Polyamide resin composition
A technology of polyamide resin and composition, which is applied in the field of polyamide resin composition, and can solve problems such as the inability to obtain a uniformly dispersed resin composition and the inability to fully improve the properties of the resin composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
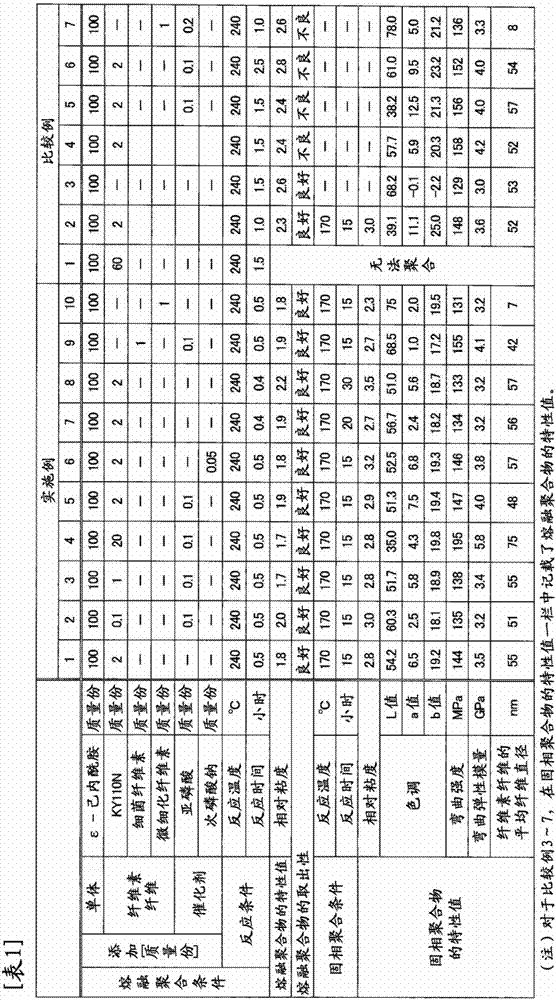
Embodiment 1
[0071] [Adjustment of aqueous dispersion of cellulose fiber]
[0072] As the aqueous dispersion of cellulose fibers, CELISH KY110N (an aqueous dispersion containing 15% by mass of cellulose fibers having an average fiber diameter of 125 nm manufactured by Daicel FineChem Co., Ltd.) was used. Purified water was added to this aqueous dispersion and stirred with a mixer to prepare an aqueous dispersion having a cellulose fiber content of 3% by mass.
[0073] [melt polymerization]
[0074] 70 parts by mass of the obtained aqueous dispersion of cellulose fibers and 100 parts by mass of ε-caprolactam were further stirred and mixed with a mixer until a uniform dispersion was obtained. The pressure was raised to 240° C. over 4 hours while stirring the mixed dispersion liquid while controlling the pressure at 0.7 MPa. Then the pressure was released to atmospheric pressure, and melt polymerization was carried out at 240°C for 0.5 hours.
[0075] After the end of the melt polymerizati...
Embodiment 2~8、 comparative example 2
[0080] [melt polymerization]
[0081] Compared with Example 1, the content of cellulose fibers, whether or not to use a polymerization catalyst, its type and content, and reaction time were changed as described in Table 1. Except for this, melt polymerization was performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0082] After the end of the melt polymerization, the polyamide resin composition was taken out, cut and pelletized.
[0083] [Refining, solid state polymerization]
[0084] Using the obtained pellets, refining and solid phase polymerization were carried out in the same manner as in Example 1.
Embodiment 9
[0086] [Adjustment of aqueous dispersion of cellulose fiber]
[0087] Inject 50 mL of a culture medium consisting of 0.5% by mass glucose, 0.5% by mass polypeptone, 0.5% by mass of yeast extract, and 0.1% by mass of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate into a 200-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Perform steam sterilization at 120°C for 20 minutes. Gluconacetobacter xylinus (NBRC 16670) propagated on a test tube slant agar medium was inoculated with 1 platinum ear, and cultured statically at 30° C. for 7 days. After 7 days, white gel film-like bacterial cellulose was formed on the upper layer of the culture solution.
[0088] The obtained bacterial cellulose was pulverized with a mixer, then soaked in water and washed repeatedly to replace it with water to prepare an aqueous dispersion having a cellulose fiber content of 4.1% by mass. The average fiber diameter of the cellulose fibers was 60 nm.
[0089] [melt polymerization]
[0090] Compared with Example 1, 24.4 parts by mass of the obtain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com