Genetically engineered bacterium for efficiently expressing high-molecular weight nitrile hydratase and application of genetically engineered bacterium
A nitrile hydratase, high molecular weight technology, applied in bacteria, lyase, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problem of not being used in a balanced or random manner, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, high-efficiency expression, and improving product purity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: Acquisition of high molecular weight nitrile hydratase gene nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G
[0036] (1) Firstly, the original high molecular weight nitrile hydratase gene (bag) (Genbank ID: X86737.1) derived from Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 was obtained by searching the GenBank database in NCBI.
[0037] (2) Among the sequences obtained in the database, the sequences between B and A of the nitrile hydratase gene and between A and G were replaced with the SD sequence (AAGGA) and spacer sequence (GATATAGAT) of Escherichia coli.
[0038] (3) The nitrile hydratase gene sequence designed through transformation in the previous step is optimized according to the codon preference of Escherichia coli to obtain the sequence of the nitrile hydratase target gene nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G, such as SEQ ID NO. 6, and enzyme cutting sites Nde Ⅰ and EcoR Ⅰ were added to the upstream and downstream ends of the gene fragment respectively.
[0039] (4) Send the gene sequence finally obtained in the...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Construction of expression vector pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G
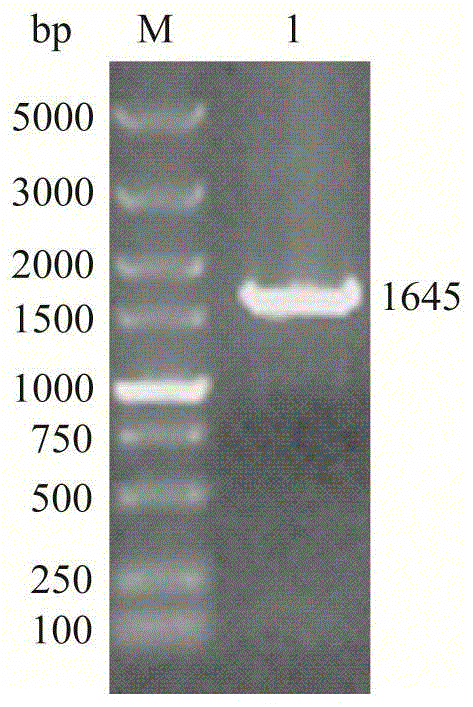
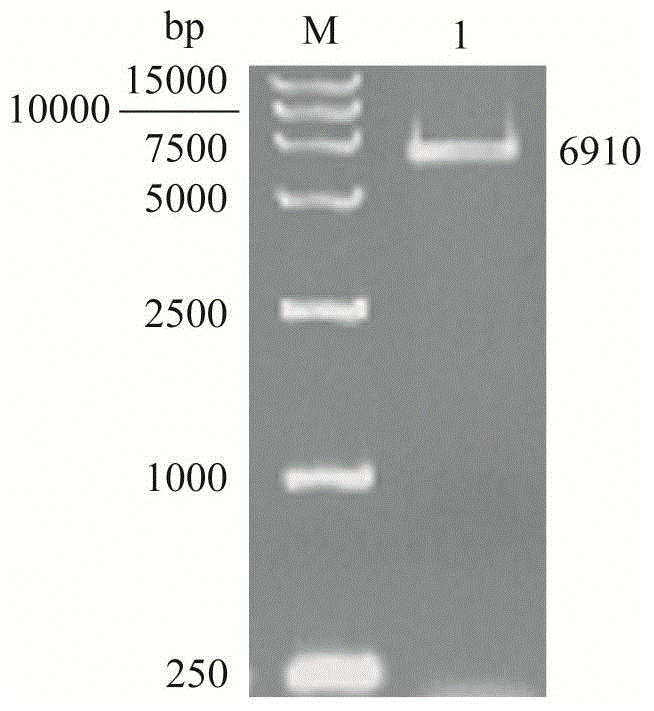
[0041] The chemically synthesized target gene fragment was cloned into the Nde I and EcoR I restriction sites of pET24a(+), transformed into E.coli JM109, and recombinants were screened on the 2YT plate containing kanamycin resistance. Extract the recombinant plasmid and perform PCR verification (eg figure 1 shown), a 1645bp electrophoresis band was obtained, which was the same size as the target gene; the recombinant plasmid was digested with EcoR Ⅰ to obtain a 6910bp electrophoresis band (such as figure 2 shown), indicating that the pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G recombinant plasmid was successfully constructed.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Induced expression of BL21 / pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G
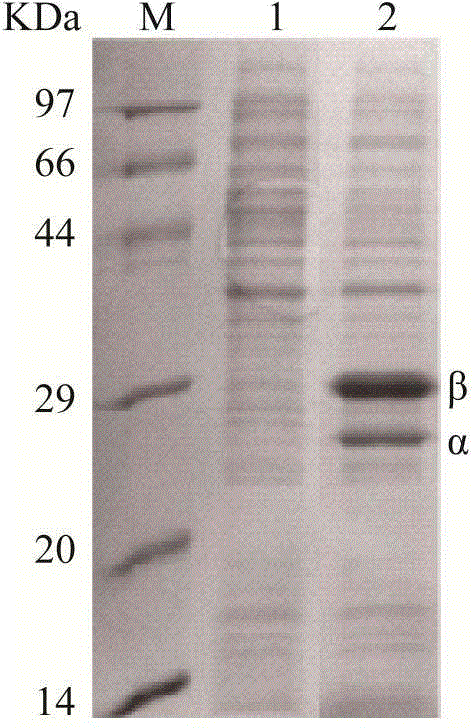
[0043] The recombinant plasmid pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G was transformed into E. coli BL21 to obtain BL21 / pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G. BL21 / pET24a(+)-nhhB(rbs)A(rbs)G recombinant single colony was inoculated into 5mL of 2YT medium and cultured at 37°C for 10h, then 1mL of the culture solution was transferred to 100mL of 2YT medium and cultured at 37°C until OD 600 When the concentration is 0.6-0.8, add IPTG and 0.1g / L CoCl to a final concentration of 0.4mM 2 ·6H 2 O, after 16 hours of induced expression at 24°C, the bacteria were collected by centrifugation, and the expression was detected by SDS-PAGE. The results are shown in image 3 , which is consistent with the theory that the α subunit is 26KDa and the β subunit is 29KDa.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com