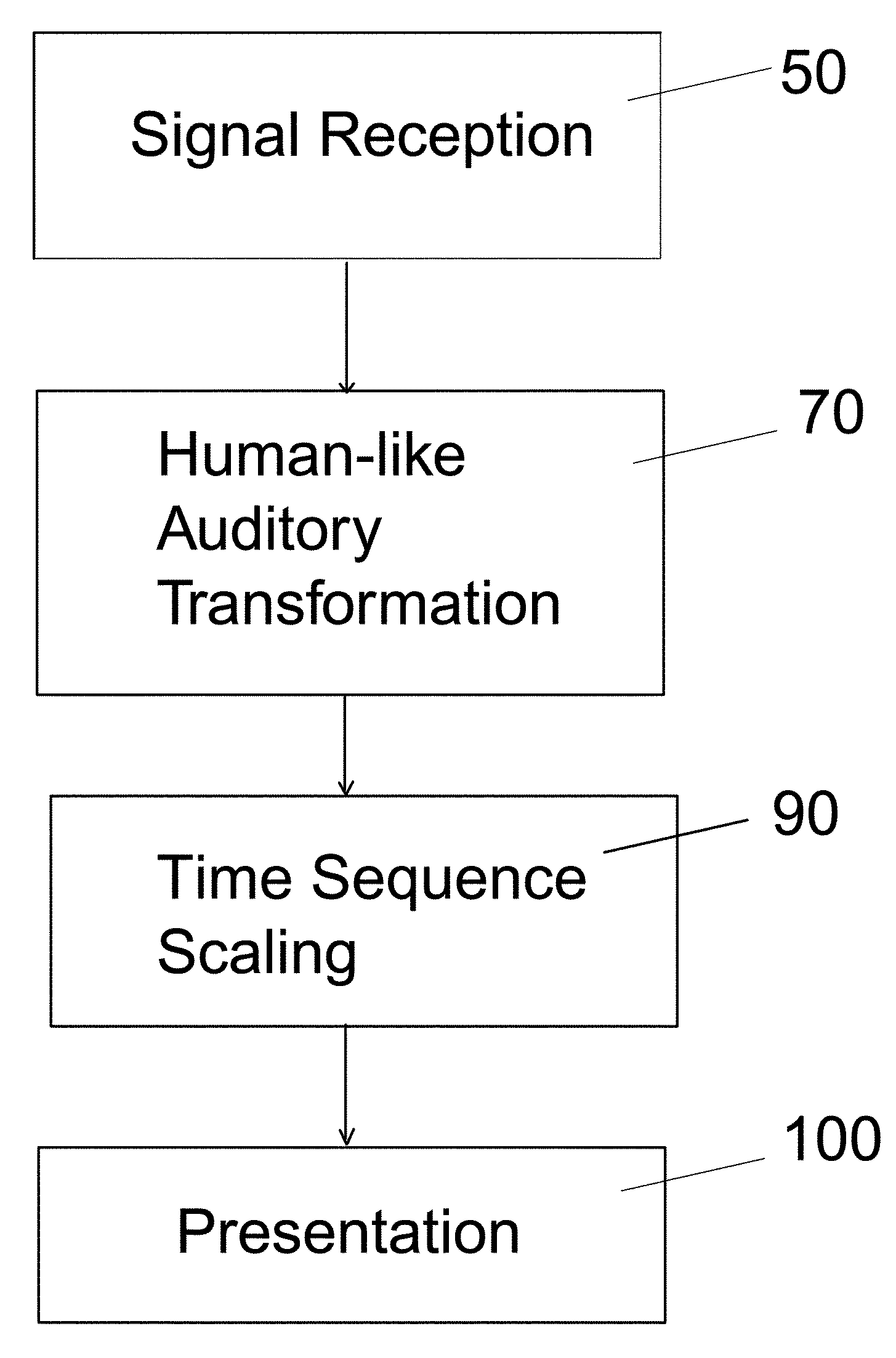
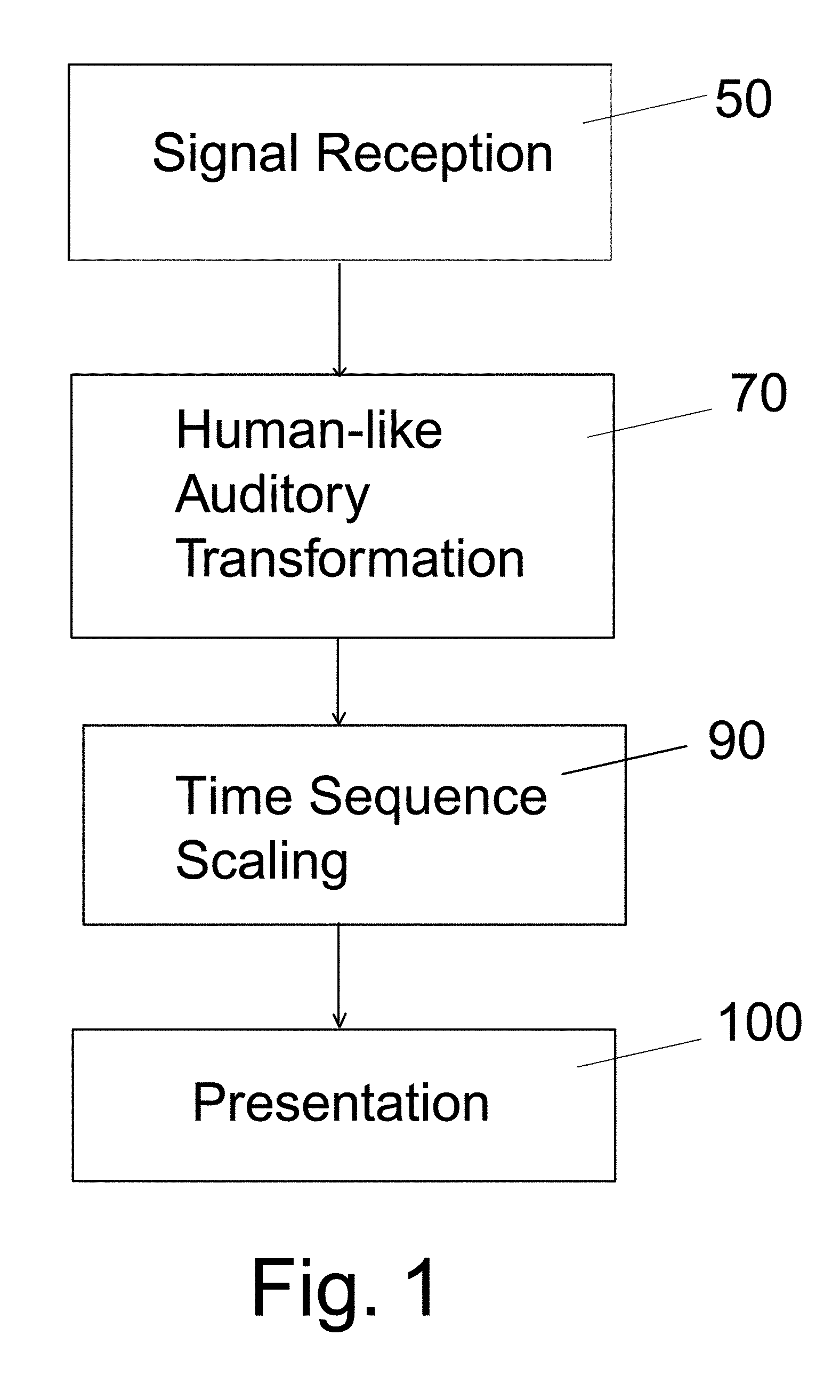
Acoustic presentation system and method
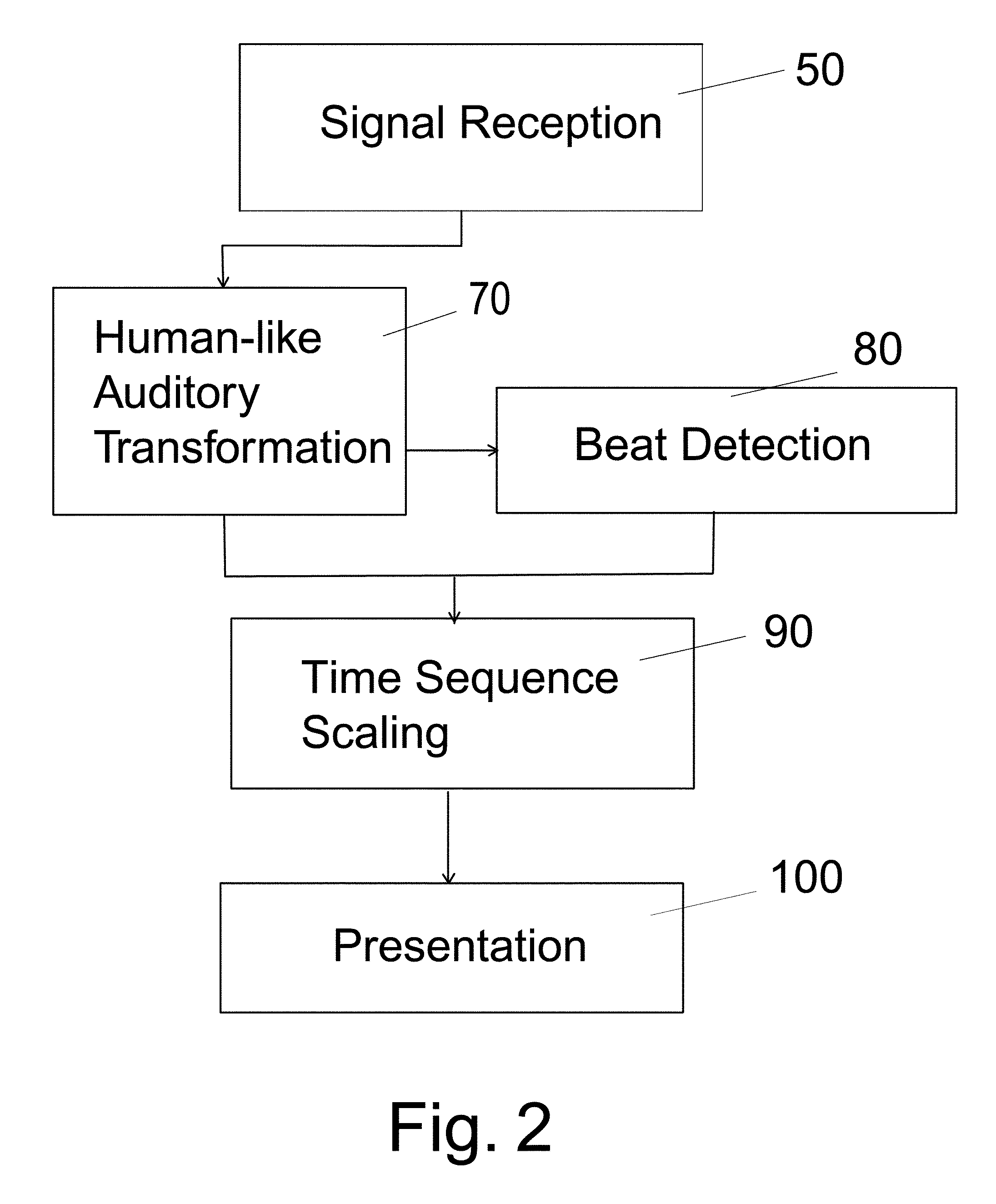
InactiveUS7451077B1Complete understandingSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsVisual presentationAnimation
Complex acoustic information, such as music, is presented as visual information or as movement of an object in a manner simulating the reception of the complex acoustic information by the human auditory system including a complexity of tempo, rhythms, intensity variation from highs to lows, and silences of the audio, providing a synchronicity with these characteristics. The acoustic information is processed by an acoustic human-like auditory transformation. The transformation may be varied depending on the presentation controlled by the device. The transformed signal is then applied to a tactile or visual presentation. The audience reception of the invention is through light, color, or animation of an image or object complementing the reception of the acoustic information.
Owner:LINDAU FELICIA +2
Digital audio signal processing method
A digital audio signal processing method disclosed by the present invention is characterized in that by embedding other content of a fixed format in a digital audio signal, a purpose of transmitting the digital information reconditely is achieved. The method mainly utilizes a masking effect of a human auditory system, so that the digital audio signal carries the predetermined data. By the method of the present invention, the data needing to be transmitted can be embedded at an appropriate position of the digital audio signal, and when the digital audio signal is played, an audio signal used for representing the relevant data information at the embedded position can be masked, so that human ears can not perceive the audio signal, but the audio signal can be received by a device possessing the audio signal processing capability.
Owner:北京音图数码科技有限公司
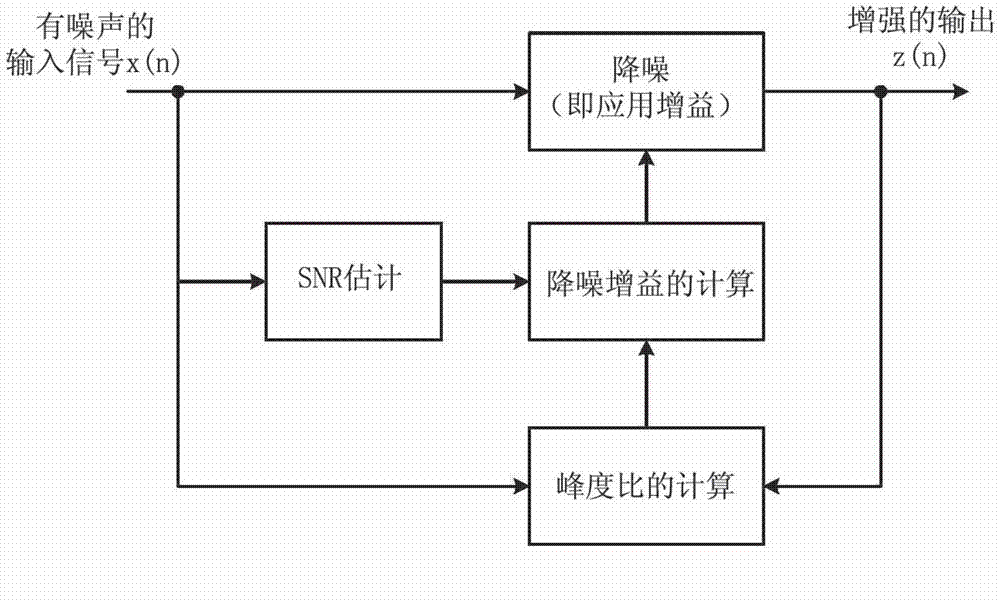
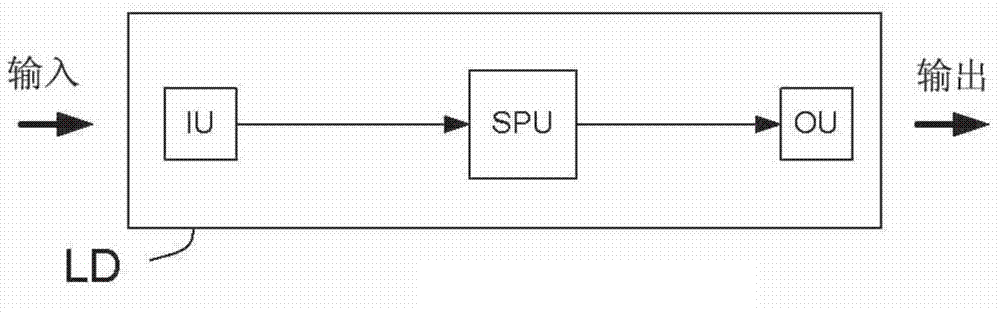
Audio processing device comprising reduced artifacts
The invention discloses an audio processing device comprising reduced artifacts. The audio processing device comprises a forward path and an analysis path. The forward path comprises an input unit for conveying a time-varying electrical input signal representing an audio signal, a signal processing unit for applying a processing algorithm on the electrical input signal and providing a processed signal, and an output unit for transmitting an output signal on the basis of the processed signal; and the electrical input signal comprises a target signal part and a noises signal part. The analysis path comprises a model unit comprising a perceptual model of a human auditory system and providing audibility measurement, an artifact identification unit for identifying the artifacts introduced by the processing algorithm to the processed signal and providing the artifact identification measurement, and a gain control unit for controlling a gain of a signal, which is applied by the processing algorithm to the forward path, on the basis of inputs from the model unit and the artifact identification unit. The audio processing device has the advantage of dynamic optimization of noise reduction aiming at audibility of the artifacts.
Owner:OTICON
Temporal masking in audio coding based on spectral dynamics in frequency sub-bands
An audio coding technique based on modeling spectral dynamics is disclosed. Frequency decomposition of an input audio signal is performed to obtain multiple frequency sub-bands that closely follow critical bands of human auditory system decomposition. Each sub-band is then frequency transformed and linear prediction is applied. This results in a Hilbert envelope and a Hilbert Carrier for each of the sub-bands. Because of application of linear prediction to frequency components, the technique is called Frequency Domain Linear Prediction (FDLP). The Hilbert envelope and the Hilbert Carrier are analogous to spectral envelope and excitation signals in the Time Domain Linear Prediction (TDLP) techniques. Temporal masking is applied to the FDLP sub-bands to improve the compression efficiency. Specifically, forward masking of the sub-band FDLP carrier signal can be employed to improve compression efficiency of an encoded signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
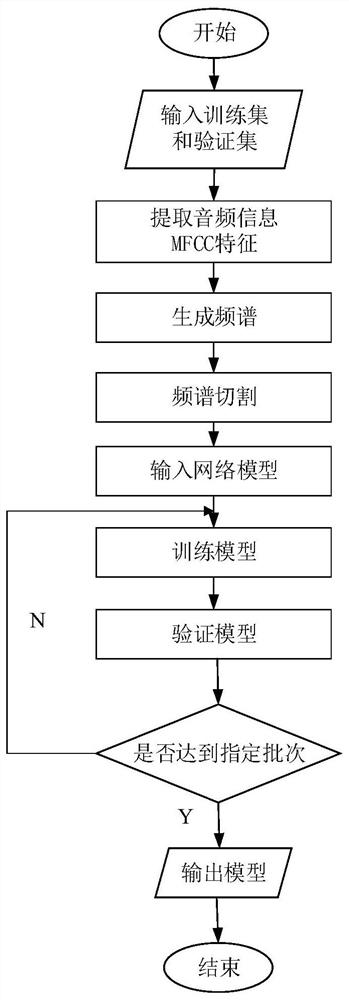
Improved DCNN music genre classification method
PendingCN112466329ASimple calculationSignificant performance gainElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumHuman auditory system
The invention discloses an improved DCNN music genre classification method. The method comprises the steps of inputting a training set and a verification set, extracting MFCC features of the audio information, generating a frequency spectrum, carrying out frequency spectrum cutting, inputting a network model, training a model, verifying the model, judging whether a specified batch is reached or not, and outputting a model. According to the method, self-adaption of channel dimensions is achieved through a function, so that the coverage range of interaction of local area cross channels is ensured, an ECA module is more effectively integrated into an existing DCNN architecture, obvious performance gain is brought to a network model, and then the working efficiency of music genre classification is improved. Through the Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient, the perception characteristics of a human auditory system are simulated, and the classification precision is further improved.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
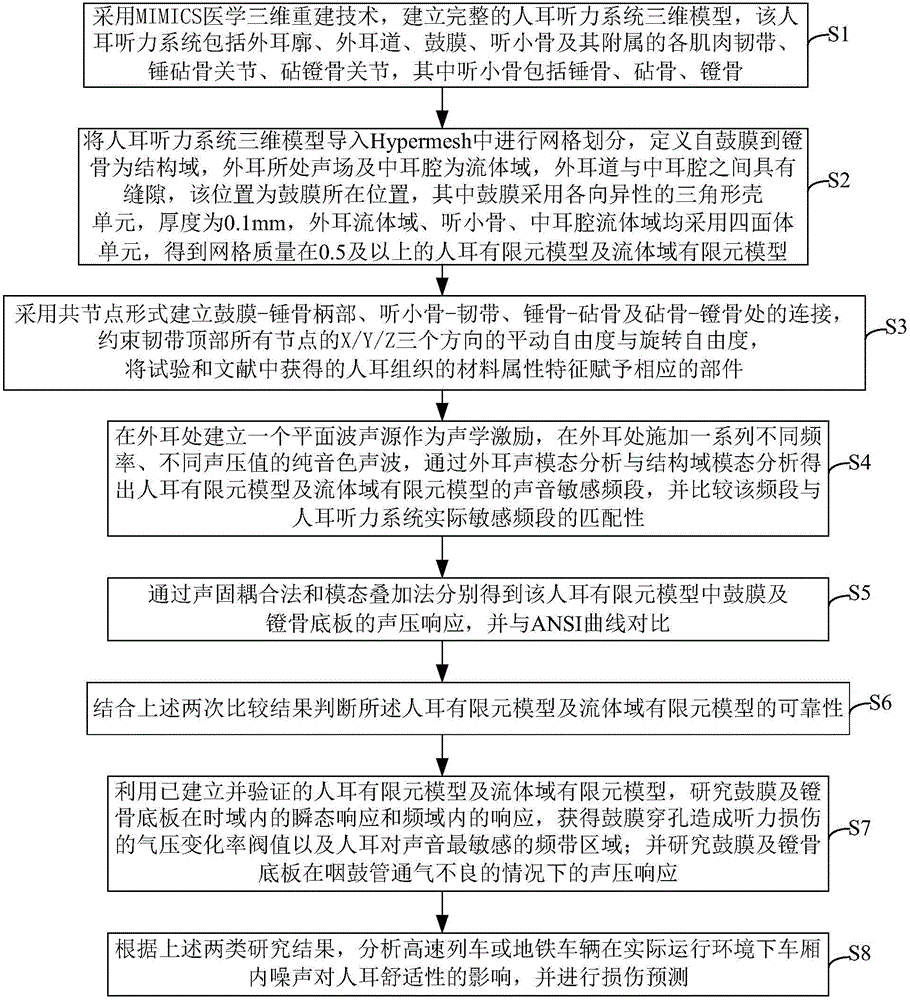
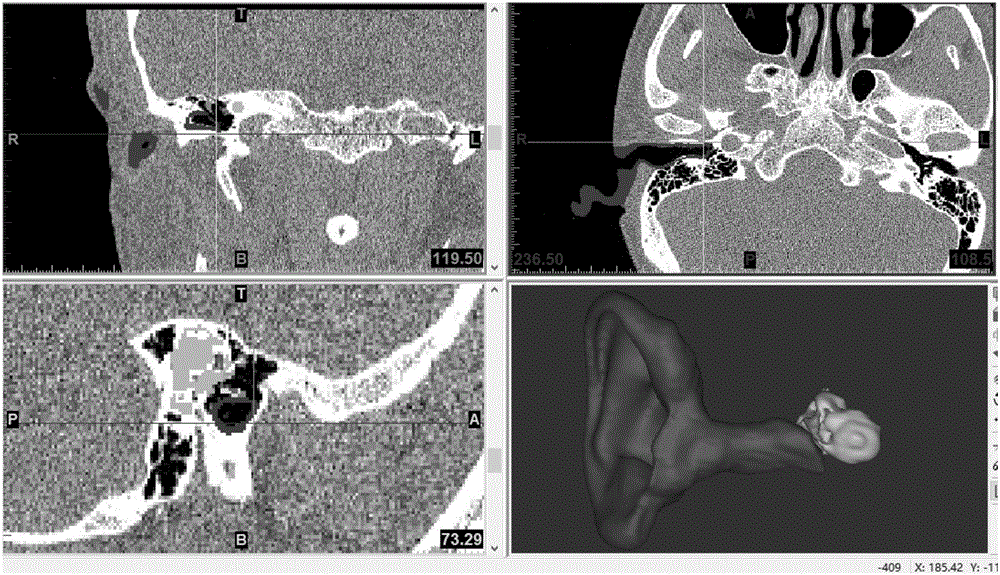
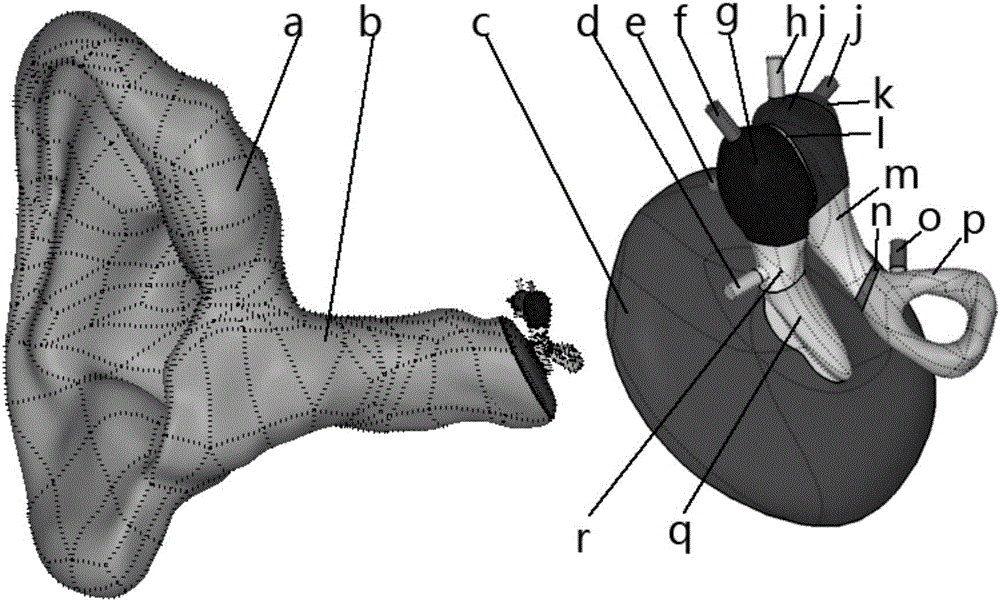
Biomechanical research, modeling, verification and application of human ear for railway vehicles
ActiveCN106326586ASustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationExternal earsElement model
The invention discloses a biomechanical research, modeling, verification and application of human ear for railway vehicles to provide thoughts and basis for the design and evaluation of noise comfort of the railway transit equipment. The verification method includes establishing a plane wave source in the external ear as the acoustic excitation and applying pure timbre of a series of different frequency and sound pressure level in the external ear. Based on the acoustic modal analysis of external ear and the domain modal analysis, the ear finite element model and the sound sensitive band of the fluid domain finite element model are obtained and the matching between the sound sensitive band and the actual sensitive band of the human auditory system is compared. And based on the acoustic solid coupling method and the mode superposition method, the tympanic membrane and the acoustic response of stapes footplate are respectively obtained, and compared with the ANSI curve. The reliability of the ear finite element model and the fluid domain finite element model are determined by combining the results of the above two comparisons.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
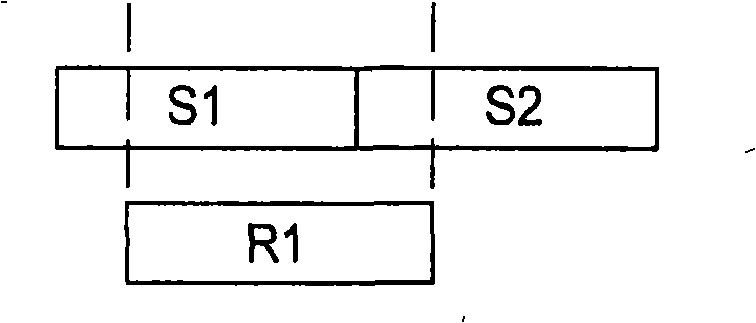
Method and apparatus for correlating two data sections
InactiveCN101405804ALow data rateSmall scaleSpeech analysisRecord information storageData segmentHuman auditory system
Watermarking of audio signals intends to manipulate the audio signal in a way that the changes in the audio content cannot be recognised by the human auditory system. The watermark data are decoded from the received watermarked audio signal by correlation with corresponding candidate reference sequences. One or more of the sync symbols (S1, S2, S3) are embedded twice in the watermark data frame in the encoder. Thereafter a circular correlation is calculated instead of a standard correlation.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Inserting watermarks into audio signals that have speech-like properties
ActiveUS9626977B2Speech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumHuman auditory system
A method for a machine or group of machines to watermark an audio signal includes receiving an audio signal and a watermark signal including multiple symbols, and inserting at least some of the multiple symbols in multiple spectral channels of the audio signal, each spectral channel corresponding to a different frequency range. Optimization of the design incorporates minimizing the human auditory system perceiving the watermark channels by taking into account perceptual time-frequency masking, pattern detection of watermarking messages, the statistics of worst case program content such as speech, and speech-like programs.
Owner:TLS CORP
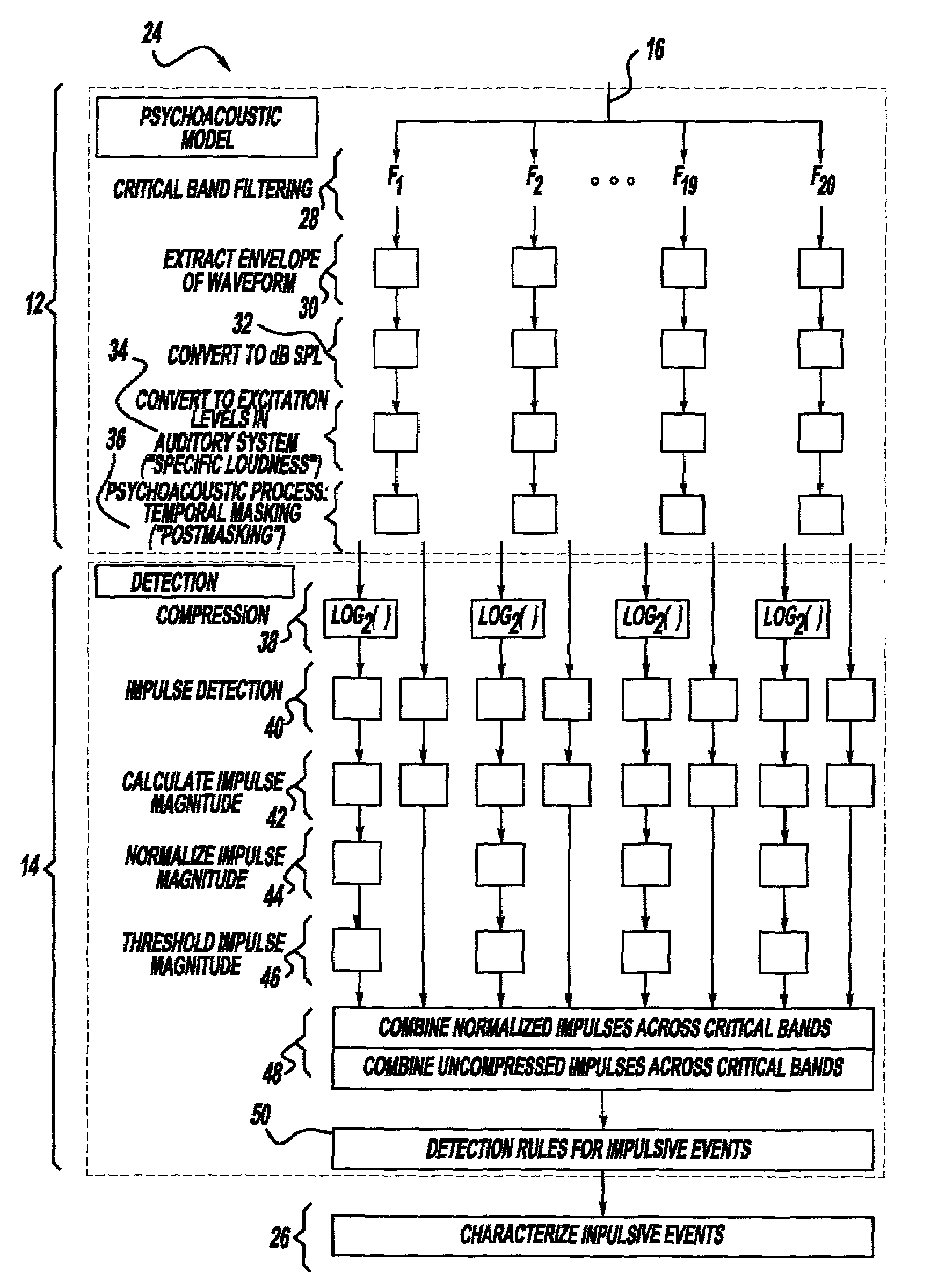
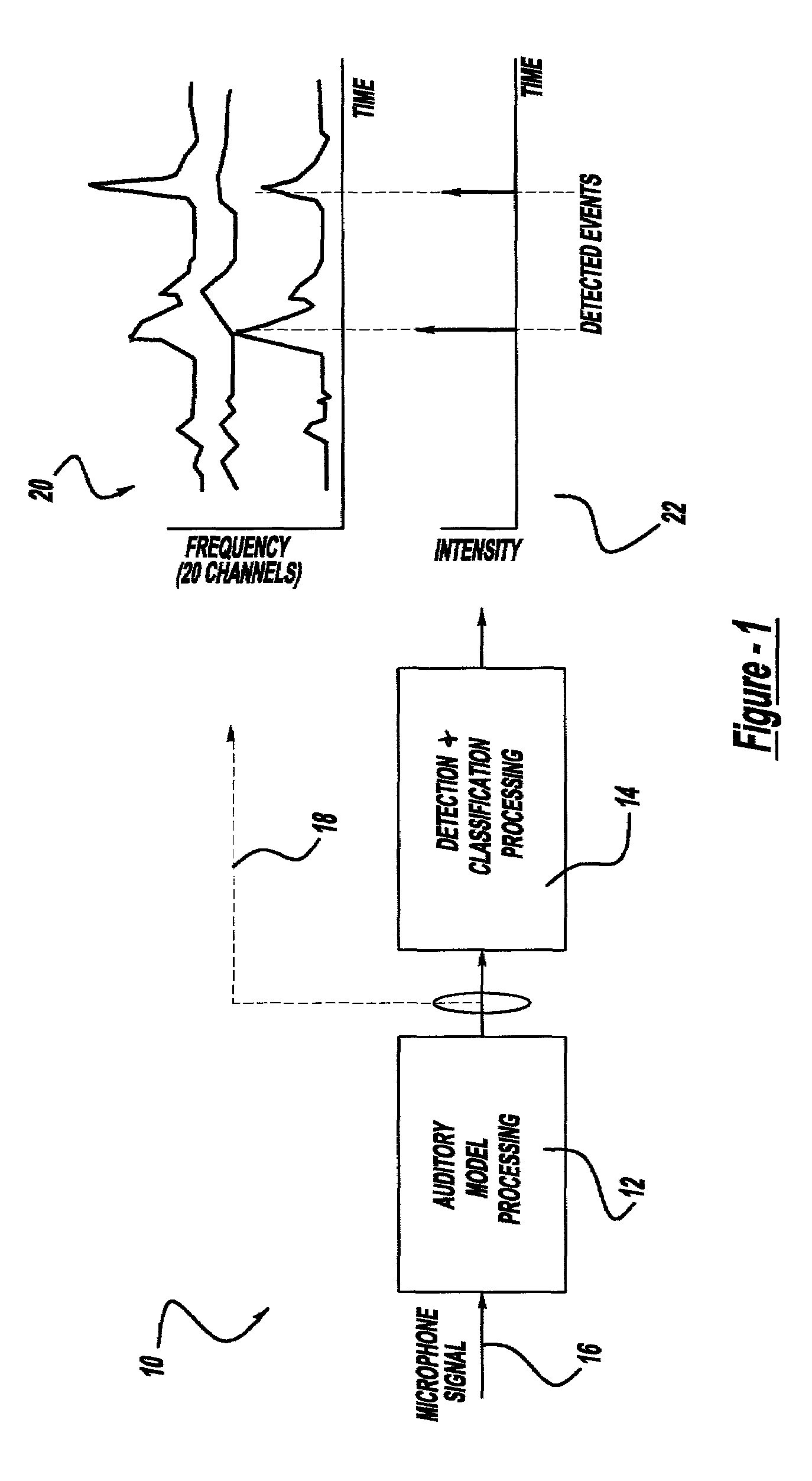
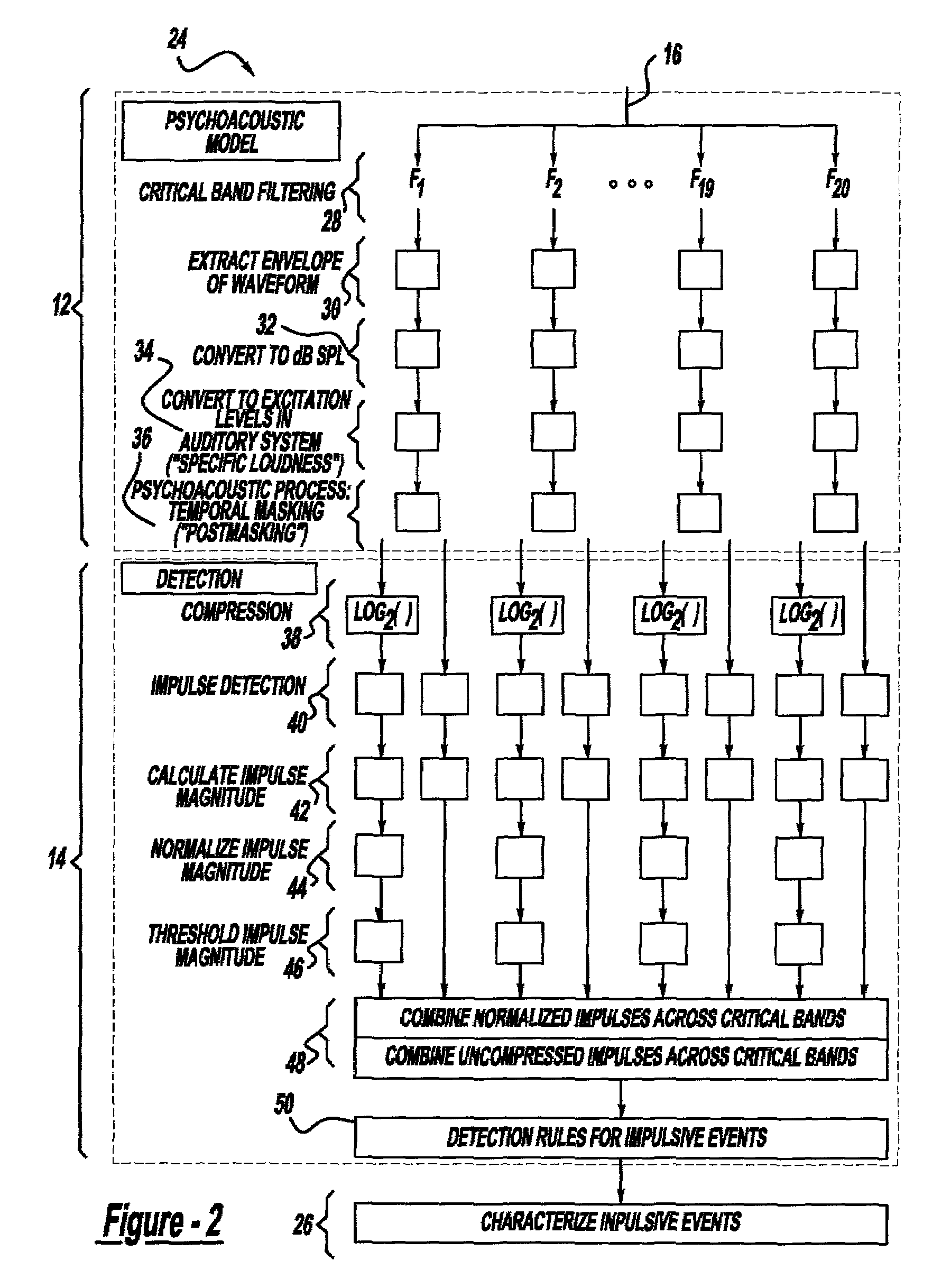
Method and implementation for detecting and characterizing audible transients in noise
A method and implementation for detecting and characterizing audible transients in noise includes placing a microphone in a desired location, producing a microphone signal wherein the microphone signal is indicative of the acoustic environment, processing the microphone signal to estimate the acoustic activity that takes place in the human auditory system in response to the acoustic environment, producing an excitation signal indicative of the estimated acoustic activity, processing the excitation signal to identify each impulsive sound frequency-dependent activity as a function of time, producing a detection signal indicative of audible impulse sounds, processing the detection signal to identify an audible impulsive sound, and characterizing each impulsive sound.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com