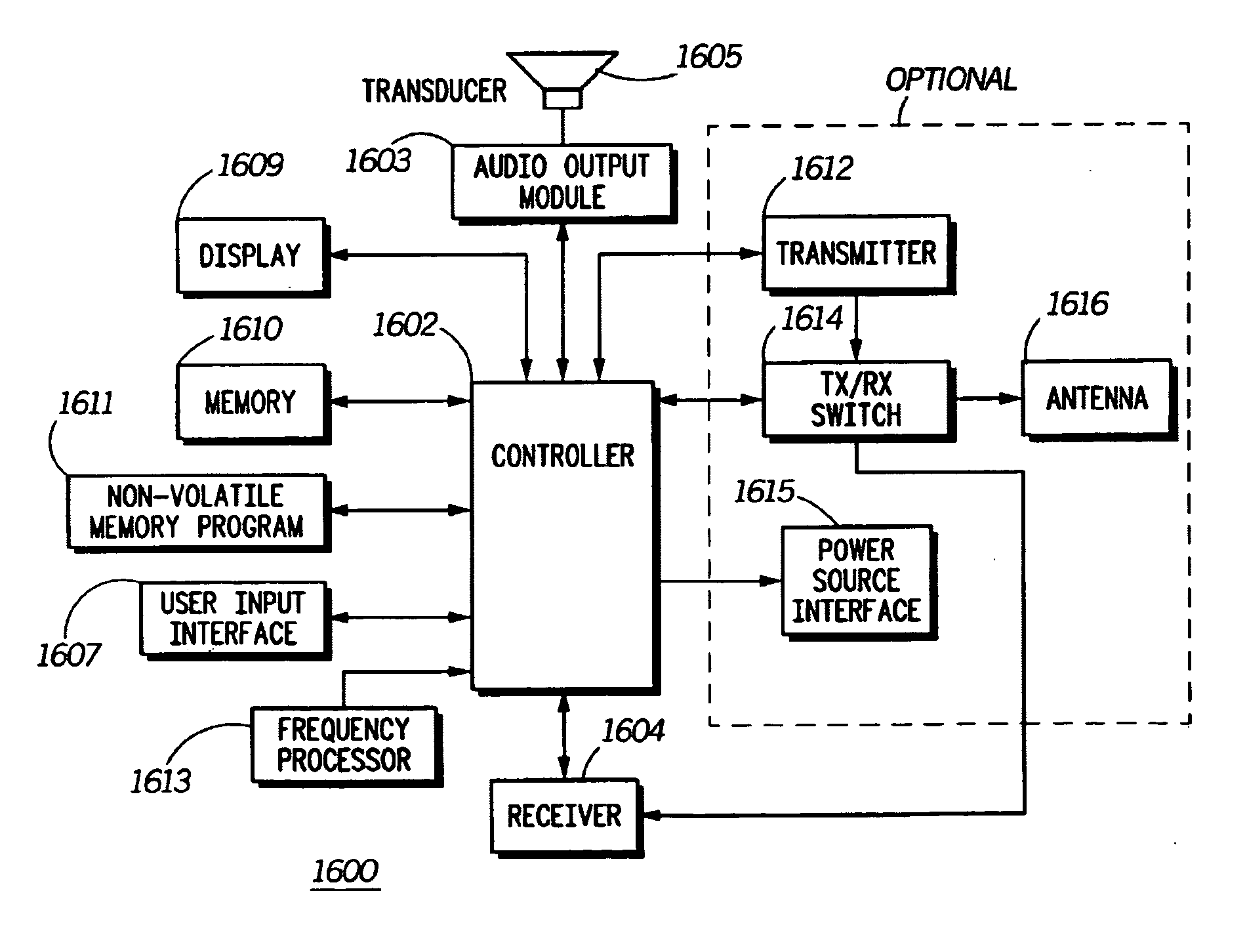
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Critical band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
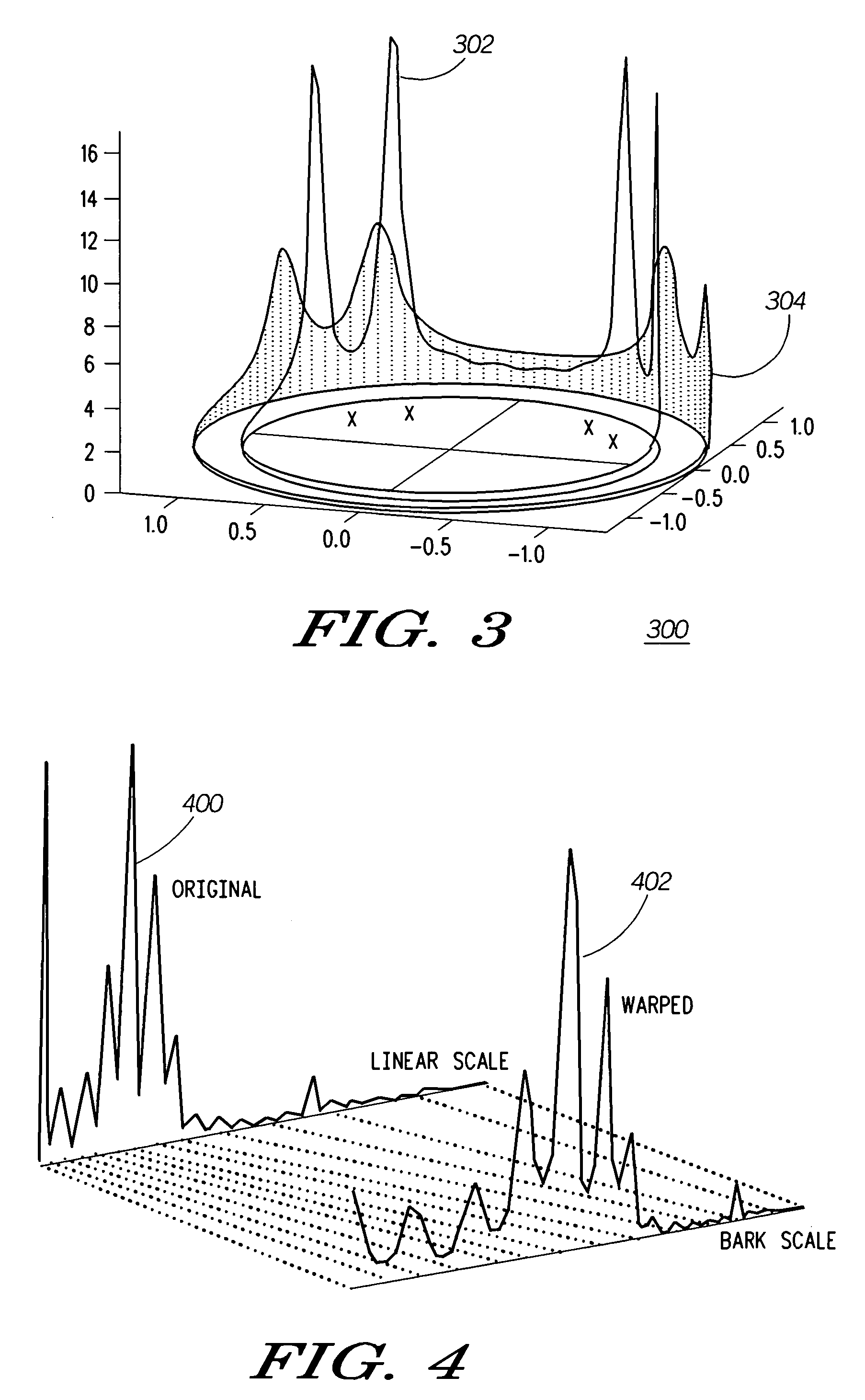
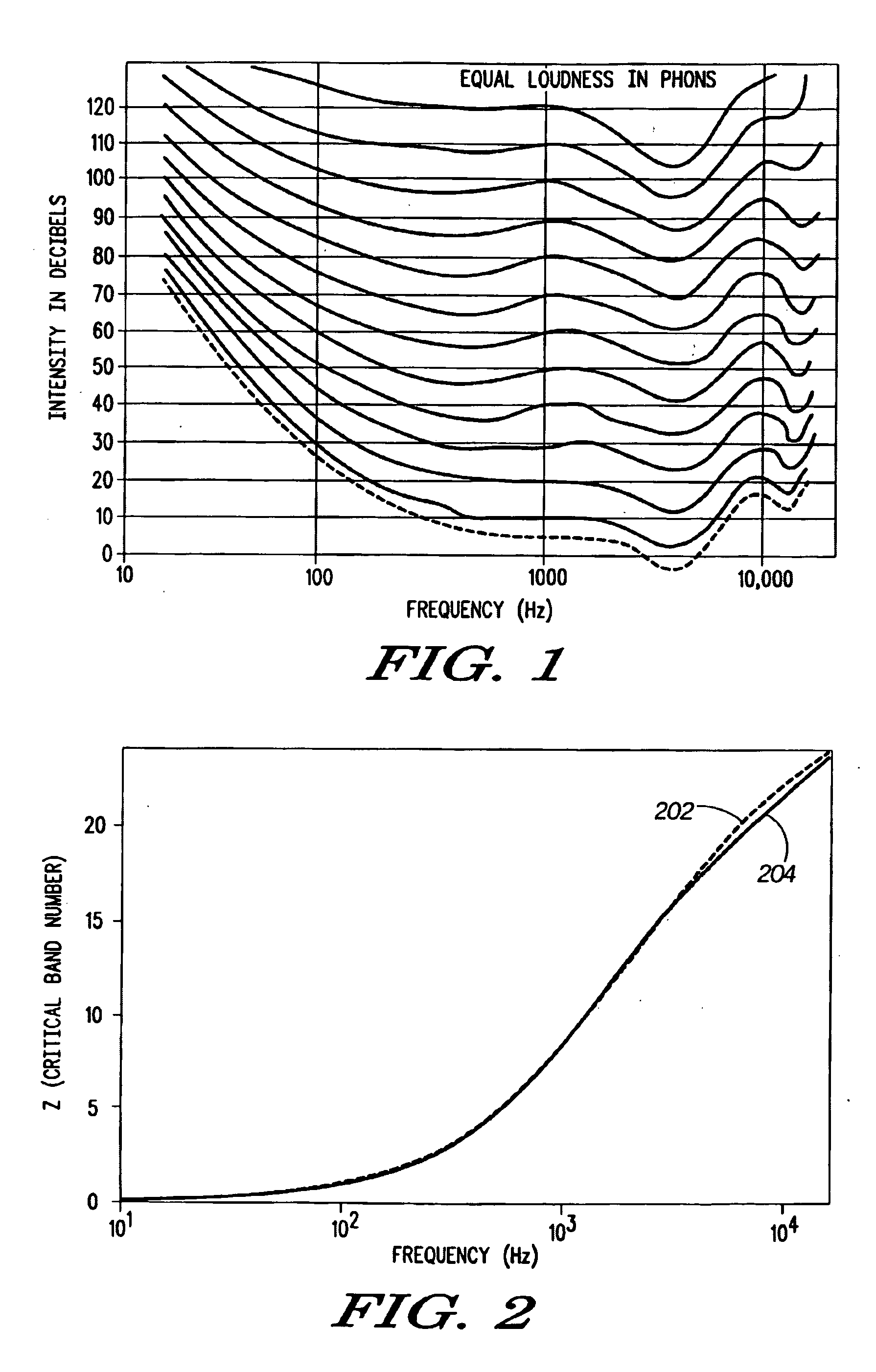
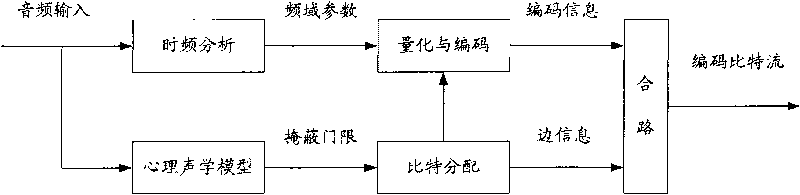
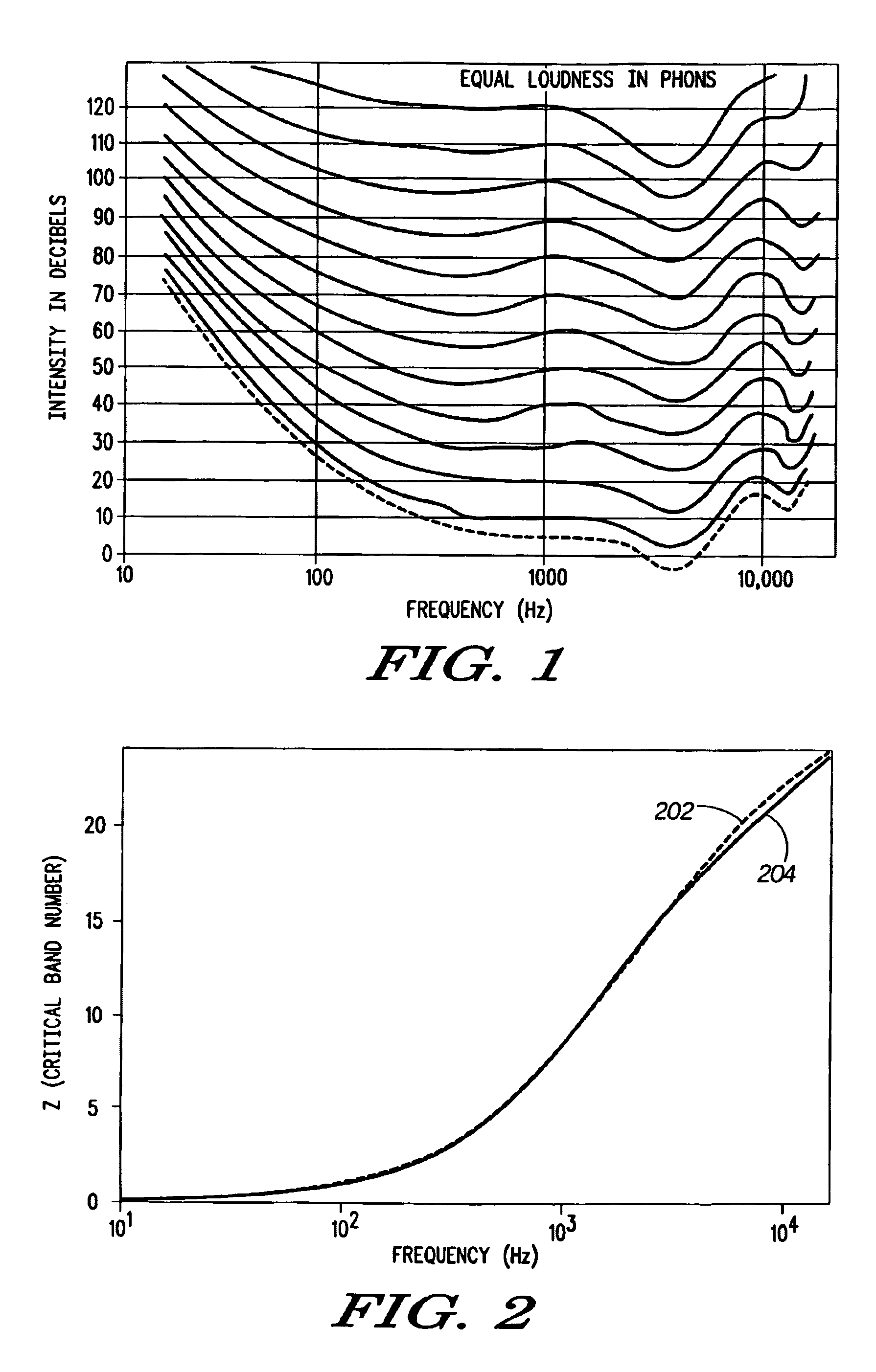
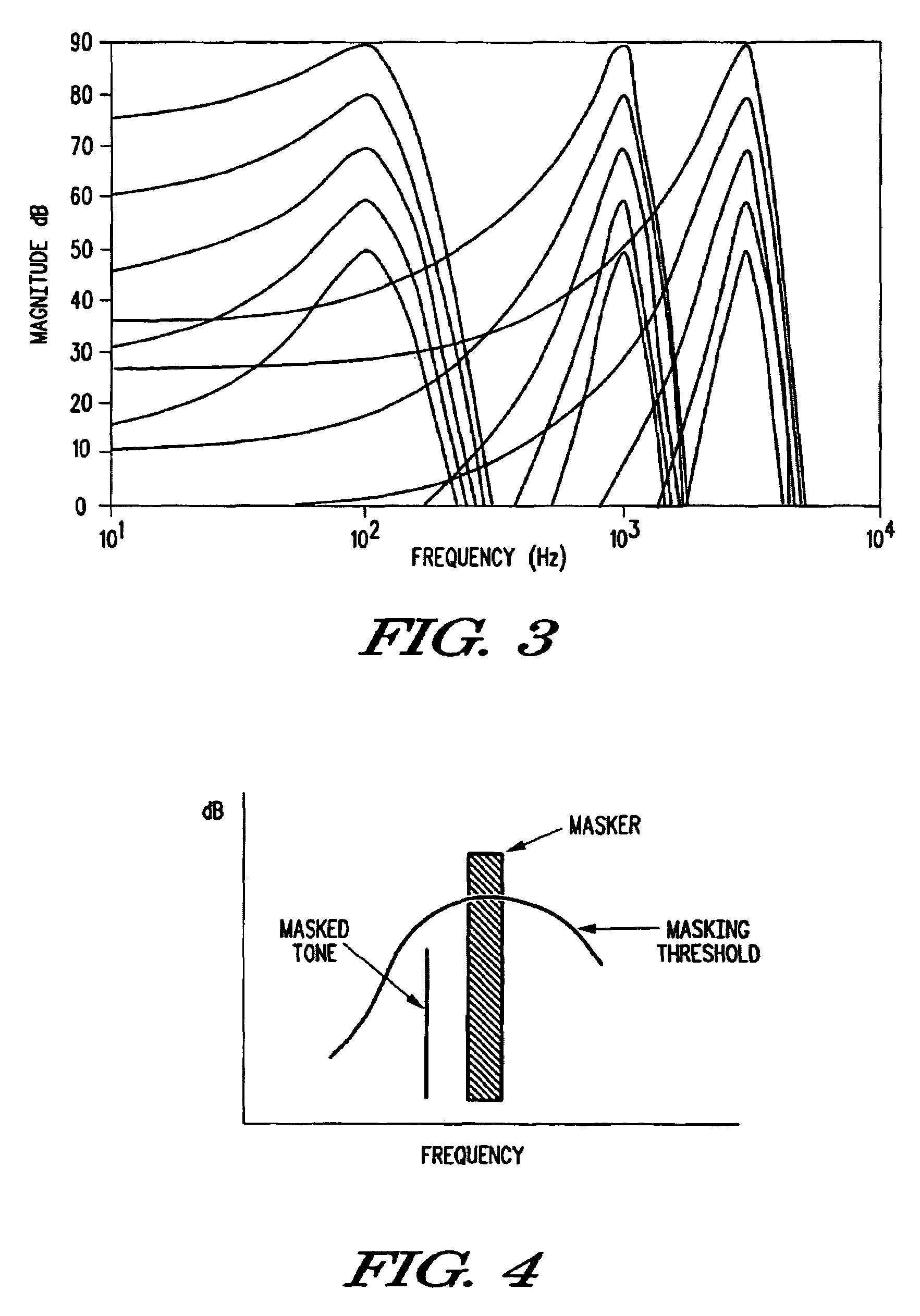
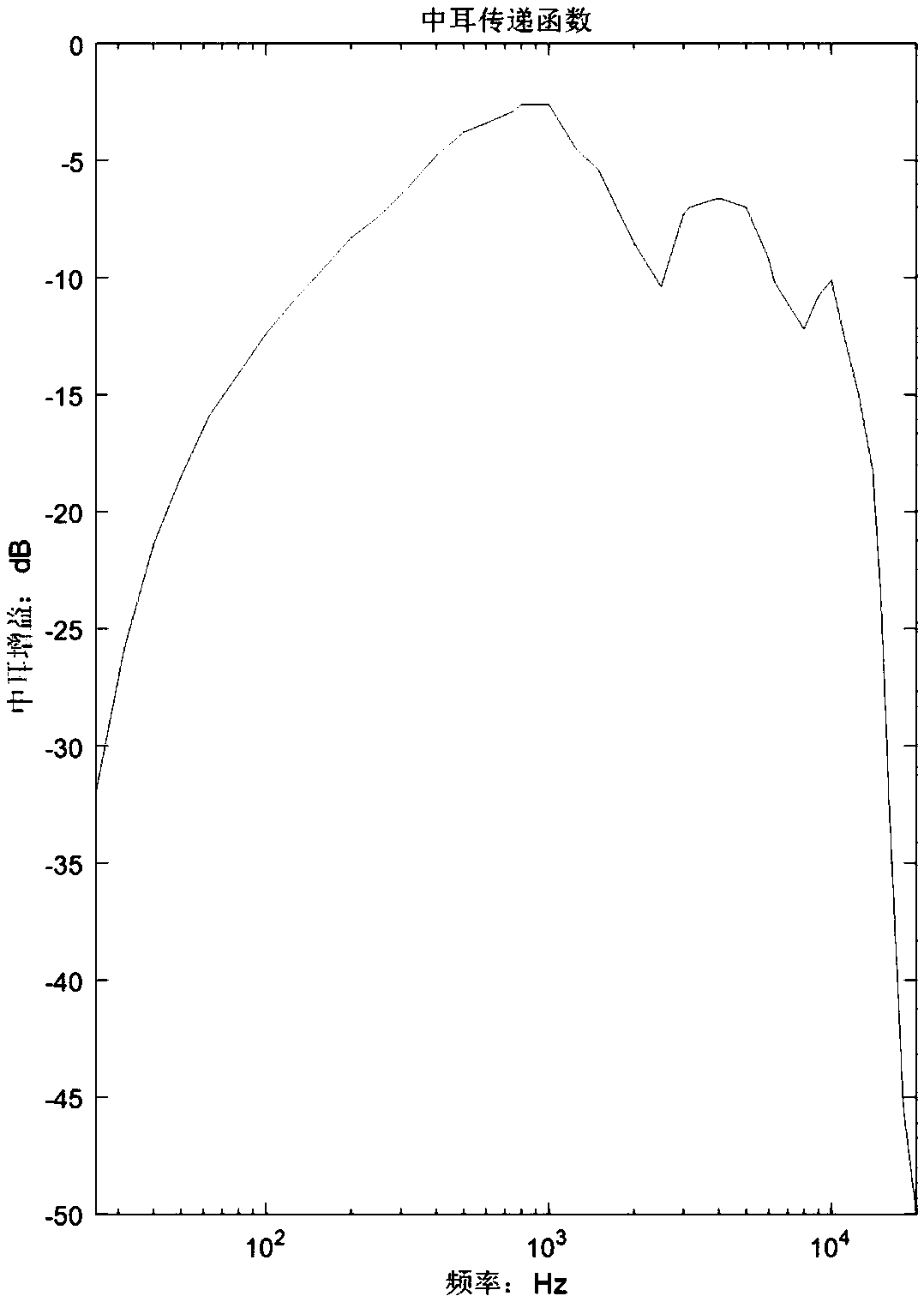
In audiology and psychoacoustics the concept of critical bands, introduced by Harvey Fletcher in 1933 and refined in 1940, describes the frequency bandwidth of the "auditory filter" created by the cochlea, the sense organ of hearing within the inner ear. Roughly, the critical band is the band of audio frequencies within which a second tone will interfere with the perception of the first tone by auditory masking.
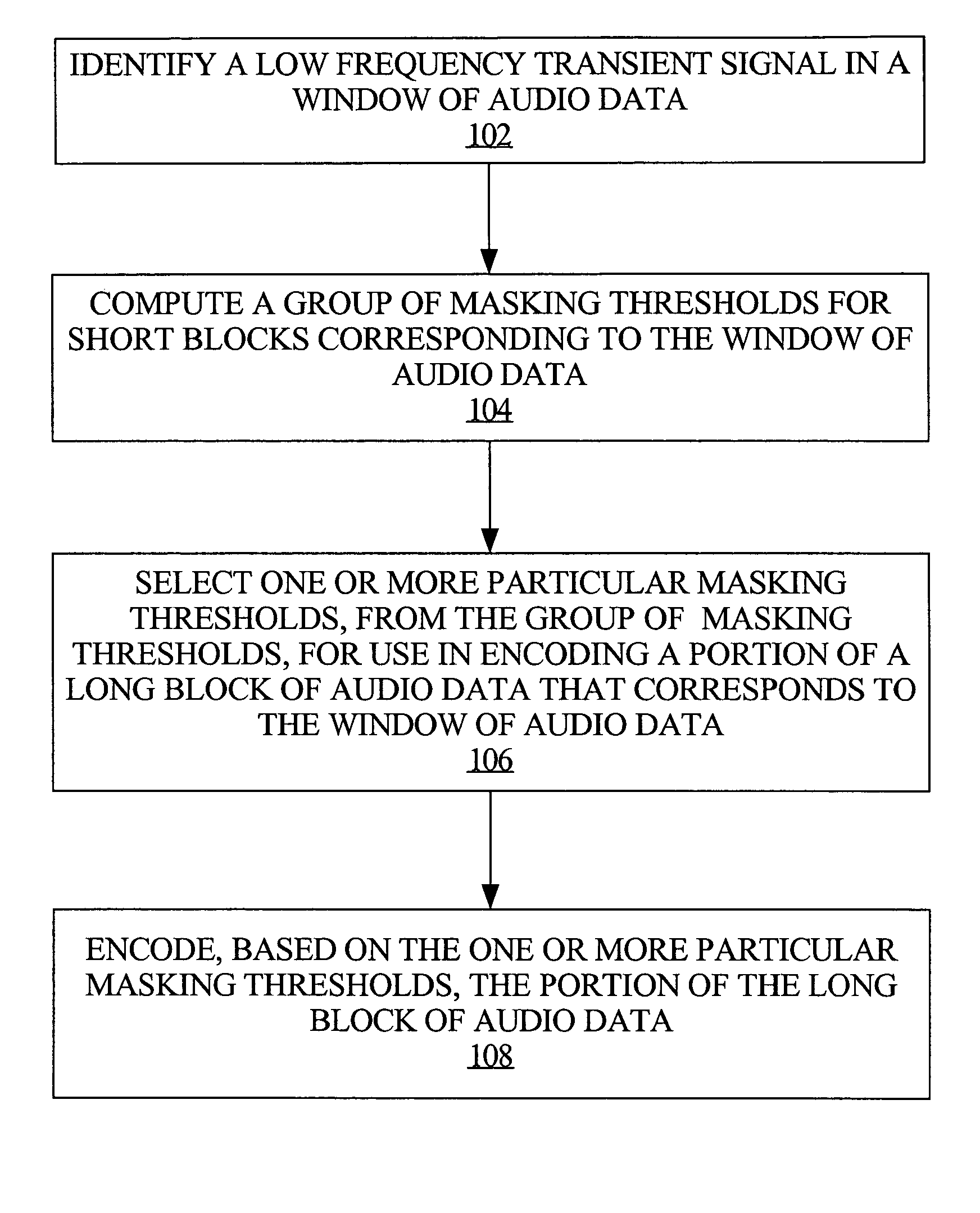
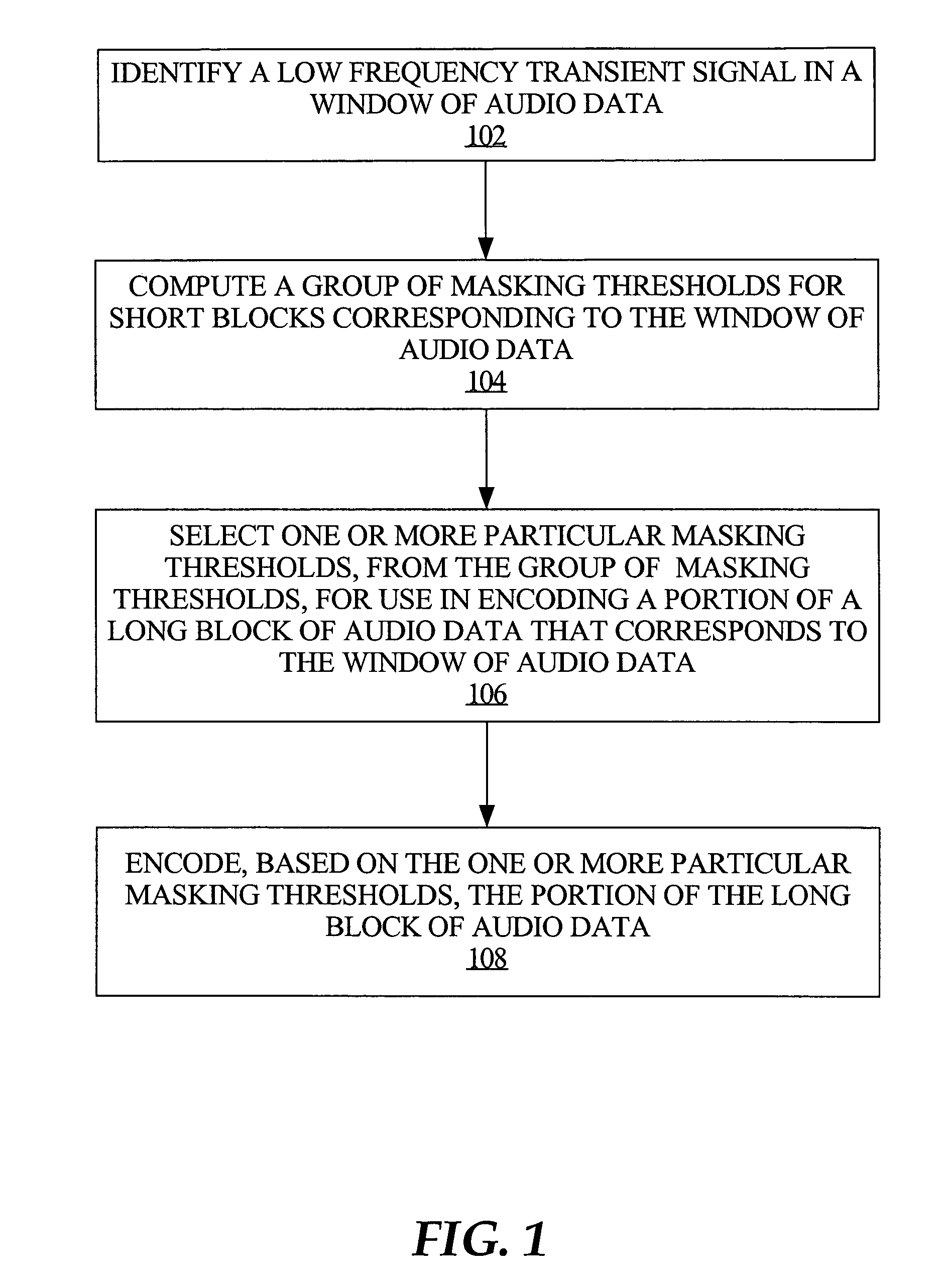
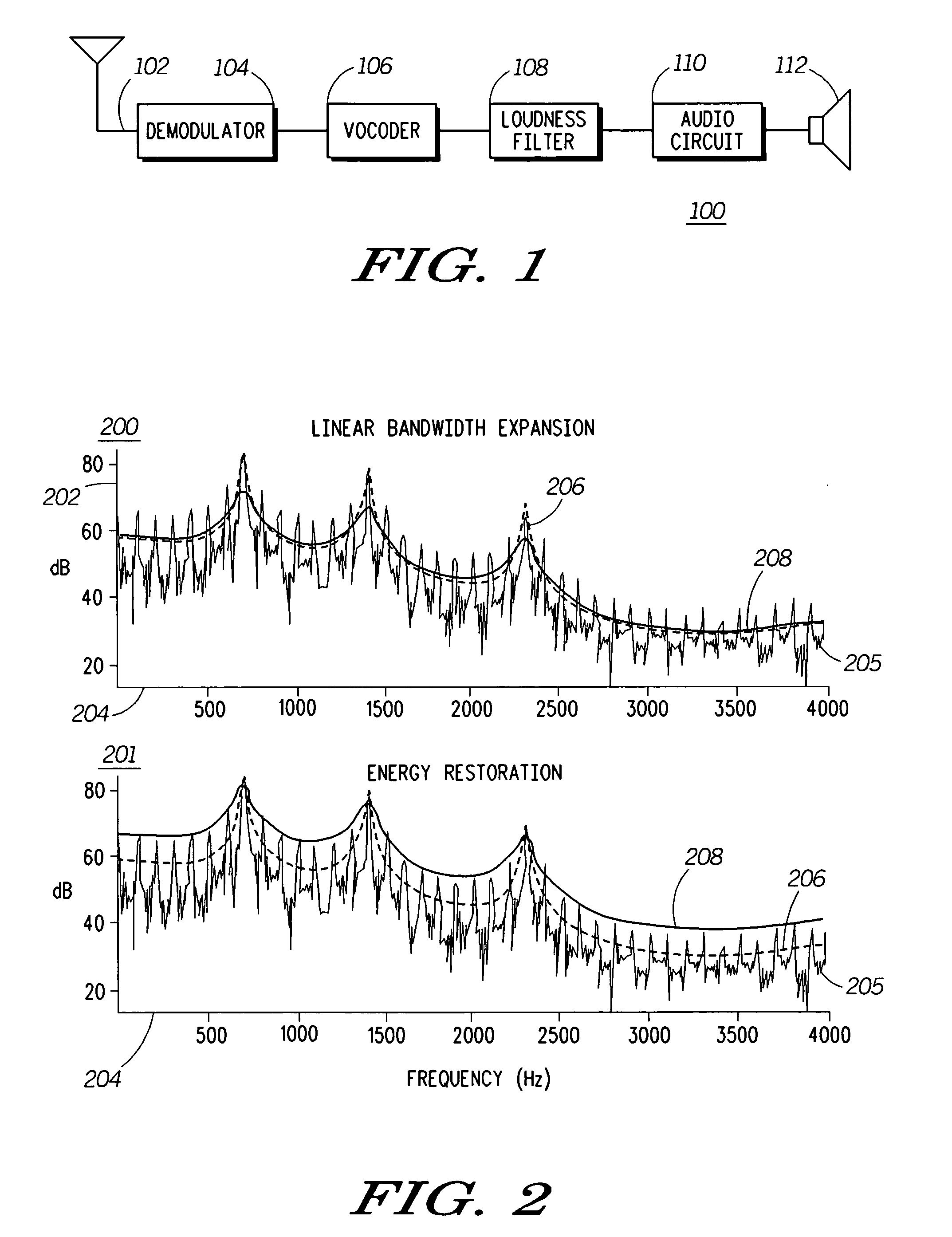
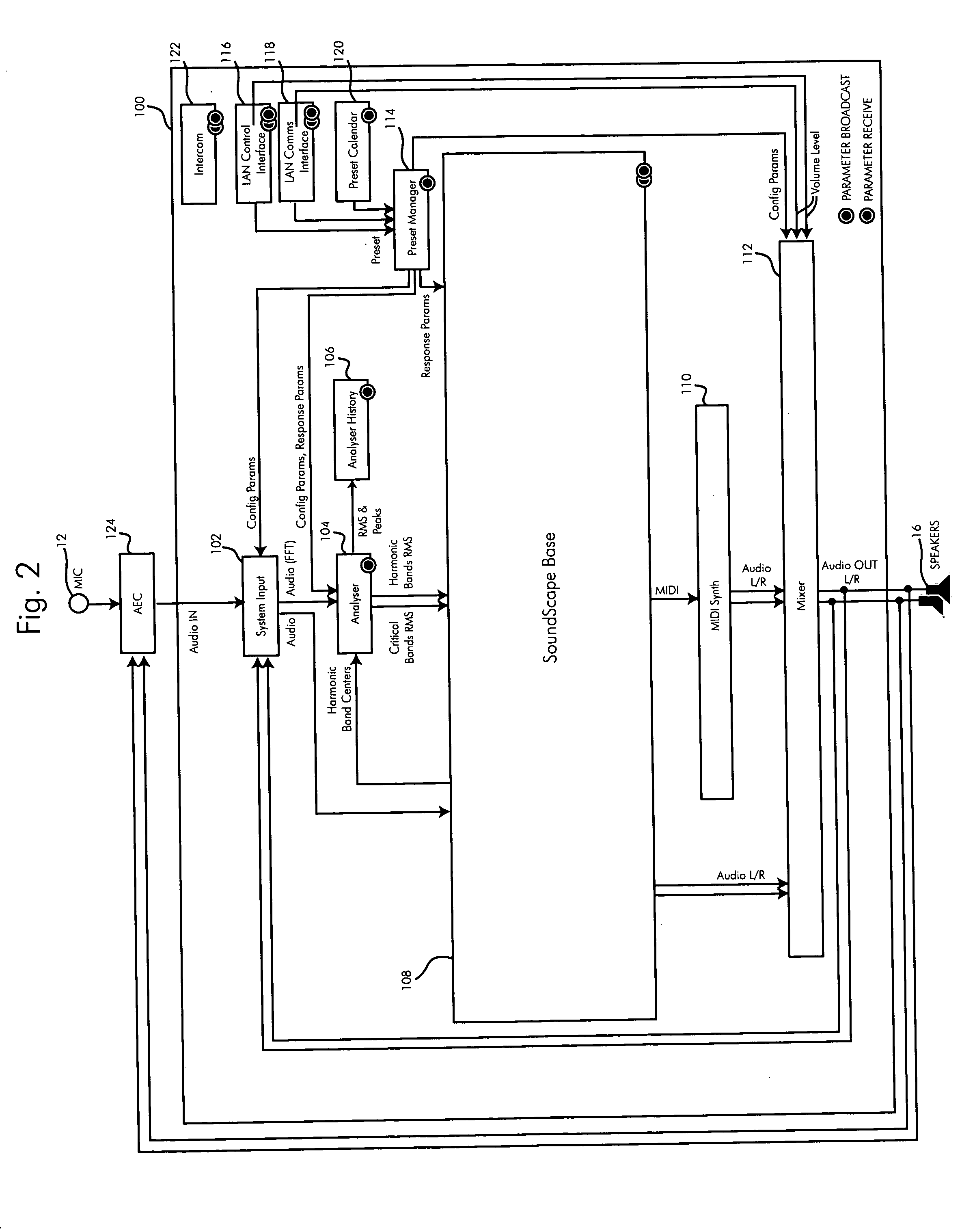
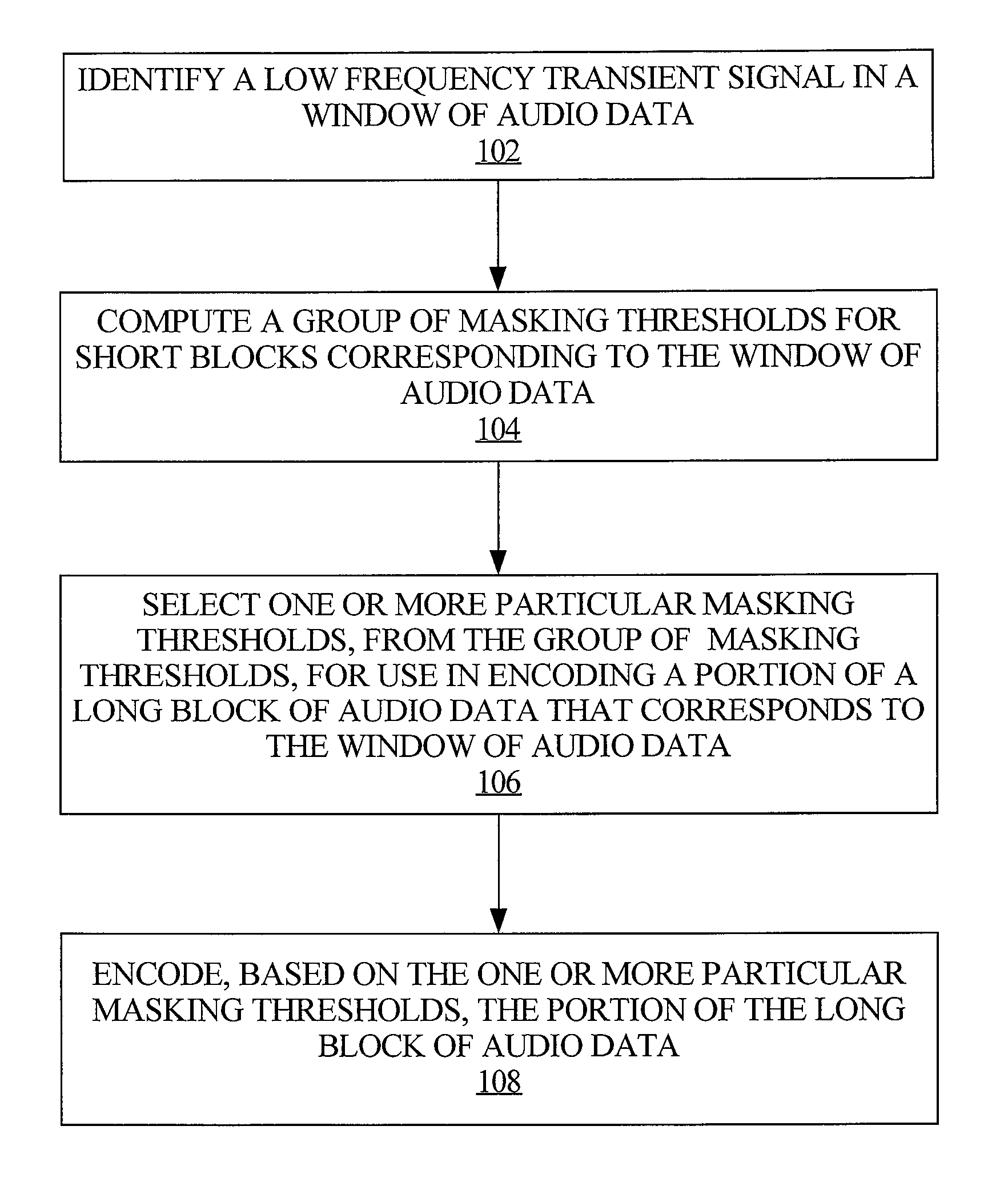
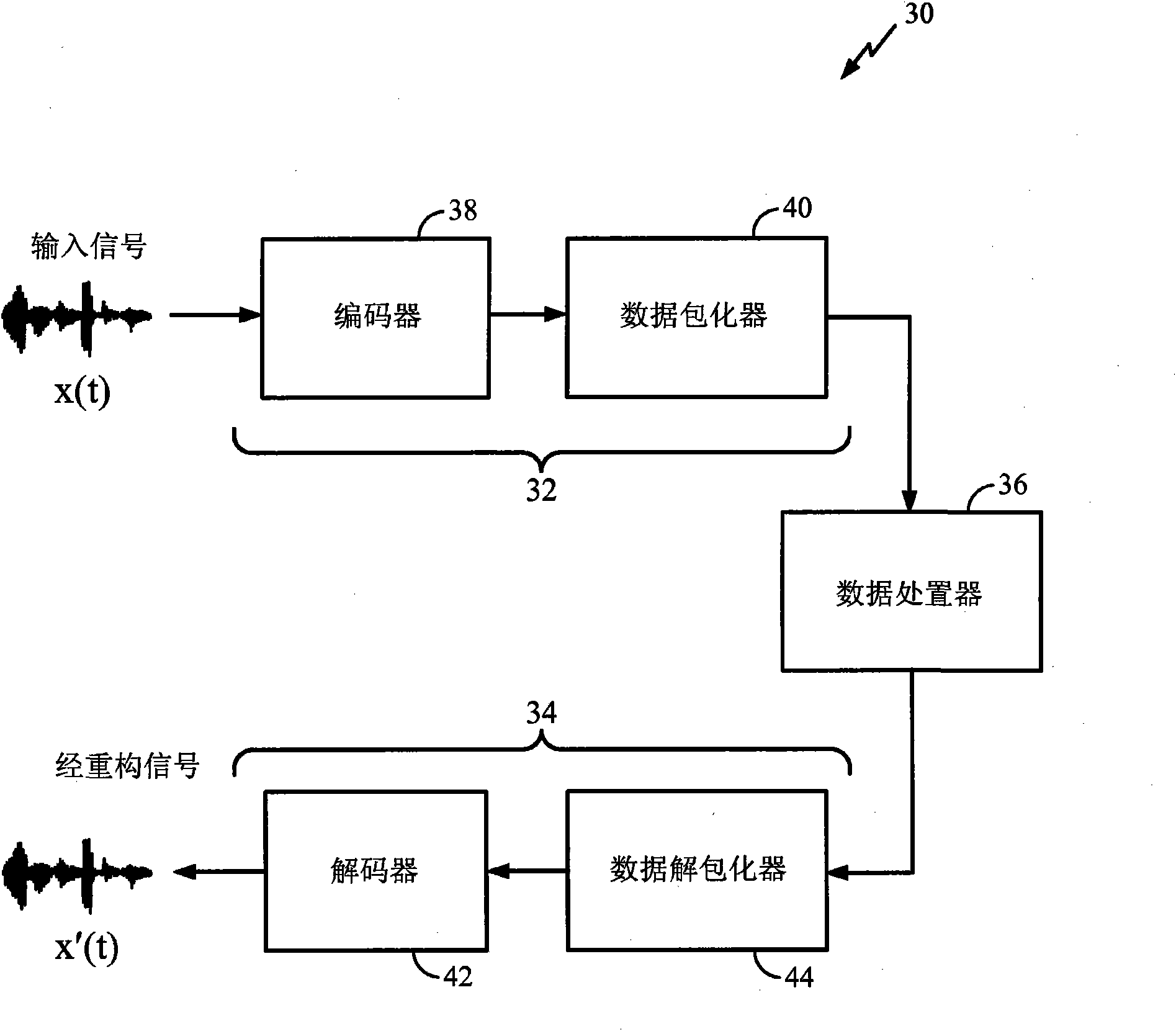
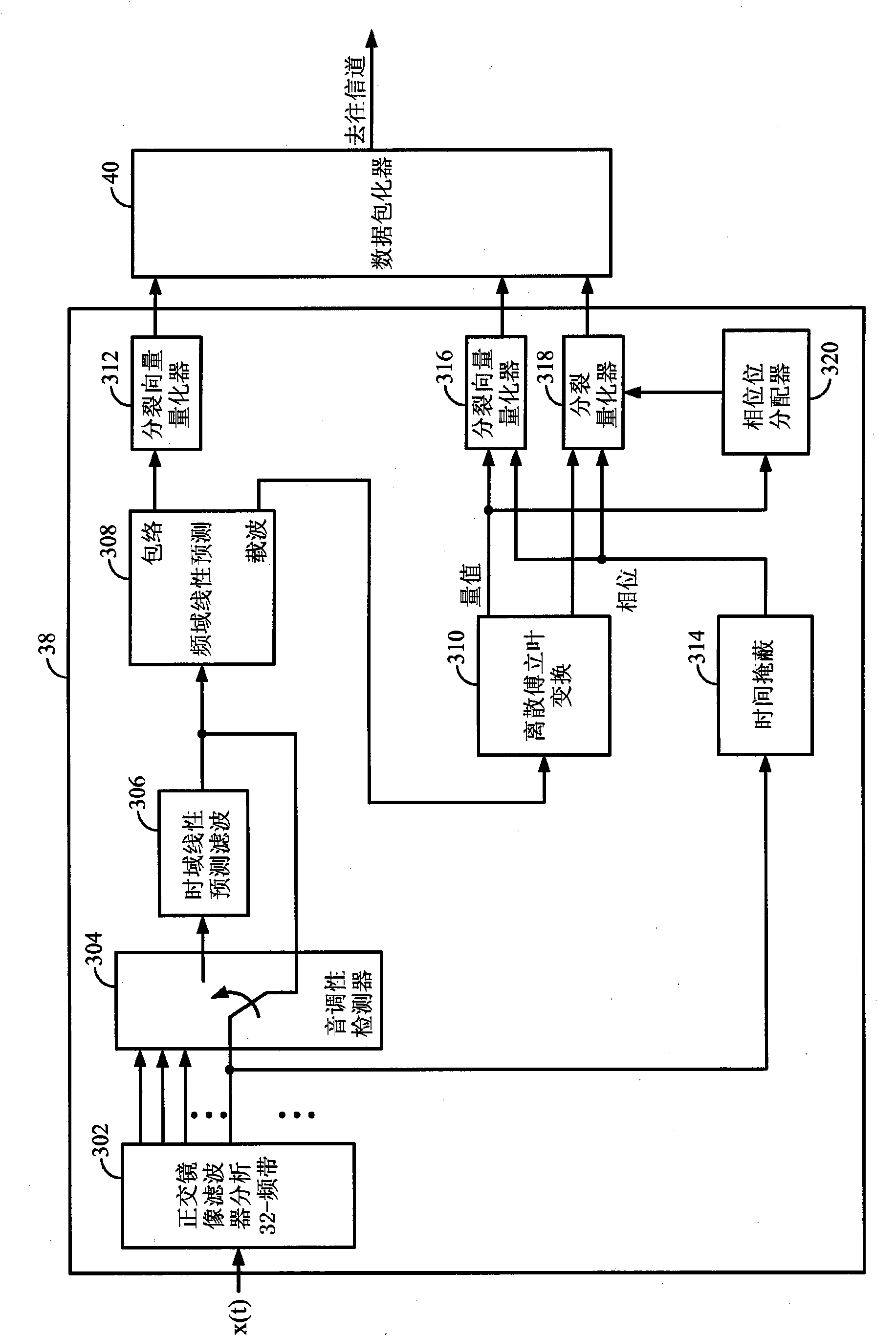
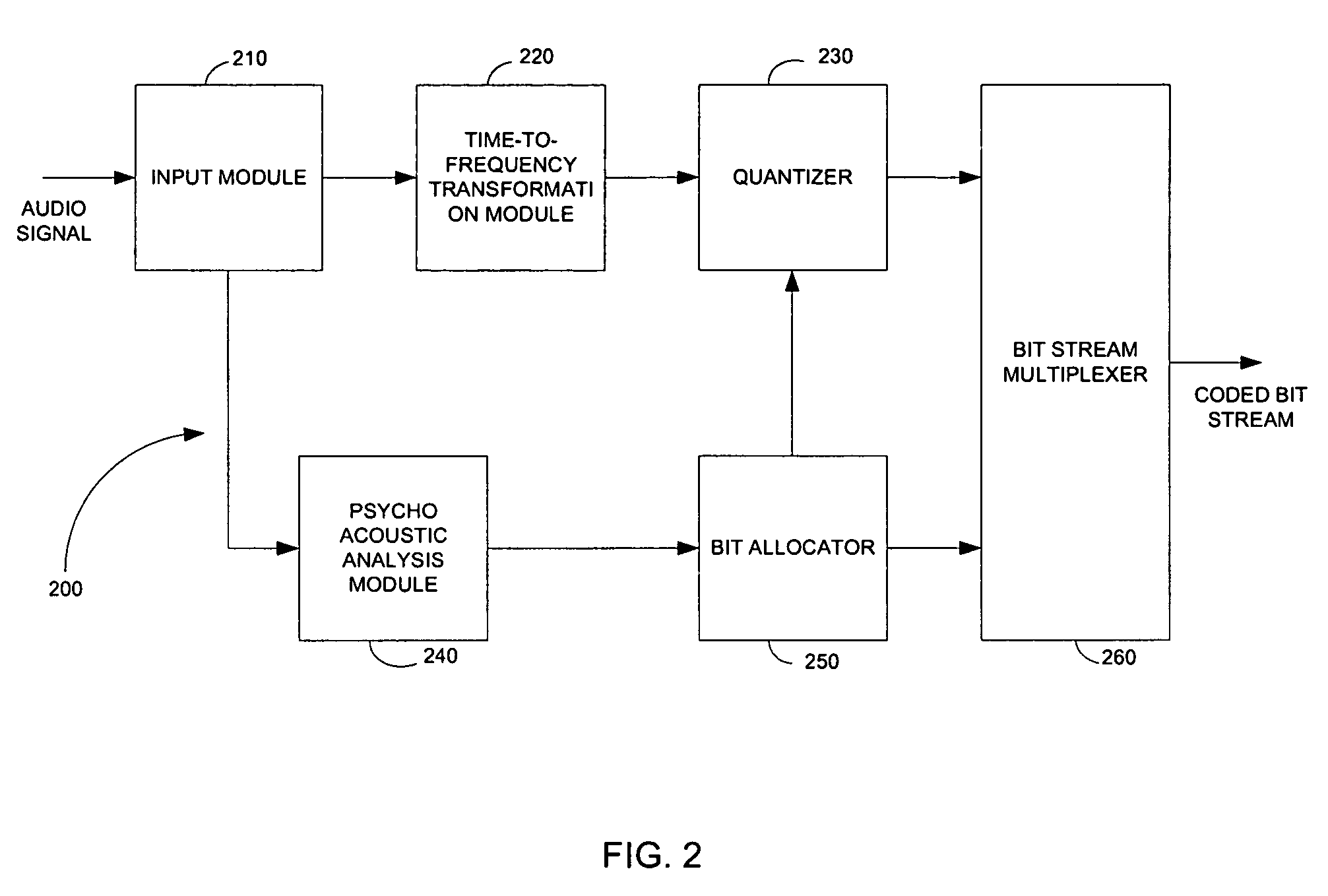
Adapting masking thresholds for encoding a low frequency transient signal in audio data
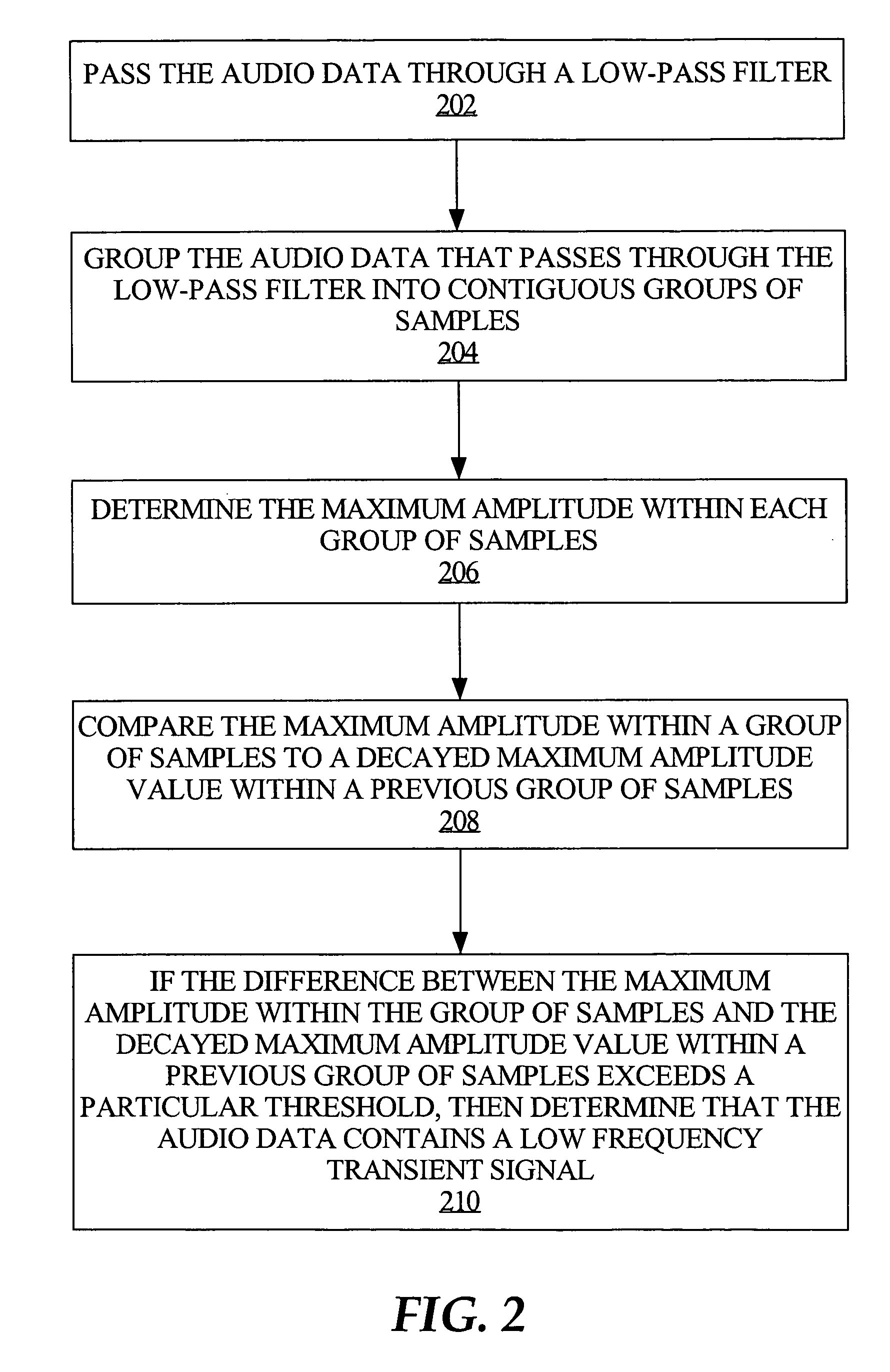
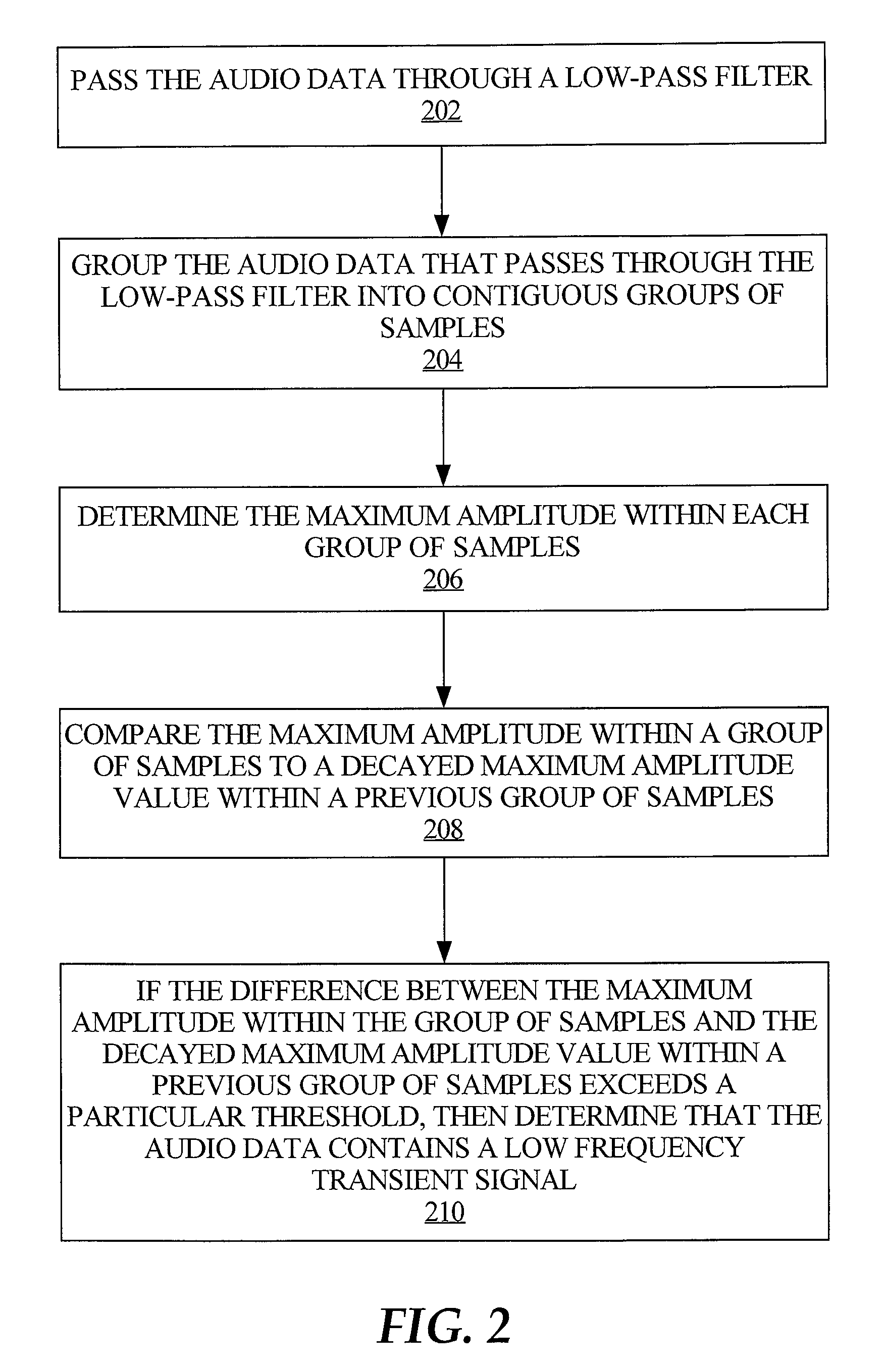
An improved audio coding technique encodes audio having a low frequency transient signal, using a long block, but with a set of adapted masking thresholds. Upon identifying an audio window that contains a low frequency transient signal, masking thresholds for the long block may be calculated as usual. A set of masking thresholds calculated for the 8 short blocks corresponding to the long block are calculated. The masking thresholds for low frequency critical bands are adapted based on the thresholds calculated for the short blocks, and the resulting adapted masking thresholds are used to encode the long block of audio data. The result is encoded audio with rich harmonic content and negligible coder noise resulting from the low frequency transient signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
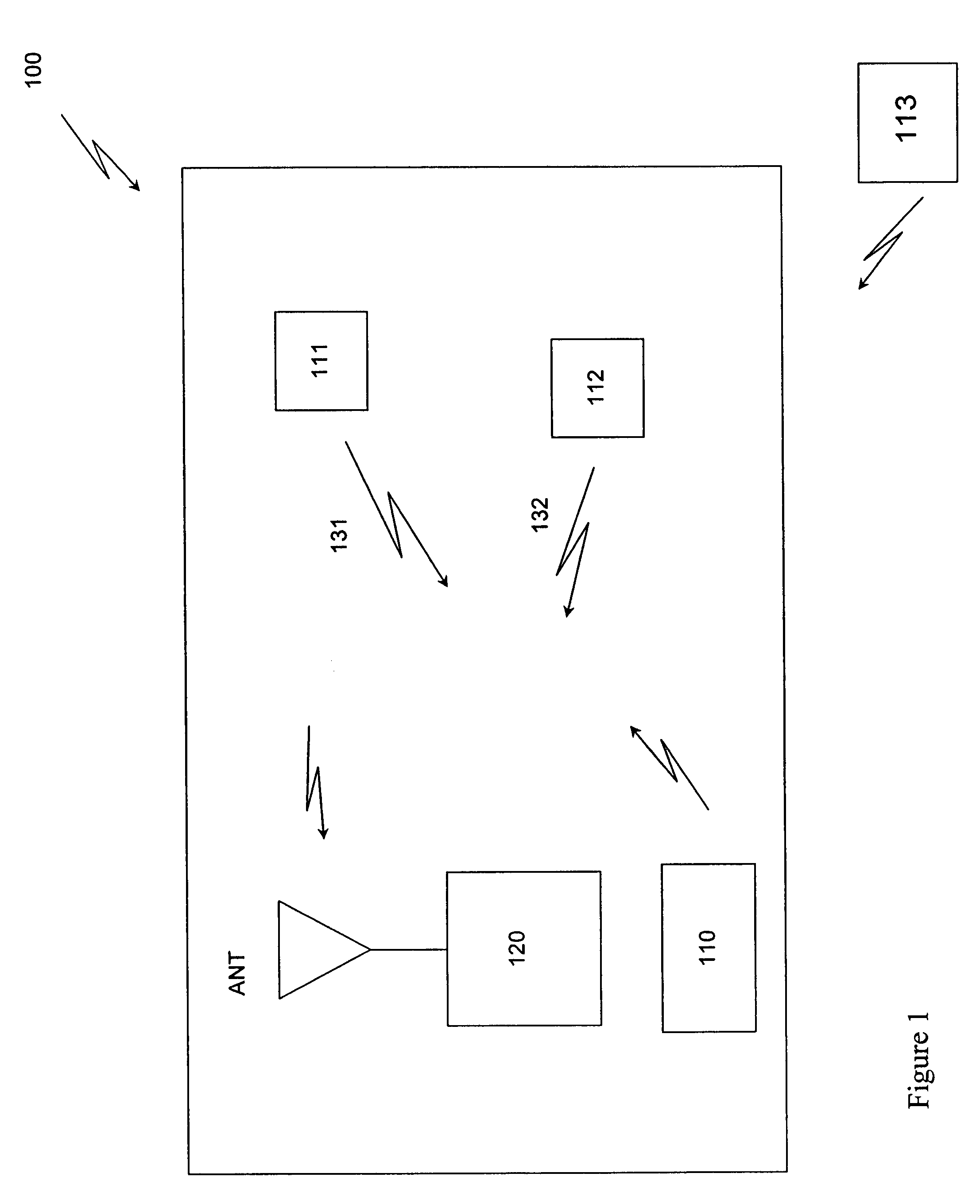
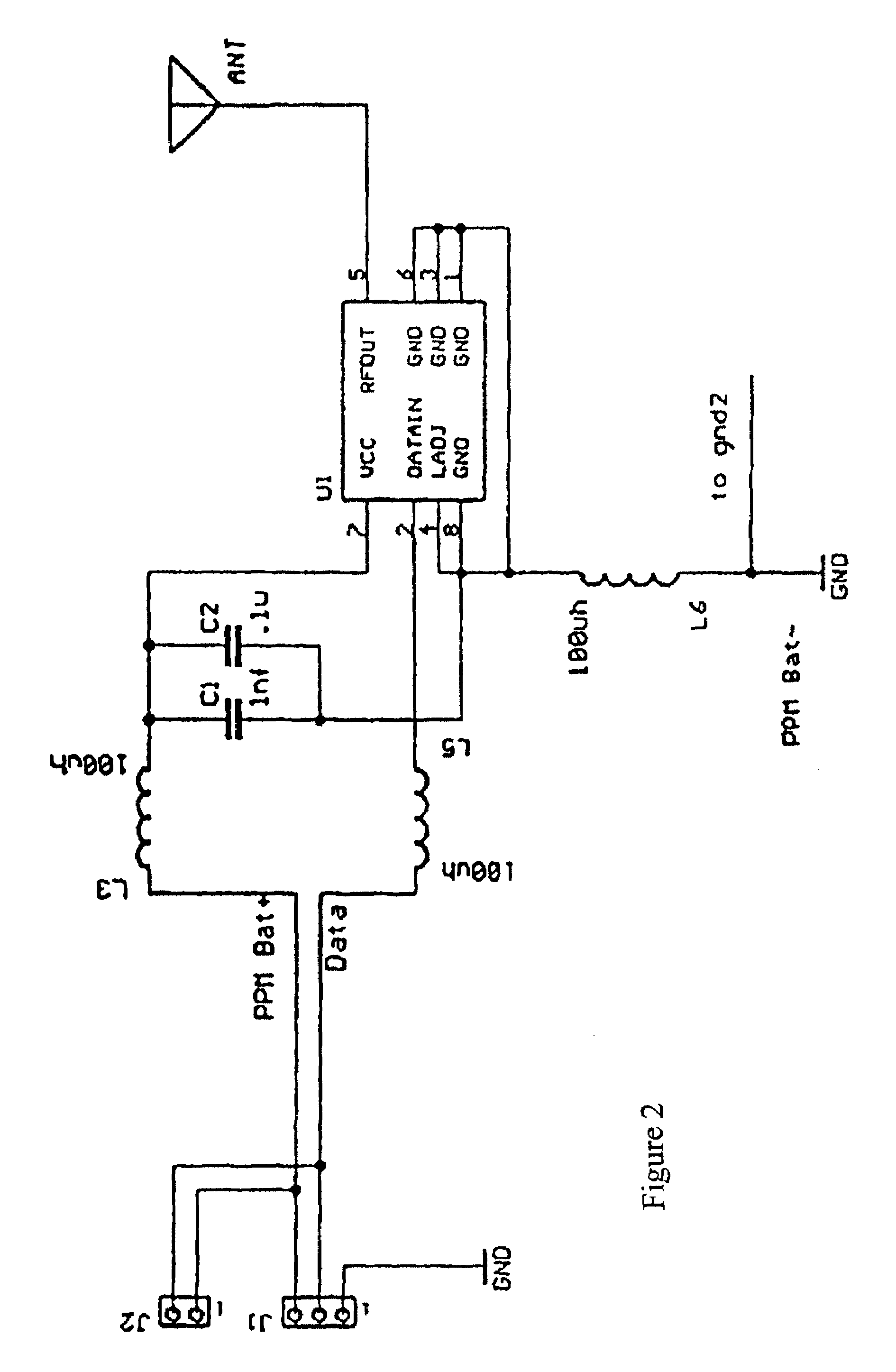
Radio frequency proximity detection and identification system and method
ActiveUS7460827B2System can be further enhancedAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionControl signalEngineering
Disclosed herein is a critical band encoding technology (CBET) system having at least one portable people meter (PPM) and a home base station and / or household hub, the CBET system containing a radio frequency (RF) proximity detection and identification system, comprising at least one RF transmitter for receiving a control signal, modulating an RF signal to a present modulation frequency upon receipt of the control signal, and wireless transmitting the modulated signal; and an RF receiver for receiving the wirelessly transmitted modulated signal, determining the modulation frequency, and transmitting the modulation frequency to a remote location, wherein the transmission power of the RF transmitter is preset to transmit the modulated data within a predetermined range.
Owner:NIELSEN HLDG NV +1
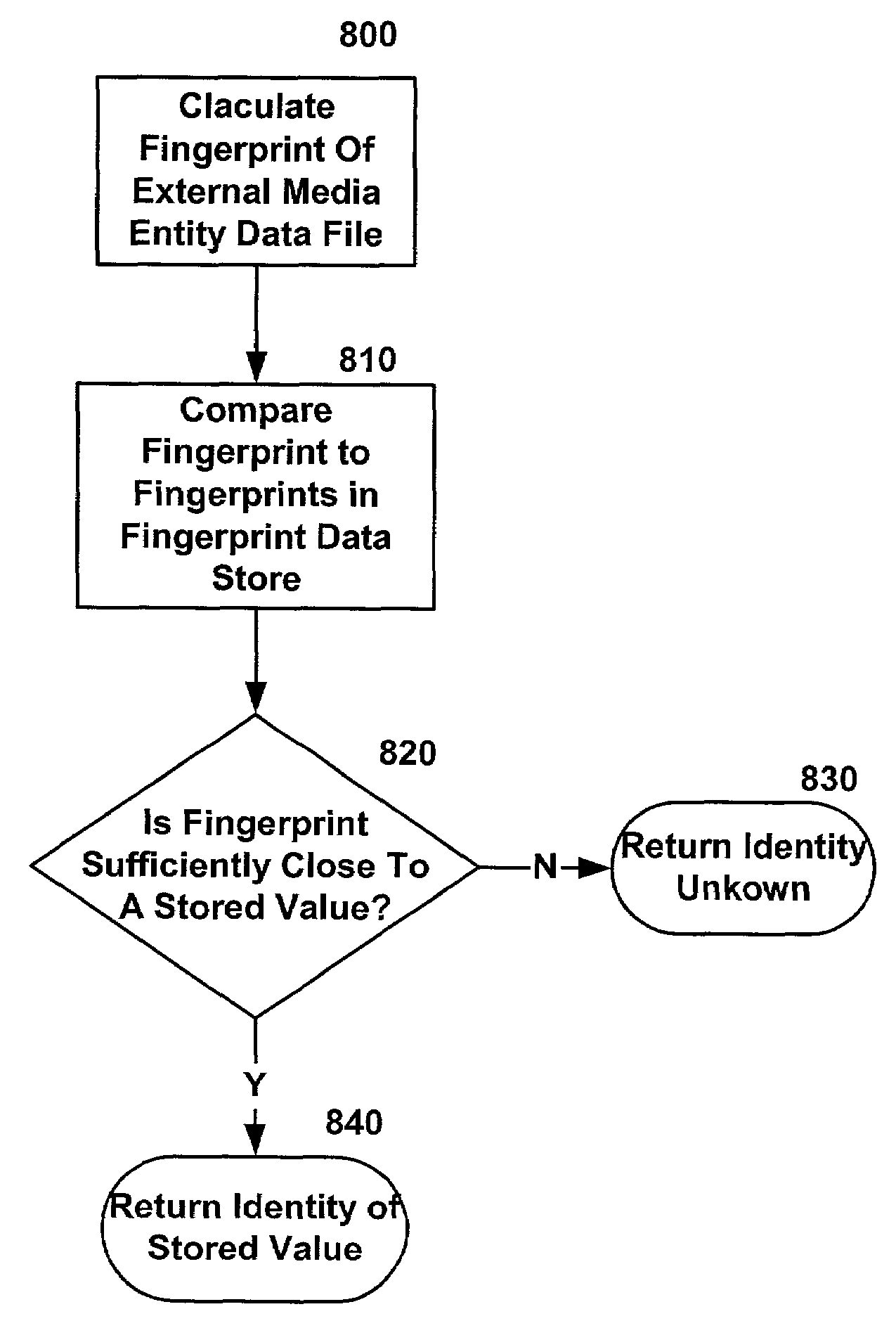
System and method for audio fingerprinting
InactiveUS6963975B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital signal processingInformation density
A system and methods for the creation, management, and distribution of media entity fingerprinting are provided. In connection with a system that convergently merges perceptual and digital signal processing analysis of media entities for purposes of classifying the media entities, various means are provided to a user for automatically processing fingerprints for media entities for distribution to participating users. Techniques for providing efficient calculation and distribution of fingerprints for use in satisfying copyright regulations and in facilitating the association of meta data to media entities are included. In an illustrative implementation, the fingerprints may be generated and stored allowing for persistence of media from experience to experience. In various non-limiting embodiments, the processing of fingerprints includes calculating the average information density of the media entities, determining the standard deviation of the calculated information of the media entities, calculating the average critical band energy of the media entities, calculating the average standard deviation of the critical band energy of the media entities, determining the play-time of the media entities and processing the information density, the standard deviation of the information density, the critical band energy, the standard deviation of the critical band, and the play time to produce a bit-sequence representative of the fingerprint.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Sound device and sound control device
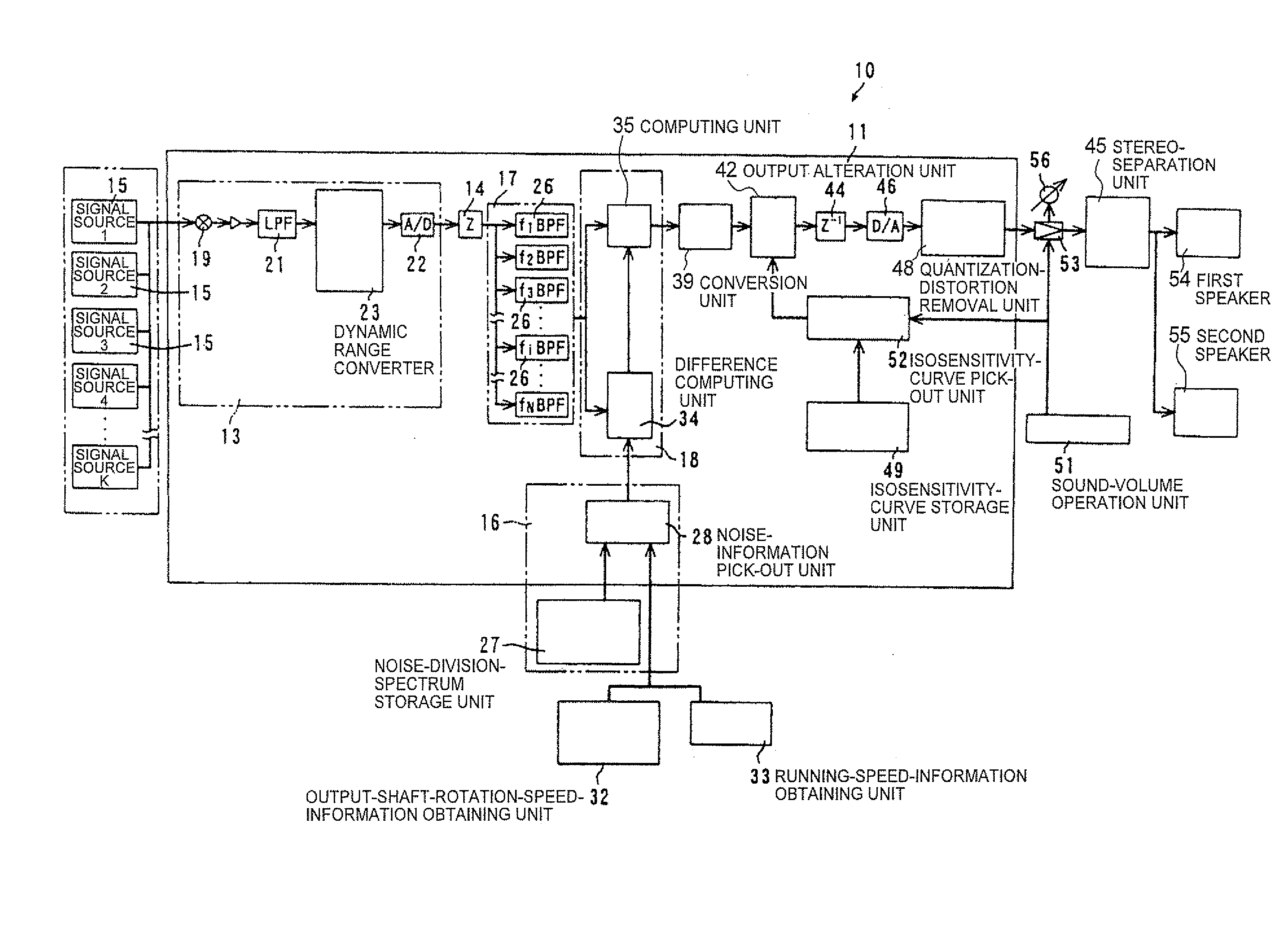
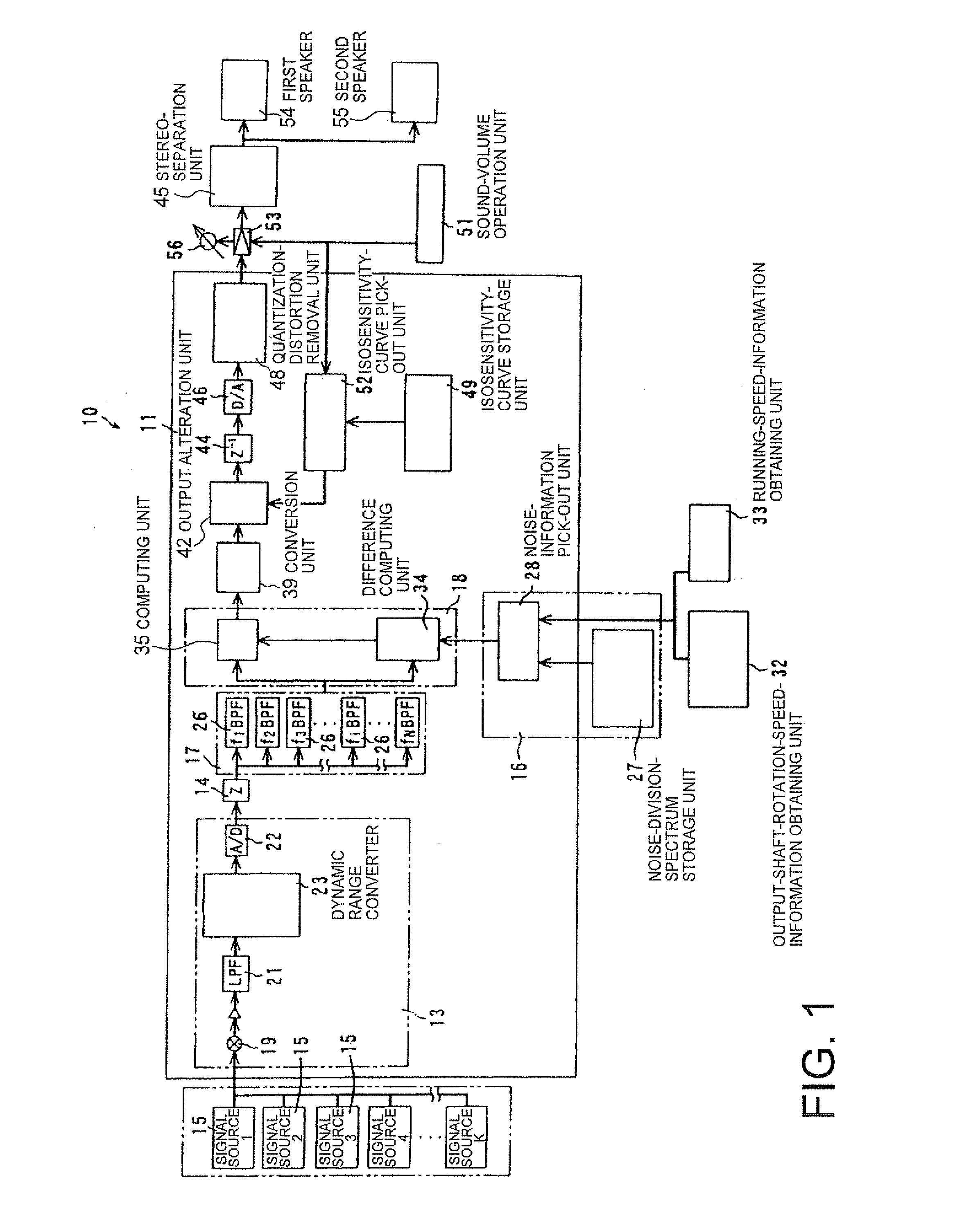
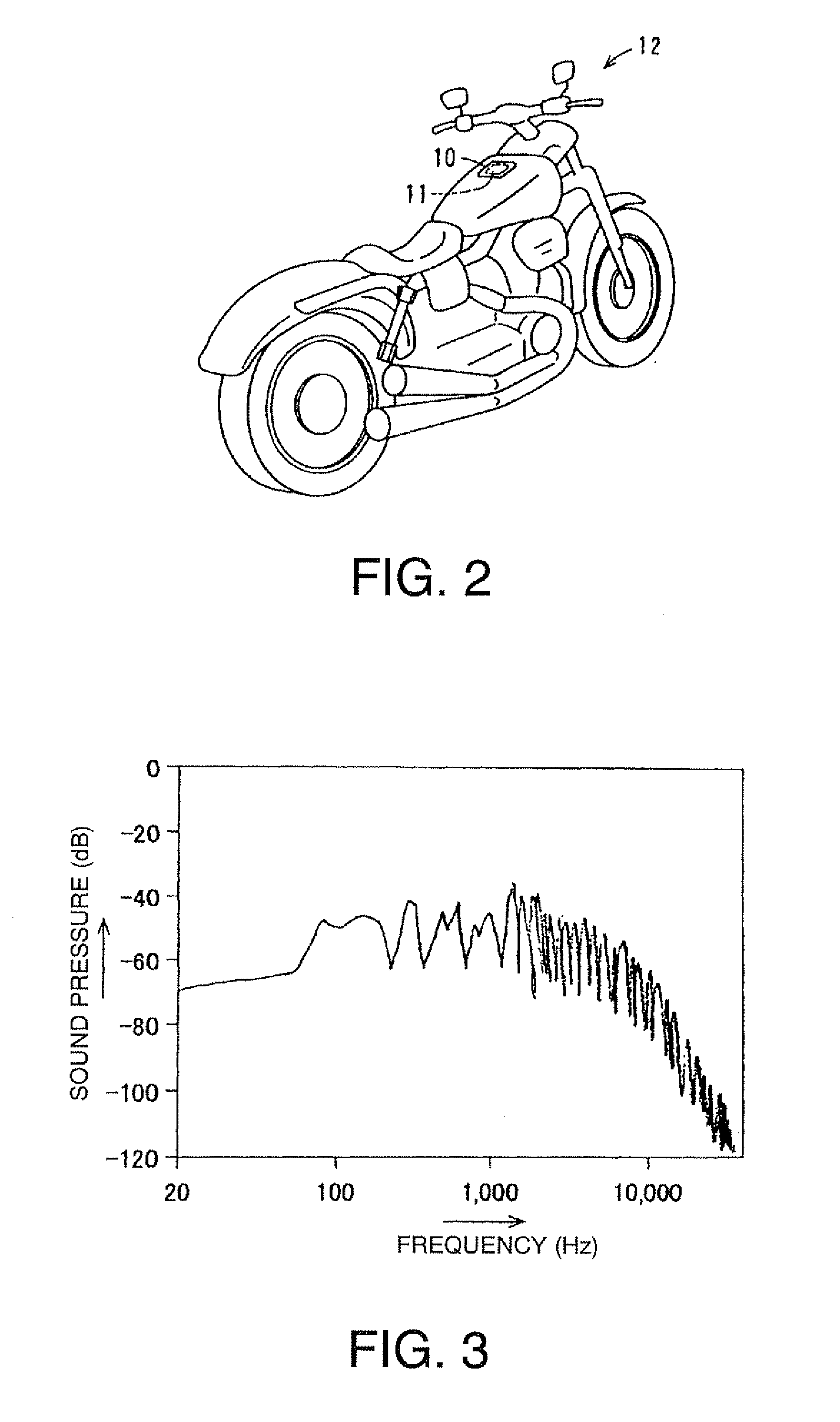
The sound device includes an audio-information output unit, an analysis unit, an audio-division-spectrum output unit, a noise-division-spectrum output unit and a correction unit. The analysis unit receives audio information from the audio-information output unit, and then outputs sound spectrum information. The noise-division-spectrum output unit outputs sound-volume information for each critical band width of a noise, and the audio-division-spectrum output unit outputs the sound-volume information for each critical band width of the sound-spectrum information. The correction unit corrects the information from the audio-division-spectrum output unit based on the information from the noise-division-spectrum output unit. The audio-signal properties can be well corrected corresponding to the auditory-sense properties of the human, and thus the audio sound, in which an uncomfortable feeling to the auditory sense of the human has been adequately controlled, can be transmitted to a user.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
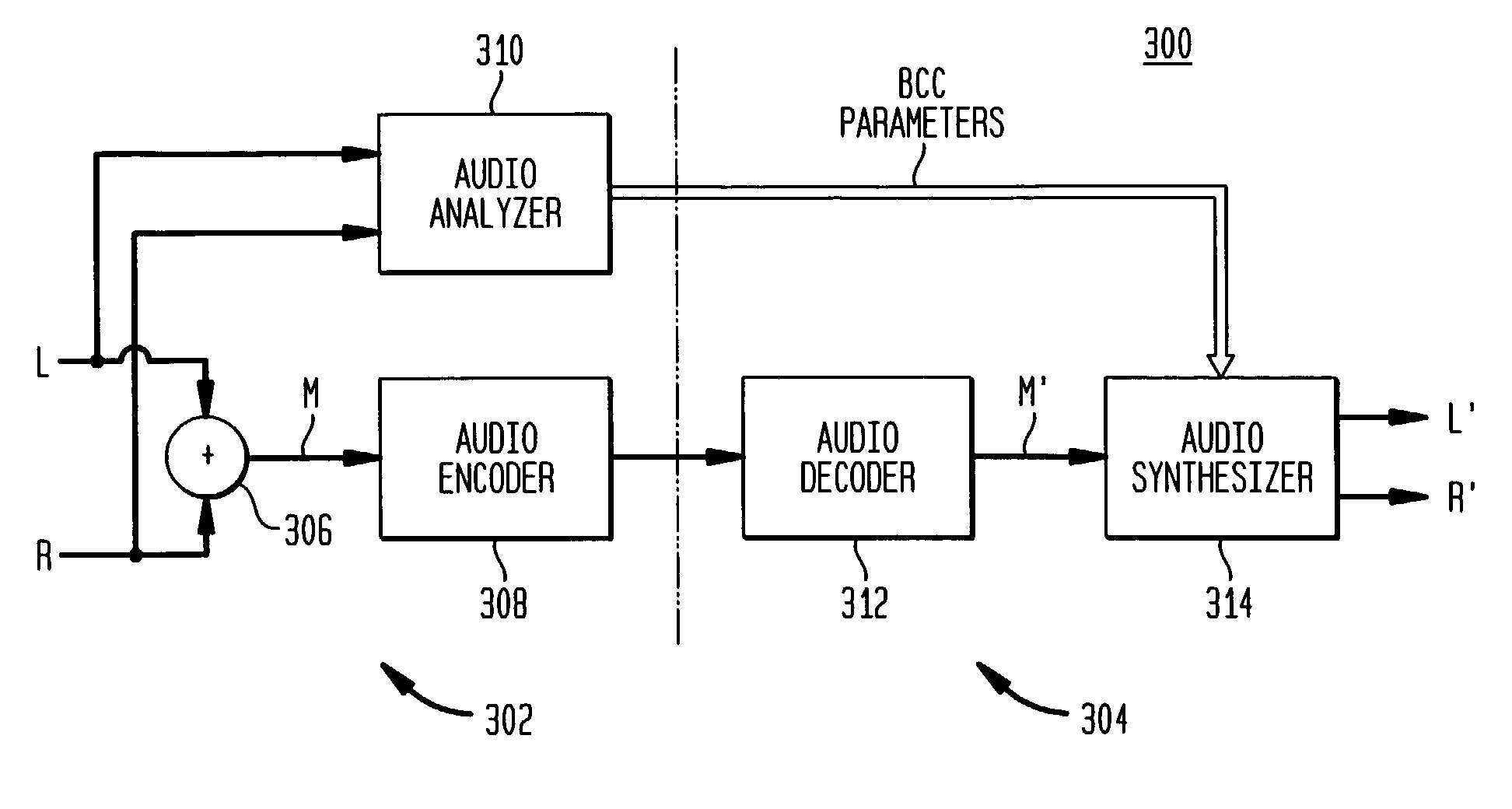
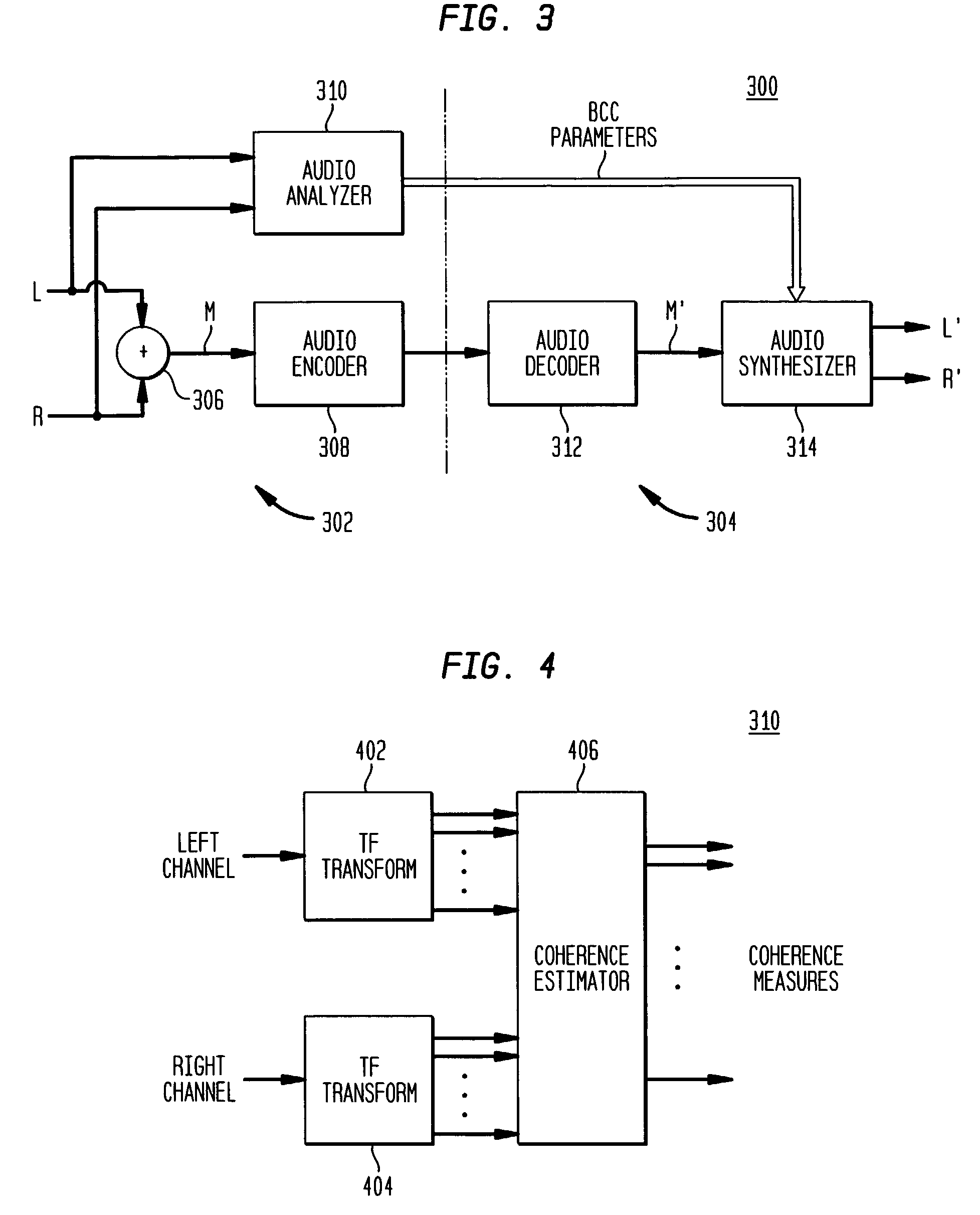
Coherence-based audio coding and synthesis
InactiveUS7006636B2Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsInteraural time differenceVocal tract
An auditory scene is synthesized from a mono audio signal by modifying, for each critical band, an auditory scene parameter (e.g., an inter-aural level difference (ILD) and / or an inter-aural time difference (ITD)) for each sub-band within the critical band, where the modification is based on an average estimated coherence for the critical band. The coherence-based modification produces auditory scenes having objects whose widths more accurately match the widths of the objects in the original input auditory scene.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
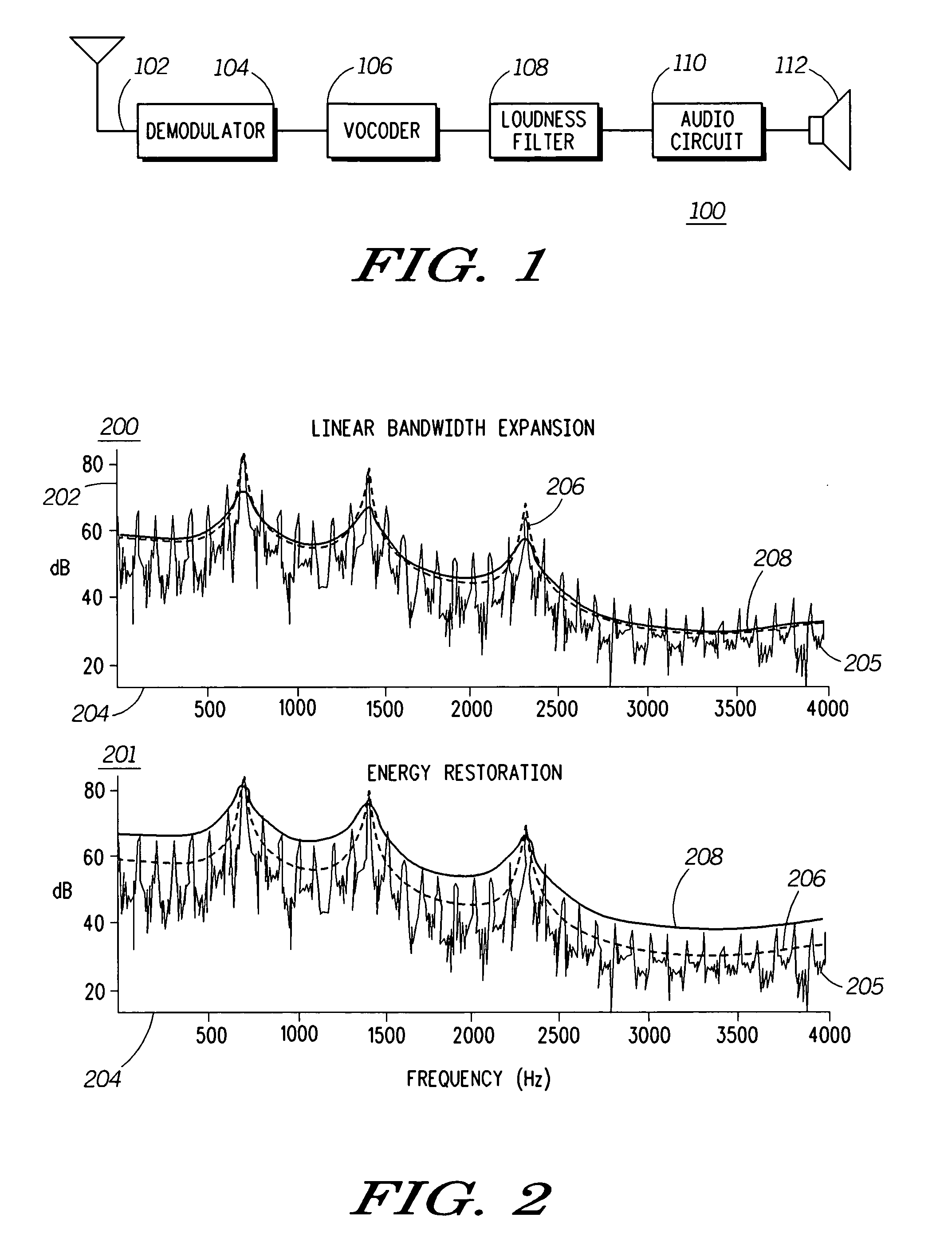
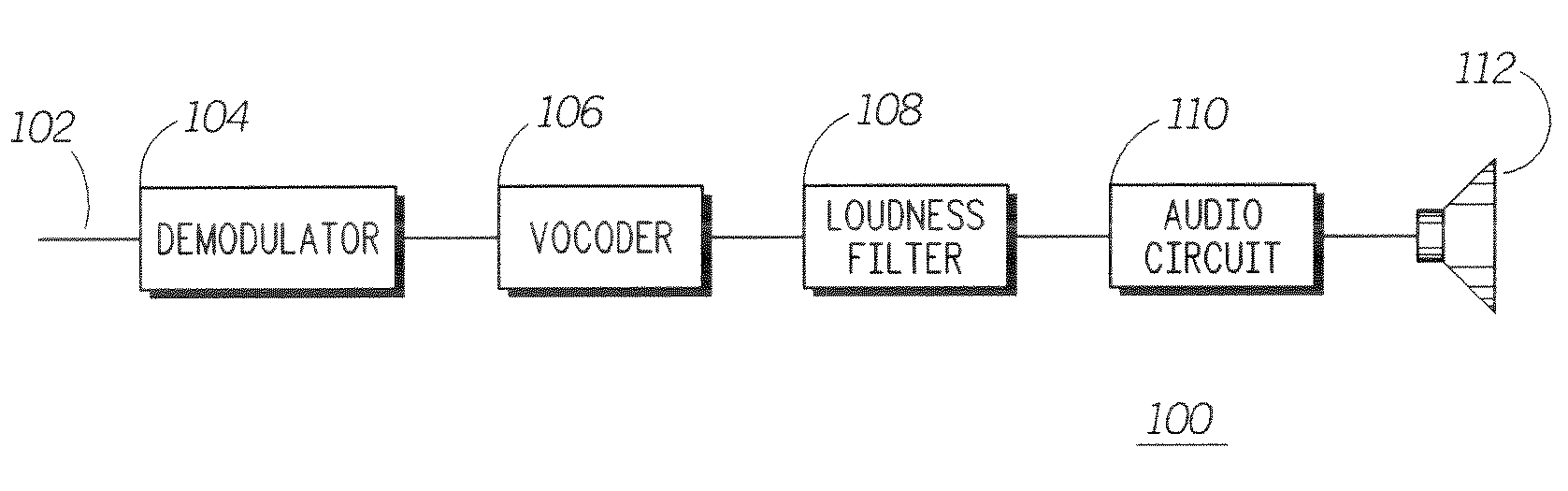
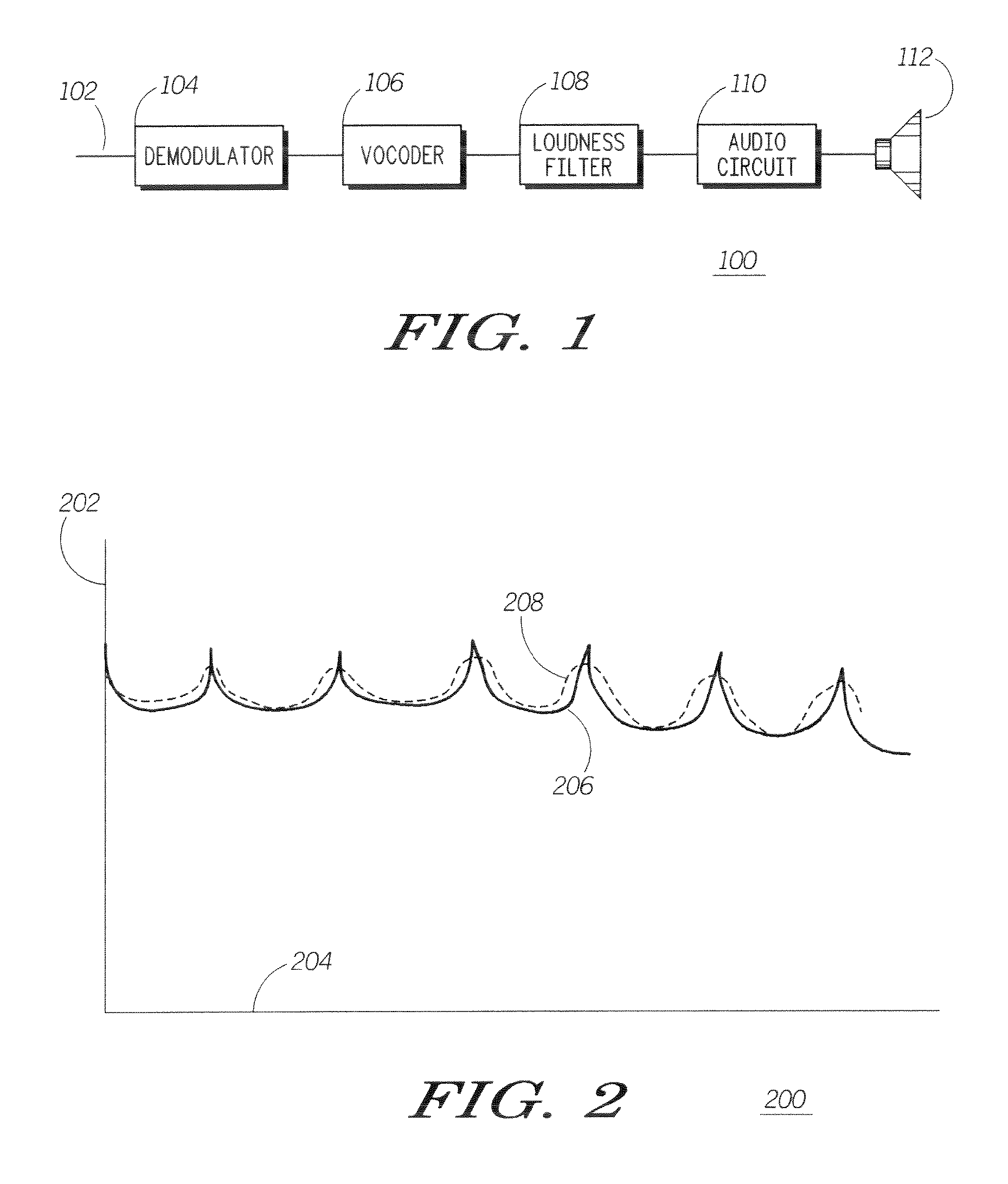
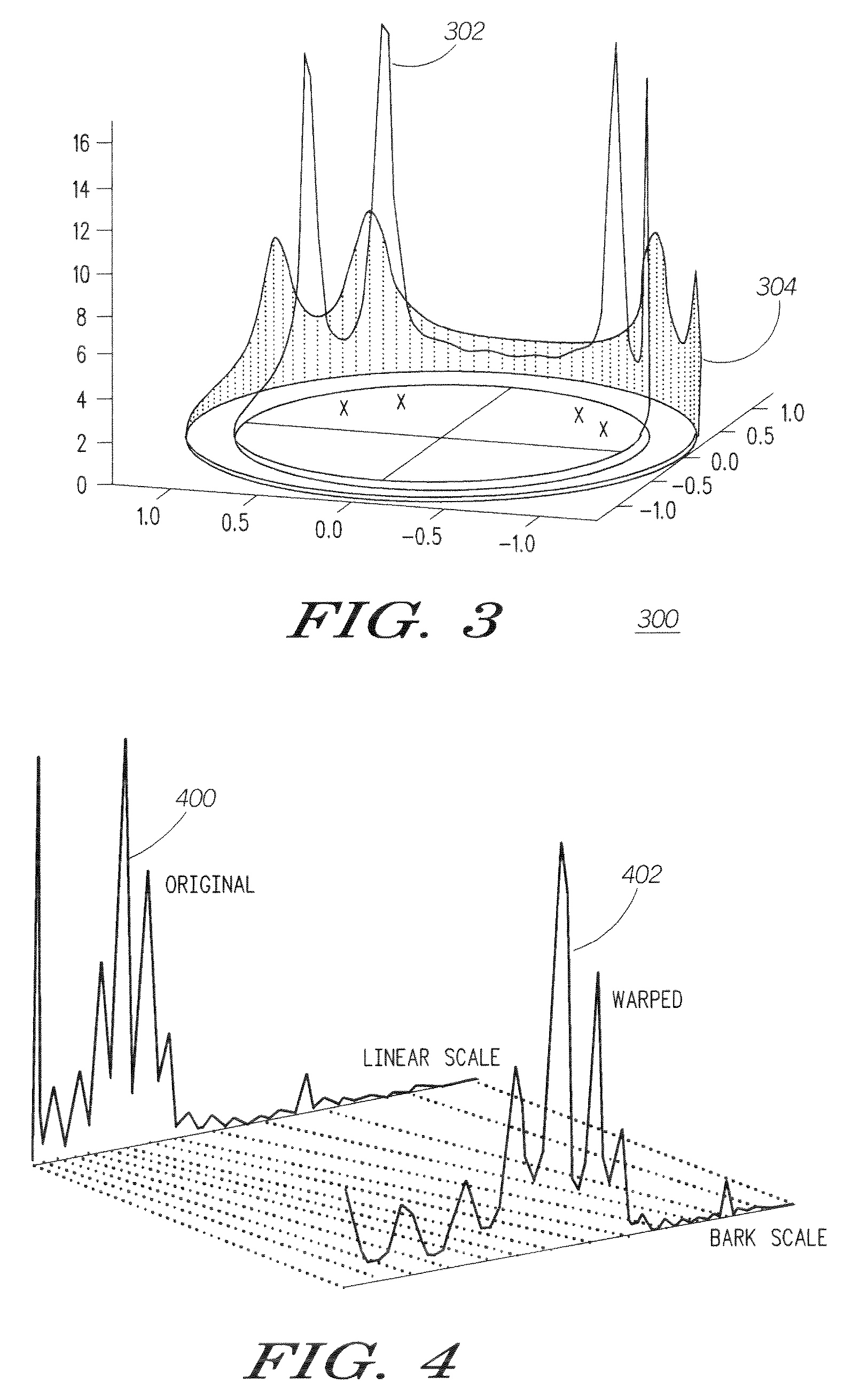
Method and apparatus for enhancing loudness of a speech signal
A speech filter (108) enhances the loudness of a speech signal by expanding the formant regions of the speech signal beyond a natural bandwidth of the formant regions. The energy level of the speech signal is maintained so that the filtered speech signal contains the same energy as the pre-filtered signal. By expanding the formant regions of the speech signal on a critical band scale corresponding to human hearing, the listener of the speech signal perceives it to be louder even though the signal contains the same energy.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Electronic sound screening system and method of accoustically impoving the environment
A flexible apparatus for, and method of, acoustically improving an environment permits manual adjustment by one or more local or remote users using a simple graphical interface and automatic adjustment of the system parameters once the manual adjustment is performed. The inputs are weighted by distance from the physical apparatus. The apparatus includes a receiver, a converter, an analyser, a processor and a sound generator. The acoustic energy impinges on the receiver and is converted to an electrical signal by the converter. The analyser receives the electrical signal from the receiver, analyzes the electrical signal, and generates data analysis signals in response to the analyzed electrical signal. The processor produces sound signals based on the data analysis signals from the analyser in each critical band. The sound generator provides sound based on the sound signals. This permits the users to define the sound heard in a set space.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF ART +1
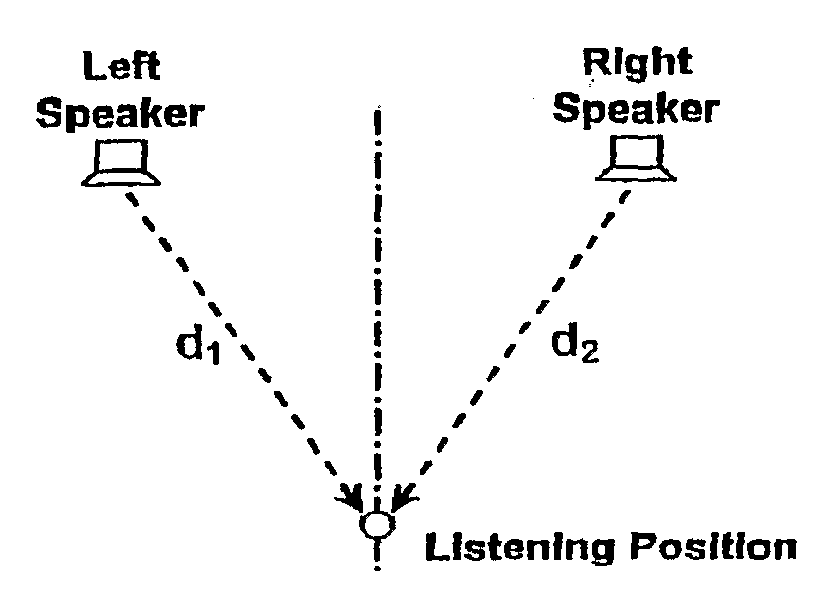
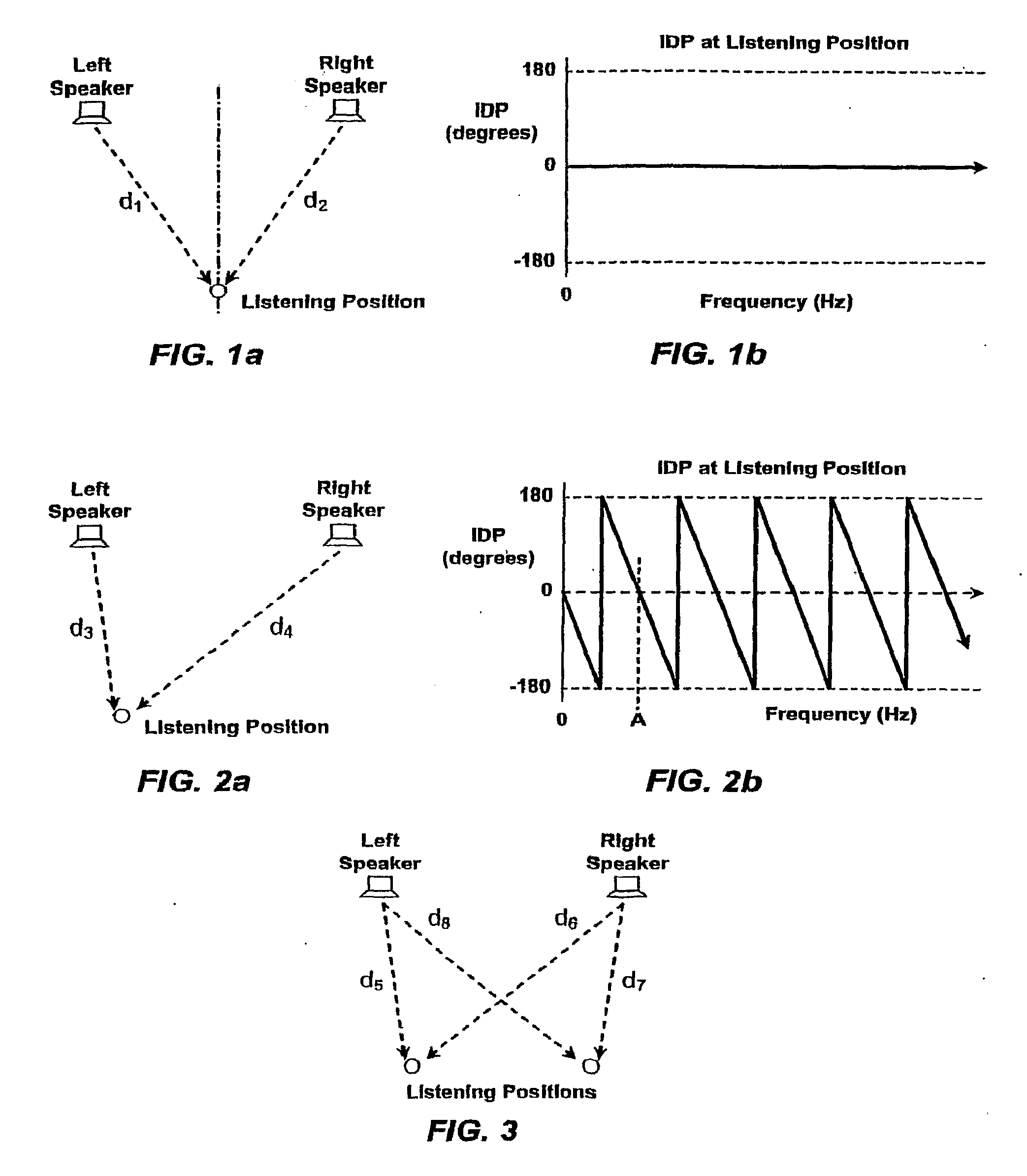
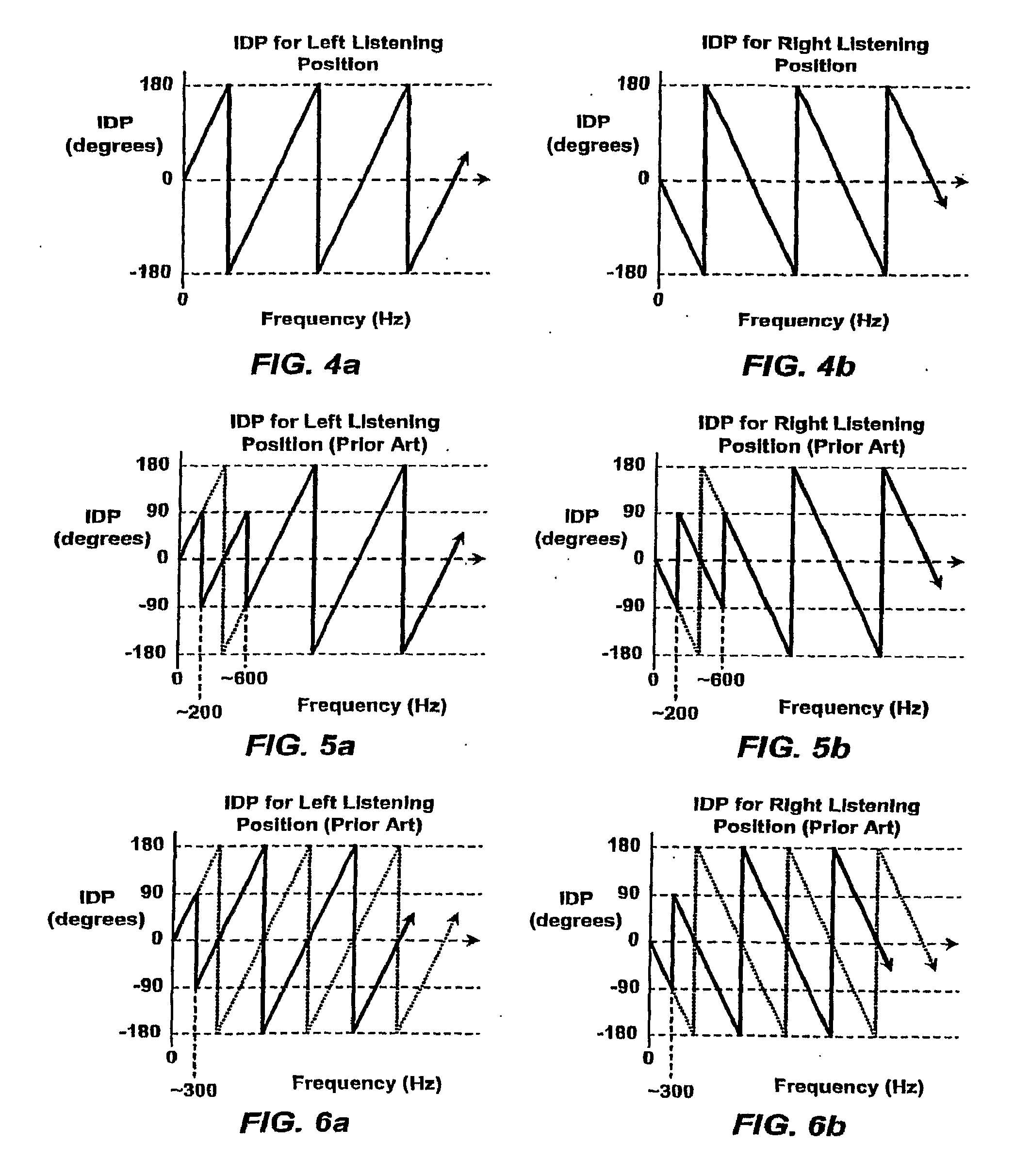
Stereophonic Sound Imaging
InactiveUS20090304213A1Improve perceived imaging of audio signalPseudo-stereo systemsTwo-channel systemsPhase differenceVocal tract
A method for reducing phase differences varying with frequency occurring at certain listening positions with respect to loudspeakers reproducing respective ones of multiple sound channels in a listening space, the phase differences occurring in a sequence of frequency bands in which the phase differences alternate between being predominantly in-phase and predominantly out-of-phase, comprises adjusting the phase in multiple frequency bands in which the multiple sound channels are out-of-phase at such listening positions. Such adjustment of phase includes the frequency bands in which the width of comb filtering pass bands and notches resulting from phase differences at such listening positions would be greater than or commensurate with the critical band width if the phase adjustment were not applied. The listening space may be the interior of a vehicle.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Digital deaf-aid frequency response compensation method based on mask curve
InactiveCN1870135AResolve claritySolve the problem of decreased intelligibilitySpeech analysisDeaf-aid setsMasking thresholdFrequency response
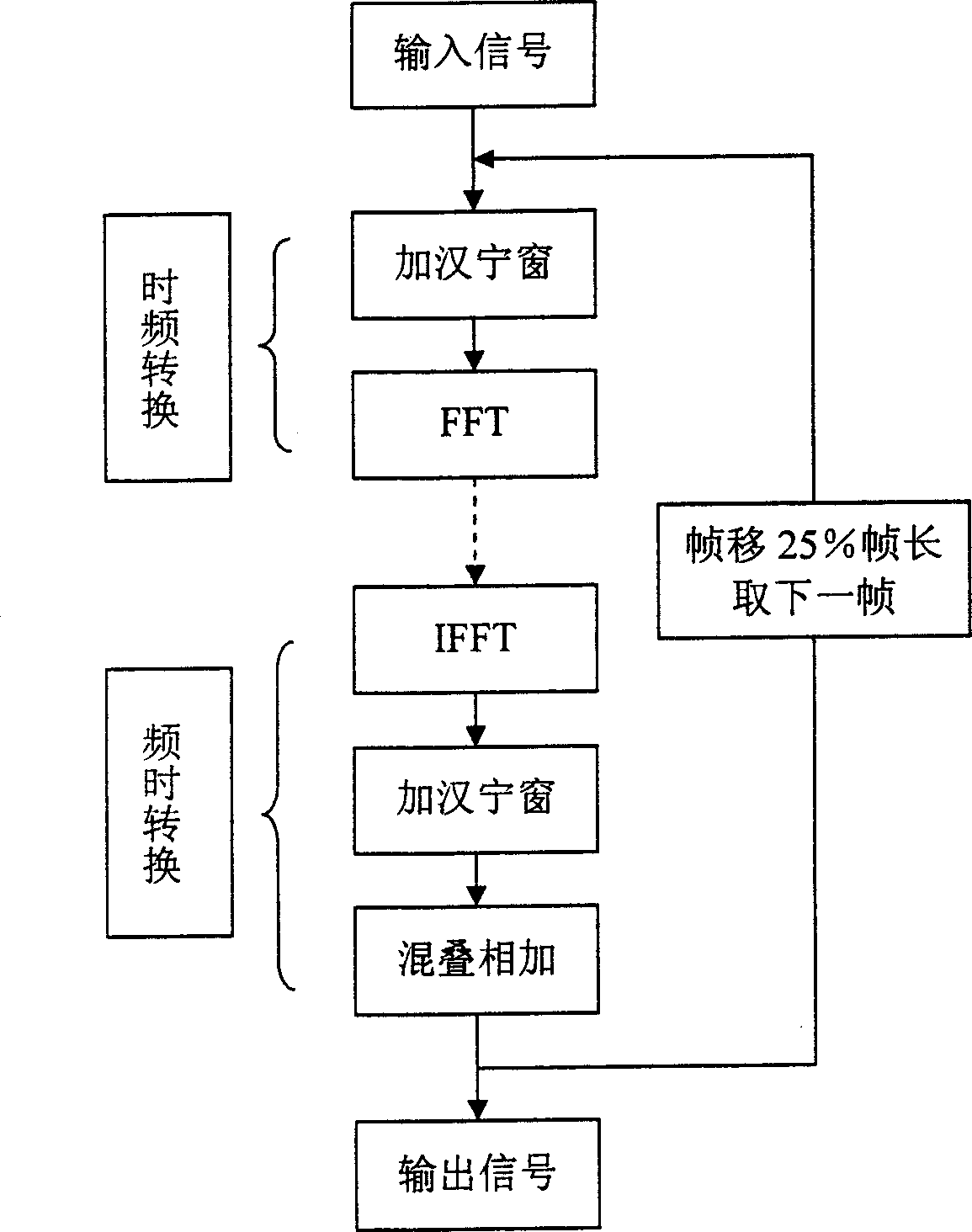
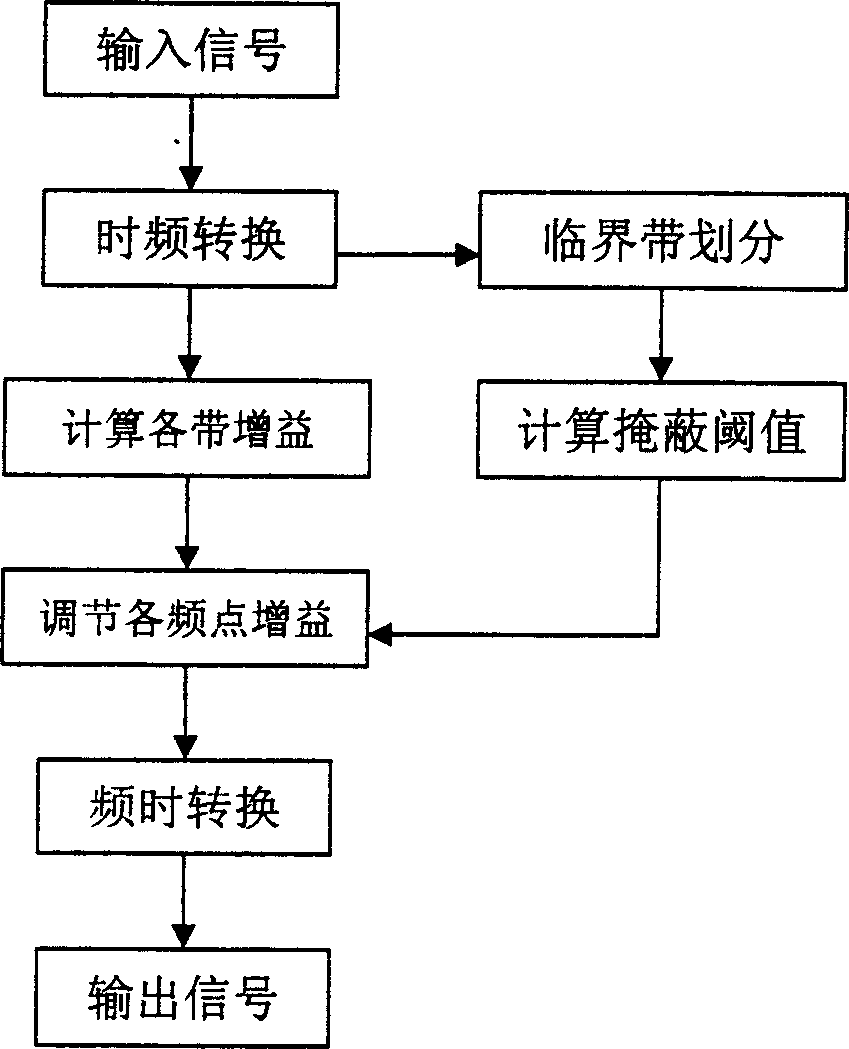
A method for compensating frequency response of digital deaf-aid based on masked curve includes techniques of time frequency domain switch-over, critical band division, masking threshold calculation and frequency response compensation to improve hearing threshold rising phenomenon caused by hearing-masking effect.
Owner:北达万坤(北京)科技发展有限公司
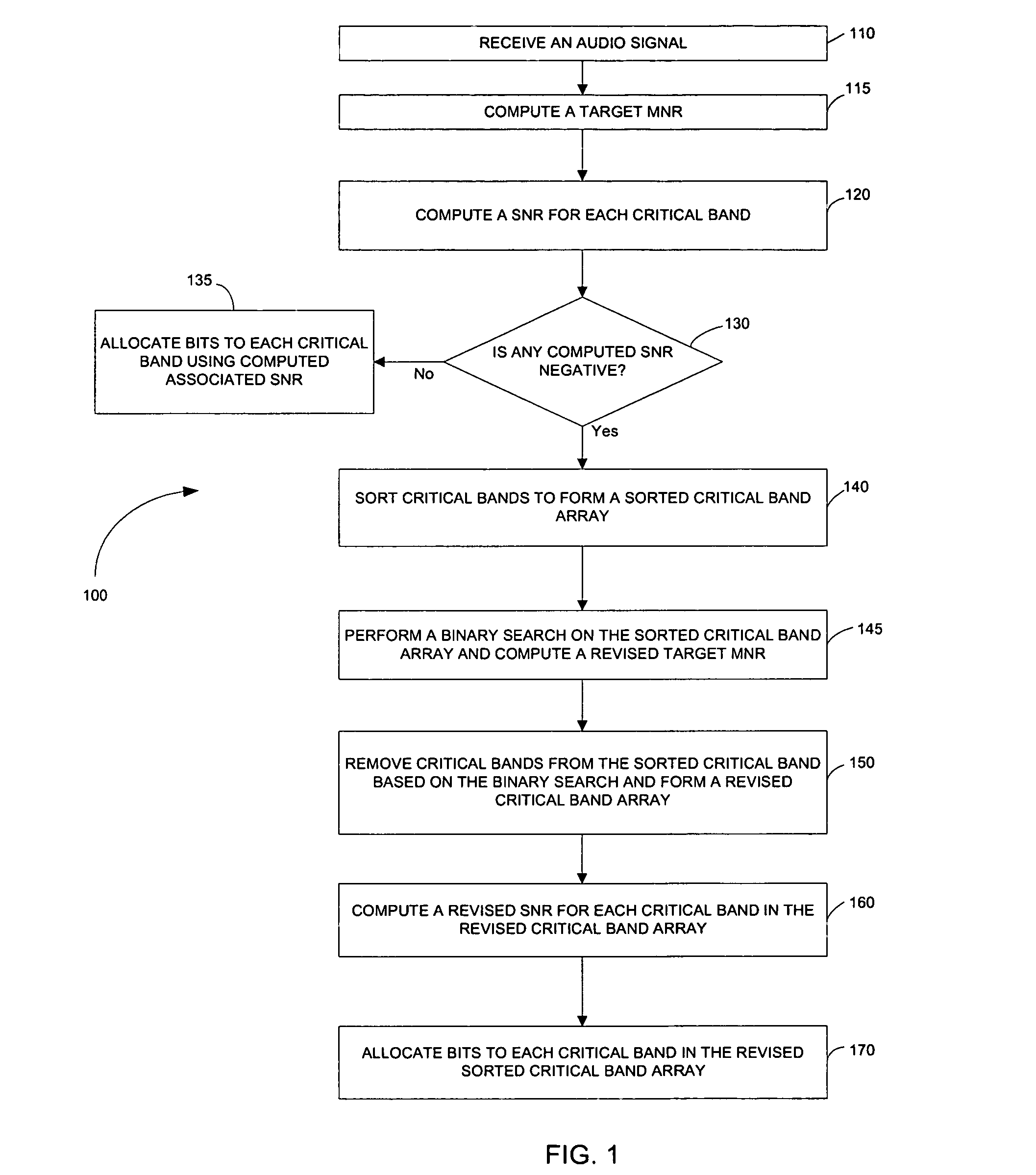
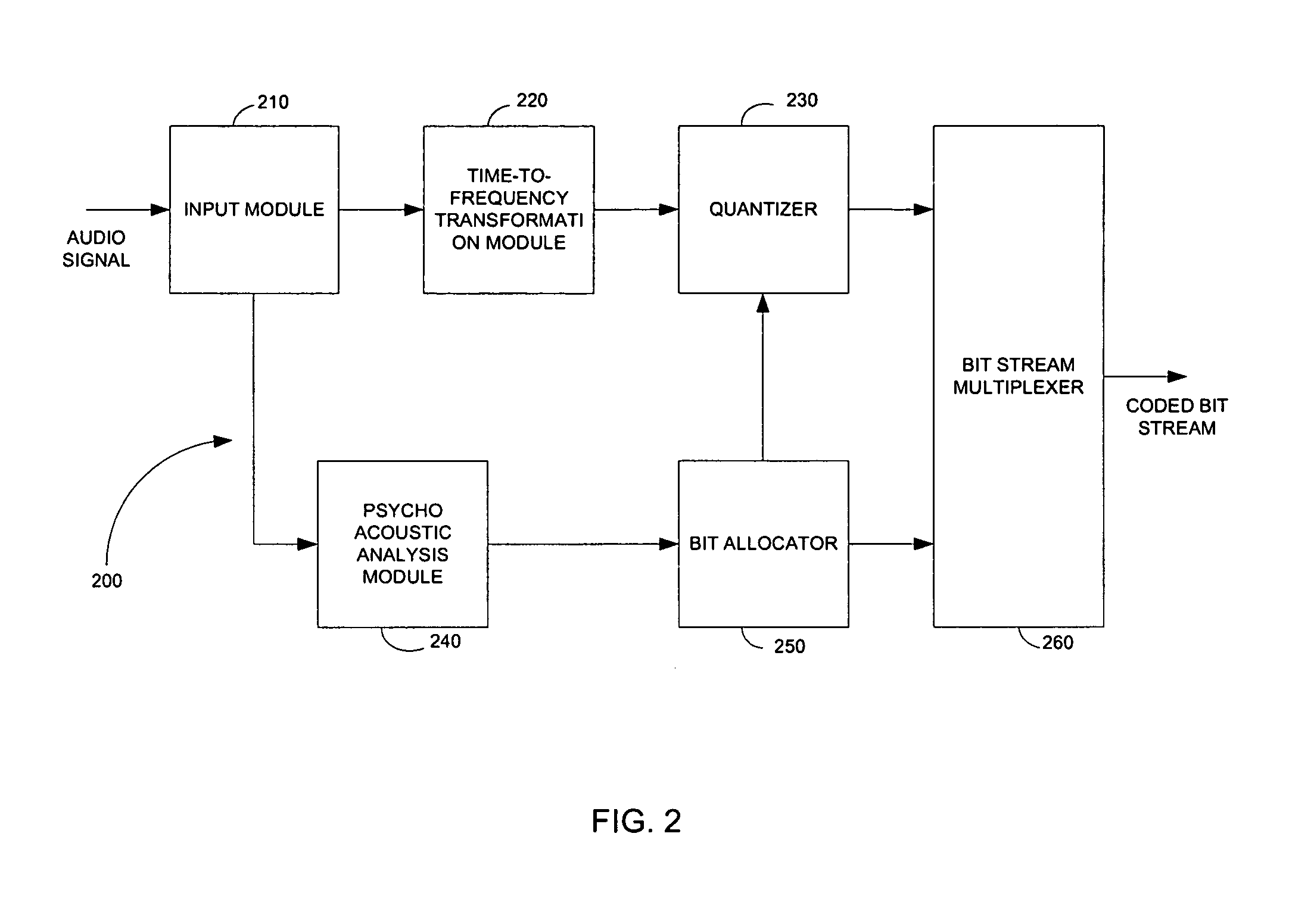
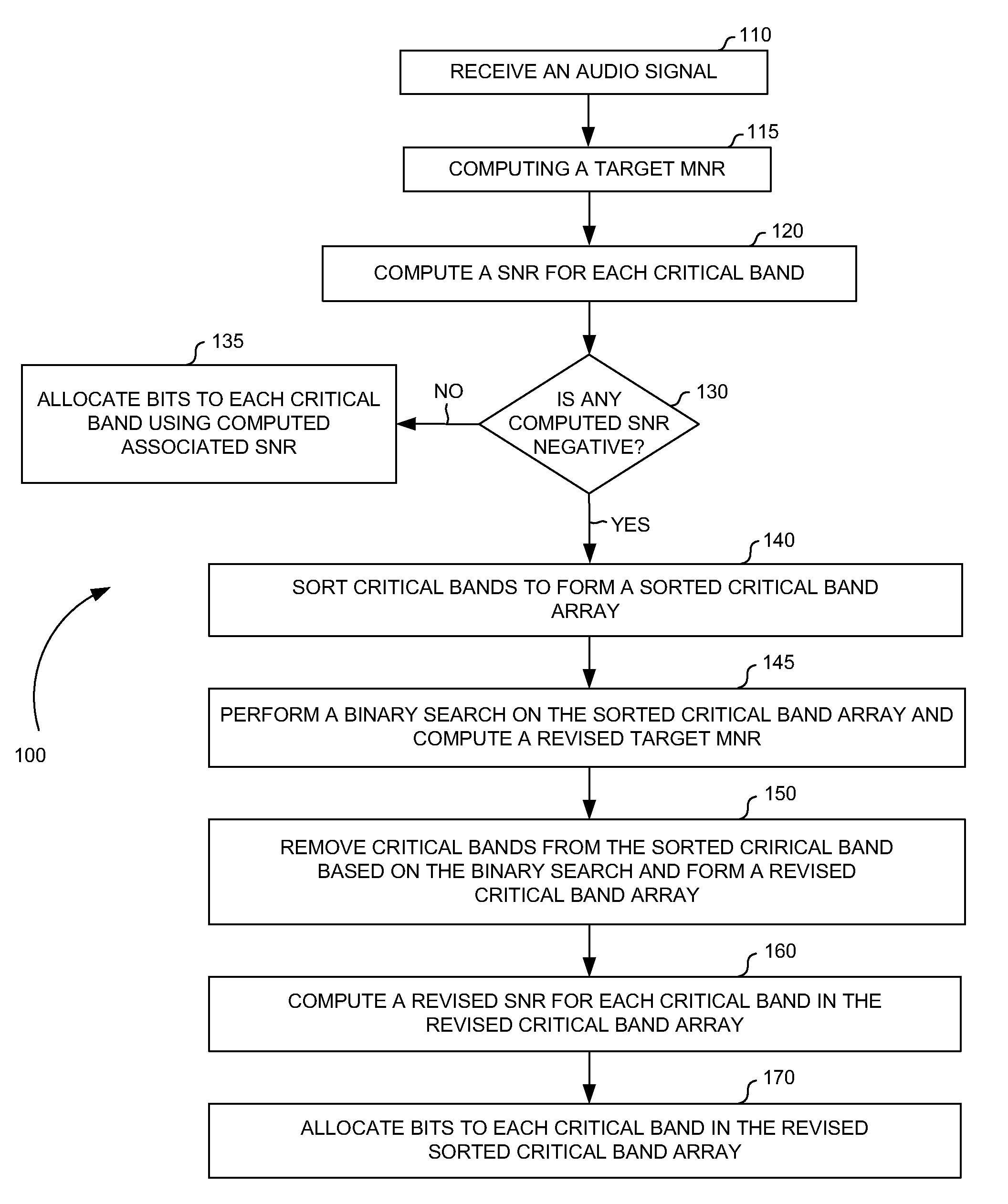
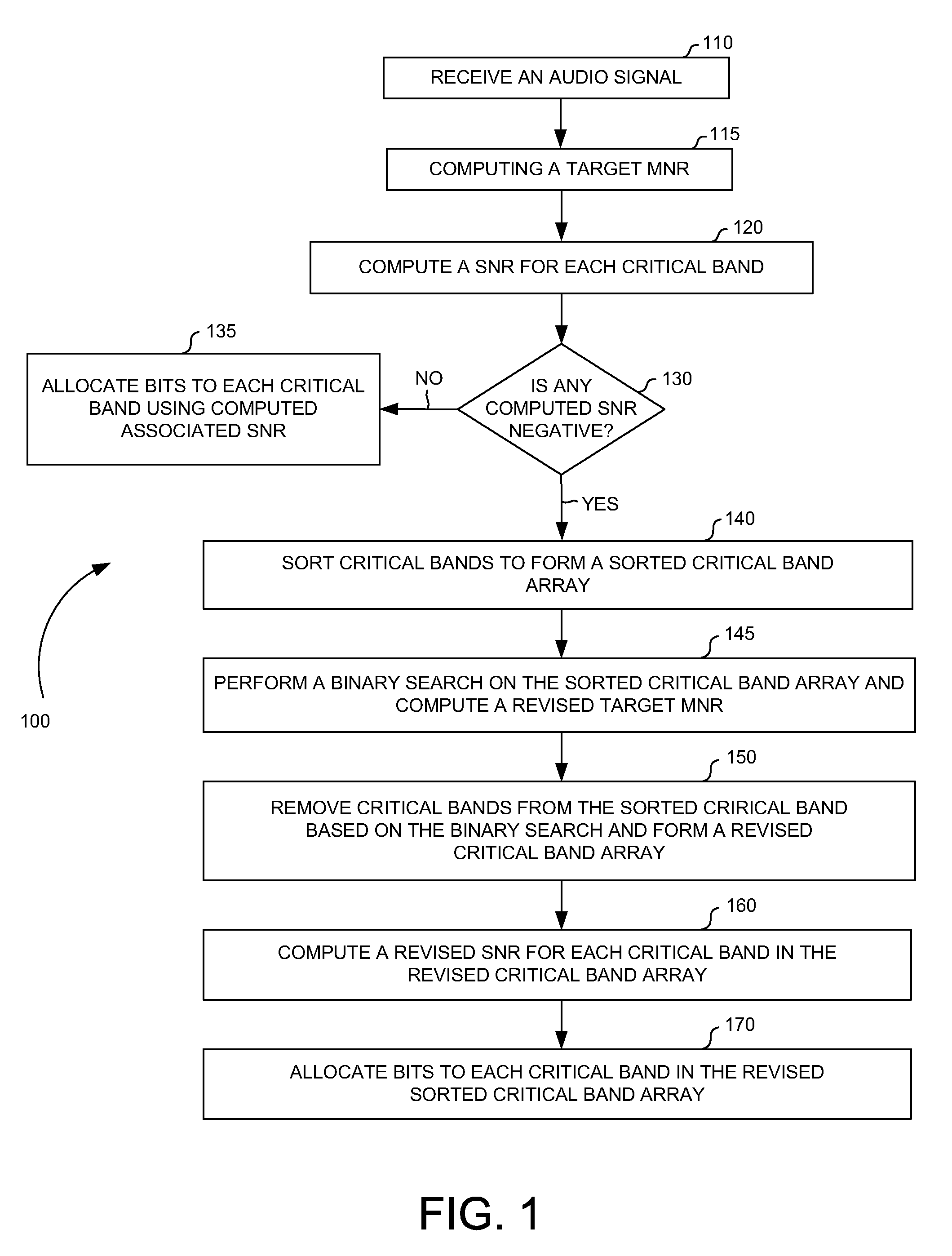
Method, system and apparatus for allocating bits in perceptual audio coders
ActiveUS20060069555A1Reduce computational complexityReduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBit allocationUniform quantization
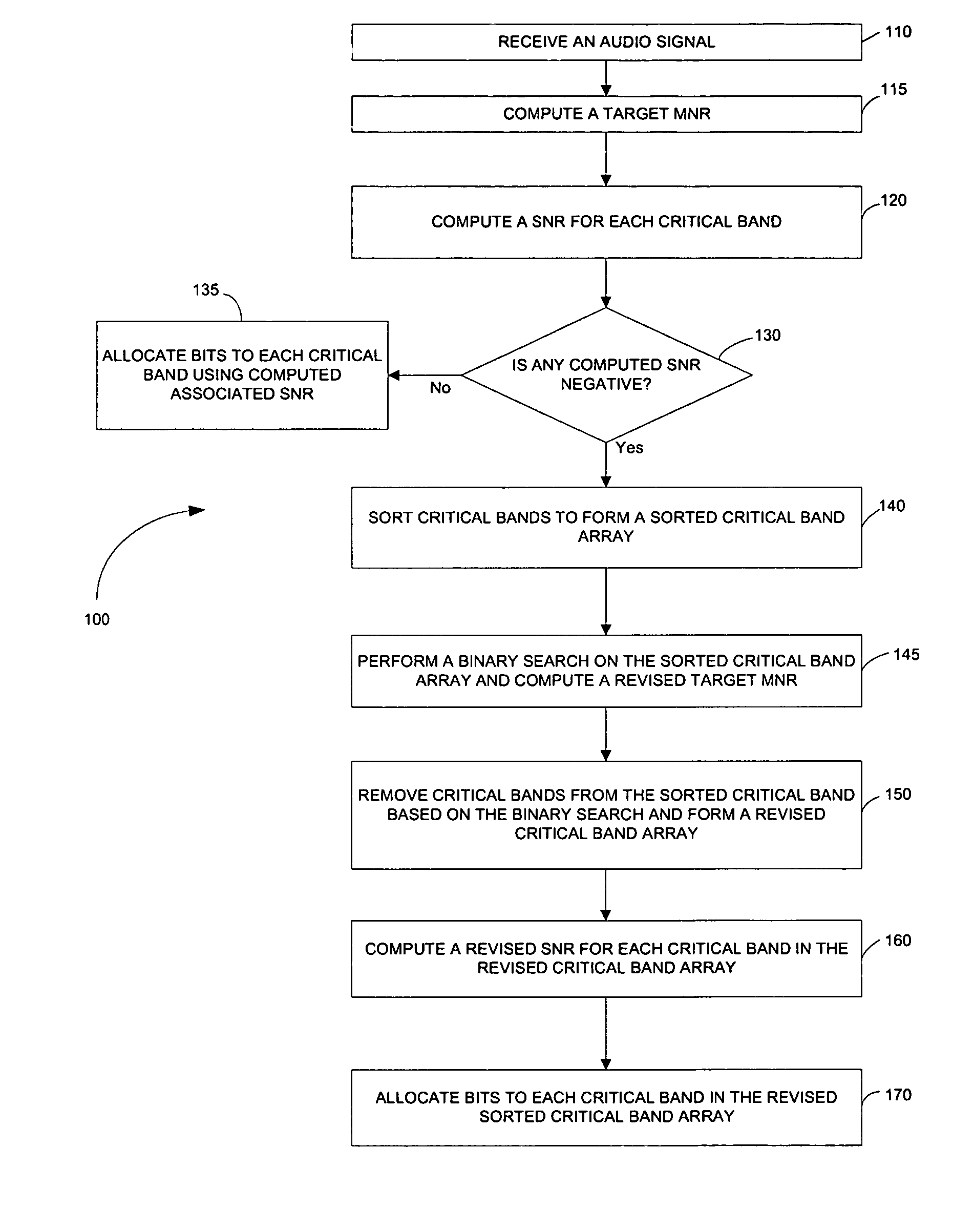
A non-iterative and computationally efficient bit allocation technique for perceptual audio coders employing uniform quantization schemes. This is achieved by computing a target MNR for all critical bands in a frame using a target bit rate and associated SMRs. Associated SNRs are then computed for the critical bands using the computed target MNR and the associated SMRs. Bits are then allocated to the critical bands based on the computed associated SNRs.
Owner:ITTIAM SYST P
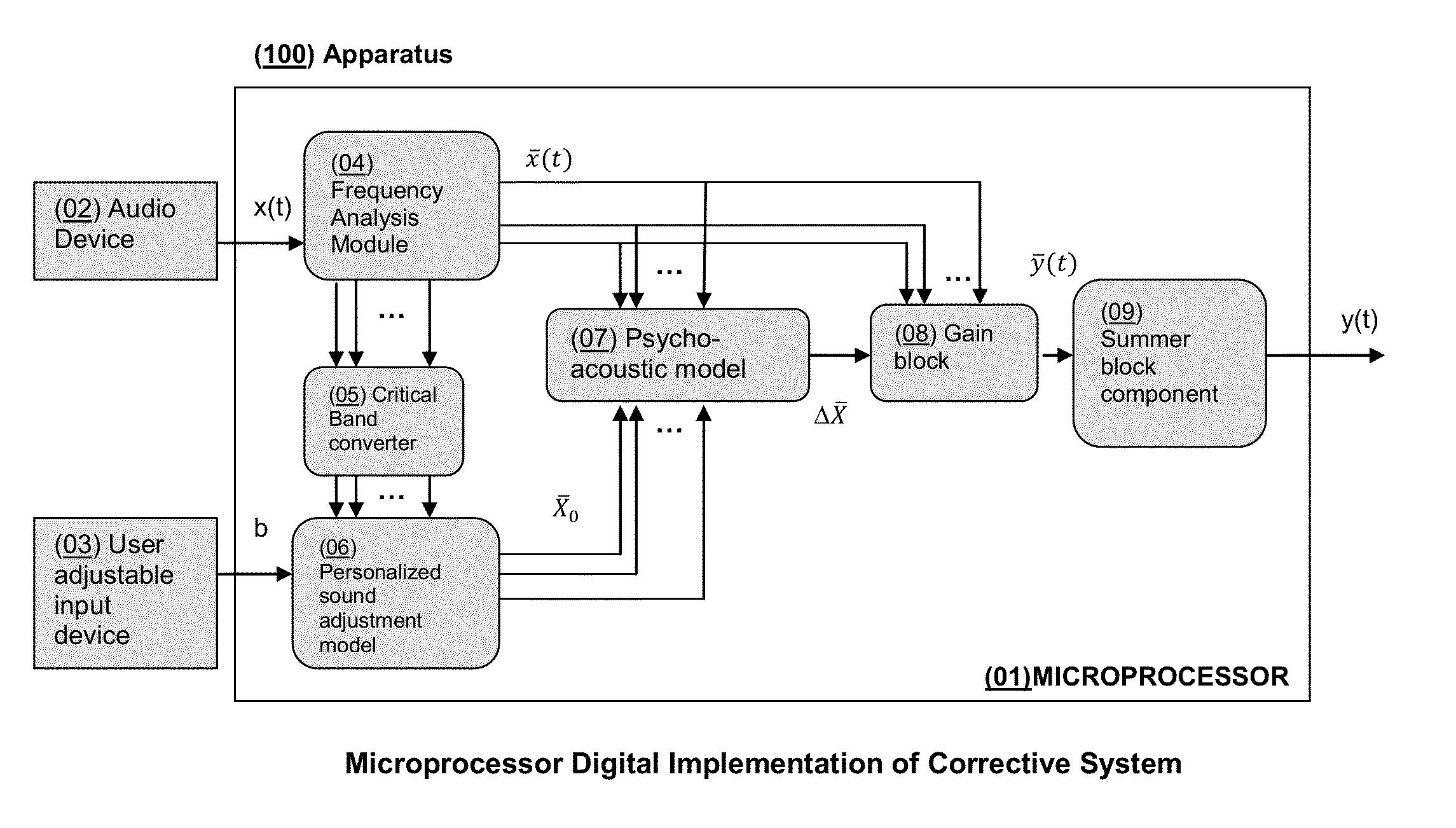
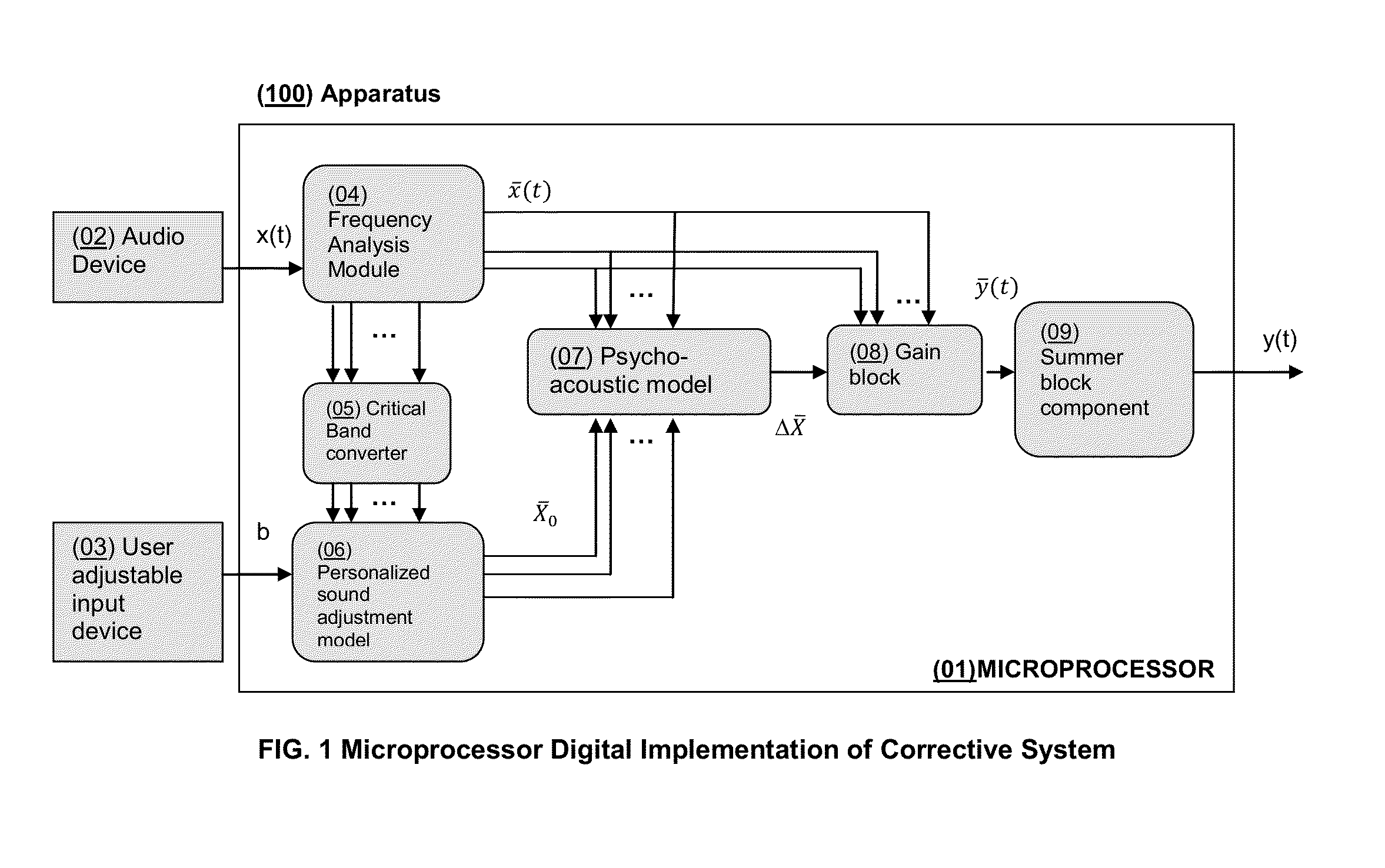
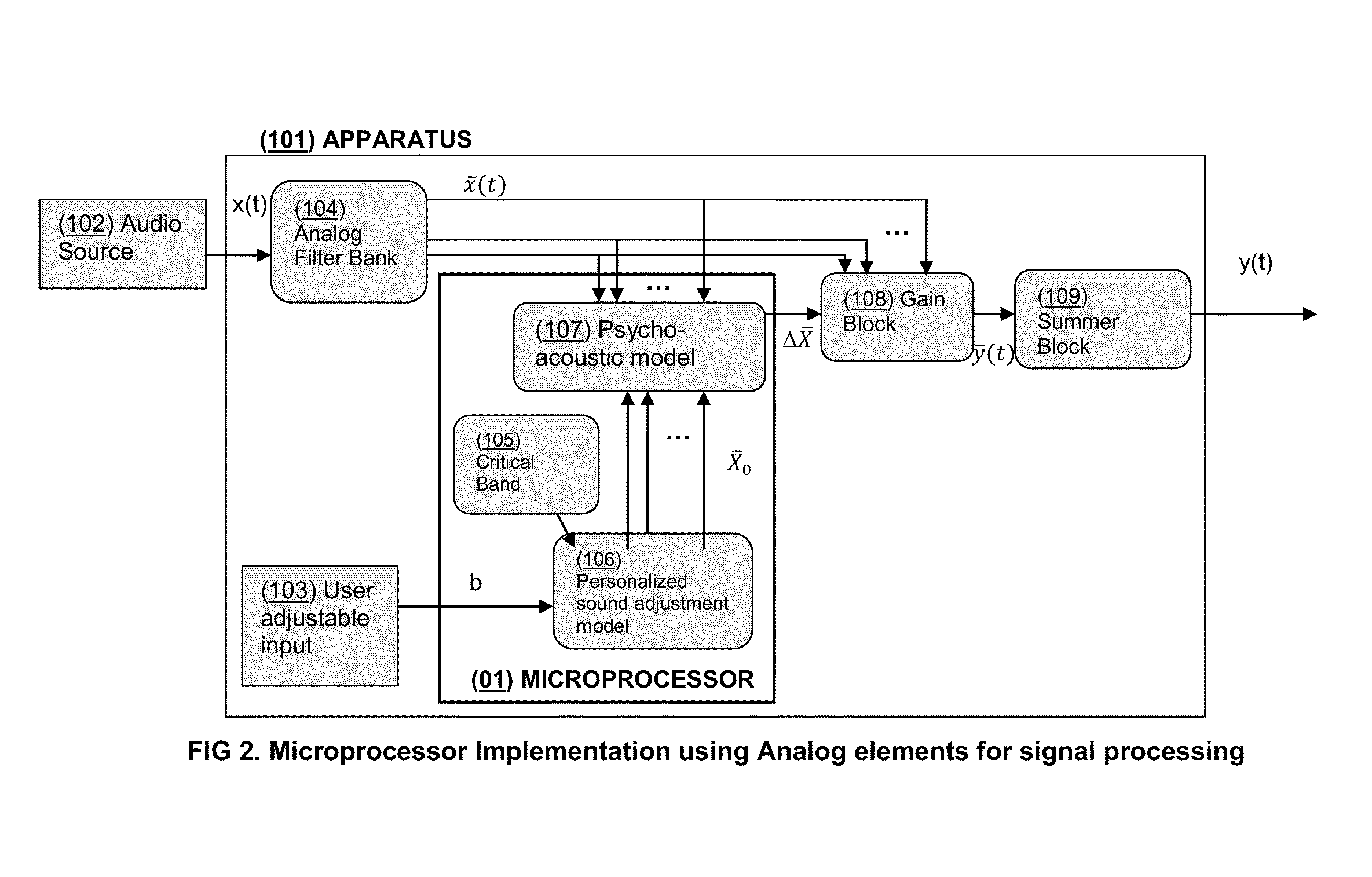
System and Method for Spectral Personalization of Sound
InactiveUS20130136282A1Gain controlDigital/coded signal combination controlPersonalizationFrequency spectrum
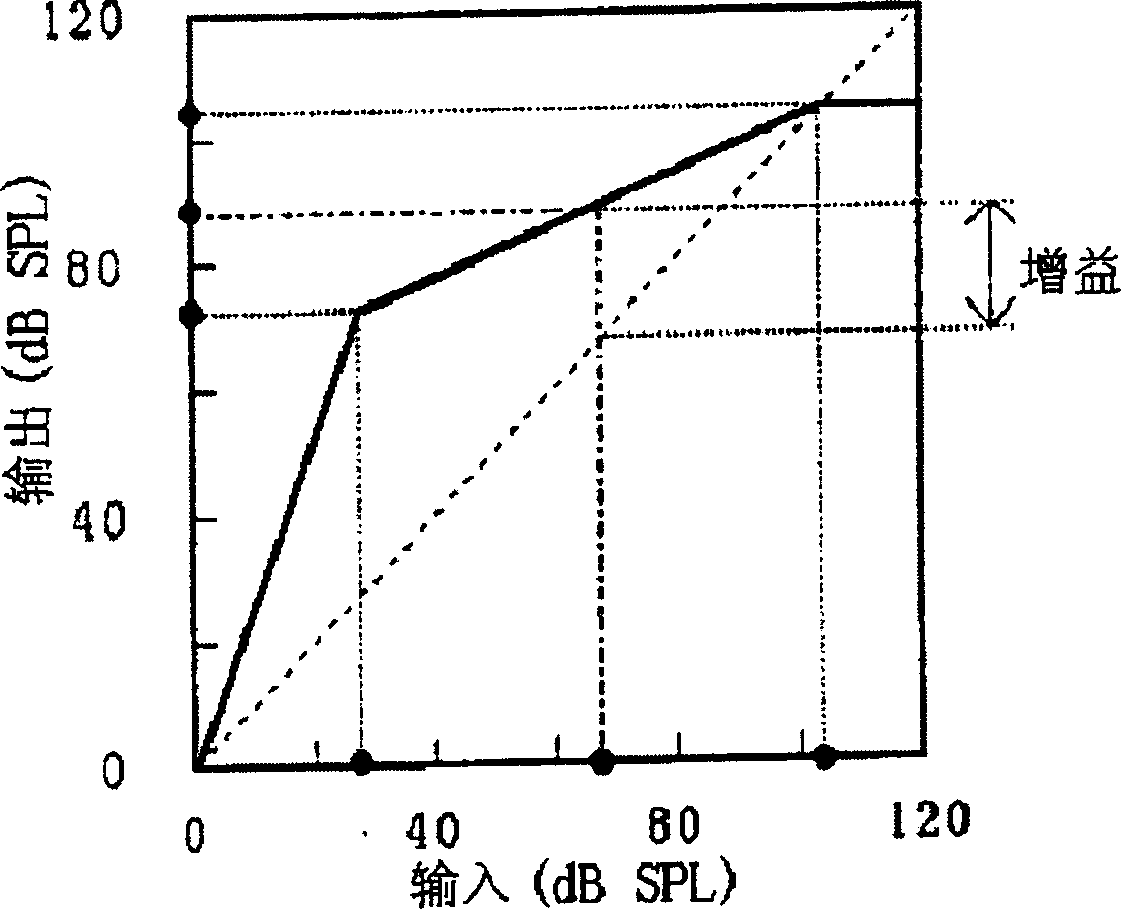
The present invention features systems for enhancing audio signals to correct across a spectrum of frequencies according to a model of the spectral characteristics of hearing loss. The methods of the present invention estimate hearing loss using a linear function of the critical band center frequency. The systems of the present invention compute a user-determined degree of correction to sounds at varying frequencies, allowing a listener to hear sounds, across varying frequencies, as the listener wishes to hear them without needing to raise the volume of the sounds to potentially damaging levels. Systems may be incorporated into apparatuses including but not limited to personal communications devices, virtual audio ports / channels and media players.
Owner:MCCLAIN DAVID
Method and apparatus for enhancing loudness of a speech signal
InactiveUS7676362B2Speech analysisVacuum gauge using compression chambersSignal onHearing perception
A speech filter (108) enhances the loudness of a speech signal by expanding the formant regions of the speech signal beyond a natural bandwidth of the formant regions. The energy level of the speech signal is maintained so that the filtered speech signal contains the same energy as the pre-filtered signal. By expanding the formant regions of the speech signal on a critical band scale corresponding to human hearing, the listener of the speech signal perceives it to be louder even though the signal contains the same energy.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for enhancing loudness of an audio signal
Human hearing perceives loudness based on critical bands corresponding to different frequency ranges. As a sound's frequency spectrum increases beyond a critical band into a previously unexcited critical band, the perception is that the sound has increased in loudness. To take advantage of this principle, a filter is applied to a speech signal so as to expand the formant bandwidths of formants in the speech sample.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
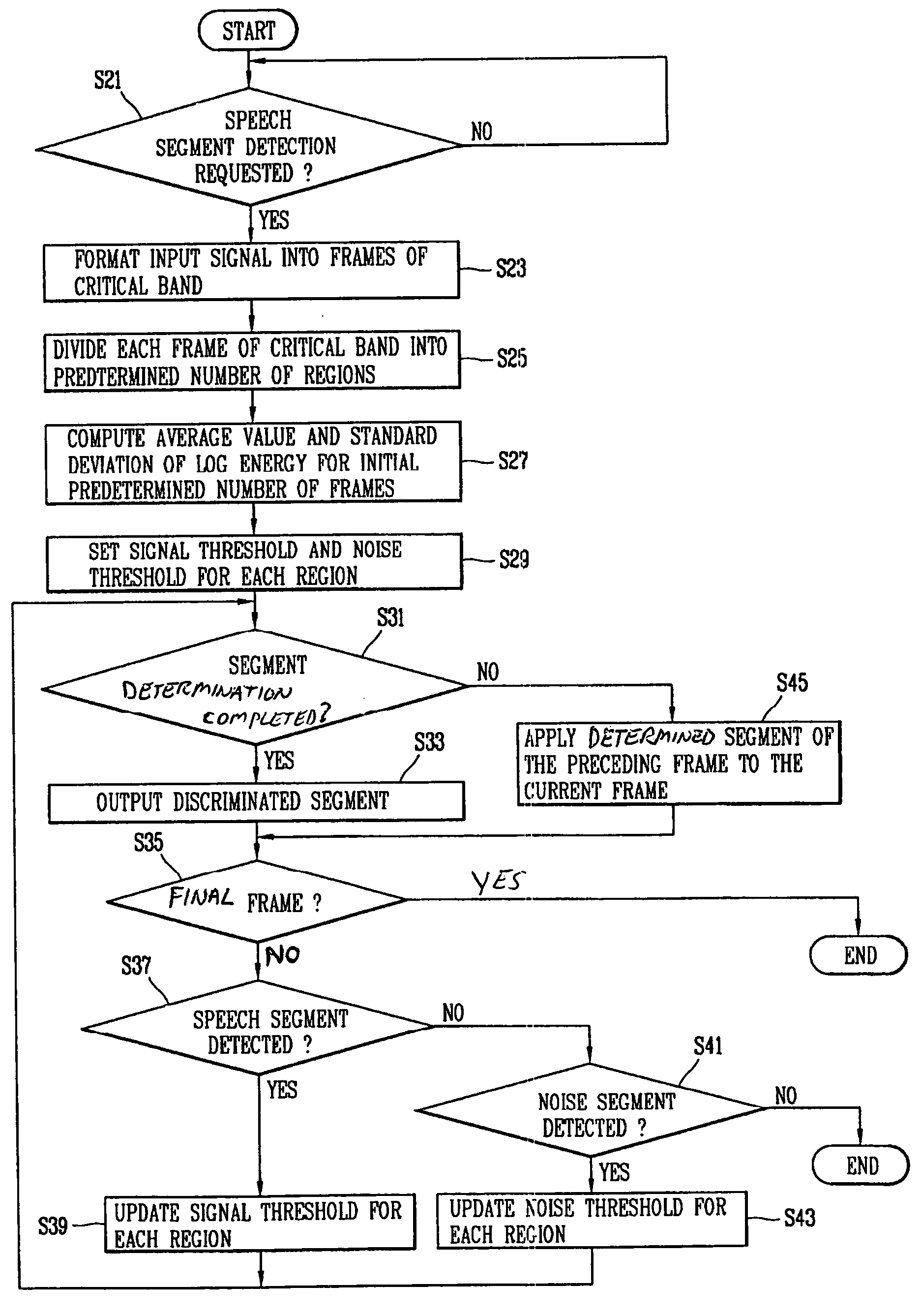
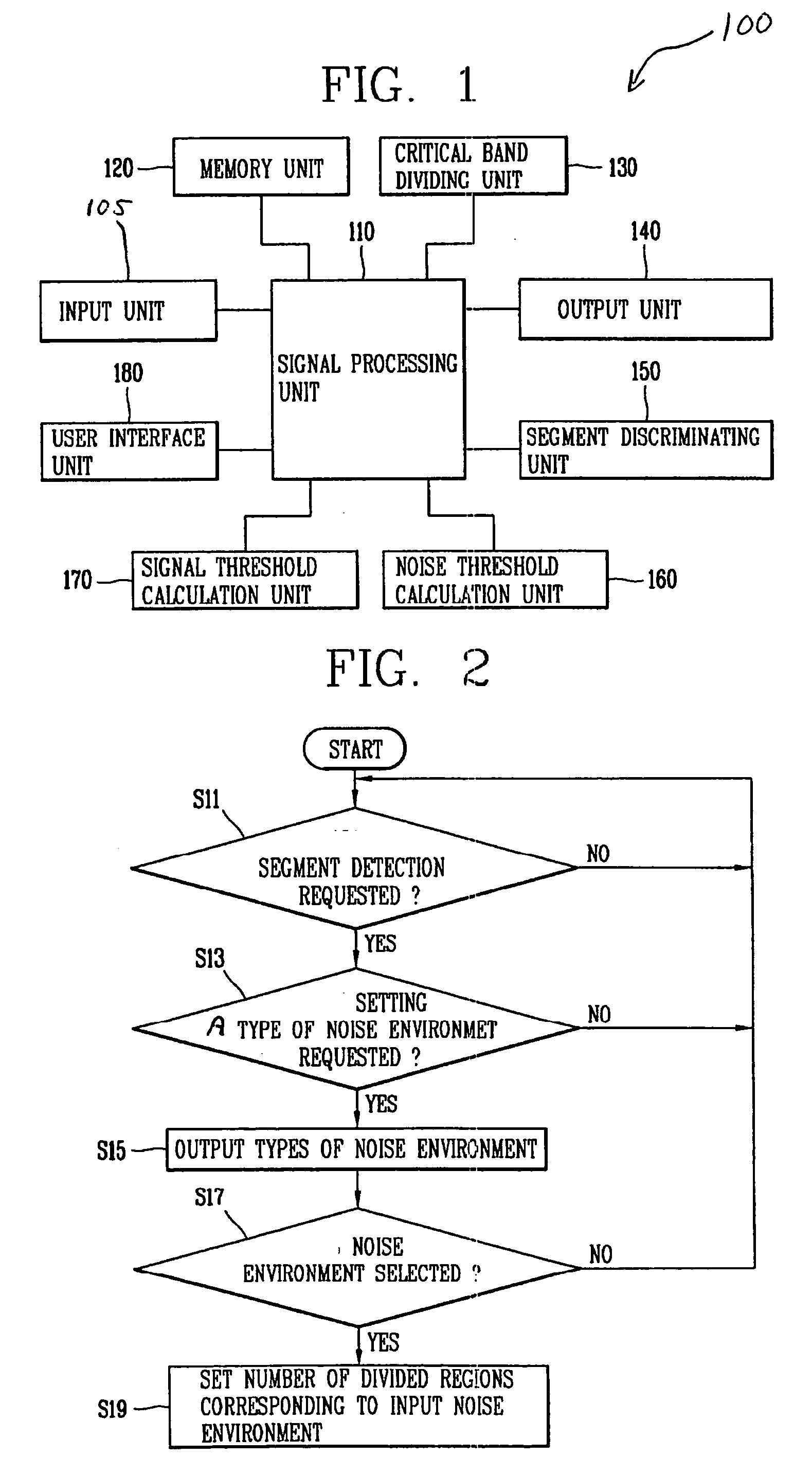
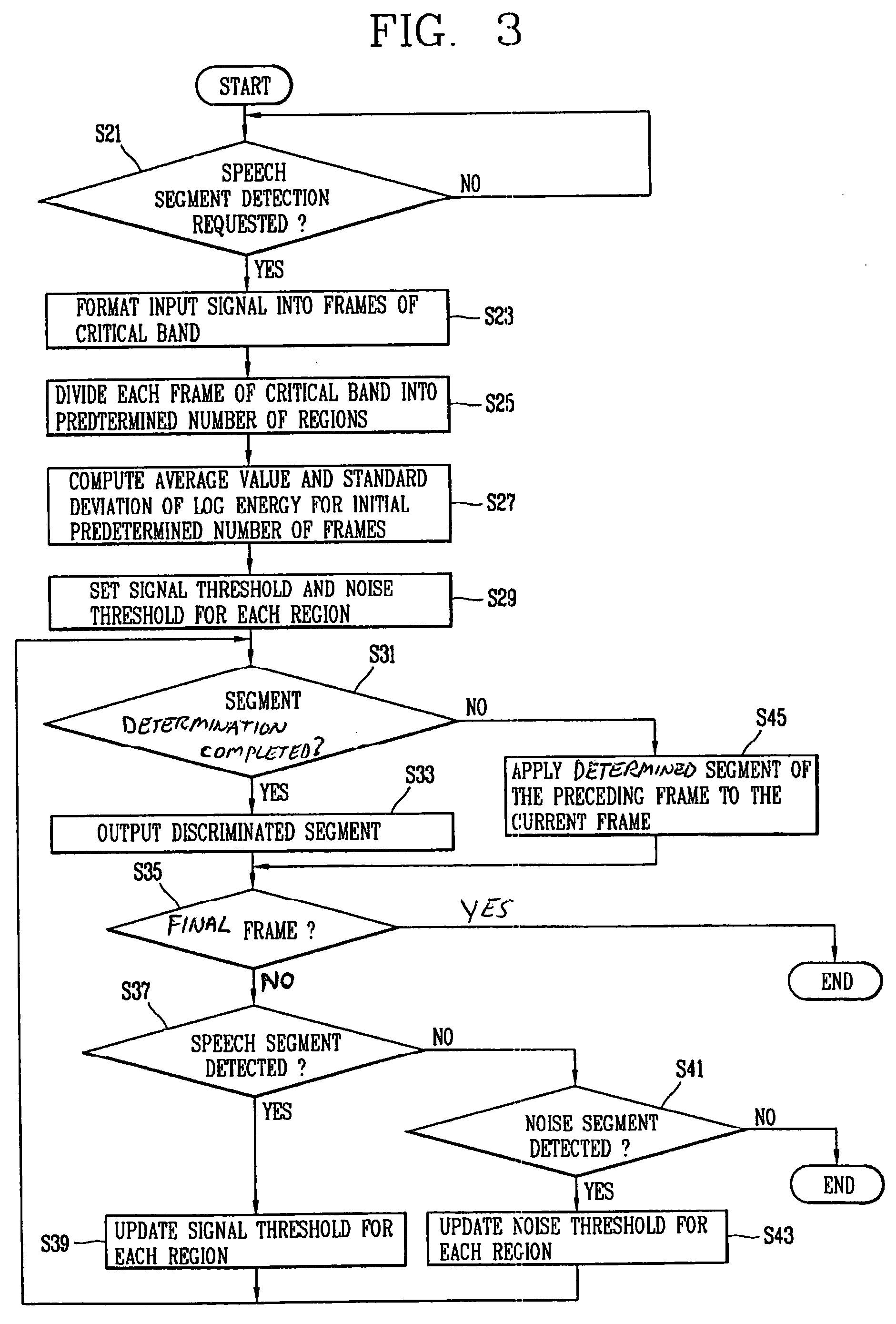
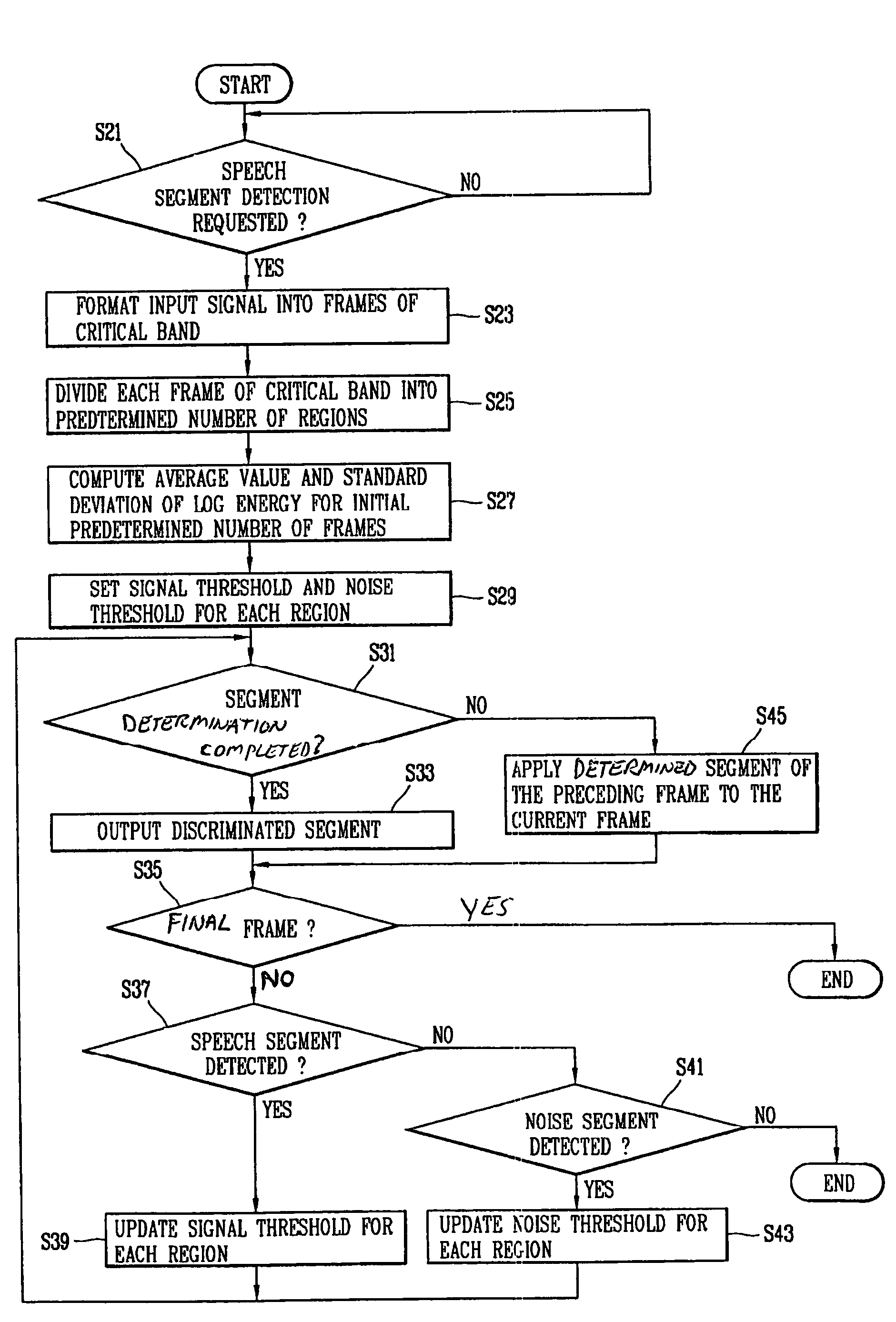
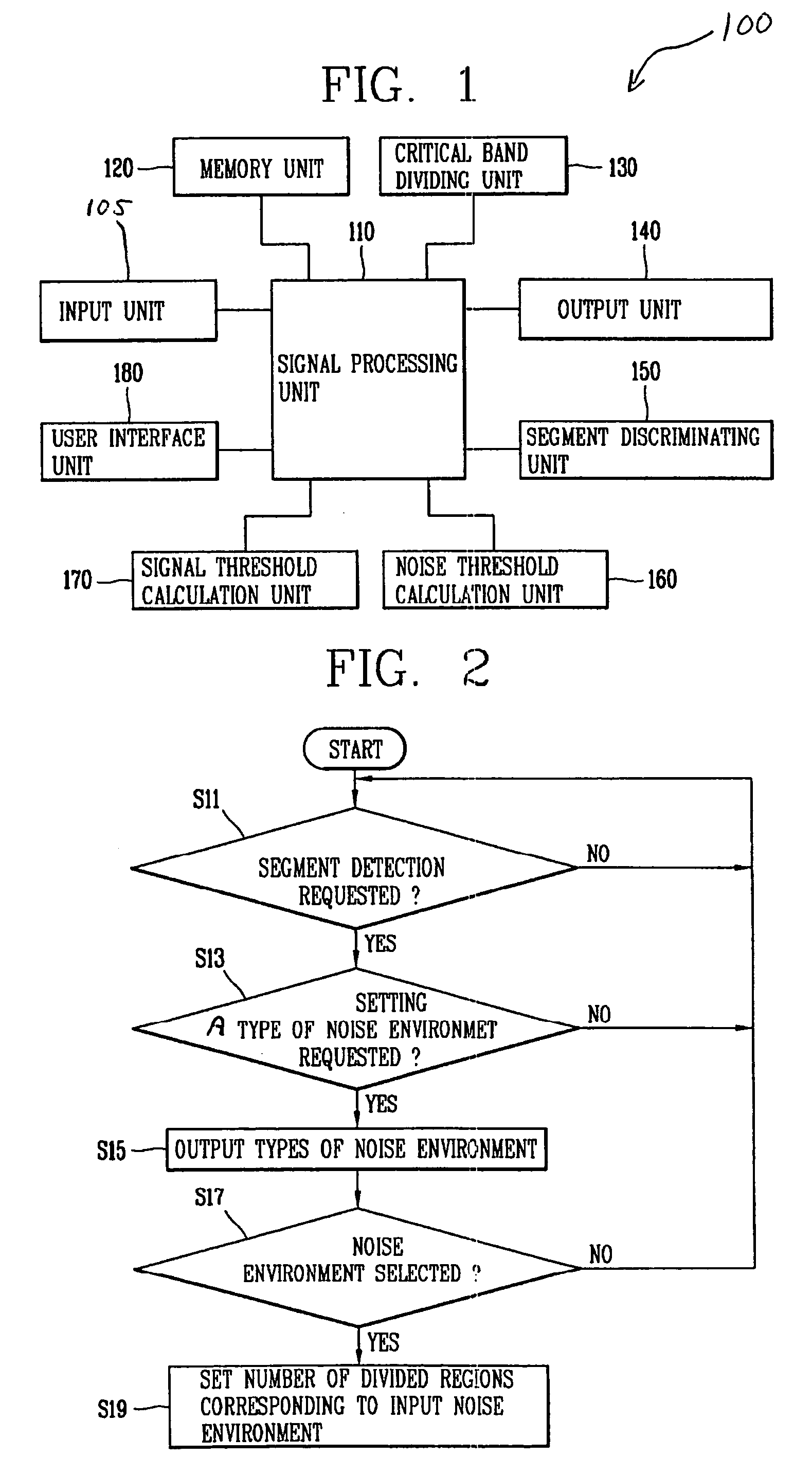
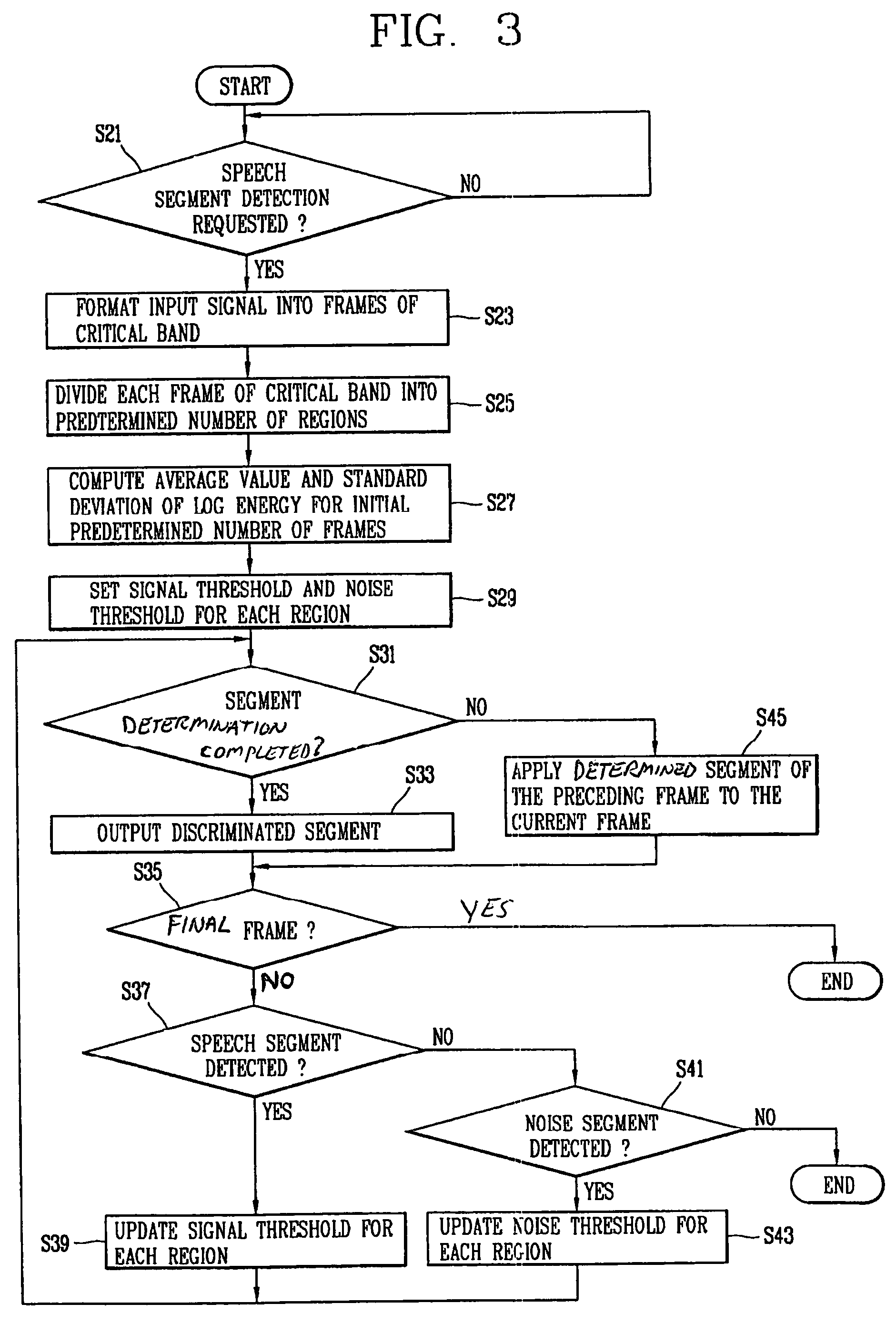
Method and apparatus for detecting speech segments in speech signal processing
InactiveUS20060111901A1Accurate detectionSmall amount of calculationSpeech recognitionVolume compression/expansionFrequency characteristicComputer science
A method and apparatus for detecting speech segments of a speech signal processing device is provided. A critical band is divided into a certain number of regions according to noise frequency characteristics, a signal threshold and a noise threshold are set for each of the regions, and it is determined whether each frame is a speech segment or noise segment by comparing the log energy calculated for each region to the corresponding signal threshold and noise threshold. Therefore, a speech segment can be detected rapidly and accurately by using a small number of operations even in a noise environment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
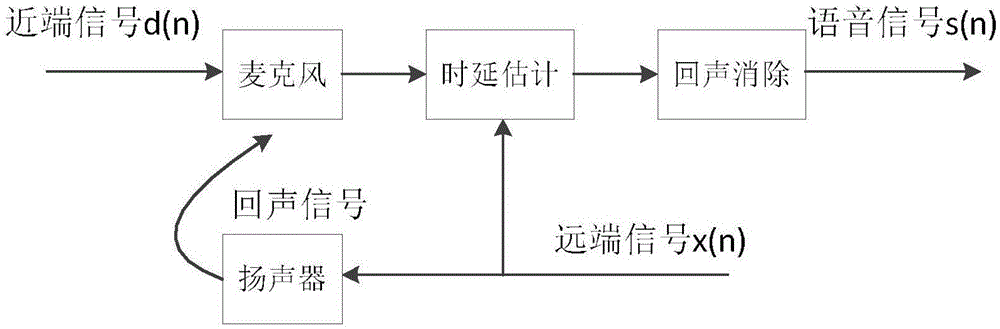
Speech signal time delay estimation method and system used for echo cancellation
ActiveCN105872275AQuality improvementSimple calculationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsDecompositionProximal point
The invention discloses a speech signal time delay estimation method and system used for echo cancellation. The method comprises the following steps of respectively obtaining a far-end signal and a near-end signal of a voice signal received by a microphone in a call and generating a corresponding far-end frequency domain signal and a corresponding near-end frequency domain signal; adopting a critical band based on the auditory masking effect to respectively carry out sub-band decomposition in the frequency band on the far-end frequency domain signal and the near-end frequency domain signal and obtaining a power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the far-end frequency domain signal and a power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the near-end frequency domain signal; respectively extracting local binary features of the power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the far-end frequency domain signal and the power spectrum of each critical frequency point of the near-end frequency domain signal, respectively matching and generating and outputting a time delay estimation result. According to the method and the system, the correlation between the far-end signal and the near-end signal is counted based on the auditory masking effect, the computation is simple, and the accurate time delay estimation can be obtained to bring great convenience for echo cancellation.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Stereophonic sound imaging
A method for reducing phase differences varying with frequency occurring at certain listening positions with respect to loudspeakers reproducing respective ones of multiple sound channels in a listening space, the phase differences occurring in a sequence of frequency bands in which the phase differences alternate between being predominantly in-phase and predominantly out-of-phase, comprises adjusting the phase in multiple frequency bands in which the multiple sound channels are out-of-phase at such listening positions. Such adjustment of phase includes the frequency bands in which the width of comb filtering pass bands and notches resulting from phase differences at such listening positions would be greater than or commensurate with the critical band width if the phase adjustment were not applied. The listening space may be the interior of a vehicle.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and system for increasing audio perceptual tone alerts
InactiveUS20050278165A1Increases audio perceptual loudnessReduced Power RequirementsMultiplex communicationSpeech analysisLoudnessAudio frequency
A method, system and computer readable medium for increasing the audio perceptual loudness includes shifting at least one frequency of a first audio signal to create a second audio signal so as to increase the audio perceptual loudness. The power level of the second audio signal is not more than a power level of the first audio signal. The method also includes generating high-audio perceptual loudness tone alert sequences based on psychoacoustic and audiometric data. It further includes acquiring a listener's threshold audio profile; adding the listener's audio profile to the loudness sensitivity curve for producing the listener's tonal sensitivity curve; determining a required dB scaling for critical band tones from the listener's tonal sensitivity curve; normalizing the tonal sensitivity curve for creating a decibel curve; selecting a frequency range of the tones by using the tonal sensitivity curve; and spacing the sequence of tones along a critical band scale.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
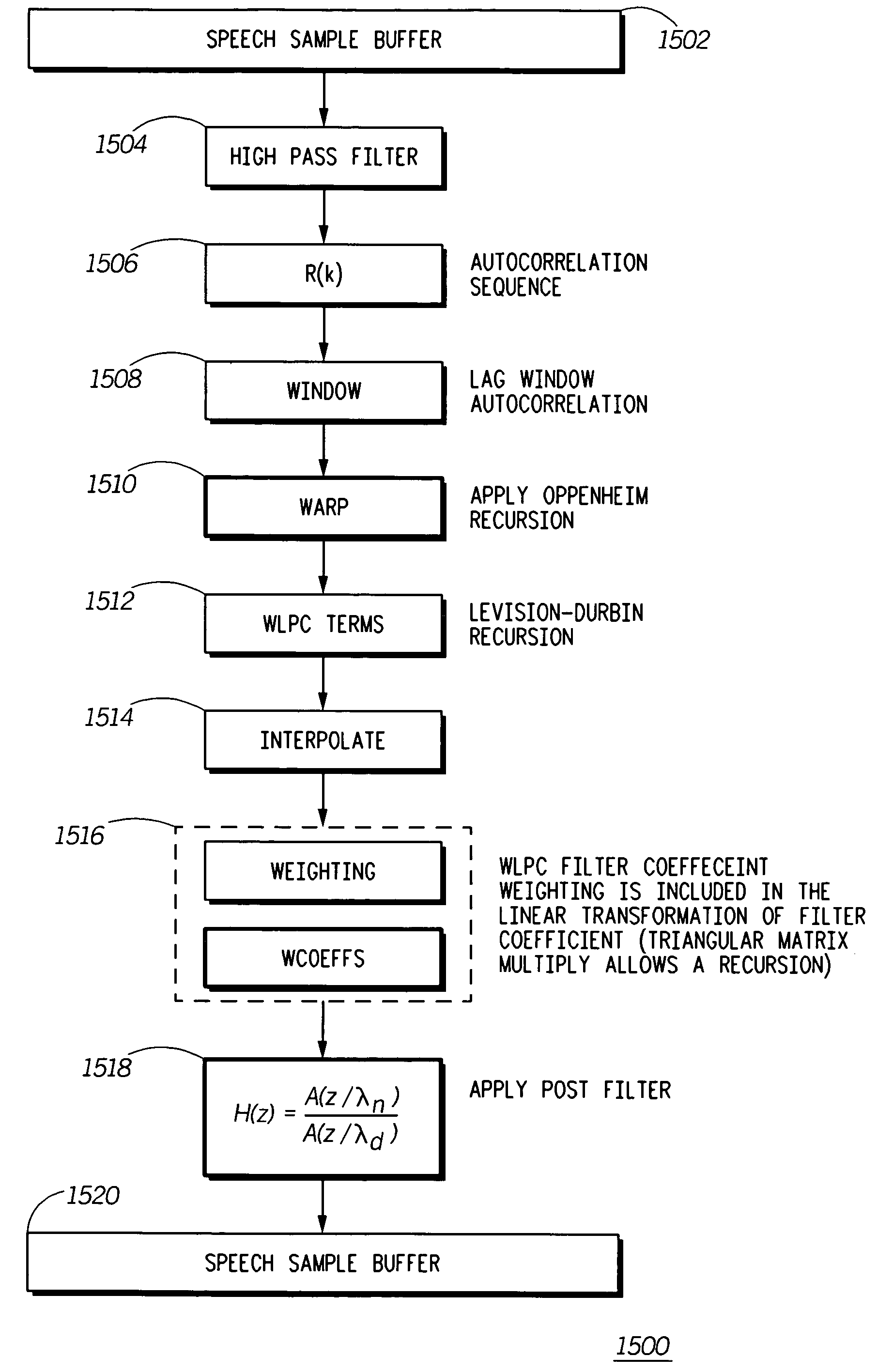
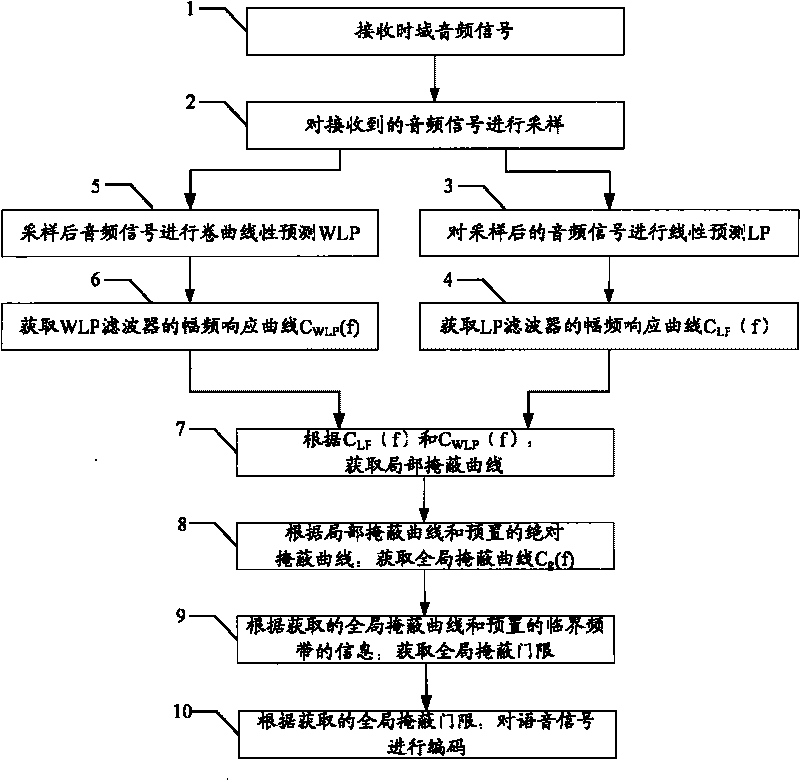
Audio coding method and audio coder
InactiveCN101740033AGet masking thresholdReduce complexitySpeech analysisMasking thresholdAudio signal flow
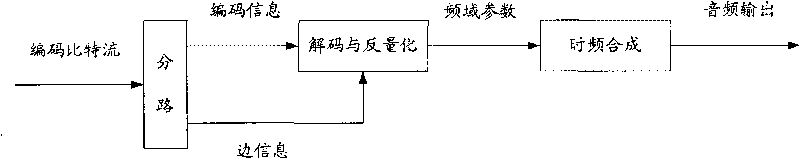
The invention discloses an audio coding method and an audio coder method. The embodiment of the invention also provides a corresponding audio coder. As the feature that the frequency resolution characteristics of linear prediction (LP) and winding linear prediction (WLP) are very close to the critical band and masking characteristic in human auditory characteristic is utilized in the technical scheme of the invention, a psychoacoustics module is built, the masking threshold is obtained, and coding is carried out on audio signals according to the obtained masking threshold, thereby decreasing the complexity of building the psychoacoustic model, being realized easily, decreasing the hardware implementation cost of the psychoacoustic model, and lowering power consumption of hardware.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
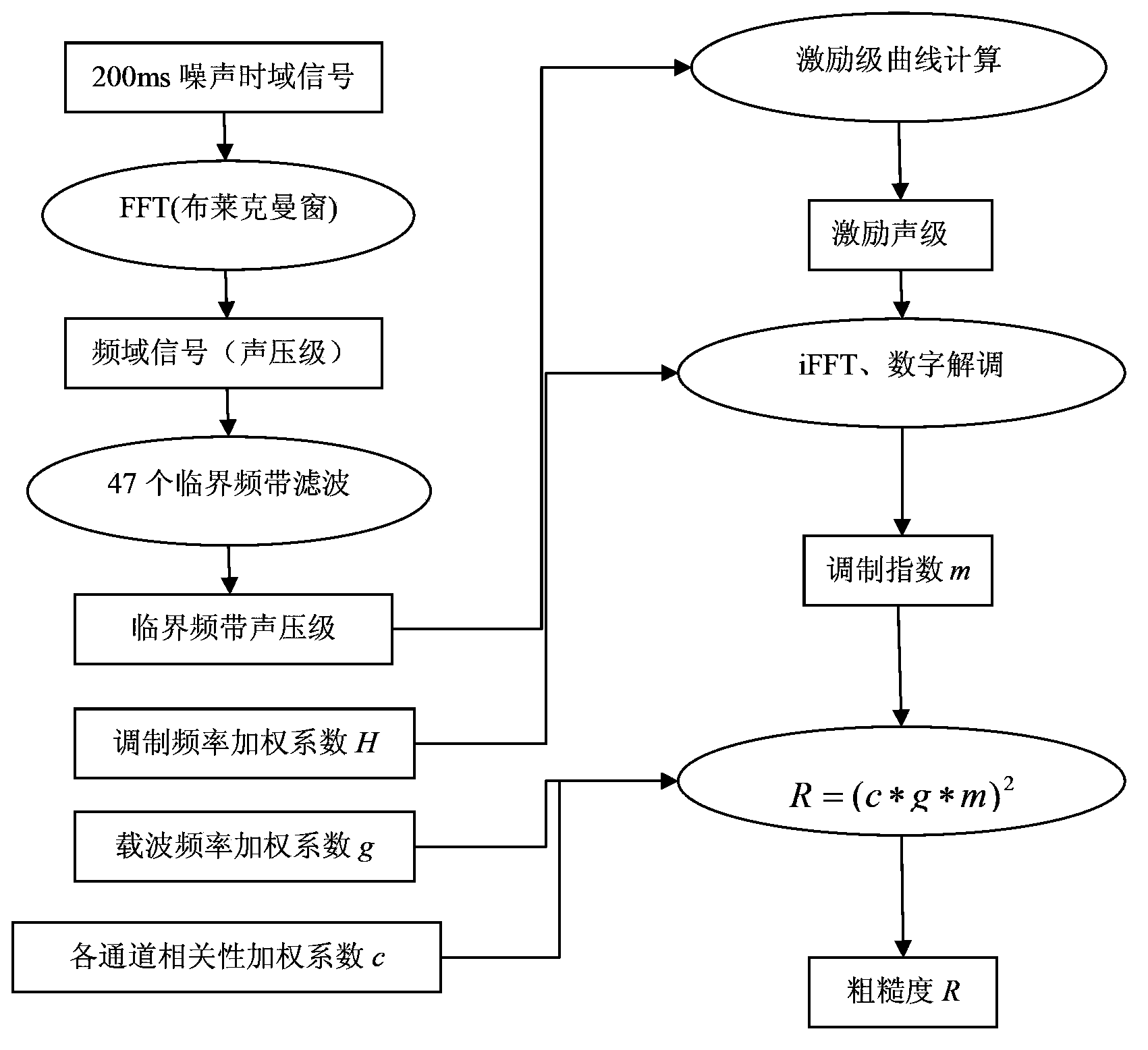
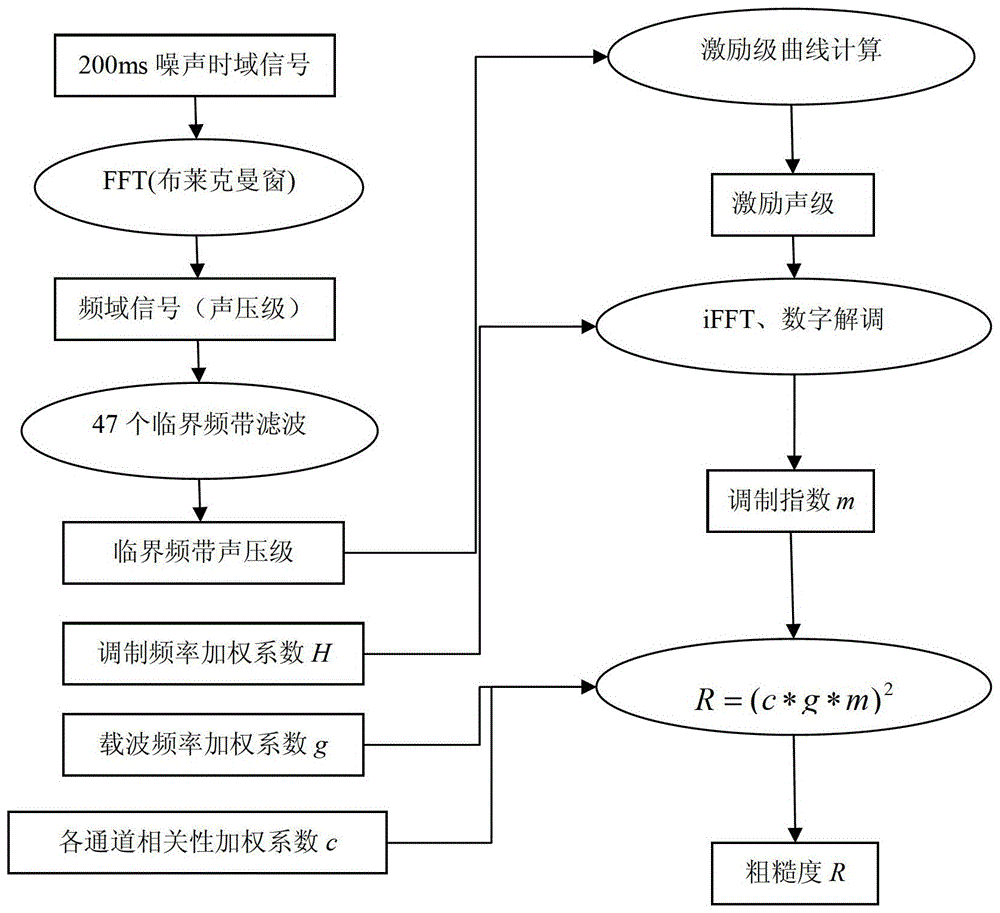
Vehicle noise sound quality roughness information processing method
ActiveCN104102803AThe calculation method is clearHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingSignal on
The invention relates to a vehicle noise sound quality roughness information processing method which comprises the following steps: (1), segmenting noise signals and windowing; (2), carrying out Fourier transformation to the noise signals after windowing, calculating out the exciting sound level of noise signals on a critical band; (3), designing mutually superimposed passages on the critical band, dividing the exciting sound level onto the passages so as to form sub noise signals, then carrying out inverse Fourier transform to the noise signals, so as to obtain time domain sub signals at the exciting sound level; (4), carrying out inverse Fourier transform after demodulation to the time domain sub signals at the exciting sound level, so as to obtain a signal time domain value after modulation, and then calculating out the modulation indexes of each passage; (5), calculating out the related coefficient and the carrier frequency weighting factor among the noise signals of all the passages; (6), calculating out the roughness of the noise signals on each passage and calculating out the total roughness. Compared with the prior art, the vehicle noise sound quality roughness information processing method provided by the invention takes auditory perception characteristics of human ears into consideration, and has the advantages of easiness in method understanding, high precision and the like.
Owner:上海鹊音科技有限公司
Adapting masking thresholds for encoding a low frequency transient signal in audio data
Owner:APPLE INC
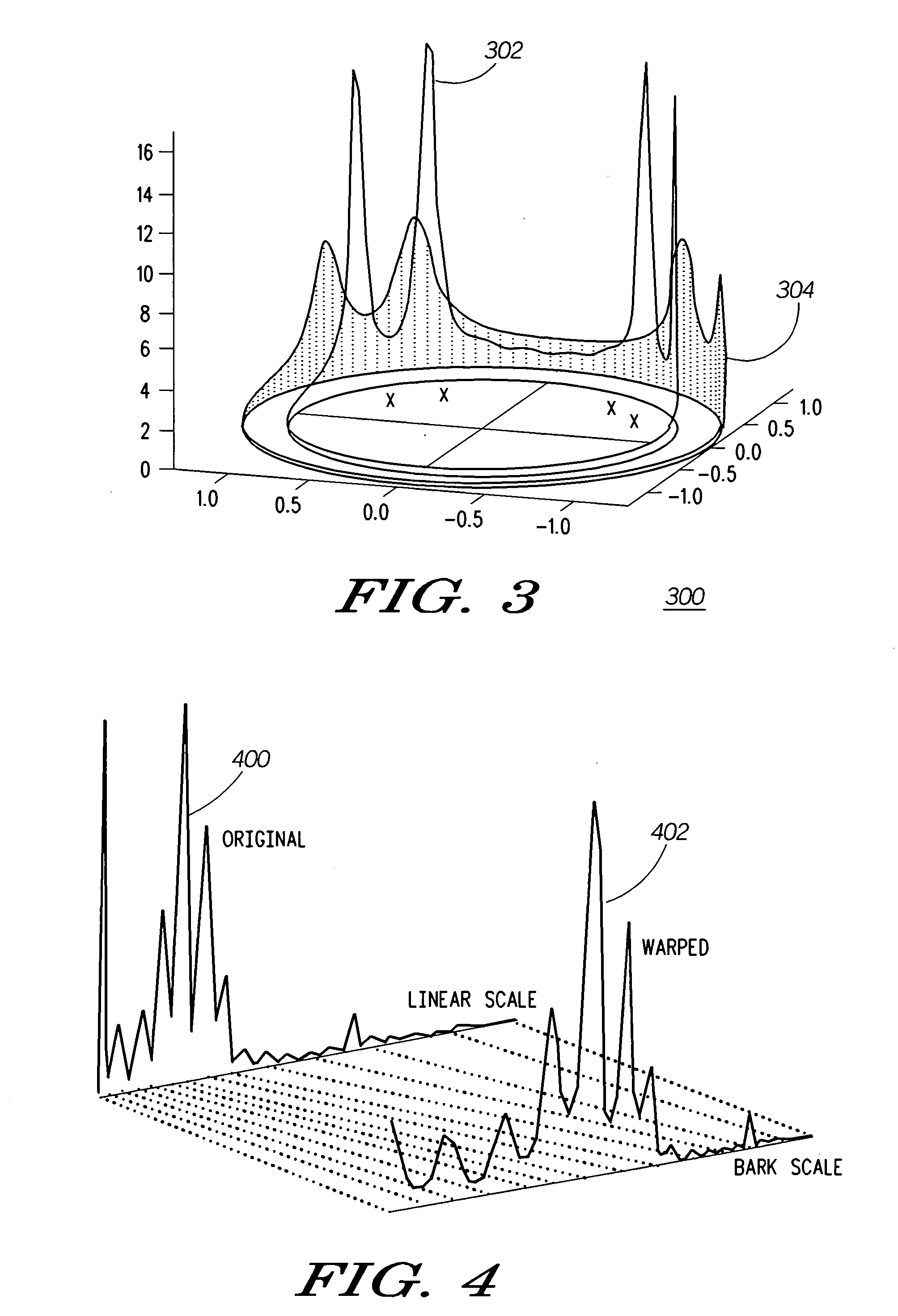
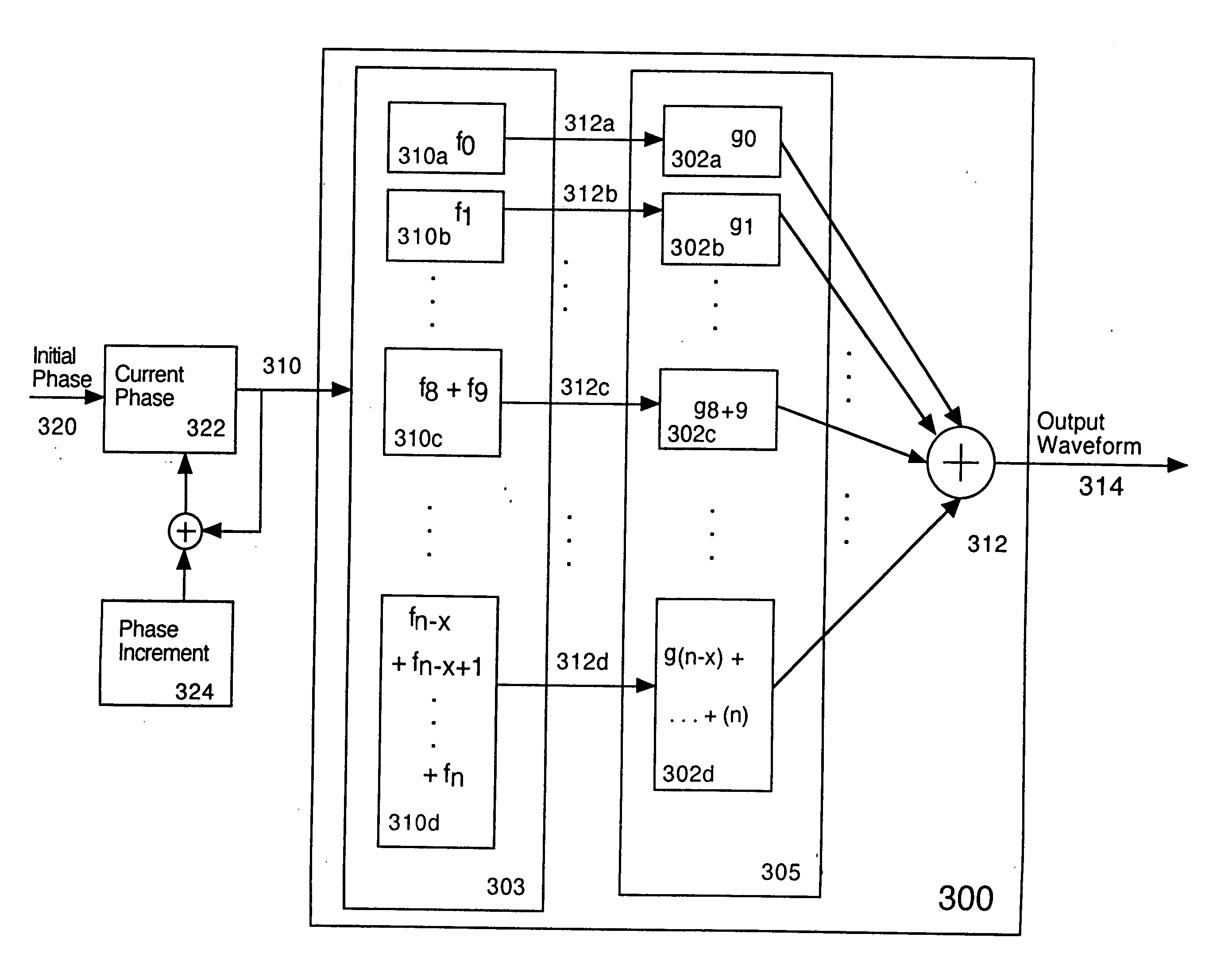
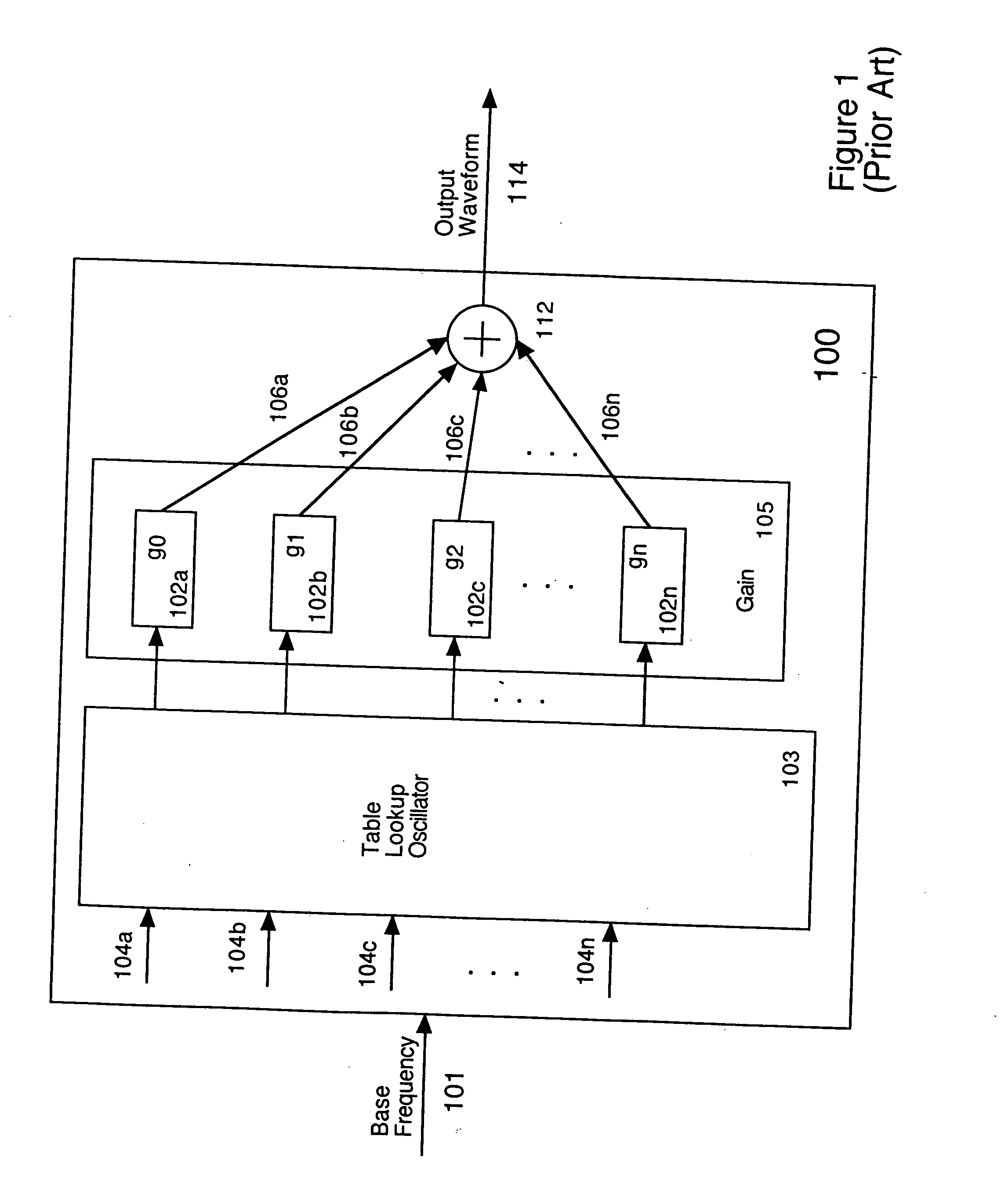
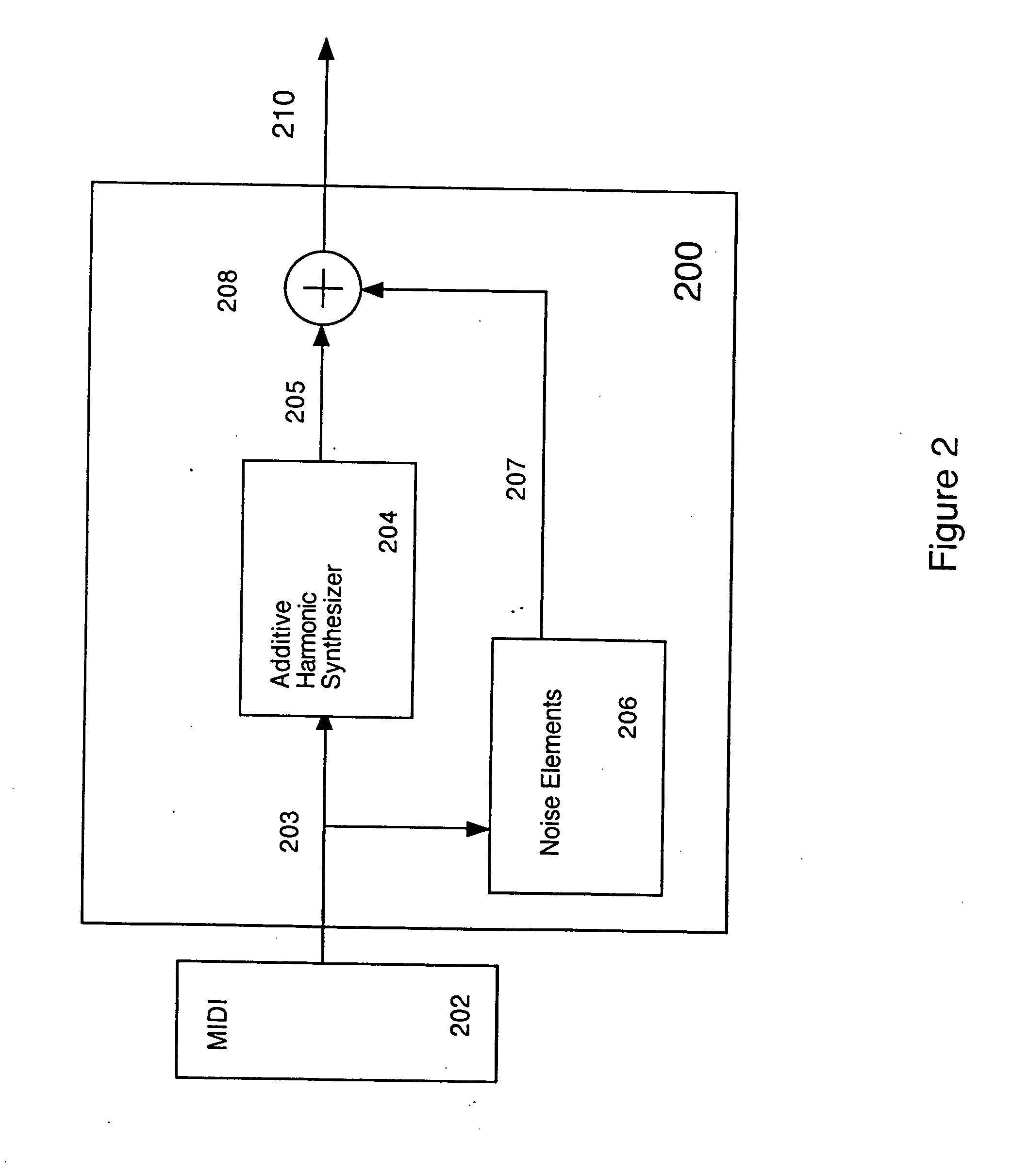
Critical band additive synthesis of tonal audio signals
InactiveUS20060217984A1Reduce calculationFew parametersElectrophonic musical instrumentsMovable seatsAdditive synthesisHarmonic
An efficient synthesizer of tonal audio signals is disclosed. The tonal audio signal synthesizer utilizes additive synthesis of harmonics of the base frequency. Rather than generating and summing all of the individual frequency sinusoidal harmonics as in traditional additive synthesis, critical band signals (comprising multiple harmonics added together) are generated, and the critical bands are summed based upon the Critical Bands resolvable by human hearing. Each critical band signal comprises the combination of from one to many sinusoids, generally of equal amplitude. Generally only a single harmonic is included in the lowest critical band, or the lowest several critical bands. As the frequency increases, the number of harmonics in each critical band increases as well. A gain is applied to each critical band signal.
Owner:LINDEMANN ERIC
Method and system for increasing audio perceptual tone alerts
InactiveUS7089176B2Increase the loudnessMaximal loudnessMultiplex communicationSpeech analysisLoudnessPsychoacoustics
A method, system and computer readable medium for increasing the audio perceptual loudness includes shifting at least one frequency of a first audio signal to create a second audio signal so as to increase the audio perceptual loudness. The power level of the second audio signal is not more than a power level of the first audio signal. The method also includes generating high-audio perceptual loudness tone alert sequences based on psychoacoustic and audiometric data. It further includes acquiring a listener's threshold audio profile; adding the listener's audio profile to the loudness sensitivity curve for producing the listener's tonal sensitivity curve; determining a required dB scaling for critical band tones from the listener's tonal sensitivity curve; normalizing the tonal sensitivity curve for creating a decibel curve; selecting a frequency range of the tones by using the tonal sensitivity curve; and spacing the sequence of tones along a critical band scale.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
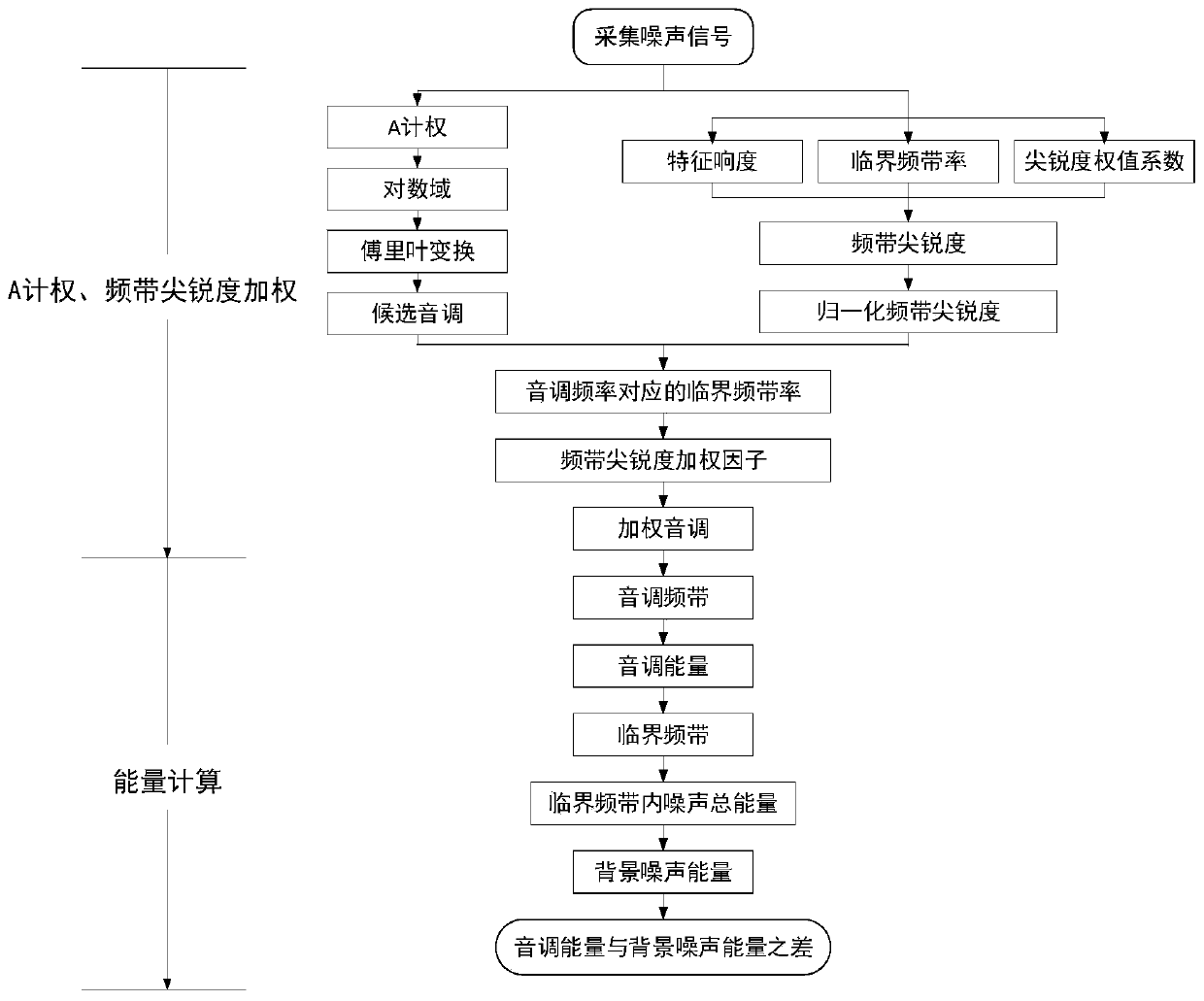
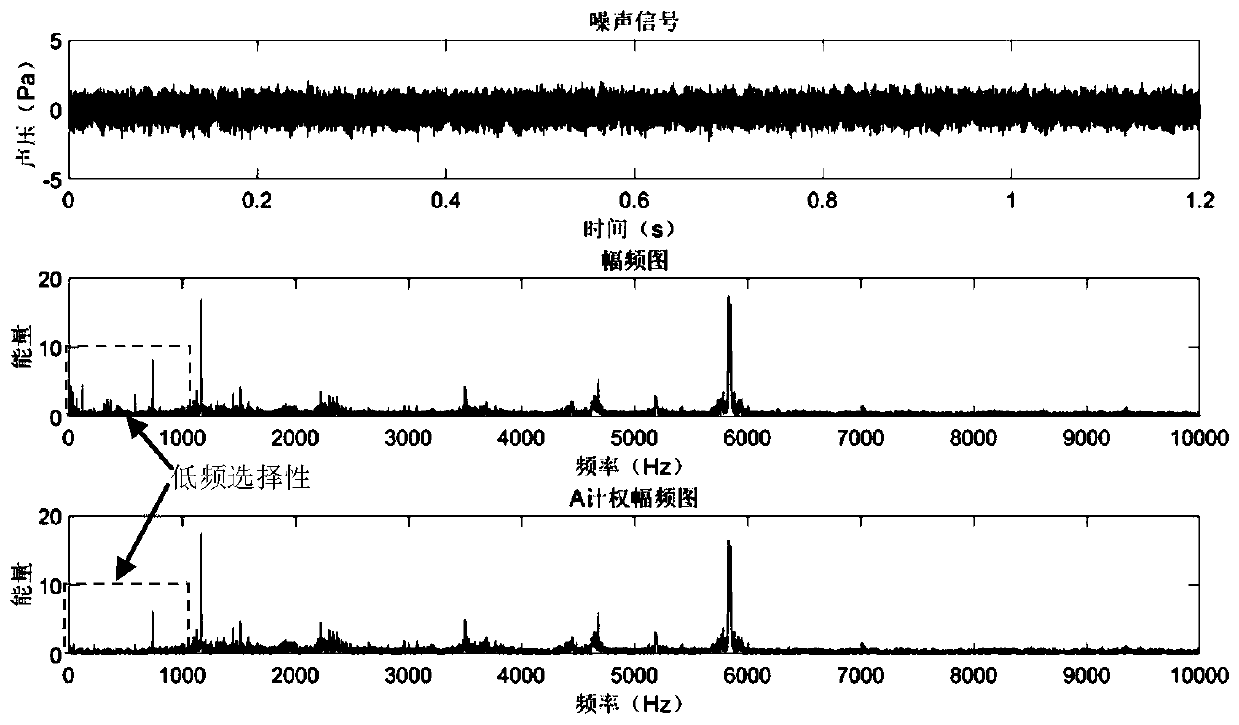
Tune energy and human ear frequency selectivity based squeal judgment method for speed reducers/changers
ActiveCN109920439AImprove the attenuation effectObvious gain effectSpeech analysisHuman earBackground noise
The invention relates to a tune energy and human ear frequency selectivity based squeal judgment method for speed reducers / changers. The method comprises the steps: firstly, sampling noise signals ofa speed reducer / changer, carrying out A weighting on the noise signals, converting processed signals to log domains, and carrying out Fourier transformation, so as to obtain energy-amplitude frequencycurves; then, calculating feature loudness and critical band rate of the noise signals, calculating frequency band acuity of each feature loudness, and subjecting frequency band acuity to normalizingtreatment; subjecting the energy-amplitude frequency curves to frequency interval Gauss smoothing processing to obtain background noises, and selecting candidate tunes; calculating a frequency band acuity weighting factor according to a corresponding relationship between the critical band rate and frequency, and carrying out weighting, so as to obtain the energy-amplitude frequency curves of thenoise signals; calculating tune energy in bandwidth of the tunes, background noise energy and difference between the tune energy and the background noise energy, and carrying out primary and secondarysequencing on abnormal noise frequencies affecting squeal. According to the method, a low-frequency region becomes a non-sensitive region, and a high-frequency region highlights acuity attribute, andthus, a subjective sensation of human ears to squeal is effectively simulated.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for detecting speech segments in speech signal processing
InactiveUS7620544B2Accurate detectionSmall amount of calculationSpeech recognitionVolume compression/expansionFrequency characteristicComputer science
A method and apparatus for detecting speech segments of a speech signal processing device is provided. A critical band is divided into a certain number of regions according to noise frequency characteristics, a signal threshold and a noise threshold are set for each of the regions, and it is determined whether each frame is a speech segment or noise segment by comparing the log energy calculated for each region to the corresponding signal threshold and noise threshold. Therefore, a speech segment can be detected rapidly and accurately by using a small number of operations even in a noise environment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
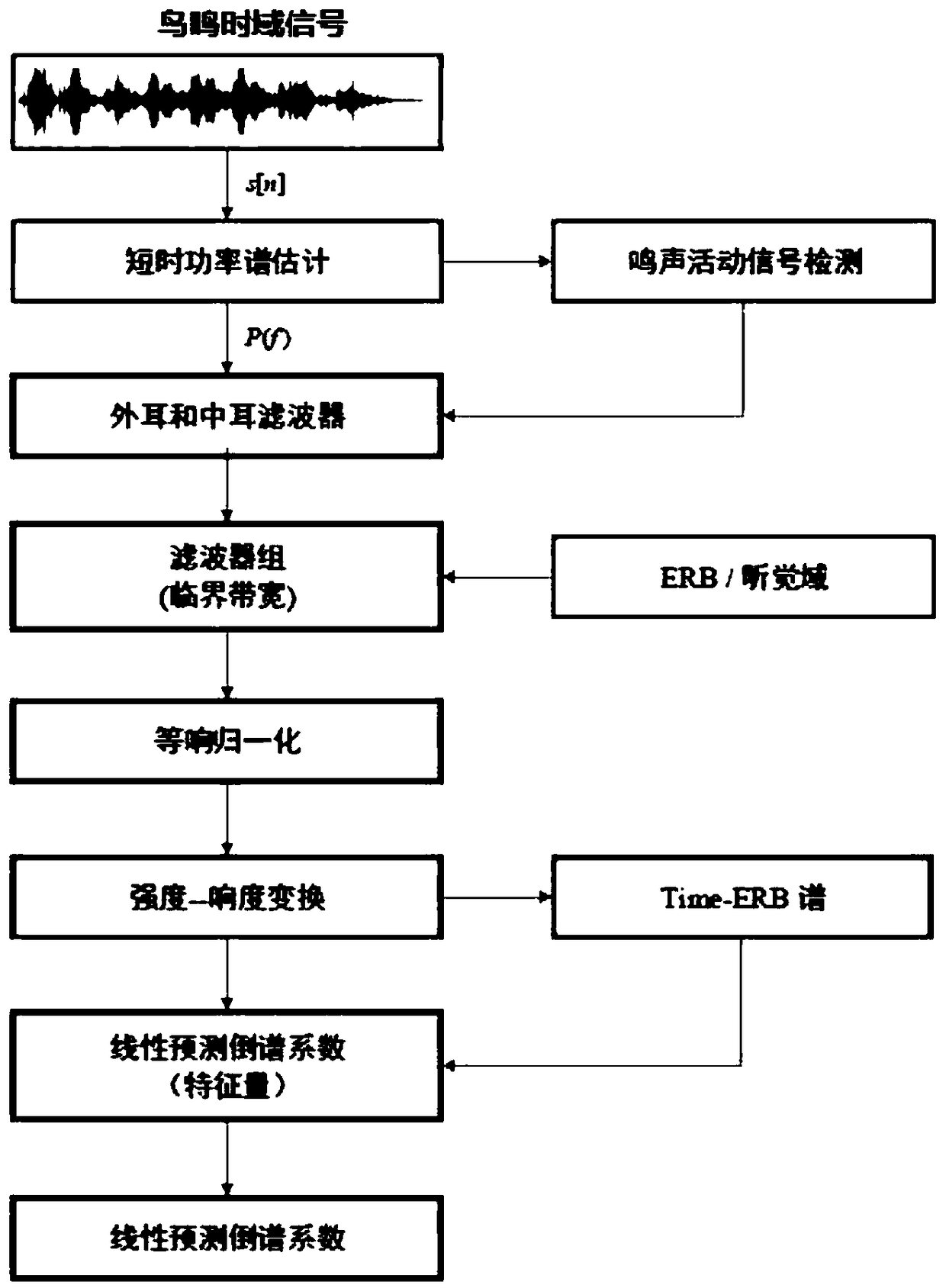
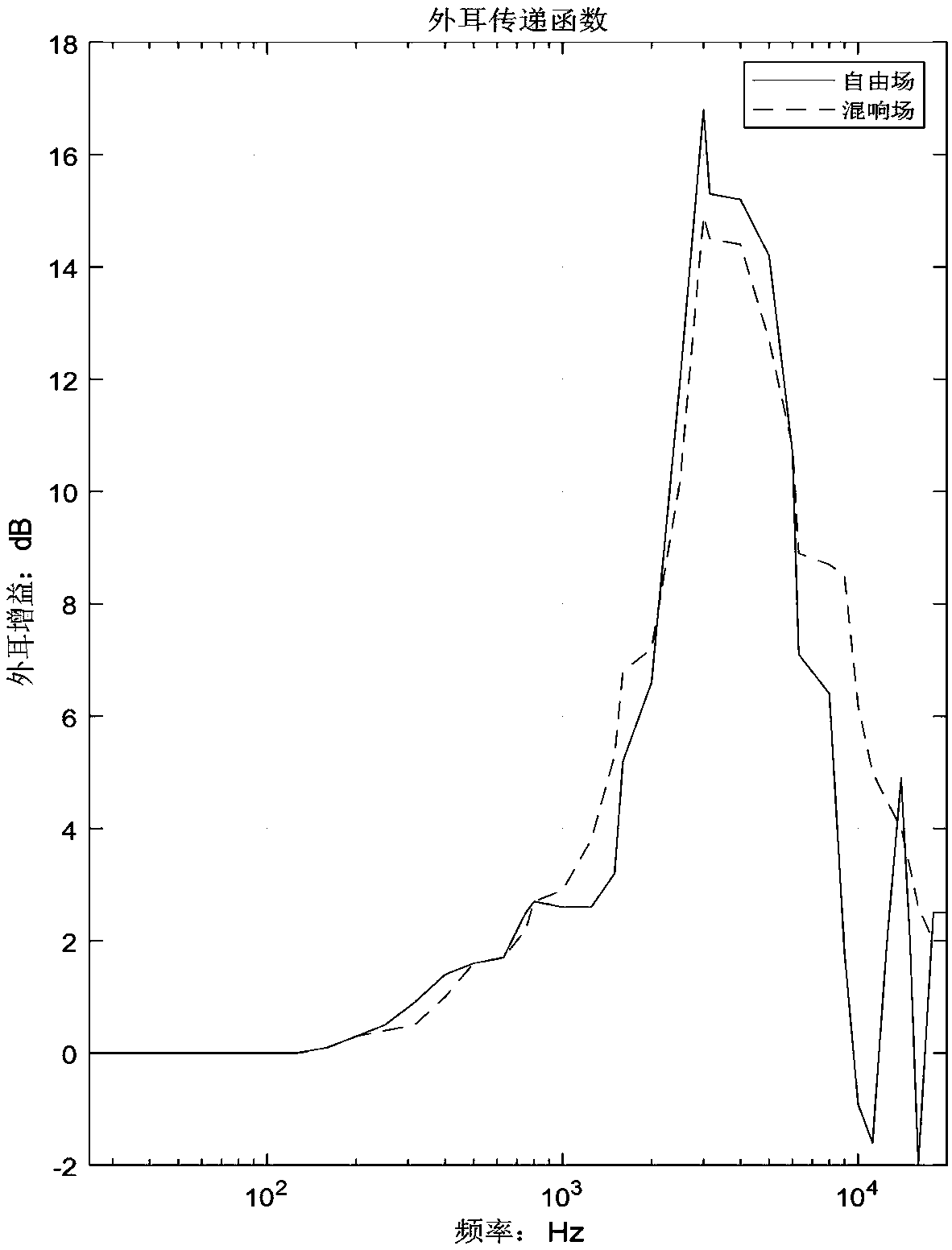
A bird species identification method based on bird whistling
InactiveCN109409308AImprove legibilityDistinguish nuancesSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMiddle earHuman ear
The invention discloses a bird species identification method based on bird whistling, which comprises the following steps of: 1) performing short-time power spectrum transformation on bird whistling signals with noise in a training set, and detecting and screening out activity signals; 2) inputting the active signal into an external ear filter model and a middle ear filter model to obtain an enhanced auditory domain signal; Step 3) transforming the auditory domain signal into a critical band domain to obtain a time-critical band loudness spectrum; 4) extracting a linear prediction cepstrum coefficient of the loudness spectrum as a feature recognition quantity, and inputting the feature recognition quantity into a hidden Markov-deep neural network classifier for training to obtain a trainedbird buzzing classifier; and 5) extracting the linear prediction cepstrum coefficient of the loudness spectrum of the bird whistle to be identified as a feature identification quantity, and inputtingthe feature identification quantity into a trained bird whistle classifier to realize bird whistle identification. The method simulates the sound processing process of human ears, and solves the technical bottleneck of bird whistle automatic identification in a complex background noise environment.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
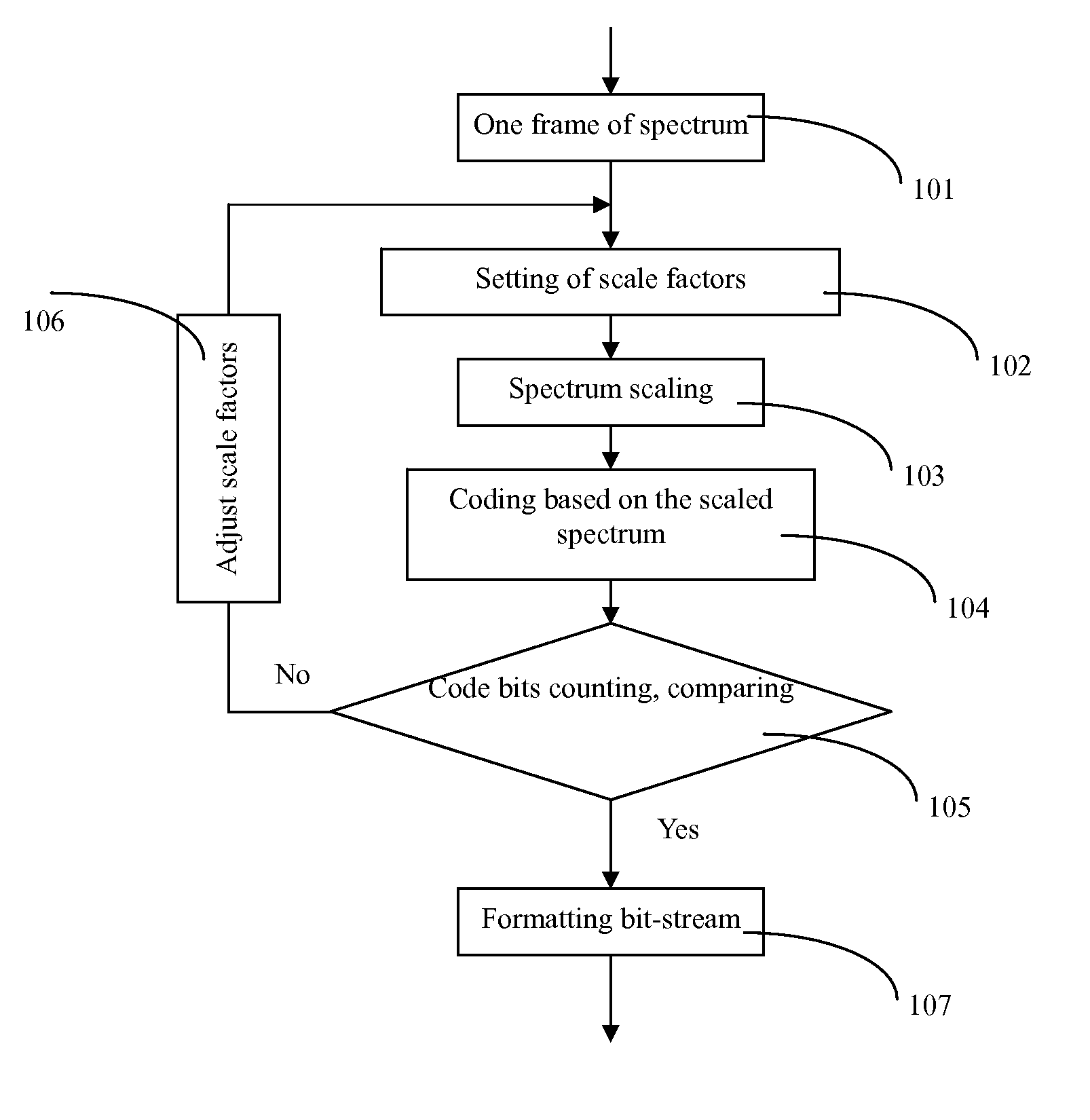
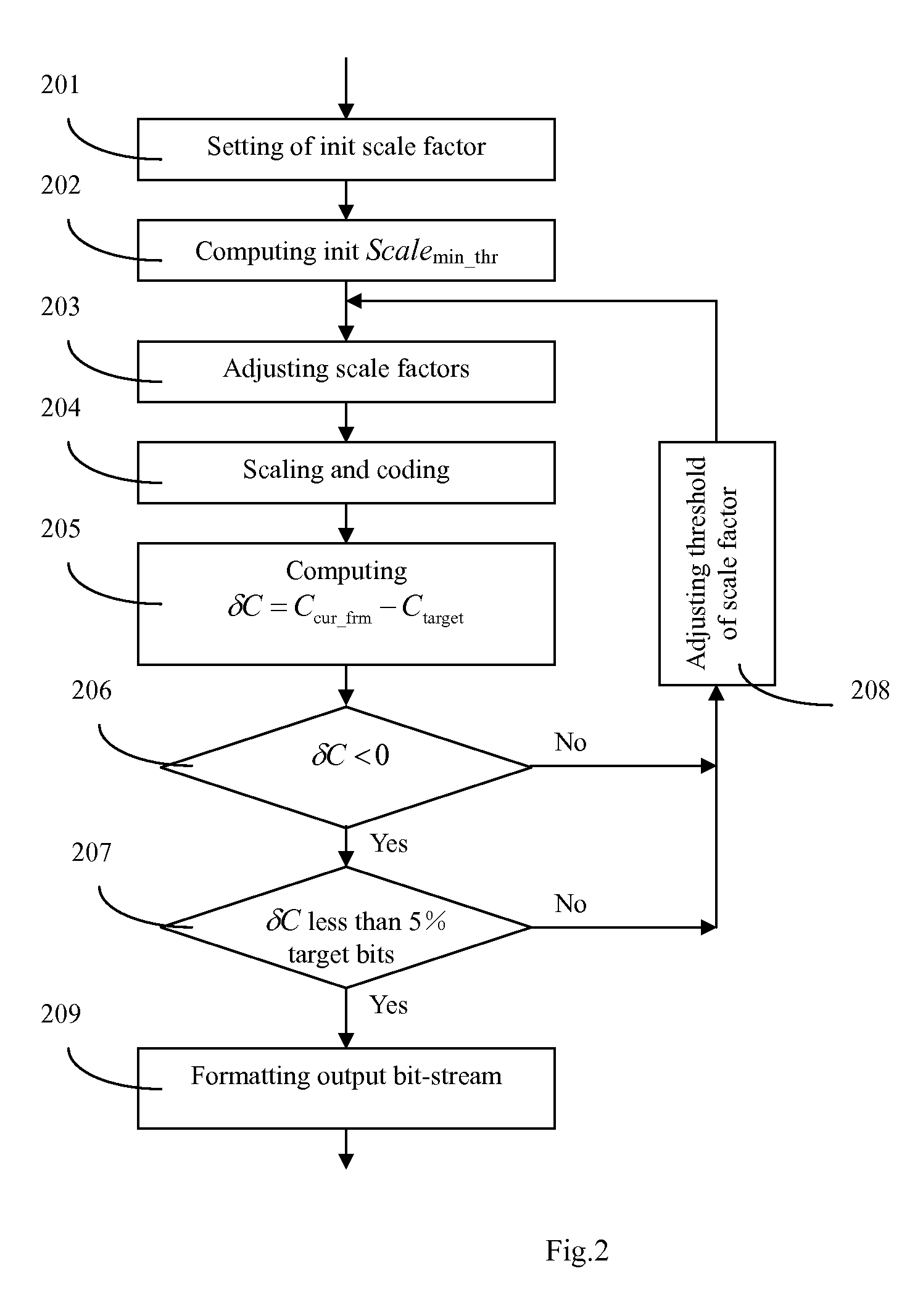
Method of bitrate control and adjustment for audio coding
InactiveUS20070033022A1Improve encoding speedQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumComputer science
This invention discloses a method of bit-rate control and adjustment for audio coding, which comprises following steps: obtain the spectrum of the current audio frame and compute the maximum absolute value of each Bark (Bark: in the unit of critical band) frequency band; calculate the initial value of the minimum scale factor threshold and set the scale factor for each Bark band; Scale the spectrum of each audio frame with different scale factor, encode the quantized spectrum and calculate the coded bit of the current frame; Determine whether or not the coded bits of current frame is within the expected range of the bits, if yes, the bitstream is formatted and outputted, otherwise the minimum scale factor threshold is adjusted and repeat the above steps until the requirement is met. This method can significantly improve the encoding speed and reduce the coding loss of audio.
Owner:SHANGHAI JADE TECH
Electronic sound screening system and method of accoustically impoving the environment
A flexible apparatus for, and method of, acoustically improving an environment permits manual adjustment by one or more local or remote users using a simple graphical interface and automatic adjustment of the system parameters once the manual adjustment is performed. The inputs are weighted by distance from the physical apparatus. The apparatus includes a receiver, a converter, an analyser, a processor and a sound generator. The acoustic energy impinges on the receiver and is converted to an electrical signal by the converter. The analyser receives the electrical signal from the receiver, analyzes the electrical signal, and generates data analysis signals in response to the analyzed electrical signal. The processor produces sound signals based on the data analysis signals from the analyser in each critical band. The sound generator provides sound based on the sound signals. This permits the users to define the sound heard in a set space.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF ART +1
Temporal masking in audio coding based on spectral dynamics in frequency sub-bands
An audio coding technique based on modeling spectral dynamics is disclosed. Frequency decomposition of an input audio signal is performed to obtain multiple frequency sub-bands that closely follow critical bands of human auditory system decomposition. Each sub-band is then frequency transformed and linear prediction is applied. This results in a Hilbert envelope and a Hilbert Carrier for each of the sub-bands. Because of application of linear prediction to frequency components, the technique is called Frequency Domain Linear Prediction (FDLP). The Hilbert envelope and the Hilbert Carrier are analogous to spectral envelope and excitation signals in the Time Domain Linear Prediction (TDLP) techniques. Temporal masking is applied to the FDLP sub-bands to improve the compression efficiency. Specifically, forward masking of the sub-band FDLP carrier signal can be employed to improve compression efficiency of an encoded signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method, system and apparatus for allocating bits in perceptual audio coders
ActiveUS7725313B2Reduce complexitySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBit allocationUniform quantization
A non-iterative and computationally efficient bit allocation technique for perceptual audio coders employing uniform quantization schemes. This is achieved by computing a target MNR for all critical bands in a frame using a target bit rate and associated SMRs. Associated SNRs are then computed for the critical bands using the computed target MNR and the associated SMRs. Bits are then allocated to the critical bands based on the computed associated SNRs.
Owner:ITTIAM SYST P
A method for processing roughness information of vehicle noise sound quality
ActiveCN104102803BThe calculation method is clearHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingSignal on
The invention relates to a vehicle noise sound quality roughness information processing method which comprises the following steps: (1), segmenting noise signals and windowing; (2), carrying out Fourier transformation to the noise signals after windowing, calculating out the exciting sound level of noise signals on a critical band; (3), designing mutually superimposed passages on the critical band, dividing the exciting sound level onto the passages so as to form sub noise signals, then carrying out inverse Fourier transform to the noise signals, so as to obtain time domain sub signals at the exciting sound level; (4), carrying out inverse Fourier transform after demodulation to the time domain sub signals at the exciting sound level, so as to obtain a signal time domain value after modulation, and then calculating out the modulation indexes of each passage; (5), calculating out the related coefficient and the carrier frequency weighting factor among the noise signals of all the passages; (6), calculating out the roughness of the noise signals on each passage and calculating out the total roughness. Compared with the prior art, the vehicle noise sound quality roughness information processing method provided by the invention takes auditory perception characteristics of human ears into consideration, and has the advantages of easiness in method understanding, high precision and the like.
Owner:上海鹊音科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com