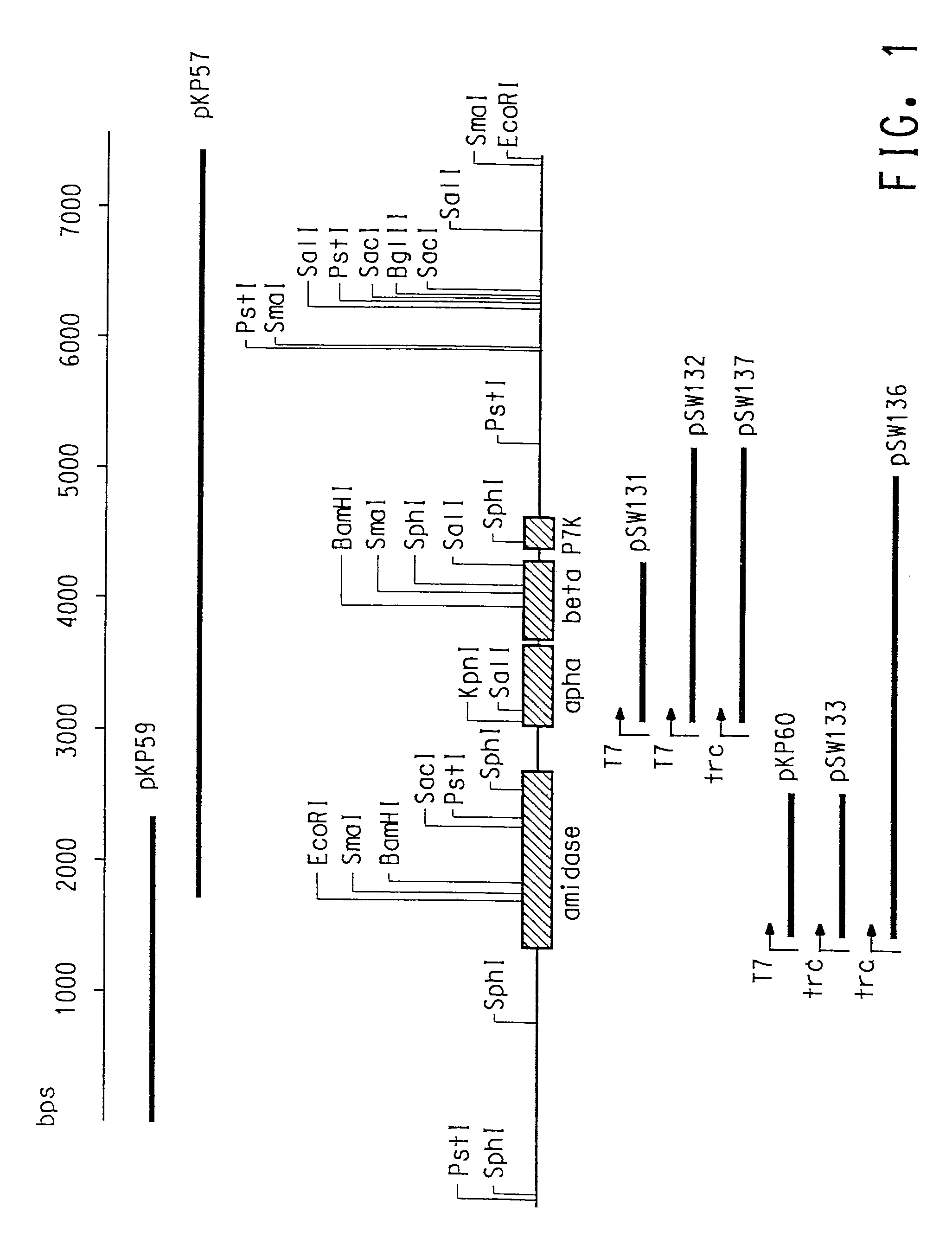
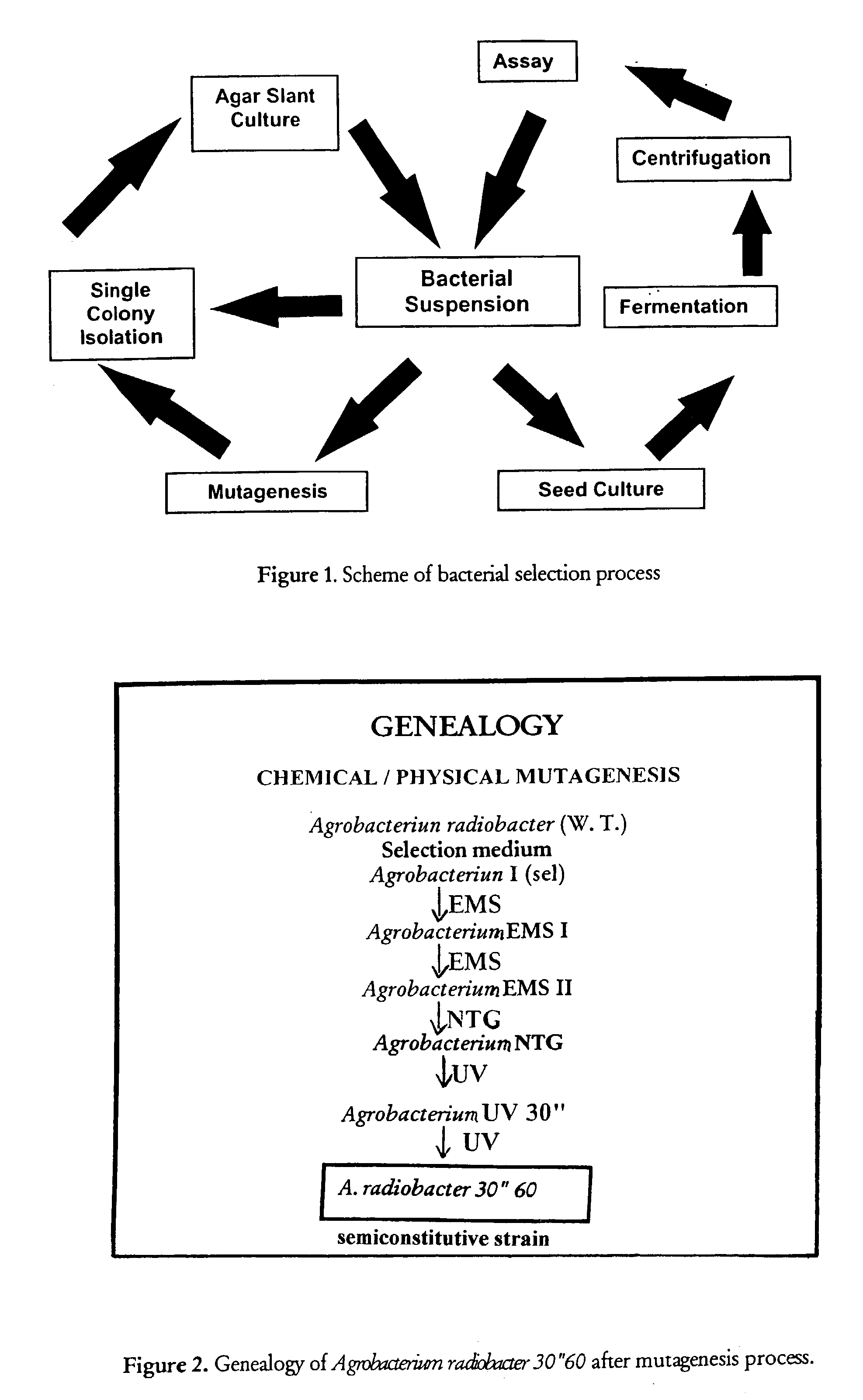
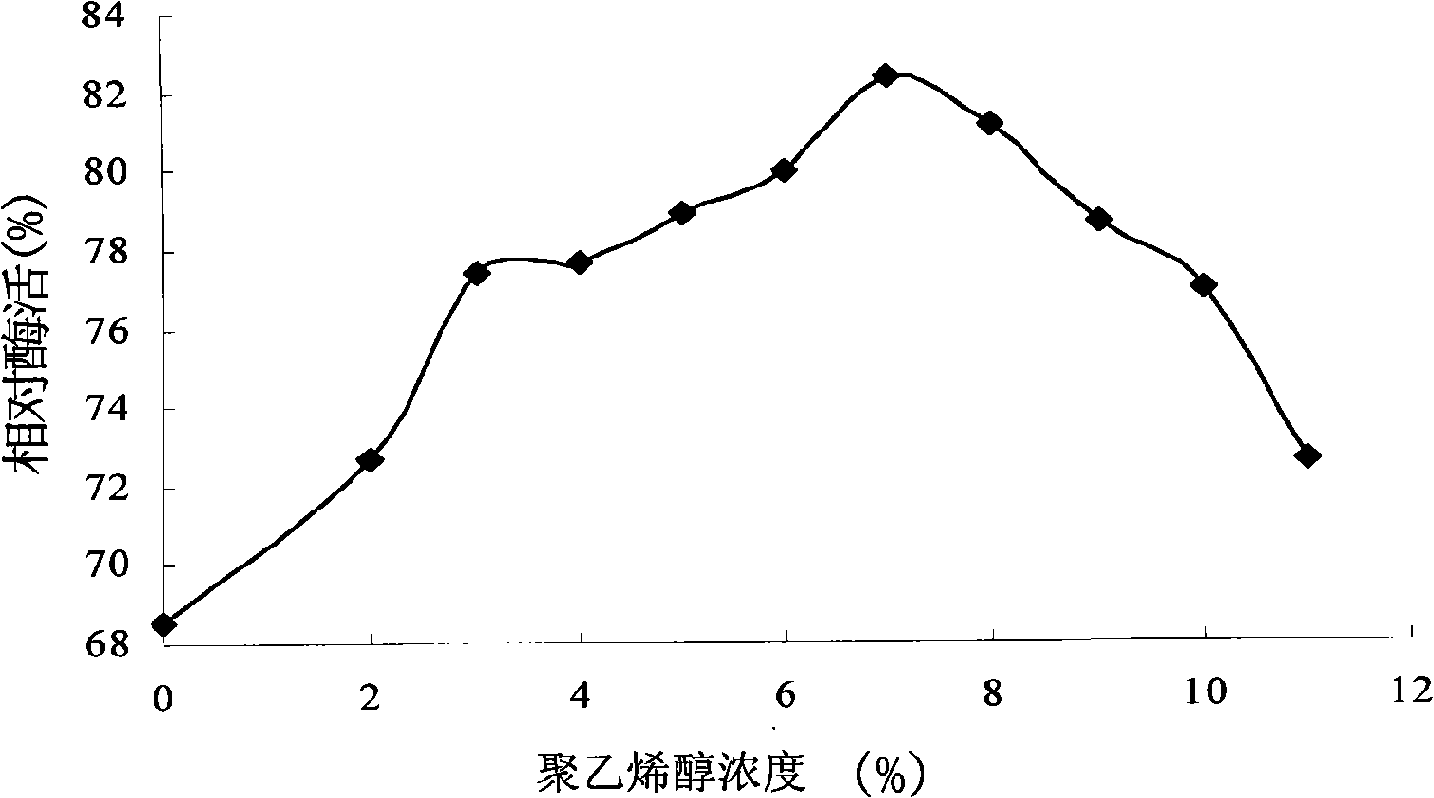
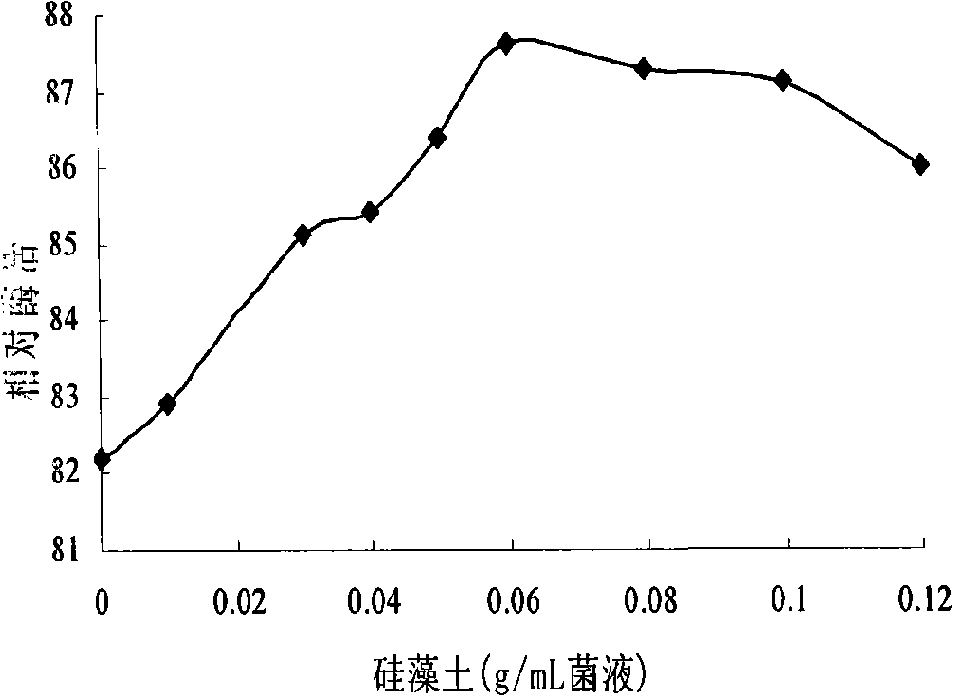
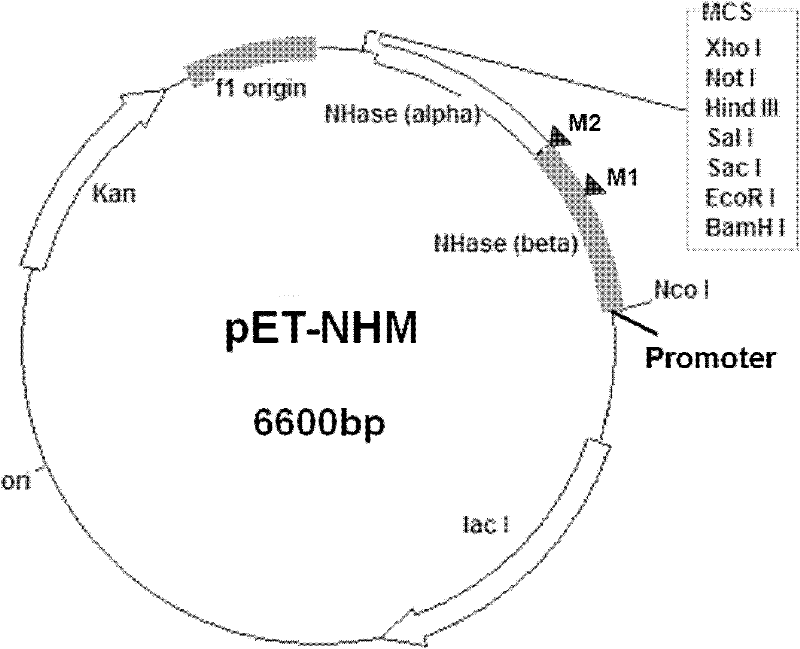
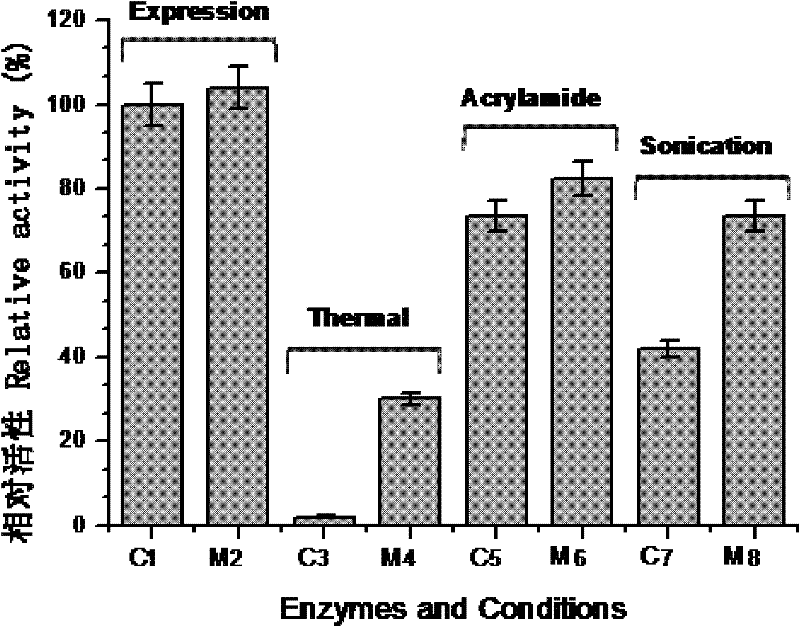
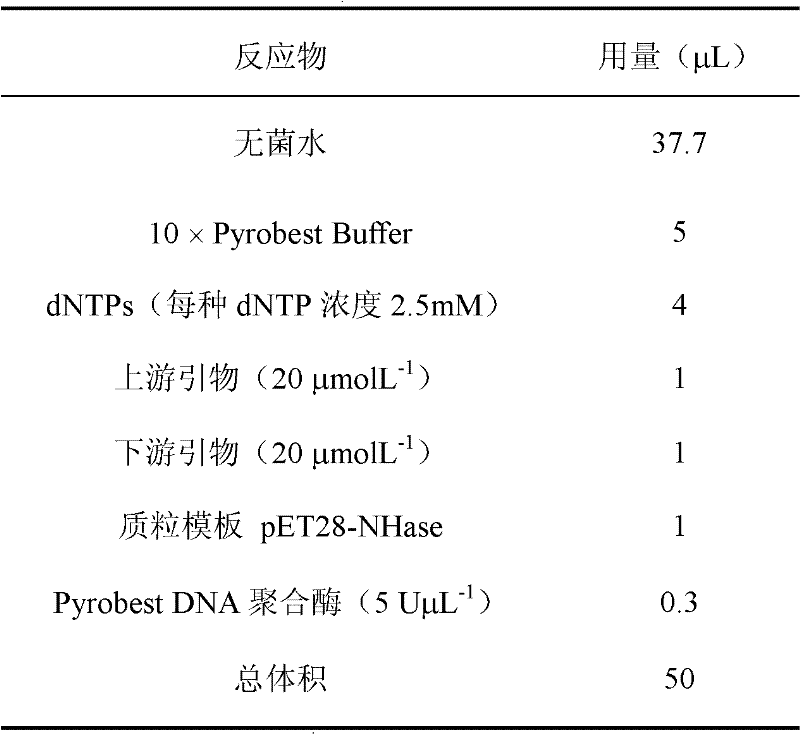
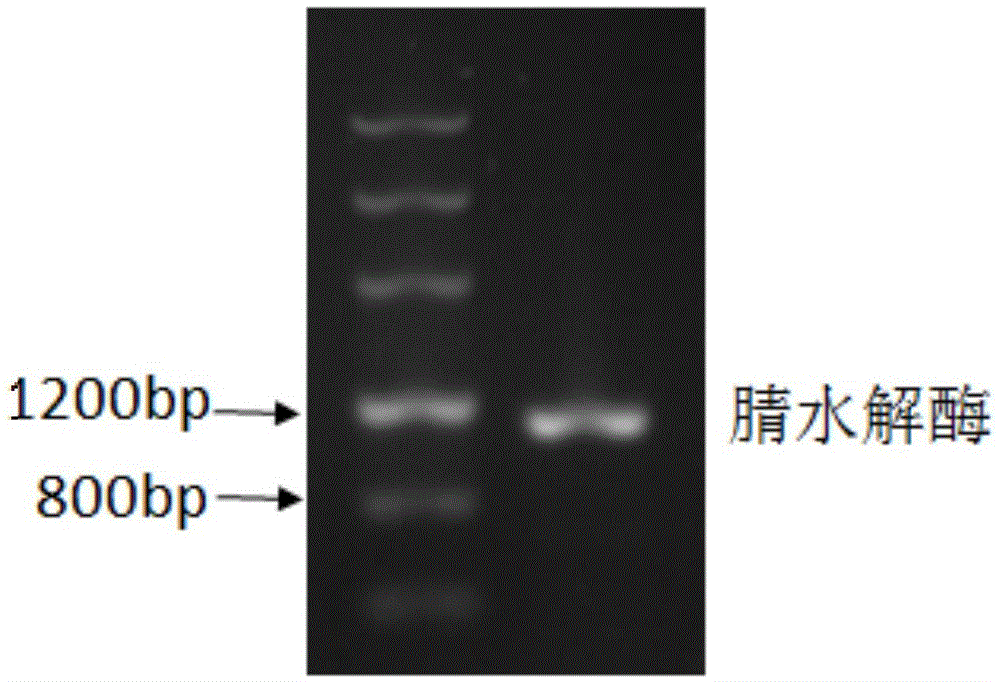
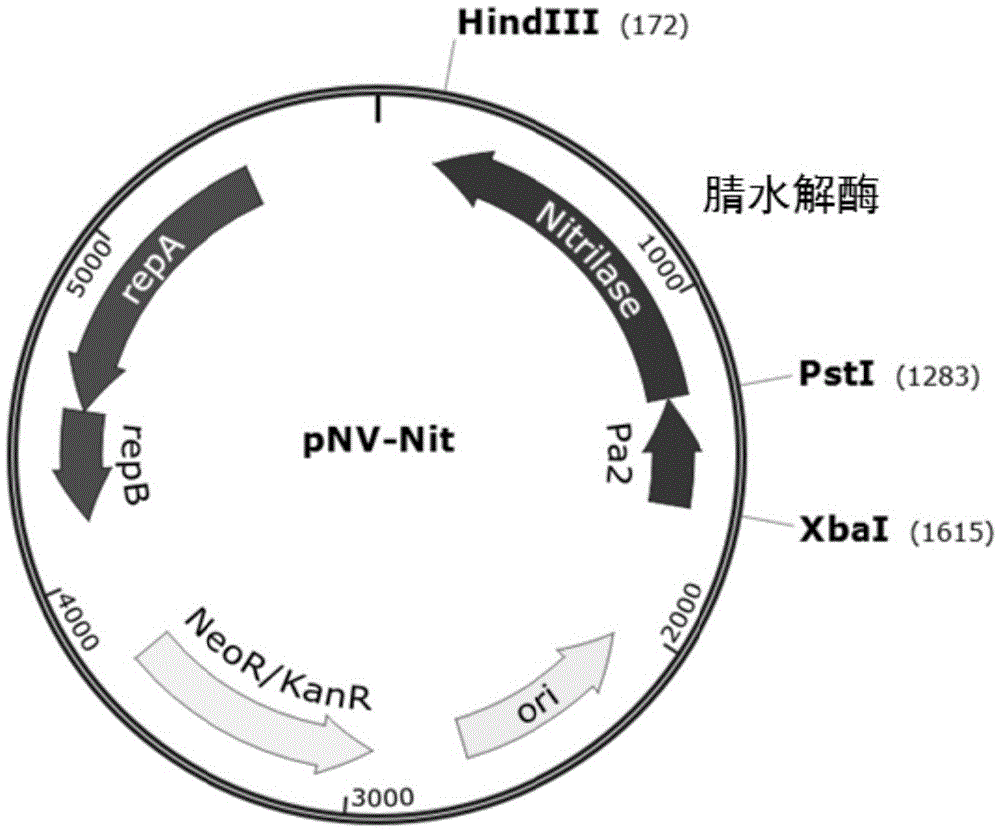
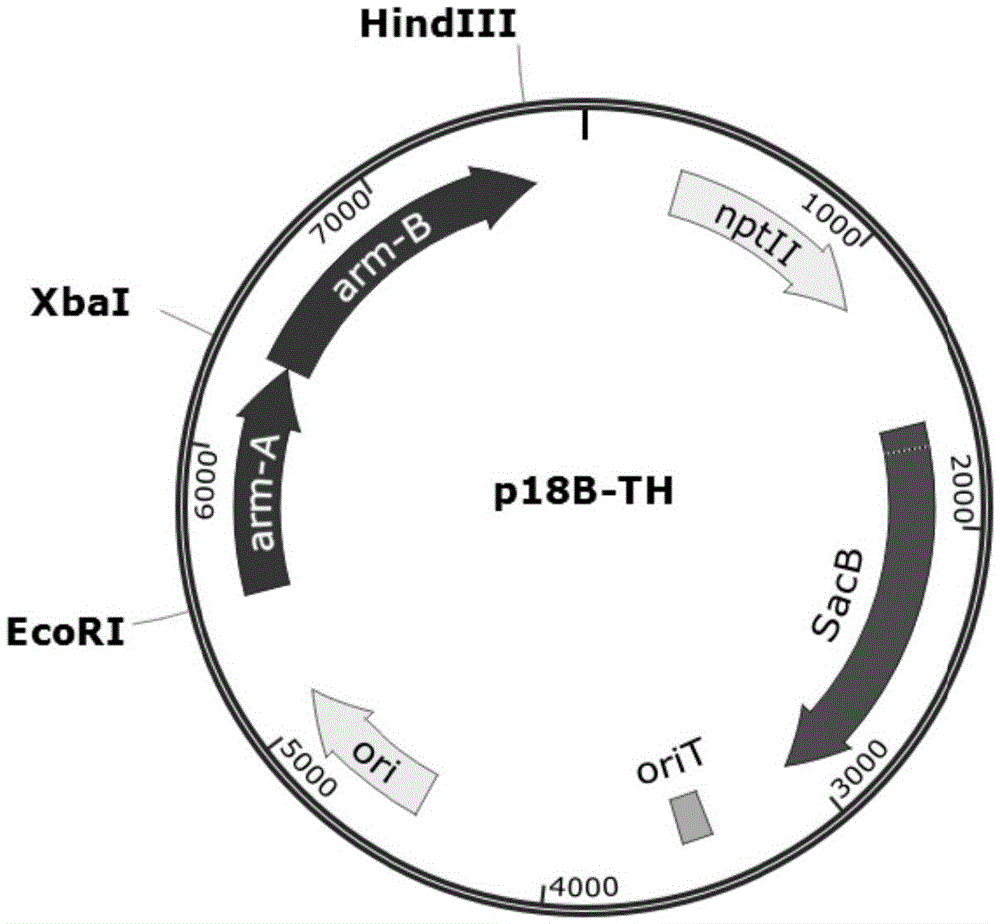
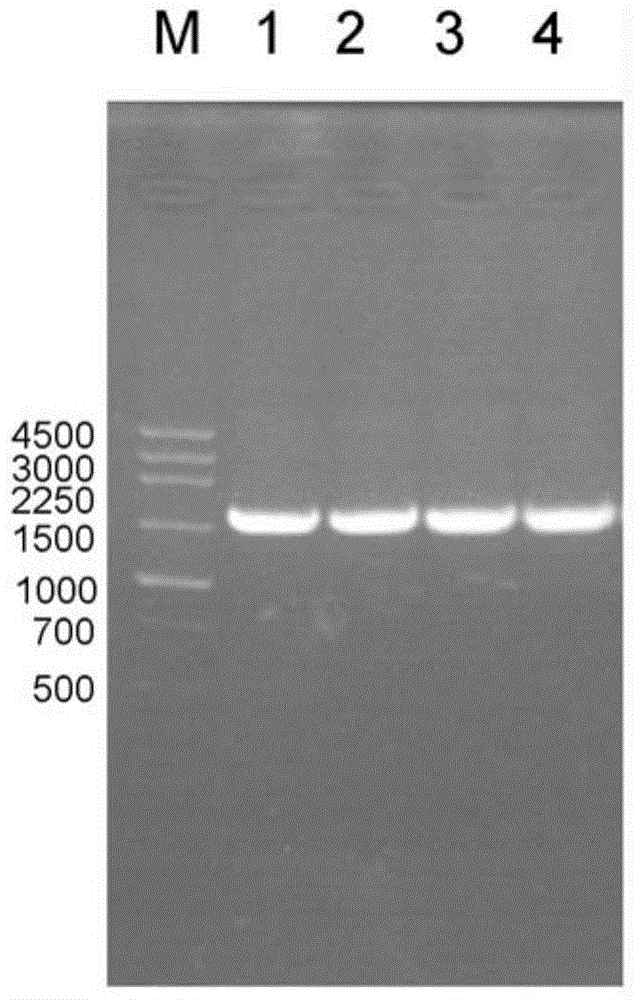
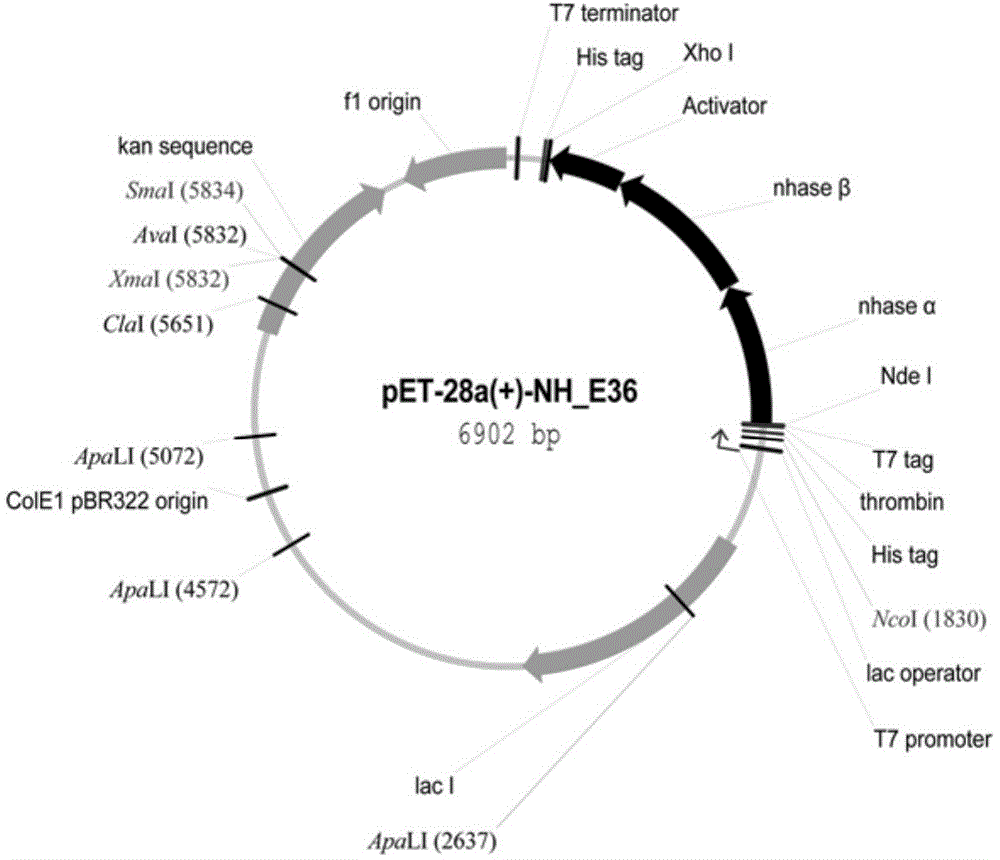
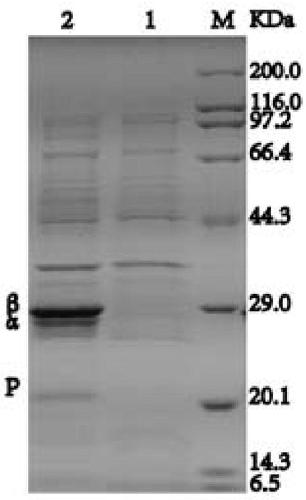
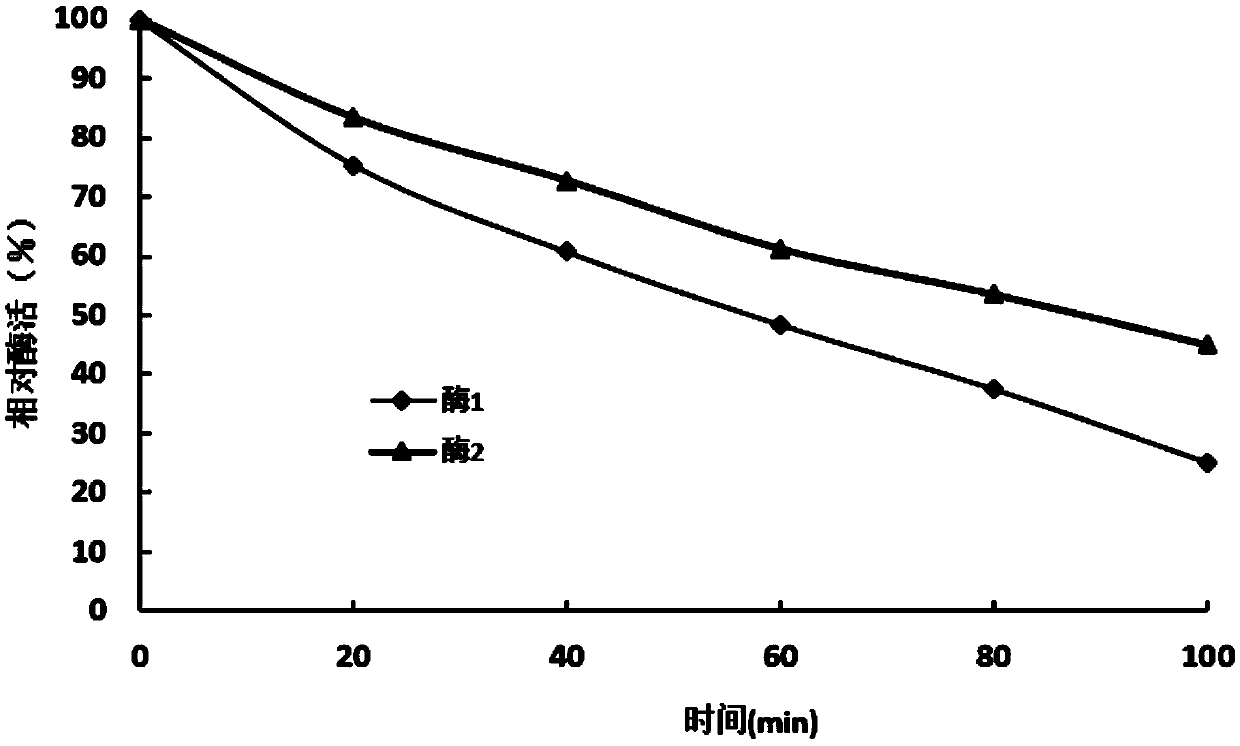
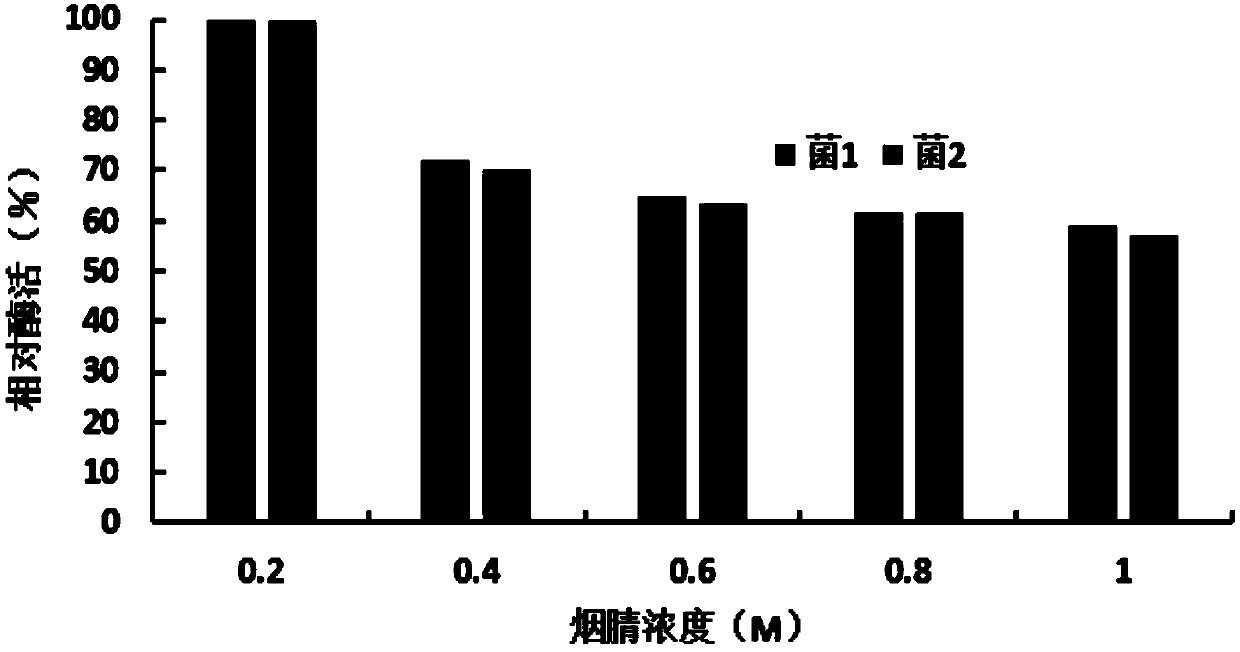
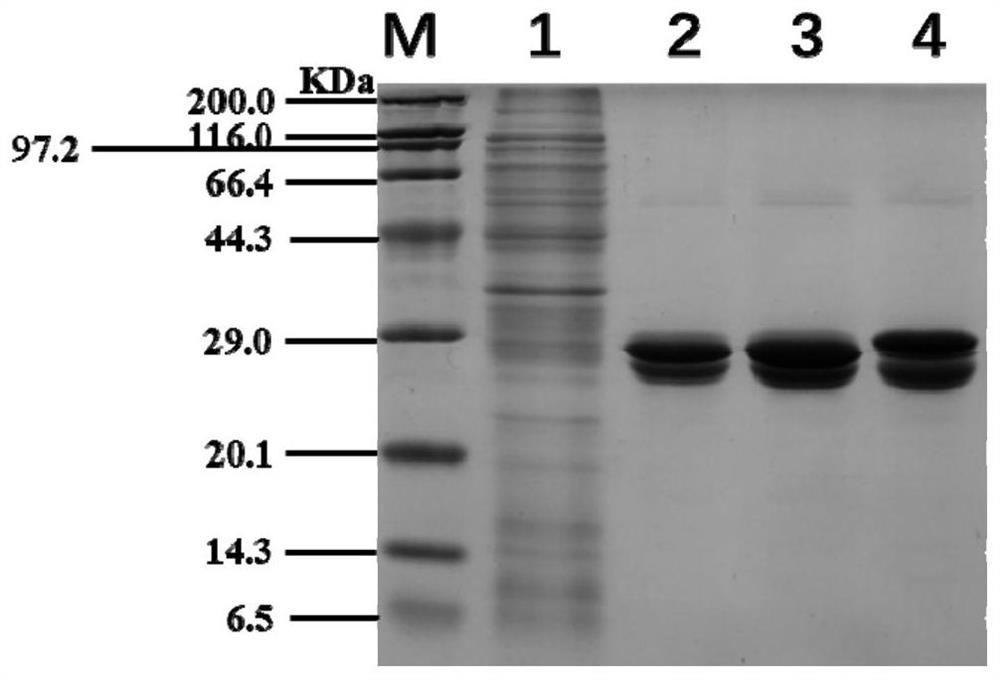
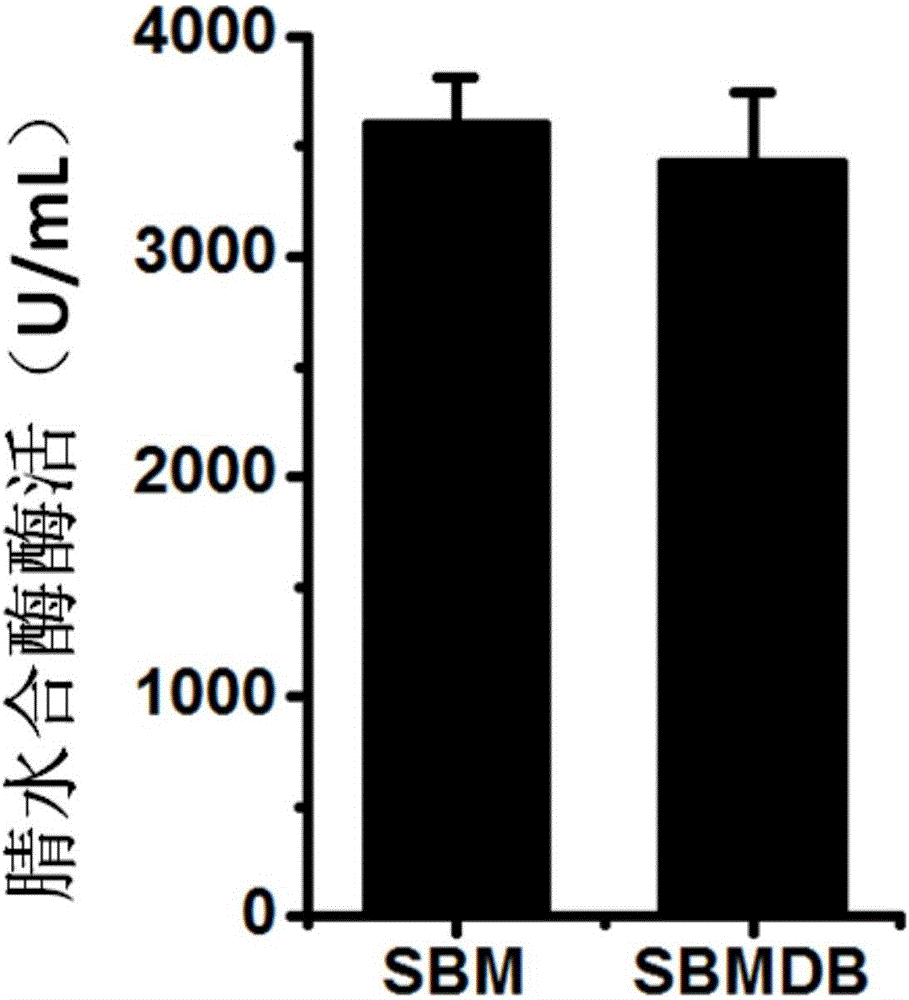
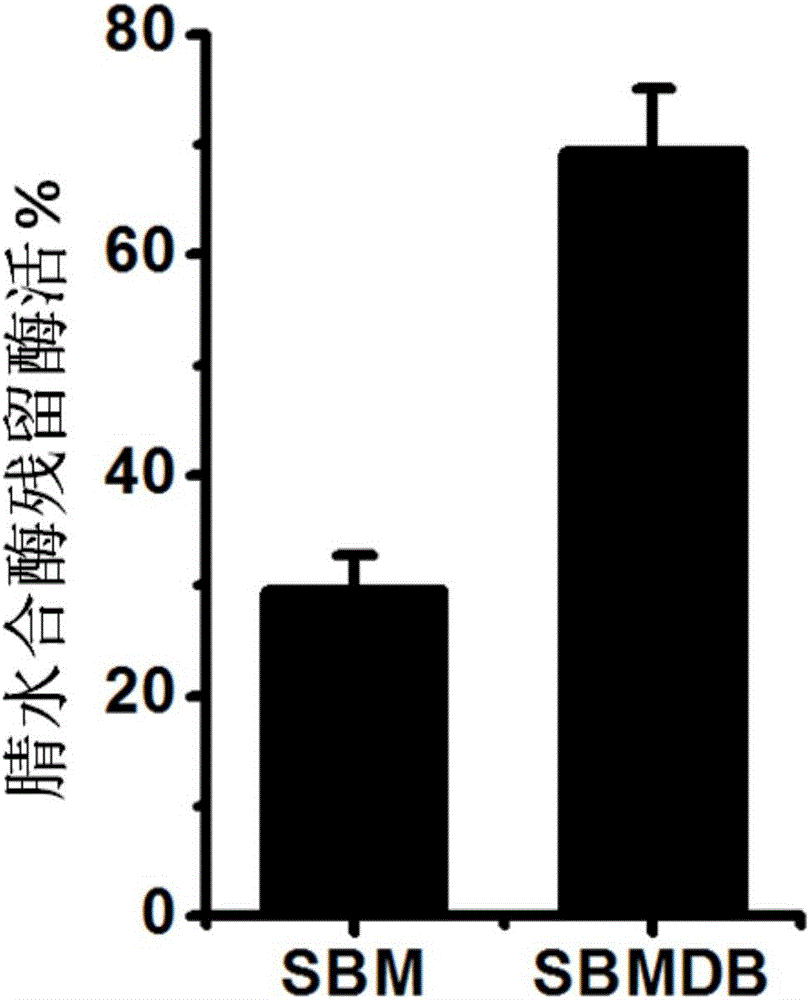
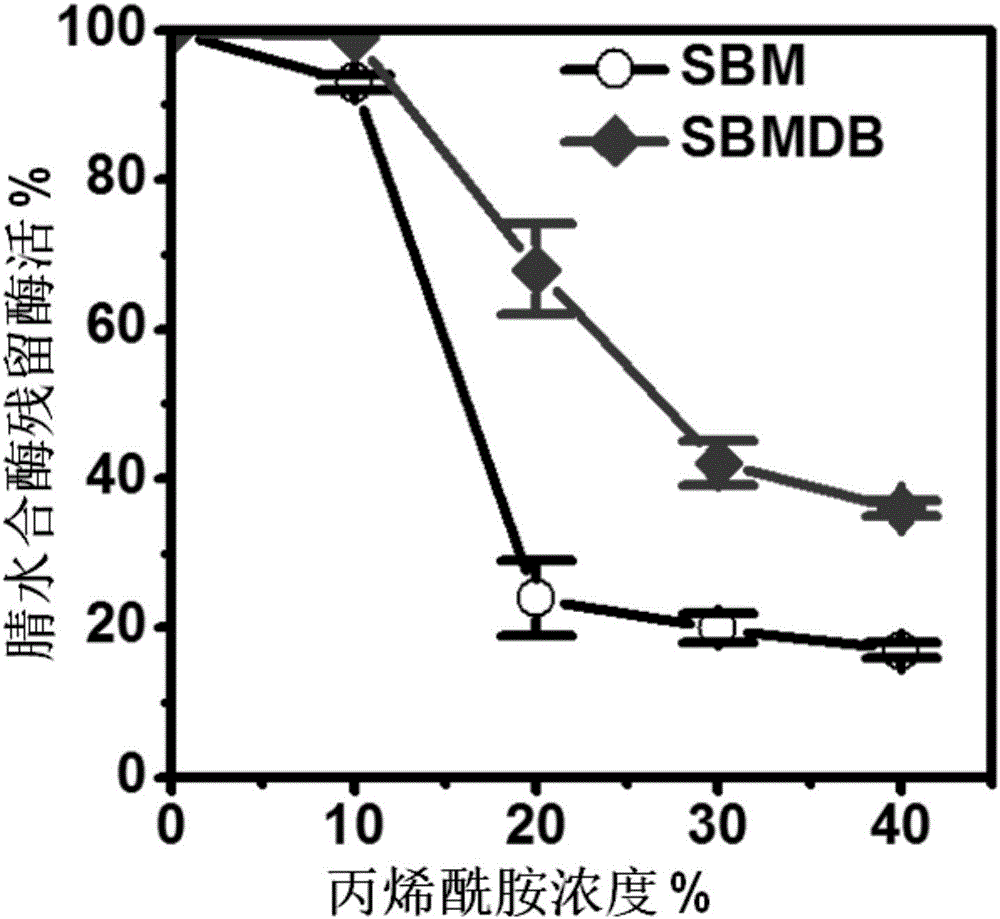
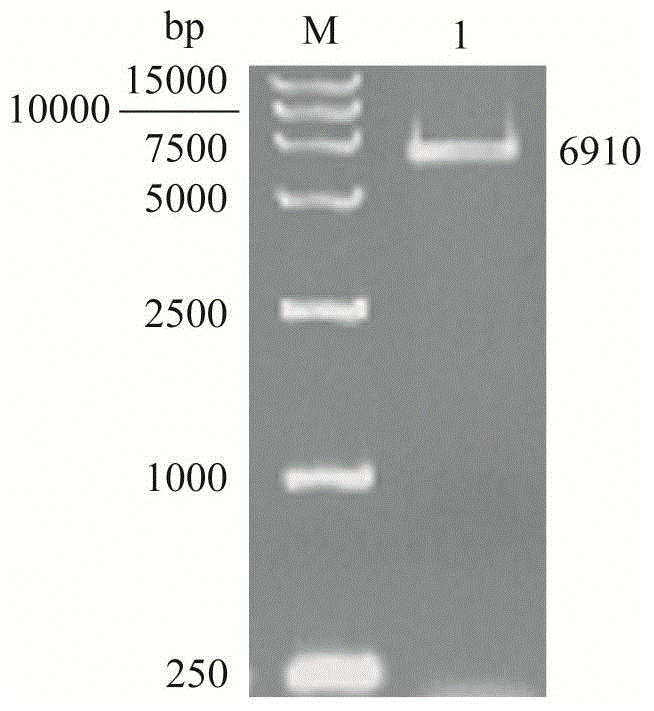
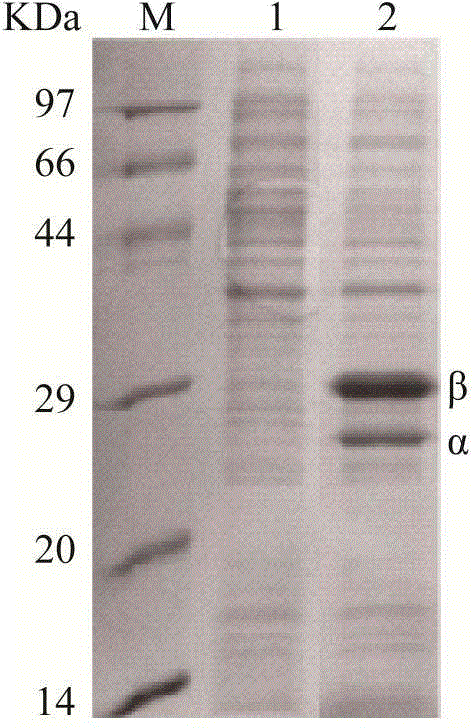
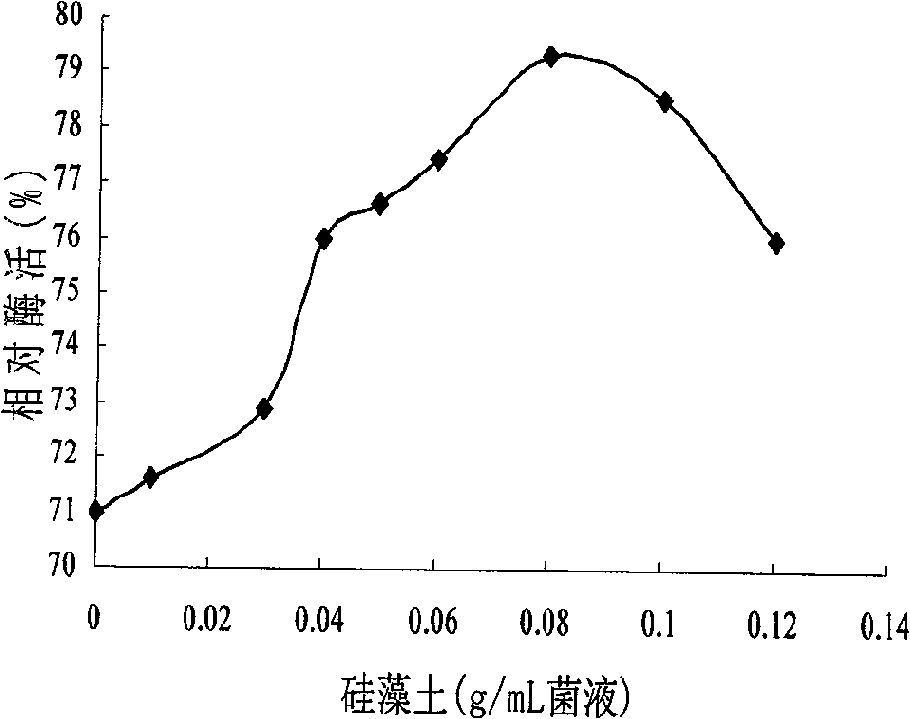
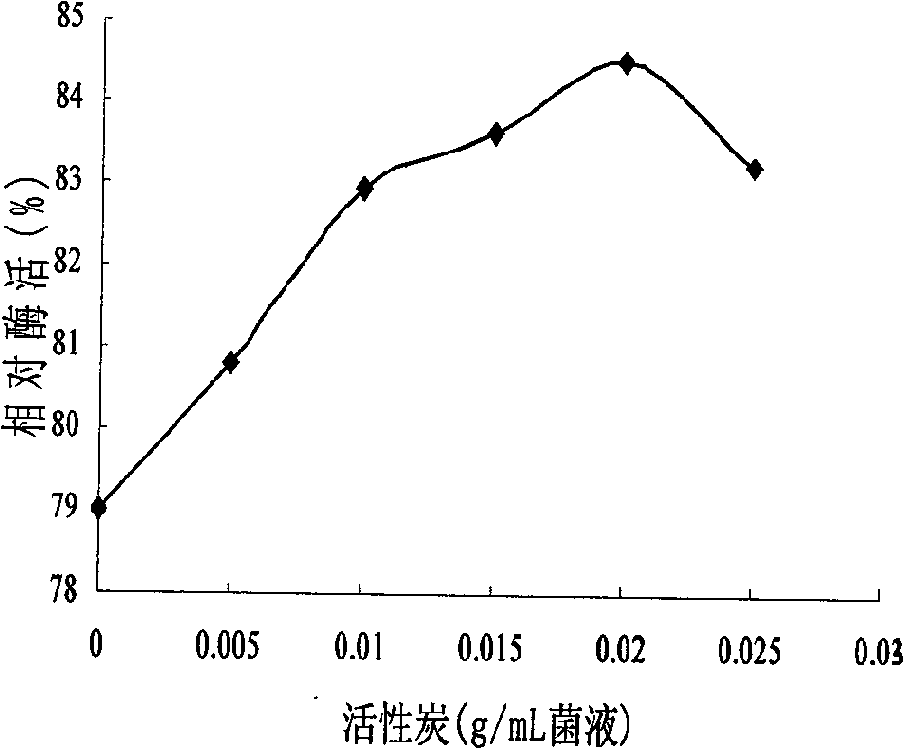
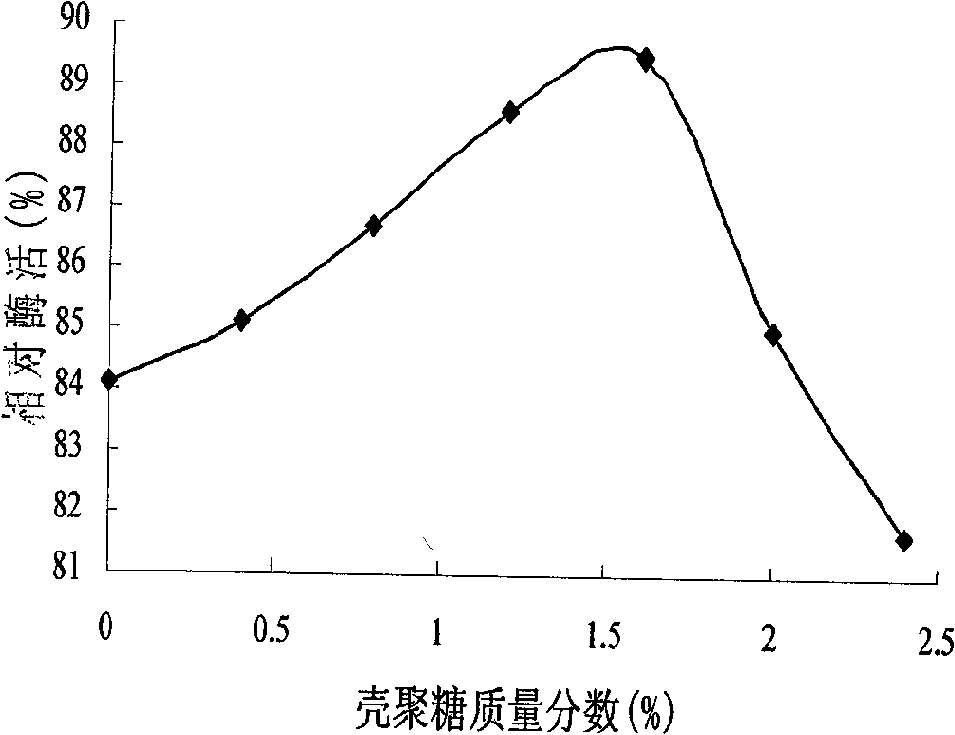
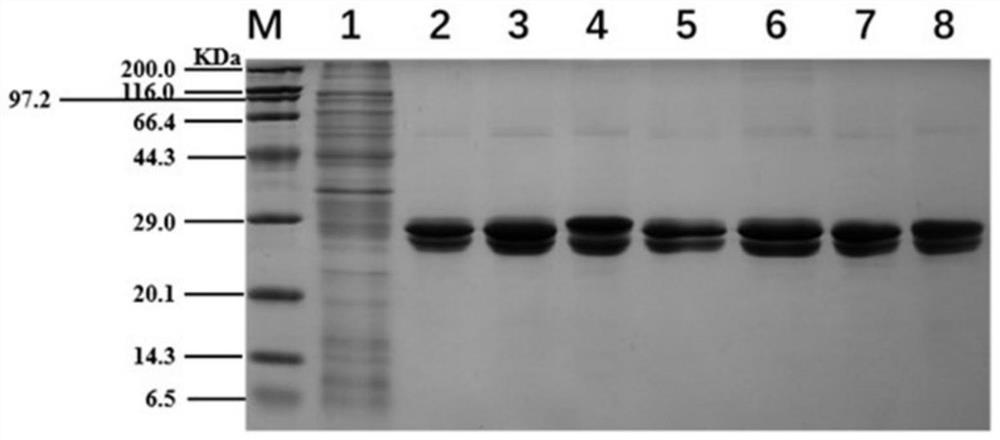
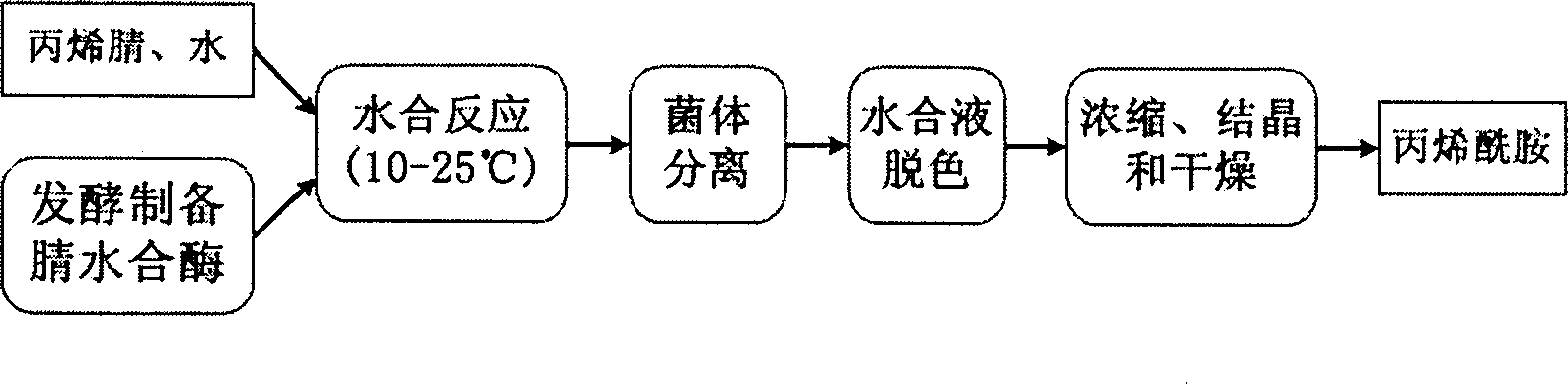
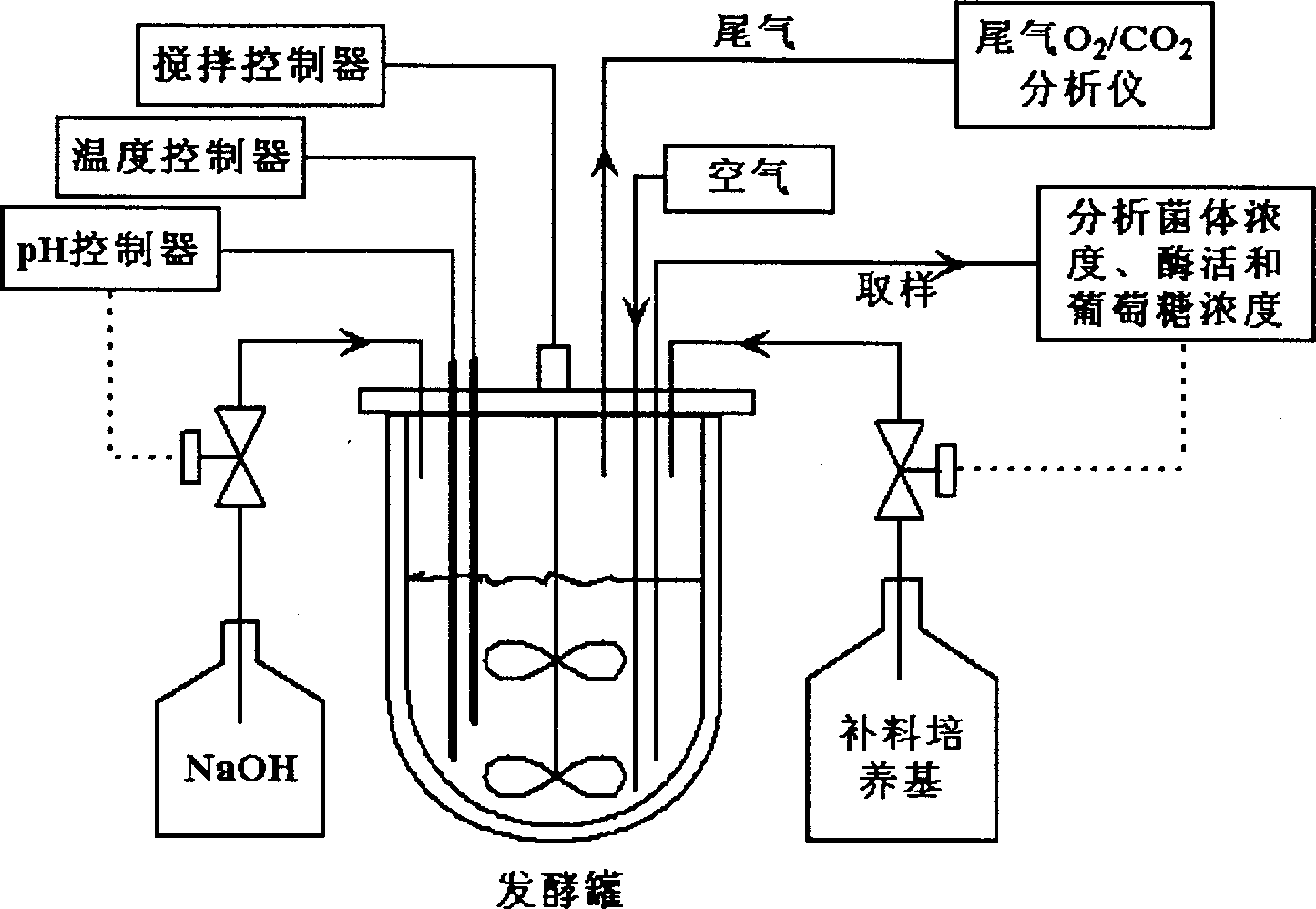
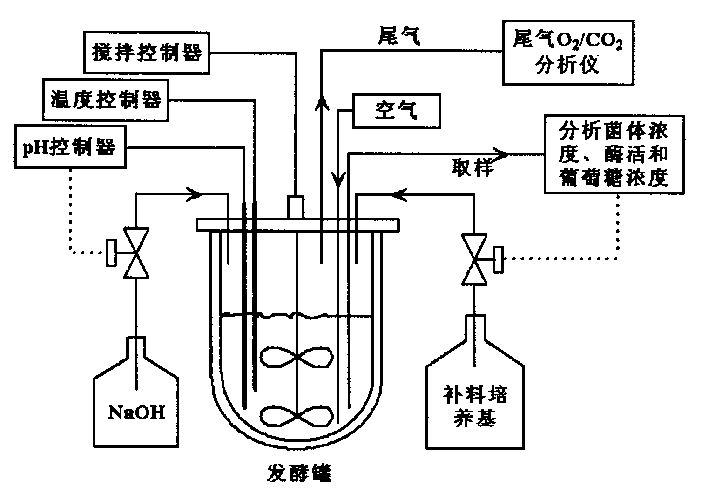
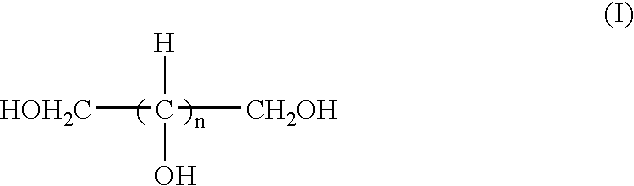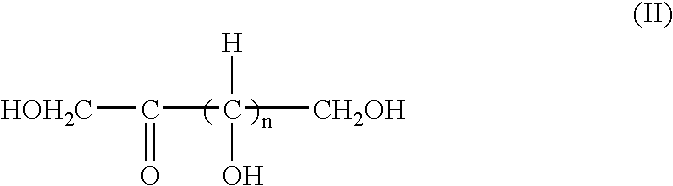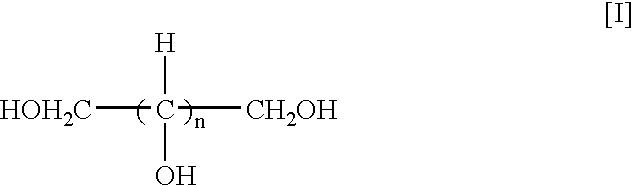Patents
Literature
160 results about "Nitrile hydratase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, nitrile hydratases (NHases; EC 4.2.1.84) are mononuclear iron or non-corrinoid cobalt enzymes that catalyse the hydration of diverse nitriles to their corresponding amides...
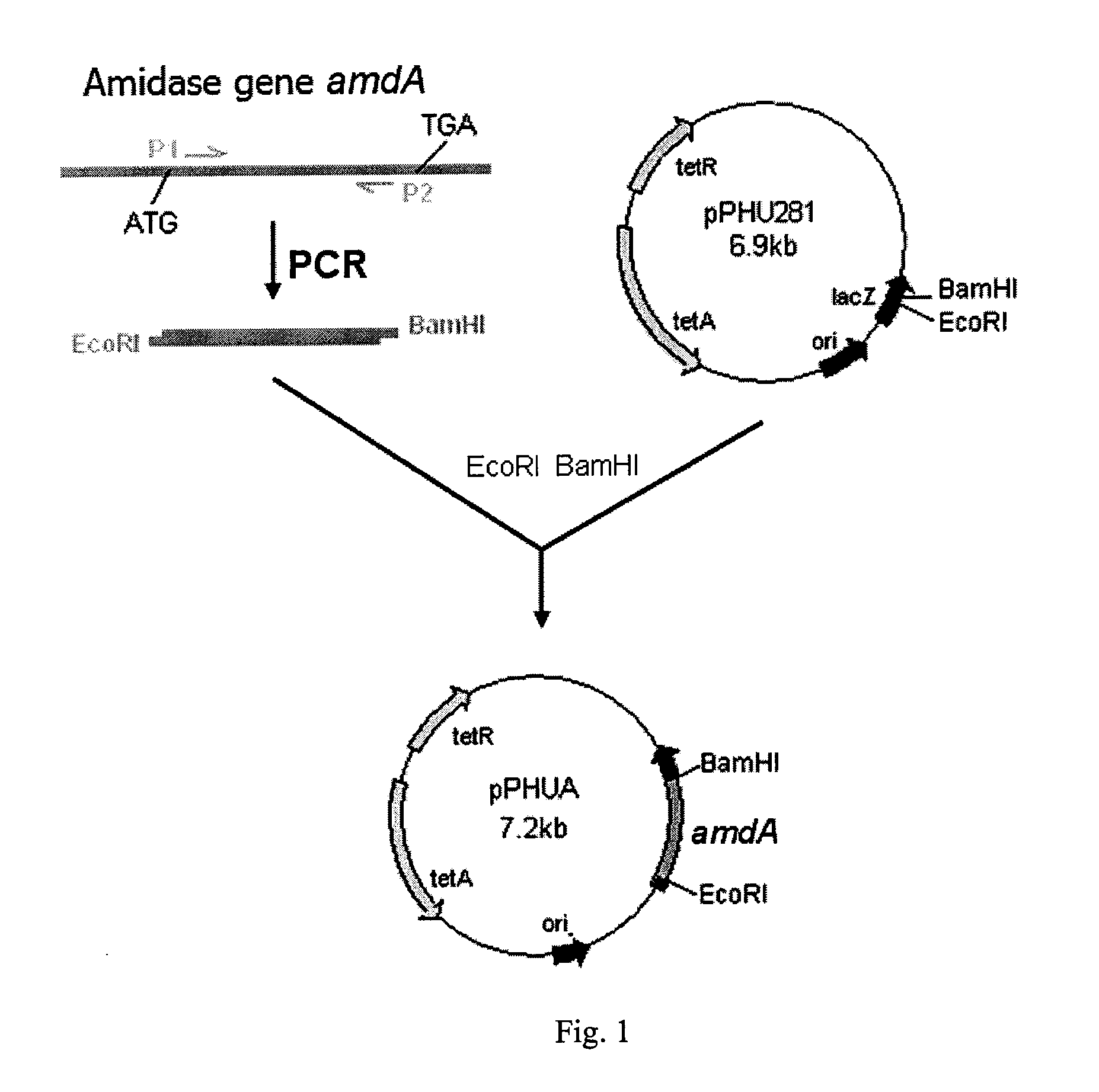
Engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium with amidase gene koucked-out, the construction and the use thereof
ActiveUS20110104690A1Inhibit expressionNot affect performance of strainBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesLarge fragment
An engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium and its construction method as well as its applications, wherein the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium is a mutant strain of an original nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium strain obtained by knocking-out or inhibiting the amidase gene in the original strain. The construction method of the engineered bacterium is to block the expression of the amidase gene by inserting the large fragment of a recombinant suicide plasmid carrying an amidase gene fragment into a wild-type strain through the homologous recombination between the recombinant suicide plasmid and the amidase gene of the wild-type strain. Compared to the corresponding wild-type bacterium strain, both the cell growth and the nitrile hydratase expression of the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium according to the invention are increased. In the process of catalyzing the hydration of acrylonitrile to produce acrylamide, the yield of the product, acrylamide, is significantly increased, while the yield of the by-product acrylic acid is significantly decreased. The engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium of the present invention has wide application prospect in the production of acrylamide by microbiological process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing aldinamide by biological catalysis of 2-cyano pyrazine and bacterial strain thereof
ActiveCN101481713AEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydration reactionPyrazine
The invention provides a method of producing 2-cyanopyrazine by biocatalysis to produce pyrazinamide and a new strain, Serratia marcescens ZJB-09104, which is used in the preparation process. In the method, the pyrazinamide is obtained through the catalytic hydration reaction under the conditions that the pH is 6.0-8.0 and the temperature is 20-40 DEG C in a reaction system which uses 2-cyanopyrazine as a substrate and nitrile hydratase which is obtained by the culturing of the Serratia marcescens as a catalyst. The method applies the Serratia marcescens ZJB-09104 to the experiments producing pyrazinamide by biocatalysis. Results show that the strain has a wide application prospect in the field of producing pyrazinamide by biocatalysis as the strain can effectively produce the pyrazinamide by biocatalysis and the transformation ratio of the 2-cyanopyrazine.attains 83.8 percent within 12h.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Novel rhodococcus, rhodococcus-origin nitrilase gene, nitrilehydratase gene and amidase gene and process for producing carboxylic acids by using the same
InactiveCN1340101AHigh puritySuitable for industrial productionBacteriaHydrolasesChemical compoundCarboxylic acid
The present invention relates to a novel Rhodococcus bacterium and to a process of hydrolyzing a cyano group of a nitrile compound using a novel Rhodococcus bacterium to produce the corresponding carboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to a process of producing carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids using a transformant transformed with a plasmid containing a nitrilase gene, a nitrile hydratase gene and an amidase gene derived from Rhodococcus bacteria capable of exhibiting particularly excellent position selectivity for the cyano group of aromatic polynitrile compounds, to such a transformant, such a plasmid, to such genes, to a process of producing an enzyme using the transformant, and to enzymes obtained by the process. The carboxylic acids, in particular cyano carboxylic acids obtained by the present invention are useful as starting materials for the synthesis of drugs, agrochemicals, dyestuffand other chemicals.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Method of culturing microorganism
In cultivating a microorganism having nitrile hydratase production ability, by allowing at least one of a ketose, such as fructose, and a sugar alcohol, such as mannitol, to be present, growth inhibition by cobalt ion is prevented, thereby achieving cultivation at a high concentration and with a high activity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Micro-organism possessing enantioselective and regioselective nitrile hydratase/amidase activities
InactiveUS20030049807A1Improve enzymatic activityBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismRegioselectivity
The present invention is concerned with new micro organisms, preferably mutagenised, belonging to the genus Agrobacterium radiobacter able to convert nitriles and / or amides into their respective acids, in addition to conversion processes utilising said micro-organisms.
Owner:IST BIOCHIM ITALANO GIOVANNI LORENZINI
Method for fixing nitrile hydratase strain by sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol
InactiveCN101358185ARealize industrialized continuous productionOn/in organic carrierPolyvinyl alcoholBoric acid
The present invention discloses a method for fixing Nitrile hydratase strain by adopting sodium alginate and polyvinyl alcohol, which relates to a method for fixing Nitrile hydratase strain. The present invention resolves the problems that the loss of the enzymatic activity of the Nitrile hydratase strain fixed by the prior method is large and that the number of reaction batches is little. The method includes the following steps: after sodium alginate, polyvinyl alcohol, Nitrile hydratase suspension, diatomite and active carbon are uniformly mixed, the mixture is dipped into saturated boric acid solution containing CaCl2; the produced pellets are solidified under the temperature of 4 DEG C for 24 hours; and the pellets are filtered out and then put into glutaraldehyde solution to be crosslinked for 20 minutes. The relative enzymatic activity of the sodium-alginate-and-polyvinyl-alcohol-fixed pellets produced by the method is increased by 24.8 percent compared with the sodium alginate embedding method, and increased by 30.8 percent compared with the polyvinyl alcohol embedding method. Meanwhile, the fixed Nitrile hydratase obtained by the method for fixing Nitrile hydratase strain by adopting the sodium alginate and the polyvinyl alcohol can carry out seven batches of continuous reactions, thus realizing industrialized continuous production.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nucleic acid fragments encoding nitrile hydratase and amidase enzymes from comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D and recombinant organisms expressing those enzymes useful for the production of amides and acids
The invention relates to the isolation, sequencing, and recombinant expression of genes encoding either a nitrile hydratase (NHase) or amidase (Am) from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D, where the NHase is useful for catalyzing the hydration of nitriles to the corresponding amides, and the amidase is useful for hydrolysis of amides to the corresponding carboxylic acids. Also provided are transformed host cells containing polynucleotides for expressing the nitrile hydratase or amidase enzymes from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
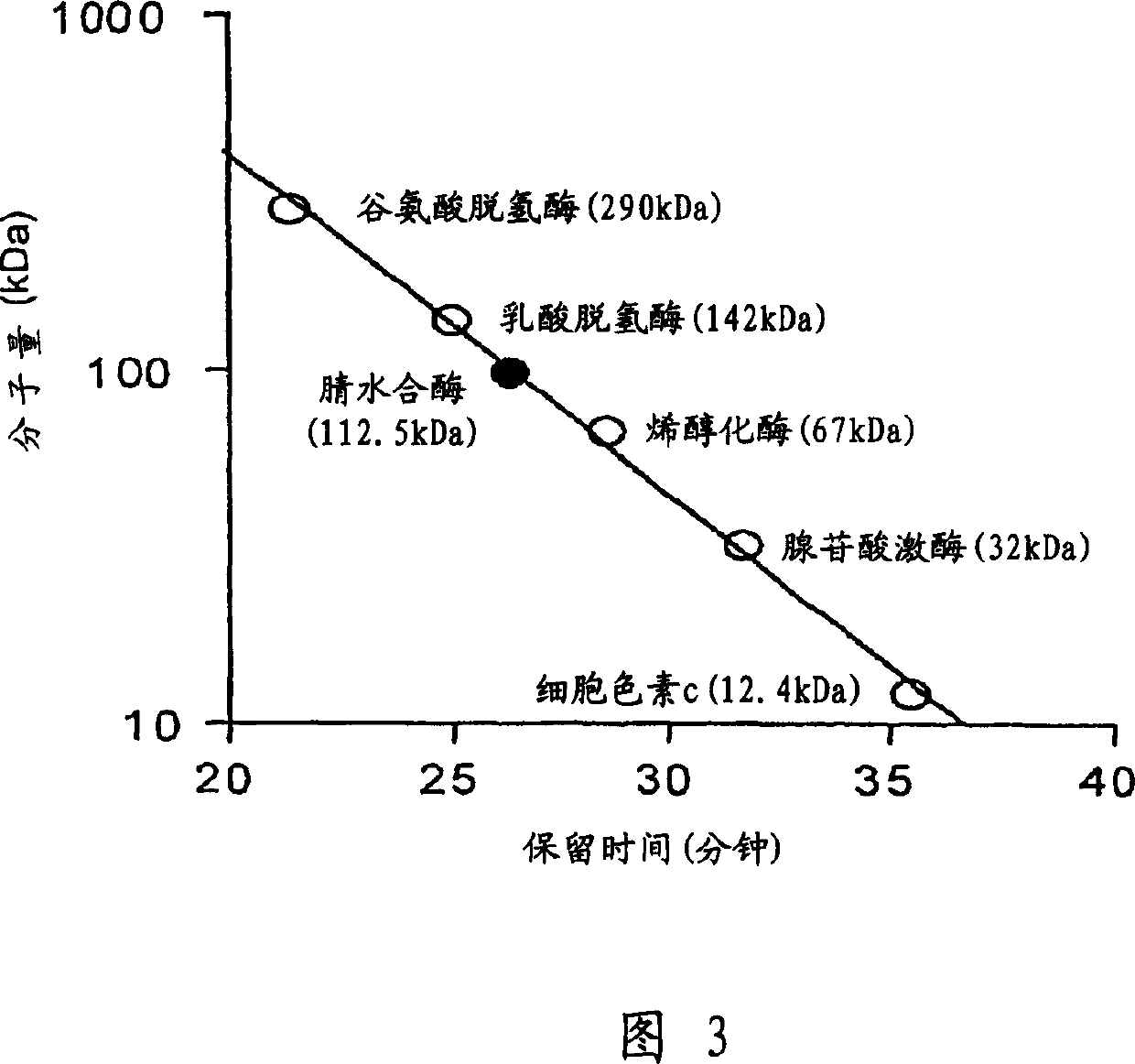
Mutant nitrile hydratase
ActiveCN102517271AImprove stress resistanceImprove heat resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiological TechniquesNitrile hydratase
The invention discloses a heat and ultrasound tolerant mutant nitrile hydratase which belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and industrial microbes. The mutant nitrile hydratase is obtained by displacing at least one residue of amino acid residues in the nitrile hydratase with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 and adding 1-2 residues to a position behind the terminal residue of the amino acid sequence represented by the SEQ ID NO:1, and the displaced residue corresponds with 141Ser, 143Ser and 144Leu in the amino acid sequence represented by the SEQ ID NO:1. The stress resistance of the mutant nitrile hydratase is good, and the heat tolerance, the survivability and the ultrasonic survivability of the mutant nitrile hydratase are substantially improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Double knockout recombinant rhodococcus as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105420154AHigh expression activityQuality improvementBacteriaHydrolasesSaccharumLevansucrase
The invention discloses a construction method of double knockout recombinant rhodococcus. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) primers are designed according to nitrile hydratase gene sequence of the rhodococcus for respective amplification of an upstream sequence and a downstream sequence of a nitrile hydratase gene, and an upstream fragment and a downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are obtained; (2) the upstream fragment and the downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are inserted into a suicide plasmid, and a recombinant suicide plasmid is obtained, wherein the suicide plasmid carries a kanamycin resistant gene and a levansucrase gene; (3) competent cells of recombinant rhodococcus of an amidase gene are knocked out through transformation of the recombinant suicide plasmid, and the double knockout recombinant rhodococcus is obtained: first screening is performed through kanamycin resistance, and a first recombinant colony is obtained and subjected to second screening through a sucrose plate. The invention further discloses recombinant rhodococcus with high nitrilase expression, a construction method of the recombinant rhodococcus and a method for preparing acrylamide.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
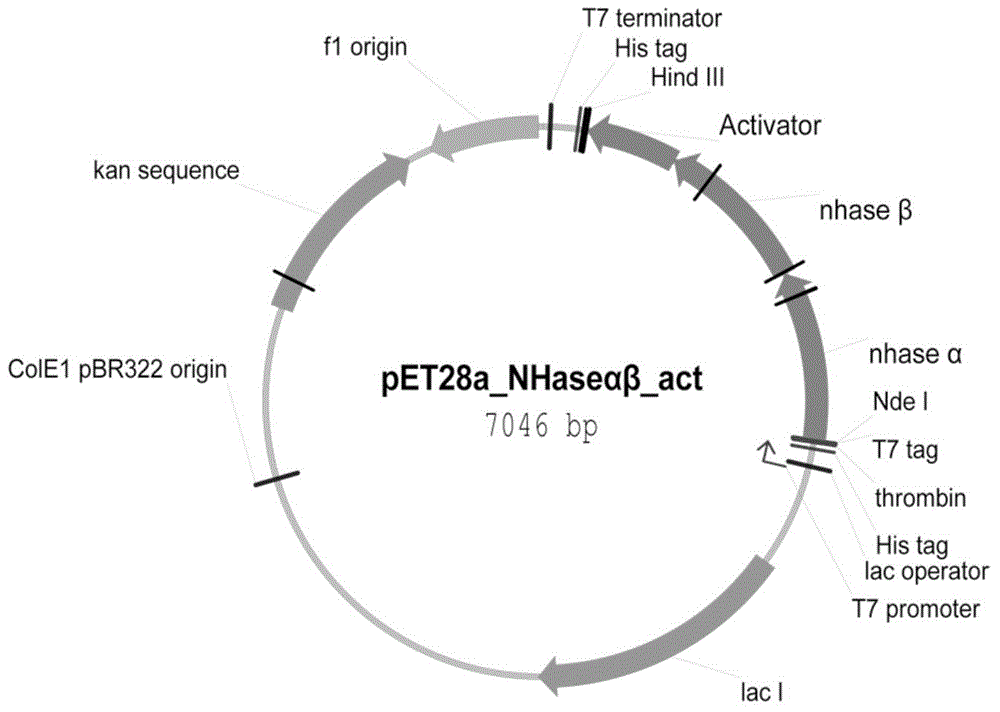
Nitrile hydratase gene, encoded enzyme, vector, engineering bacterium as well as application of engineering bacterium to preparation of amide compound
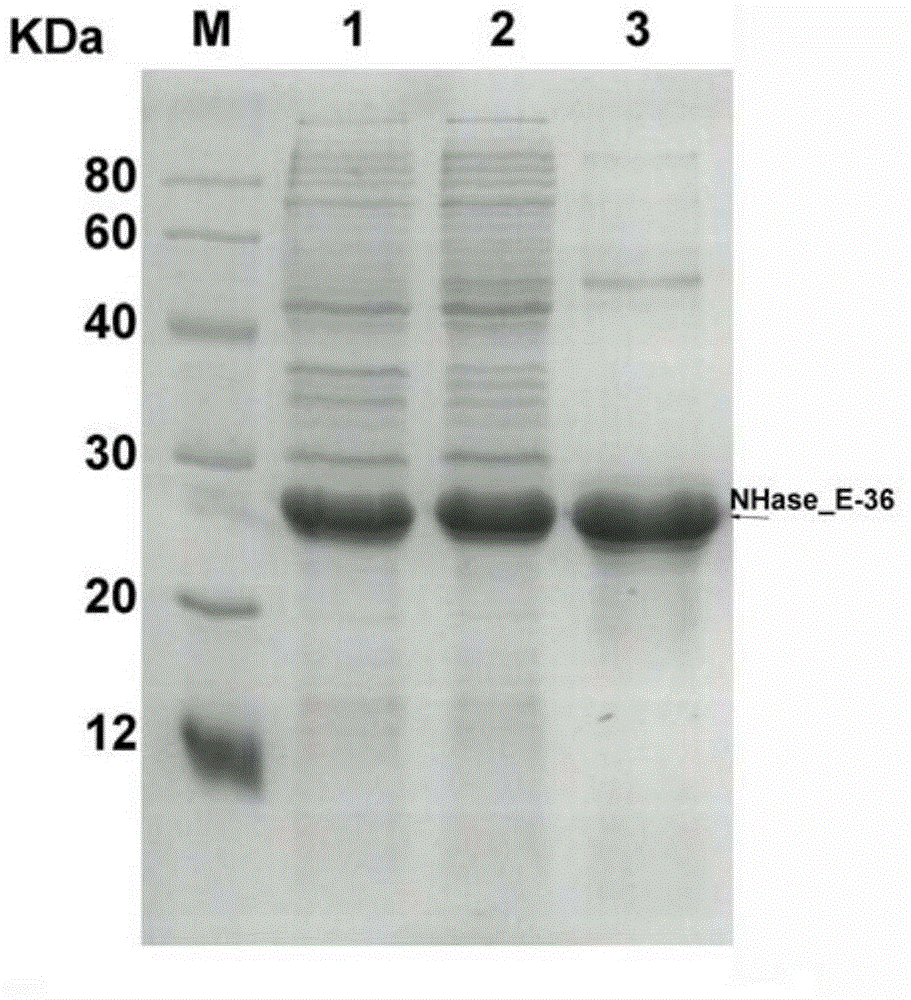
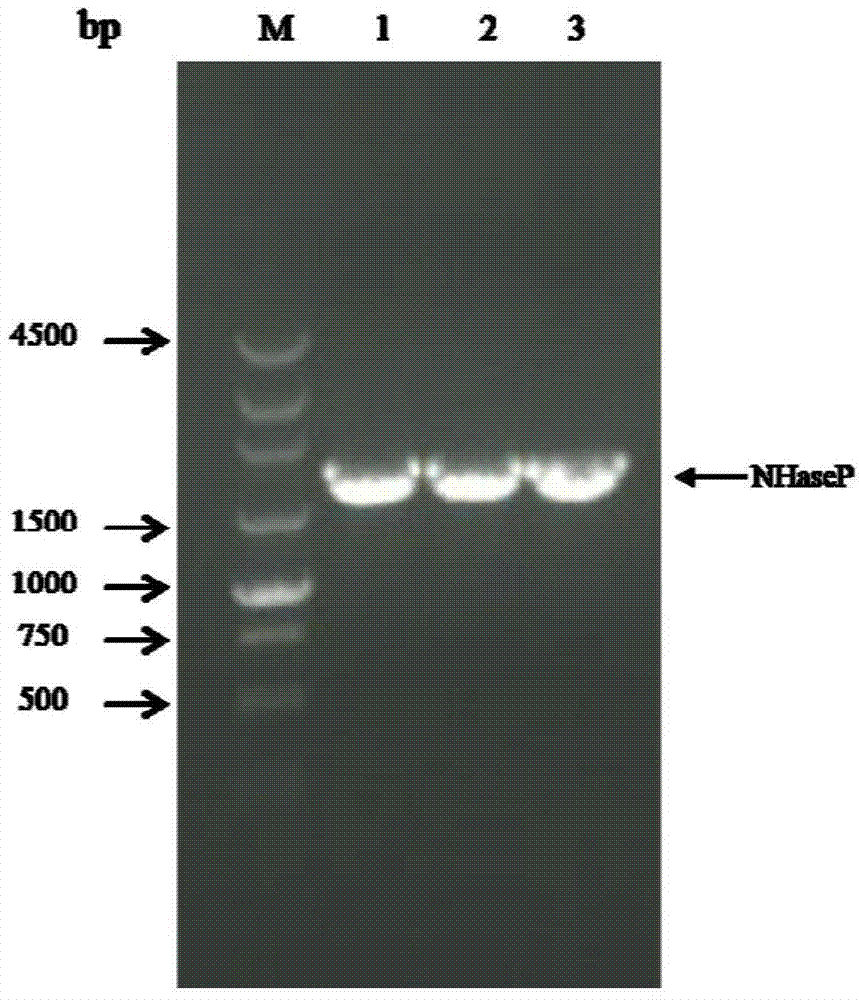
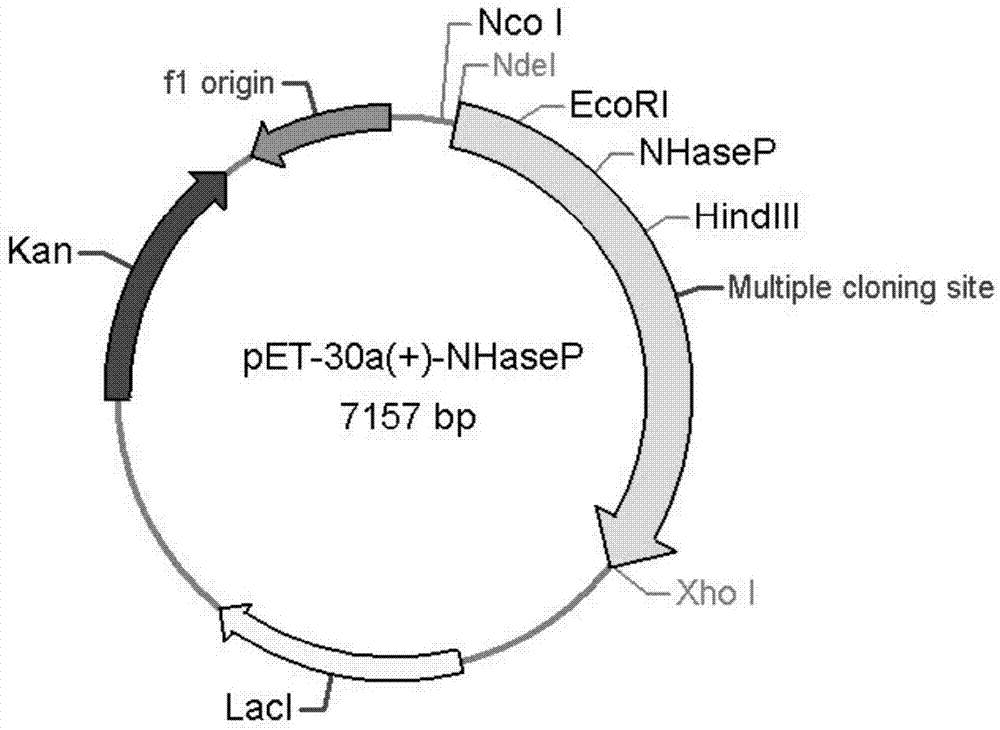
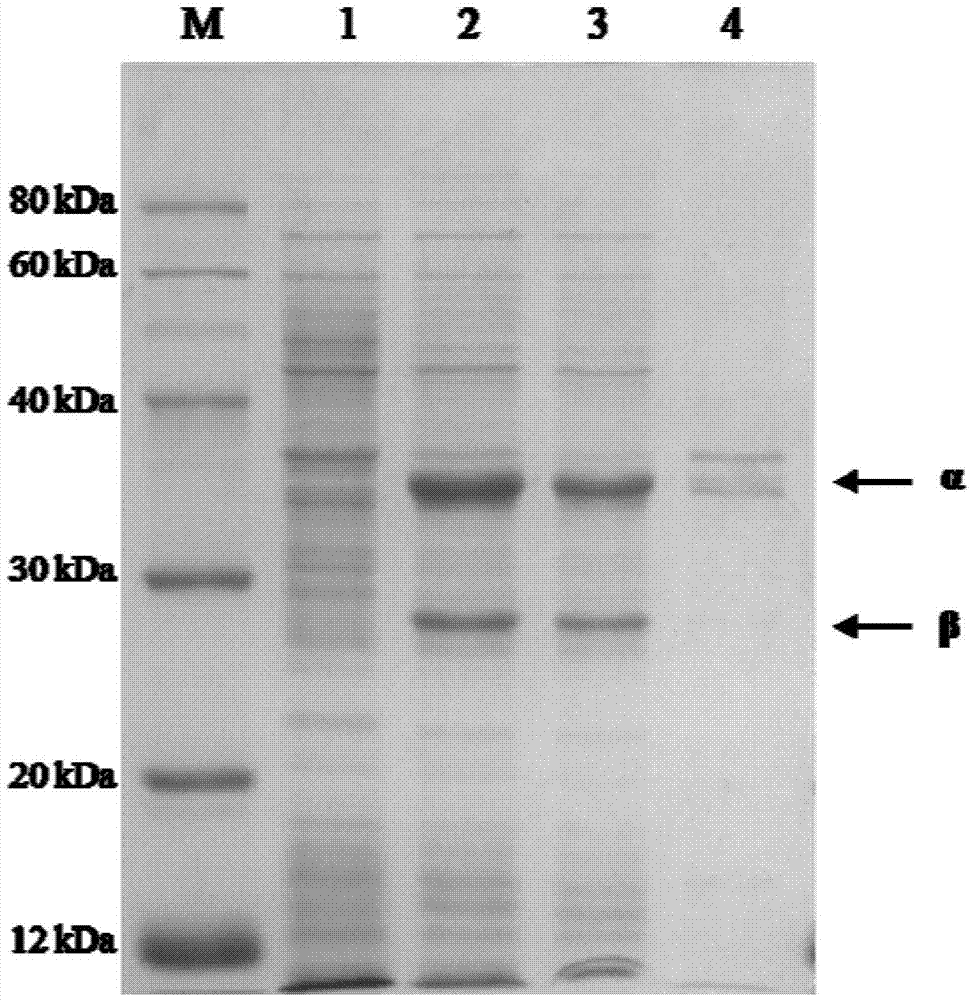
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase gene, an encoded enzyme, a vector, an engineering bacterium as well as an application of the engineering bacterium to preparation of an amide compound. The recombinant nitrile hydratase gene is formed by sequentially connecting an alpha subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.2, a beta subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and an activation element shown in SEQ ID NO.4. The functional expression of the tentative nitrile hydratase gene from sulfitobacter sp E-36 in Escherichia coil cells is realized, the gene engineering bacterium for expressing the nitrile hydratase efficiently is provided, and aromatic nitrile can be converted into the corresponding amide compound efficiently.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Nitrile hydratase variant
ActiveUS20110212506A1RiskStable productionSugar derivativesBacteriaAmino acid substitutionNitrile hydratase
A nitrile hydratase variant of the present invention comprises substitution of at least one amino acid with another amino acid to improve two or more properties of nitrile hydratase by substitution of one amino acid.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Nitrile hydratase and application thereof
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase and an application thereof. The nitrile hydratase is composed of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit, wherein an amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit is as shown in SEQ ID NO.6; the amino acid sequence of the beta subunit is as shown in SEQ ID NO.7. The nitrile hydratase is cloned to a nitrile hydratase gene from Burdett bacteria DSM 12804 (Bordetella petrii DSM 12804); the nitrile hydratase which is high in expression quantity, high in activity, wide in substrate spectrum and good in chiral selectivity is successfully obtained after gene expression. An existing nitrile hydratase is relatively high in activity on aliphatic acrylic compounds in general, and is low in activity on aromatic nitrile compounds in general. The nitrile hydratase disclosed by the invention has relatively high catalytic activity on the aromatic nitrile compounds, especially 2-isopropyl-4-chlorophenyl acetonitrile.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nitrile hydratase mutant, genetically engineered bacteria containing mutant and application of mutant
ActiveCN109593750AImprove thermal stabilityImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycineHigh density
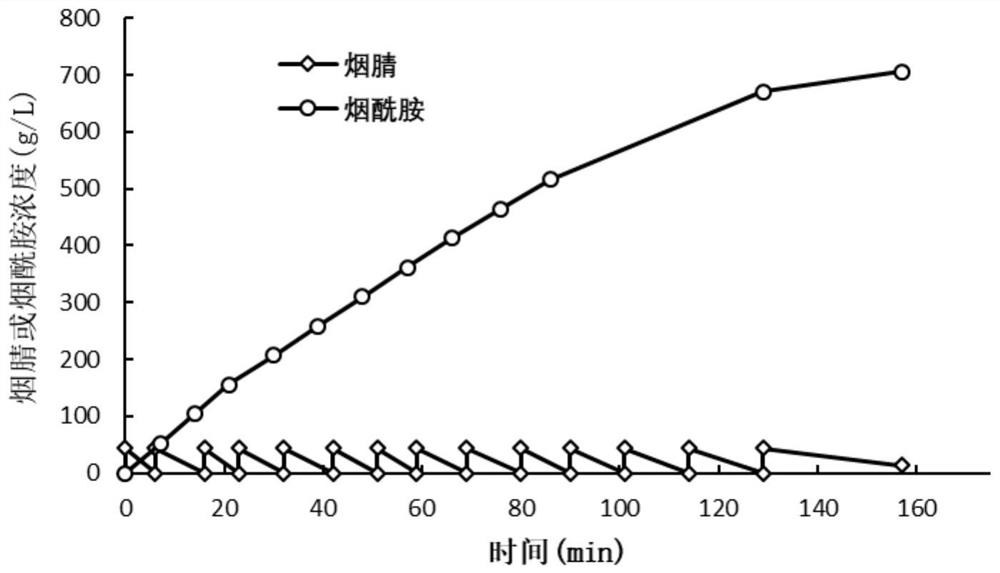
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase mutant, genetically engineered bacteria containing the mutant and application of the mutant, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a 47th glycine of the nitrile hydratase mutant alphaL6T / A19V / F126Y-betaM46K / E108R / S212Y (disclosed in the invention patent CN102216455A) mutates into asparagine; the obtained new mutant enzyme has better temperature tolerance and product tolerance, which is conducive to industrial production in the future; a recombinant strain containing the nitrile hydratase mutant is fermented at a high density, and nicotinonitrile is used as a substrate to perform whole-cell catalytic reaction to prepare nicotinamide. Compared with a chemical production method, the method is safe andclean in production process and free of environmental pollution; and compared with an enzymatic method, the method has low price of the substrate and high catalysis efficiency, obtains a final productnicotinamide at a yield of over 95% and a concentration up to 680 g / L, and simplifies separation and purification steps of the product.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrile hydratase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN112501151AHigh catalytic activityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNitrile hydrataseNicotinamide
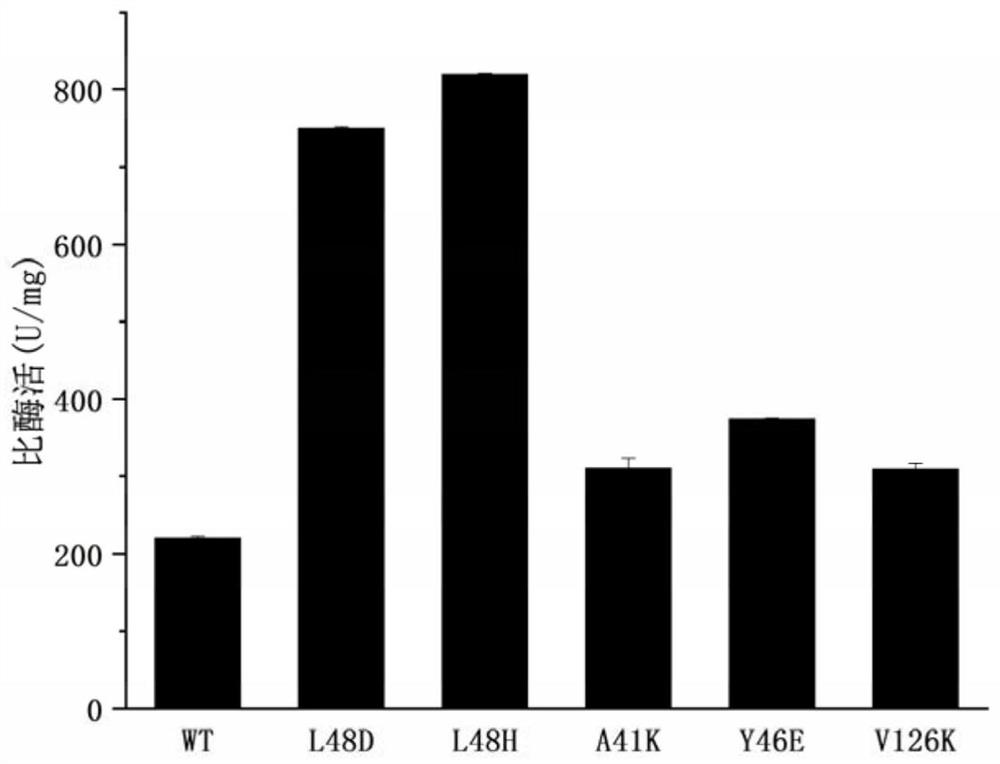
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the nitrile hydratase mutant, the enzyme activity of a single-point mutant L48D and the enzyme activity of a single-point mutant L48H constructed on by the 48th on a beta subunit in the amino acid motif of the nitrile hydratase are 750.26 + / -1.63 U / mg and 820.01 + / -0.98 U / mg respectively, and the enzyme activity of the single-point mutant L48D and the enzyme activity of the single-point mutant L48H are obviously improved in comparison with the specificenzyme activity 220.30 + / -2.28 U / mg of unmodified wild nitrile hydratase. the enzyme activity of the mutant L48D and the enzyme activity of the mutant L48H are respectively 3.4 times and 3.7 times ofthat of the wild nitrile hydratase mutant. The mutation of the two amino acid residues significantly improves the catalytic activity of nitrile hydratase, is beneficial to the production of industrialfine chemicals such as nicotinamide, improves the catalytic efficiency and reduces the production cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrile hydratase and a method for producing amides
An objective of the present invention is to provide a nitrile hydratase capable of producing 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutyroamide. The present invention provides a novel nitrile hydratase producing alpha-hydroxyamide using, alpha-hydroxnitrile as the substrate, and the encoding DNA thereof. The enzyme can be obtained from Rhodococcus sp. Further, the enzymatic activity of the enzyme can he maintained stably during the reaction. The present invention provides a method for producing amide compounds, the method comprising the step of reacting this enzyme to nitrile compounds. According to the present invention, from hydroxy nitrile compounds, corresponding amide compounds can be produced biochemically without reducing the enzyme activity of nitrile hydratase.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method of producing nicotinamide by catalysis of rhodococcus
InactiveCN104762338AHigh total enzyme activityHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydration reactionPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the field of bio-chemical engineering and discloses a method of producing nicotinamide by catalysis of rhodococcus. In the method, by means of nitrile hydratase generated by the rhodococcus, a catalytic reaction is carried out between the nitrile-production hydratase and a substrate, 3-cyanopyridine, to produce the nicotinamide. In the reaction process, a method of adding the substrates and the catalyst in batches is employed for increasing the conversion rate. In the invention, a novel nitrile hydratase is employed so that the method is simple and convenient in operation processes and is less in environmental pollution. The nicotinamide product is easy to separate and is high in purity. The method is good in industrial application prospect.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
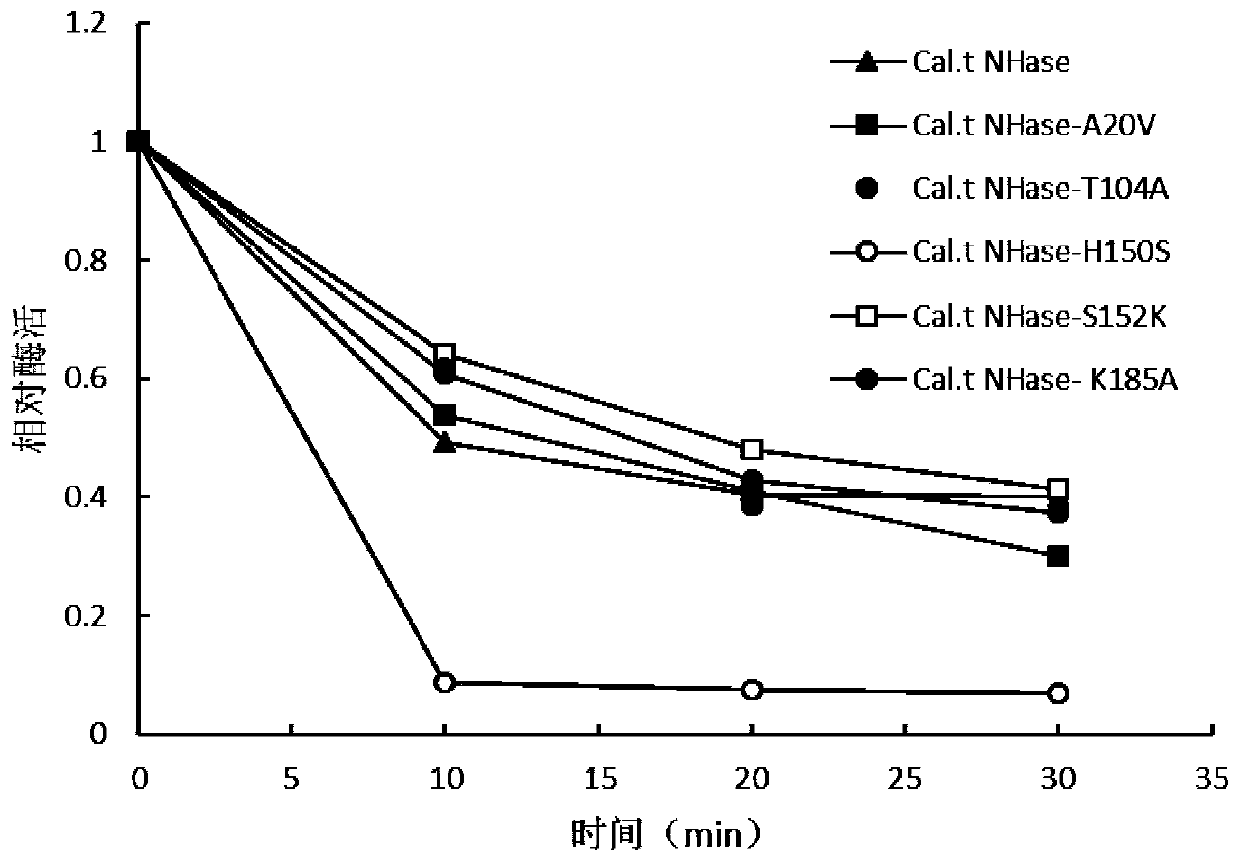
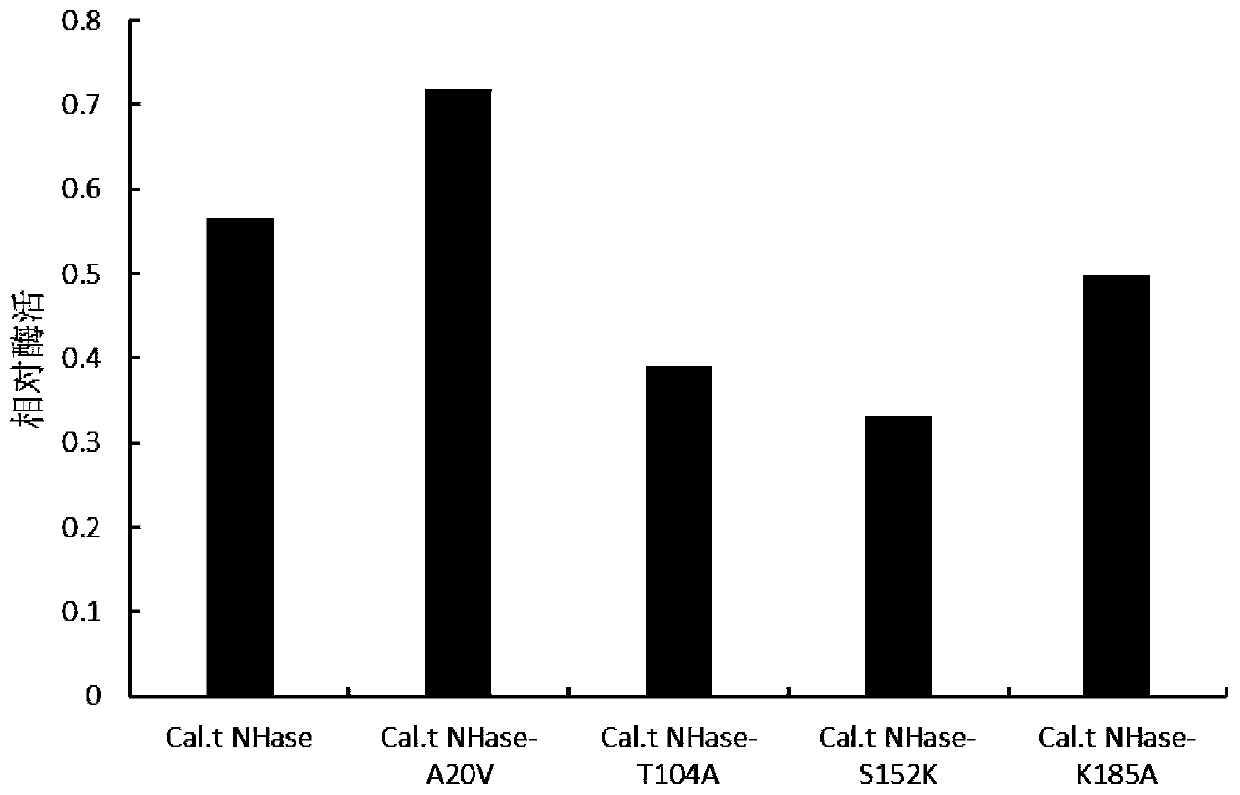
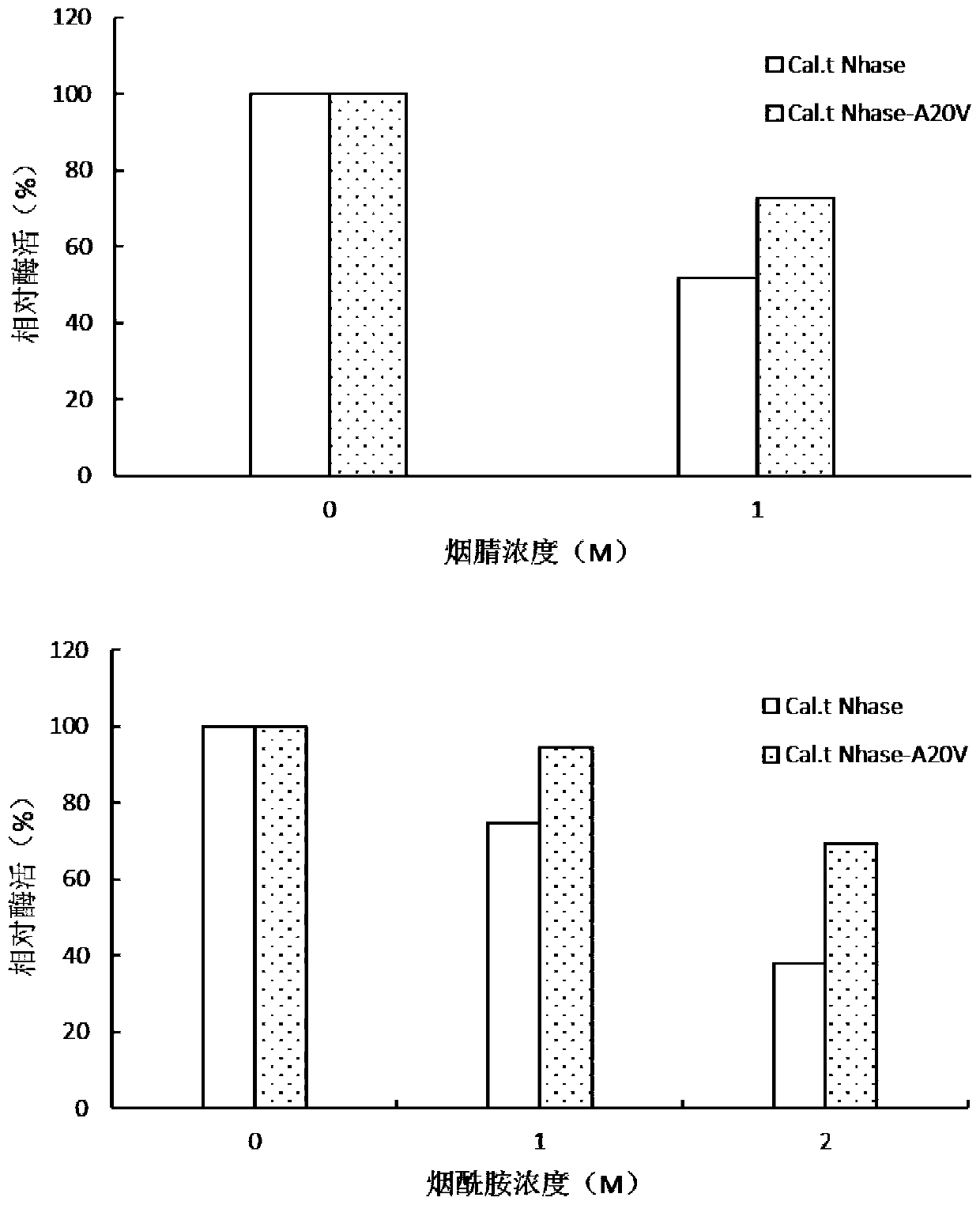
Mutant of nitrile hydratase derived from caldalkalibacillus thermarum
ActiveCN110938616AGood substrate toleranceGood enzymatic propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSpecific enzymeSporolactobacillus
The invention discloses a mutant of nitrile hydratase derived from caldalkalibacillus thermarum, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The half-life period of the nitrile hydratasemutant Cal.t Nhase-A20V at 70 DEG C is about 10 min, the thermal stability of the mutant Cal.t Nhase-A20V has no too large change compared with that of a wild enzyme, and the specific enzyme activityof the mutant Cal.t Nhase-A20V is 128% of that of the wild enzyme. At the same time, the mutant also has better substrate tolerance and product tolerance, the final yield of nicotinamide produced bywhole-cell catalysis reaches 598 g / L; therefore, the nitrile hydratase mutant Cal.t Nhase-A20V provided by the invention has very good enzymatic properties, and is beneficial to industrial productionin future.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Modified nitrile hydratase and application thereof
ActiveCN107177581AImprove stress resistanceImprove heat resistanceBacteriaFermentationHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses modified nitrile hydratase and application thereof in the technical field of enzyme engineering and industrial microorganisms. A method for obtaining the modified nitrile hydratase disclosed by the invention is that Pro of 133 site of a alpha subunit of an amino acid sequence shown as by a sequence table SEQ ID NO:2 and Asp of 215 site of a beta subunit of an amino acid sequence shown as by a sequence table SEQ ID NO:1 are respectively replaced with Cys, so that a disulfide bond is formed between the two subunits. Stress resistance and heat resistance of the modified nitrile hydratase disclosed by the invention and product tolerance are all obviously improved, and activity of the nitrile hydratase is not lowered. The modified nitrile hydratase can be catalyzed to obtain a high-concentration acrylamide product, and can be recycled repeatedly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High efficient expression method for actinomyces-based nitrile hydratase gene in escherichia coli
ActiveCN103320458AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high efficient expression method for an actinomyces-based nitrile hydratase gene in escherichia coli, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering technology. The method processes high efficiency and safety. It is benefit for large scaled nitrile hydratase extraction and purification, and further theoretical research about nitrile hydratase that a large amount of soluble nitrile hydratase can be obtained in a short expression period by applications of the method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-glufosinate ammonium preparation method
ActiveCN109384811AEasy to operateLow costGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFermentationGlufosinate-ammoniumHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for obtaining L-glufosinate ammonium with single configuration by catalytically hydrolyzing an inexpensive and easily-available glufosinate ammonium cyanamide intermediate with biological enzyme through a one-pot method, wherein the hydrolyzing process specifically comprises: 1, obtaining a glufosinate ammonium amide racemate from a racemic glufosinate ammonium cyanamide intermediate under the action of non-selective nitrile hydratase; 2, selectively hydrolyzing the L-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate with L-amide hydrolase to obtain L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate while racemizing the unhydrolyzed D-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate under the action of ACL racemase to continuously convert into the L-glufosinate ammonium amide intermediate, such that the single L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate is finally obtained through the DKR process; and 3, hydrolyzing the L-glufosinate ammonium phosphonate under the action of dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain the L-glufosinate ammonium.
Owner:SICHUAN LIER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
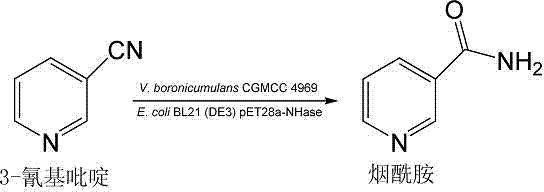
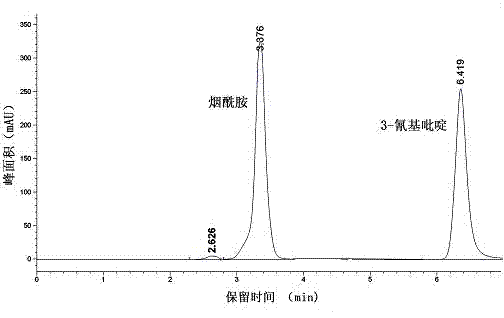
Vaporophage bacterium cgmcc4969 and its application in the biotransformation of 3-cyanopyridine to nicotinamide
The invention discloses the use of variovoraxboronicumulans CGMCC 4969 in bioconversion of 3-cyanopyridine for forming nicotinamide. The nitrile hydratase gene cluster produced by the strain consists of a DNA sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table; the DNA consisting of the sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1 is recombined onto a pET28a plasmid and can be induced to express in EscherichiacoliBL21(DE3) strain; and the Escherichia coli cells containing expressed proteins and cell extracting solution can convert 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinamide.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
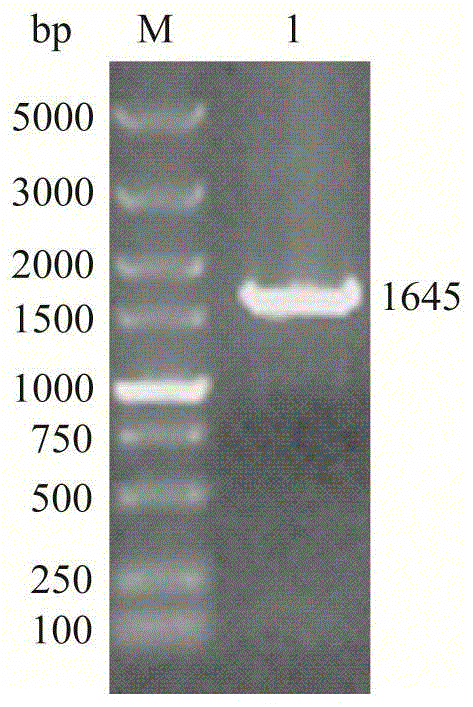
Genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently expressing high-molecular weight nitrile hydratase and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN104830747AReduce incubation timeShorten fermentation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently expressing high-molecular weight nitrile hydratase and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of microbiological genetic engineering. The high-molecular weight nitrile hydratase gene nhhB (rbs) A (rbs) G is obtained from a nitrile hydratase gene bag based on an R.rhodochrous J1 source through codon optimization, express element transformation and chemical synthesis. The whole length of the gene is 1645bp; the gene is encoded with 533 amino acids and can be successfully expressed in escherichia coli; the method is efficient and safe; 96.7U / mL soluble nitrile hydratase can be obtained by inducing at 24 DEG C for 16 hours; the specific enzyme activity can be up to 234U / mg after purification; and the method is beneficial to extraction and purification of the nitrile hydratase and efficient enzymatic synthesis of amide substances in the production process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for fixing nitrile hydratase strain by sodium alginate-chitosan microcapsules
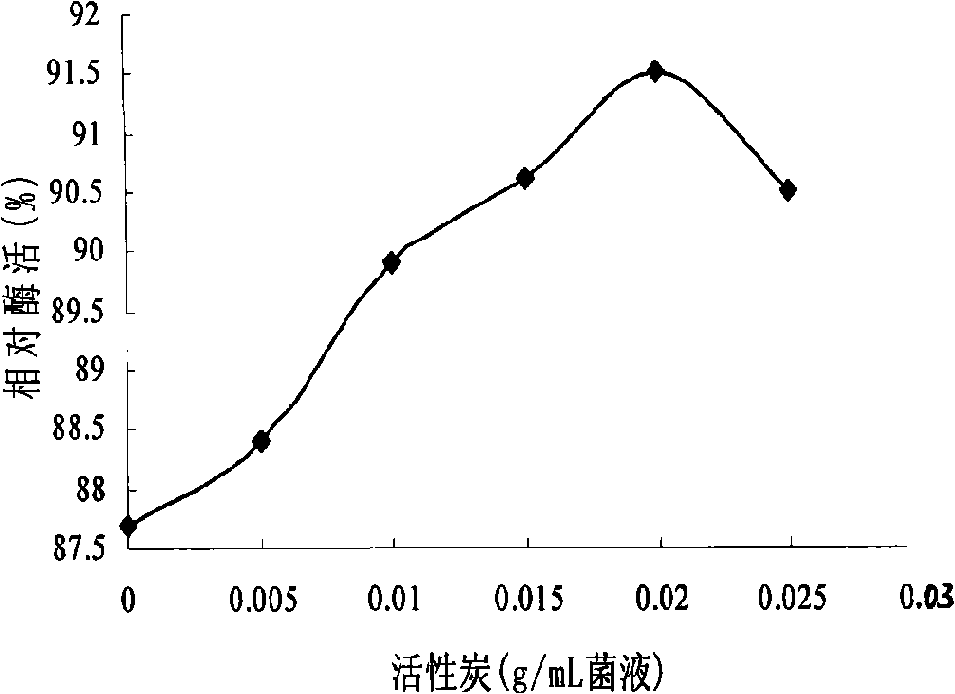
InactiveCN101358186AHigh relative enzyme activityIncreased relative enzyme activityOn/in organic carrierAcetic acid solutionOperational stability
The present invention discloses a method for fixing Nitrile hydratase strain by adopting sodium alginate and chitosan microcapsules, which relates to a method for fixing Nitrile hydratase strain. The present invention resolves the problems that the loss of the enzymatic activity of the Nitrile hydratase strain fixed by the prior method is large and that the number of reaction batches is little. The method includes the following steps: after sodium alginate, Nitrile hydratase suspension, diatomite and active carbon are uniformly mixed, the mixture is dipped into CaCl2 solution; the produced pellets are solidified under the temperature of 4 DEG C for 24 hours; and the pellets are filtered out and then put into chitosan acetic acid solution to be filmed. The sodium alginate and the chitosan microcapsules, which are obtained by the method, have the highest relative enzymatic activity, reaching 91.6 percent, increased by 23.3 percent compared with the relative enzymatic activity of the sodium alginate and the chitosan microcapsules obtained by the sodium alginate embedding method. The Nitrile hydratase strain obtained by the method can realize ten batches of reactions, and compared with the sodium alginate embedding method, the method has better operation stability and continuity and can realize industrialized continuous production.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
BACTERIAL STRAIN RHODOCOCCUS AETHERIVORANS VKM Ac-2610D PRODUCING NITRILE HYDRATASE, METHOD OF ITS CULTIVATION AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING ACRYLAMIDE
The invention relates to a bacterial strain belonging to the genus Rhodococcus which is a producer of a nitrile hydratase. The invention also relates to a method for producing acrylamide by hydration of acrylonitrile using a biomass of the bacterial strain and to a method of culturing the bacterial strain.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Method for cultivation of the nitrile-hydratase-producing strain Rhodococcus rhodochrous M33
The invention relates to a method for cultivation of the nitrile-hydratase-producing strain Rhodococcus rhodochrous M33, using a culture medium which is based on a 12 to 60 mM phosphate buffer, covers the demand of the cells for phosphorus and maintains the pH in the range of 5.5 to 9.0 during cultivation, and to which acetic acid is added in doses as the new source of carbon after consumption of the initially supplied quantity of glucose. The invention also relates to the culture medium used in the method.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Method of producing acrylamide
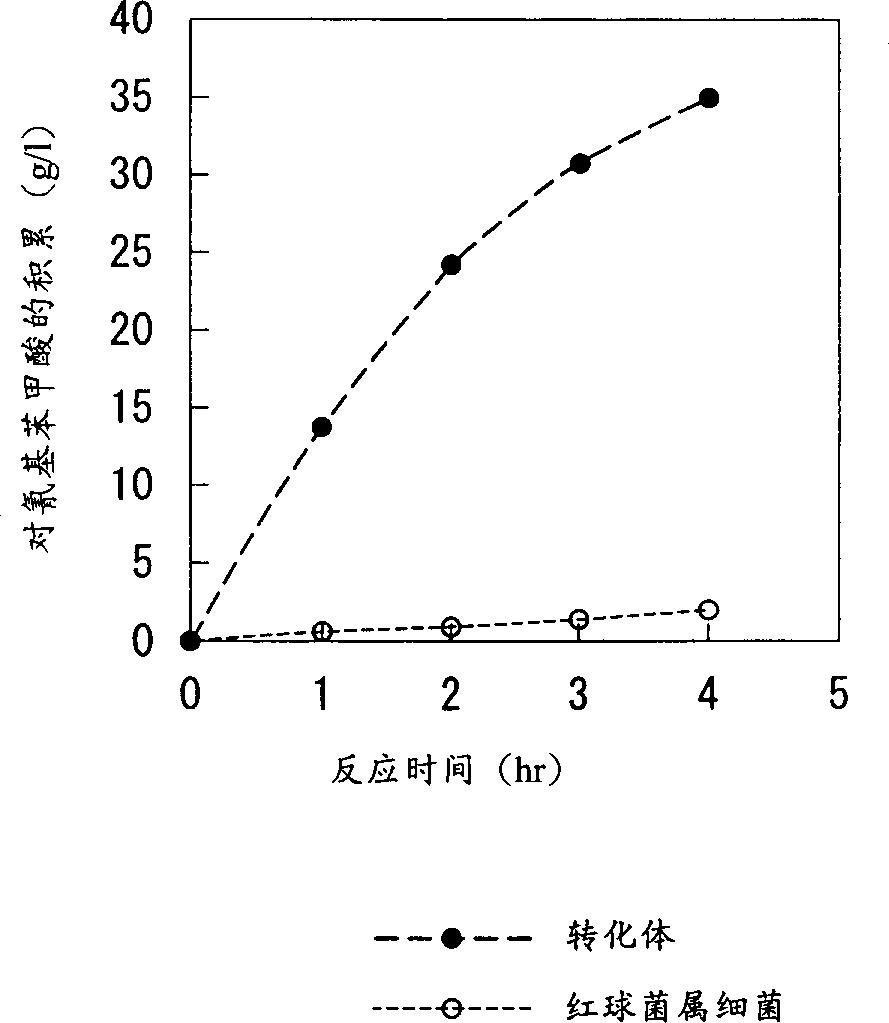
InactiveCN101410527AEfficient manufacturingImprove qualityFermentationHydration reactionAcrylonitrile
It is intended to provide a method of producing acrylamide having improved qualities at an elevated efficiency by using, for example, a microbial catalyst containing nitrile hydratase. Namely, acrylamide can be produced by subjecting acryl nitrile to a hydration reaction with the use of microbial cells or processed microbial cells containing nitrile hydratase under such conditions as allowing the presence of a compound having at least one active methylene group and / or at least a salt of this compound.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Modification and application of nitrile hydratase amino acid motif
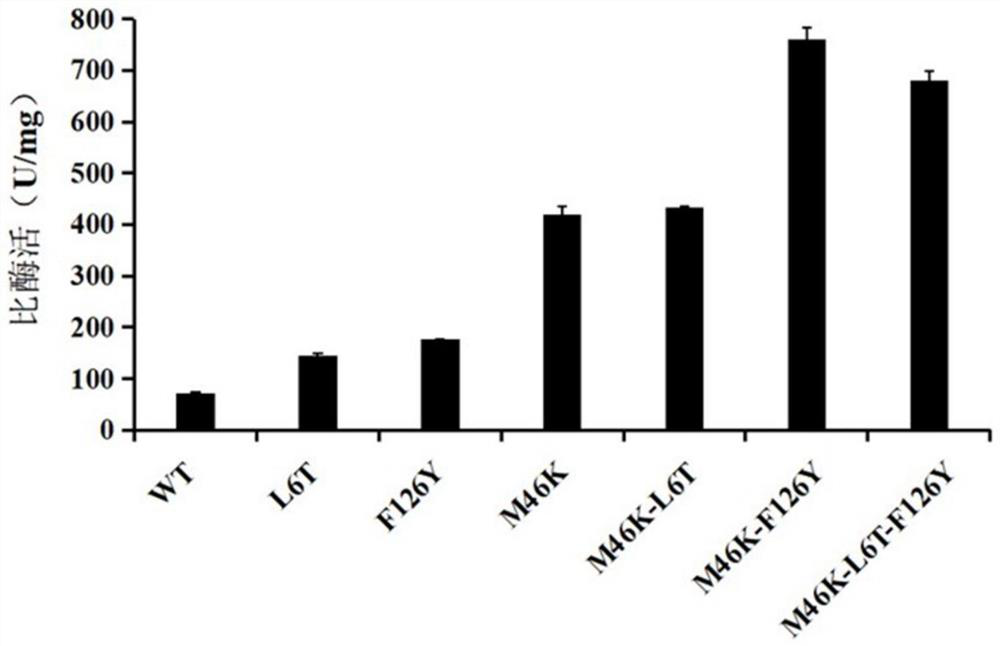
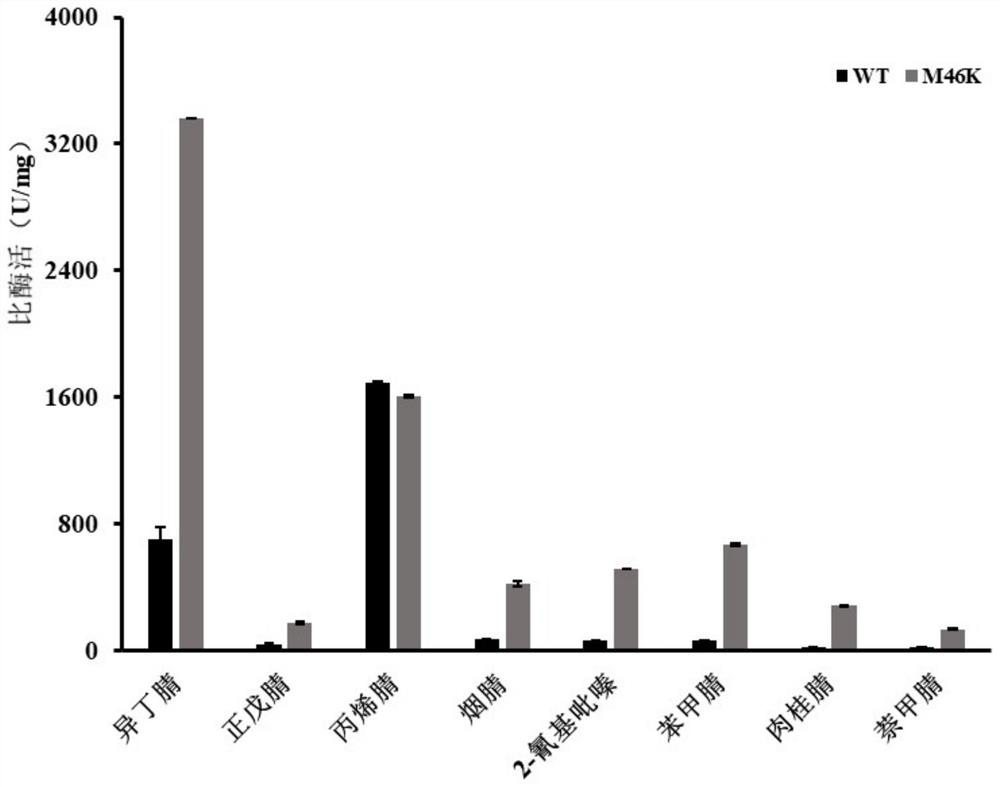
InactiveCN112522245AIncreased specific enzyme activityImprove catalytic performanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeCatalytic effect
The invention provides modification and application of nitrile hydratase amino acid motif, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, nitrile hydratase derived from pseudonocardia thermophila is modified, the NO.46 site on a beta subunit and the NO.6 site and NO.126 site on an alpha subunit of a wild type are mutated respectively, and the specific enzyme activity of a constructed mutant is remarkably improved and can be improved by 1-5 times compared with that of the wild type. Moreover, the substrate spectrum is also broadened, the mutant has a very goodcatalytic effect on isobutyronitrile, n-valeronitrile, acrylonitrile, nicotinonitrile, 2-cyanopyrazine, benzonitrile, cinnamonitrile, naphthonitrile and the like, and the catalytic performance on corresponding substrates is also remarkably improved. Therefore, the obtained nitrile hydratase mutant can be suitable for more production scenes, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Heat-resistant recombinant nitrile hydratase gene, encoded enzyme, engineering bacterium and application of gene engineering bacterium
InactiveCN104561065AHigh expressionHigh activityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliBiological activation
The invention discloses a heat-resistant recombinant nitrile hydratase gene, an encoded enzyme, a vector, an engineering bacterium and an application of the gene engineering bacterium to catalysis of a nitrile compound to produce amide and a biodegradation herbicide, that is, dichlobenil. The functional expression of the tentative nitrile hydratase gene from bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 is realized, and the crucial role of an activation element of the nitrile hydratase in the expression process is proved. Meanwhile, the invention provides a method for constructing the nitrile hydratase gene engineering bacterium in Escherichia coli, and the nitrile hydratase with the high expression quantity and the high activity is obtained from the nitrile hydratase gene with the participation of the activation element.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Technique method for preparing hydratase of carbonitrile mitrile by using glucose-CO2+ coupling adding ferment
InactiveCN1446913AEasy to synthesizeIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesGlucose polymersD-Glucose
A process for preparing nitrile hydratase from glucose and Co ions includes coupling glucose with Co ions and fermenting, and features that the output of nitrile hydratase is positivity dependent to the consumptions of glucose and Co ions. Its advantages are high enzyme activity and simple process. The said product can be used for preparing acrylamide.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com