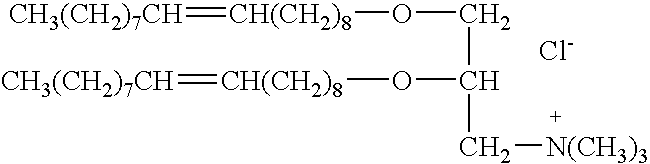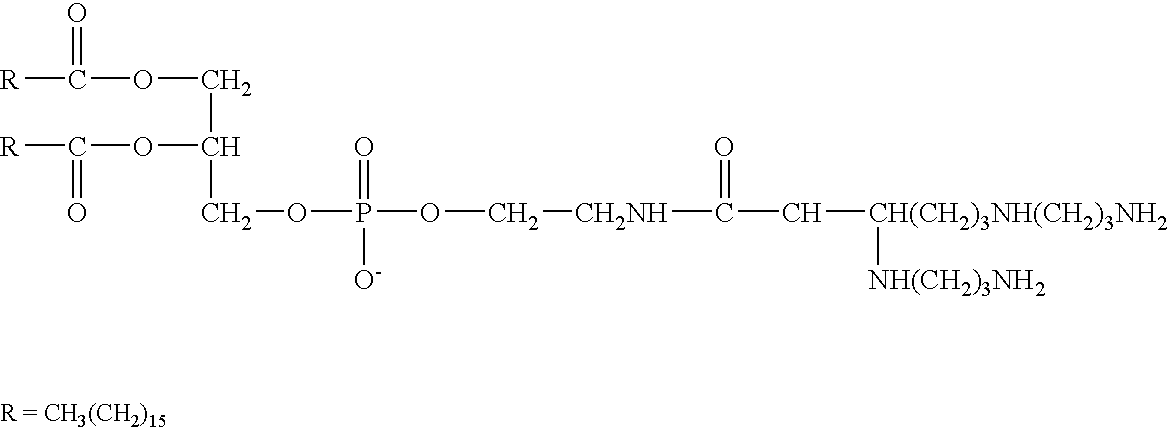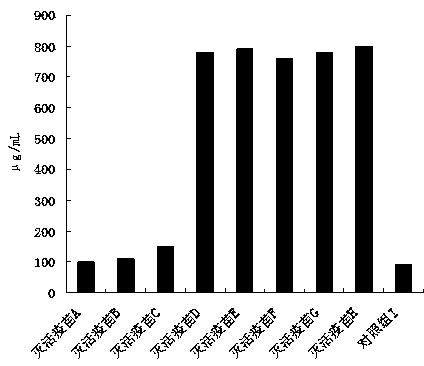Patents
Literature
128 results about "Lipid A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
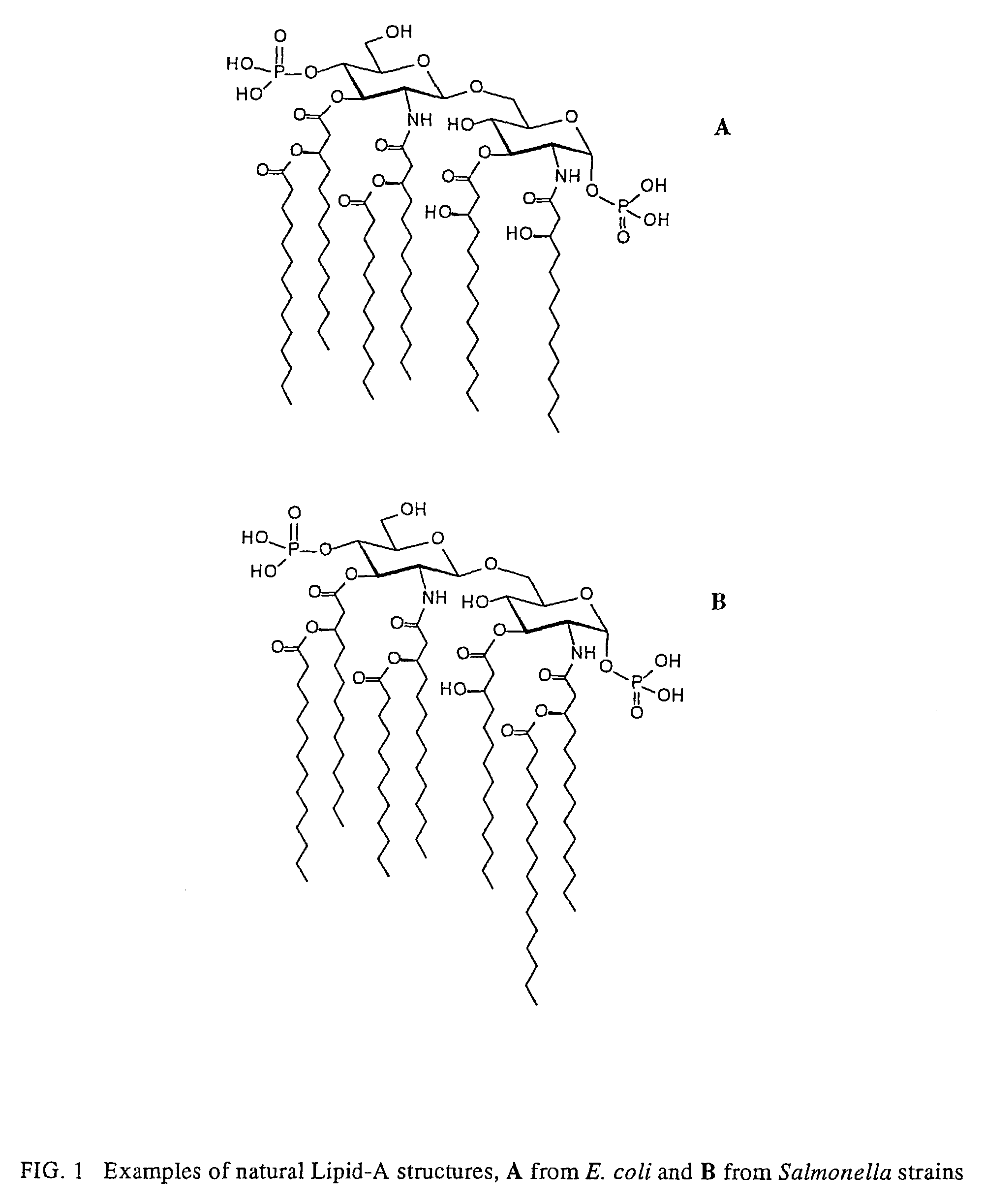
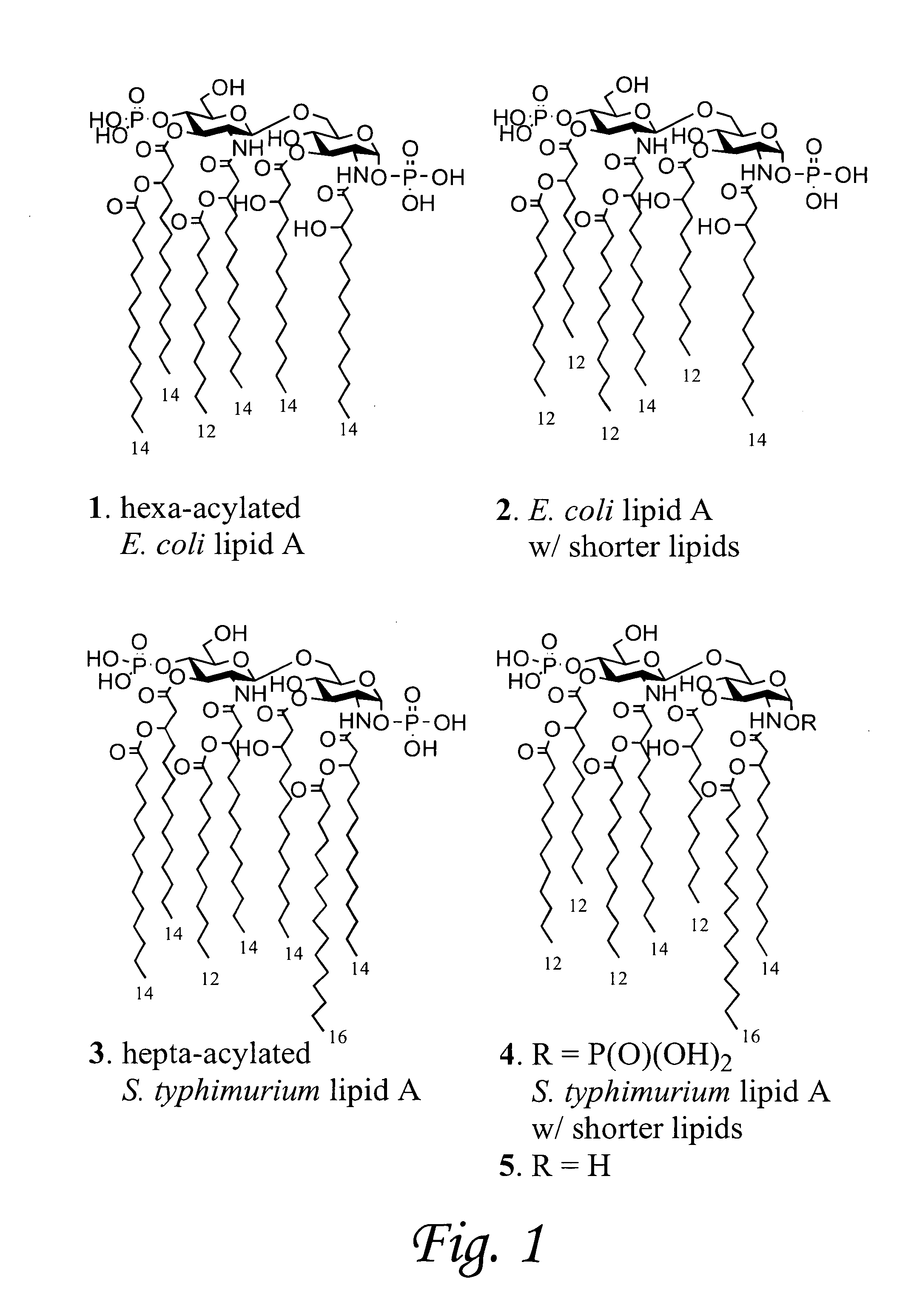
Lipid A is a lipid component of an endotoxin held responsible for the toxicity of gram-negative bacteria. It is the innermost of the three regions of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also called endotoxin molecule, and its hydrophobic nature allows it to anchor the LPS to the outer membrane. While its toxic effects can be damaging, the sensing of lipid A by the human immune system may also be critical for the onset of immune responses to gram-negative infection, and for the subsequent successful fight against the infection.
Rinse-off personal care compositions containing high modulus lipids
InactiveUS20060239953A1Clean skinHigh modulusCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPersonal careLipid formation
A rinsable personal care composition comprises (a) 0 to 75 weight percent of a surfactant; (b) 0.01 to 99 weight percent of a skin benefit agent comprising a high modulus lipid and an ester; and (c) 0 to 99 weight percent water.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Genetic immunization with cationic lipids
InactiveUS6890554B2Elicit immune responseOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLipid formationEpitope mapping
A method for immunization using genetic material is disclosed. Compositions for genetic immunization comprising cationic lipids and polynucleotides are also disclosed. Methods for using genetic immunization to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are also disclosed. A method for epitope mapping is also disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Bone graft material incorporating demineralized bone matrix and lipids
InactiveUS6565884B2Good osteoinductivityEasy to operateBiocidePowder deliveryHydrophilic polymersVitamin C
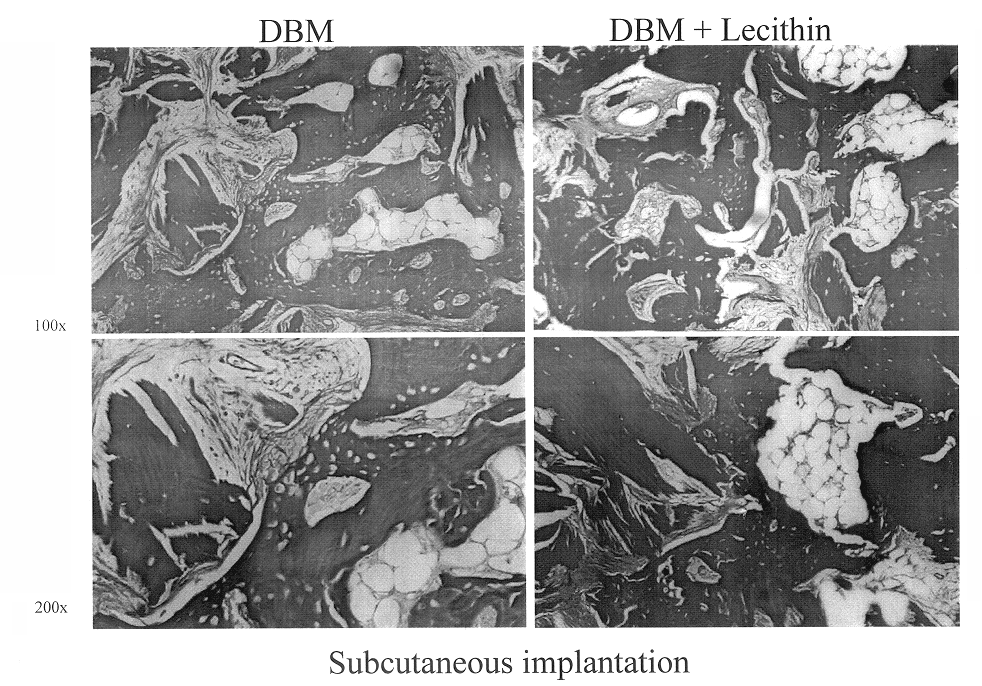
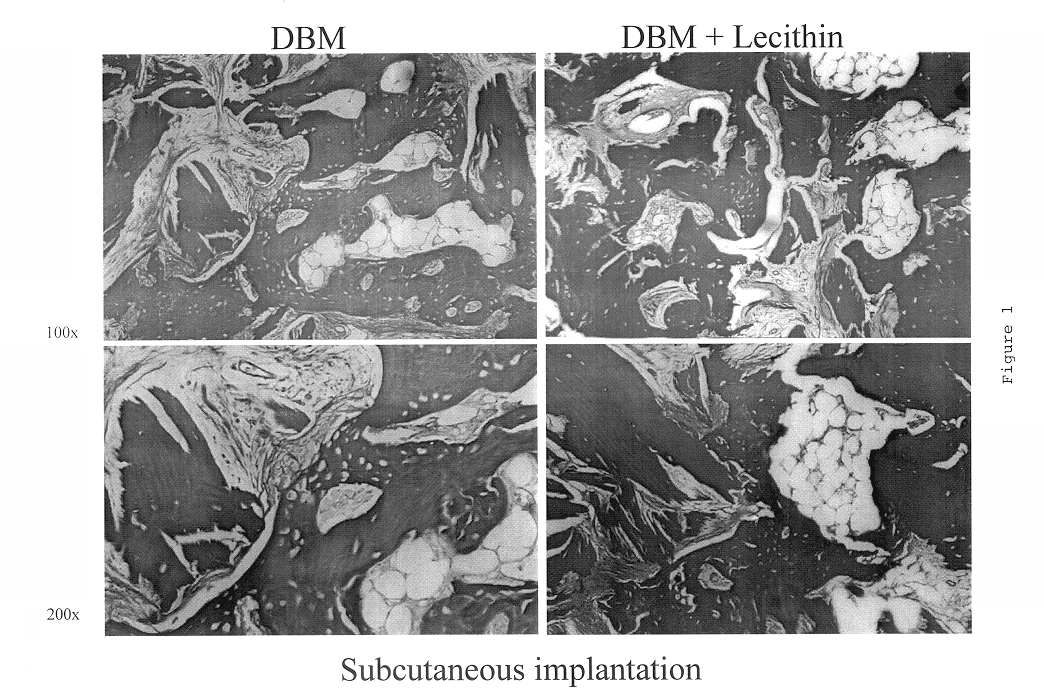
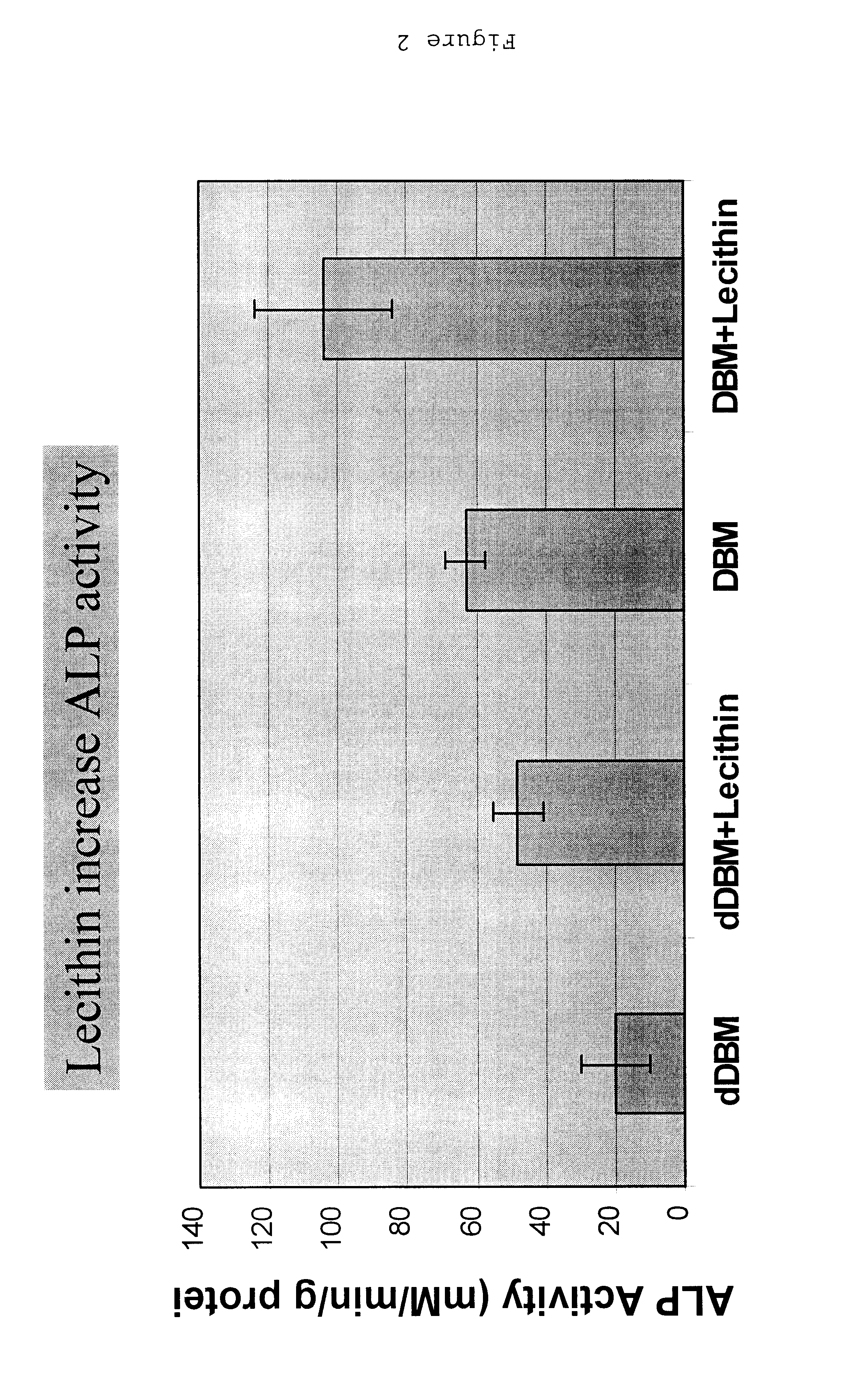
A demineralized bone putty composition comprises: (1) demineralized bone matrix (DBM); and (2) a lipid fraction selected from the group consisting of lecithin and a mixture of lecithin and triglycerides containing unsaturated fatty acids. The putty composition is moldable, biocompatible, slowly resorbable, and soluble in tissue fluids, and non-extrudable. The composition delivers a biologically active product to animals and humans that will enhance bone formation at sites where bone is lost, deficient, or present in suboptimal amounts. The composition can further comprise calcium, an antioxidant such as Vitamin E or Vitamin C, or a hydrophilic polymer such as methylcellulose or hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Genetic immunization with cationic lipids
InactiveUS7166298B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedEpitope mappingGenetic Materials
A method for immunization using genetic material is disclosed. Compositions for genetic immunization comprising cationic lipids and polynucleotides are also disclosed. Methods for using genetic immunization to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are also disclosed. A method for epitope mapping is also disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Lipopolysaccharide fractions of vitreoscilla filiformis useful for stimulating the synthesis of Anti-microbial peptides of the skin
InactiveUS20090035294A1Prevent skinImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsAnti microbial peptideMicroorganism
Specific fractions of Vitreoscilla filiformis comprising its Lipid A are useful for stimulating the synthesis of anti-microbial peptides of the skin.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Lipid A and other carbohydrate ligand analogs
Owner:ONCOTHYREON
Method for evaluating lipid a analog-containing injections
InactiveUS6828155B1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLipid formationMembrane fluidity
The present invention provides an evaluation method and preparation process of injection containing a lipid A analog. Specifically, it provides, in an injection preparation containing a lipid A analog or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, forecasting and evaluating methods of the pharmacokinetics of the lipid A analog, and quality evaluating method and preparation process of the injection, which each comprises measuring membrane fluidity and / or circular dichroism.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
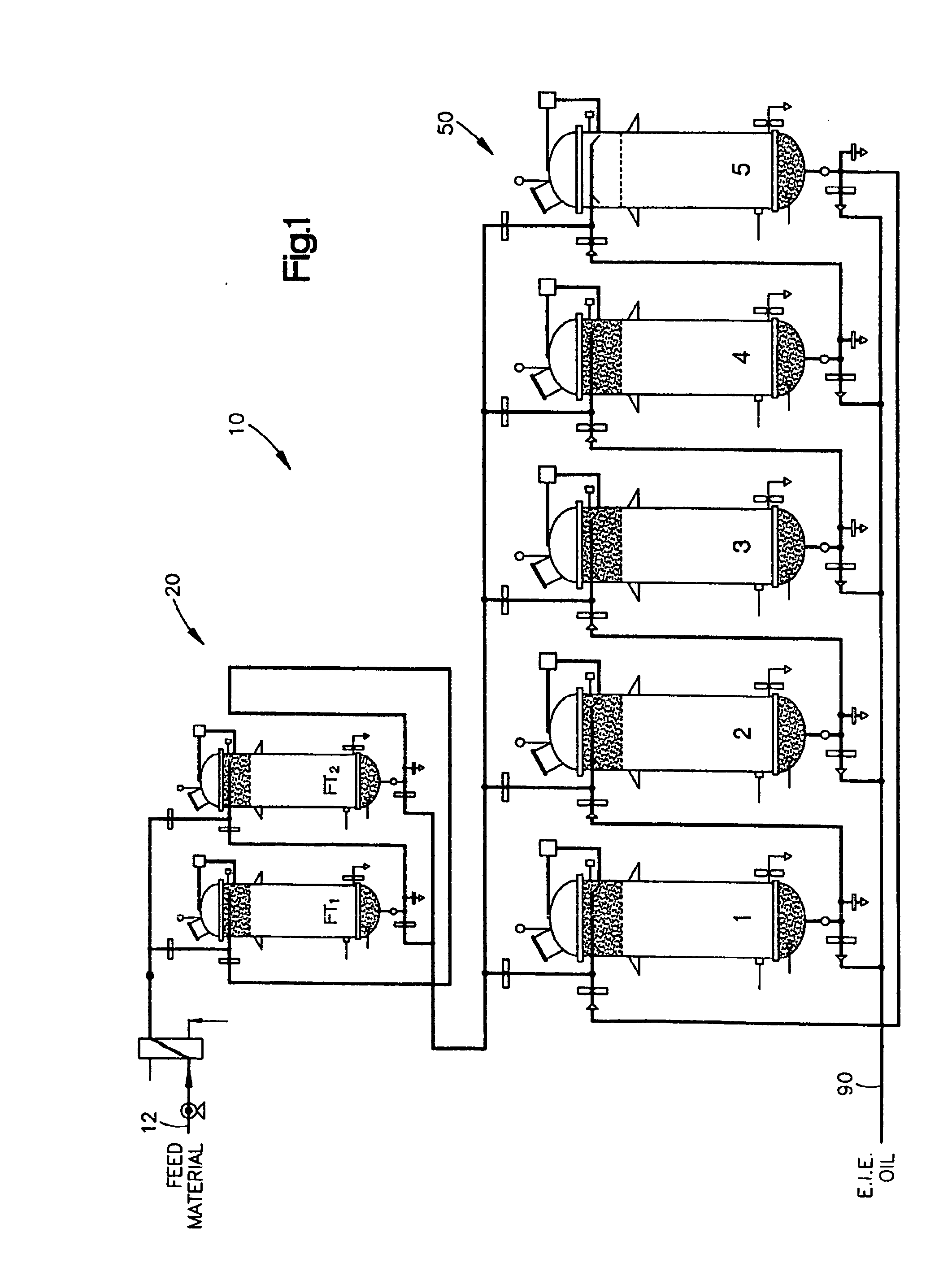
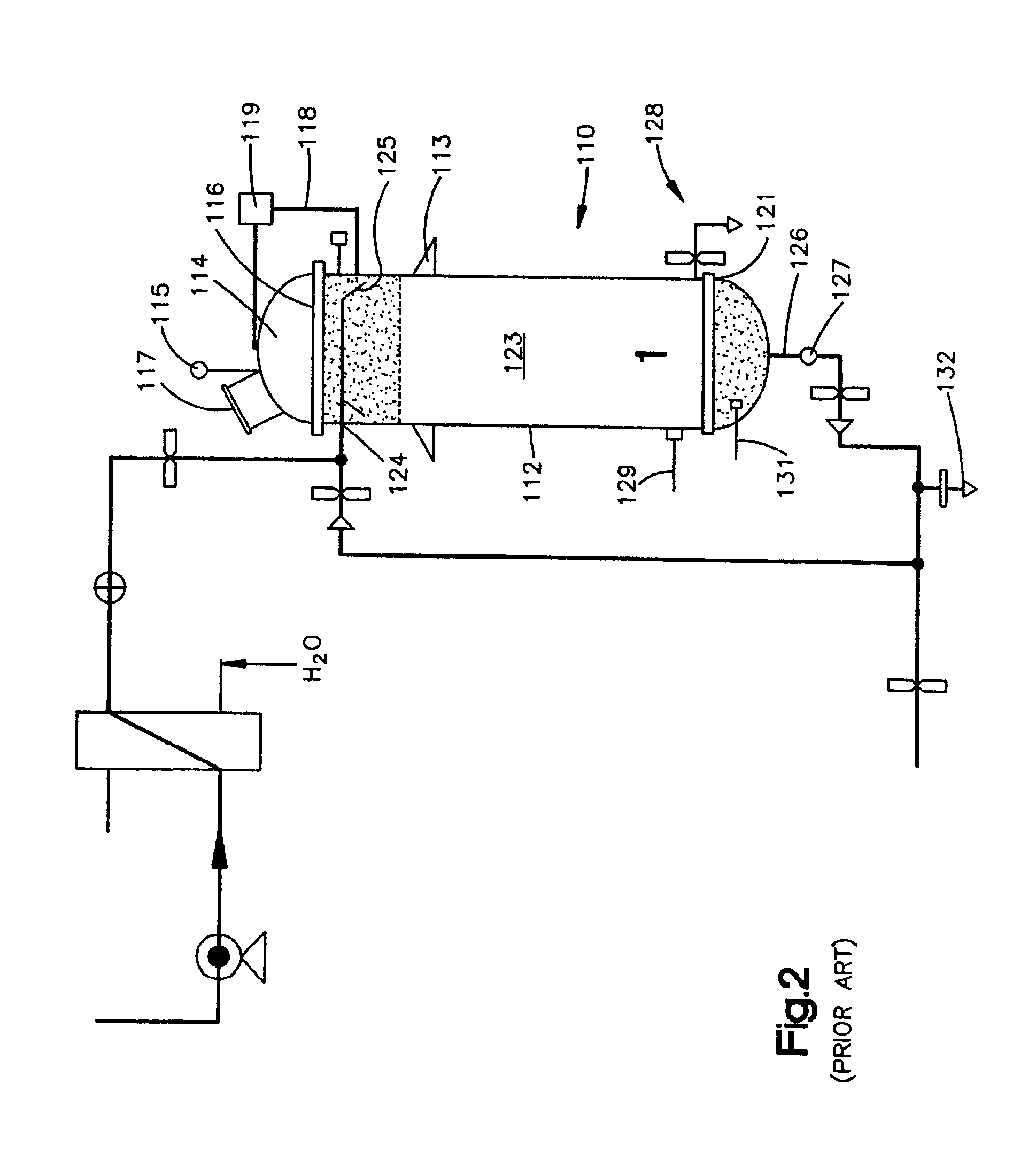
Continuous Process and Apparatus for Enzymatic Treatment of Lipids
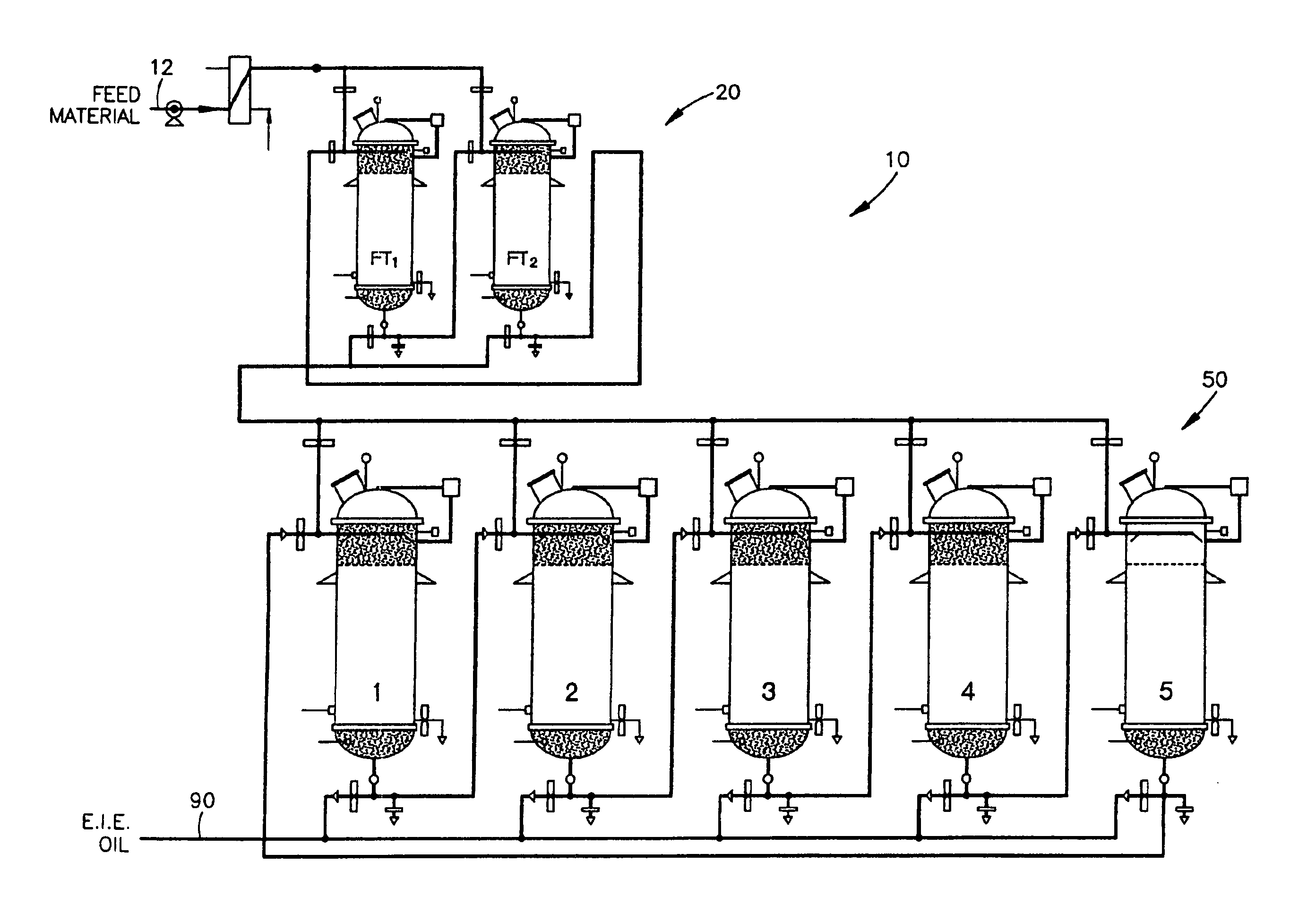
ActiveUS20080138867A1Constant flowLess operator monitoringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationFixed bed
A method and system for the enzymatic treatment of a lipid containing feedstock comprises contacting the feedstock with a processing aid, then causing the feedstock to pass at a substantially constant flow rate through a treatment system comprising a plurality of enzyme-containing fixed bed reactors connected to one another in series. The fixed bed reactors can be individually serviceable, the flow rate of the feedstock remaining substantially constant through the system when one of the fixed bed reactors is taken off line for servicing. In the most preferred embodiment, the processing aid is a substantially moisture-free silica. The processing aid can be placed in one or more of the fixed bed reactors, disposed above the enzyme in the reactor, or it can be in a pre-treatment system which can comprise one or more reactors.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
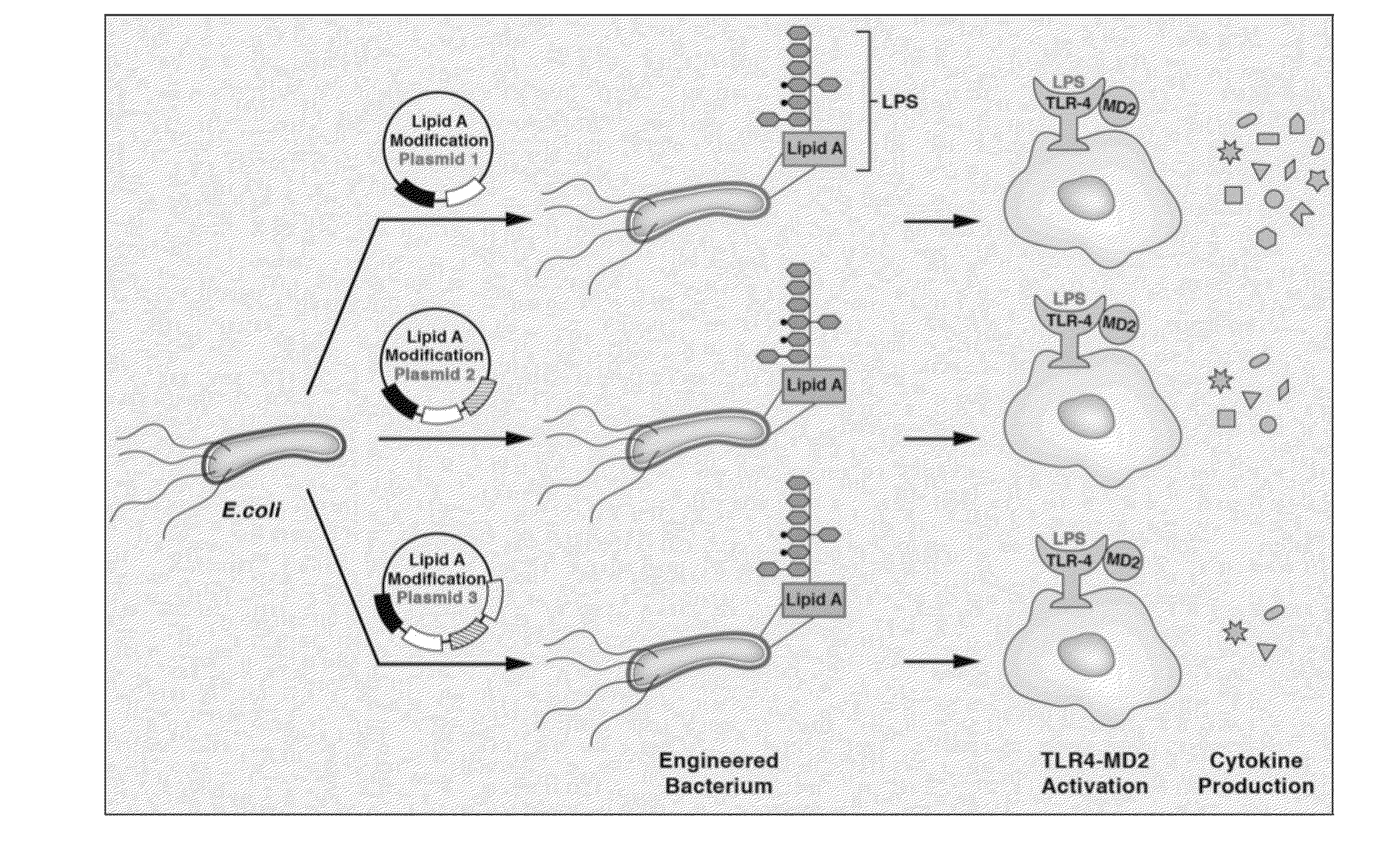
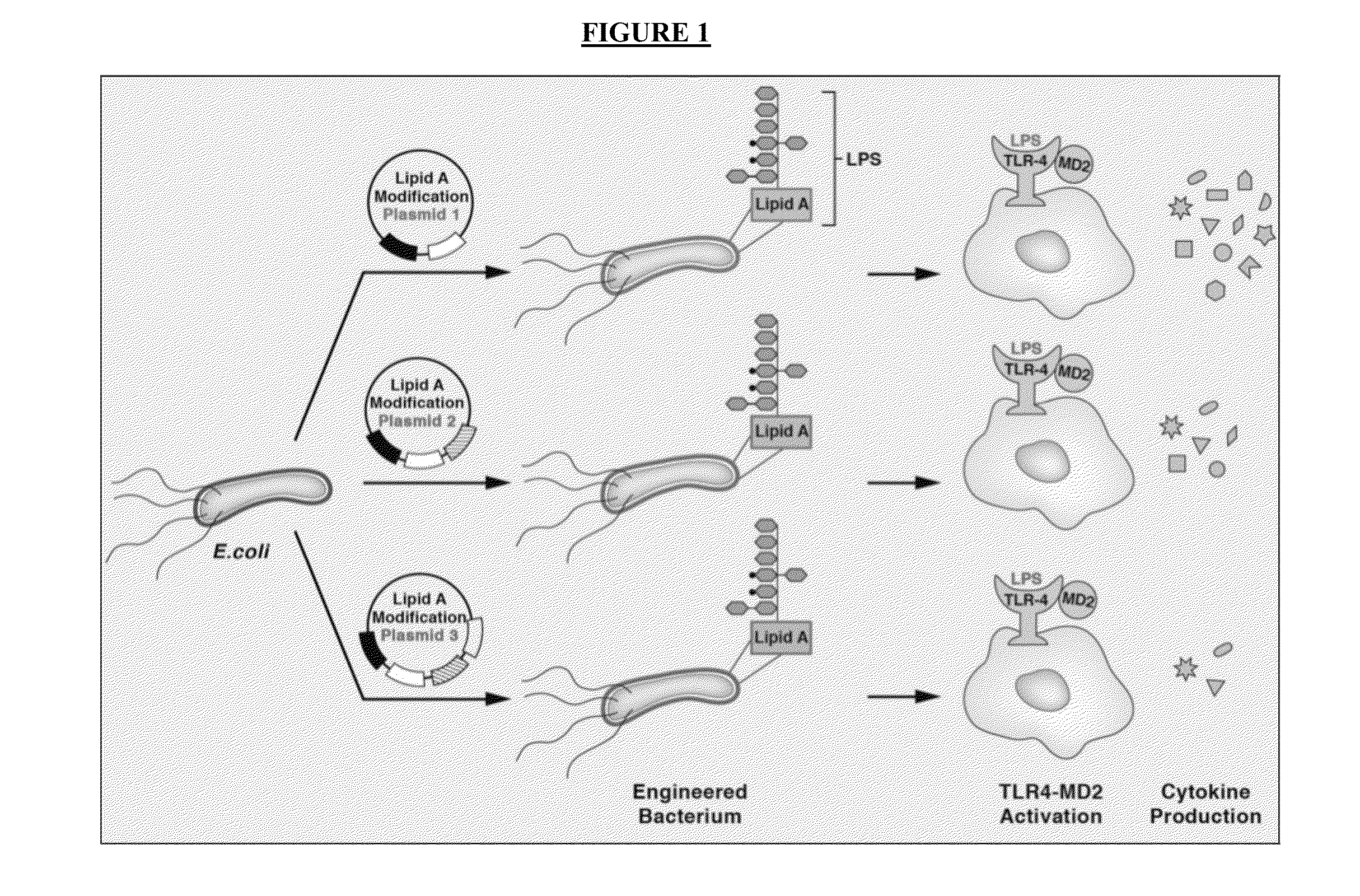
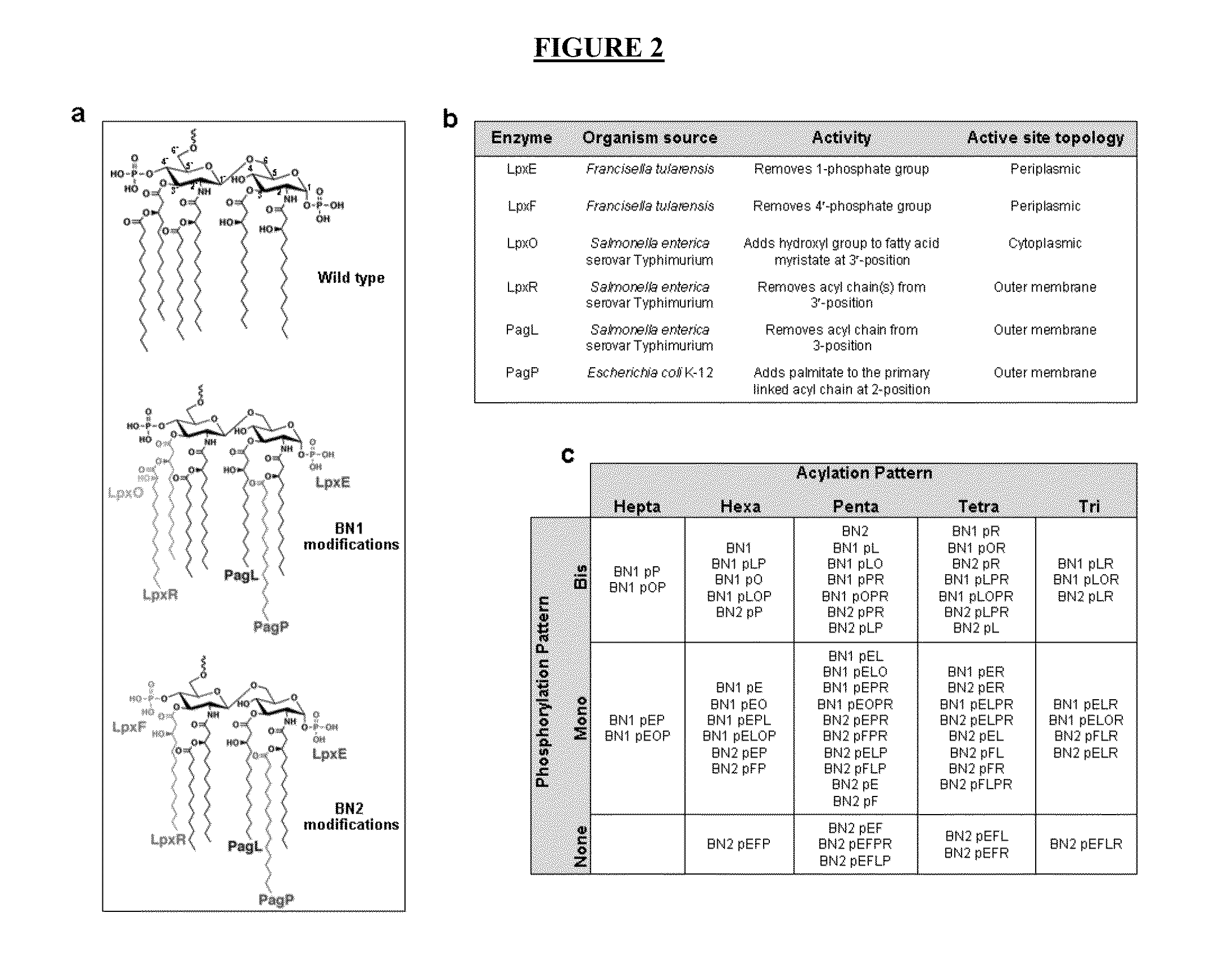
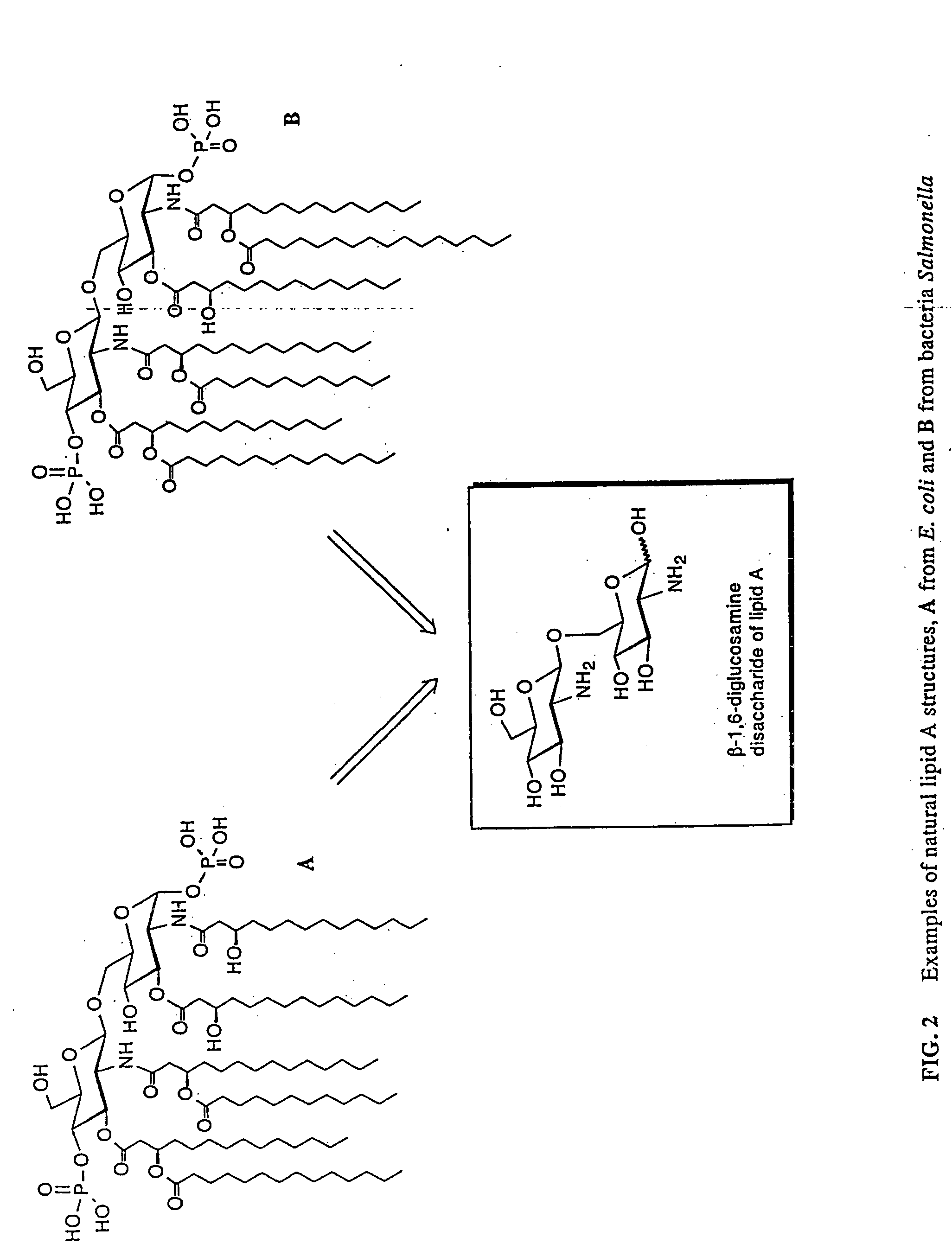
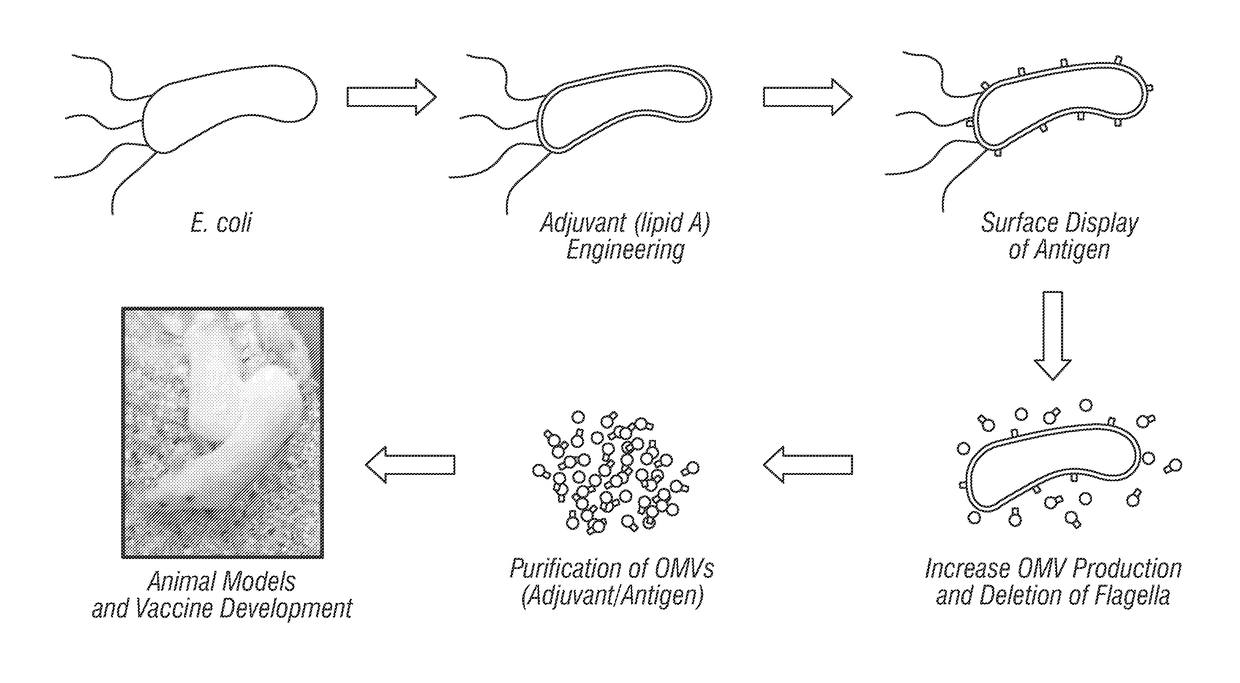
Synthetic lipid biology for combinatorial engineering of endotoxin
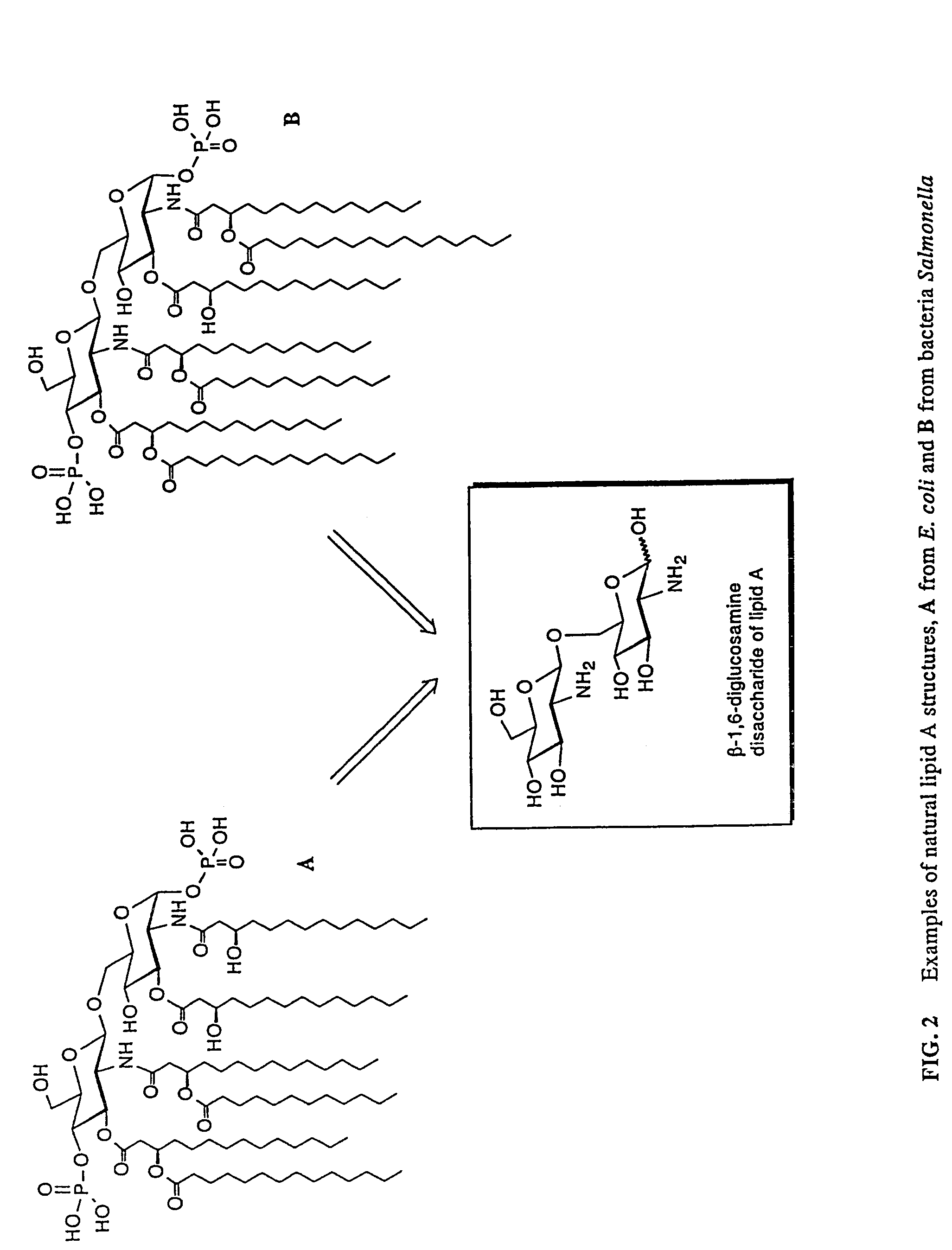
The present disclosure generally relates to genetic engineering of bacteria. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to genetic engineering of Gram-negative bacteria expressing different species of lipid A on their surface. In one embodiment, the present disclosure provides for an engineered strain of E. coli according to Table 1. In another embodiment, the present disclosure provides for a lipopolysaccharide purified from an engineered strain of E. coli according to Table 1.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Quil a fraction with low toxicity and use thereof
ActiveUS20060239963A1Improve the level ofBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunomodulationsCell Wall Skeleton
Owner:NOVAVAX
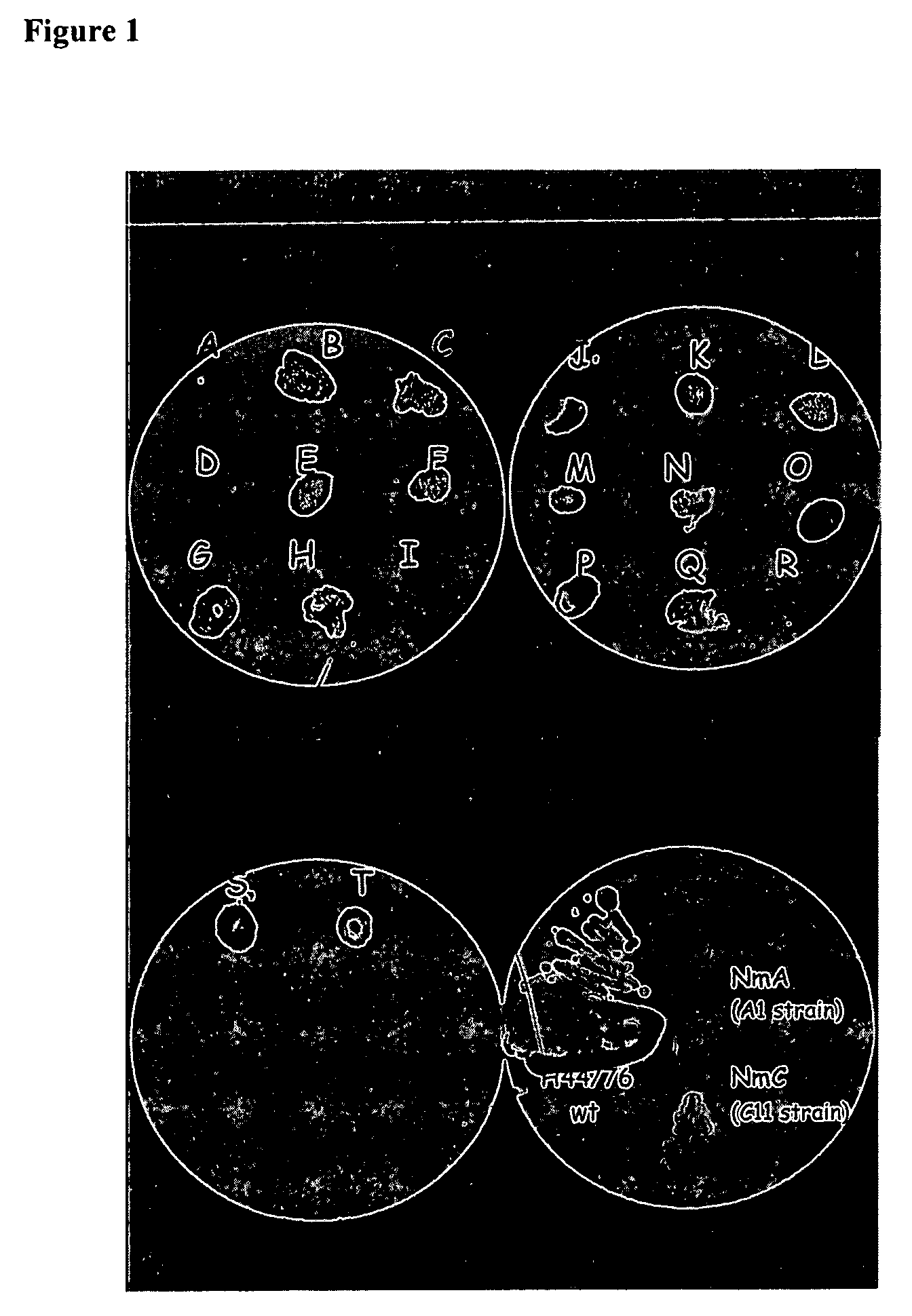
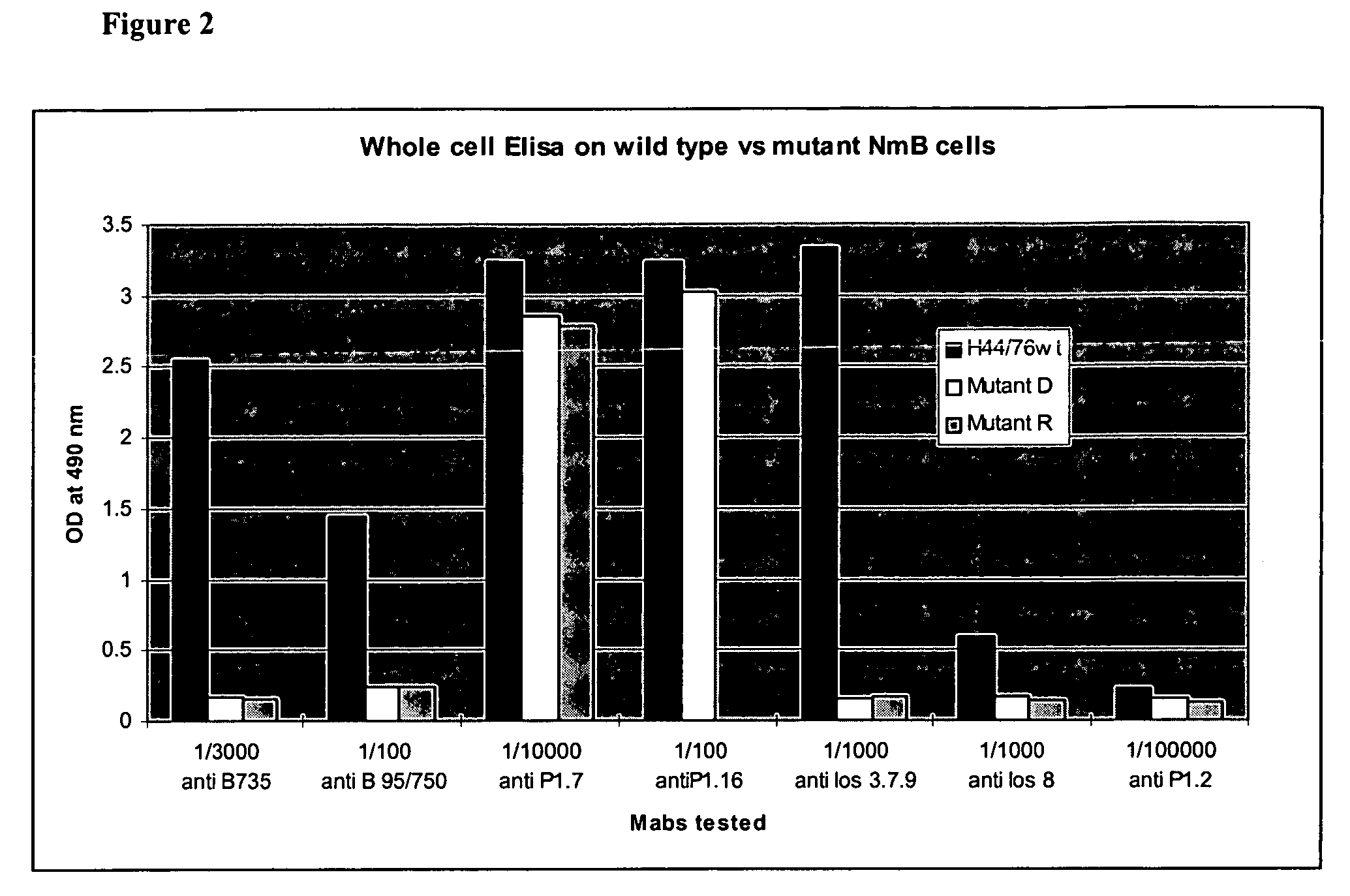
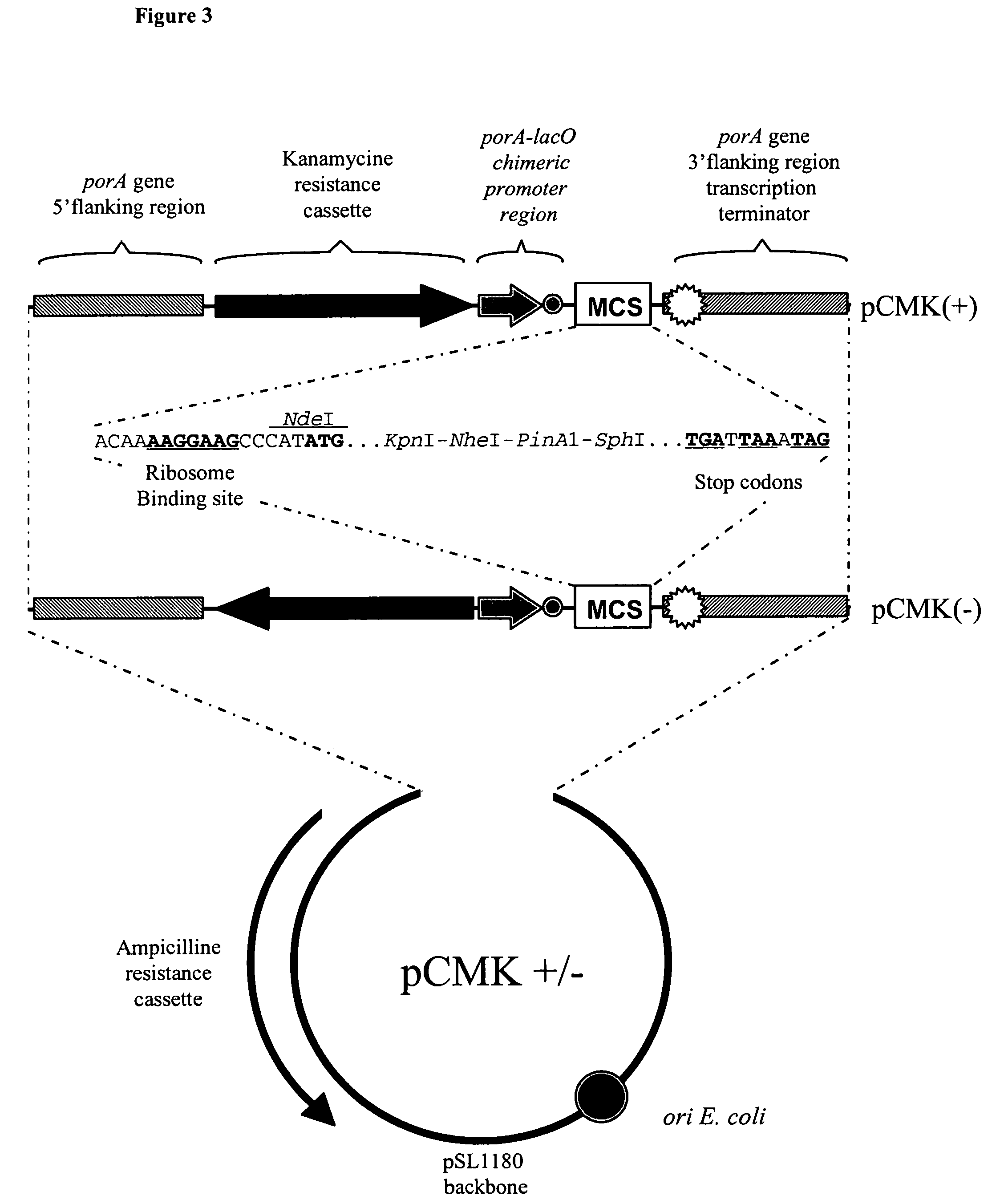
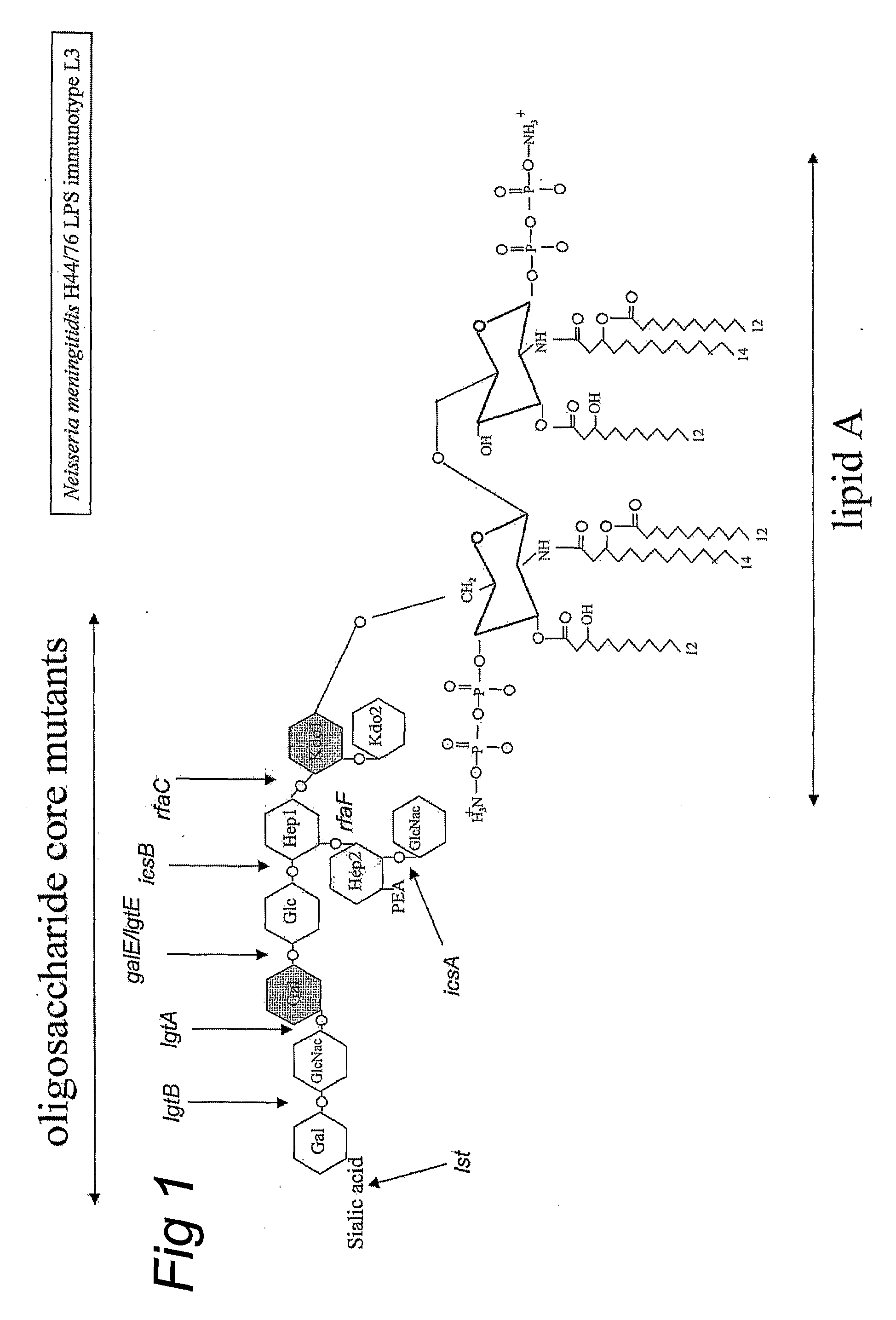
Neisseria mutants, lipooligosaccharides and immunogenic compositions
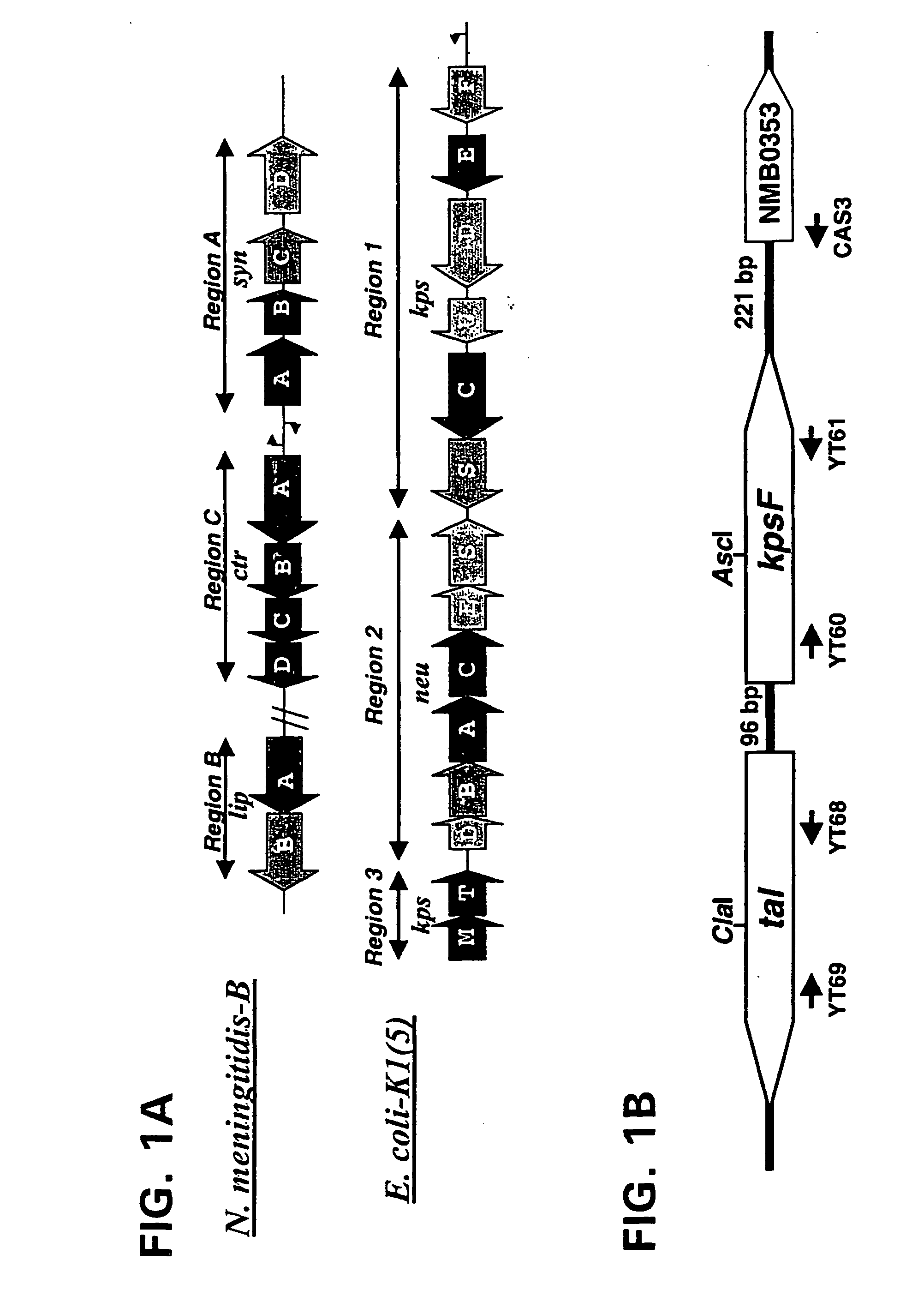
Provided herein are mutant strains of Neisseria meningitidis which produce Kdo-free lipid A as well as the Kdo-free lipid A molecules and immunogenic compositions containing such Kdo-free lipid A molecules from a Neisseria strain containing a genetically stable mutation which inactivates a gene selected from the group consisting of genes encoding arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase, CMP-Kdo synthetase and CMP-Kdo transferase. N. meningitidis NMB206 is a specifically exemplified strain which harbors a stable insertion mutation in the gene (ApsF) encoding A5P isomerase; strain NMB-249 is a specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdtA) encoding CMP-Kdo synthetase, and strain NMB259 is specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdsB) encoding CMP-Kdo transferase. Also provided by the present invention are methods for the production of Lipid A flee of 3-keto-3-deoxyoctanoic acid using these genetically stable N. meningitidis mutants. Also describes is pYT250, a plasmid functional in neisseriae and in enterics such as Escherichia coli.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for solid phase extraction of lipids
ActiveUS20100291688A1Overcome limitationsOther chemical processesComponent separationPhosphateFiltration
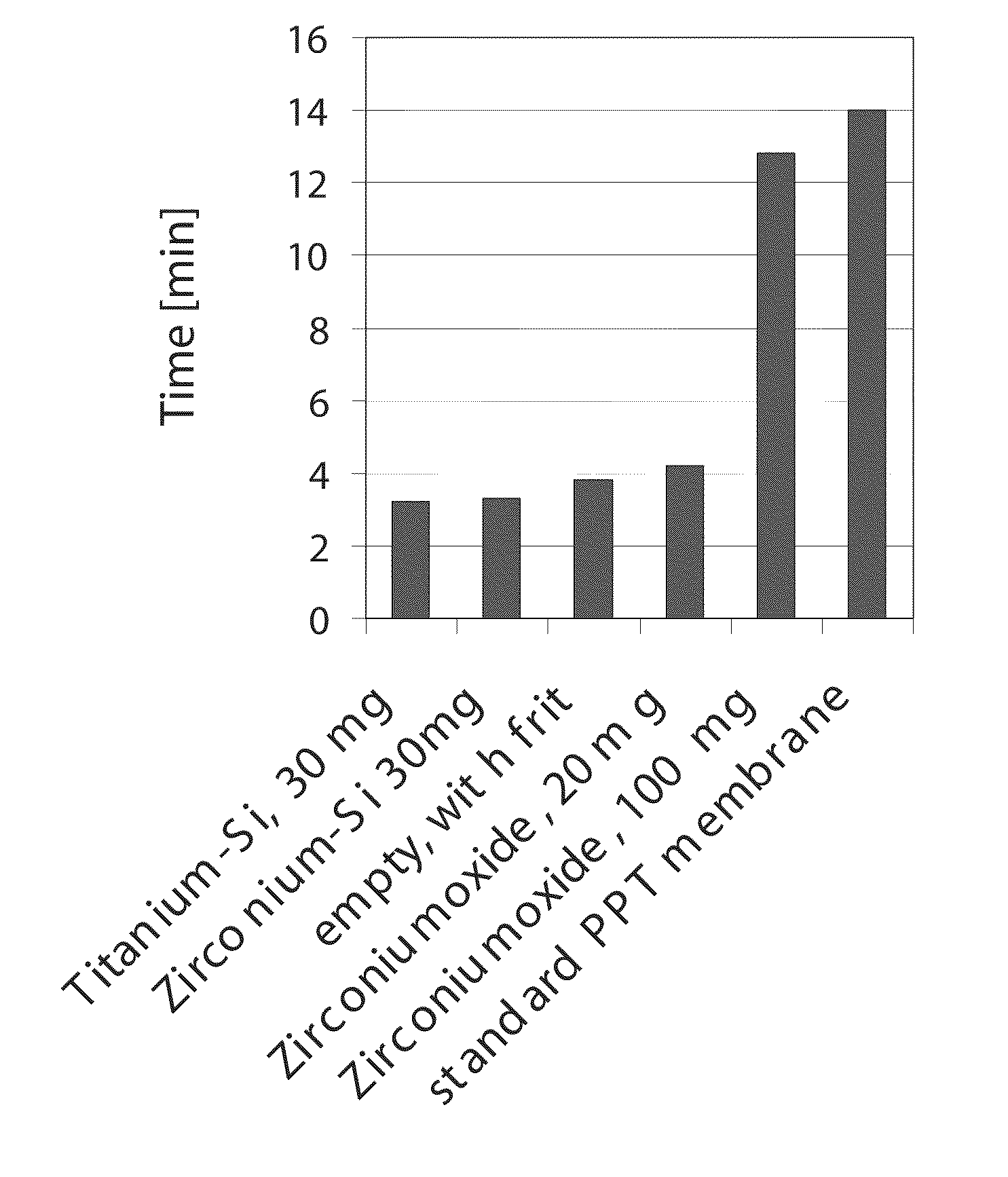
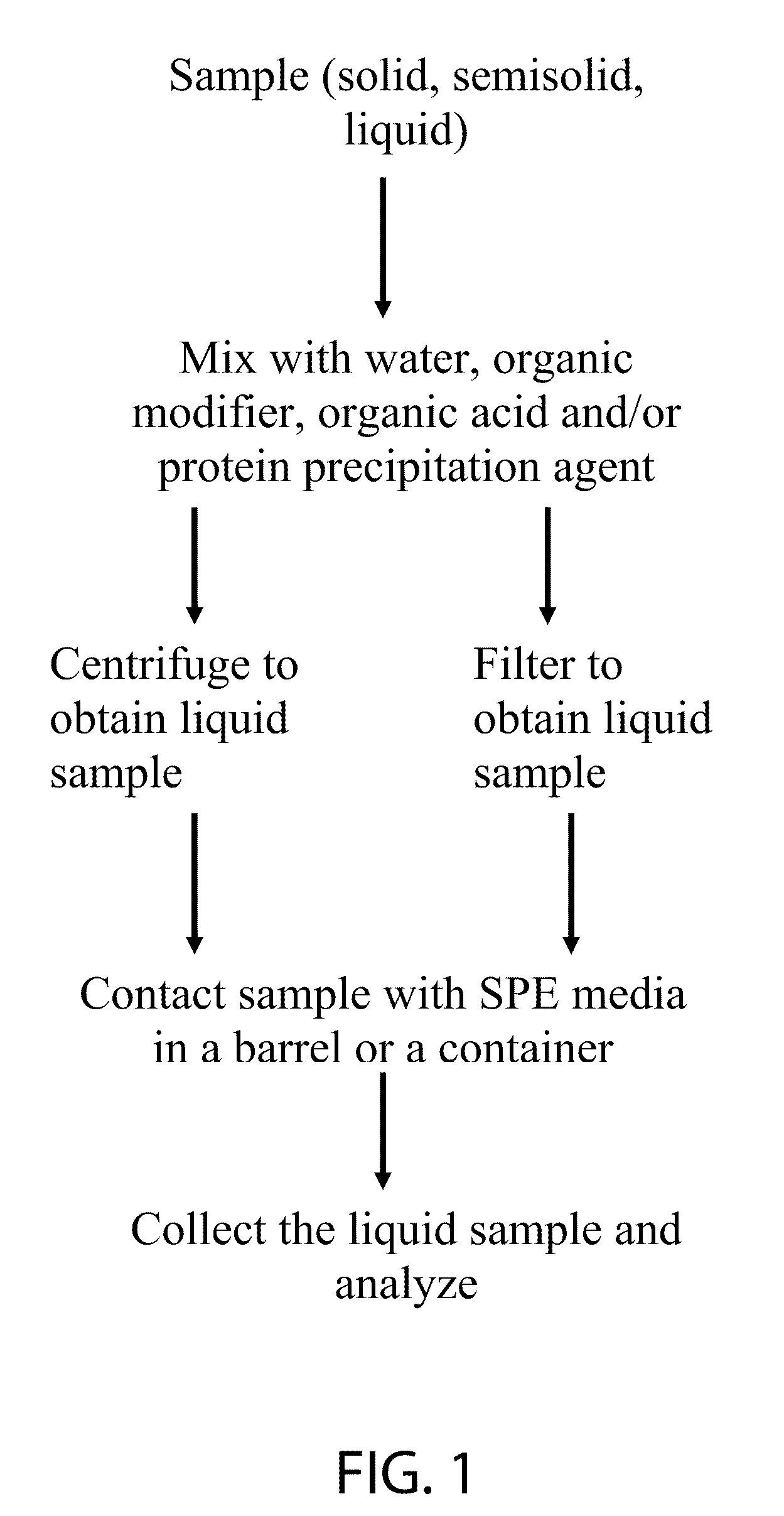
A composition, method and device for the preparation of biological samples for subsequent instrumental analyses, such as GC, GC-MS, LC and LC-MS analysis, using a solid phase extraction (SPE) process is described. Through SPE process alone or an integrated combination of protein precipitation, filtration, and SPE using a hydrophobic zirconia-coated chromatographic media, interfering compounds, such as proteins, glycerides and phosphate-containing compounds, are eliminated from the biological, food, environmental and biotechnology samples, affording an enhanced analyte response during the instrumental analysis.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
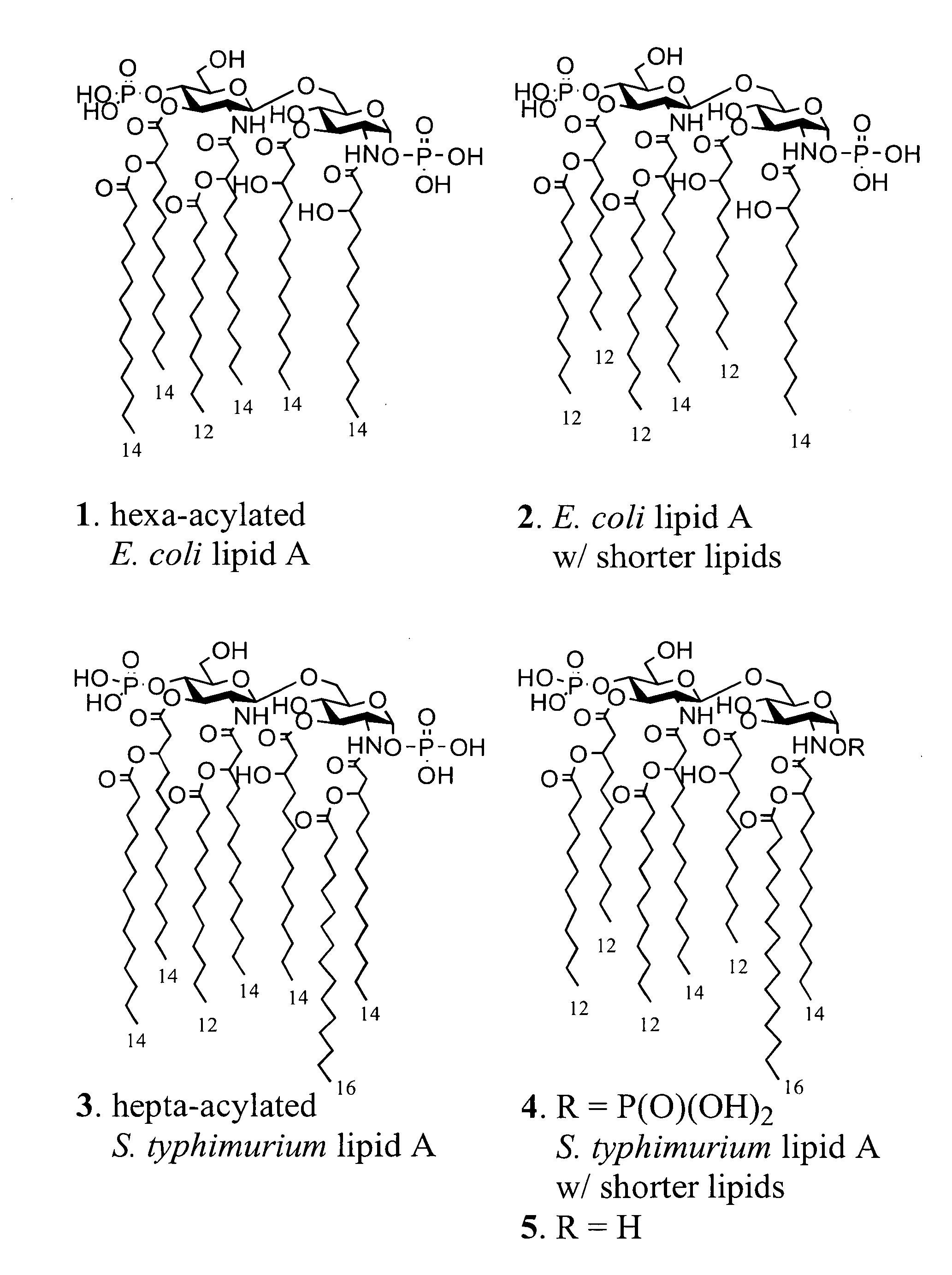
Synthetic lipid-a-analogs and uses thereof
InactiveUS7491707B1Reduce doseEasy to adaptOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLipid formationComparative test
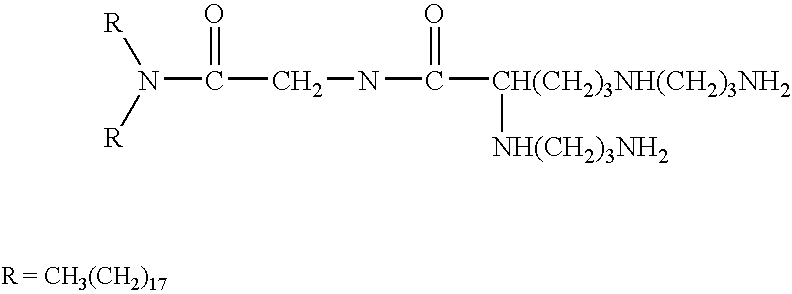
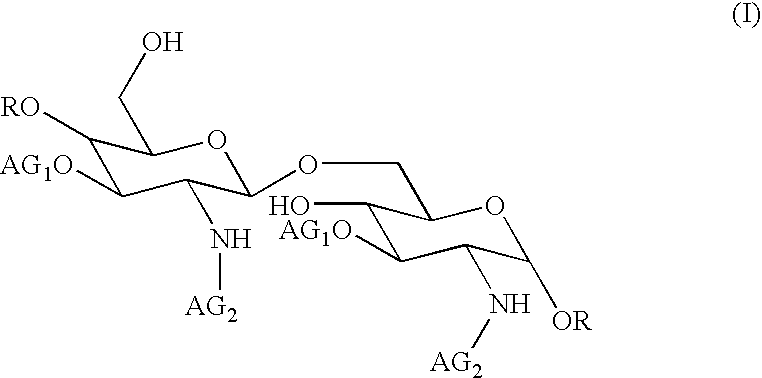
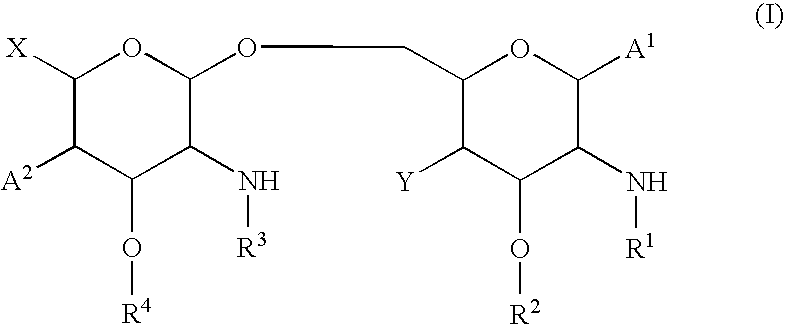
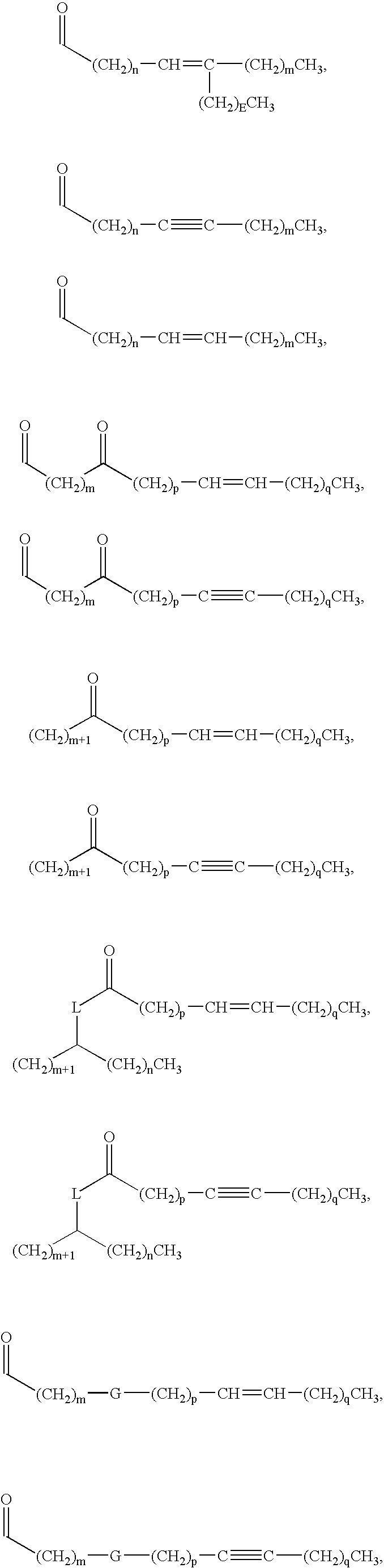
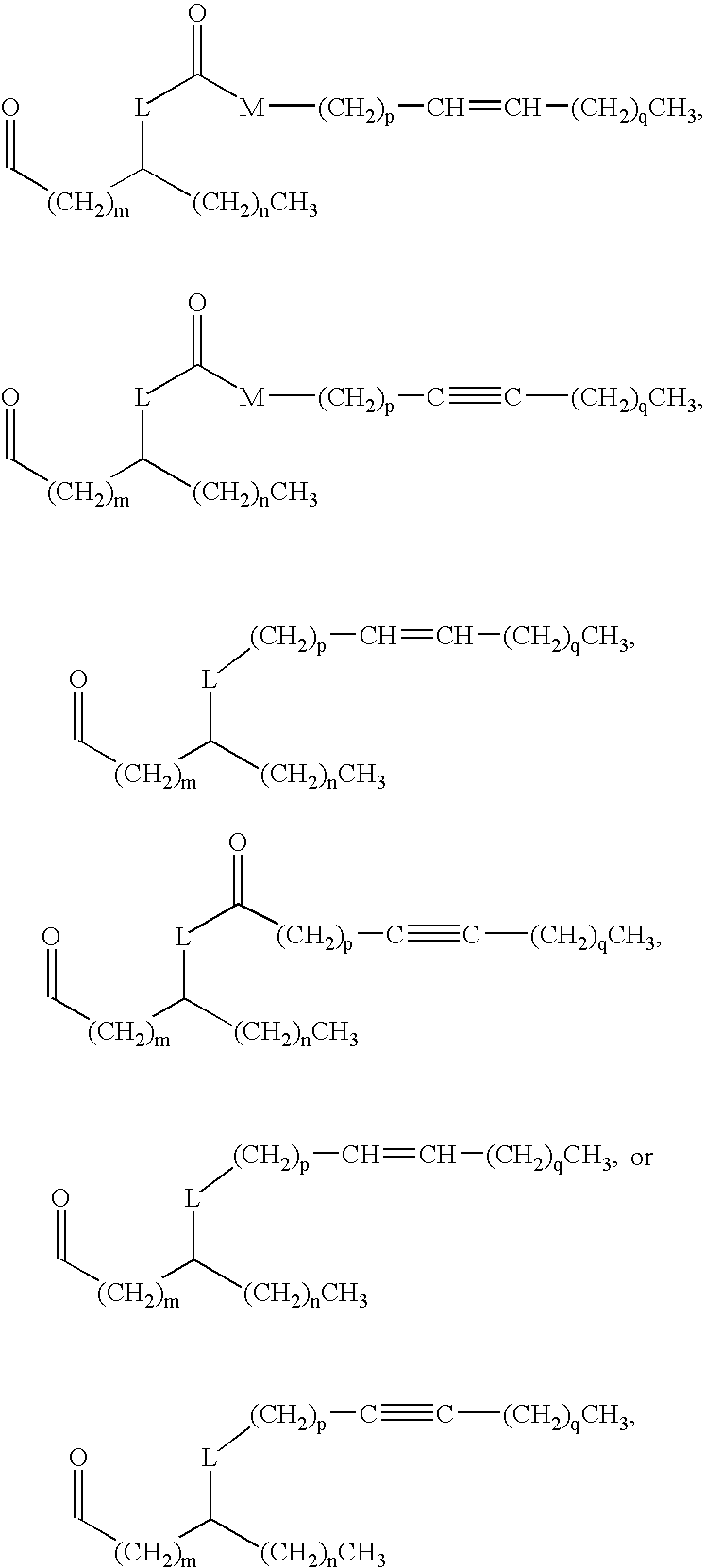
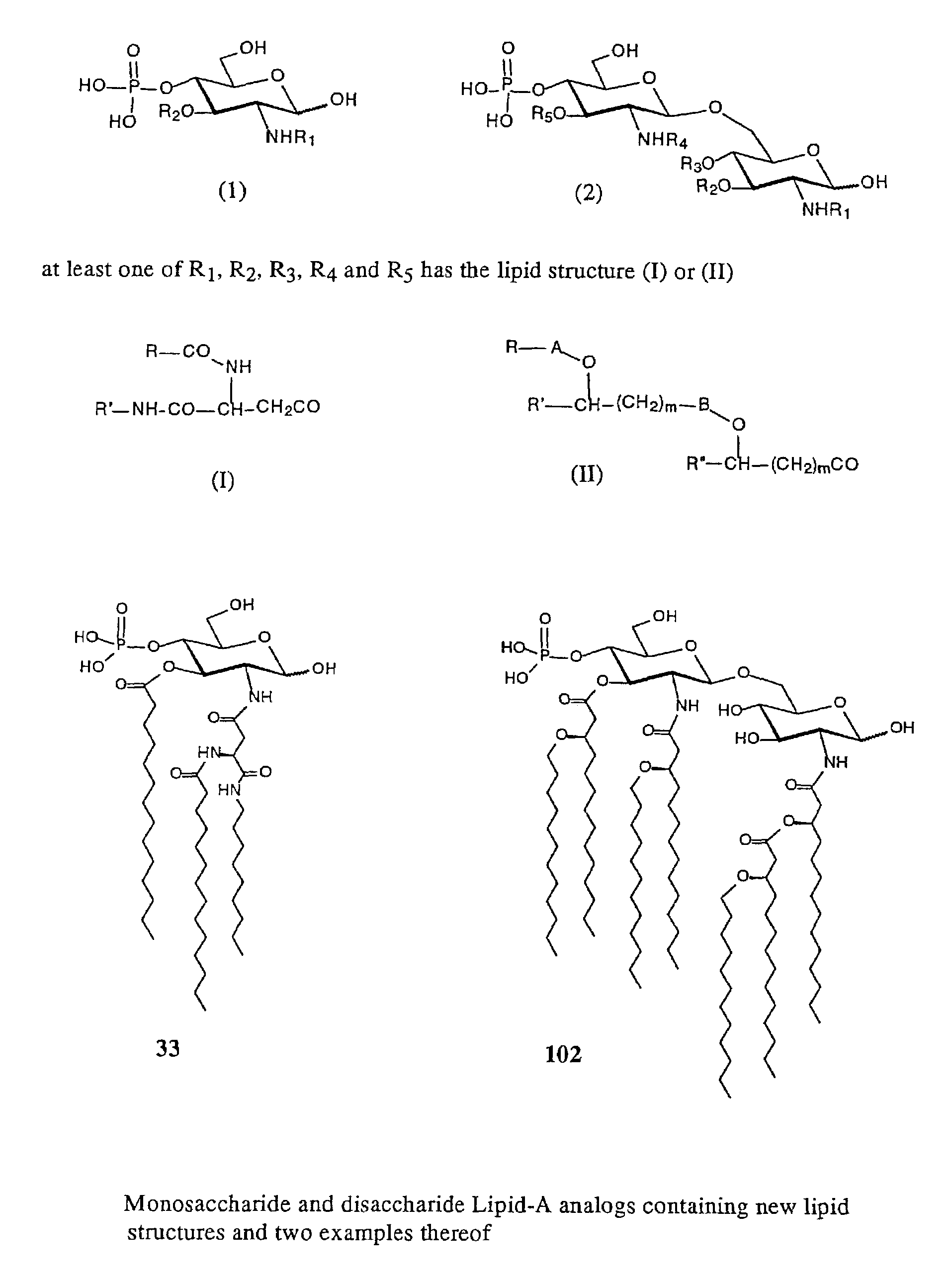
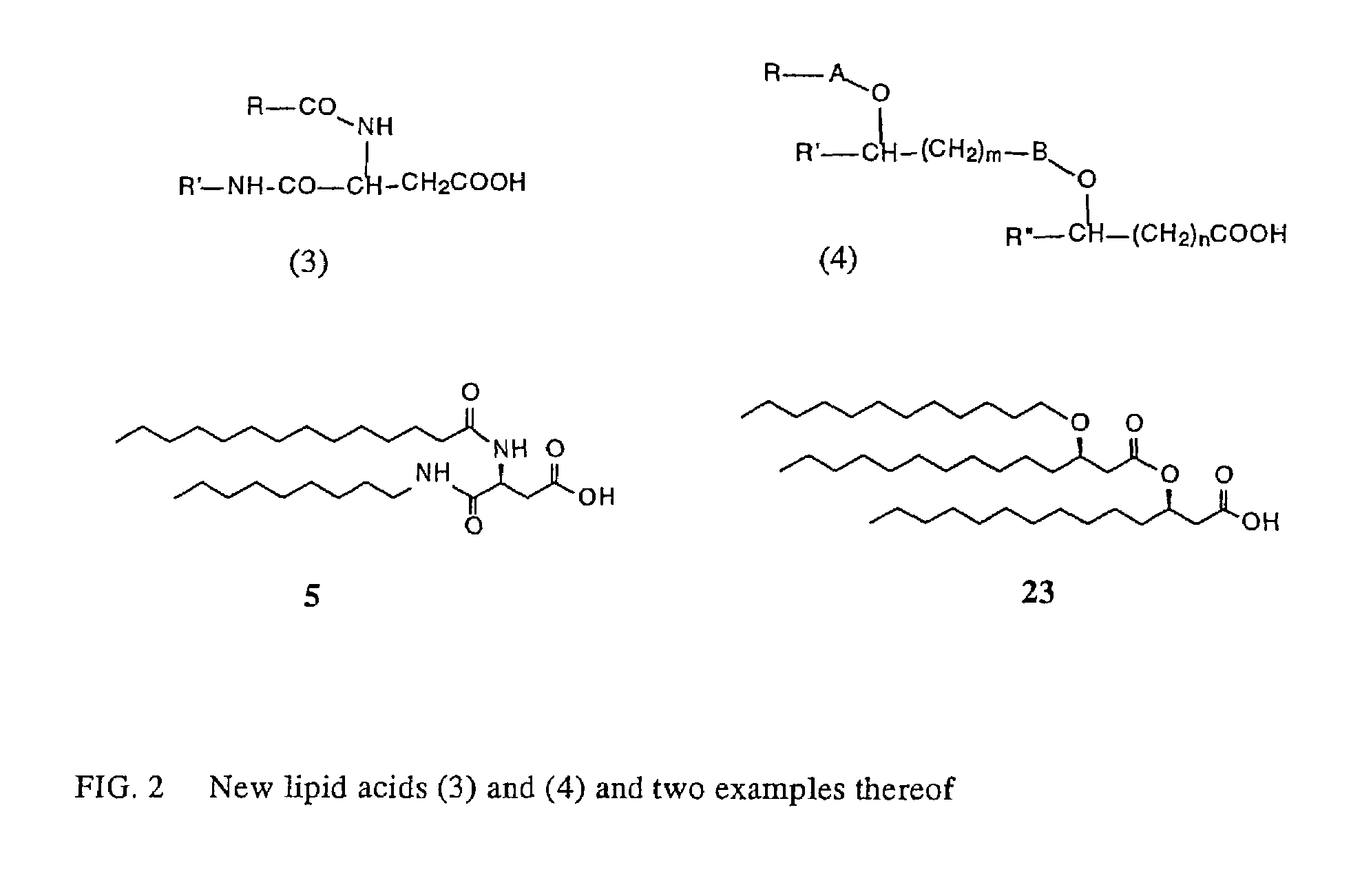
New synthetic Lipid-A analogs based on monosaccharide (1) and disaccharide (2) derivatives were designed and prepared in the present invention. Both structures (1) and (2) incorporate novel lipid structures (3) and (4) that are not found in nature. Also, novel disaccharide Lipid-A structures (2) that incorporate novel contingents of uniform lipids and where R1, R4 and R5 are the same substitution group of structure (III) were synthesized. Liposome formulations containing totally synthetic components such as synthetic Lipid-A and synthetic lipopeptide derived from tumor-associated MUC1 mucin are described along with their therapeutic utility. Comparative test results of immunostimulating properties and toxicity of Lipid-A analogs (1) and (2) are included.
Owner:ONCOTHYREON
Vaccine composition
InactiveUS20060216307A1UpregulationReducing lipid A toxicityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderProtective antigenBacteroides
The present invention relates to an immuno-protective and non-toxic Gram-negative bleb vaccine suitable for paediatric use. Examples of the Gram-negative strains from which the blebs are made are N. meningitidis, M. catarrhalis and H. influenzae. The blebs of the invention are improved by one or more genetic changes to the chromosome of the bacterium, including up-regulation of protective antigens, down-regulation of immunodominant non-protective antigens, and detoxification of the Lipid A moiety of LPS.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
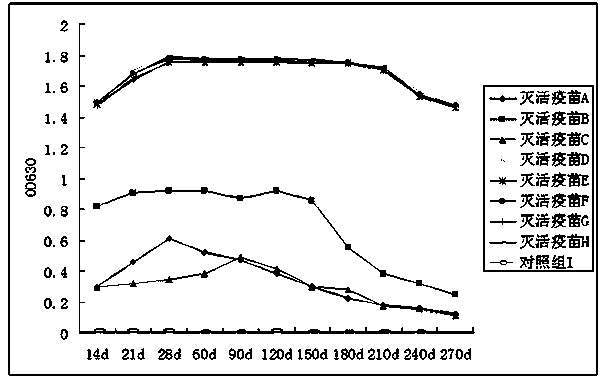
PED (Porcine Epedemic Diarrhea) inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104383528AEnhance immune responseImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesDipeptide
The invention provides a PED (Porcine Epedemic Diarrhea) inactivated vaccine and a preparation method thereof and relates to the field of biopharmacy. The PED inactivated vaccine comprises inactivated PEDV (Porcine Epedemic Diarrhea Virus), and is characterized in that the PED inactivated vaccine comprises 0.05-10 mg / mL Beta-glucosylceramide, 0.1-21 mg / mL monophosphoryl lipid A, 1.5-125 mg / mL muramyl dipeptide and 0.7-4.5 mg / mL Beta-glucan. According to the ingredients of the PED inactivated vaccine, Beta-glucosylceramide, monophosphoryl phosphoryl lipid A, muramyl dipeptide and Beta-glucan have the synergistic effect, the immune response of animals to antigens in the vaccine is significantly improved, the immune window phase is shortened, the antibody production duration of the animal body is obviously prolonged, the serum antibody level is improved, and the level of total intestinal mucosa secretory antibodies (the total SIgA) is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
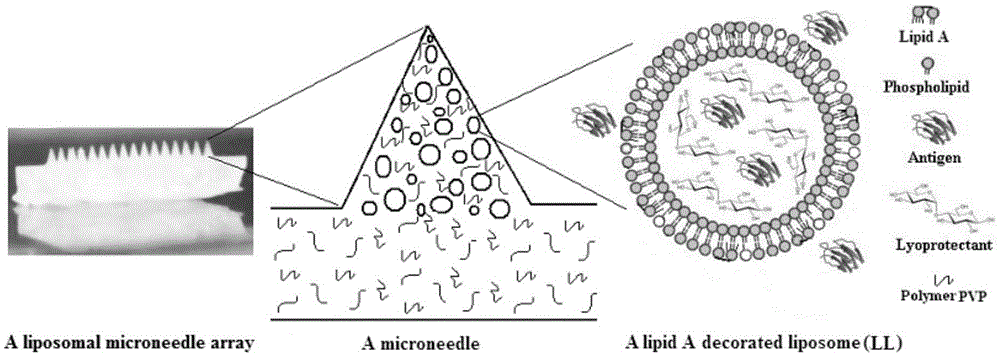
Microneedle array vaccine adjuvant transmission system built by using lipid modifying carrier
InactiveCN104083759AImprove stabilityEnhance internal and external stabilityImmunological disordersAntibody medical ingredientsExcipientTransmission system
The invention discloses a microneedle array which contains lipid modifying carrier and is used for a vaccine adjuvant transmission system. The microneedle array comprises a substrate and a plurality of microneedles fixed on the substrate, wherein the substrate is composed of saccharides, povidone, cellulose, or starch auxiliary materials; each microneedle comprises lipid A modifying carrier, the auxiliary materials (excipients) and vaccine ingredients; the lipid A modifying carrier can be lipidosome, lipid, micro-capsule or nanoparticle, and the like; the vaccine ingredients mainly refer to causative agent antigen proteins. Compared with the existing vaccine preparations, the lipid A-modified lipidosome microneedle array vaccine adjuvant transmission system can contain different vaccine ingredients to form vaccines aiming to different pathogens and therefore has a wide application scope. Biodegradable materials are selected and therefore the safety is high. The microneedle array vaccine adjuvant transmission system is a solid preparation which is high in stability and convenient to inoculate. Inoculation can be completed by a user self through oral mucosa, the vaccine can be prevented from running away along with saliva, and a body can be induced to establish mucosal immunity.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
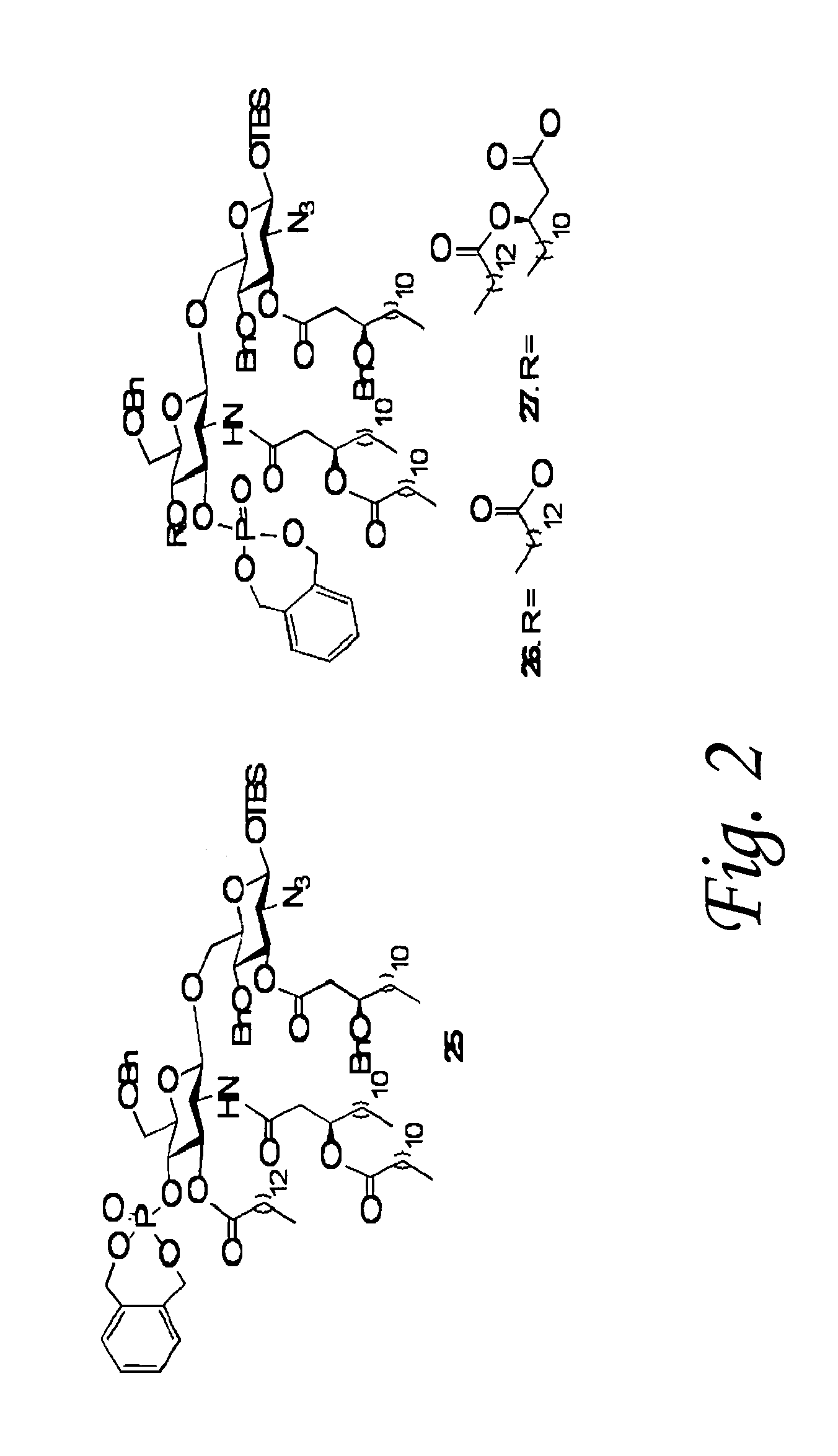
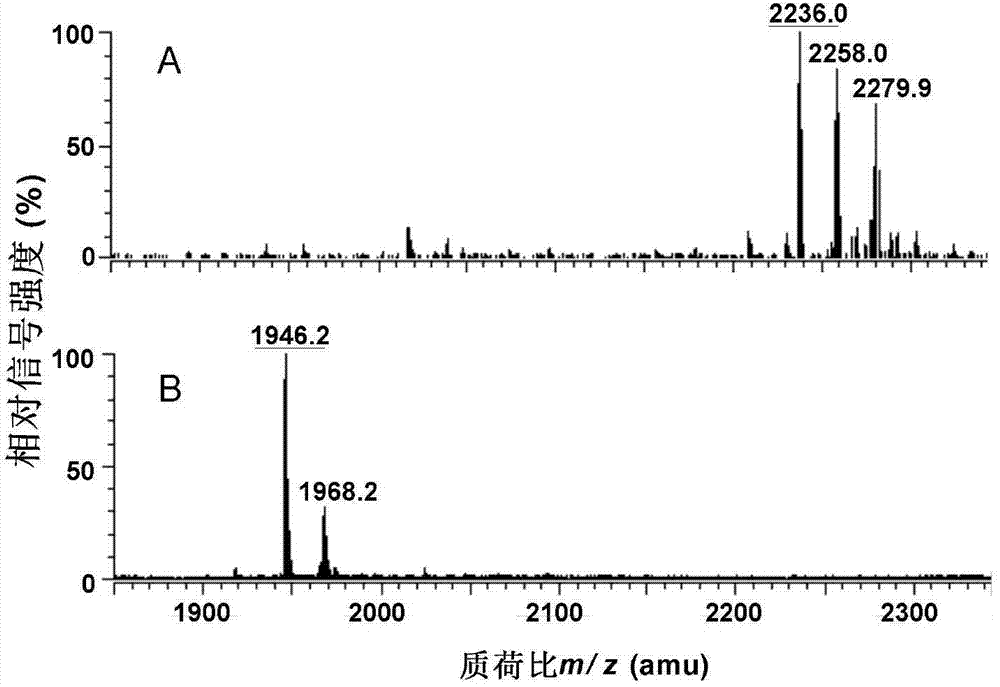
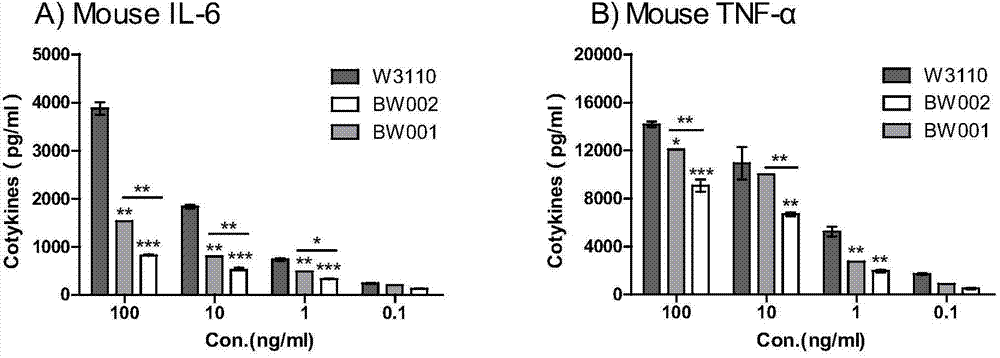
Preparation and application of low-toxicity Kdo2-monophosphoryl lipid A containing five fatty acid chains
ActiveCN104844665ALow cytotoxicityImprove solubilityEsterified saccharide compoundsBacteriaEscherichia coliImmunocompetence
The invention discloses preparation and application of a low-toxicity Kdo2-monophosphoryl lipid A containing five fatty acid chains, belonging to the field of bioengineering. By modifying Escherichia coli, a special-structure low-toxicity five-chain Kdo2-monophosphoryl lipid A is synthesized, and the Kdo2-lipid A molecule is not connected with the core polysaccharide long chain, and only composed of two 2-one-3-desoxyoctoic acids, five fatty acid chains and a C4' site single phosphoric acid. The Kdo2-lipid A is amphiphilic, is convenient for separation, extraction and purification, can be detected and directly identified, maintains the biological immunocompetence of the lipid A part, has obvious toxicity attenuation effect as compared with wild type W3110 LPS, and is a vaccine adjuvant with great development potential. Meanwhile, the method for extracting and purifying the Kdo2-lipid A is simple in steps and easy to operate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
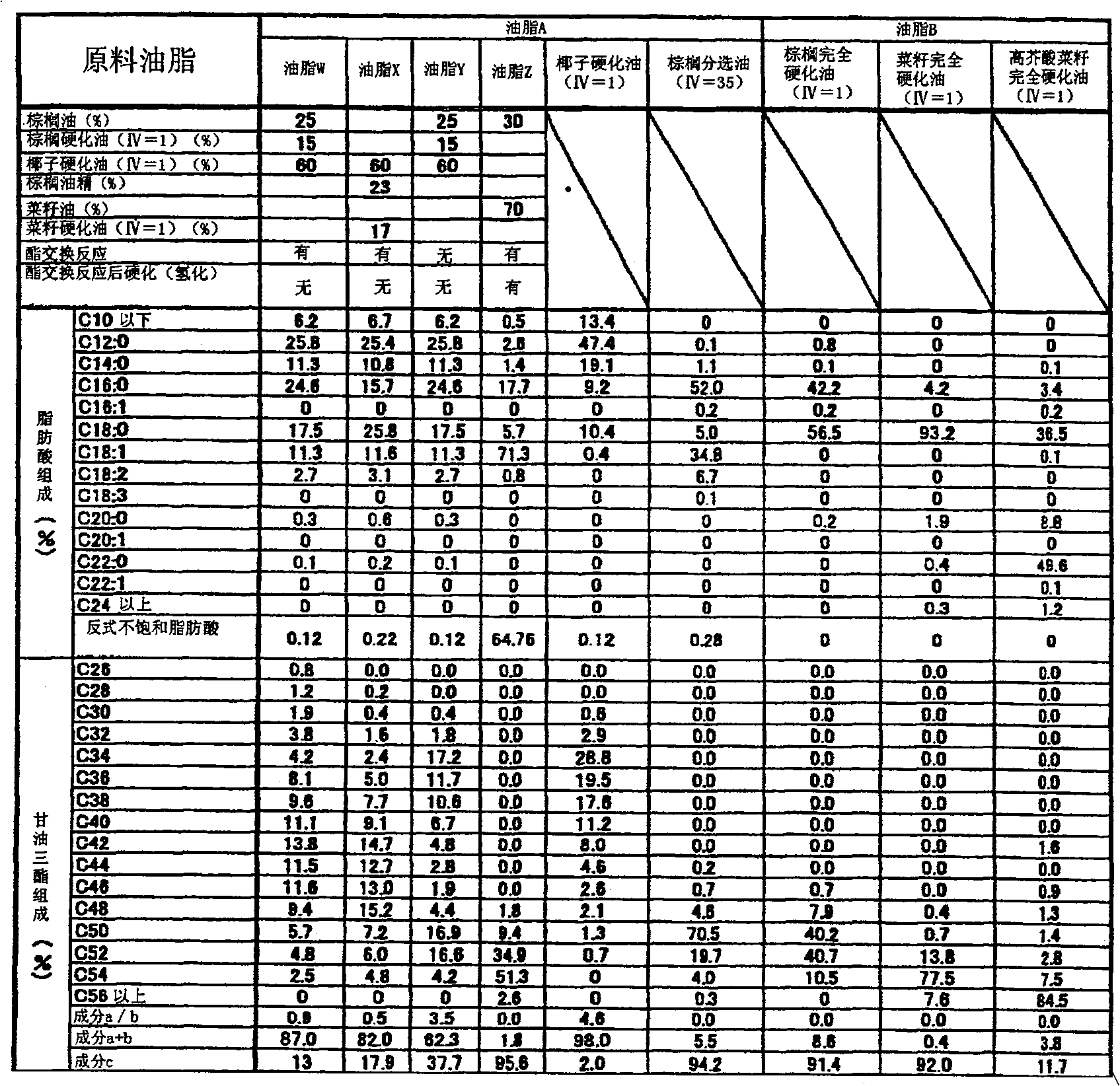
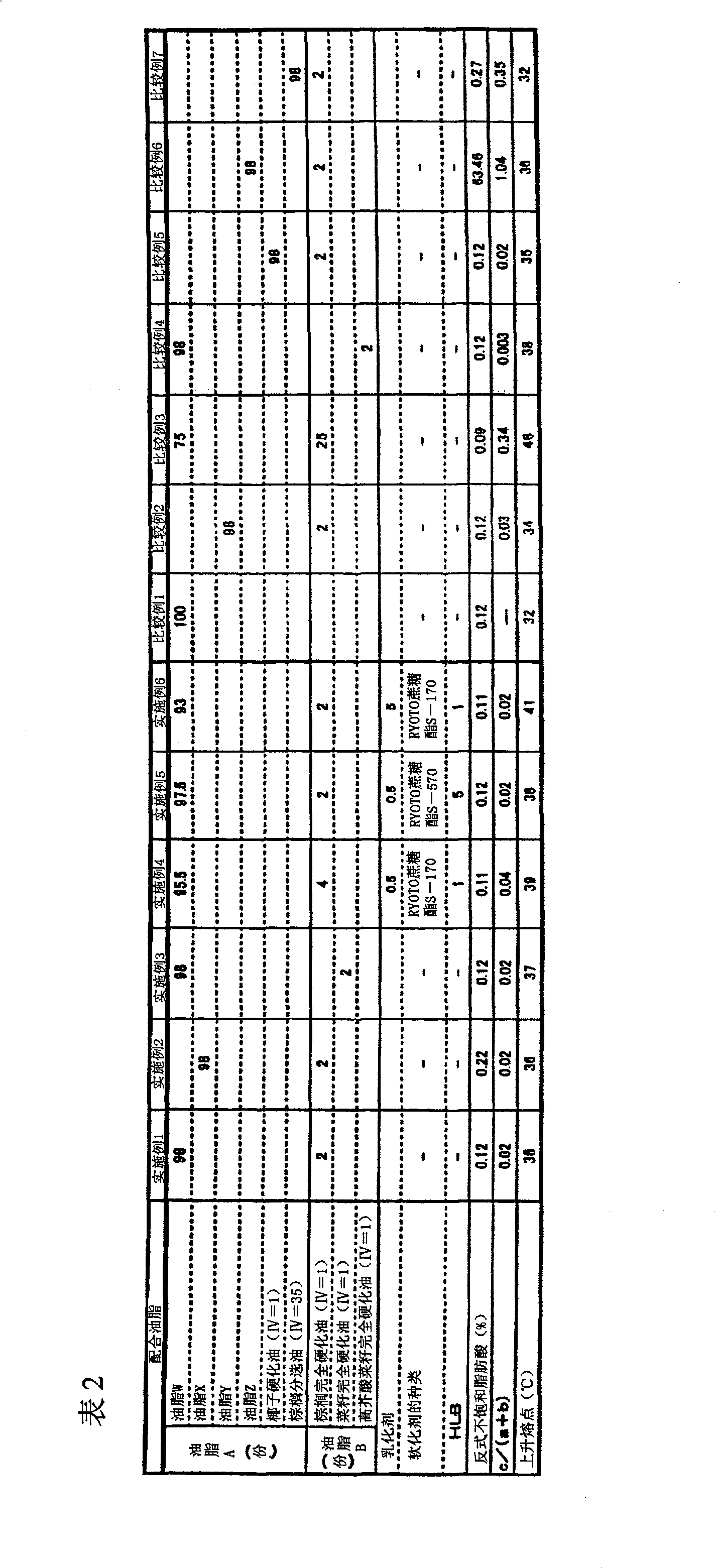
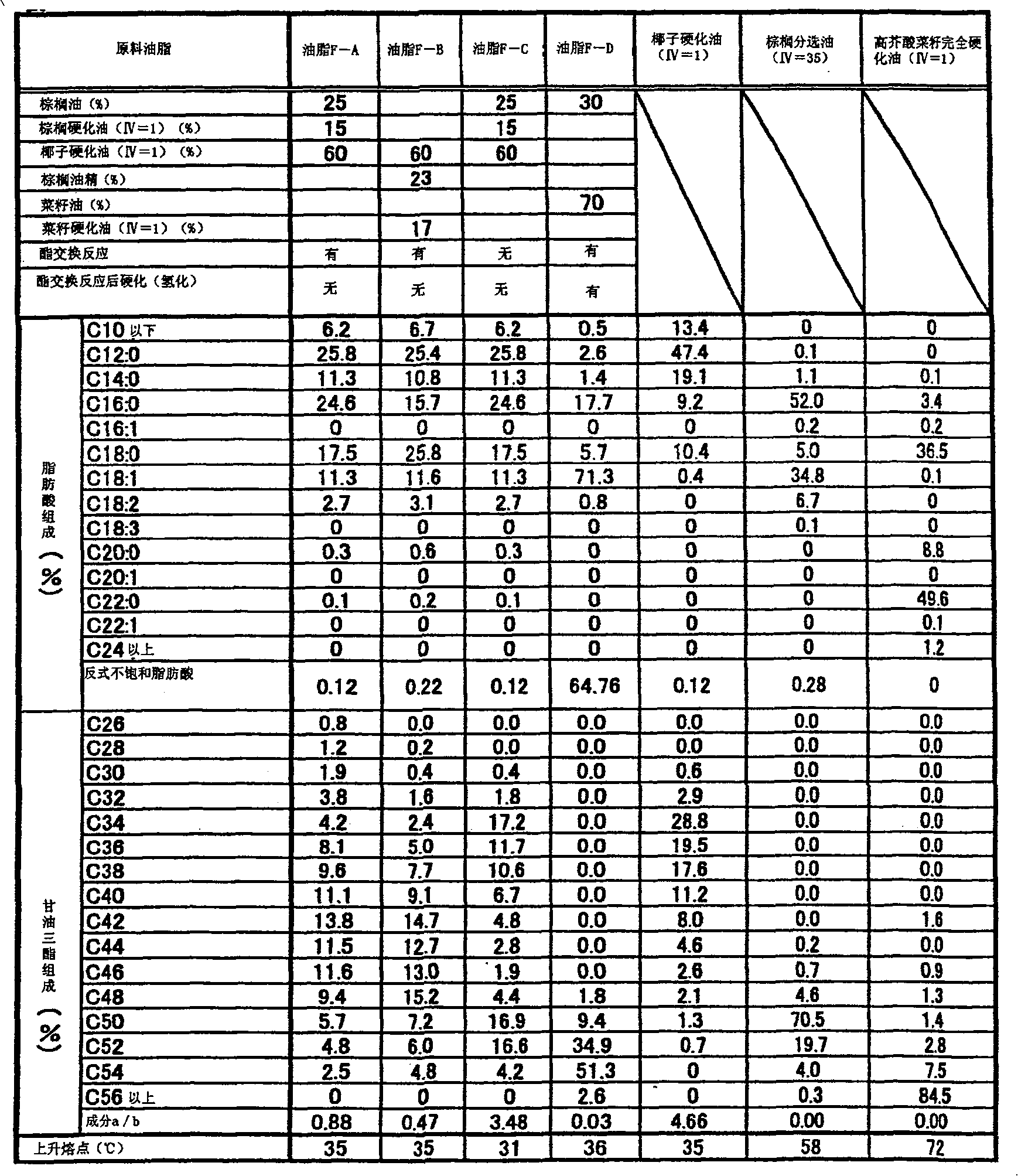
Hard fat and chocolate
The invention provides hard fat comprising a lipid composition and chocolate comprising the hard fat. The lipid composition comprises lipid A and lipid B. Trans unsaturated fatty acids account for 5% in mass of all the fatty acids composed of lipid. Mass ratio of components a and b in lipid A to component c in lipid B is shown in following formula: c / a+b=0.001-0.3. Referring to lipid A: (1) in the composing fatty acids, saturated fatty acids with number of carbon atom less than 14 account for 25-60% in mass, and saturated fatty acids with carbon atom number more than 20 account for less than 1% in mass, (2) in triglyceride of the fatty lipid, mass ratio of triglyceride (component a) with number of carbon atoms composing the fatty acid being less than 40 to triglyceride (component b) with number of total carbon atoms composing the fatty acid being 42-48 is shown in the following formula: a / b=0.2-1; referring to lipid B: (3) in the composing fatty acids, saturated fatty acids account for 95% in mass, and fatty acids with carbon number more than 20 account for less than 5% in mass, (4) in triglyceride of lipid, triglyceride with number of carbon atom composing the fatty acids being 50-54 account for 80% in mass.
Owner:KAO CORP
Lipid a and other carbohydrate ligand analogs
InactiveUS20060040891A1Improve vaccine efficacyEnhancing innate immunityAntibacterial agentsBiocideLipid formationCell adhesion
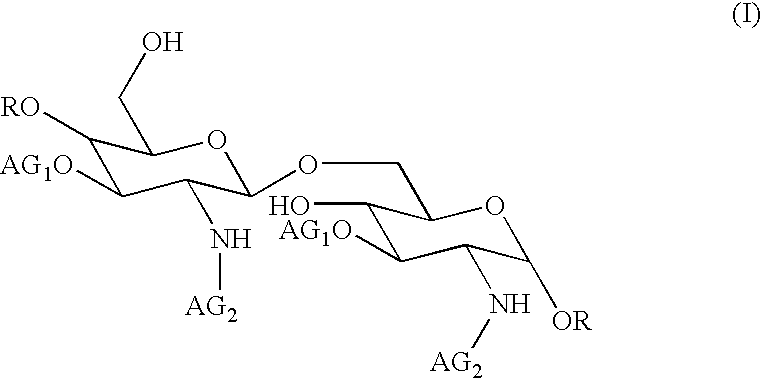
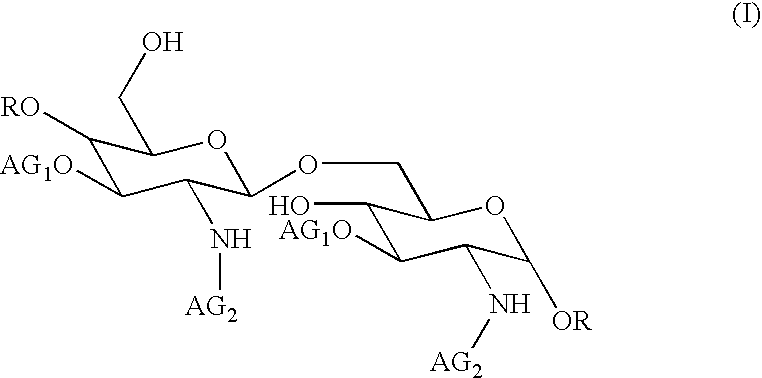
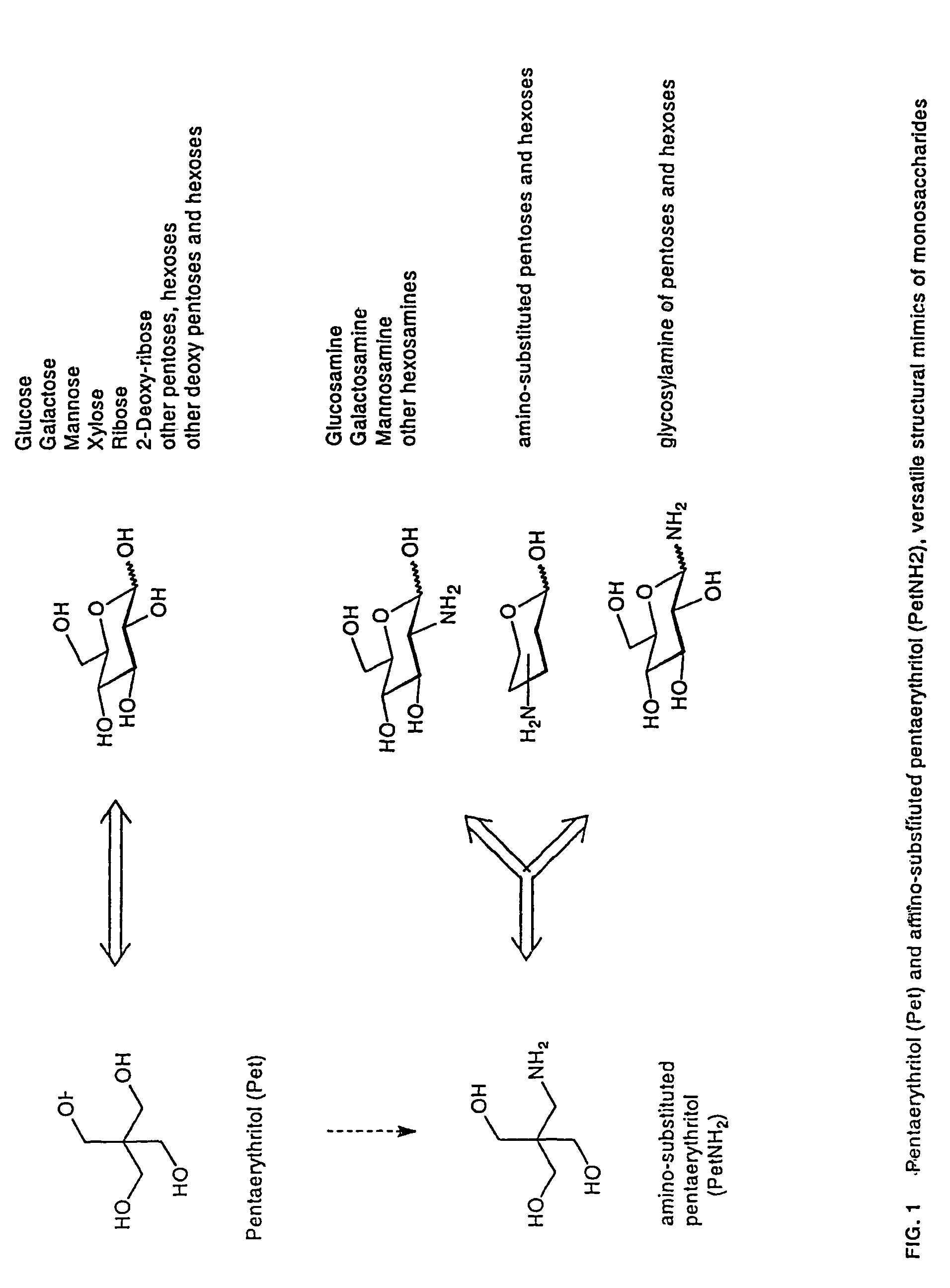
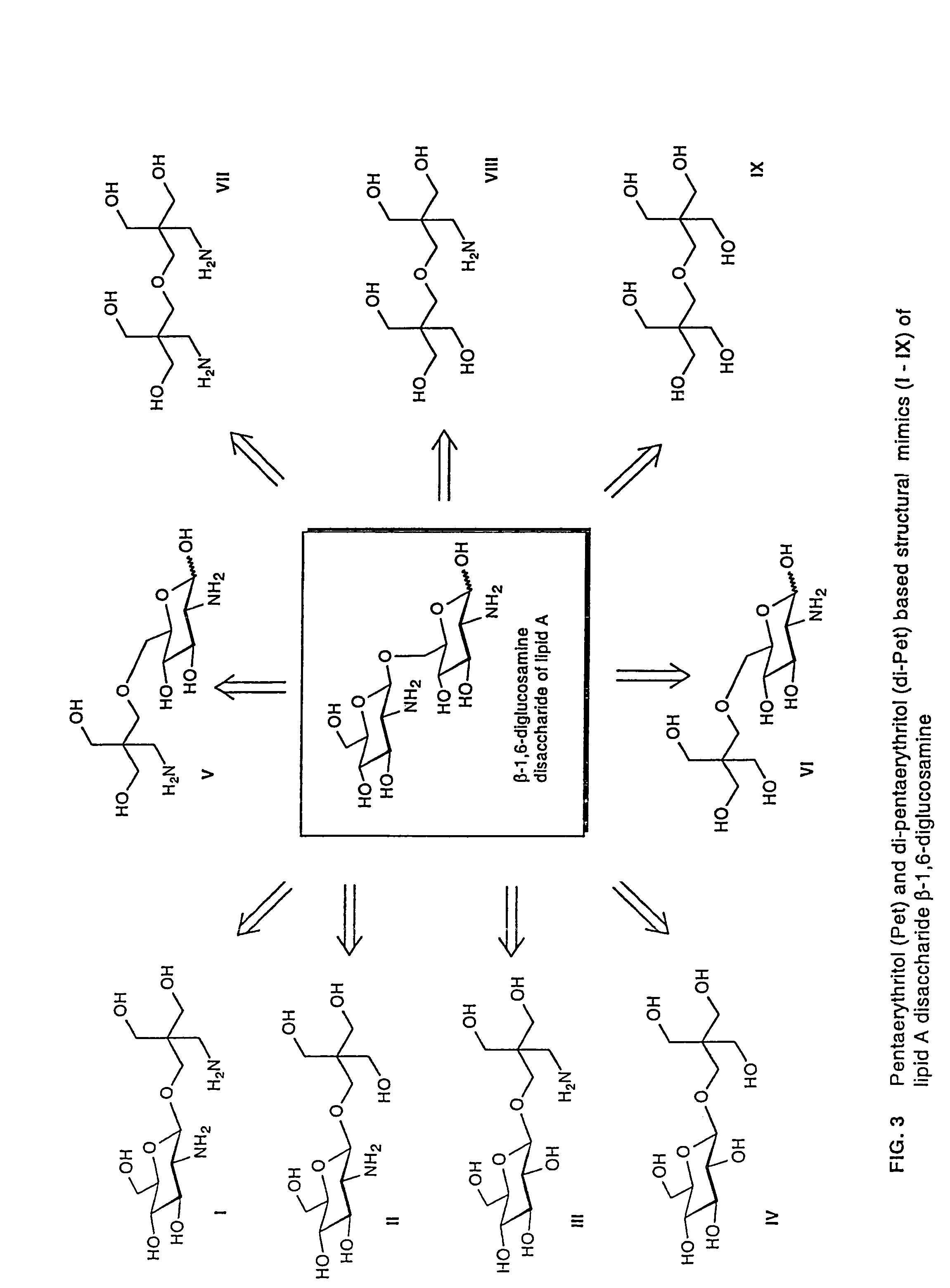
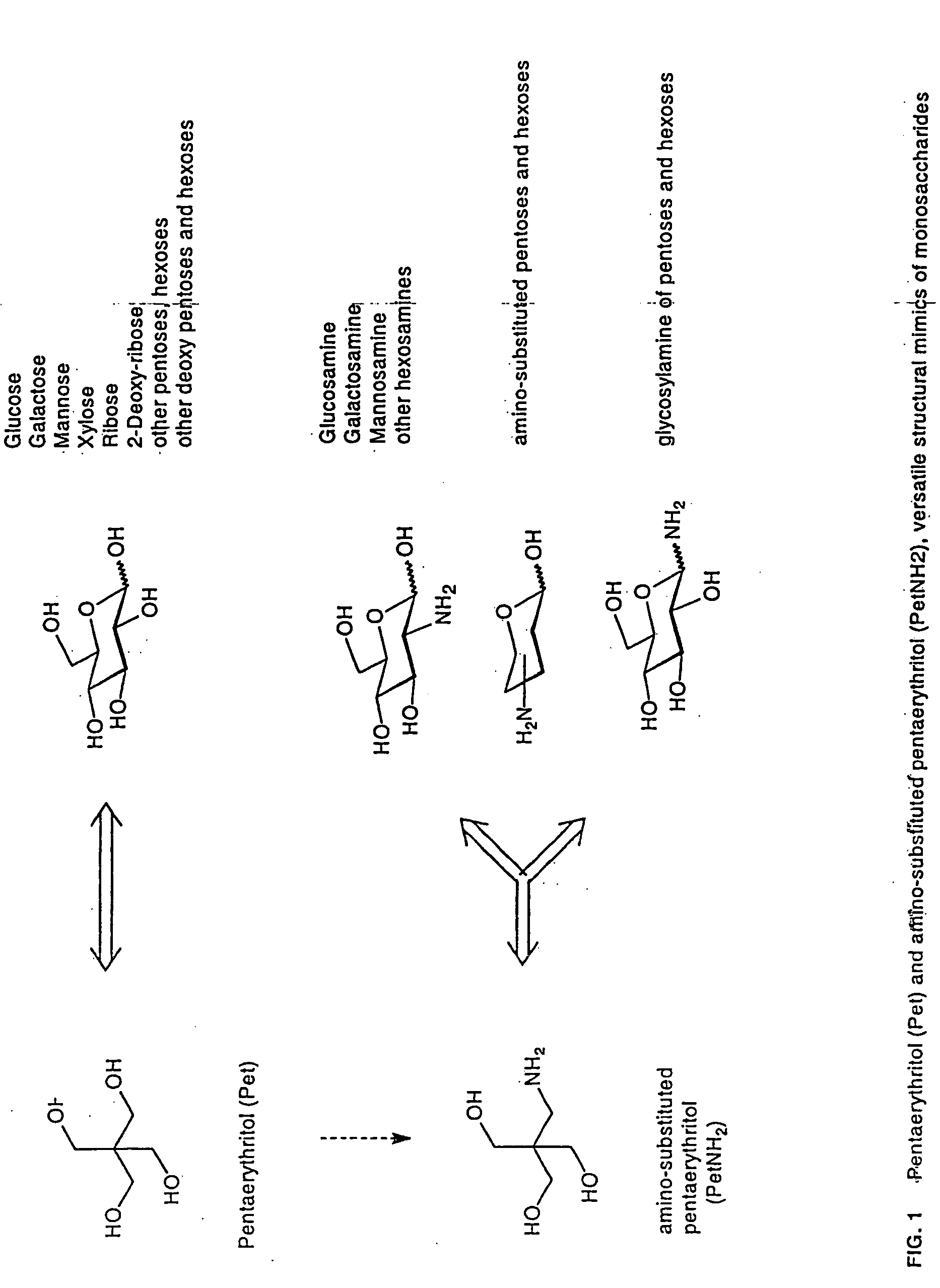
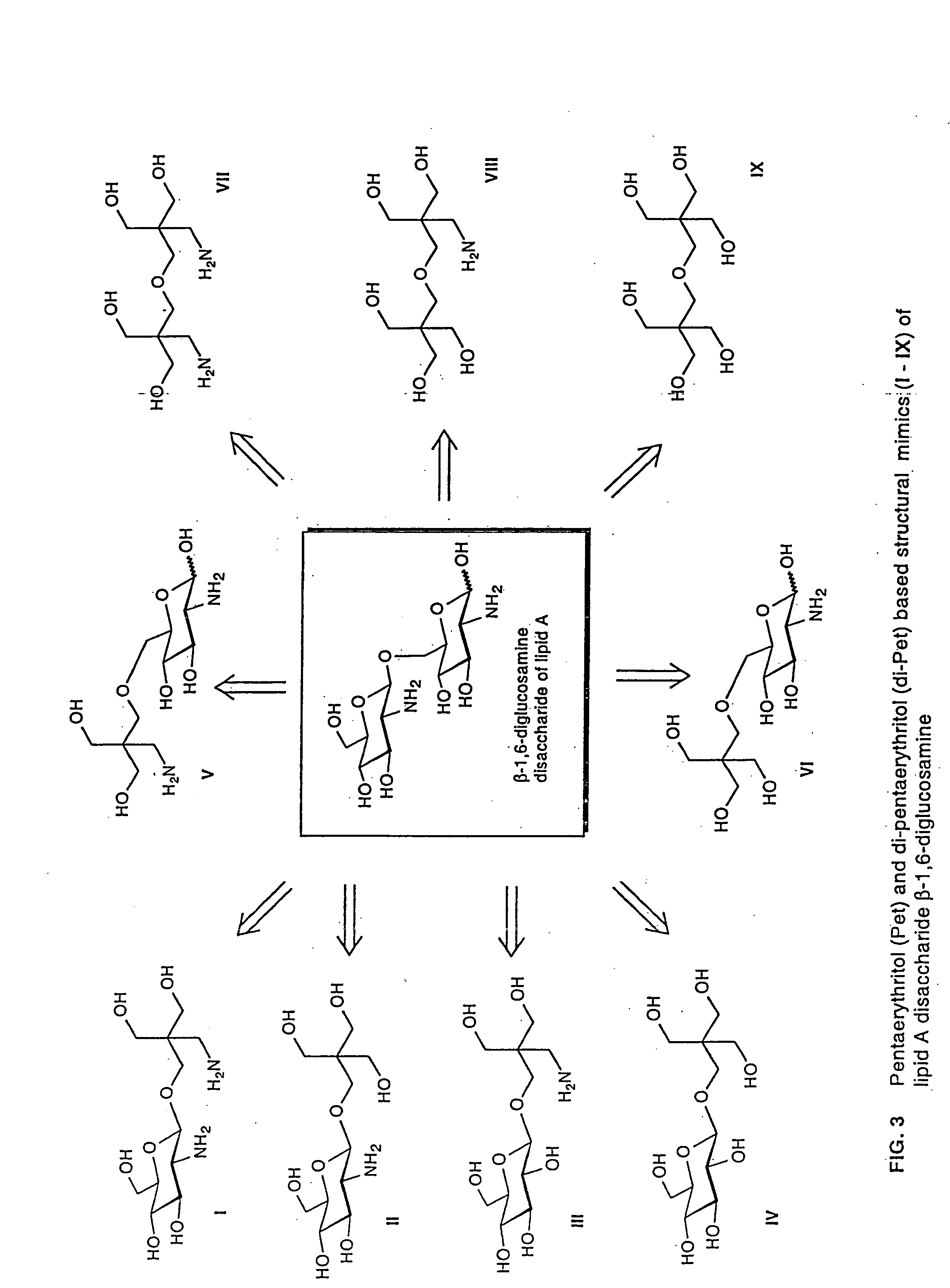
The core structure of pentaerythritol has been used as a replacement for one or both sugars in lipid A, leading to the generation of a series of lipid A analogs. These lipid A analogs may further differ from lipid A with respect to, e.g., the number, nature and location of negatively charged groups, and the number, nature and location of the lipid chains. The lipid A analogs may be lipid A agonists useful as immunostimulatory agents, or lipid A antagonists useful in the treatment of septic shock. In a like manner, a residue of pentaerythritylamine may be used as a replacement for an amino sugar residue in a carbohydrate ligand having a biological activity of interest, generating a series of ligand analogs. These are useful, e.g., as haptens, inhibitors of bacterial-host cell adhesion, etc.
Owner:ONCOTHYREON
Method of improving immune function in mammals using lactobacillus strains with certain lipids
A method of improving immune-function in mammals using selected 3-HPA producing lactic acid bacteria with a medium chain triglyceride (MCT) oil.
Owner:BIOGAIA AB
Genetic Immunization with Cationic Lipids
A method for immunization using genetic material is disclosed. Compositions for genetic immunization comprising cationic lipids and polynucleotides are also disclosed. Methods for using genetic immunization to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are also disclosed. A method for epitope mapping is also disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Neisseria meningitidis lgtb Los as Adjuvant
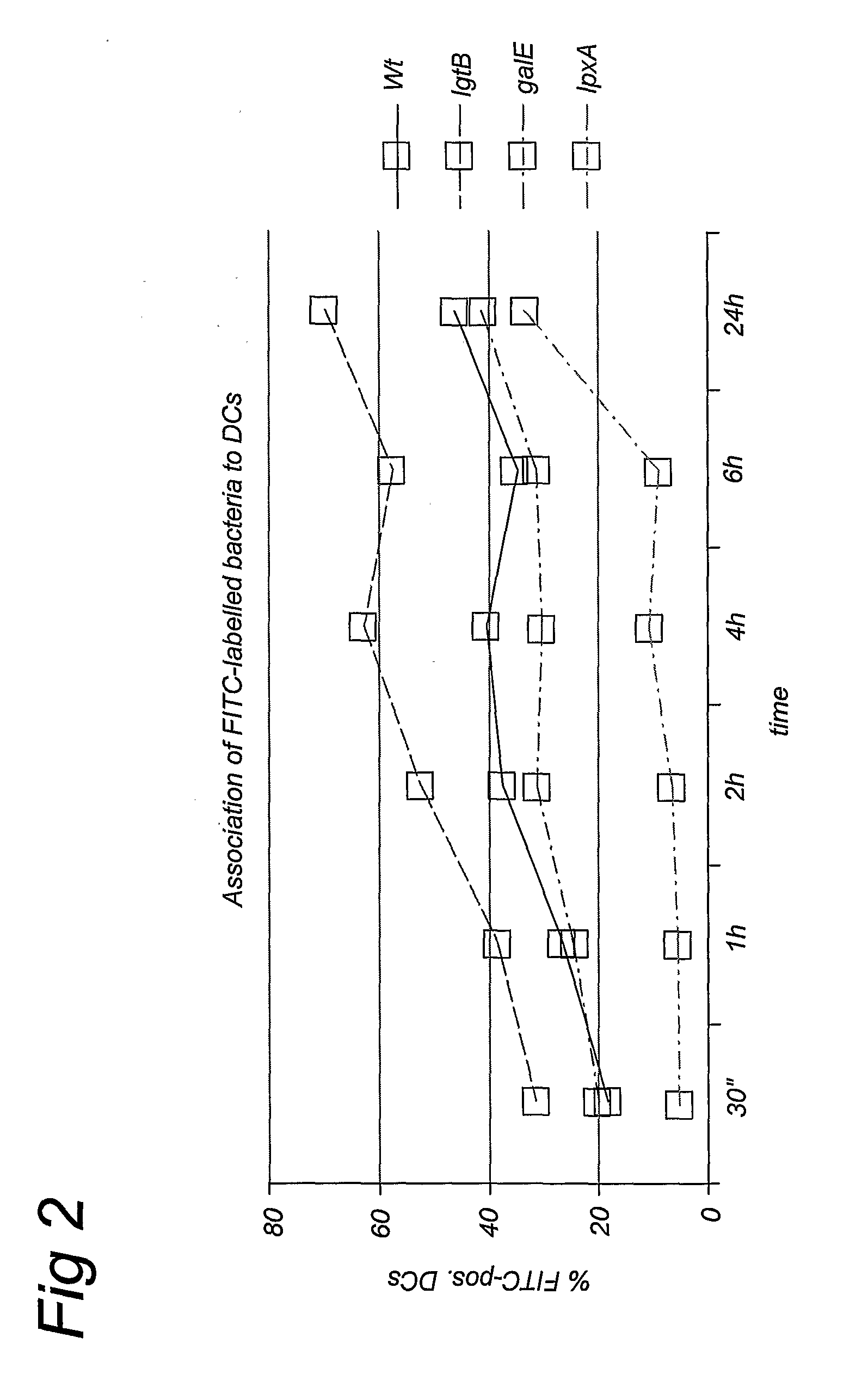
InactiveUS20080138359A1Improve bindingIncreased internalisationCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntiinfectivesAdjuvantDC-SIGN
The present invention relates to Neisserial Lipo-Oligo-Saccharides (LOS) that comprise a tri-saccharide outer core that shows increased binding to the DC-SIGN receptor on dendritic cells, as a result of which the Neisserial LOS's of the invention have increased immunostimulatory activity. The tri-saccharide outer core of the Neiserial LOS's combined with a Lipid A moiety with reduced toxicity is useful as an adjuvant in vaccine preparations.
Owner:DE STAAT DER NEDERLANDEN VERT DOOR DE MINIST VAN VWS
Quil A fraction with low toxicity and use thereof
ActiveUS8821881B2Improve the level ofSnake antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsMedicineCell Wall Skeleton
Fraction A of Quil A can be used together with at least one other adjuvant for the preparation of an adjuvant composition, where the included adjuvant components act synergistically to enhance level of immune response and have synergistic immunomodulating activity on the co-administered antigens or immunogens.Other adjuvants can comprise saponins, naturally occurring, synthetic or semisynthetic saponin molecules; e.g. saponins and saponin fractions from Quil A, cell wall skeleton, blockpolymers, TDM, lipopeptides, LPS and LPS-derivatives, Lipid A from different bacterial species and derivatives thereof, e.g., monophosphoryl lipid A. CpG variants, CT and LT or fractions thereof.
Owner:NOVAVAX
Saccharide conjugates
The invention provides a series of novel Lipid A analogs that are structually simple, synthetically accessible, and capable of blocking the cellular receptor within the signal transduction pathway. The novel Lipid A analogs can include a monosaccharide core with hydrophobic side chains and amino acid ionic motif. The invention further provides methods of using the compounds and compositions thereof in various therapeutic methods.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
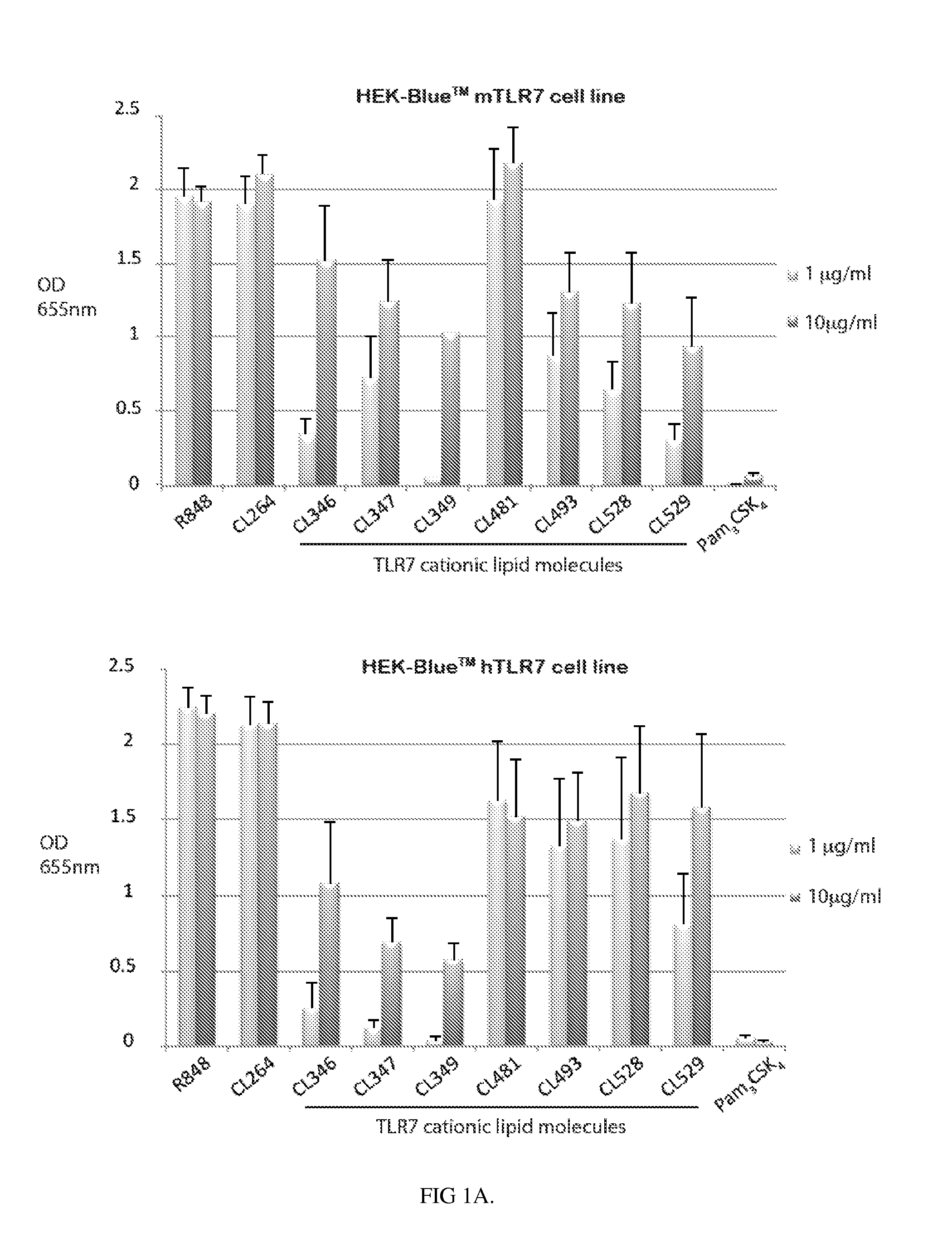
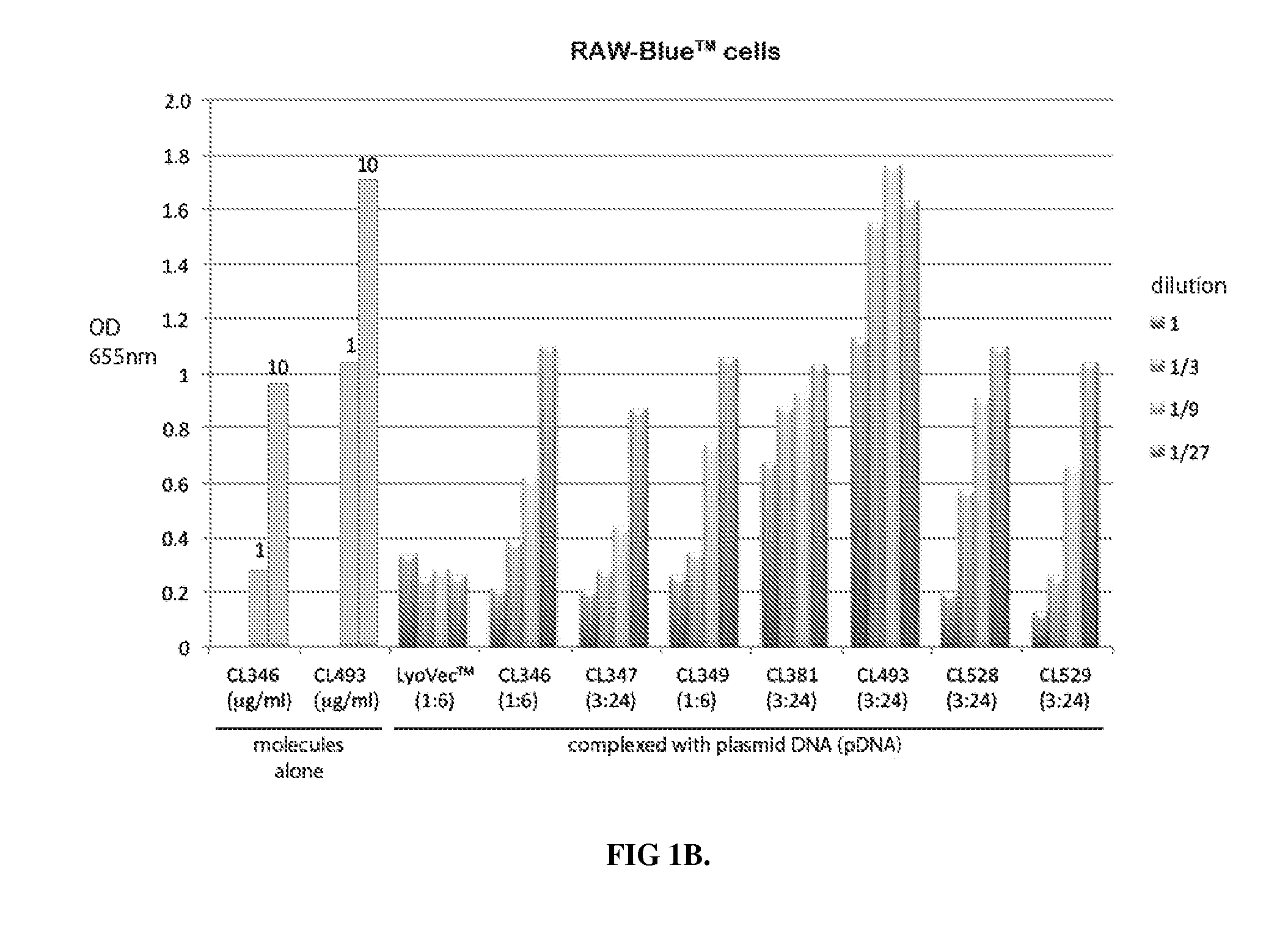
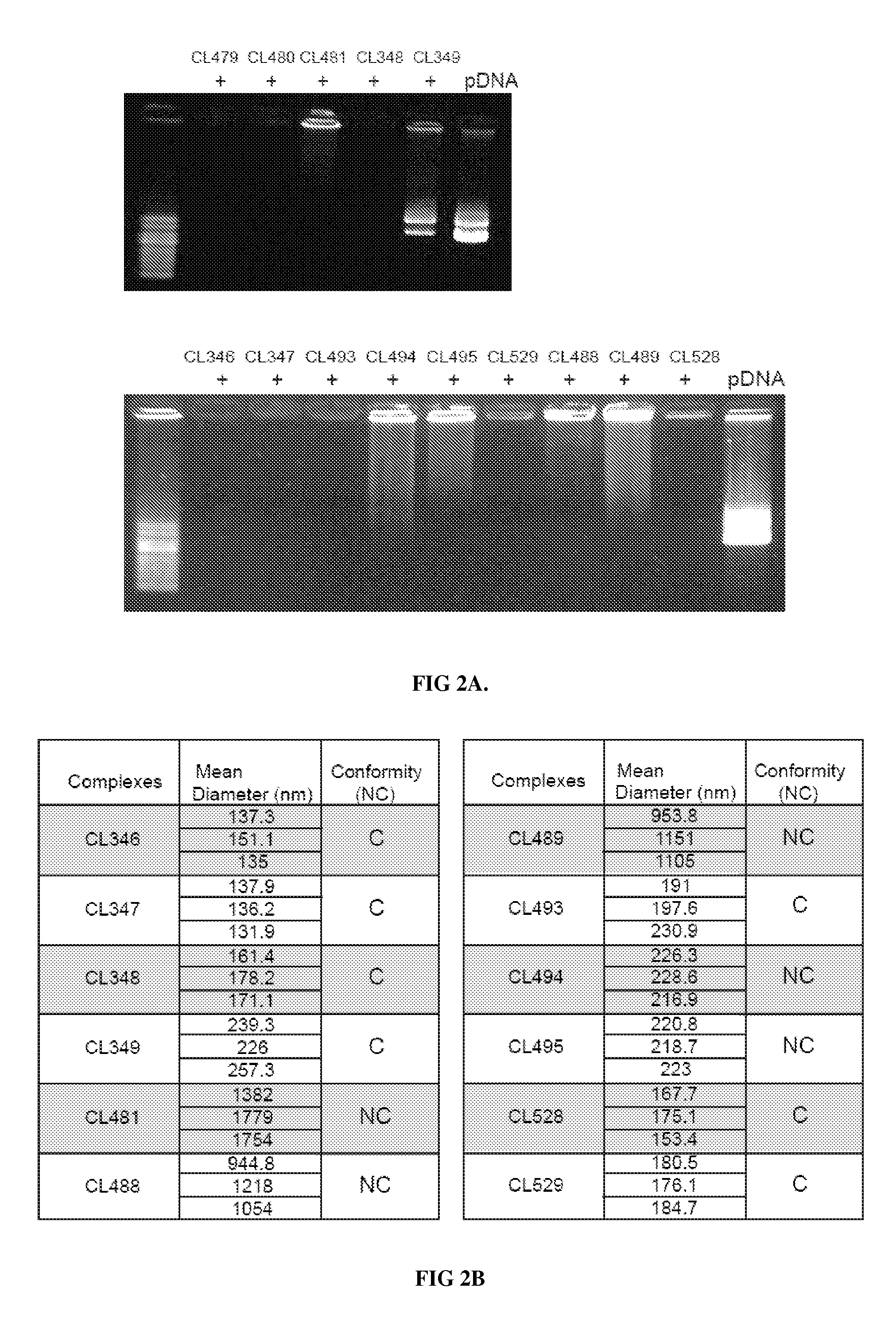
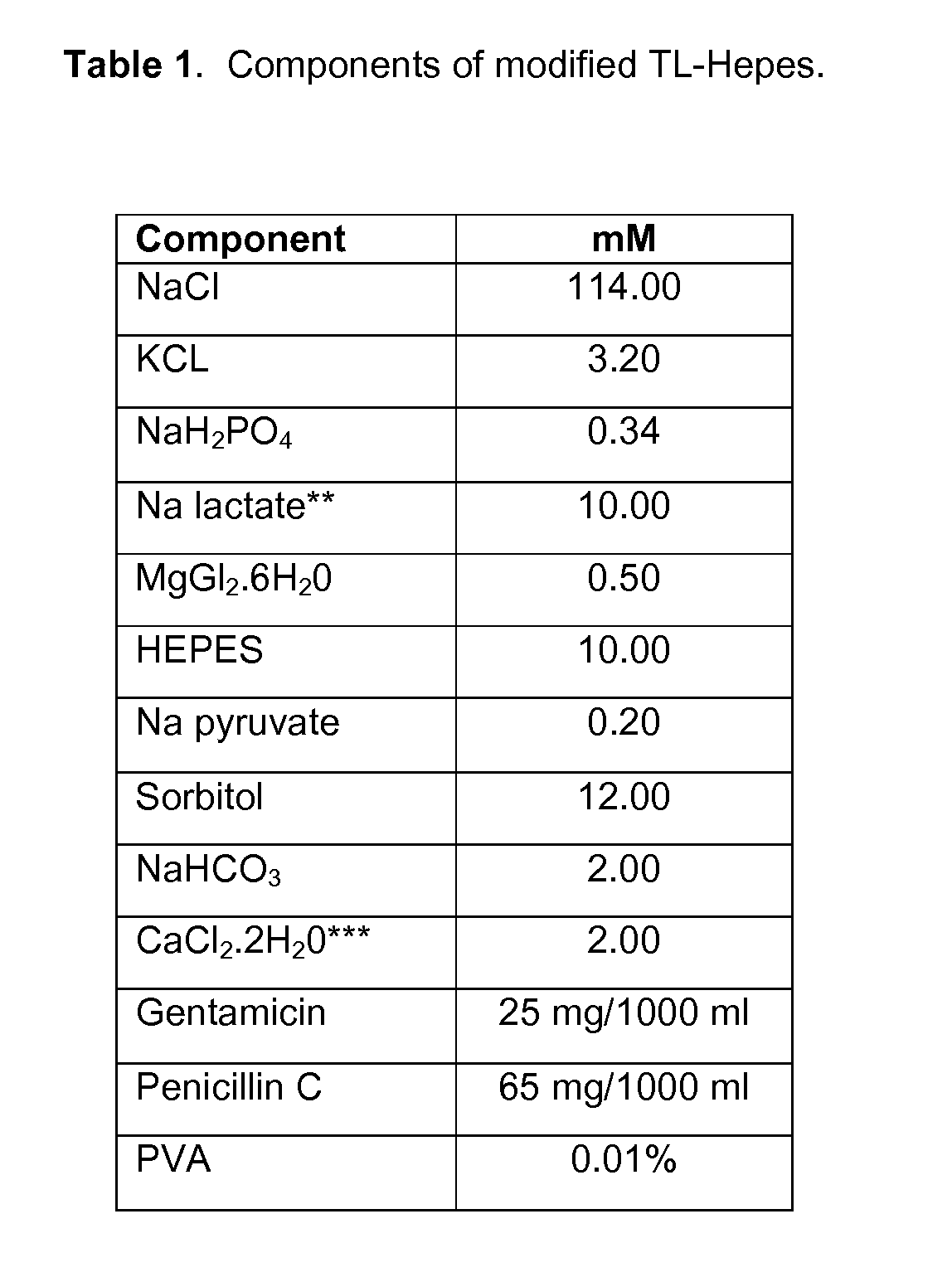
Novel compositions of tlr7 and/or tlr8 agonists conjugated to lipids
ActiveUS20130336996A1Reduce usageEffectively eliminate tumorBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAgonistOrganic chemistry
A conjugated compound of formula Q-Z—R4 wherein Q is a TLR7 and / or TLR8 agonist and Z—R4 is a lipid covalently linked to an amino acid or peptide coupled to a polyamine group, and a process for the manufacture of the conjugated compound, as well as a complex formed between the conjugated compound and a polyanionic molecule and a pharmaceutical composition containing the conjugated compound or complex. Also described is the use of the conjugated compound or complex in the treatment of infection, cancer or immune disorders or for use in vaccines.
Owner:INVIVOGEN
Methods for the Cryopreservation of Animal Cells that Contain High Levels of Intracellular Lipids
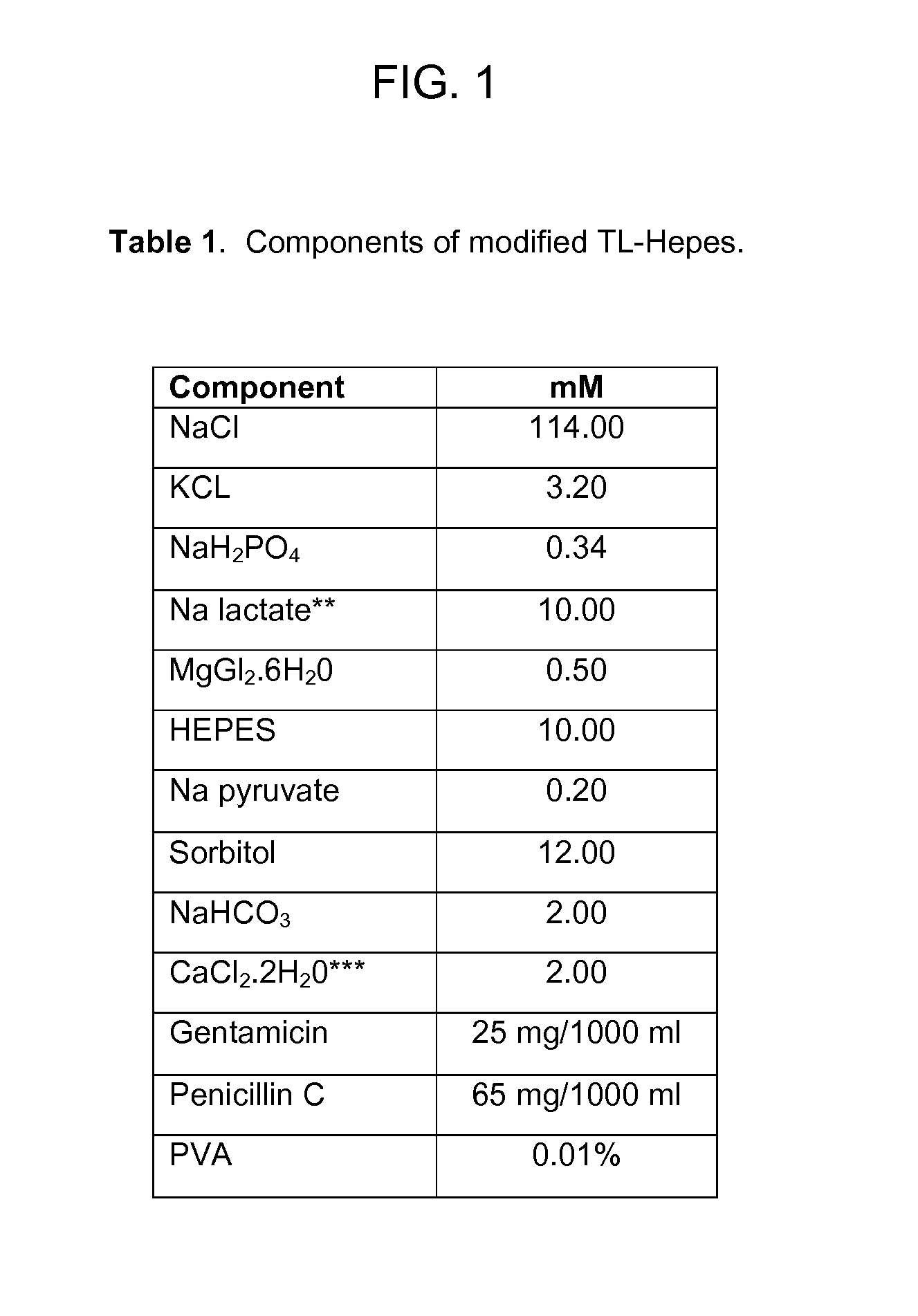
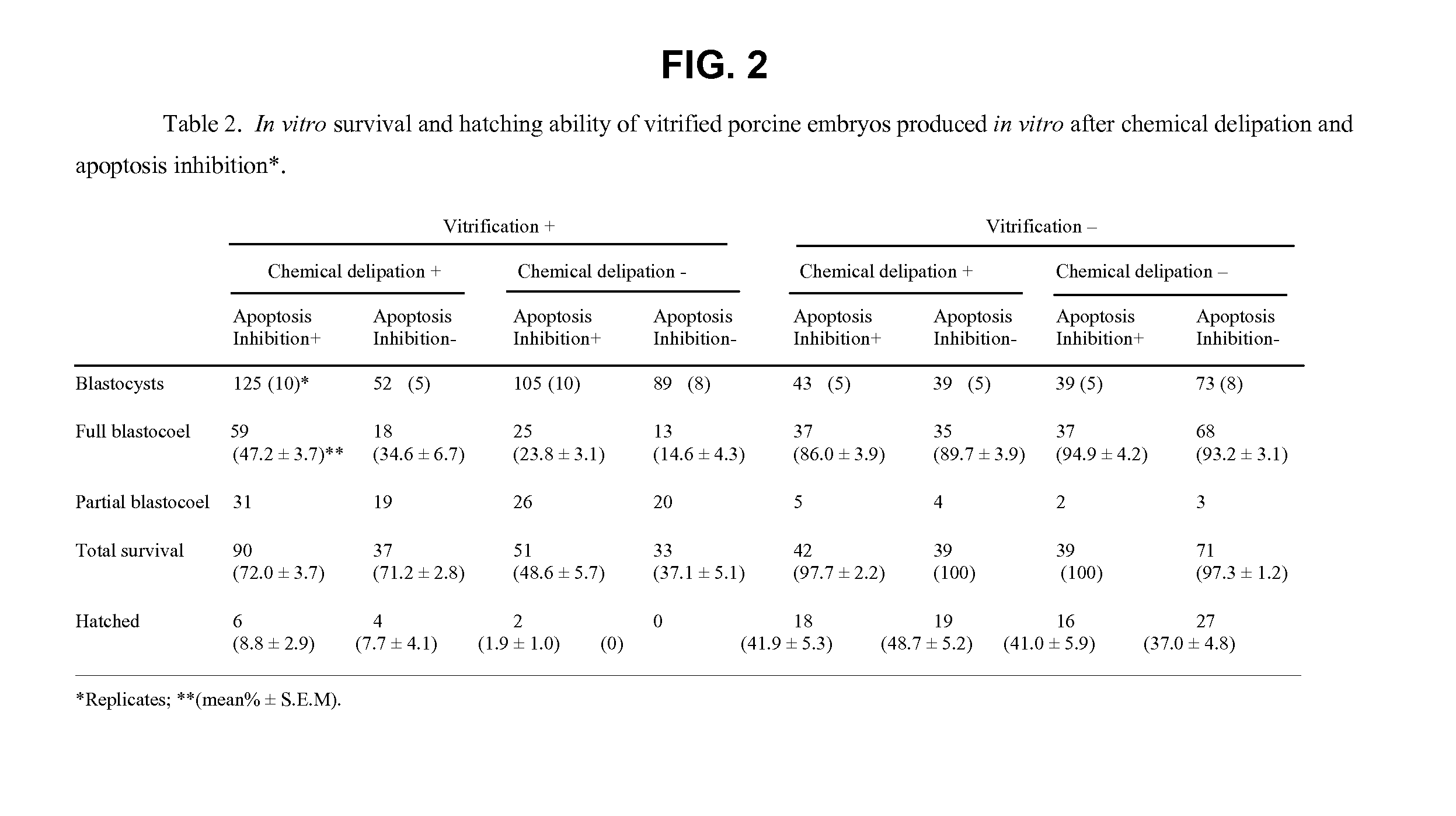
A method for cryopreservation of animal cells with high level of intracellular lipid content, comprises the steps of conducting a delipation procedure using one or more lipolytic agent(s) and / or lipogenesis inhibitors during culture of the animal cells to stimulate the hydrolysis of intracellular lipids to reduce the lipid content, and vitrifying the treated animal cells using a modified vitrification solution and a modified warming solution.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Process for producing hydrocarbons from microbial lipids
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Factor c for treating gram-negative bacterial infection
InactiveUS20080085865A1Strong antibacterial effectSuppress LPS-induced cytokinesAntibacterial agentsBiocideEndotoxin removalClearance rate
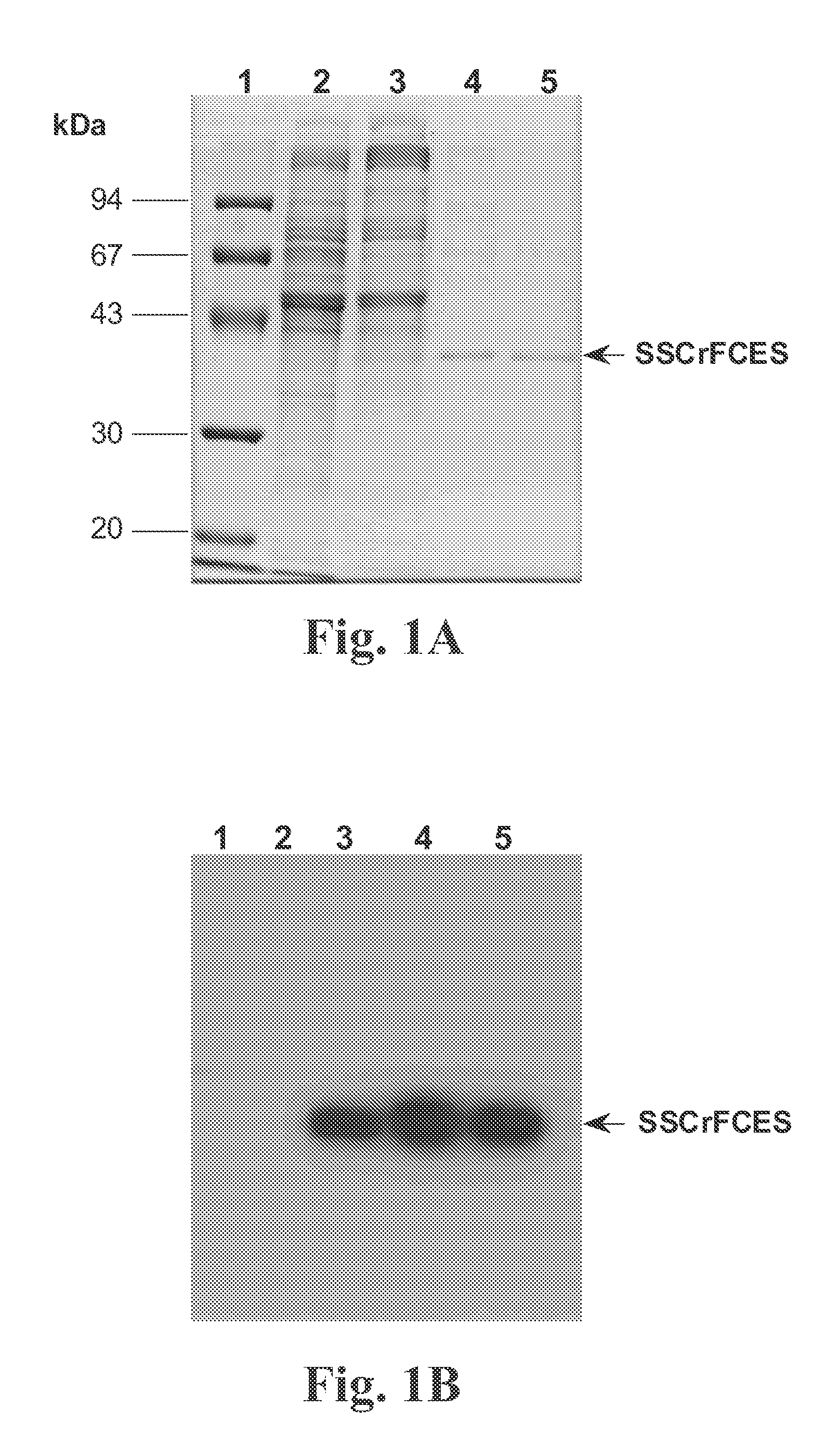
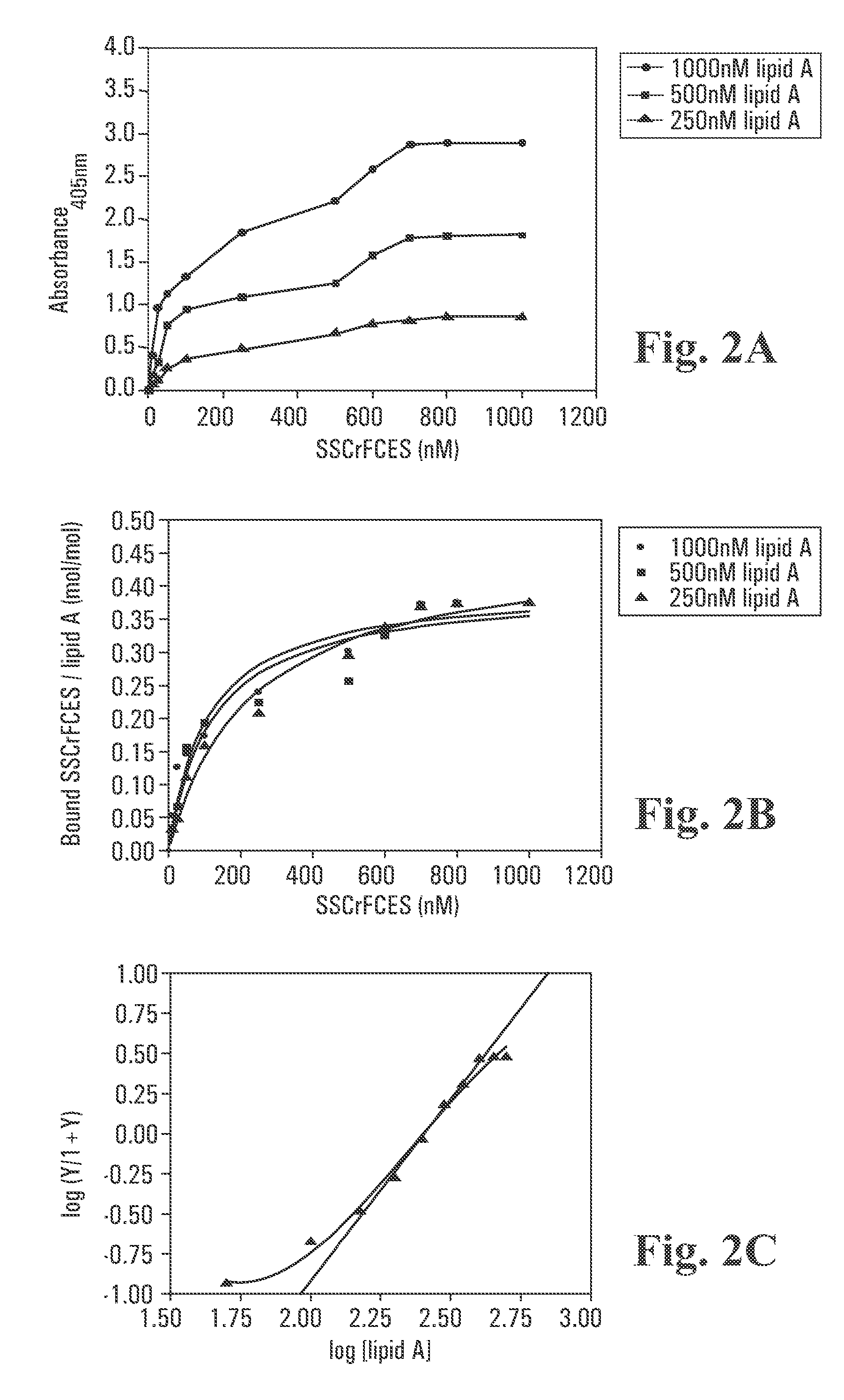
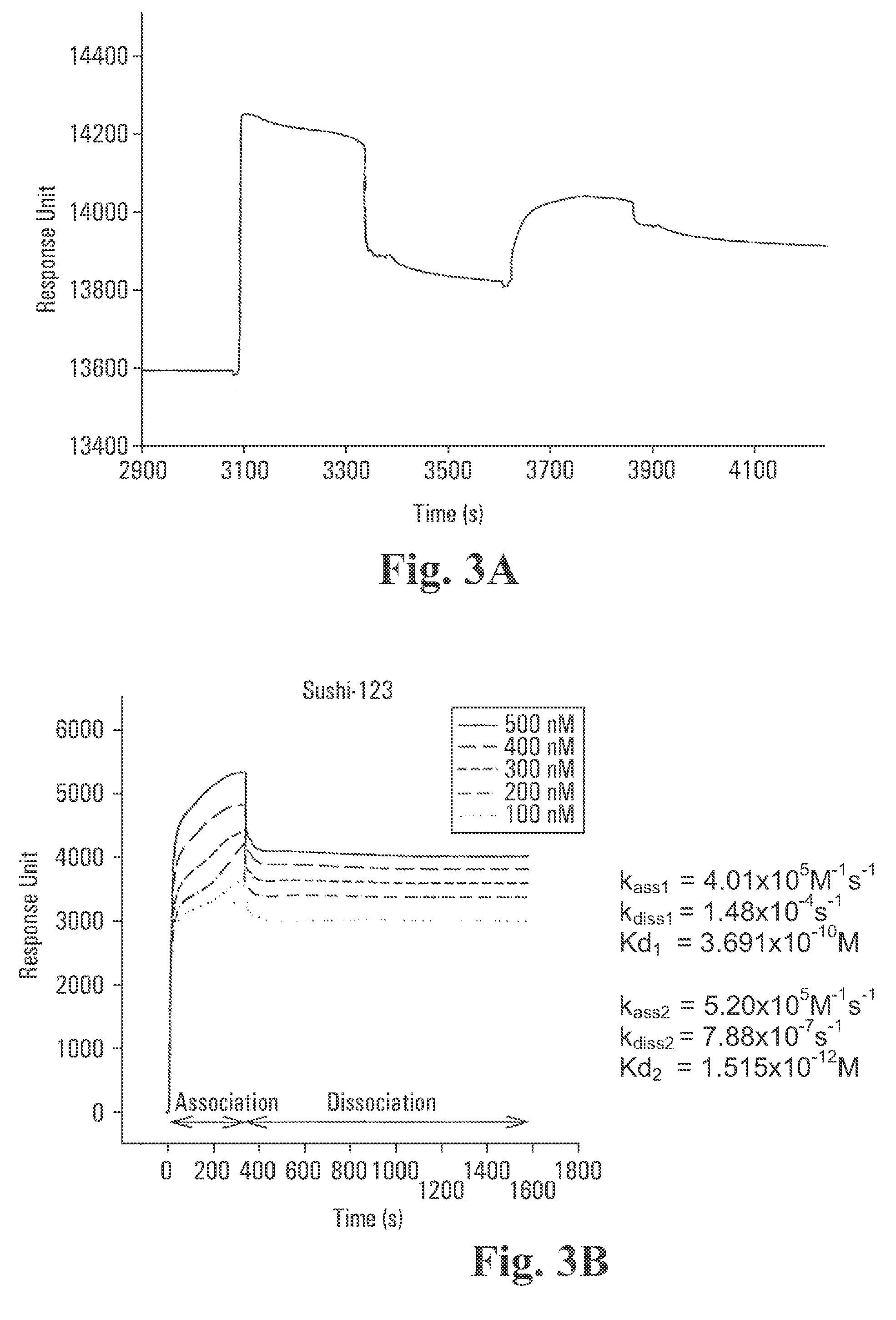
Recombinant fragments of Factor C are disclosed. These proteins and peptides show great potency in recognizing, binding to, neutralizing and removing endotoxin. These molecules can thus be used for anti-microbial, anti-endotoxin, and anti-sepsis therapy. SSCrFCES is a 38 kDa protein representing the LPS-binding domain of Factor C. The ability of SSCrFCES to bind lipid A was analyzed using an ELISA-based assay as well as surface plasmon resonance. Surface plasmon resonance similarly carried out for SSCrFC-sushi-1,2,3-GFP, SSCrFC-sushi-1GFP, and SSCrFC-sushi-3GFP confirmed their superior affinity for endotoxin. The 50% endotoxin-neutralizing concentration of SSCrFCES against 200 EU of endotoxin is 0.069 μM, suggesting that SSCrFCES is an effective inhibitor of LAL coagulation cascade. Although partially attenuated by human serum, as low as 1 μM of SSCrFCES inhibits the LPS-induced secretion of hTNF-α and hIL-8 by THP-1 and human pheripheral blood mononuclear cells with a potency more superior than polymyxin B. SSCrFCES is non-cytotoxic, with a clearance rate of 4.7 ml / minute. The LD90 of SSCrFCES for LPS lethality in mice is achieved at 2 μM. These results demonstrate the endotoxin-neutralizing capability of SSCrFCES in vitro and in vivo, as well as its potential for use in the treatment of endotoxin-induced septic shock. Also embodied in this application is the use of the sushi peptides and their mutant derivatives as potent antimicrobials.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Combinatorial platform for the display of surface adjuvants and antigens
ActiveUS20170080080A1Low costLess timeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyAdjuvant
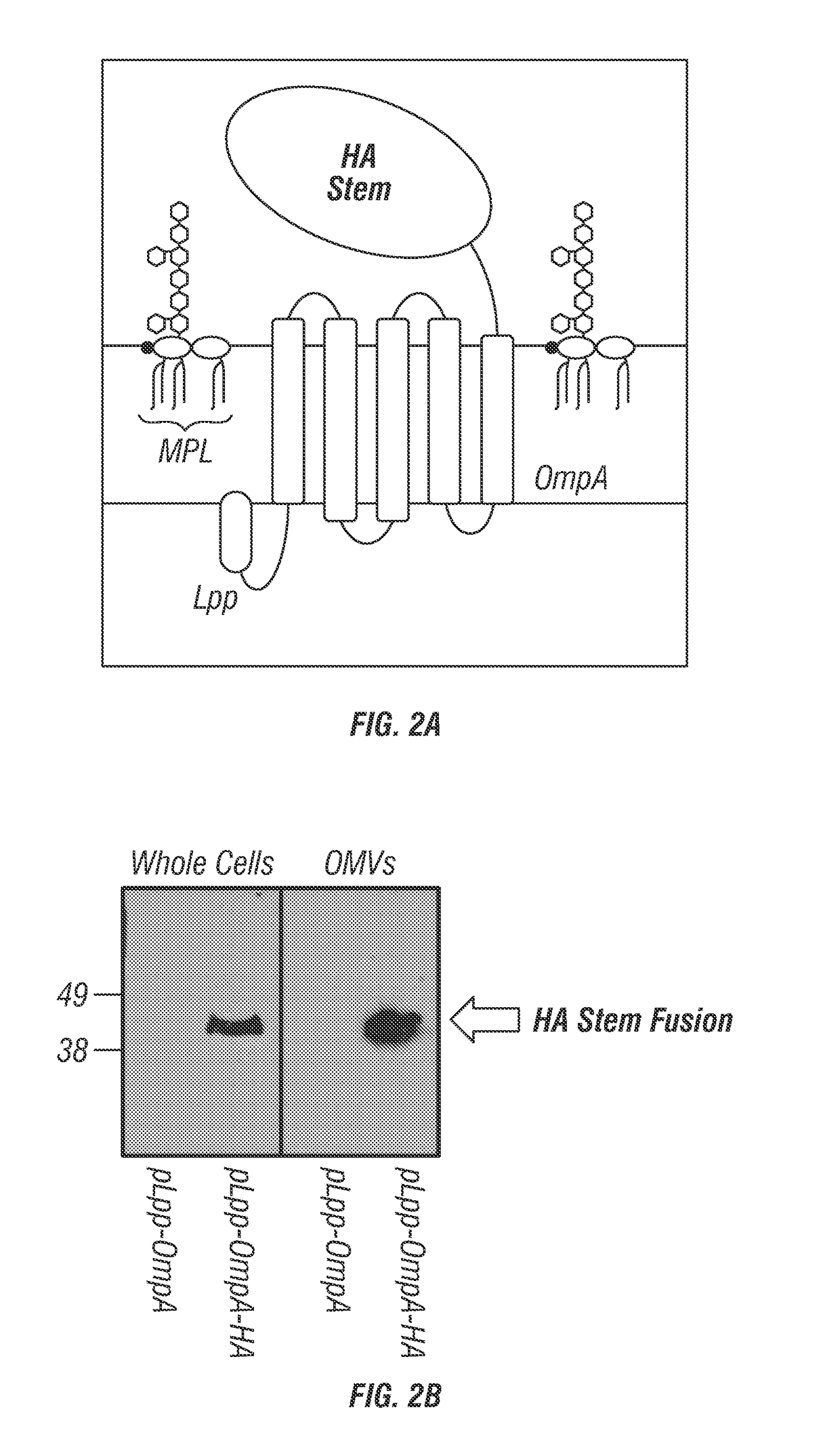
Engineered bacteria are provided that produce modified lipid A and a polypeptide or polysaccharide antigens. In some aspects, immunogenic compositions are provided comprising a modified a lipid A and a polypeptide or polysaccharide antigen.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com