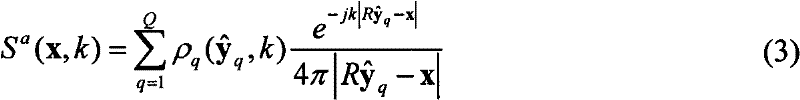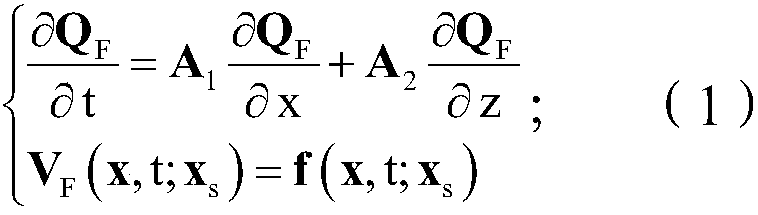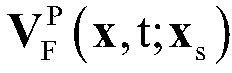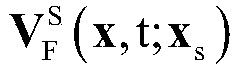Patents
Literature
72 results about "Wave field synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
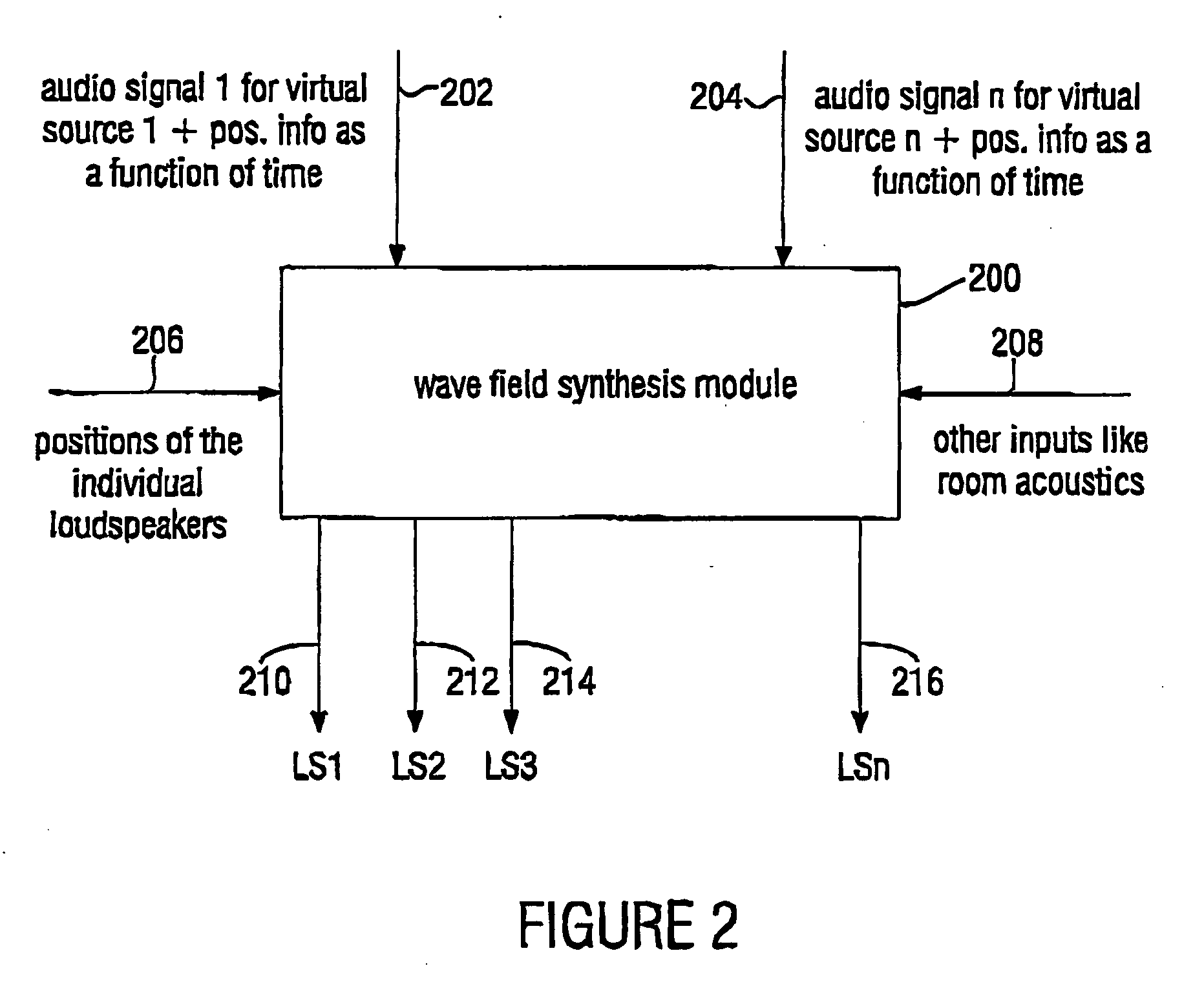
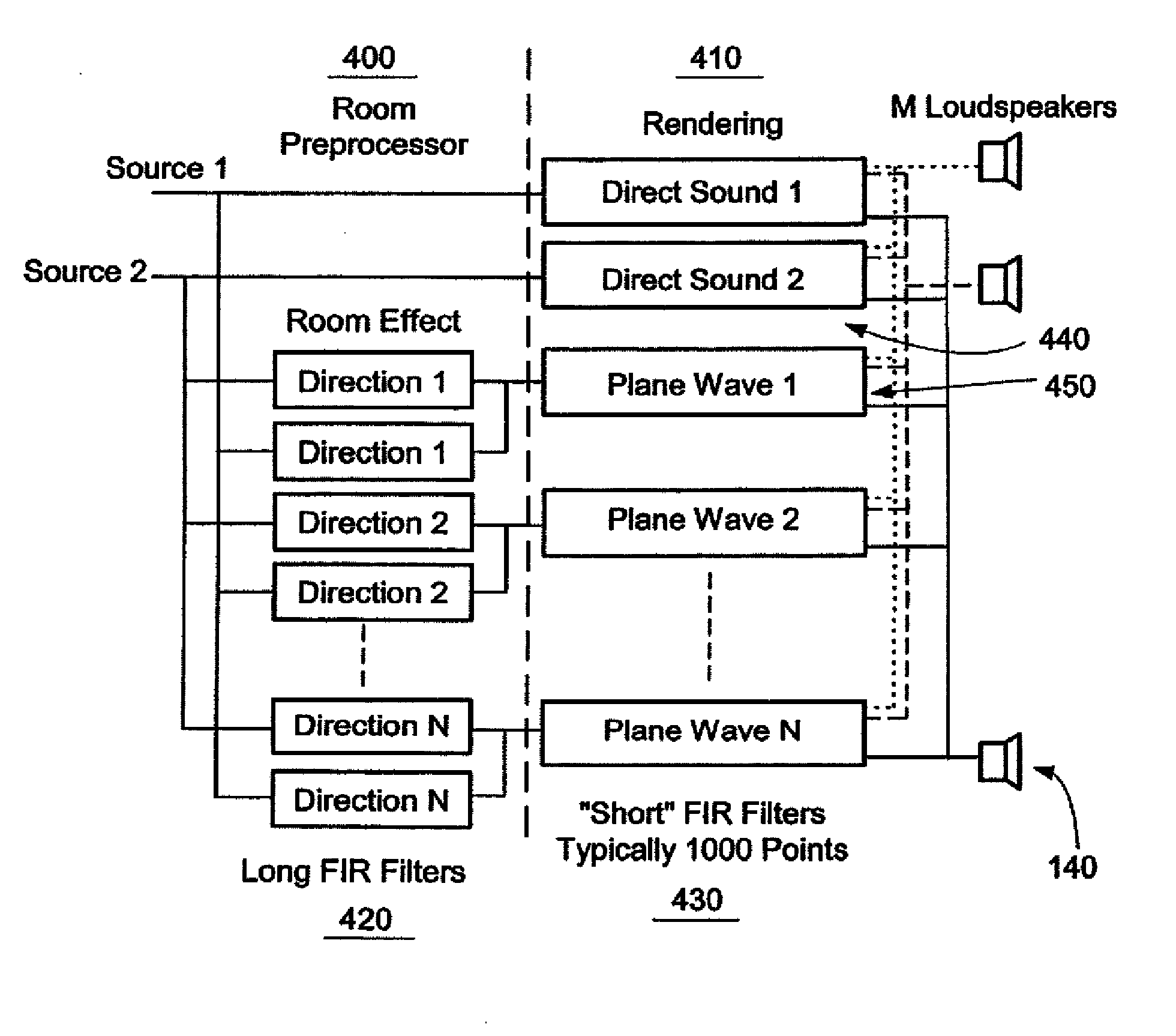
Wave field synthesis (WFS) is a spatial audio rendering technique, characterized by creation of virtual acoustic environments. It produces artificial wavefronts synthesized by a large number of individually driven loudspeakers. Such wavefronts seem to originate from a virtual starting point, the virtual source or notional source. Contrary to traditional spatialization techniques such as stereo or surround sound, the localization of virtual sources in WFS does not depend on or change with the listener's position.
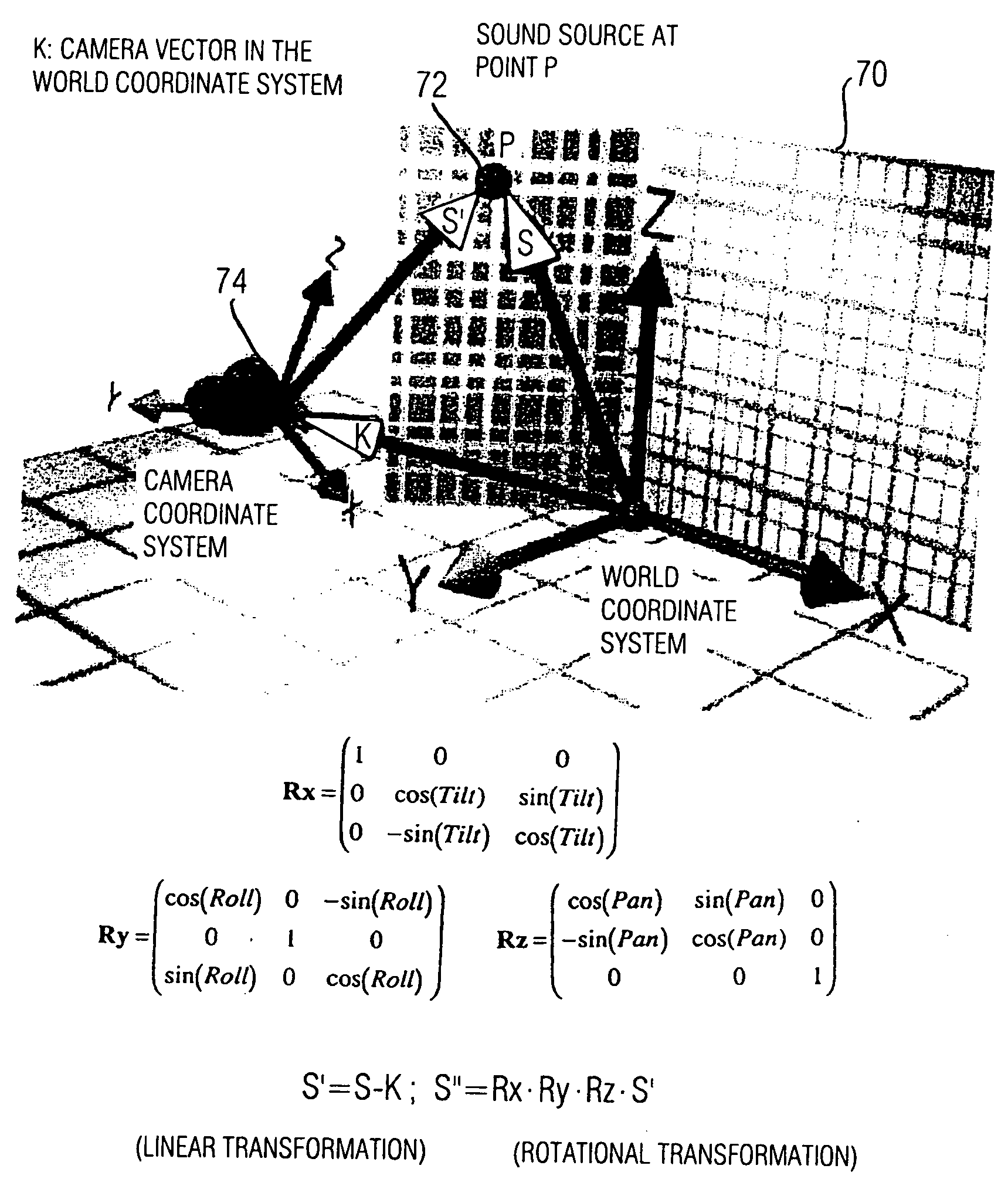
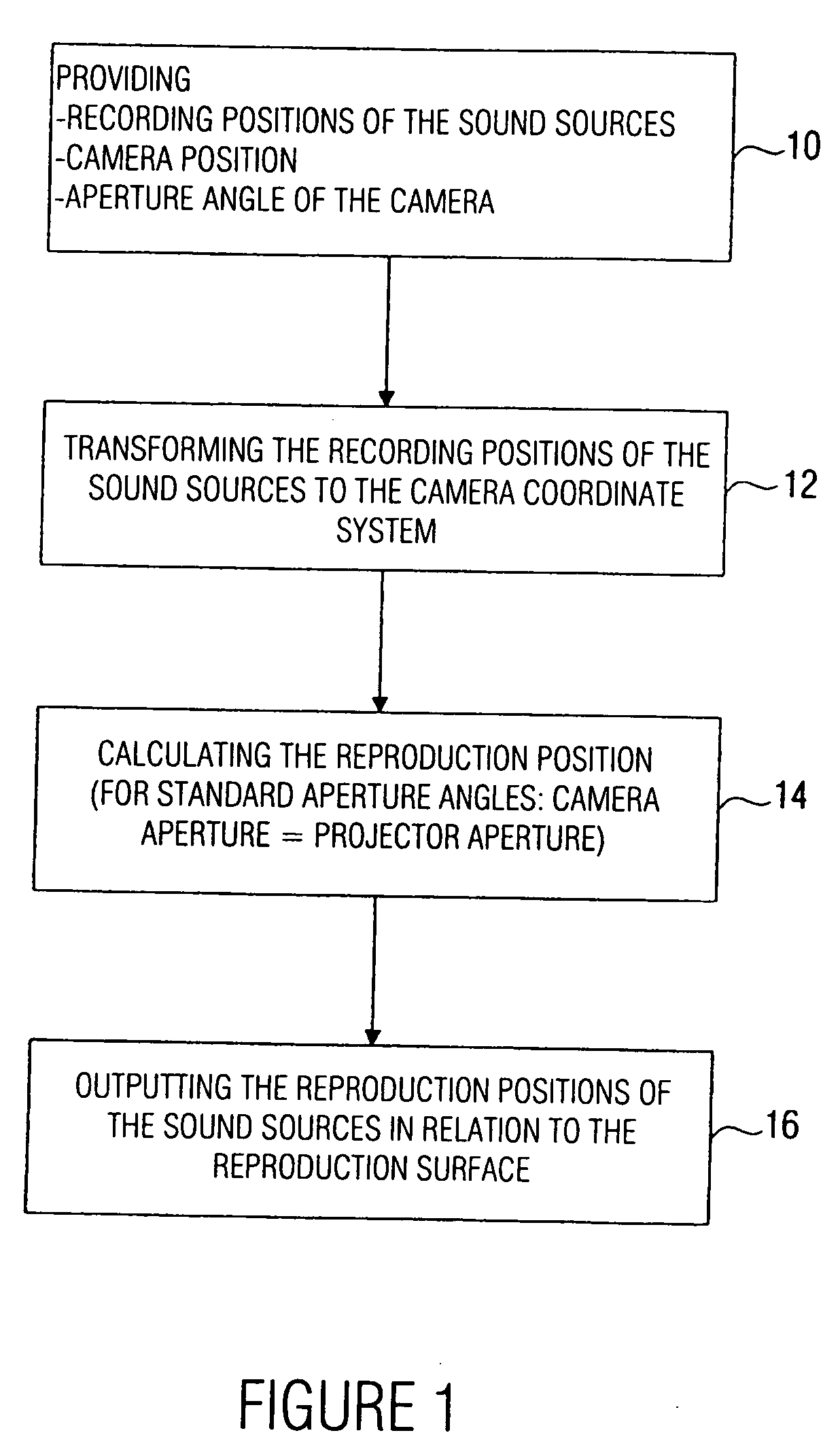
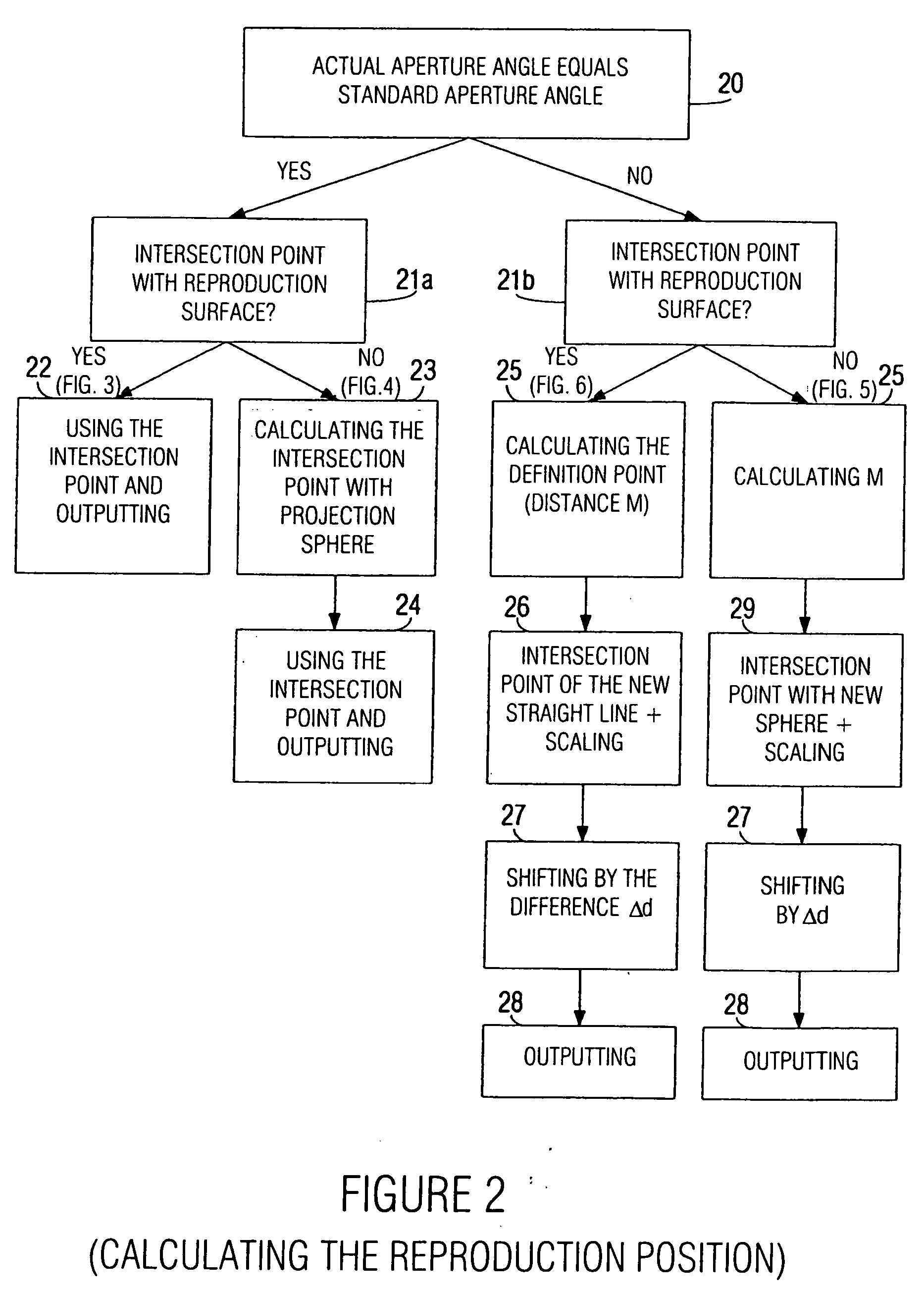
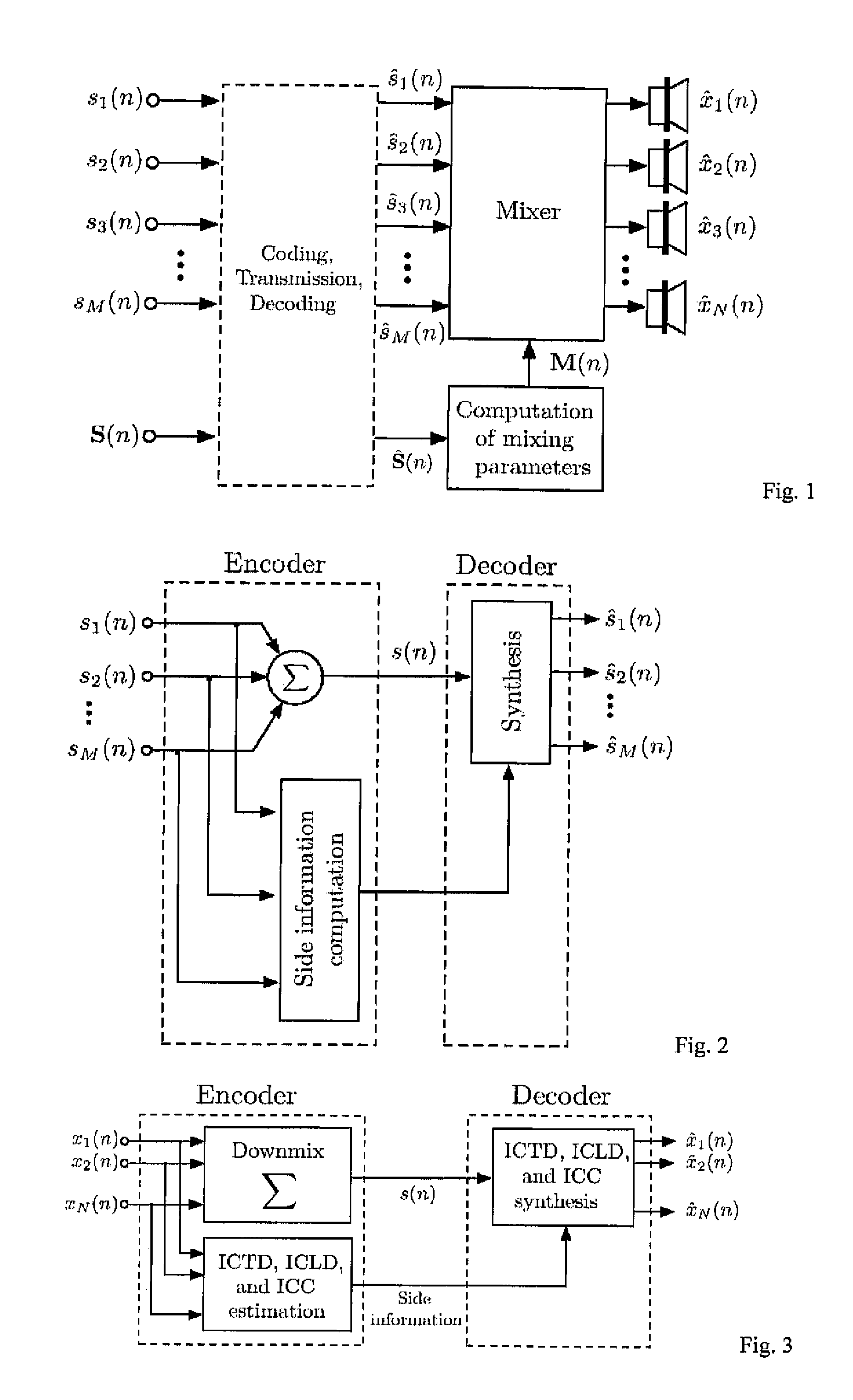
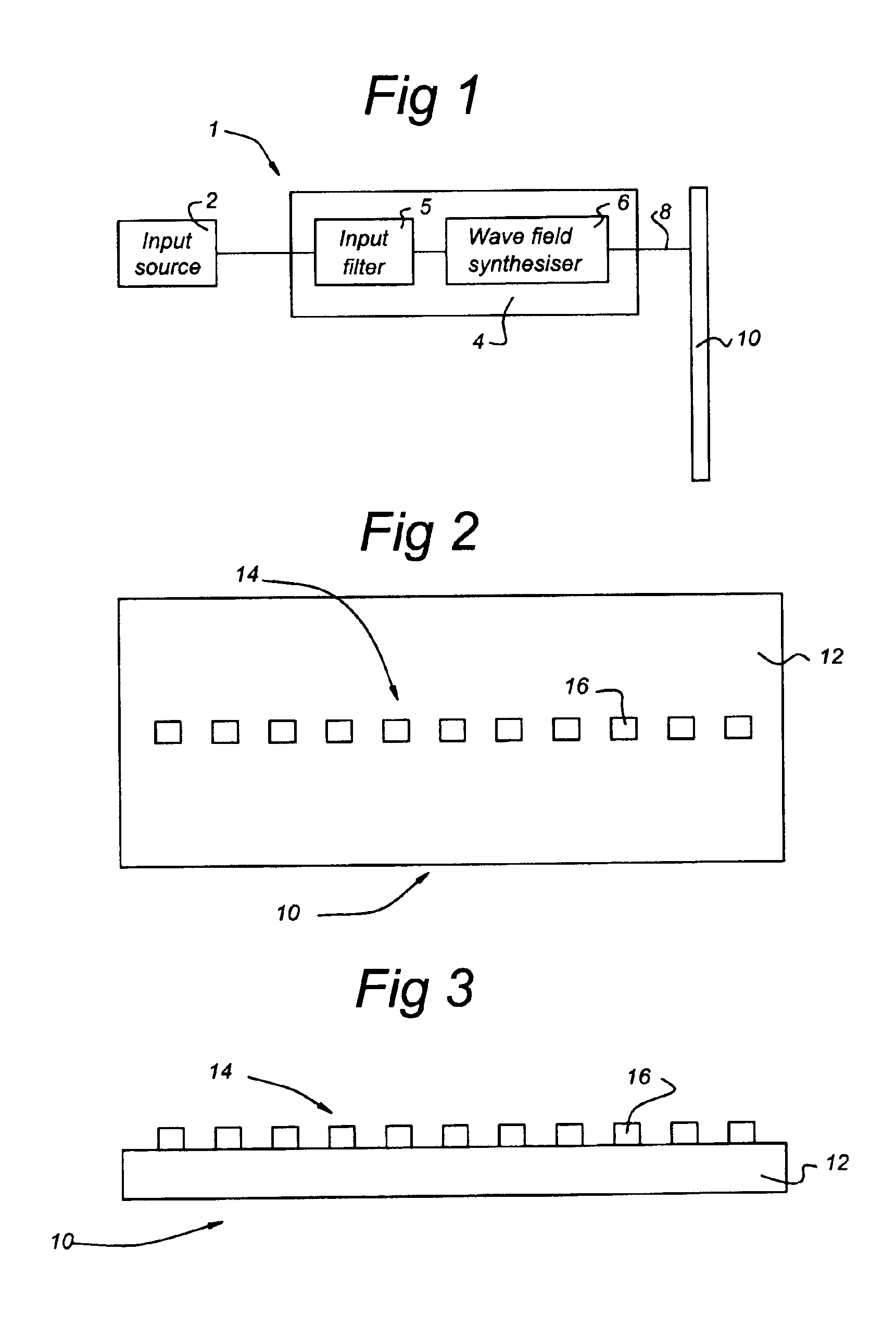
Device and method for determining a reproduction position
ActiveUS20050147257A1Readily availablePrecise positioningTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionSound sourcesComputer graphics (images)
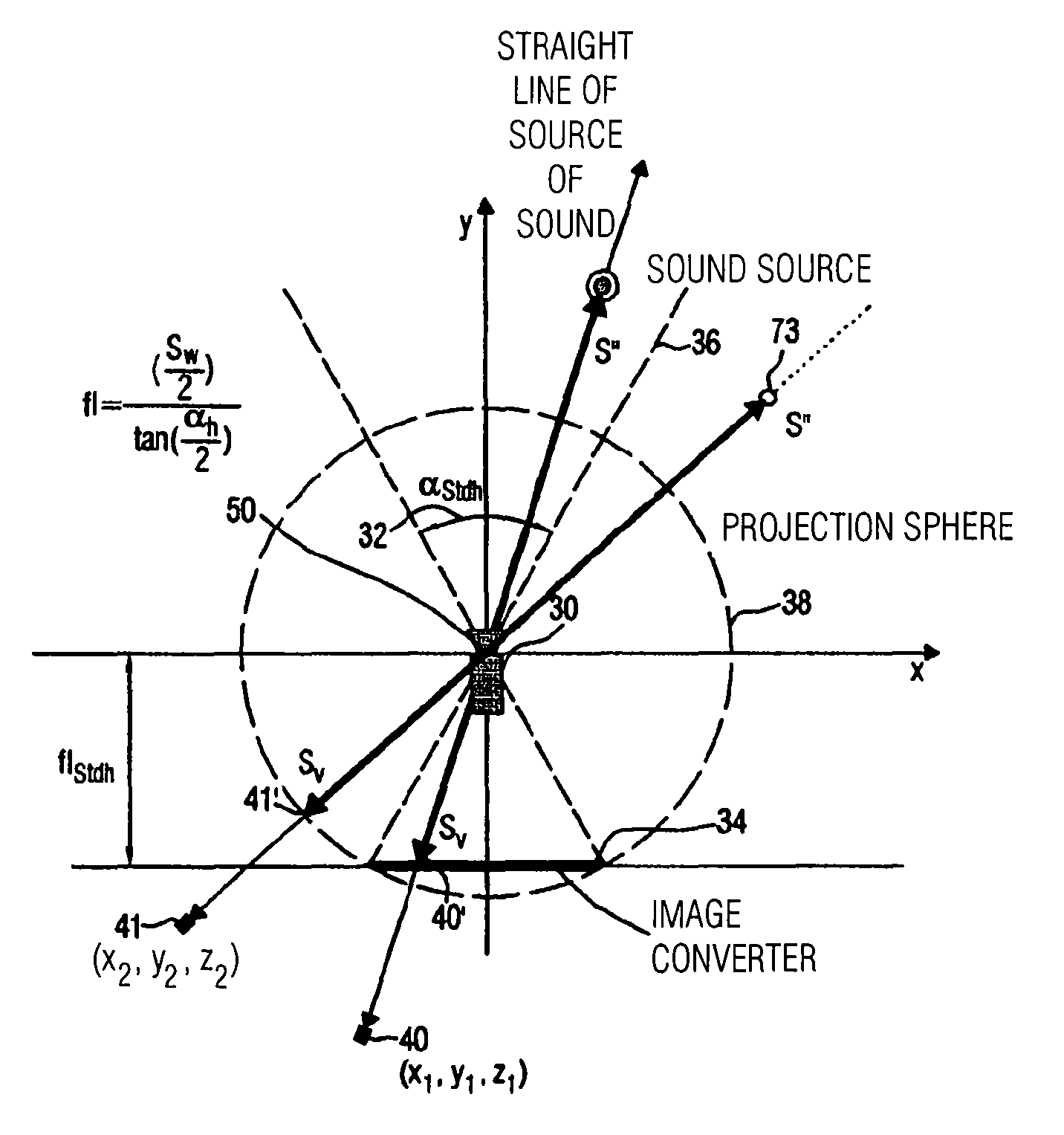
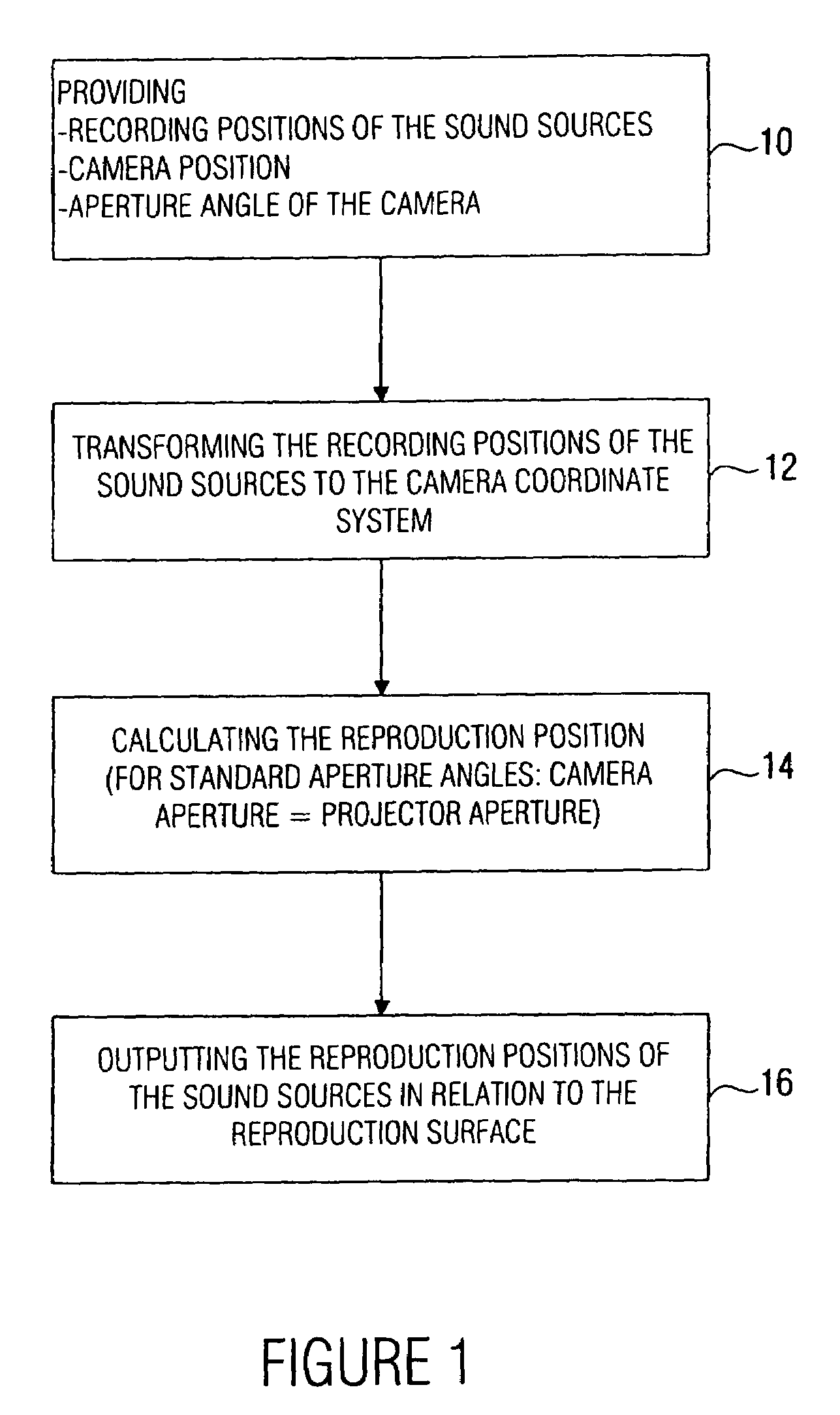
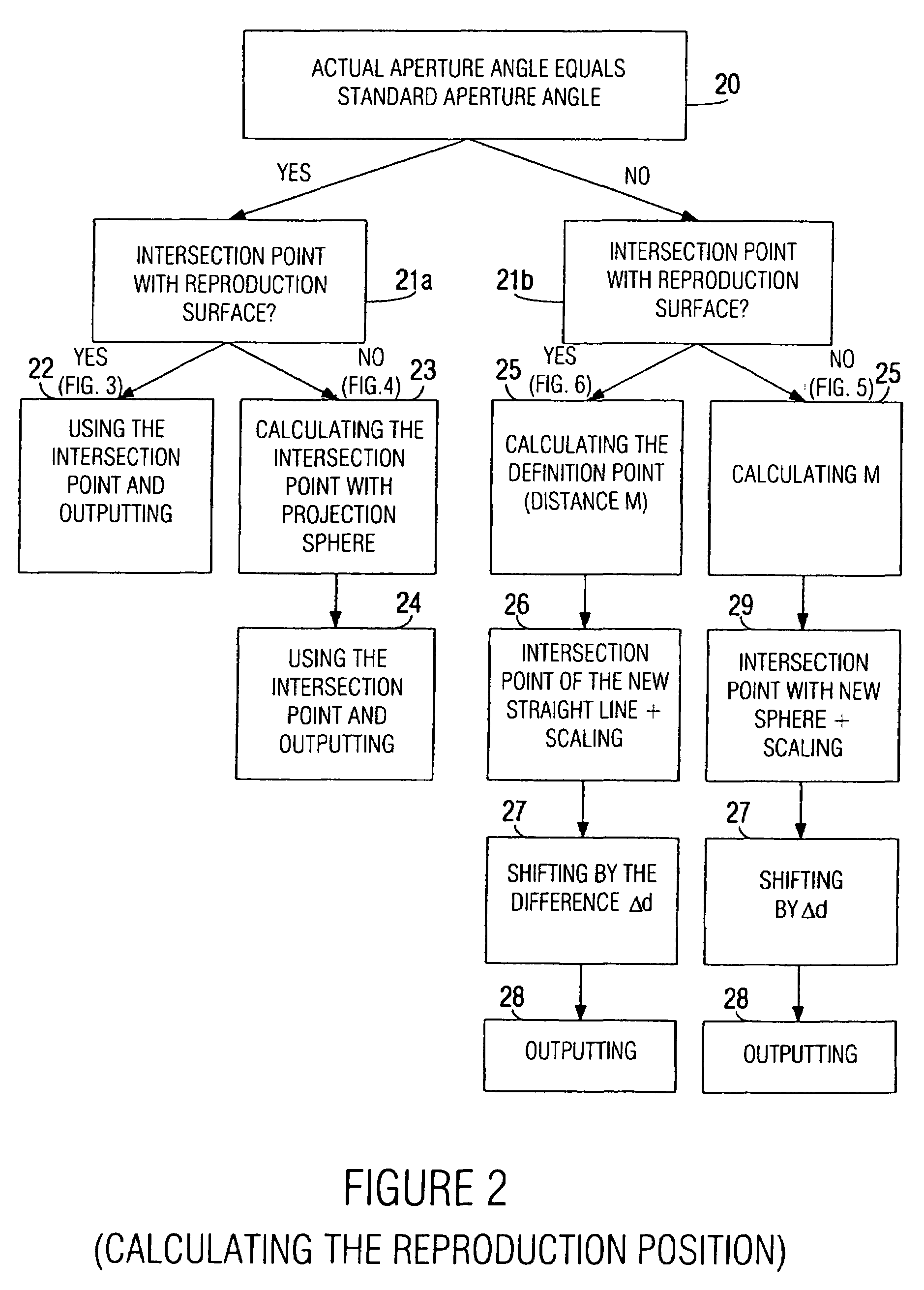
A device for determining a reproduction position of a source of sound for audio-visual reproduction of a film scene from a plurality of individual pictures with regard to a reproduction surface having a predetermined width and a projection source having a projection reference point comprises means for providing a recording position of the source of sound, a camera position during recording, and an aperture angle of the camera during recording. In addition, provision is made of means for transforming the recording position of the source of sound to a camera coordinate system, the origin of which is defined, in relation to a camera aperture, to obtain a recording position of the source of sound in the camera coordinate system. Means for calculating the reproduction position of the source of sound in relation to the projection reference point determines whether the aperture angle of the camera equals a predetermined aperture angle, and whether or not a source of sound is located within the visual range of the camera. If the current aperture angle of the camera differs from the predetermined standard aperture angle, the reproduction position of the source of sound is spaced toward a viewer, or away from the viewer, by a distance which depends on the ratio of the standard aperture angle to the current aperture angle. Hereby, automatable sound-source positioning is achieved so as to provide not only a visually realistic, but also an acoustically realistic situation in a reproduction room using wave-field synthesis methods.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Parametric joint-coding of audio sources
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
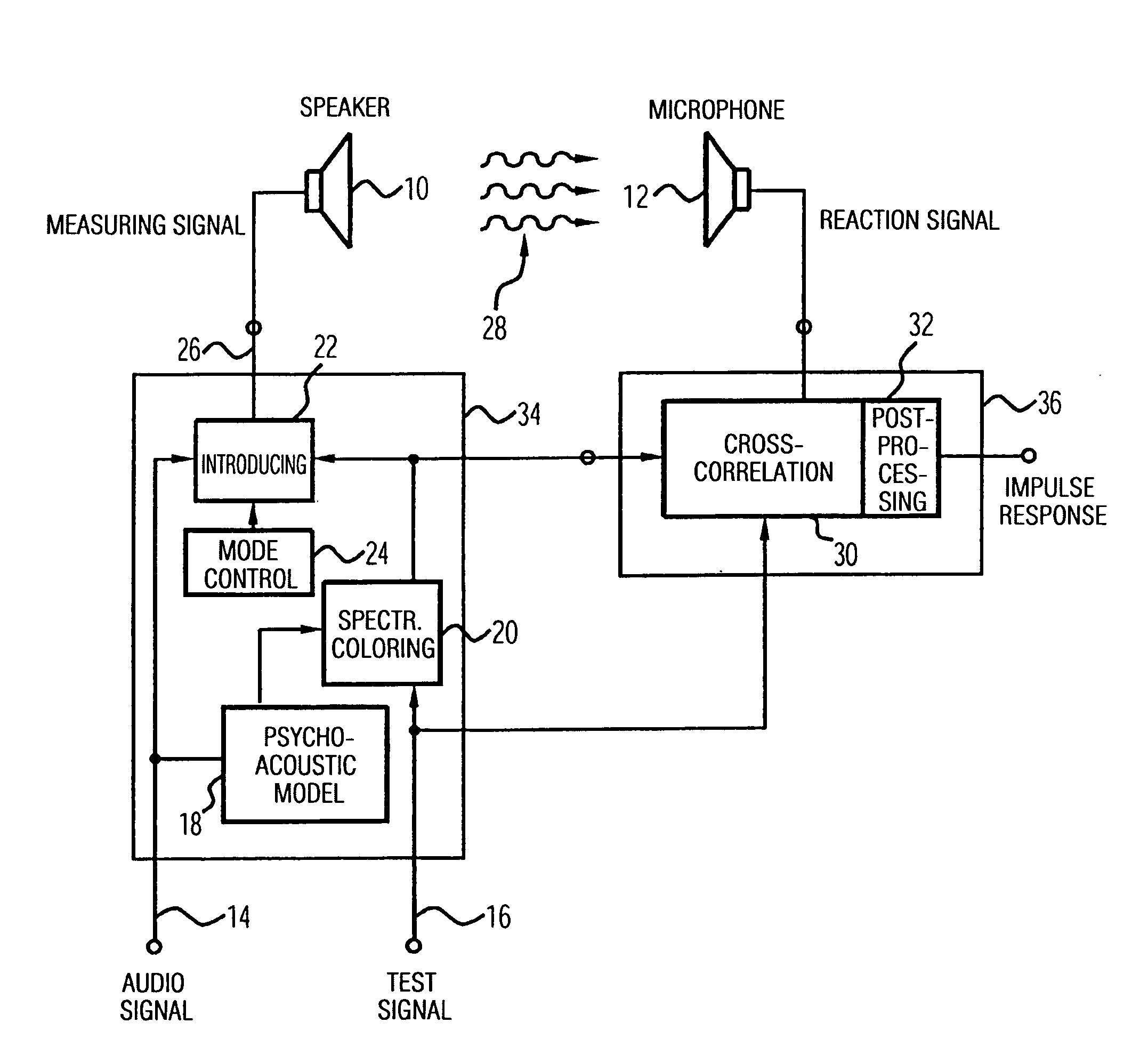
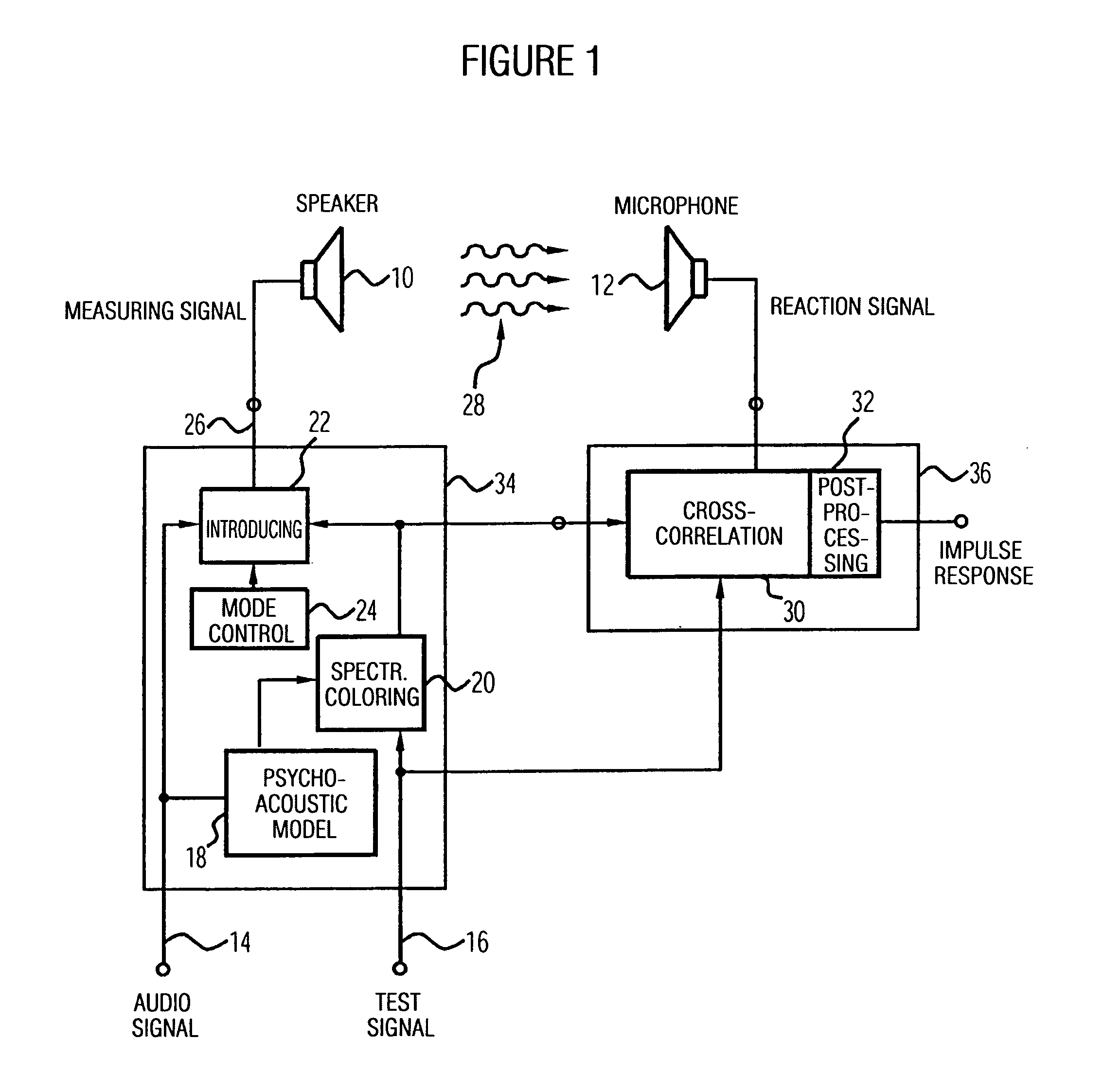
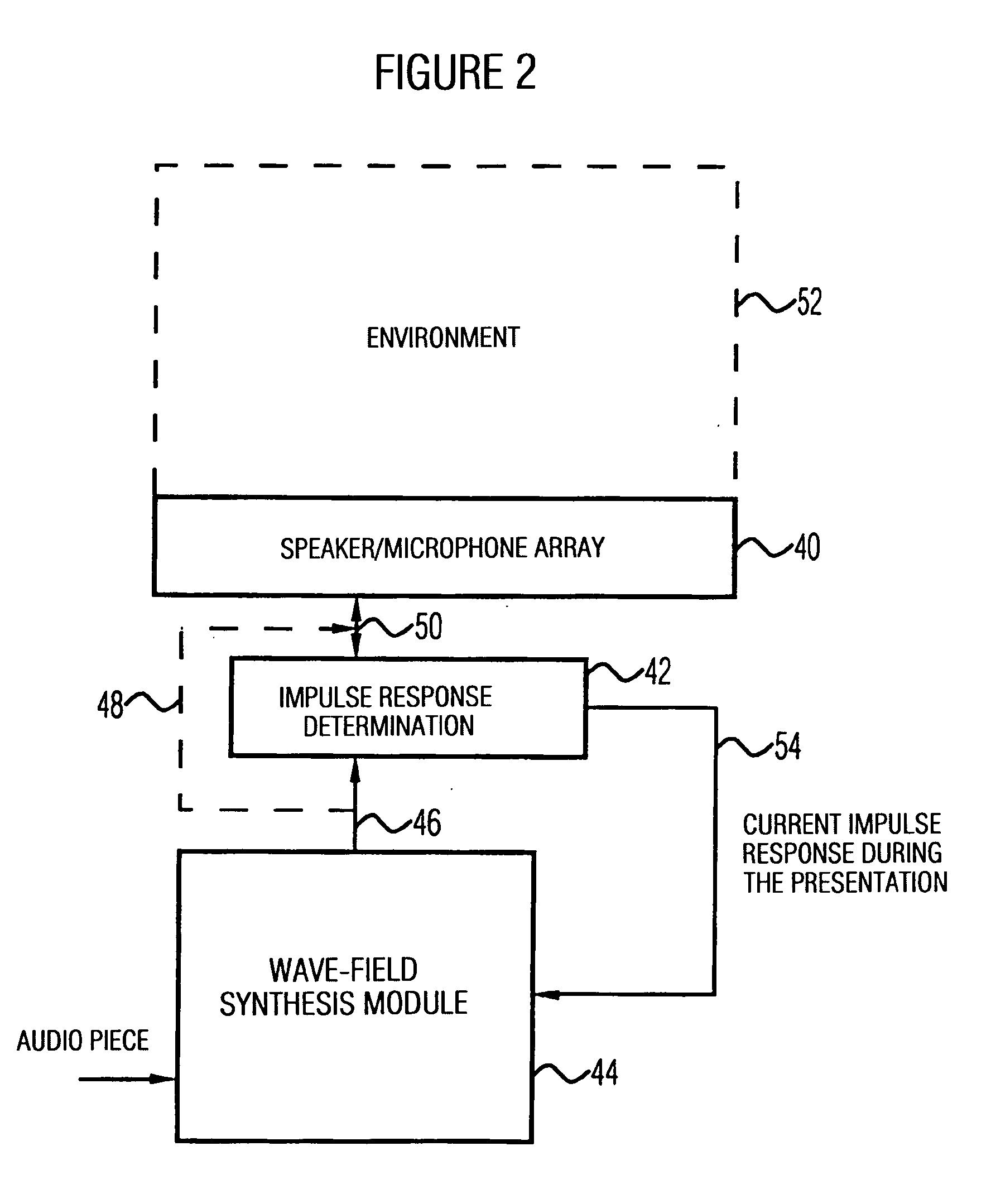
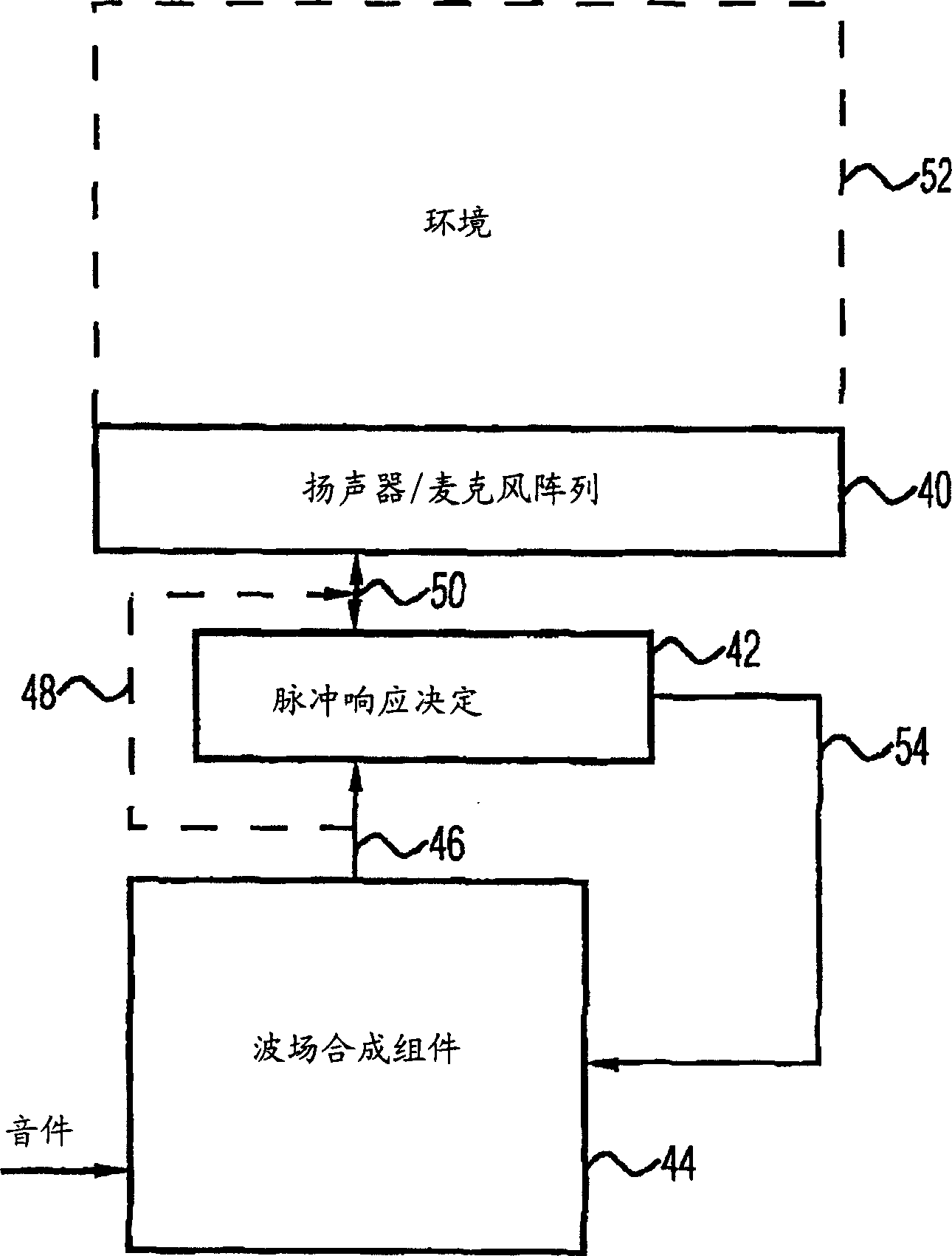
Apparatus and method of determining an impulse response and apparatus and method of presenting an audio piece
InactiveUS20050207592A1Accurate impulse responseImprove sound qualityTransmission noise suppressionStereophonic systemsFrequency spectrumWave field synthesis
The apparatus for determining an impulse response in an environment in which a speaker and a microphone are placed works using an audio signal. Means for spectrally coloring a test signal, which preferably is a pseudonoise signal, works using a psychoacoustic masking threshold of the audio signal to obtain a colored test signal, which is embedded in the audio signal to obtain a measuring signal, which can be fed to the speaker. Means for determining the impulse response preferably performs a cross-correlation of a reaction signal received via the microphone from the environment and the test signal or the colored test signal. With this, an impulse response of an environment may also be determined during the presentation of an audio piece to provide an optimal description of environment for a wave-field synthesis.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
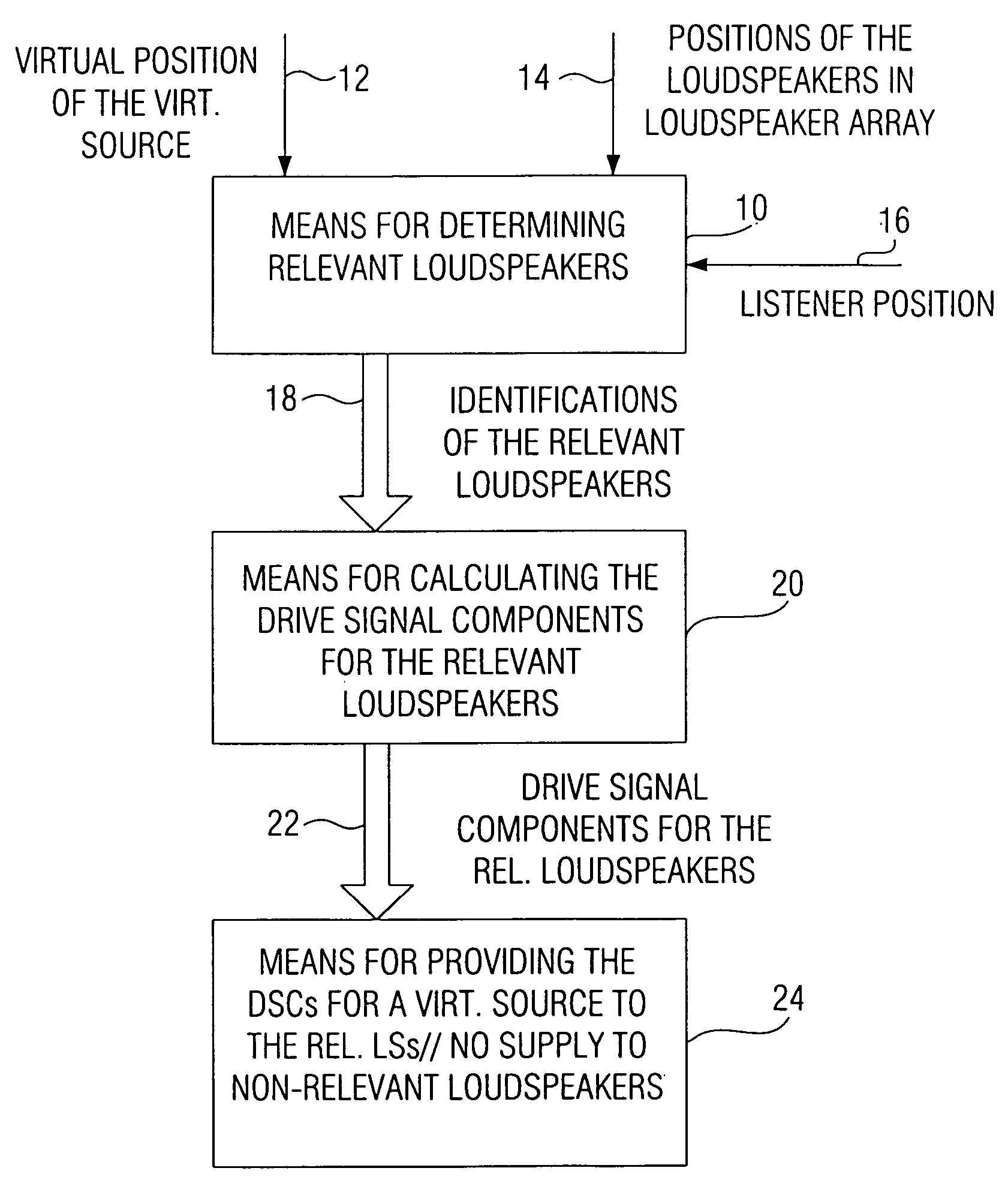
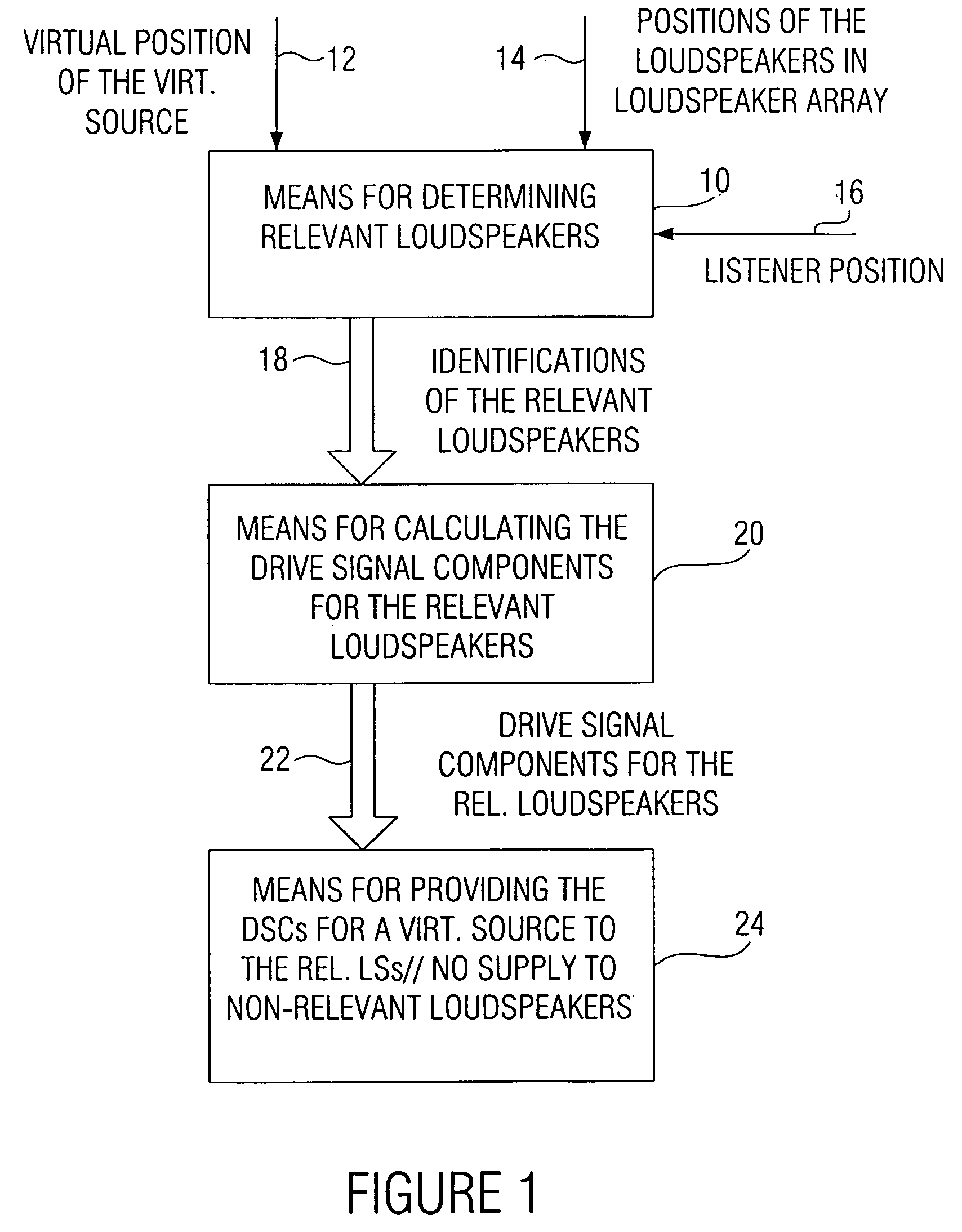
Wave field synthesis apparatus and method of driving an array of loudspeakers
ActiveUS20060098830A1Reduce artifactsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsLine-transmissionWave field synthesisWave field
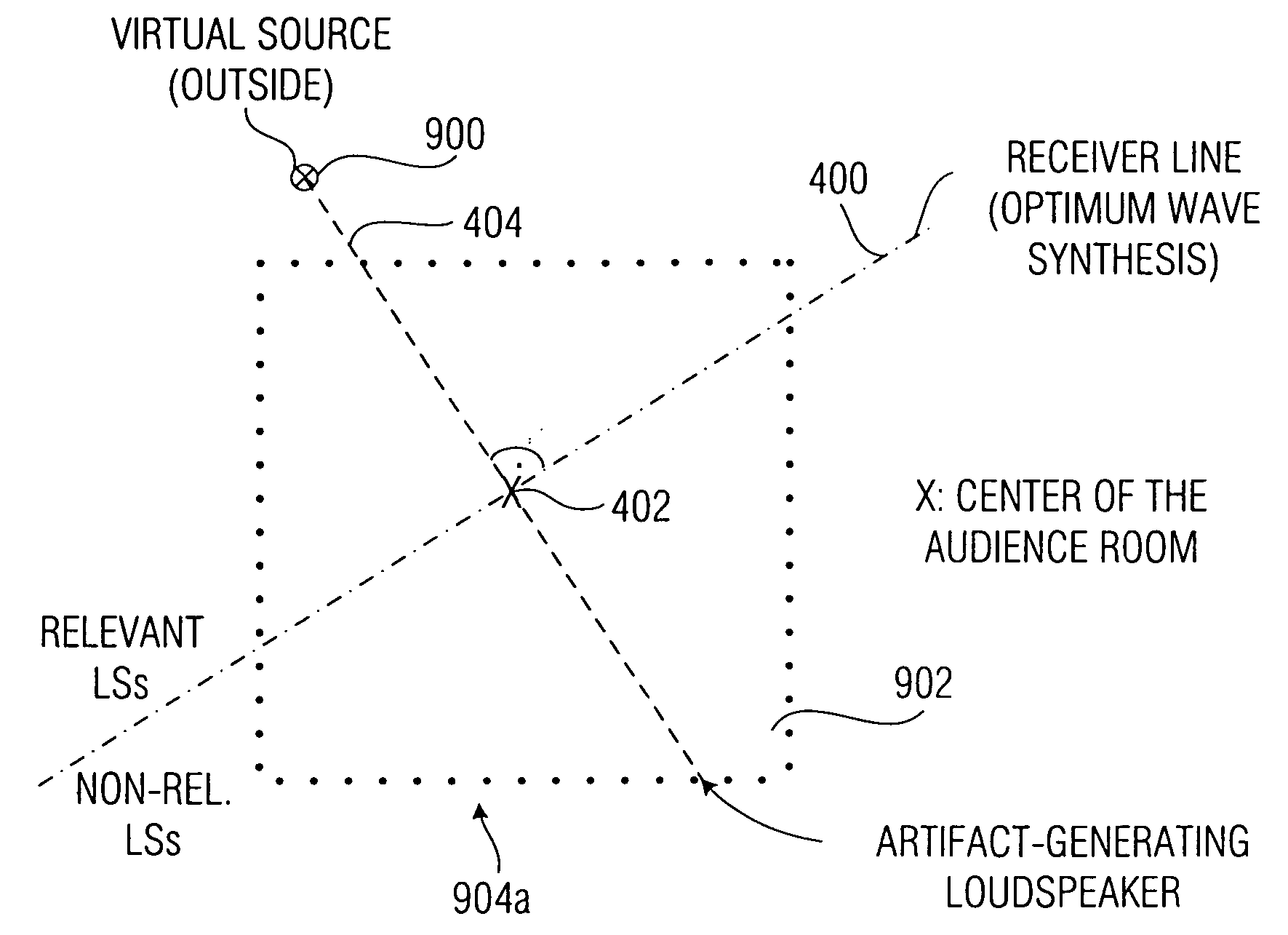
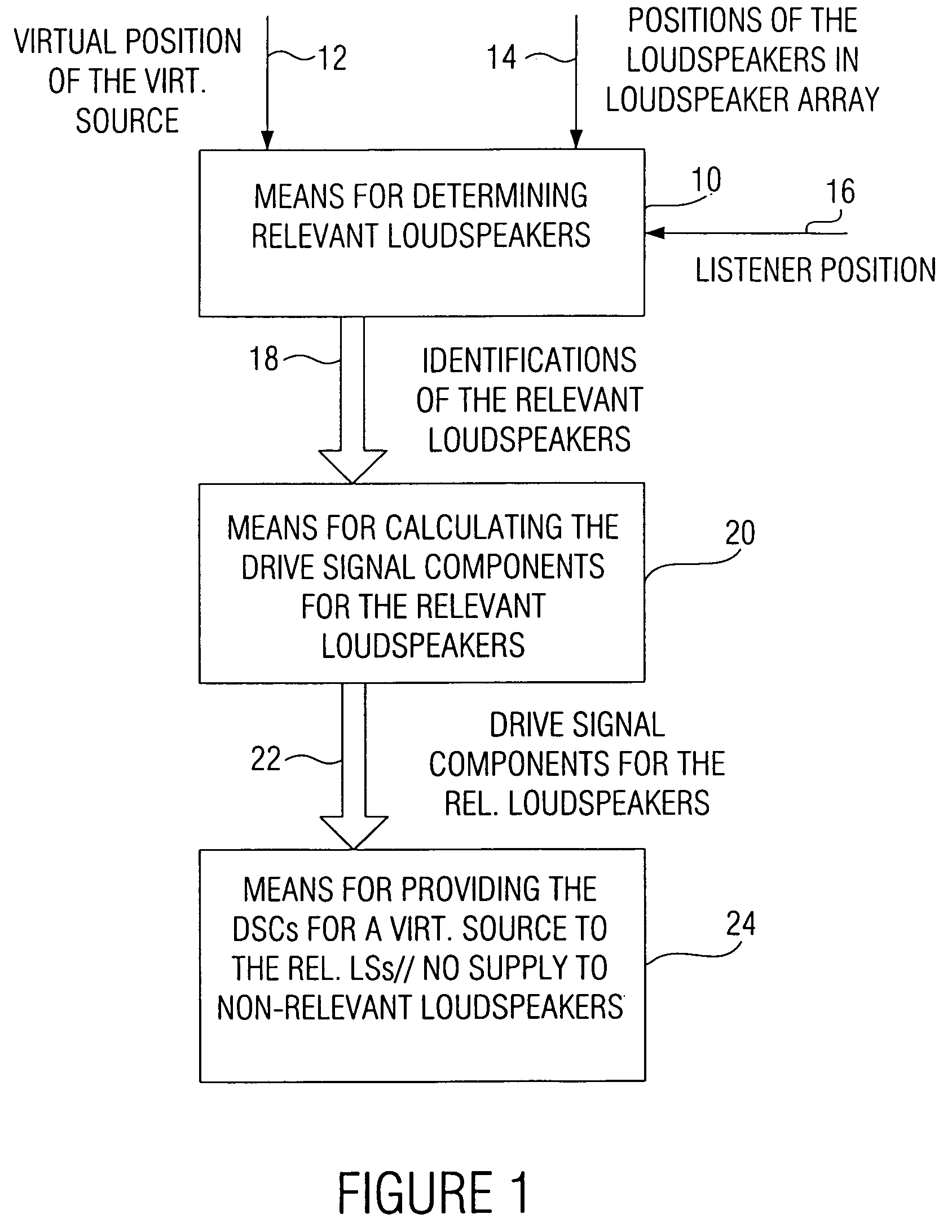
In a wave field synthesis apparatus for driving an array of loudspeakers with drive signals, the loudspeakers being arranged at different defined positions, a drive signal for a loudspeaker being based on an audio signal associated with a virtual source having a virtual position with reference to the loudspeaker array and on the defined position of the loudspeaker, at first relevant loudspeakers of the loudspeaker array are determined on the basis of the position of the virtual source, a predefined listener position, and the defined positions of the loudspeakers, so that artifacts due to loudspeaker signals moving opposite to a direction from the virtual source to the predefined listener position are reduced. Downstream to means for calculating the drive signal components for the relevant loudspeakers and for a virtual source, there is means for providing the drive signal components for the relevant loudspeakers for the virtual source to the relevant loudspeakers, wherein no drive signals for the virtual source are provided to loudspeakers of the loudspeaker array not belonging to the relevant loudspeakers. With this, artifacts in an area of the audience room due to a generation wave field are suppressed, so that in this area only the useful wave field is heard in artifact-free manner.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
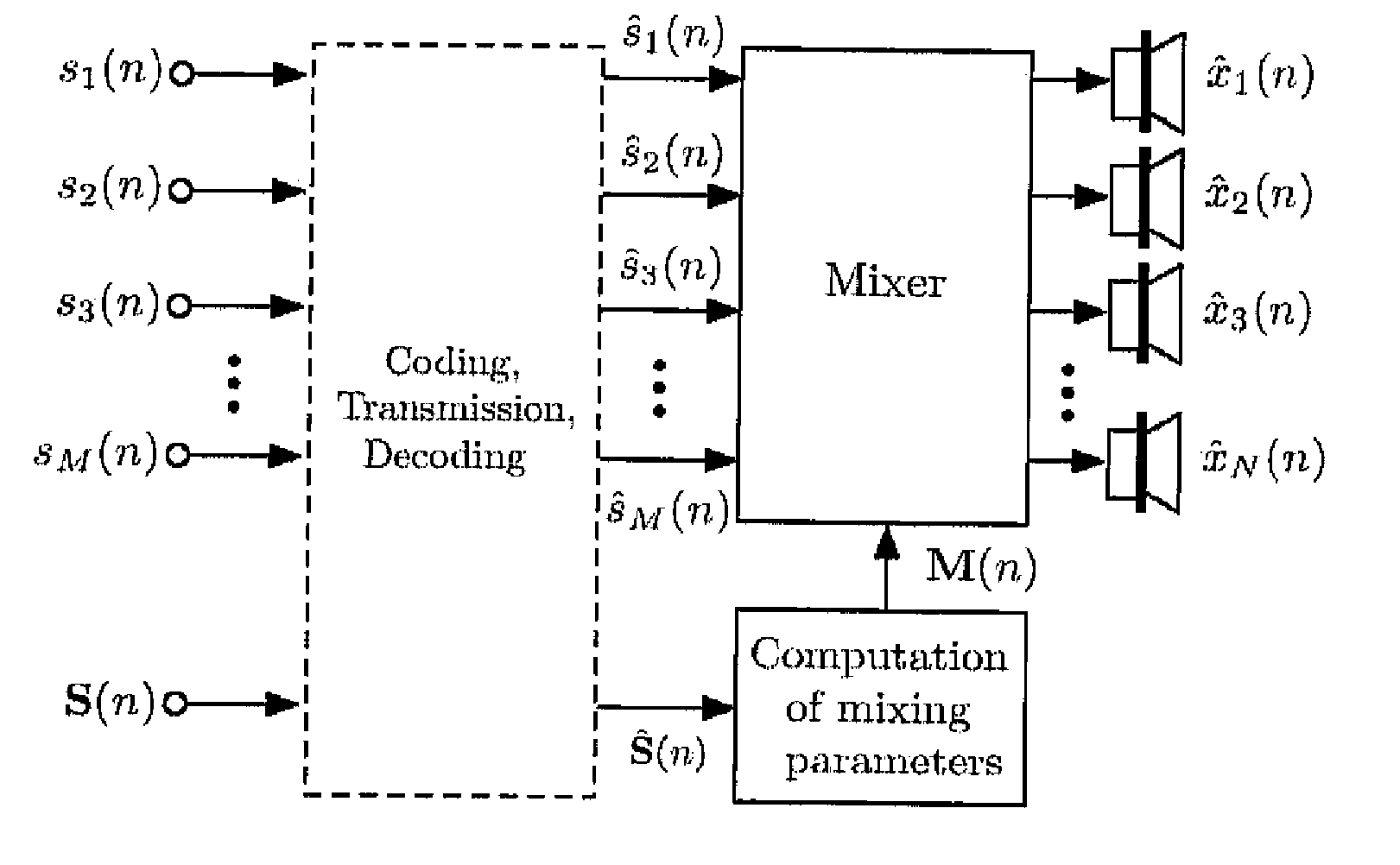
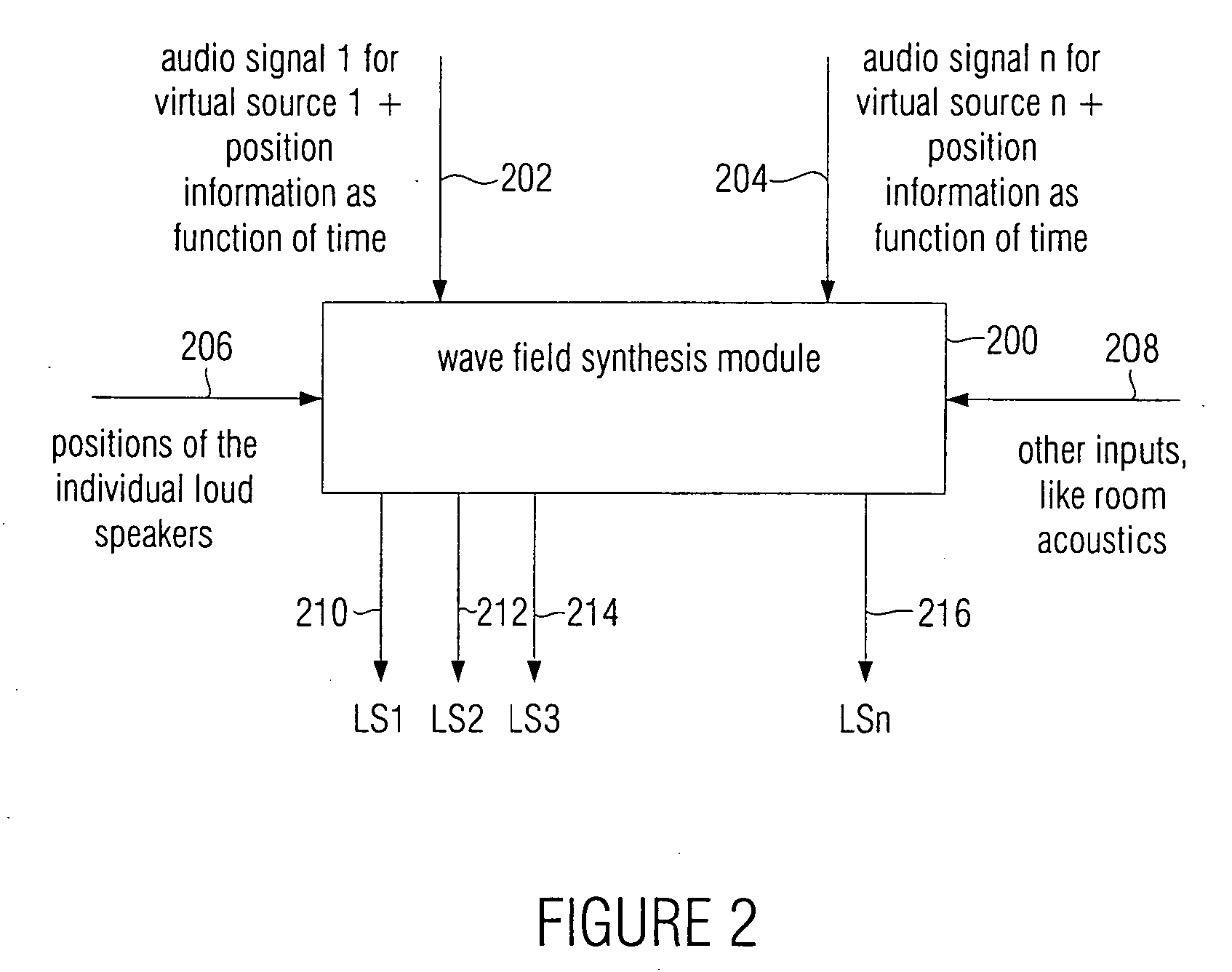
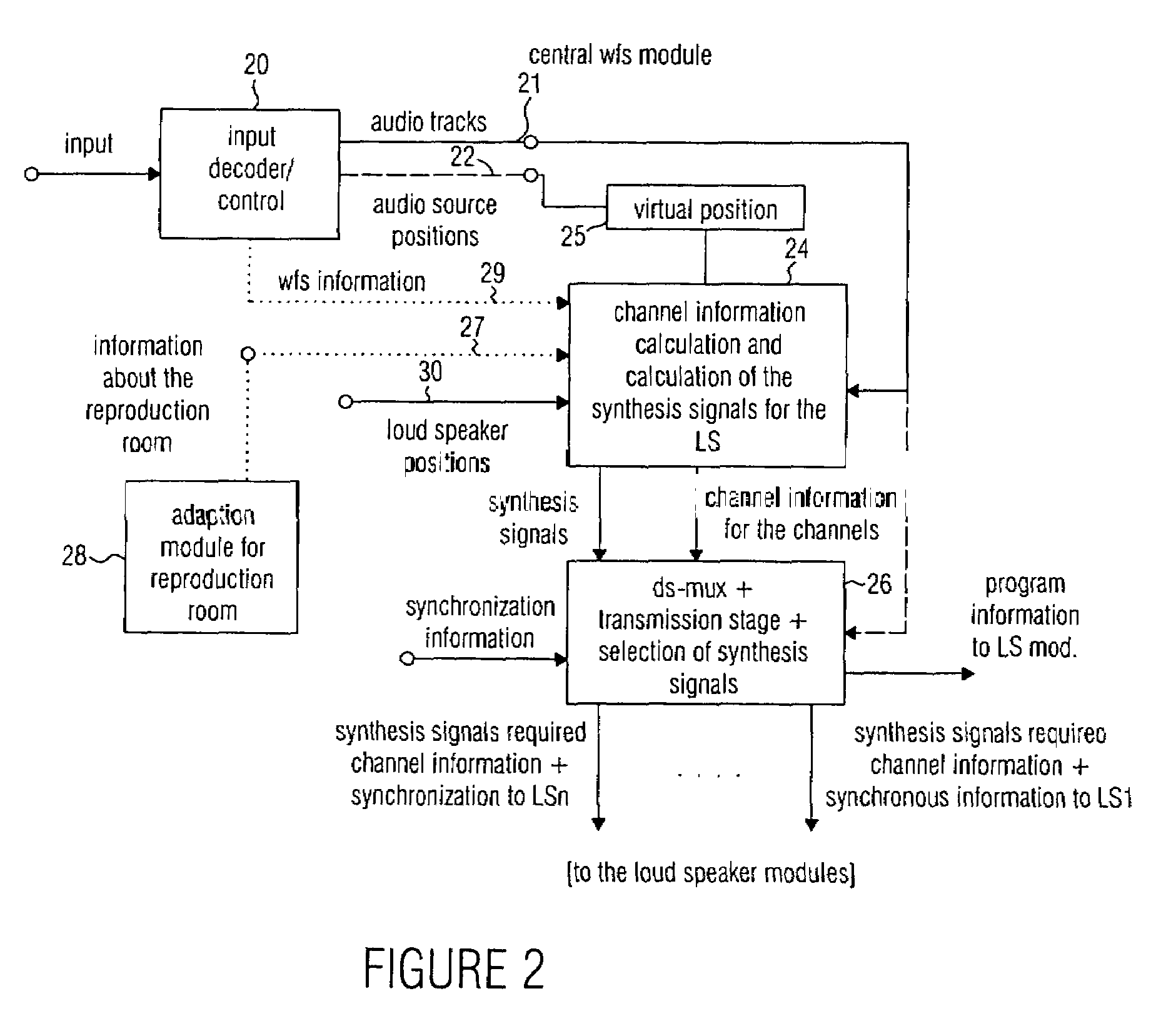
Audio reproduction system and method for reproducing an audio signal
ActiveUS20050175197A1High market acceptanceLow costLoudspeaker signals distributionFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsWave field synthesisWave field
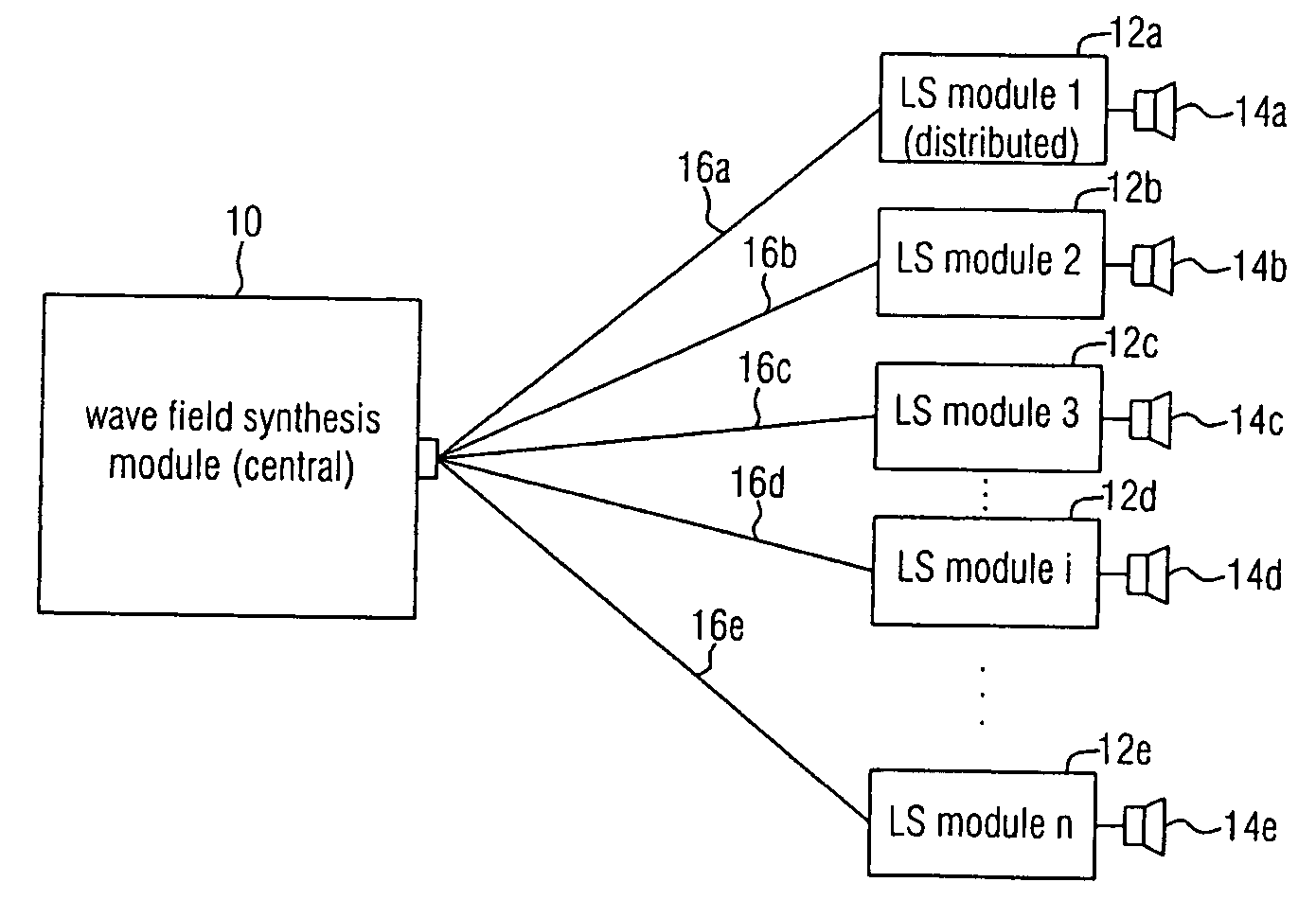
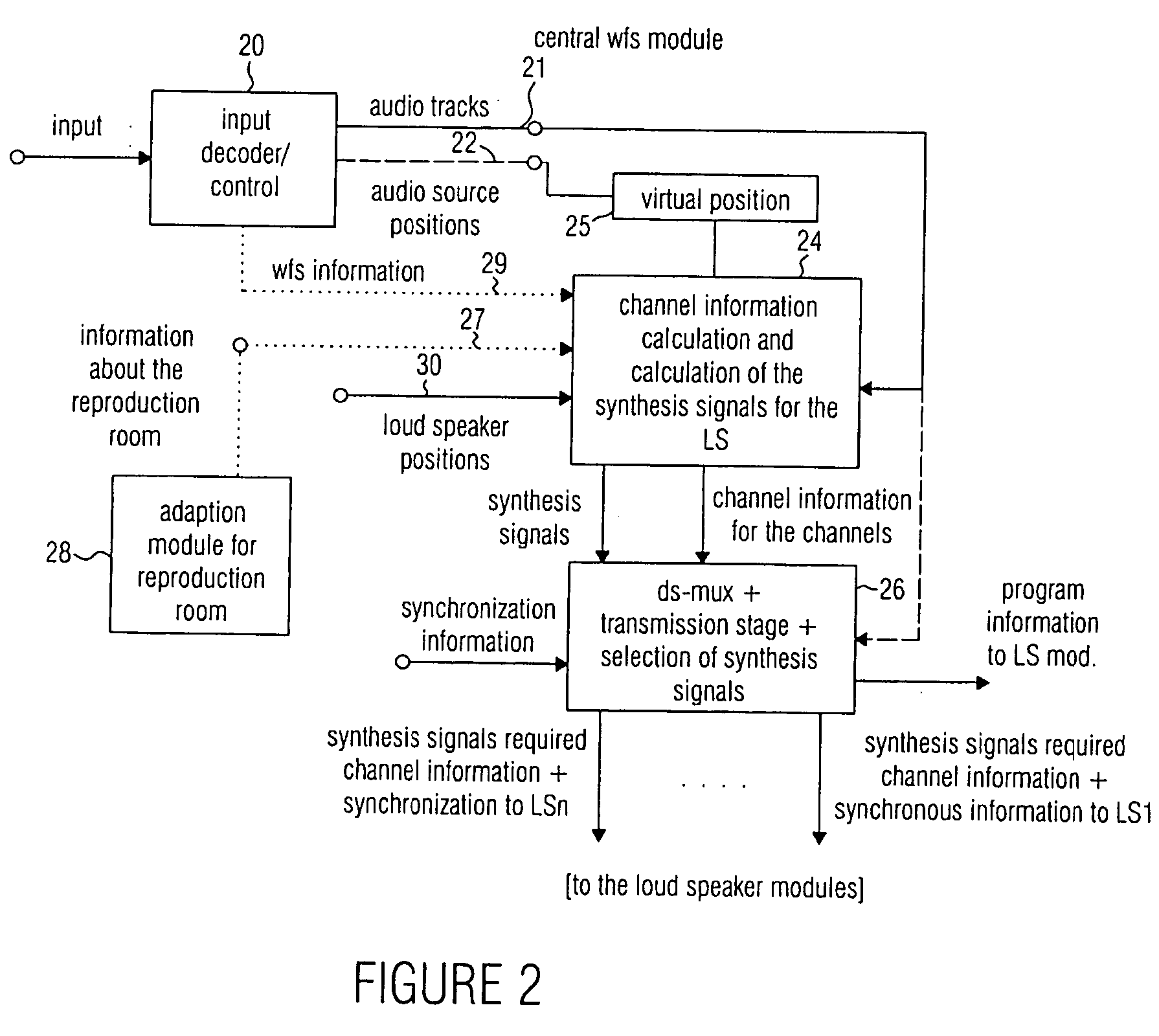
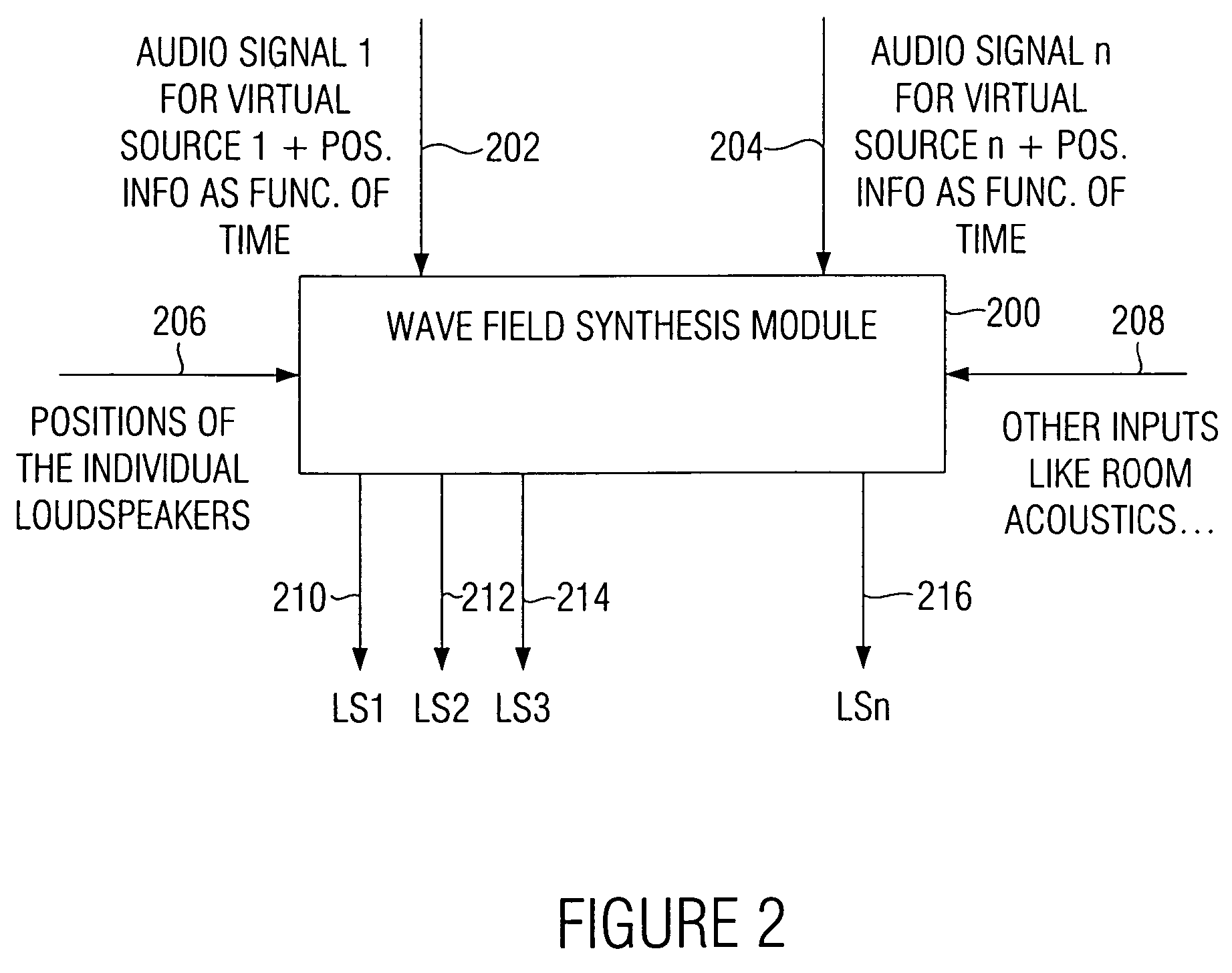
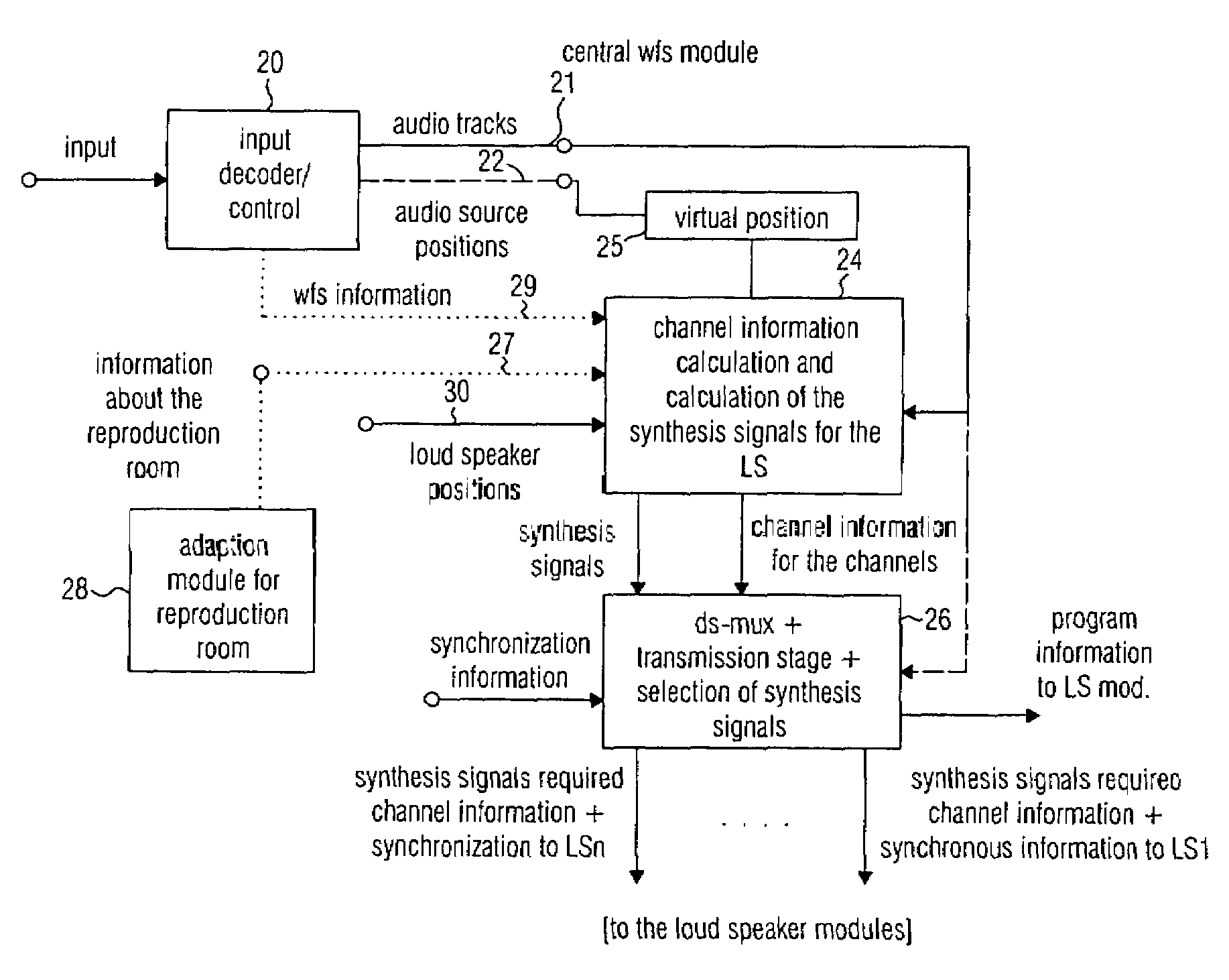
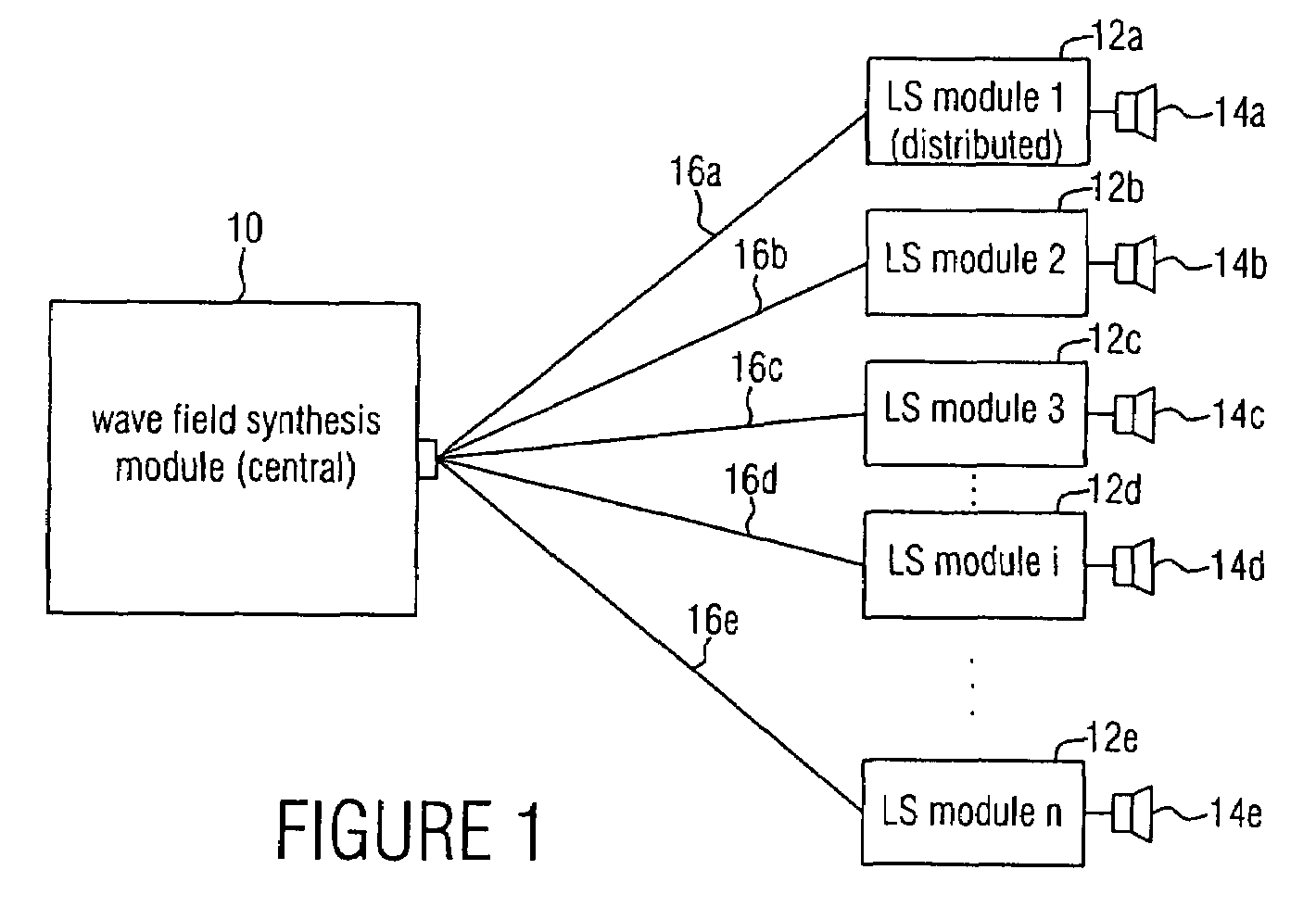
An audio reproduction system is divided into a central wave-field synthesis module and a plurality of loudspeaker modules disposed in a distributed way, wherein synthesis signals for the individual loudspeakers as well as corresponding channel information associated to the synthesis signals are calculated in the central wave-field synthesis module. The synthesis signals for a loudspeaker as well as associated channel information will then be transmitted to respective loudspeaker modules via a transmission path, wherein every loudspeaker module obtains the synthesis signals and associated channel information intended for the loudspeaker associated to the loudspeaker module. A distributed audio rendering and digital / analog converting takes place in the loudspeaker module to generate the actually analog loudspeaker signals in a distributed way in spatial proximity to every loudspeaker. The division into a central wave-field synthesis module and the plurality of distributed loudspeaker modules allows that audio reproduction systems that are scalable with regard to the price can be generated in order to offer systems of different size scalable in price particularly for cinema reproduction rooms varying strongly in size.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
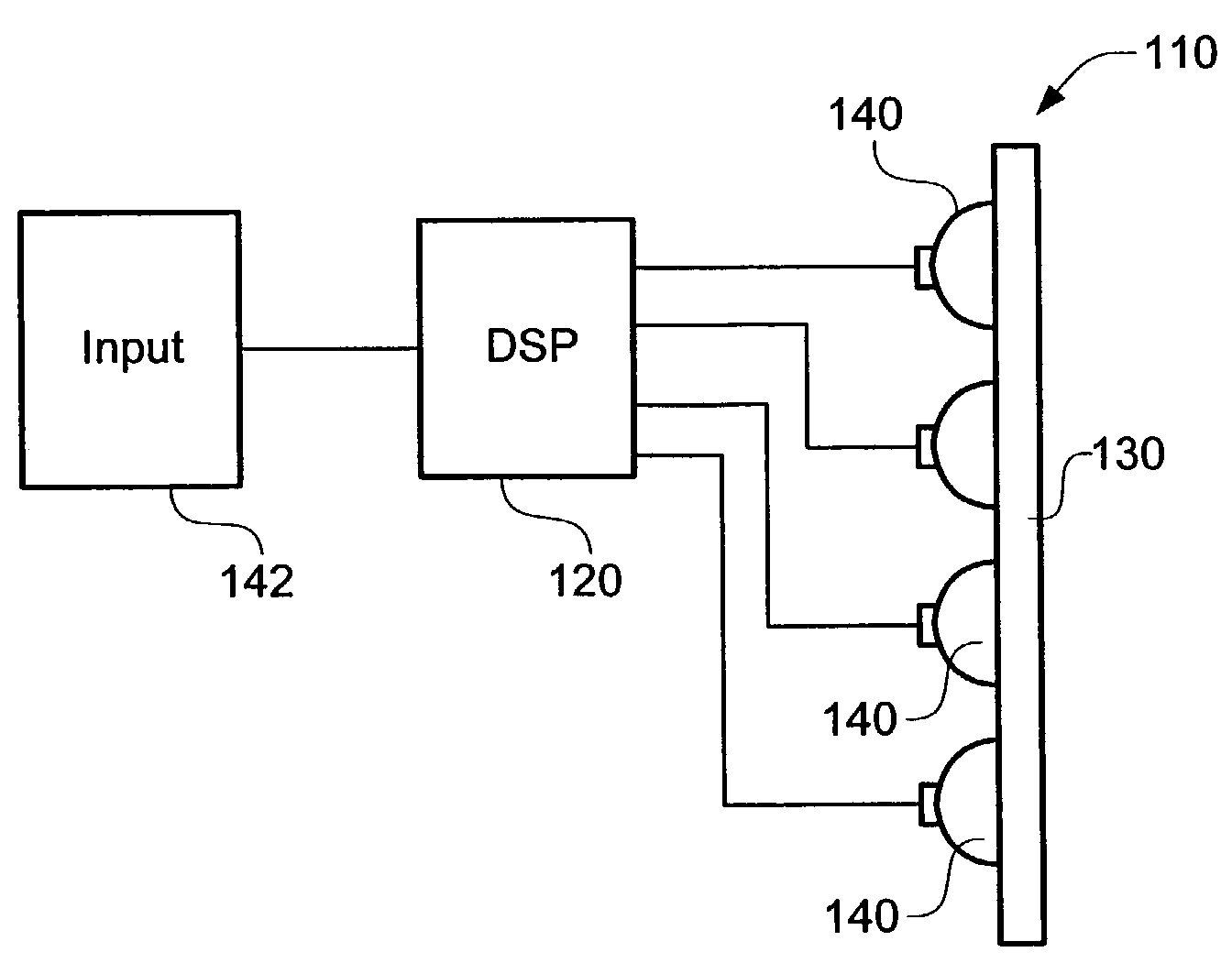
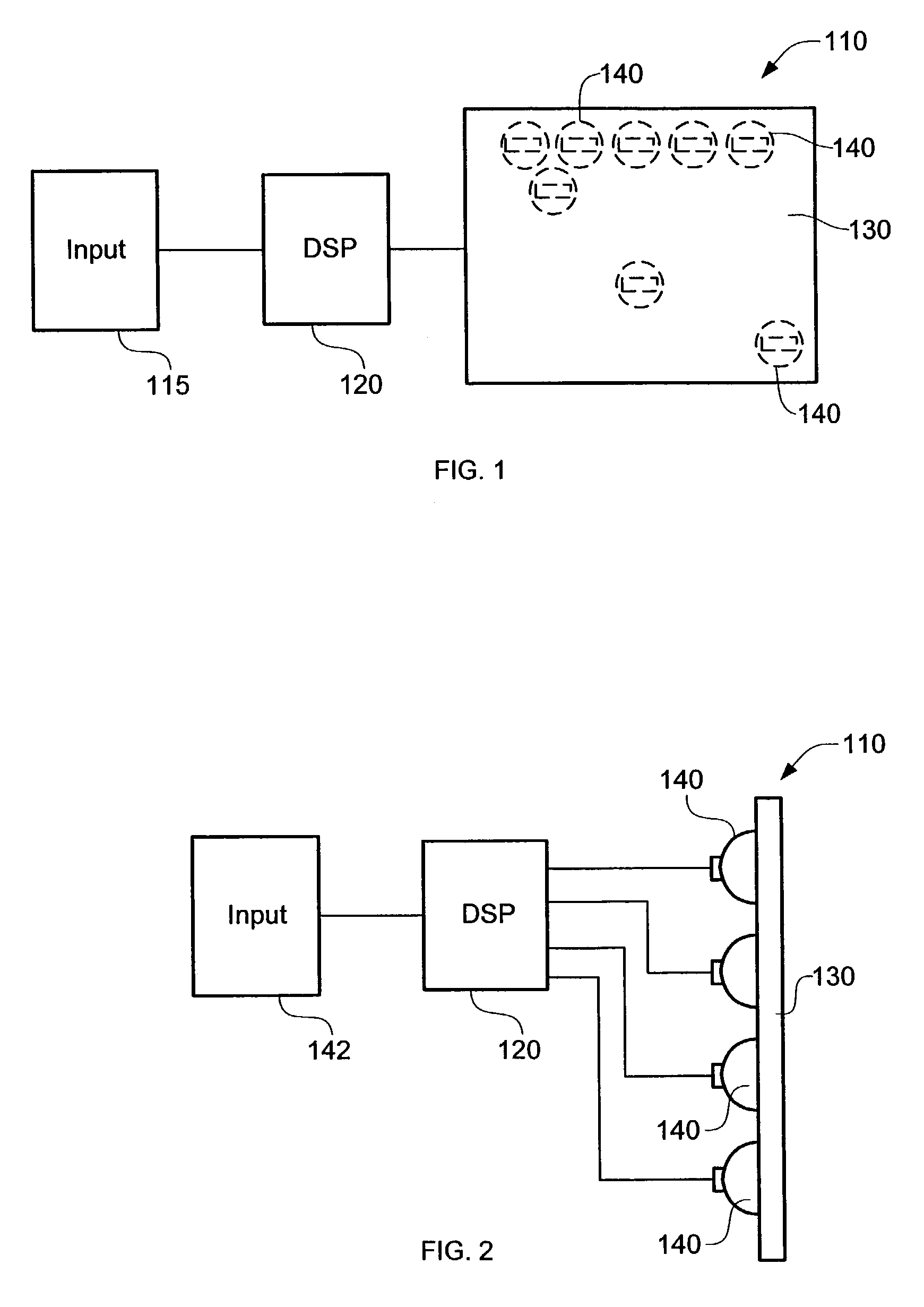
Sound reproduction system
InactiveUS6959096B2Easy to installExtension of timeGain controlPseudo-stereo systemsWave field synthesisTransducer
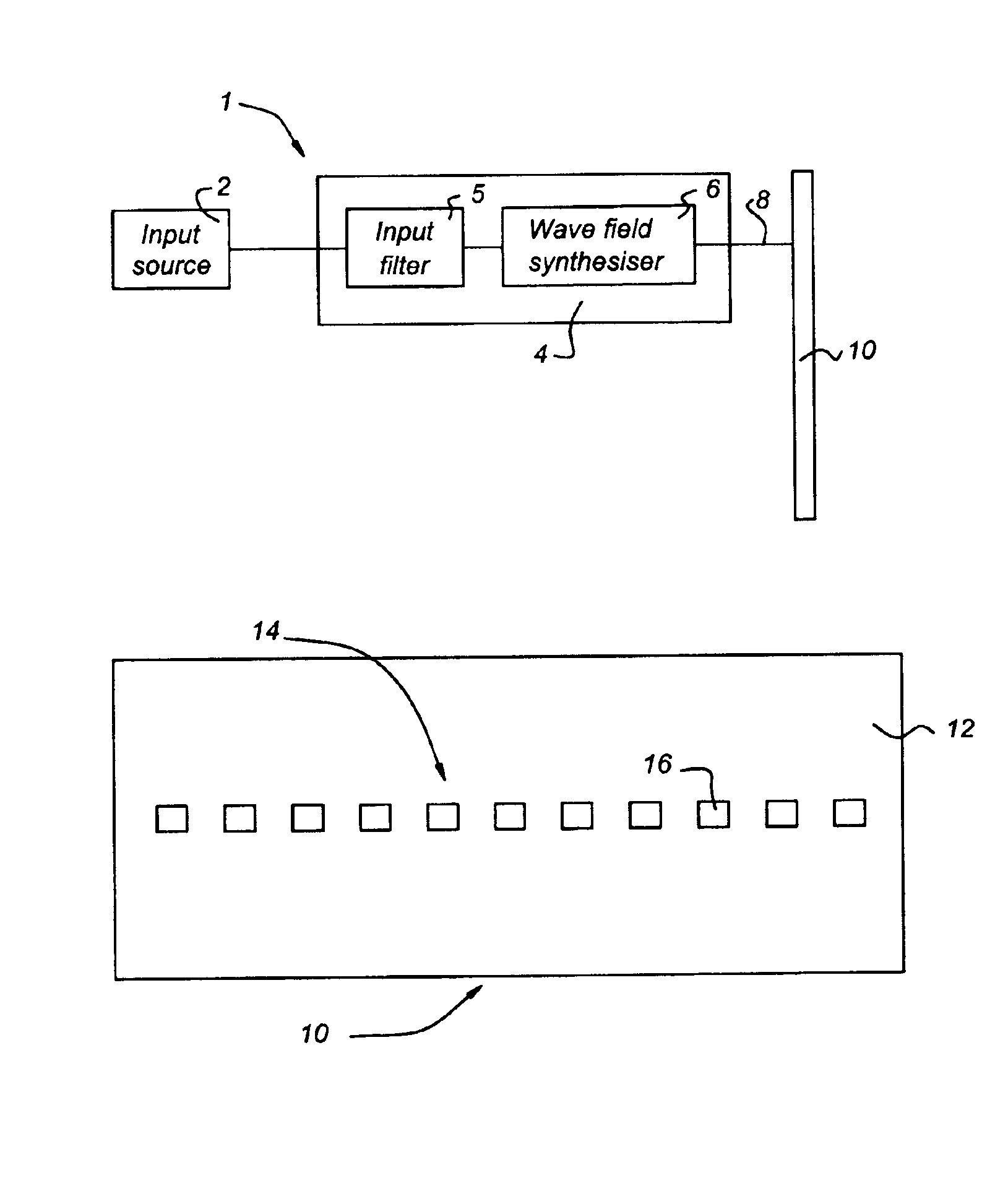
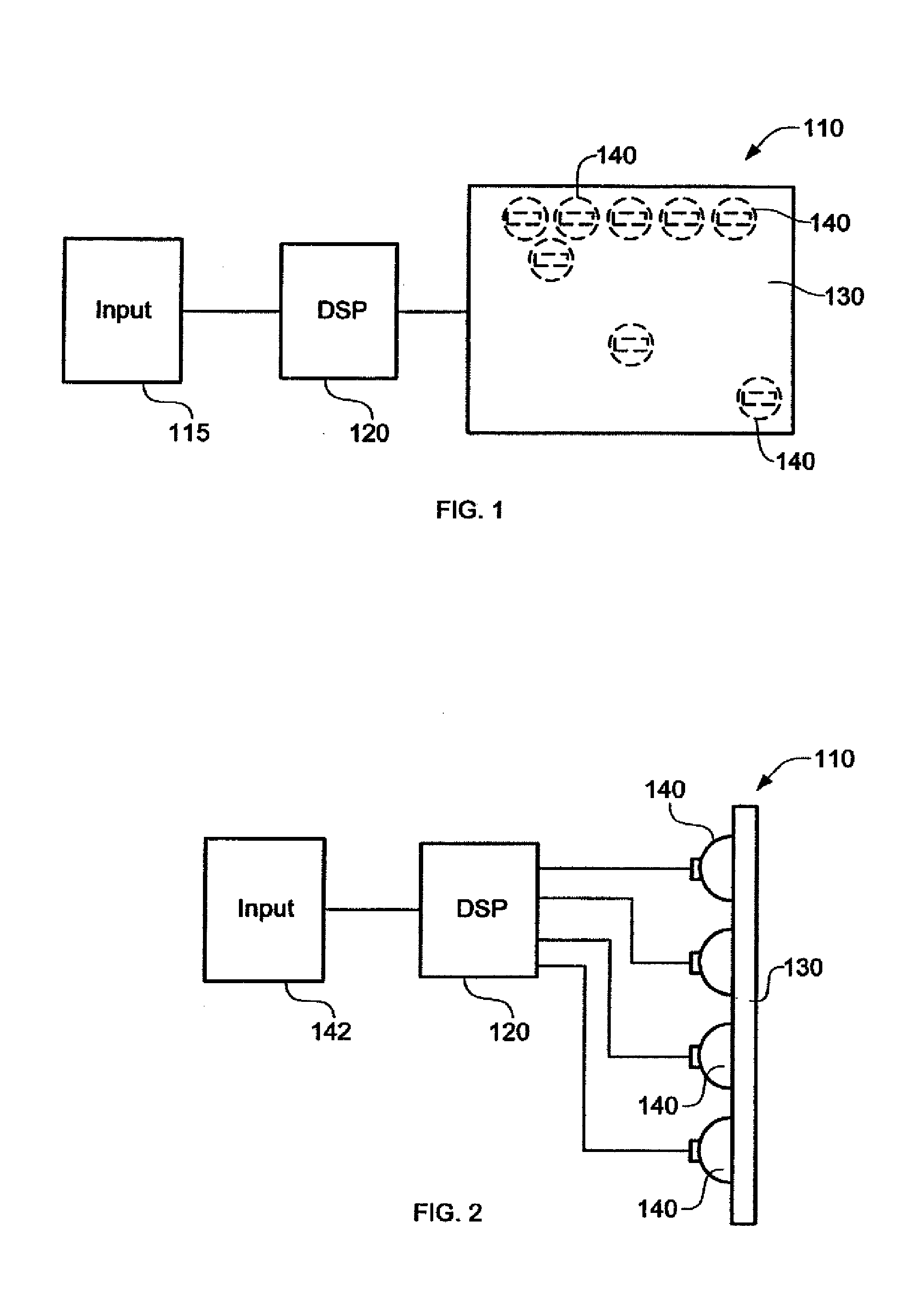
Arrangement of a sound reproduction system (1), including at least one input (2), a sound field generator (4), a loudspeaker panel (10); the at least one input (2) connected to the sound field generator (4), and the sound field generator (4) connected to the loudspeaker panel (10); the at least one input (2) arranged for generating an audio signal; the sound field generator (4) including a wave field synthesizer (6) arranged for generating a spatially perceptible sound field for the audio signal and for outputting the spatially perceptible sound field to the loudspeaker panel (10), the loudspeaker panel (10) being a multi-exciter Distributed Mode Loudspeaker panel (10) consisting of a plate (12) and a plurality of transducers (16), arranged within an array (14) on the large plate (12) for reproducing the spatially perceptible sound field from the wave field synthesizer (6) by exciting bending waves in the plate (12).
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
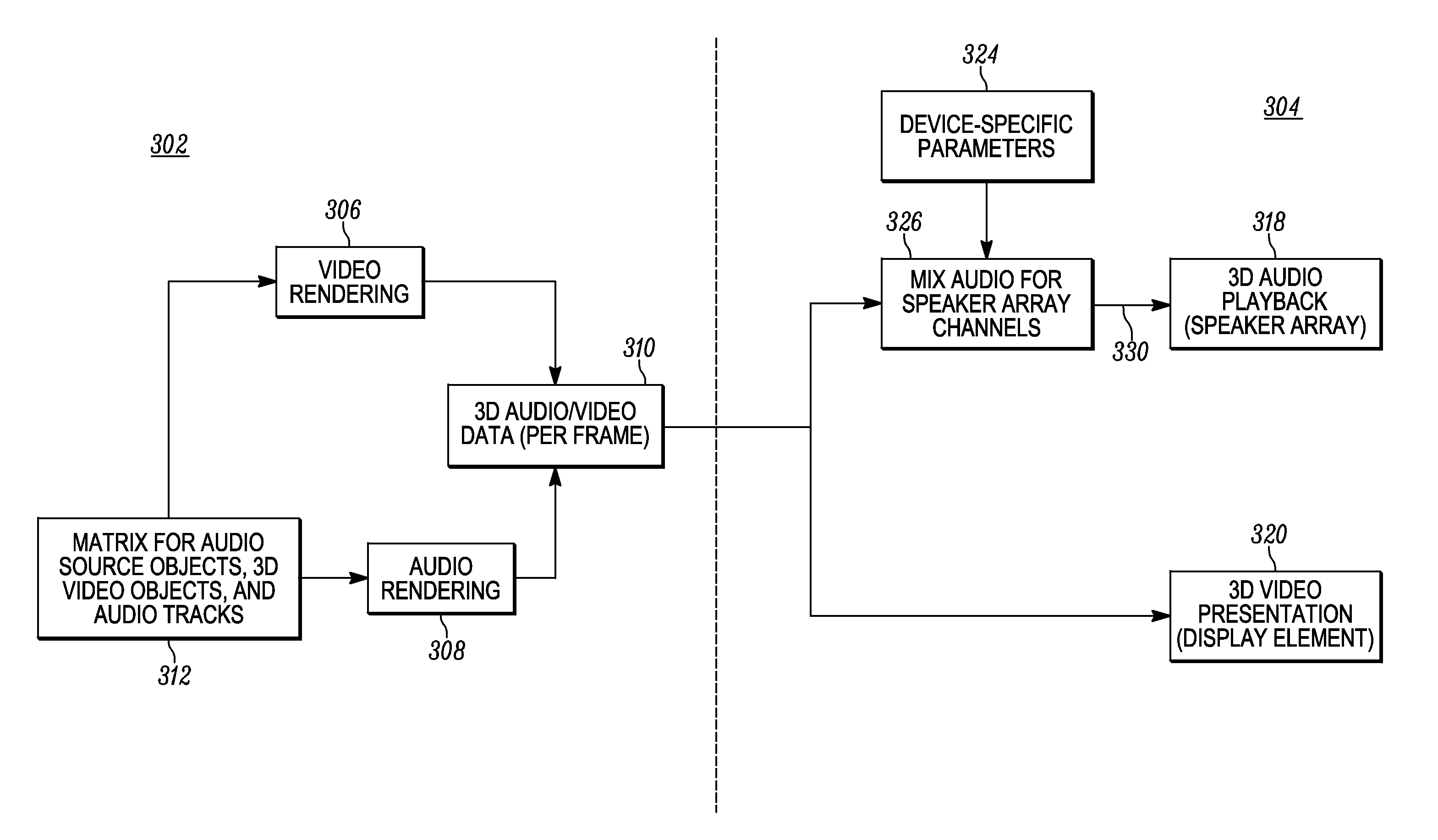
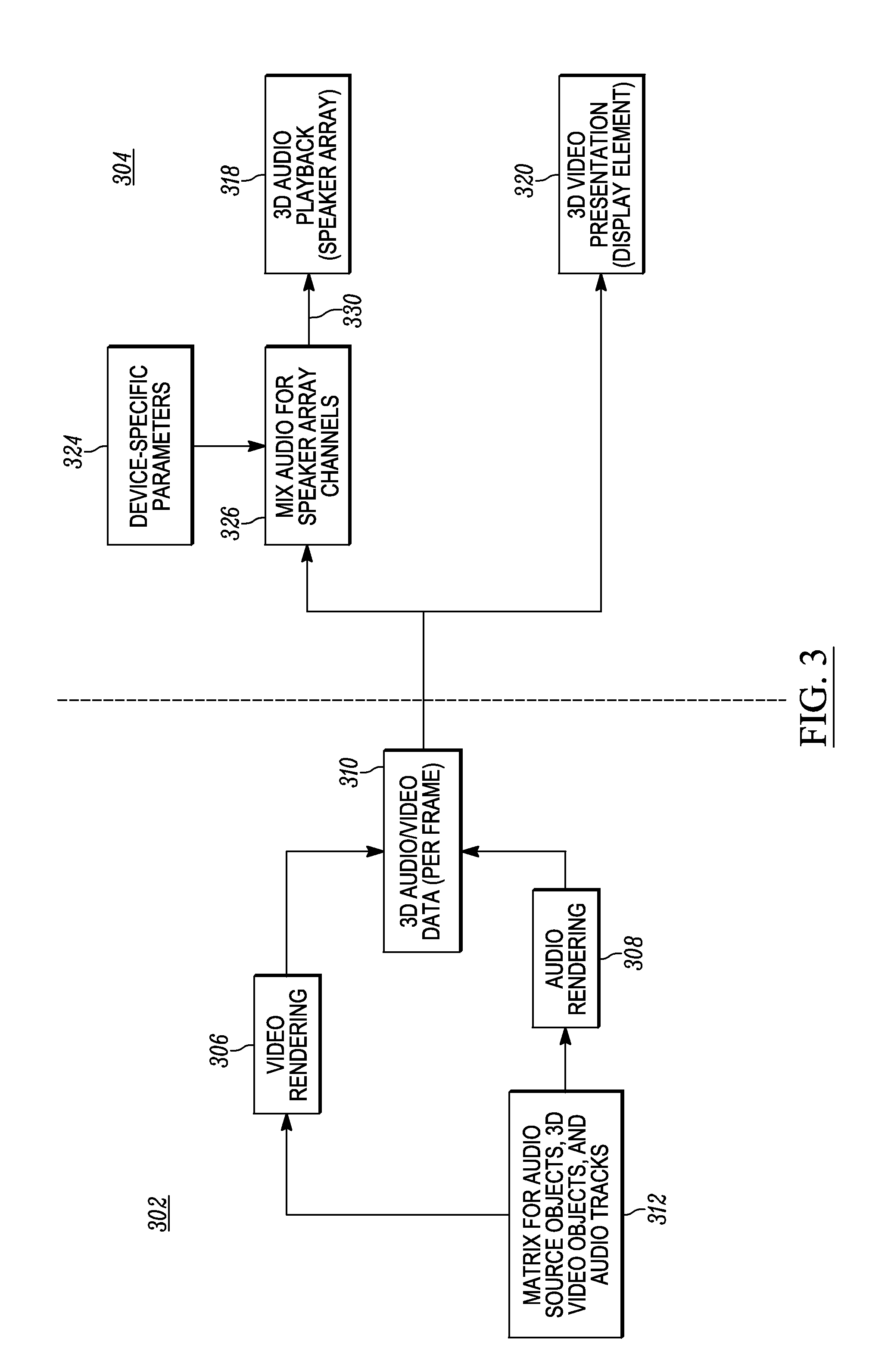
Three-dimensional audio rendering techniques
ActiveUS20150131966A1Audio/video recordingColor television signals processingComputer graphics (images)Wave field synthesis
Three-dimensional (3D) audio content creation and rendering systems and methodologies are presented here. A disclosed method of processing 3D audio assigns audio source objects to 3D video objects, links audio tracks to assigned audio source objects, and performs wave field synthesis on the linked audio tracks to generate 3D audio data representing a 3D spatial sound field. A disclosed method of processing 3D audio during playback of 3D video content obtains 3D audio data and 3D video data for a frame of 3D video content, applies device-specific parameters to the 3D audio data to obtain transformed 3D audio data scaled to a presentation device, and processes the transformed 3D audio data to render audio information for an array of speakers associated with the presentation device.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
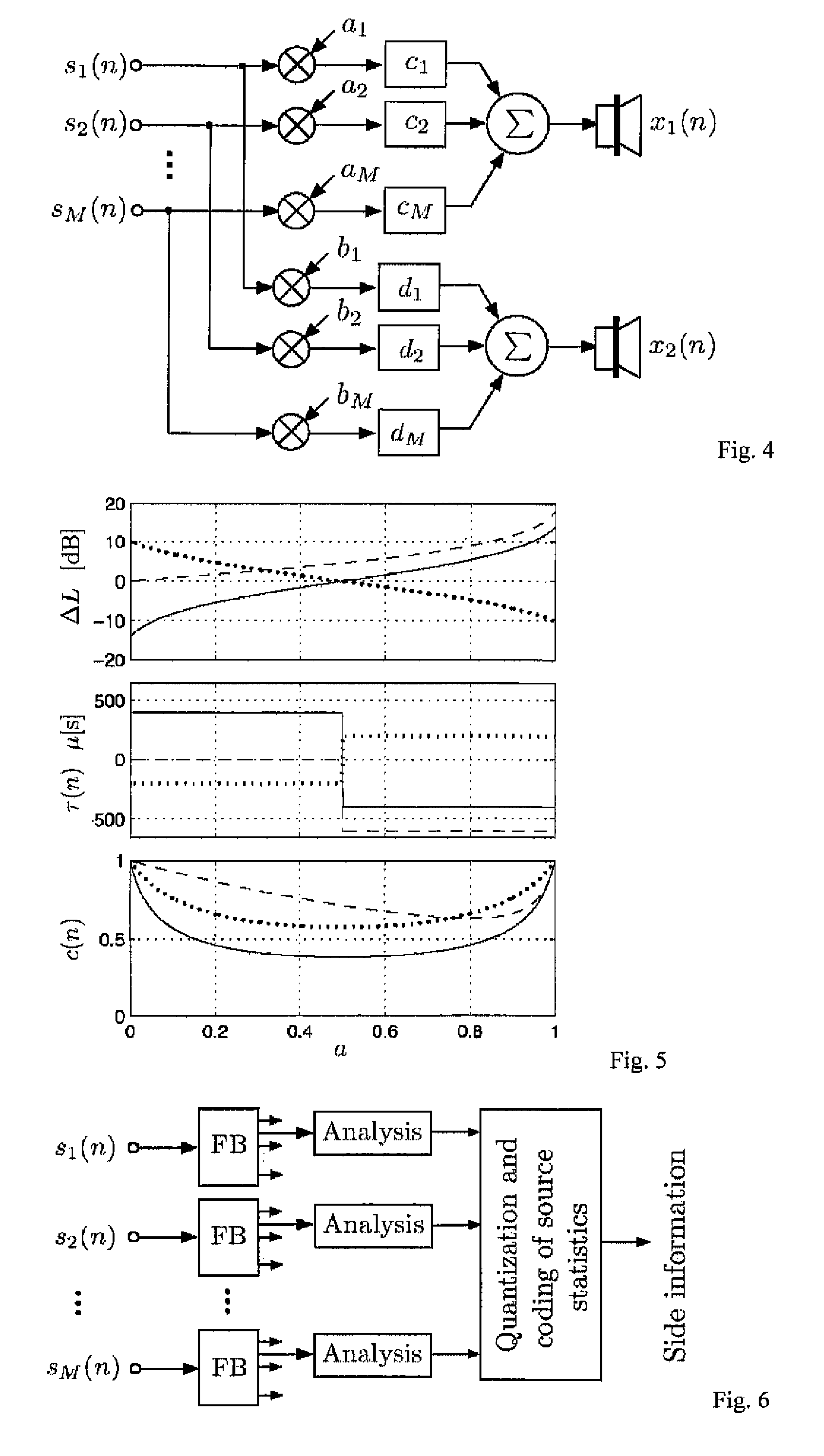
Method to Generate Multi-Channel Audio Signal from Stereo Signals
ActiveUS20080267413A1Good sound experienceSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsWave field synthesisDecomposition
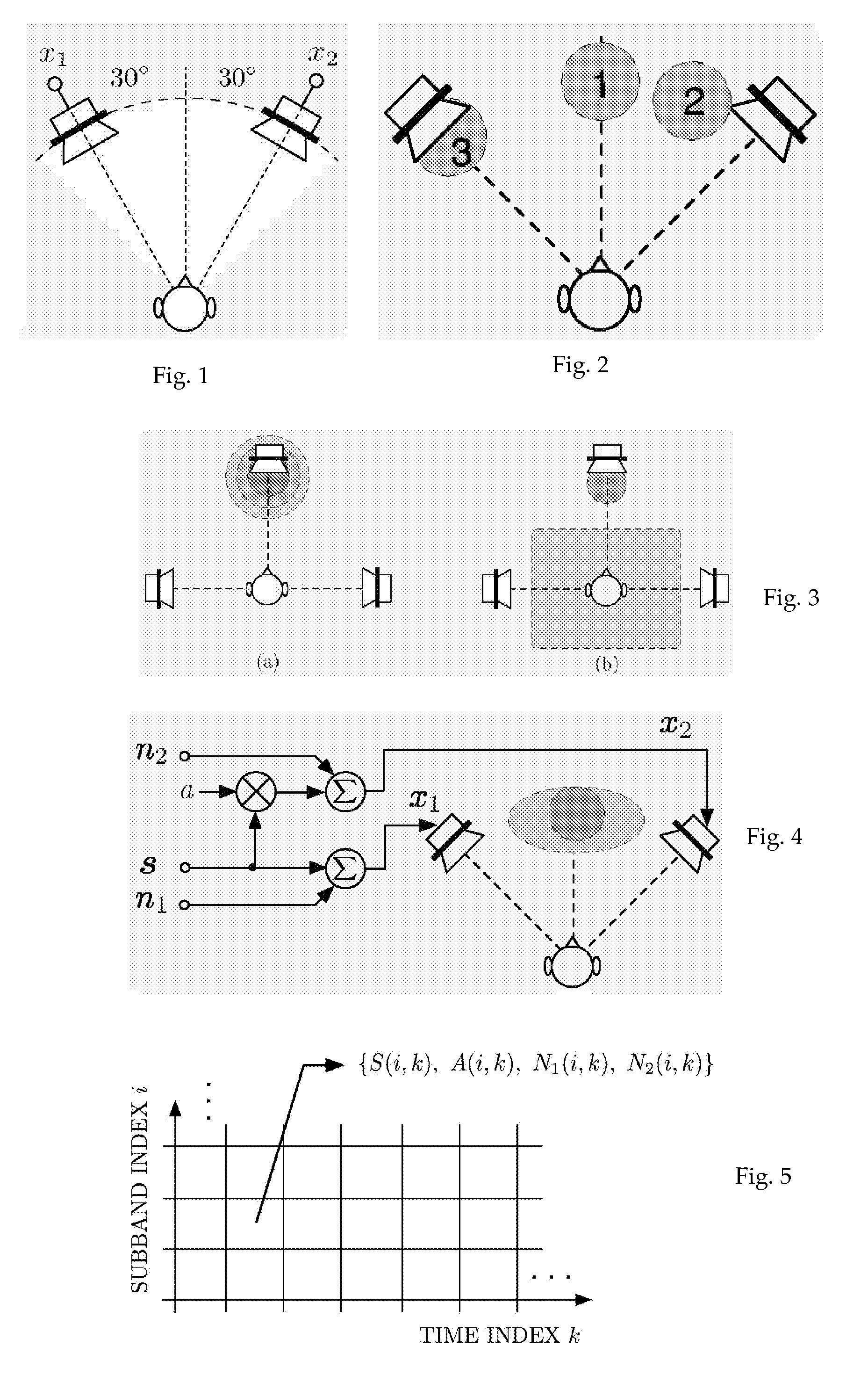
A perceptually motivated spatial decomposition for two-channel stereo audio signals, capturing the information about the virtual sound stage, is proposed. The spatial decomposition allows to re-synthesize audio signals for playback over other sound systems than two-channel stereo. With the use of more front loudspeakers, the width of the virtual sound stage can be increased beyond + / −30° and the sweet spot region is extended. Optionally, lateral independent sound components can be played back separately over loudspeakers on the two sides of a listener to increase listener envelopment. It is also explained how the spatial decomposition can be used with surround sound and wavefield synthesis based audio system. According to the main embodiment of the invention applying to multiple audio signals, it is proposed to generate multiple output audio signals (y1 . . . yM) from multiple input audio signals (x1, . . . , xL), in which the number of output is equal or higher than the number of input signals, this method comprising the steps of: —by means of linear combinations of the input subbands X1(i), . . . , XL(i), computing one or more independent sound subbands representing signal components which are independent between the input subbands, —by means of linear combinations of the input subbands X1(i), . . . , XL(i), computing one or more localized direct sound subbands representing signal components which are contained in more than one of the input subbands and direction factors representing the ratios with which these signal components are contained in two or more input subbands, —generating the output subband signals, Y1(i) . . . YM(i), where each output subband signal is a linear combination of the independent sound subbands and the localized direct sound subbands—converting the output subband signals, Y1(i) . . . YM(i), to time domain audio signals, y1 . . . yM.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Device for level correction in a wave field synthesis system
ActiveUS20060109992A1Significant positive effectIncrease the number ofMechanical record carriersRecord information storageWave field synthesisWave field
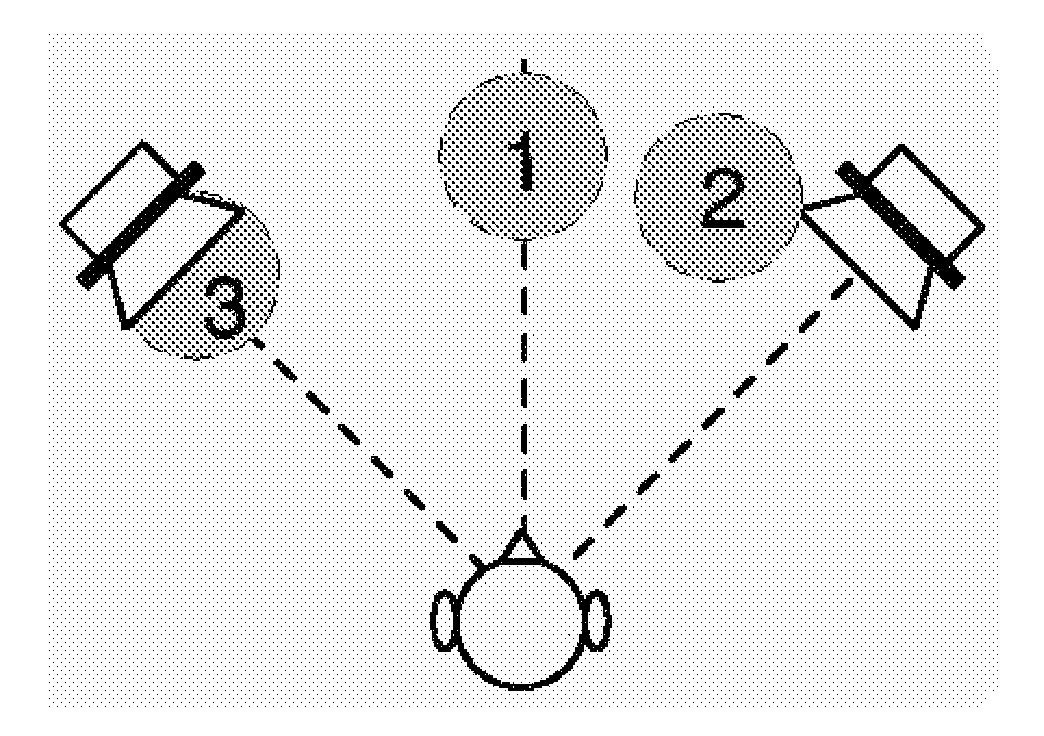
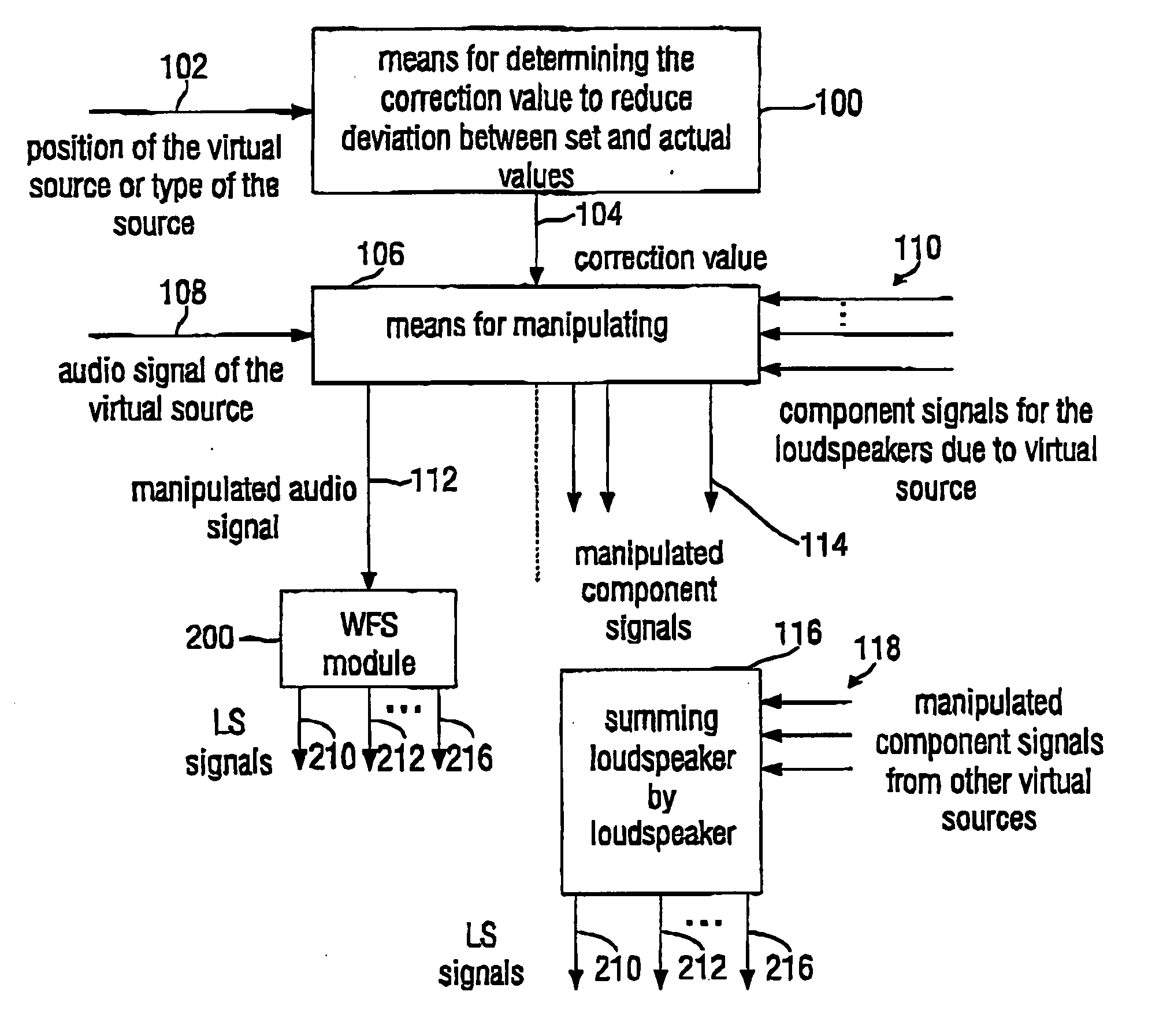
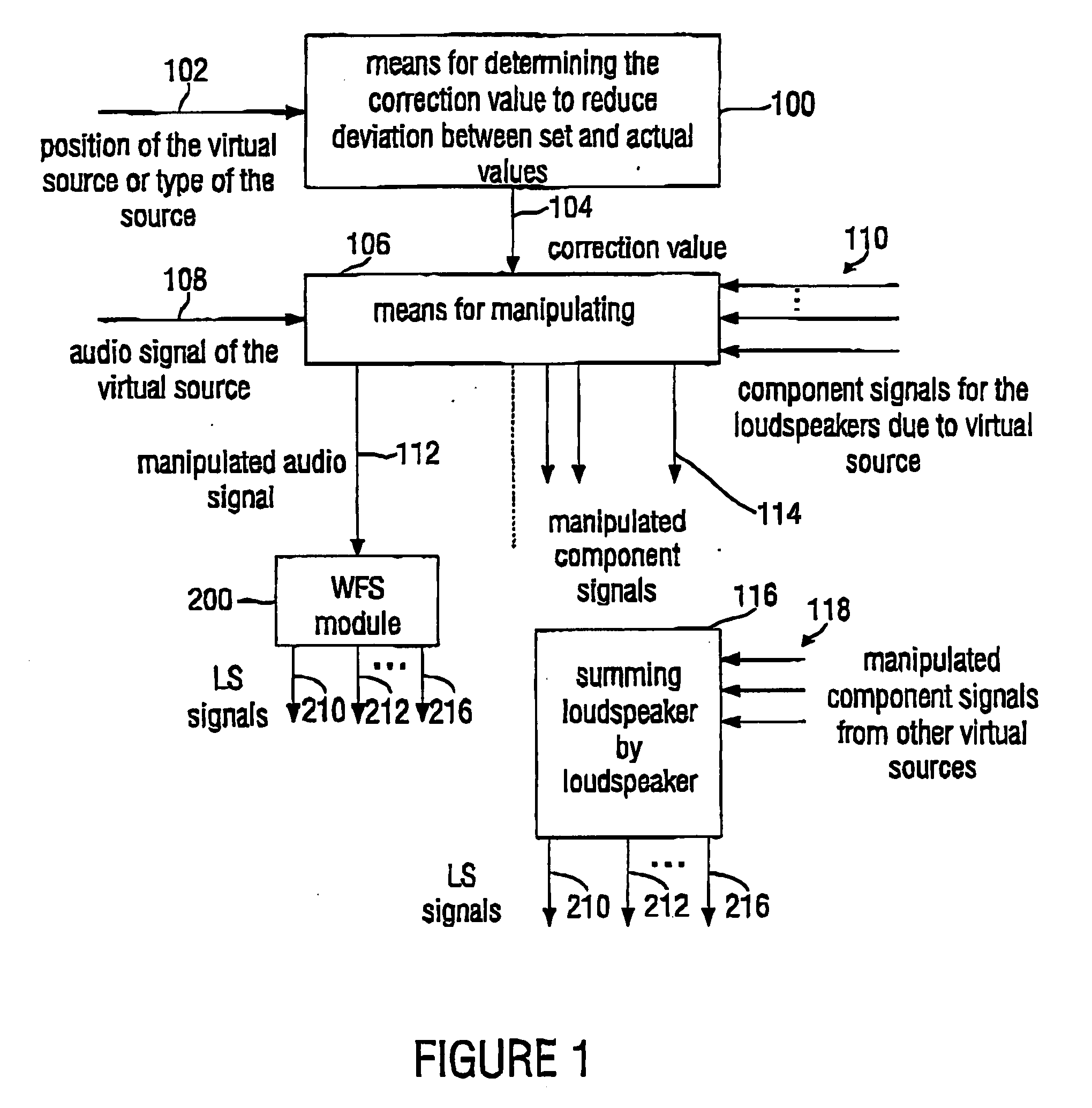
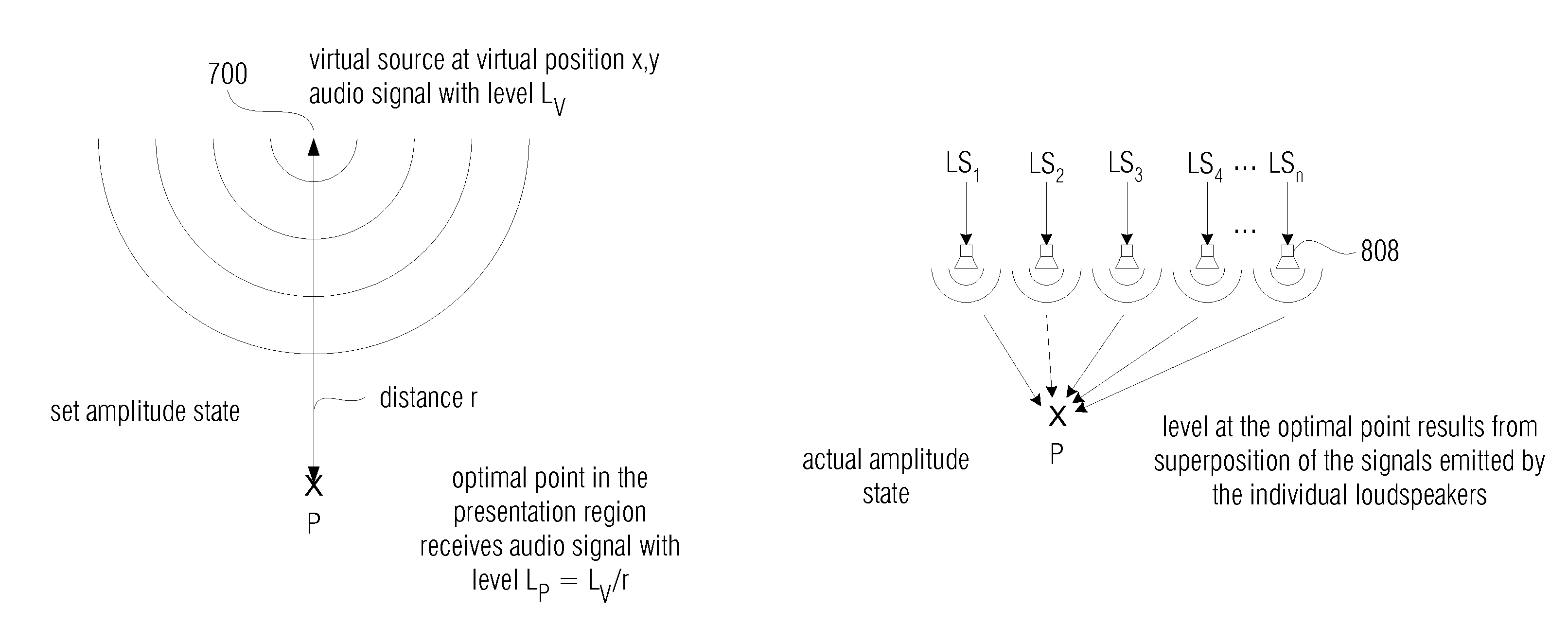
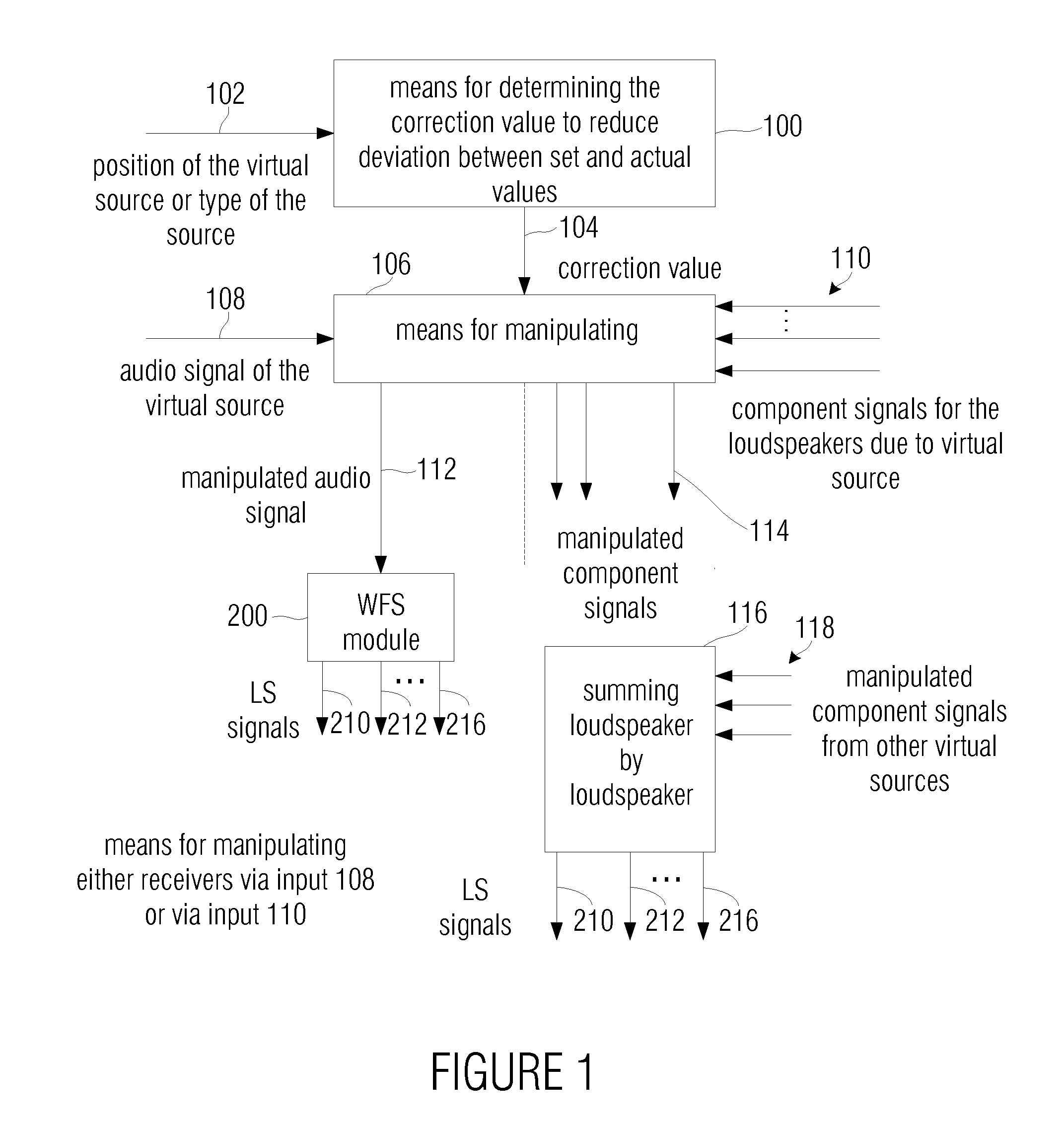
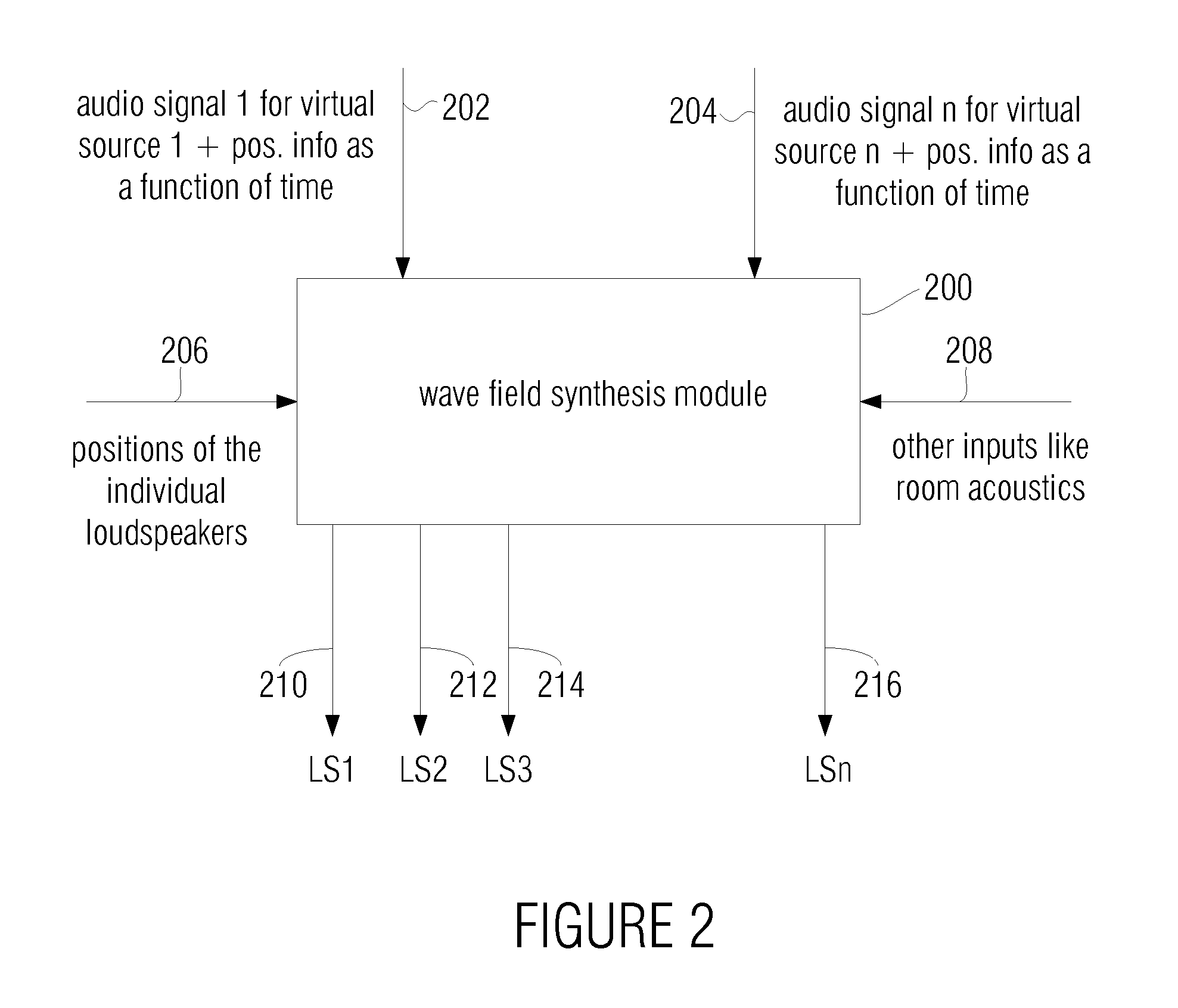
For a level correction in a wave field synthesis system having a wave field synthesis module and an array of loudspeakers for providing sound to a presentation region, a correction value which is based on a set amplitude state in a presentation region is determined, the set amplitude state depending on a position of the virtual source or a type of the virtual source, and the actual amplitude state in the presentation region depending on the component signals for the loudspeakers due to the virtual source. The correction value determined is fed to a manipulator manipulating the audio signal associated to the virtual source before feeding to the wave field synthesis module, or the component signals for the individual loudspeakers due to the virtual source are manipulated to reduce a deviation between a set amplitude state and an actual amplitude state at one point or several points in the presentation region. Thus, level artifacts due to the finite number of loudspeakers in a wave field synthesis system are at least reduced such that a more pleasant sound experience for a listener is obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
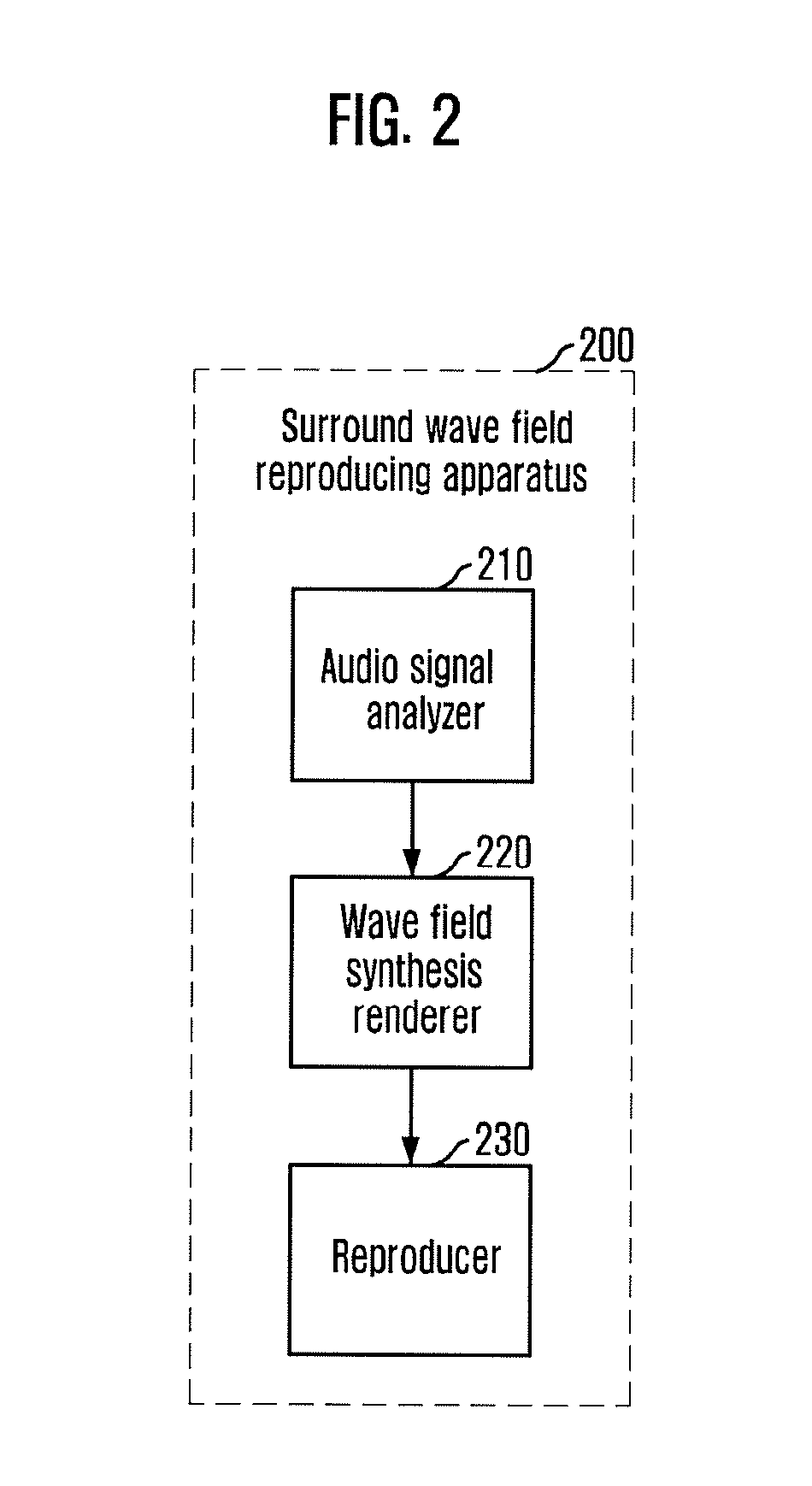
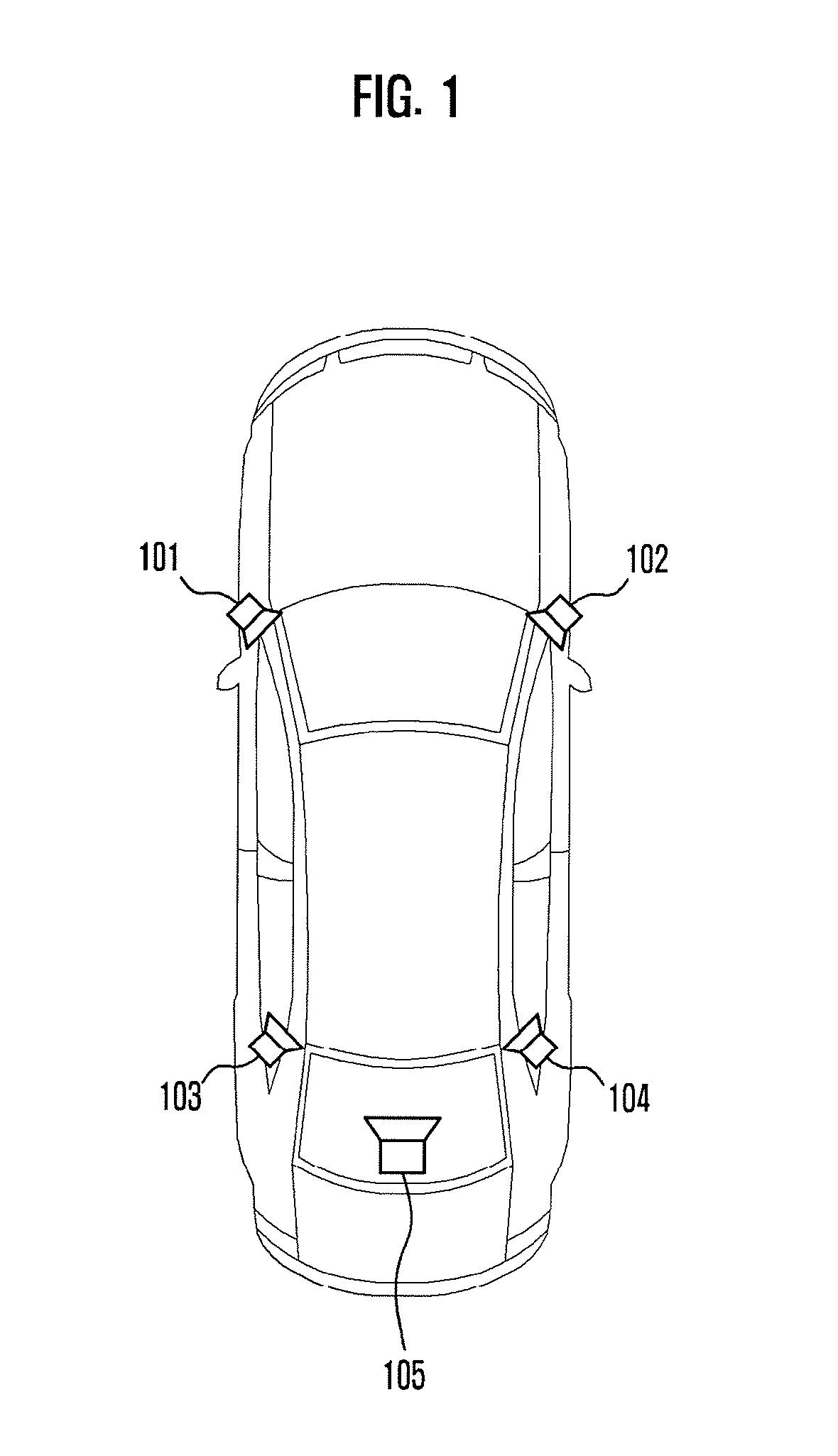
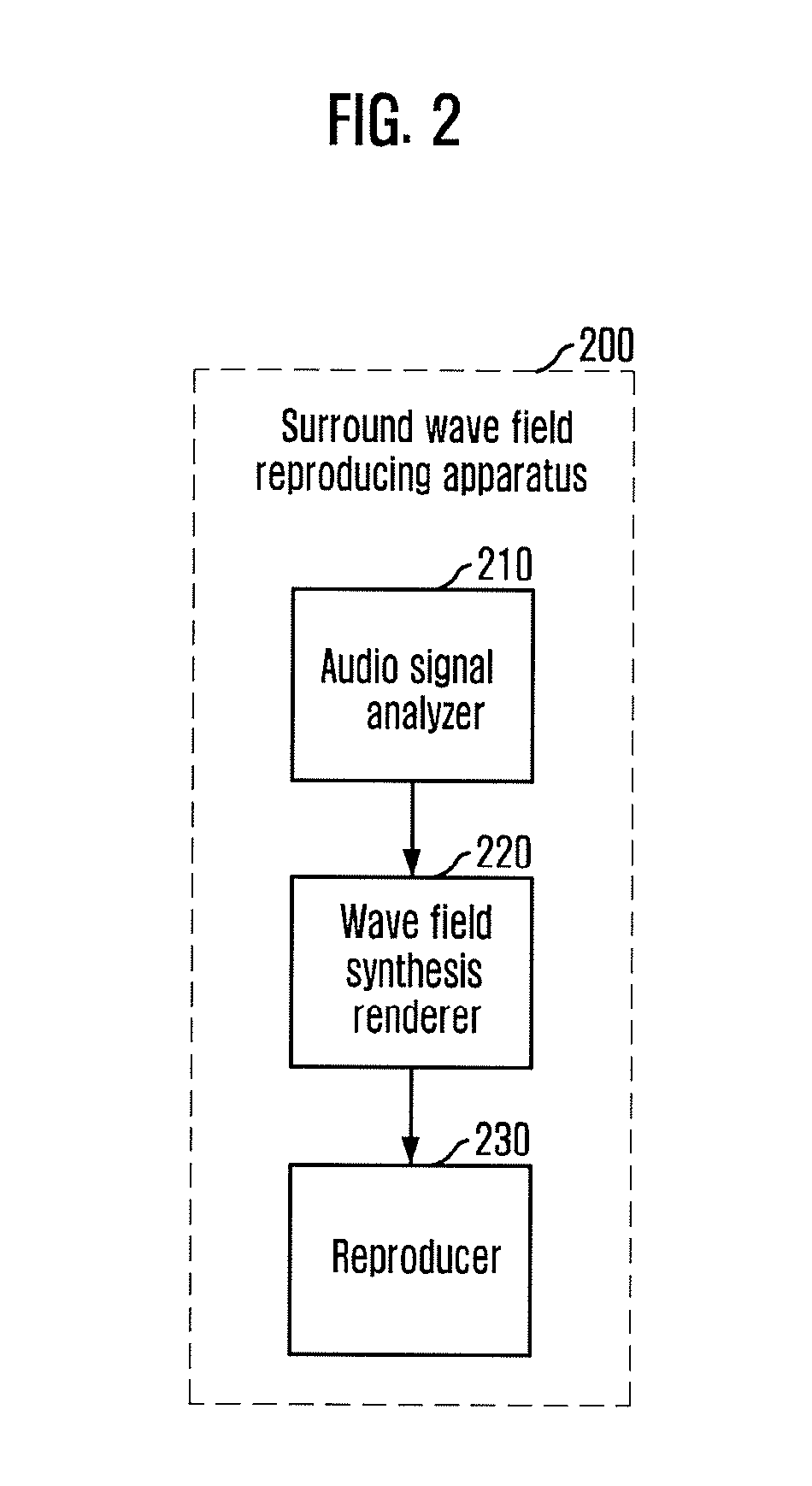
Apparatus and method for reproducing surround wave field using wave field synthesis
Provided are an apparatus and a method for reproducing a surround wave field using wave field synthesis. The apparatus includes an audio signal analyzer for analyzing a received multi-channel audio signal to check the number of audio signal channels, and extracting a sound source signal for each checked channel from the multi-channel audio signal; a wave field synthesis renderer for localizing the extracted sound source signal for each channel at a virtual sound image outside a narrow space using wave field synthesis so that the extracted sound source signal is suitable for the number of the checked audio signal channels; and an audio reproducer for reproducing the localized virtual sound source signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
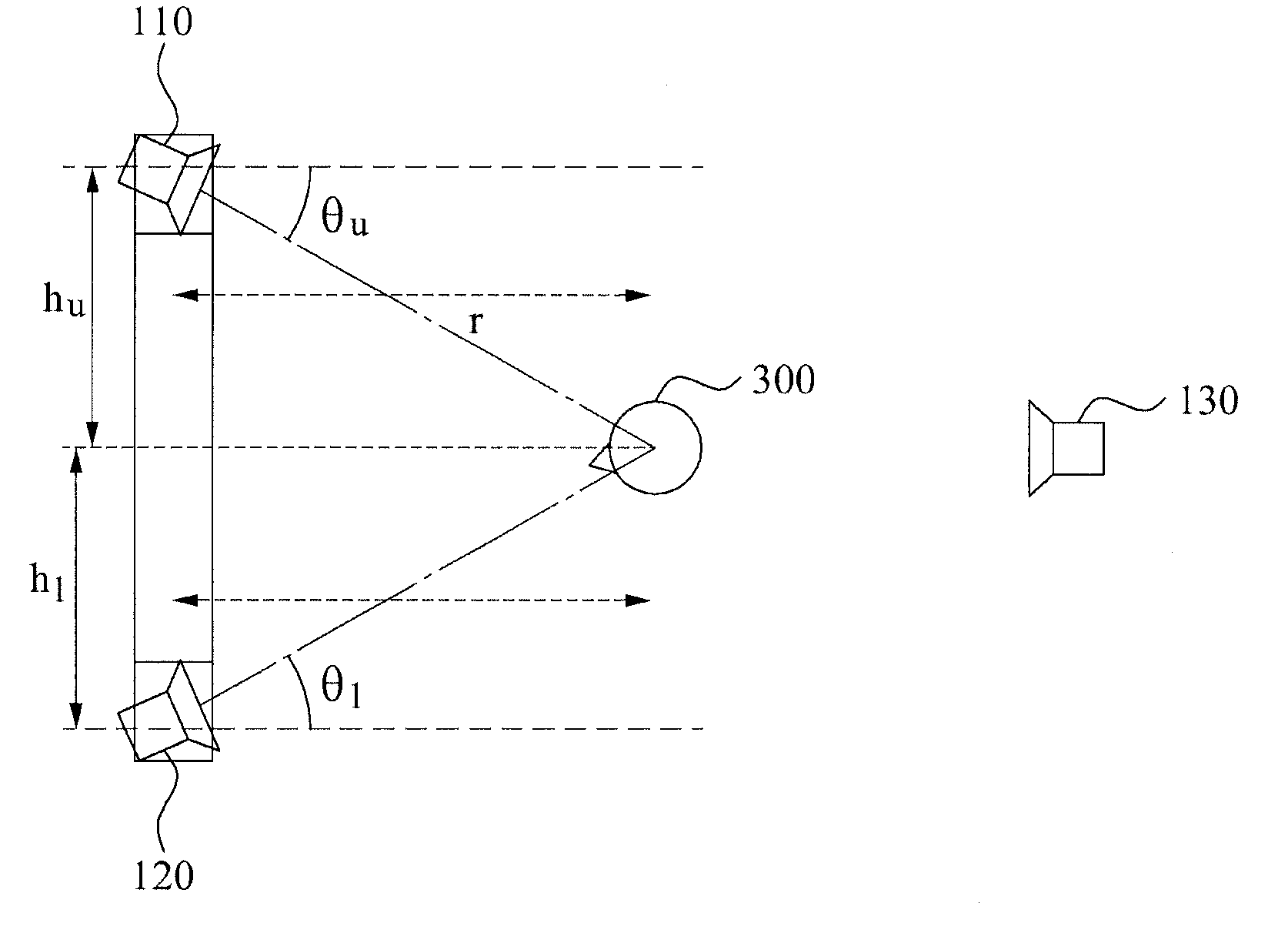
Apparatus for reproducting wave field using loudspeaker array and the method thereof
ActiveUS20120070021A1Easy to installPromote reproductionDigital recording/reproducingStereophonic systemsSound sourcesSound image
Provided is an apparatus and method for reproducing a wave field using a loudspeaker array. A loudspeaker array may be configured in front of and behind a listener, and a wave field synthesis rendering and a three-dimensional sound image localization rendering may be performed based on a position of a sound source.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wave field synthesis apparatus and method of driving an array of loudspeakers
ActiveUS7684578B2Reduce artifactsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsWave field synthesisVirtual position
In a wave field synthesis apparatus for driving an array of loudspeakers with drive signals, the loudspeakers being arranged at different defined positions, a drive signal for a loudspeaker being based on an audio signal associated with a virtual source having a virtual position with reference to the loudspeaker array and on the defined position of the loudspeaker, at first relevant loudspeakers of the loudspeaker array are determined on the basis of the position of the virtual source, a predefined listener position, and the defined positions of the loudspeakers, so that artifacts due to loudspeaker signals moving opposite to a direction from the virtual source to the predefined listener position are reduced. Downstream to means for calculating the drive signal components for the relevant loudspeakers and for a virtual source, there is means for providing the drive signal components for the relevant loudspeakers for the virtual source to the relevant loudspeakers, wherein no drive signals for the virtual source are provided to loudspeakers of the loudspeaker array not belonging to the relevant loudspeakers. With this, artifacts in an area of the audience room due to a generation wave field are suppressed, so that in this area only the useful wave field is heard in artifact-free manner.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
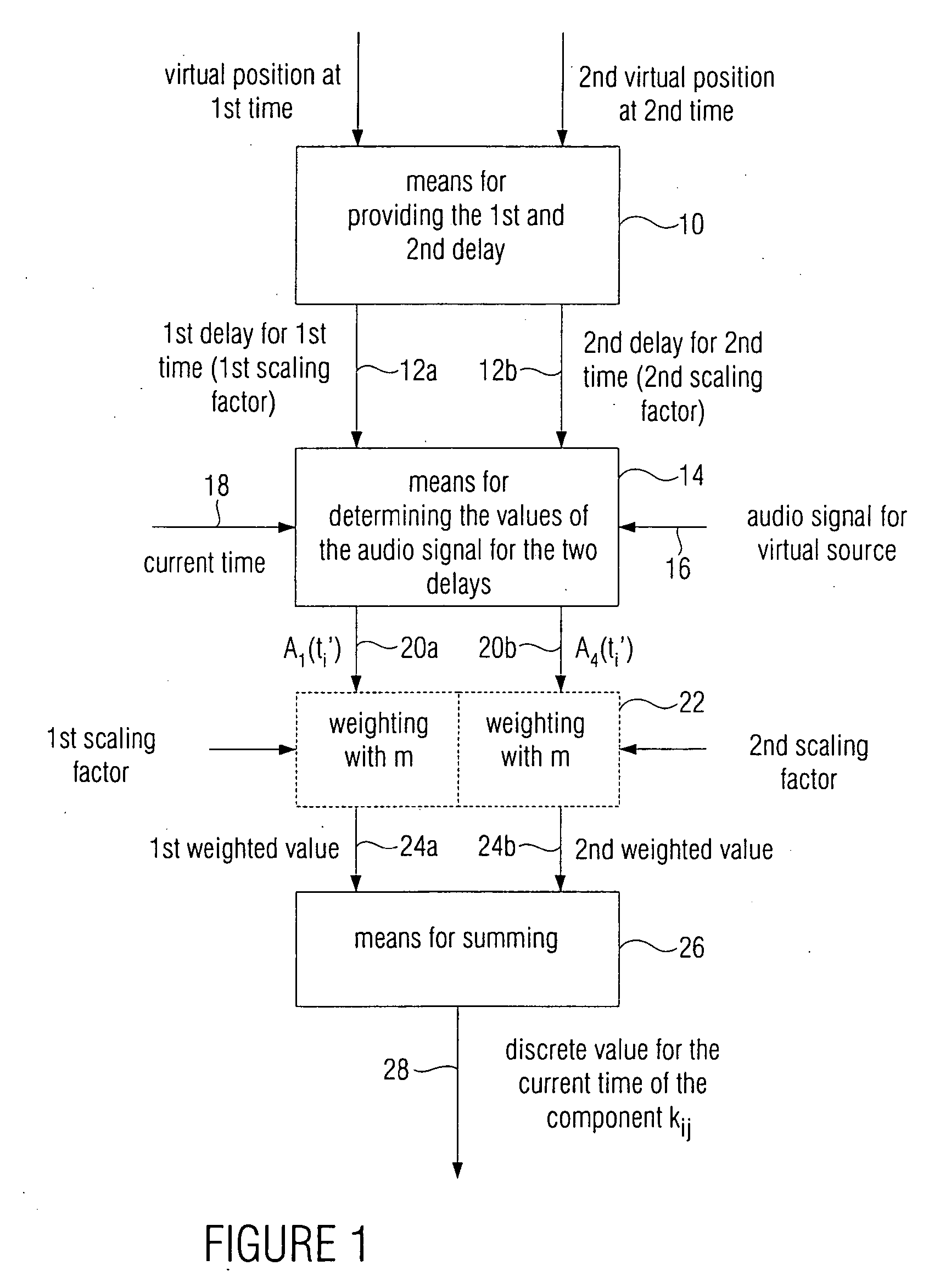
Apparatus and method for calculating a discrete value of a component in a loudspeaker signal
ActiveUS20060092854A1Reduce artifactsAvoid spaceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWave field synthesisAudio frequency
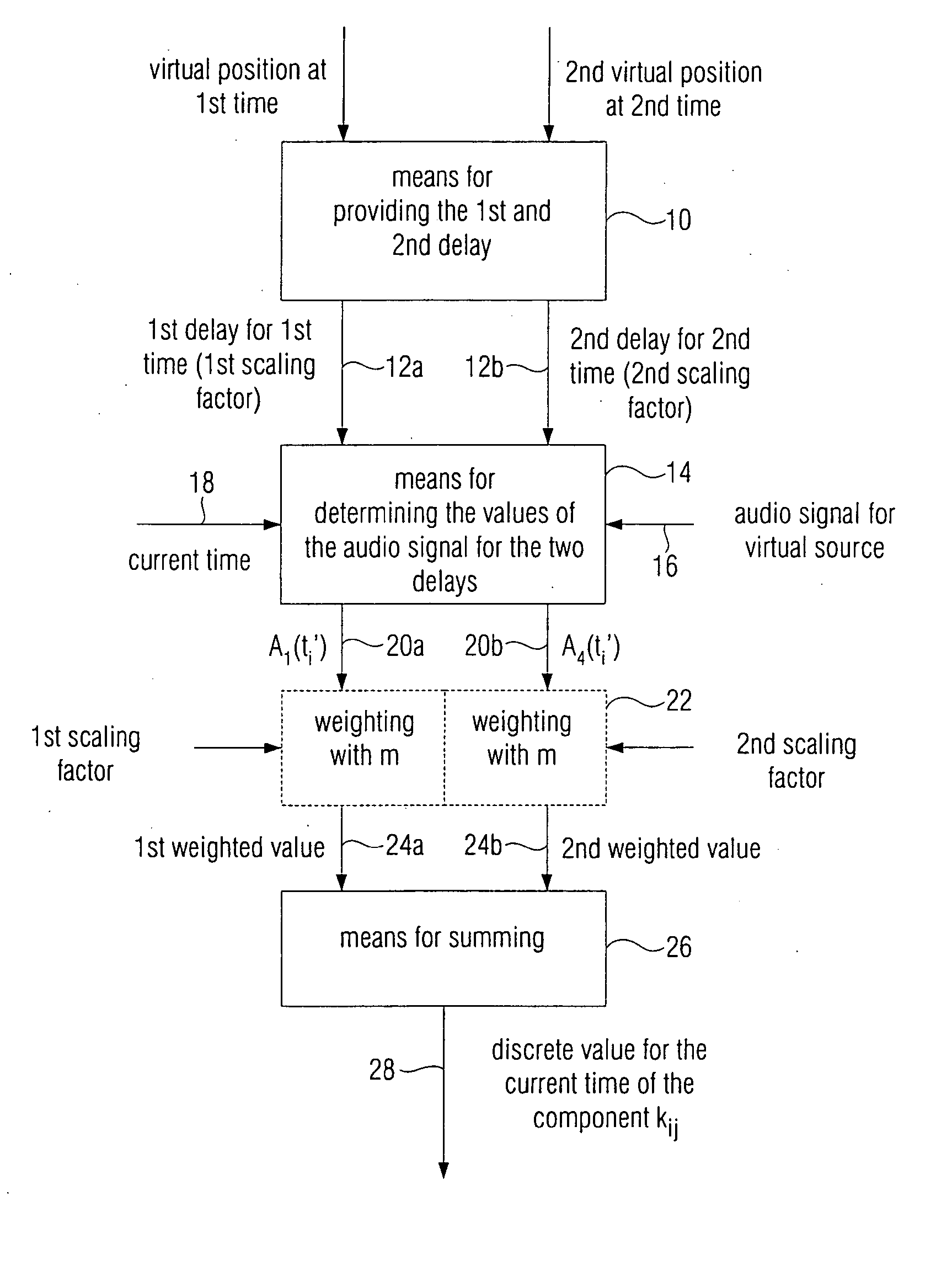
For reducing Doppler artifacts in the wave-field synthesis due to delay changes from one time to a second time, first, the delay for the first time and the delay for the second time are determined. Then, a value of an audio signal delayed by the first delay for the current time and the value for the audio signal delayed by the second delay for the current time are determined. Then, the first value is weighted by a first weighting factor and a second value is averaged with a second weighting factor, whereupon the two weighted values are added up to obtain a discrete value for the current time of the component in a loudspeaker signal for a loudspeaker based on a virtual source. Thus, by knowing a delay present at a later time, panning is obtained from a delay to a subsequent delay, which reduces undesired Doppler artifacts.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
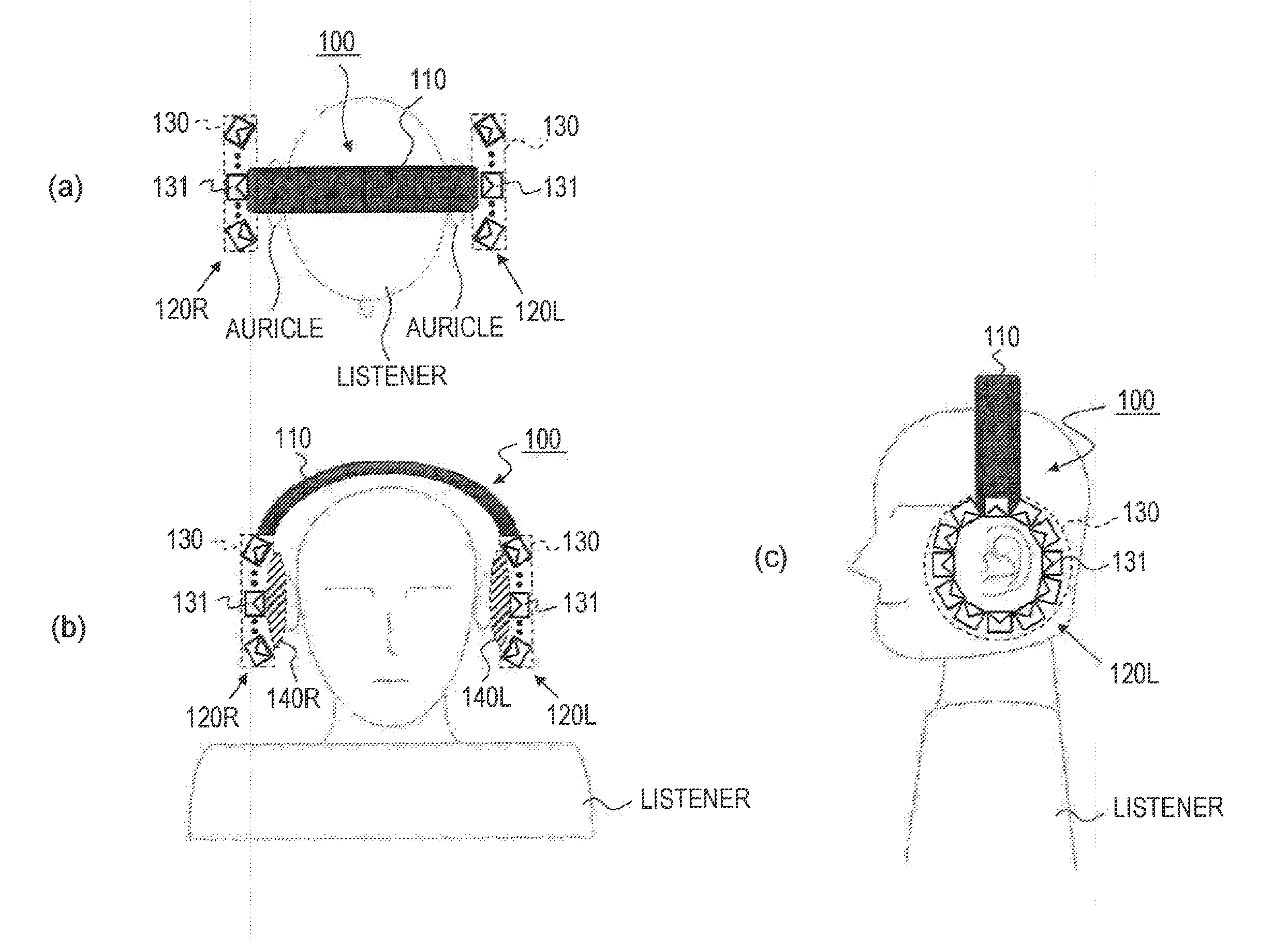
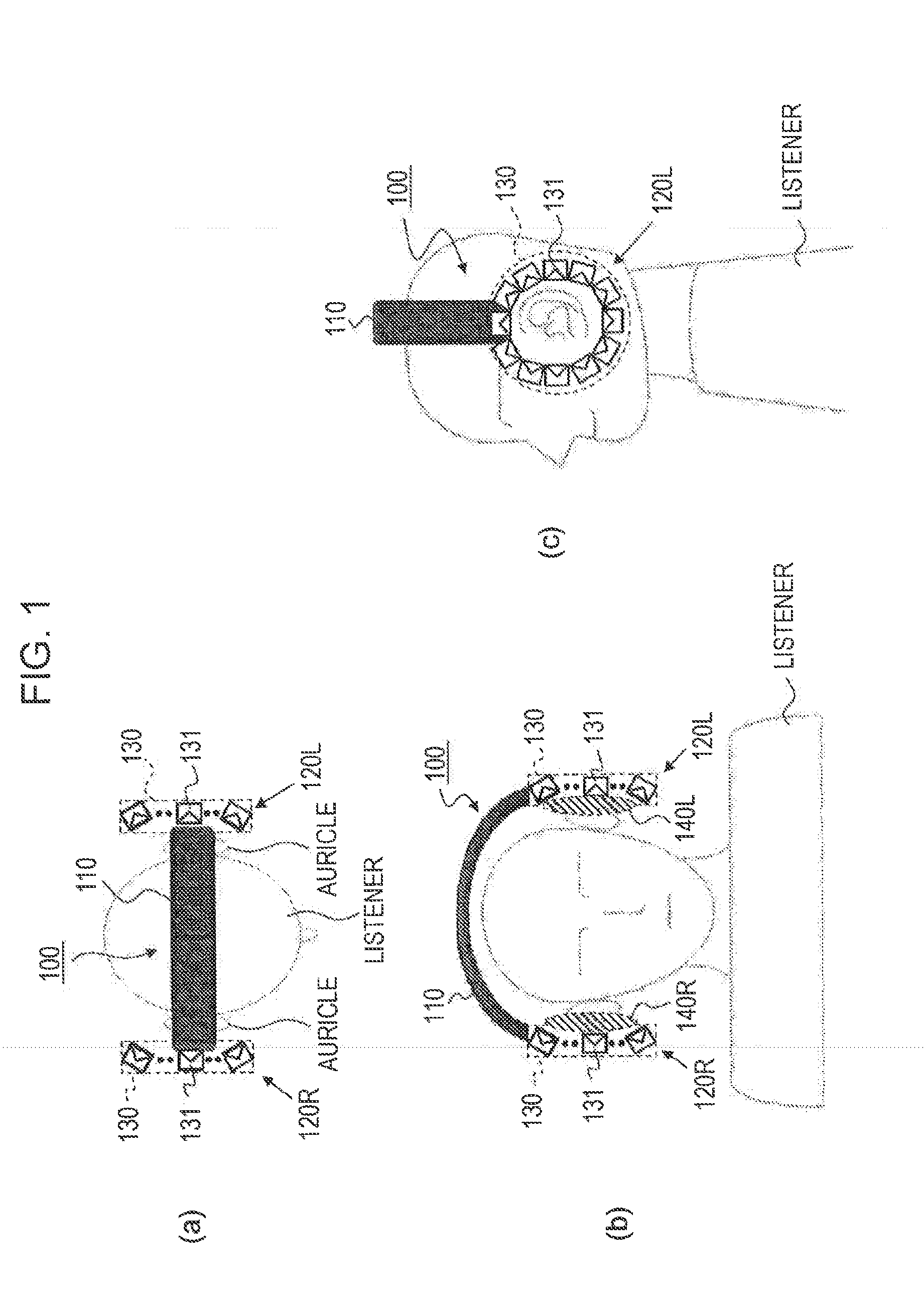
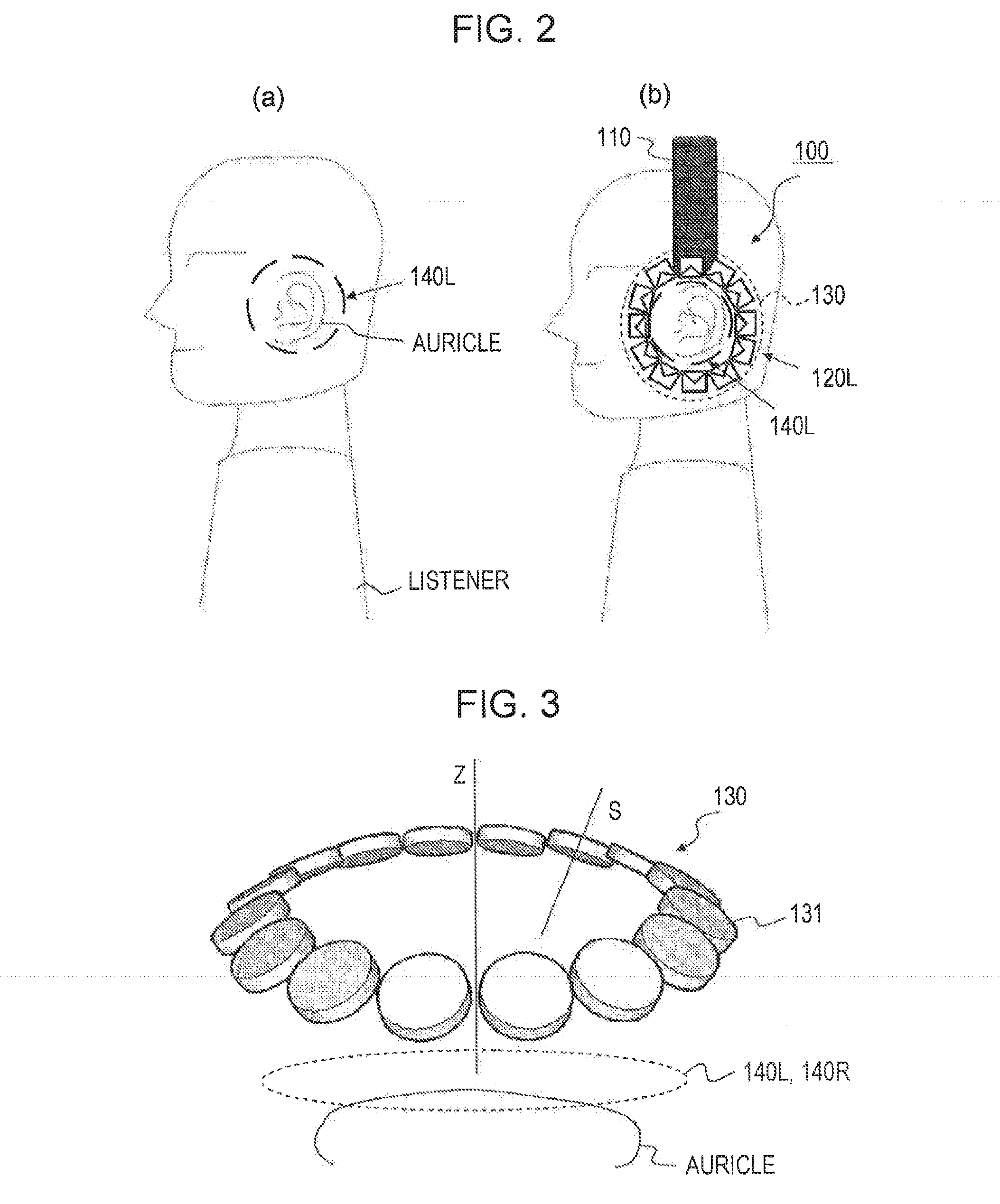
Headphone device
ActiveUS20130216074A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationSupra/circum aural earpiecesDiffraction effectEar Auricle
[Object] To provide a headphone device in which the influence of individual differences in virtual sound field reproduction is less likely to occur and which may listen external sounds naturally,[Solution] A left-side headphone body and a right-side headphone body include speaker arrays which are formed of a plurality of speaker units which are arranged to surround auricles, respectively. The speaker array of the headphone body reproduces a sound field inside a closed curved surface in the vicinity of the auricle using wave field synthesis, and since reverberation or a diffraction effect occurs in the ear of each individual, the influence caused by individual differences is less likely to occur. In addition, the speaker array has the plurality of the speaker units arranged to surround the auricle and is not of a shape that blocks the ear of the listener, and then the external sound can be heard naturally.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method to generate multi-channel audio signals from stereo signals
A perceptually motivated spatial decomposition for two-channel stereo audio signals, capturing the information about the virtual sound stage, is proposed. The spatial decomposition allows to re-synthesize audio signals for playback over other sound systems than two-channel stereo. With the use of more front loudspeakers, the width of the virtual sound stage can be increased beyond + / - 30 DEG and the sweet spot region is extended. Optionally, lateral independent sound components can be played back separately over loudspeakers on the two sides of a listener to increase listener envelopment. It is also explained how the spatial decomposition can be used with surround sound and wavefield synthesis based audio system. According to the main embodiment of the invention applying to multiple audio signals, it is proposed to generate multiple output audio signals (y1,..., yM) from multiple input audio signals (x1, ..., xL), in which the number of output is equal or higher than the number of input signals , this method comprising the steps of: by means of linear combinations of the input subbands (X1(i), ..., XL(i)), computing one or more independent sound subbands representing signal components which are independent between the input subbands, by means of linear combinations of the input subbands (X1(i), ..., XL(i)), computing one or more localized direct sound subbands representing signal components which are contained in more than one of the input subbands and direction factors representing the ratios with which these signal components are contained in two or more input subbands, generating the output subband signals (Y1(i)...YM(i)), where each output subband signal is a linear combination of the independent sound subbands and the localized direct sound subbands, converting the output subband signals (Y1(i)...YM(i)), to time domain audio signals (y1,..., yM).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
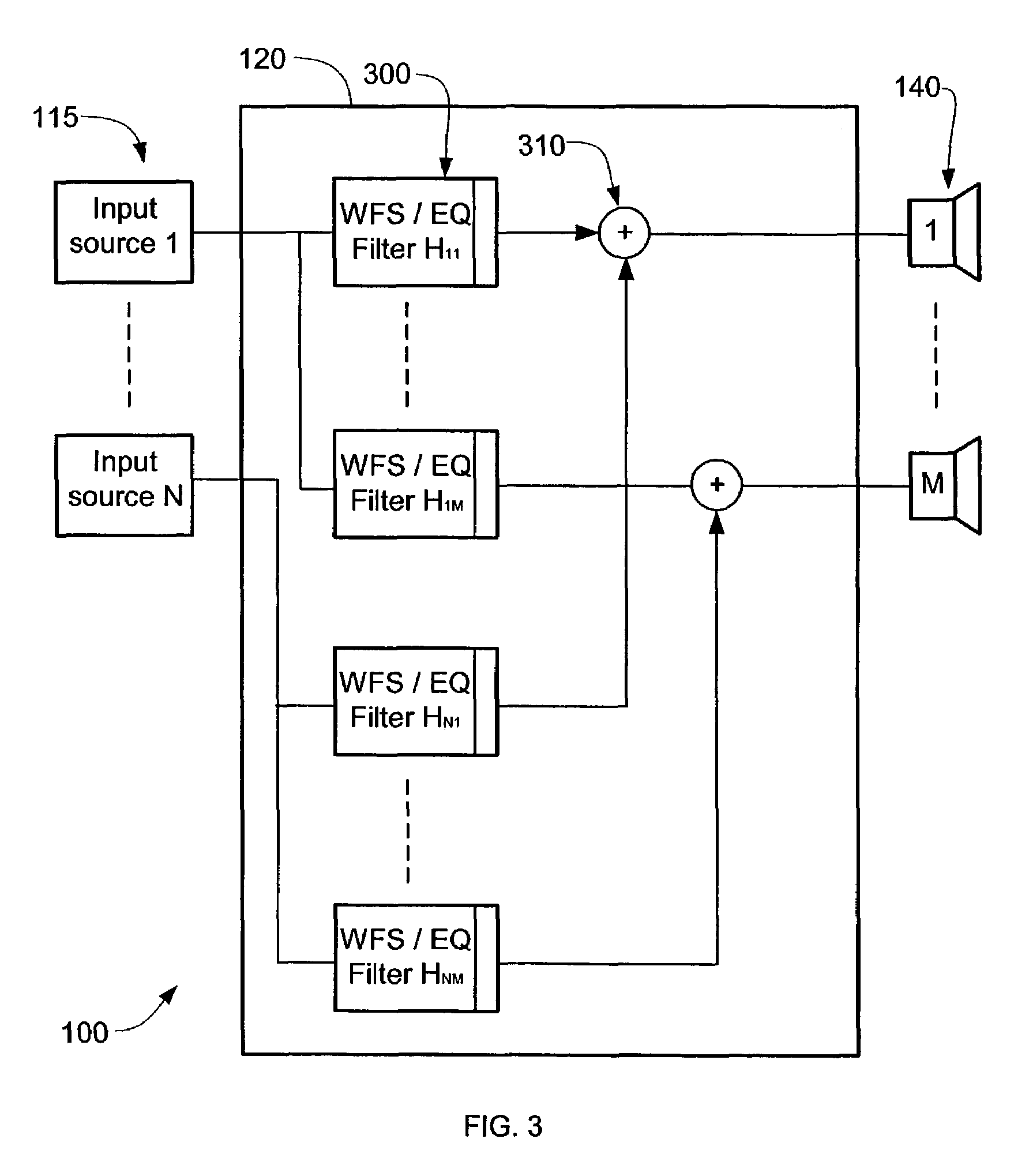
Loudspeaker system for virtual sound synthesis
ActiveUS20080101620A1Microphones signal combinationLoudspeaker signals distributionFinite impulse responseSound sources
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method of reproducing surround wave field using wave field synthesis based on speaker array
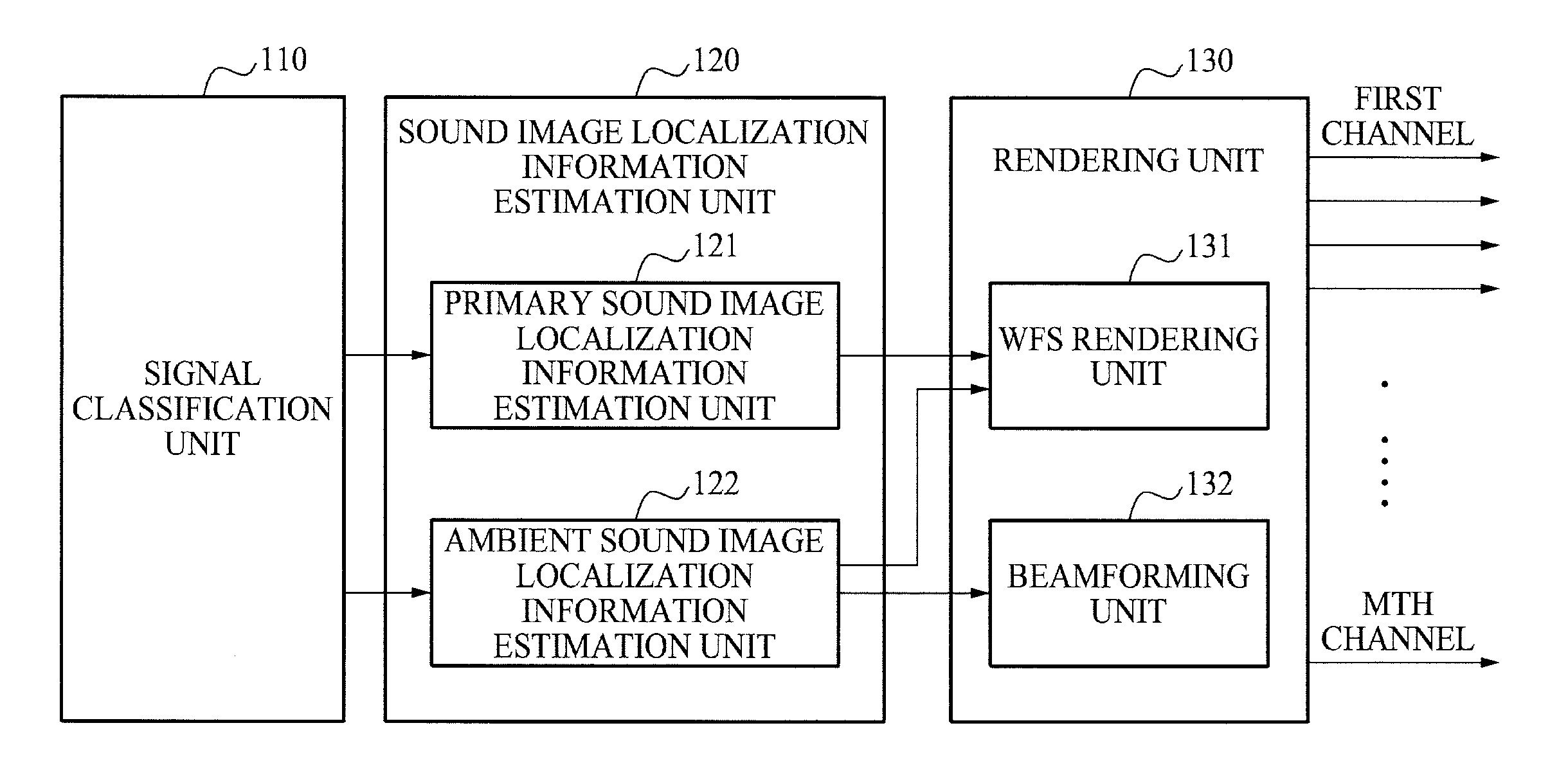
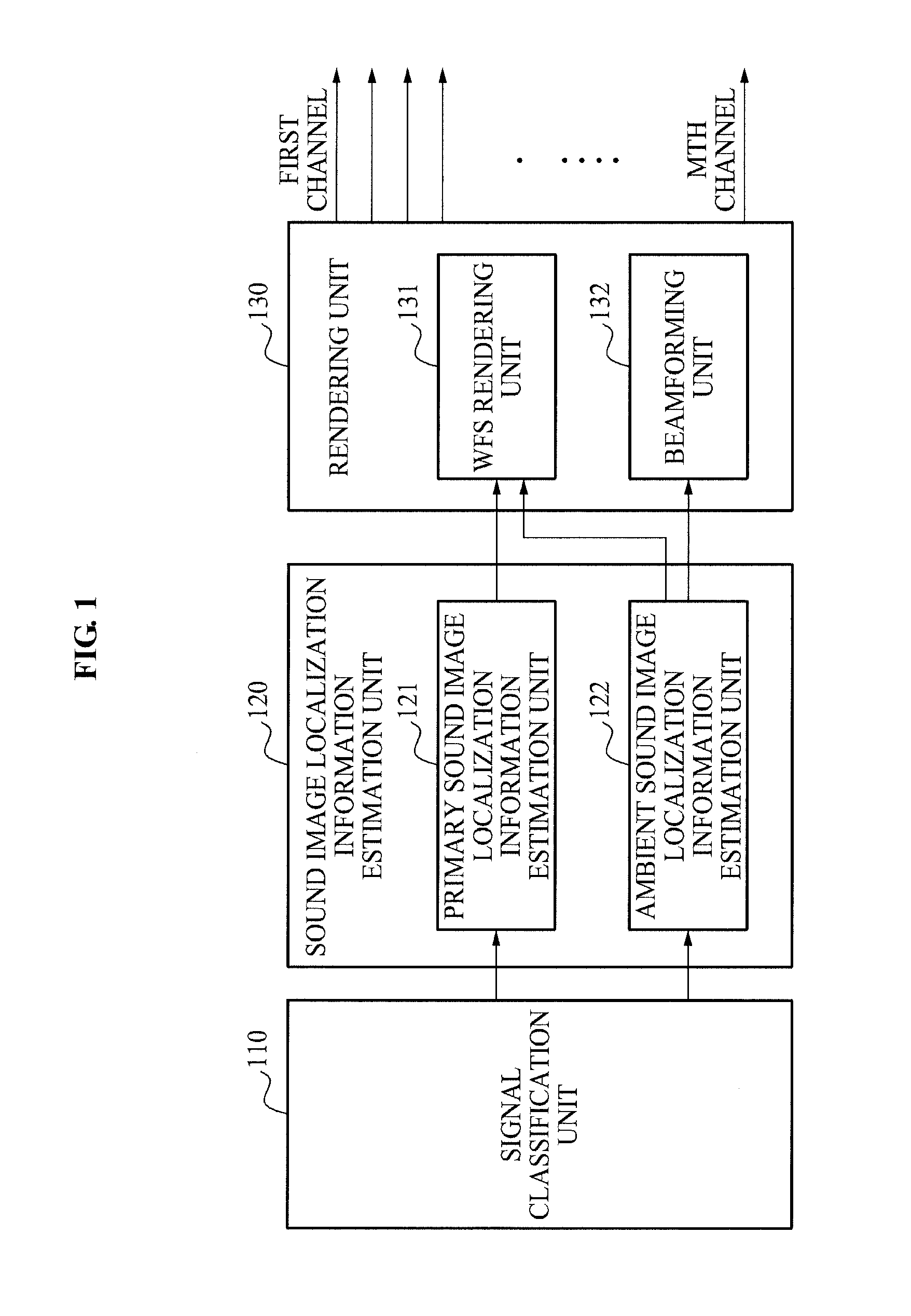
ActiveUS8958582B2Minimize distortionMinimize informationLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsStereophonic systemsSound imageSignal classification
Disclosed are an apparatus and method of surround wave field synthesizing a multi-channel signal excluding sound image localization information. A wave field synthesis and reproduction apparatus may include a signal classification unit to classify an inputted multi-channel signal into a primary signal and an ambient signal, a sound image localization information estimation unit to estimate sound image localization information of the primary signal and sound image localization information of the ambient signal, and a rendering unit to render the primary signal and the ambient signal based on the sound image localization information of the primary signal, the sound image localization information of the ambient signal, and listener environment information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Audio reproduction system and method for reproducing an audio signal
ActiveUS7706544B2High market acceptanceLow costLoudspeaker signals distributionFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsWave field synthesisEngineering
An audio reproduction system is divided into a central wave-field synthesis module and a plurality of loudspeaker modules disposed in a distributed way, wherein synthesis signals for the individual loudspeakers as well as corresponding channel information associated to the synthesis signals are calculated in the central wave-field synthesis module. The synthesis signals for a loudspeaker as well as associated channel information will then be transmitted to respective loudspeaker modules via a transmission path, wherein every loudspeaker module obtains the synthesis signals and associated channel information intended for the loudspeaker associated to the loudspeaker module. A distributed audio rendering and digital / analog converting takes place in the loudspeaker module to generate the actually analog loudspeaker signals in a distributed way in spatial proximity to every loudspeaker. The division into a central wave-field synthesis module and the plurality of distributed loudspeaker modules allows that audio reproduction systems that are scalable with regard to the price can be generated in order to offer systems of different size scalable in price particularly for cinema reproduction rooms varying strongly in size.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Loudspeaker system for virtual sound synthesis
ActiveUS7336793B2Accurate equalizationEar treatmentMicrophones signal combinationFinite impulse responseSound sources
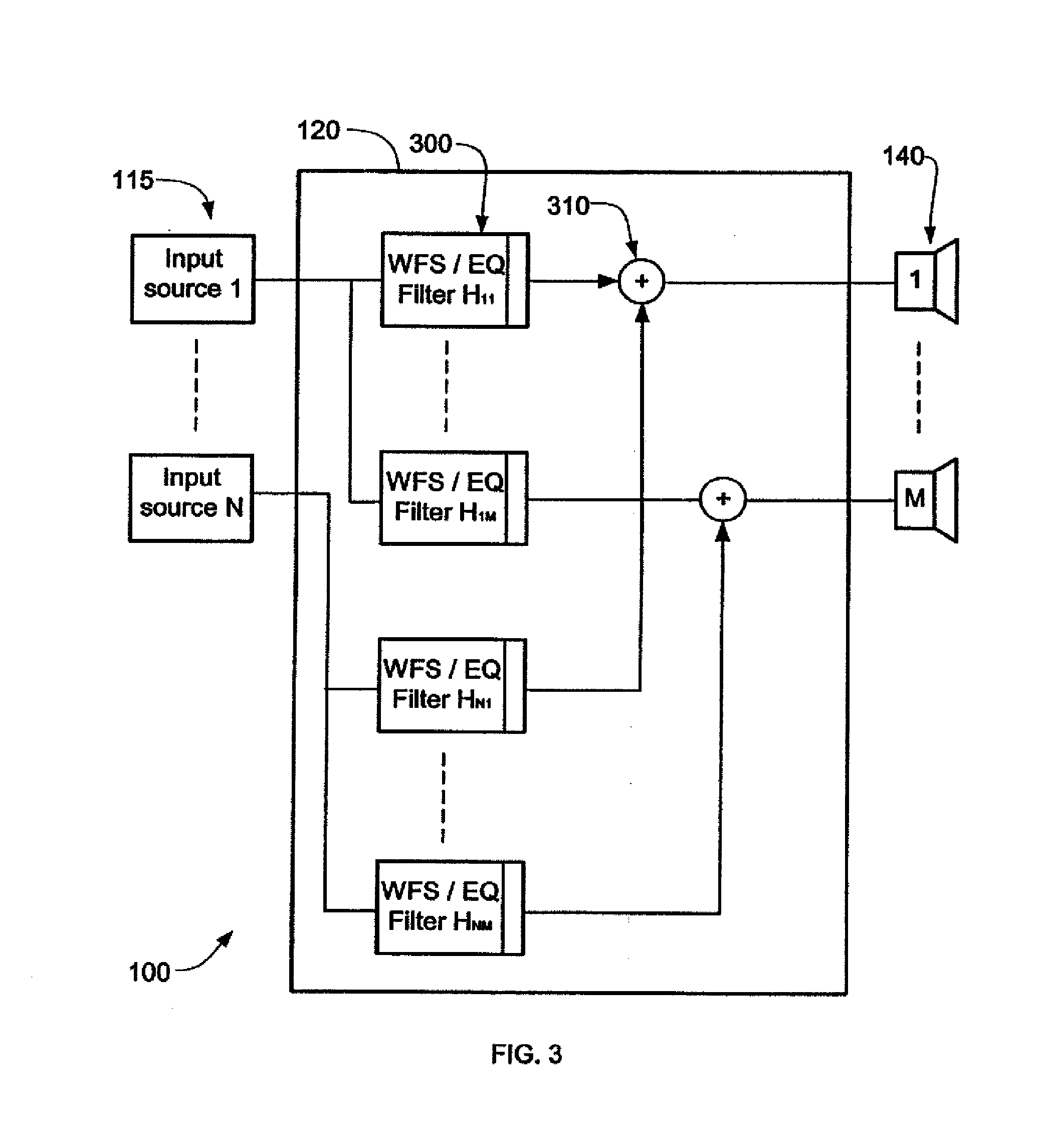
A sound system obtains a desired sound field from an array of sound sources arranged on a panel. The desired sound field allows a listener to perceive the sound as if the sound were coming from a live source and from a specified location. Setup of the sound system includes arranging a microphone array adjacent the array of sound sources to obtain a generated sound field. Arbitrary finite impulse response filters are then composed for each sound source within the array of sound sources. Iteration is applied to optimize filter coefficients such that the generated sound field resembles the desired sound field so that multi-channel equalization and wave field synthesis occur. After the filters are setup, the microphones may be removed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method for simulating a wave field synthesis system
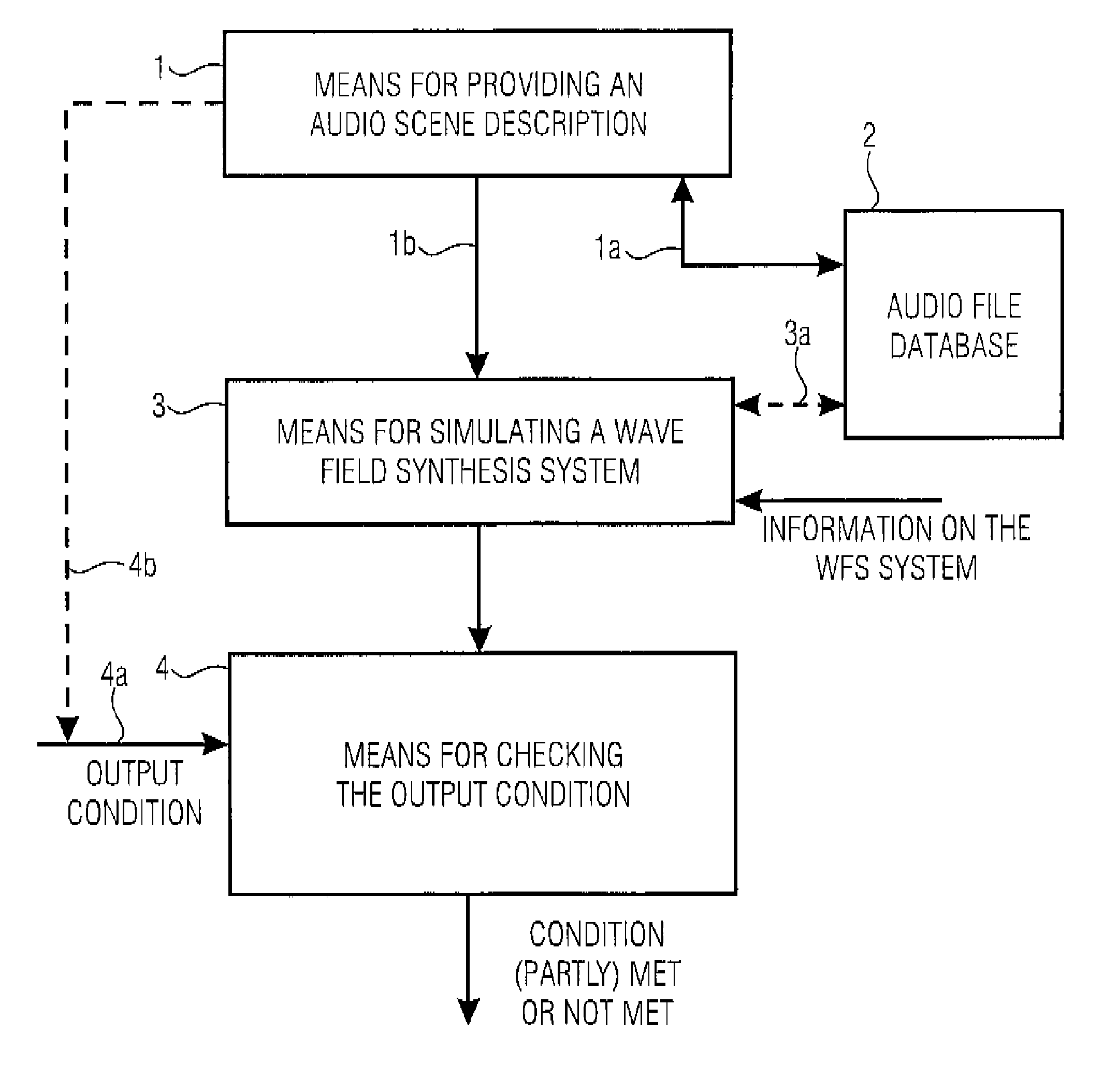
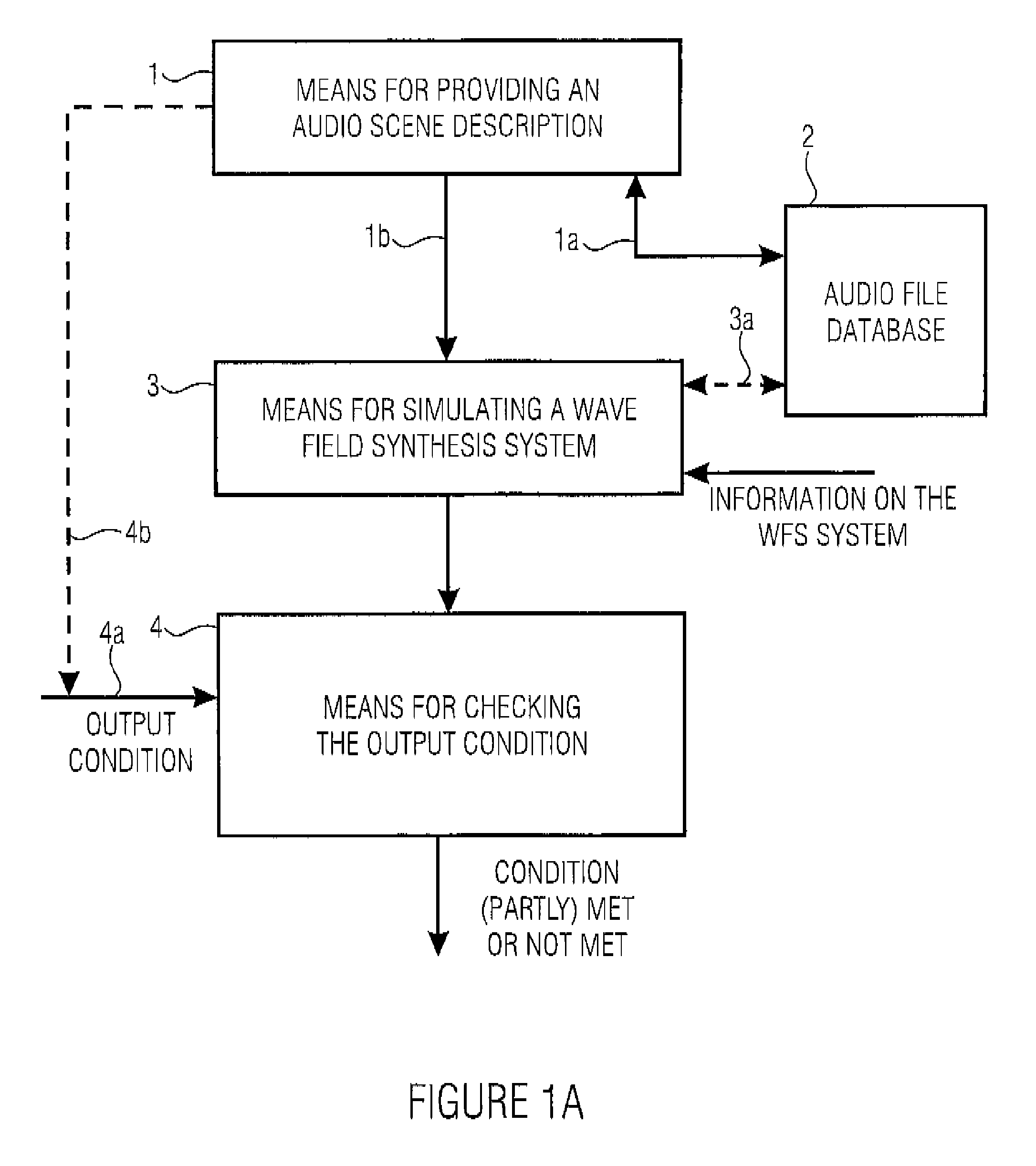
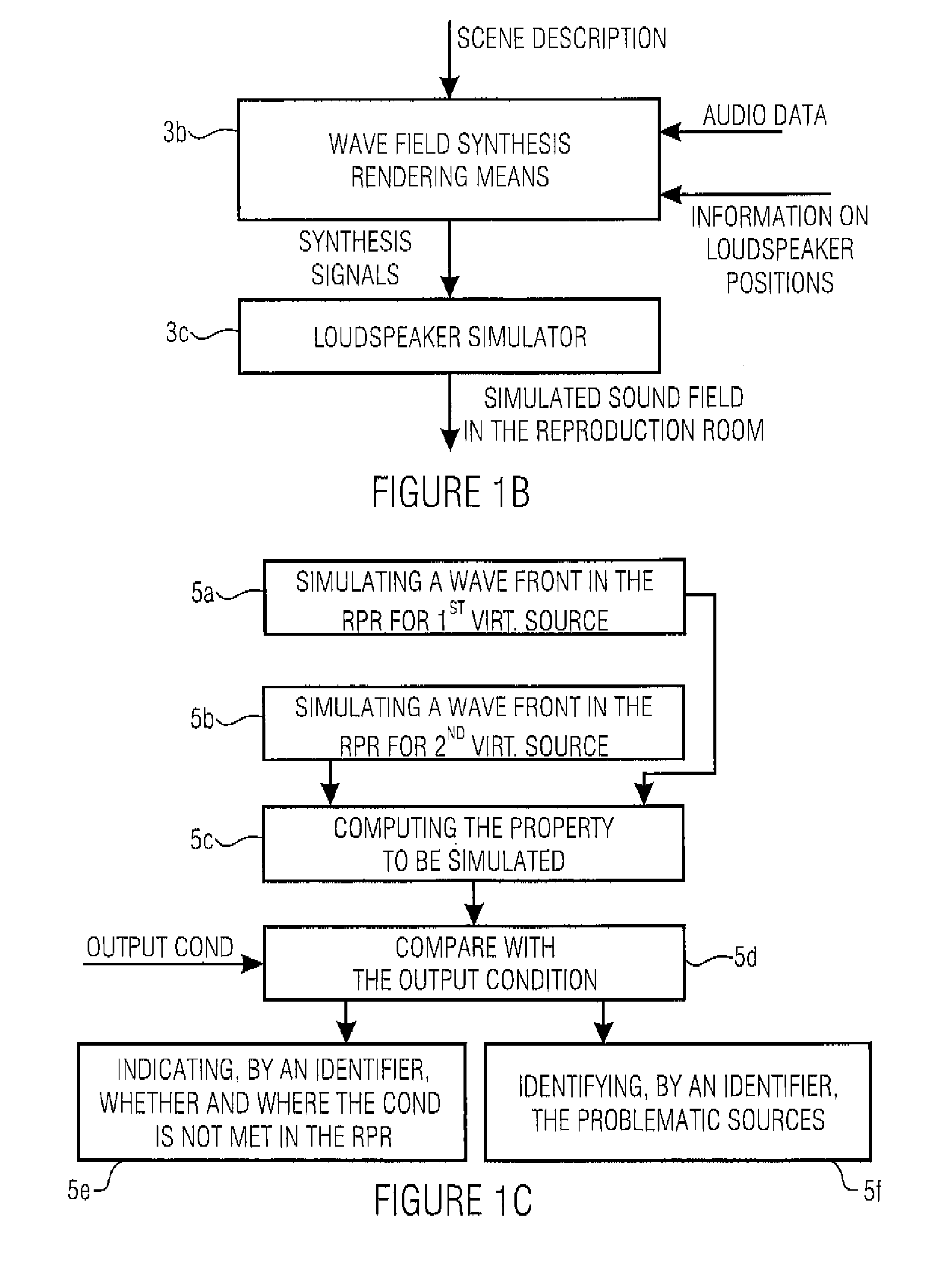
ActiveUS7809453B2High simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStereophonic systemsWave field synthesisWave field
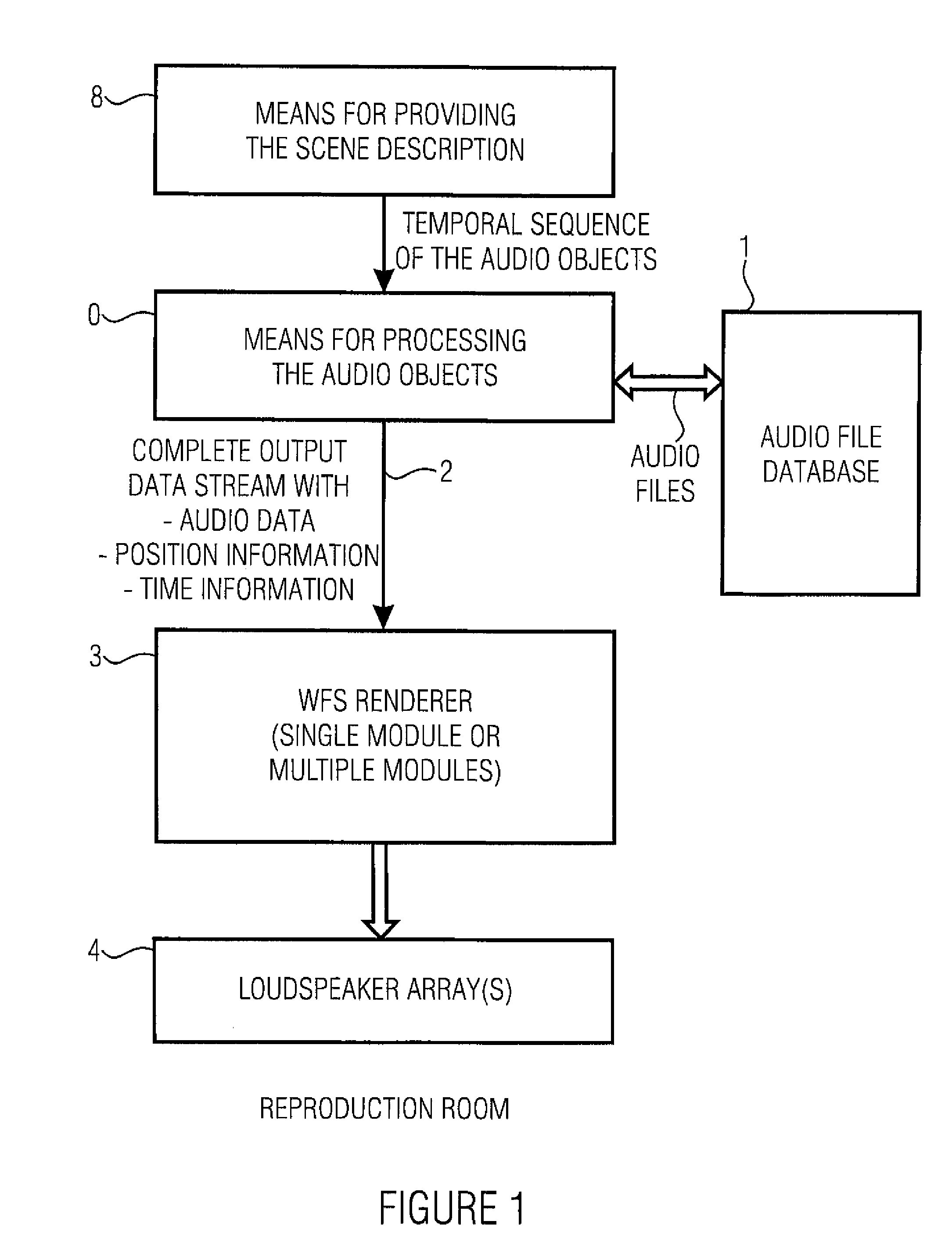
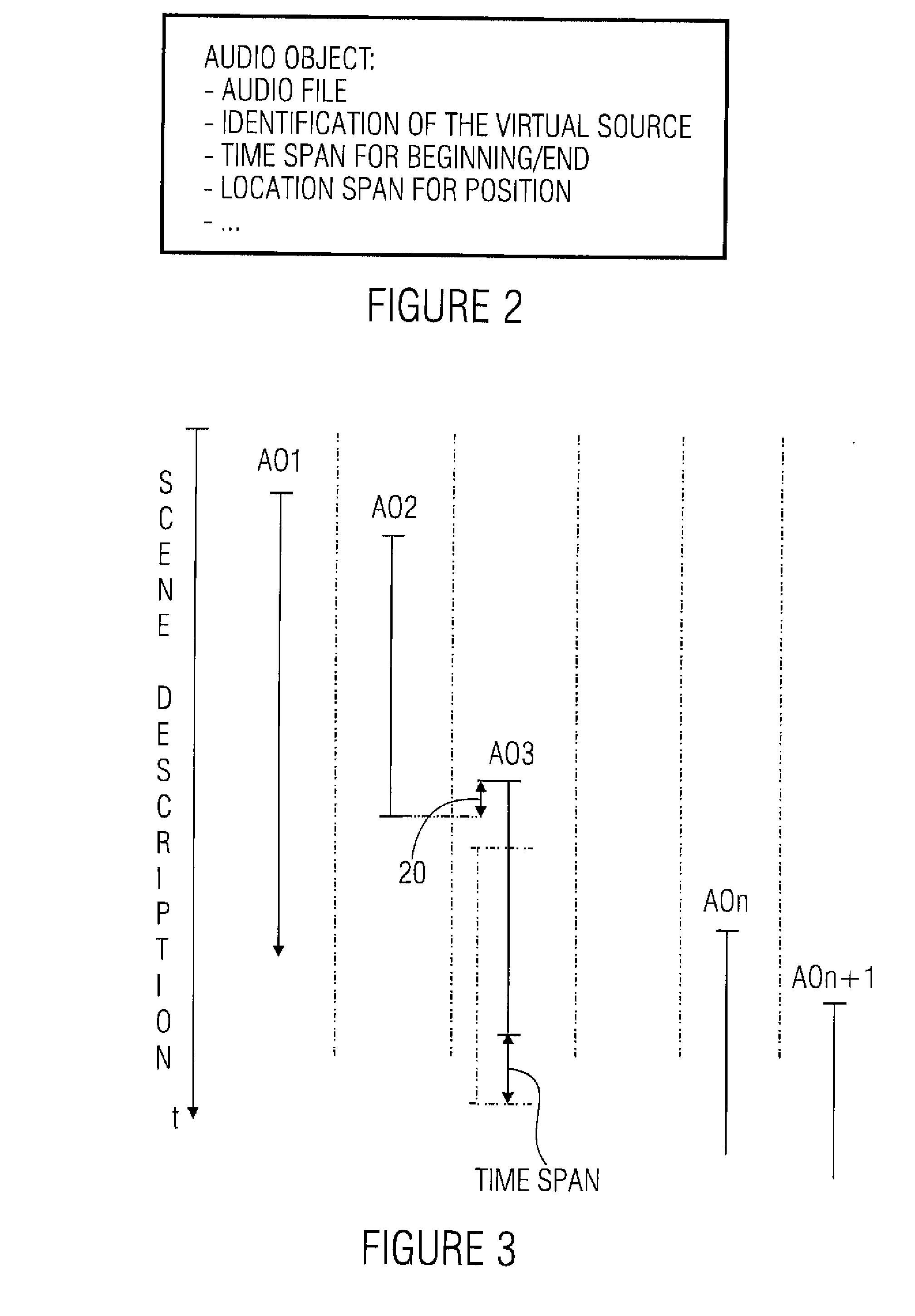
For simulating a wave field synthesis system, an audio scene description defining a temporal sequence of audio objects is provided, an audio object having an audio file for a virtual source or a reference to the audio file and information on a source position of the virtual source. Furthermore, an output condition the wave field synthesis system is to satisfy is given. Furthermore, a simulator for simulating the behavior of the wave field synthesis system for the audio scene description, using the audio data and the source positions as well as information on the wave field synthesis system, is provided. Finally a checker performs a check to determine if the simulated behavior of the wave field synthesis system satisfies the output condition. This achieves more flexible audio scene description creation as well as flexible portability of an audio scene description developed for one system to another wave field synthesis system.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Replay method of sound fields in three-dimensional local space based on continuous sound source concept
The invention discloses a replay method of sound fields in a three-dimensional local space. In the method, based on a continuous sound source concept, to-be-replayed sound fields and replay sound fields from continuously-distributed replay sound sources are expanded to form spherical harmonic functions; coefficients of the spherical harmonic functions are matched to acquire driving functions of the continuously-distributed replay sound sources; the continuously-distributed replay sound sources and the driving functions thereof are discretized to obtain driving functions of an actually-discretized replay sound source array; and the driving functions are fed back to the replay sound sources for replaying the sound fields and suitable for any type of sound sources. Compared with a spherical harmonic function expansion method, the replay method is used to avoid the problems of matrix inversion and errors possibly caused by the matrix inversion and expand replay regions; and compared with a wave field synthesis method, the replay method can be used to improve the replay accuracy in micro-regions in which replay centers are contained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Device for level correction in a wave field synthesis system
ActiveUS7751915B2Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageWave field synthesisComputer module
For a level correction in a wave field synthesis system having a wave field synthesis module and an array of loudspeakers for providing sound to a presentation region, a correction value which is based on a set amplitude state in a presentation region is determined, the set amplitude state depending on a position of the virtual source or a type of the virtual source, and the actual amplitude state in the presentation region depending on the component signals for the loudspeakers due to the virtual source. The correction value determined is fed to a manipulator manipulating the audio signal associated to the virtual source before feeding to the wave field synthesis module, or the component signals for the individual loudspeakers due to the virtual source are manipulated to reduce a deviation between a set amplitude state and an actual amplitude state at one point or several in the presentation region.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
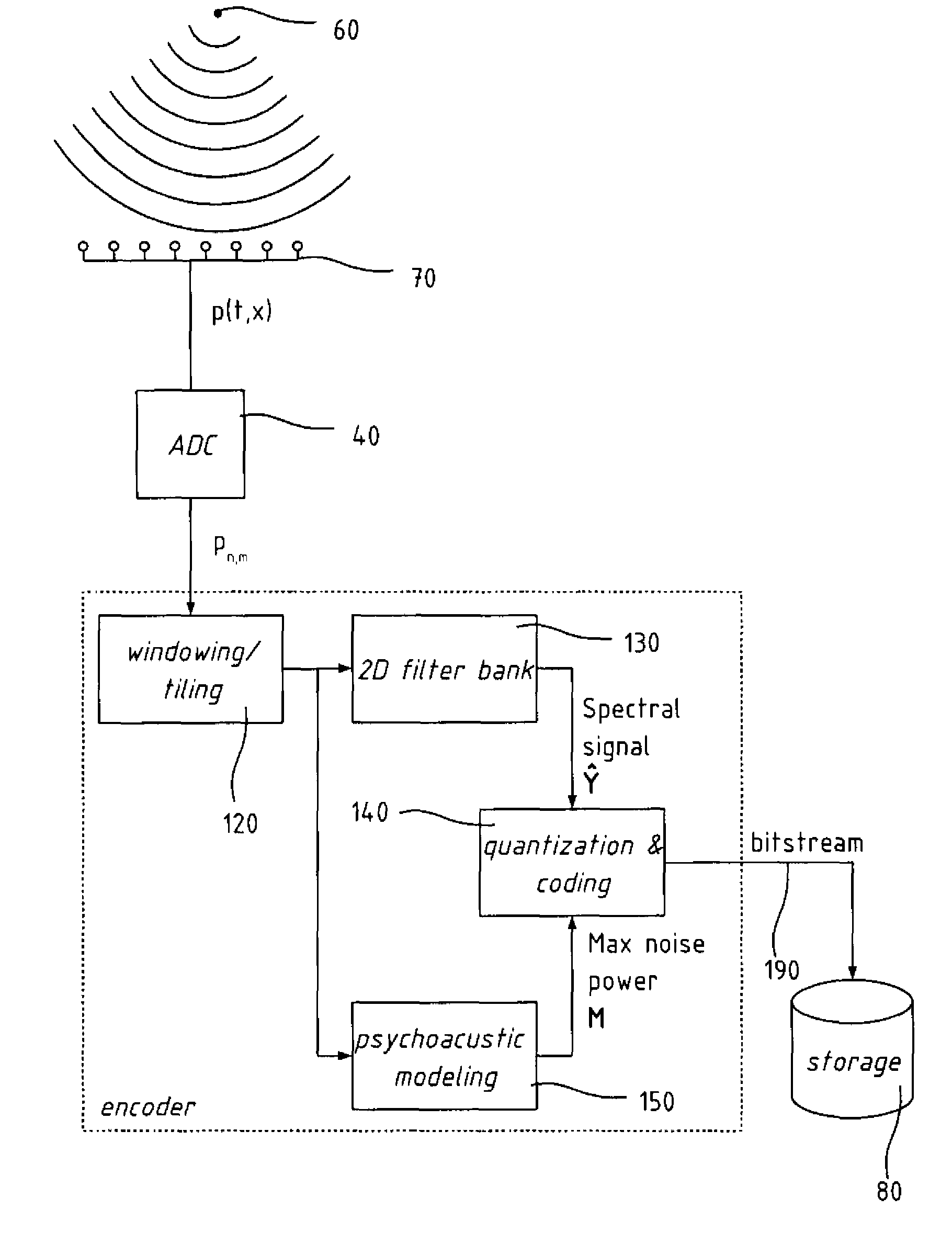
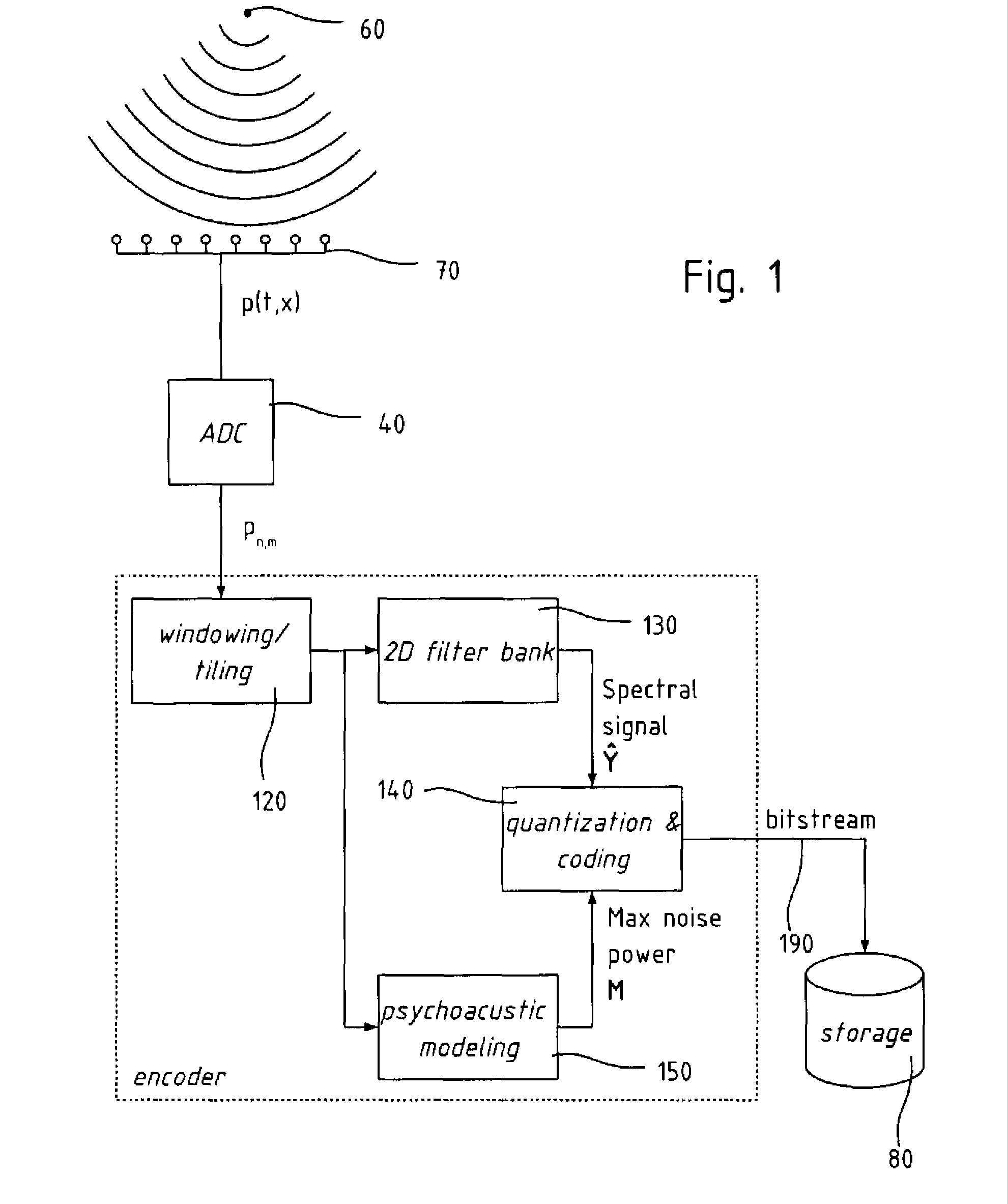
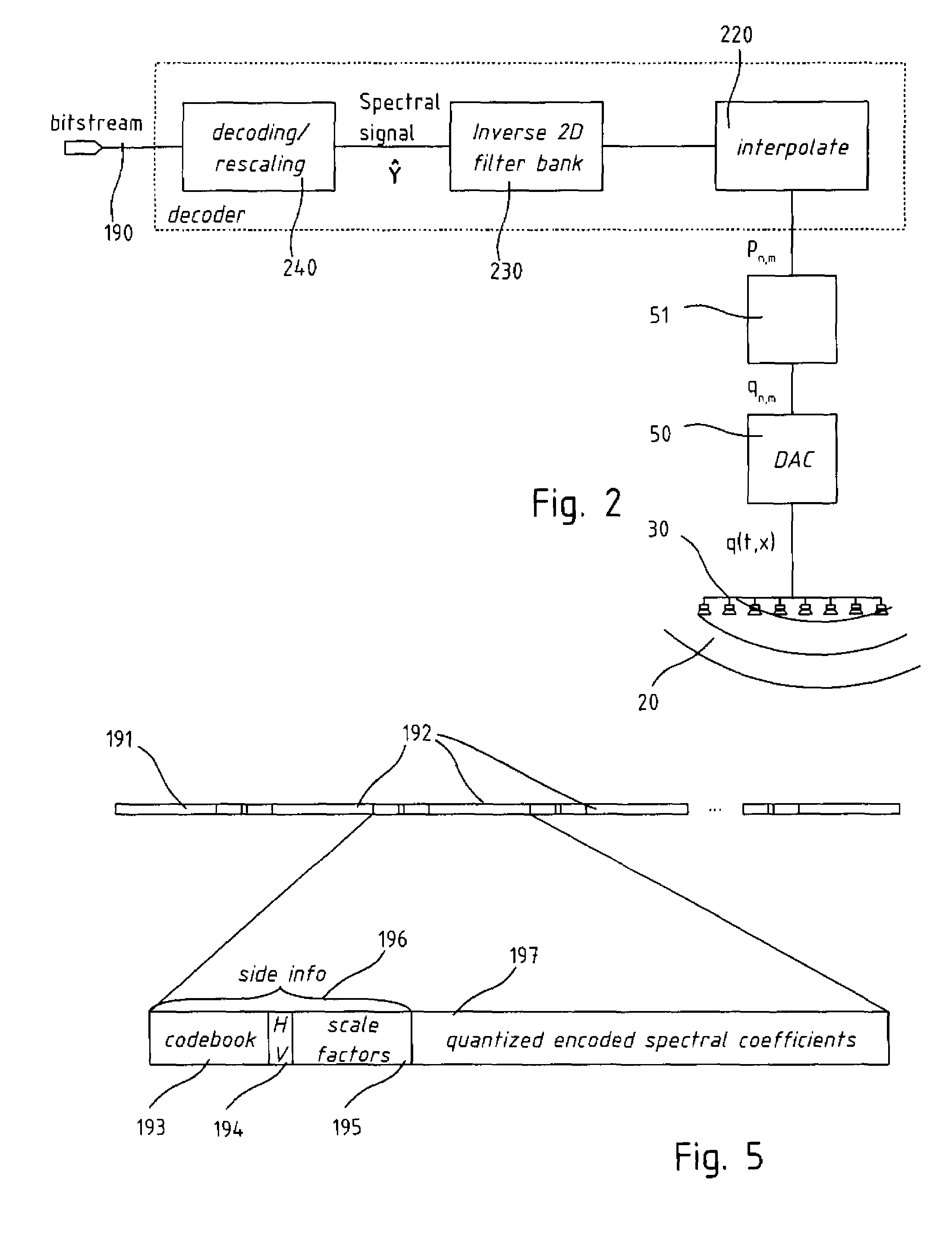
Audio wave field encoding
An encoder / decoder for multi-channel audio data, and in particular for audio reproduction through wave field synthesis. The encoder comprises a two-dimensional filter-bank to the multi-channel signal, in which the channel index is treated as an independent variable as well as time, and and the resulting spectral coefficient are quantized according to a two-dimensional psychoacoustic model, including masking effect in the spatial frequency as well as in the temporal frequency. The coded spectral data are organized in a bitstream together with side information containing scale factors and Huffman codebook identifiers.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Apparatus and method for reproducing surround wave field using wave field synthesis
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
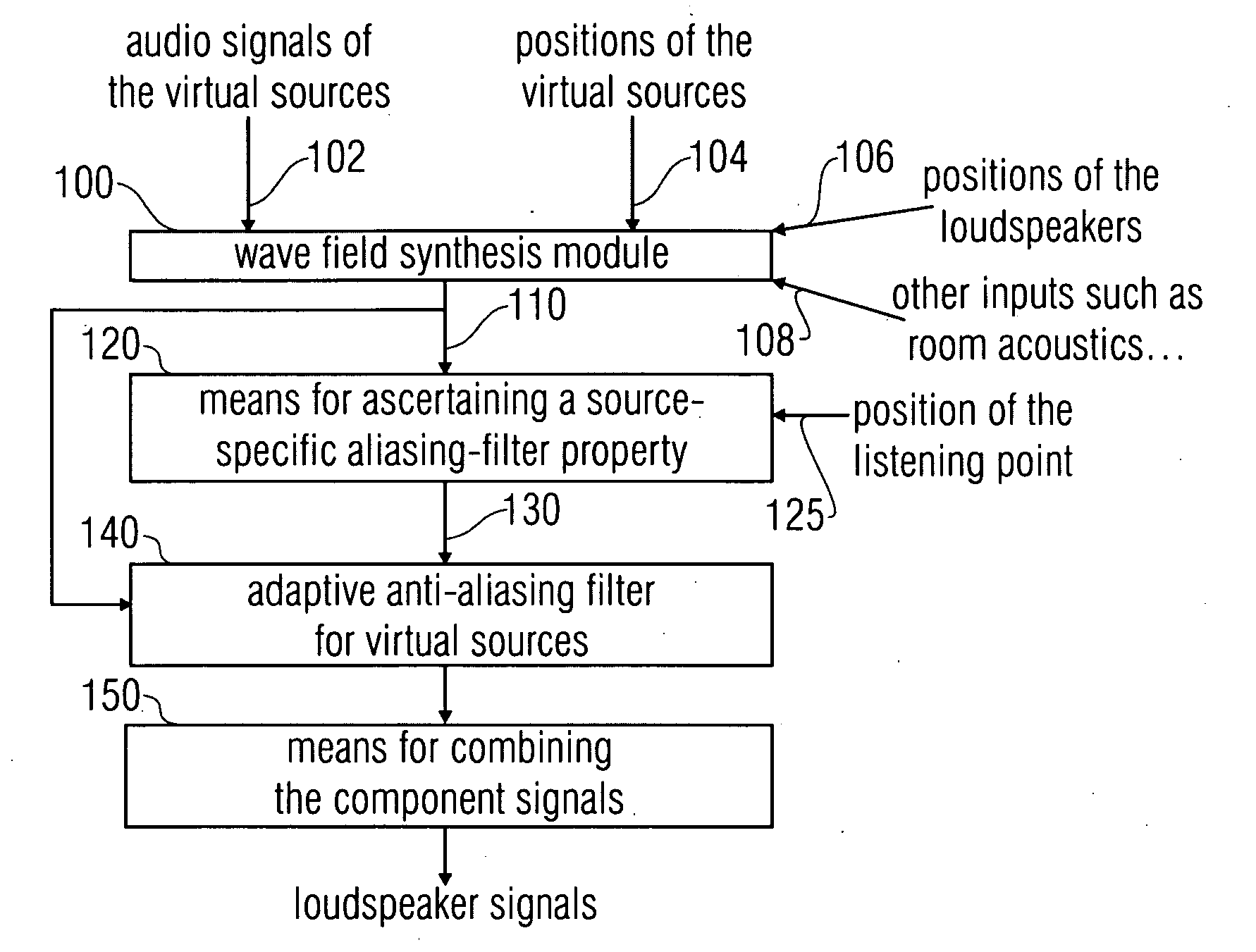
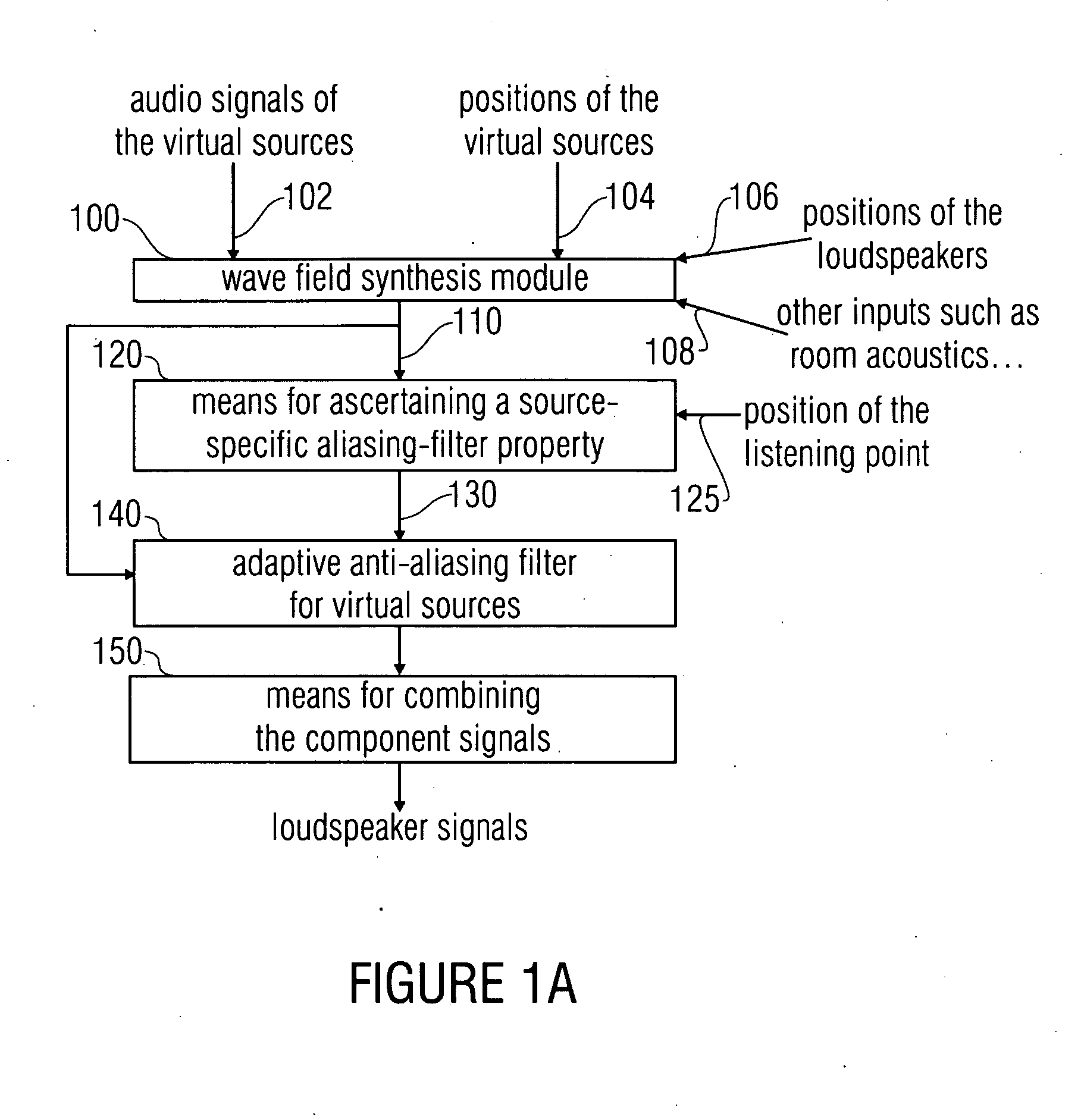
Device and method for simulation of wfs systems and compensation of sound-influencing properties
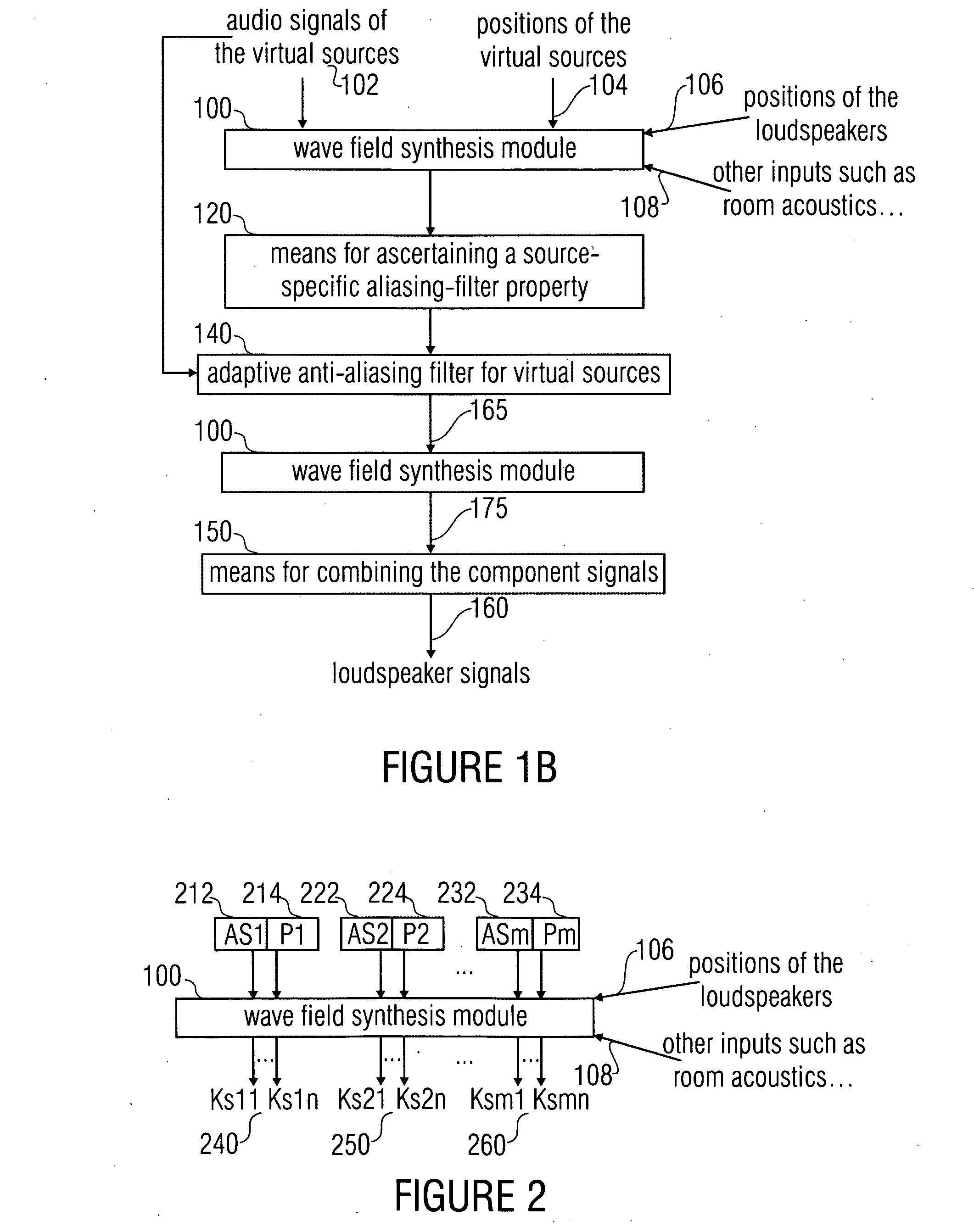
ActiveUS20090220111A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsWave field synthesisWave field
An aliasing correction in a wave field synthesis system is achieved by ascertaining the aliasing filter property specific for a virtual source. This aliasing filter property, which, for example, may be the aliasing frequency is ascertained by help of the source position information. This aliasing filter property is used for an adaptive anti-aliasing filter for adaptive filtering of the audio signal associated with the source or the component signals associated with the source.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
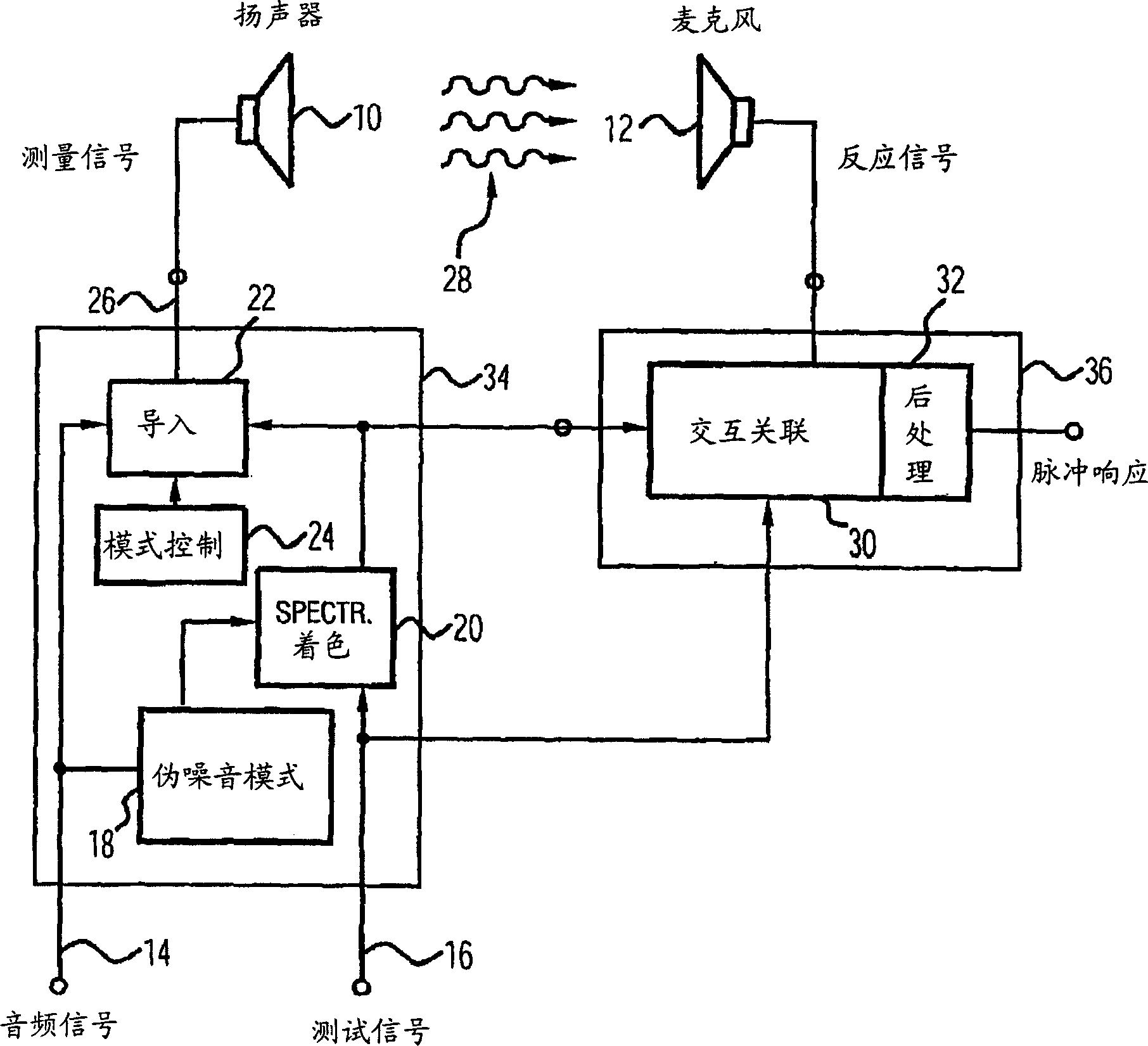
Apparatus and method of determining an impulse response and apparatus and method of presenting an audio piece
The invention relates to a device, which is provided for determining a pulse response in an environment, inside of which a loudspeaker (10) and a microphone (12) are placed, and which operates while using an audio signal. A device (20) for effecting the spectral coloring of a test signal, which is preferably a pseudo noise signal, operates while using a psychoacoustic masking threshold of the audio signal in order to obtain a colored test signal that is embedded in the audio signal in order to obtain a measurement signal that can be fed to the loudspeaker (10). A device (30, 32) for determining the pulse response preferably carries out a cross-correlation of a reaction signal, which is received from the environment via the microphone, and of the test signal or of the colored test signal. This enables a pulse response of an environment to be determined even while playing an audio piece in order to provide an optimal description of the environment for a wavefield synthesis.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Device and method for determining a reproduction position
ActiveUS7606372B2Readily availablePrecise positioningTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionSound sourcesComputer graphics (images)
A method and device are provided for determining a reproduction position of a source of sound for audio-visual reproduction of a film scene from a plurality of individual pictures with regard to a reproduction surface having a predetermined width, and with regard to a projection source having a projection reference point. A recording position of the source of sound, a camera position during recording, and an aperture angle of the camera during recording are obtained and the determined recording position is transformed to a camera coordinate system. A reproduction position for the source of sound is calculated and used to produce sound-source positioning in a reproduction room using wave-field synthesis methods.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
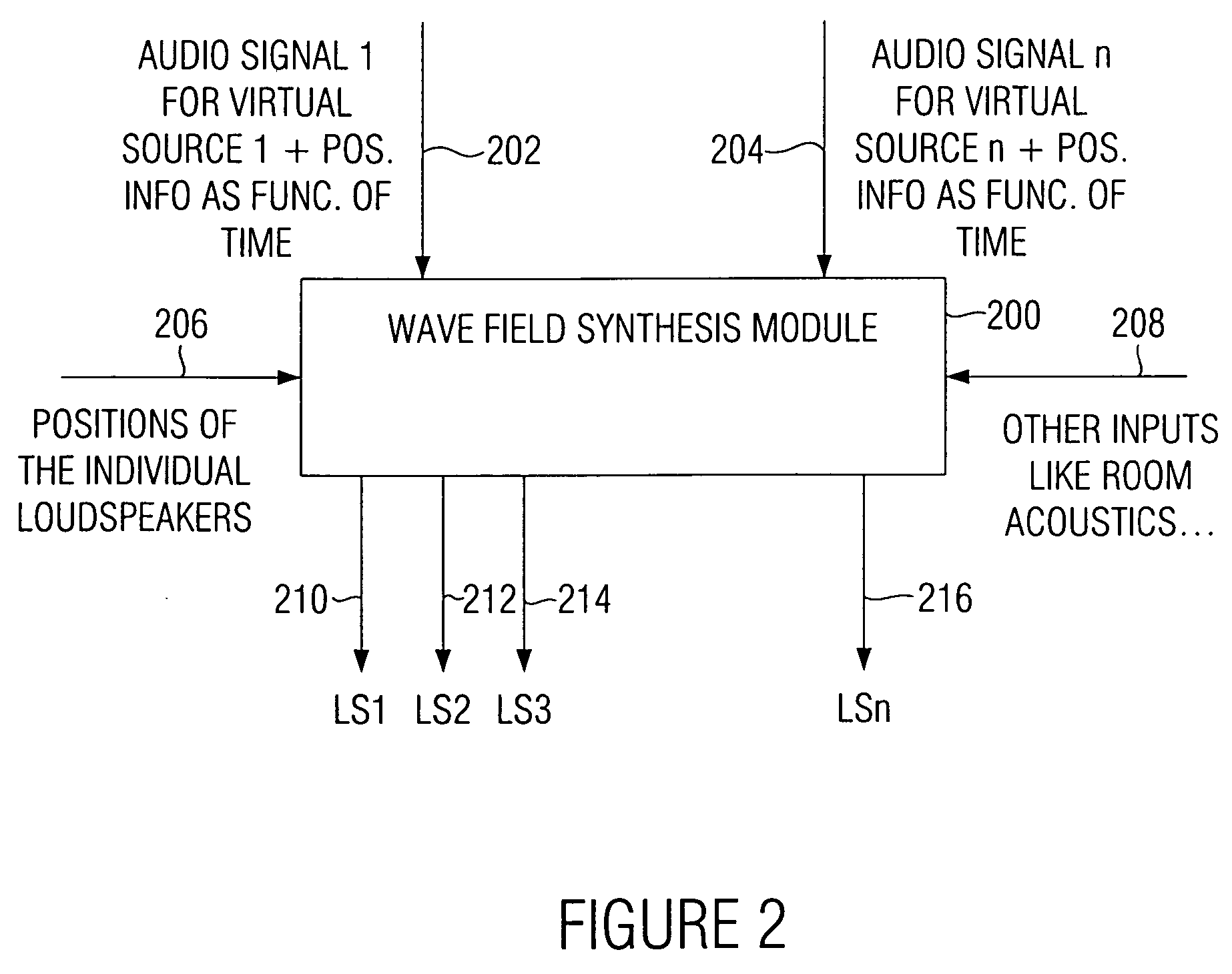
Apparatus and method for controlling a wave field synthesis renderer means with audio objects
ActiveUS20080123864A1Increase flexibilityImprove portabilityMechanical record carriersRecord information storageData streamWave field synthesis
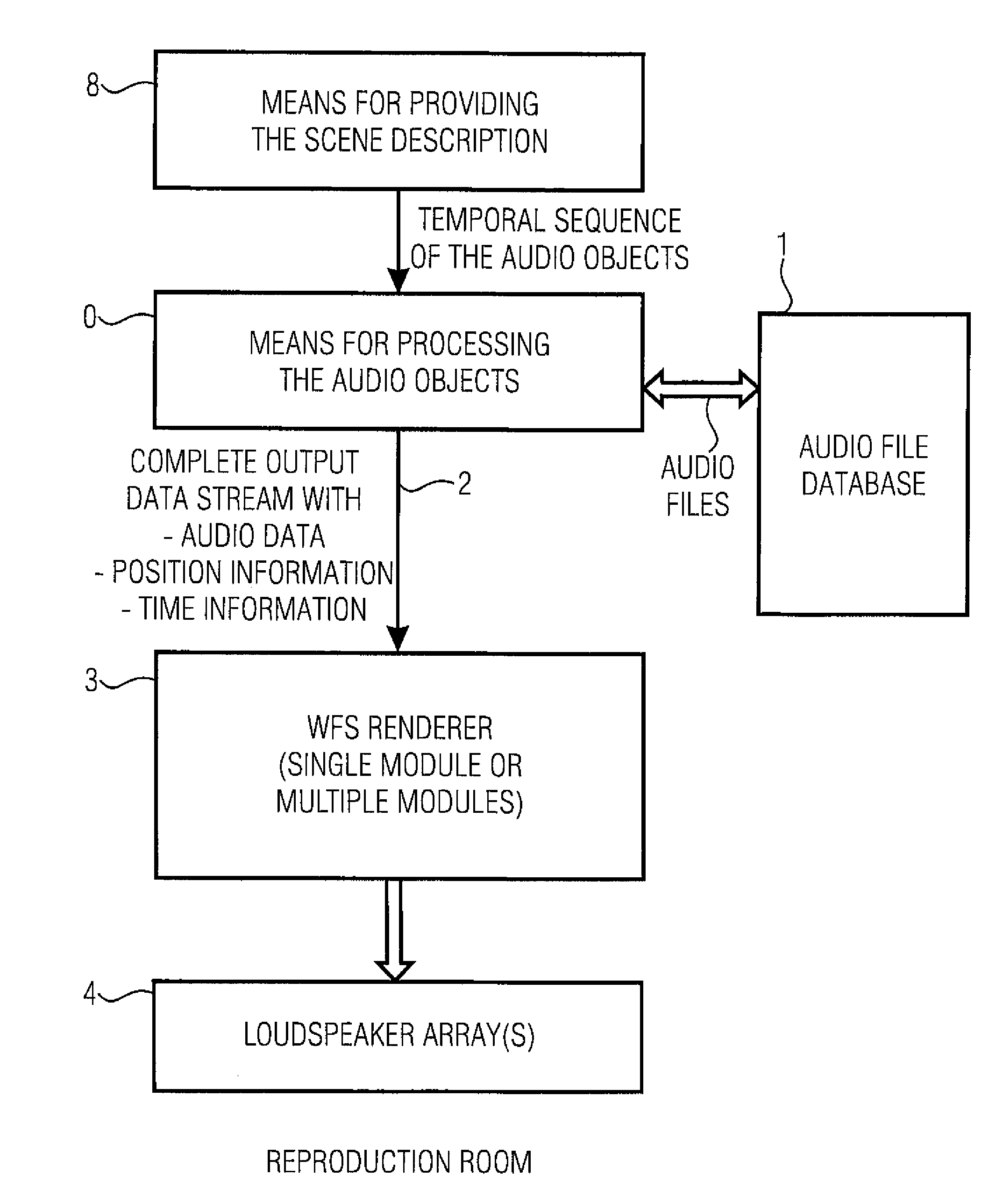
An apparatus for controlling a wave field synthesis renderer with audio objects includes a provider for providing a scene description, wherein the scene description defines a temporal sequence of audio objects in an audio scene and further includes information on the source position of a virtual source as well as on a start or an end of the virtual source. Furthermore, the audio object includes at least a reference to an audio file associated with the virtual source. The audio objects are processed by a processor, in order to generate a single output data stream for each renderer module, wherein both information on the position of the virtual source and the audio file itself are included in mutual association in this output data stream. With this, high portability on the one hand and high quality due to secure data consistency on the other hand are achieved.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for driving an array of loudspeakers with drive signals
ActiveUS20180098175A1Enhance listening experienceLoudspeaker signals distributionStereophonic systemsWave field synthesisWave field
A wave field synthesis apparatus for driving an array of loudspeakers with drive signals, the apparatus includes a sound field synthesizer for generating sound field drive signals for causing the array of loudspeakers to generate one or more sound fields at one or more audio zones, a binaural renderer for generating binaural drive signals for causing the array of loud-speakers to generate specified sound pressures at at least two positions, wherein the at least two positions are determined based on a detected position and / or orientation of a listener, and a decision unit for deciding whether to generate the drive signals using the sound field synthesizer or using the binaural renderer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
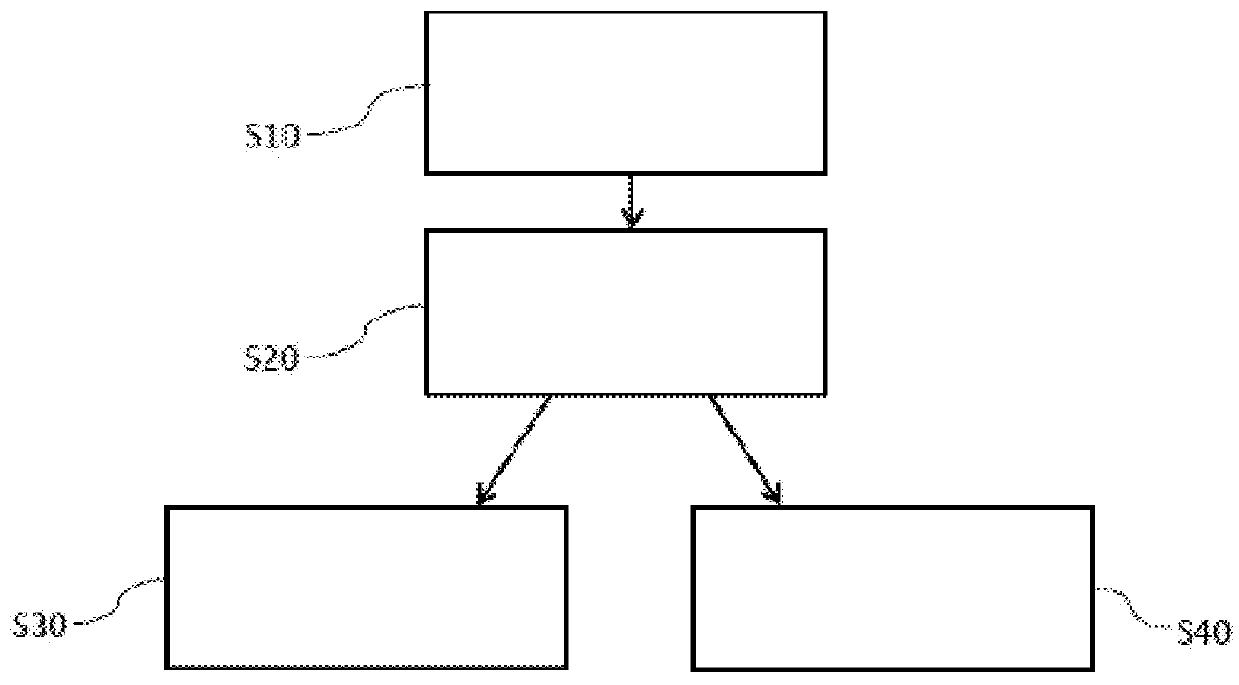
Two-dimensional multi-component seismic data migration imaging method and system
ActiveCN109557582AHigh precisionHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingReverse timeImaging condition
The invention discloses a two-dimensional multi-component seismic data migration imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a vector wave field continuation operator; constructing a scalar imaging condition based on a vector wave field decomposition operator, establishing a gradient calculation equation; constructing a predicted reflection wave field continuation equation based on a vector and a scalar wave field continuation operator, obtaining a predicted multi-component wave field by utilizing a wave field synthesis operator; and establishing an objective function and an inversion process. The invention introduces least squares inversion into a multi-component data pre-stack depth inverse time migration imaging method, and can obtain a multi-component pre-stack depth inverse time migration profile of high precision, high resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio, and amplitude fidelity by establishing accurate multi-component wave field pre-stackdepth inverse time migration and inverse time inverse migration operators. The migration profile and the multi-component data pre-stack depth reverse time migration have the consistent physical significance, which directly reflects the reflection coefficient information of the longitudinal wave and the converted transverse wave of the underground medium. The method has high imaging precision, amplitude fidelity of the offset profile, and clear physical significance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com