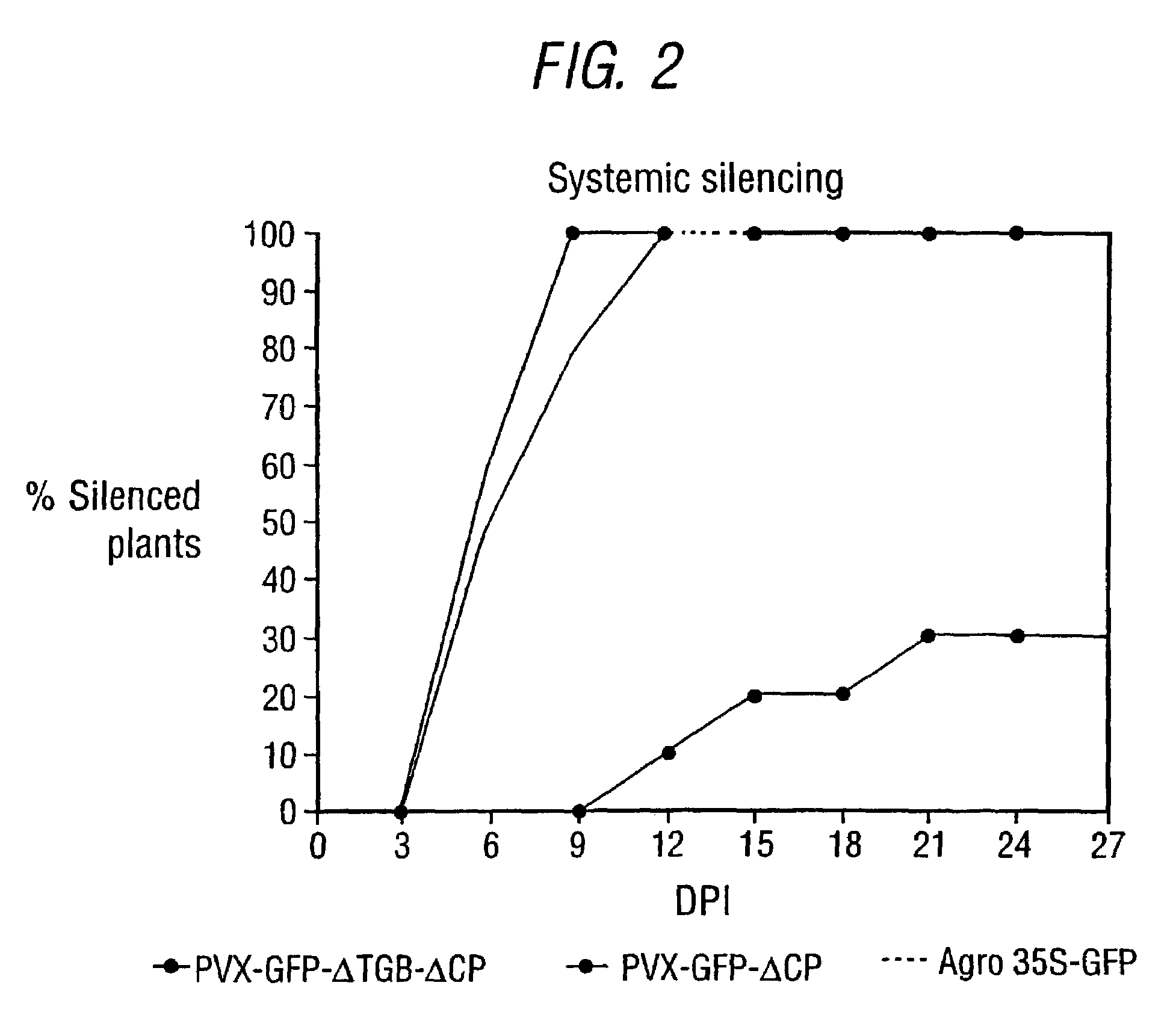
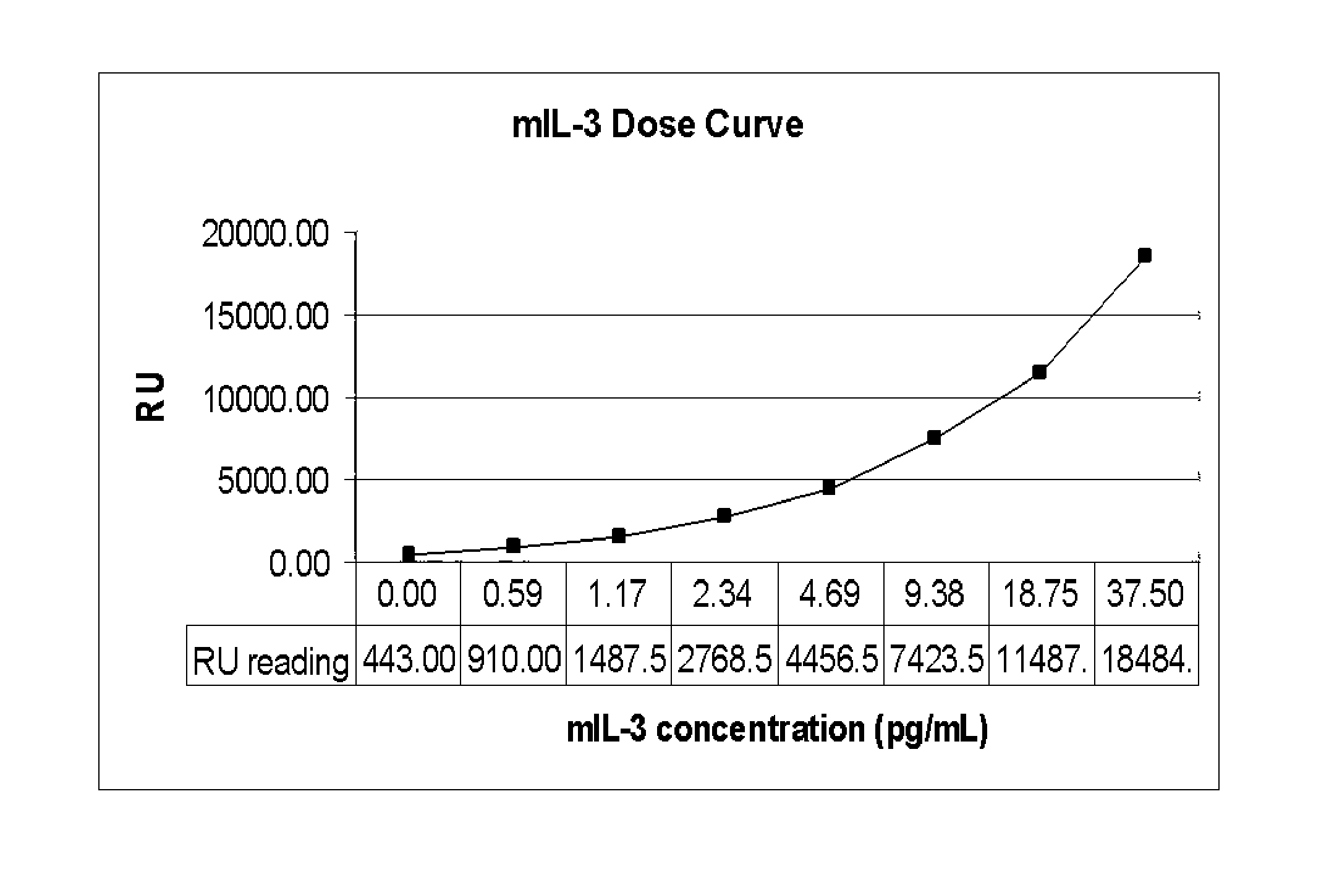
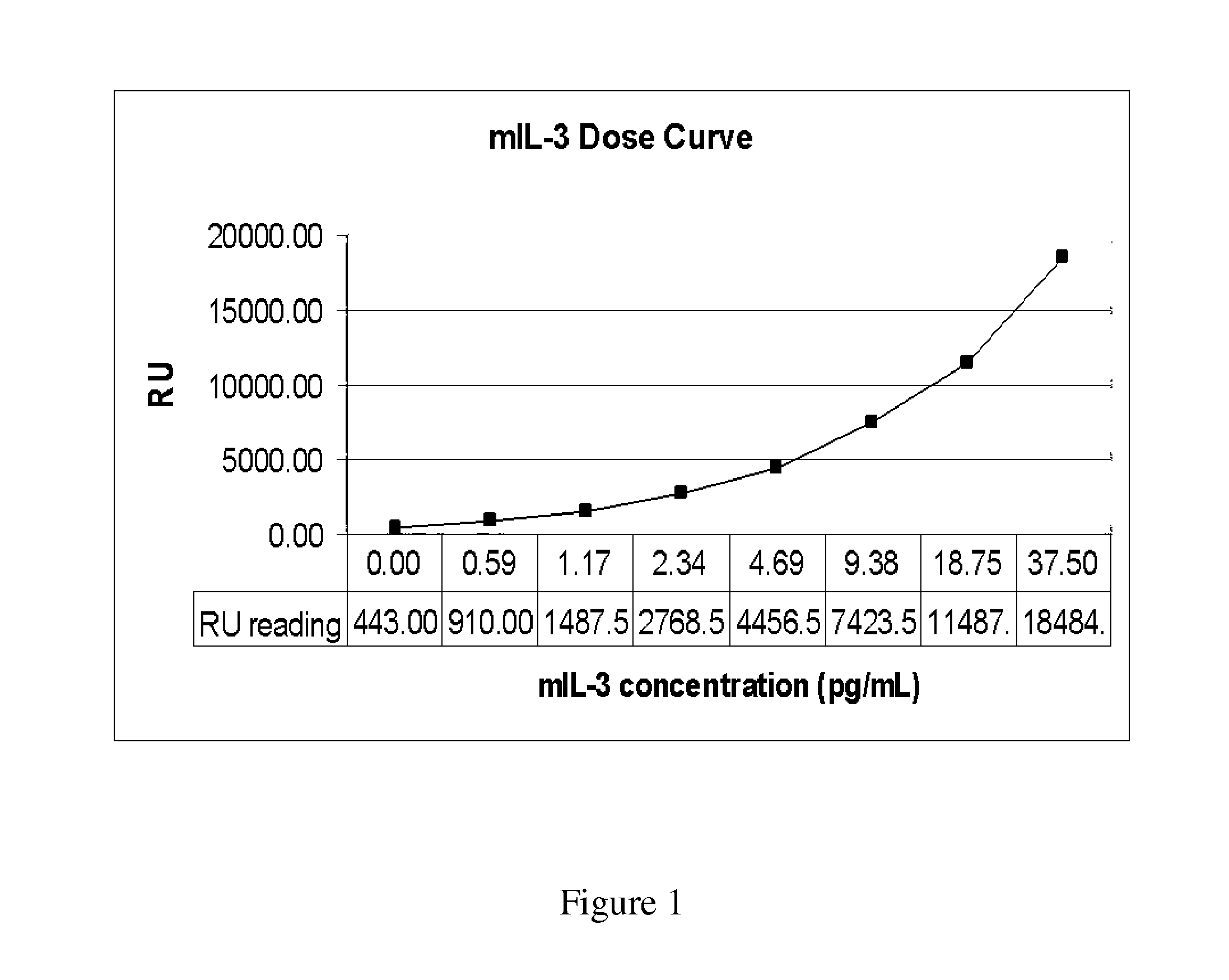
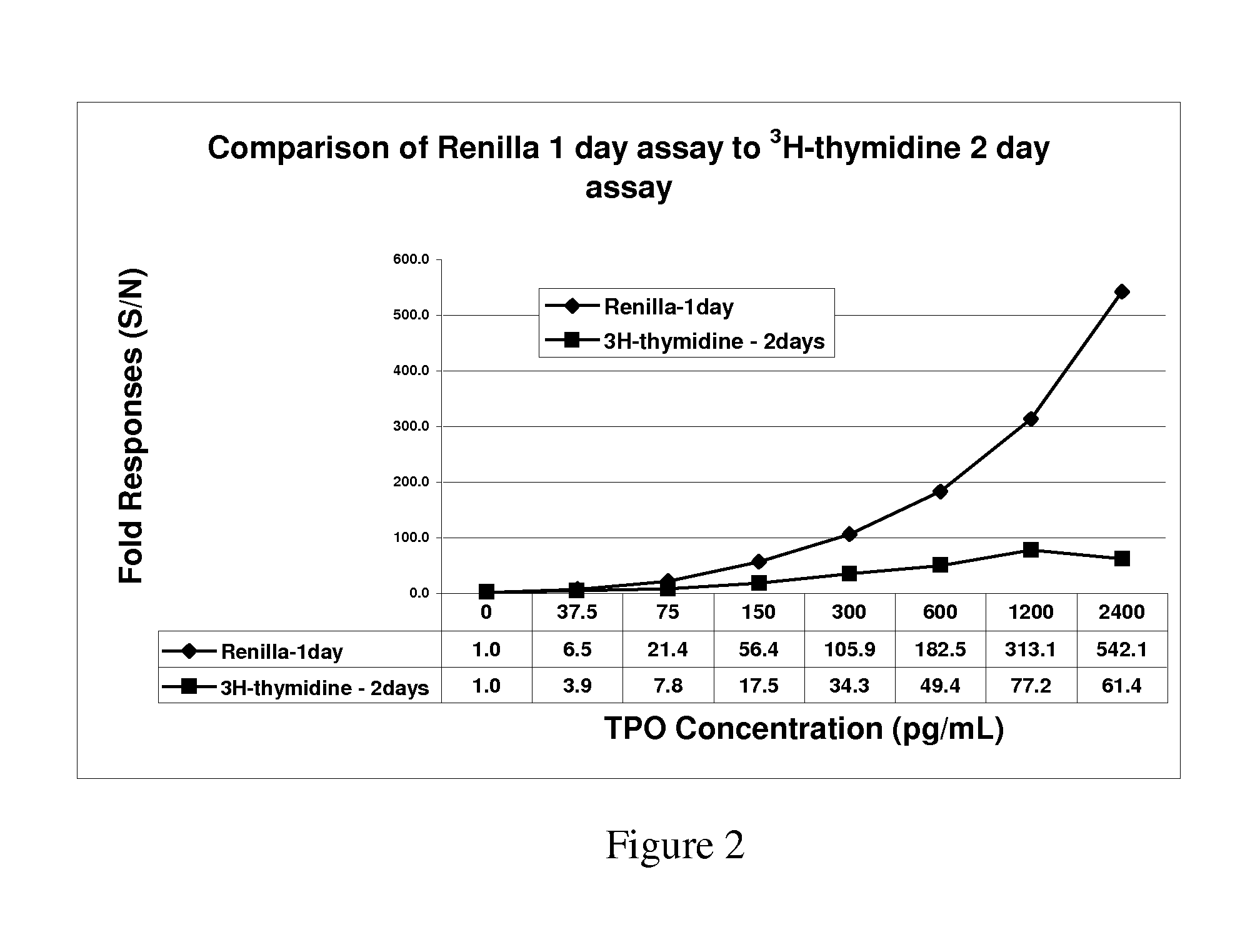
Patents
Literature
299 results about "Synexpression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
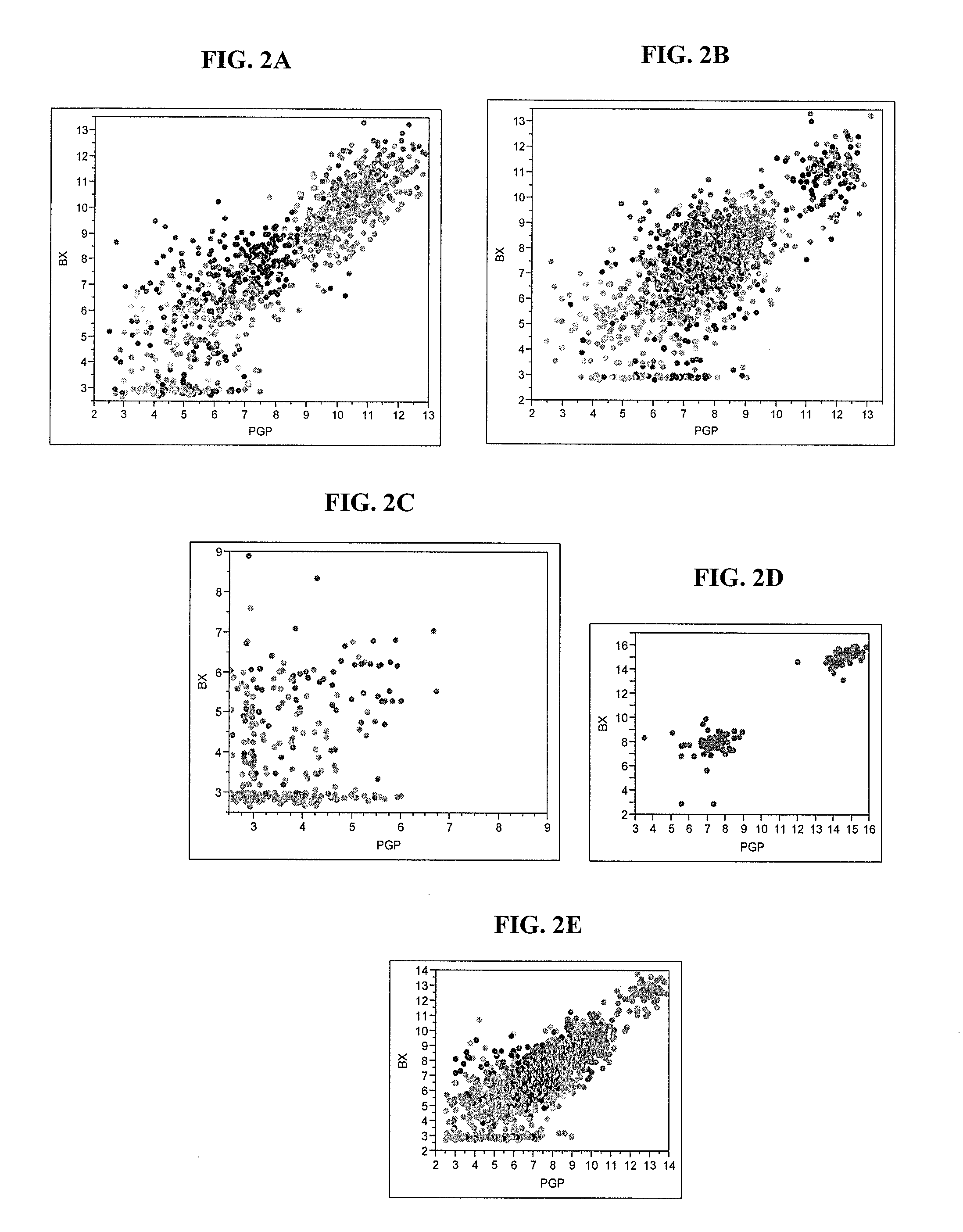
Synexpression is a type of non-random eukaryotic gene organization. Genes in a synexpression group may not be physically linked, but they are involved in the same process and they are coordinately expressed. It is expected that genes that function in the same process be regulated coordinately. Synexpression groups in particular represent genes that are simultaneously up- or down-regulated, often because their gene products are required in stoichiometric amounts or are protein-complex subunits. It is likely that these gene groups share common cis- and trans-acting control elements to achieve coordinate expression.
Methods for producing soluble, biologically-active disulfide-bond containing eukaryotic proteins in bacterial cells
InactiveUS6027888AEfficient productionFold preciselyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsDisulfide bondingZymogen
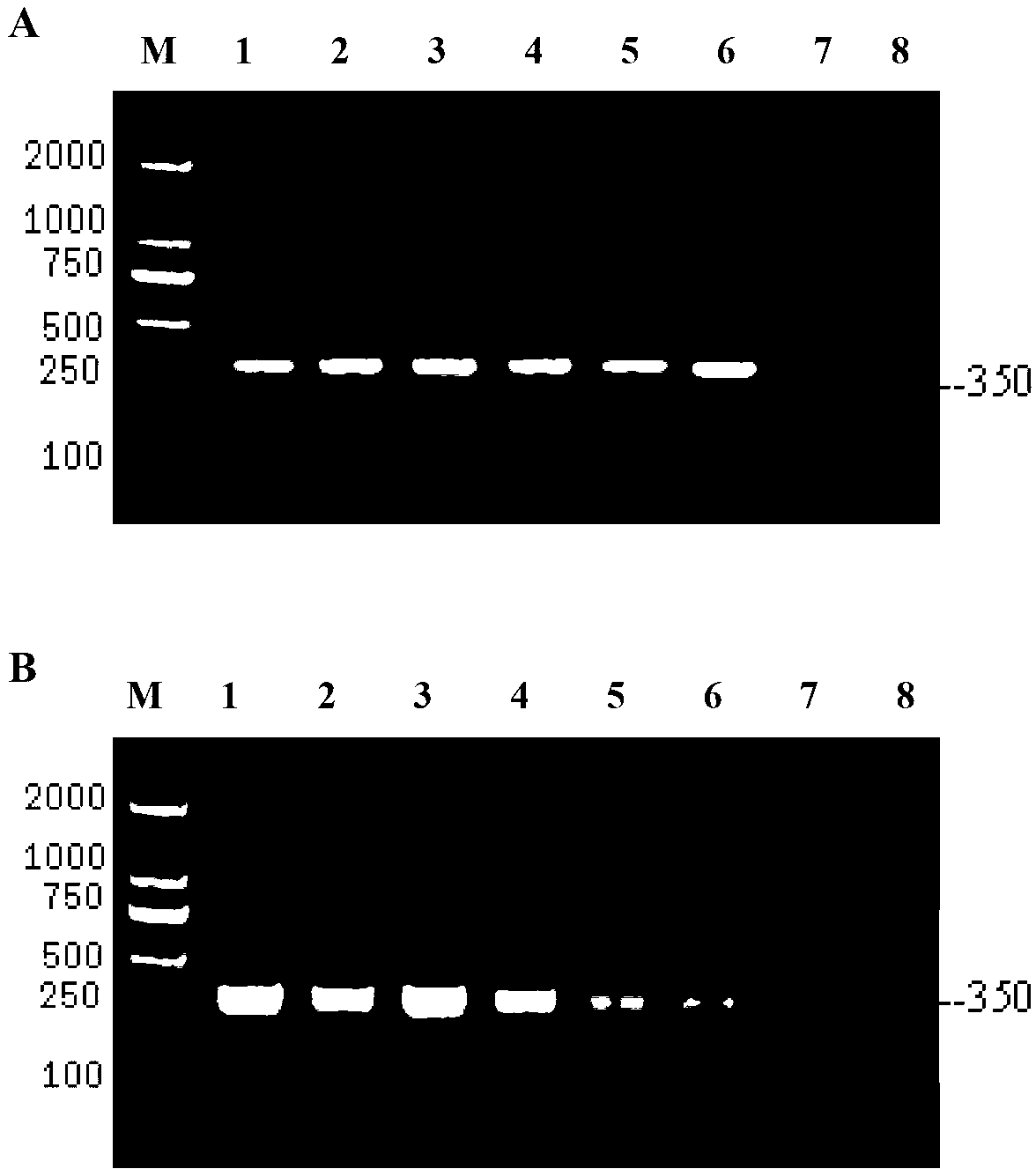
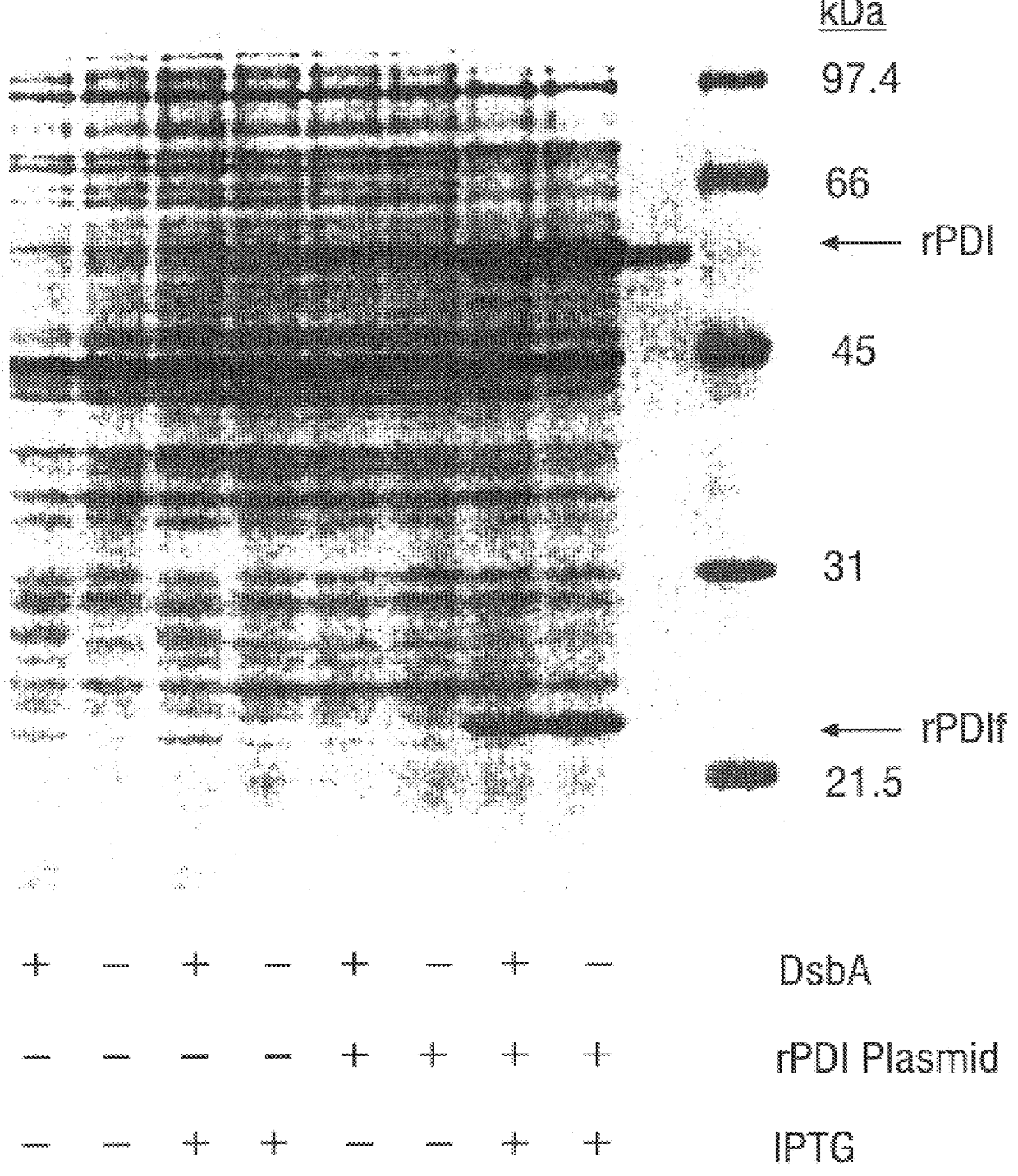
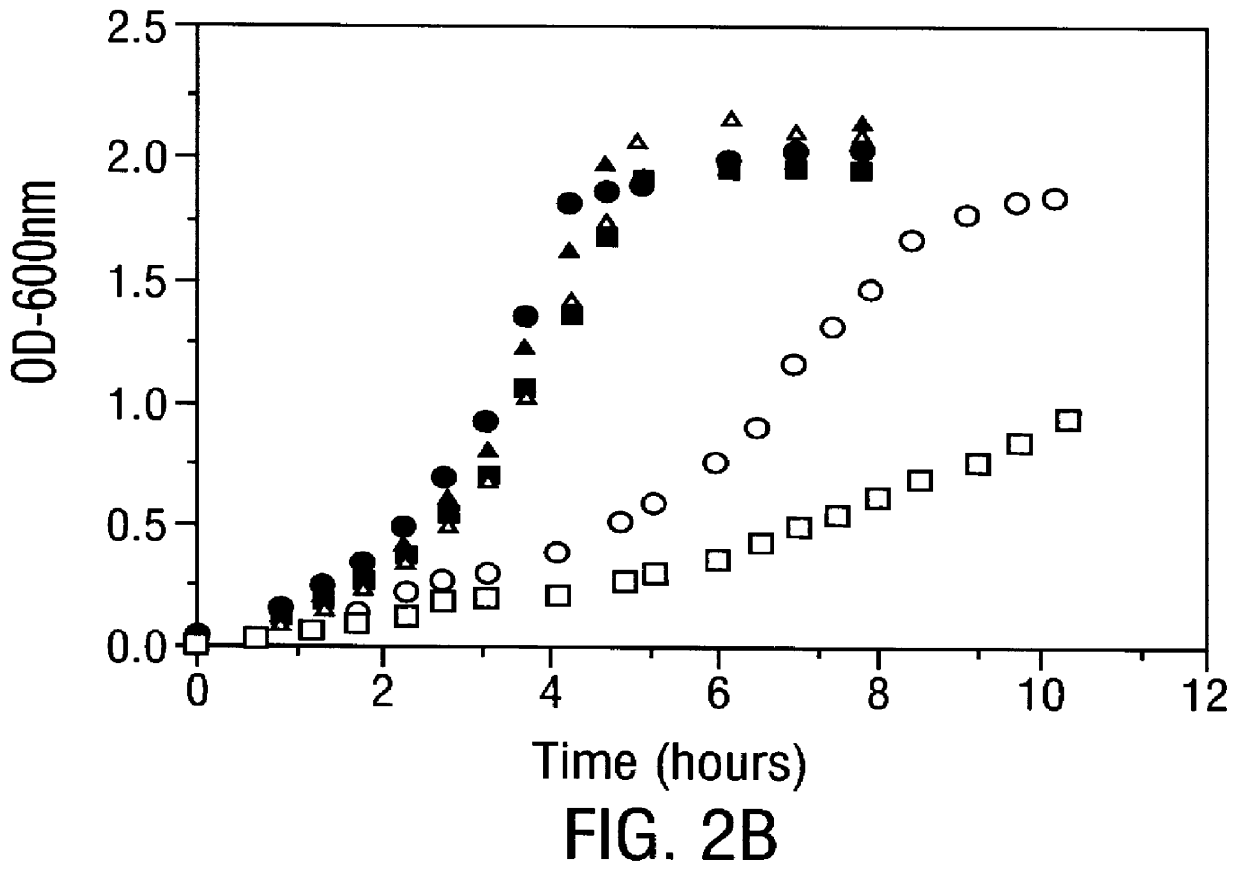
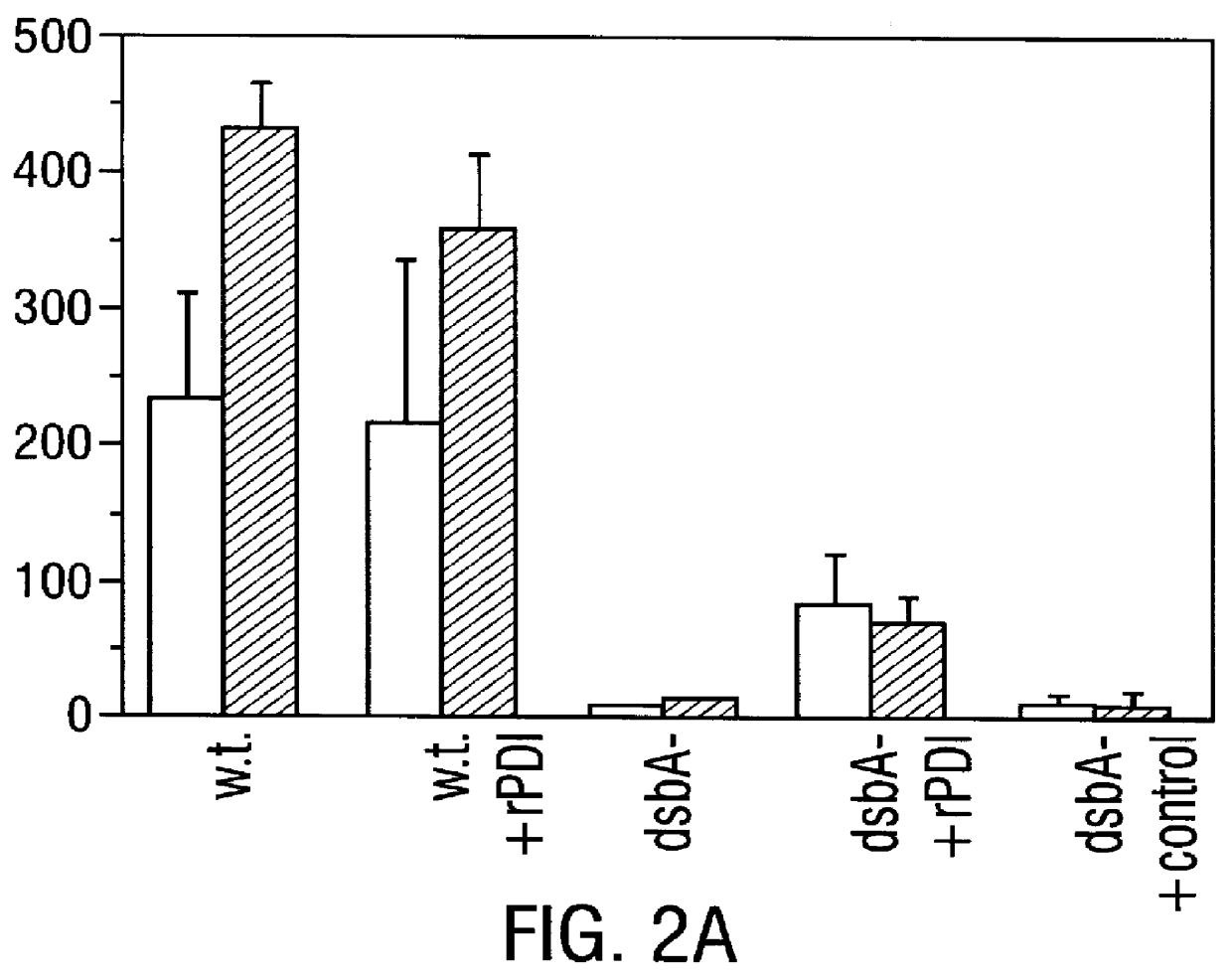
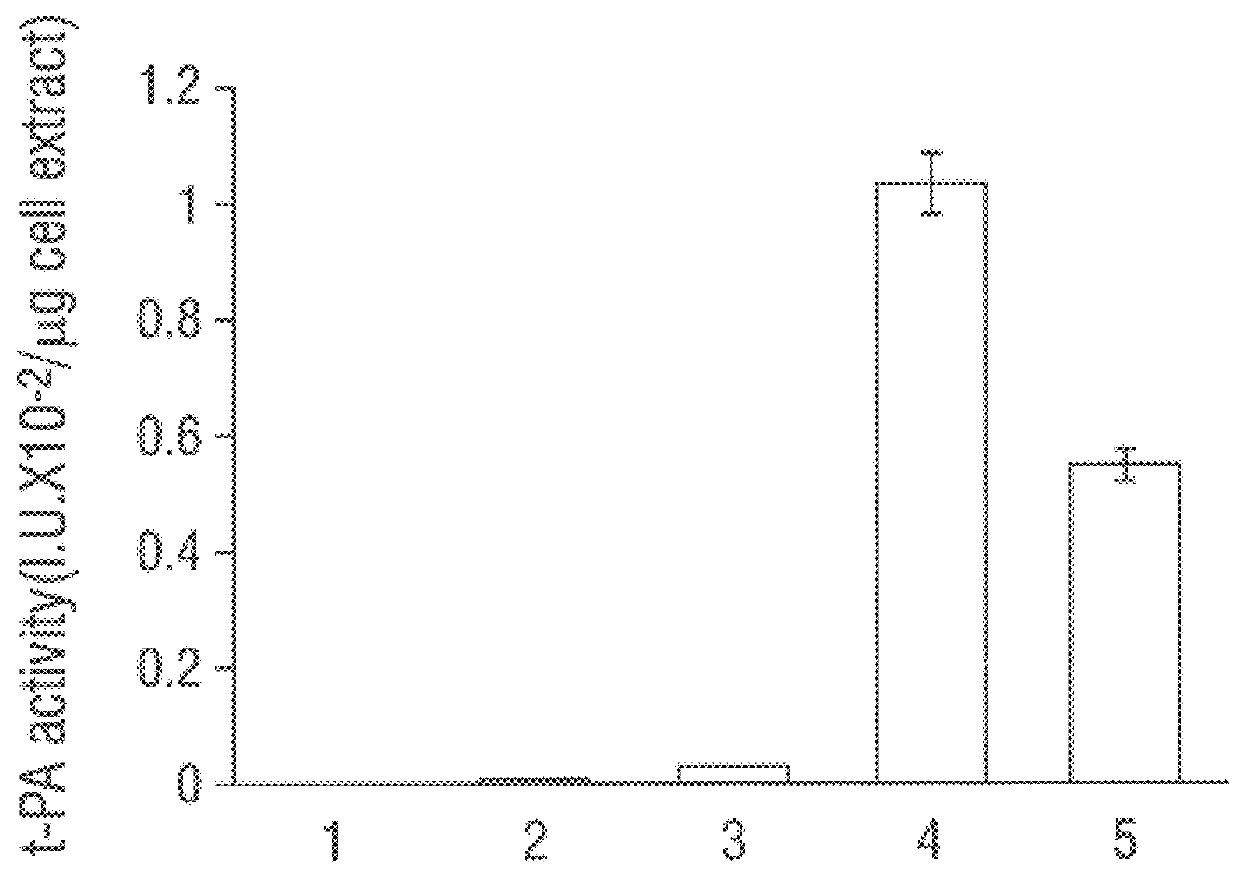
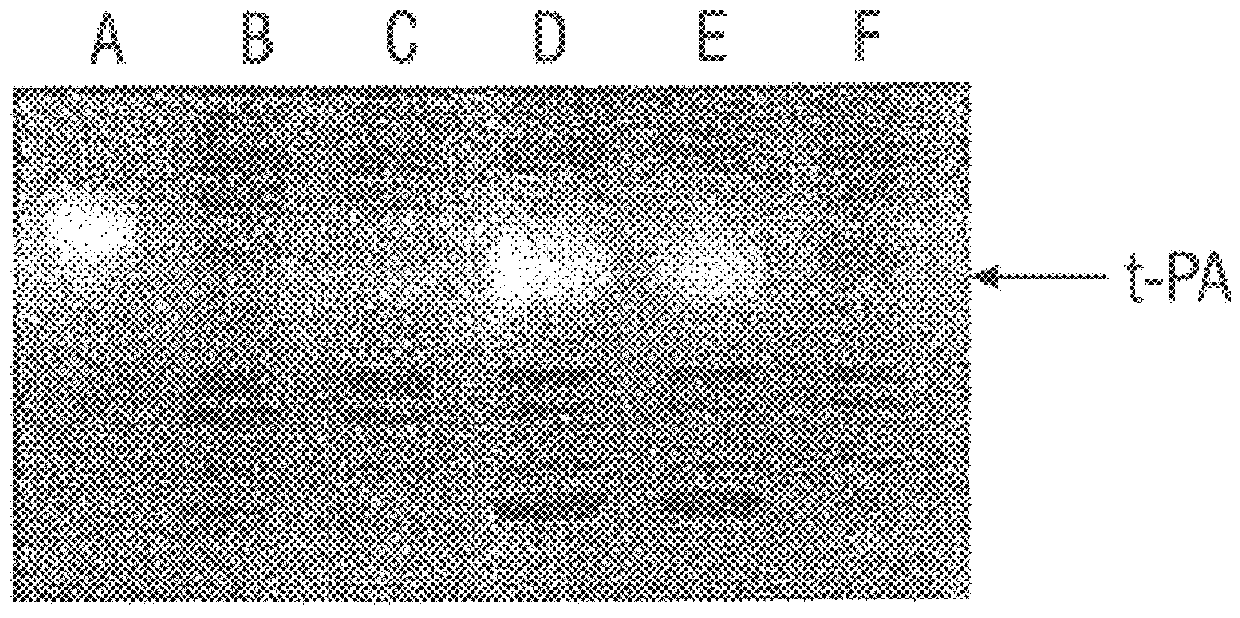
Disclosed are methods of producing eukaryotic disulfide bond-containing polypeptides in bacterial hosts, and compositions resulting therefrom. Co-expression of a eukaryotic foldase and a disulfide bond-containing polypeptide in a bacterial host cell is demonstrated. In particular embodiments, the methods have been used to produce mammalian pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) in soluble, biologically-active forms, which are isolatable from the bacterial periplasm. Also disclosed are expression systems, recombinant vectors, and transformed host cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for producing heterologous disulfide bond-containing polypeptides in bacterial cells
InactiveUS6083715AEfficient productionFold preciselyBacteriaUnicellular algaeMolecular biologyDisulfide bond
Disclosed are methods and compositions for producing heterologous disulfide bond containing polypeptides in bacterial cells. In preferred embodiments the methods involve co-expression of a prokaryotic disulfide isomerase, such as DsbC or DsbG and a gene encoding a recombinant eukaryotic polypeptide. Exemplary polypeptides disclosed include tissue plasminogen activator.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Basic group editing system as well as constructing and applying methods thereof
ActiveCN106916852AImprove efficacyReduce insertionStable introduction of DNADNA/RNA fragmentationComputer graphics (images)Genome
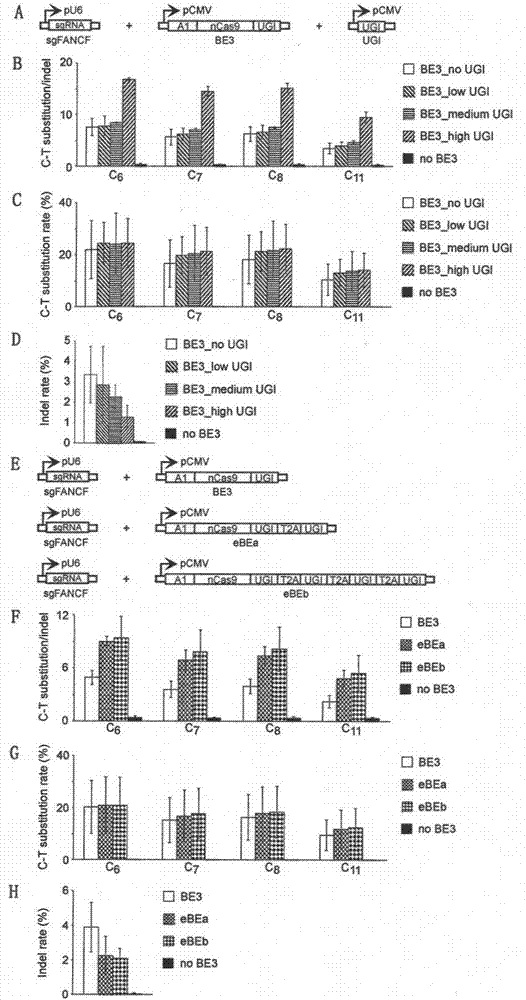
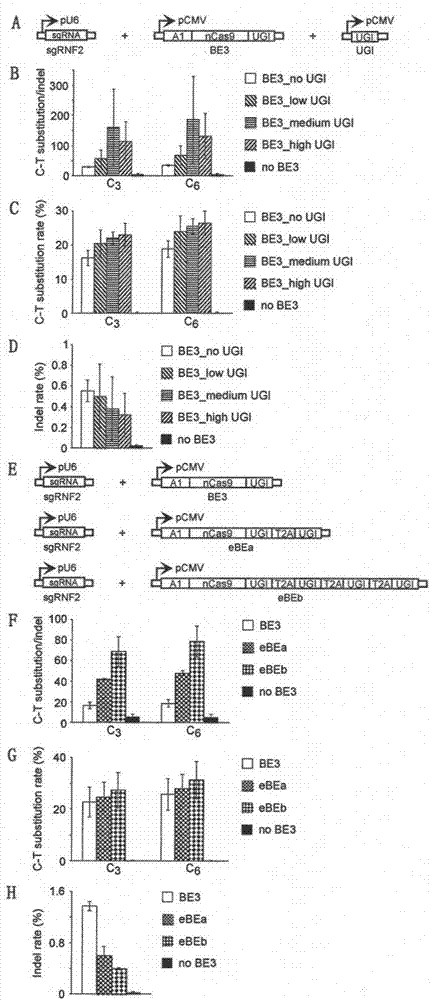
The invention provides a basic group editing system as well as constructing and applying methods of the basic group editing system. The basic group editing system is characterized y comprising a UGI expression vector and a BE3 expression vector, or a UGI and BE3 coexpression vector. According to the basic group editing system as well as the constructing and applying methods of the basic group editing system, for the first time, the C-T editing ratio generated by a CRISPR basic group editor is increased and the basic group insertion or loss ratio caused by the CRISPR system is reduced internationally, then the efficacies of the CRISPR basic group editor is enhanced, and thus a novel method and a novel thought are provided for the implementation of the accurate and safe basic group editing of the CRISPR basic group editor in the genomes of the various species.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Methods and compositions for gene silencing
InactiveUS20070130653A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesDevelopmental stageHeterologous
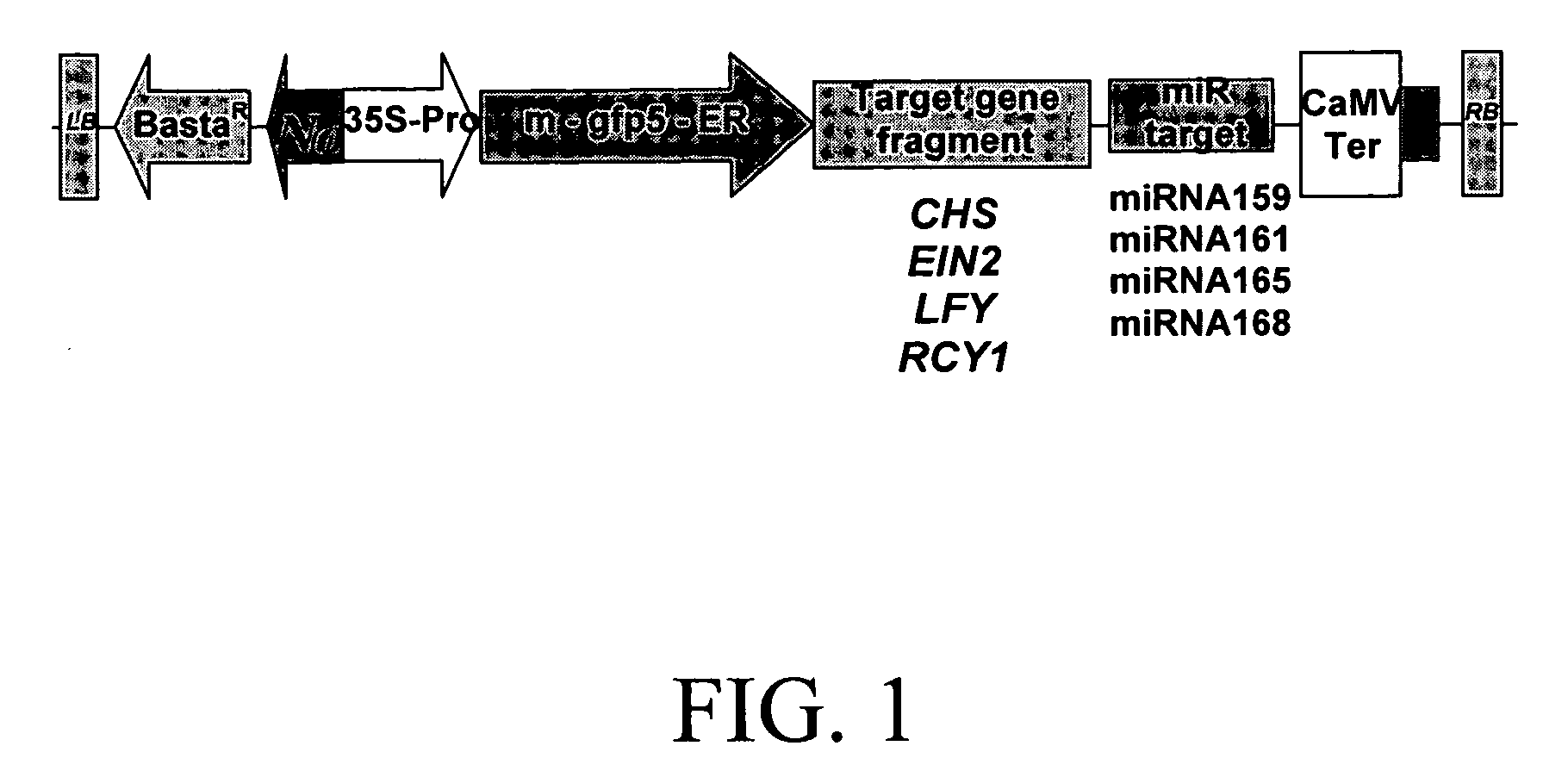
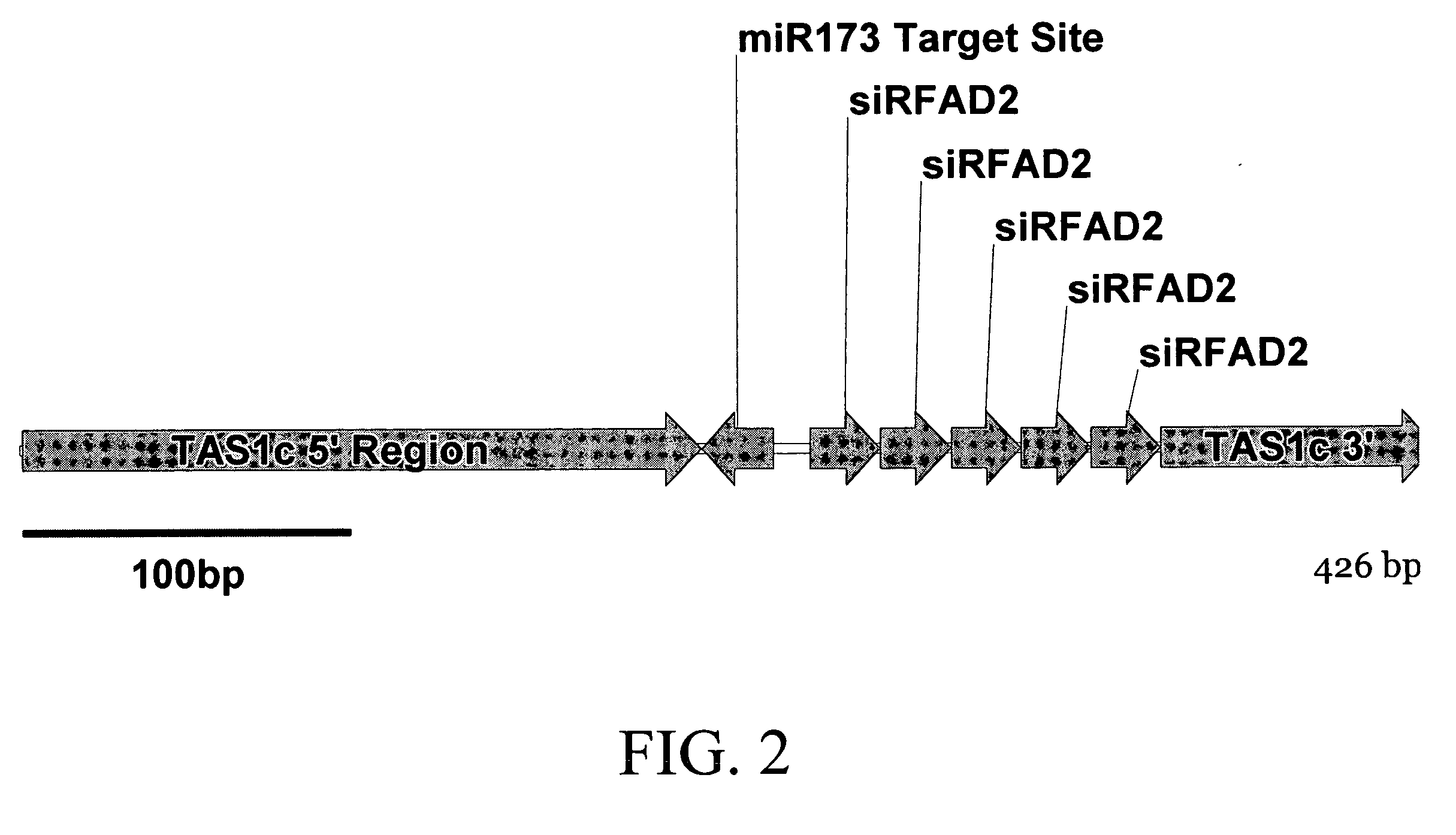
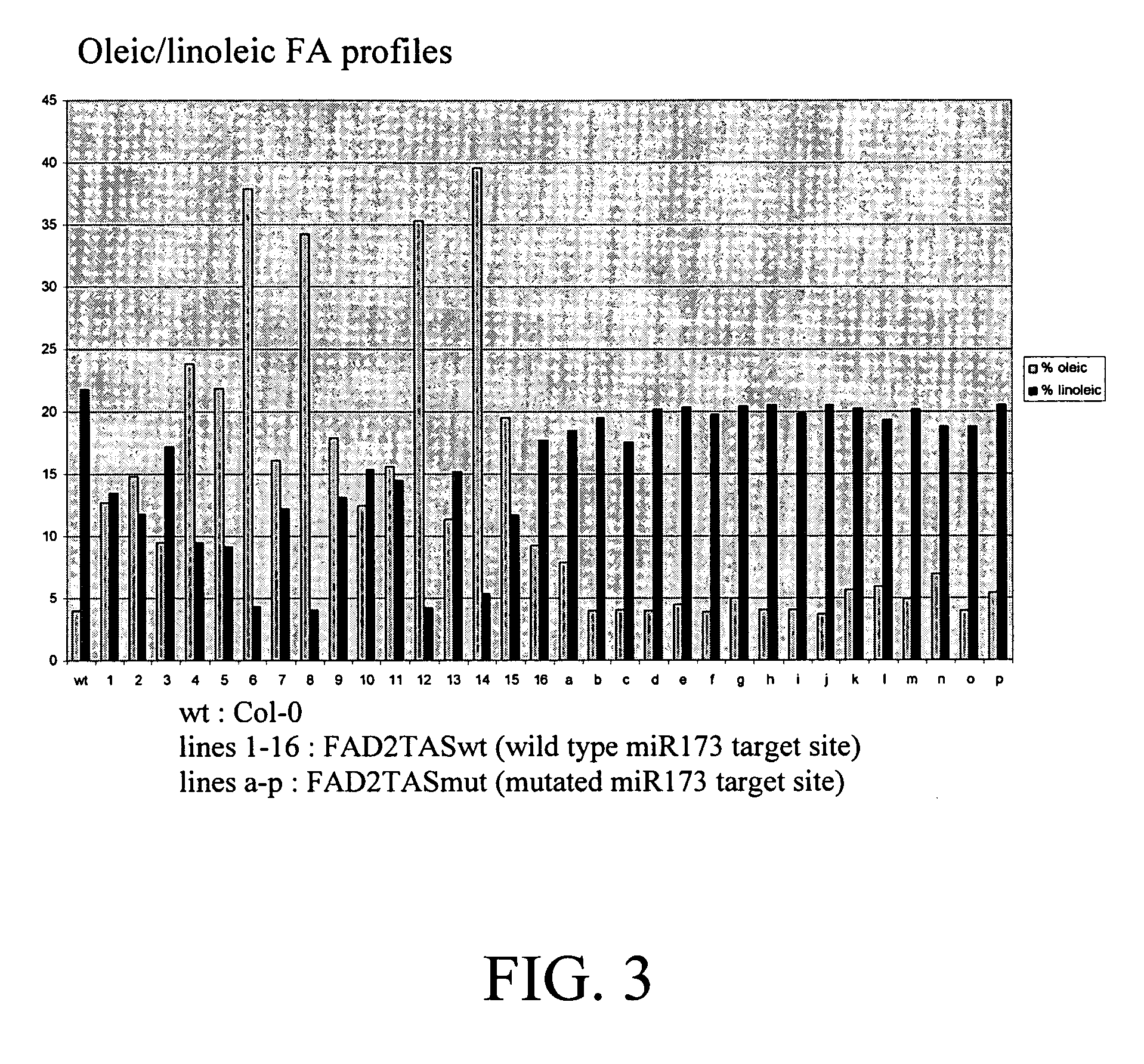
Methods and compositions are provided for reducing the level of expression of a target polynucleotide in an organism. The methods and compositions selectively silence the target polynucleotide through the expression of a chimeric polynucleotide comprising the target for a sRNA (the trigger sequence) operably linked to a sequence corresponding to all or part of the gene or genes to be silenced. In this manner, the final target of silencing is an endogenous gene in the organism in which the chimeric polynucleotide is expressed. In a further embodiment, the miRNA target is that of a heterologous miRNA or siRNA, the latter of which is coexpressed in the cells at the appropriate developmental stage to provide silencing of the final target when and where desired. In a further embodiment, the final target may be a gene in a second organism, such as a plant pest, that feeds upon the organism containing the chimeric gene or genes. Compositions further comprise vectors, seeds, grain, cells, and organisms, including plants and plant cells, comprising the chimeric polynucleotide of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
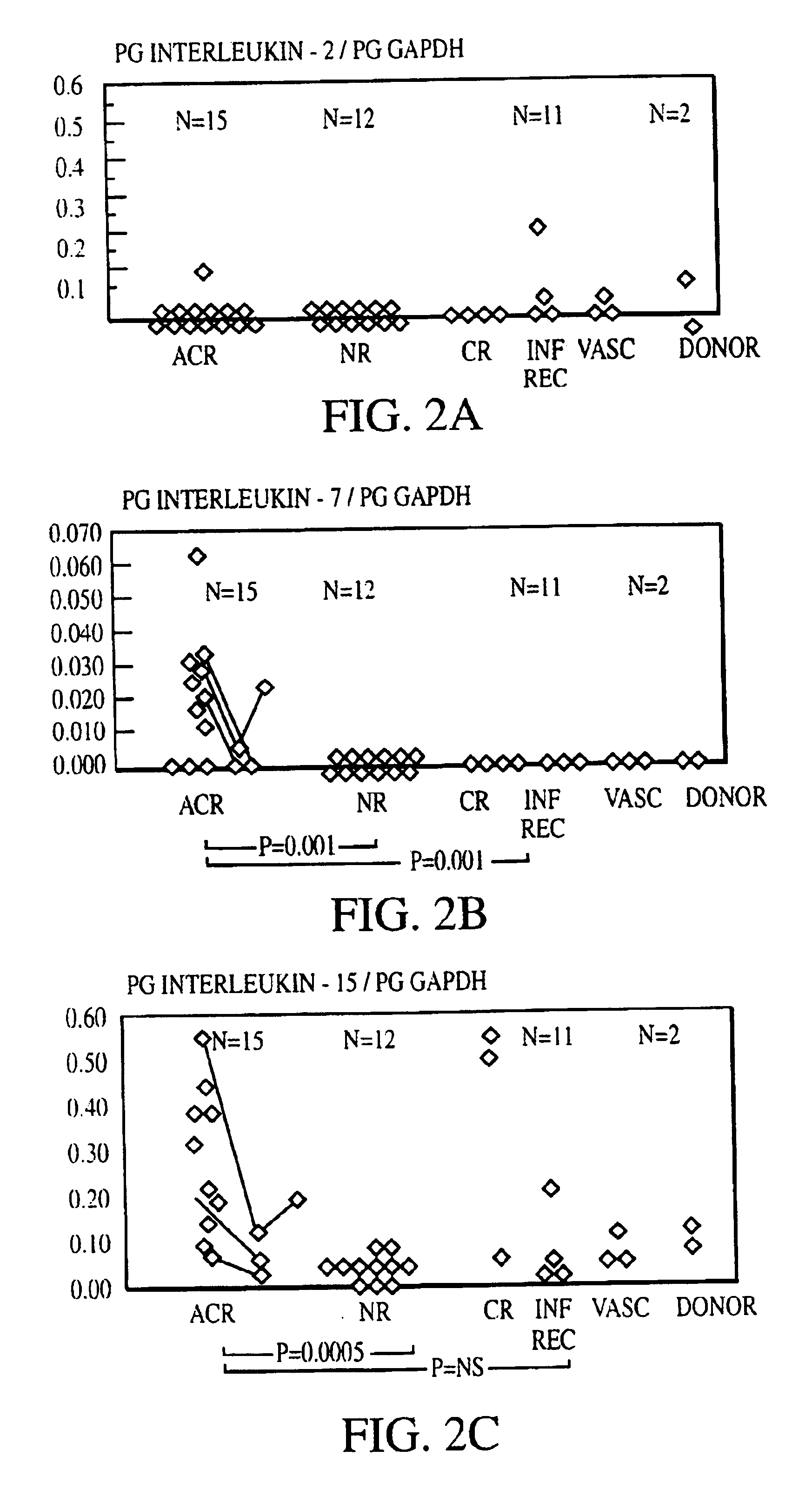
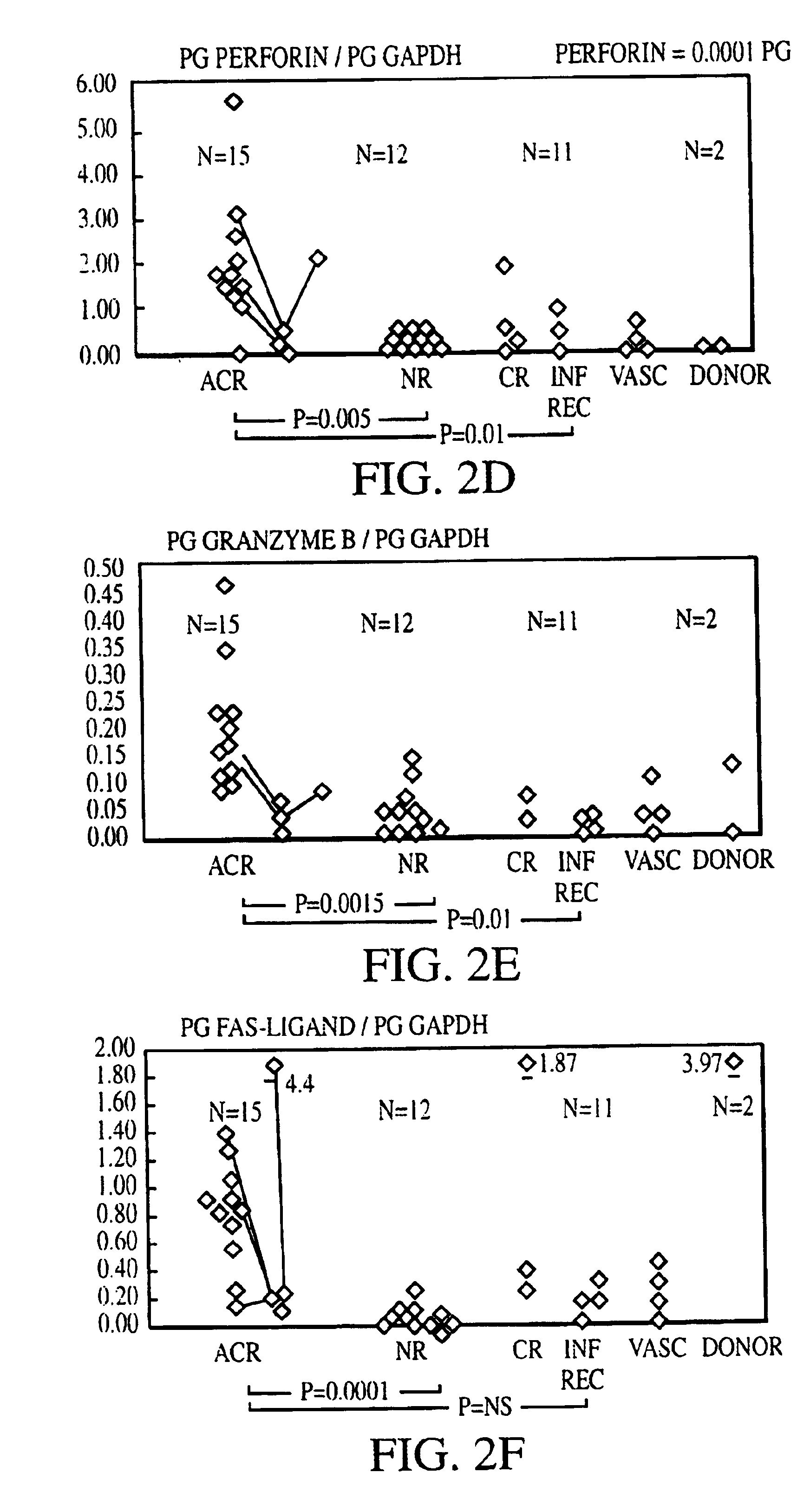
Measurement of protective genes in allograft rejection
InactiveUS6900015B2Quantitative precisionAccurately allograft rejectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCytotoxicityAllograft rejection
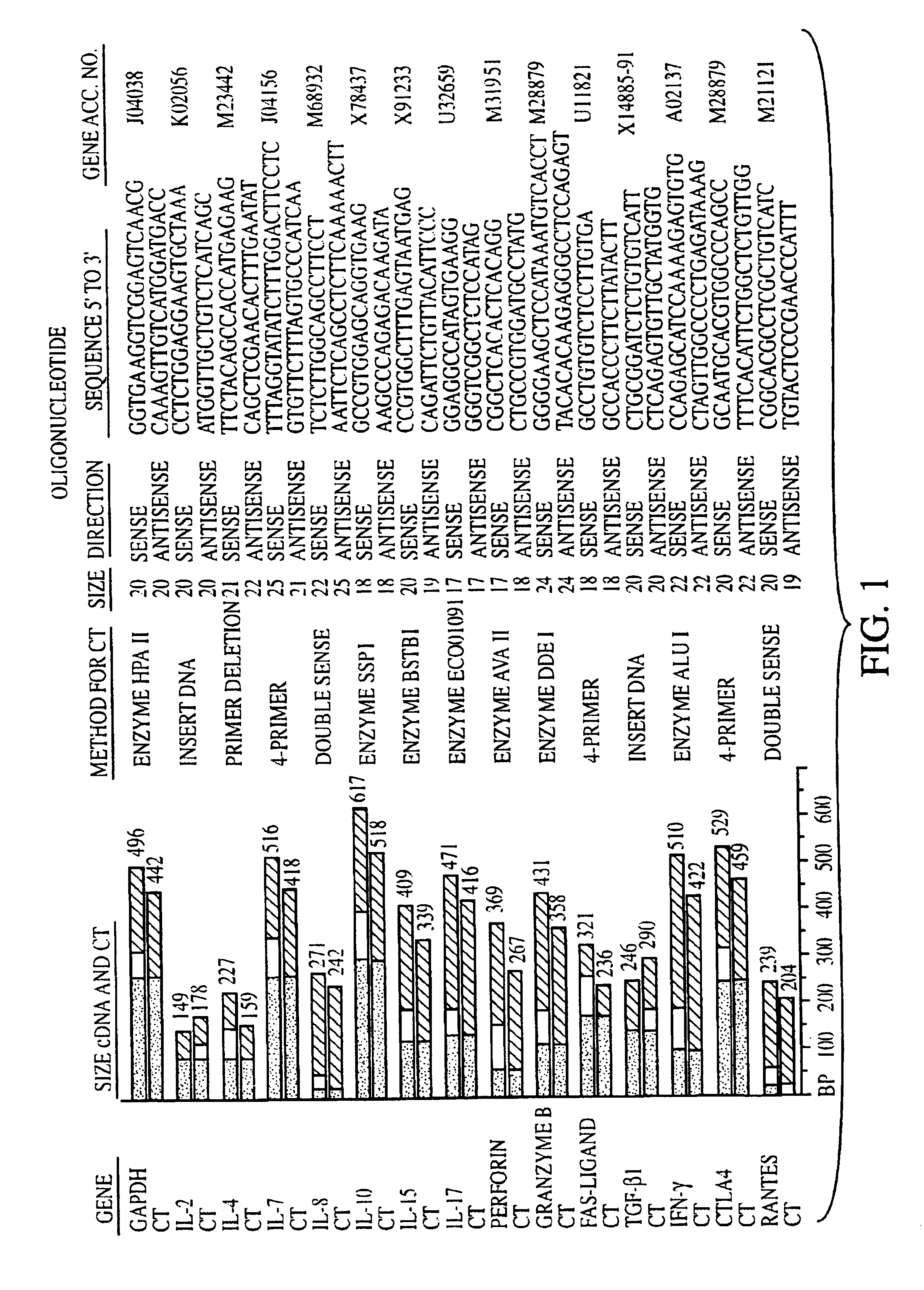
The invention relates to methods of evaluating transplant rejection in a host comprising determining a heightened magnitude of gene expression of genes in rejection-associated gene clusters. The disclosed gene clusters include genes that are substantially co-expressed with cytotoxic lymphocyte pro-apoptotic genes, cytoprotective genes and several other cytokine and immune cell genes.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Coordinate in vivo gene expression
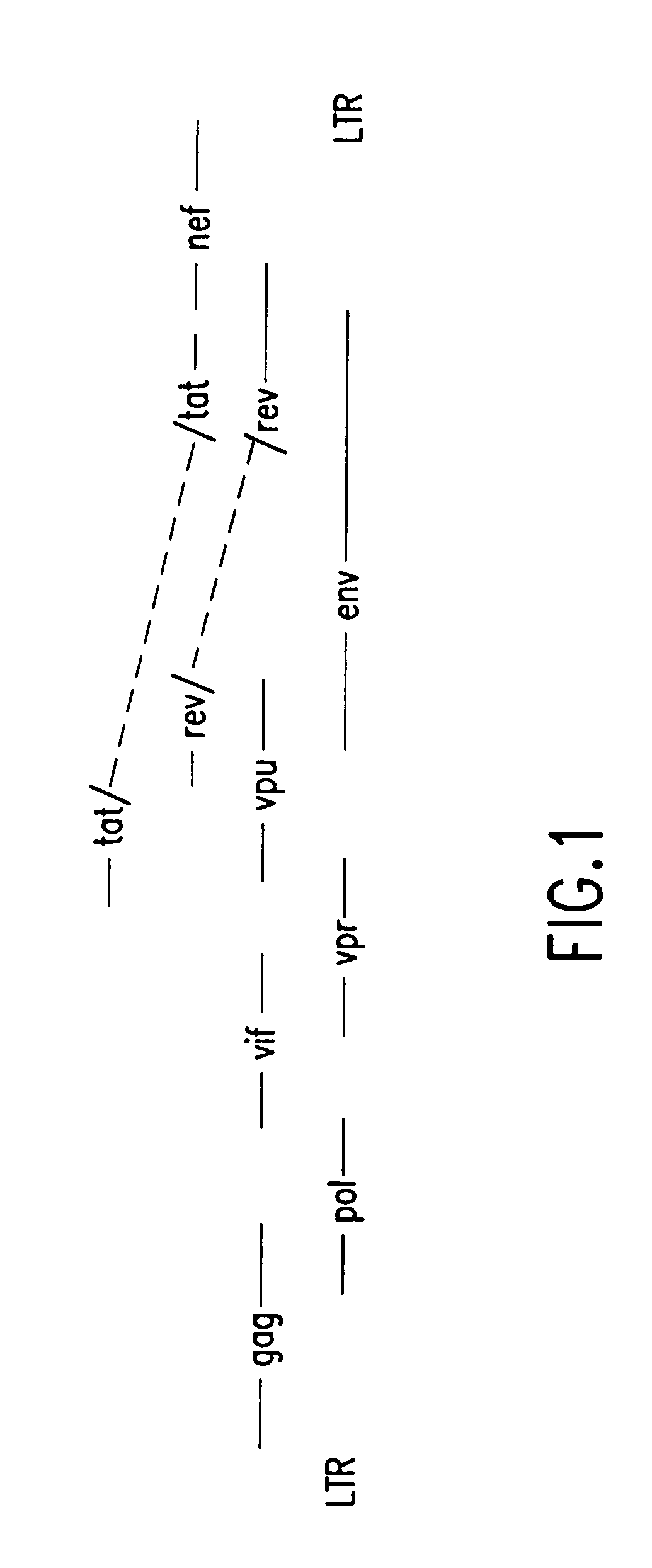
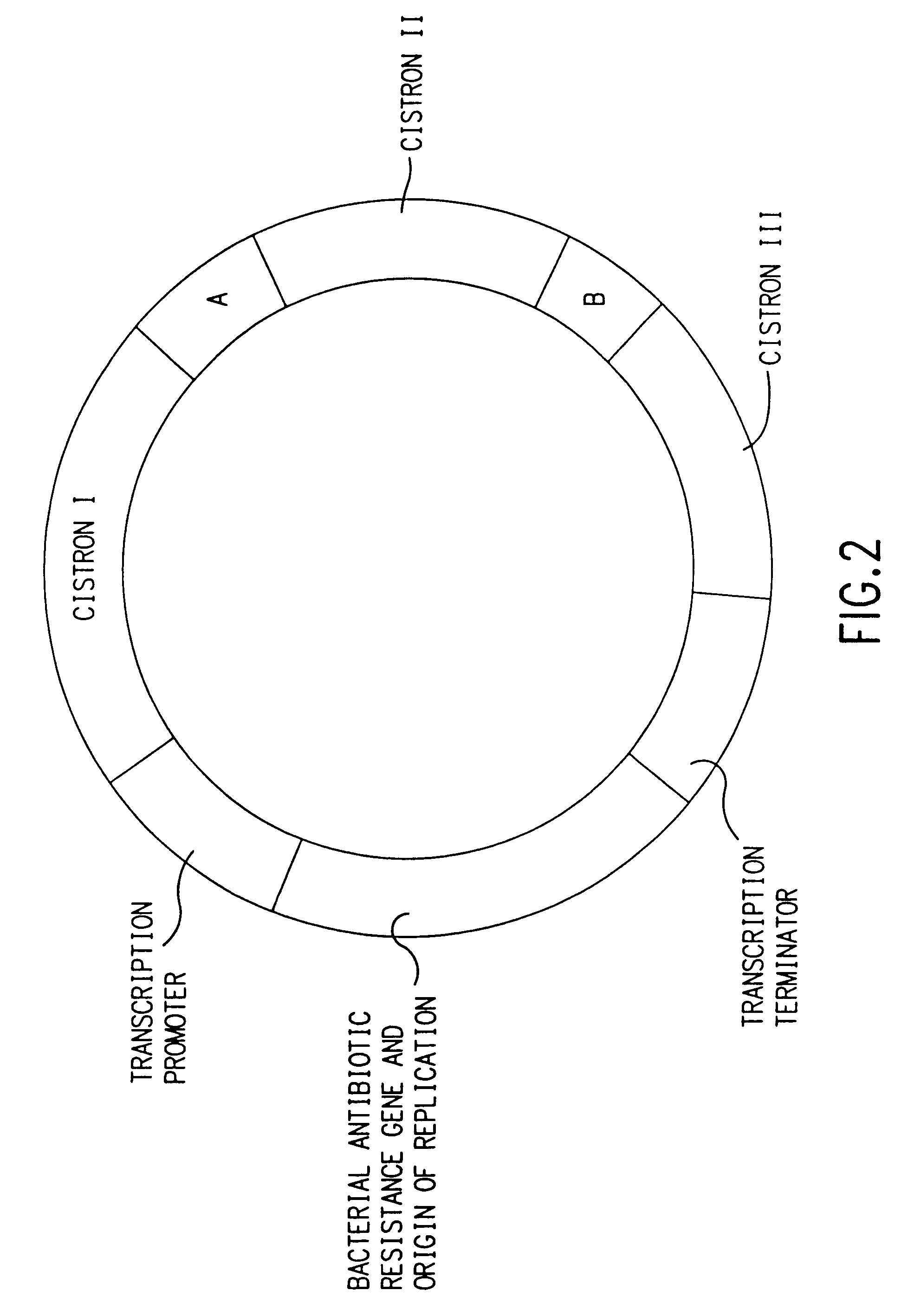
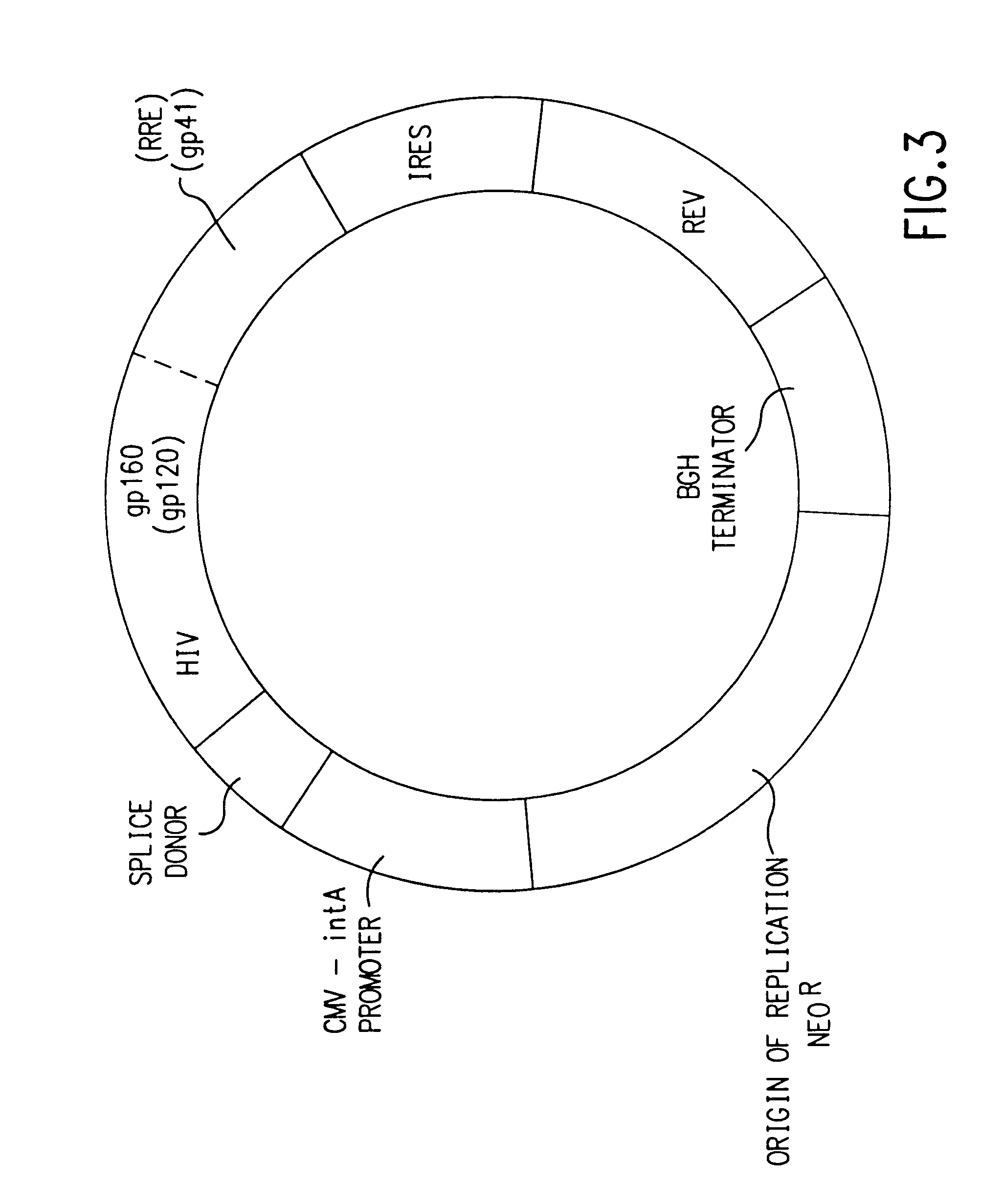
Nucleic acids, including DNA constructs and RNA transcripts, capable of inducing coordinate expression of two to three cistrons upon direct introduction into animal tissues, are bi- or tri-cistronic polynucleotides of this invention include those encoding and co-expressing HIV gene products, genes encoding antigens unrelated to HIV, and immunostimulatory gene products, including but not limited to GM-CSF, interleukins, interferon and members of the B7 family of proteins which act as T-cell costimulatory elements. The methods and polynucleotides of this invention are generally applicable to co-ordinate expression in vivo of any two or more genes in a single cell.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
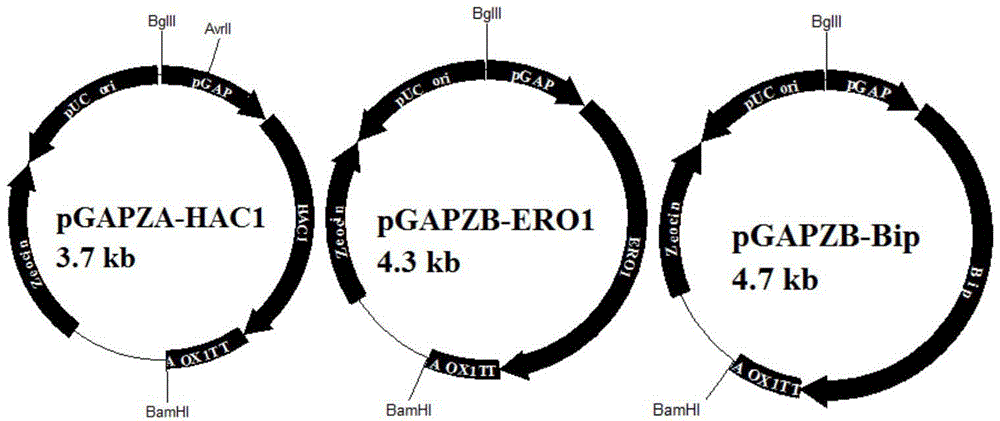
Method for improving expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris
ActiveCN104152484AHigh expressionPromotes proper foldingFungiMicroorganism based processesForeign proteinSecretion expression
The invention aims to provide a method for improving the expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris. Byintracellular co-expression of double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 or three genes of HAC1, ERO1 and BIP in pichia pastoris, the expression amount of secretory foreign protein in pichia pastoris is effectively improved. According to the invention, double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 or three genes of HAC1, ERO1 and BIP are transformed into pichia pastoris secreting and expressing exogenous xylanase to obtain recombinant pichia pastoris strains, thereby significantly increasing the expression amount of the exogenous xylanase. During co-expression of double genes of HAC1 and ERO1 in pichia pastoris, the secretion expression amount of exogenous xylanase is generally increased by 15%-25% compared with the initial level; and during the co-expression of three genes HAC1, ERO1 and BIP, the secretion expression amount of xylanase is increased by 45%-57% compared with the initial level.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Complex formation for the stabilisation and purification of proteins of interest
InactiveUS20050059053A1Increase volumeReduce degradation rateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccinesAntigenPost translational
A method is described for altering the properties such as the accumulation, the stability and / or integrity, the subcellular localisation, the post-translational modifications, the ability to get purified, and the phase partitioning behaviour of natural or recombinant target proteins expressed in a host organism. The method involves the co-expression of natural or recombinant proteins along with a specific binding partner that sequesters the target recombinant protein into a complex. The binding partner is supplied as a separate protein allowing formation of intermolecular complexes or is fused to the protein of interest, allowing the formation of intramolecular complexes. The binding partner can also be used to alter the subcellular localisation without modifying the sequence or structure of the target protein itself. This can be achieved by either incorporating appropriate targeting signals into the binding ligand, which are then linked to the target protein through complex formation, or complex formation itself may alter the subcellular localisation. The same strategy can be used to provide an affinity tag to facilitate protein purification. The principle of the invention is demonstrated by the coexpression of an unstable antibody and its cognate antigen.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Gene Expression Profile Algorithm and Test for Determining Prognosis of Prostate Cancer
ActiveUS20130196321A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementProstate cancerOncology
The present invention provides algorithm-based molecular assays that involve measurement of expression levels of genes, or their co-expressed genes, from a biological sample obtained from a prostate cancer patient. The genes may be grouped into functional gene subsets for calculating a quantitative score useful to predict a likelihood of a clinical outcome for a prostate cancer patient.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
Expression system
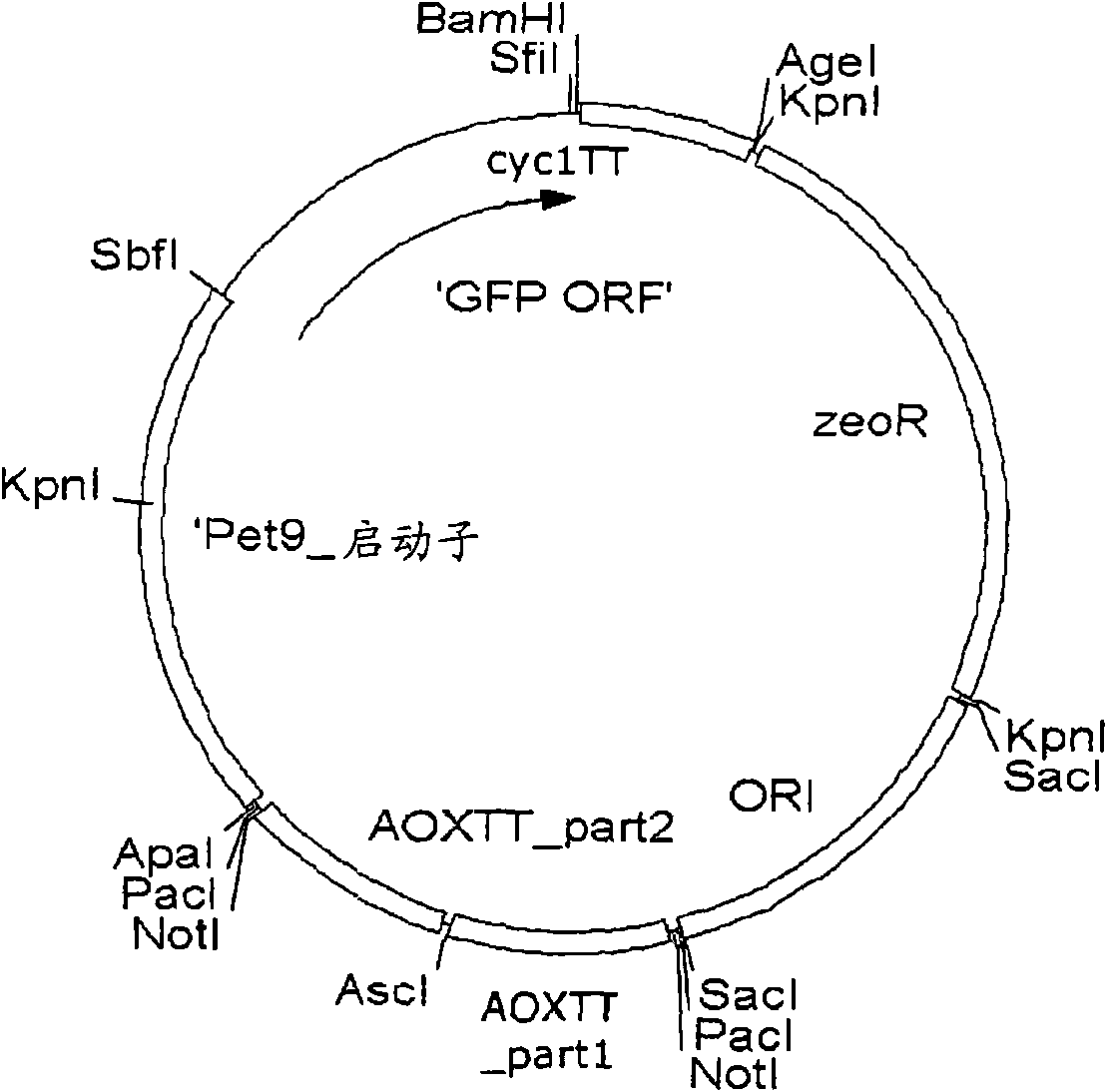
The present invention relates to methods for increasing the secretion of a protein of interest (POI) from a eukaryotic cell comprising co-expression of a POI and of at least one protein that enhancesprotein secretion, said enhancing protein being selected from the group consisting of BMH2, BFR2, C0G6, C0Y1, CUP5, IMH 1, KIN2, SEC31, SSA4 and SSE1. The invention further relates to a yeast promotersequence, in particular to a promoter sequence of the PET9 gene of P. pastoris, having, under comparable conditions, an increased promoter activity relative to a promoter sequence of the GAP protein.The invention further relates to an expression vector comprising such a promoter sequence and to the use of such an expression vector for expression of a POI in a host cell. The invention further relates to new yeast promoter sequences of genes from P. pastoris, which are useful for expression of a POI in yeast.
Owner:POLYMUN SCI IMMUNBIOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG
Tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication
InactiveCN106295246ASimple processSimple methodBiostatisticsProteomicsDifferential codingPredictive marker
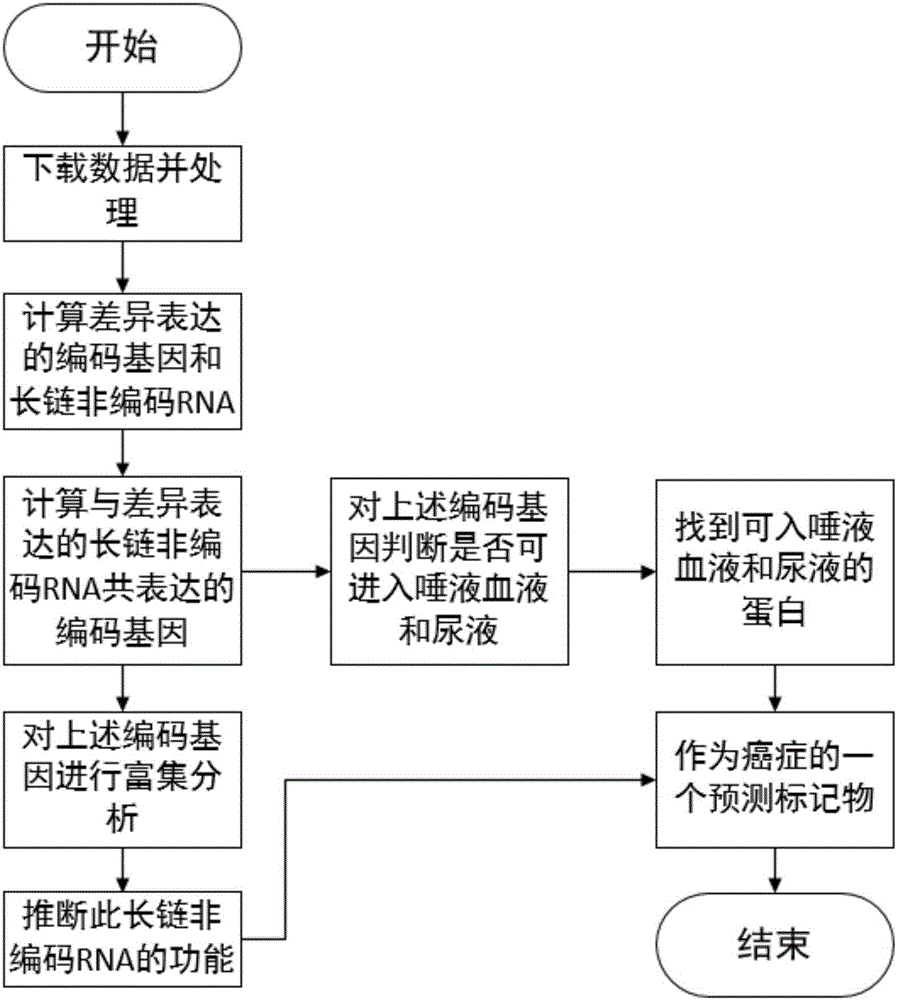
The invention relates to tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication. By taking differential expression of IncRNA in tumors as diagnosis references, a process for finding a relation between IncRNA and tumors includes: step one, downloading data from GEO database, processing the data to obtain expression data of part of IncRNA and exons; step two, subjecting the processed expression data to differential expression analysis; step three, analyzing co-expression and differential coding genes and IncRNA for IncRNA in differential expression; step four, subjecting the coding genes to probe platform annotation; step five, further screening the IncRNA in differential expression to select out most obviously differential IncRNA; step six, performing enrichment analysis to obtain a GOBP process and pathyway, and speculating IncRNA functions through coding gene related biological processes; step seven, analyzing whether common coding genes obtained at the step six can enter blood, saliva and urine or not, analyzing genes which are allowed to enter, and taking the genes and IncRNA as potential predication marks of cancers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Enhanced transgene expression by co-expression with a suppressor of post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)
InactiveUS7217854B1Minimize the possibilityHigh expressionTransferasesStable introduction of DNATransgeneNucleic acid sequence
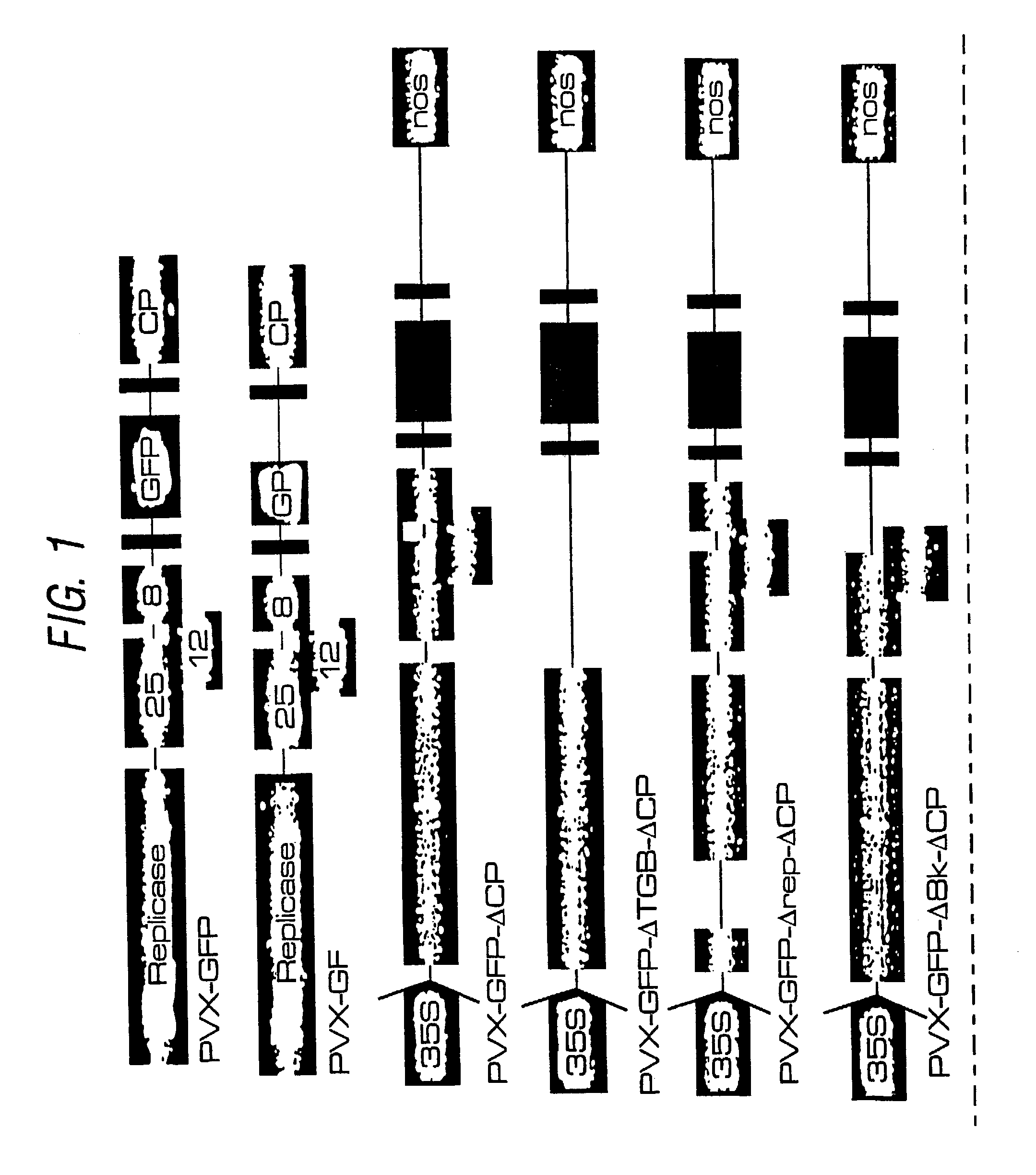
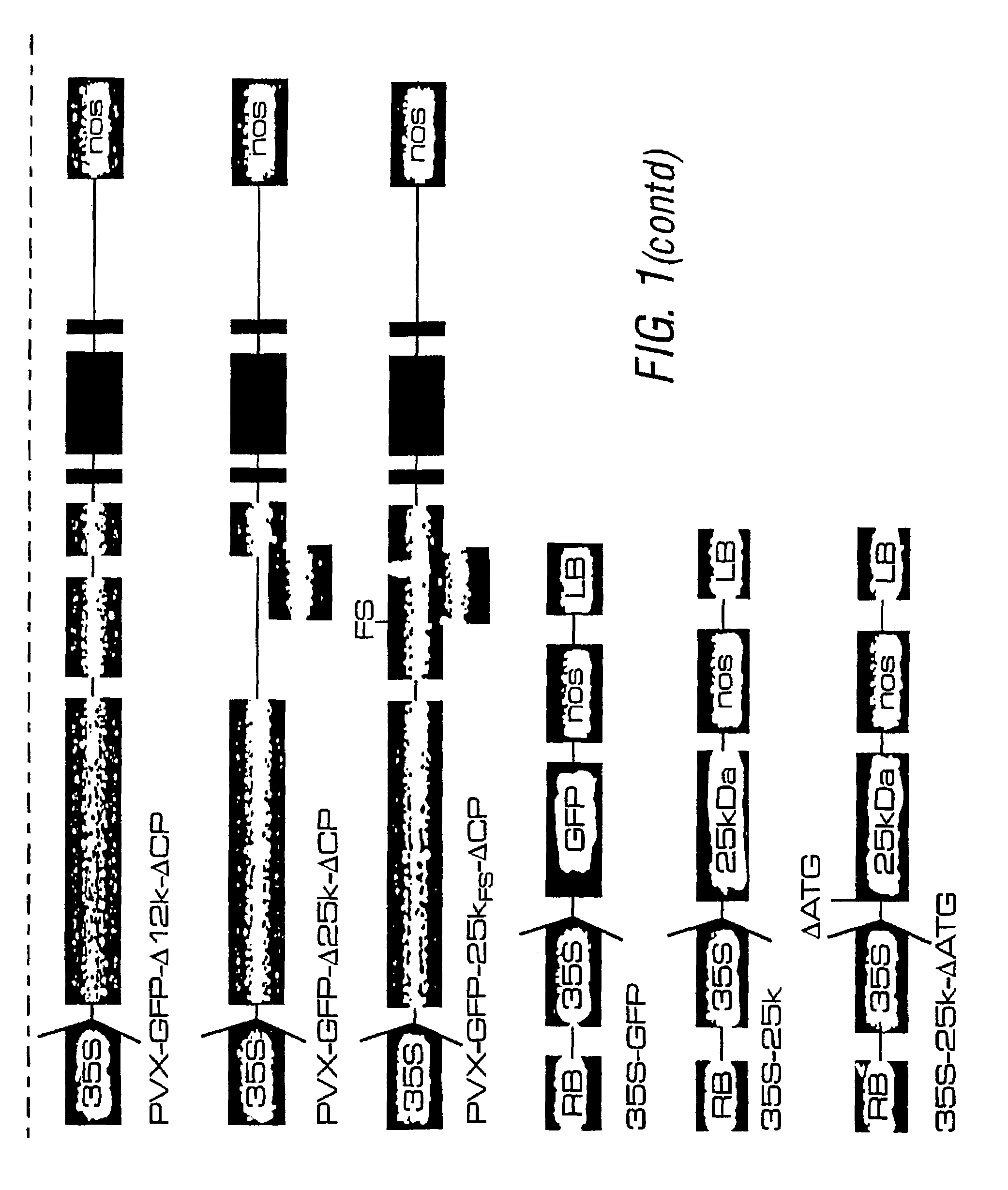
Disclosed are a variety of methods for achieving enhanced expression from a target nucleotide sequence in a plant e.g. comprising the step of transiently introducing into a tissue of a plant (e.g. a leaf) a first nucleic acid comprising the target nucleotide sequence and a second nucleic acid encoding a Post Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS) suppressor protein (preferably of viral or plant origin), wherein the first and second nucleic acids are comprised within a single binary vector construct, or the first and second nucleic acid sequences are comprised within a first binary vector and a second binary vector construct respectively. The plant tissue may then be harvested for the protein. Such methods can give much higher levels of gene expression than are obtainable using stable transgenes, or certain replicating vectors. Also disclosed are specific PTGS suppressor proteins: potato virus X (pvx) p25 protein; african cassava mosaic virus (acmv) AC2 protein; rice yellow mottle virus (rymv) P1 protein; tomato bushy stunt virus (tbsv) 19K protein; plus variants of these. These suppressors may be used in any PTRS context, including the enhancement of transient expression systems.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Cell systems and methods for detecting proliferation acitvity
The invention provides proliferative response indicator cell having a vertebrate cell having a luciferase encoding nucleic acid and a heterologous proliferation factor receptor encoding nucleic acid, wherein each of the encoding nucleic acids are operationally linked to expression elements for co-expression of a luciferase polypeptide and a heterologous proliferation factor receptor. The invention also provides a method of determining a cell proliferative response to a proliferation factor. The method includes: (a) contacting a vertebrate cell expressing luciferase and a proliferation factor receptor with a proliferation factor for sufficient time for the proliferation factor to bind to the proliferation factor receptor; (b) culturing the contacted cell expressing luciferase for at least one generation, and (c) measuring the amount of light emission, wherein the luciferase expression is driven from a promoter non-responsive to the proliferation factor and the light emission directly correlates with proliferation factor-mediated cell proliferation. The proliferation factor can be a growth factor, a cytokine or a hormone or an agonist or antagonist thereof. The methods of the invention additionally include determining the effect of an inhibitor of the proliferation factor. Cells used in the method are contacted with a proliferation factor in the presence of a sample suspected of containing an inhibitor of the proliferation factor. The inhibitor can be neutralizing antibody, or binding fragment thereof, to the proliferation factor. The methods of the invention also are applicable as an indicator of cell health or viability. The invention further provides a diagnostic system. The diagnostic system includes a plurality of different vertebrate cell lines each encoding a luciferase gene and a different proliferation factor receptor, the luciferase gene being operationally linked to a promoter non-responsive to a proliferation factor bound by the proliferation factor receptor, wherein light emission from each of the different cell lines being characterized as directly correlating with proliferation factor-mediated cell proliferation.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method for establishing recombinant adenovirus vector with Africa swine fever EP153R and P54 gene coexpression and packaging adenovirus
PendingCN109735567AEnhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsGene coexpressionMultiple cloning site
The invention provides a method for establishing a recombinant adenovirus vector with Africa swine fever EP153R and P54 gene coexpression and packaging adenovirus and belongs to the technical field ofgene engineering. According to the adenovirus vector of coexpression of the EP153R gene and the P54 gene, with a pShuttle-CMV eukaryotic expression vector as a basis, the CTLA4, EP153R and P54 genesare introduced at multiple cloning sites. The invention further provides recombinant adenovirus with coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes. The established pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-P54 vector is used for achieving the adenovirus packaging process, the adenovirus which can directly infect animals or eukaryocyte is obtained, the aim of coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes in eukaryocyte is achieved, and the basis is laid for research on adenovirus vaccines of coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Construction of EP153R and EP402R gene co-expression recombinant adenovirus vector and adenovirus packaging method
InactiveCN109652449ADirect infectionEnhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesMultiple cloning siteCloning Site
The invention provides construction of an EP153R and EP402R gene co-expression recombinant adenovirus vector and a adenovirus packaging method, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Based on a pShuttle-CMV eukaryotic expression vector, an EP153R gene and EP402R gene overexpression adenovirus vector pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-EP402R is introduced with CTLA4, EP153R and EP402Rgenes at multiple cloning sites. The invention also provides recombinant adenovirus for co-expressing EP153R and EP402R genes, and the adenovirus packaging process is achieved by utilizing the constructed pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-EP402R vector to obtain the adenovirus capable of directly infecting animal or eukaryotic cells, thereby achieving the purpose of co-expressing EP153R and EP402R genes in eukaryotic cells, and laying a foundation for researching the adenovirus vaccine for achieving the co-expression of EP153R and EP402R genes.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Hansenula polymorpha expression system, hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha
ActiveCN103045492AThe mutation site is clearLow back mutation rateFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh level expressionGenetic engineering
The invention provides a hansenula polymorpha expression system, a hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha. The expression system contains uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501, of which the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7013. The uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501 provided by the invention has the advantages of definite mutation site, low reverse mutation frequency, good hereditary stability, high biological expression quantity and the like, plays a significant role in researching and producing gene engineering vaccine, has the advantages of higher yield and low cost as compared with other eukaryotic expression systems adopted at present. The invention further provides an expression vector applied to the hansenula polymorpha expression system and a construction method of the expression vector. Two or more genes can be expressed simultaneously through the expression vector. Two target genes can be expressed in a hansenula polymorpha auxotroph cell at a high level without interference.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
Gene knockout method and its sgRNA fragment and application thereof
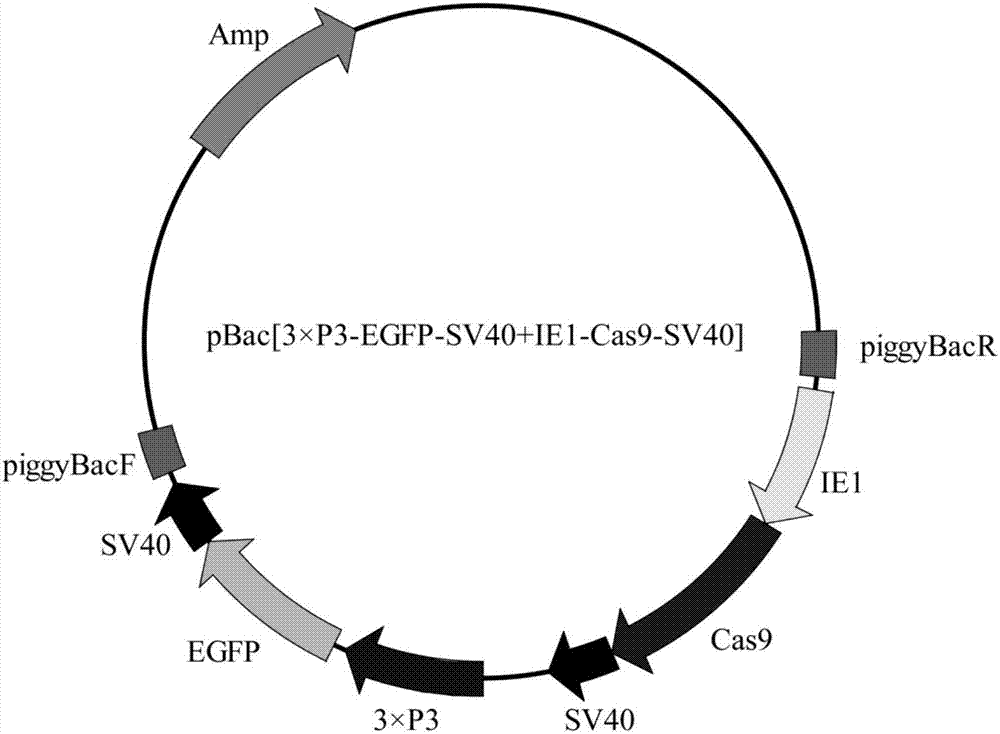
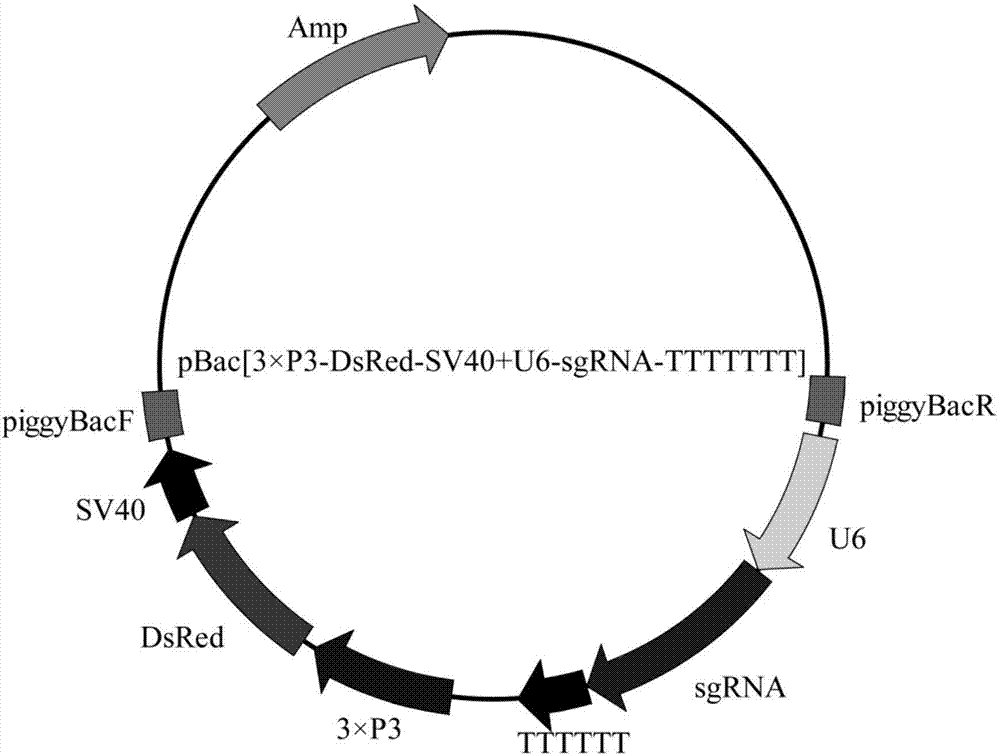
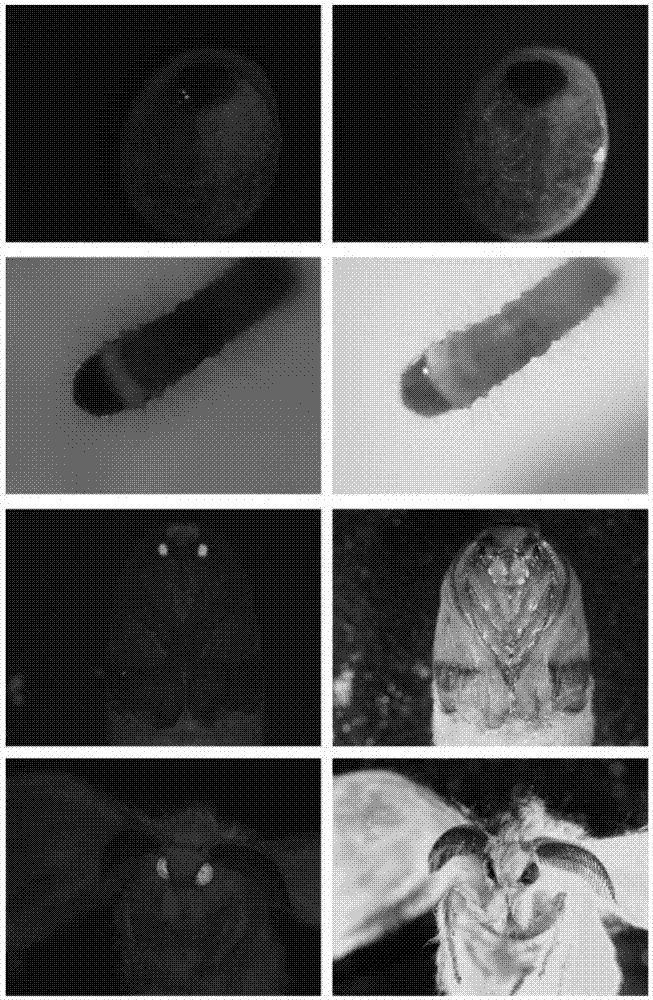
ActiveCN107043782ASimplify build technologyImprove injection efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAGenetically modified organismCas9
The invention provides a gene knockout method and its sgRNA fragment and an application thereof. The gene knockout method comprises the steps of respectively obtaining genetically modified organisms capable of expressing Cas9 and sgRNA, two genetically modified organisms are subjected to hybridization to obtain co-expression positive individual. According to the invention, a carrier construction technology is simplified, injection efficiency is increased, target sequence editing can be carried out after fertilization is completed, and the editing efficiency is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
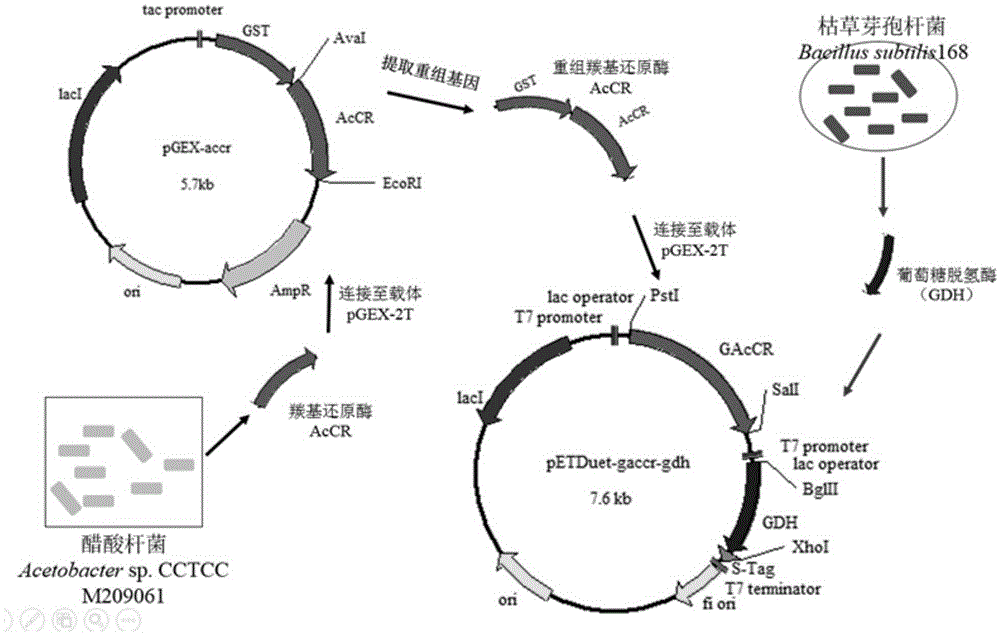
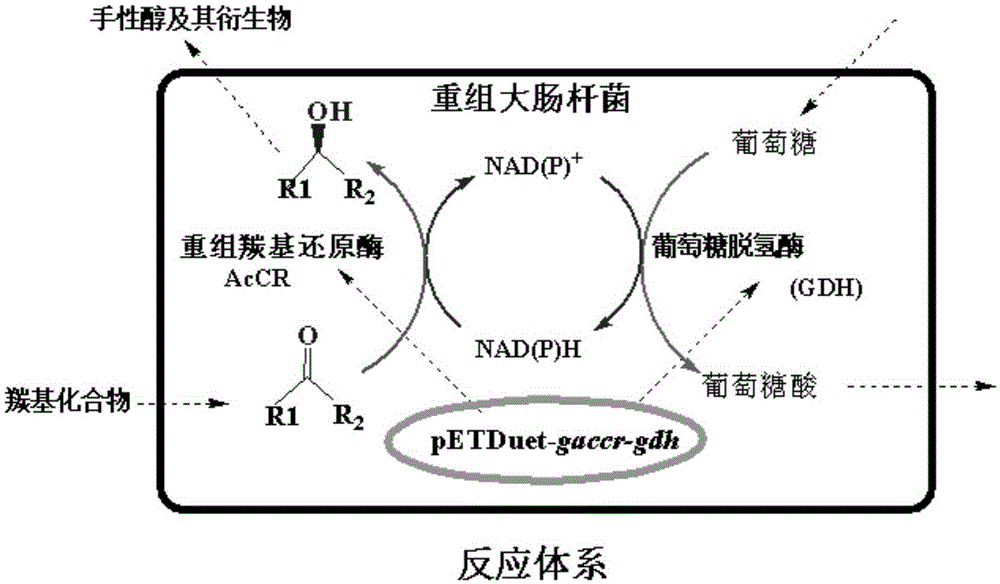
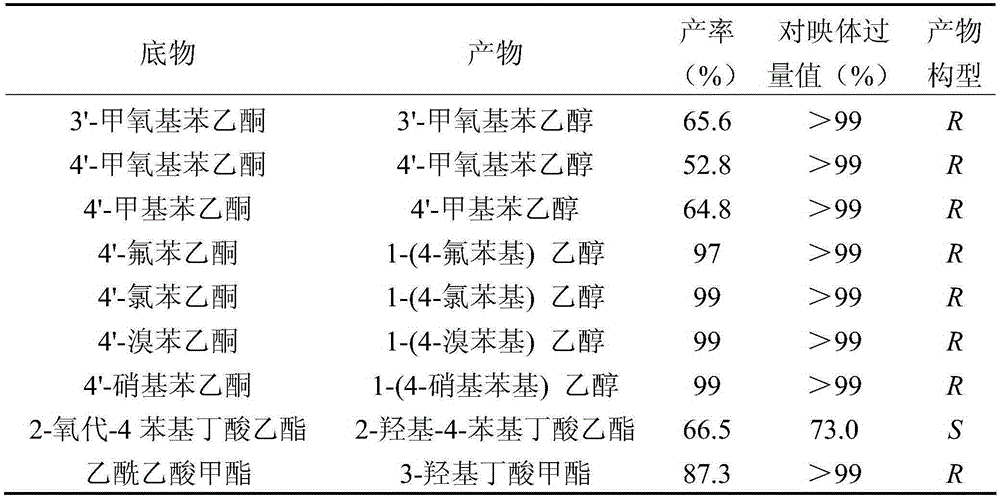
Carbonyl reductase AcCR and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105349503ACan be catalyzed to generateAchieve in situ regenerationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholEnantiomer
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and particularly relates to carbonyl reductase AcCR and an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the carbonyl reductase AcCR is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for encoding the carbonyl reductase AcCR is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The carbonyl reductase AcCR comes from bacillus aceticus XZY003 and can catalyze 13 carbonyl compounds to generate corresponding chiral alcohol of single enantiomers. The carbonyl reductase AcCR and glucose dehydrogenase GDH are co-expressed in a prokaryotic expression system or a eukaryotic expression system, the biological reaction process of biological catalytic conversion is conducted through the carbonyl reductase, in-situ regeneration of coenzyme is achieved, production cost is greatly reduced, the optical purity of an obtained product is high, the reaction process is efficient, and conditions are moderate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
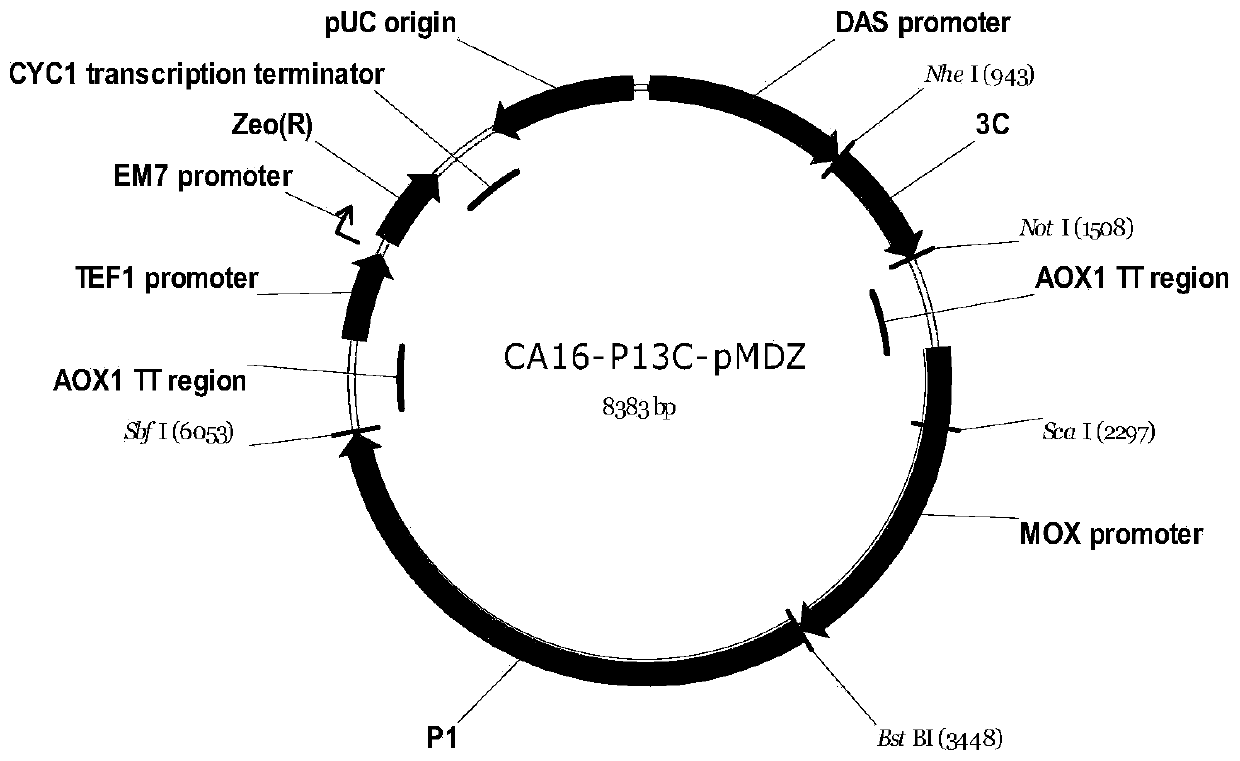
Method for preparing recombinant coxsackievirus A16 type virus-like particles
ActiveCN103436553AUniform shapeStable traitsInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsOpen reading frameCoxsackievirus a16
The invention relates to the field of immunity technology, and particularly relates to a method for preparing recombinant coxsackievirus A16 type virus-like particles. In the method, the PI protein and 3C protein of CA16 are expressed in a double-expression plasmid through a yeast expression system. In order to realize the preparation of CA16 virus-like particles, according to the method provided by the invention, an expression vector and an expression system for CA16 virus-like particles are established, wherein the expression vector comprises two open reading frames which respectively contain a P1 protein expression sequence and a 3C protein expression sequence of CA16. According to the invention, a method for preparing recombinant coxsackievirus-like particle protein by use of co-expression of 3C protease and P1 protein is established through codon optimization; and the method can obtain virus particles with high purity, uniform form and stable characters, is used for preparing a hand-foot-and-mouth disease vaccine, and has a great market value.
Owner:上海博唯生物科技有限公司 +1
Construction of coenzyme efficient regeneration system and application thereof
InactiveCN105238807AImprove conversion efficiencyLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliThreonine
The invention relates to a method for preparing alpha-aminobutyric acid by utilizing series connection amino acid dehydrogenase and codon optimization formate dehydrogenase recombinant escherichia coli. First, codon optimization is performed on a Candida boidinii formate dehydrogenase gene sequence according to the codon preference of the escherichia coli. After codon optimization on formate dehydrogenase, the expression quantity of formate dehydrogenase in the escherichia coli can be improved remarkably, the yield of alpha-aminobutyric acid is increased, and in the escherichia coli, co-expression formate dehydrogenase and L-amino acid dehydrogenase can promote circulation of cofactors in mycetome without needing the adding of any exogenous cofactors. In addition, the process of utilizing whole-cell transformation bulk chemical L-threonine to produce alpha-aminobutyric acid is simple and quick, and the cost is low. In a 5 L fermentation tank, the yield of alpha-aminobutyric acid obtained through the method can be 81.5 g / L, and an actually effective strategy is provided for industrial production of alpha-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
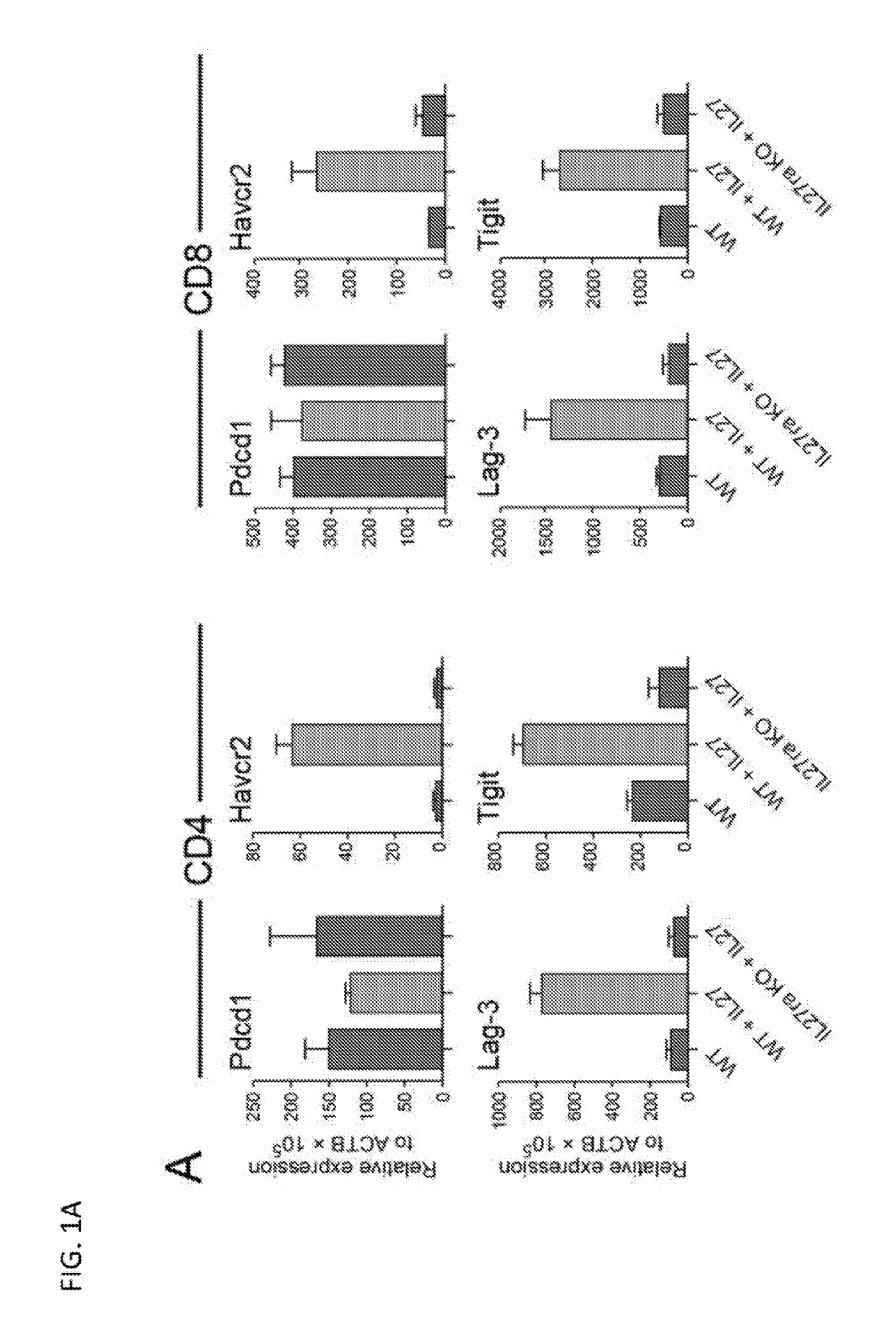
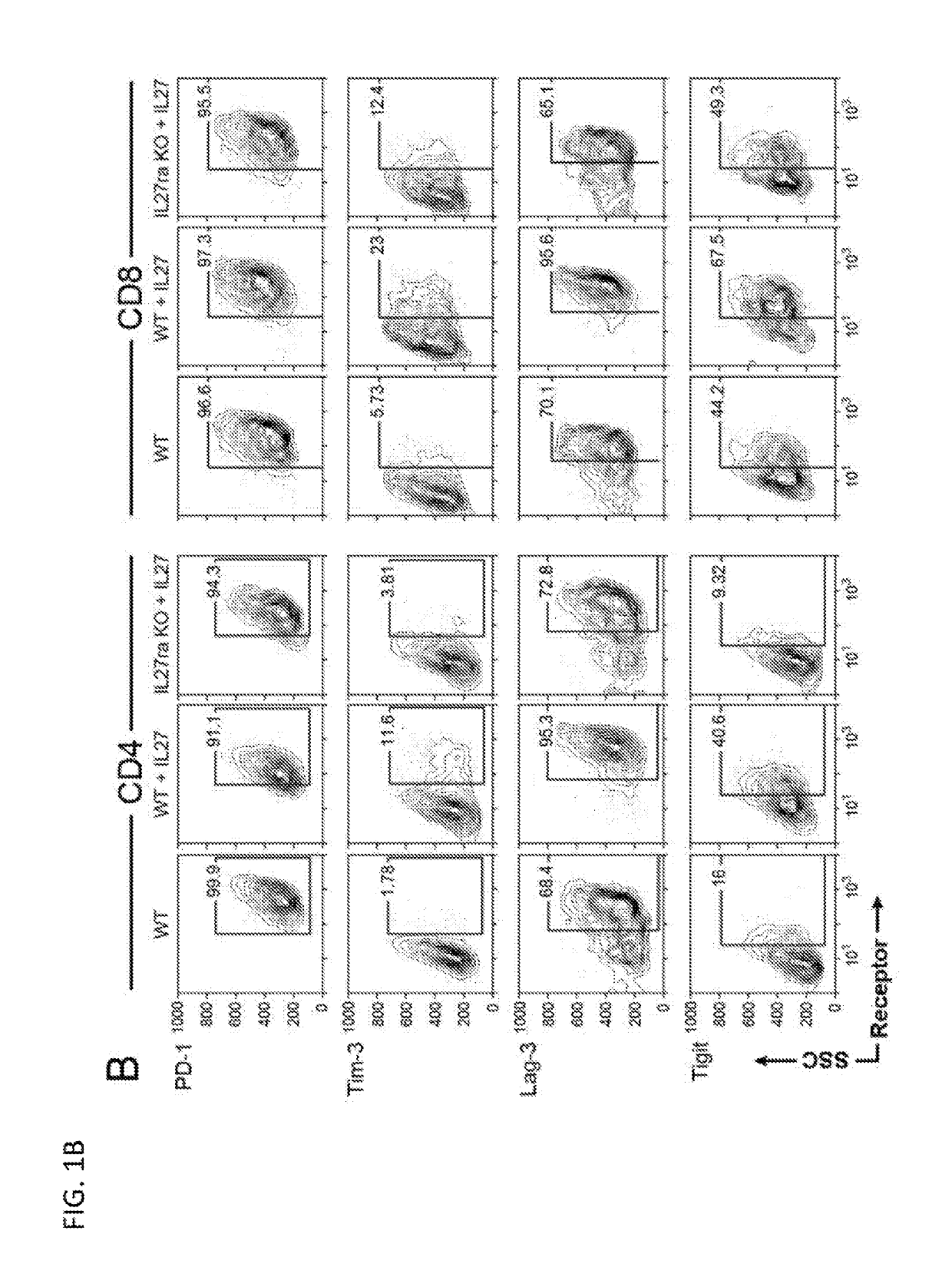
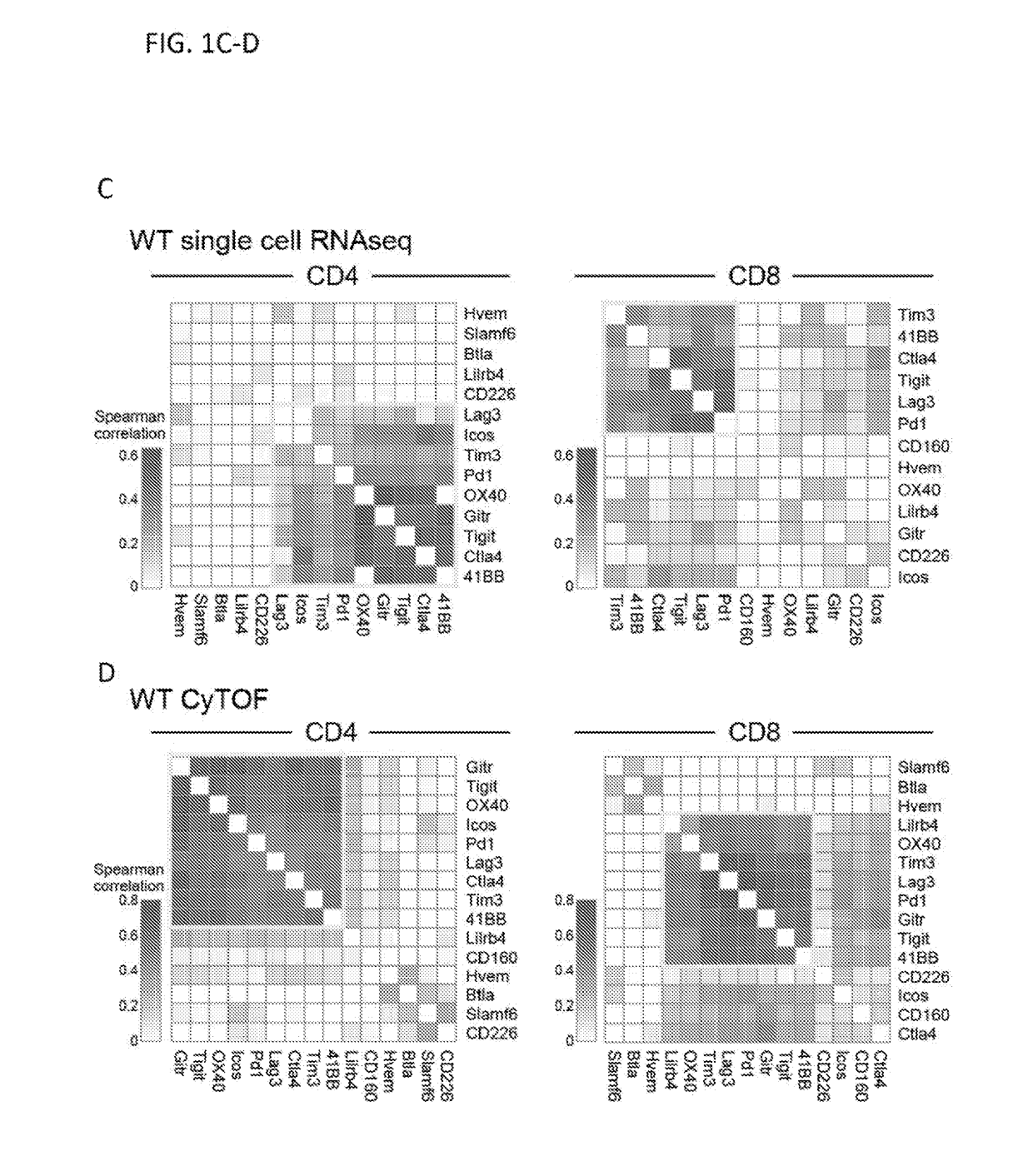
Modulation of novel immune checkpoint targets
PendingUS20190255107A1Decrease in exhausted T cell phenotypeIncrease T cell activationAntibacterial agentsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseClinical efficacy
Dysfunctional or exhausted T cells arise in chronic diseases including chronic viral infections and cancer, and express high levels of co-inhibitory receptors. Therapeutic blockade of these receptors has clinical efficacy in the treatment of cancer. While co-inhibitory receptors are co-expressed, the triggers that induce them and the transcriptional regulators that drive their co-expression have not been identified. The immunoregulatory cytokine IL-27 induces a gene module in T cells that includes several known co-inhibitory receptors (Tim-3, Lag-3, and TIGIT). The present invention provides a novel immunoregulatory network as well as novel cell surface molecules that have an inhibitory function in the tumor microenvironment. The present invention further provides the novel discovery that the transcription factors Prdm1 and c-Maf cooperatively regulate the expression of the co-inhibitory receptor module. This critical molecular circuit underlies the co-expression of co-inhibitory receptors in dysfunctional T cells and identifies novel regulators of T cell dysfunction.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +2
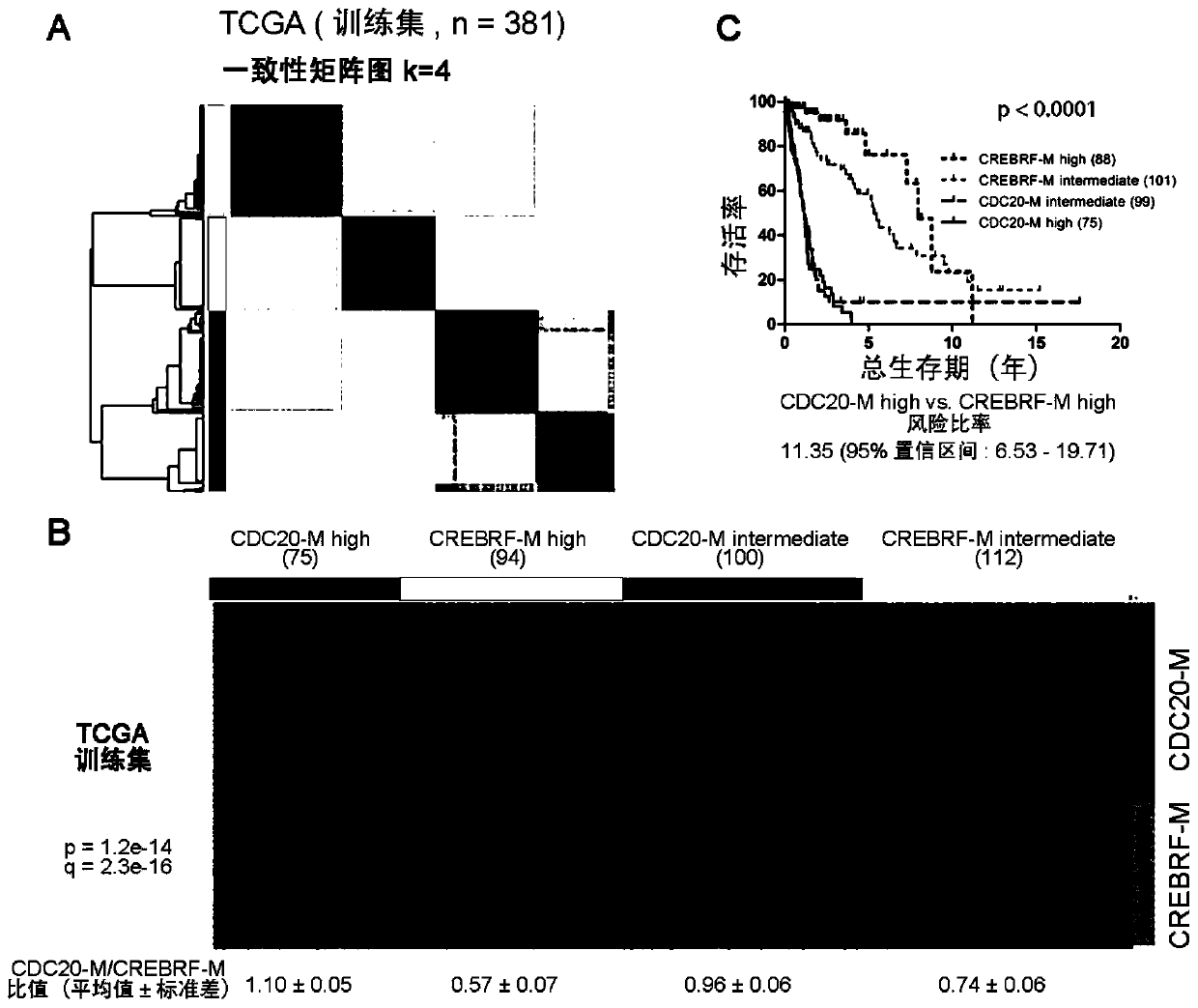
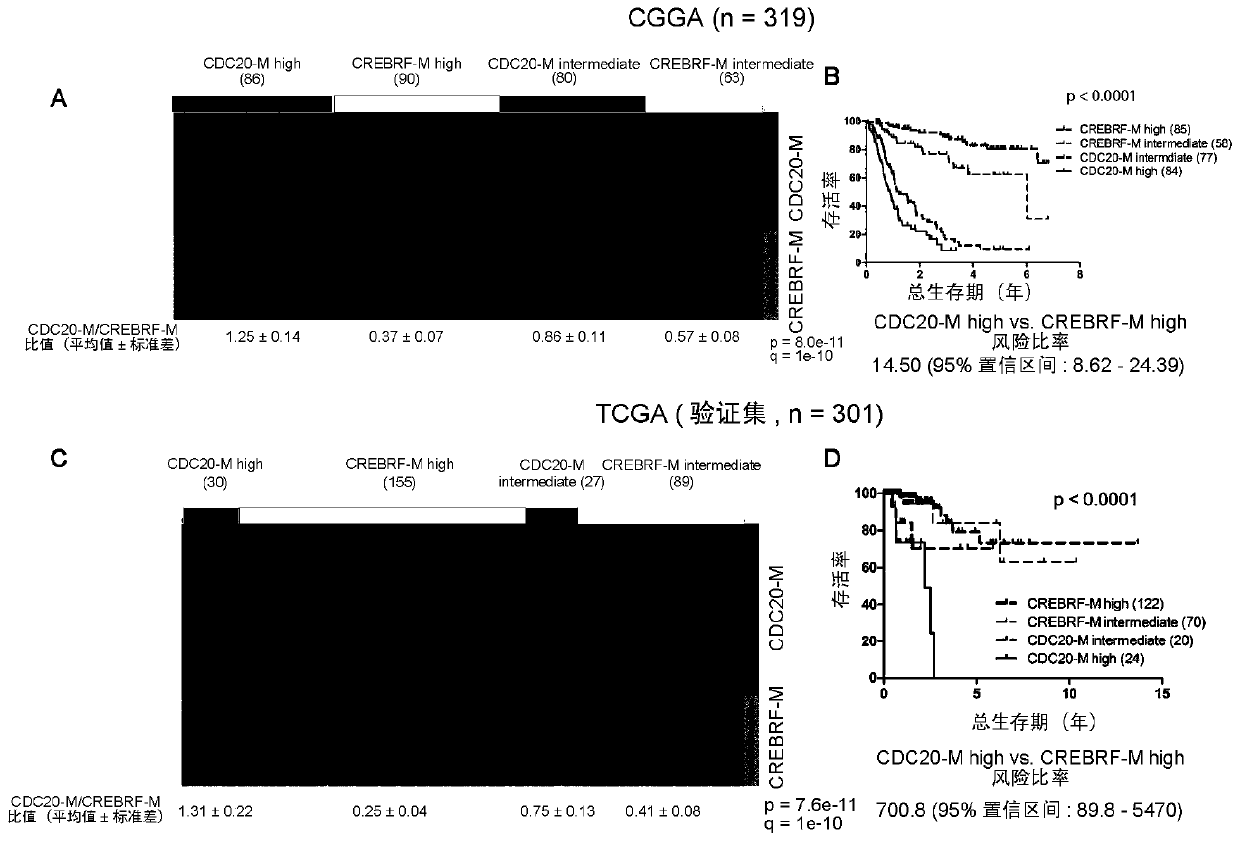
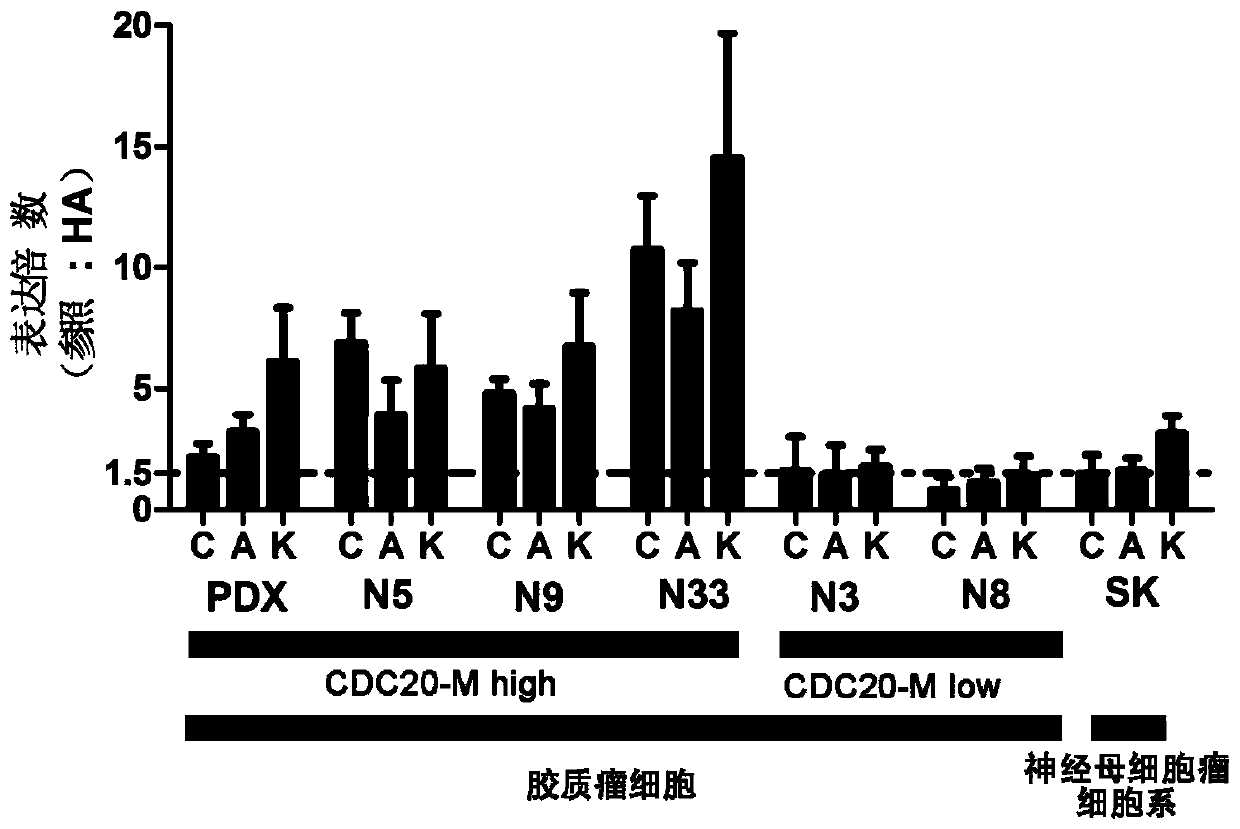
Application of CDC20 co-expression gene network as glioma treatment target
The invention discloses an application of CDC20 co-expression gene network as a glioma treatment target. The invention provides an application of an inhibitor in any of the following: (A1) preparing aproduct for treating glioma; (A2) treating glioma, wherein the inhibitor is a substance capable of reducing the expression activity and / or expression level of the following genes or encoded proteinsthereof: AURKA gene, CDC20 gene and / or KIF2C gene. The application proves that CDC20-M is a sensitive marker of genomic instability and poor prognosis in glioma, and finds potential glioma treatment targets in experimental analysis of main members of CDC20-M, and thus a new idea is provided for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
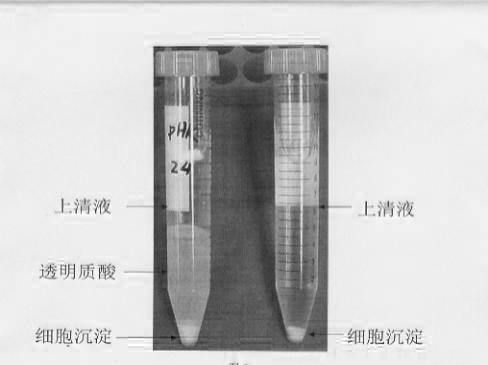
Preparation method of hyaluronic acid
ActiveCN102154405AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcyl CoA dehydrogenaseSynexpression
The invention provides a preparation method of hyaluronic acid. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a recombinant expression vector into the colibacillus to obtain engineering colibacillus by constructing the recombinant expression vector of which hyaluronic acid synzyme gene Has and uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase gene are jointly expressed in the colibacillus; and fermenting the engineering colibacillus to obtain the hyaluronic acid. After the method is used, the production yield of the hyaluronic acid achieves 2.5g / L. compared with the prior art, the yield of the highest HA (hyaluronic acid) obtained by gram positive chained coccus HA synthetic gene spHas expressed in the colibacillus is approximately improved by 10 times.
Owner:MICROBIAL FERMENTATION ENG RES CENT CO LTD OF YUNNAN PROVINCE
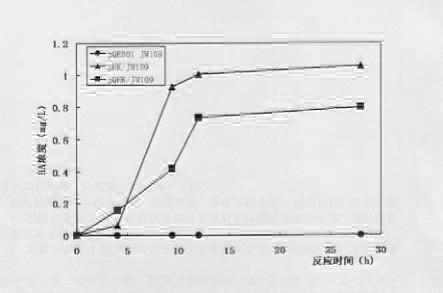
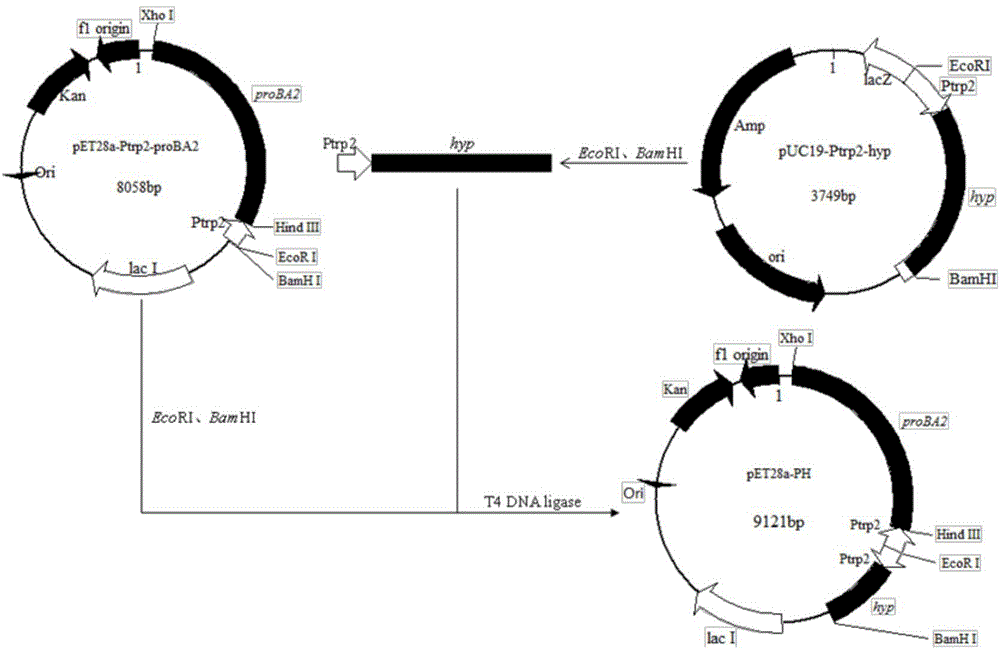
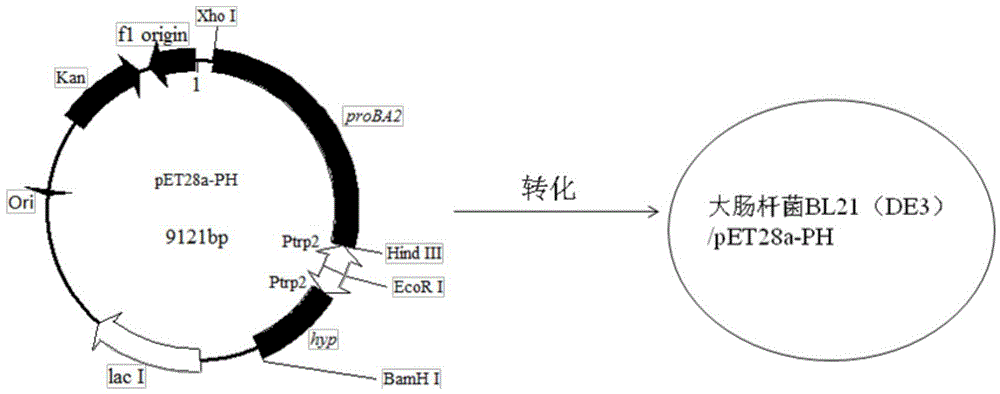
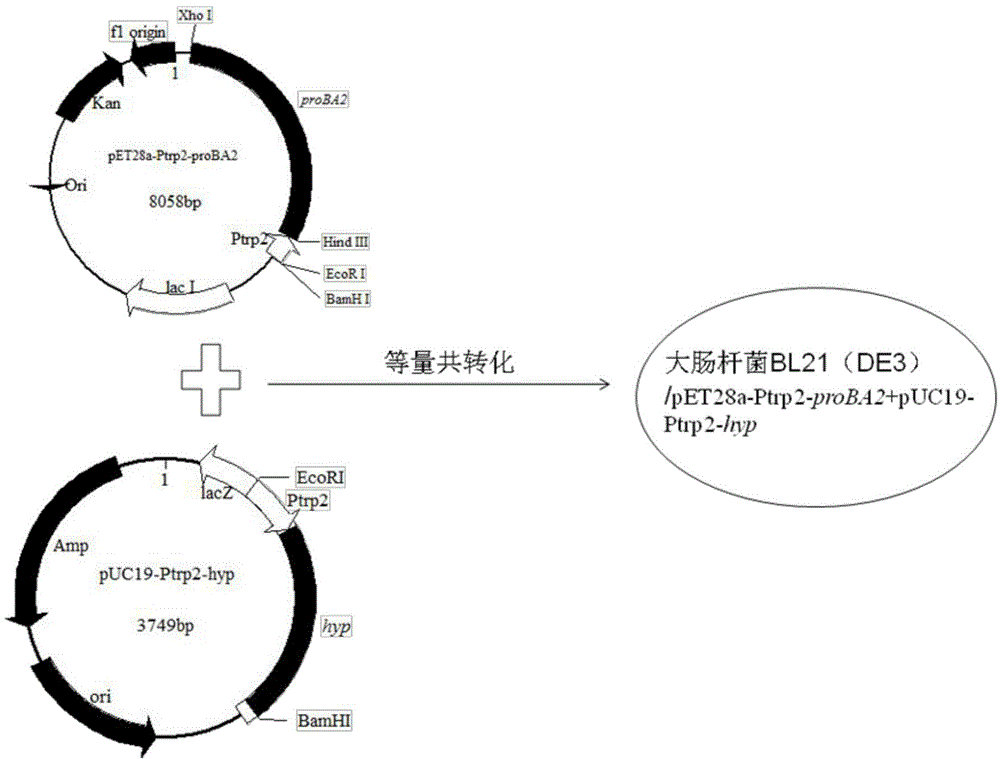
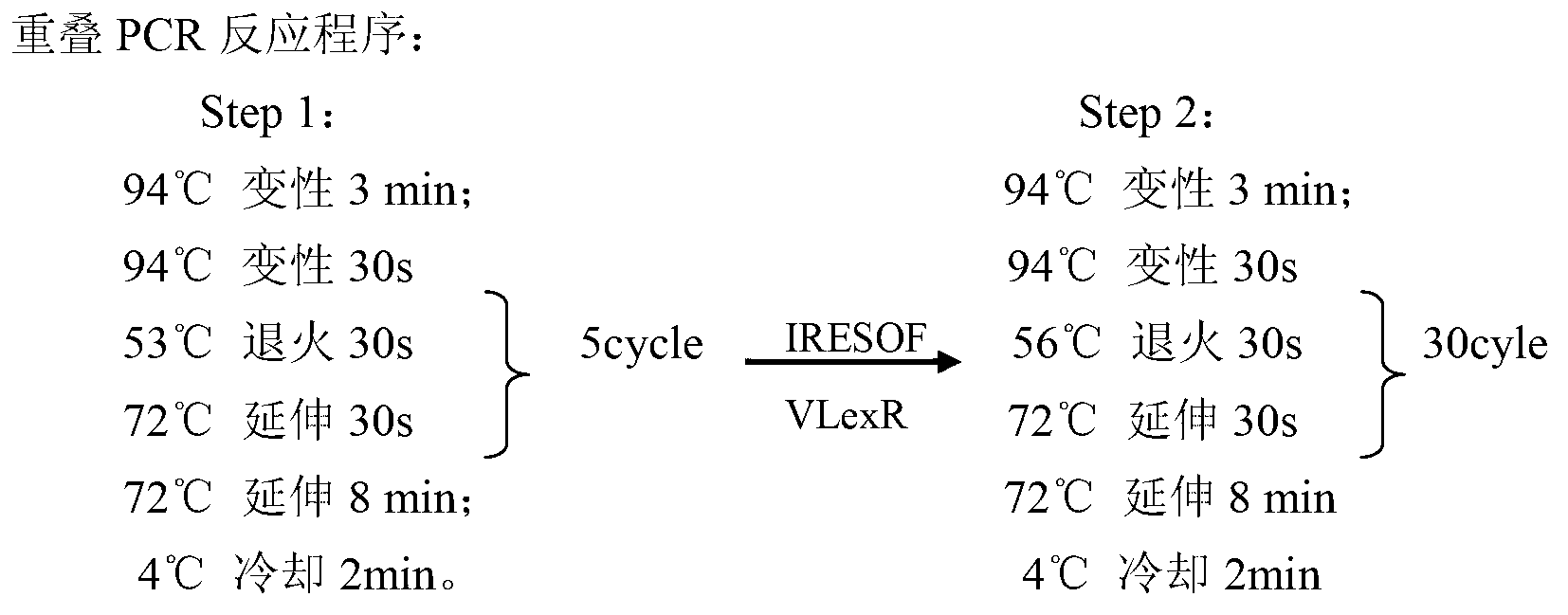
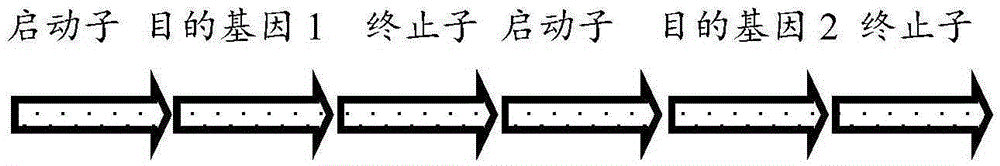
Method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in fermentation manner
The invention discloses a method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in a fermentation manner by virtue of recombinant Escherichia coli without adding exogenous L-proline. A recombinant plasmid carried by the recombinant Escherichia coli has a mutant gene proBA2 and hyp (4-hydroxyproline), wherein proBA2 is mutated on a glutamyl kinase encoding gene proB, and the inhibition effect of L-proline on glutamyl kinase encoded by the mutated gene is remarkably reduced. proBA2 and hyp are co-expressed, and trans-4-hydroxyproline can be produced directly from glucose in the fermentation manner without adding exogenous L-proline. The recombinant plasmid is obtained by recombining proBA2 and hyp onto the same expression plasmid or by co-transforming recombinant plasmids which contain the two genes respectively and have different resistances. The invention further discloses the application of the Escherichia coli to the production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Staphylococcal enterotoxin gene engineering reshaped antibody and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN103224560AOvercome the defects in the detection meansImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a staphylococcal enterotoxin gene engineering reshaped antibody and its preparation method and use. The staphylococcal enterotoxin gene engineering reshaped antibody has an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. Through construction of light and heavy chain eukaryotic co-expression vectors of the staphylococcal enterotoxin monoclonal antibody, a high-efficiency expression and stable-secretion mammalian cell line and the gene engineering reshaped antibody having high singularity and strong affinity are obtained. The staphylococcal enterotoxin gene engineering reshaped antibody can be used in staphylococcal enterotoxin detection, cell indirect immunofluorescence detection and flow cytometry detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Microalgae multigene co-expression vector and multigene co-expression microalgae
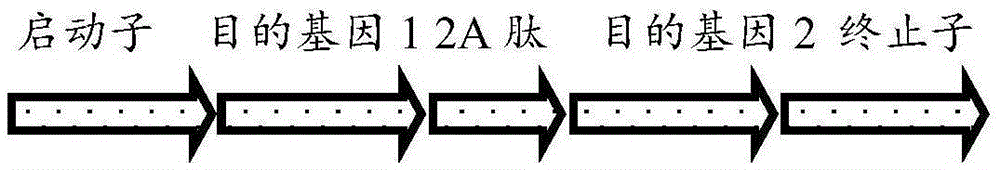
The invention discloses a microalgae multigene co-expression vector which is characterized in that the open reading frame of the expression vector adopts a Ubi promotor, an Nos promotor or an Hsp70A promotor; target genes are connected through 2A peptide sequences and built in one open reading frame of the expression vector.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Staphylococcal enterotoxin micromolecule antibody and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN103224561AImmunoglobulins against bacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionDisulfide bondingNatural antibody
The invention discloses a staphylococcal enterotoxin micromolecule antibody and its preparation method and use. The staphylococcal enterotoxin micromolecule antibody has an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. The preparation method comprises the following steps of designing and constructing eukaryotic mono-promoter co-expression vectors of staphylococcal enterotoxin monoclonal antibody light chain and heavy chain variable region genes, introducing cysteine residues to C- ends of the light chain and the heavy chain to form interchain disulfide bonds by an intracellular peptide fragment self-assembling principle, and simulating antigen binding domain spatial conformation of natural antibodies to obtain high-efficiency expression stable-secretion mammal cell line and the high-singularity strong-affinity micromolecule antibody. The staphylococcal enterotoxin micromolecule antibody can be used for staphylococcal enterotoxin detection, cell indirect immunofluorescence detection and flow cytometry detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
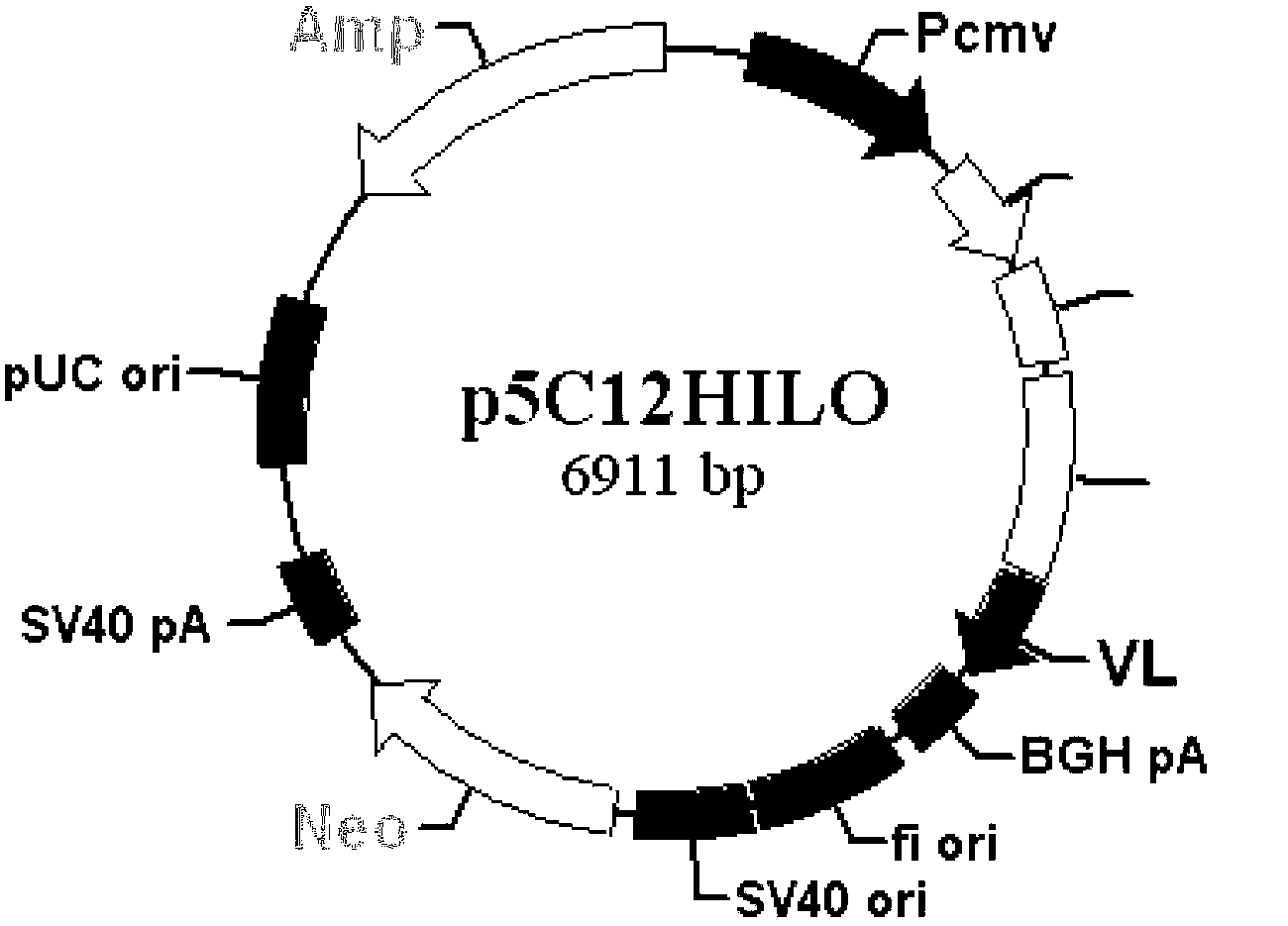
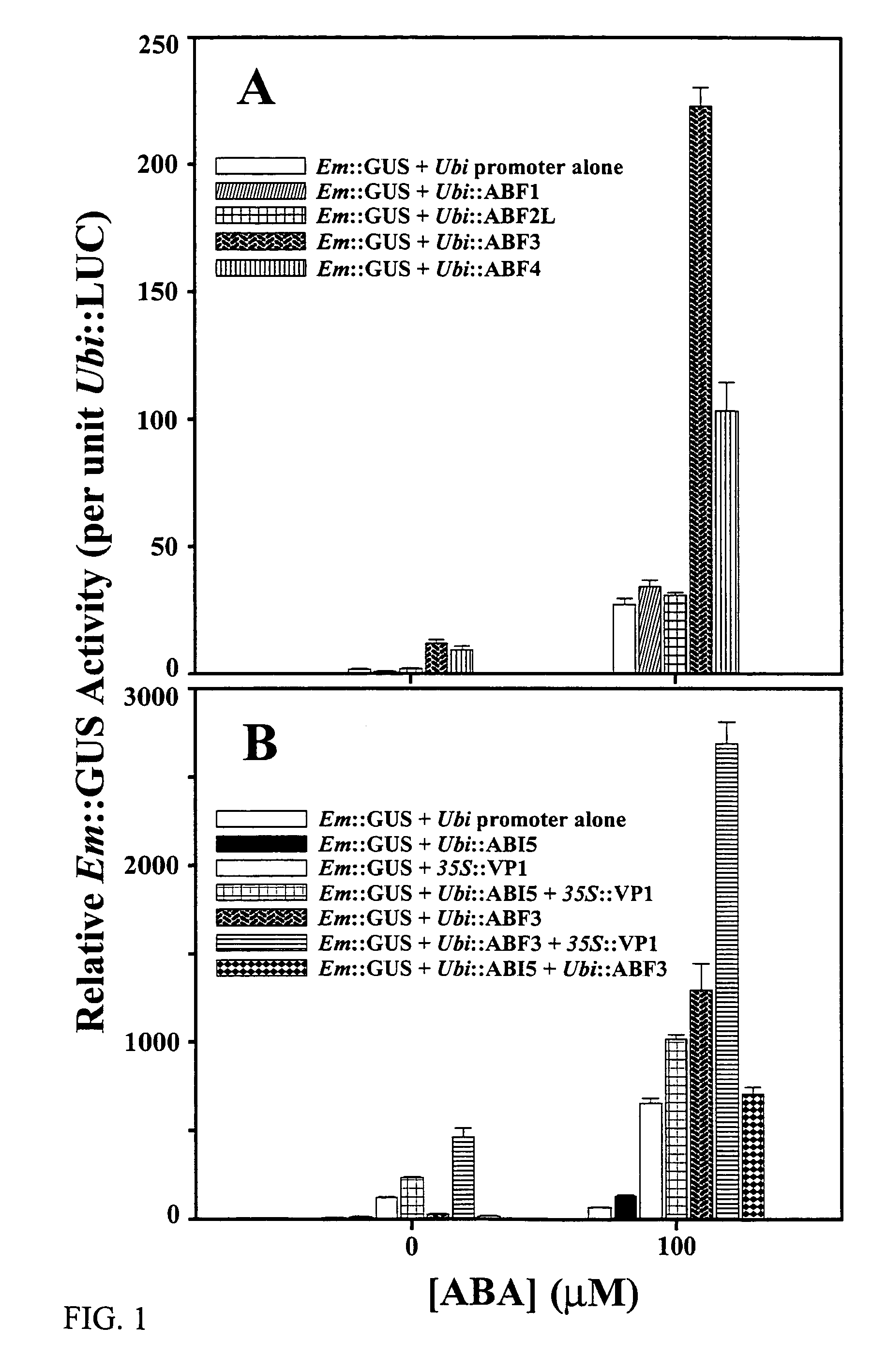
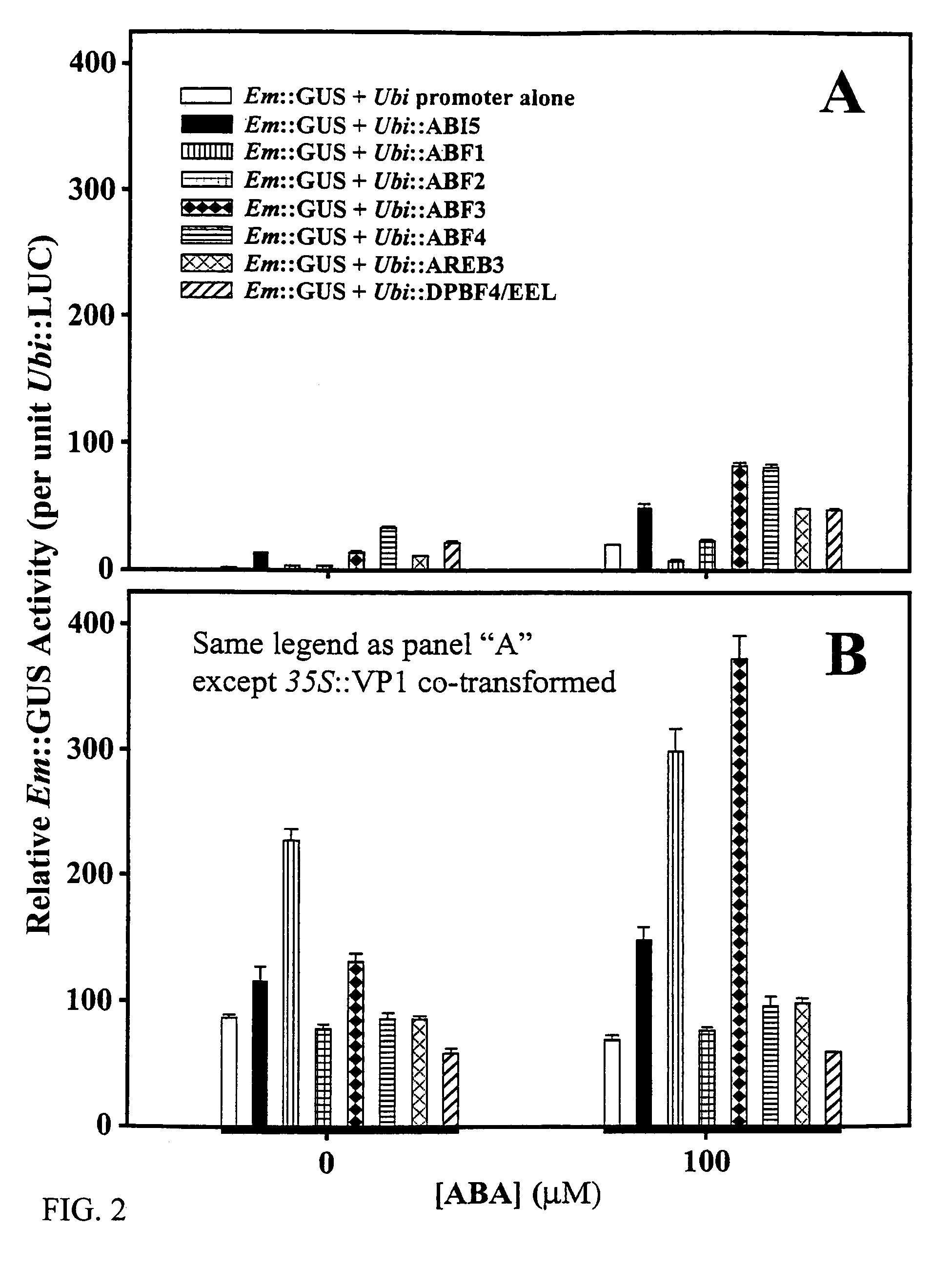
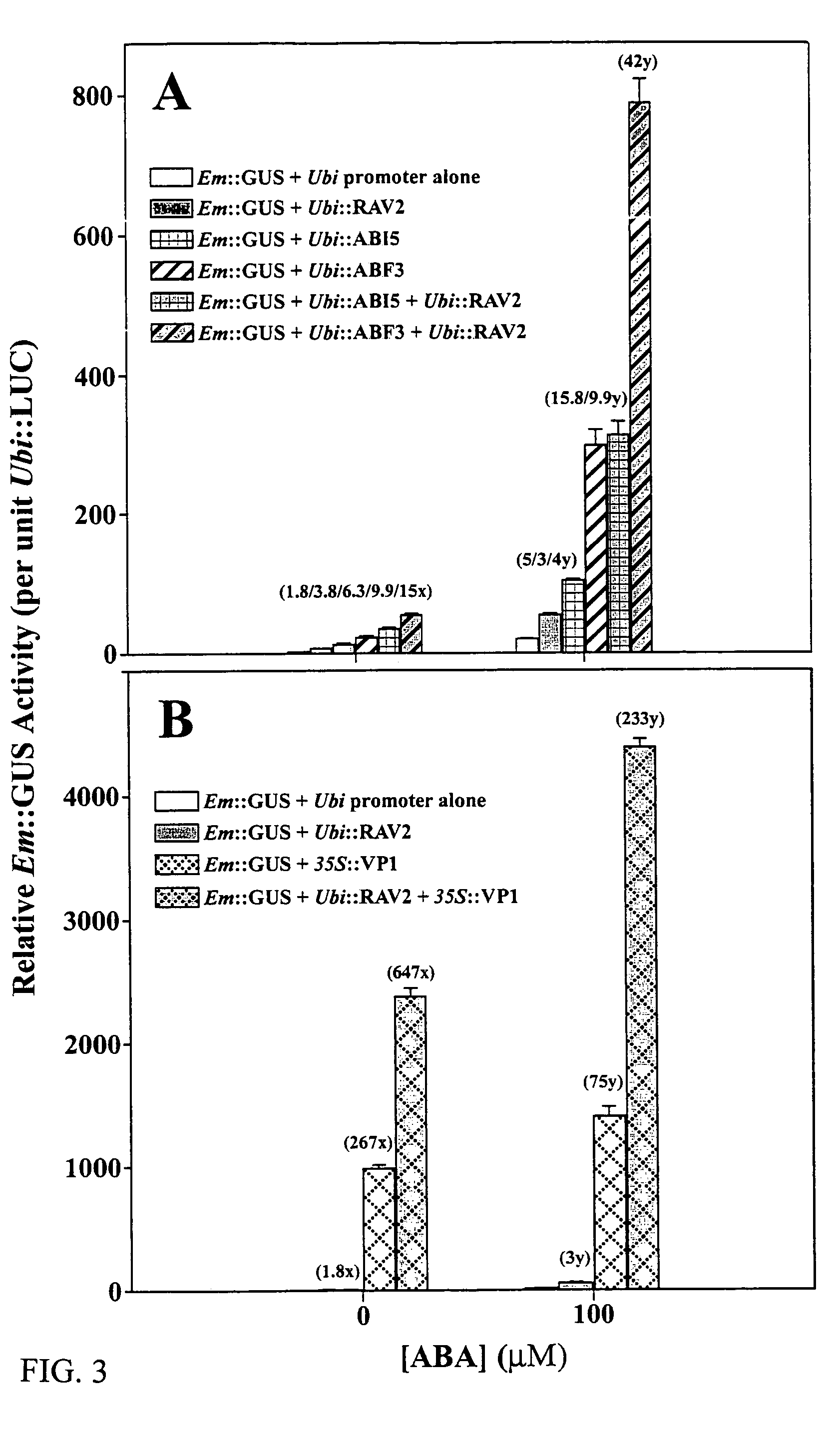
Transcription factors, DNA and methods for introduction of value-added seed traits and stress tolerance
Abscisic acid-inducible gene expression in different plant tissues is enhanced synergistically by the co-expression of a B3-domain transcription factor and various bZIP-domain transcription factors, or a different B3-domain transcription factor. Using these transcription factors in novel formulations, as shown by examples, will confer value-added traits to transgenic plants, including, but not limited to, higher levels of heterologous gene expression, drought and salt tolerance, viability and productivity under stress, and enhanced nutrient reserves and seed properties.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY
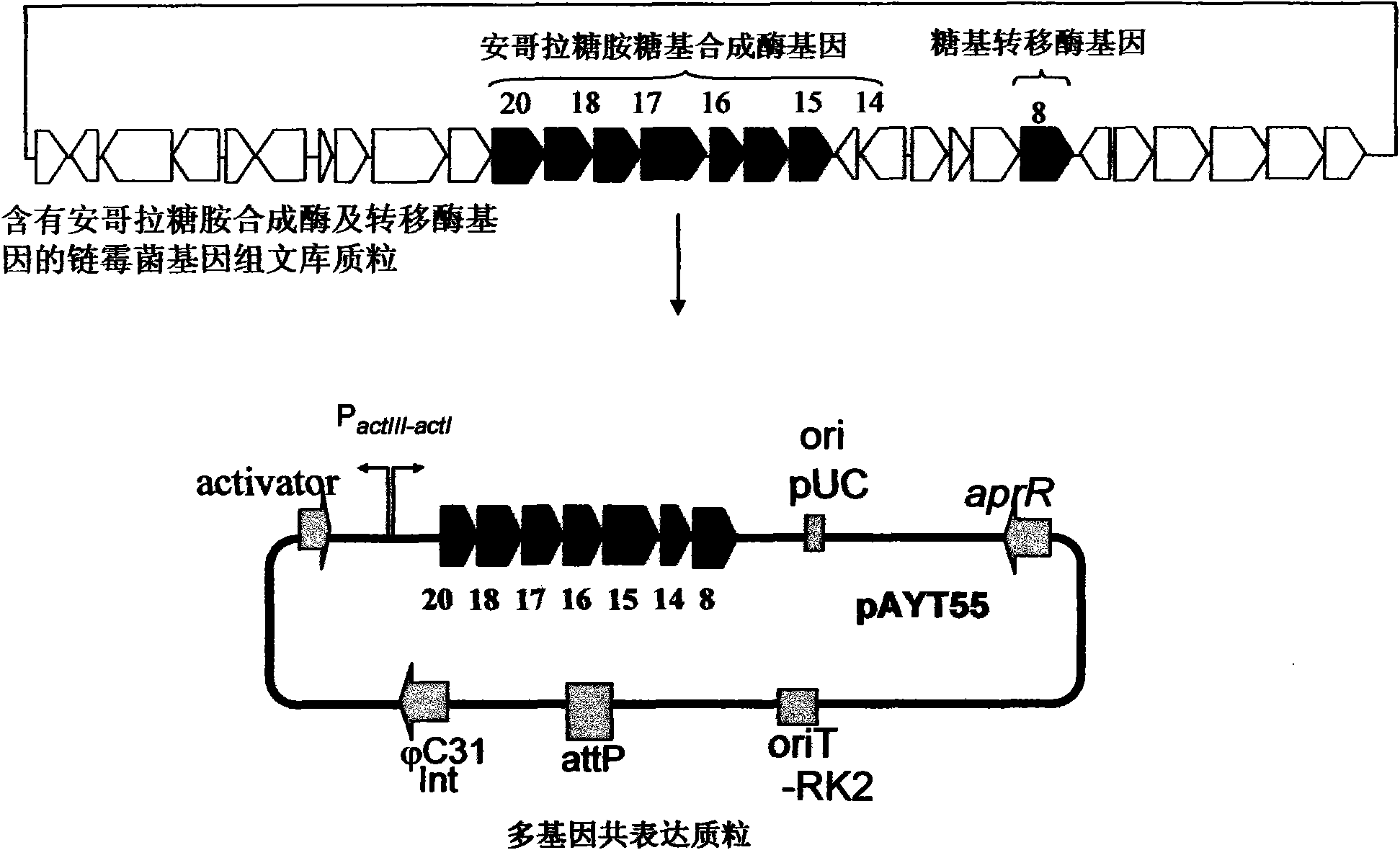
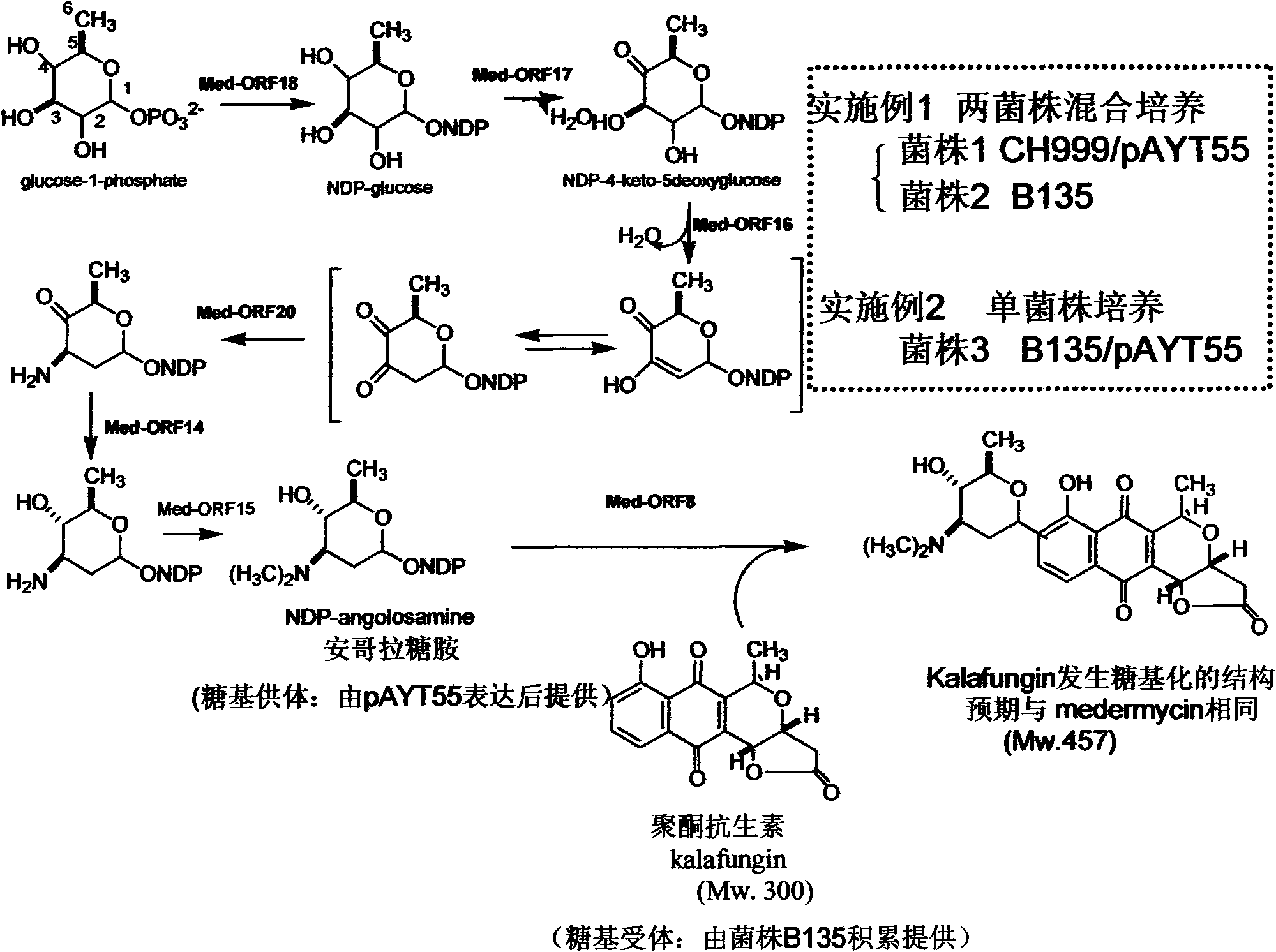
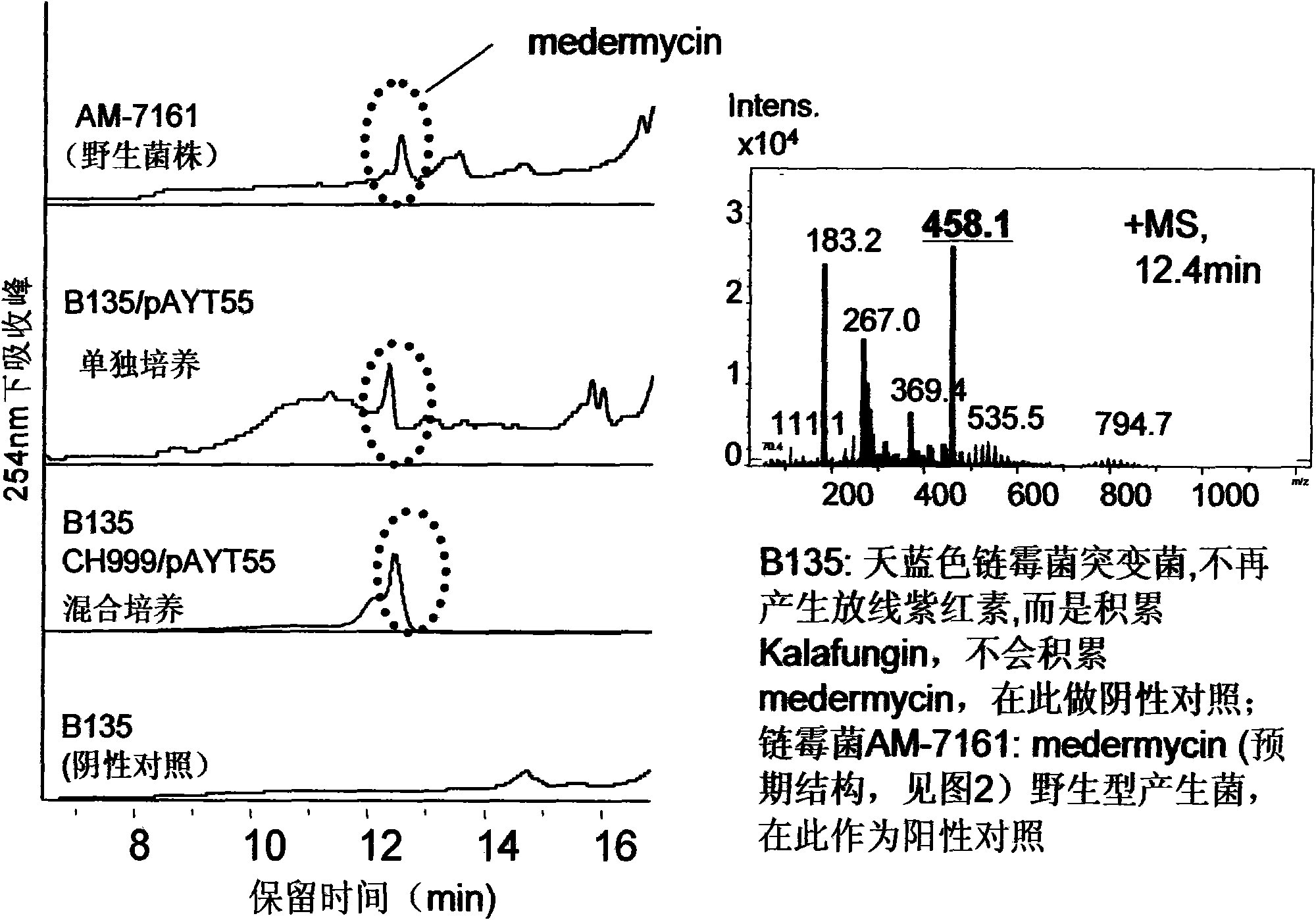
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
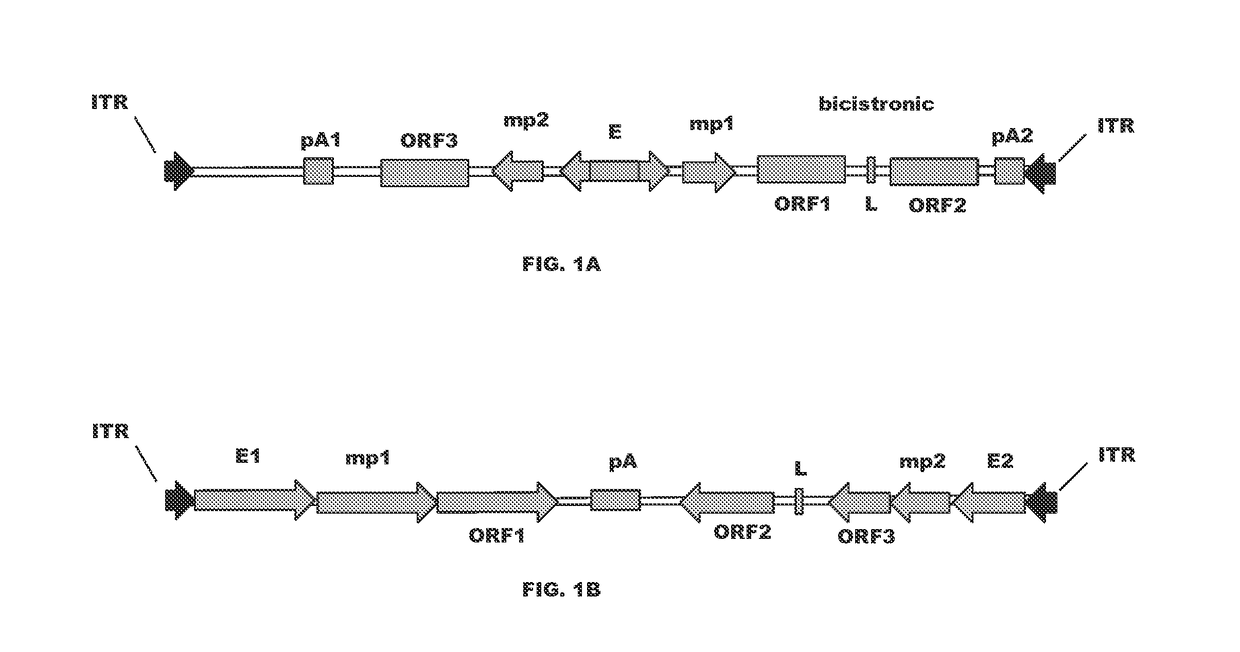
Compositions comprising aav expressing dual antibody constructs and uses thereof
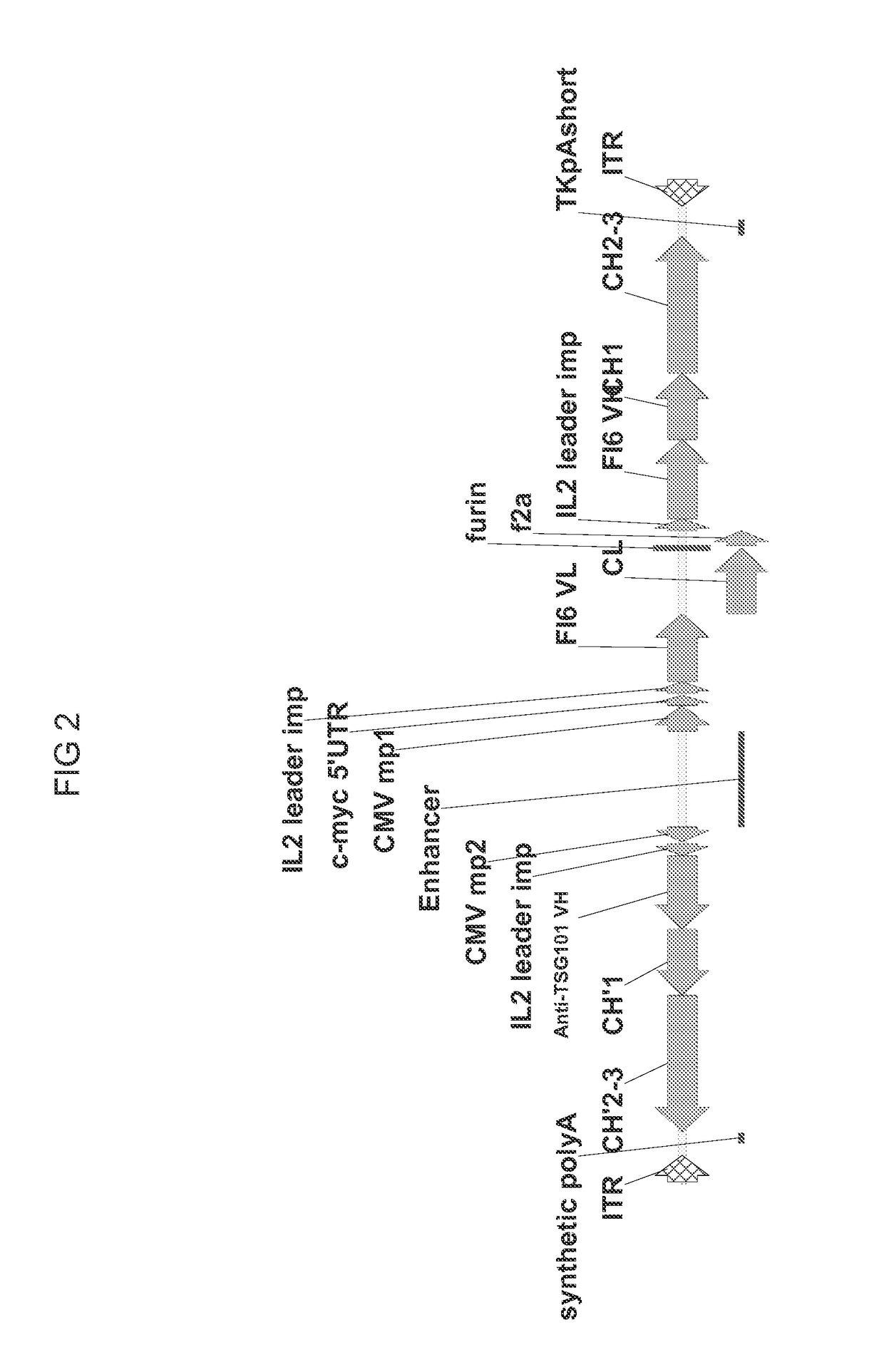
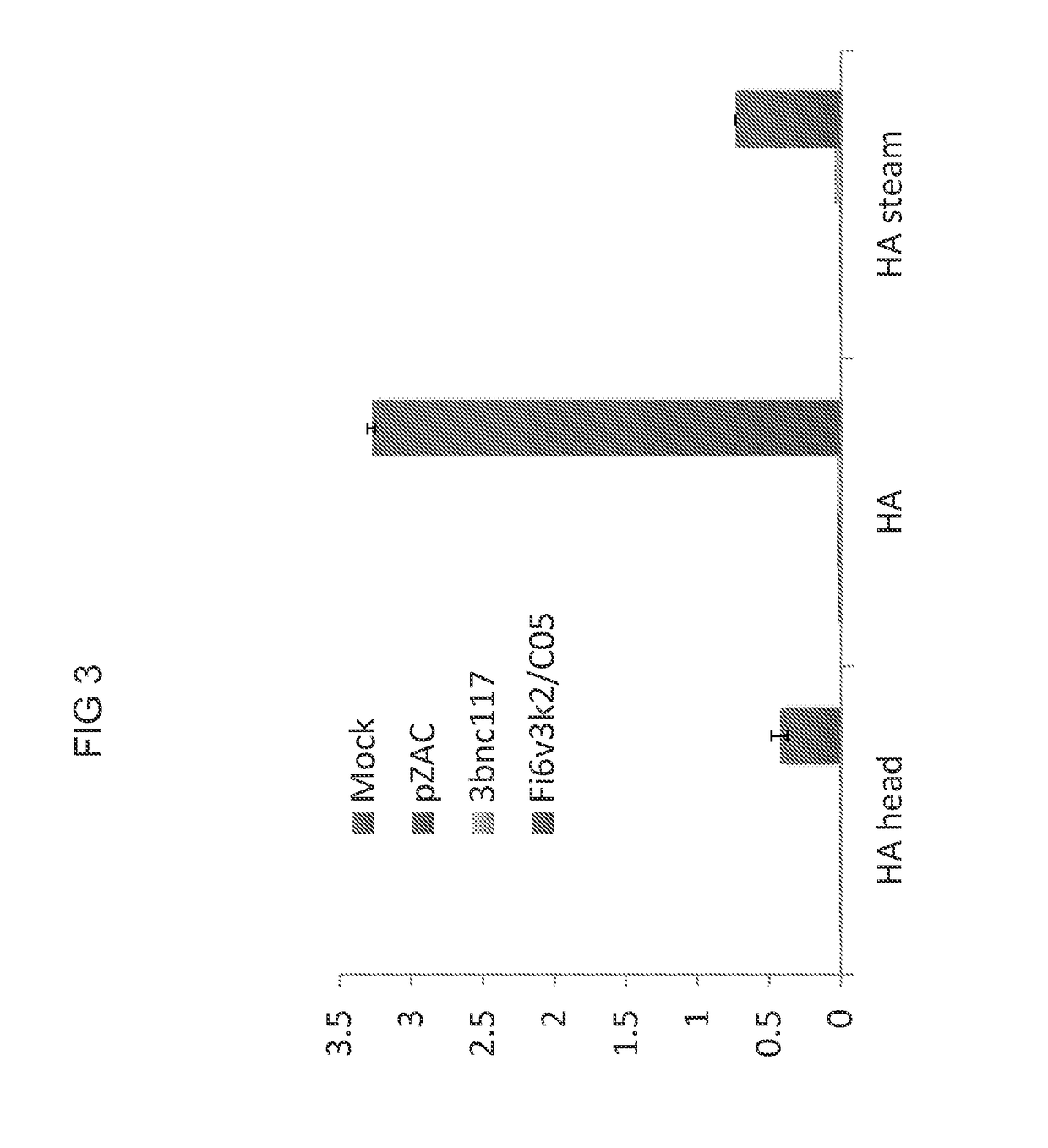
A recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) having an AAV capsid and packaged therein a heterologous nucleic acid which expresses two functional antibody constructs in a cell is described. Also described are antibodies comprising a heavy chain and alight chain from a heterologous antibody. In one embodiment, the antibodies are co-expressed from a vector containing: a first expression cassette which encodes at least a first open reading frame (ORF) for a first immunoglobulin under the control of regulatory control sequences which direct expression thereof; and a second expression cassette which comprises a second ORF, a linker, and a third ORF under the control of regulatory control sequences which direct expression thereof, wherein the second and third ORF encode a second and third immunoglobulin construct. The vector co-expressing these two antibody constructs is in one embodiment an AAV, in which the 5′ and 3′ ITRs flank the expression cassettes and regulatory sequences.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com