Patents
Literature
257 results about "Coli cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Escherichia coli or E. coli is a bacterium that can be found in human intestines. Scientists have studied E. coli very well, and know more about how E. coli cells work than any other organism.
Method for exposing peptides and polypeptides on the cell surface of bacteria
InactiveUS7186524B2High varianceMaintain good propertiesBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGramCell membrane
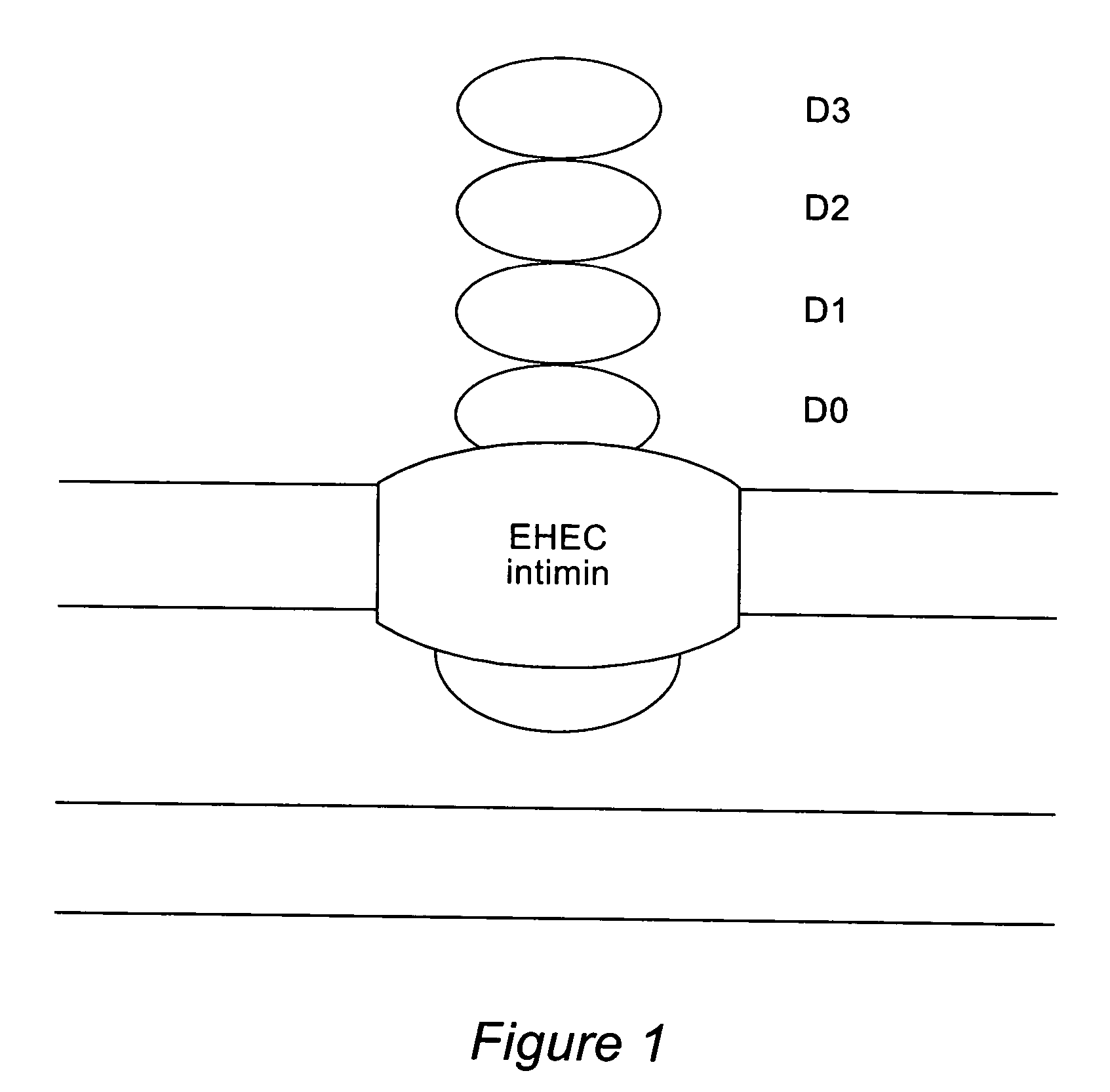
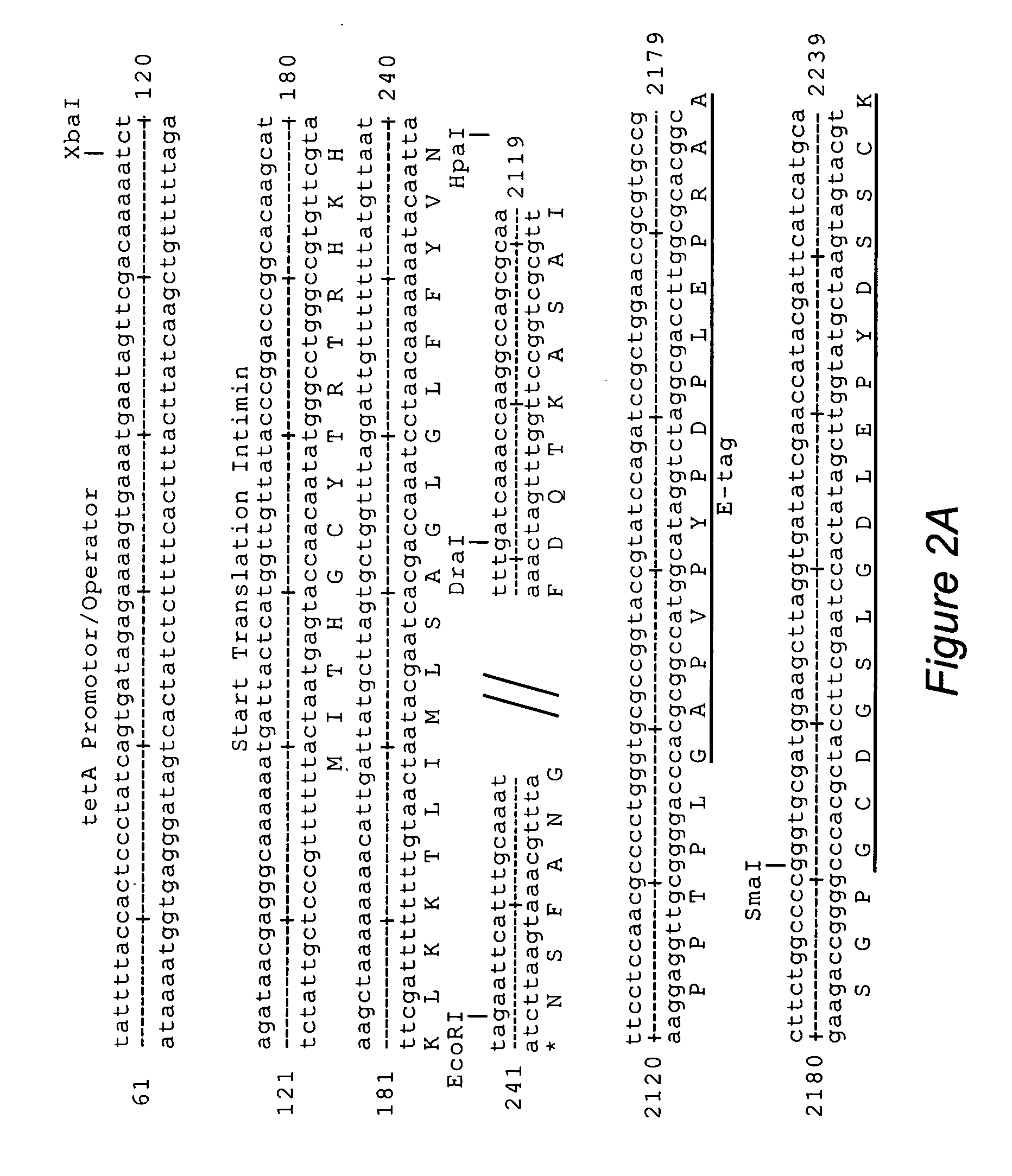
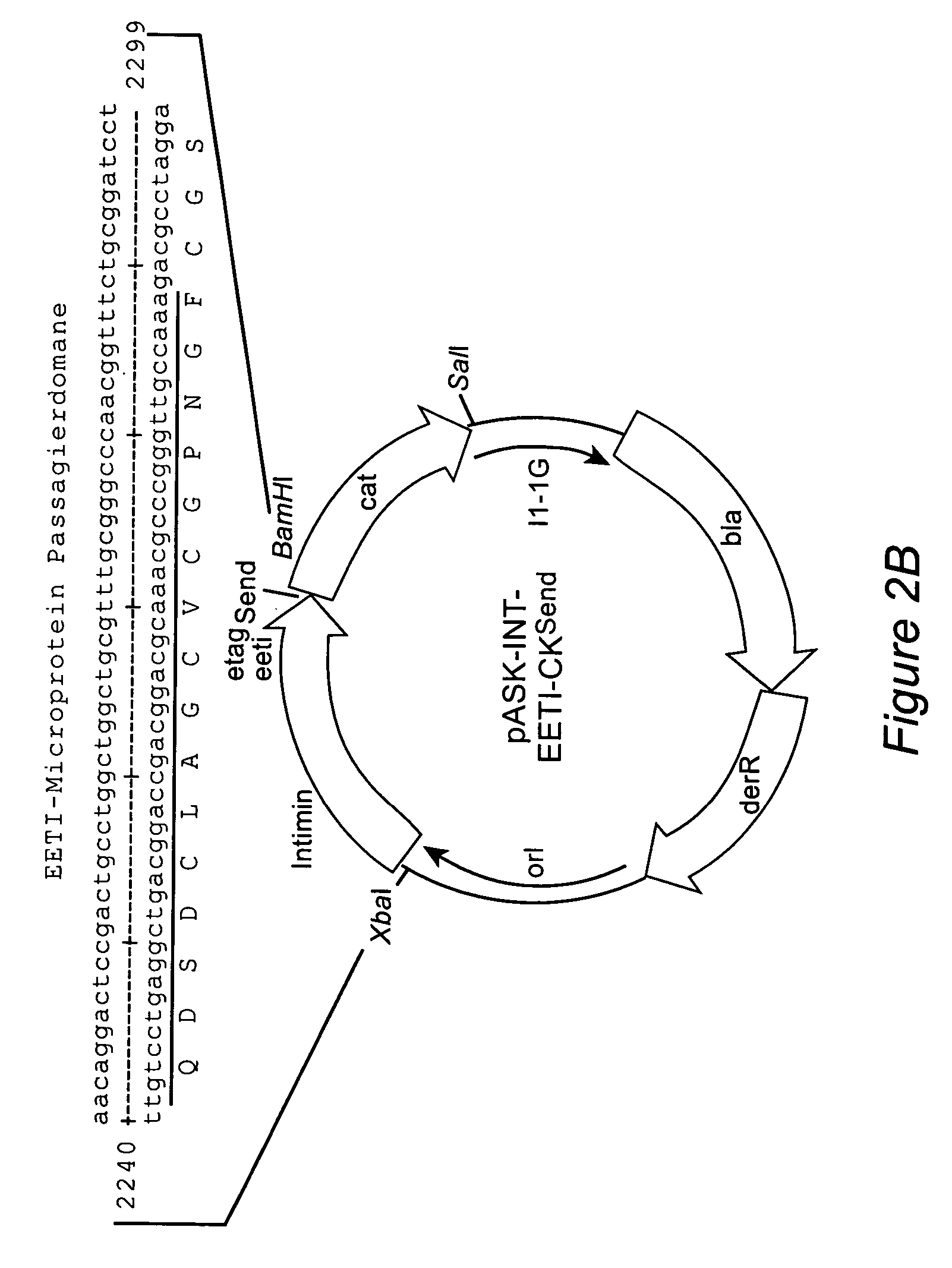
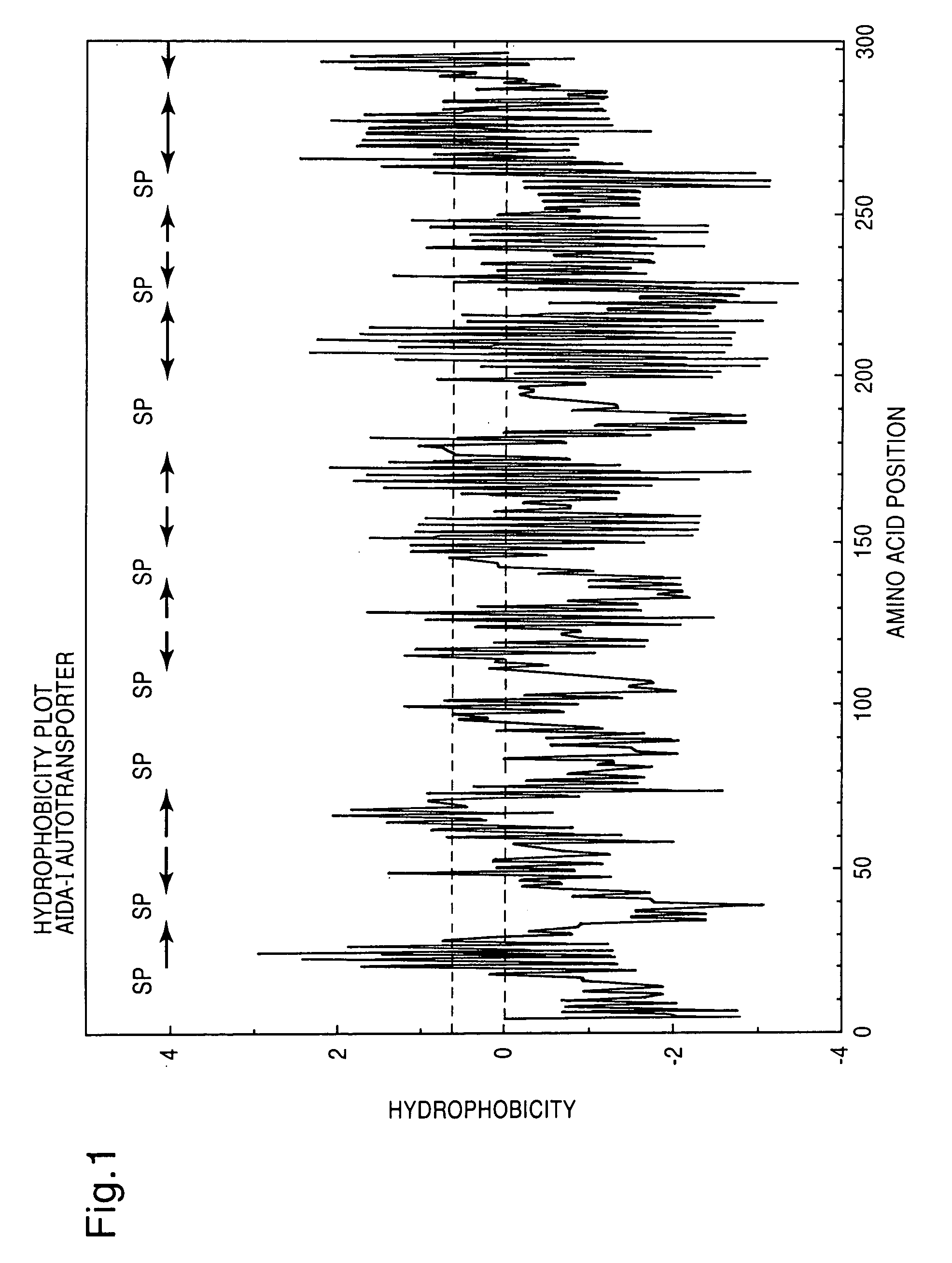
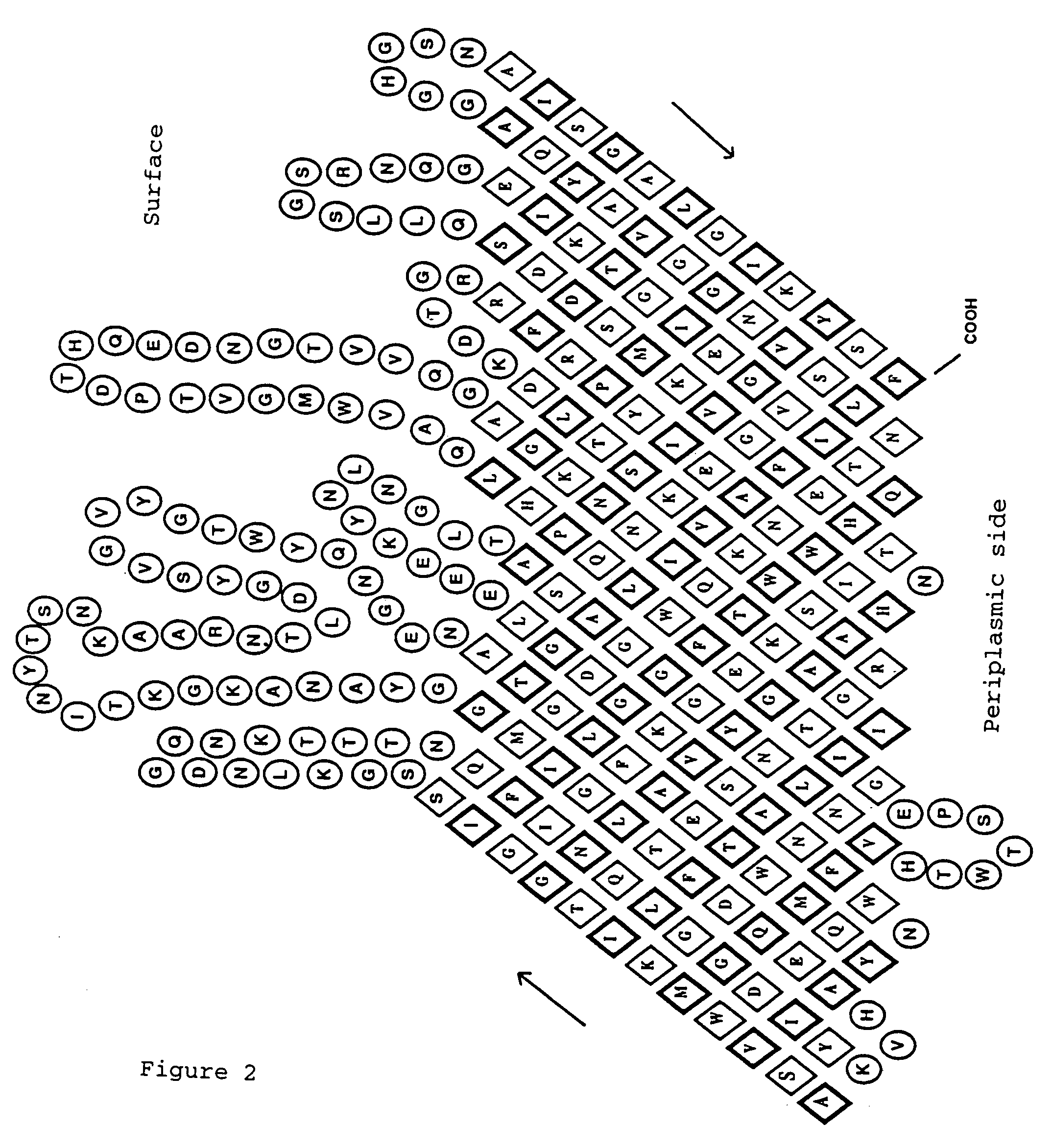
The inventive method allows peptides or polypeptides to be exposed on the surface of gram-negative host bacteria using specific intimin-based anchor modules. Intimins with shortened carboxy terminals have been found to be particularly suitable anchor modules for passenger domains in the exterior E. coli cell membrane. According to the method, host bacteria are transformed using vectors, on which are located a fused nucleic acid sequence consisting of a sequence segment which codes for an intimin with a shortened carboxy terminal and a nucleic acid sequence segment which codes for the passenger peptide that is to be exposed. The invention permits a particularly large number of passenger domains to be exposed on the cell surface of the bacteria, without adversely affecting the viability of the bacteria.
Owner:BIONTECH AG
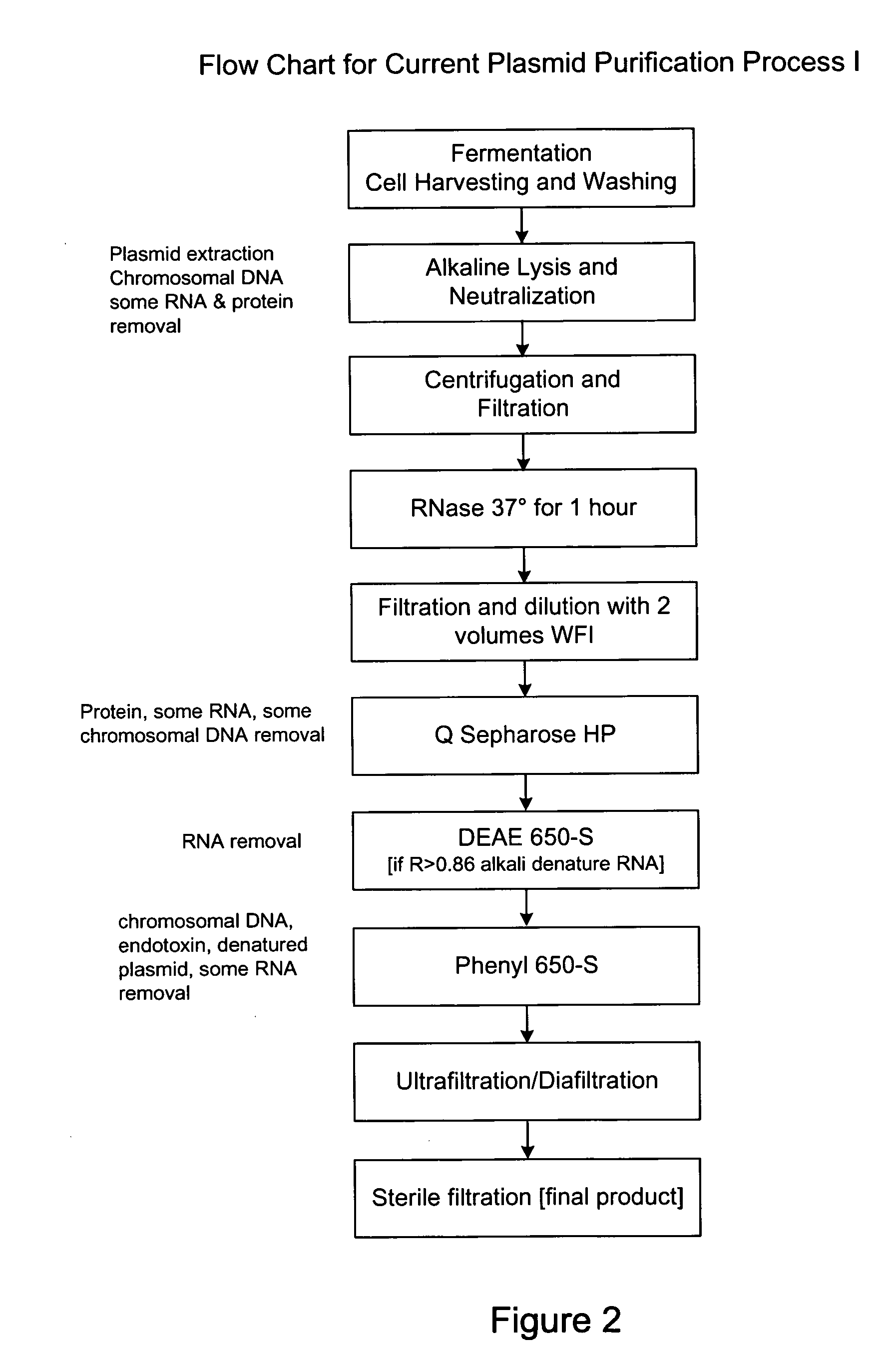
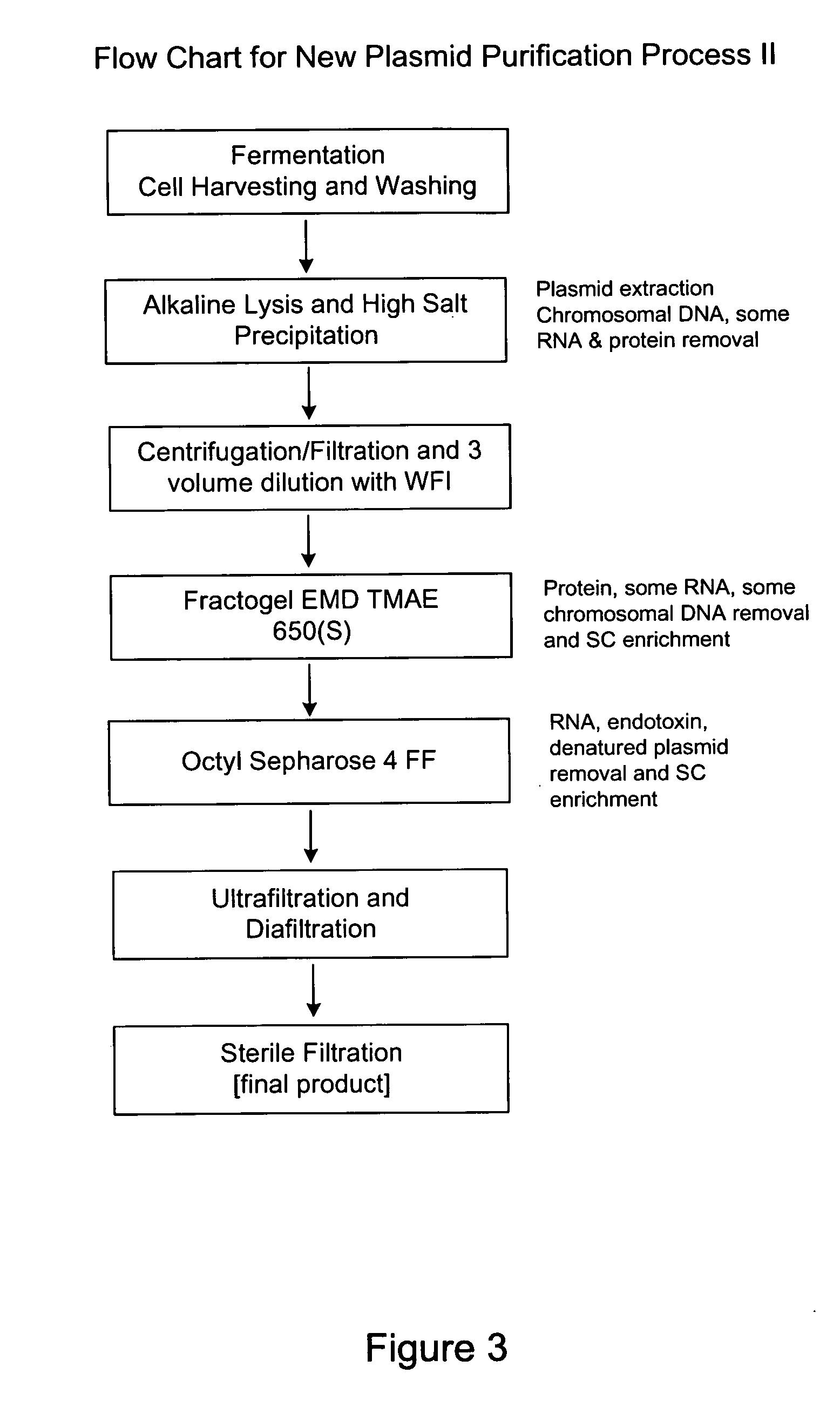
Process and equipment for plasmid purfication
InactiveUS20060106208A1Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationLysisGram
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
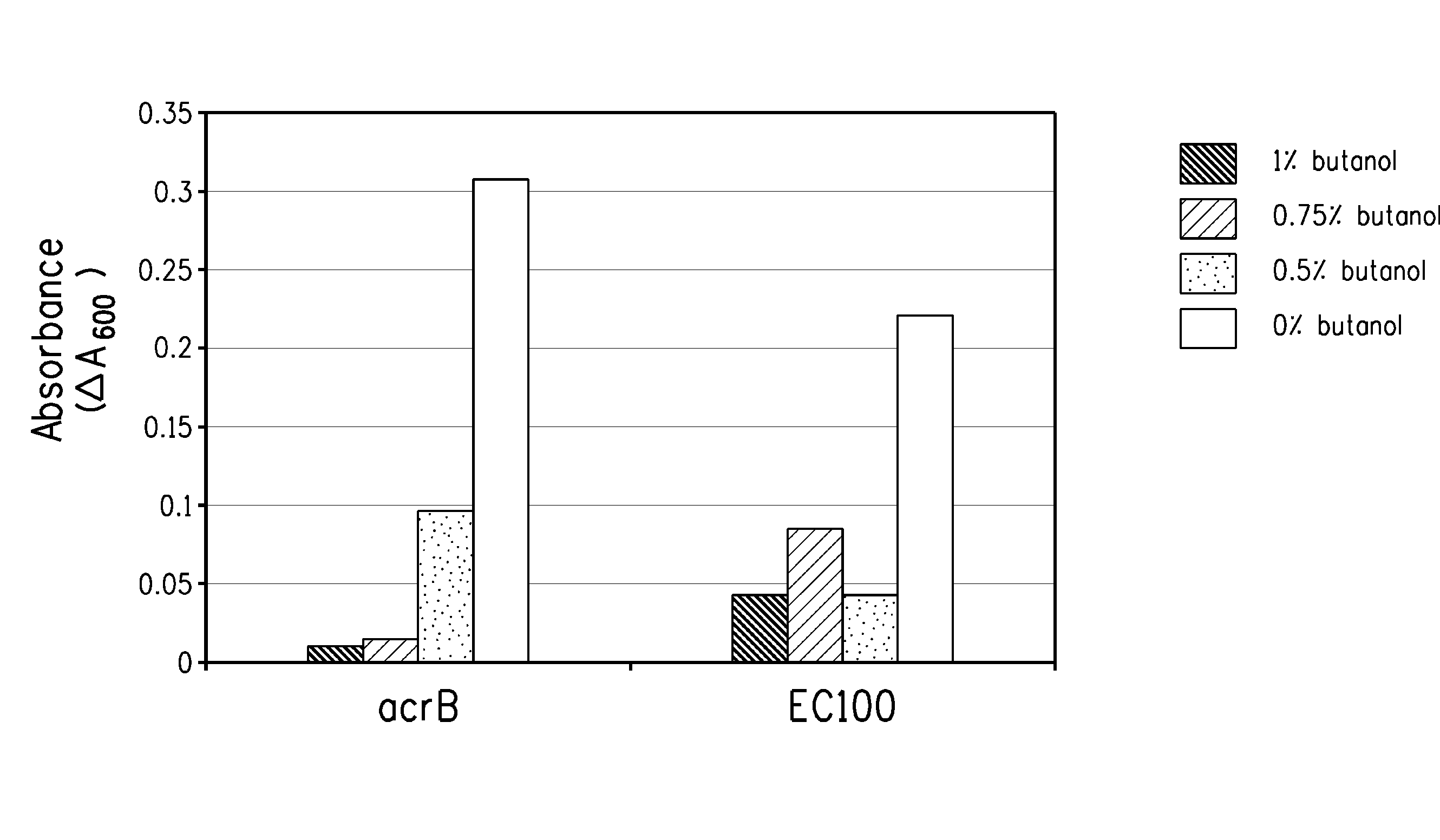
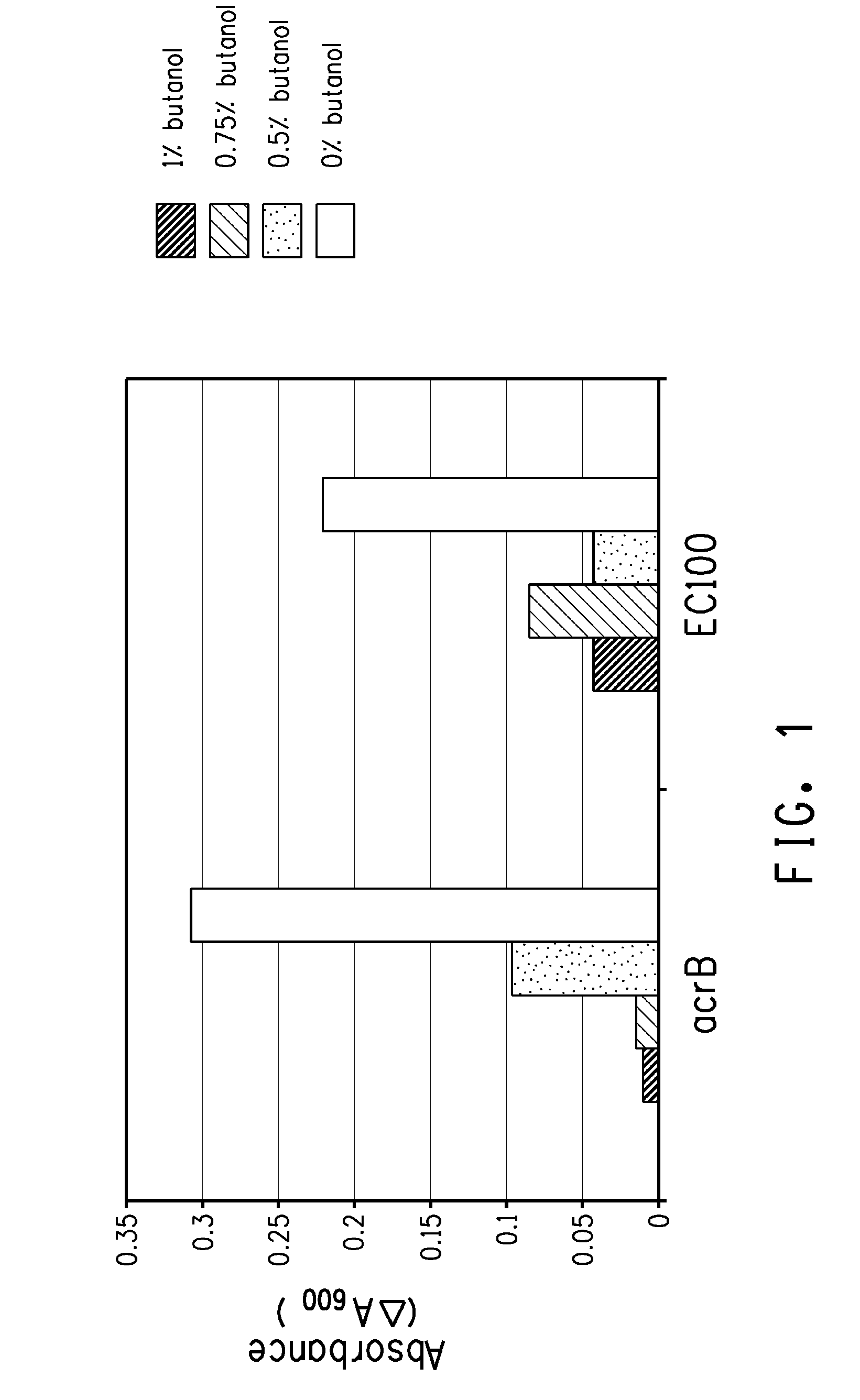
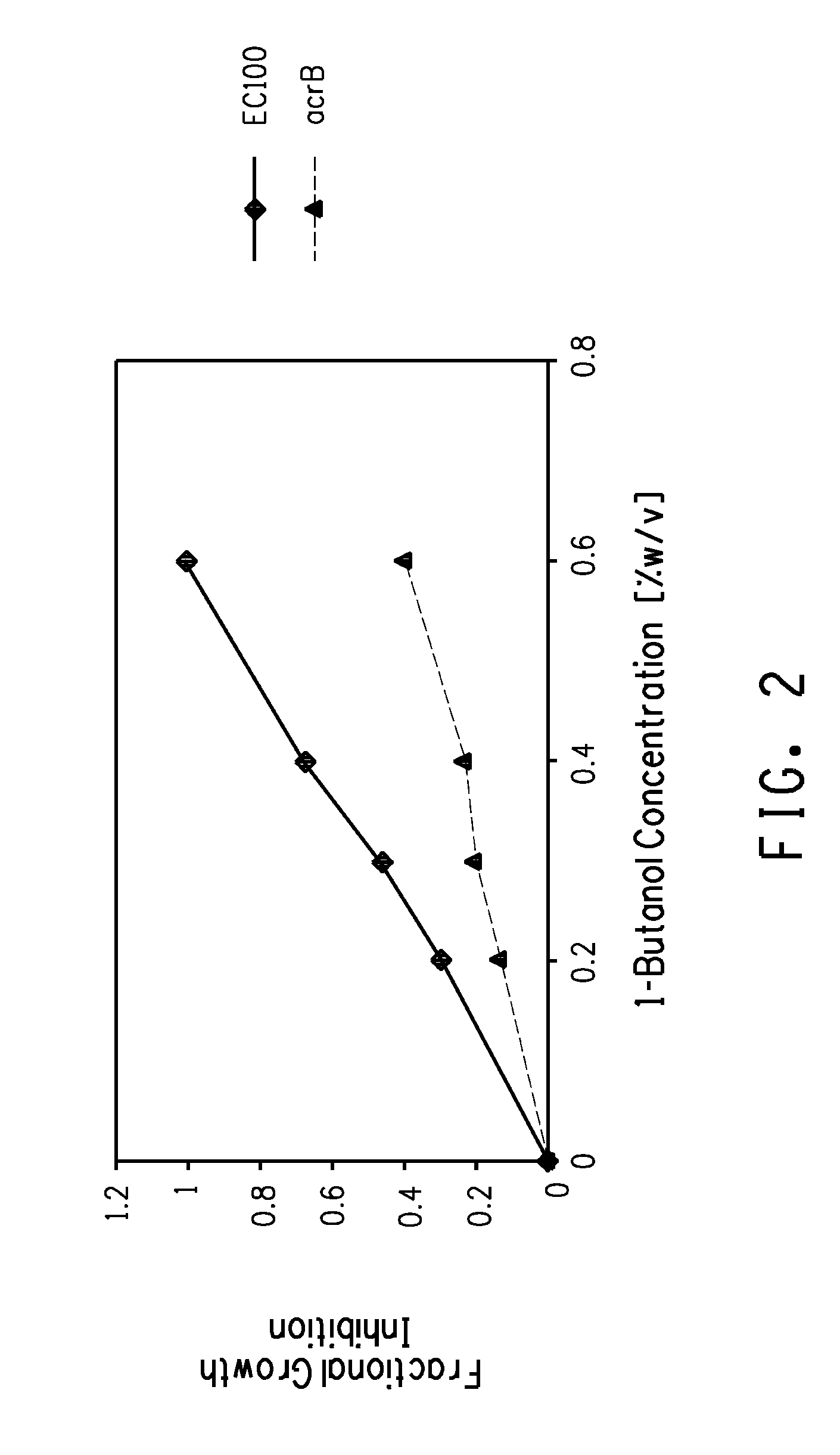
Strain for butanol production
Using screening of transposon random insertion mutants, genes involved in a complex that is a three-component proton motive force-dependent multidrug efflux system were found to be involved in E. coli cell response to butanol. Reduced production of the AcrA and / or AcrB proteins of the complex confers increased butanol tolerance. E. coli strains with reduced AcrA or AcrB production and having a butanol or 2-butanone biosynthetic pathway are useful for production of butanol or 2-butanone.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
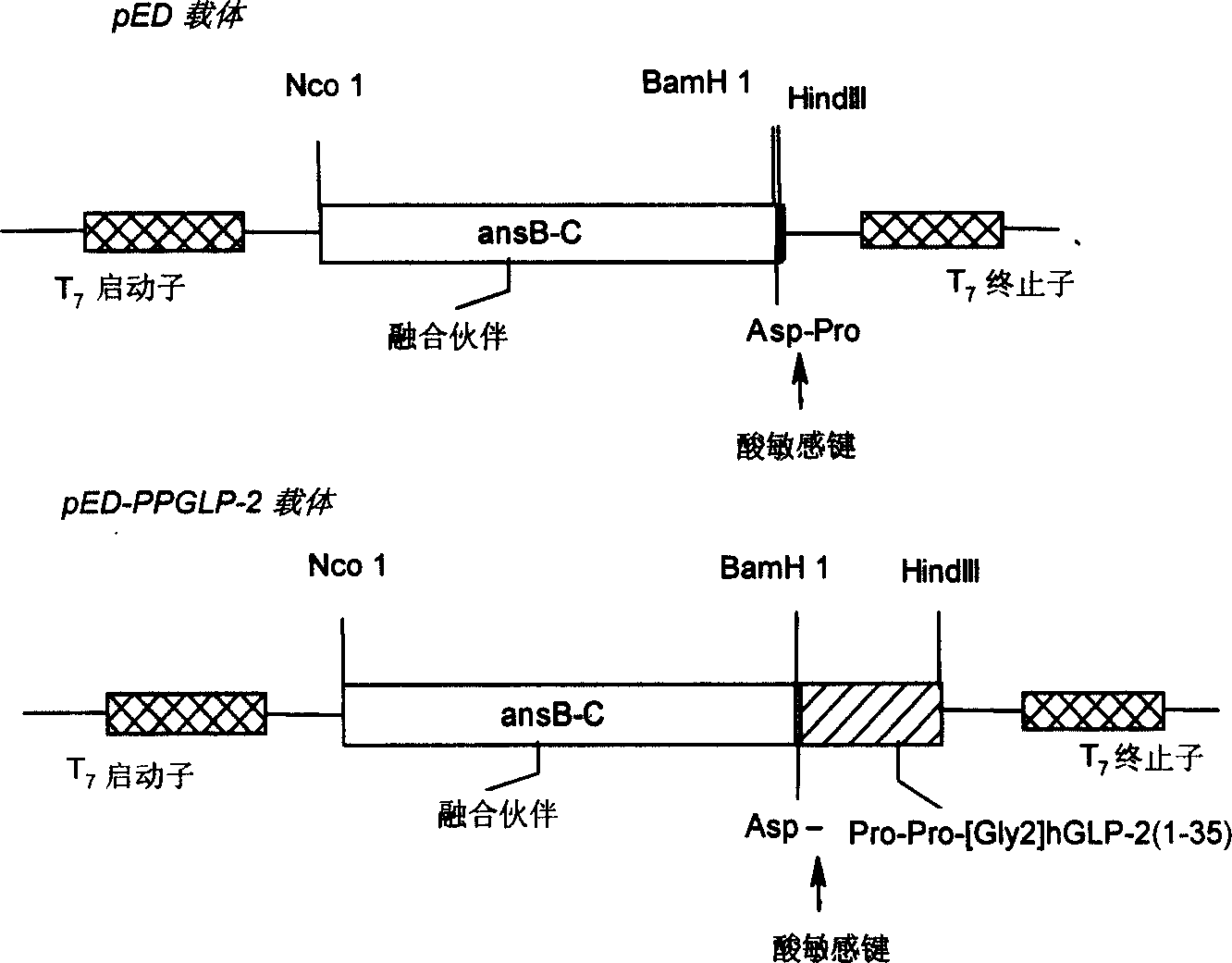
Human pancreas hyperglycemiacin relative peptide-2 analogue
A human glucagon associated peptide-2 analog Pro-Pro-h[Gly2]GLP-2(1-35) for treating the short bowel syndrome and malabsorption of stomach and intestine is prepared through configuring genetic engineering bacterium for effective expression of Pro- Pro-h[Gly2]GLP-2(1-35) in colibacillus cell, splitting, washing, dissolving urea, depositing in alcohol, separating fusion protein, hydrolyzing it, chromatography by DEAE-52 column, separating by HPLC, and freeze drying.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Bioprocess for the production of recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody
A process for producing recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody comprising the steps of fermenting recombinant E. Coli cells in broth, concentrating the cells by removing the broth, crushing the concentrated cells, separating a permeate derived from the crushed cells from cell debris, purifying a recombinant antibotulinum antibody (Fab) from said permeate, and separating said Fab from impurities by diafiltration.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Preparation method of liraglutide intermediate polypeptide
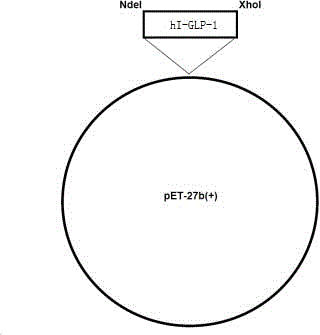
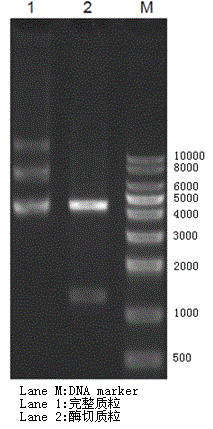
The invention belongs to the technical field of polypeptide preparation and relates to a preparation method of a liraglutide intermediate GLP-1(7-37). The preparation method utilizes a genetic recombination technology. Compared with chemical synthesis, the preparation method reduces impurities and improves purity and a yield. The preparation method comprises the following steps of introducing plasmids with hI-GLP-1(7-37) gene sequences into cells of escherichia coli by a gene engineering method to construct recombinant engineering bacteria, carrying out fermentation induction to obtain a hI-GLP-1(7-37) expression fusion protein, and carrying out renaturation, digestion conversion and separation purification to obtain GLP-1(7-37).
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
Export systems for recombinant proteins
InactiveUS7129060B1Quick modificationImprove stabilityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOmpTCarrier protein
The present invention relates to vectors, host-vector combinations and processes for preparing stable fusion proteins consisting of a carrier protein and a passenger protein, where expression of the fusion proteins leads to exposure of the passenger domains on the surface of bacterial cells, especially Escherichia coli cells. If required, the passenger domains can be released into the medium by proteases, for example by selected host factors such as, for example, OmpT.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method for synthesizing beta-alanine by biological catalysis
InactiveCN102851333AImprove qualityLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-AspartateGenus Catellibacterium
The invention provides a method for synthesizing beta-alanine by biological catalysis, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The method comprises the following steps: culturing escherichia coli microbe to obtain aspartase and L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase, mixing the enzyme-containing escherichia coli cells with an ammonium fumarate aqueous solution, performing an enzyme reaction to generate beta-alanine. The method of the invention is cheap and easily available in raw materials, simple in production process, safe, environment-friendly, mild in reaction condition, high in efficiency, low in production cost, and high in product quality, and has significant economic benefits and environmental protection benefits when compared with traditional methods.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Diffraction-based cell detection using a micro-contact-printed antibody grating
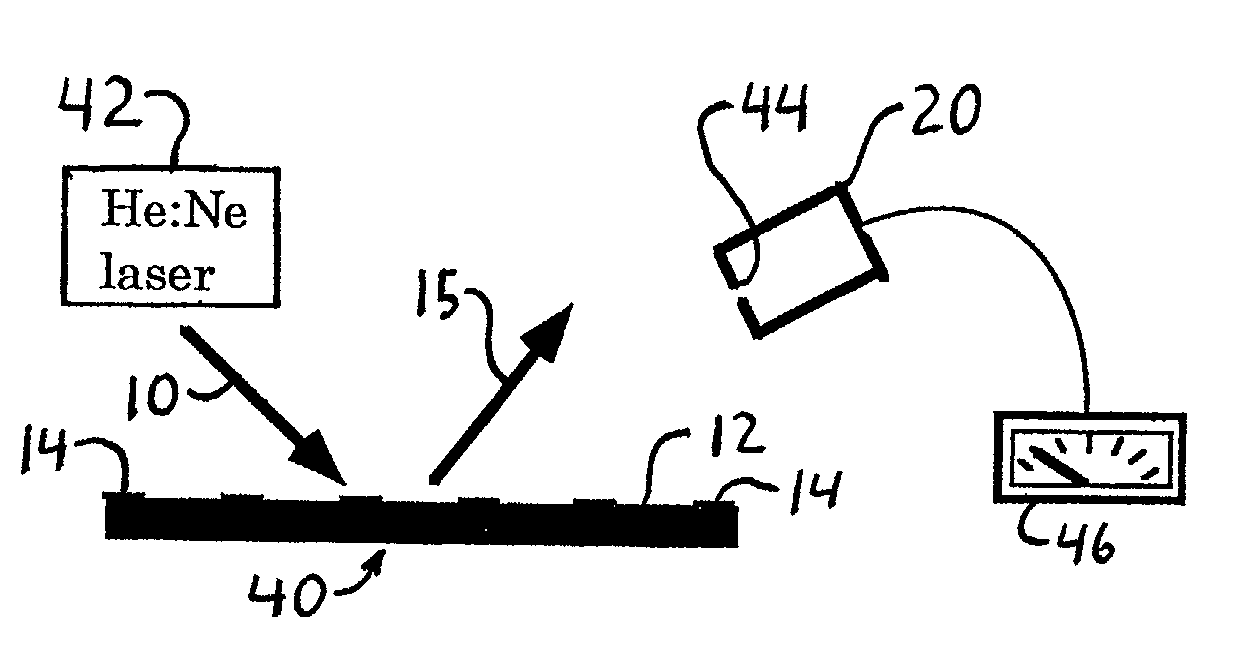
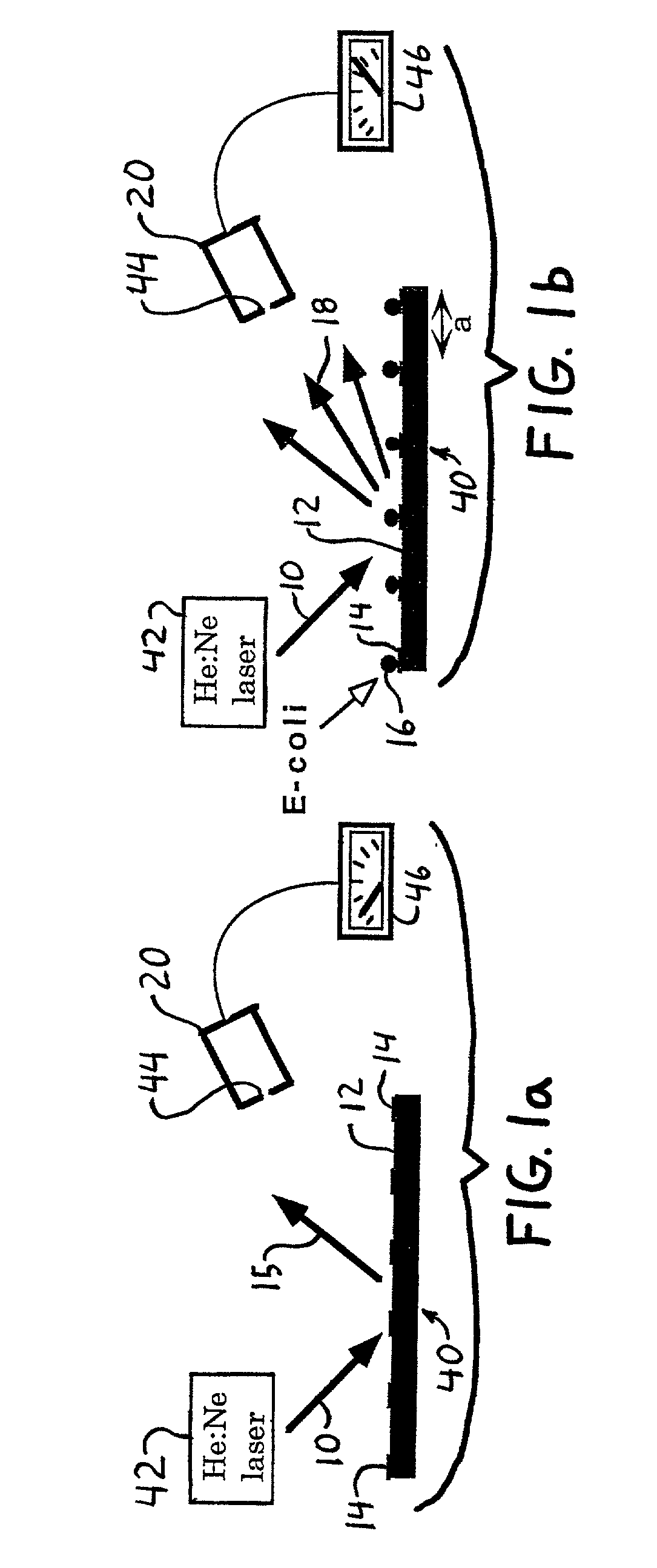
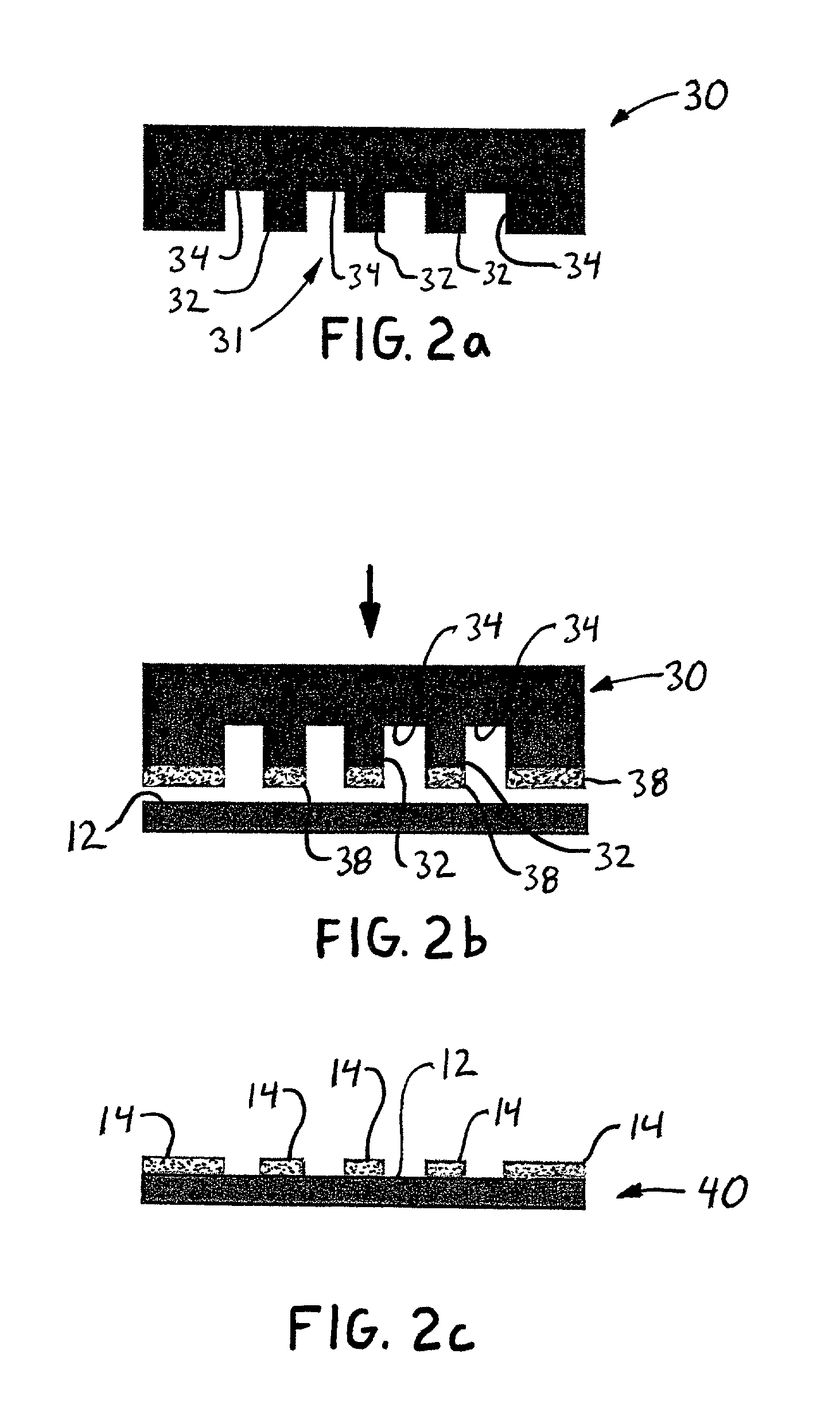
InactiveUS20020037593A1Material nanotechnologyScattering properties measurementsMicrocontact printingEscherichia coli
An optical biological detector is able to bind specific targeted bacterial cells by stamping an antibody grating pattern onto a silicon surface. The antibody grating alone produces insignificant optical diffraction, but upon immunocapture of the targeted cells, the optical phase change produces a diffraction pattern. Micro-contact printing provides a method for placing the antibody grating pattern directly onto a substrate surface with no additional processes or binding chemicals. Antibodies or other biologically active material may be stamped directly onto clean native oxide silicon substrates with no other chemical surface treatments. Direct binding of the antibodies to the silicon occurs in a way that still allows them to function and selectively bind antigen. The performance of the sensor was evaluated by capturing Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells on the antibody-stamped lines and measuring the intensity of the first order diffraction beam resulting from the attachment of cells. The diffraction intensity increases in proportion to the cell density bound on the surface.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for biologically preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester with recombinant escherichia coli expressed ketoreductase
InactiveCN103173503AHigh optical purityGenerate efficientlyMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidEthyl acetate
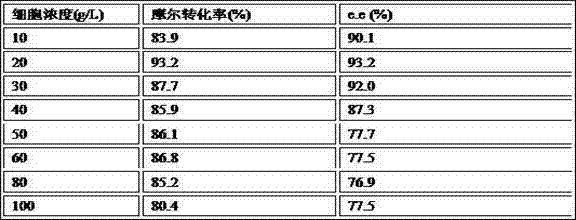
The invention discloses a method for biologically preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester with recombinant escherichia coli expressed ketoreductase and application thereof in preparing (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester through asymmetric reduction of 4-chloroacetoacetic acid ethyl ester. The recombinant escherichia coli for expressing the gene of the ketoreductase (KRED) is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) so that the escherichia coli cell is recombined into a catalyst; efficient preparation of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyric acid ethyl ester through asymmetric reduction of 4-chloroacetoacetic acid ethyl ester in a single water phase is realized no matter in the presence of or in the absence of coenzyme NAD(P)H; and the molar transformation rate is higher than 92% and the enantiomer excess (e.e.) of the product is 100%.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV +1
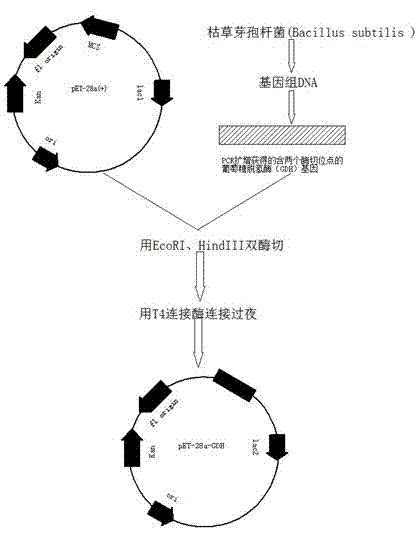
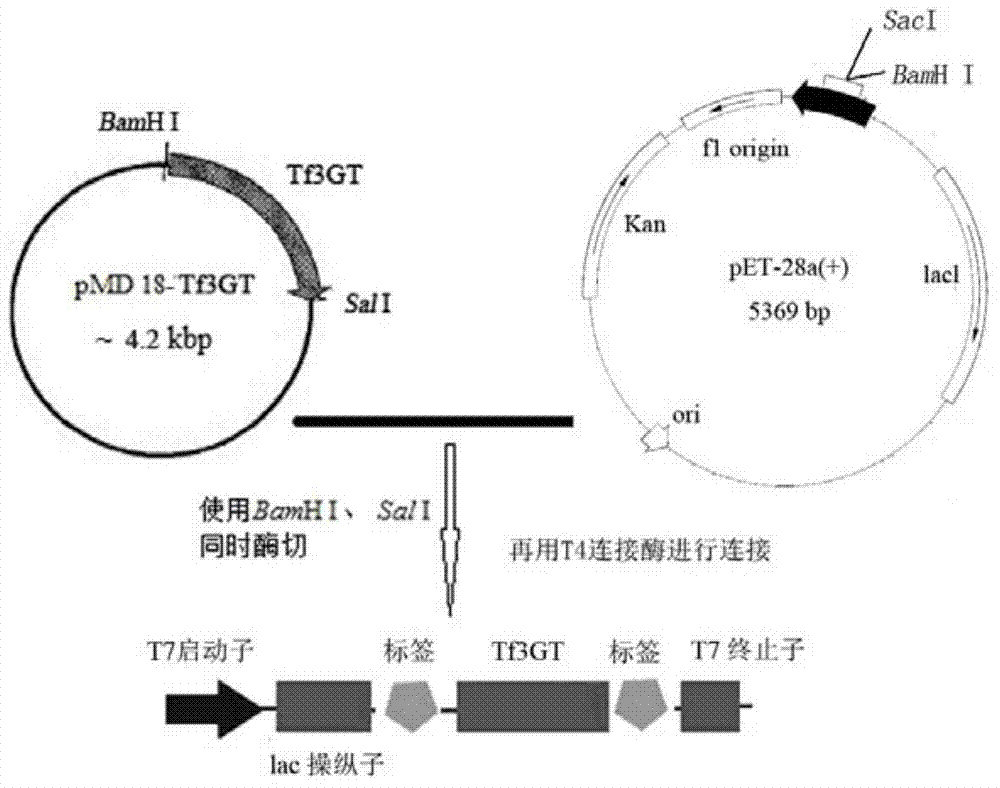
Tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and coding gene thereof
InactiveCN103695382AImprove viewing valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityTransgene
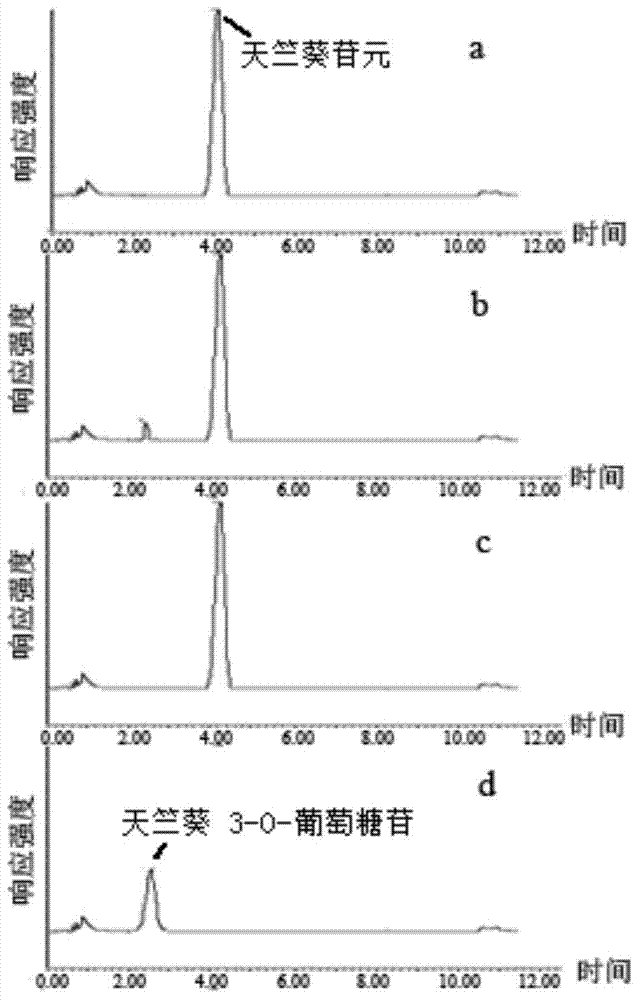
The invention discloses a tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein is a protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2, or a protein with tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase activity obtained by substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids on the basis of the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 for coding the protein. When the tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT gene is expressed in Escherichia coli cells, the recombinant flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase protein can promote anthocyanin and UDP-glucose to react and generate the anthocyanin. The Tf3GT coding sequence has application value in modification of varieties by a transgenic technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, and encoded protein and application of the same
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase gene, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a host converted by the vector, an expression product produced by utilization of the converted body, and the application of the product. Staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, brucella, and nitrite reductase gene of escherichia coli serve as references for a primer design, genome DNA extracted by Lactobacillus plantarum serves as a template, and the gene segments of Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase are amplified via the PCR technique; the segments are connected to a pET-32a(+) expression vector and then transferred to escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells; and after IPTG induction, expression of Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase (NiRL) protein is carried out, finally obtaining Lactobacillus plantarum nitrite reductase protein.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by microbial catalysis
A method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by microbial catalysis relates to a method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of engineering escherichia coli cells. The method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of engineering escherichia coli cells comprises the following steps of: compounding, inducing, selecting and optimizing anti-phloroglucinol mutant strains by employing HNO2 and LiCl; carrying out PCR amplification by taking the genome DNA of bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 as a template to obtain a polyketide synthase gene (phlD); connecting with a pET carrier after cleavage, transferring to the anti-phloroglucinol mutant strains, and inudcing and expressing a target protein by using IPTG to obtain the engineering escherichia coli for catalyzing and synthesizing the phloroglucinol. The phloroglucinol can be obtained in the fermentation liquor after the engineering escherichia coli are fermented, and the phloroglucinol is extracted and concentrated to get the finished phloroglucinol. The invention first provides the method for synthesizing phloroglucinol by catalysis of the engineering escherichia coli, and lays a solid foundation for catalyzing and synthesizing phloroglucinol by an environment-friendly synthetic process in future.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
Nitrile hydratase gene, encoded enzyme, vector, engineering bacterium as well as application of engineering bacterium to preparation of amide compound
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase gene, an encoded enzyme, a vector, an engineering bacterium as well as an application of the engineering bacterium to preparation of an amide compound. The recombinant nitrile hydratase gene is formed by sequentially connecting an alpha subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.2, a beta subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and an activation element shown in SEQ ID NO.4. The functional expression of the tentative nitrile hydratase gene from sulfitobacter sp E-36 in Escherichia coil cells is realized, the gene engineering bacterium for expressing the nitrile hydratase efficiently is provided, and aromatic nitrile can be converted into the corresponding amide compound efficiently.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacterium, construction thereof and method for preparing D-valine by using the same
InactiveCN101260381APrevent oxidationImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneValine
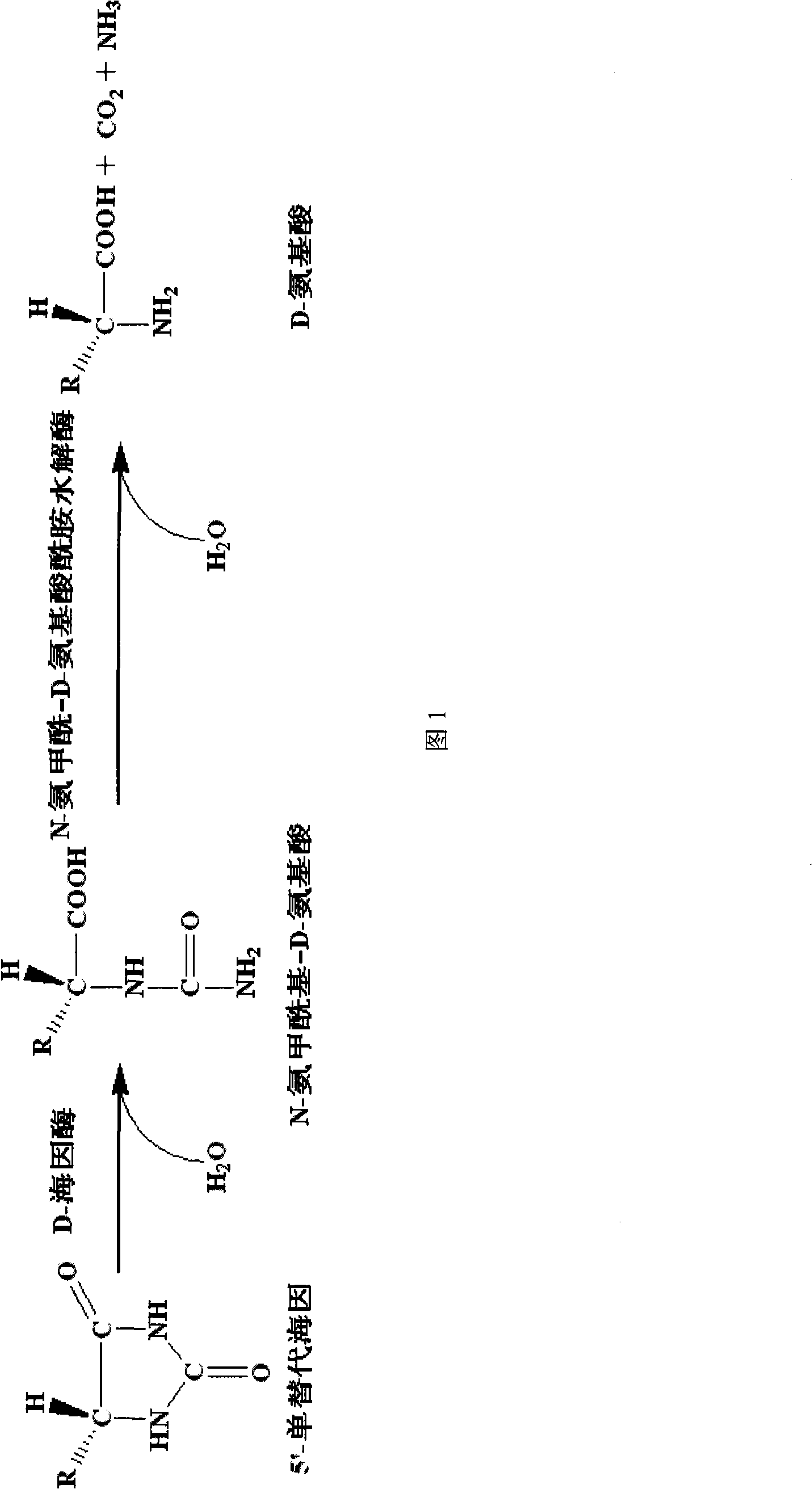
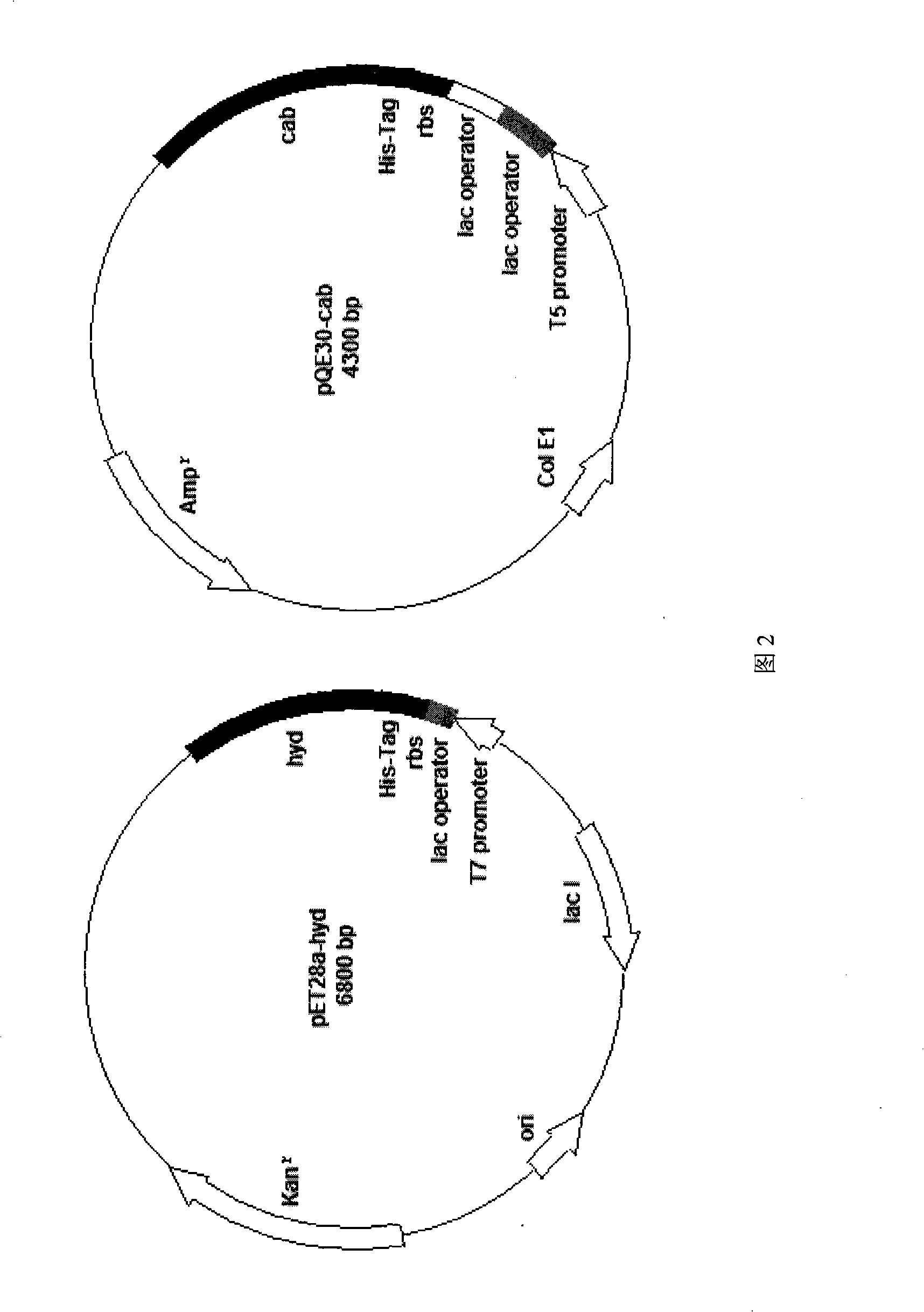
The invention provides an engineering strain, which can simultaneously express D-hydantoin enzyme and N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase. The construction method of the invention is as follows: a D-hydantoin enzyme gene is cloned to a plasmid ET-28a and an N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase gene is cloned to a plasmid pQE-30, and then two recombinant plasmids pET28a-hyd and pQE30-cab are shifted into the same Escherichia coli cell by utilization of a co-conversion technology. The invention also provides a method for producing D-valines by utilization of the engineering strain to convert 5'-opropyl hydantoin. The method is characterized by high optical purity of products, simple manufacturing technique, and environmental protection and so on; moreover, compared with the prior market products, the method is low in production cost.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
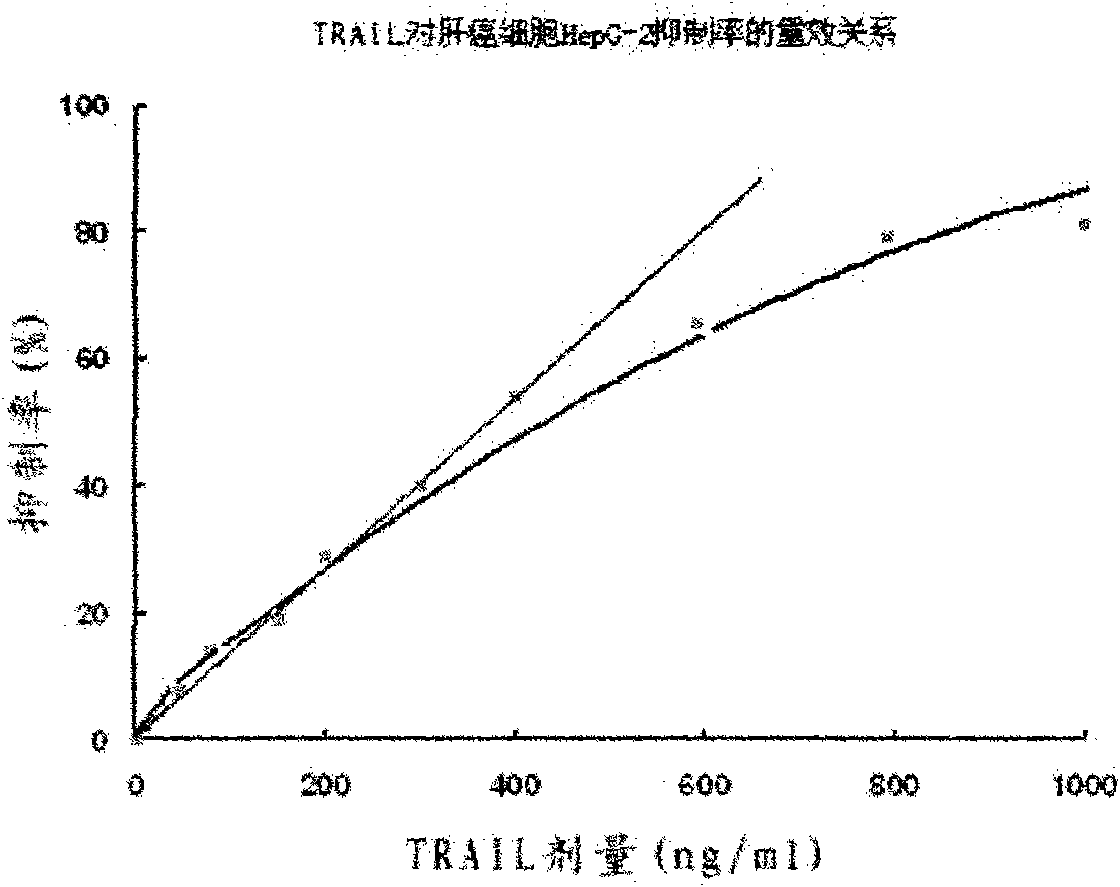
Preparation method for soluble truncated human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) active protein
InactiveCN102021173ATruncated soluble expressionShort fermentation timeCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsHumaninInclusion bodies
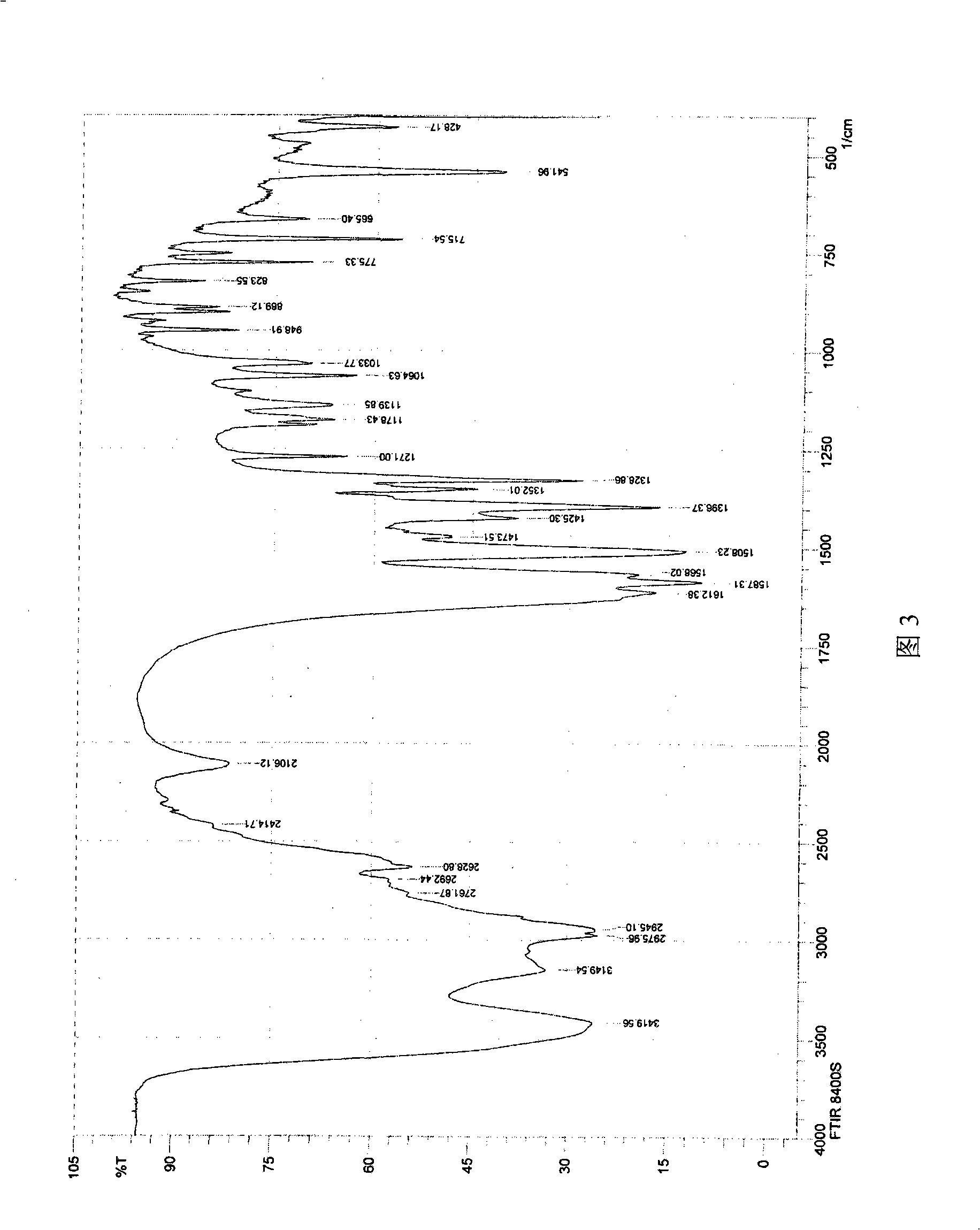
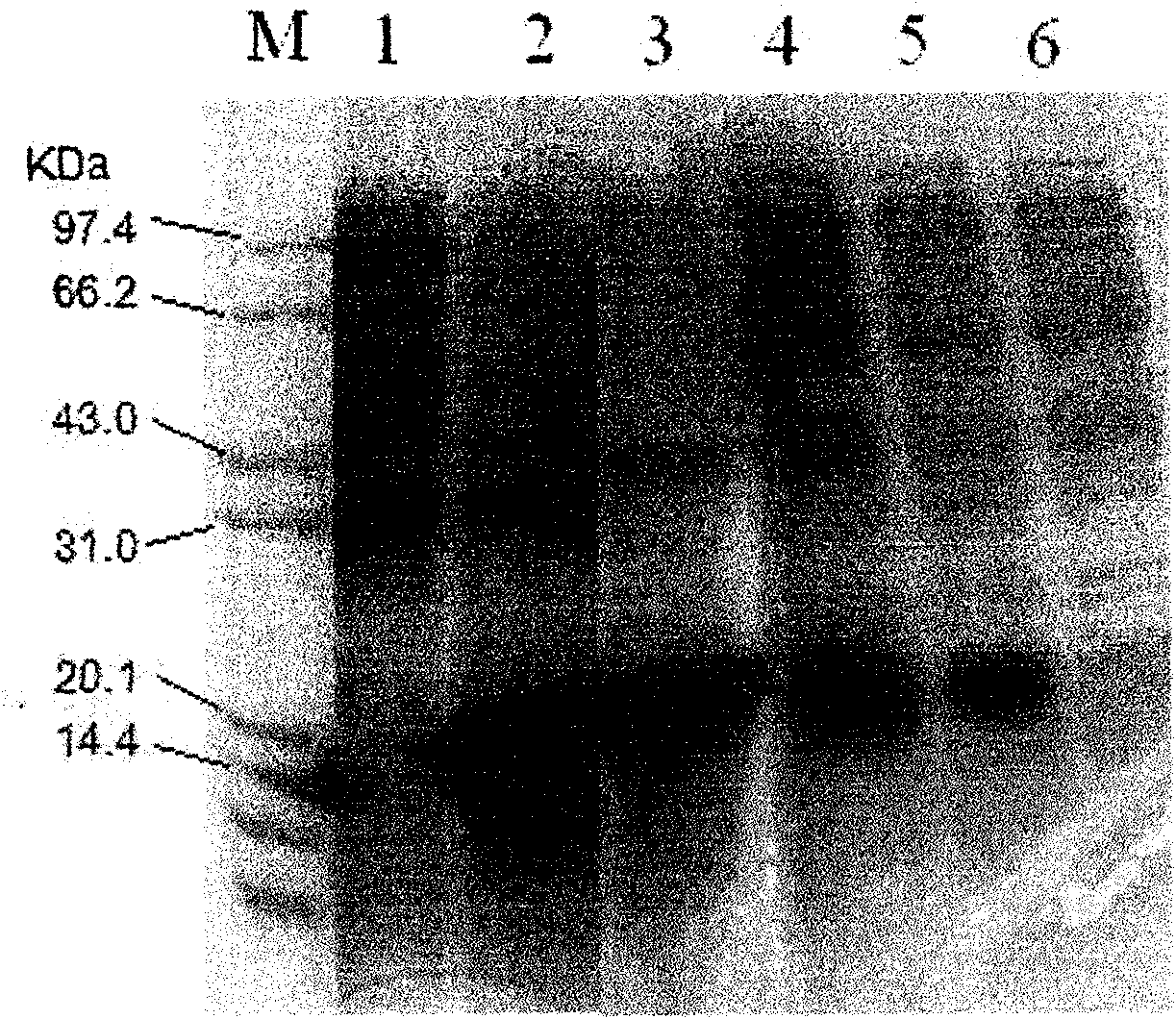
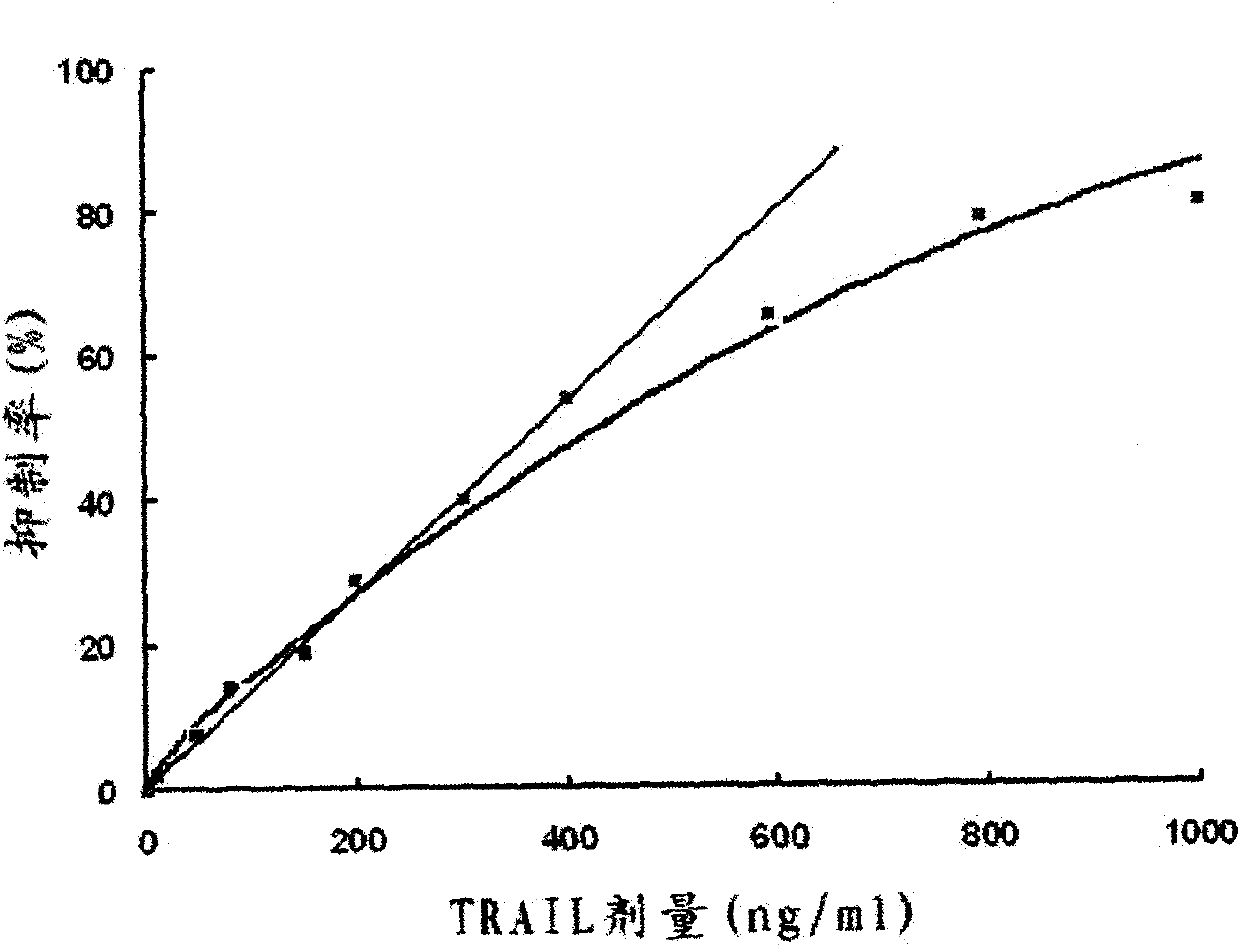
The invention provides a preparation method for a soluble truncated human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) active protein, comprising the following steps of: (A) designing and synthetizing an oligomerization deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) single-stranded segment according to the amino acid sequence of the human TRAIL protein issued by a Genebank by the preference of a bacterium genetic code; (B) synthetizing a complete double stranded DNA by three-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR); (C) carrying out amplification by utilizing a T-carrier, and inserting the amplified double stranded DNA segment into an expression carrier and screening a positive transformant; (D) expressing the truncated human TRAIL protein in escherichia coli at low temperature; (E) purifying the protein by using a three-step method; and (F) determining the truncated TRAIL protein. The invention realizes that the truncated human TRAIL protein is efficiently expressed in an escherichia coli cell and a purification preparation technique thereof and overcomes the problem that an infusible inclusion body is easy to form in the prior art. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short fermentation time and easy purification, and moreover, the protein is ensured not to have any modification, and the protein reaches electrophoretically pure. The invention can be directly used for the research work of biochemistry and molecular biology and the oncology and the preclinical stage of tumor treatment or the development of clinical drugs.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
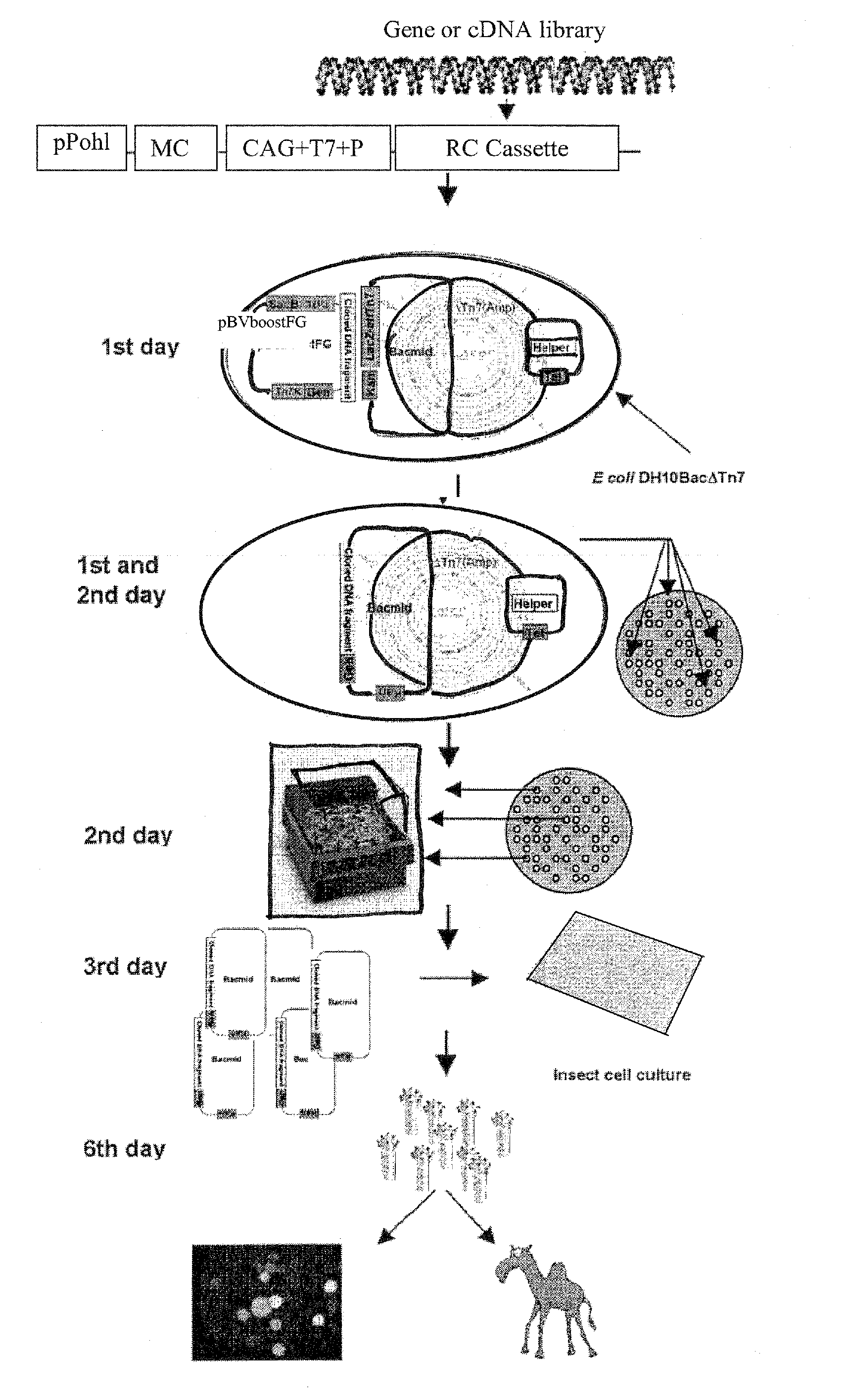
Engineered Baculoviruses and Their Use
InactiveUS20090176660A1Improve the display effectEasy and fast productionAnimal cellsVectorsHeterologousGene product
Baculovirus is engineered so that the capsid displays one or more heterologous peptides or protein. Such baculovirus can be used to deliver therapeutics, and in functional genomics.Also a method for generating recombinant baculoviruses comprises:(i) incorporating a lethal gene into a donor plasmid comprising an expression cassette;(ii) transposing the expression cassette from the donor plasmid into a bacmid in E. coli cells to form a recombinant bacmid, wherein the lethal gene product kills the cells still harbouring the donor vector;(iii) extracting the recombinant bacmids; and(v) transfecting insect cells with recombinant bacmids to form recombinant baculoviruses.
Owner:ARK THERAPEUTICS
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and production method
PendingCN114480240AGrow fastImprove expression levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell factory
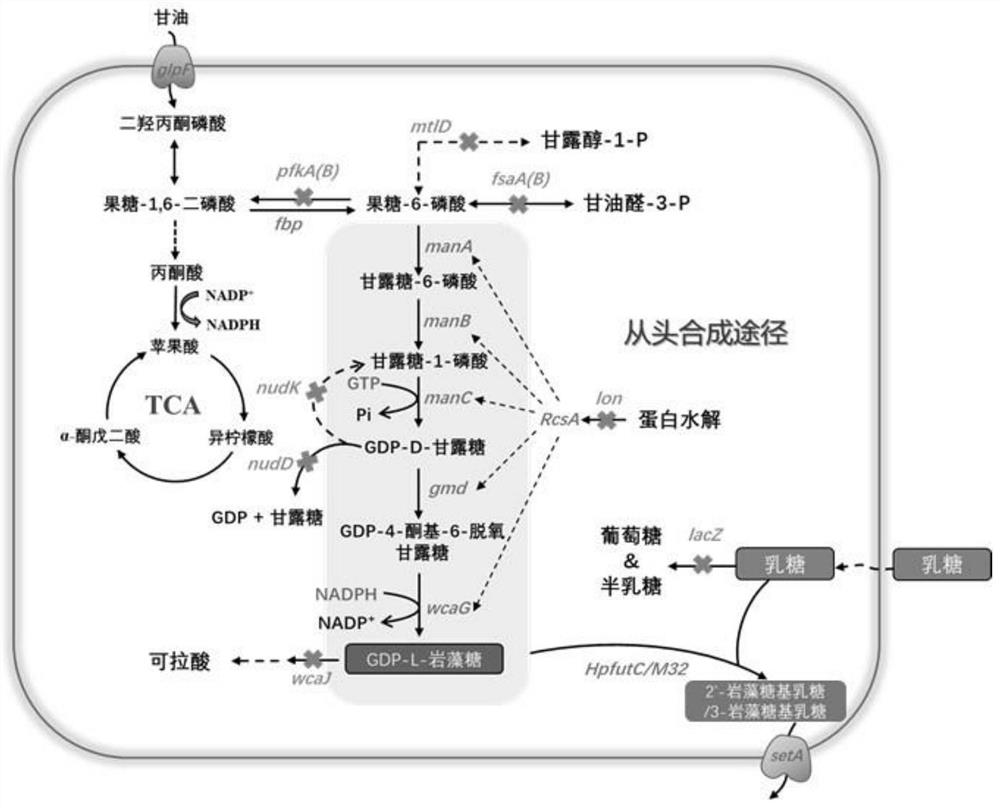
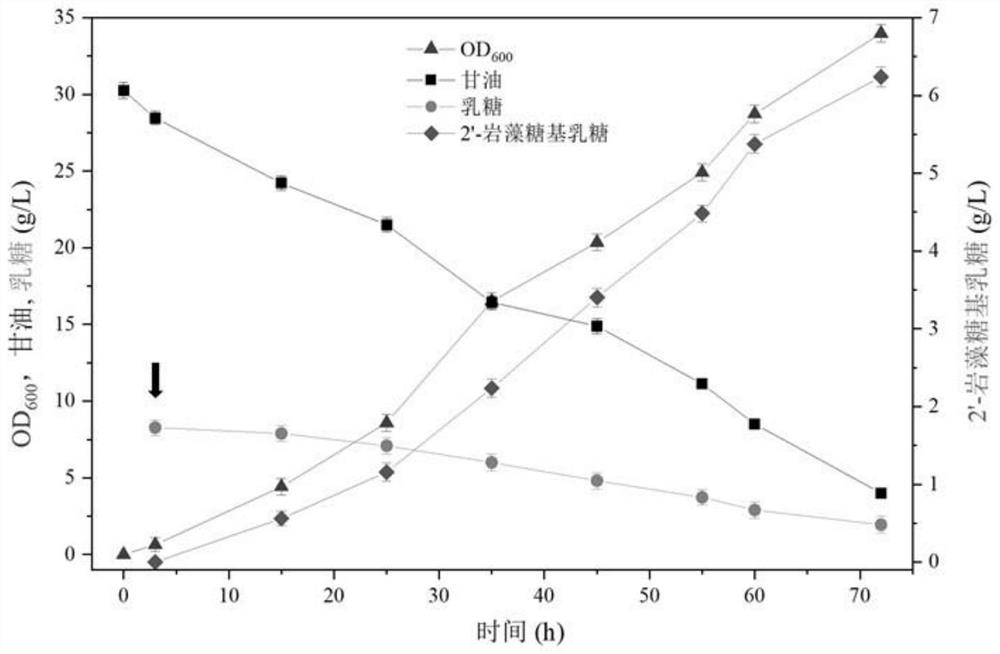
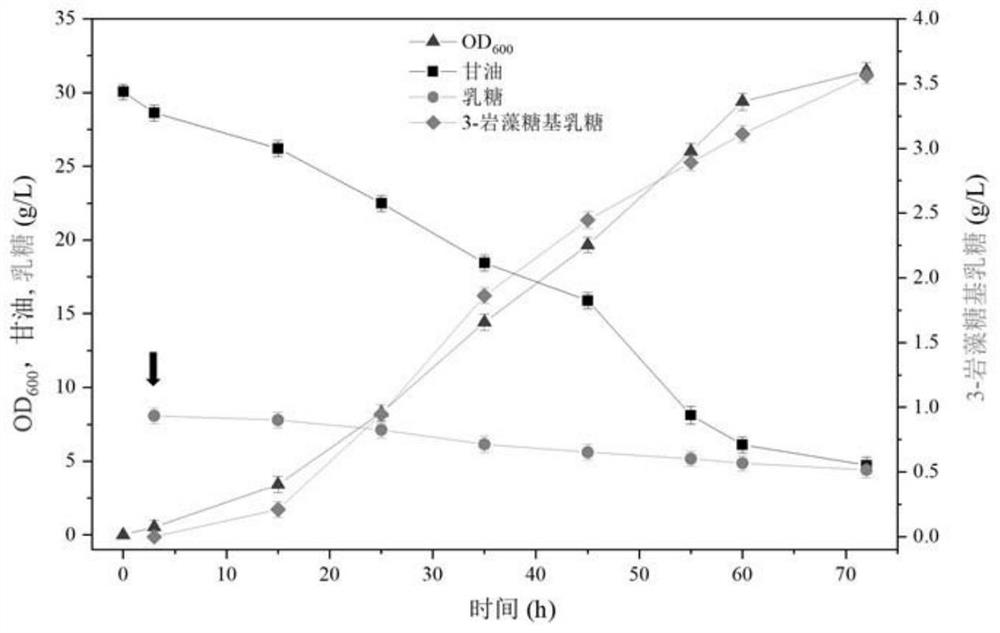
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and a production method of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to metabolic engineering and food fermentation technologies. According to the invention, a synthetic biological means is utilized, an escherichia coli cell factory of fucosyllactose is constructed based on a de novo synthetic route, bypass related genes lacZ, wcaJ, nudD, pfkA and lon in host cells are knocked out by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, and genes manB, manC, gmd and wcaG are assembled through a multi-plasmid expression system, so that the fucosyllactose is obtained. Constructing expression vectors with different copy numbers to increase the expression level of key genes; fucosyltransferase from different sources is screened, so that the activity of rate-limiting enzyme is improved. The constructed recombinant escherichia coli can be used for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose by utilizing glycerol, is stable in heredity and high in expression level, and has obvious industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
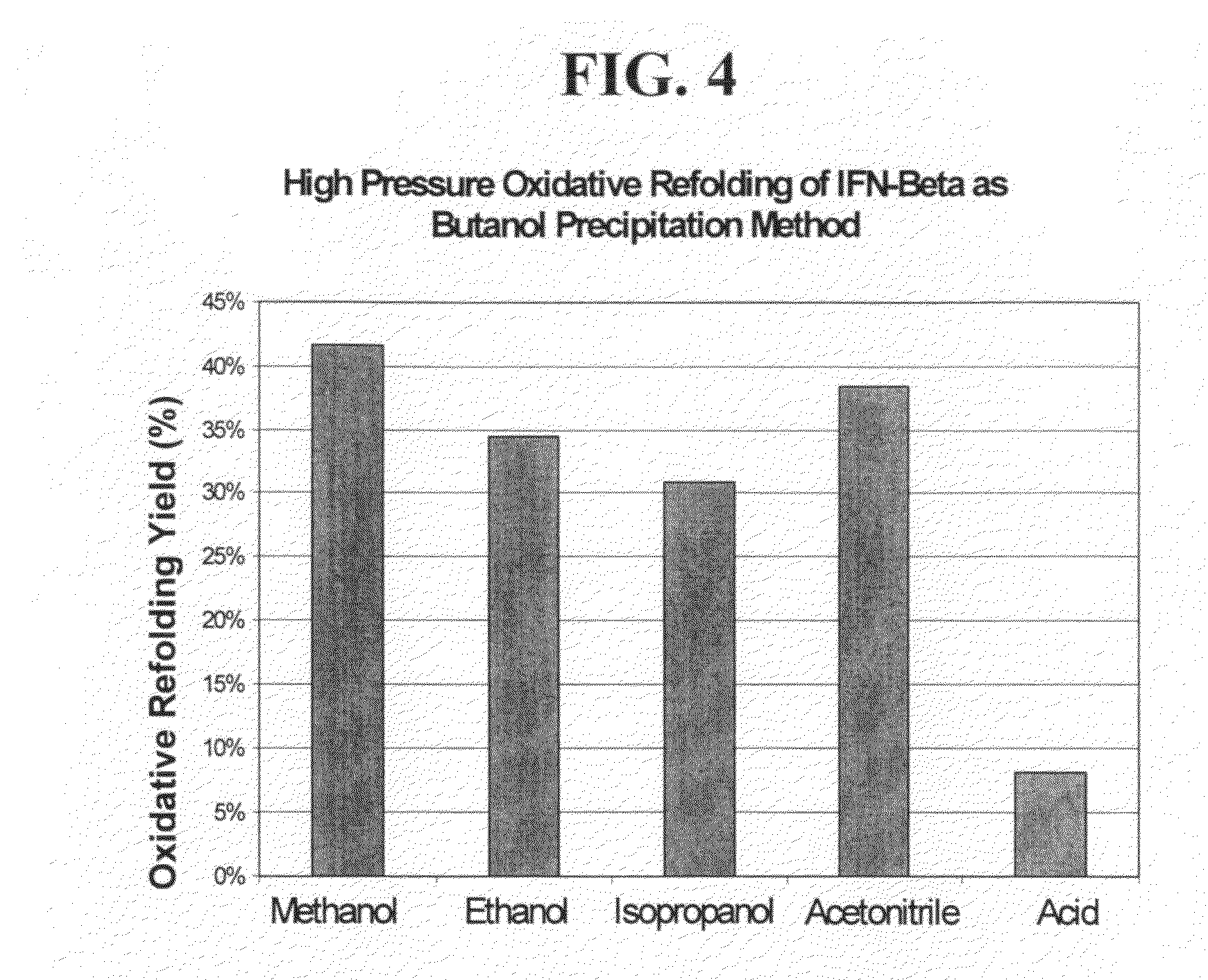
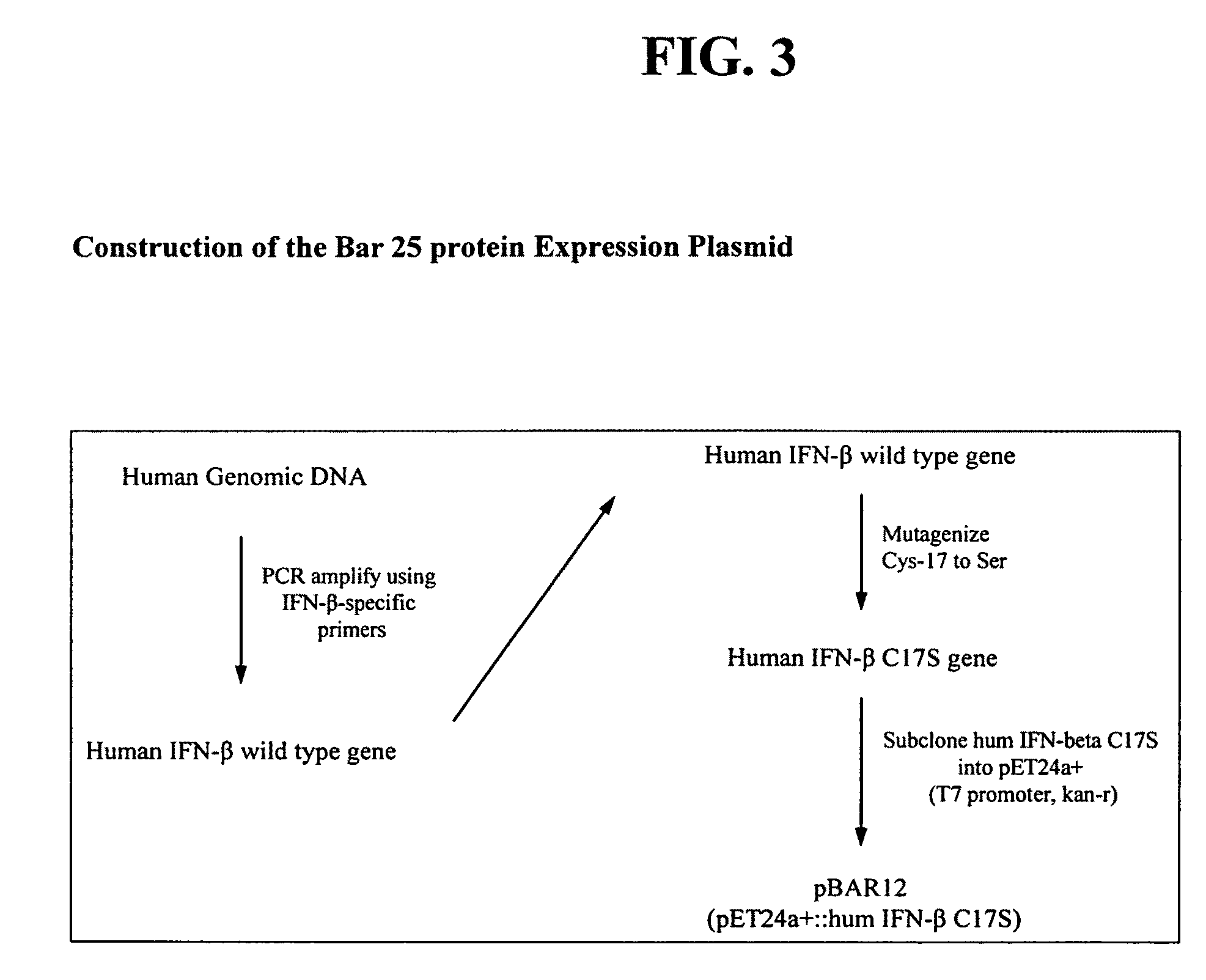
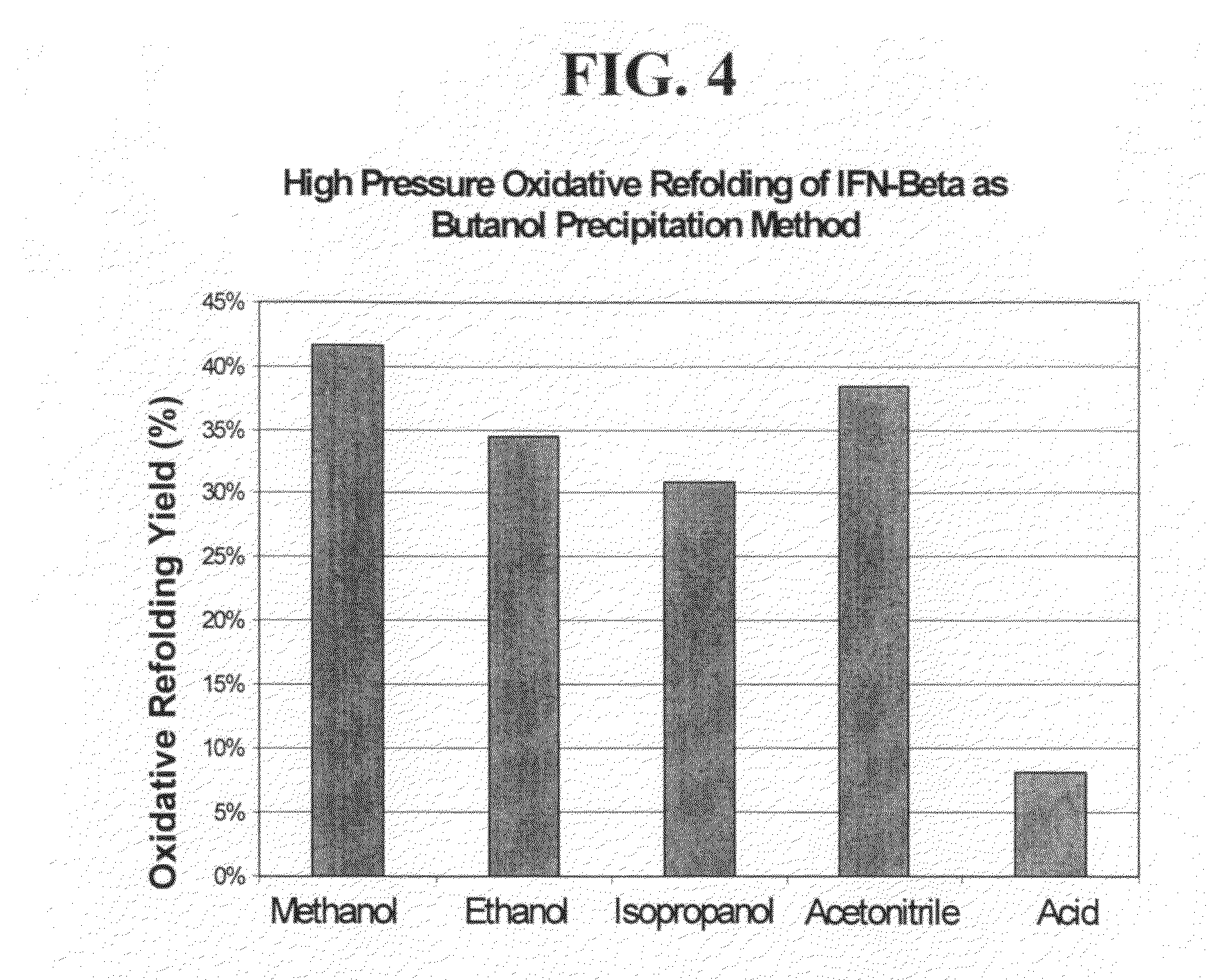
High pressure treatment of aggregated interferons
InactiveUS20090208453A1High yieldImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesInclusion bodiesCell Aggregations
High pressure to treat aggregated interferons, particularly recombinant human interferon-β, to reduce the aggregate content of interferon material. Highly pure, soluble monomeric recombinant interferon-β is prepared in representative embodiments. Multiple strategies may be used in combination that make nonglycosylated IFN-β more amenable to high pressure treatment. It has been found that refolding yields of high pressure treatment can be significantly improved by use of a combination of strategies, including, or example a pre-treatment of the IFN-β that involves solubilizing and then precipitating the protein. This pre-treatment is particularly effective with respect to recombinant IFN-β inclusion bodies recovered from host cells such as E. coli cells. According to another strategy, refolding under high pressure is much more effective when the refolding reagent incorporating the IFN-β incorporates a zwitterionic surfactant and / or a cholate salt. When a solubilization and precipitation pre-treatment is used, the effectiveness of the high pressure treatment is further enhanced when the refolding reagent incorporating the protein incorporates a disulfide shuffling chemistry such as cysteine / cystine. According to still yet another strategy, high pressure treatment is more effective when using atypically high treatment pressures. When coupled with purification techniques, these strategies singly or in combination provide a low aggregate or substantially aggregate free, biologically active solution. Biologically active solutions comprising nonglycosylated interferon, said interferon comprising less than about 5 weight percent of protein aggregation has been found to exhibit improved PK / PD characteristics.
Owner:NURON BIOTECH
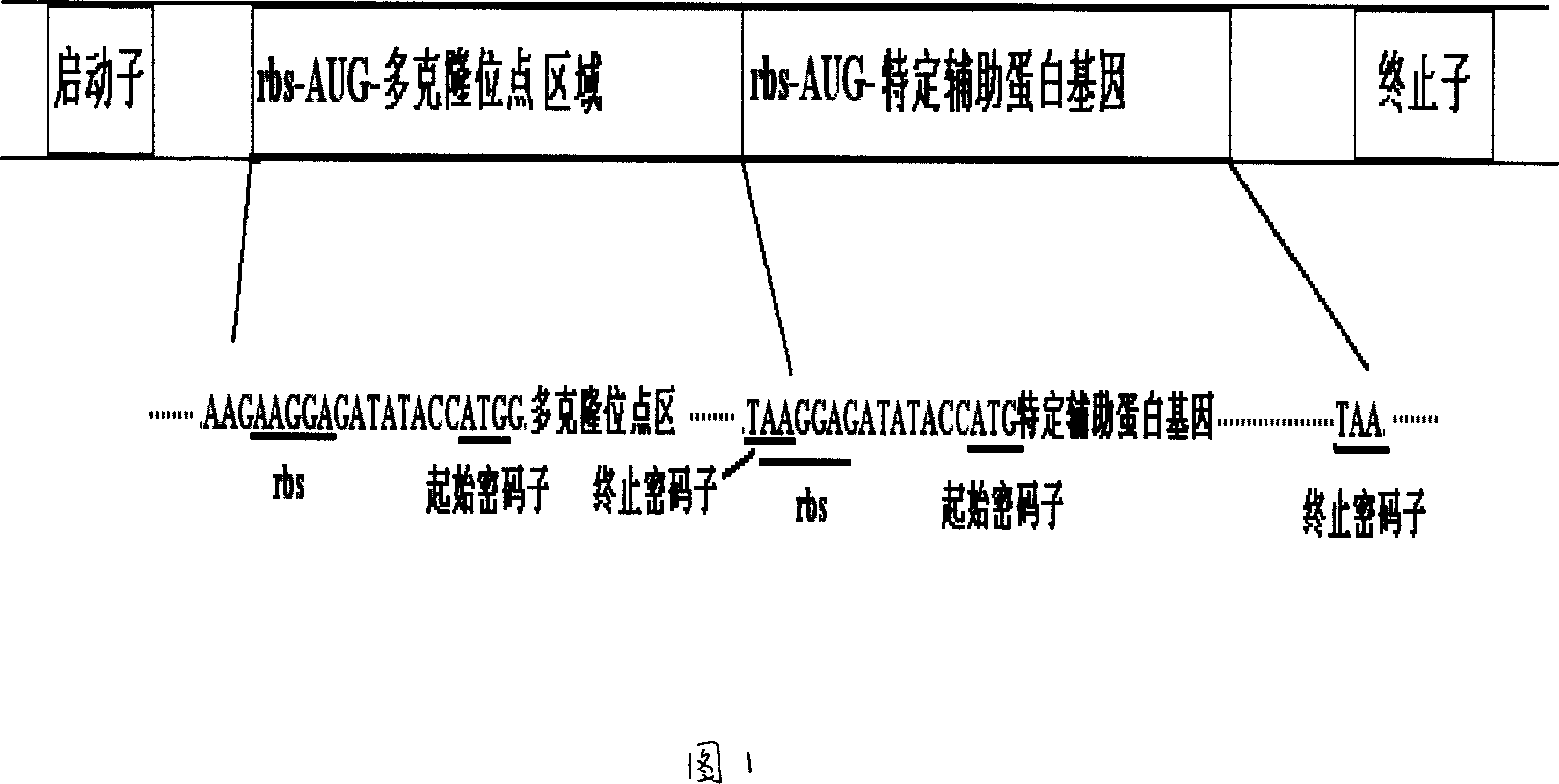
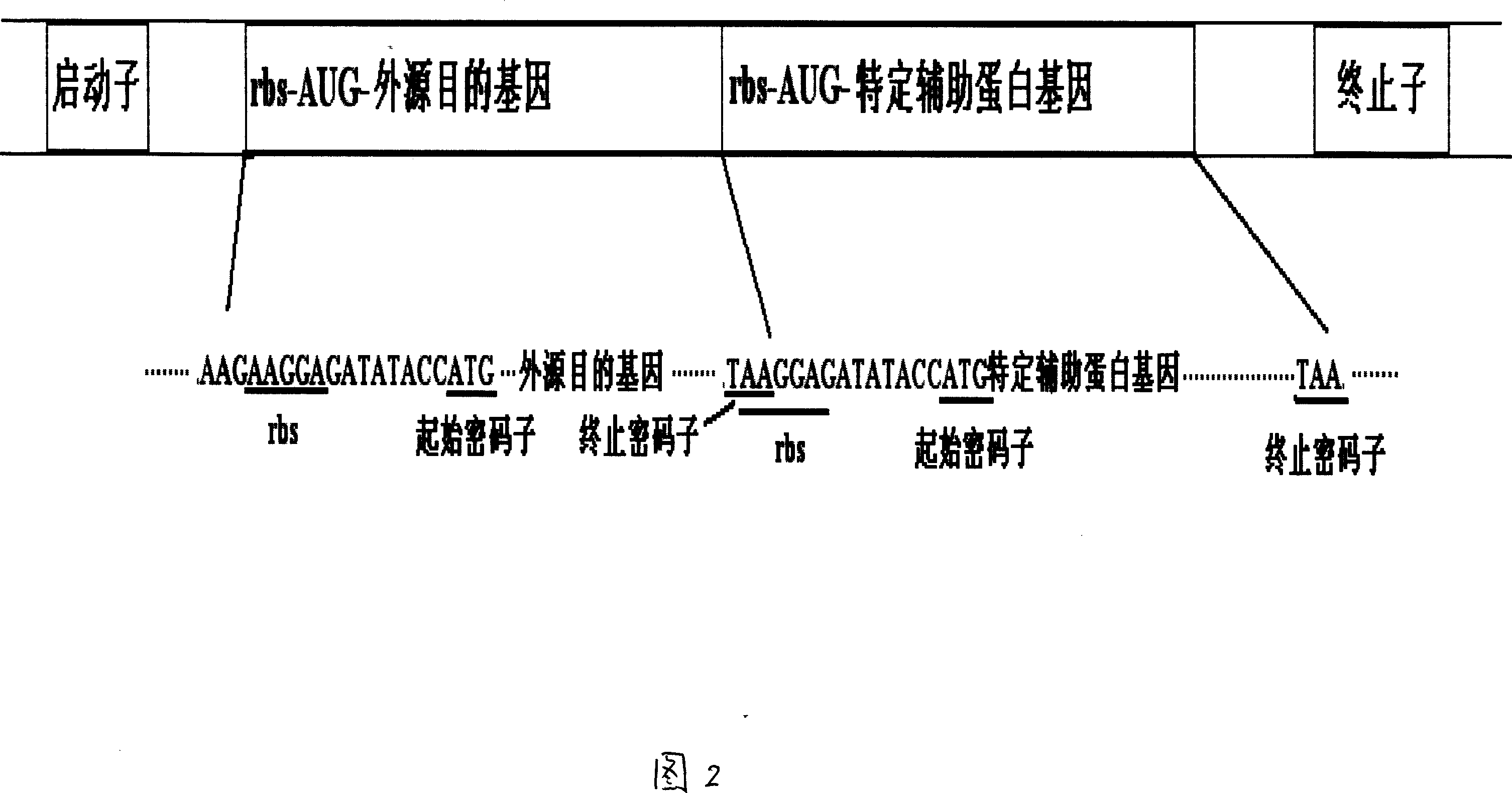
Prokaryotic cell non-fusion soluble expression system
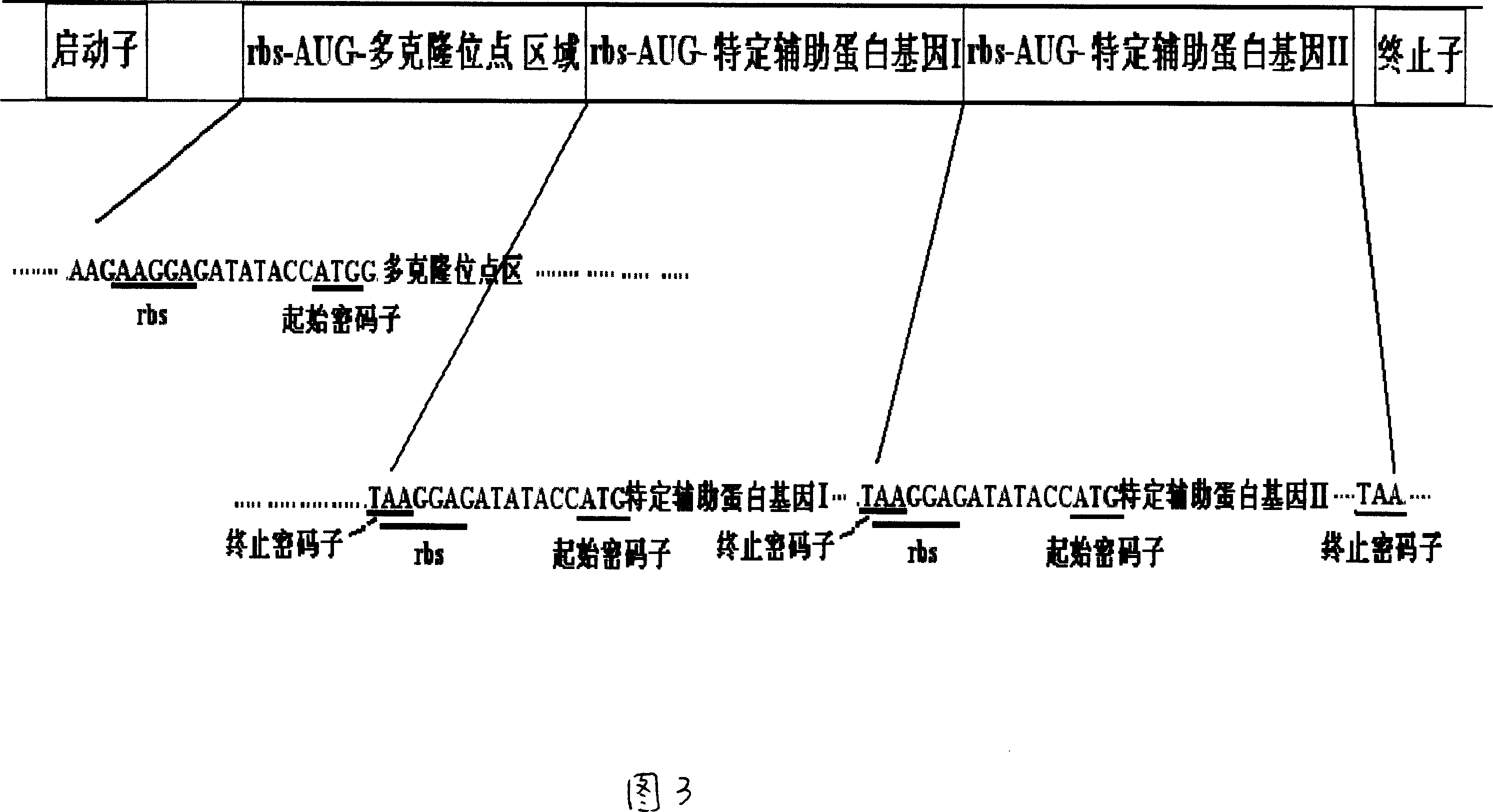
The invention discloses a procaryotic cell non-merge solubility pressing system, which comprises the following steps: building one type auxiliary protein gene or two type auxiliary protein gene and pre-expressing exogenesis goal gene in a transcription unit; proceeding intracellular co-express through each self-contained translational control system of auxiliary protein gene and pre-expressing exogenesis goal gene in the same pronucleus expression host cell; utilizing the auxiliary protein to realize non-merge solubility expression especially to realize non-merge solubility expression with multiple disulfide bond peptide chain. This system can make the expressing quantity of procaryotic cell occupy above 105 of thallus total protein under the normal condition.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
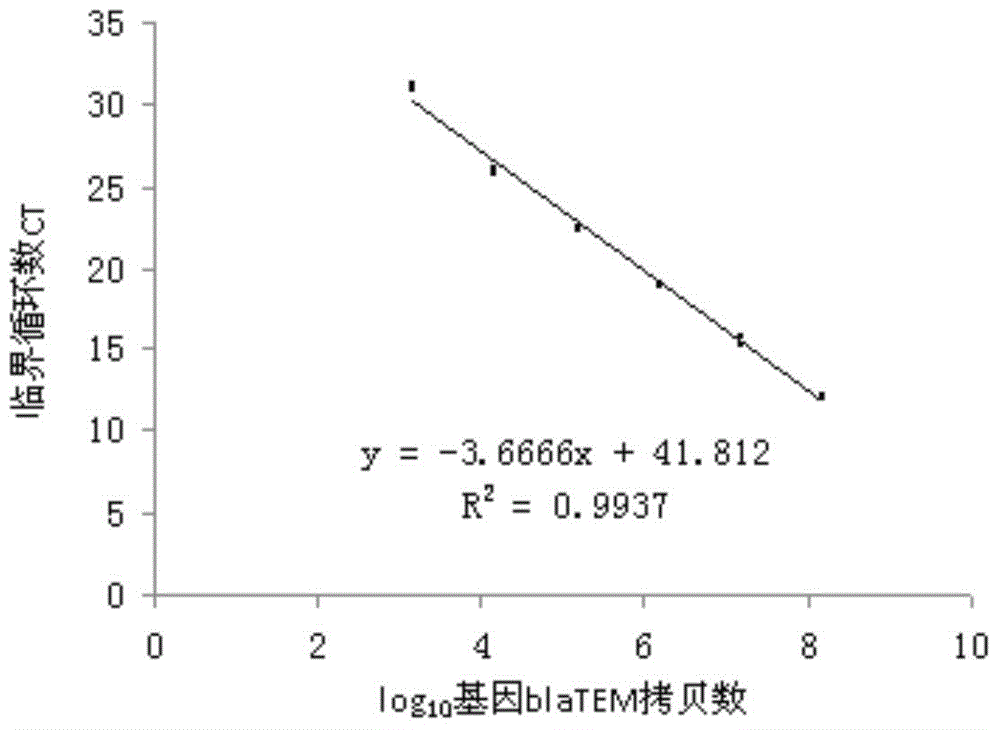
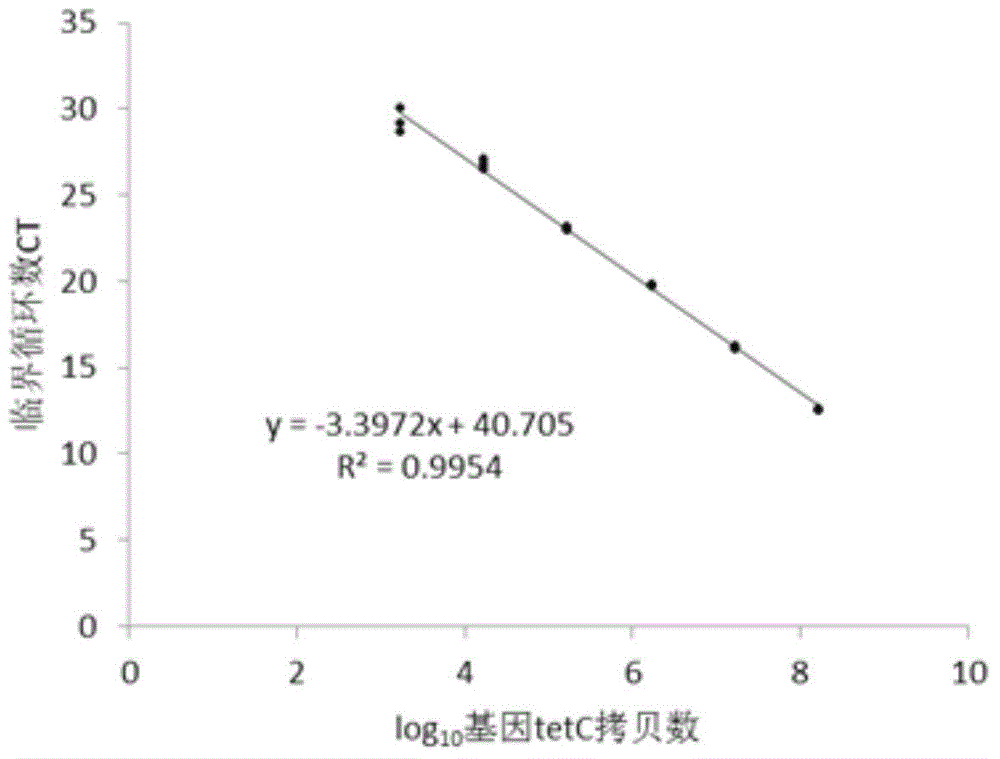
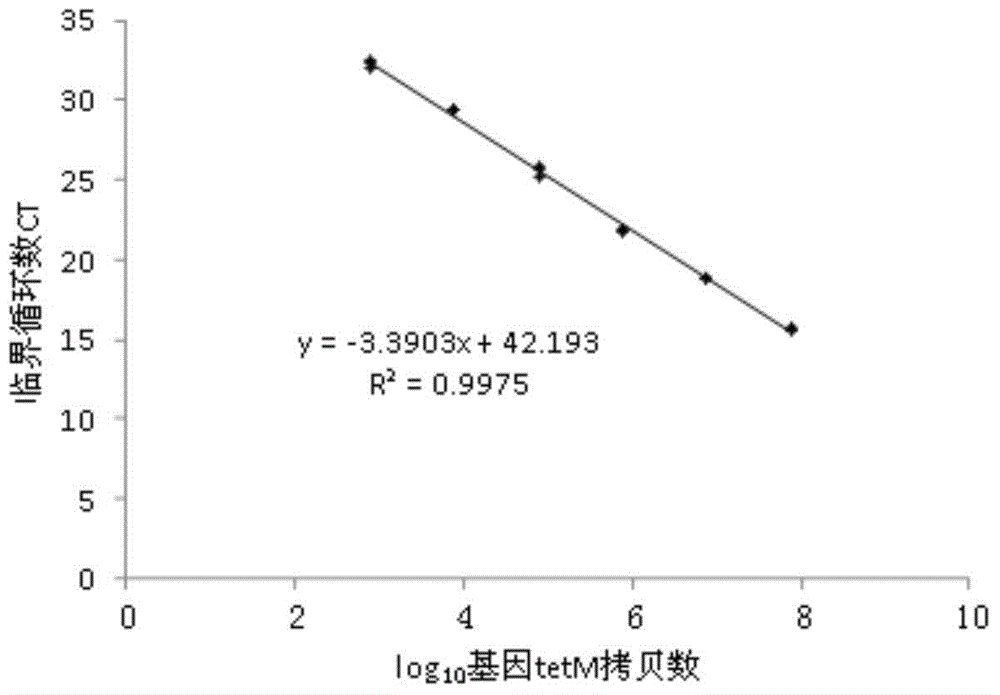
Quantitative detection method of antibiotics resistance gene in soil
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method of antibiotics resistance gene in soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting pigs which usually eat antibiotics, taking the pig manure DNA as the template, amplifying the target resistance gene sections by PCR; (2) carrying out gel extraction and purifying the amplified target resistance gene, inoculating the resistance gene onto a T carrier, converting to competence colibacillus cells, coating the cells on a LB plate, selecting the positive clones; (3) detecting the quality of amplified culture bacterium liquid through an agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE) method, extracting plasmids from bacterium liquid in which target resistance gene has been successfully cloned, measuring the plasmid concentration, calculating the copy number of the resistance genes carried by the plasmids, diluting the bacterium liquid as the resistance gene standard for later use by taking 10 times as the dilution gradient; (4) extracting soil genome DNA, simultaneously carrying out quantitative PCR amplification on the soil sample DNA and the resistance gene standard, and finally figuring out the copy number of the resistance gene in the soil sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process for protein extraction
ActiveUS6967241B2Reduced pHReduce the amount requiredPowder deliveryBacteriaSolubilityCellular Debris
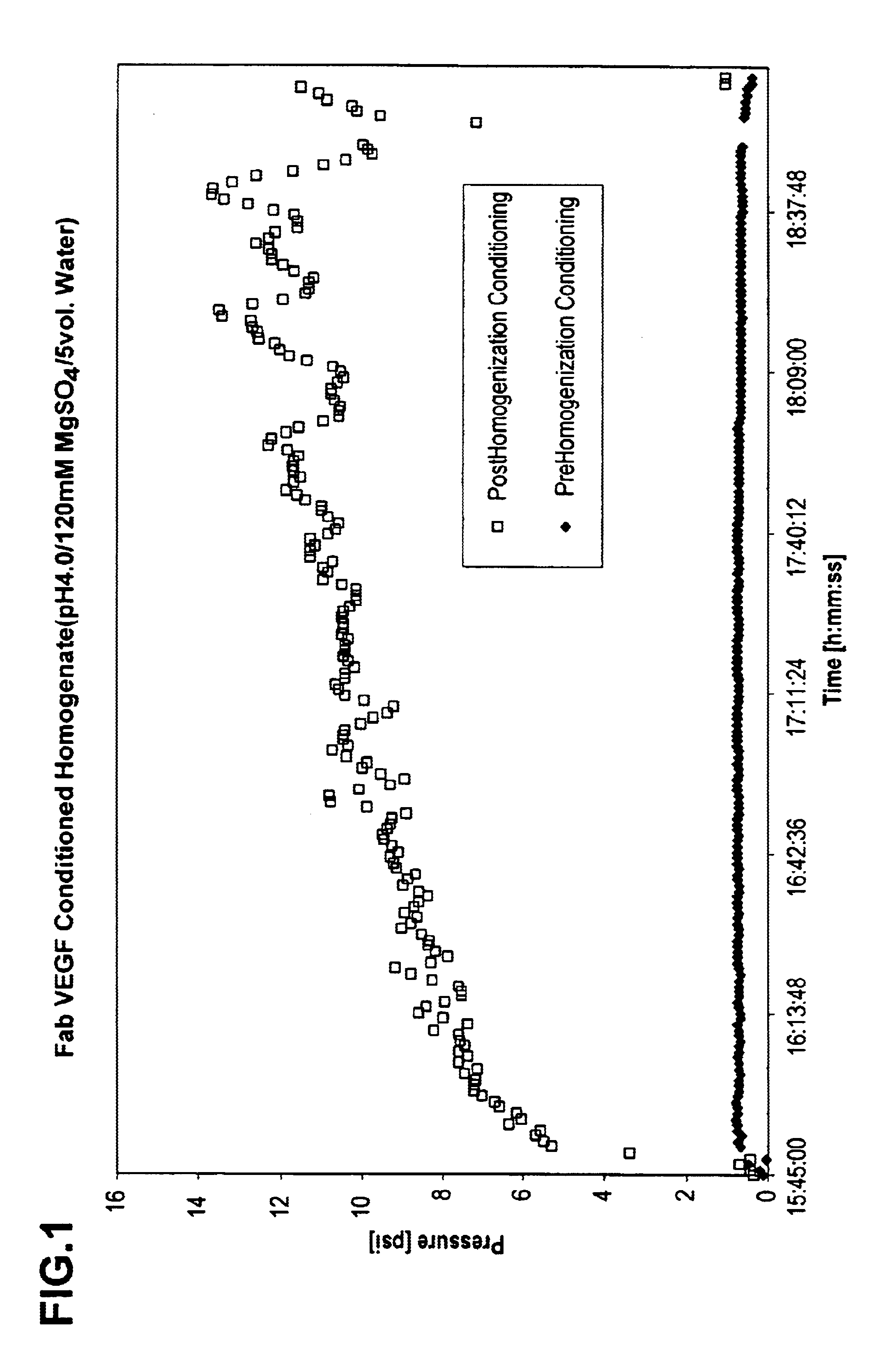
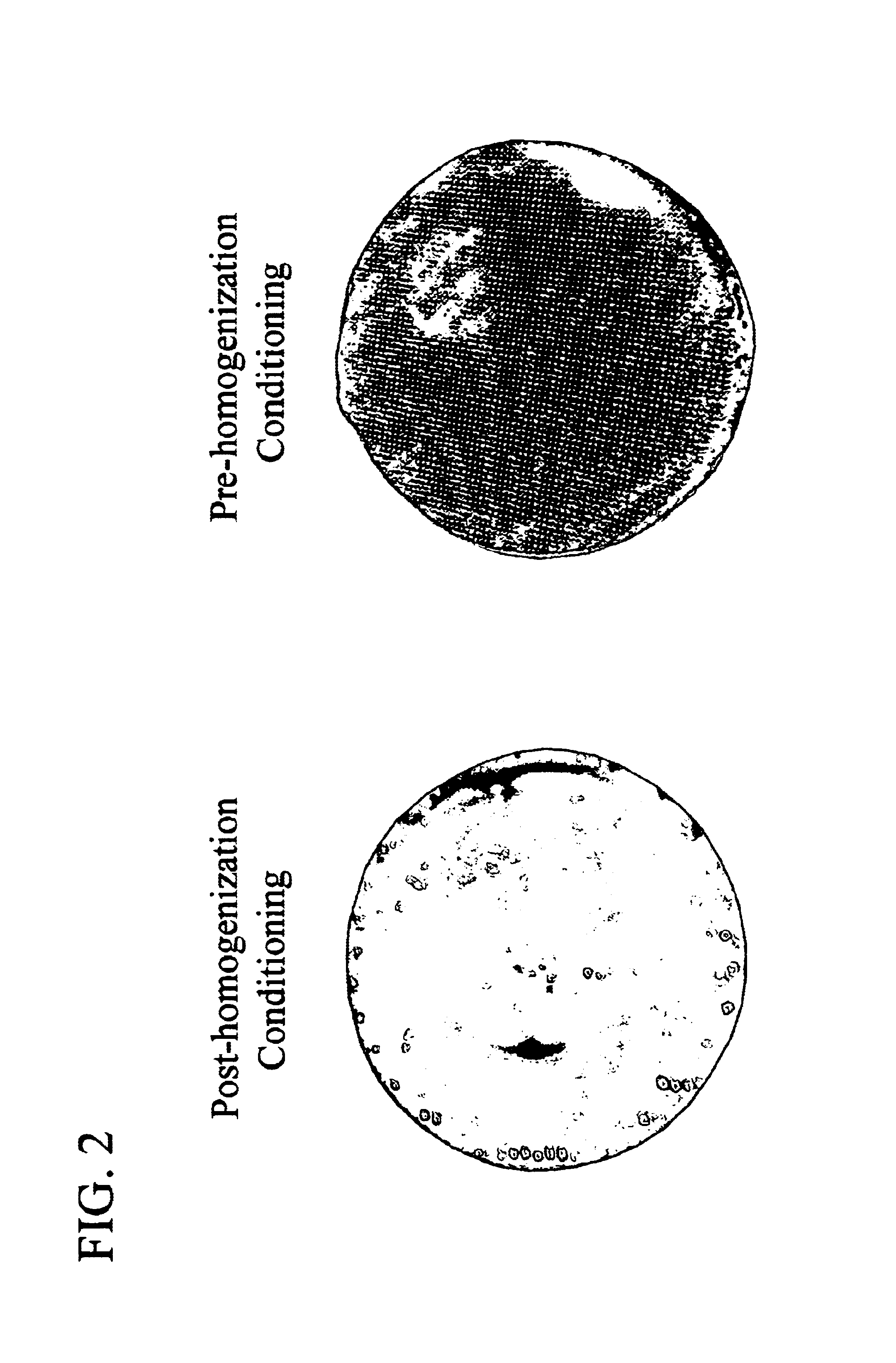
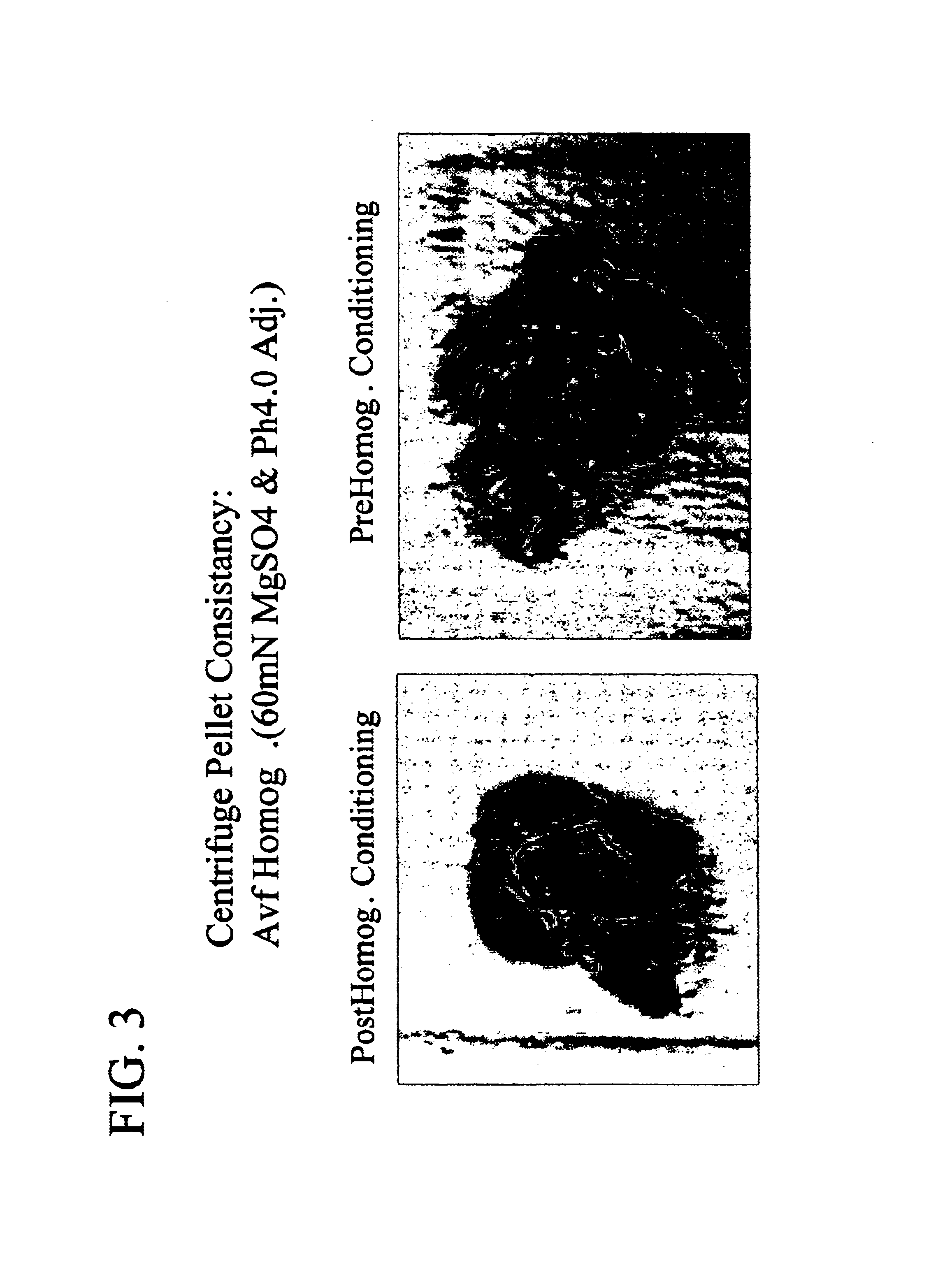
The invention includes a process for extracting a target protein from E. coli cells that includes lowering the pH of a whole E. coli cell solution to form an acidic solution, disrupting the cells to release the protein into the acidic solution, and separating the cellular debris from the released protein to obtain a protein product enriched in the heterologous target protein. The invention also includes addition of a solubility enhancer.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
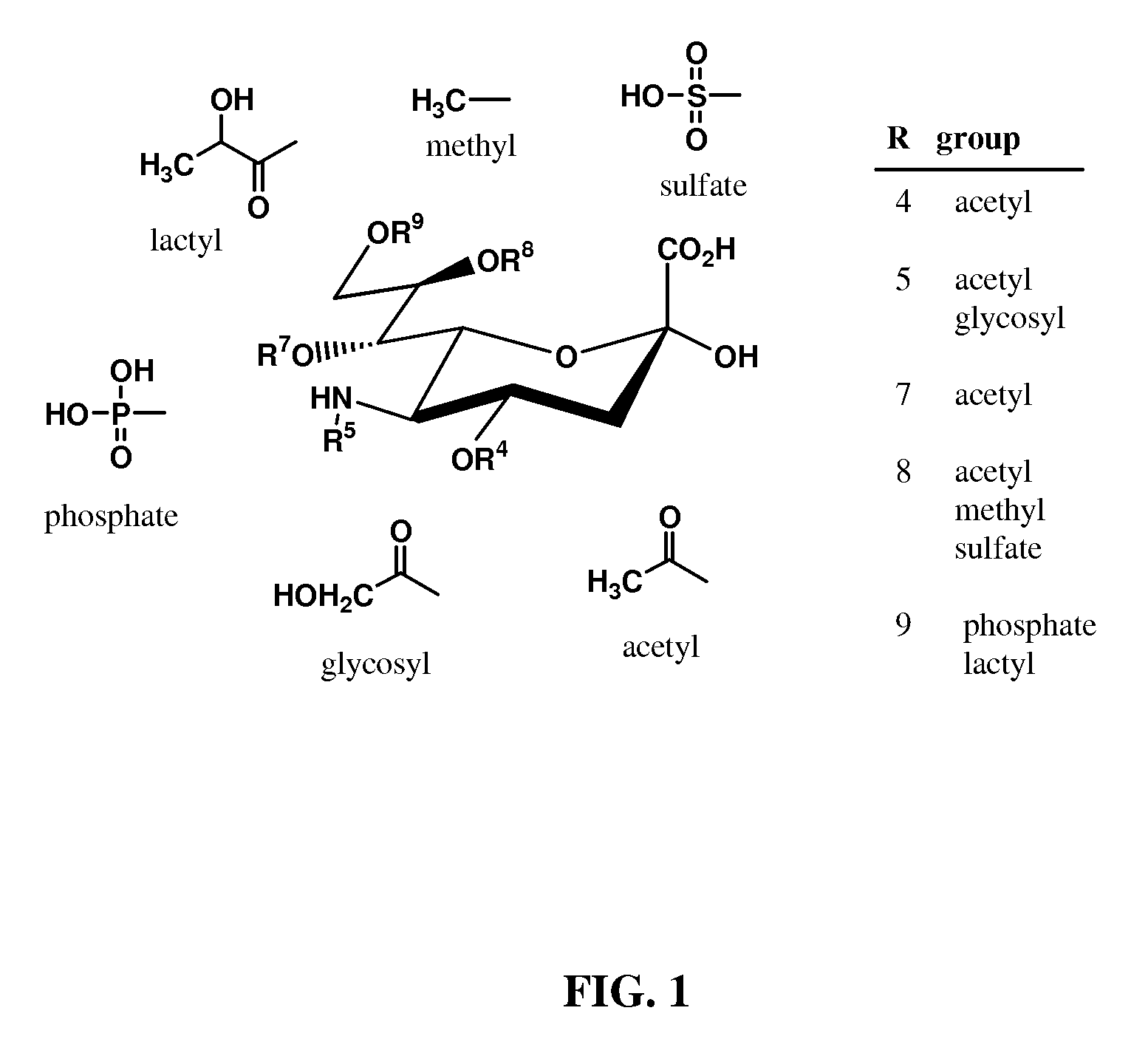
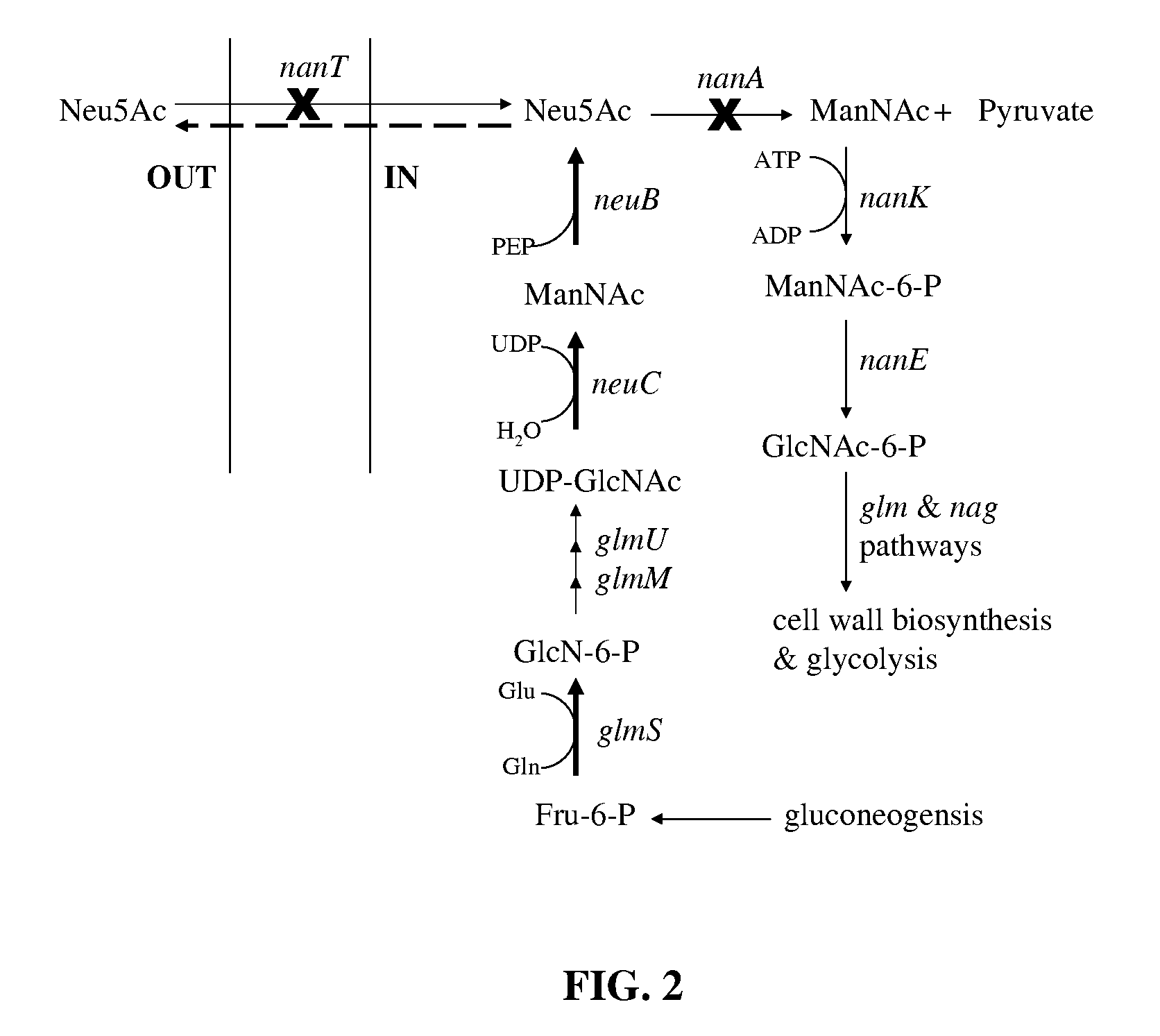
Metabolically Engineered Escherichia Coli For Enhanced Production of Sialic Acid
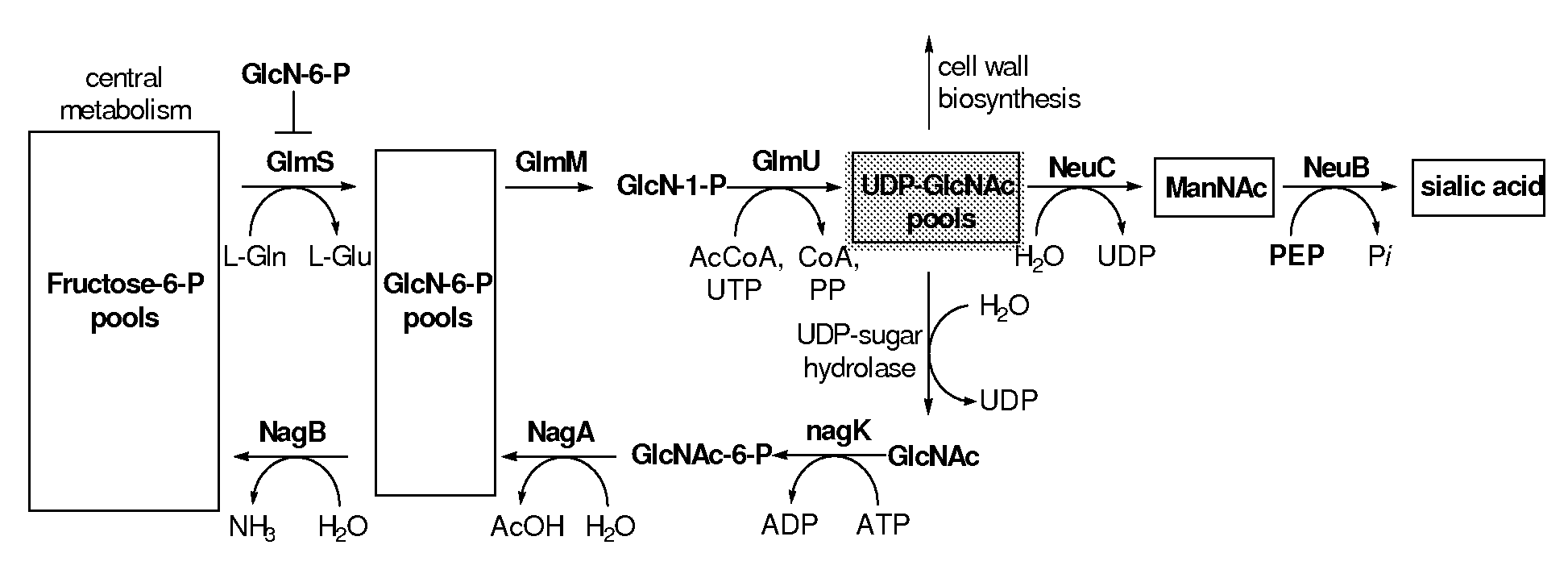
A metabolically engineered E. coli strain which produces sialic acid and a method of making said strain. In the engineered E. coli cells, the nanT (sialic acid transporter) and nanA (sialic acid adolase) genes are inactivated, and the neuC and neuB genes of sialic acid biosynthesis in Neisseria meningitidis group B are introduced and overexpressed in the nanT− nanA− E. coli cell. In addition, the glucosamine synthase gene, glmS, of E. coli is co-overexpressed with neuB and neuC.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
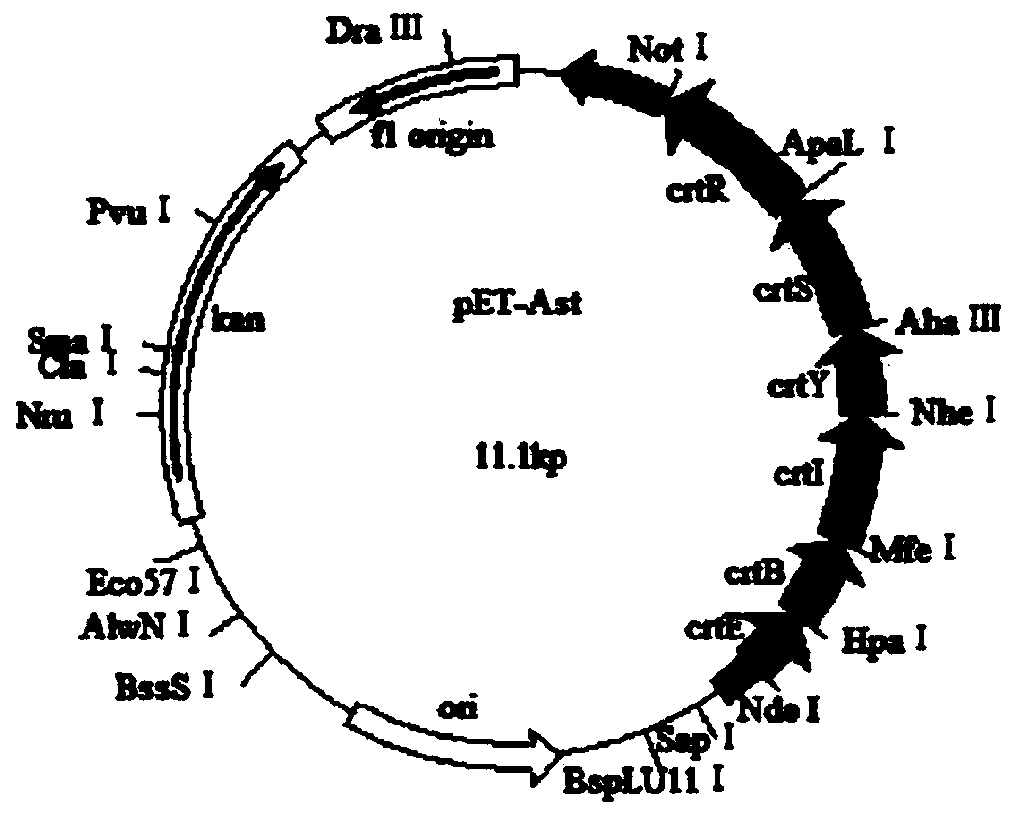
Astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid as well as preparation method and application of astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid
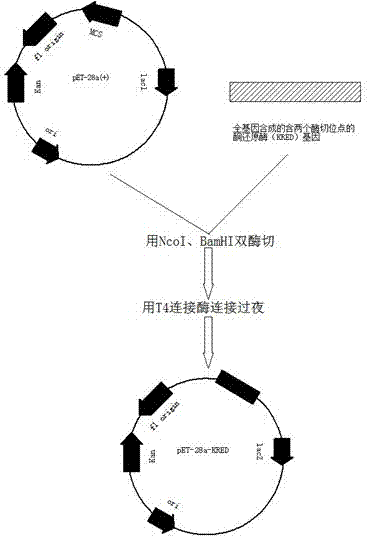
InactiveCN103805623ARealize accumulationBuild accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAstaxanthinBetaxanthins
The invention discloses an astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast with a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast, an application of the recombinant plasmid pET-Ast to the detection of astaxanthin synthetase activity of a target receptor, and an application method. After the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast provided by the invention is introduced to an Escherichia coli BL21 strain, the accumulation of astaxanthin in a cell body of Escherichia coli is successfully realized, so that an astaxanthin production strain can be accurately and rapidly established. The preparation method of the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast is simple and convenient, easy to operate and low in cost. By using the method disclosed by the invention, a gene sequence to be detected in the target receptor can be replaced with a related gene sequence in the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast through digestion and connection, and then, the function of a gene to be detected in the target receptor can be simply and effectively detected and verified through detecting whether the astaxanthin is accumulated in a host cell body.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Nanofiber biological membrane immobilized bi-enzyme system and trehalose catalytic synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN105838704AImprove conversion efficiencyImprove efficiencyBacteriaChemical industryAmylaseEnzyme system
The invention provides a nanofiber biological membrane immobilized bi-enzyme system and a trehalose catalytic synthesis method thereof. A starchiness nanofiber biological membrane is arranged on the surface of an escherichia coli cell generating high-temperature-resistant trehalose synthase through fermentation, polypeptide tag SpyTag-SpyCatcher capable of gene coding is used for specificity covalent binding and efficient immobilization recombination of beta-amylase, a trehalose synthase-beta amylase bi-enzyme catalytic system is constructed autonomously, and finally extracellular and intracellular two-step catalysis is conducted continuously. The immobilization efficiency of beta-amylase can reach 50-62%, maltose is generated by 20-25wt% of soluble starch under catalysis of beta-amylase on the extracellular biological membrane, enters the cell and reacts with trehalose synthase to generate trehalose, and the conversion rate of starch can reach 45-55% after the immobilized cell is reused for 10-16 times.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
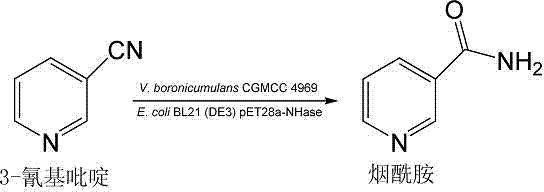
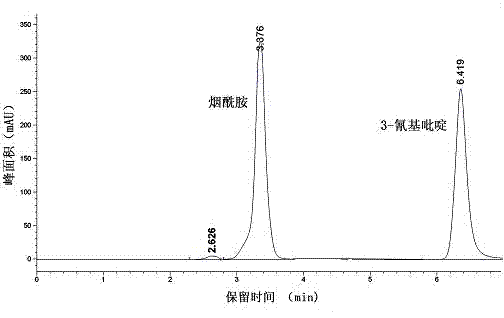
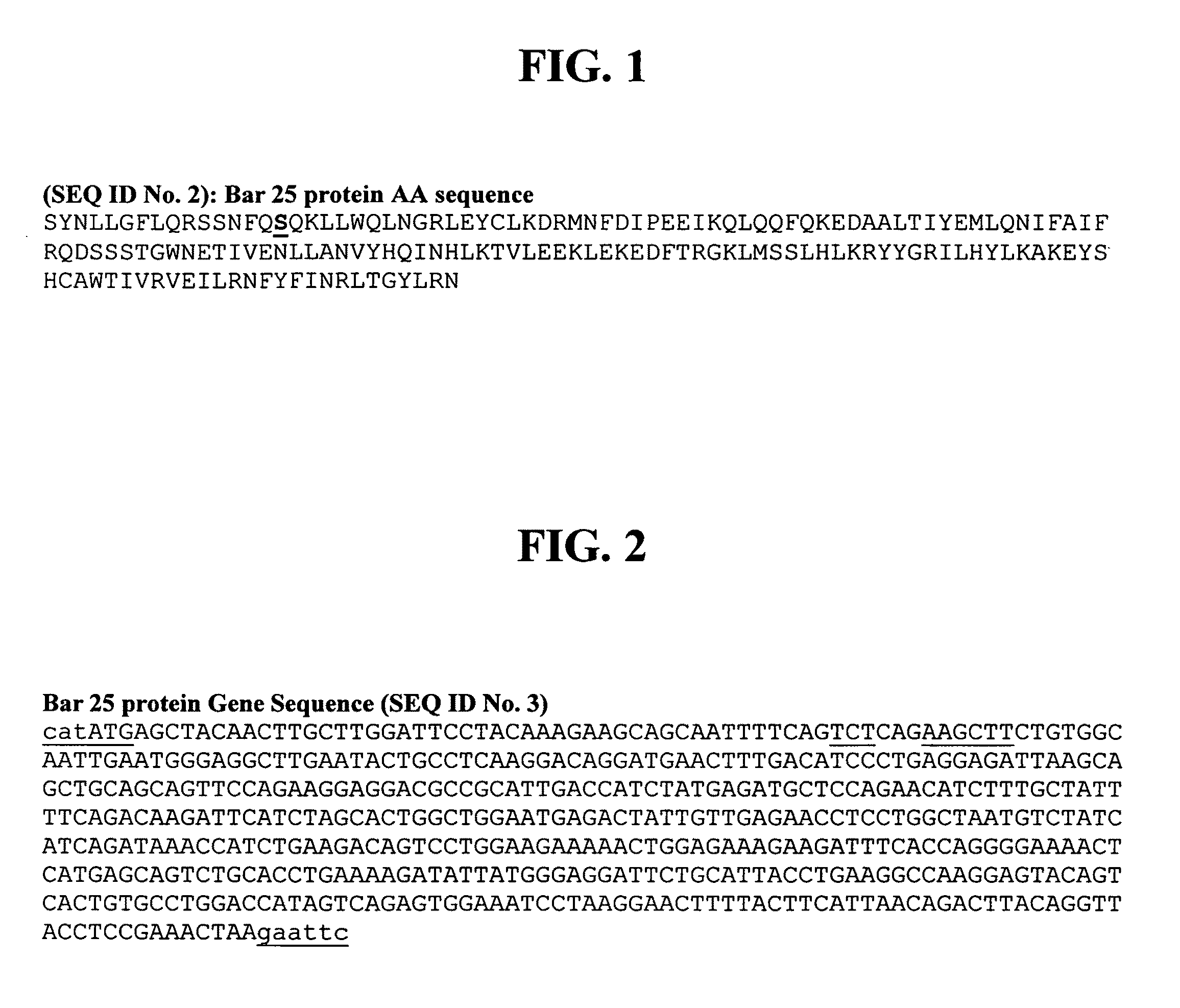
Vaporophage bacterium cgmcc4969 and its application in the biotransformation of 3-cyanopyridine to nicotinamide
The invention discloses the use of variovoraxboronicumulans CGMCC 4969 in bioconversion of 3-cyanopyridine for forming nicotinamide. The nitrile hydratase gene cluster produced by the strain consists of a DNA sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table; the DNA consisting of the sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 is recombined onto a pET28a plasmid and can be induced to express in EscherichiacoliBL21(DE3) strain; and the Escherichia coli cells containing expressed proteins and cell extracting solution can convert 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinamide.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High pressure treatment of aggregated interferons
InactiveUS8273561B2High yieldImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesInclusion bodiesCell Aggregations
High pressure to treat aggregated interferons, particularly recombinant human interferon-β, to reduce the aggregate content of interferon material. Highly pure, soluble monomeric recombinant interferon-β is prepared in representative embodiments. Multiple strategies may be used in combination that make nonglycosylated IFN-β more amenable to high pressure treatment. It has been found that refolding yields of high pressure treatment can be significantly improved by use of a combination of strategies, including, or example a pre-treatment of the IFN-β that involves solubilizing and then precipitating the protein. This pre-treatment is particularly effective with respect to recombinant IFN-β inclusion bodies recovered from host cells such as E. coli cells. According to another strategy, refolding under high pressure is much more effective when the refolding reagent incorporating the IFN-β incorporates a zwitterionic surfactant and / or a cholate salt. When a solubilization and precipitation pre-treatment is used, the effectiveness of the high pressure treatment is further enhanced when the refolding reagent incorporating the protein incorporates a disulfide shuffling chemistry such as cysteine / cystine. According to still yet another strategy, high pressure treatment is more effective when using atypically high treatment pressures. When coupled with purification techniques, these strategies singly or in combination provide a low aggregate or substantially aggregate free, biologically active solution. Biologically active solutions comprising nonglycosylated interferon, said interferon comprising less than about 5 weight percent of protein aggregation has been found to exhibit improved PK / PD characteristics.
Owner:NURON BIOTECH
Method for isolation and identification of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 and plating media for said process
InactiveUS6087156AReduce percentageLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAdditive ingredientPH indicator
A solid plating medium for the presumptive detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 which comprises (1) an ingredient which promotes growth of Escherichia coli cells under incubation, (2) an ingredient which inhibits growth of gram positive microorganisms under incubation, (3) an ingredient that inhibits growth of Proteus sp. under incubation, (4) an ingredient which inhibits the growth of strains of Escherichia coli other than Escherichia coli 0157:H7 under incubation, (5) a carbohydrate medium that under incubation is not fermented by Escherichia coli 0157:H7 but which is fermented by other microorganisms including other strains of Escherichia coli, (6) a pH indicator dye which changes the plating media to a first color when the pH of the medium changes, (7) a chromogenic beta-galactosidase substrate that produces precipitate of a second color responsive to beta-galactosidase, the first color contrasting with the second color and the first and second colors blending to produce a third color which contrasts with the first and second colors, and (8) a mass of agar sufficient to solidify the mixture. Also, the method of detecting the presence of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 comprising inoculating the solid plating medium set forth above with a test sample containing Escherichia coli including Escherichia coli 0157:H7, then incubating said plating medium for a period sufficient to obtain colonies of microorganisms and generating one or more of the colors produced by the plating medium, and then examining the surface of the medium for the presence of colonies of the second color.
Owner:R&F PROD
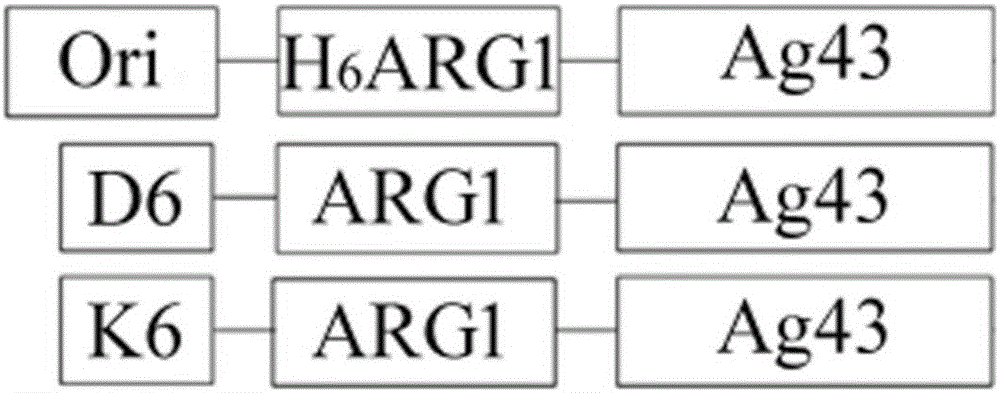
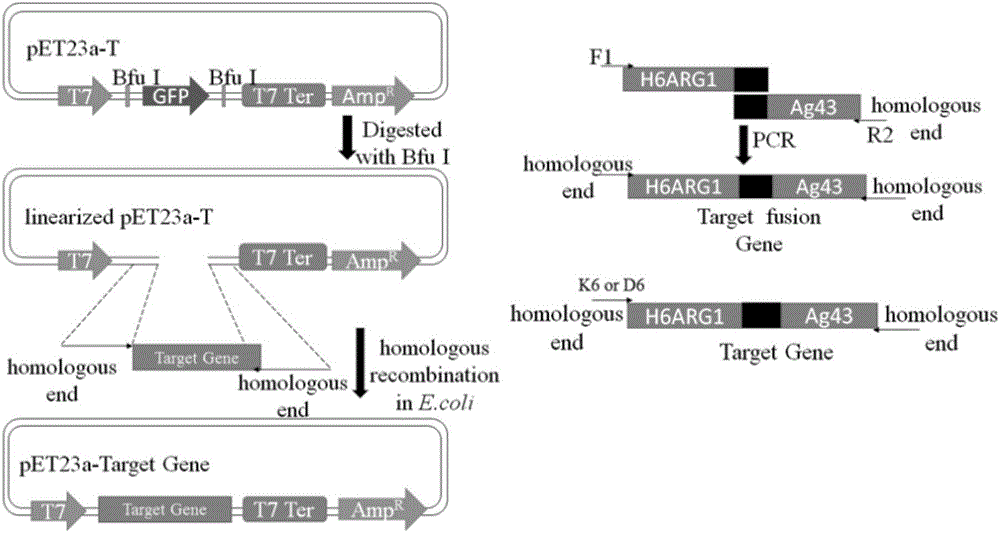
Method for displaying human arginase1 on surfaces of escherichia coli
InactiveCN105886491AImprove display efficiencyIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesAntigenCompetent cell
The invention provides a method for displaying human arginase1 on surfaces of escherichia coli. The method comprises steps as follows: 1) recombinant plasmids for surface display of human arginase1 are constructed; 2) the recombinant plasmids are converted into escherichia coli competent cells, and genetic engineering strains are obtained; 3) the recombinant strains are subjected to shake-flask culture, and the display efficiency and enzyme activity of human arginase1 are detected; 4) L-Arginine (L-arginine, L-Arg) is efficiently converted by means of the recombinant strains for synthesis of L-Ornithine (L-ornithine, L-Orn). Human arginase1 is effectively displayed on surfaces of escherichia coli cells through improved Type V self-transport protein (Antigen 43), and industrial application of human arginase1 is realized more rapidly. By comparison with an original Type V self-transport protein (Antigen 43) display system, the display efficiency and the enzyme activity of human arginase1 are remarkably improved; by comparison with an existing chitin immobilization method, the synthesis cost is reduced, the technological process is shortened, and the purification procedures are simplified.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
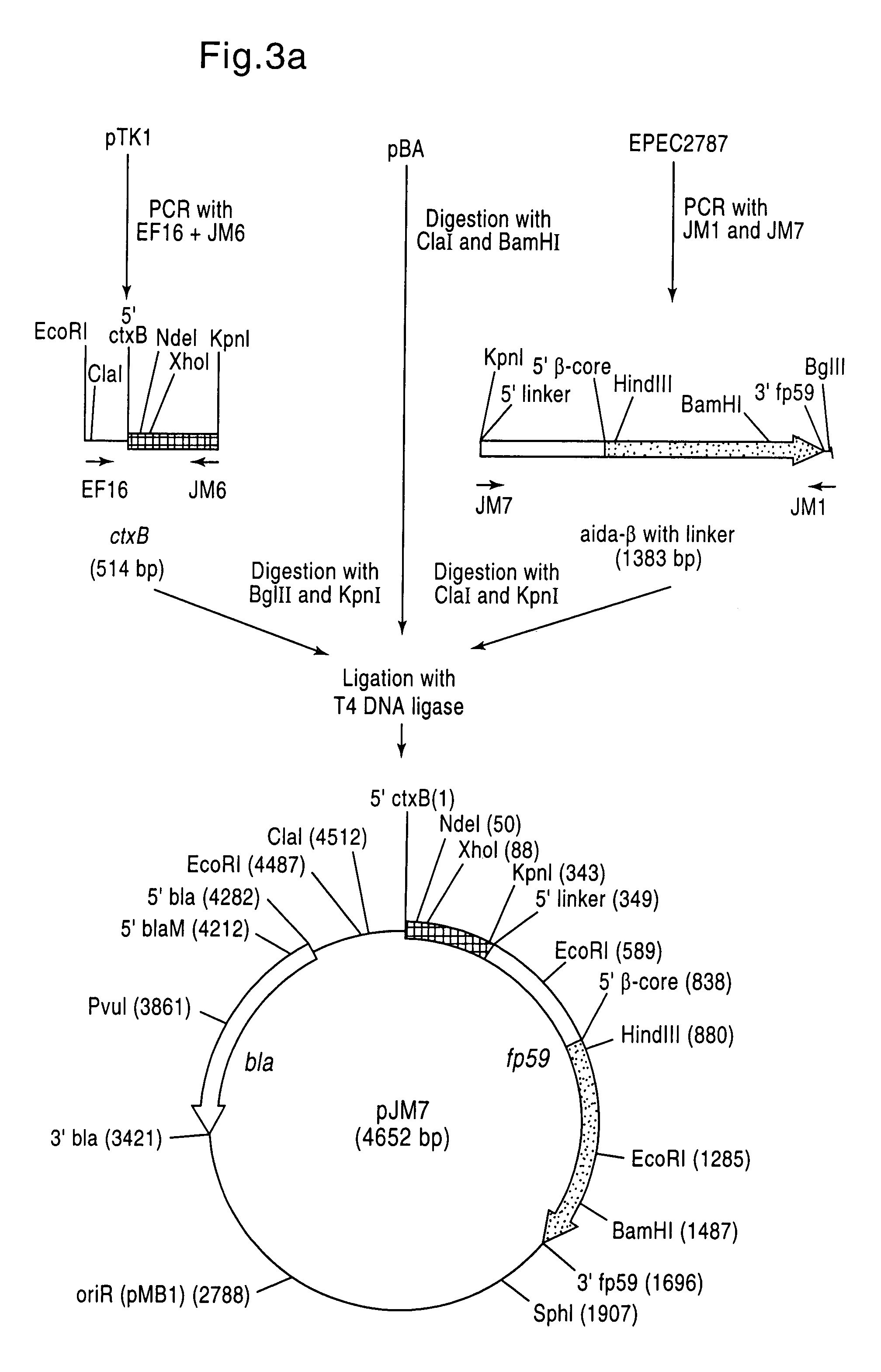
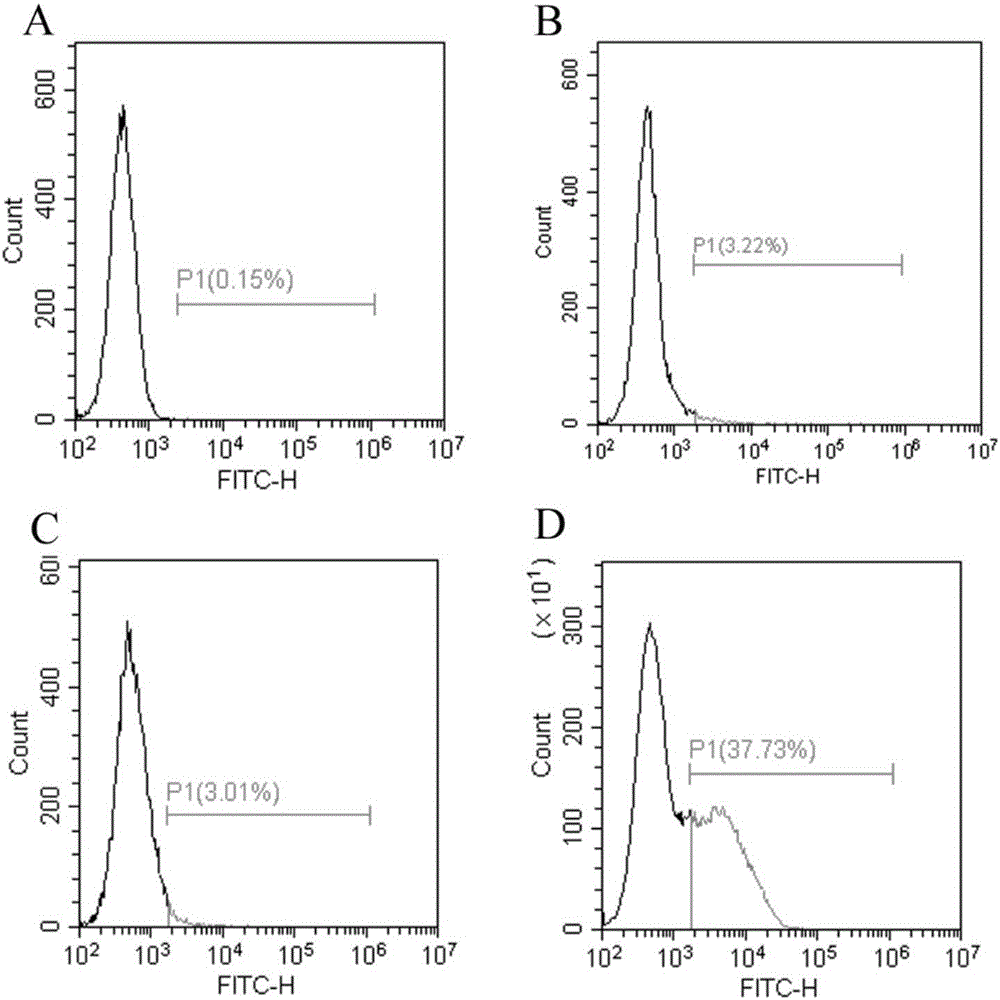
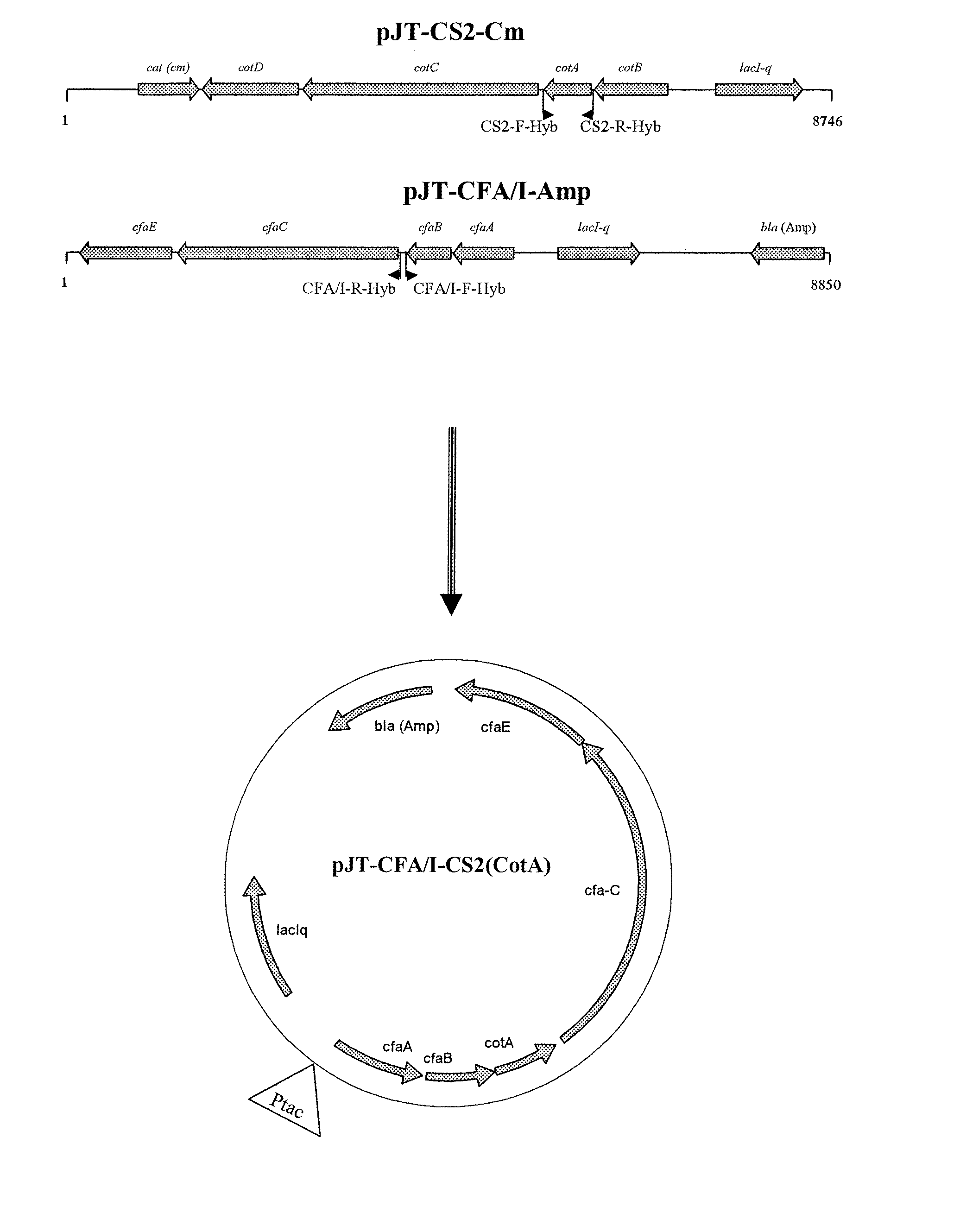
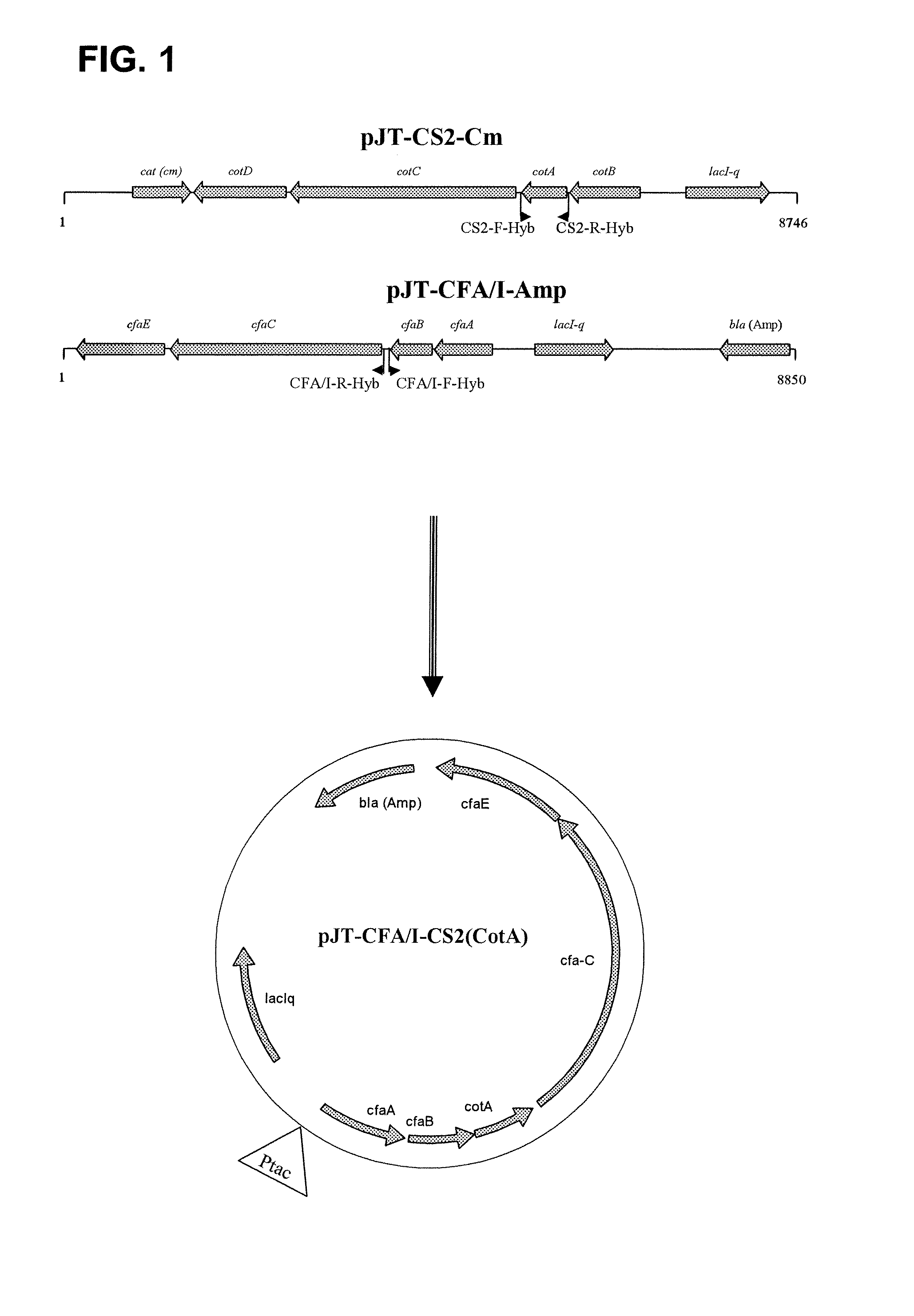
Hybrid operon for expression of colonization factor (CF) antigens of enterotoxigenic escherichia coli
InactiveUS20100136059A1Reduce in quantityAvoid restrictionsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenVaccine Production
A recombinant operon comprising a gene assembly wherein there are at least two structural genes coding for at least two major subunits of colonization factor antigens (CFs) associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli bacteria (ETEC), is disclosed. Further disclosed is a host cell, such as an Escherichia coli cell, genetically engineered to comprise such a recombinant operon, wherein said operon is located on an episomal element, such as a plasmid, or integrated in the chromosome of said host cell. Also disclosed is a method of producing a host cell capable of expressing from said operon at least two major subunits of colonization factor antigens (CFs) associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli bacteria (ETEC). In addition, a vaccine composition against diarrhea comprising at least one such host cell together with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, buffers, and / or diluents is disclosed. Finally is disclosed the use of said operon in the production of such a vaccine.
Owner:GOTOVAX AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com