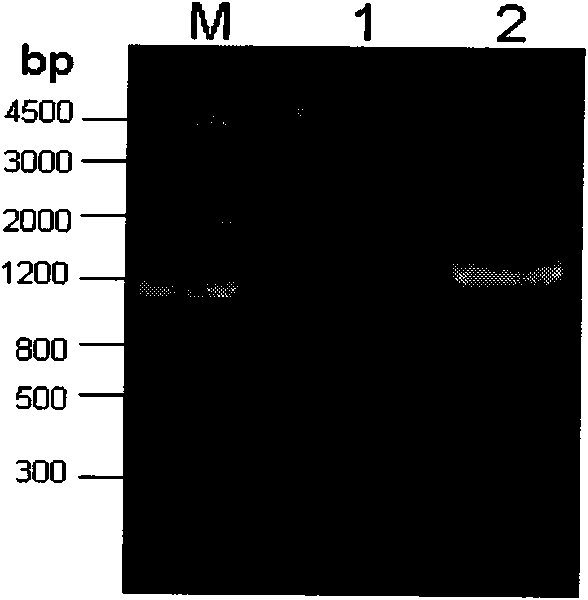
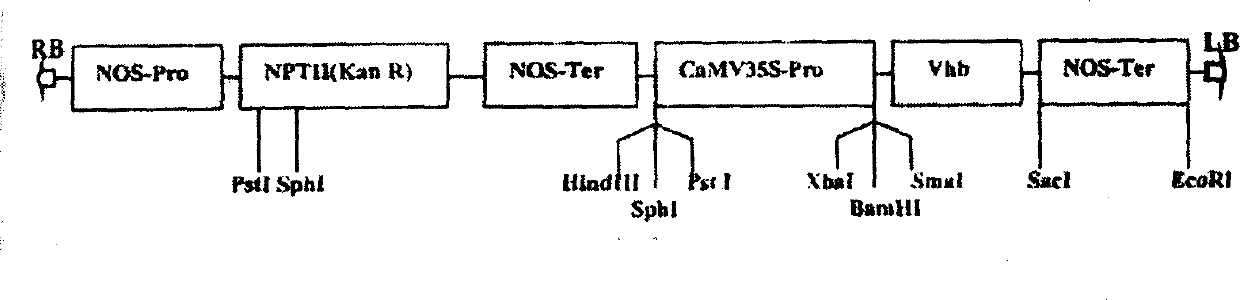
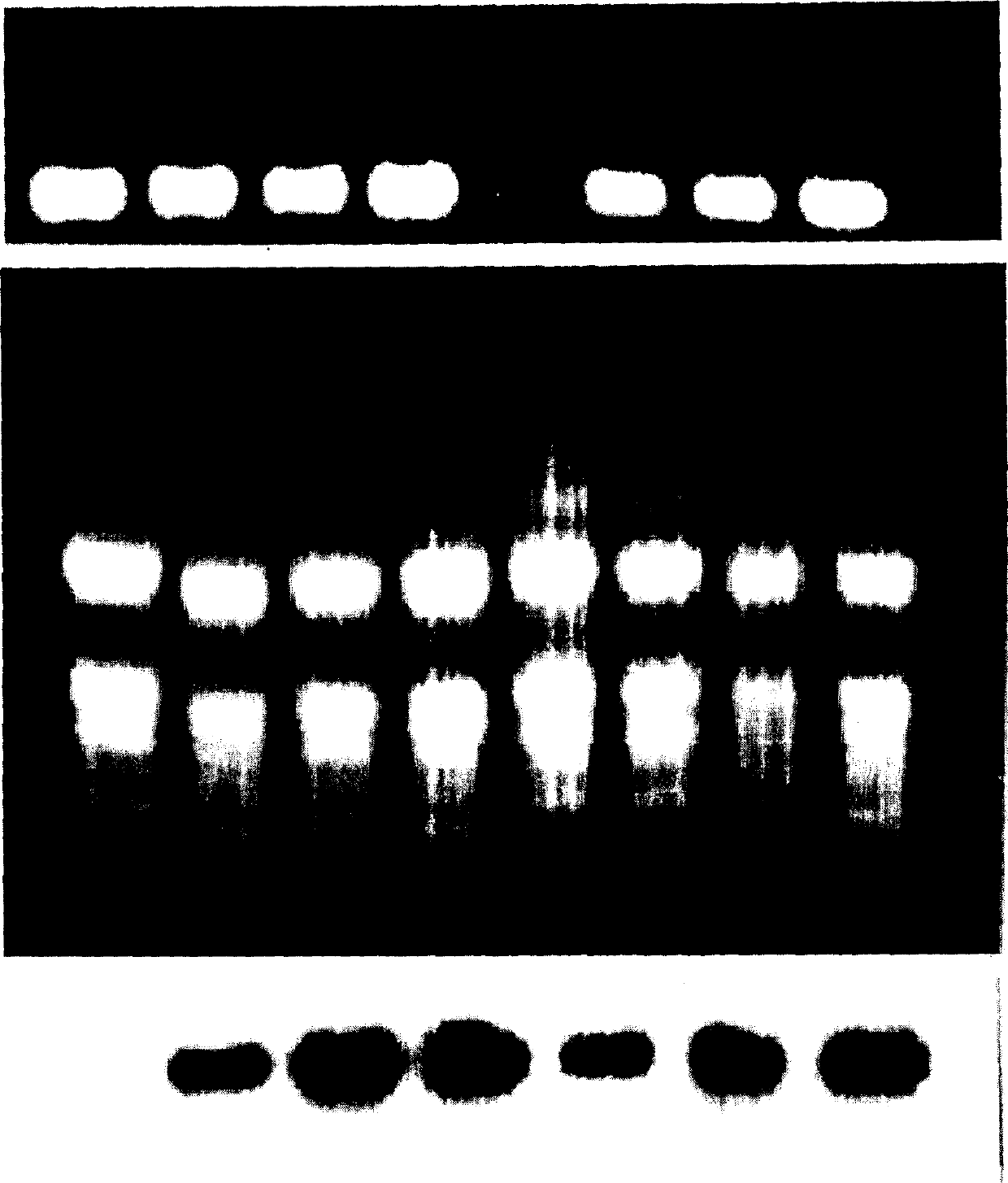
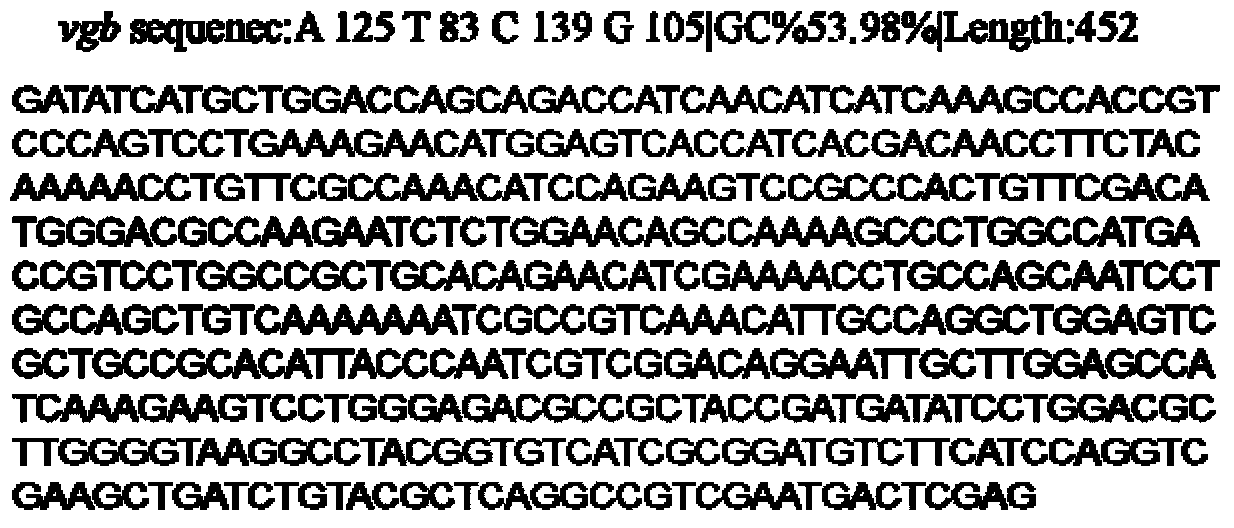Patents
Literature
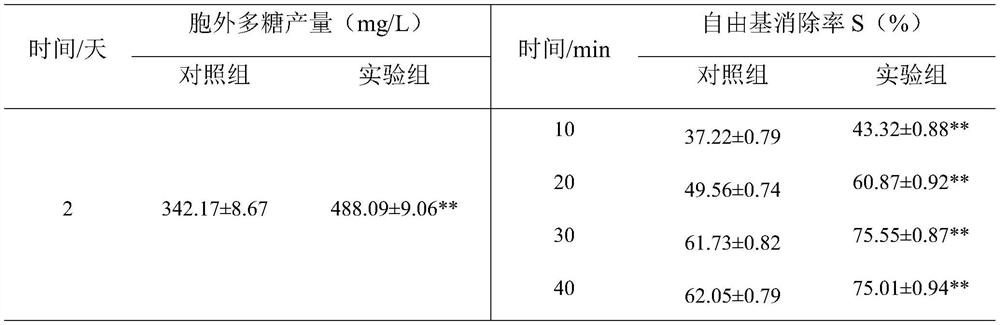
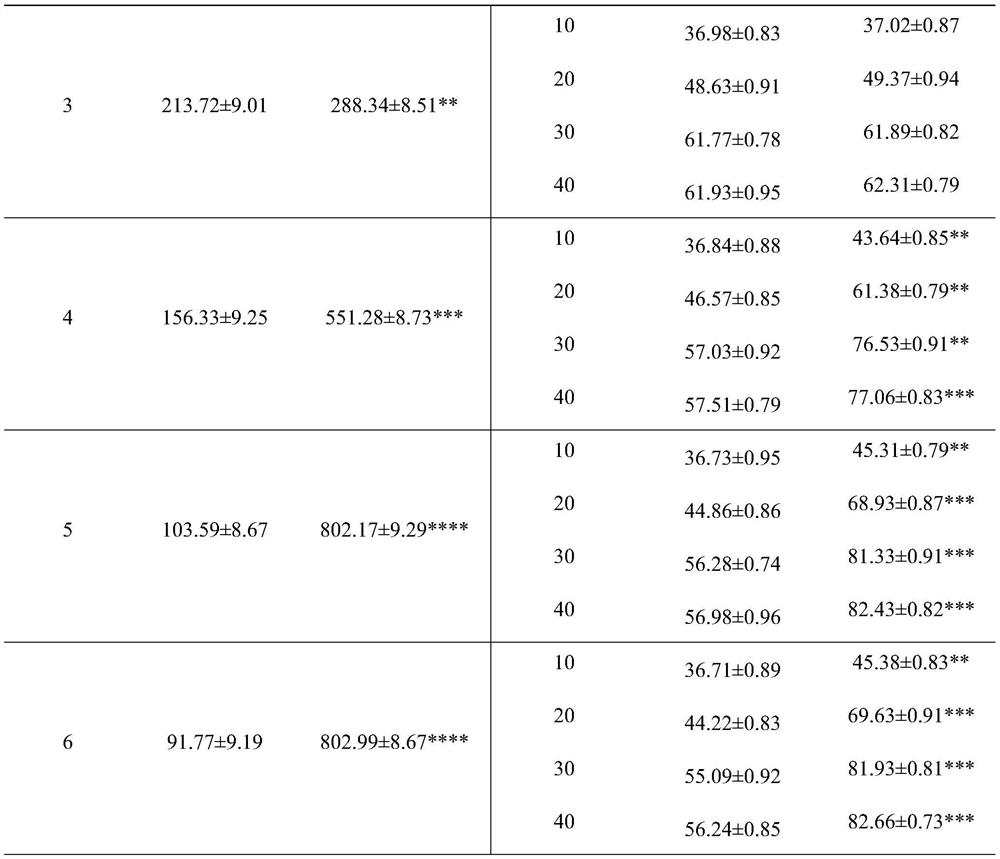
33 results about "Vitreoscilla" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vitreoscilla is a genus of Gram-negative aerobic bacterium. The bacterial haemoglobin (VHb) was first discovered from Vitreoscilla, and VHb is found to have a wide range of biological and biotechnological applications including promotion of cell growth, protein synthesis, metabolite productivity, respiration, cellular detoxification, fermentation, and biodegradation.
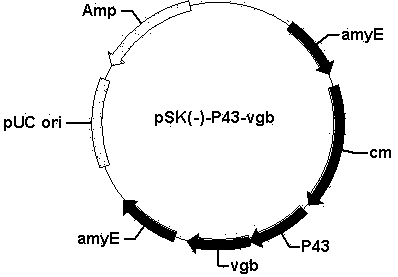
Gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial and method for producing high-yield gamma-polyglutamic acid through gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial
ActiveCN103881954AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMonosodium glutamateGenetic engineering
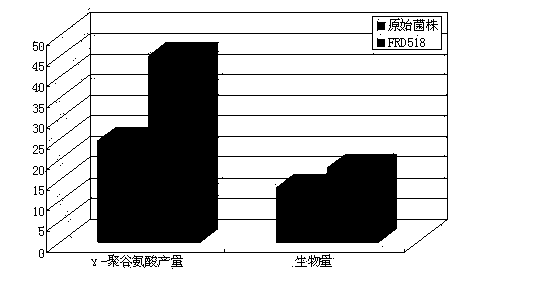
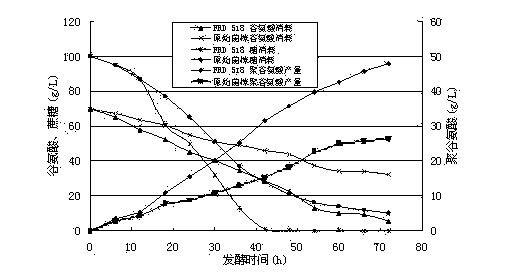
The present invention discloses a high-yield gamma-polyglutamic acid production gene engineering bacterial and a fermentation production method thereof. The gene engineering bacterial is named Bacillus subtilis FRD518, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC NO.6772, and the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb) is recombined and integrated on the chromosome of the gene engineering bacterial, such that the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin VHb can be successfully and highly expressed so as to significantly improve the oxygen utilization rate of the recombinant Bacillus subtilis under a low dissolved oxygen condition. According to the present invention, during a fermentation process, a carbon source, sodium glutamate, a yeast extract and other components are added in a flow manner, such that the gene engineering bacterial can efficiently produce the gamma-polyglutamic acid in a high yield manner, wherein the yield achieves more than 65 g / L, and is increased by 147% compared with the yield of the single batch culture of the original wild strain; and with the gene engineering bacterial, the problems of low yield, more by-products, long period, high energy consumption and the like of fermentation of the gamma-polyglutamic acid gene engineering bacterial under high viscosity and dissolved oxygen limiting conditions are solved, and the gamma-polyglutamic acid gene engineering bacterial can be applied for large-scale industrial production of gamma-polyglutamate acid.
Owner:SHANDONG FREDA BIOTECH
Genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and application thereof
InactiveCN102041264ASolve the problem of insufficient oxygen supplyPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDihydroxyacetoneGluconobacter oxydans
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid for expressing vitreoscilla hemoglobin in a cell and a construction method of the recombinant plasmid, a genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a construction method and application of the genetic engineering bacterium. The recombinant plasmid comprises a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb, a PtufB promoter of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a suitable carrier, wherein the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by transforming recombinant plasmid into a host bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can be used for expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin in the cell, can be used for improving the yield of biomass and catalysate 1, 3-dihydroxyacetone under the condition of not changing the existing equipment and energy consumption pressure and provides an effective path for solving the problem of in sufficient oxygen supply in the cell cultivation and catalytic process of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans).
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of Vitreoscilla hematoglobin gene in improving waterlogging resistance of plant
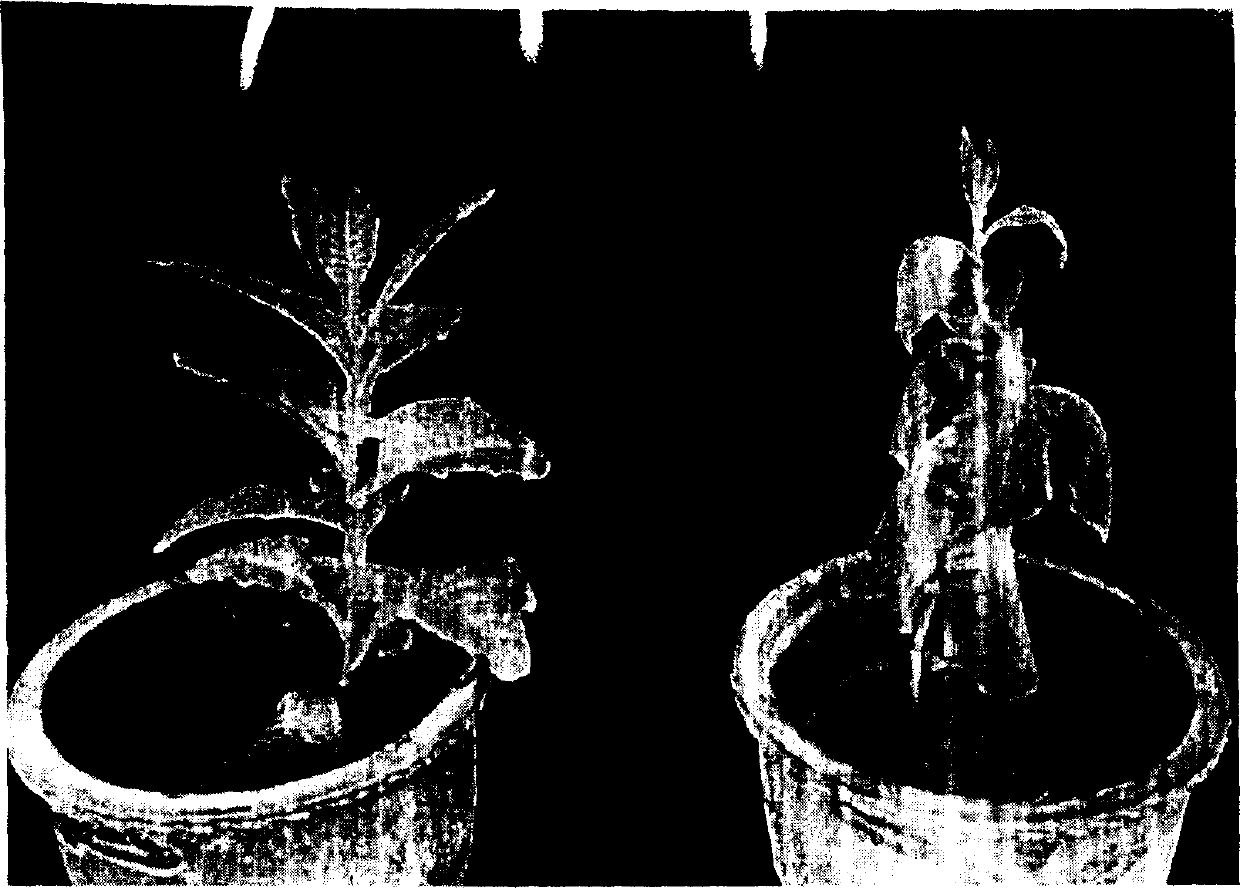
An application of vitreoscilla hematoglobin gene in improving the waterlogging resistance of plant is disclosed. Said gene is constructed in the expression vector, which is then transferred to plant cells to make said gene be expressed in plant cells. The resultant transgenic plant has high resistance to waterlogging.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
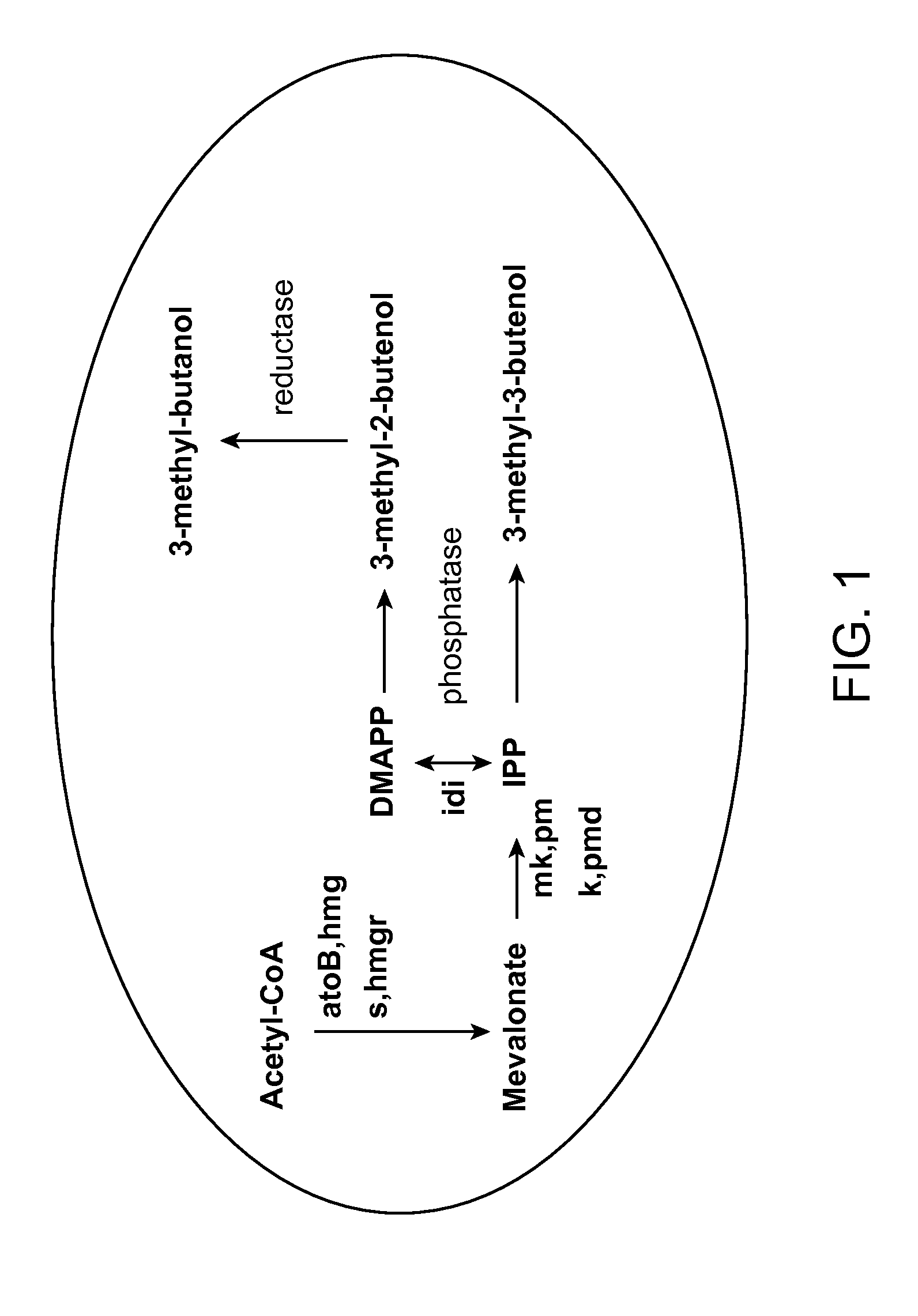
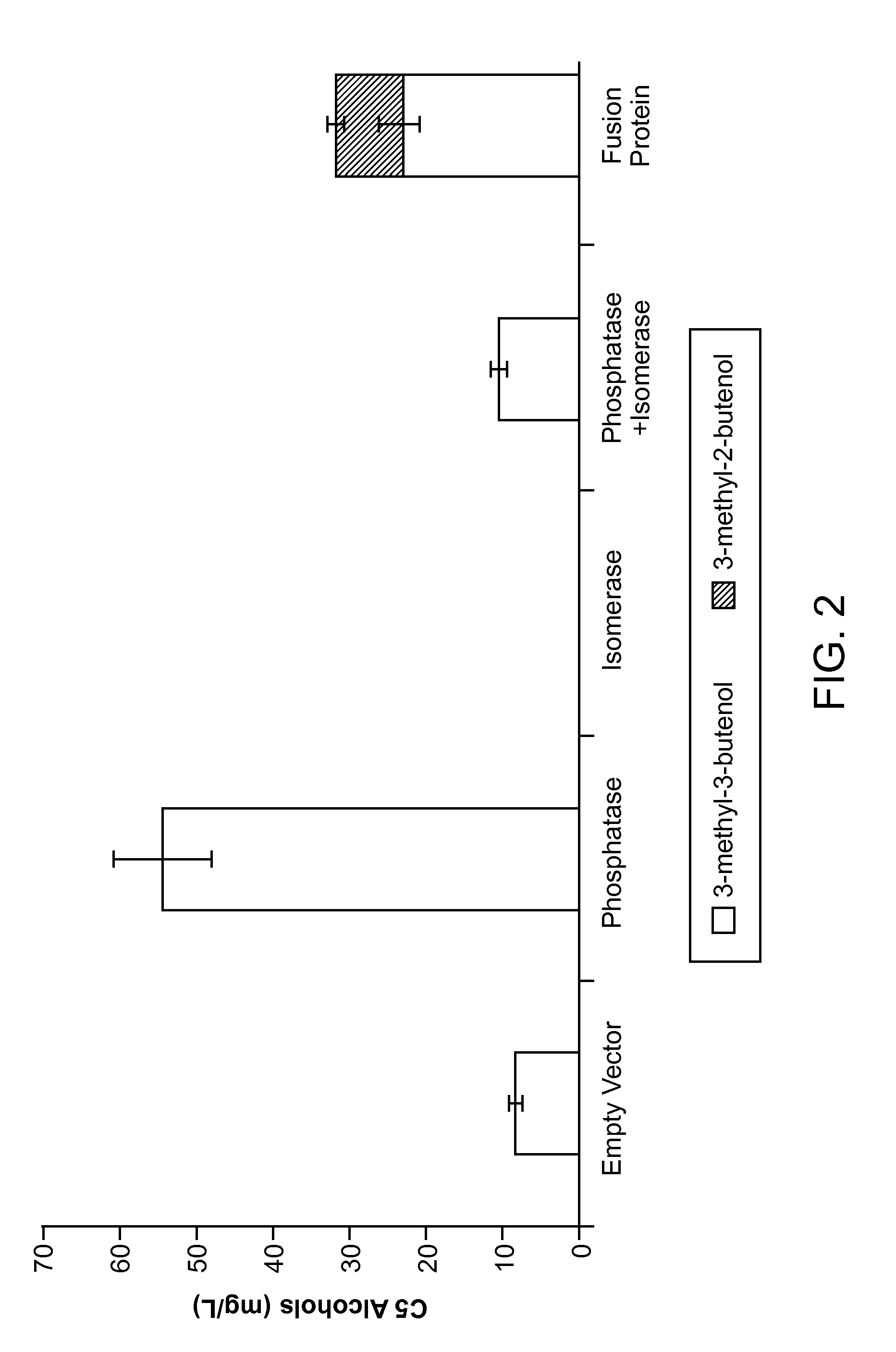
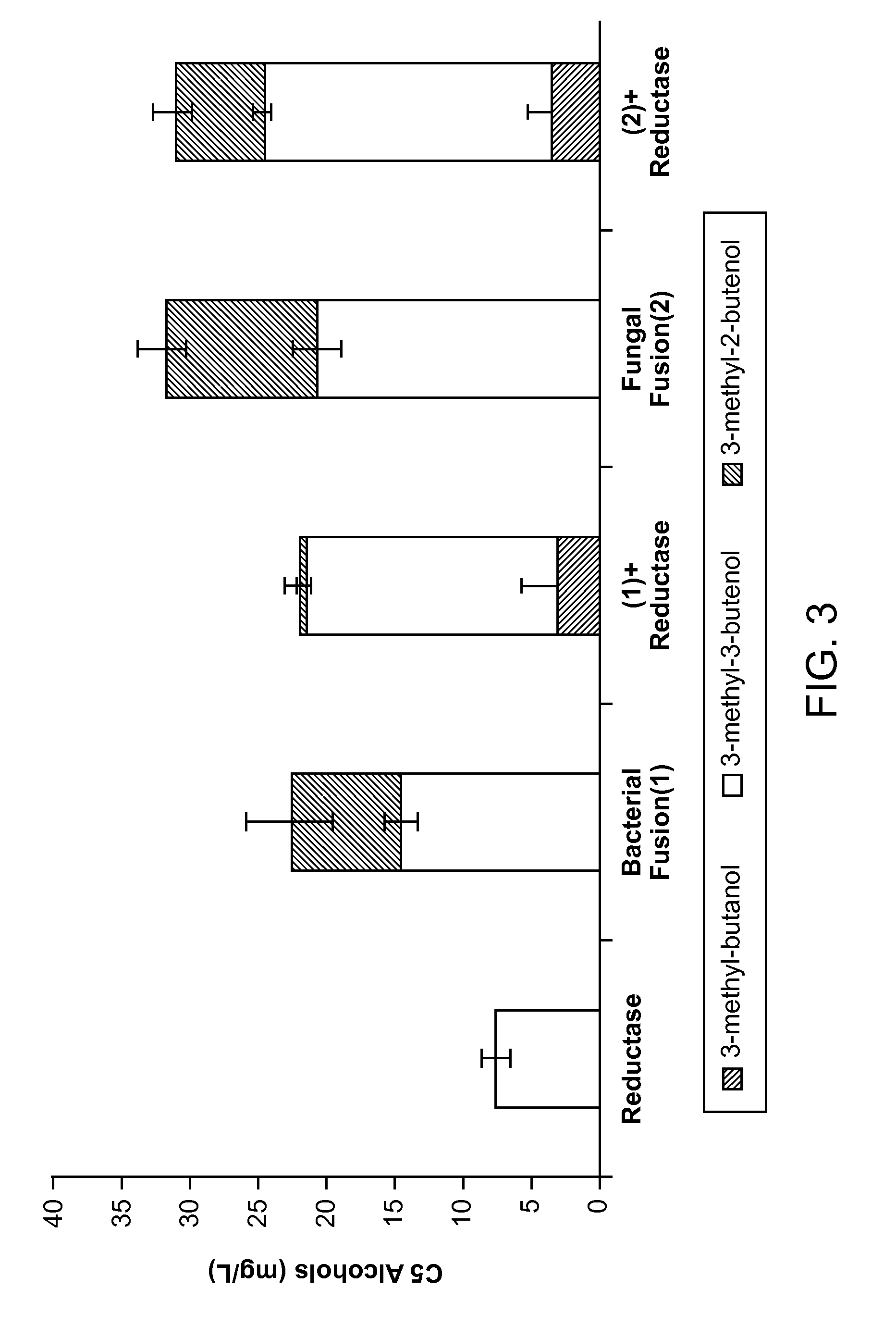
Methods for increasing production of 3-methyl-2-butenol using fusion proteins
The invention relates, in part, to nucleic acid constructs, genetically modified host cells and methods employing such constructs and host cells to increase the production of 3-methyl-2-butenol from IPP. Thus, in some aspects, the invention provides a genetically modified host cell transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fusion protein comprising a phosphatase capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) linked to an IPP isomerase capable of converting IPP to DMAPP, wherein the nucleic acid construct is operably linked to a promoter. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell 5 further comprises a nucleic acid encoding a reductase that is capable of converting 3-methyl-2-butenol to 3-methyl-butanol. In some embodiments, the reductase is encoded by a nucleic acid construct introduced into the cell. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type I isomerase. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type II isomerase. In some embodiments, the host cell is selected from a group of taxonimcal classes consisting of 20 Escherichia, Enterobacter, Azotobacter, Erwinia, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Rhizobia, Vitreoscilla, Synechococcus, Synechocystis, and Paracoccus taxonomical classes. In some embodiments, the host cell is an Escherichia coli cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is a fungal cell, such as a yeast cell. In some embodiments, the yeast cell is a Saccharomyces sp. cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is an algal, insect or mammalian cell line. In some embodiments, the phosphatase is nudB from E. coli. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is encoded by an idi gene from E. coli or idil gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
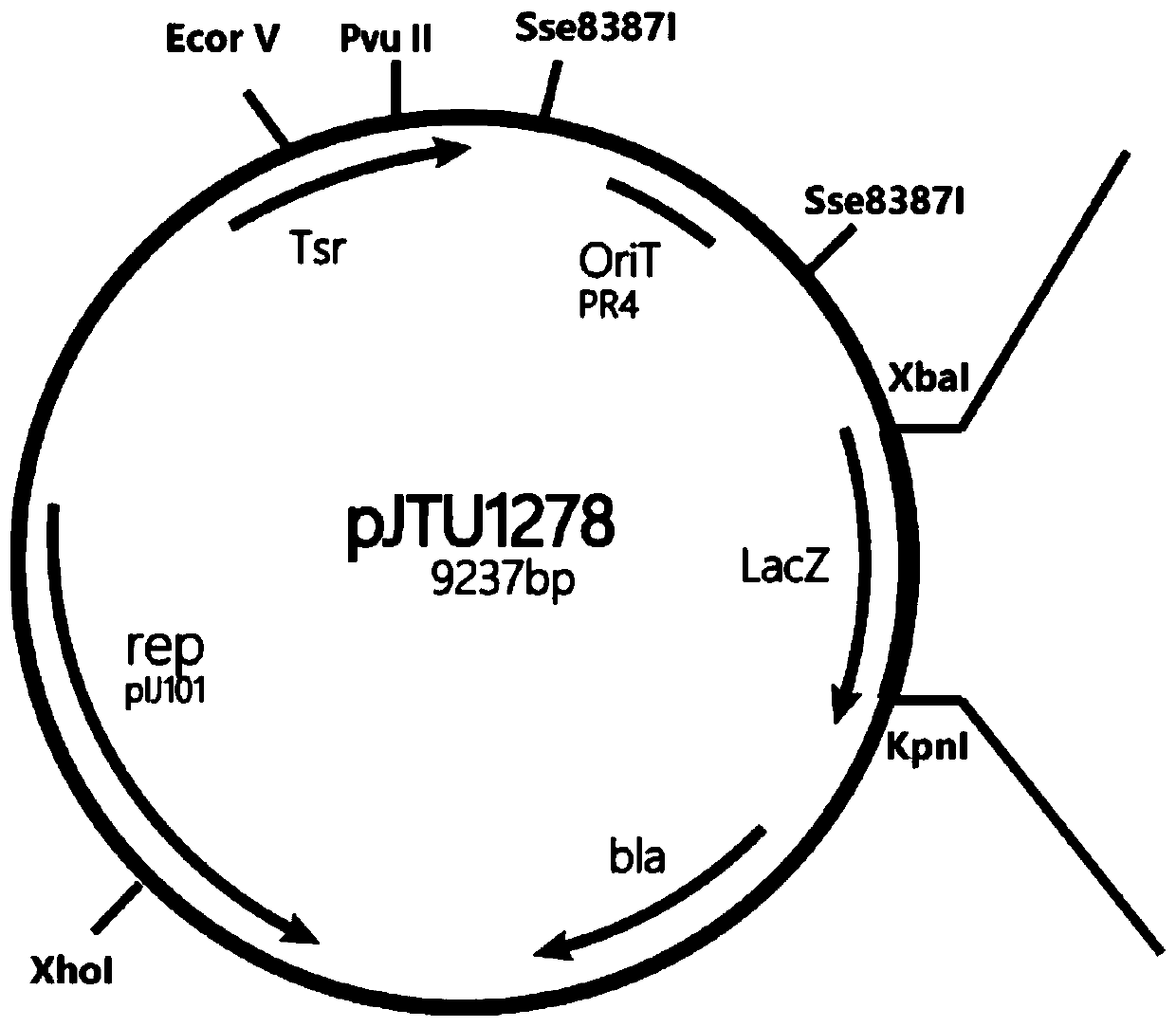
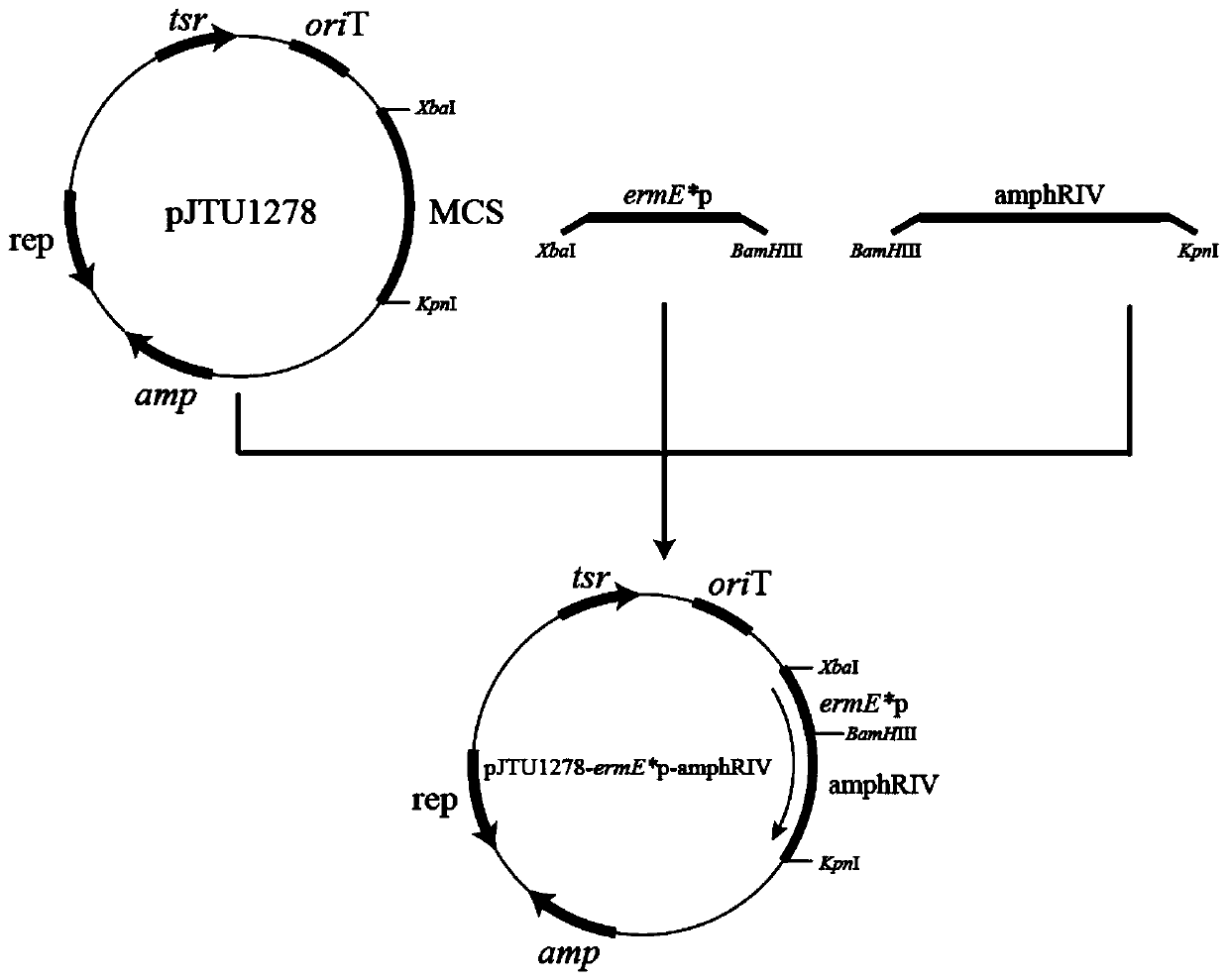
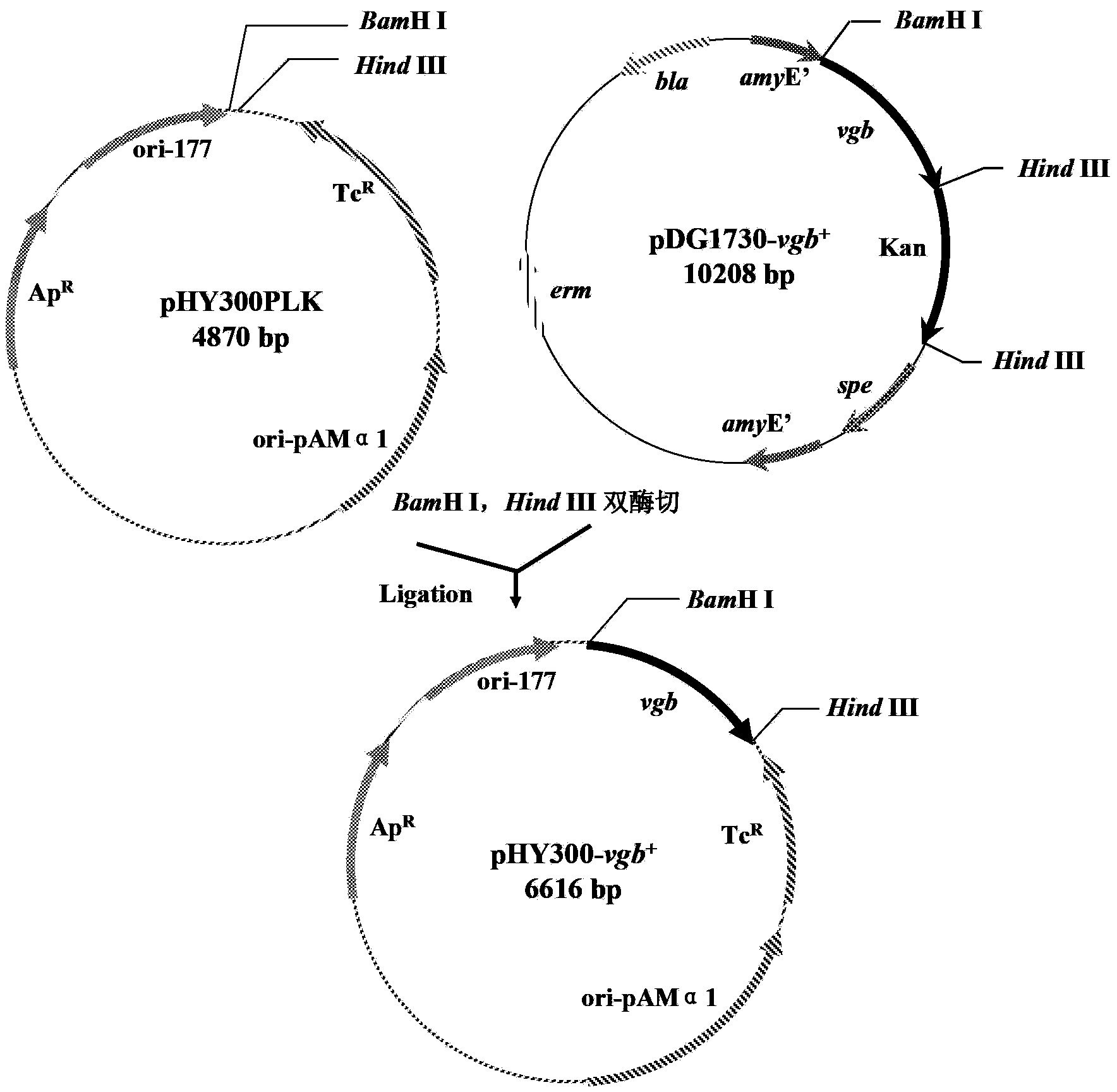
Method for constructing saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb)
InactiveCN102234660AIncrease intakeImprove utilizationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPrimary metabolismProtein
The invention provides a method for cloning a saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb), belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. In the method, based on the fact that VHb (hemoglobin) can be combined with oxygen to form an oxygenated state, the VHb intervenes the oxygen related metabolic pathway of cells, thereby changing the original biological metabolism mode of the cells under oxygen-limited conditions, promoting the cell growth and protein synthesis under oxygen-deficient conditions, directly or indirectly affecting the action principles of primary metabolism and secondary metabolism of aerobes, firstly constructing an Escherichia coli expression plasmid pQEV, expressing the VHb with biological activity, and further constructing the saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV). In order to realize high-density culture of cells and high-yield fermentation of metabolic products under oxygen-limited conditions, the invention provides an important pathway for homologous recombination of vgb gene elements and saccharopolyspora erythraea chromosome genomes.
Owner:邢安辉 +2
Ganoderic acid high-producing engineering strain kmust-VGB-1
ActiveCN105296367ALabor savingShorten the production cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesGanoderic acidMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a ganoderic acid high-producing engineering strain kmust-VGB-1, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with preservation number of CGMCC NO. 11301. The lucid ganoderma engineering strain kmust-VGB-1 for high production of ganoderic acid is prepared by expressing a vitreoscilla hemoglobin VGB gene through a lucid ganoderma strong promoter P-gpd; through a fermentation experiment in a shaking flask, under the circumstance of avoiding influence on cell growth, yield of monomer ganoderic acids GA-Me, GA-T, GA-Mk and GA-S produced by the VGB converter strain are respectively 3.1 times, 3.2 times, 2.1 times and 3.6 times that of monomer ganoderic acids produced by a WT strain; therefore, the high-producing strain, as an engineering strain for producing the ganoderic acid, has a broad application prospect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant bacillus subtilis, construction method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103421725ASolve the problem of dissolved oxygenIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyBacillus sp. BI
The invention relates to a recombinant bacillus subtilis, a construction method and applications thereof. The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb, and the bacillus subtilis can generate gamma-polyglutamic acid. The invention also discloses a construction method that recombinant plasmid containing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb sections is transferred into the bacillus subtilis to obtain the recombinant bacillus subtilis, which contains the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb and is capable of expressing gamma-polyglutamic acid. The recombinant bacillus subtilis can achieve the goal of high yield production of gamma-polyglutamic acid under the conditions of high viscosity culture medium and low dissolved oxygen, solves the problem of requirement on high dissolved oxygen in mass production of gamma-polyglutamic acid, and thus the production cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Tylosin gene engineering strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102690775AIncrease productionIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShuttle vectorEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a tylosin gene engineering strain. The construction method for the tylosin gene engineering strain comprises the following steps: cloning tylosin through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to synthesize crucial rate-limiting enzyme gene TylF and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin VHb gene, constructing a recombinant plasmid by using an E. coli-streptomyces shuttle vector, importing the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002, performing conjugal transfer culture on the Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002 and streptomyces fradiae spores, converting streptomyces, screening a converter through apramycin resistance, further confirming the converter by using PCR, and finally obtaining the gene engineering strain. The tylosin gene engineering strain can be directly used in the industrial production of tylosin; and compared with the tylosin gene engineering strain used in the conventional industrial production, the tylosin gene engineering strain has the advantages that the yield of the tylosin can be obviously improved to be 17,000-18,000u / ml and the content of a component A in the tylosin is effectively improved to be 94-95 percent.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
A kind of recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum expressing vgb gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106591210BImprove fermentation yieldRelease substrate inhibitionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAureobasidium sp.Bacillus thuringiensis
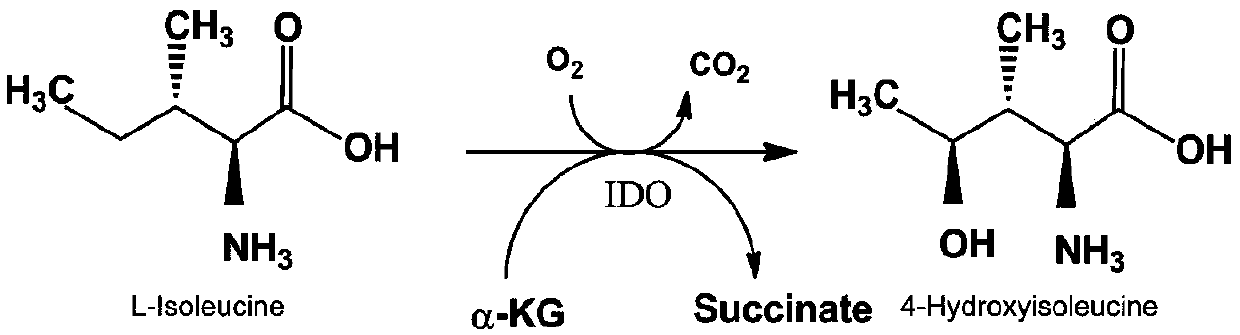
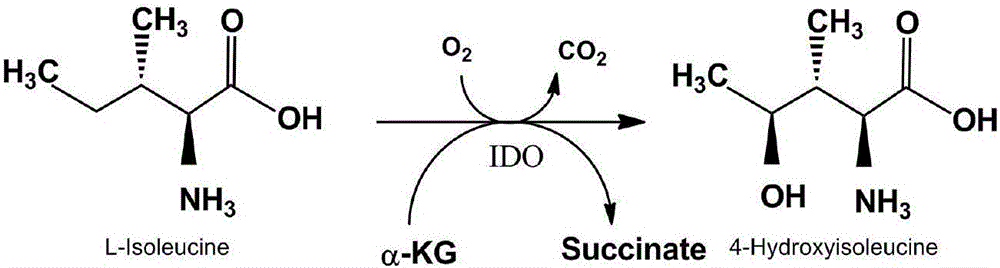
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum expressing a vgb gene and an application of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. An isoleucine dioxygenase gene ido from bacillus thuringiensis and a hemoglobin gene vgb from vitreoscilla are co-expressed to construct an expression vector pJYW-4-ido-vgb of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum; the expression vector is electrically transferred into corynebacterium glutamicum ssp.lactofermentum SN01 for producing L-isoleucine, and the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum SN01 / pJYW-4-ido-vgb is obtained. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum can relieve inhibition of a substrate of IDO by L-isoleucine in the production process of 4-HIL (4-hydroxyisoleucine) with L-isoleucine taken as the substrate, so that the fermentation yield of 4-HIL is increased by 50.0%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction method and application of recombinant bacterium for producing chitosanase
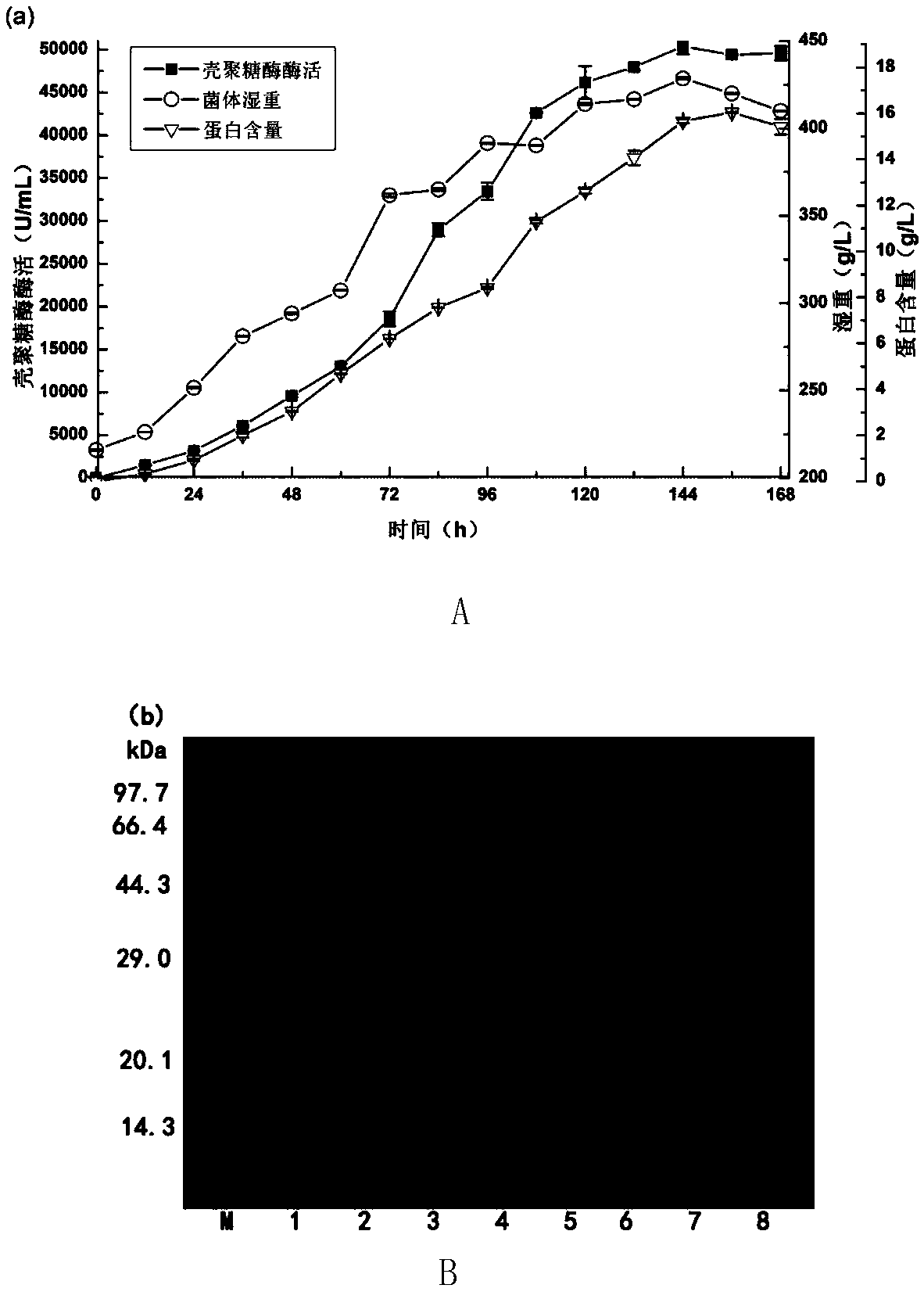
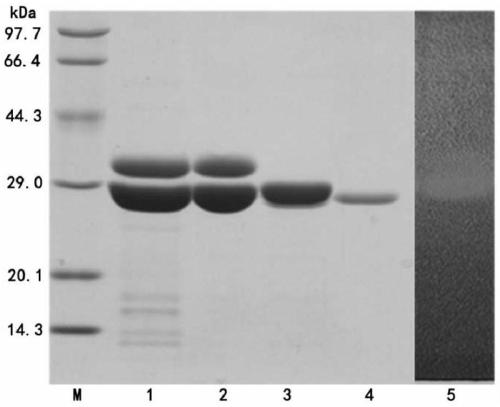
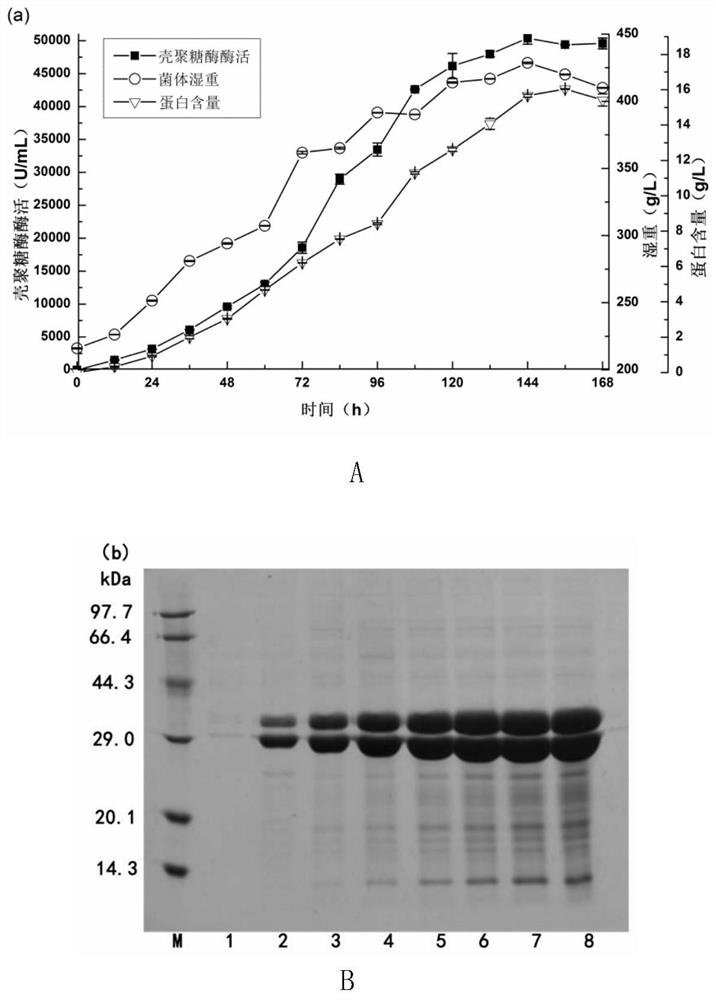
ActiveCN109652437AEfficient expressionExcellent hydrolysis propertiesBacteria peptidesEnzymesChitosanaseHigh concentration
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a recombinant bacterium for producing chitosanase. According to the method, a bacillus subtilis chitosanase gene and a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene are co-expressed in pichia pastoris, and a recombinant strain is used for efficiently preparing the chitosanase through a high-density fermentation strategy. The enzyme activity of the chitosanase prepared through the method is as high as 50000 U / mL or above, and the protein content is up to 16.0 mg / mL. The specific enzyme activity of recombinant enzyme is 4065.7 U / mg, the optimum pHvalue is 6.0, and the optimum temperature is 55 DEG C. The enzyme is used for hydrolyzing high-concentration (larger than or equal to 10%) chitosan to prepare chitosan oligosaccharide, the yield of chitosan oligosaccharide is larger than 75%, and main products are disaccharide, trisaccharide and tetraose. The enzyme production level of the chitosanase preparation method is much higher than that reported in existing literature and patents, and the produced enzyme has excellent hydrolysis characteristics and has very good application value in industrial production of chitosanase and preparationof chitosan oligosaccharide.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum expressing vgb gene and application of recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveCN106591210AImprove fermentation yieldRelease substrate inhibitionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsBacillus thuringiensisAureobasidium sp.
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum expressing a vgb gene and an application of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. An isoleucine dioxygenase gene ido from bacillus thuringiensis and a hemoglobin gene vgb from vitreoscilla are co-expressed to construct an expression vector pJYW-4-ido-vgb of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum; the expression vector is electrically transferred into corynebacterium glutamicum ssp.lactofermentum SN01 for producing L-isoleucine, and the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum SN01 / pJYW-4-ido-vgb is obtained. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum can relieve inhibition of a substrate of IDO by L-isoleucine in the production process of 4-HIL (4-hydroxyisoleucine) with L-isoleucine taken as the substrate, so that the fermentation yield of 4-HIL is increased by 50.0%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Streptomyces diastatochromogenes engineering strain for producing toyocamycin, as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103243062AImprove the problem of dissolved oxygenIncrease bacterial concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHemoglobin hbToyocamycin
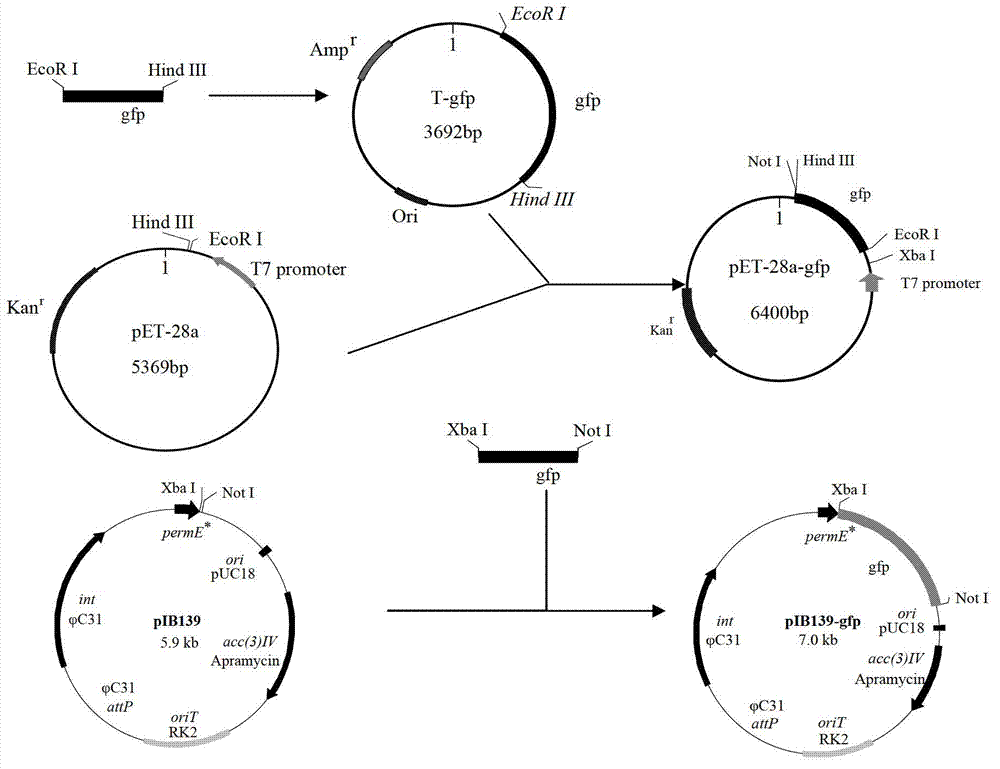
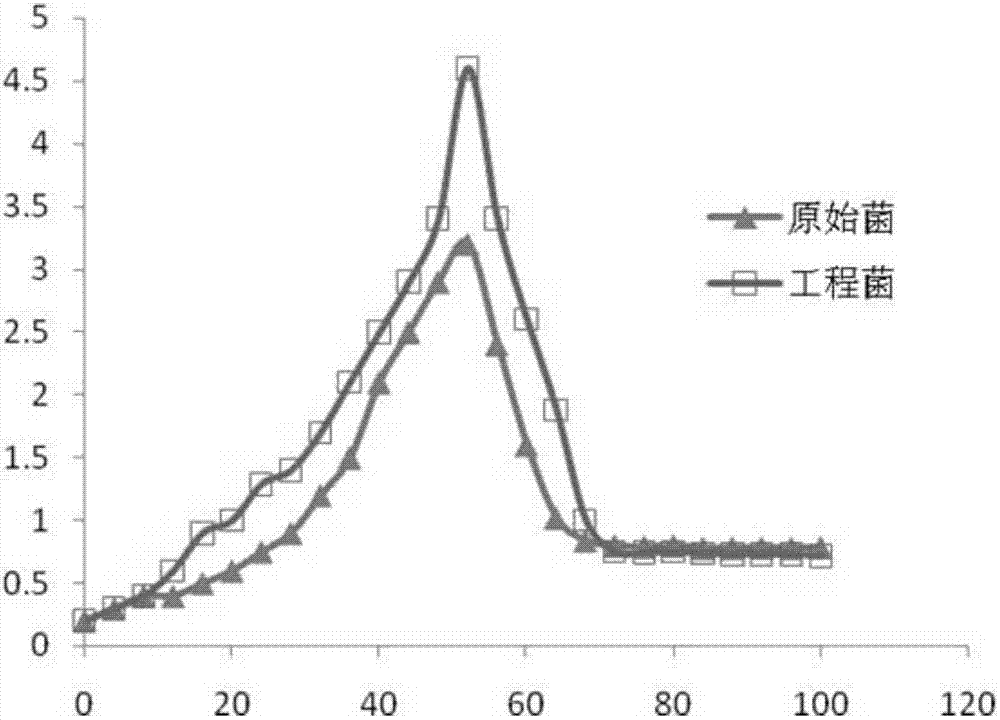
The invention discloses a streptomyces diastatochromogenes engineering strain for producing toyocamycin, as well as a construction method and application thereof. Vitreoscilla hemoglobingene (vgb) is integrated on a chromosome of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes engineering strain, so that the toyocamycin expression capability is higher than that of streptomyces diastatochromogenes 1628. The construction process is as follows: 1) constructing an expression vector pIB139-vgb; and 2) utilizing a conjugation method to integrate the expression vector into the chromosome of streptomyces diastatochromogenes to obtain the engineering strain. A promoter permE* on the pIB139 vector is utilized to start the expression of the vgb gene, and the conjugation method is utilized to integrate the specificity of the vector pIB139-vgb into the chromosome of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes 1628 to obtain the engineering strain with stable inheritance. Compared with an original strain, the yield of the recombinant toyocamycin is at least improved by 21.2%, and the concentration of the strain is improved by 11.6%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102776147AIncrease profitImprove liquidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEngineered geneticPromoter
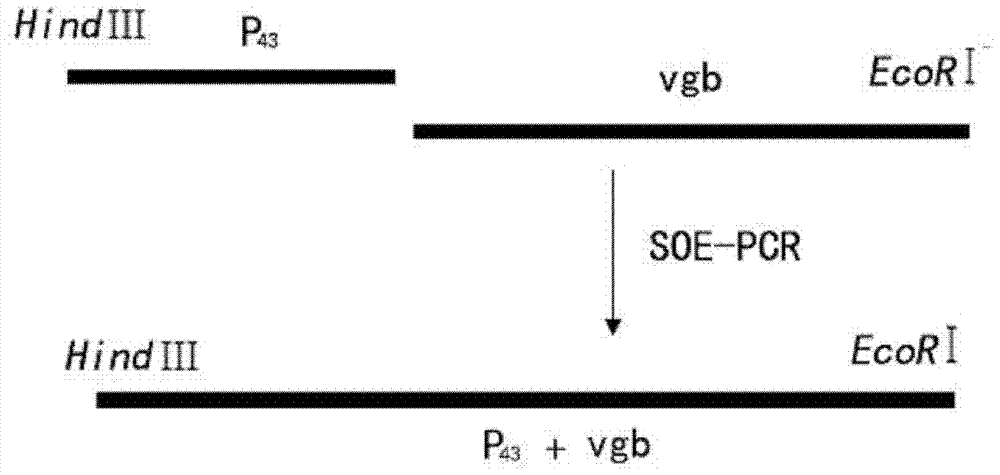
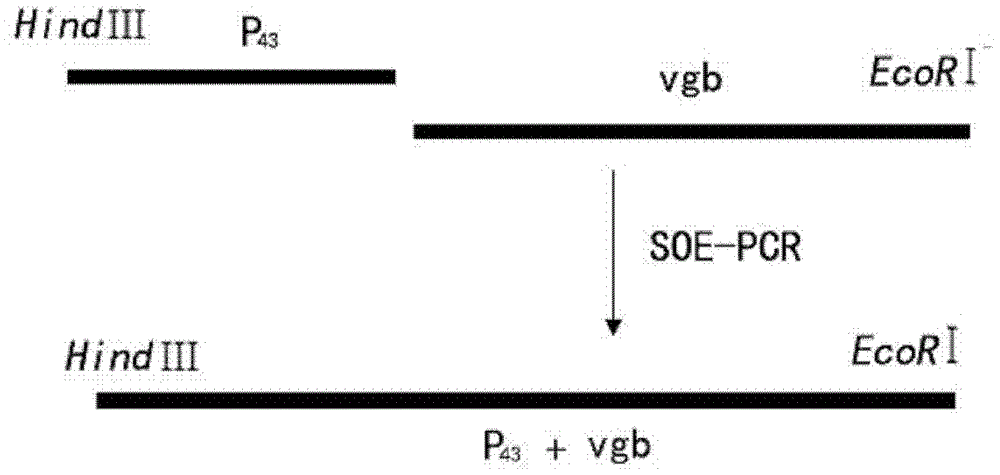
The invention discloses a gene-engineered bacterium of gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and a construction method and application of the gene-engineered bacterium. Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus BC39 with vitreoscilla hemoglobin regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter is constructed by constructing a gene-recombination integrative vector with a peoriae paenibacillus LXH-B-1 strain as host bacteria. The gene-engineered bacterium of the gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus is capable of intracellularly expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, so that the utilization rate of oxygen by the peoriae paenibacillus, the cell biomass liveweight and the yield of catalysate polypeptide antibiotics can be improved; and the yield of the catalysate polypeptide antibiotics of the engineering strain is increased by 45% compared with that of the original strain; and therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the problem of insufficient oxygen supply in the cell culture and catalysis process of the peoriae paenibacillus.
Owner:杨凌静玥生物科技有限公司
Genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently synthesizing riboflavin and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN113073074AIncrease productionIncreased maximum yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyEngineered genetic
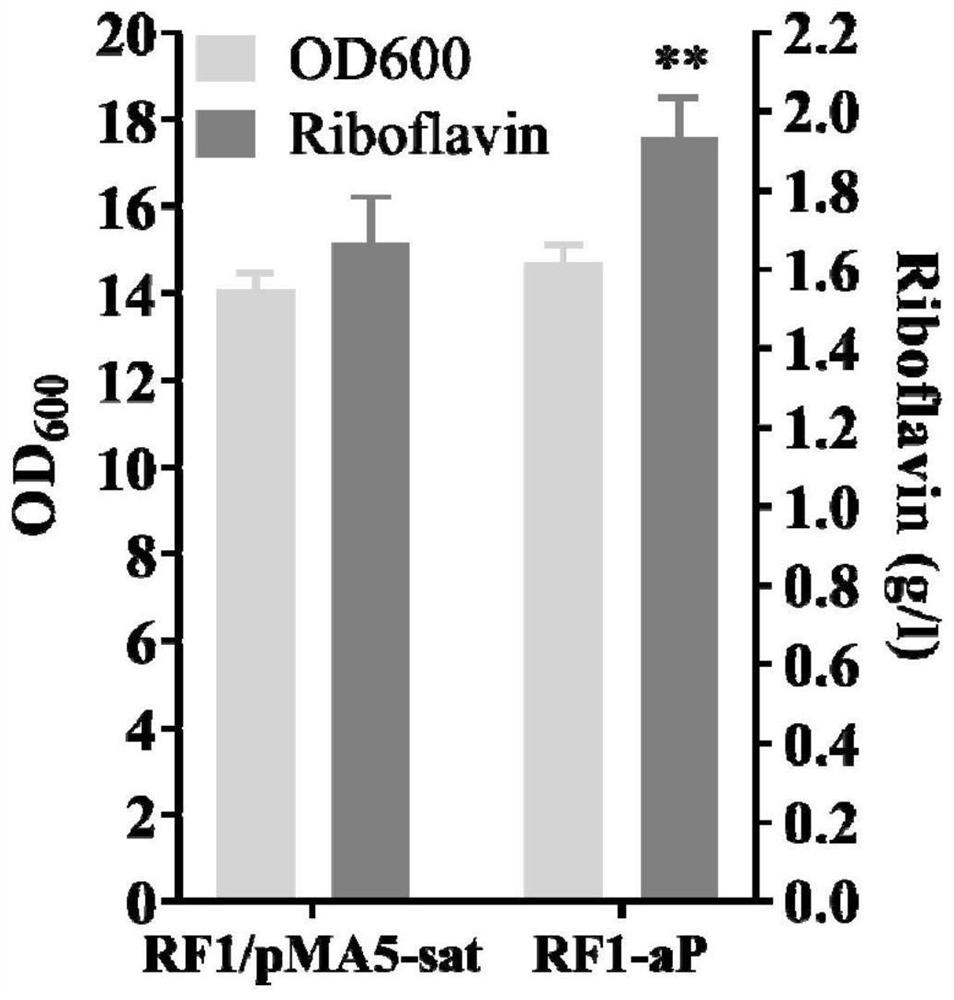
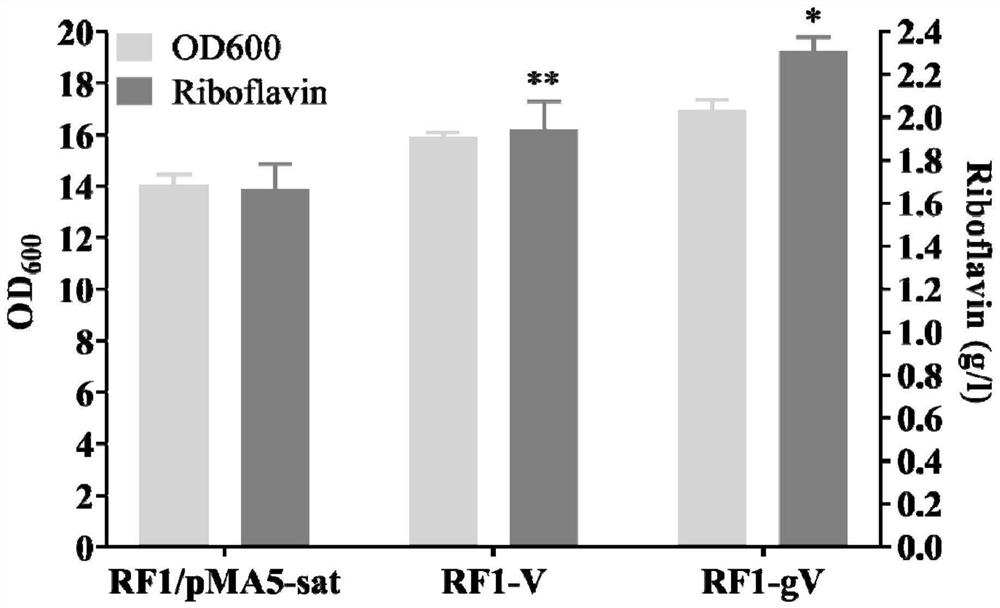
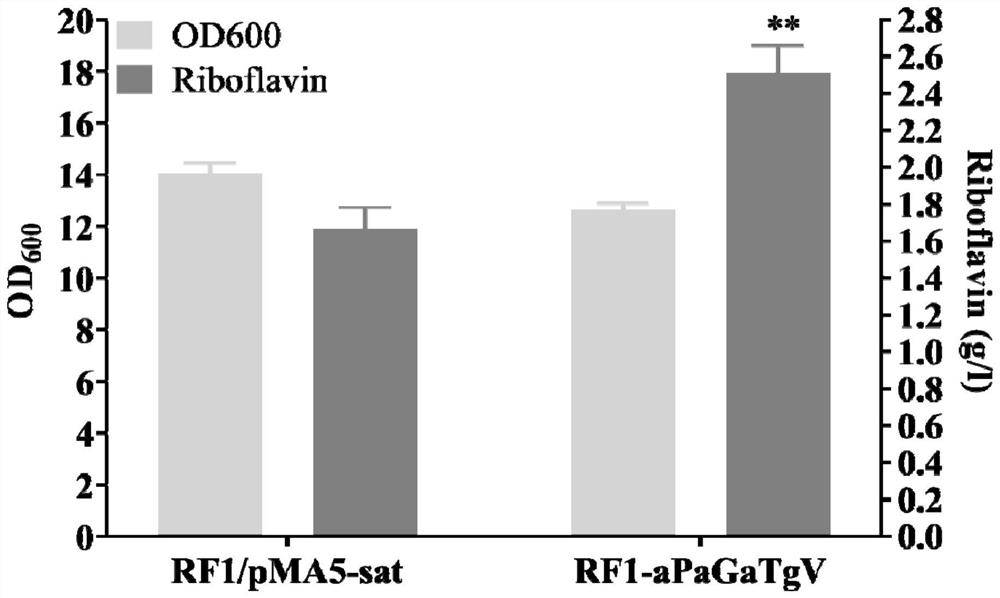
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently synthesizing riboflavin and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation. The genetically engineered bacterium has the advantages that genes for encoding purR are knocked down, genes for encoding glnR and tnrA are knocked down, hemoglobin from vitreoscilla is overexpressed, dissolved oxygen limitation in the fermentation process is relieved, the energy consumption in the fermentation process is reduced, and the riboflavin yield is increased; and the riboflavin yield of the constructed engineered strain RF1-aPaGaTgV is increased by 50.78% at a shake flask stage, and reaches 2.51 g / L. At the 5-L fermentation level, the highest yield of the riboflavin obtained by adopting the constructed RF1-aPaGaTgV is increased by 45.51% and reaches 10.71 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of microbial water purifying agent for black fish culture water and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104276665BSuitable for online processingEasy to settleBiological water/sewage treatmentSynechococcusThiothrix
The invention discloses a microbial water purifying agent for snakehead culture water and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding 20-40 parts by weight of surface-modified C8 and C18 alkyl-chain magnetic silicon balls into 200-400 parts by weight of water; adding 80-100 parts by weight of microbial reagent, including 60-80 parts of Synechococcus, 60-80 parts of Oscillatoria, 10-30 parts of Nitrosococcus, 10-30 parts of Nitrosolobus, 10-20 parts of iron bacteria, 10-20 parts of Leptothrix, 1-5 parts of Thiothrix, 1-5 parts of Vitreoscilla, 30-70 parts of paramecium, 30-70 parts of infusorian, 30-50 parts of Tetraselmis and 30-50 parts of blue algae; and adding 50-90 parts by weight of beef extract peptone agar culture medium, and culturing. The microbial water purifying agent can be added into a snakehead culture tank to achieve the goal of purifying culture tank water.
Owner:贺兰县晶诚水产养殖有限公司
A kind of construction method and application of recombinant bacteria producing chitosanase
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a recombinant bacterium producing chitosanase. The invention co-expresses the Bacillus subtilis chitosanase gene and the hyaline hemoglobin gene in Pichia pastoris, and the recombinant strain efficiently prepares the chitosanase through a high-density fermentation strategy. The enzyme activity of the chitosanase prepared by the method is as high as 50000 U / mL, and the protein content is as high as 16.0 mg / mL. The specific enzyme activity of the recombinant enzyme is 4065.7U / mg, the optimum pH is 6.0, and the optimum temperature is 55°C. The enzyme hydrolyzes high-concentration (≥10%) chitosan to prepare chitosan oligosaccharides, the chitosan oligosaccharide yield is greater than 75%, and the main products are disaccharides, trisaccharides and tetrasaccharides. The chitosanase preparation method of the present invention produces enzyme level far higher than the reports of existing documents and patents, and the produced enzyme has excellent hydrolysis characteristics, and has good performance in industrial production of chitosanase and preparation of chitosan oligosaccharides. application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
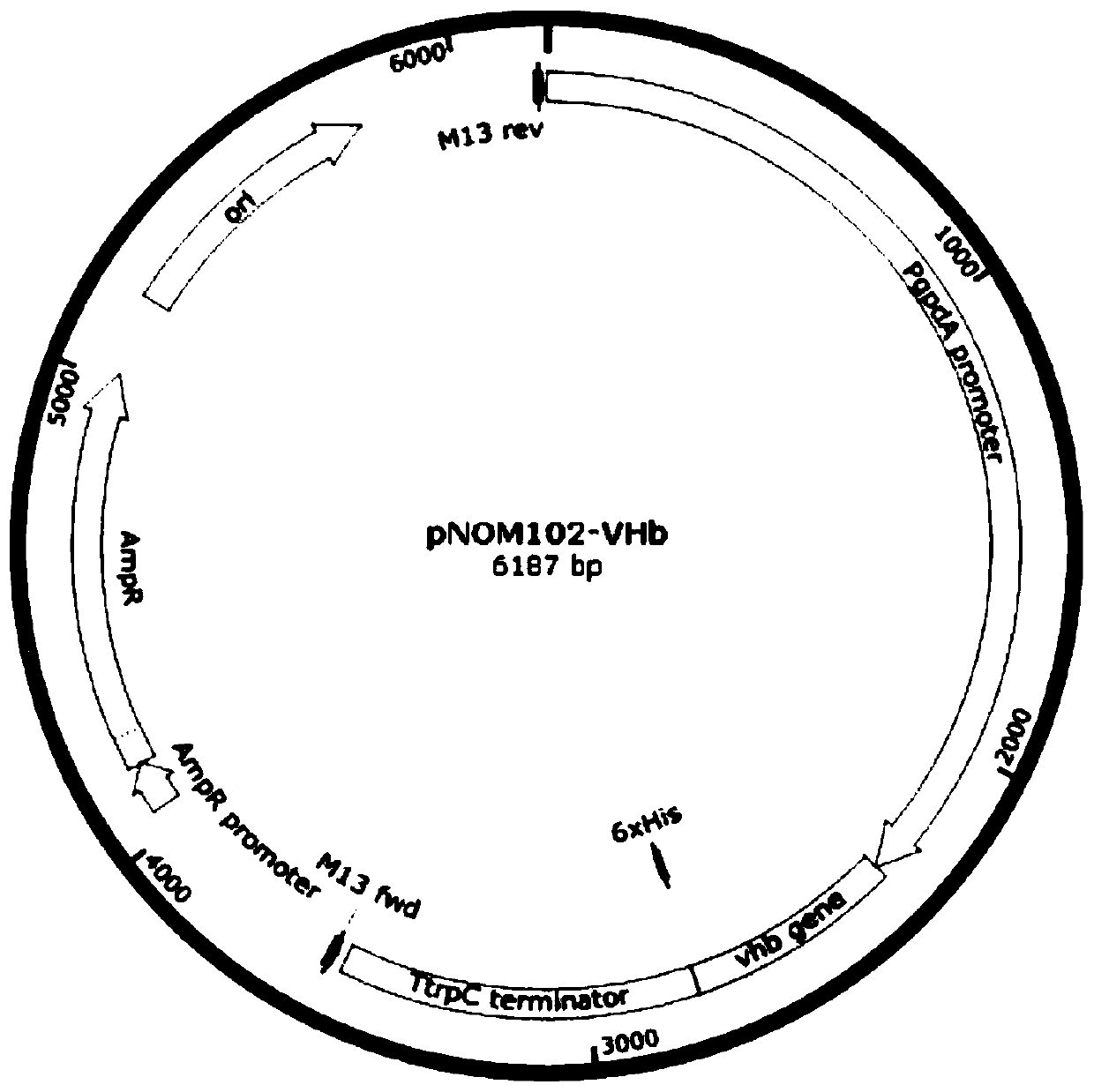
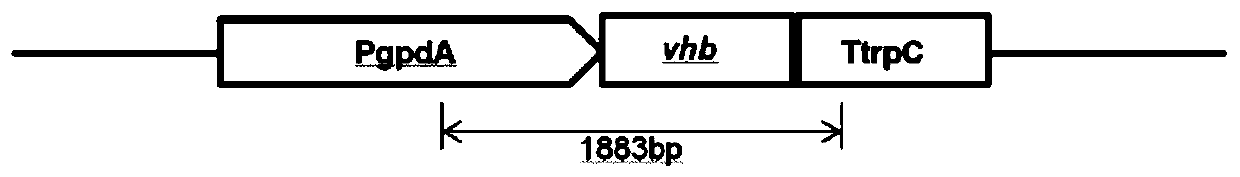
Recombinant paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 and application thereof
InactiveCN103484386AIncrease gene copy numberGood colonization effectBiocideFungiPaecilomyces lilacinusNematode
The invention relates to a paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 for expressing the hemoglobin VHb of vitreoscilla and the application of the paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8. The recombinant paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 is collected in the China center for type culture collection with the collection number of CCTCC No:M 2013296. The paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 is obtained by optimizing a codon, a promoter and a gene structure, successfully integrating the hemoglobin VHb from the vitreoscilla into a chromosome of a wild paecilomyces lilacinus strain ACSS which has a plant parasitic nematode killing effect and is provided by the agricultural culture collection of China, and performing screening. Compared with the wild paecilomyces lilacinus strain ACSS, the paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 has the advantages that more extracellular proteases, chitinase, alpha-amylases and the like can be generated, and meanwhile, the biomass and the cell yield are improved; after the paecilomyces lilacinus strain PNVT8 is applied as a product, the growth rate during field planting under a soil micro-aerobic condition also is increased to further improve the nematode larva killing activity.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A kind of recombinant bacteria and its application in producing cellulase
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria and applications of the recombinant bacteria in production of cellulase. According to the present invention, the recombinant bacteria are obtained by introducing a specific DNA molecule into Trichodermareesei, wherein the specific DNA molecule has a gpdA promoter and the encoding gene of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin, and the expression of the encoding gene of the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin is initiated by the gpdA promoter; the cellulase yield of the recombinant bacteria is high, and compared to the starting strain, the filter paper enzyme activity is increased by 54.87%, and the extracellular total protein yield is significantly improved; and the great value is provided for the production of cellulase, and the important significance is provided for therelieving of energy crisis and environmental pollution.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium and use thereof in synthesis of miglitol intermediate
InactiveCN112592879AIncreased dehydrogenase activityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcyl CoA dehydrogenaseResting Cell
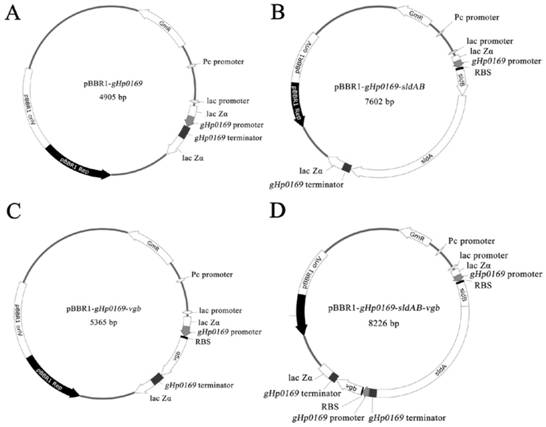
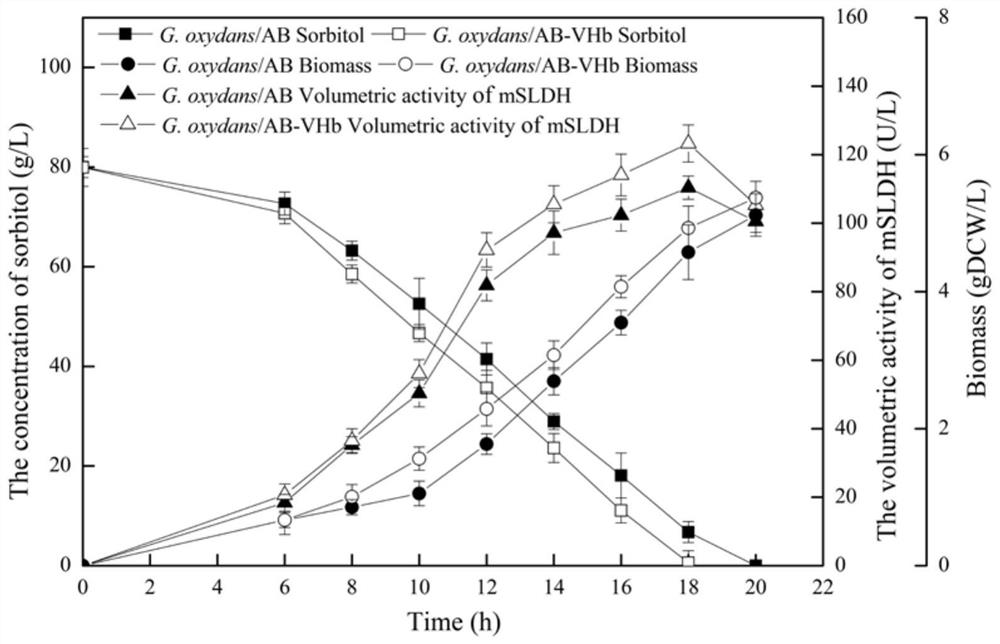
The invention discloses a recombinant gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium and use thereof in a synthesis of a miglitol intermediate. The recombinant gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacteriumis constructed by jointly transferring a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vhb and a sorbitol dehydrogenase gene sldAB into a host bacterium. The host bacterium is gluconobacter oxydans. A growth rate ofthe recombinant gluconobacter oxydans and a final activity of a sorbitol dehydrogenase are both improved. Resting cells are used to produce 6-deoxy-6-amino (N-ethoxyl)-alpha-L-furan sorbose. The recombinant gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium shows a higher catalytic capacity, can catalytically synthesize 96.1 g / L of 6NSL in a single batch within 24 h, and improves yield of the 6NSL by 9.5% under the same condition compared with G.oxydans / pBBR-sldAB constructed by a patent CN110016455A.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant Paecilomyces lilacinus strain pnvt8 and its application
InactiveCN103484386BIncrease gene copy numberGood colonization effectBiocideFungiPaecilomyces lilacinusNematode
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of vitreoscilla hemoglobin in improving expression quantity of cephalosporin C acylase
The invention relates to an application of vitreoscilla hemoglobin in improving expression quantity of cephalosporin C acylase, and discloses a method for improving cephalosporin C acylase expressionquantity, which comprises the step of co-expression of a cephalosporin C acylase gene and a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene in escherichia coli.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Vitella hyaline hemoglobin expression cassette suitable for bacillus and application
ActiveCN111549050BImprove expression efficiencyExtensive industrial productionHaemoglobins/myoglobinsMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisAmylase
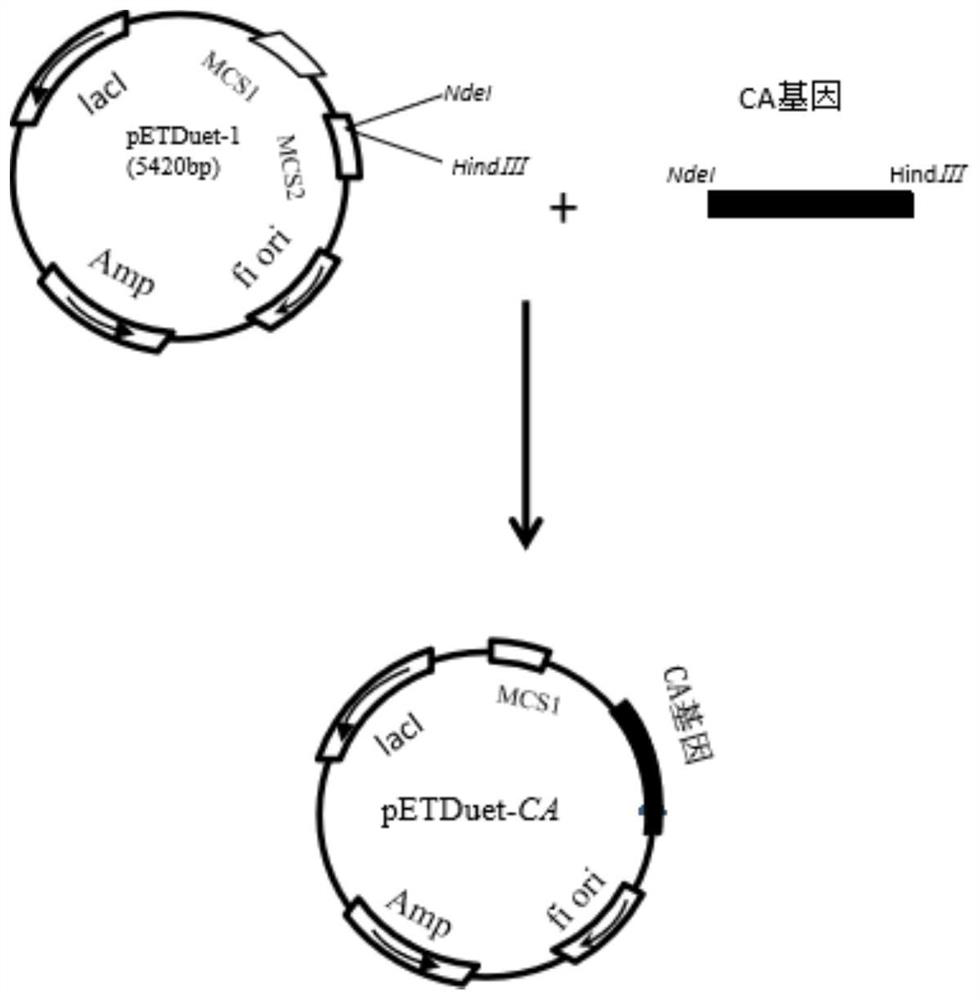
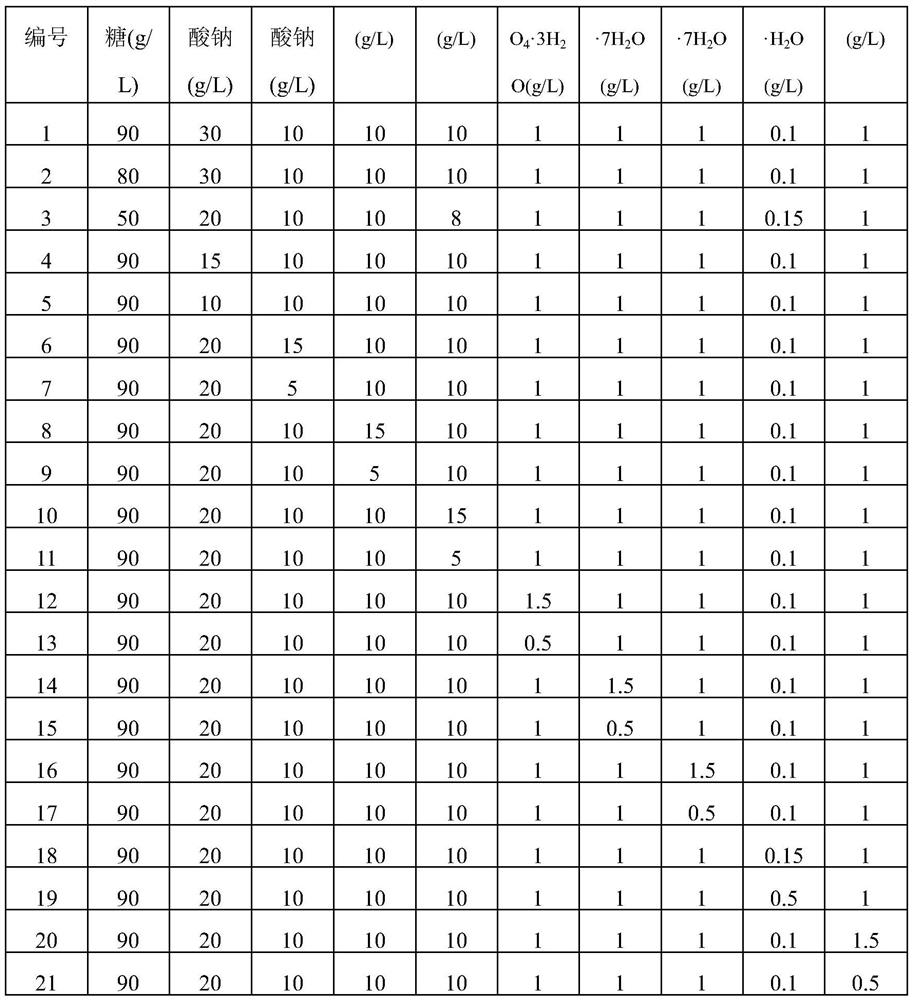
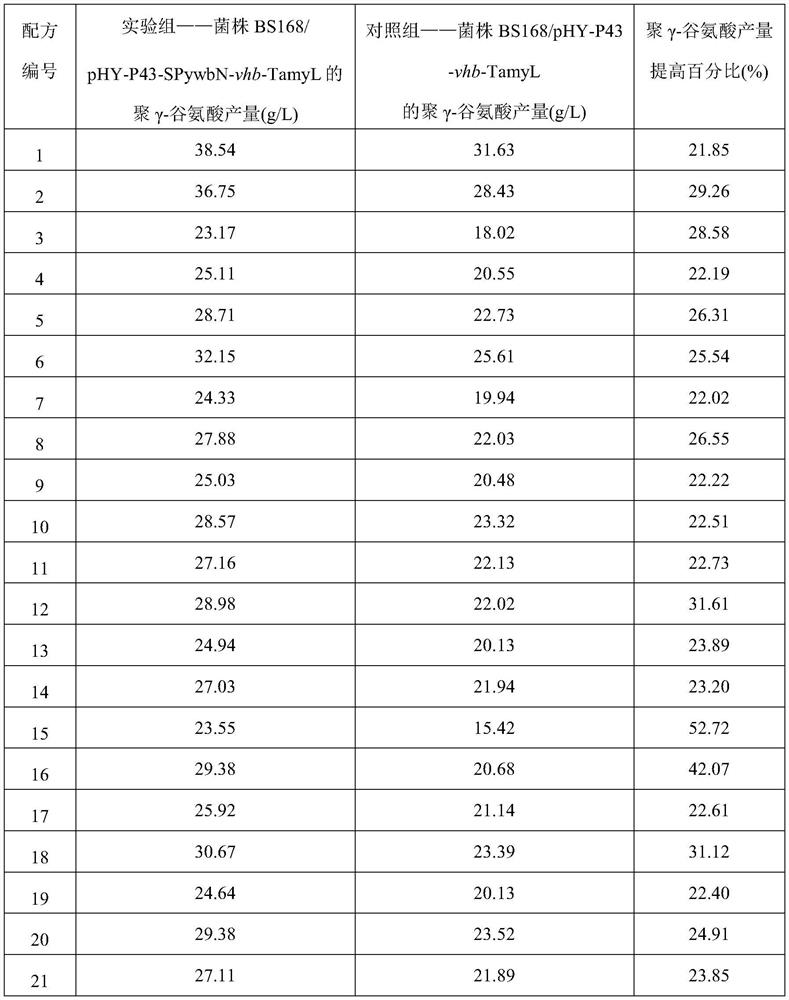
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and fermentation engineering, and provides an expression cassette suitable for Bacillus hyaline hemoglobin and its application. The invention combines the signal peptide SPywbN of YwbN in Bacillus subtilis and the promoter of Bacillus subtilis P43 is connected with the amylase terminator TamyL in Bacillus licheniformis to form a VHb protein expression cassette P43‑SPywbN‑ vhb‑ Tamy L. The expression cassette was applied to three kinds of Bacillus (Bacillus subtilis 168, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LX‑12, Bacillus licheniformis DW2), compared with the conventional single enhanced expression VHb strains, the poly-γ-glutamic acid , Iturin A, and bacitracin yields increased by 21.85%, 18.77% and 23.40%, and the invention provides theoretical guidance for the high-efficiency expression and wide application of Vitiligo hyaline hemoglobin VHb in Bacillus.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
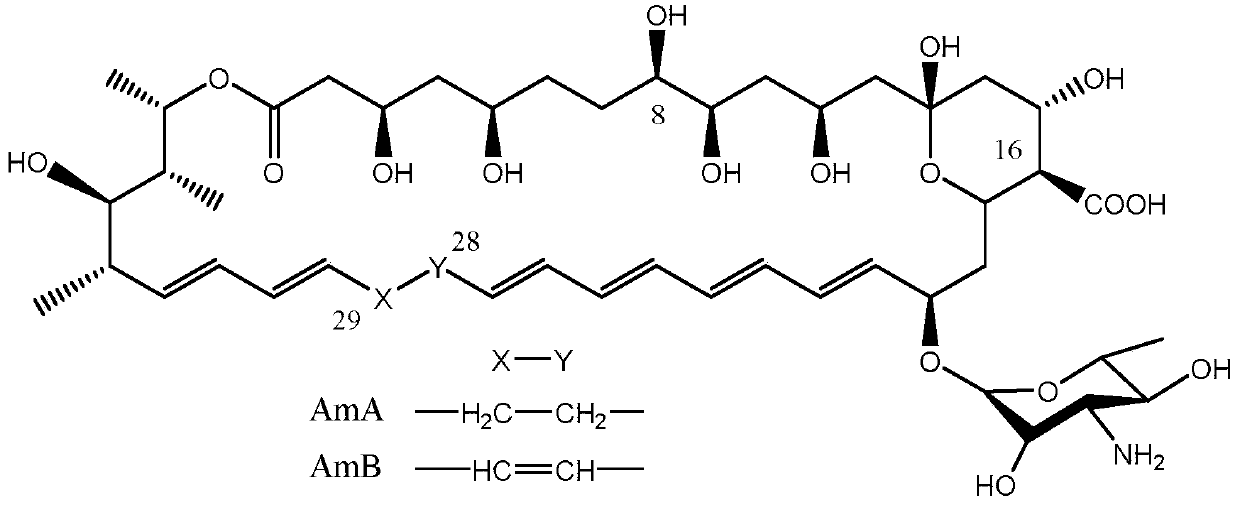
A kind of recombinant Streptomyces tuberculosis producing amphotericin B and its application
ActiveCN108441459BQuality improvementIncrease production capacityBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsS-Adenosyl-l-methionineStreptomyces nodosus
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
An anti-oxidant moisturizing essence rich in fermented products of Vitella hyaline, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110151675BSimple production processIncrease productivityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyAntioxidant
The invention discloses an anti-oxidation moisturizing essence rich in fermented products of Vitella hyalineus and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cosmetics. The moisturizing essence is composed as follows in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of pure water, 60-80 parts of transparent vitriol Bacteria fermentation product 3‑6 parts, tremella polysaccharide 5‑8 parts, pantothenic acid 0.05‑0.2 parts, tea extract 0.5‑2 parts, purslane extract 1‑3 parts, ascorbic acid 1.5‑3 parts, seaweed extract 2‑ 5 parts, 0.01-0.06 parts of carbomer, 1.5-3.5 parts of squalane, 2-5 parts of propylene glycol, 0.35-0.5 parts of phenoxyethanol, 0.05-0.15 parts of essence. The present invention is not only oriented to improve the polysaccharide product, but also significantly improves the antioxidant activity of the fermented product of Vitella hyaline through the selection of different carbon sources, nitrogen sources, salt solutions and enzymes in the culture medium, and aims to significantly improve the concentration of the essence through the fermentation method. Antioxidant, at the same time, the addition of tremella polysaccharide, tea extract, purslane extract and other compounds significantly improves the effect of moisturizing essence to delay skin aging and make the skin smooth and shiny.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant rhamnolipid-producing strain and application thereof
PendingCN113355266AHigh oxygen utilizationIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPseudomonas
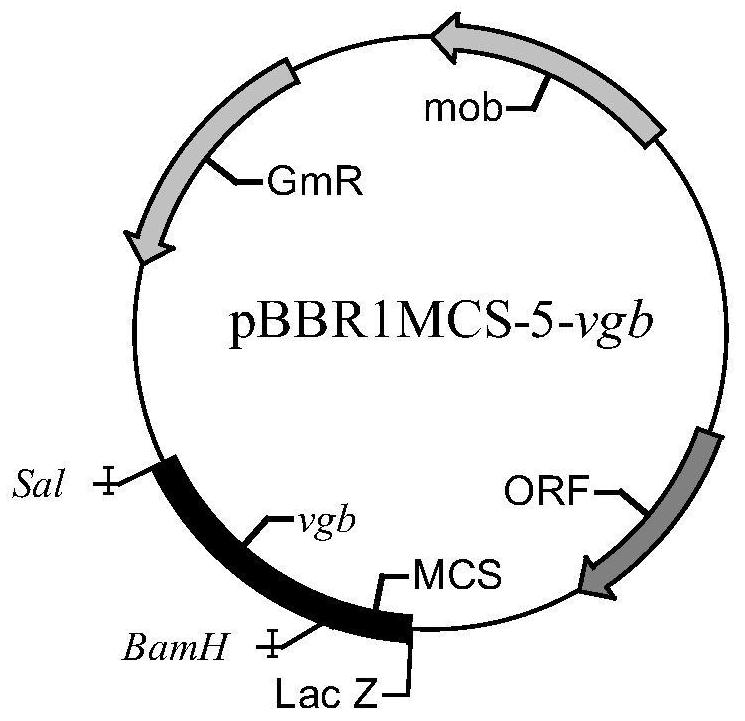
The invention relates to the technical field of applied microbiology and genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a recombinant rhamnolipid-producing strain and application thereof in fermentation production of rhamnolipids. According to the method in the invention, a hemoglobin gene vgb from Vitreoscilla stercoralis is connected to an expression vector to construct a recombinant vector PBBR1MCS-5-vgb, the recombinant expression vector is transformed into pseudomonas aeruginosa, the expression of hemoglobin promotes the growth of thalli and the synthesis of rhamnolipids, the ventilatory capacity and fermentation temperature required by fermentation are reduced, and a new technical scheme is provided for effectively reducing the fermentation production cost of rhamnolipids.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant gene which enhances the ability of fish to tolerate low dissolved oxygen stress and the use thereof
InactiveUS8546644B2Improve hypoxia toleranceHigh dissociation rate constantVectorsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsResearch ObjectBlunt snout bream
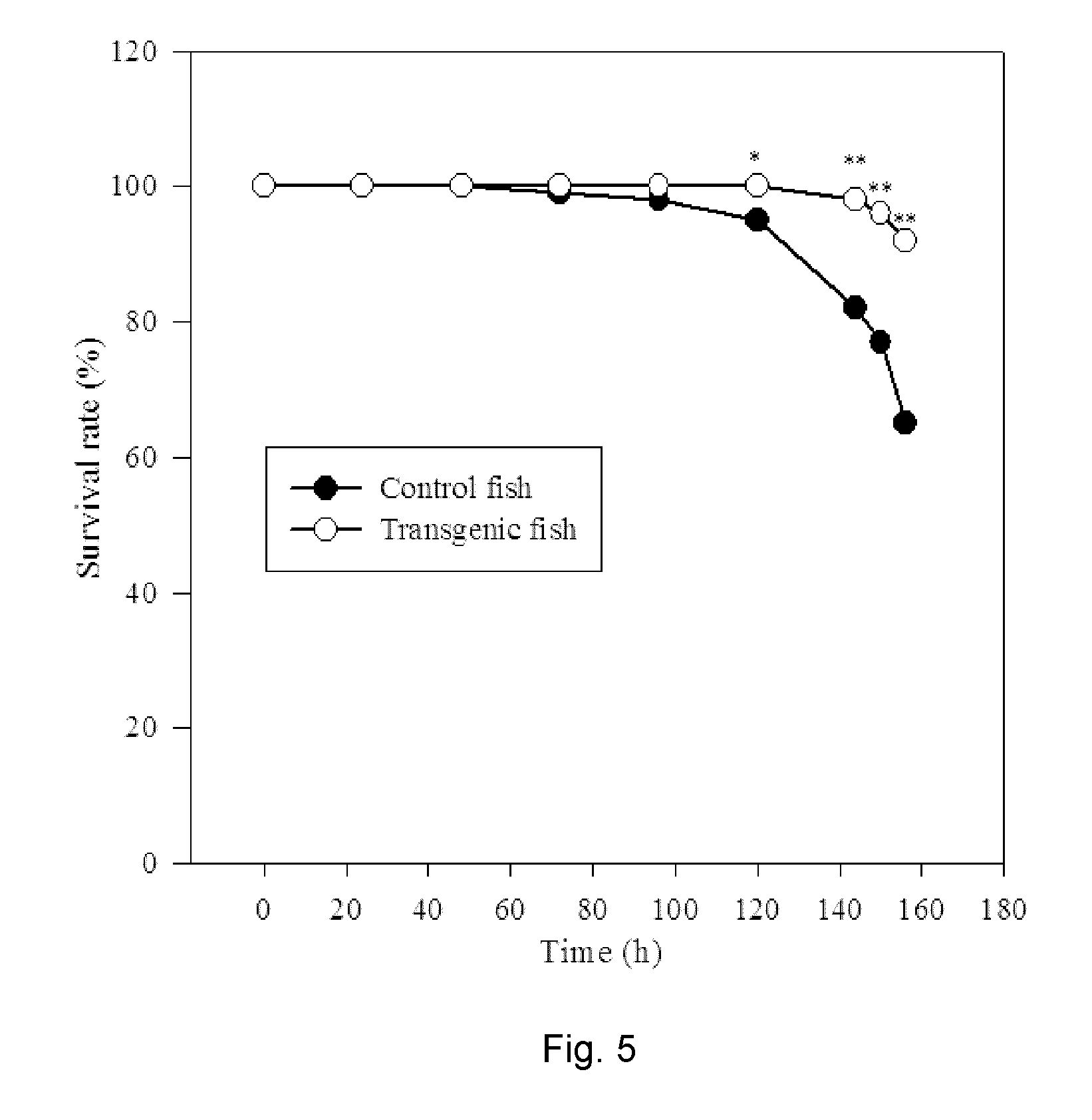
The invention discloses a recombinant gene which enhances the ability of fish to tolerate low dissolved oxygen (DO) stress and the use thereof. Carp β-actin gene promoter is used as a promoter and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene is used as a target gene, so as to construct the recombinant Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene driven by carp β-actin promoter. The modeling organism zebrafish is used as the research object, and the recombinant gene is microinjected into zygotes of zebrafish. After PCR screening and 156 h low DO stress test, transgenic fish are obtained with a survival rate of 92%, which is significantly different from the survival rate of 65% of the control fish group. The vhb transgenic zebrafish obtain hypoxia tolerance. When the recombinant gene is applied to the economically farmed species, i.e., blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), it enhances their hypoxia tolerance as well. Such genetically improved breeding technique may be widely used for breeding new excellent farmed species with the hypoxia tolerance.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin expression cassette suitable for streptomyces fradiae and application thereof
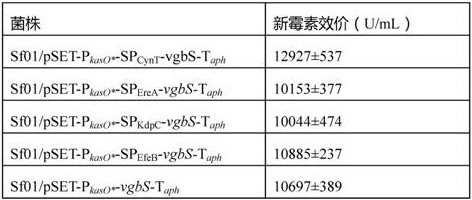
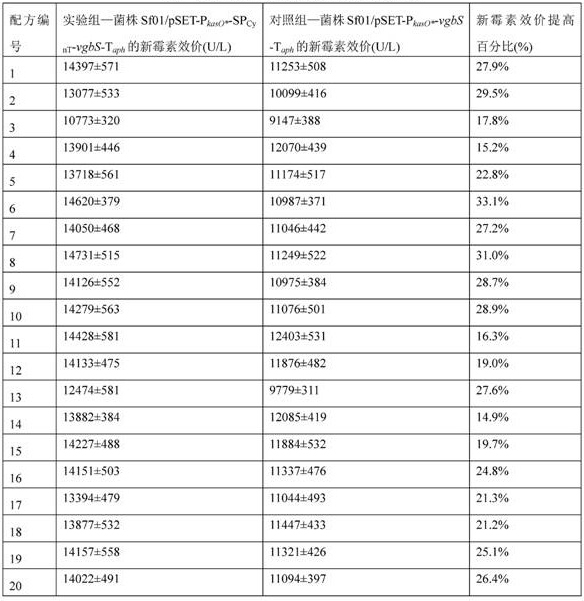
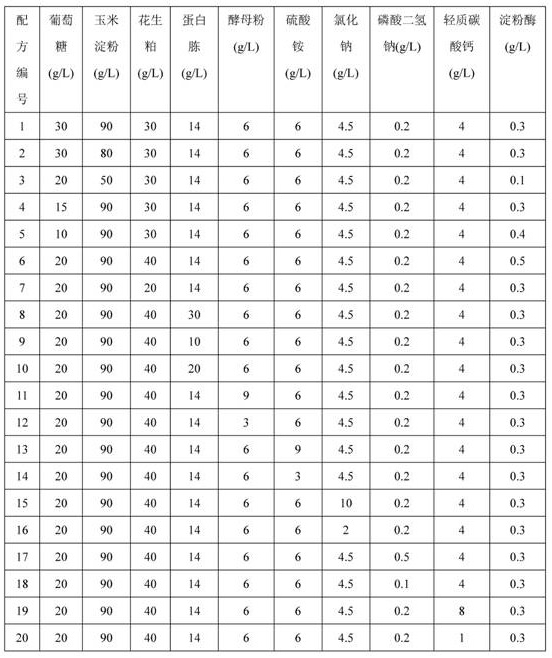
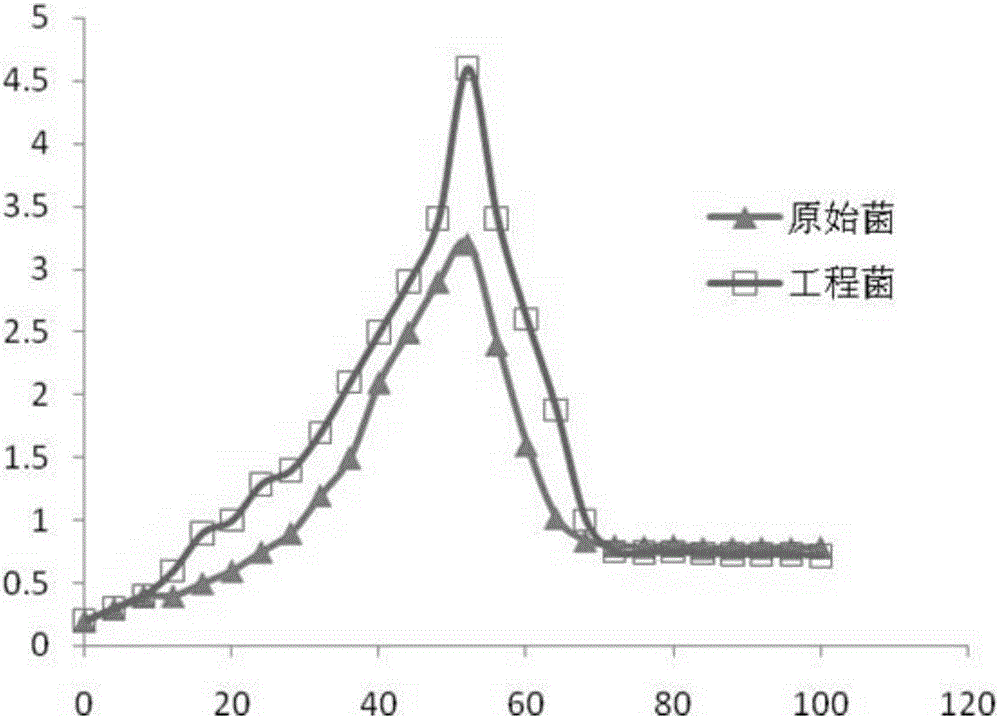
kasO*The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and fermentation engineering, and provides a vitreoscilla hemoglobin expression cassette suitable for streptomyces fradiae and application thereof.The vitreoscilla hemoglobin expression cassette is obtained by connecting a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgbS with a signal peptide SPCynT of carbonic anhydrase CynT in streptomyces fradiae, a streptomyces constitutive strong promoter PkasO * and a streptomyces fradiae terminator Taph; a VHb protein expression cassette PkasO *-SPCynT-vgbS-Taph is formed, and the nucleotide sequence of the expression cassette is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The VHb protein expression cassette PkasO *-SPCynT-vgbS-Taph disclosed by the invention has more efficient VHb expression capacity, and when the VHb protein expression cassette PkasO *-SPCynT-vgbS-Taph is applied to streptomyces fradiae, the VHb expression effect is better, the fermentation product yield of the streptomyces fradiae is higher, and the yield of neomycin is at least increased by 14.9%.
Owner:LIFECOME BIOCHEM
Gene recombined Paenibacillus russica and its construction method and application
ActiveCN102776147BIncrease profitImprove liquidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic YGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a gene-engineered bacterium of gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and a construction method and application of the gene-engineered bacterium. Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus BC39 with vitreoscilla hemoglobin regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter is constructed by constructing a gene-recombination integrative vector with a peoriae paenibacillus LXH-B-1 strain as host bacteria. The gene-engineered bacterium of the gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus is capable of intracellularly expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, so that the utilization rate of oxygen by the peoriae paenibacillus, the cell biomass liveweight and the yield of catalysate polypeptide antibiotics can be improved; and the yield of the catalysate polypeptide antibiotics of the engineering strain is increased by 45% compared with that of the original strain; and therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the problem of insufficient oxygen supply in the cell culture and catalysis process of the peoriae paenibacillus.
Owner:杨凌静玥生物科技有限公司
Recombinant corynebacterium crematum by expression of vitreoscilla haemoglobin gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101397548BImprove acid production performanceIncrease bacterial concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCorynebacterium crenatumGenetic engineering
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Bacterial strain of bacillus licheniformis with vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene as well as construction method and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103146629BImprove oxygen uptakeIncrease oxygen supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
Owner:LIFECOME BIOCHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com