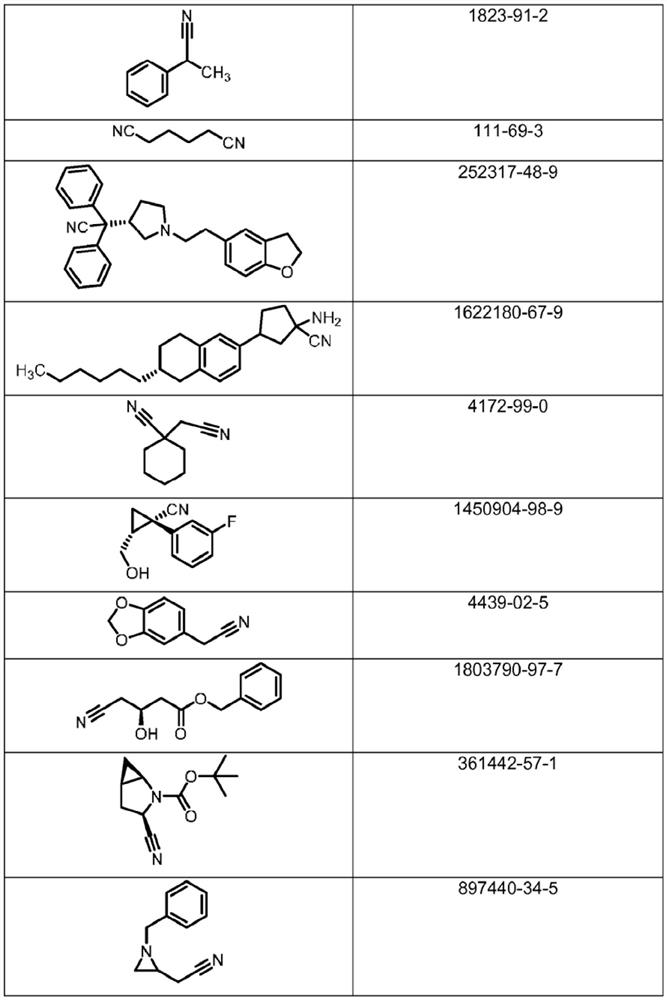
Patents
Literature
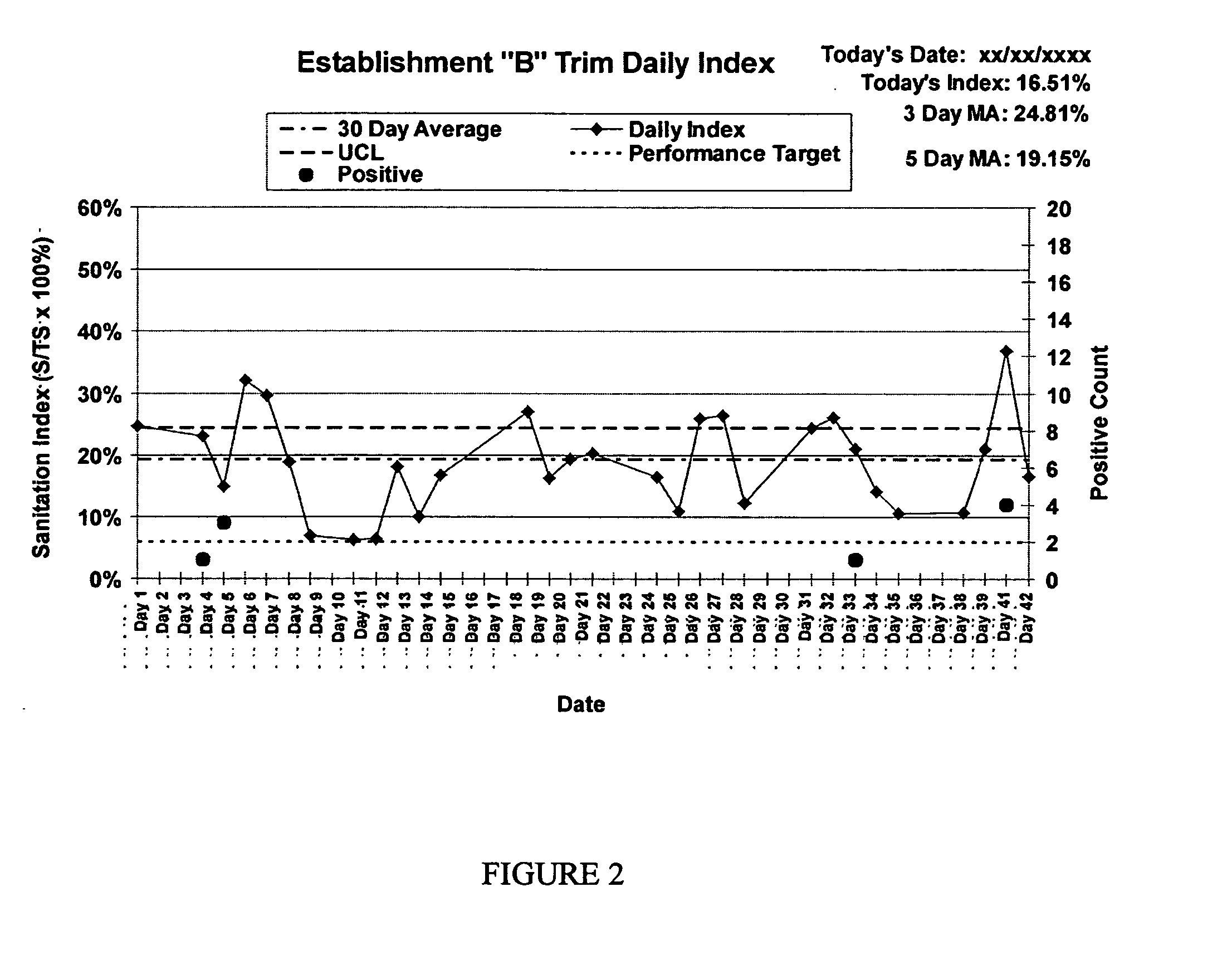
52 results about "Microbiological Processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What does microbiological processes mean? Definitions for microbiological processes mi·cro·bi·o·log·i·cal pro·cess·es Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word microbiological processes.
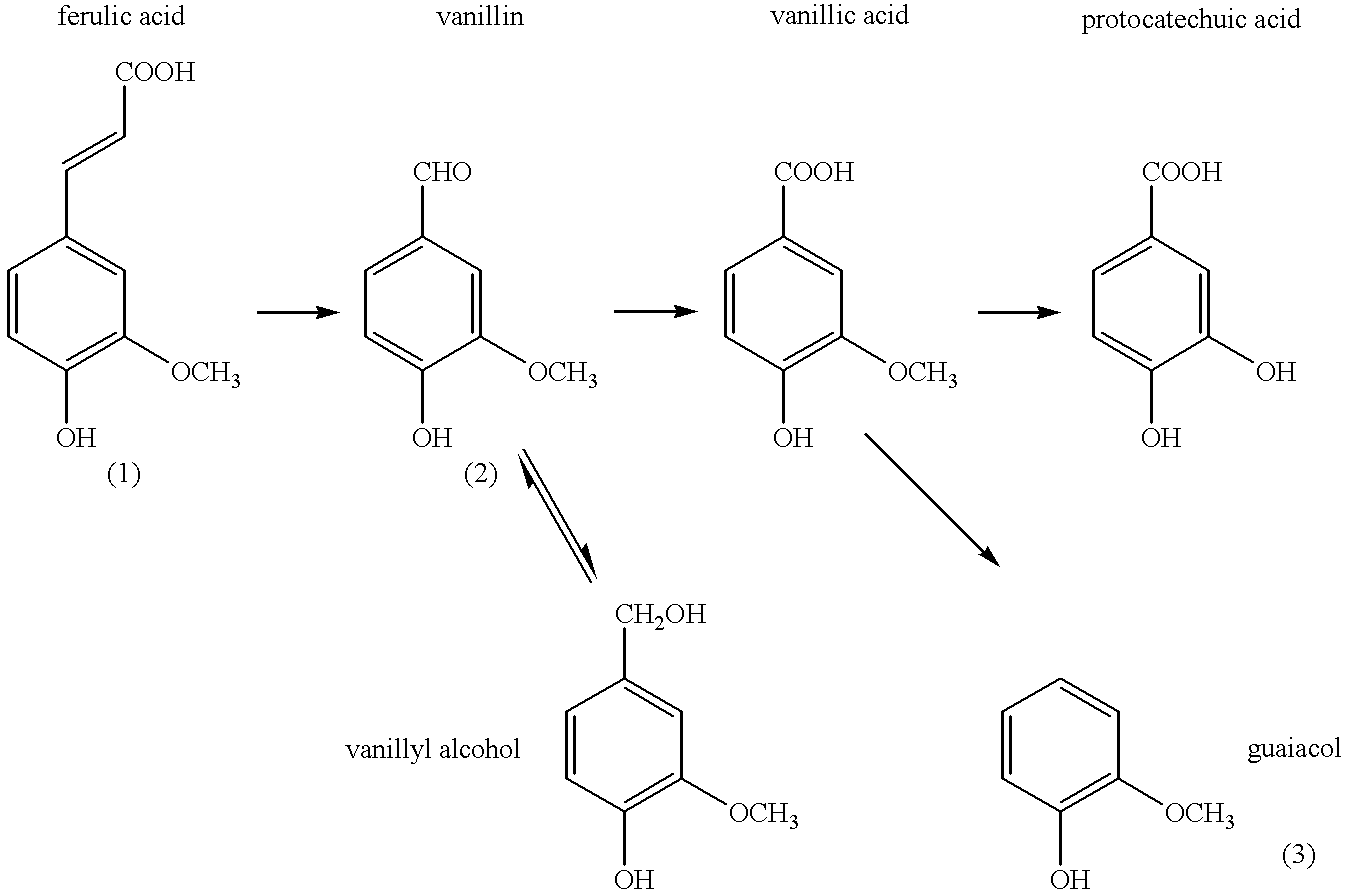
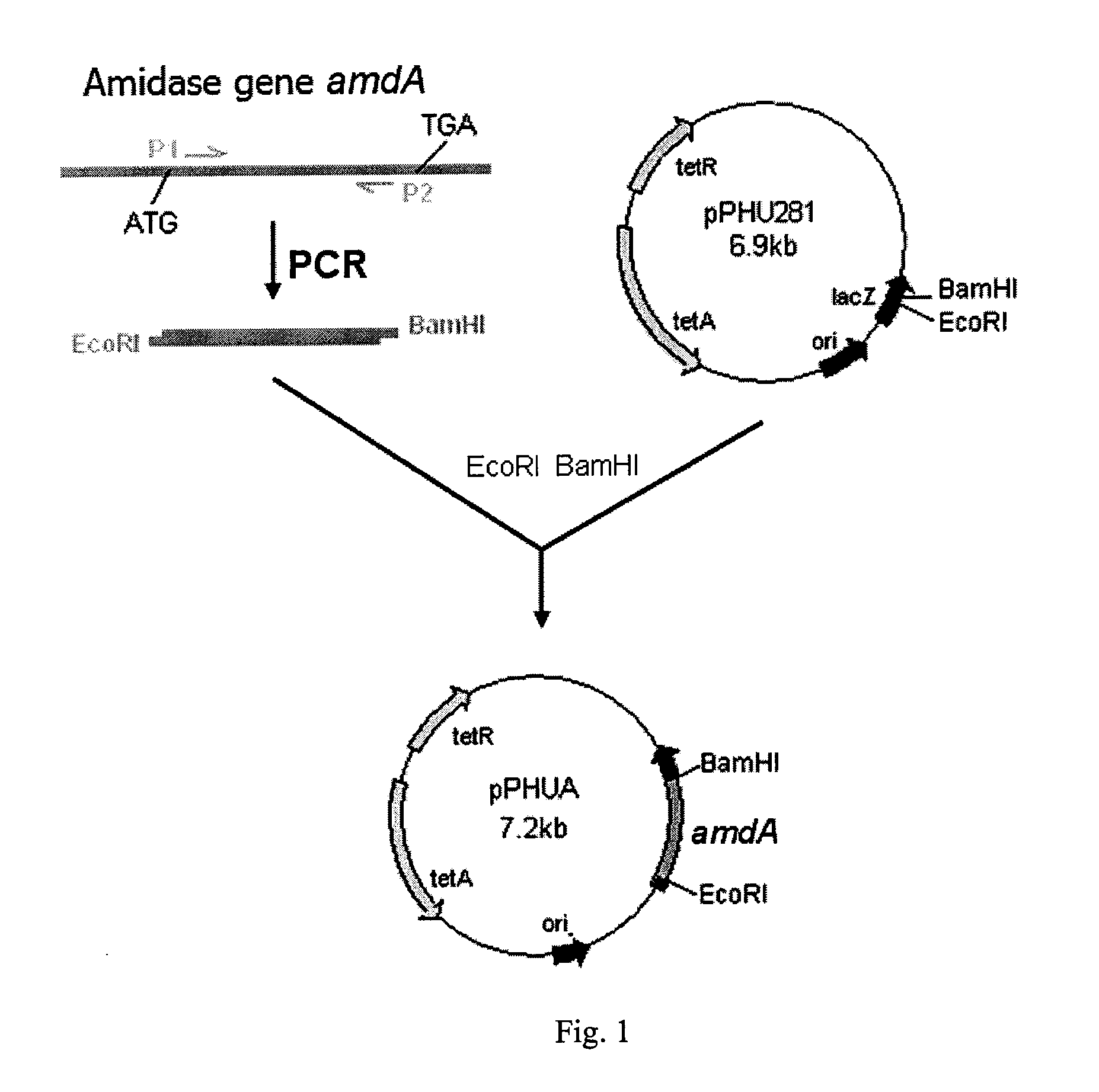
Microbiological process for producing vanillin
InactiveUS6235507B1High-yieldMicroorganism based processesEssential-oils/perfumesMicroorganismGuaiacol
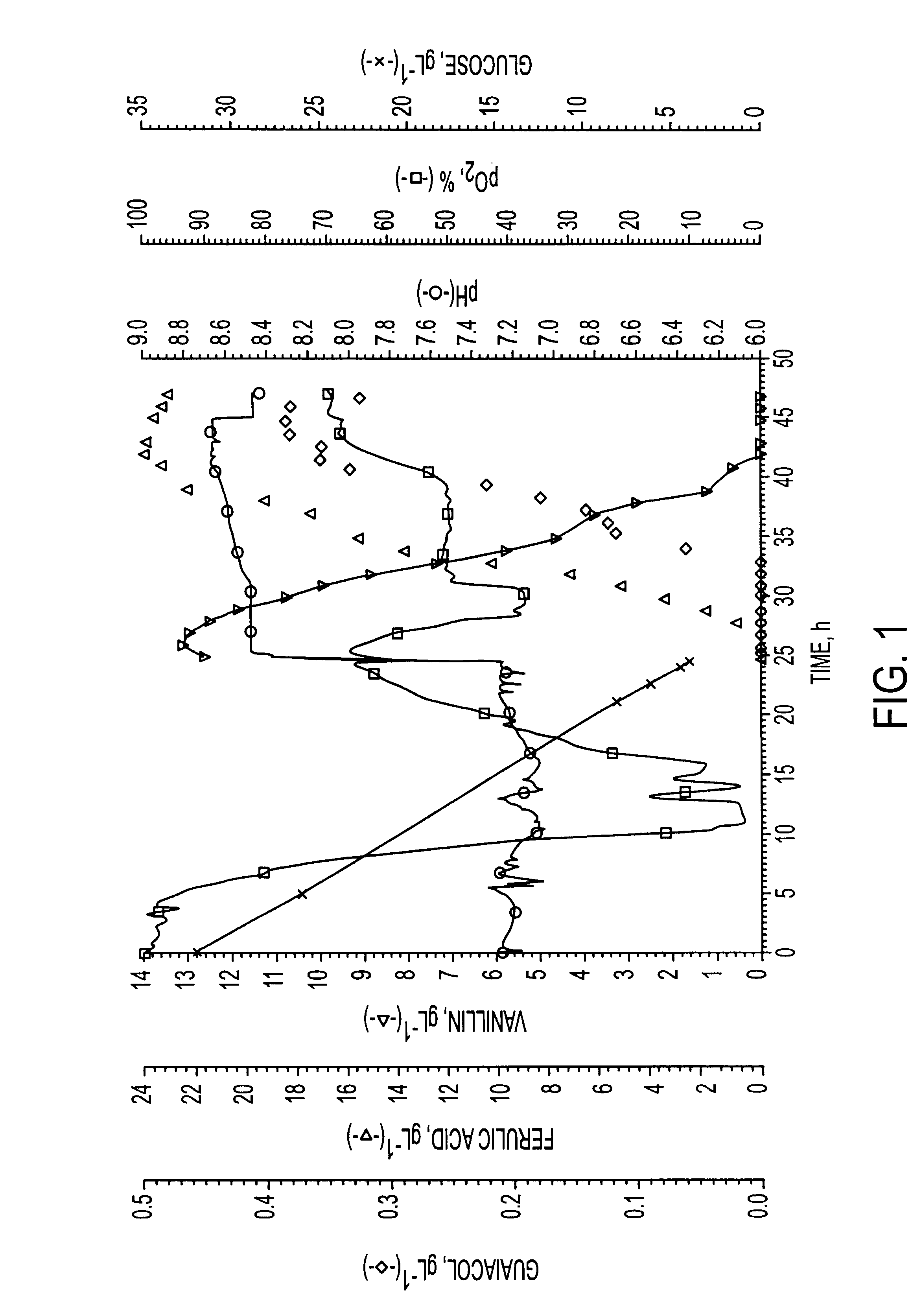
A microbiological process for producing vanillin and other useful products from ferulic acid is disclosed. Vanillin and guaiacol are recovered from the process using a differential pH extraction where the guaiacol is recovered at a pH of greater than 9 and the vanillin is recovered at a pH of from about 5 to about 8.
Owner:GIVAUDAN SA
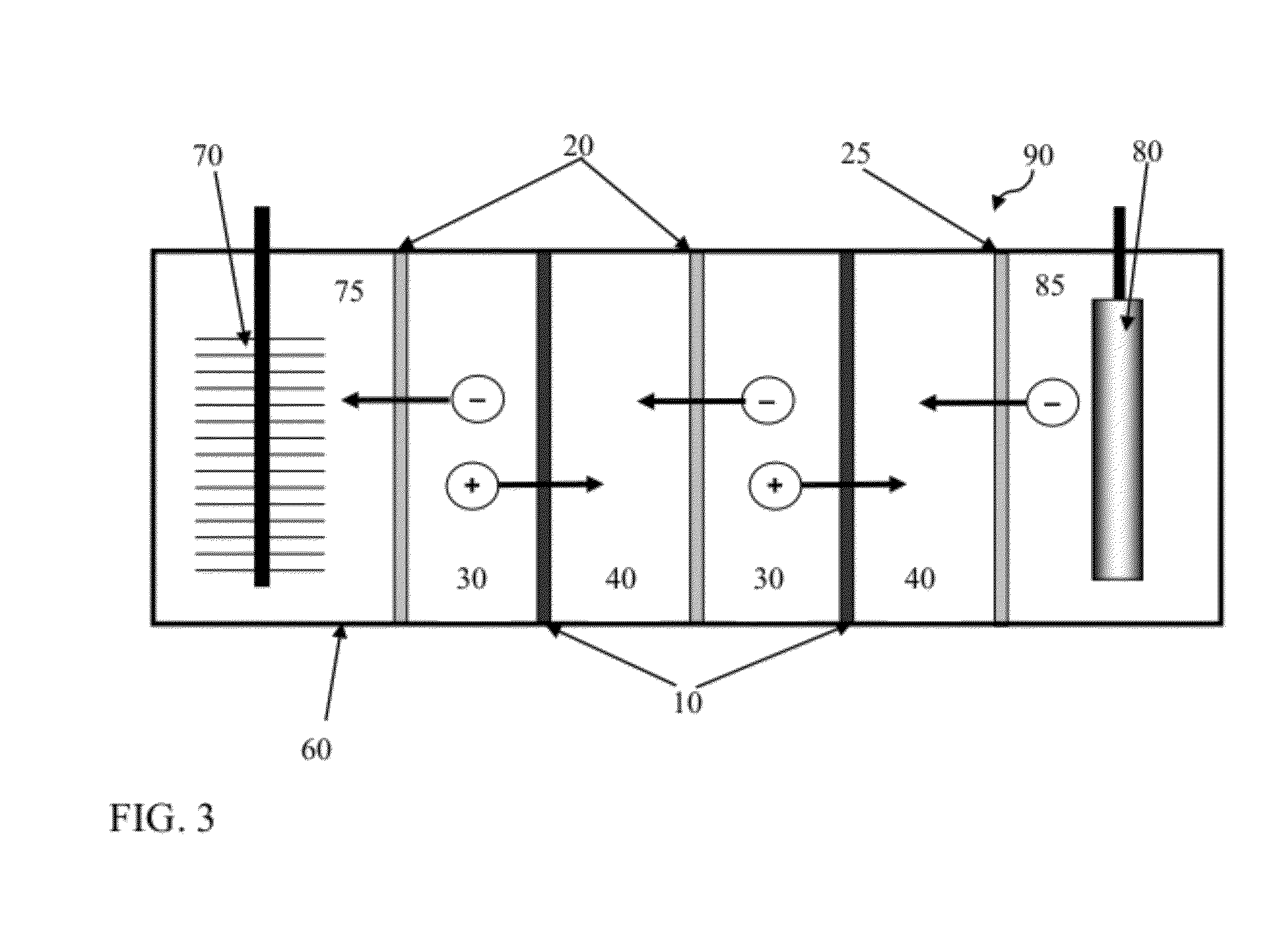
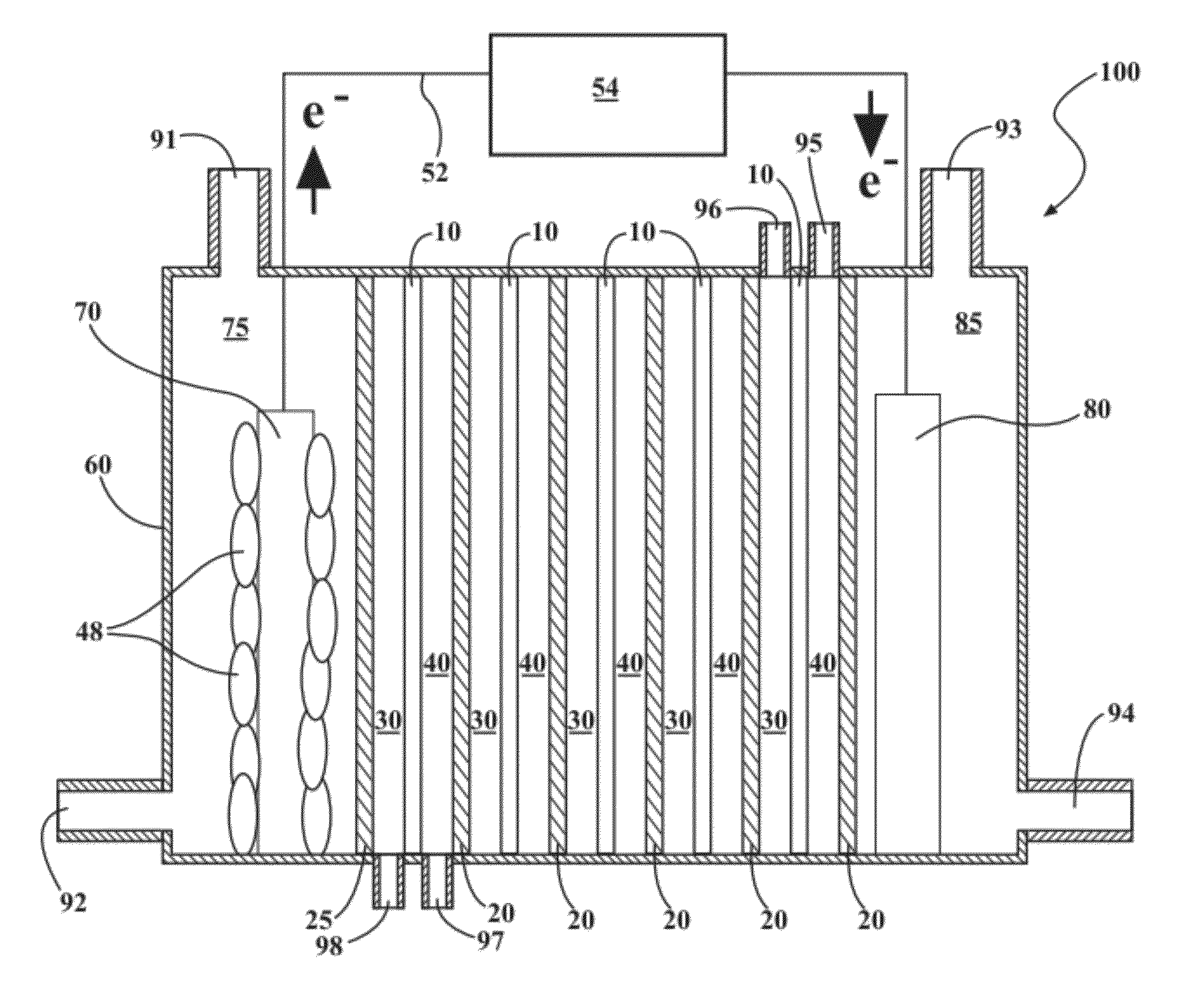
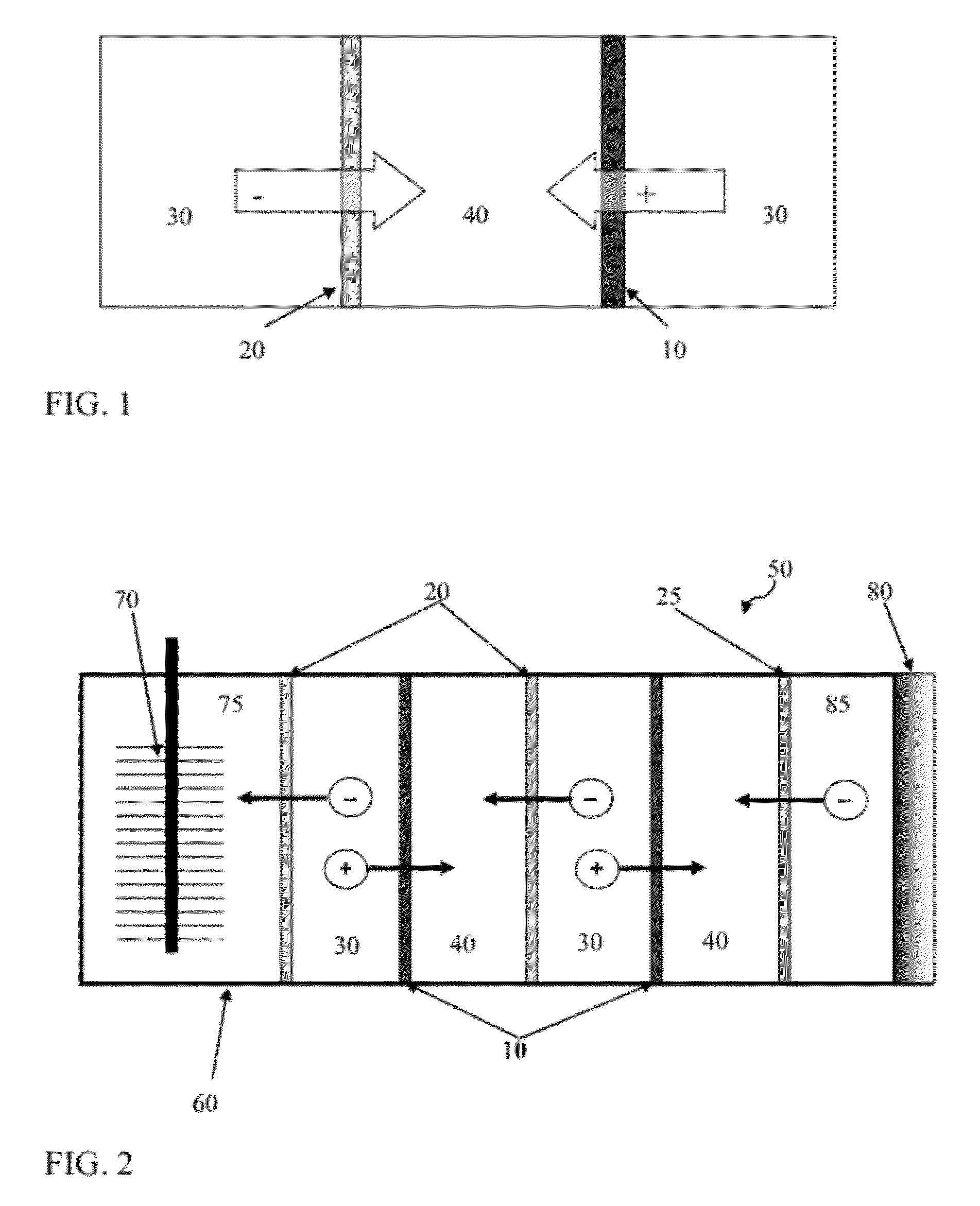
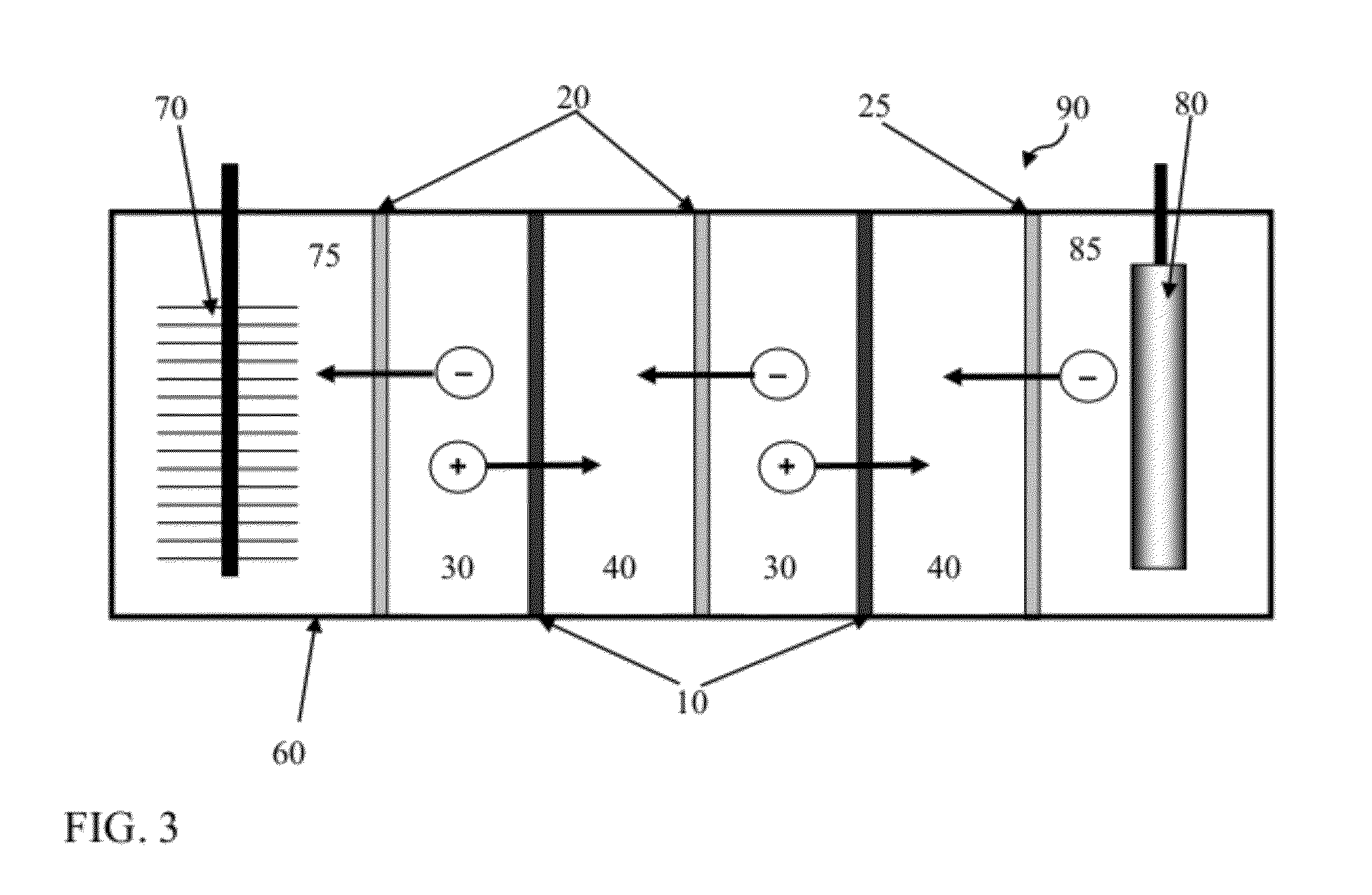
Reverse electrodialysis supported microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells
ActiveUS20120292187A1Raise the potentialSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrobiological ProcessesElectron
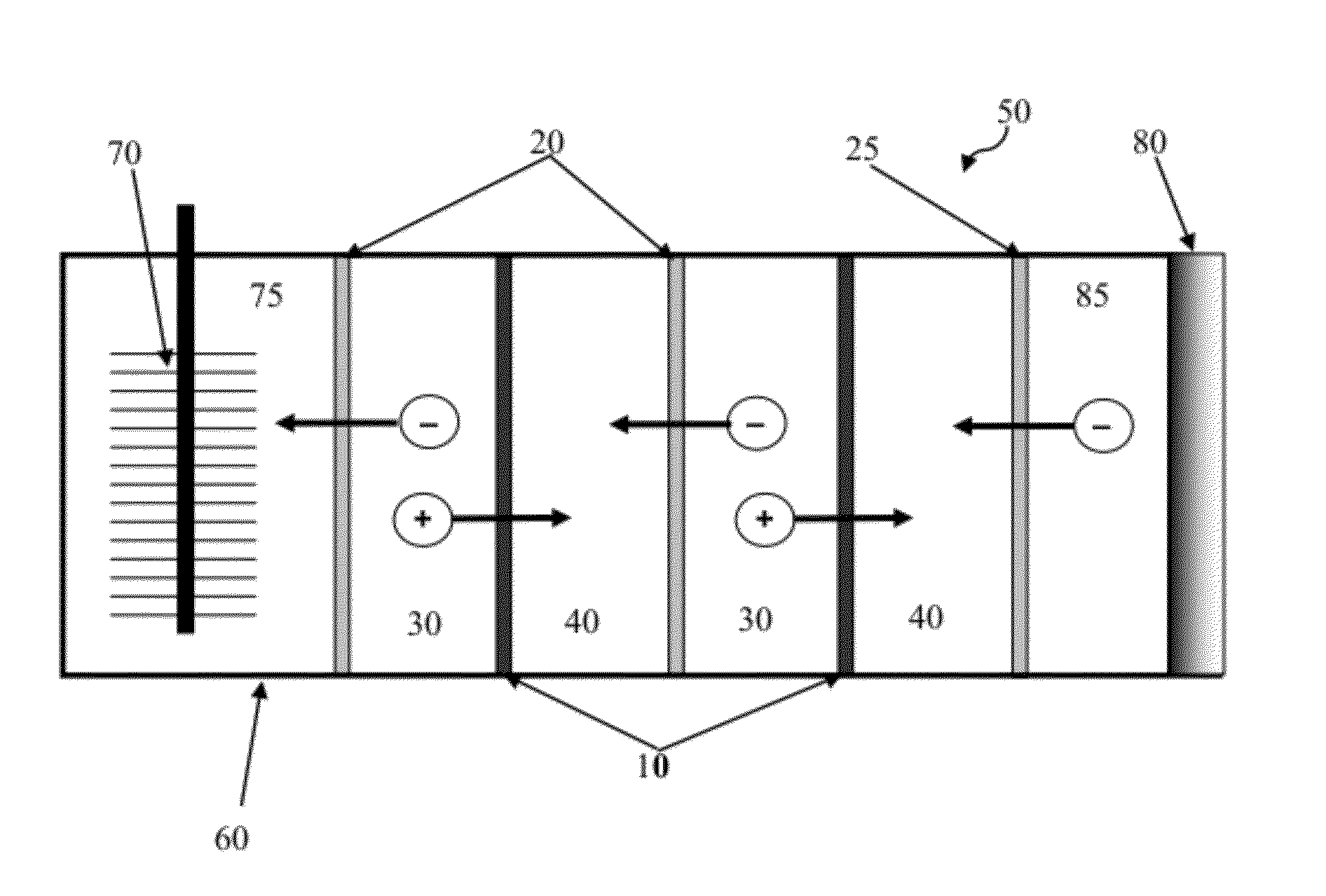
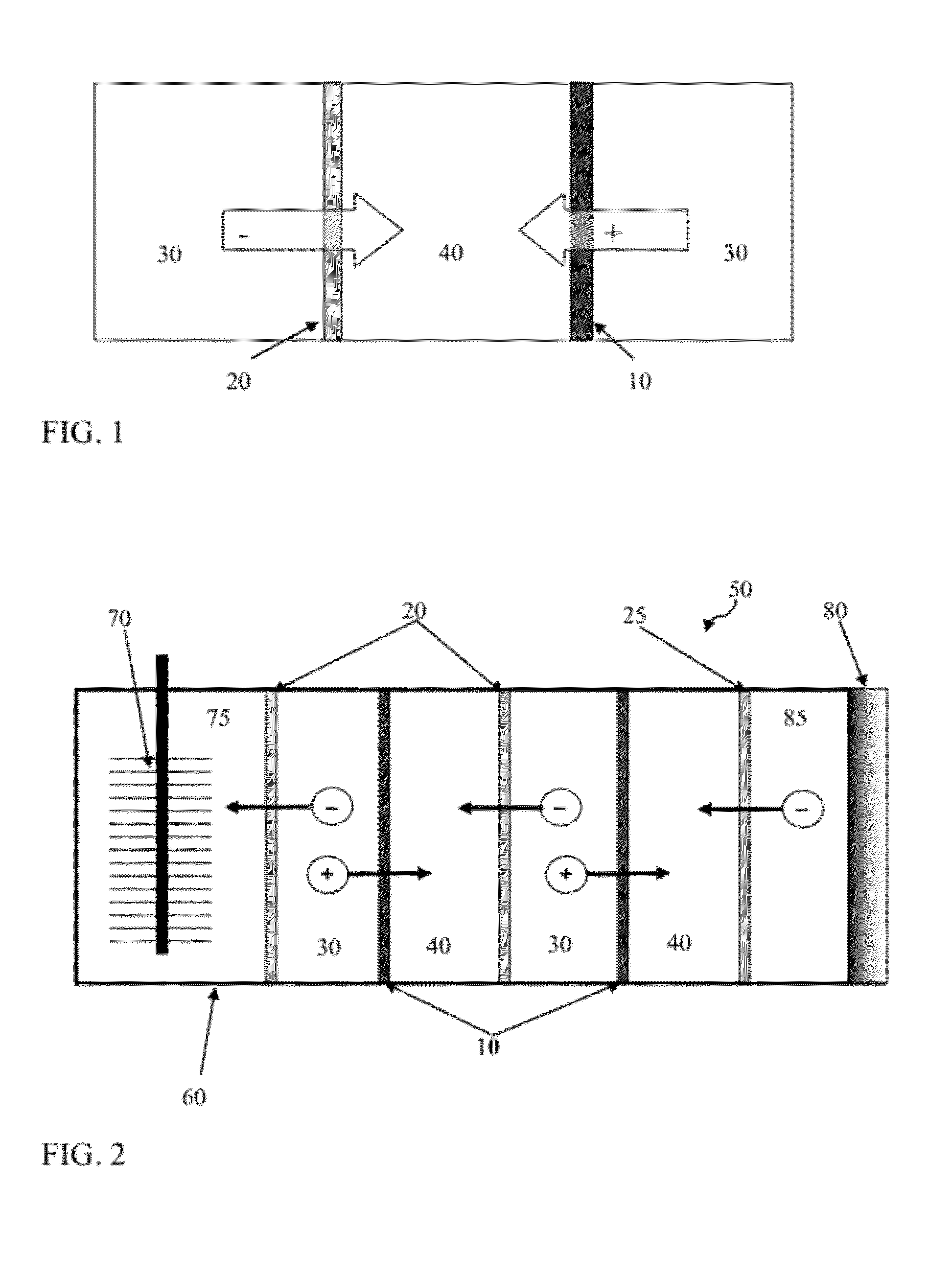
Systems and methods for microbial processes of generating products such as electrical power, hydrogen gas and methane, are provided according to aspects of the present invention which include a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reaction chamber and an exterior of the reaction chamber; an anode at least partially contained within an anode compartment of the reaction chamber; a plurality of exoelectrogenic microorganisms disposed in the anode compartment; a cathode at least partially contained within a cathode compartment of the reaction chamber; a conductive conduit for electrons in electrical communication with the anode and the cathode; and a reverse electrodialysis stack comprising a plurality of plurality of alternating anion selective barriers and cation selective barriers disposed between the anode and the cathode defining one or more saline material compartments and one or more lower-saline material compartments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium with amidase gene koucked-out, the construction and the use thereof
ActiveUS20110104690A1Inhibit expressionNot affect performance of strainBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesLarge fragment
An engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium and its construction method as well as its applications, wherein the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium is a mutant strain of an original nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium strain obtained by knocking-out or inhibiting the amidase gene in the original strain. The construction method of the engineered bacterium is to block the expression of the amidase gene by inserting the large fragment of a recombinant suicide plasmid carrying an amidase gene fragment into a wild-type strain through the homologous recombination between the recombinant suicide plasmid and the amidase gene of the wild-type strain. Compared to the corresponding wild-type bacterium strain, both the cell growth and the nitrile hydratase expression of the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium according to the invention are increased. In the process of catalyzing the hydration of acrylonitrile to produce acrylamide, the yield of the product, acrylamide, is significantly increased, while the yield of the by-product acrylic acid is significantly decreased. The engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium of the present invention has wide application prospect in the production of acrylamide by microbiological process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
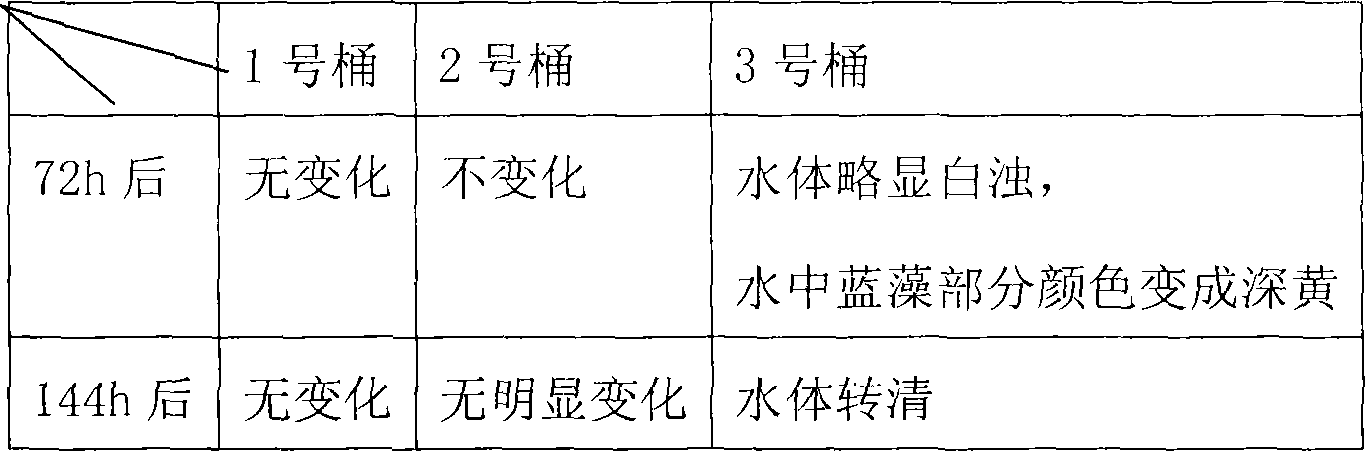
Method for treating water eutrophication and blue algae bloom through glucose enhancement microbiological process
The invention relates to a governance of water body eutrophication and blue algae breakout, belonging to environmental protection field. The invention provides the technical proposal that the application of a sugar reinforced microorganism method governs the water body eutrophication and blue algae breakout; the glucide is put into a bacterial liquid of microorganism in the eutrophied and polluted water body in weight radio of 1 to 5:1. When the bacterial liquid of microorganism plunged into the water body, putting in the glucide of a certain class and proportion can provide more feasible development condition for the ecdemic bacteria in the water body, help the ecdemic bacteria adapt to the water body environment rapidly, and simultaneously provide carbon source which the bacteria in reproduction needs in order to achieve the goals of great microorganism reproduction.
Owner:KUNMING SHENGHE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECHCO
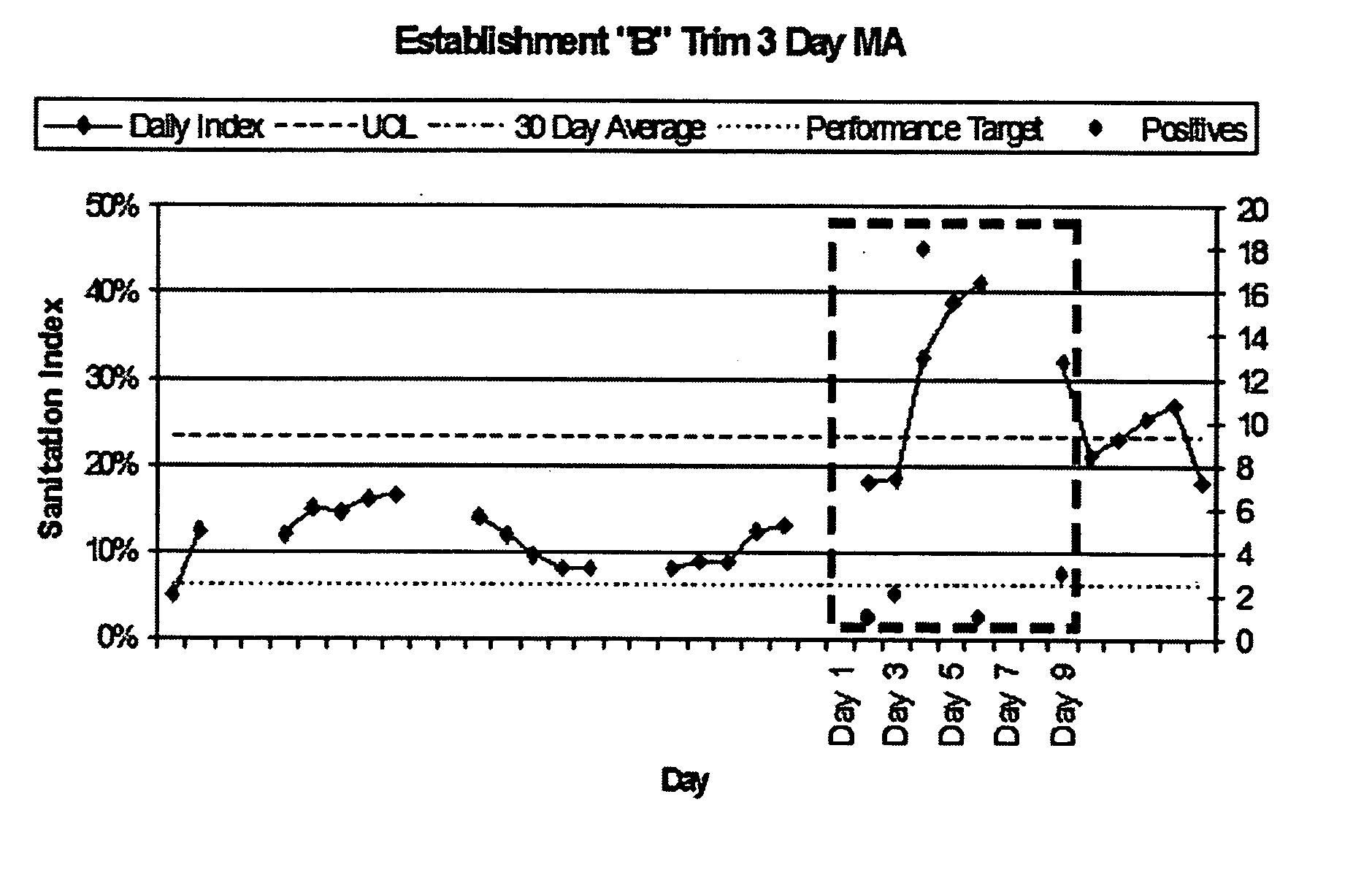
Trend analysis and statistical process control using multitargeted screening assays
ActiveUS20060115824A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiotechnologyMicrobiological Processes
Aspects of the present invention provide novel multi-targeted microbiological screening and monitoring methods having substantial utility for monitoring and control of microbial growth and contaminants, microbiological processes, predictive microbiology, and for exposure and risk assessment. Microbial markers shared by both target and index microbes are used in novel methods for microbial monitoring, monitoring of microbial performance potential, trend analysis, and statistical process control (SPC) in processes or systems that are receptive to a plurality of genetically distinct microbes.
Owner:INST FOR ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Reverse electrodialysis supported microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells
ActiveUS9112217B2Raise the potentialSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrobiological ProcessesElectron
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Microbiological culture for triggering microbiological processes in water
InactiveUS7384777B2Improve cleaning efficiencySuitable for processingBacteriaWater treatment compoundsMicroorganismMicrobiological Processes
A microbiological culture for triggering microbiological processes in bodies of water, soils, sediments, and / or muds contains chemo-lithoautotrophic bacteria that are immobilized. The bacteria are immobilized in a matrix having the form of capsules, gels, or gel spheres. The matrix material is selected from a wide range of natural and synthetic polymers.
Owner:SOLL HLDG
Dewatering method for sludge microbiologically treating life waste water
InactiveCN1781853AReduce moisture contentReduce shipping costsSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationChlorideSewage
The present invention belongs to the field of environment protection technology, and is especially process of dewatering sludge from city sewage treating microbiological process. The sludge dewatering process includes the following steps: 1. adding flyash into sludge in the amount of 0.2-0.6 g each liter of sludge, and stirring for 20-120 sec; 2. adding aluminum chloride in the amount of 4-6 wt% of dry sludge, and stirring for 20-120 sec; 3. adding polyacrylamine in the amount of 0.03-0.05 g each liter of sludge, and stirring for 20-90 sec; 4. depositing naturally for 10-600 sec; and 5. vacuum suction filtering or pressure filtering for 2-6 min. The said process can lower the water content of sludge from 99.4-99.8 % to 76.5-79.0 %, and compared with single polyacrylamine process, the present invention has higher sludge dewatering rate and low polyacrylamine consumption.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Sorbent and process for removing fermentation inhibitors
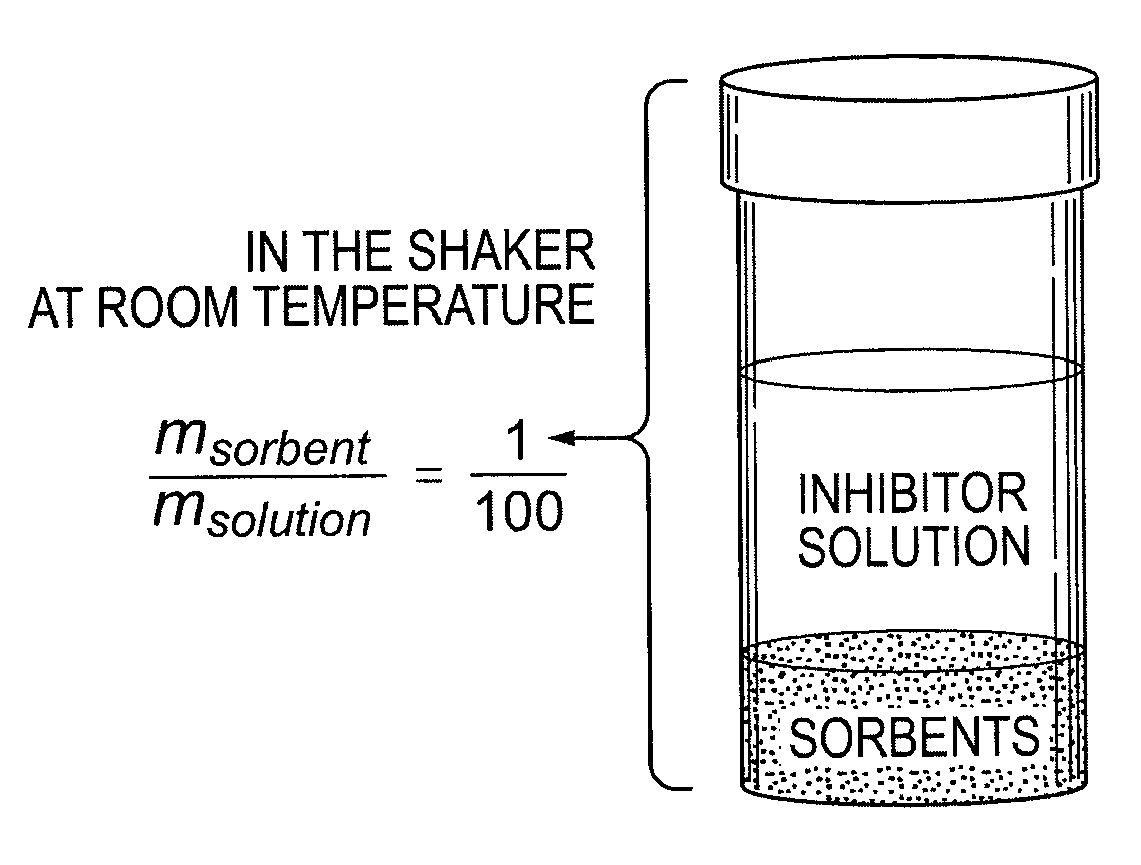
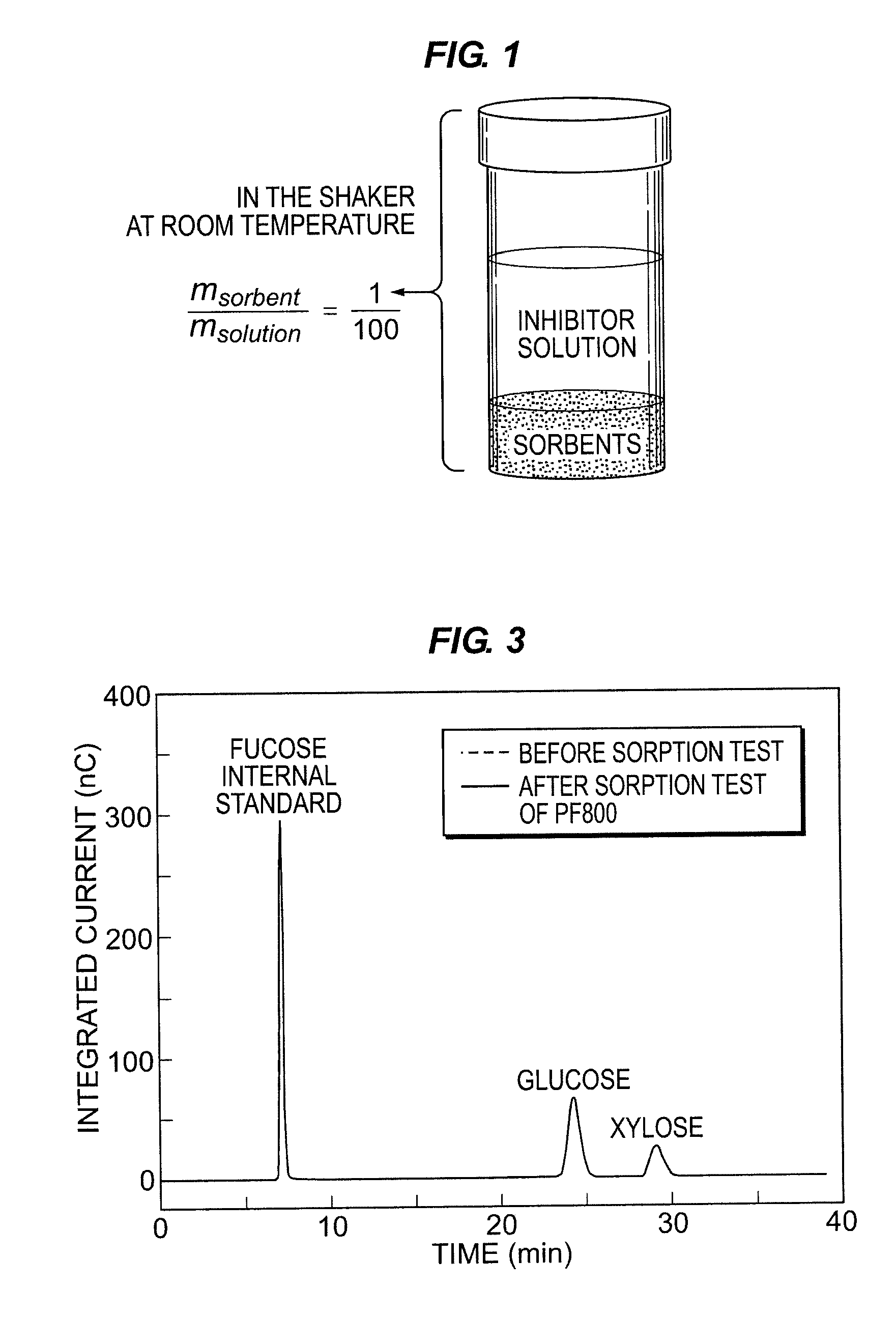
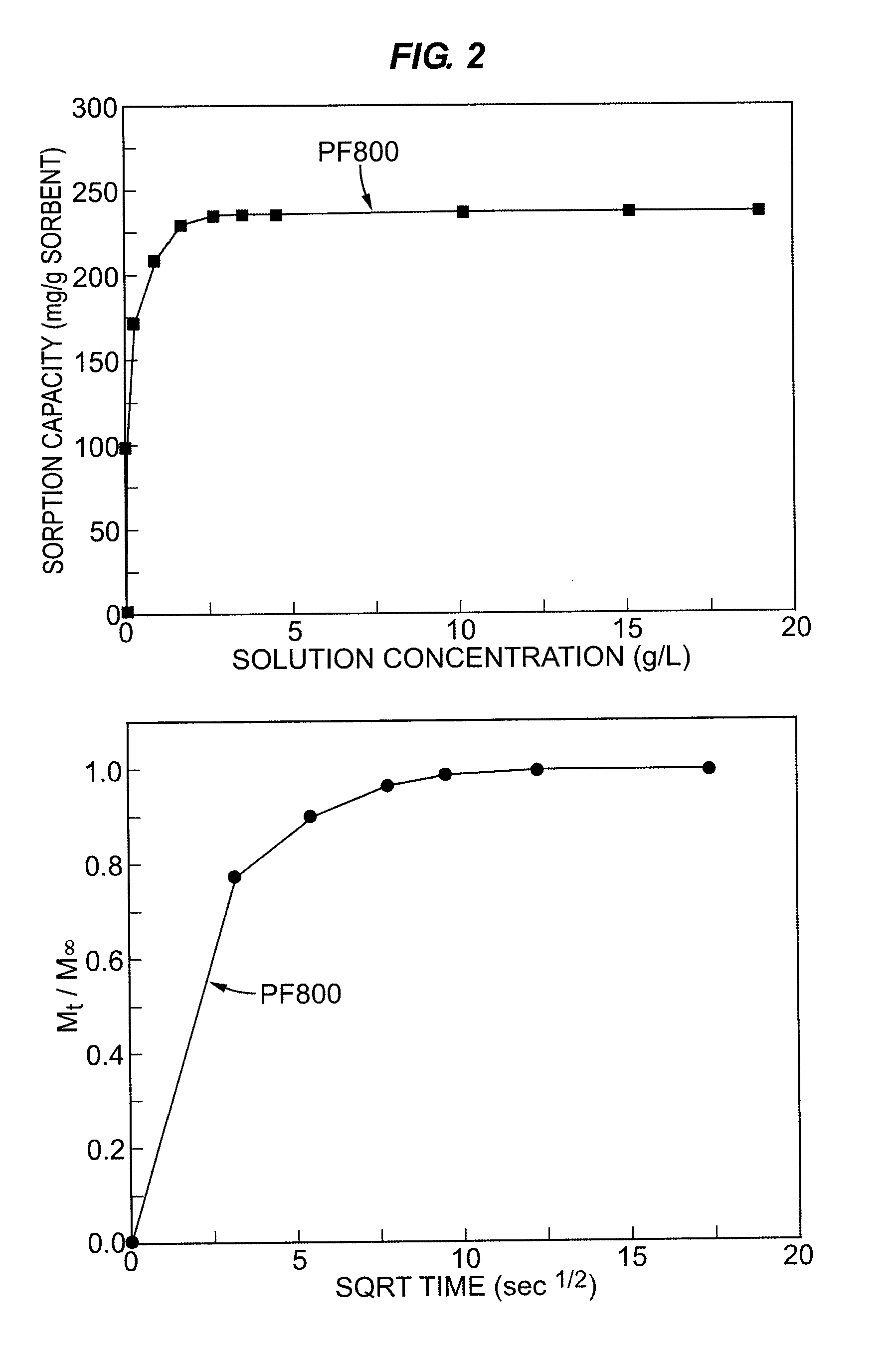
InactiveUS20120135485A1Inhibit microbial growthReducing furfuralPulp liquor regenerationSugar derivativesGramSorbent
The invention pertains to, for example, an improved sorbent and process for removing fermentation inhibitors such as furfural and / or HMF in microbial processes utilizing fermentable sugars obtained from biomass including, for example, in the production of bioalcohols. The sorbent is capable of separating one or more inhibitors from monosaccharides and is characterized by: (1) a Ksugar partition coefficient of less than about 5 and (2) one or more of the following characteristics: (a) a furfural sorption capacity of at least about 200 mg / g sorbent at a furfural solution concentration of 2.5 grams per liter of water; (b) an Mt / M∞ of at least about 0.9 at 7.5 sec1 / 2; and (c) a Kfurfural partition coefficient of greater than about 3000.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Device and method for automating microbiology processes
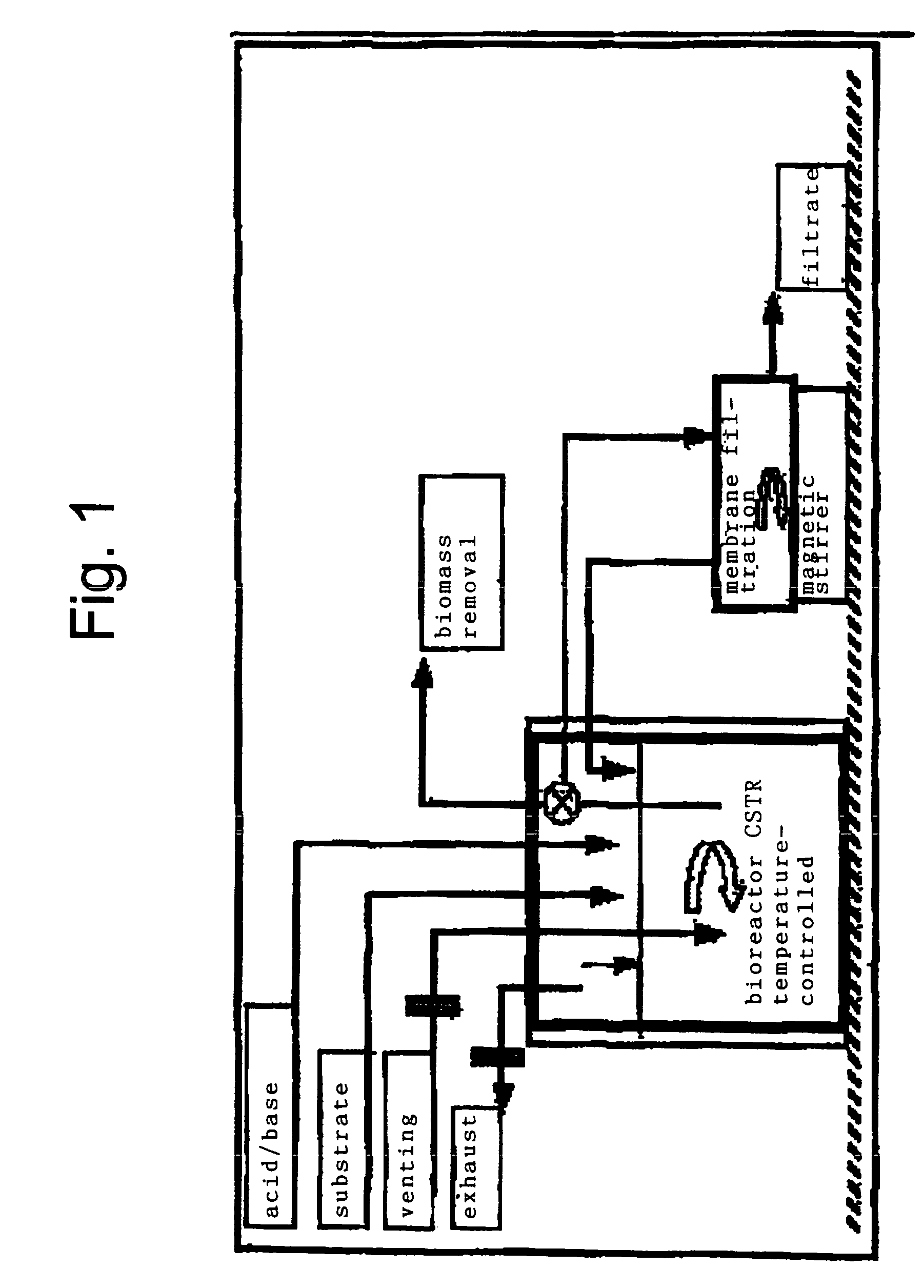
InactiveUS20090181449A1Reduce turnaround timeShorten the lengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActuatorMicrobiological Processes
A device and method for automating the handling and testing of microbiological specimens are provided. A portable specimen collection vehicle (SCV) is provided which comprises a protective housing, a specimen chamber for receiving a biospecimen sample, a plurality of culturing chambers each for receiving a portion of the biospecimen sample and each containing a different culture medium, a system of fluid ducts connecting the specimen chamber to each of the culturing chambers, and an actuator that facilitates flow of portions of the biospecimen sample from the specimen chamber through the system of fluid ducts and into each of the culturing chambers, wherein biological organisms in the biospecimen begin to grow in one or more of the culturing chambers and cultured portions of the biospecimen sample can be withdrawn selectively from the apparatus. A microbiology automation platform includes a computer system that integrates microbiology laboratory instruments and workflow logic in order to perform organism detection and susceptibilities on specimens contained in an SCV. The platform is intended to automate the work of a medical technologist which is characteristically labor intensive. The work performed by the platform includes accession of the specimen, pre-test processes, detection and susceptibility assays, post-test handling and reporting of results.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
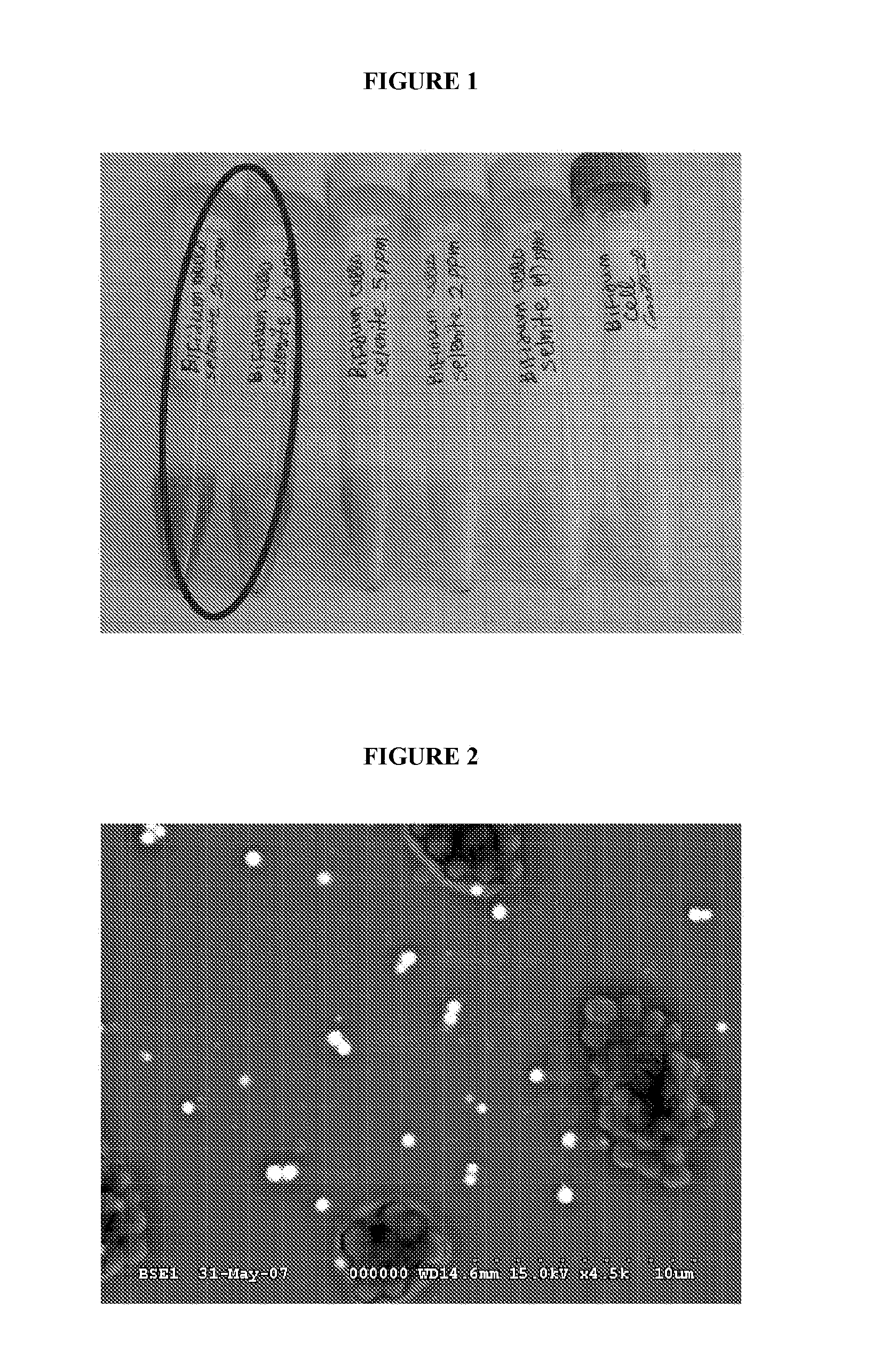
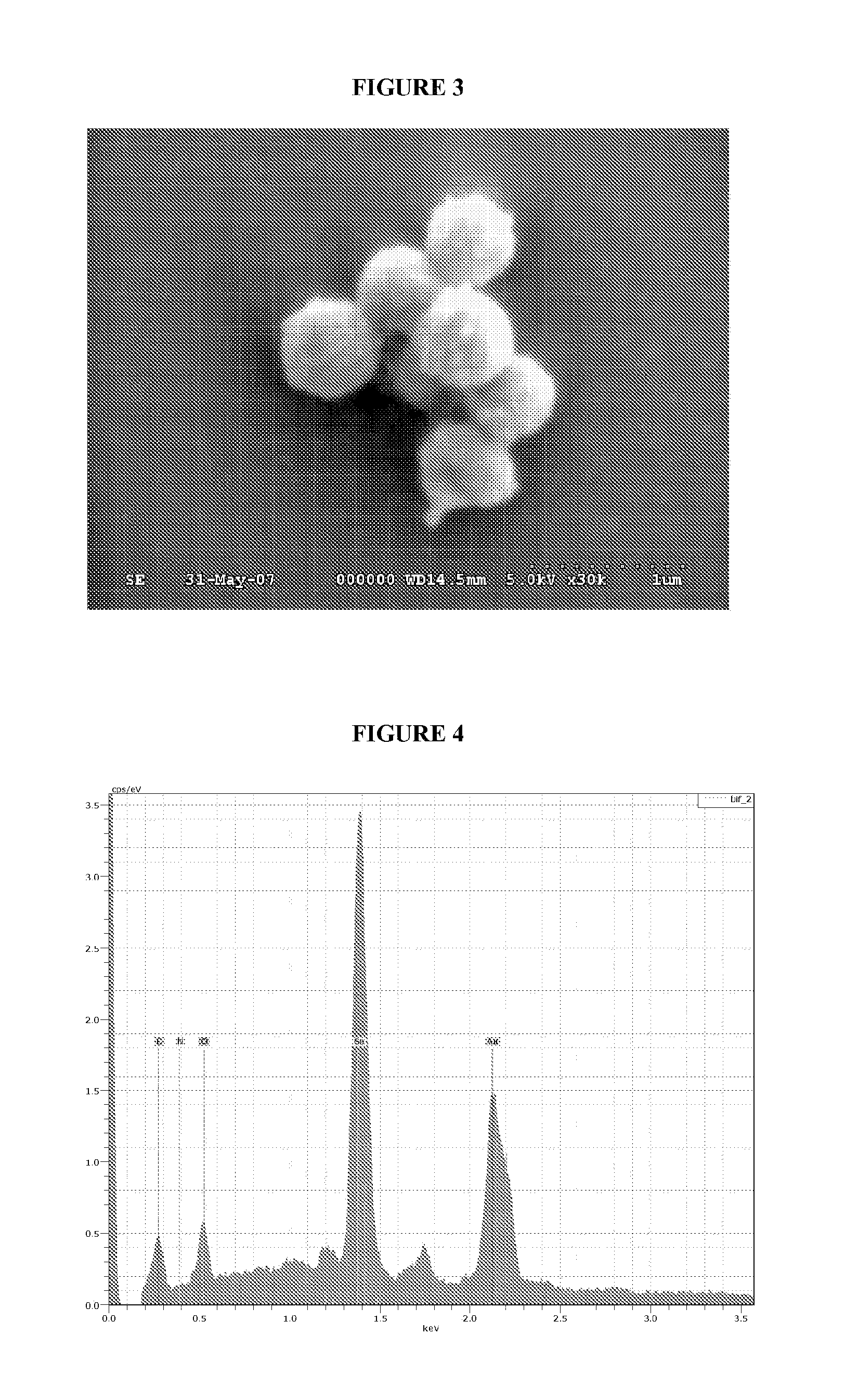
Process for producing elemental selenium nanospheres
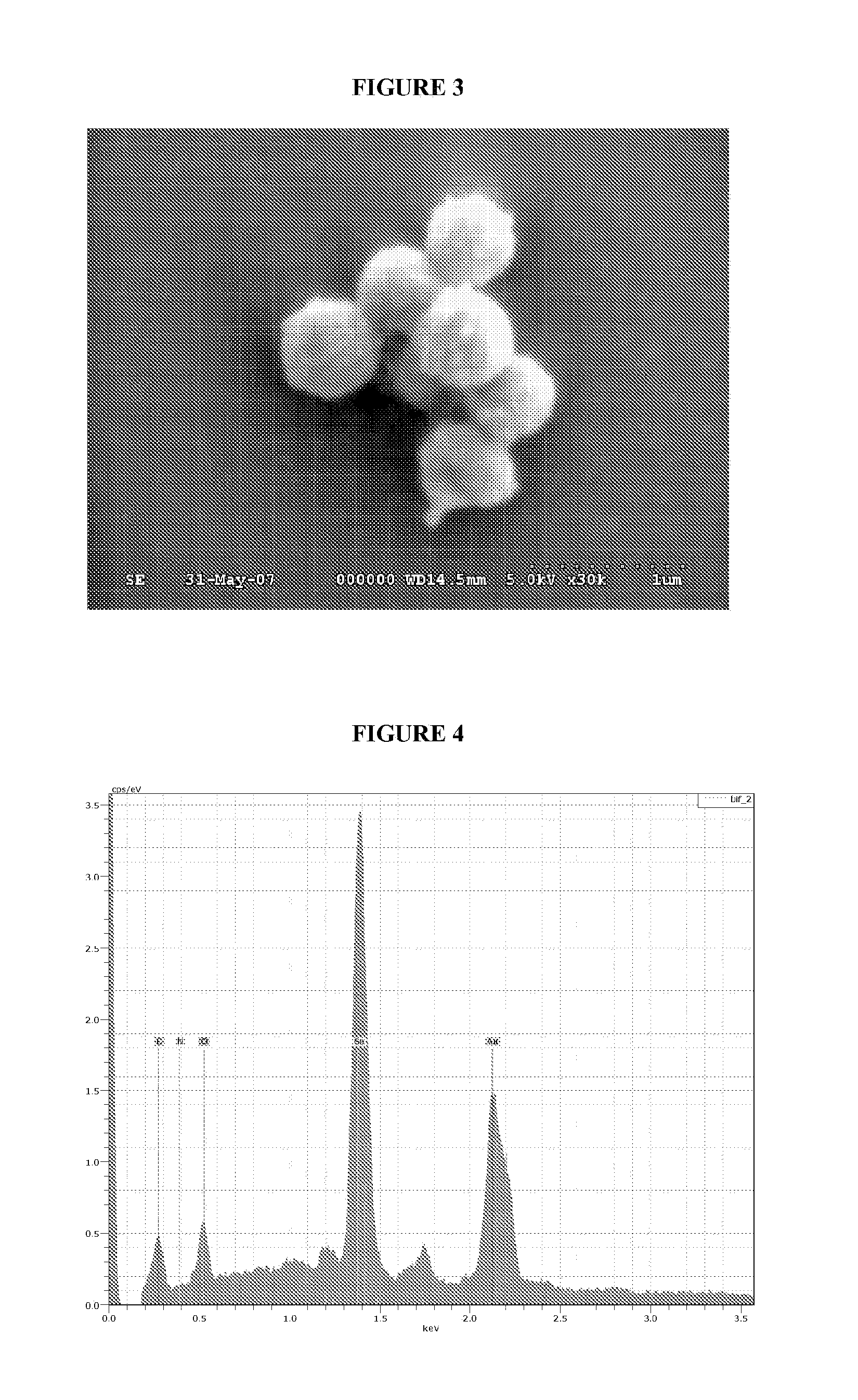
InactiveUS20100189634A1Raw materials are simpleAddress rising pricesBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFood additiveMicrobiological Processes
The invention relates to microbiological processes using non-selenium-respiring bacteria for the production of elemental selenium nanospheres having a size in the 50-500 nm range and compositions comprising said nanospheres. The invention further concerns grey elemental selenium nanospheres directly obtainable by the processes of the invention. The compositions and materials of the invention are useful, in particular, as food additives and for use as raw material in the microelectronic and optical industries.
Owner:DR ALIMENT
Composition for triggering microbiological processes in water and method of producing the same
InactiveCN103097303AWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentMicrobiological ProcessesOxidizing agent
Owner:LAVARIS TECH
Apparatus and Method for Conducting Microbiological Processes
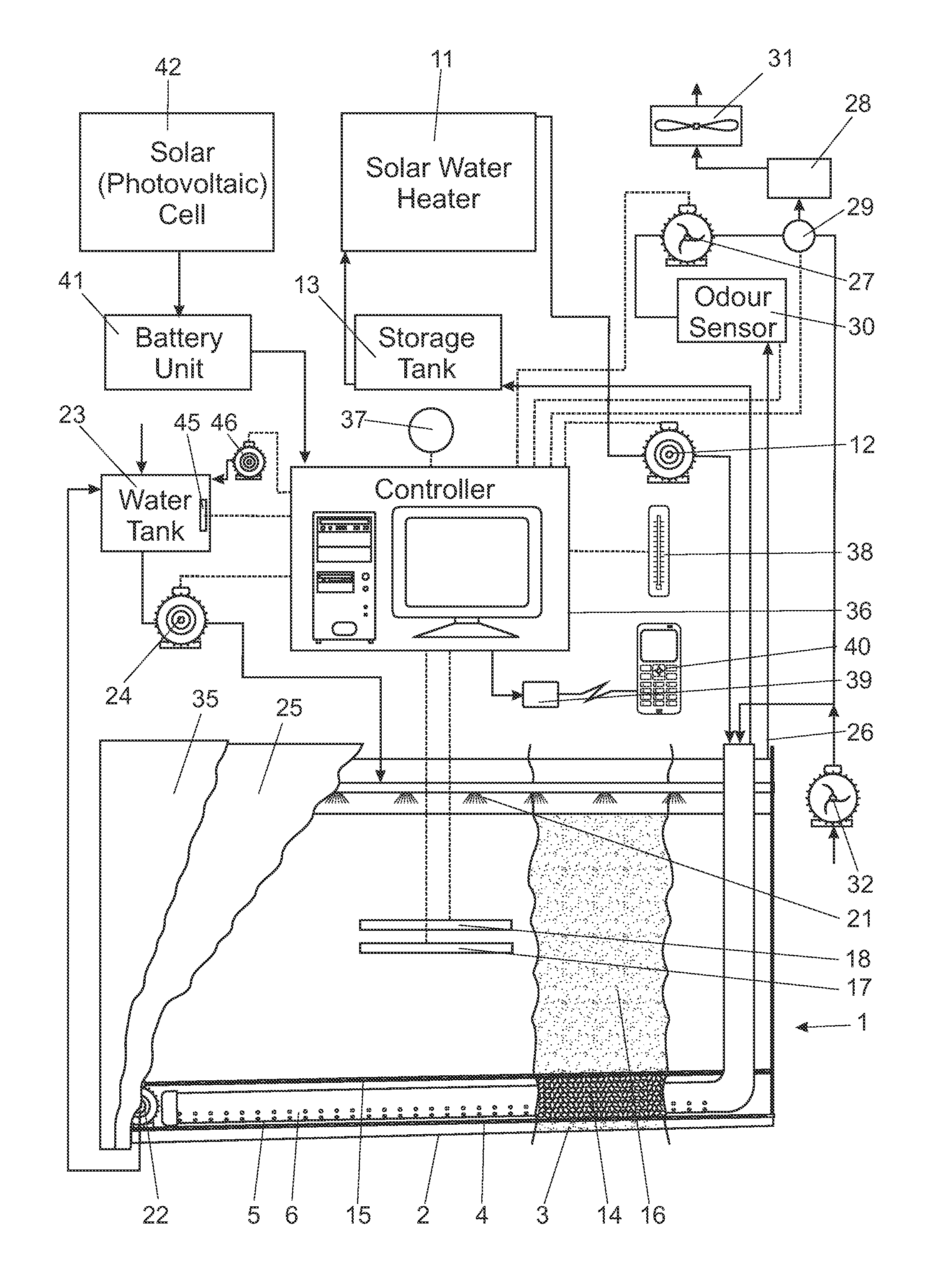
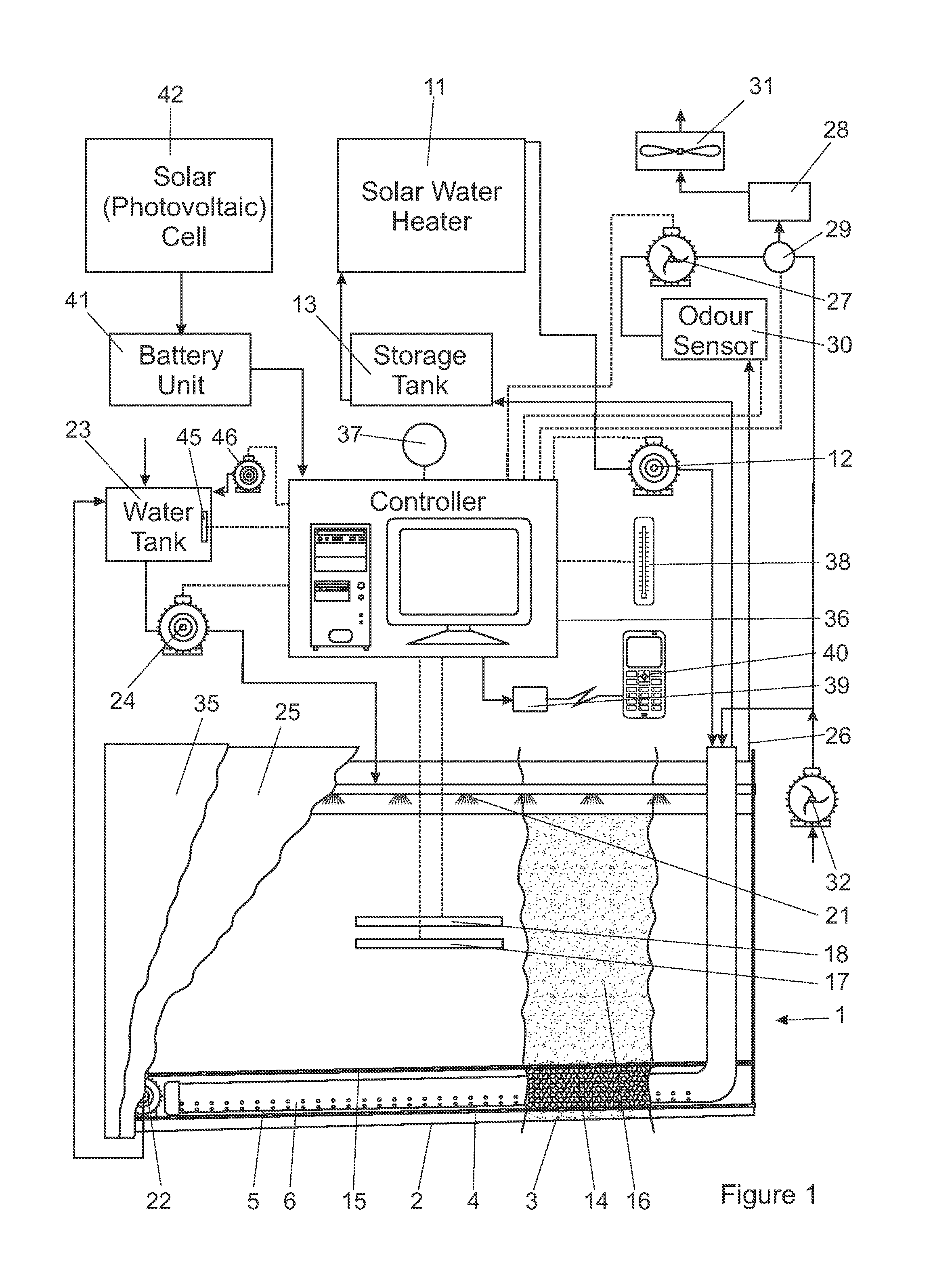
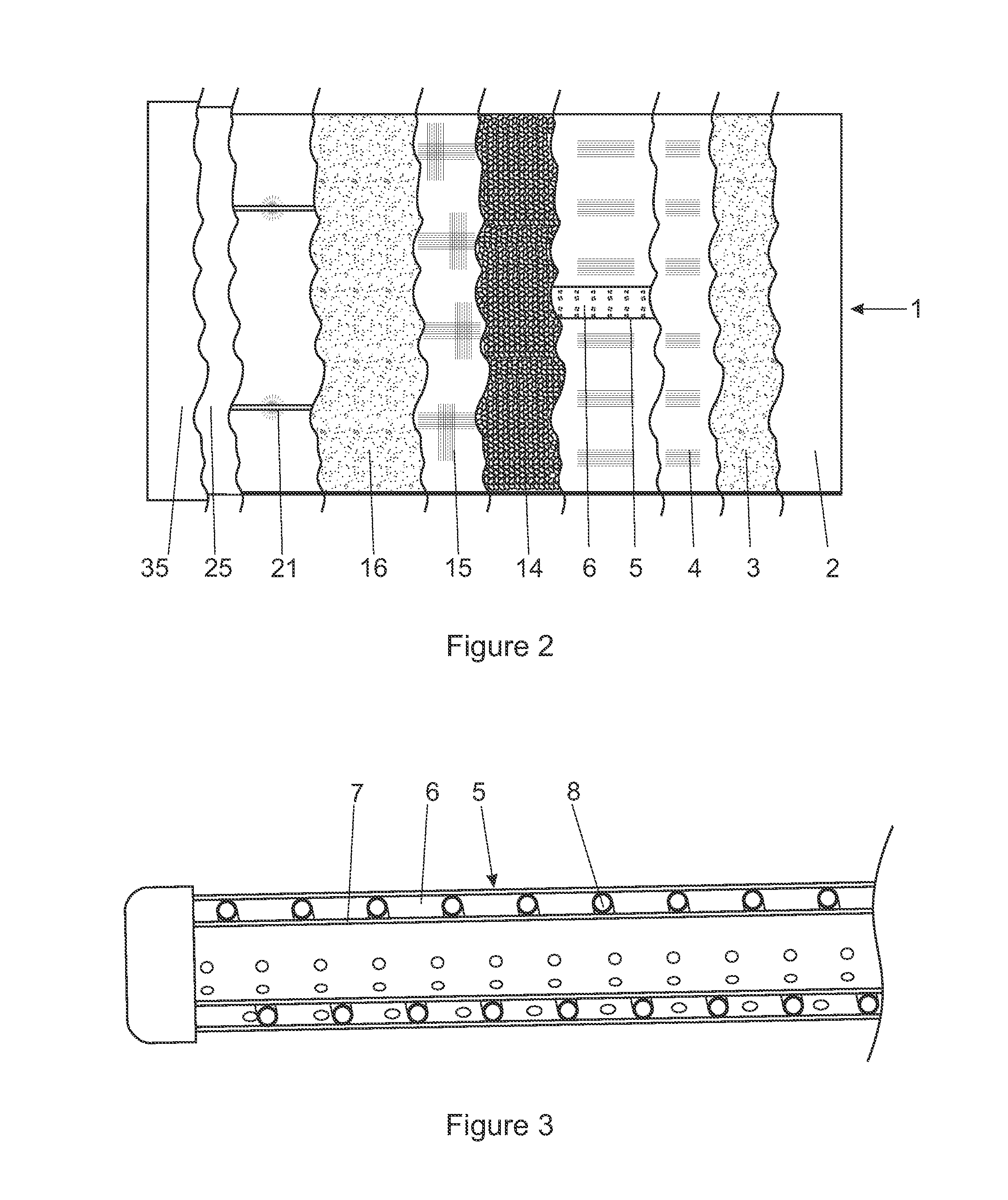
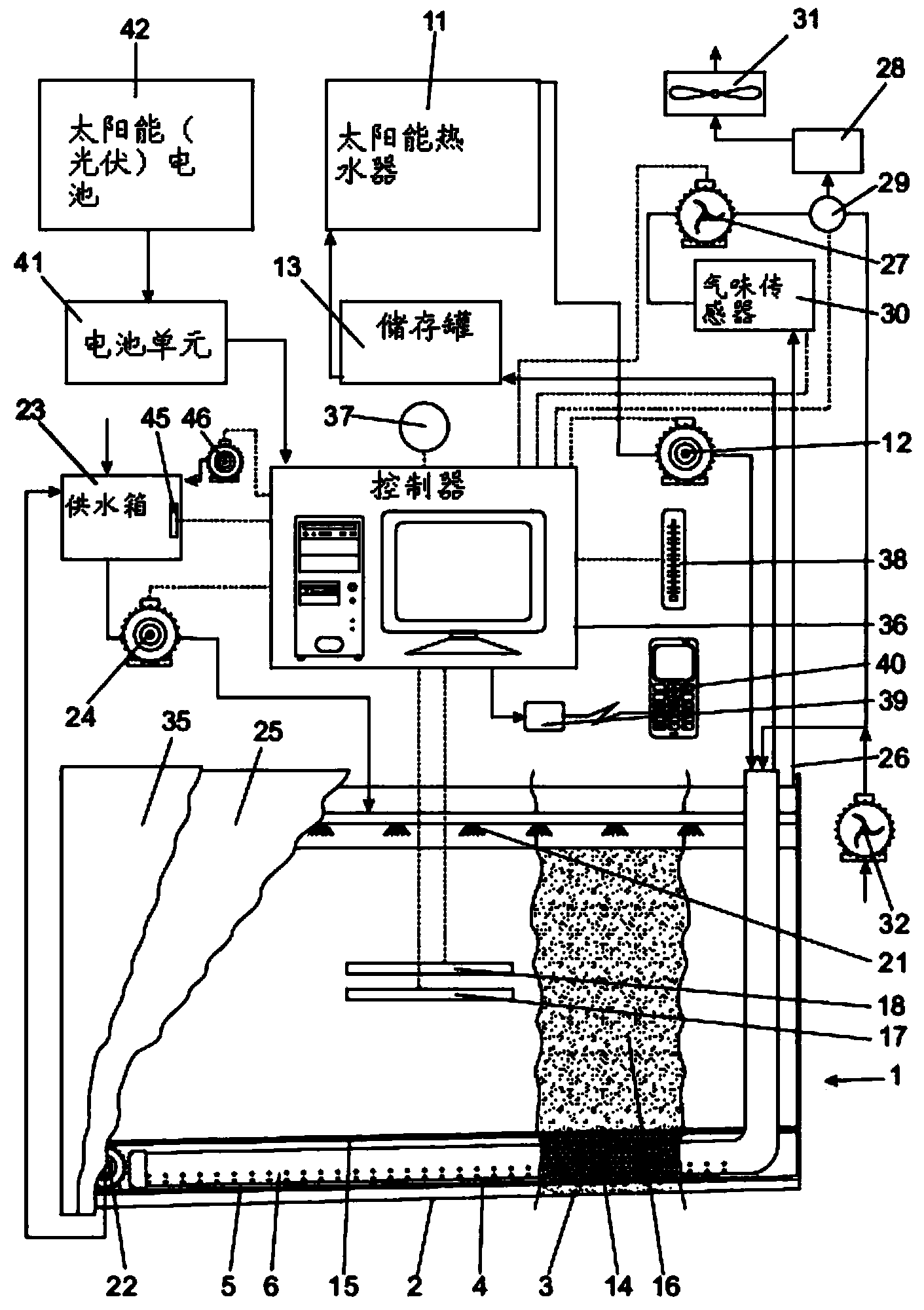
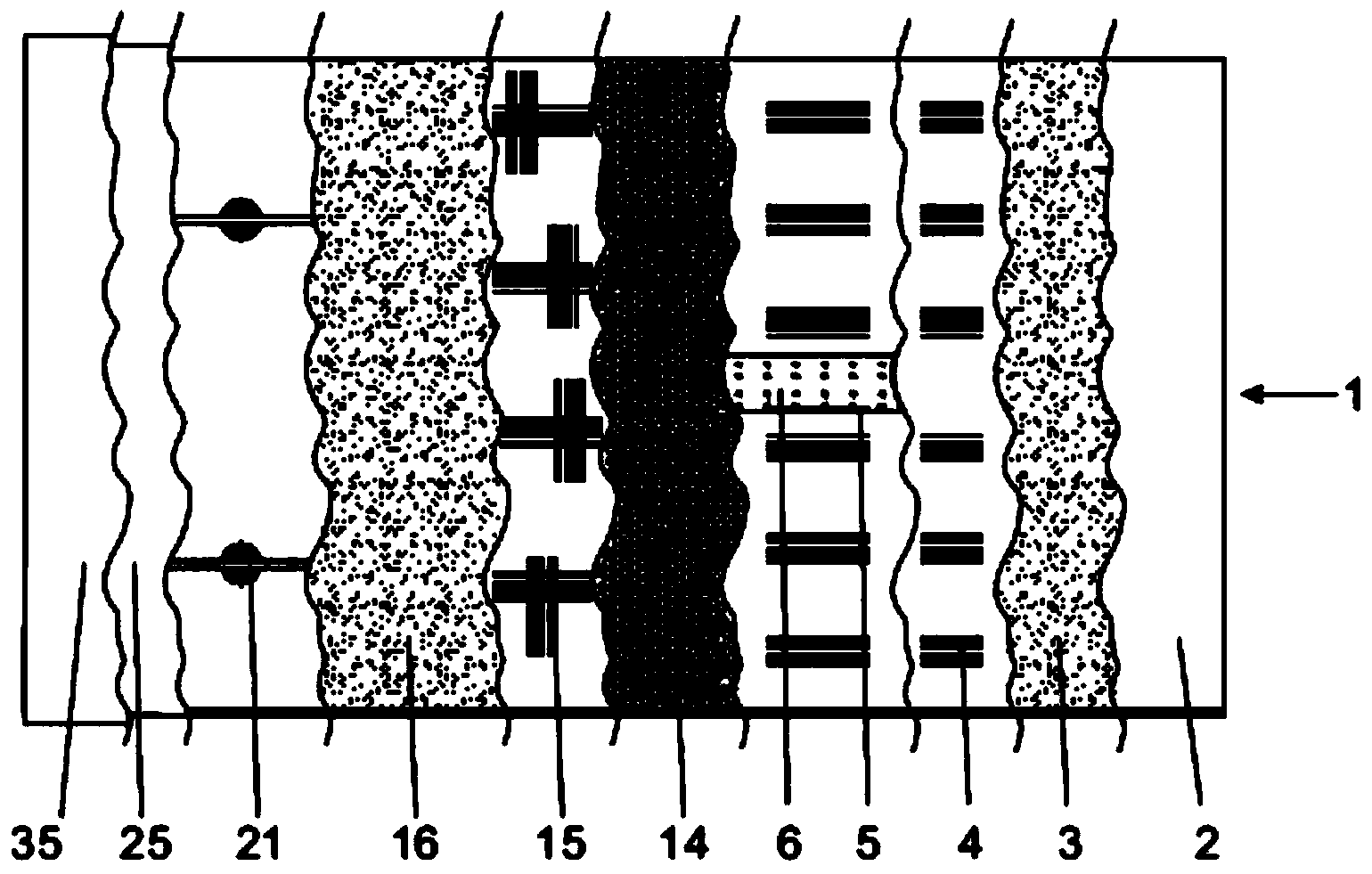
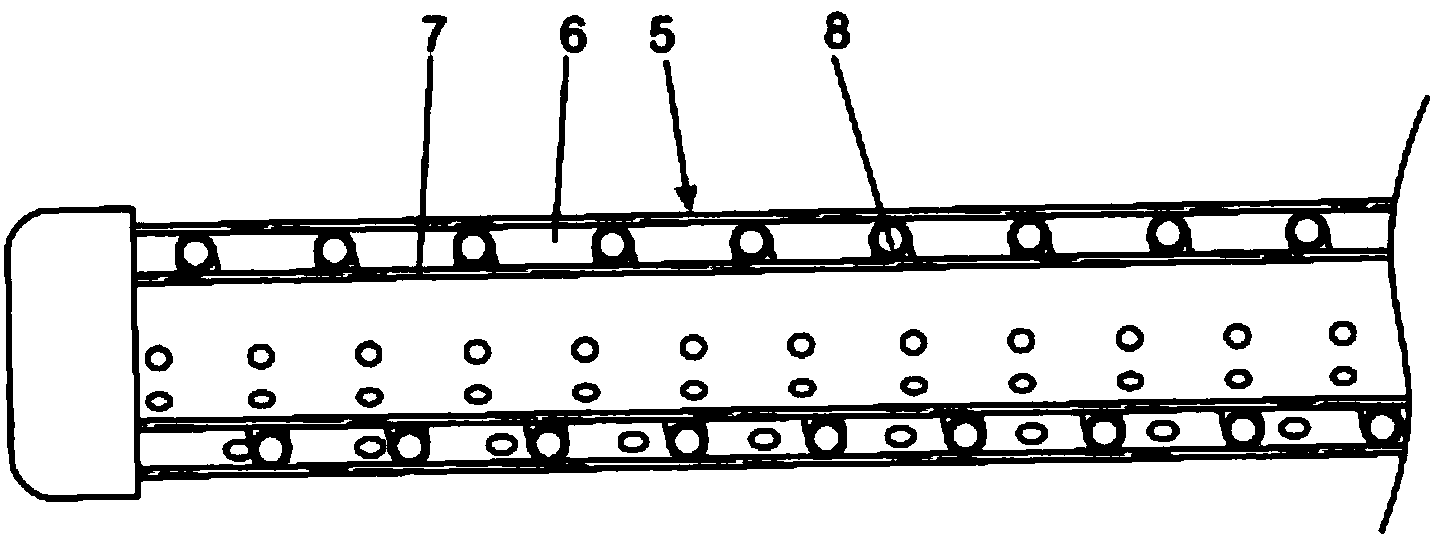
InactiveUS20130309758A1Reduces ecological footprintReduced footprintBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingTemperature controlThermal energy
A method and apparatus are provided for conducting a microbiological process on a bulk material in which a quantity of the bulk material is loaded onto a waterproof lining forming part of a bio cell with a heat transfer arrangement below the quantity of bulk material or within its volume, or both. The moisture content of the bulk material is controlled by periodic or intermittent distribution of water into the bulk material in order to promote microbiological activity within the bulk material by means of microbes that may be either naturally occurring within the bulk material or may be selected and introduced into the bulk material according to a desired result. A leachate recovery installation collects leachate draining from the bulk material. The temperature within the bulk material is monitored and the temperature controlled in order to elevate or decrease the temperature thereof to approach a target temperature associated with enhanced microbial activity of microbes present within the bulk material. The apparatus includes a controller having an electronic micro-processor with the controller having inputs for association with a temperature detector and a moisture detector. The preferred apparatus includes solar powered thermal and electrical energy units.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE FREE STATE
Column reactor for testing and evaluating refractory ores
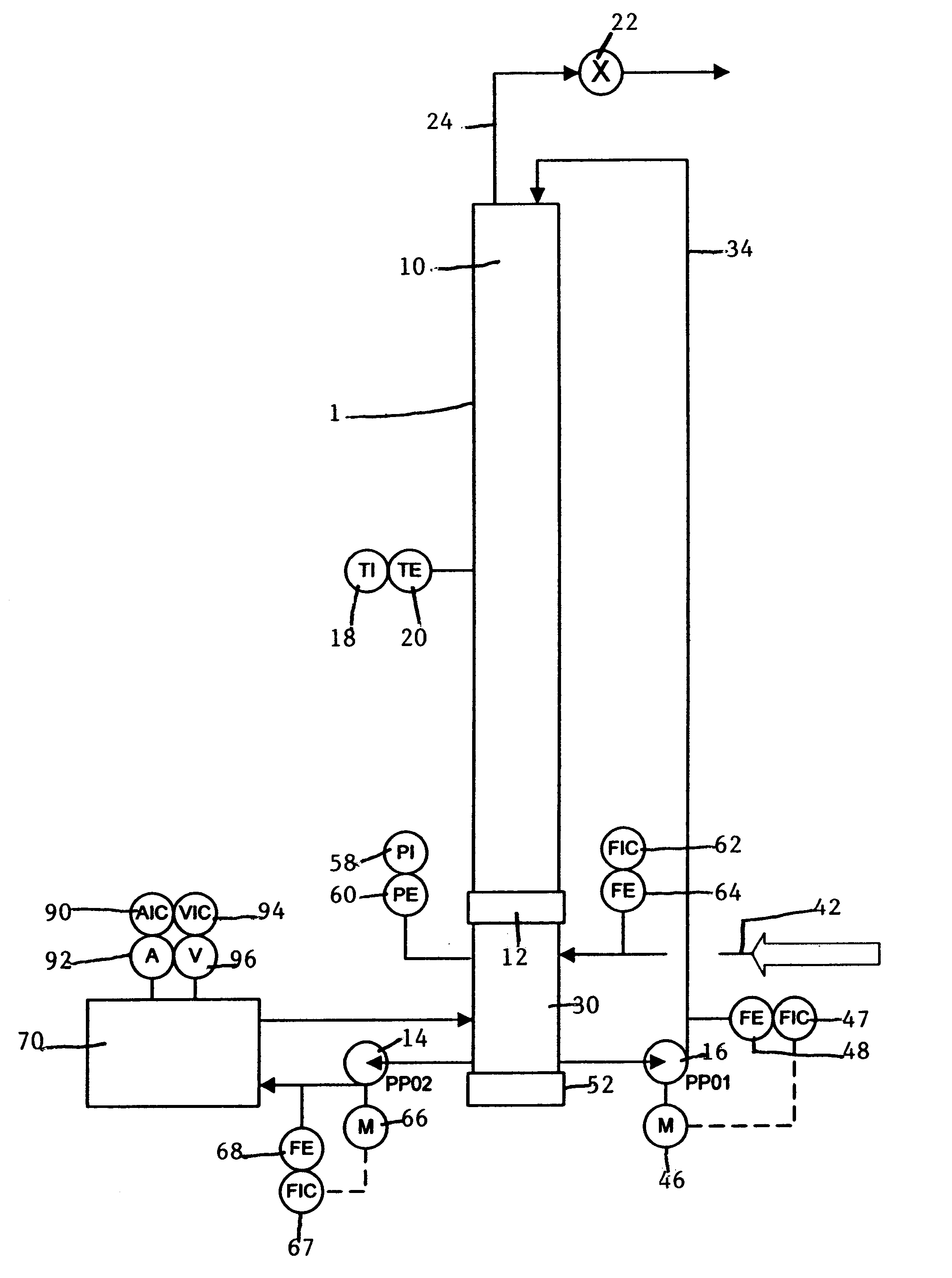
InactiveUS6498031B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVulcanizationBioleaching
The present invention is directed to microbiological processes for the oxidative treatment of refractory gold and base metal ores and concentrates, and particularly, an apparatus for testing refractory gold and sulfidic base metal ores for their suitability to heap biooxidation or bioleaching processes. The invention can be used to simulate heap biooxidation. This apparatus incorporates features of heap biooxidation and may be used to generate engineering data for creating detailed process and engineering designs. The invention can be used to develop a select population of bacteria geared to optimize biooxidation of a specific refractory ore.
Owner:OXIDOR CORP
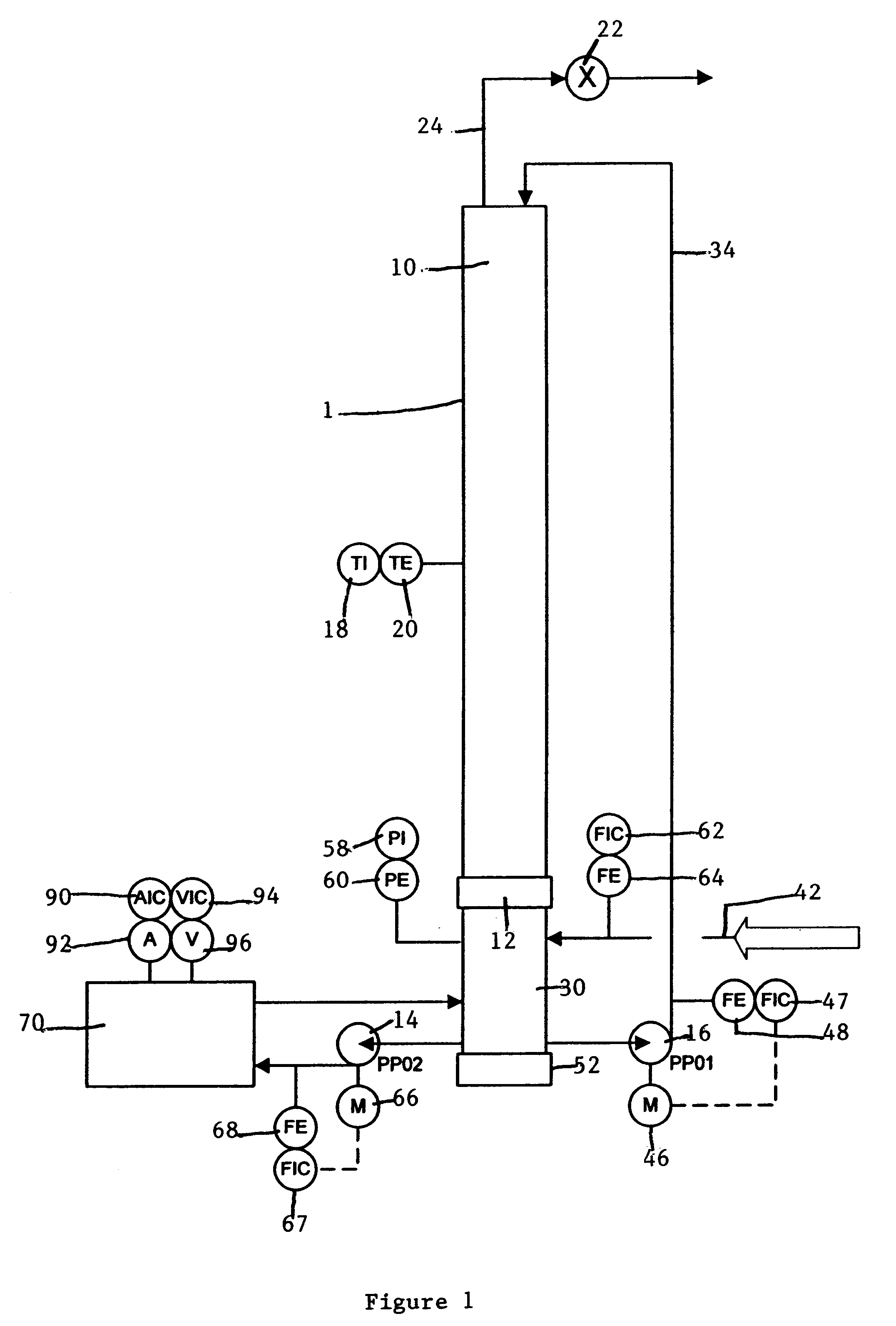
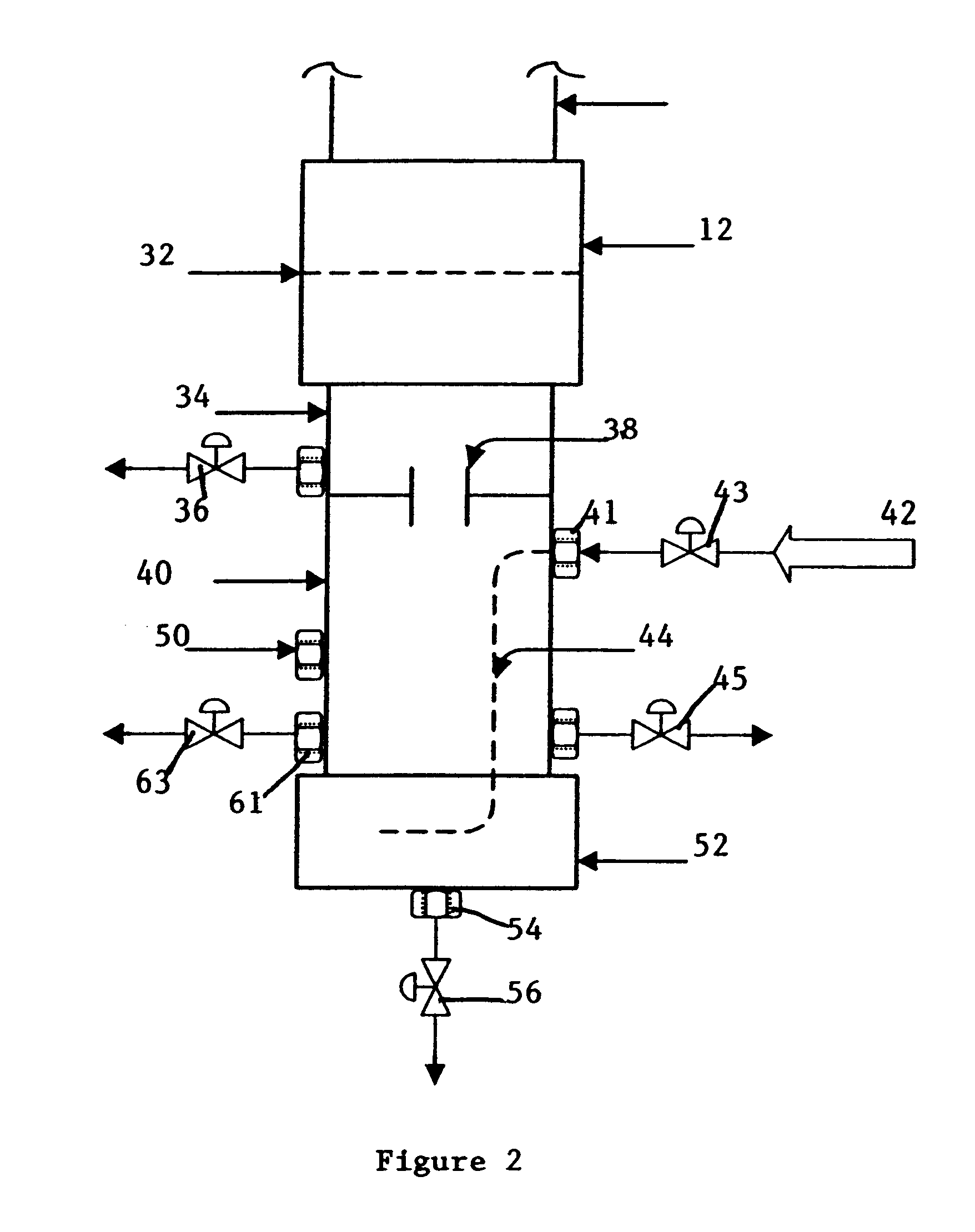
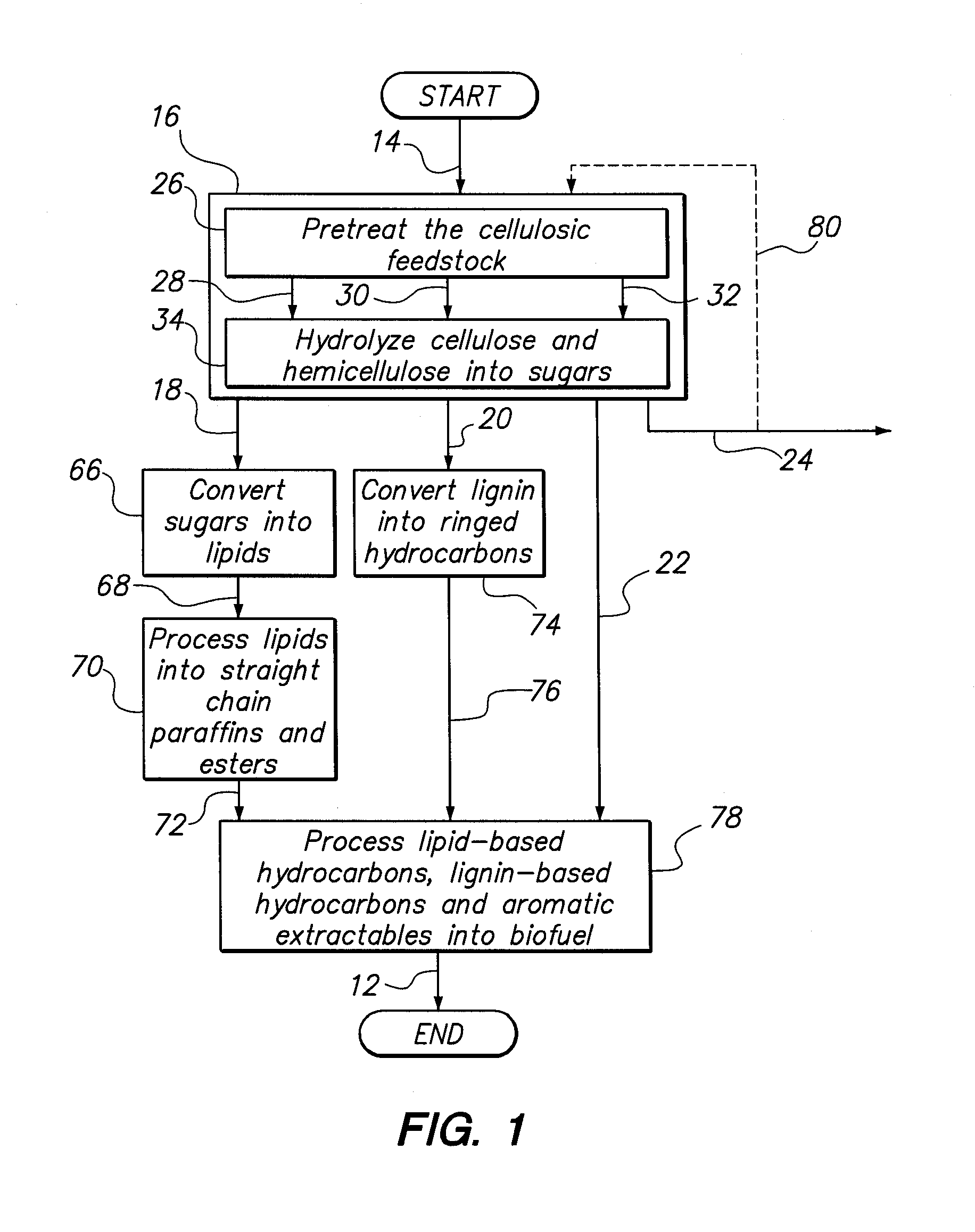
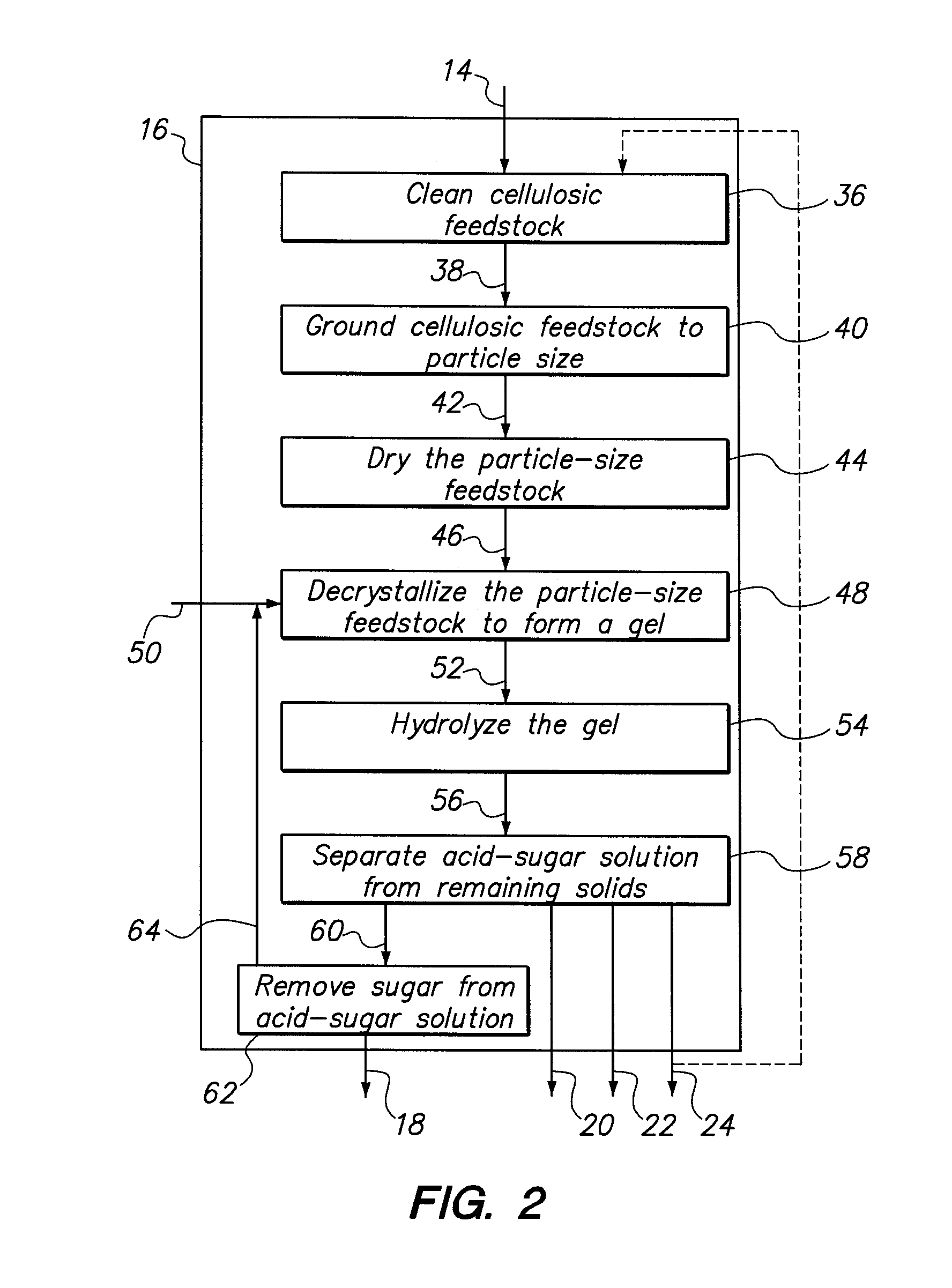
Method and system for microbial conversion of cellulose to fuel
InactiveUS20120077234A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce energy consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzymatic hydrolysisCycloparaffins
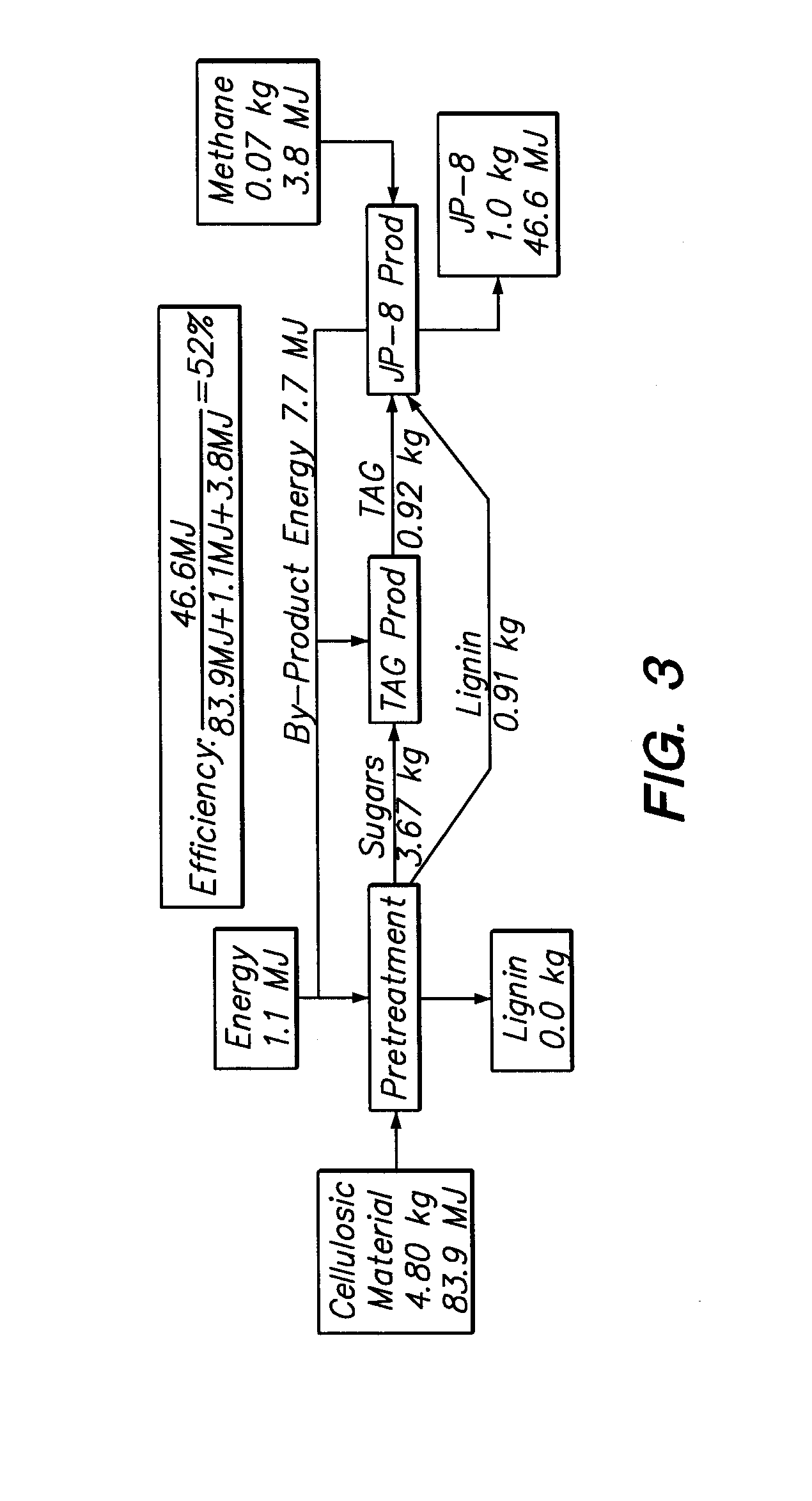
A method and system are provided for producing biofuel from cellulosic feedstock. In the method, the cellulosic feedstock is pretreated to separate cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Thereafter, the cellulose and hemicellulose are converted into sugars through enzymatic hydrolysis. Then, the sugars are converted into lipids, e.g. triglycerides, through a microbial process. Specifically, heterotrophic microalgae is grown on the triglycerides and forms triglycerides. While triglycerides are formed from the cellulose and hemicellulose, the lignin is converted into ringed hydrocarbons, such as aromatic hydrocarbons and cycloalkanes, e.g., cycloparaffins. To form the biofuel, the triglycerides and ringed hydrocarbons are processed together. During this step, the triglycerides are converted into straight chain paraffins and esters. Preferably, the biofuel is a surrogate for jet quality JP-8 fuel.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Composition for triggering microbiological processes in water and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20130180915A1Efficient and long-term degradationEfficient productionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentMicrobiological ProcessesChemistry
The present invention is directed to a composition for triggering microbiological processes in water, to a kit of parts comprising the components of said composition in distinct form, a method of producing such a composition and the use thereof for microbiologically decomposing water-immiscible substances, in particular crude oil and crude oil-derived substances.
Owner:LAVARIS TECH
Process for producing elemental selenium nanospheres
InactiveUS8003071B2Raw materials are simpleIncrease rangeBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFood additiveMicrobiological Processes
The invention relates to microbiological processes using non-selenium-respiring bacteria for the production of elemental selenium nanospheres having a size in the 50-500 nm range and compositions comprising said nanospheres. The invention further concerns grey elemental selenium nanospheres directly obtainable by the processes of the invention. The compositions and materials of the invention are useful, in particular, as food additives and for use as raw material in the microelectronic and optical industries.
Owner:DR ALIMENT
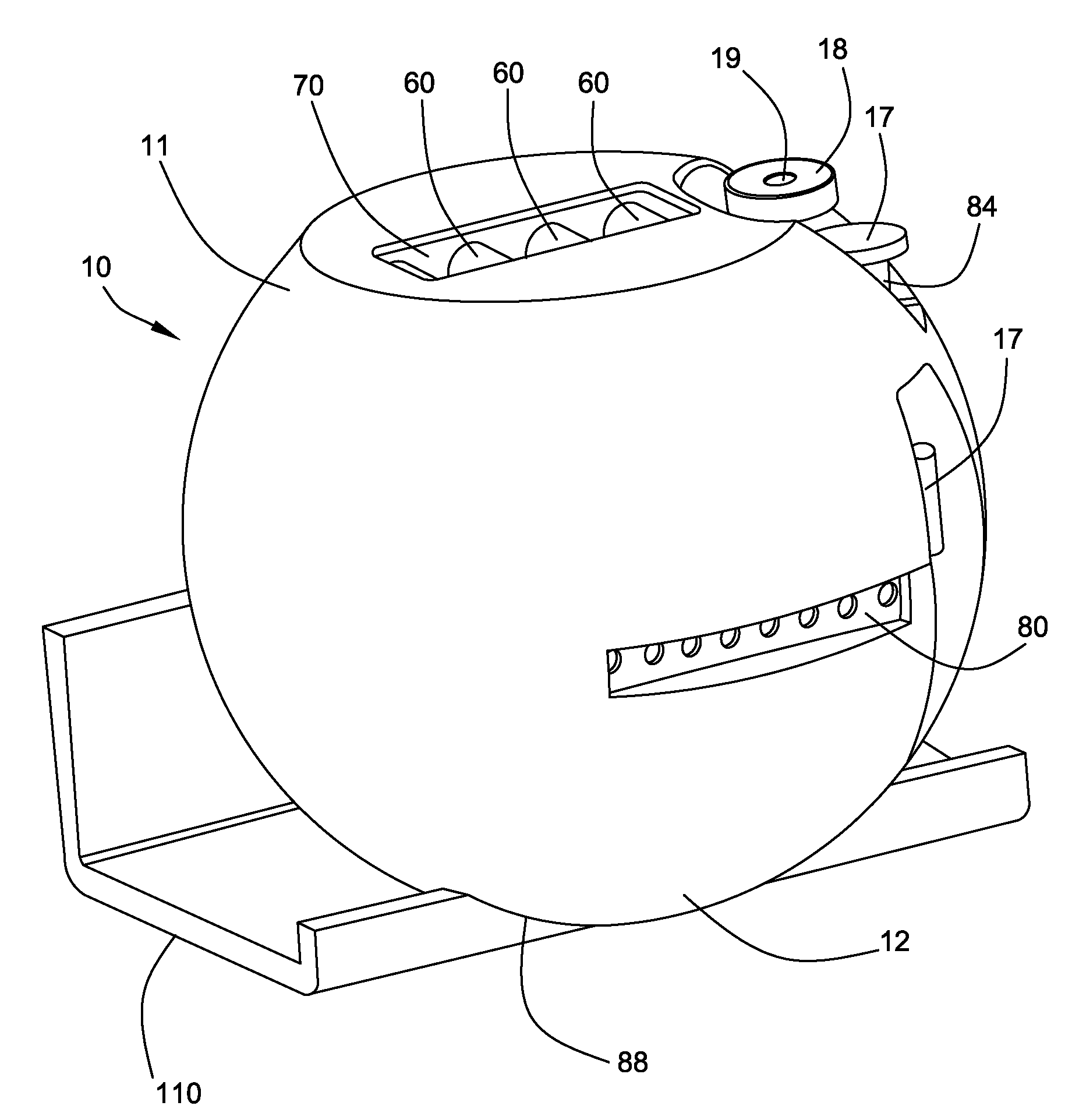
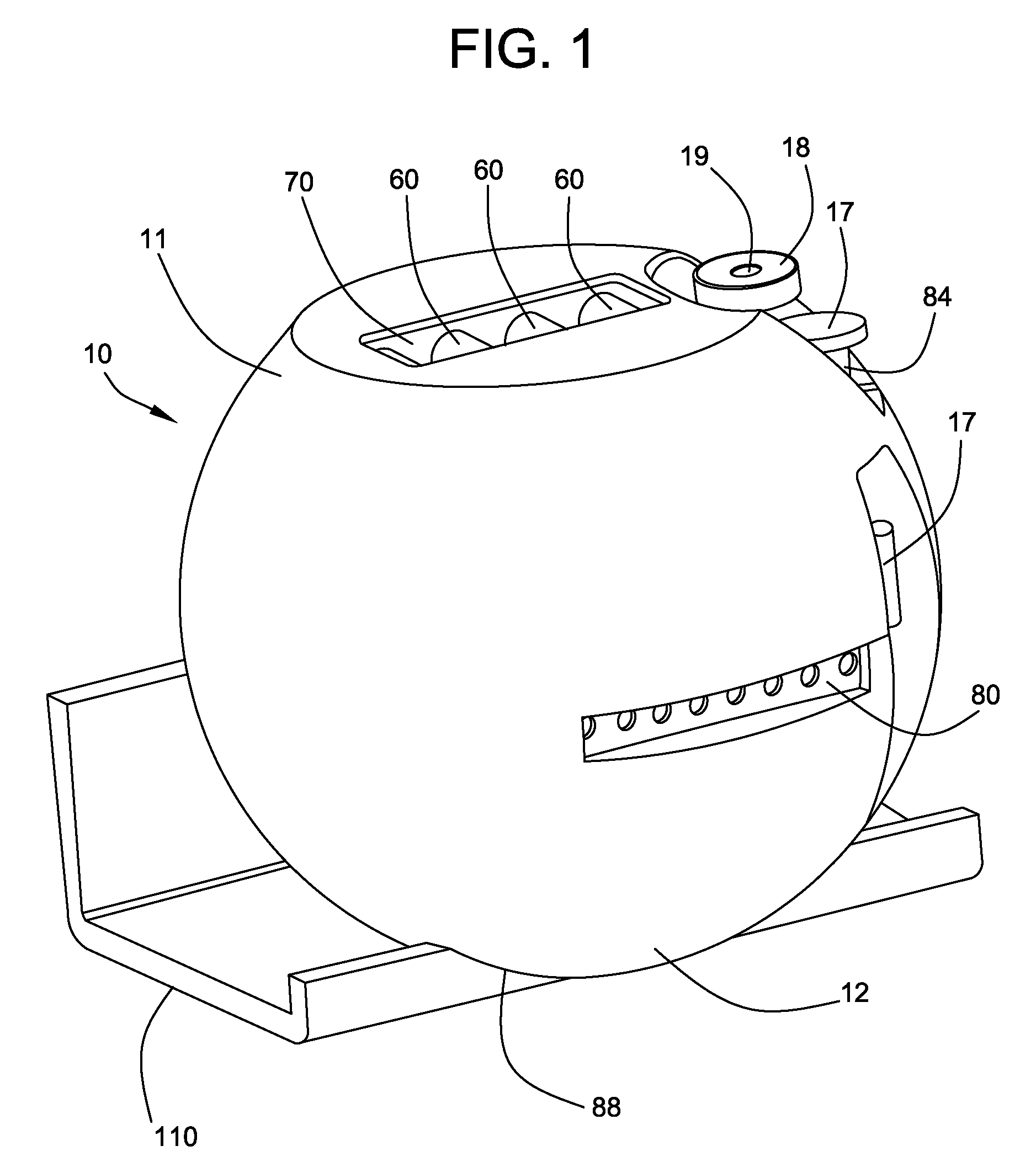
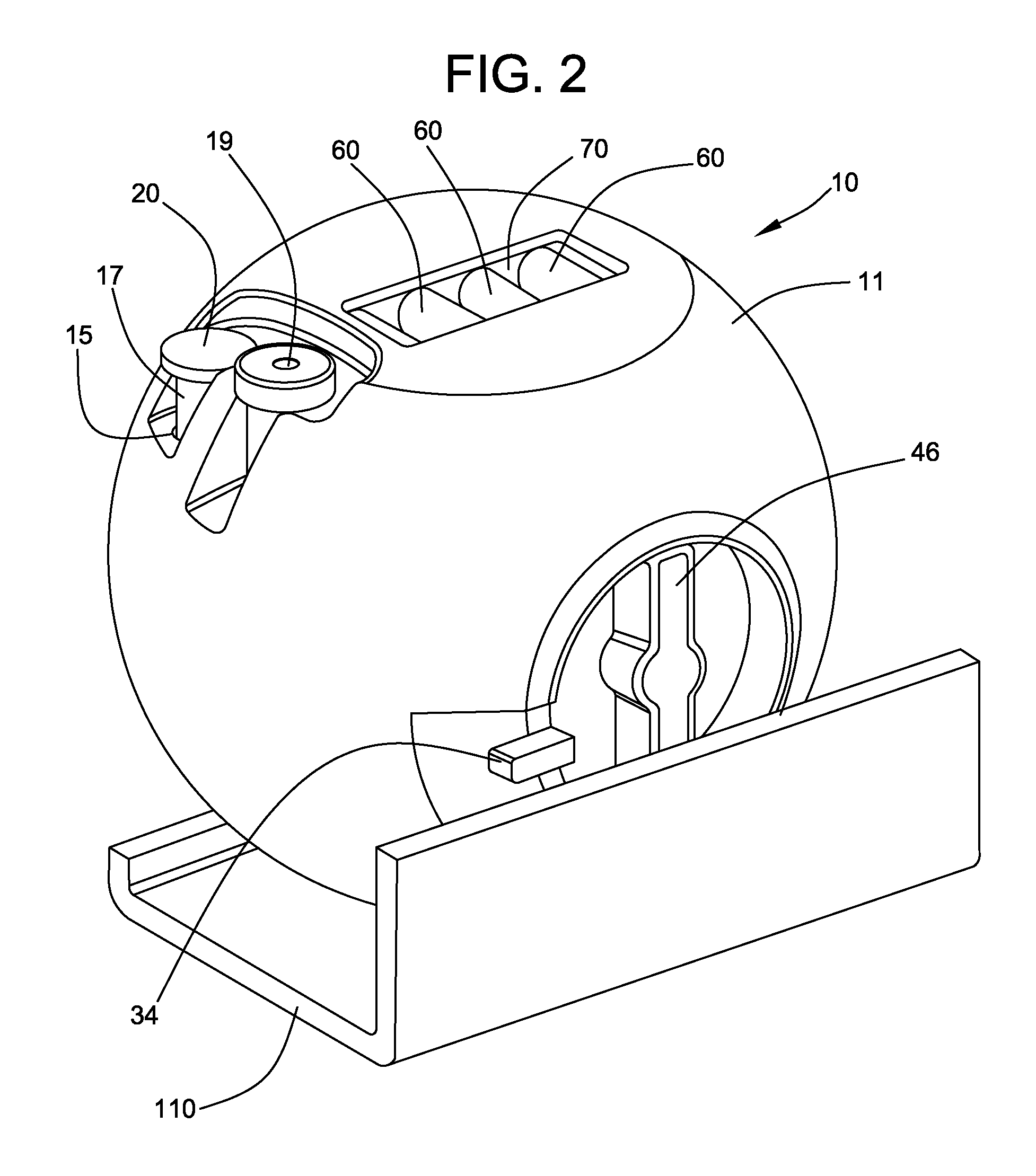
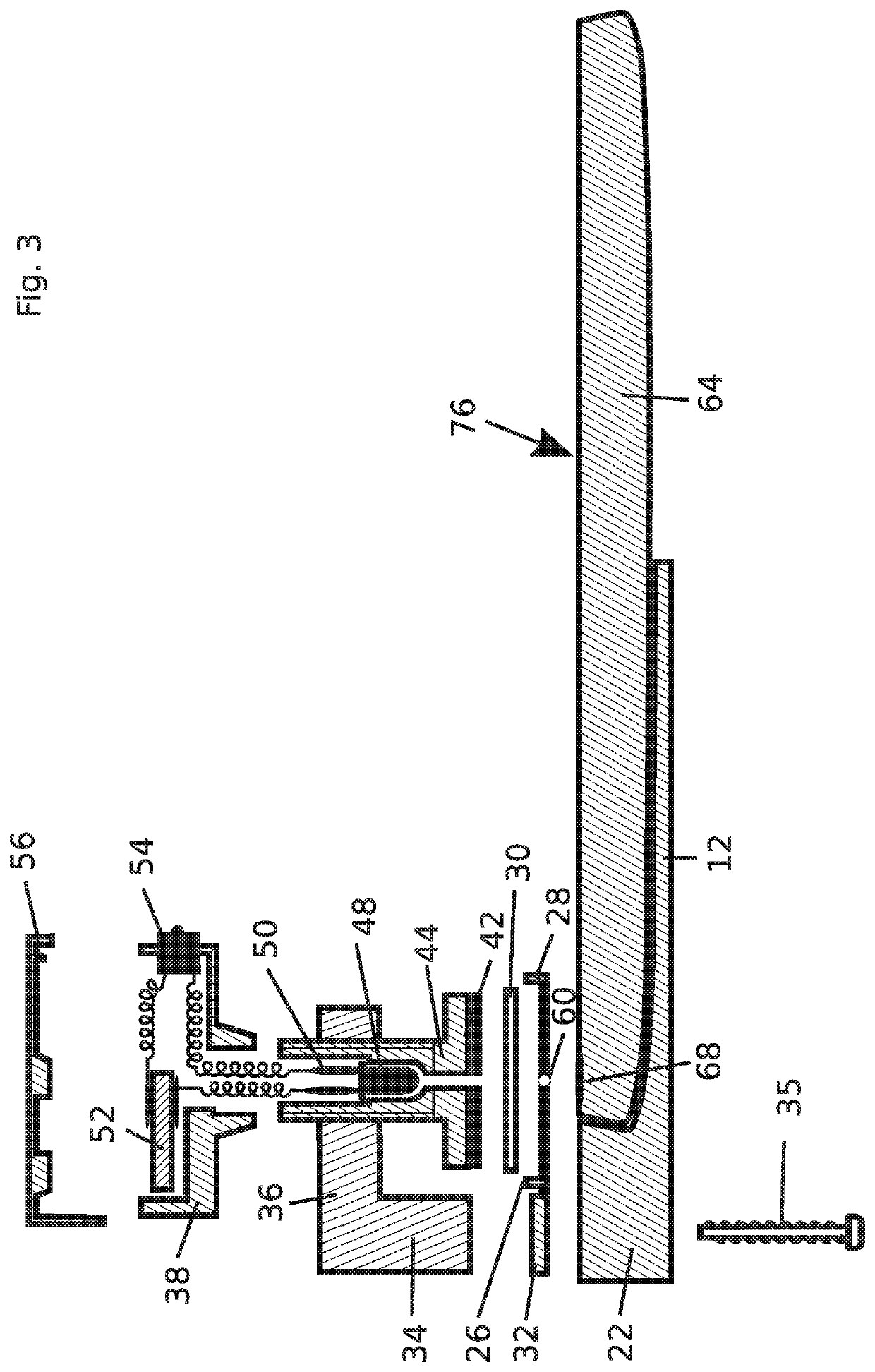
Microscope Assembly
ActiveUS20200057288A1Simple designHigh quality processingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMicroorganismEngineering
A microscope assembly can be used during microbiological processes. The microscope assembly includes a lens assembly for magnified imaging of an object range in an imaging plane along an optical path; a sample receiving unit for a sample arranged in the object range; and a camera receiving unit for receiving a camera in a range of the imaging plane the camera adapted to generate a digital image of the sample; where the lens assembly is a ball lens, a halved ball lens, or a lens in the form of a rotational spheroid; and the camera receiving unit is adapted to receive a customary mobile end device equipped with a camera or a camera cooperating with a mobile end device.
Owner:OCULYZE GMBH
DNA Microarray for Quantitative Detection of Microbial Processes in the Oilfield
InactiveUS20100323910A1Promote recoveryNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleotide
A DNA microarray having correctly designed target nucleotide sequences bound thereto generates a quantifiable signal when the microarray hybridizes a field sample nucleotide sequence that indicates a microbial process in a field sample from an oilfield, for instance from downhole. Such DNA microarrays may be designed and manufactured to detect microbial production of hydrogen sulfide, organic acids, surfactants, and gases as well as thermophilic bacterial activity. The field sample nucleotide sequences may be tagged with a fluorescent molecular label, so that the DNA microarrays may generate signals, such as fluorescent signals that may be measured and quantified to provide a more accurate way to correlate bacterial processes in the oilfield than presently available methods.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
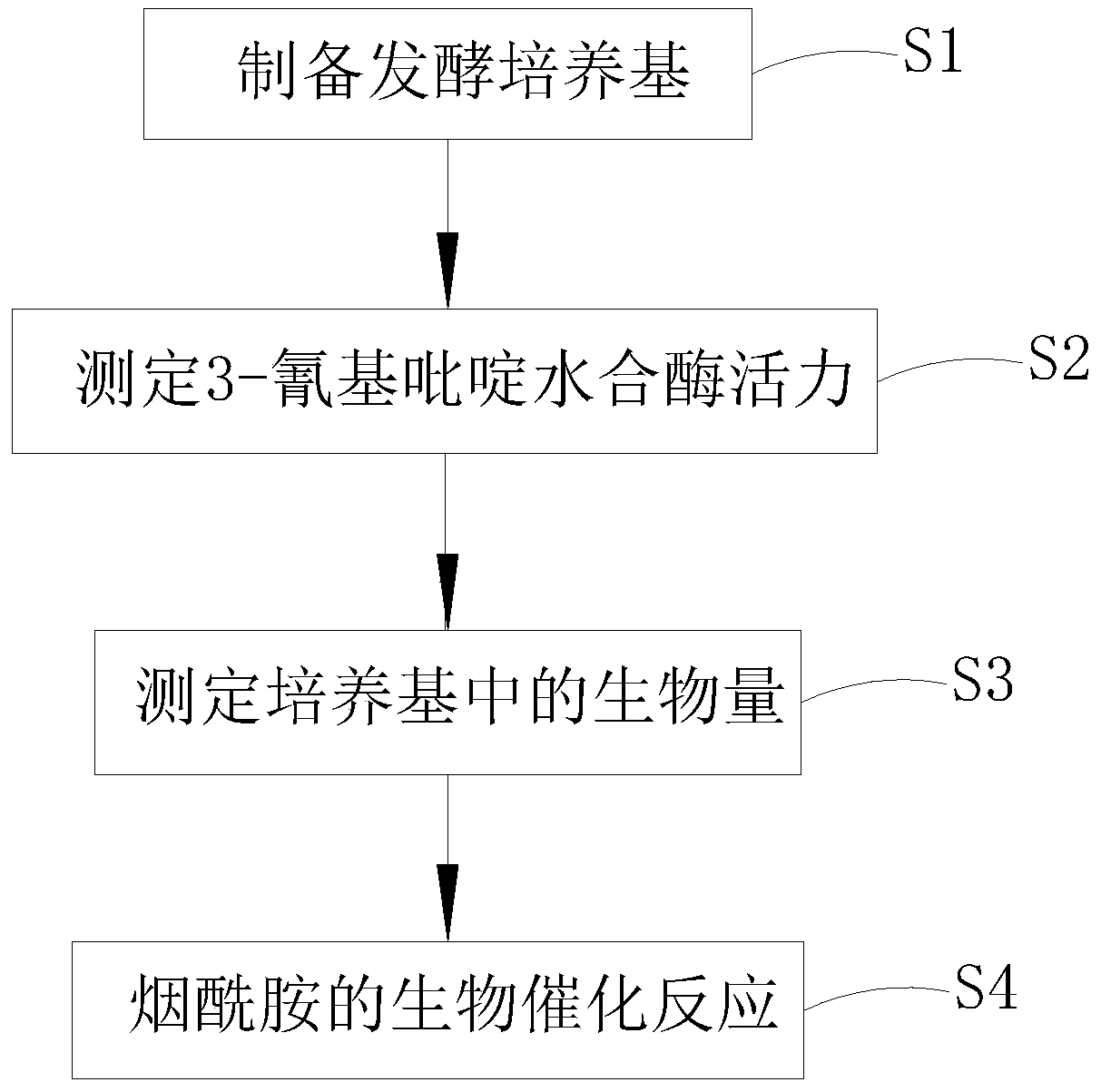
Synthesis and catalysis process of nicotinamide containing low nicotinic acid byproduct
PendingCN111039861ASolve the problem of complex and difficult to control operating conditions in batch production processSimple production processOrganic chemistryBacteriaBiotechnologyRhodococcus equi
The invention discloses a synthesis and catalysis process of nicotinamide containing a low nicotinic acid byproduct. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a fermentation culture medium,measuring the activity of 3-cyanopyridine hydratase in the culture medium, measuring biomass in the culture medium, carrying out a biological catalytic reaction on nicotinamide, and preserving strainsafter the catalytic reaction. According to the invention, research on production of nicotinamide by biotransformation of immobilized cells is carried out, the repeated utilization frequency of the immobilized cells is increased from 3 times to 6-7 times, and a conversion rate is 99.6%, moreover, the extraction process of nicotinamide is improved, crystallization yield is enabled to reach 88.6%, and total extraction yield reaches 88.5% ; according to the method, 3-cyanopyridine is taken as a substrate, Rhodococcus equi is taken as a catalytic strain, and the method for synthesizing nicotinamide by a microbiological process is simple in production process and stable and easy to control in catalytic process, and overcomes the problems of complex and difficult-to-control operation conditionsof a traditional batch production process based on a biological method.
Owner:ANHUI RUIBANG BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Special microbial feed additive for white-leg shrimps and preparation method of special microbial feed additive
ActiveCN105192432AConducive to loadLow costClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyVitamin C
The invention discloses a special microbial feed additive for white-leg shrimps and a preparation method of the special microbial feed additive and belongs to the field of microbial additives. The preparation method of the special microbial feed additive comprises steps as follows: (1), corn flour, maltodextrin and seaweed meal are disinfected for 10 s by ultraviolet light; (2), the corn flour, the soybean meal, the maltodextrin and the seaweed meal are uniformly mixed and added with water, the mixture is stirred to form paste, the paste is gradually heated to 80 DEG C, carrageenan is added, stirring is continued while heat is preserved, and mixed powdery paste is obtained; (3), sodium caseinate, edible salt, vitamin C, solanum nigrum juice, disodium succinate and fish bone meal are added to the mixed powdery paste obtained in the step (2), and then bacillus and nitrobacteria are added; stirring is performed for 5 min, and then the mixture is extruded to be granular and dried in the air. The microbe adding process is different from a common addition mode only considering the microbe content after addition, loaded substances of the microbes are considered simultaneously, the functions of the microbes are performed through the additive, and the cost is saved to the greatest extent.
Owner:SHENZHEN GELINWO ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION TECH DEV CO LTD
Method for preparing fermented tied feet
InactiveCN105029468AColor Sauce RedSuitable for salty and sweetFood ingredient as antioxidantClimate change adaptationFlavorNitrite
The present invention discloses a method for preparing fermented tied feet. The method comprises the following steps: A, raw material pretreatment; B, production of a fermentation bone meal; C, pickling; D, rolling; E, preparation of a leavening agent; F, fermentation; G, stuffing, tying and shaping; H, marinating; I, cooling and packaging; J, sterilization, cooling, cartonning and storage. The method improves a traditional production process of tied feet; the accessory materials are supplemented with fermentation bone meal, sweet corn, domestic fungus and onion; the method makes full use of nutrition and health benefits of raw materials and has broad market prospects. Compared to the traditional tied feet, fermented tied feet have very big breakthrough in taste, nutrition and storage; the fermentation process is accompanied by very complex physicochemical and microbiological processes, whereby beneficial acidification is generated and a unique flavor is formed; and the tied feet have declined pH value, increased amino nitrogen content, and significantly decreased content of nitrite.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of ramee/expanded graphite composite fiber adsorbing material
ActiveCN103506081AImprove water purification effectQuick eliminationOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesEscherichia coliLow voltage
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ramee / expanded graphite composite fiber adsorbing material. On the basis of the functions of corrosion resistance, bacterial resistance, mold resistance and the like by utilizing different degrees of inhibitory effects of ramee (containing, pyrimidine, purine and other molecules) on Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and the like, the ramee used as a matrix raw material and the expanded graphite are synthesized into a composite fiber, and the ramee / expanded graphite composite fiber and boehmite mainly comprising aluminum hydroxide are prepared into a bioactive adsorbing material. The ultrafiltration water-adsorbing material can generate positive charges, and adsorb negatively charged microbes and bacteriophages, thereby achieving the goal of almost adsorbing all the microbes and bacteriophages in water. Especially after a low-current low-voltage external power source is switched on, the water purification effect is better. The adsorbing material provided by the invention has the characteristics of accessible materials, low manufacturing cost, low requirements for the working environment and high adsorbability, and can be widely used in the fields of medicine, veterinary medicine, food industry, water and solution purification related to the microbial process, and the like.
Owner:南京意西欧环境科技有限公司
Artificial tooth cleaning film indicating cleanness by metachromatism
InactiveCN102048657AEffectively eliminateIntuitive and quick detectionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSodium bicarbonatePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an artificial tooth cleaning film indicating cleanness by metachromatism, which is characterized by comprising the components by weight percent: 40-50% of sodium bicarbonate, 10-20% of potassium monopersulfate, 20-30% of sodium perborate monohydrate, 5-10% of anhydrous citric acid, 5-10% of polyethylene glycol, 1-5per mill of sodium benzoate, 1-5per mill of lauryl sodium sulfate and 1-5per mill of indicator. The artificial tooth cleaning film of the invention has the beneficial effects of effectively removing the hackneyed bacterium and other microorganisms on false teeth, indicating a process of effectively killing the bacterium and the microorganism through the metachromatism between the indicator and an oxidant, and being capable of detecting the sterilizing effects more visually and rapidly when the color of the blue substances in aqueous solution changes from blue to colourless.
Owner:WUHE KELING HEALTHCARE TECH
Papermaking Additive
ActiveUS20080093040A1High strengthAdditional componentNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingFermentation
A new class of polymeric additives for papermaking is disclosed as well as a process for their manufacture, a method for their use and a paper sheet containing the addition. The additives can be used in paper manufacture as agents for improving retention, paper machine operation and the strength properties of the product. The additives are manufactured from the biomass that is a by-product of microbiological production of citric acid by a fermentation process using Aspergillus Niger, suitable by-product from other microbiological process, or from a biomass specifically produced for this purpose. The biomass that contains acetyl amino groups or other amides is chemically modified by hydrolysis of the amides to form primary amino groups. Under neutral or acidic conditions these primary amines become cationic, which assures a good absorption of the additive onto fibres and fines of pulp that is generally of anionic nature. Furthermore, primary amino groups can form chemical bonds with carbonyl groups, and ionic interactions with carboxyl groups. Both these groups are abundant in the fibres and fines of pulps, especially in mechanical pulps. The additive prepared in this manner might contain glucosamine polymers that might be chemically bound to a carbohydrate polymer or oligomer. Novel papermaking additives produced in this manner are particularly suitable for the production of paper from fibrous pulp suspensions produced at least partially from mechanical pulps, the high negative charge of which tends to overwhelm a majority of conventional cationic polymers.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Trend analysis and statistical process control using multitargeted screening assays
ActiveUS8956826B2Guaranteed maximum utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiotechnologyMicrobiological Processes
Aspects of the present invention provide novel multi-targeted microbiological screening and monitoring methods having substantial utility for monitoring and control of microbial growth and contaminants, microbiological processes, predictive microbiology, and for exposure and risk assessment. Microbial markers shared by both target and index microbes are used in novel methods for microbial monitoring, monitoring of microbial performance potential, trend analysis, and statistical process control (SPC) in processes or systems that are receptive to a plurality of genetically distinct microbes.
Owner:INST FOR ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Conditioning biomass for microbial growth
InactiveCN101573440AIncrease growth rateMicroorganism based processesLignin derivativesMicroorganismWoody plant
The present invention relates to methods for improving the yield of microbial processes that use lignocellulose biomass as a nutrient source. The methods comprise conditioning a composition comprisinglignocellulose biomass with an enzyme composition that comprises a phenol oxidizing enzyme. The conditioned composition can support a higher rate of growth of microorganisms in a process. In one embodiment, a laccase composition is used to condition lignocellulose biomass derived from non-woody plants, such as corn and sugar cane. The invention also encompasses methods for culturing microorganisms that are sensitive to inhibitory compounds in lignocellulose biomass. The invention further provides methods of making a product by culturing the production microorganisms in conditioned lignocellulose biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Method for producing a useful compound and treating a wastewater using pure oxygen
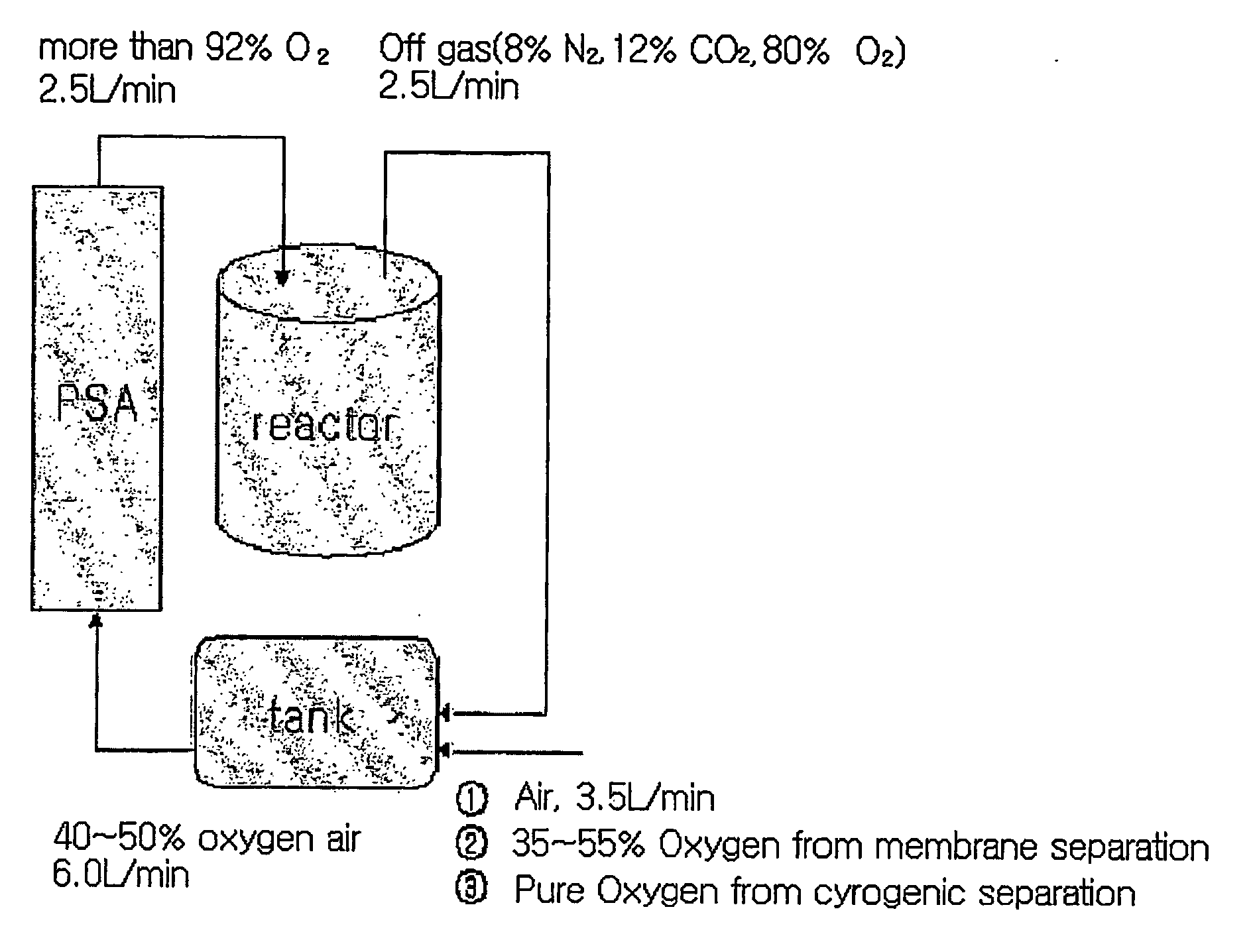
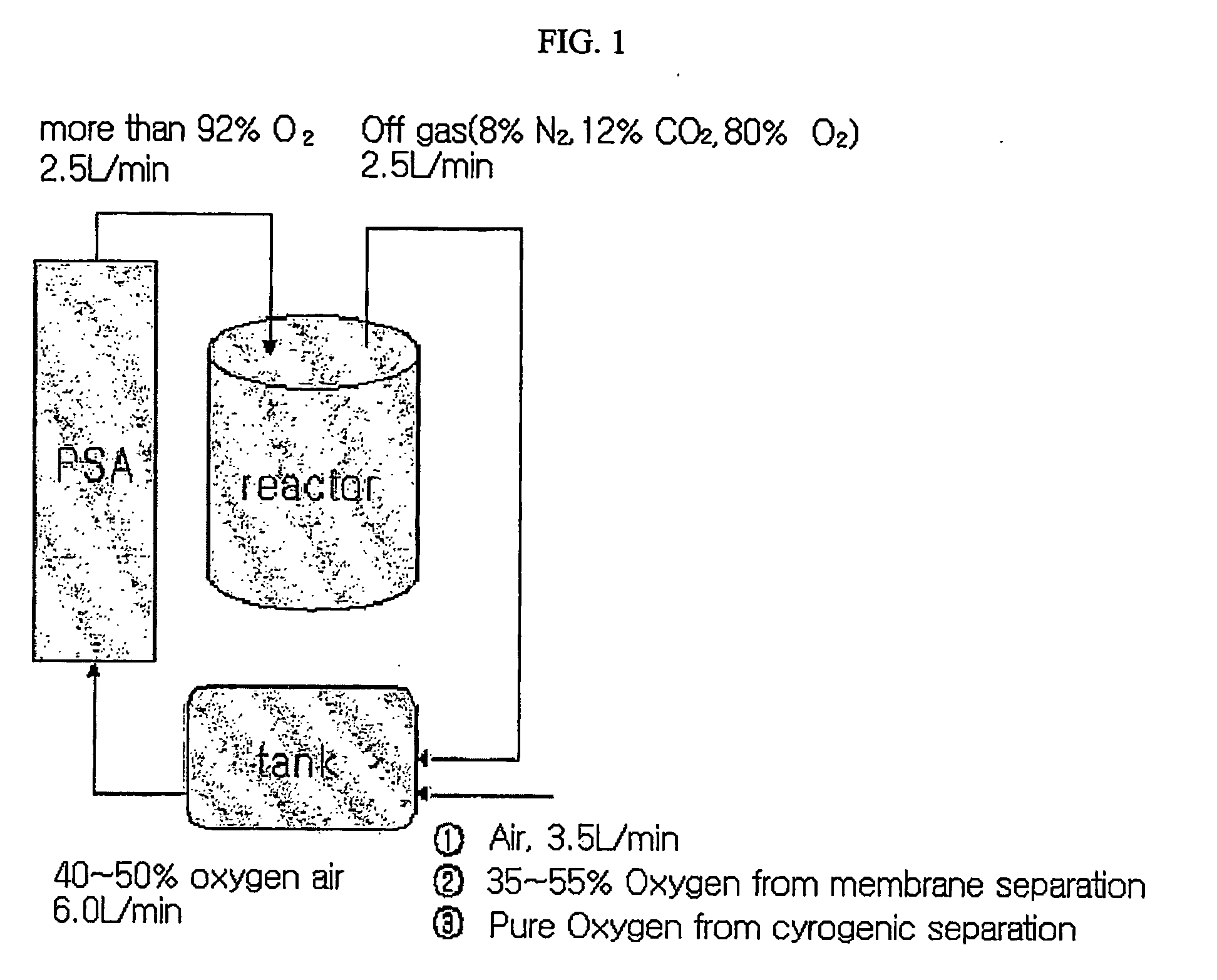
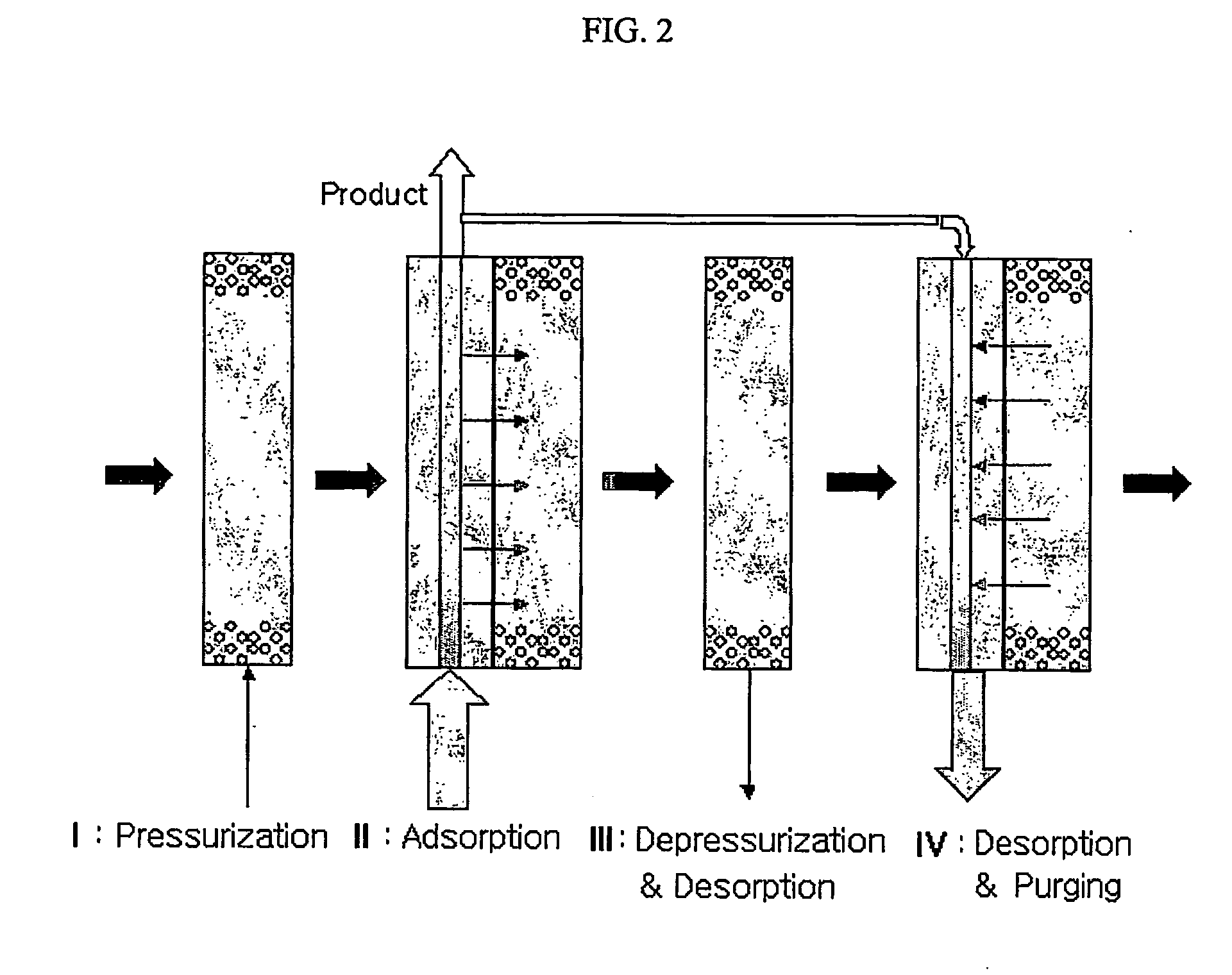
A method of using pure oxygen in microbial fermentation processes and wastewater treatment processes, in which the pure oxygen is produced by a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process from a gas mixture of air and unused oxygen-containing recycled off-gas from microbial processes which uses oxygen-containing gas in a liquid or gas state. When pure oxygen with a purity of more than 90% is used in microbial processes, microbial productivity can be about 5 times as increased as it is that in the conventional method using air with an oxygen content of 21%, and the volume of an active sludge tank in wastewater treatment processes can be reduced to at most ⅕ of the volume as compared to the conventional method. Also, the off-gas from such pure oxygen processes has a high oxygen content of about 70-80%. Thus, when the off-gas is recycled with air for the supplement of oxygen consumption, the gas mixture with an oxygen content of about 40% is used as feed gas for the PSA process, and CO2 generated by microbial breathing is also removed. Thus, the volume of a PSA column and an air compressor for supplying the feed gas can be reduced to less than ½ of the volume as compared to that of the use of air.
Owner:E1 BIOTECH +1
Microbiological process for the preparation of amides
A microbiological process for the preparation of amides from the corresponding nitriles by enzymatic hydrolysis with nitrile hydratase enzyme from a bacterial strain of Rhodococcus biphenylivorans species is described.
Owner:哥伦比亚有限公司
Apparatus and method for conducting microbiological processes
InactiveCN103443037AReduce ecological footprintBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganismTemperature control
A method and apparatus are provided for conducting a microbiological process on a bulk material in which a quantity of the bulk material is loaded onto a waterproof lining forming part of a bio cell with a heat transfer arrangement below the quantity of bulk material or within its volume, or both. The moisture content of the bulk material is controlled by periodic or intermittent distribution of water into the bulk material in order to promote microbiological activity within the bulk material by means of microbes that may be either naturally occurring within the bulk material or may be selected and introduced into the bulk material according to a desired result. A leachate recovery installation collects leachate draining from the bulk material. The temperature within the bulk material is monitored and the temperature controlled in order to elevate or decrease the temperature thereof to approach a target temperature associated with enhanced microbial activity of microbes present within the bulk material. The apparatus includes a controller having an electronic micro-processor with the controller having inputs for association with a temperature detector and a moisture detector. The preferred apparatus includes solar powered thermal and electrical energy units.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE FREE STATE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com