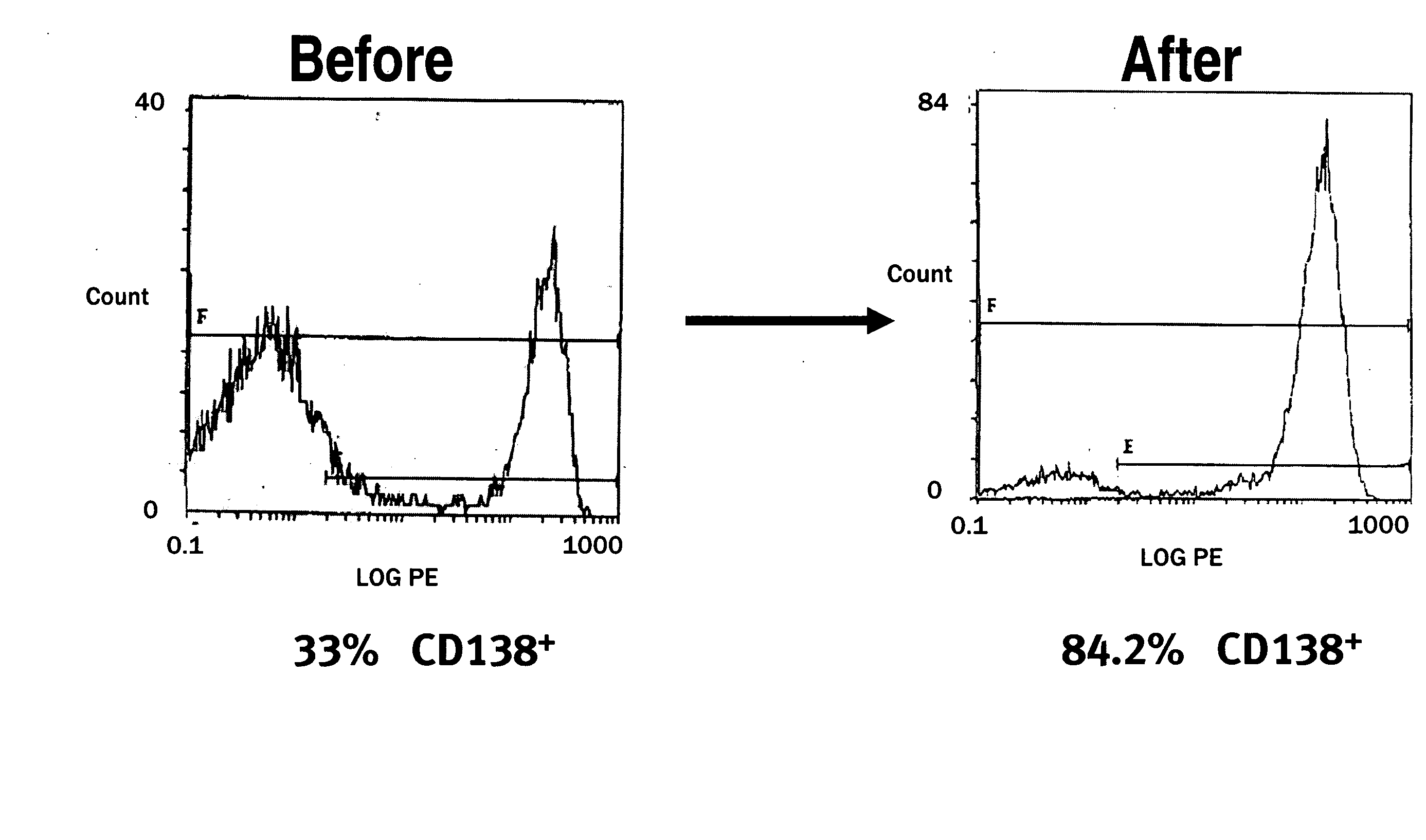
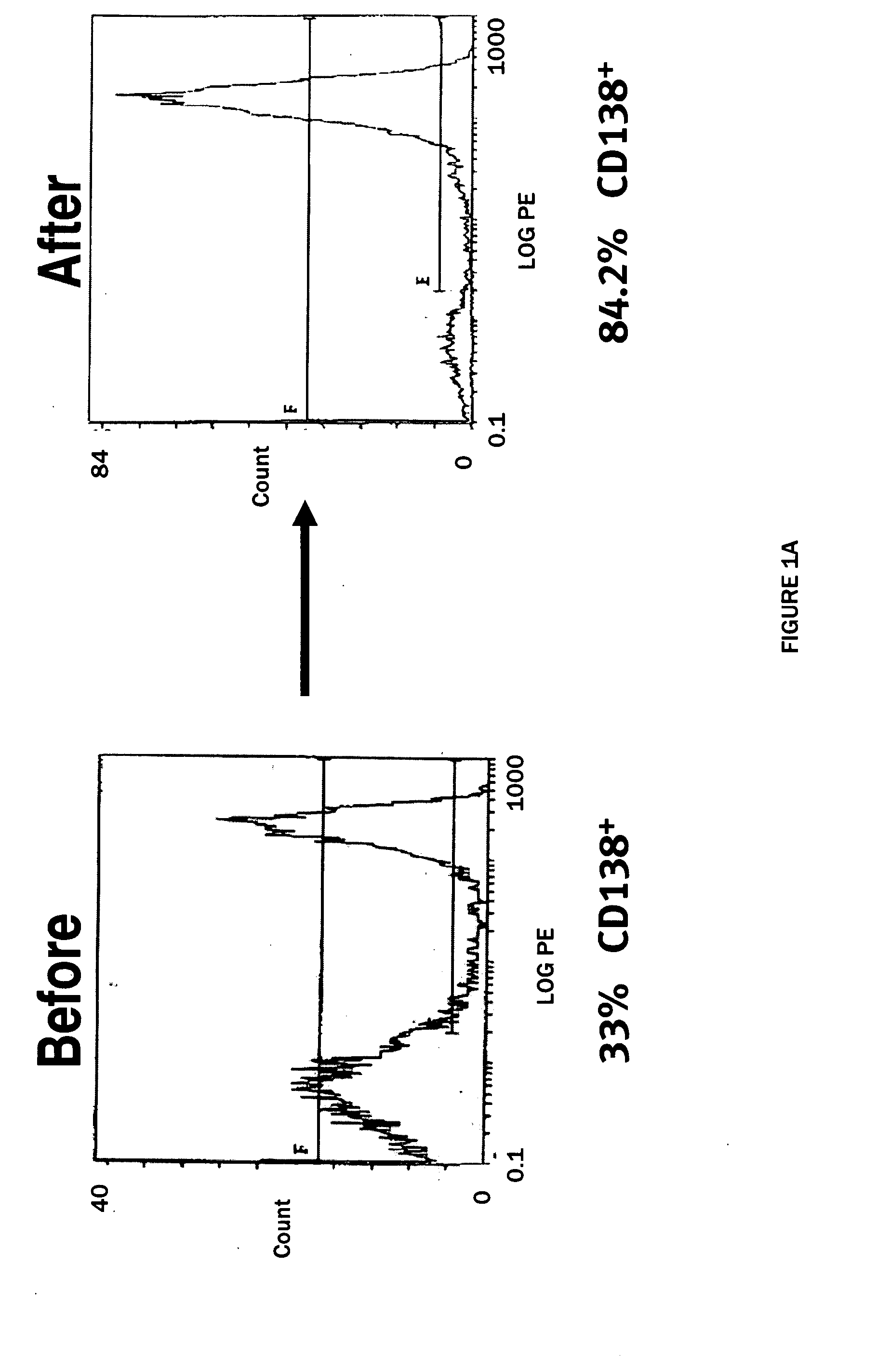
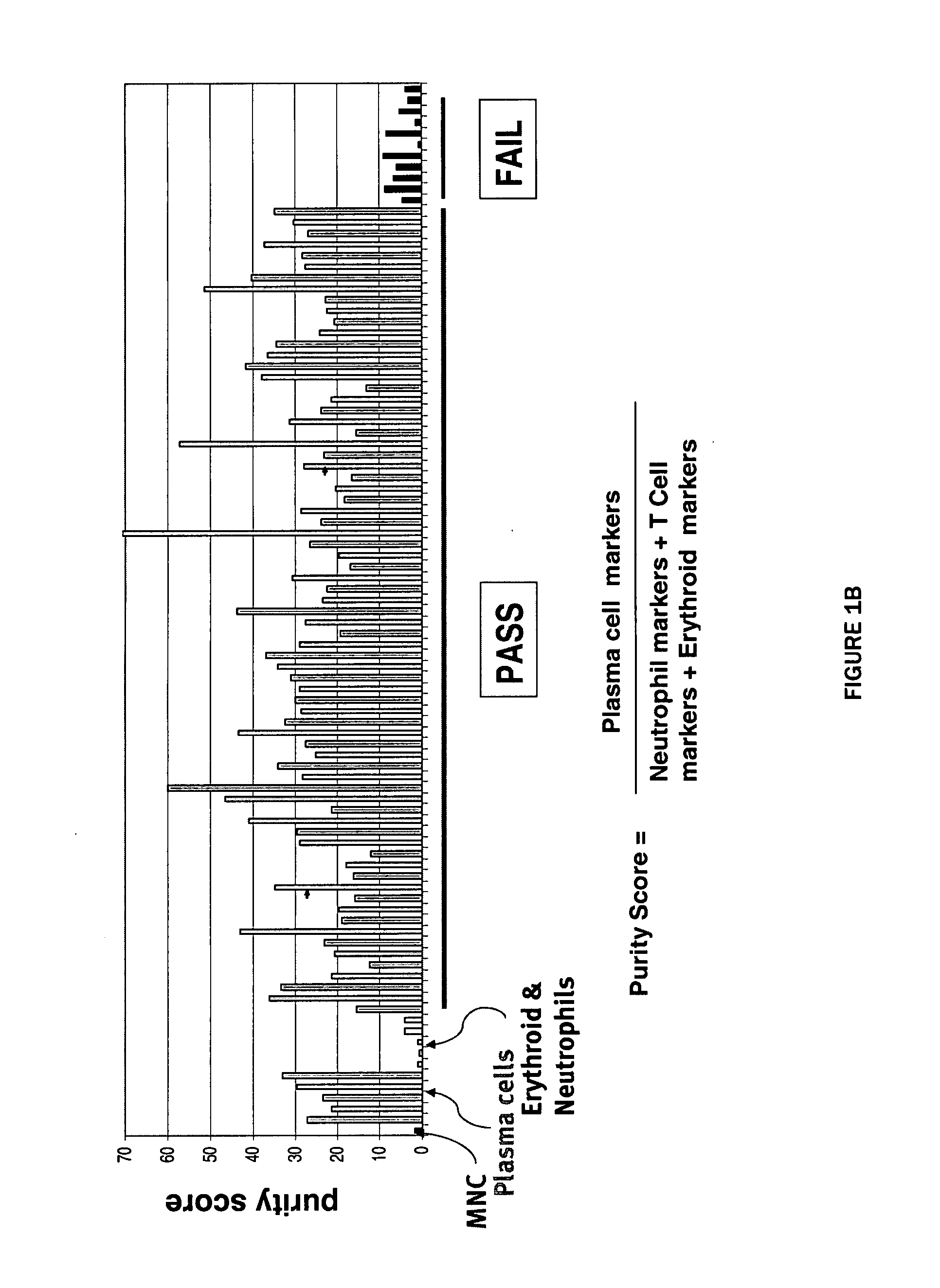
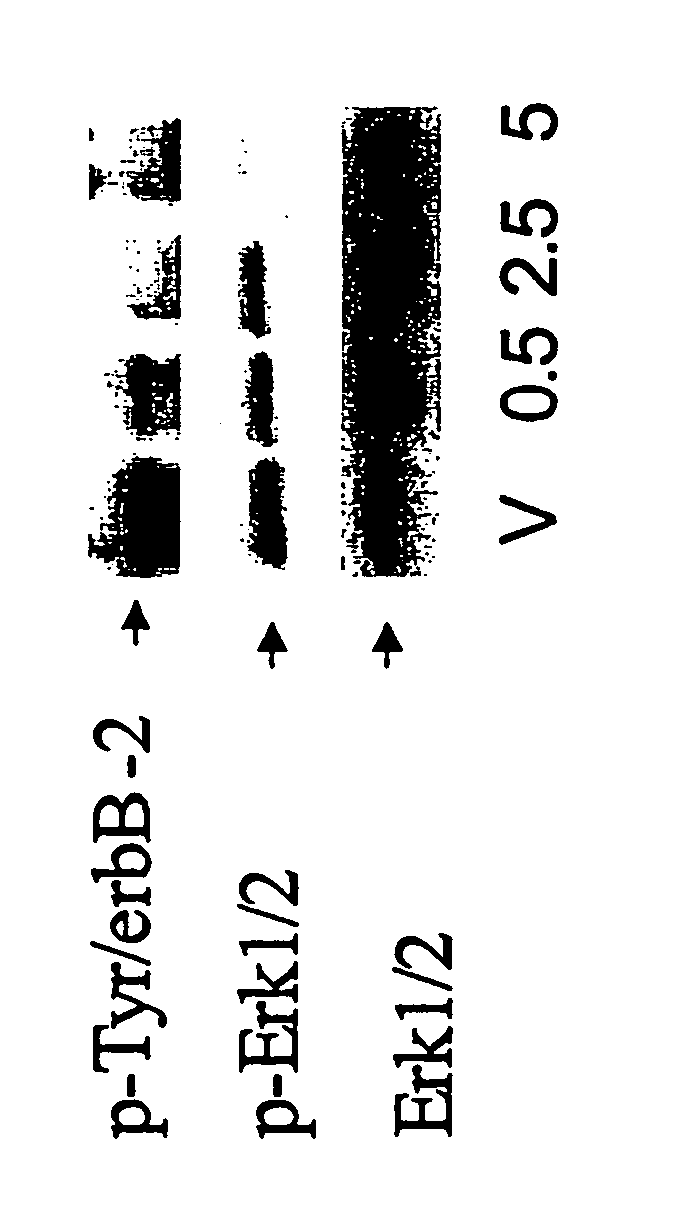
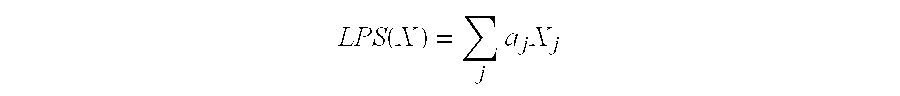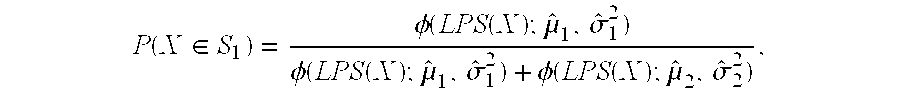Patents
Literature
95 results about "Predictive marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A predictive marker is a particular protein or gene that indicates sensitivity or resistance to a specific therapy. The use of predictive markers is becoming increasingly relevant in cancer therapy as it allows for better identification of patients who will respond positively to the therapy. In the clinical setting, predictive markers are limited to use in breast cancer. Expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors can determine the benefits of hormone therapy, whilst the benefit of treating breast cancer patients with herceptin (Trastuzumab) is determined by the expression of HER2. There are many advantages to utilizing a predictive marker in cancer therapy including better patient management minimizing unnecessary suffering from side effects with ultimately the wrong treatment choice, reducing loss of precious time whilst determining whether a therapy will provide any benefit, and a reduction in cost to both the patient and the wider health community.
Methods for the identification, assessment, and treatment of patients with cancer therapy
ActiveUS20060281122A1Reduced growth rateEliminate ineffective or inappropriate therapeutic agentsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthRegimen
The present invention is directed to the identification of predictive markers that can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to treatment. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain individual and / or combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen. Thus, by examining the expression levels of individual predictive markers and / or predictive markers comprising a marker set, it is possible to determine whether a therapeutic agent, or combination of agents, will be most likely to reduce the growth rate of tumors in a clinical setting.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Predictive markers for ovarian cancer
ActiveUS20090004687A1High precision testAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsPredictive markerPhases of clinical research
Methods are provided for predicting the presence, subtype and stage of ovarian cancer, as well as for assessing the therapeutic efficacy of a cancer treatment and determining whether a subject potentially is developing cancer. Associated test kits, computer and analytical systems as well as software and diagnostic models are also provided.
Owner:ASPIRA WOMENS HEALTH INC
Molecular Diagnostic Test for Cancer
InactiveUS20140342924A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCancer typeAntiangiogenic therapy
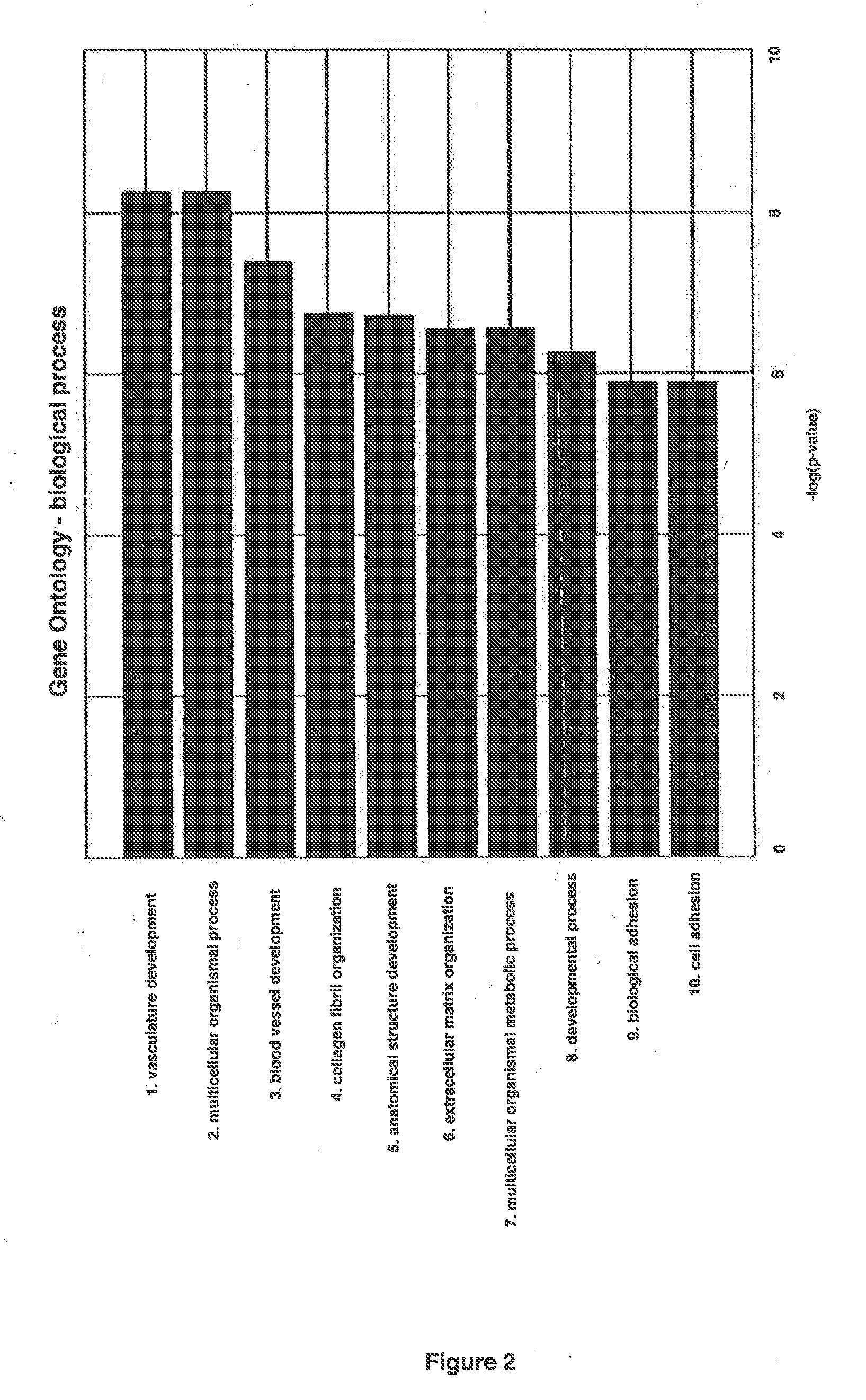
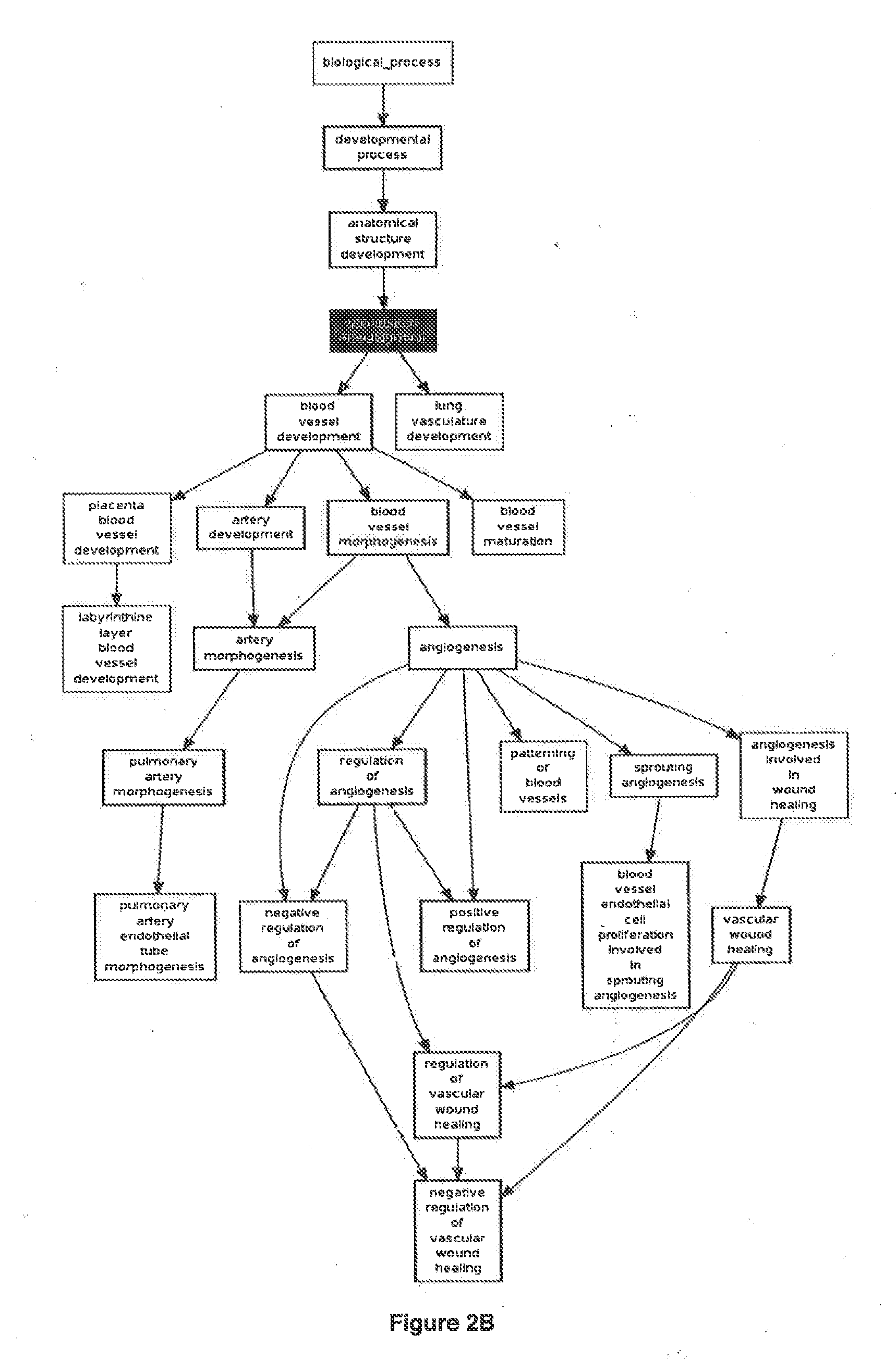
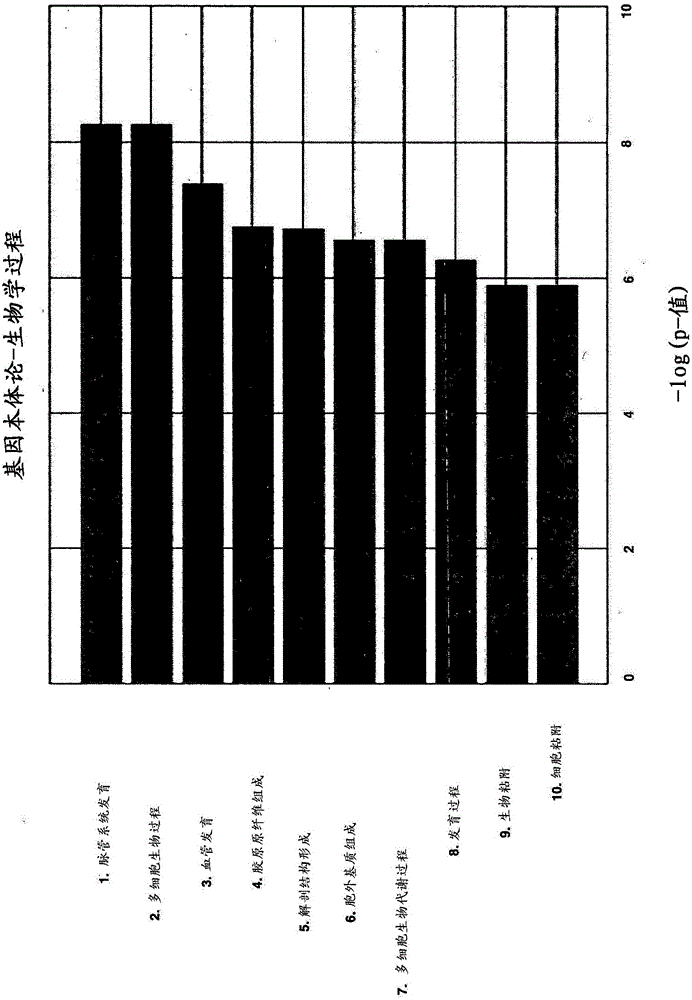
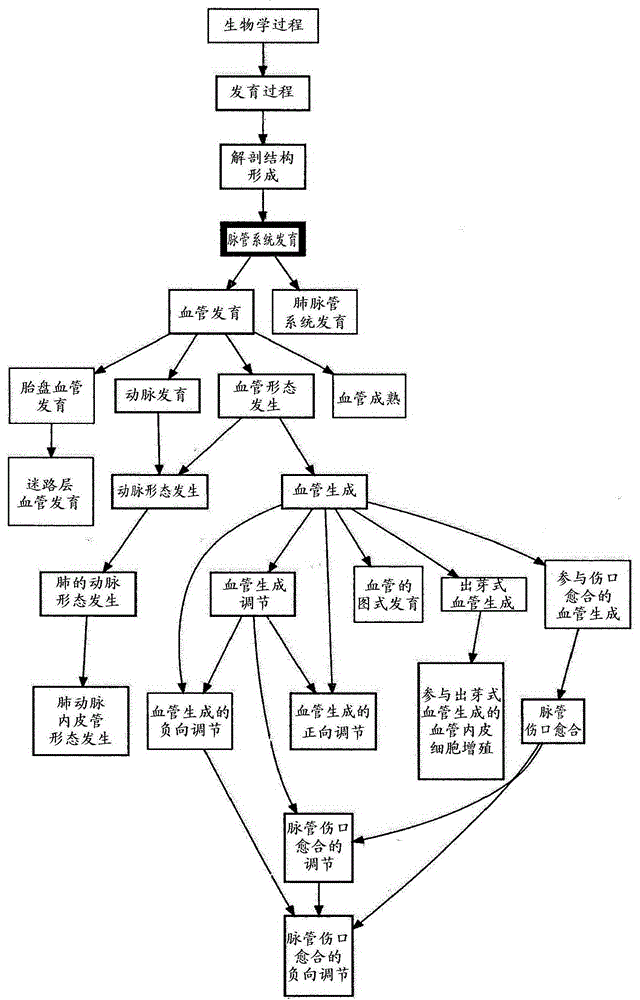
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for cancer. The test identifies cancer subtypes that are responsive to anti-angiogenesis therapeutics and enables classification of a patient within this subtype. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any anti-angiogenic agent. This test may be used in different cancer types and with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect angiogenesis or angiogenesis signalling. In addition, the present invention may be used as a prognostic indicator for certain cancer types. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS SERVICES LIMITED
Methods for the identification, assessment, and treatment of patients with cancer therapy
ActiveUS20080064055A1Prolong survival timeEliminate inefficienciesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingShort term survivalPatient survival
The present invention is directed to the identification of predictive markers that can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are expected to demonstrate long term or short term survival times. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain individual and / or combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with expected short term or long term survival. Thus, by examining the expression levels of individual predictive markers and / or predictive markers comprising a marker set, it is possible to determine predicted patient survival.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Predictive markers in cancer therapy
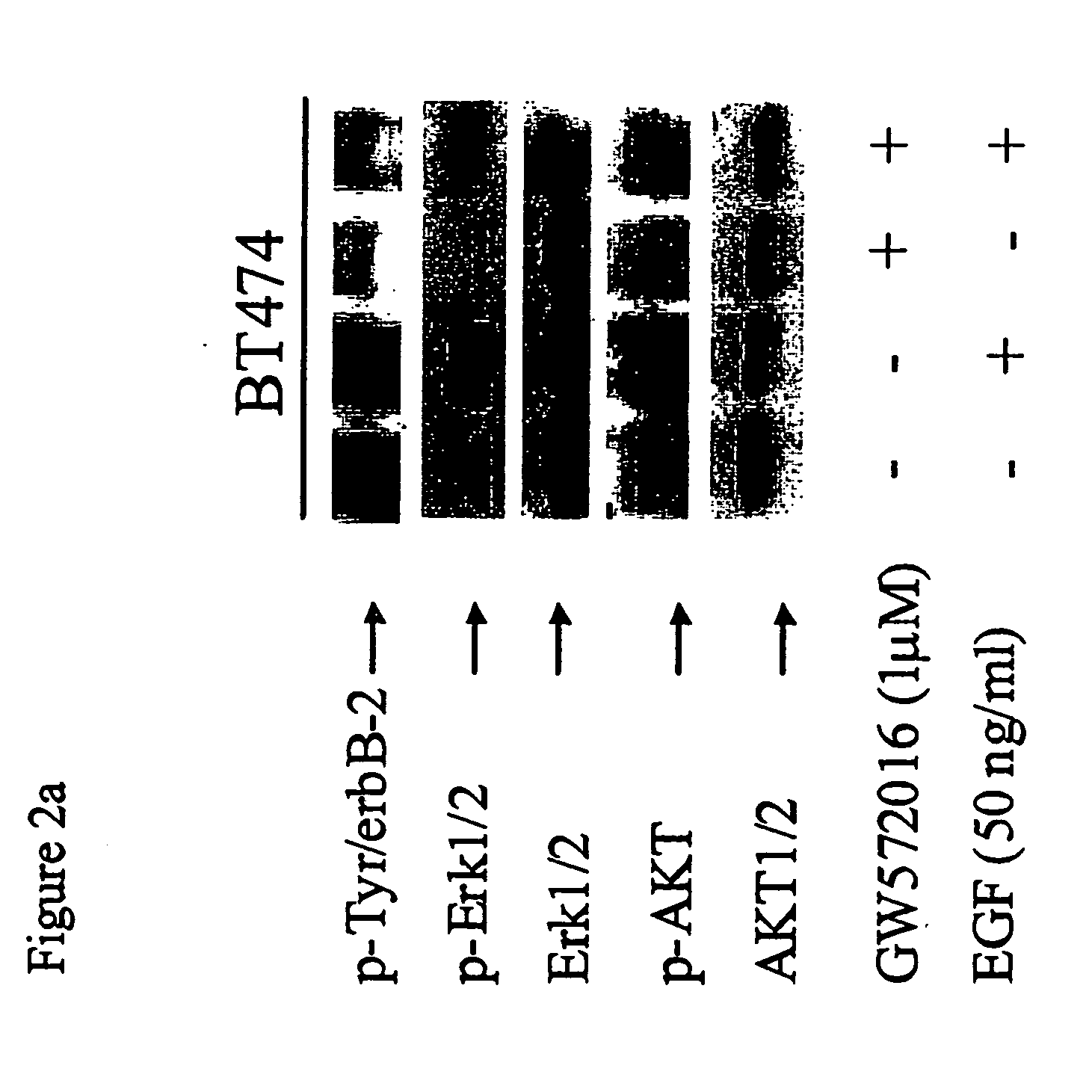
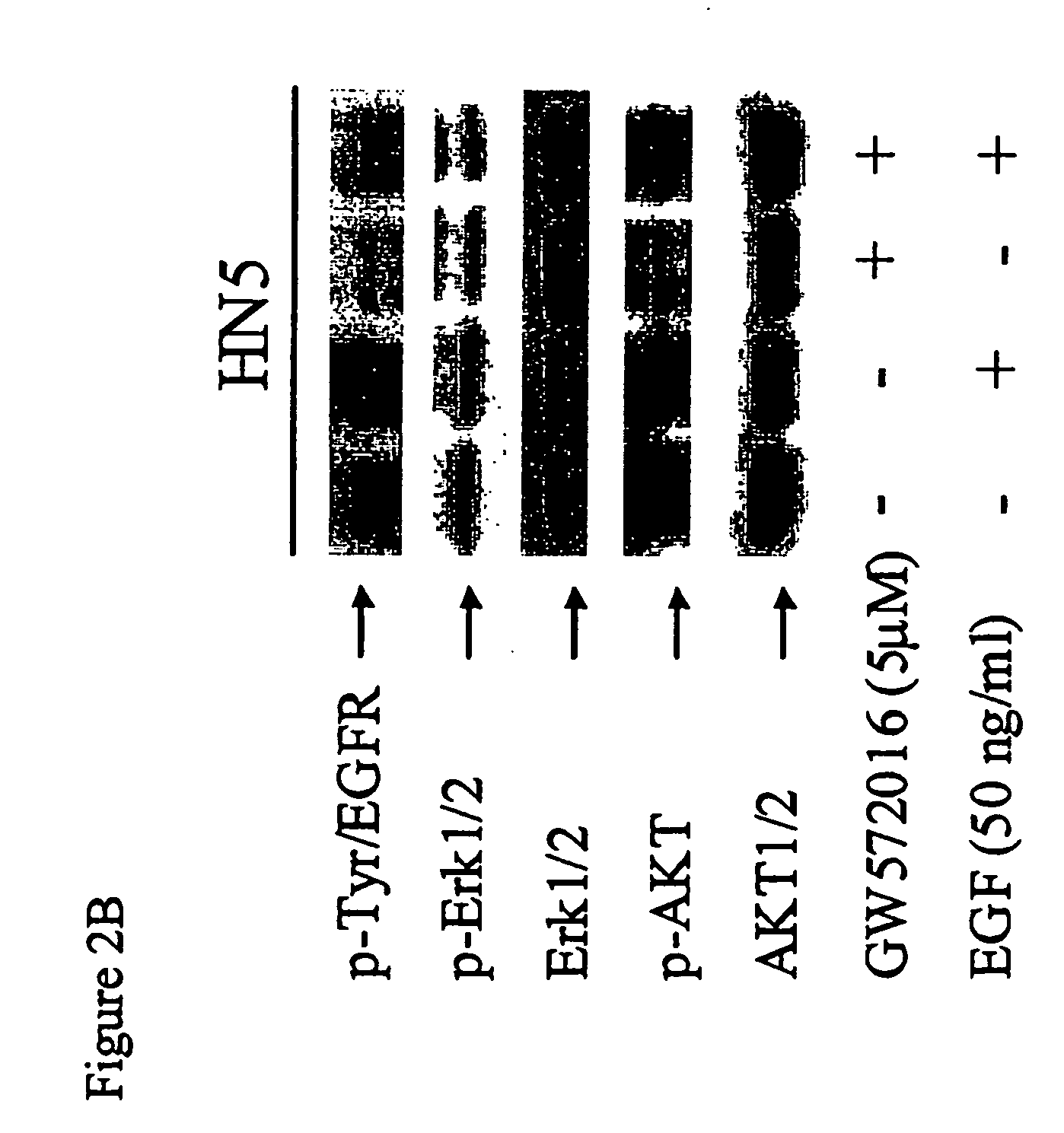
InactiveUS20060094068A1Remarkable effectMinimal toxicityBiocideBiological material analysisAbnormal tissue growthPhosphorylated erk
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Genes involved estrogen metabolism
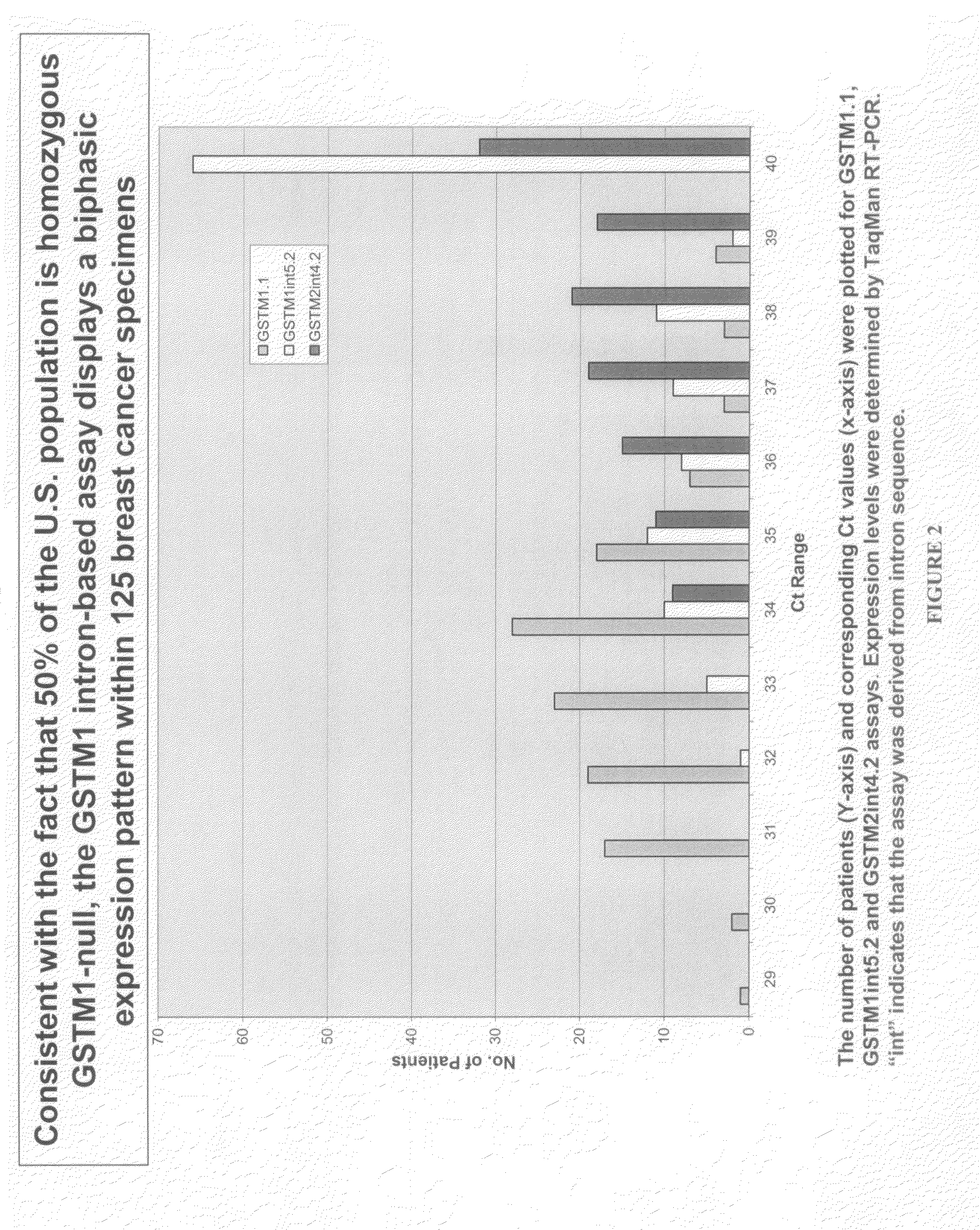
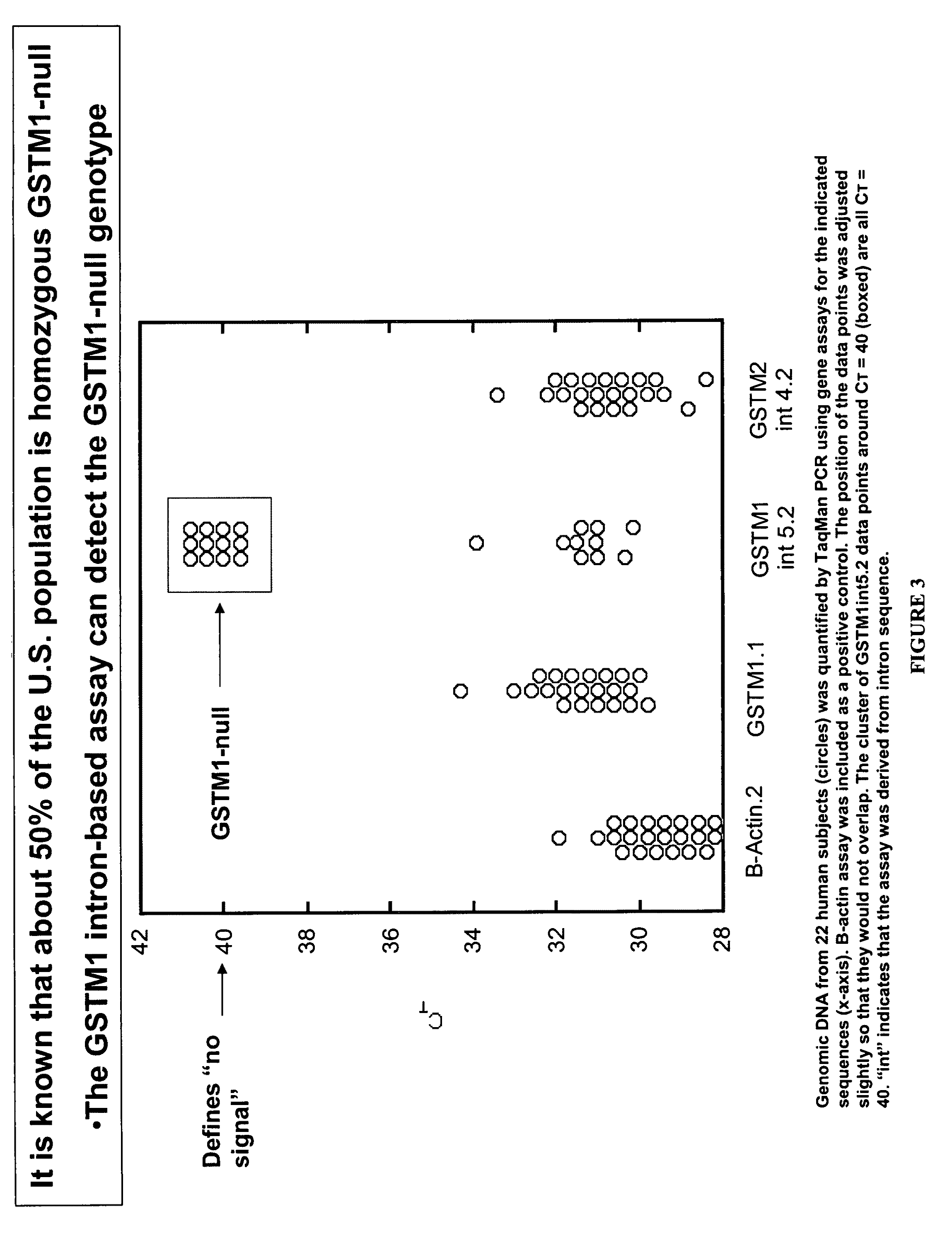
ActiveUS7888019B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEstrogen MetabolismPharmaceutical drug
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication
InactiveCN106295246ASimple processSimple methodBiostatisticsProteomicsDifferential codingPredictive marker
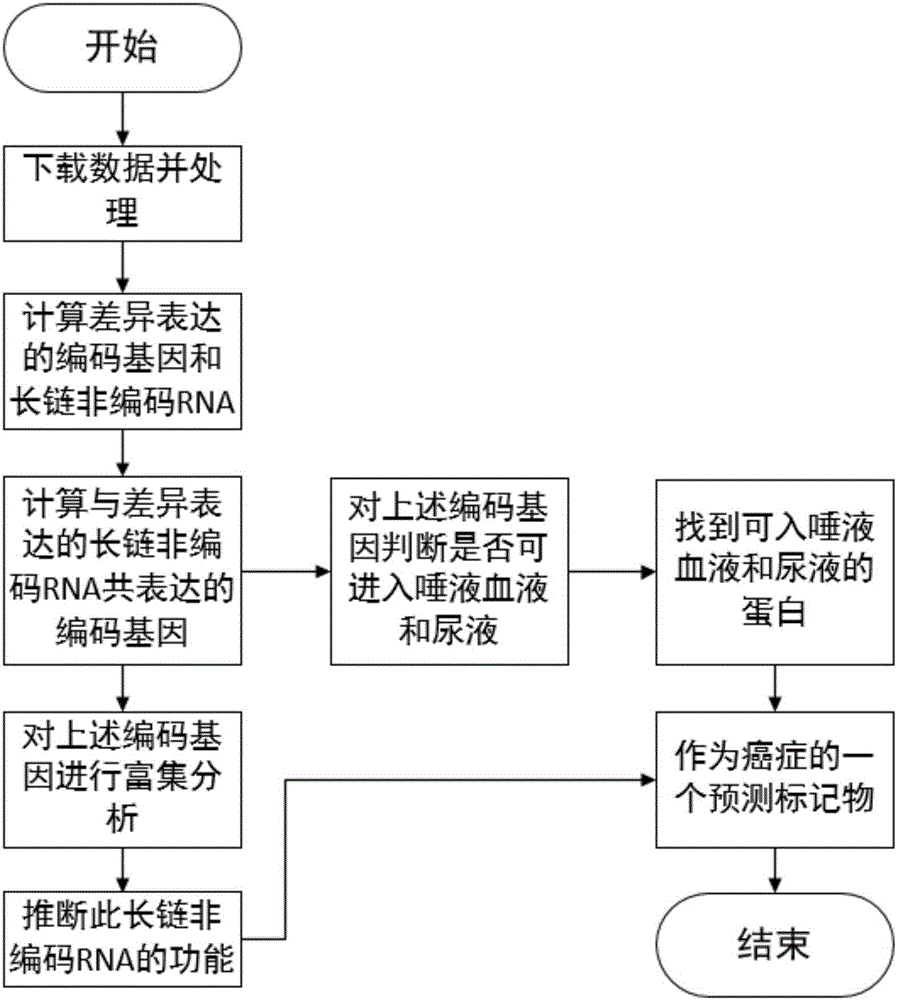
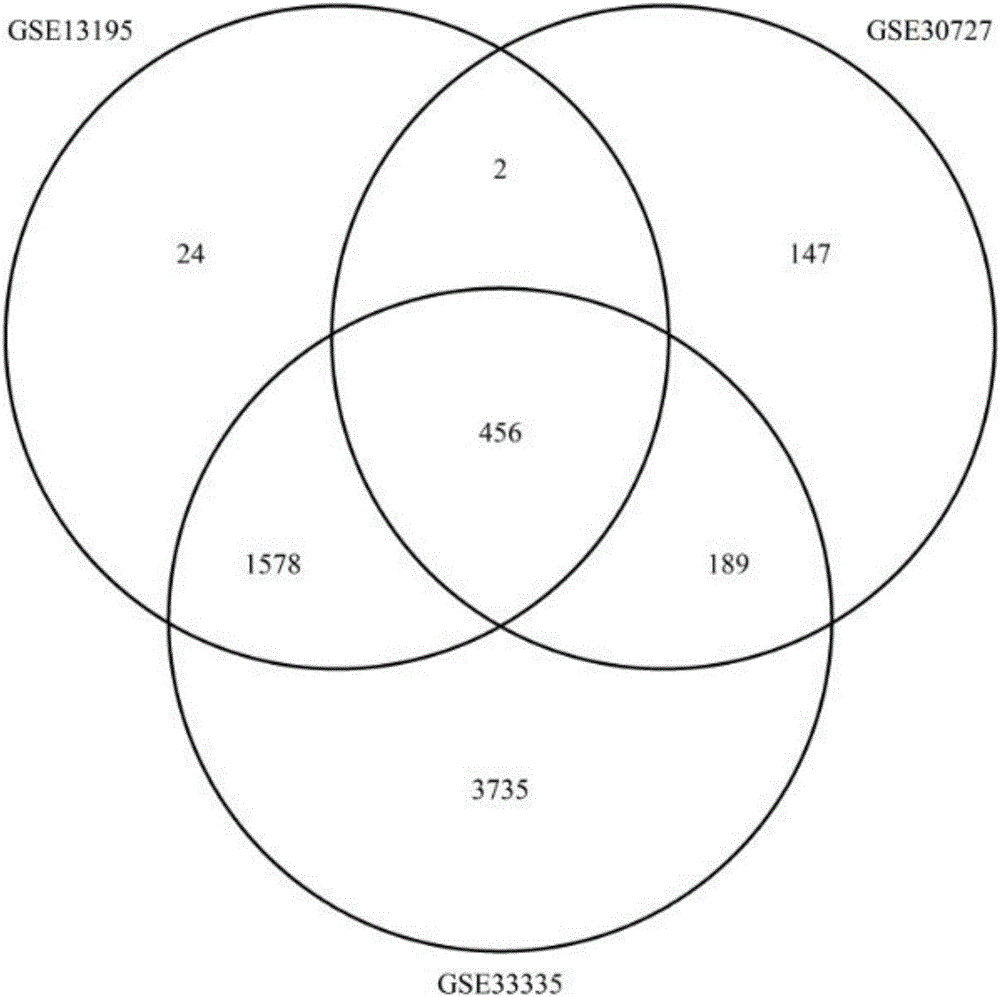
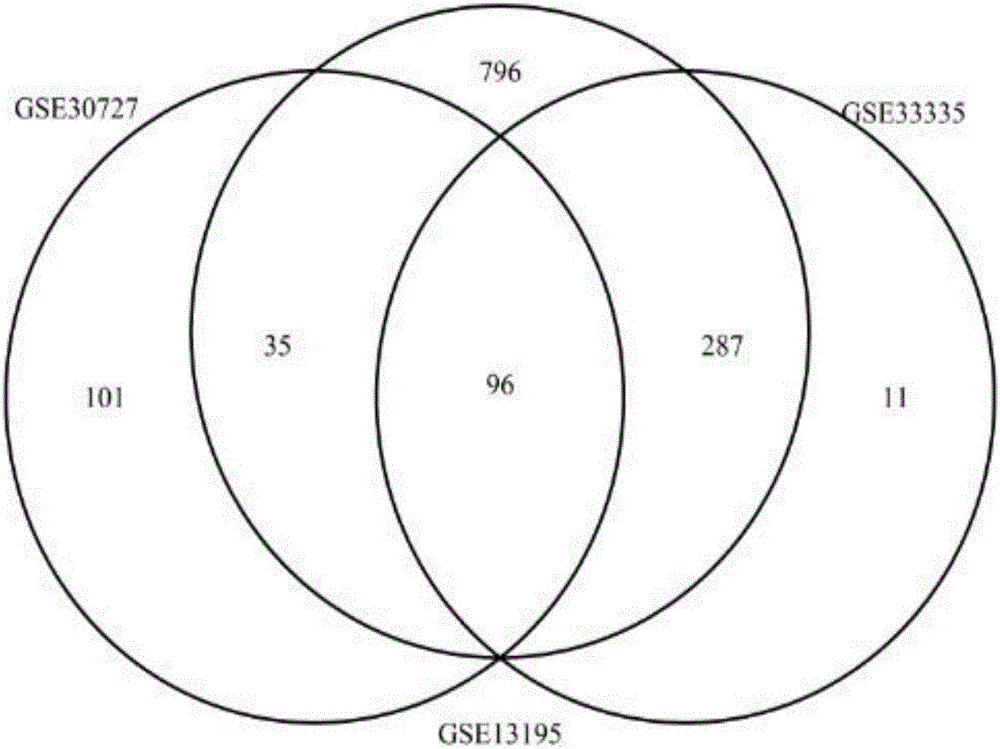
The invention relates to tumor-related IncRNA and tumor-related IncRNA function predication. By taking differential expression of IncRNA in tumors as diagnosis references, a process for finding a relation between IncRNA and tumors includes: step one, downloading data from GEO database, processing the data to obtain expression data of part of IncRNA and exons; step two, subjecting the processed expression data to differential expression analysis; step three, analyzing co-expression and differential coding genes and IncRNA for IncRNA in differential expression; step four, subjecting the coding genes to probe platform annotation; step five, further screening the IncRNA in differential expression to select out most obviously differential IncRNA; step six, performing enrichment analysis to obtain a GOBP process and pathyway, and speculating IncRNA functions through coding gene related biological processes; step seven, analyzing whether common coding genes obtained at the step six can enter blood, saliva and urine or not, analyzing genes which are allowed to enter, and taking the genes and IncRNA as potential predication marks of cancers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Molecular diagnostic test for cancer
ActiveUS20160002732A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCancer typeAngiogenesis growth factor
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for cancer. The test identifies cancer subtypes that have an up-regulation or a down-regulation in biomarker expression related to angiogenesis and vascular development. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any anti-angiogenic agent. This test may be used in different cancer types and with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect angiogenesis or angiogenesis signalling. In addition, the present invention may be used as a prognostic indicator for certain cancer types. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS SERVICES LIMITED
Molecular diagnostic test for cancer
InactiveCN105102631AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsCancer typeAngiogenesis growth factor
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for cancer. The test identifies cancer subtypes that have an up-regulation or a down- regulation in biomarker expression related to angiogenesis and vascular development. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any anti- angiogenic agent. This test may be used in different cancer types and with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect angiogenesis or angiogenesis signalling. In addition, the present invention may be used as a prognostic indicator for certain cancer types. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS LIMITED
Molecular diagnostic test for cancer
ActiveUS20140051591A1Inorganic active ingredientsHealth-index calculationCancer typeChemotherapeutic drugs
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for cancer. The test defines a novel DNA damage repair deficient molecular subtype and enables classification of a patient within this subtype. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with cancer are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any chemotherapy. This test may be used in different cancer types and with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect DNA damage or repair, such as many of the standard cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs currently in use. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS SERVICES LIMITED
Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer's Disease
The present invention relates to novel methods for the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. In addition, the invention relates to methods for assessing an individual's susceptibility or pre-disposition to Alzheimer's disease. The methods of the present invention involve the use of therapeutic targets and diagnostic and / or predictive markers within the mTOR signalling pathway. The methods also involve screening subjects for genetic polymorphisms associated with rapamycin-sensitive genes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
Predictive Markers For Cancer and Metabolic Syndrome
InactiveUS20130338027A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningVascular diseasePredictive biomarker
Disclosed are predictive biomarkers and methods of use for the determination of insulin resistance and sensitivity, in addition to cardiovascular disease and risk associated with obesity. Methods for the stratification of patients along continuum of susceptibility to cardiometabolic risk, including prediction and progression to metabolic syndrome are also provided.
Owner:NUCLEA BIOMARKERS
Circulating ve-cadherin as a predictive marker of sensitivity or resistance to Anti-tumoral treatment and improved method for the detection of soluble proteins
InactiveUS20100120171A1Reliable measurementDisease diagnosisBiological testingProtein detectionPredictive marker
The application relates to improved means for the detection of soluble protein(s), such as soluble angiogenesis-related protein(s), more particularly circulating VE-cadherin. These means notably comprise the dilution of the fluid sample (e.g., serum or plasma sample), before submitting it to protein detection. Said dilution is advantageously diluted in a surfactant-containing solution. The improved means of the invention enabled to determine that circulating VE-cadherin is a reliable prognostic marker of the sensitivity or resistance to anti-tumoral treatment. It is believed that prior art sVE-cadherin detection means did not enable such determination.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Predictive markers for ovarian cancer
ActiveUS8664358B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesEfficacyOncology
Methods are provided for predicting the presence, subtype and stage of ovarian cancer, as well as for assessing the therapeutic efficacy of a cancer treatment and determining whether a subject potentially is developing cancer. Associated test kits, computer and analytical systems as well as software and diagnostic models are also provided.
Owner:ASPIRA WOMENS HEALTH INC
Identification and use of prognostic and predictive markers in cancer treatment
InactiveUS20090304697A1Reduce recurrenceLow recurrence rateOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceTissue microarray
The present invention provides a method of screening for markers useful in predicting the efficacy of a specified cancer that includes: (a) constructing a tissue microarray from a tissue bank comprising multiple tissue samples that are annotated with clinical follow up data; (b) labeling polynucleic acid probes specific for oncogenes or cancer associated genes known to be potential amplicons; (c) performing fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis on the tissue microarray; and (d) correlating the result of the fluorescent in situ hybridization with the clinical follow up data. The present disclosure also provides methods of treating breast cancer that include screening a breast cancer patient for amplification of one or more of the genes disclosed herein, and treating a patient having amplification of one or more of these genes with a therapeutically effective amount of a compound that interferes with HER2 signaling.
Owner:NSABP FOUND INC
Gastric cancer prognosis predictive marker and application thereof
ActiveCN110187110AEffectively distinguish the lifetimeEffectively distinguish the length of lifeMaterial analysisMedicineTissue sample
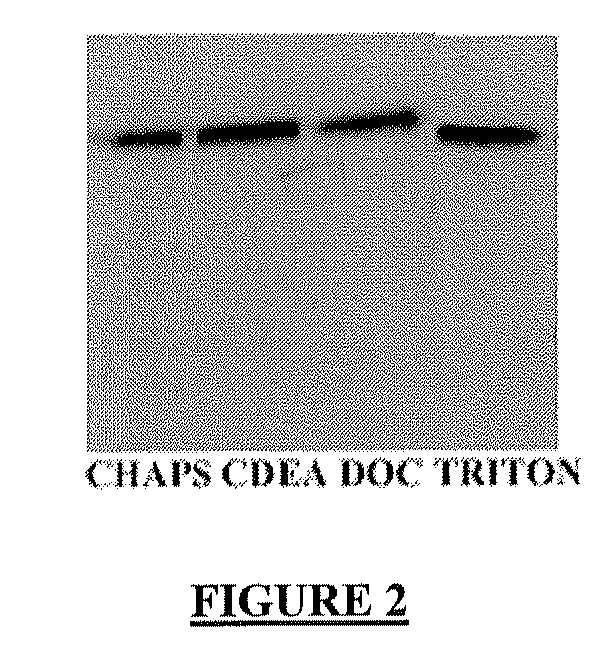
The invention belongs to the technical field of the tumor medicine, and specifically discloses a gastric cancer prognosis predictive maker-ERICH3 protein and application of a detection reagent of theERICH3 protein in preparation of a kit or reagent for gastric cancer prognosis prediction. The detection reagent of the ERICH3 protein is used for detecting whether the ERICH3 protein is expressed molecule. By detecting the expression of the ERICH3 protein in a tissue sample, the lifetime of the gastric cancer patient can be effectively distinguished, thereby providing a new path for the judgementof the gastric cancer prognosis prediction and providing reference evidence for gastric cancer condition analysis by the clinician.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV +2
Method for predicting the clinical response to chemotherapy in a subject with cancer
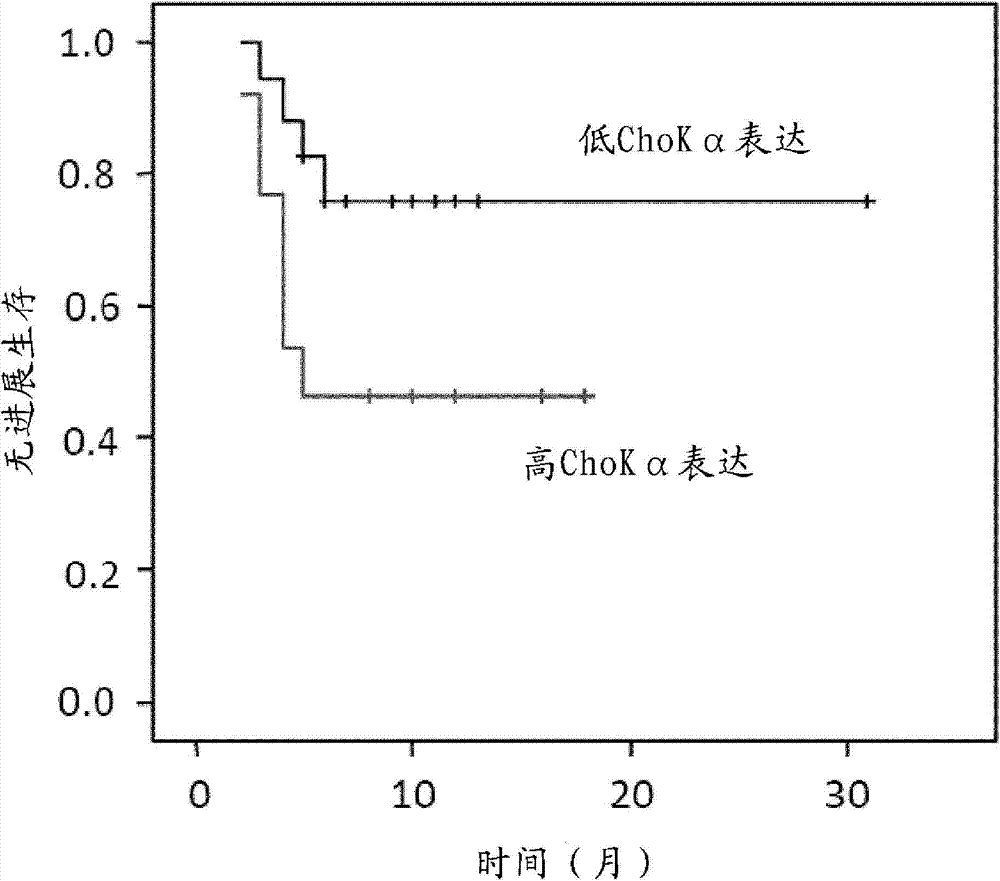
InactiveCN103687964AImprove expression levelOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsPlatinumCholine kinase alpha
The invention relates to the use of choline kinase alpha as predictive marker for the determination of the response to a chemotherapeutic treatment in a subject suffering from cancer, particularly for predicting the clinical response of a subject suffering from non-small cell lung cancer to a platinum-based chemotherapeutic treatment. The invention relates to methods for designing a personalised therapy for subjects suffering from cancer, particularly from non- small cell lung cancer, based on the expression levels of choline kinase alpha as well as to methods for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer using a platinum-based chemotherapeutic treatment based in a subject wherein the subject is selected based on the expression levels of choline kinase alpha.
Owner:TRASLATIONAL CANCER DRUGS PHARMA SL
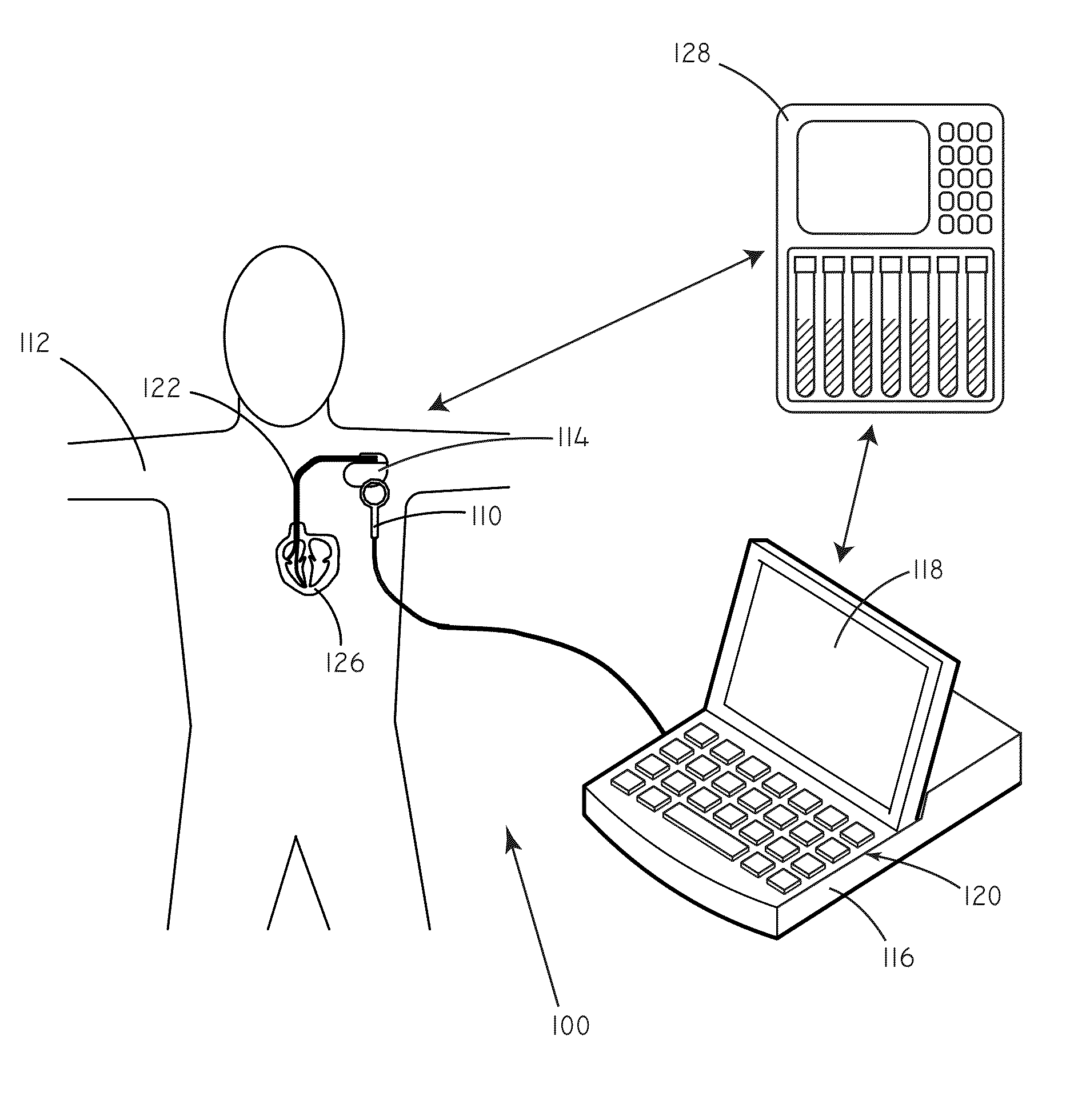
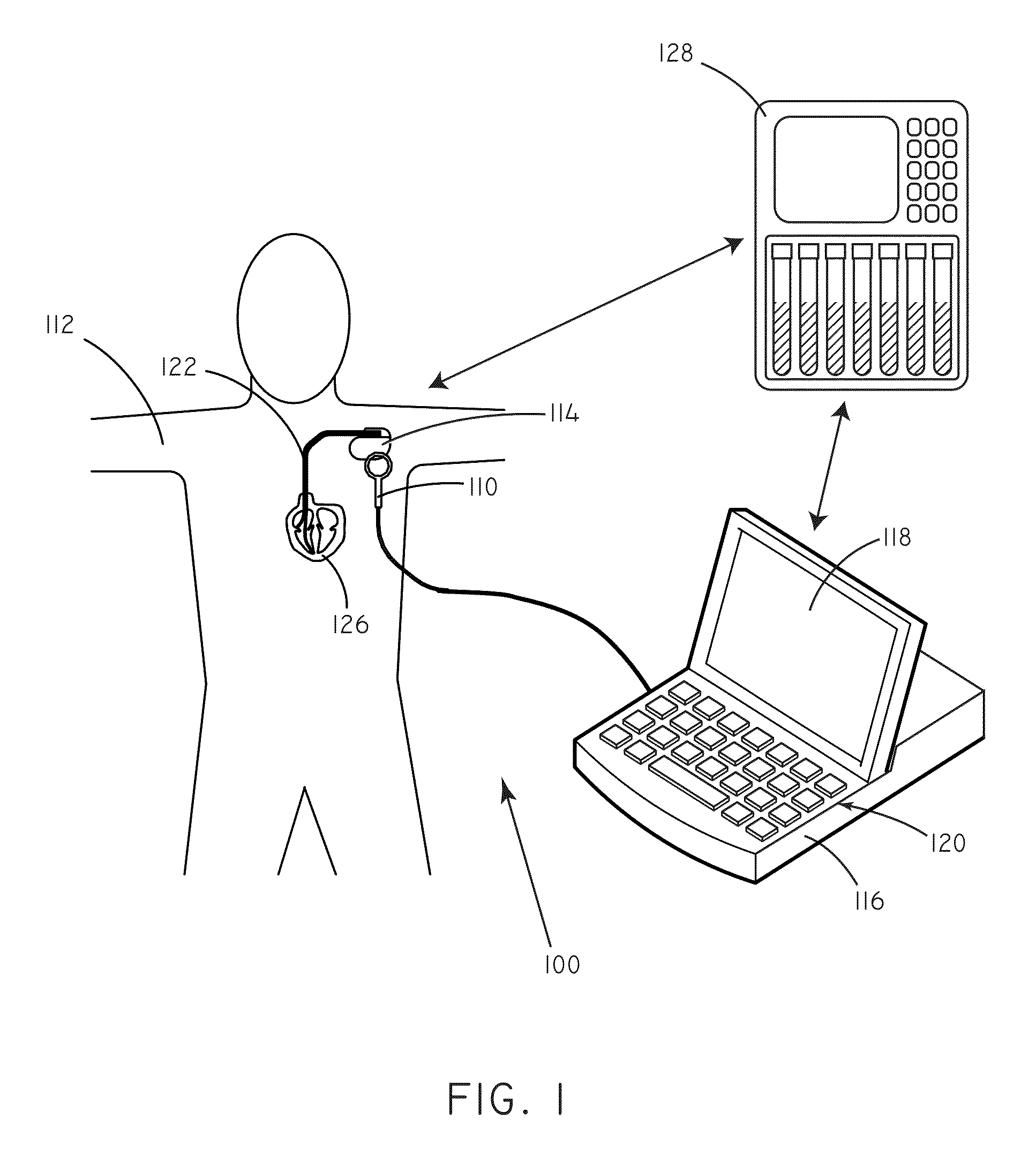
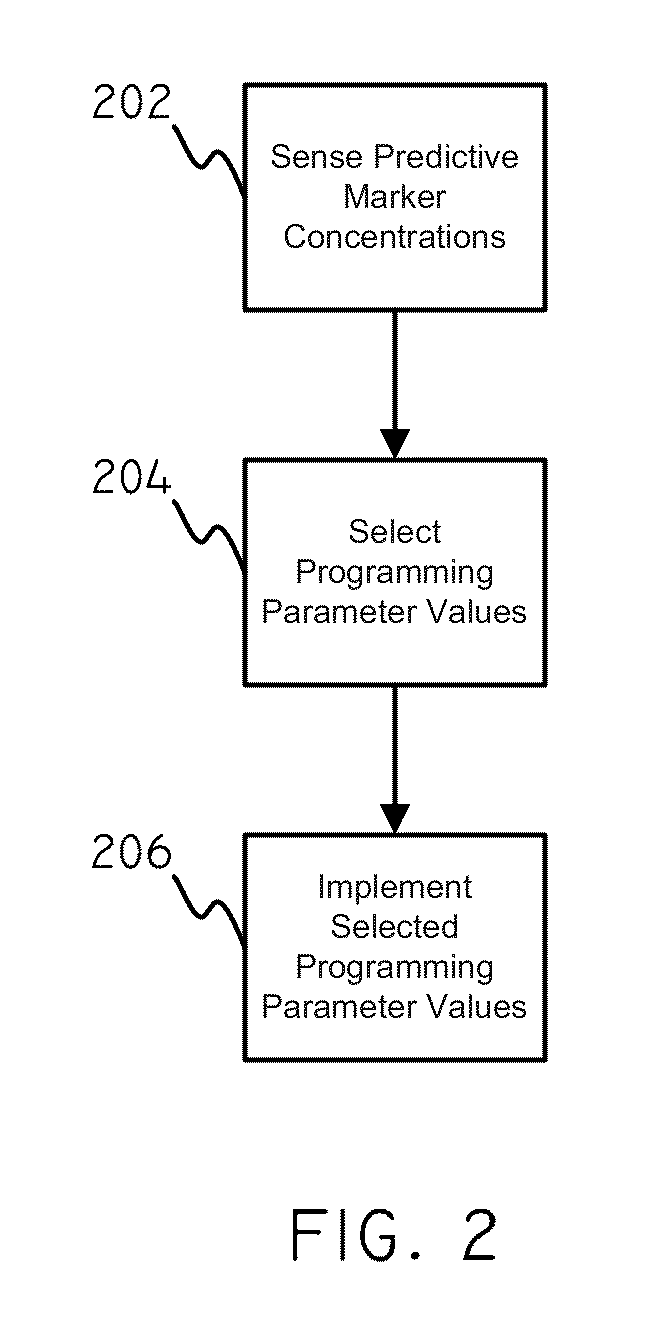
Systems and methods for setting parameters of implantable medical devices using predictive marker data
Embodiments of the invention are related to systems and methods for setting parameters of implantable medical devices, amongst other things. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method for programming an implantable medical device including sensing concentrations of a predictive marker such as ET-1 in a patient, selecting programming parameter values based on the sensed concentrations of the predictive marker, and implementing the selected programming parameter values. In an embodiment the invention includes a method for detecting arrhythmia in a patient including sensing concentrations of the predictive marker in a patient, selecting a level of stringency to be used in an arrhythmia detection module based on the sensed concentrations of the predictive marker, sensing electrical signals in the patient, and evaluating the sensed electrical signals for indicia of an arrhythmia using the arrhythmia detection module. Other embodiments are also included herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Predictive markers and biomarker panels for ovarian cancer
InactiveUS20120171694A1Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBiomarker panelBiologic marker
Methods are provided for predicting the presence, subtype and stage of ovarian cancer, as well as for assessing the therapeutic efficacy of a cancer treatment and determining whether a subject potentially is developing cancer. Associated test kits, computer and analytical systems as well as software and diagnostic models are also provided.
Owner:VERMILLION INC
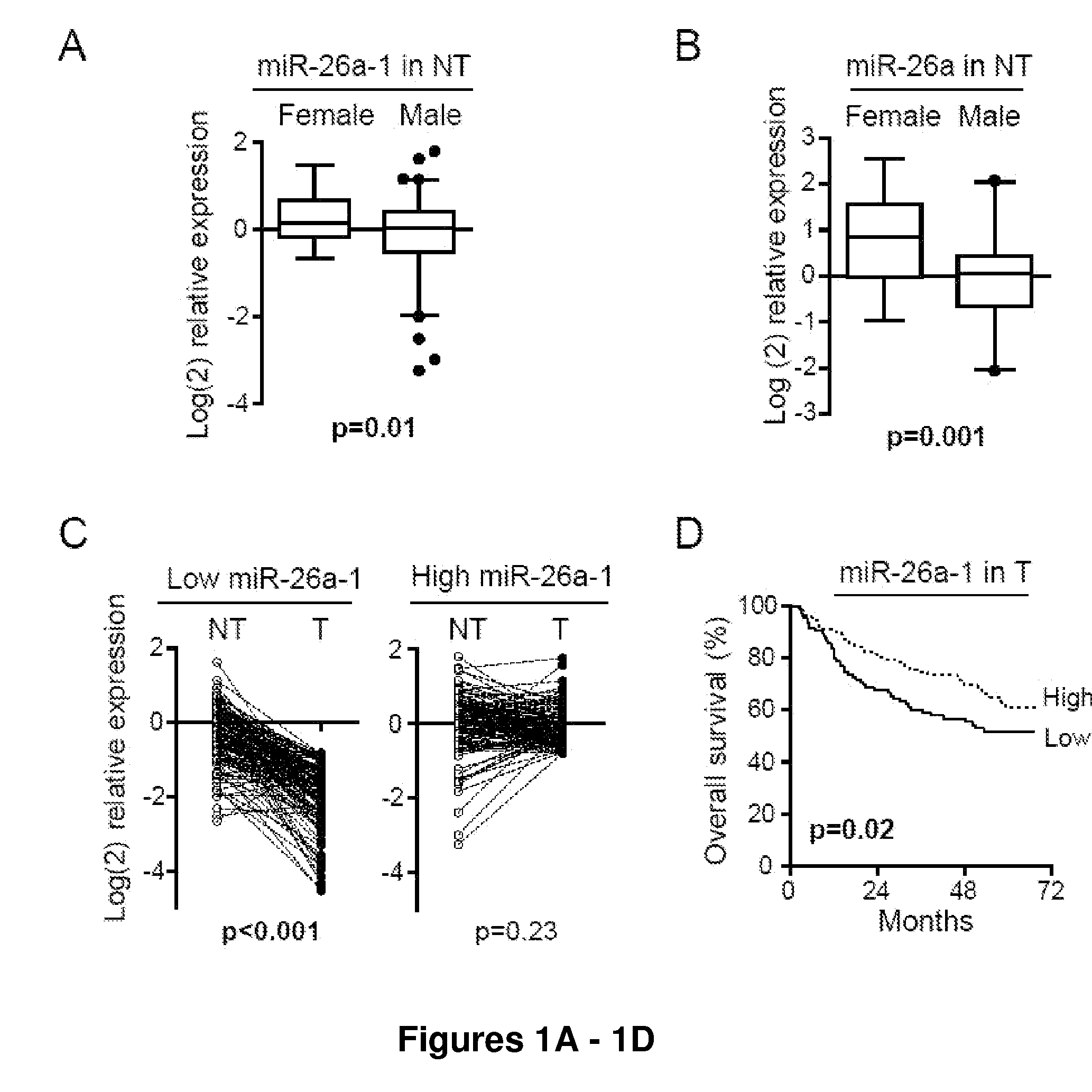
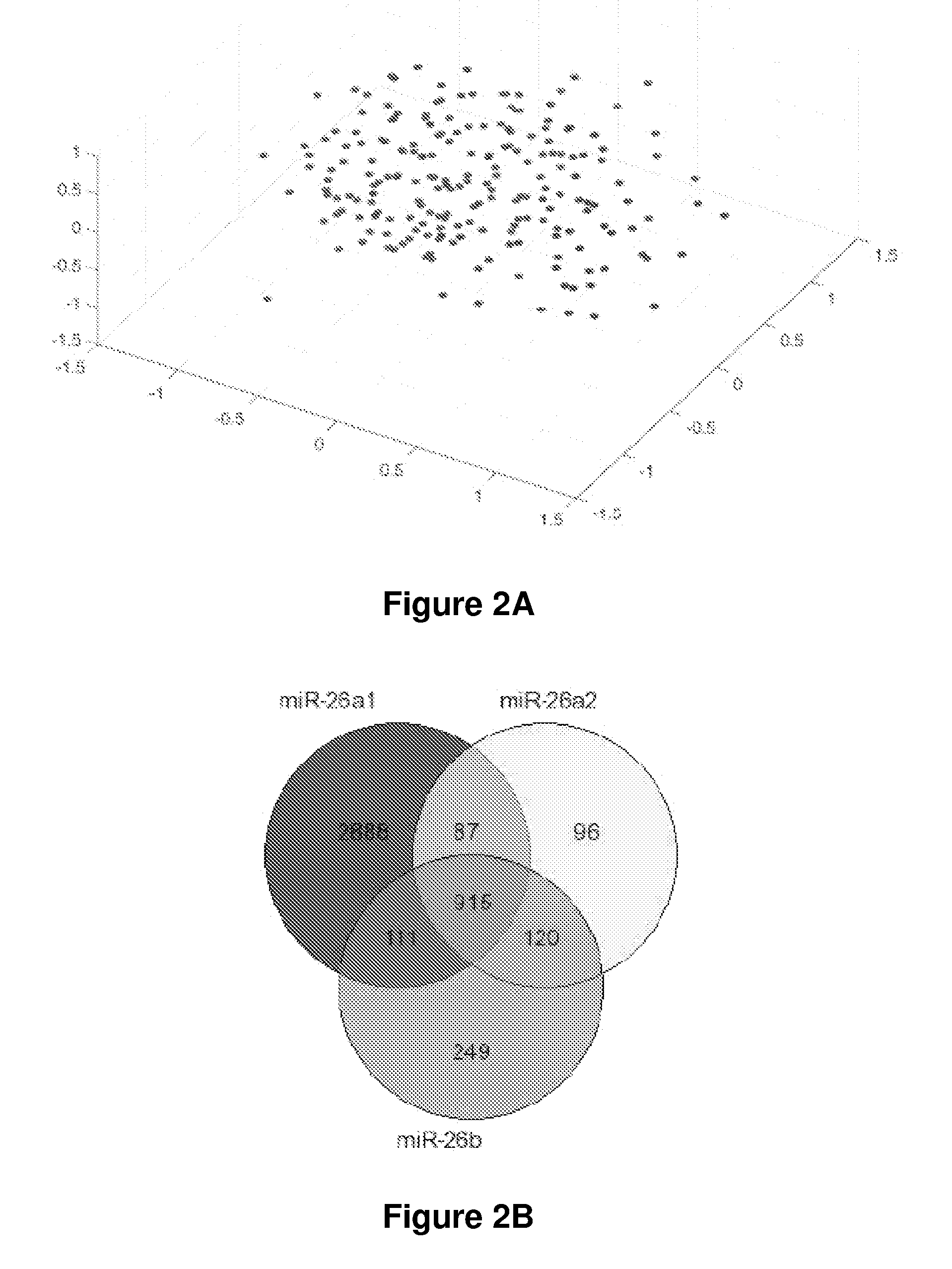
Use of MiR-26 Family as a Predictive Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Responsiveness to Therapy
InactiveUS20110124521A1Poor clinical outcomeImprove responsePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFAVORABLE RESPONSEHepatocellular carcinoma
It is disclosed herein that expression of microRNA-26 is decreased in hepatocellular (HCC) tumor tissue relative to non-cancerous tissue, and that a low level of microRNA-26 is associated with a poor clinical outcome. It is also disclosed herein that a low expression level of microRNA-26 is correlated with a favorable response to interferon (IFN)-α therapy in HCC patients. Thus, provided herein is a method of predicting the clinical outcome of a patient diagnosed with HCC comprising detecting the level of microRNA-26 expression in a sample obtained from the patient. Also provided is a method of selecting a patient diagnosed with HCC as a candidate for IFN-α therapy, comprising detecting the level of microRNA-26 expression in a sample obtained from the patient. A method of identifying therapeutic agents for the treatment of HCC, comprising screening candidate agents in vitro to select an agent that increases expression of microRNA-26 in HCC cells are also provided. Further provided are methods of treating a patient diagnosed with HCC and expressing a low level of miR-26, wherein treatment comprises IFN-α therapy.
Owner:THE U S DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +2
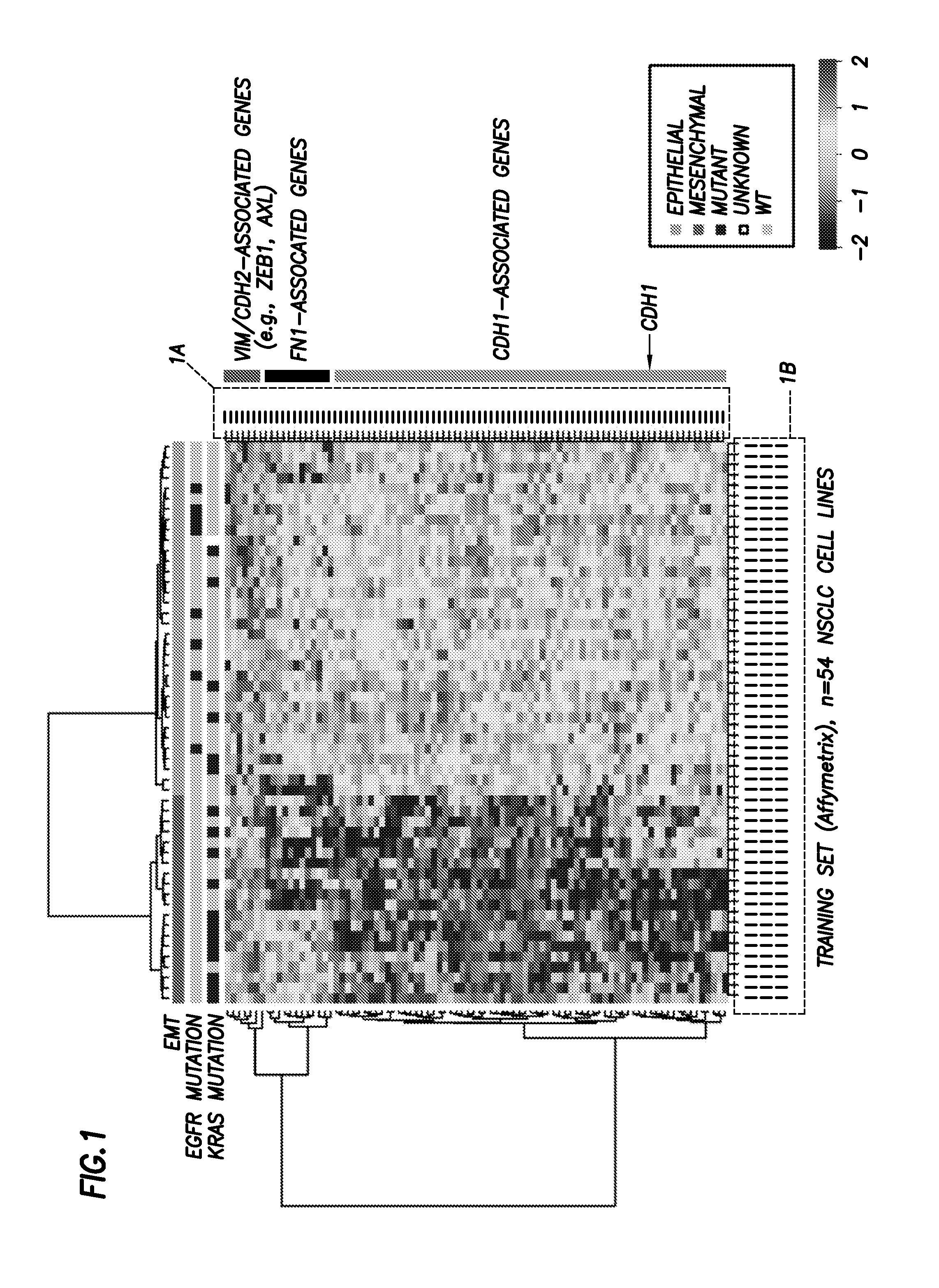
Emt signatures and predictive markers and method of using the same
InactiveUS20140155397A1Reliable resistiveAccurate classificationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDrugs responsePredictive marker
EMT signatures and markers useful for characterizing the status of epithelial cancers and for predicting drug responses in patients having non-small cell lung cancer are provided together with methods of using the same.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
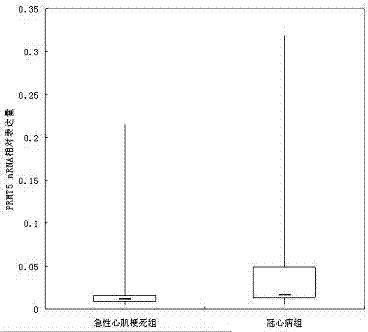
Application of PRMT5 gene serving as marker for predicting, diagnosing and treating acute myocardial infarction
InactiveCN107058554AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPRMT5 GeneMedicine
The invention discloses application of a PRMT5 gene serving as a marker for predicting, diagnosing and treating acute myocardial infarction and relates to peripheral blood acute myocardial infarction marker detection and application thereof. The PRMT5 gene or the expression product thereof is used as a new target for predicting, diagnosing and treating the acute myocardial infarction, the PRMT5 gene or the expression product thereof are used to prepare a preparation for predicting, diagnosing and treating the acute myocardial infarction, and important clinical application significance and a high development value are achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Function-driven multi-molecular marker for individualized prediction of colorectal cancer prognosis and device and evaluation method thereof
InactiveCN109486948AHelp formulateGuaranteed reliabilityHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementData setPrognostic prediction
The invention discloses a function-driven multi-molecular marker for individualized prediction of colorectal cancer prognosis and a device and an evaluation method thereof. Prognostic predictive markers are simultaneously screened from multiple cancer large sample data sets of multiple centers, and predictive effects of the multi-molecular marker are validated and comprehensively evaluated in three independent data sets. The application of the above methods and strategies ensures the reliability of the multi-molecular marker in judgment of the prognosis of a colorectal cancer patient; the multi-molecular marker combination is not affected by the batch effect of an experiment or the difference of a detection platform, thereby ensuring the stability of the multi-molecular marker in the judgment of the prognosis of the colorectal cancer patient; the multi-molecular marker combination does not need to be subjected to data standardization between multiple samples before use, thereby facilitating the use and ensuring the clinical operability of the multi-molecular marker in the judgment of the prognosis of the colorectal cancer patient.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Predictive markers and biomarker panels for ovarian cancer
InactiveUS20130267439A1Accurate measurementPeptide librariesLibrary screeningBiomarker panelPredictive marker
Methods are provided for predicting the presence, subtype and stage of ovarian cancer, as well as for assessing the therapeutic efficacy of a cancer treatment and determining whether a subject potentially is developing cancer. Associated test kits, computer and analytical systems as well as software and diagnostic models are also provided.
Owner:MANSFIELD BRIAN C +3
CIRCULATING miRNAs AS EARLY DETECTION MARKER AND PROGNOSTIC MARKER
ActiveUS20150315659A1Prevention and amelioration and treatment of onsetReduce usageNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnticarcinogenOncology
Provided is a novel method for the early detection and / or discrimination of cancer and anti-cancer agents for the prevention or early treatment of cancer. In particular, the method relates to the determination of levels of circulating miRNAs in breast cancer patients, both primary and metastatic. Furthermore, kits, devices, pharmaceutical compositions as well as methods related thereto are described.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HEIDELBERG +1
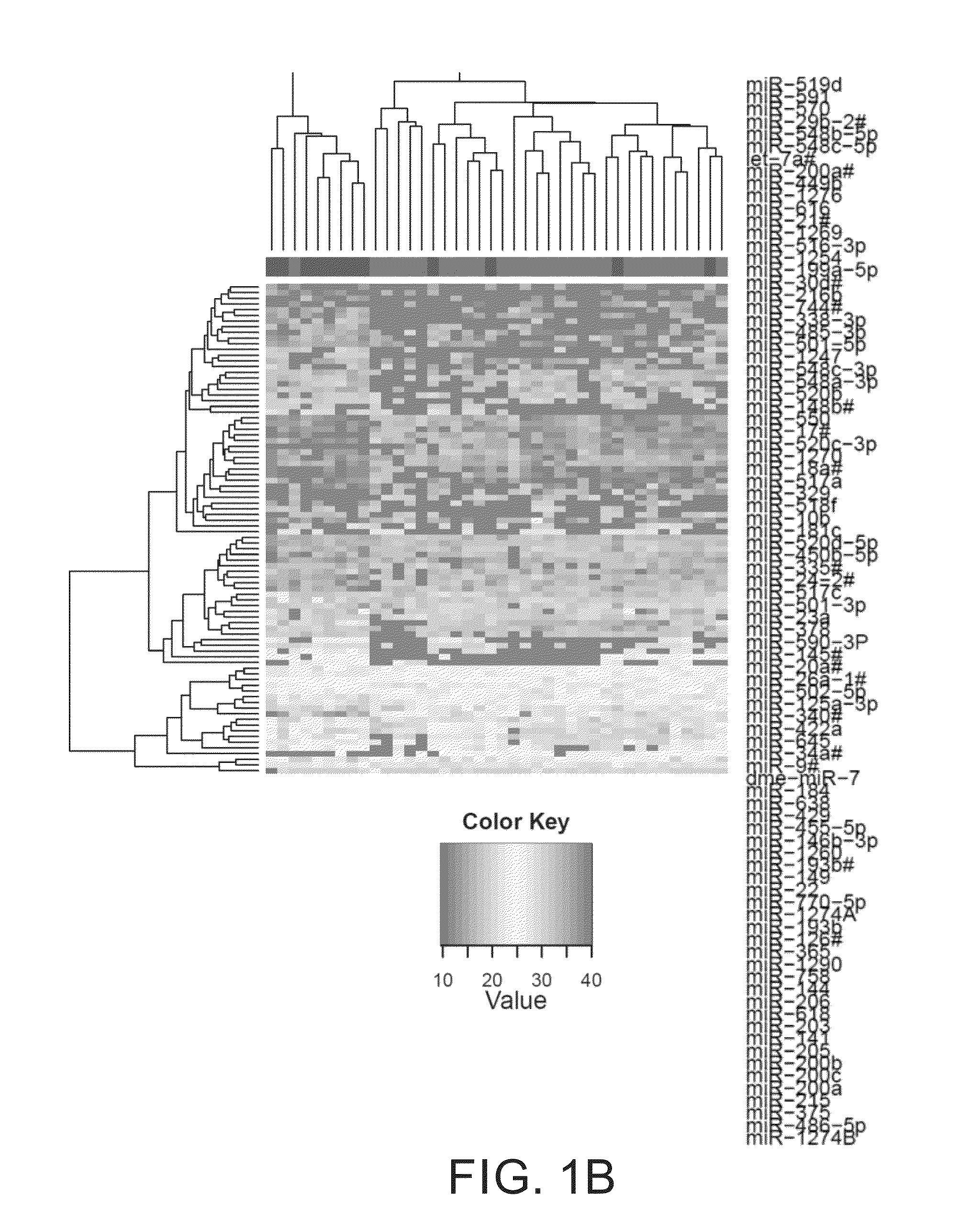
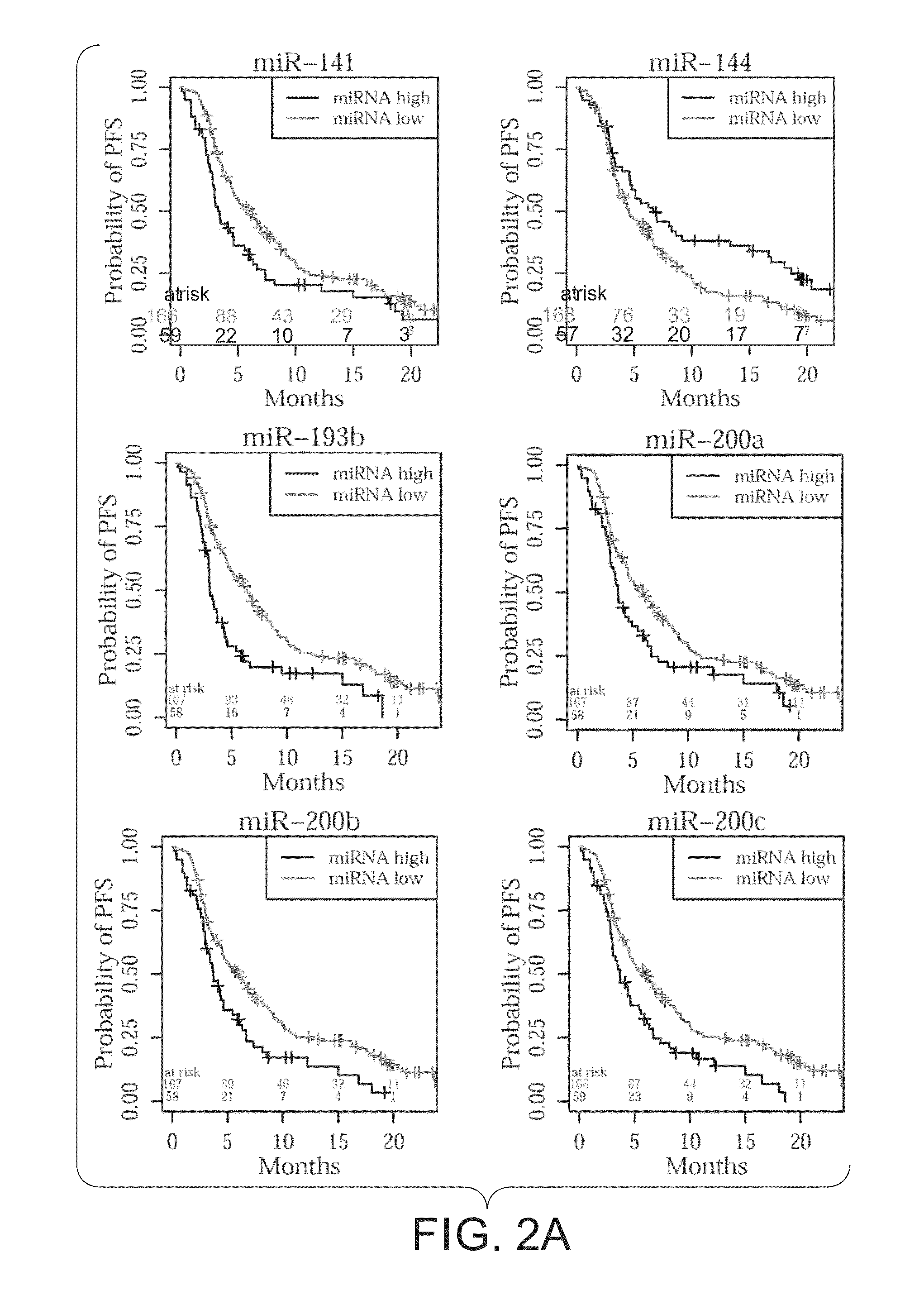
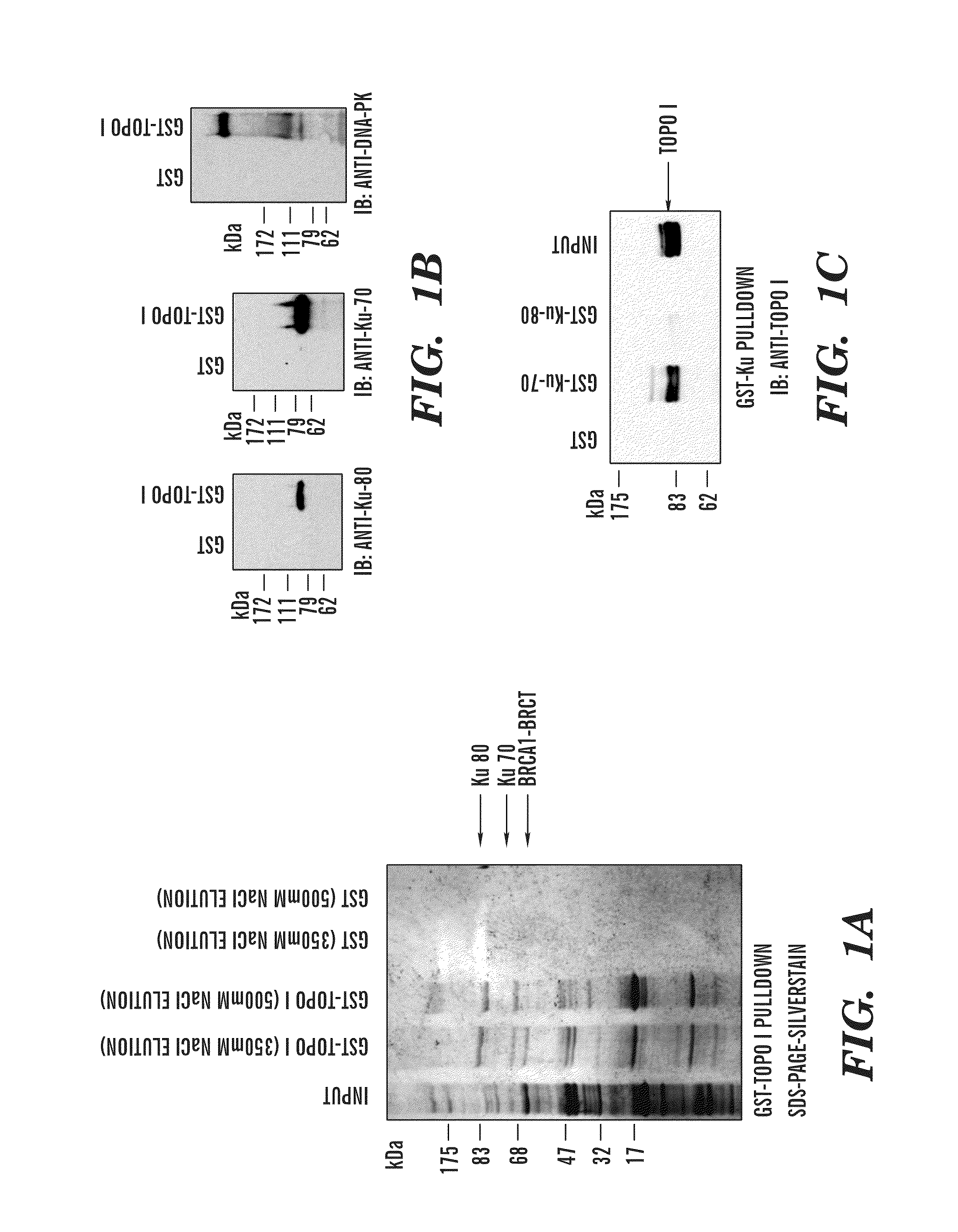
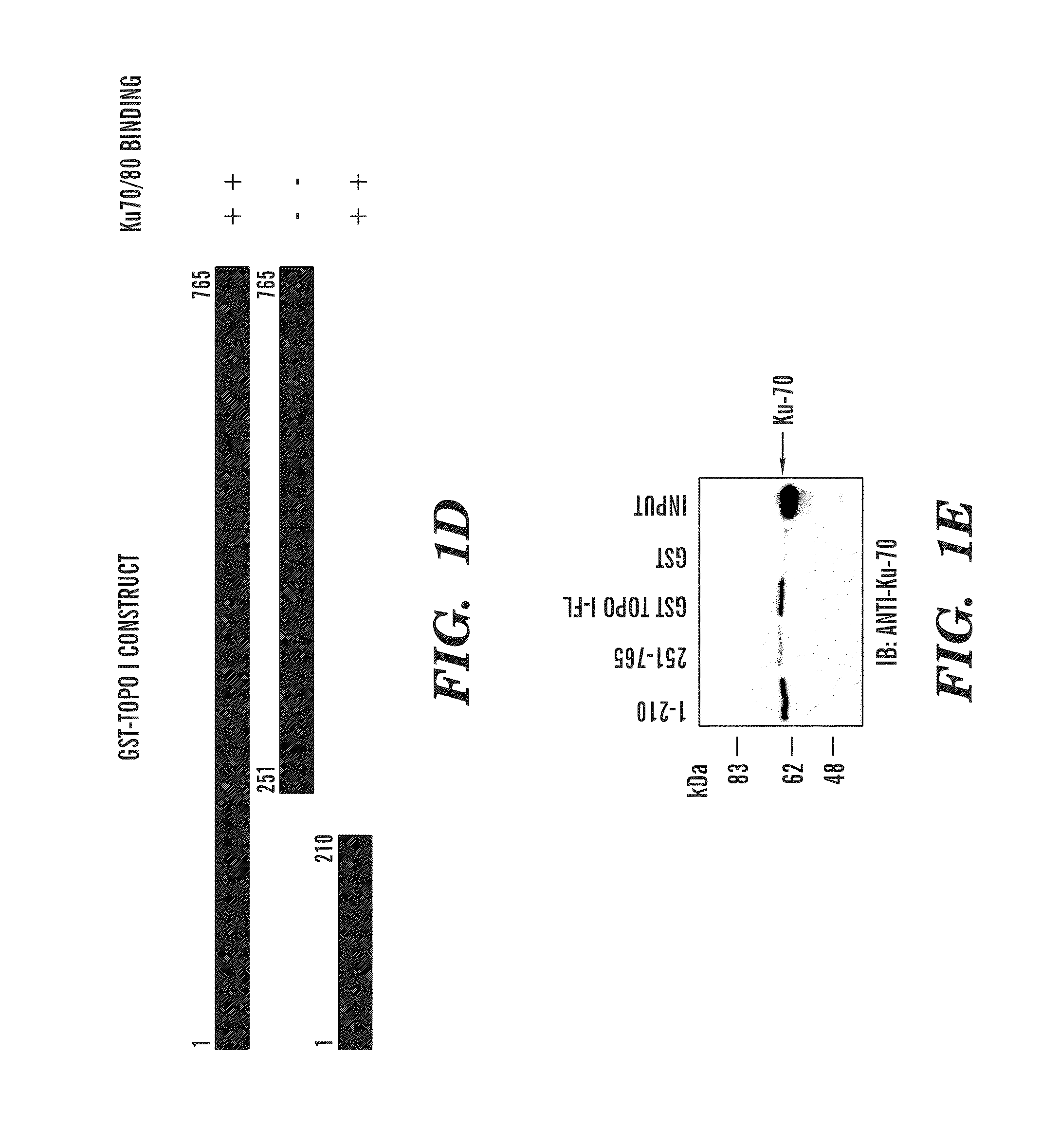
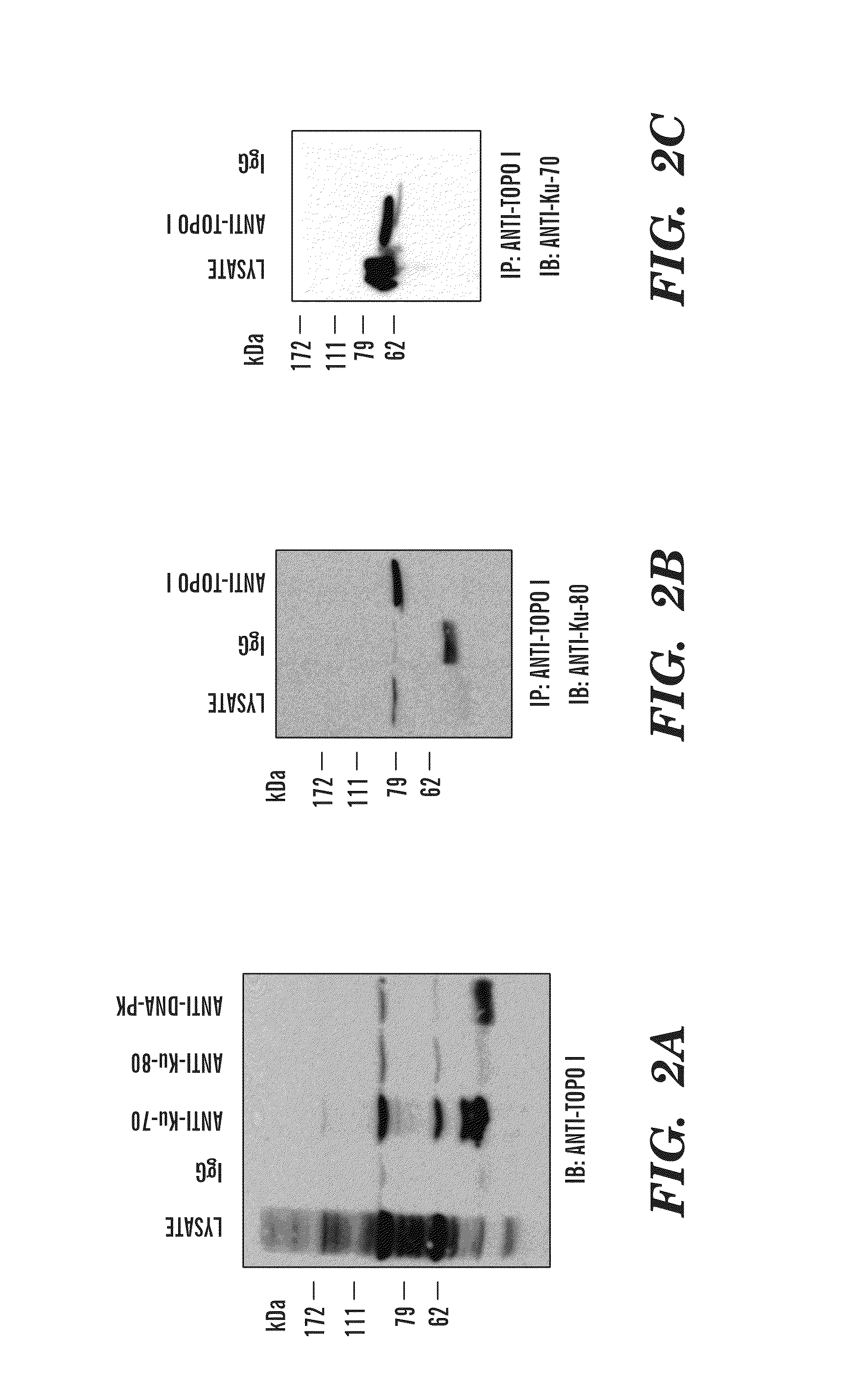
Predictive marker for topoisomerase I inhibitors
ActiveUS8993309B2Organic active ingredientsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCancer preventionPredictive marker
The present invention generally relates to the fields of cancer therapy and cancer prevention. More particularly, the present invention generally relates to a diagnostic marker for predicting the efficacy of topoisomerase I (topo I) inhibitors in the treatment of cancers. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods, machines, computer systems, computable readable media and kits which can be used to identify and determine the effectiveness of topoisomerase I (topo I) inhibitors in the treatment of cancers, and in some embodiments, the level of sensitivity or resistance of a tumor cell to a topoisomerase I inhibitor, such as camptothecin (CPT), or CTP analogues such as topotecan and irinotecan and derivatives thereof. More specifically, the present invention related to methods, machines, computer systems, computable readable media and kits which can be used to determine the presence of phosphorylation of topoisomerase I polypeptide, in some embodiments phosphorylation at residue serine 10 (S10) of a topoisomerase I polypeptide, wherein the presence of phosphorylation, in particular the phosphorylation at serine 10 of a topoI polypeptide indicates a cancer is likely to be unresponsive to a topo I inhibitor, whereas the absence of phosphorylation, in particular, the absence of phosphorylation at residue serine 10 (S10) identifies a cancer is likely to be responsive to a topo I inhibitor. Other aspect of the present invention relate to phospho-serine 10 topoisomerase I antibodies and other protein binding moieties, and uses thereof.
Owner:BOSTON MEDICAL CENTER INC
Molecular diagnostic test for lung cancer
InactiveUS20160222459A1Avoid overtreatmentRisk of severeMicrobiological testing/measurementRespiratory disorderChemotherapeutic drugsPharmaceutical drug
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of a molecular diagnostic test for lung cancer. The test defines a novel DNA damage repair deficient molecular subtype and enables classification of a patient within this subtype. The present invention can be used to determine whether patients with NSCLC are clinically responsive or non-responsive to a therapeutic regimen prior to administration of any chemotherapy. This test may be used with different drugs that directly or indirectly affect DNA damage or repair, such as many of the standard cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs currently in use. In particular, the present invention is directed to the use of certain combinations of predictive markers, wherein the expression of the predictive markers correlates with responsiveness or non-responsiveness to a therapeutic regimen.
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS LIMITED
Method of using a gene expression profile to determine cancer responsiveness to an anti-angiogenic agent
InactiveUS10260097B2Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCancer typeAntiangiogenic therapy
Owner:ALMAC DIAGNOSTICS SERVICES LIMITED
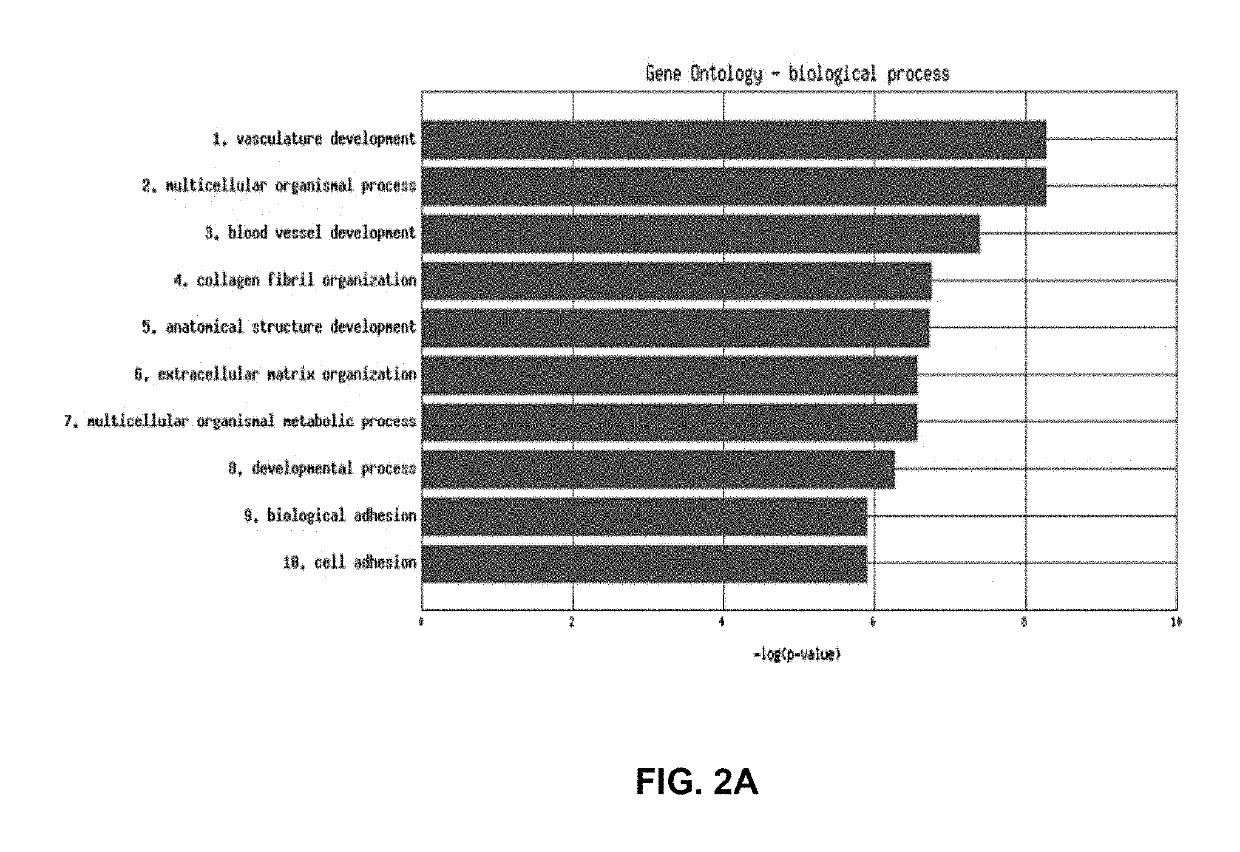
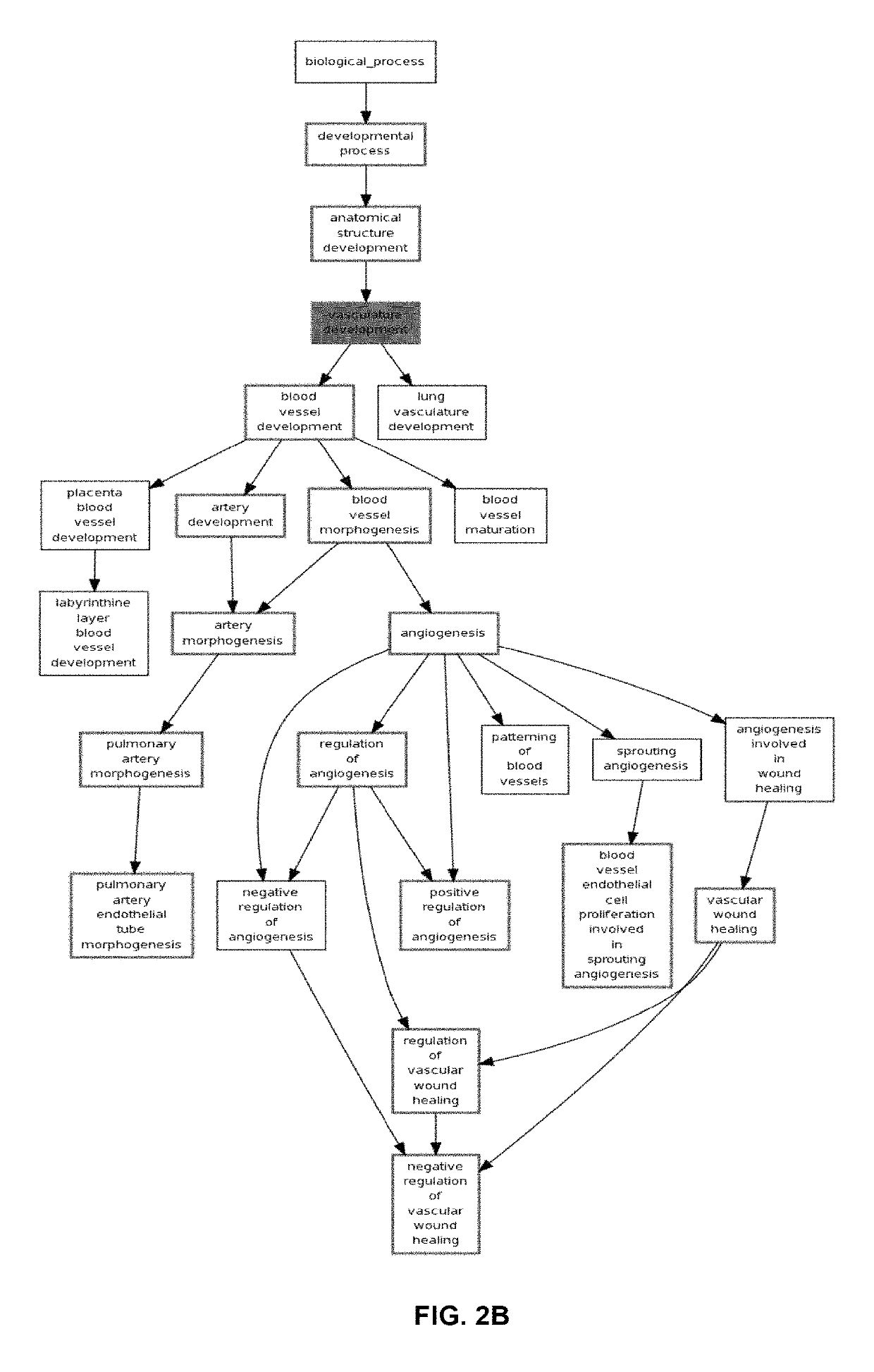
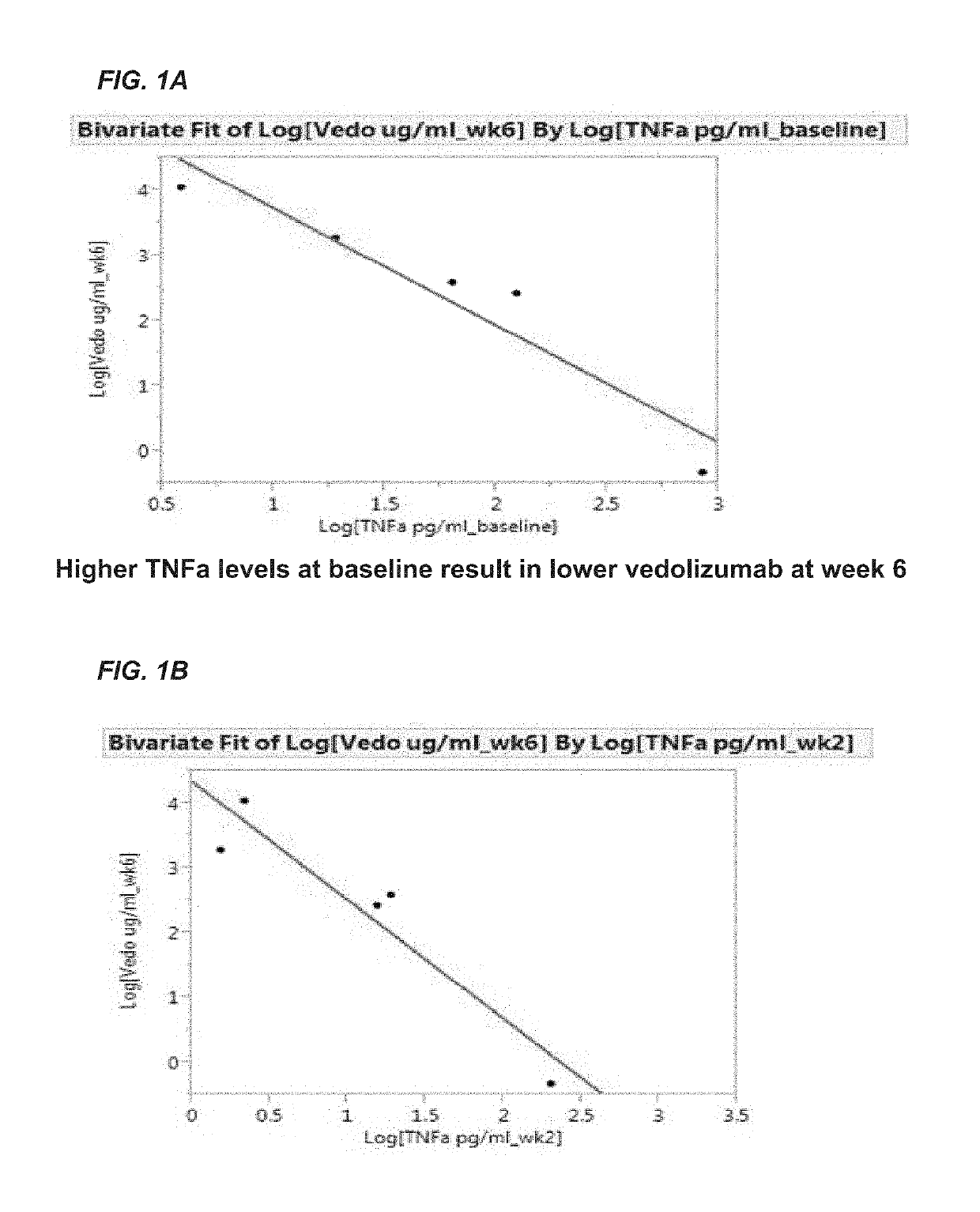
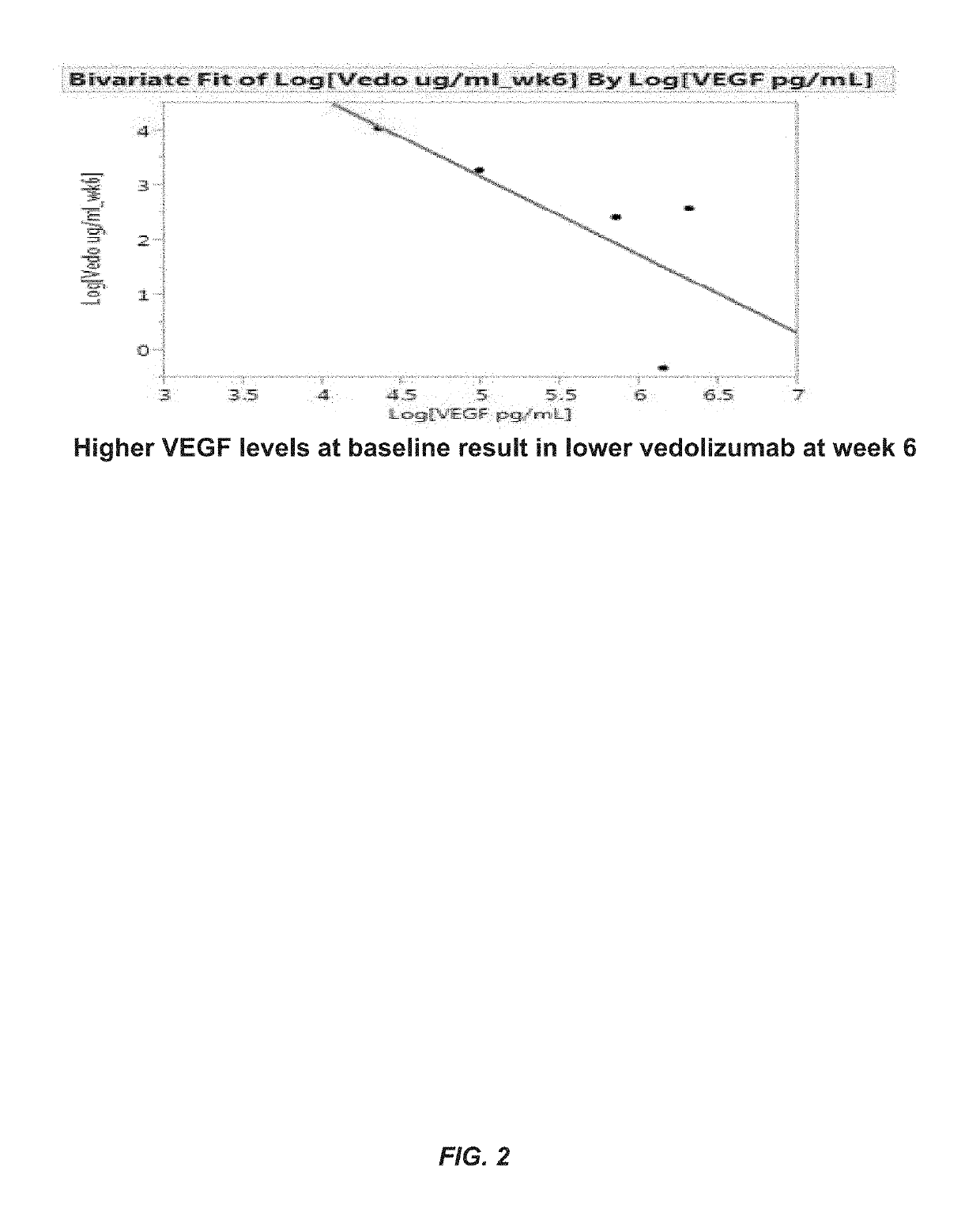
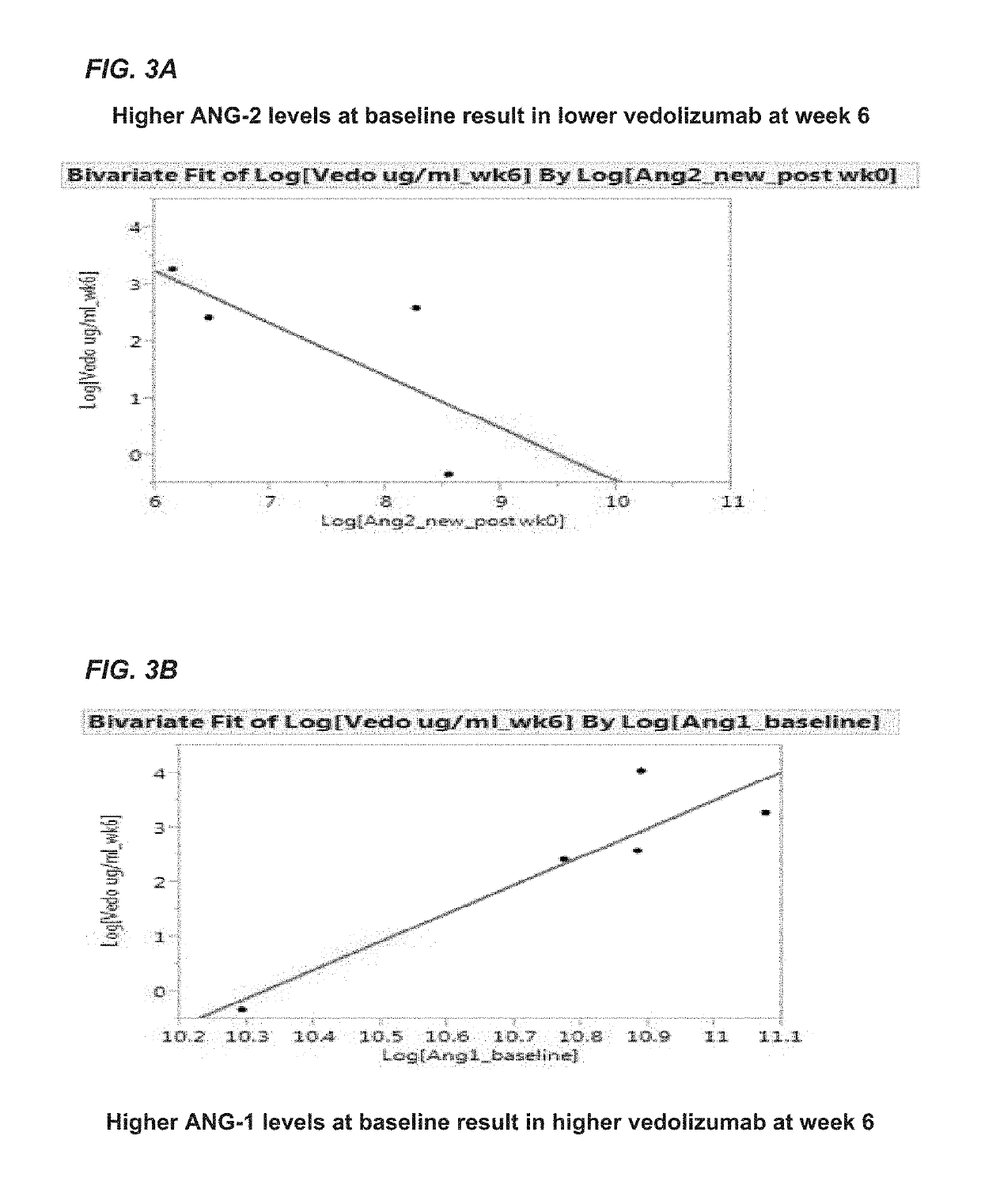
Methods for establishing a vedolizumab dosing regimen to treat patients with irritable bowel disease
The present invention provides methods for predicting whether an individual having inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is likely to respond to vedolizumab treatment. Also provided are methods for predicting whether an individual with IBD such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis will develop autoantibodies against vedolizumab. The present invention also provides a treatment regimen for an IBD patient which includes measuring the level of one or more predictive markers of response to vedolizumab prior to administering the anti-α4β7 integrin drug.
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB
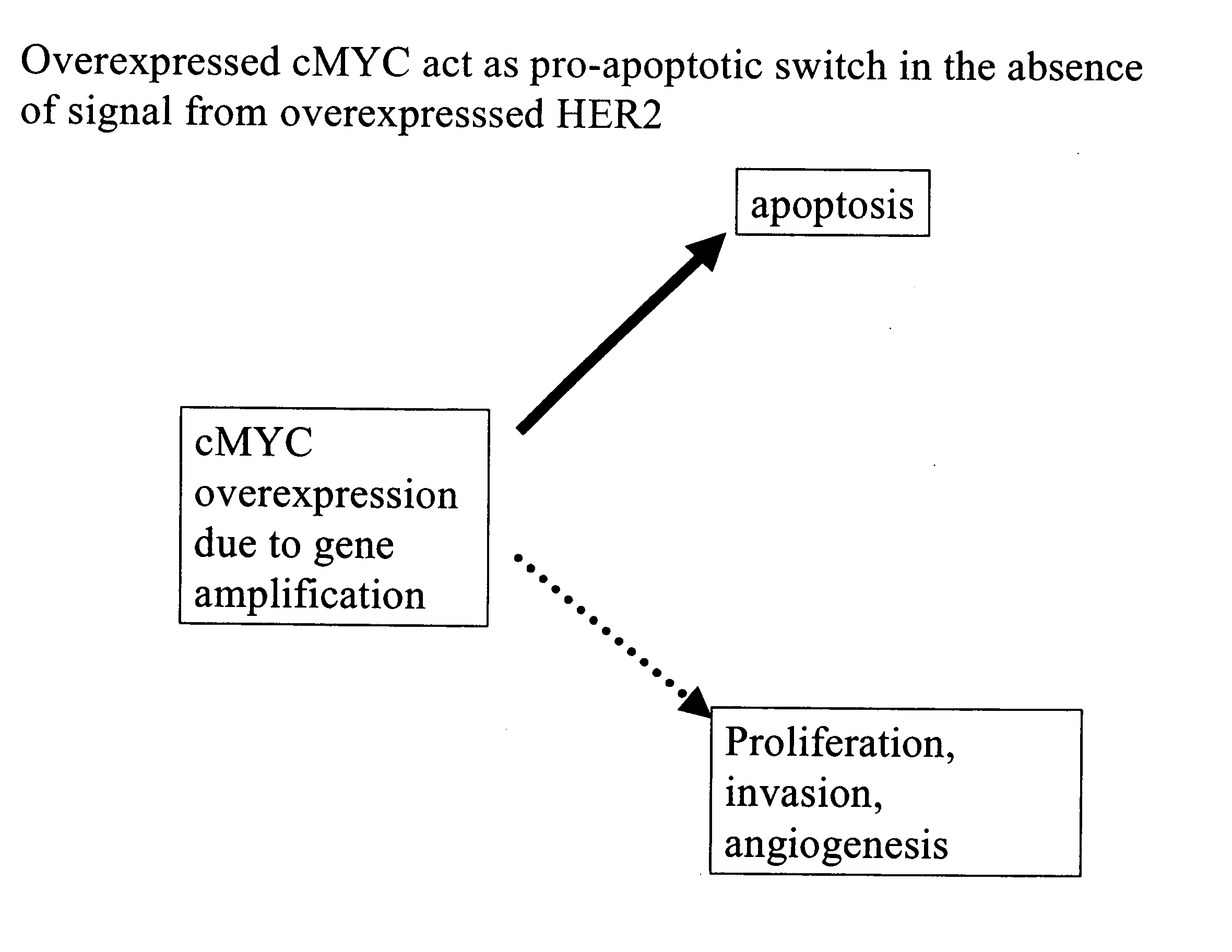
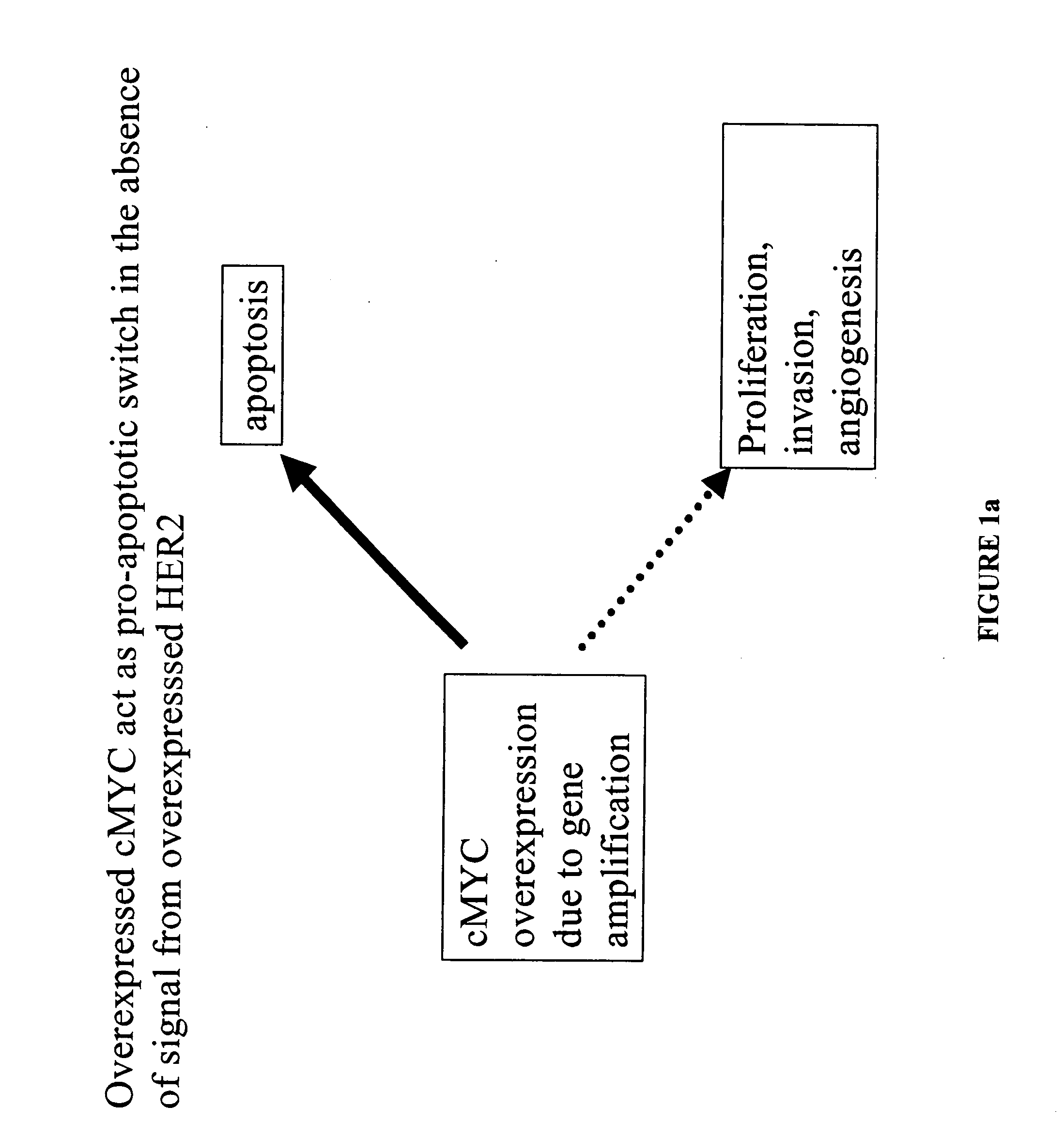
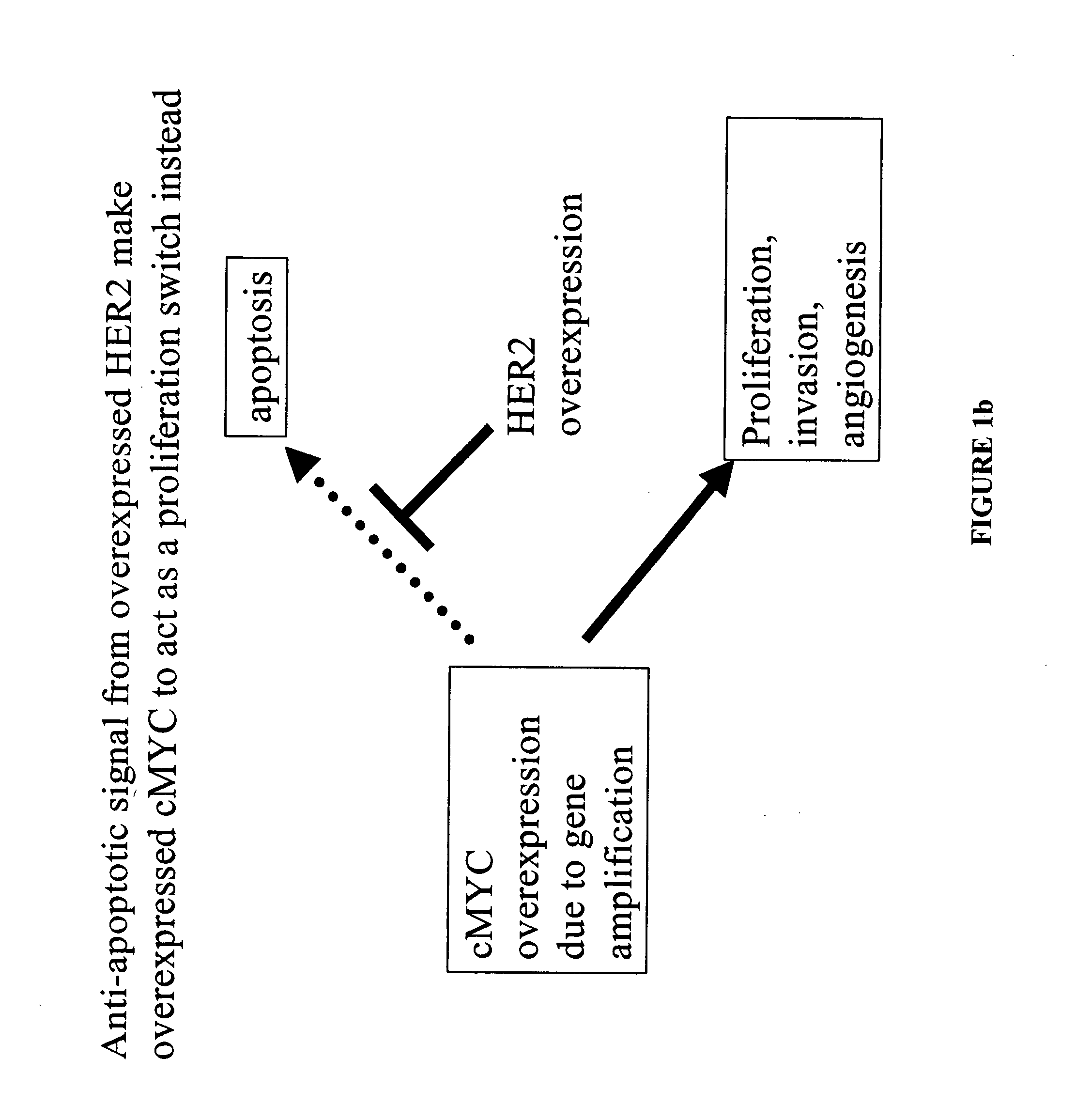
Identification and use of prognostic and predictive markers in cancer treatment
InactiveUS20060127935A1Poor prognosisReducing cancer recurrenceCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFluorescencePredictive marker
The present invention provides a method of screening for markers useful in predicting the efficacy of a specified cancer that includes: (a) constructing a tissue microarray from a tissue bank comprising multiple tissue samples that are annotated with clinical follow up data; (b) labeling polynucleic acid probes specific for oncogenes or cancer associated genes known to be potential amplicons; (c) performing fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis on the tissue microarray; and (d) correlating the result of the fluorescent in situ hybridization with the clinical follow up data. In addition, the present invention provides a method of treating breast cancer that includes measuring the expression levels or amplification of HTPAP in a patient having breast cancer and then providing a patient having increased levels of HTPAP expression or HTPAP amplification with therapeutic quantities of at least one compound that interferes with the phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity of HTPAP. The present invention also encompasses a method of treating breast cancer that includes screening a breast cancer patient for amplification of the cMYC gene and then treating a patient having amplification of the cMYC gene with therapeutic quantities of a compound that interferes with HER2 signaling.
Owner:NSABP FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com