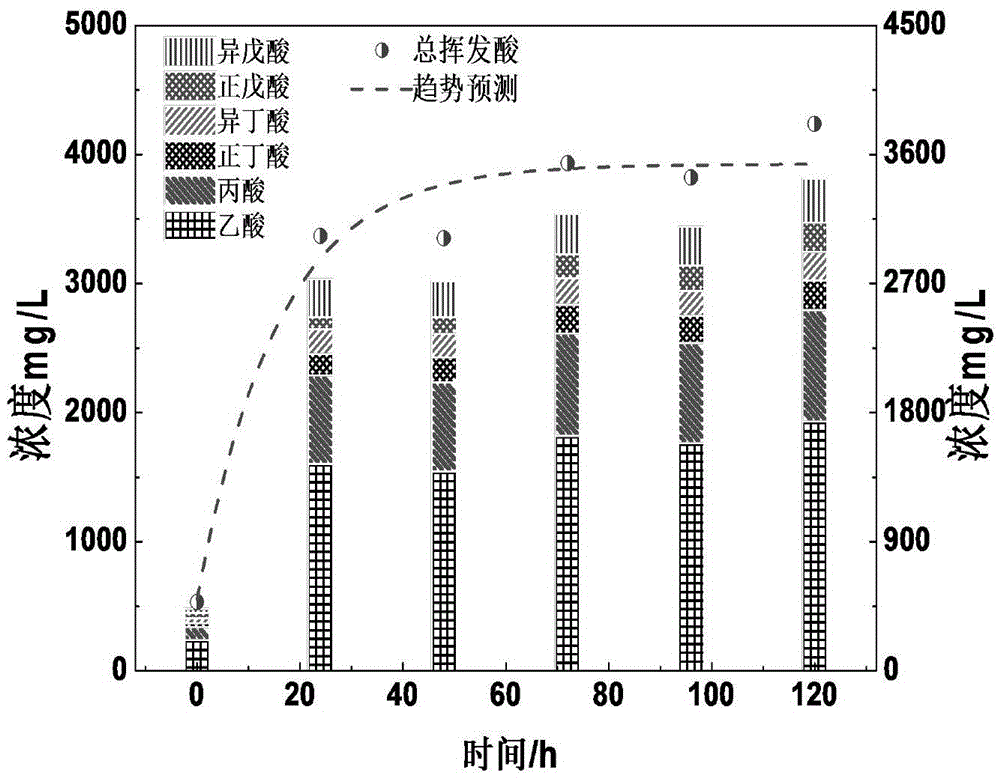
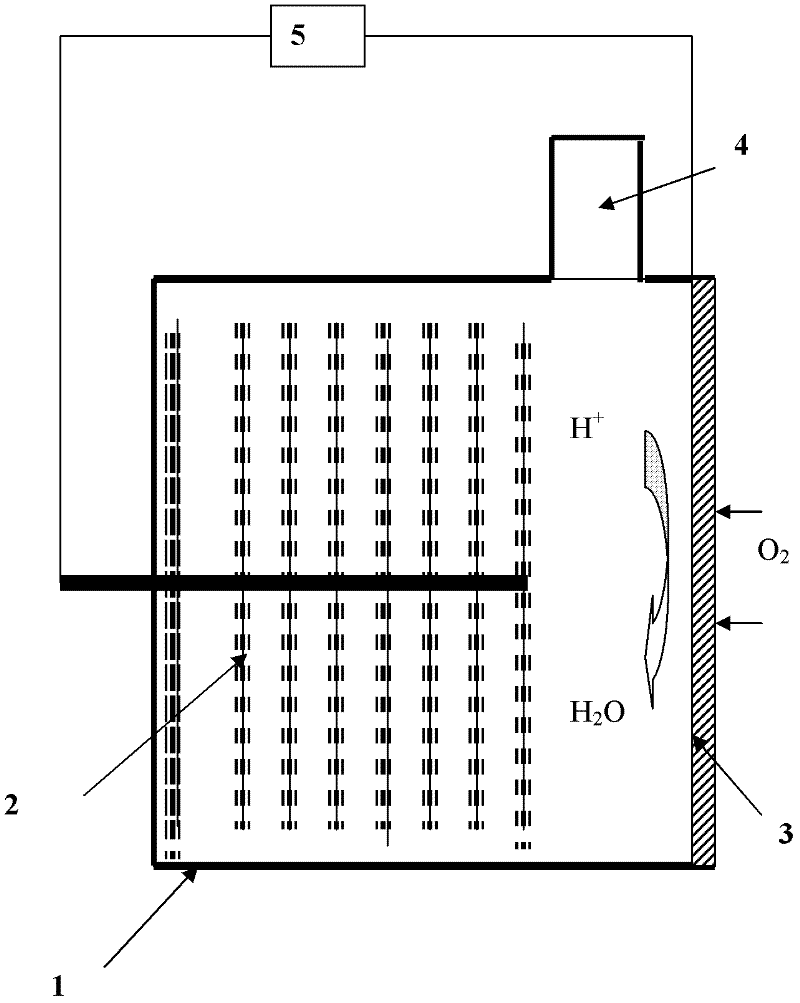
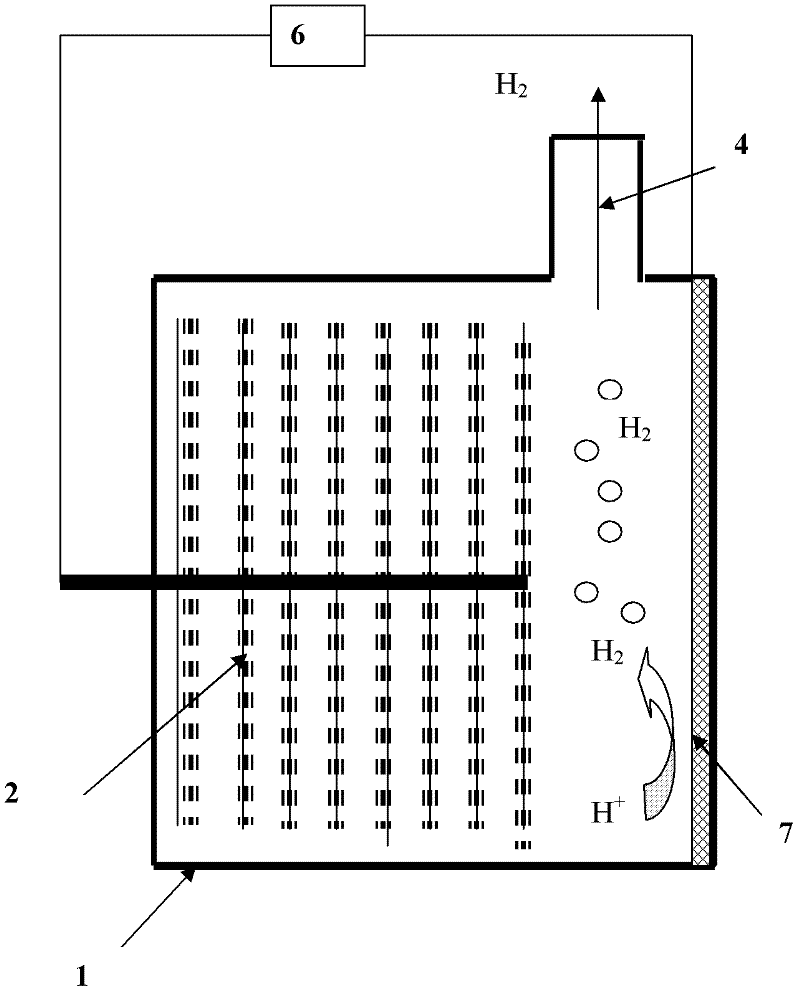
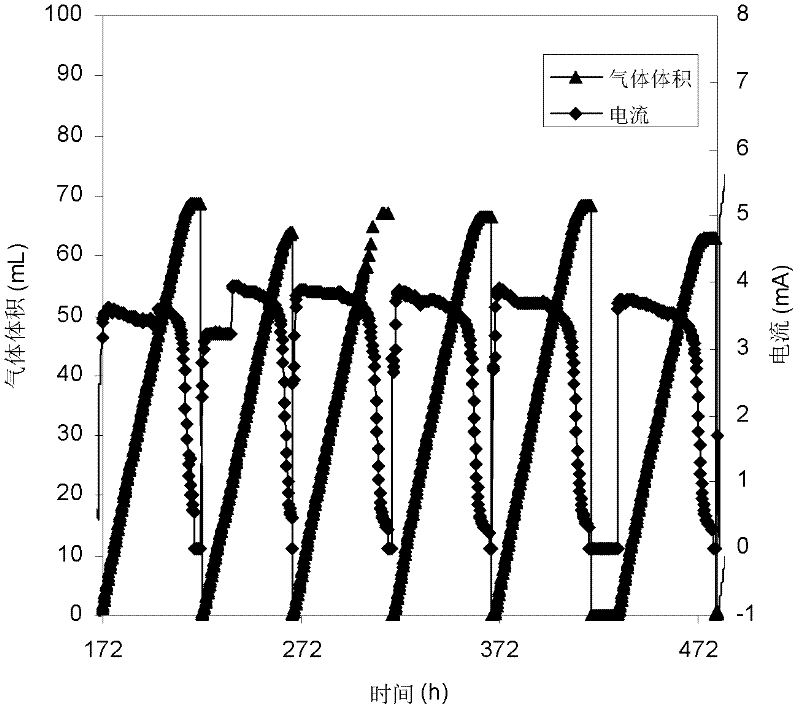
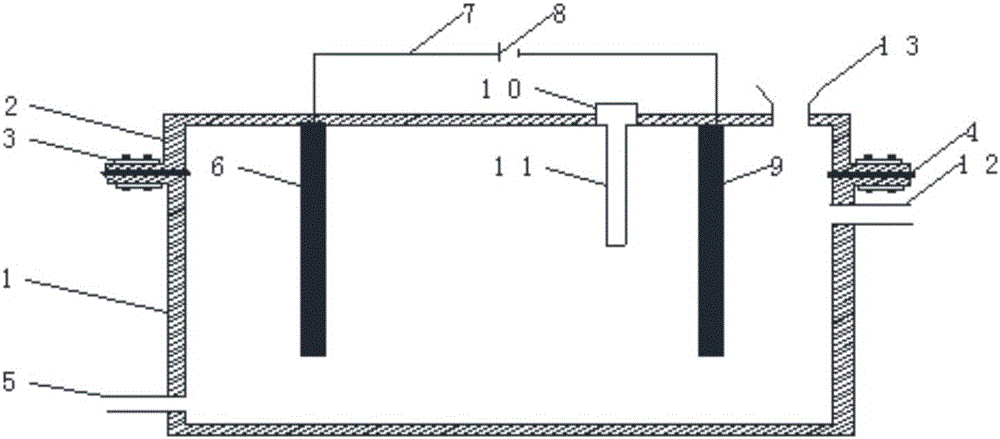
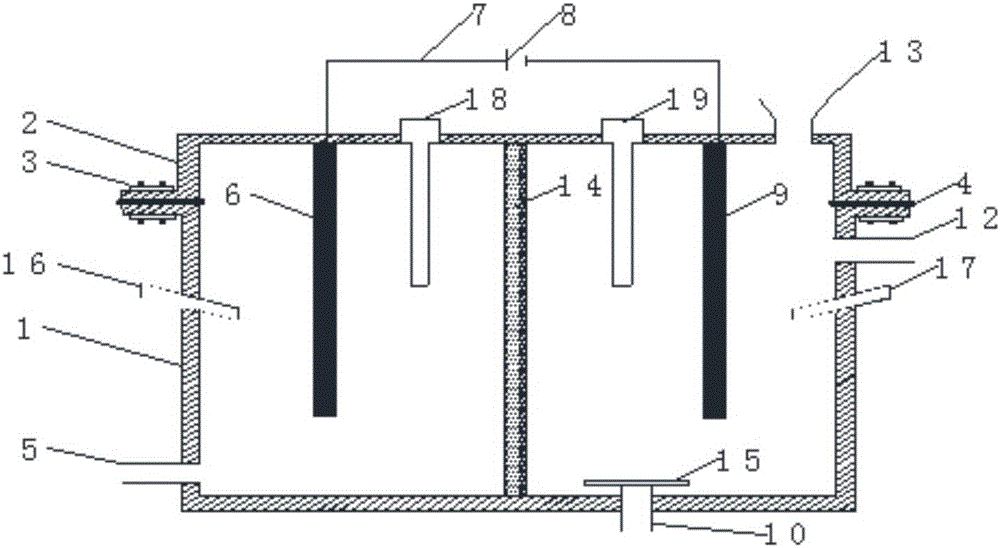
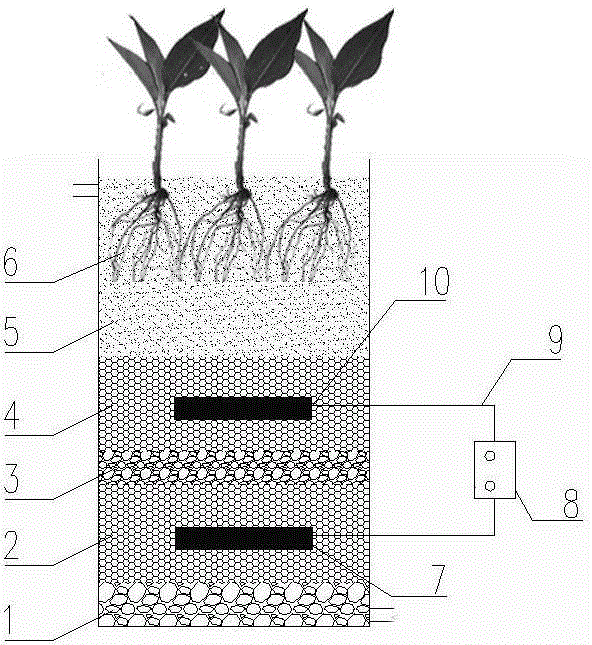
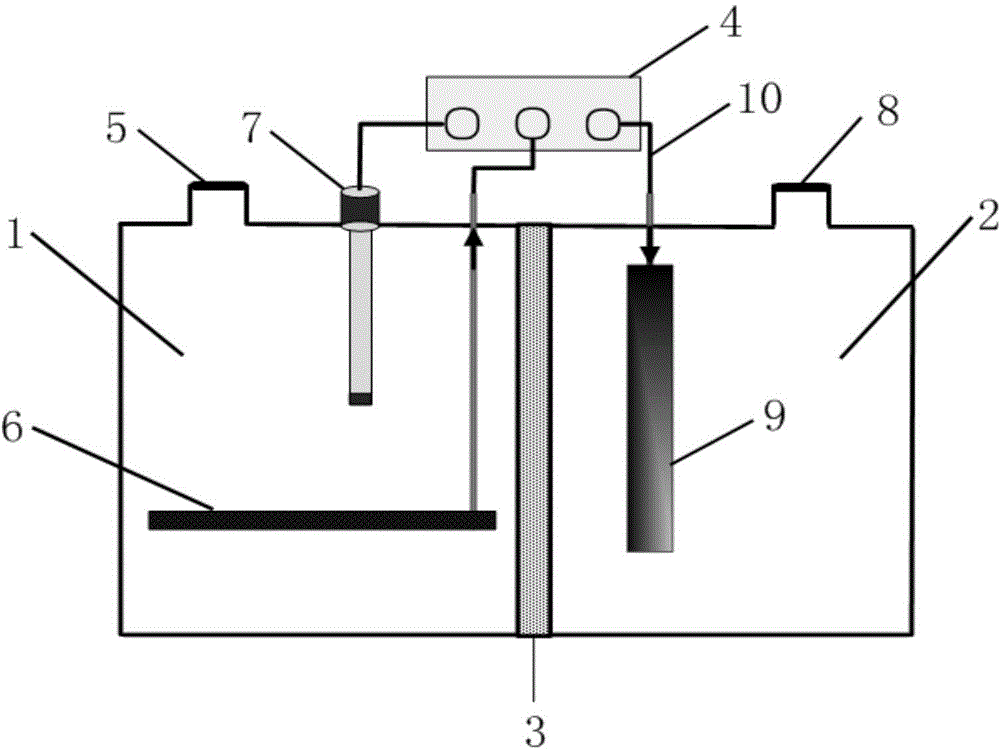
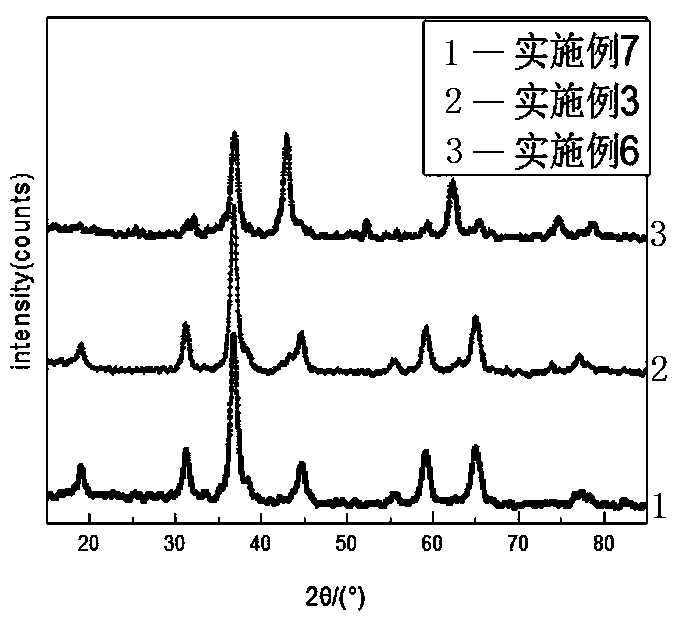
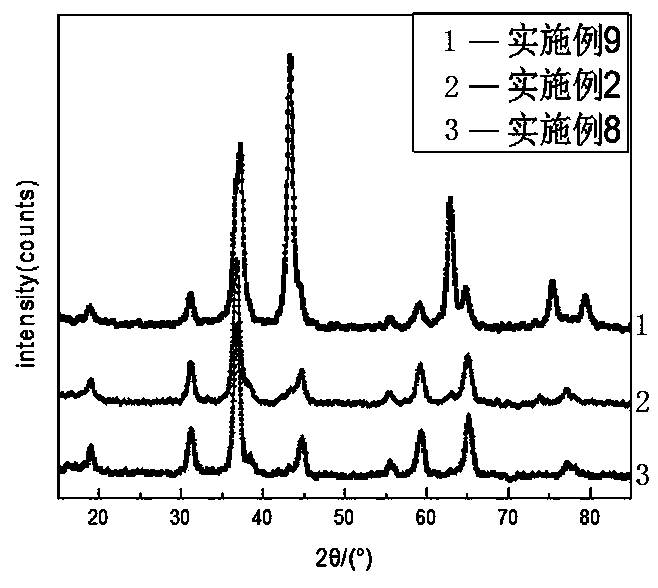
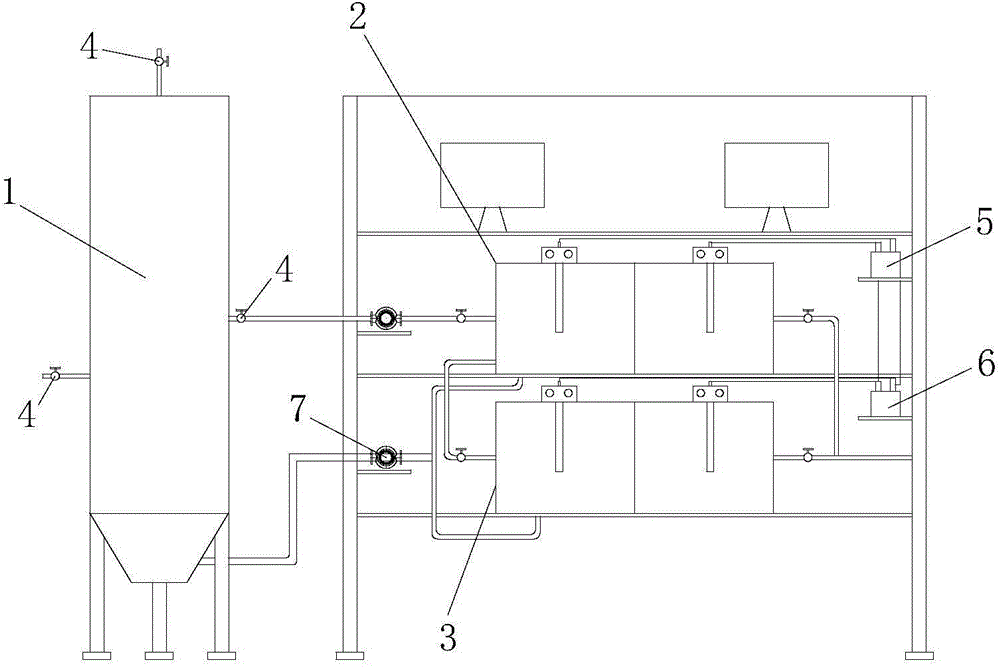
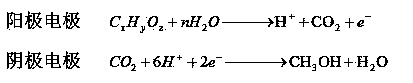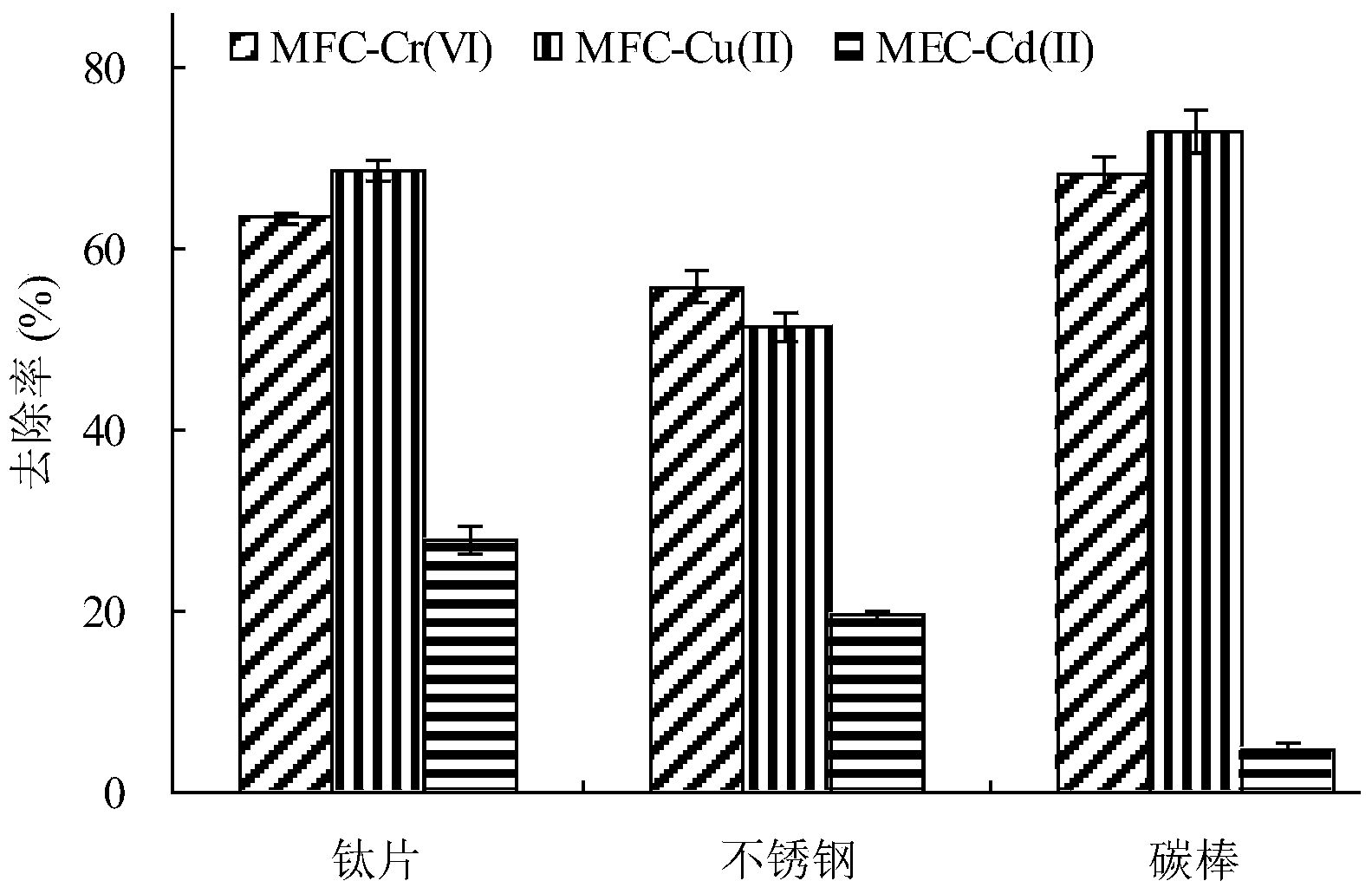Patents
Literature
227 results about "Microbial electrolysis cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
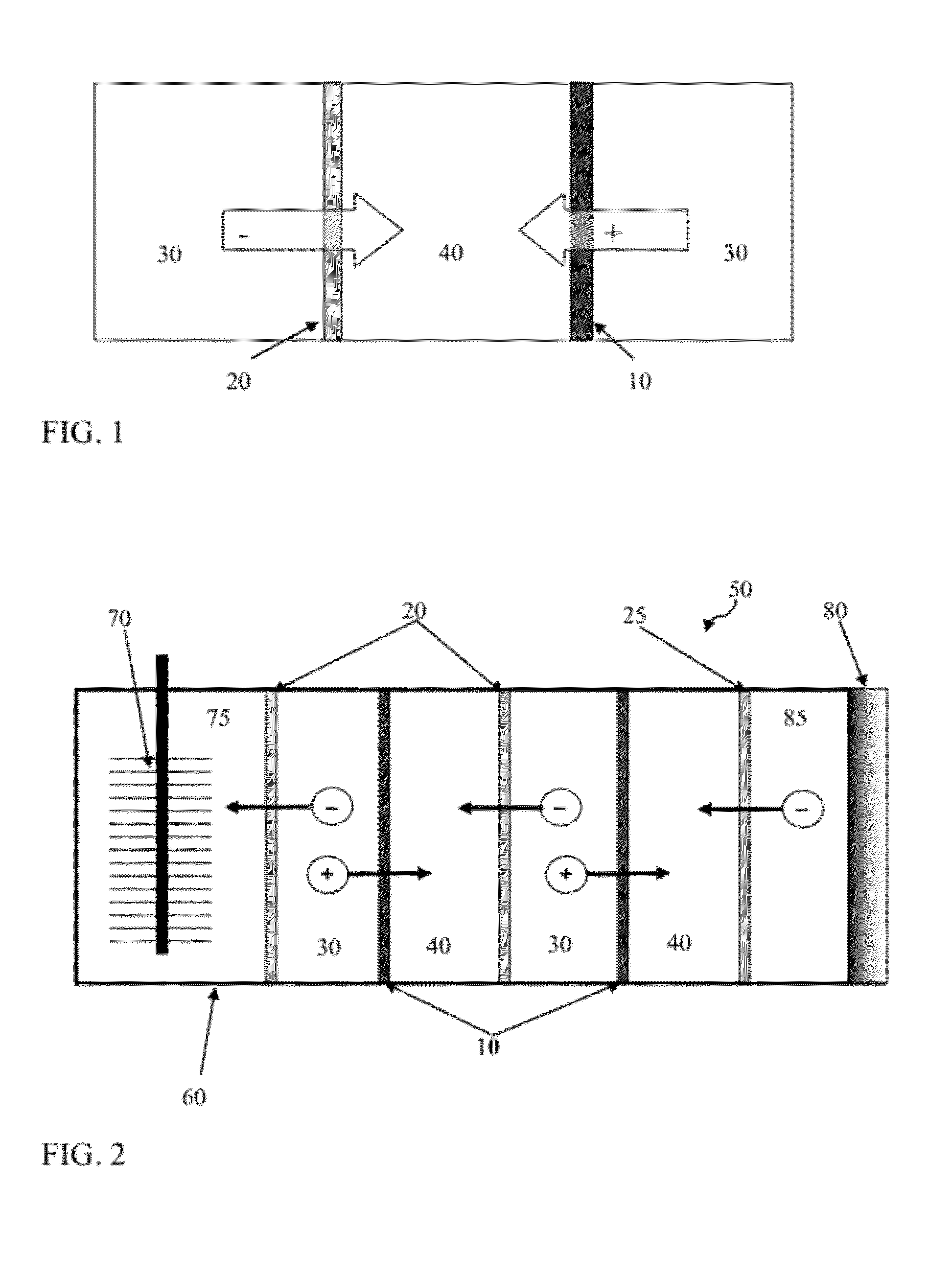
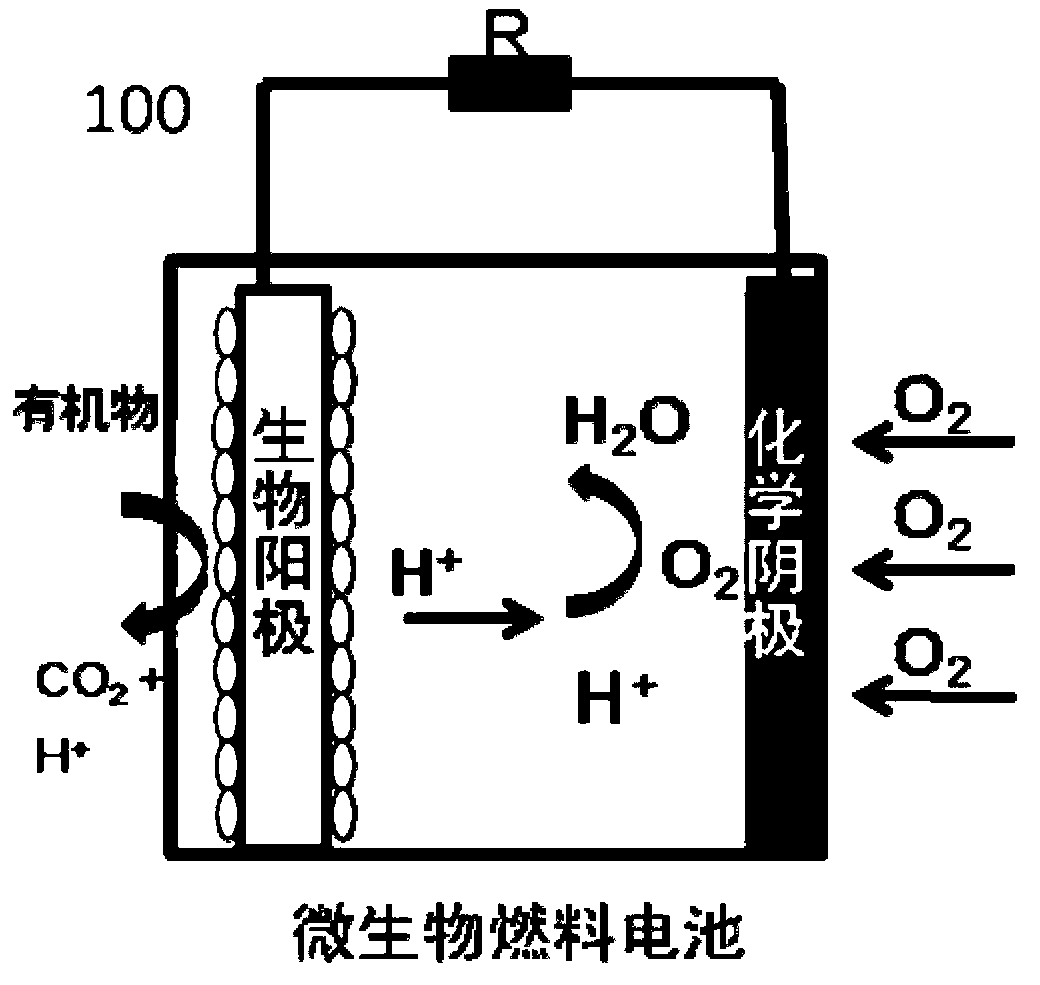
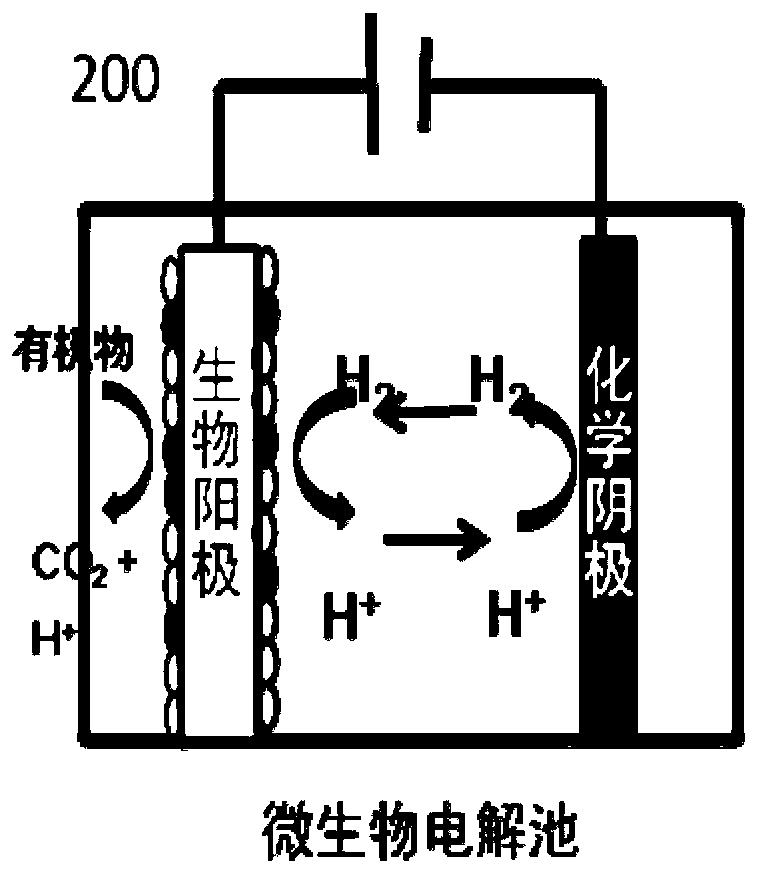
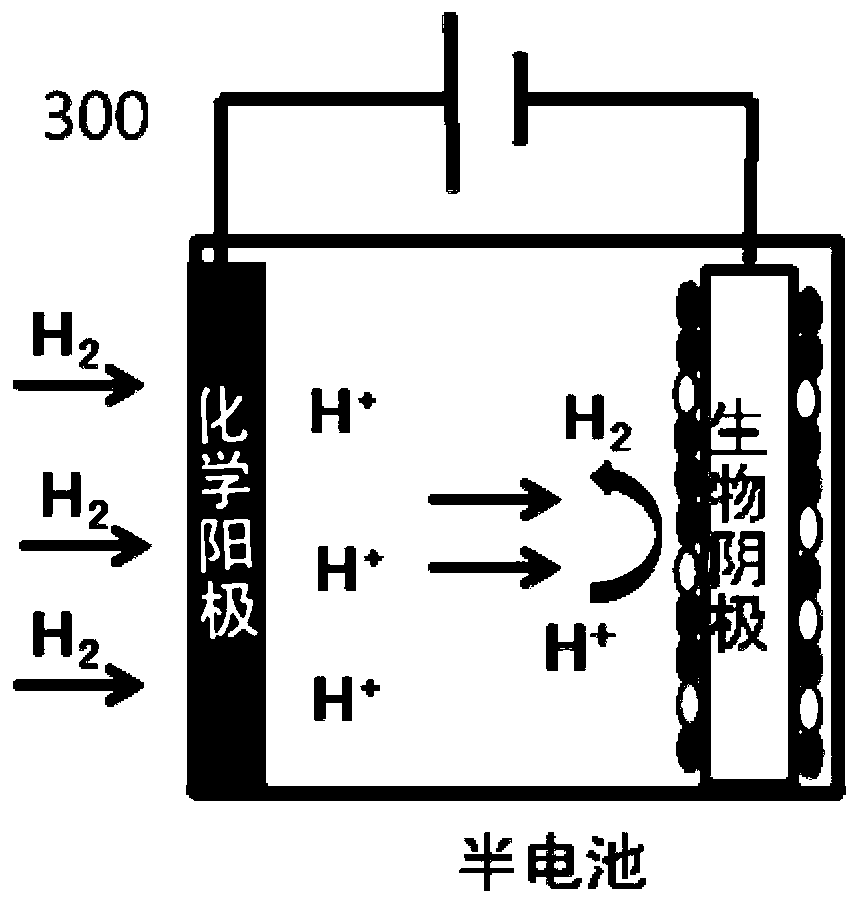
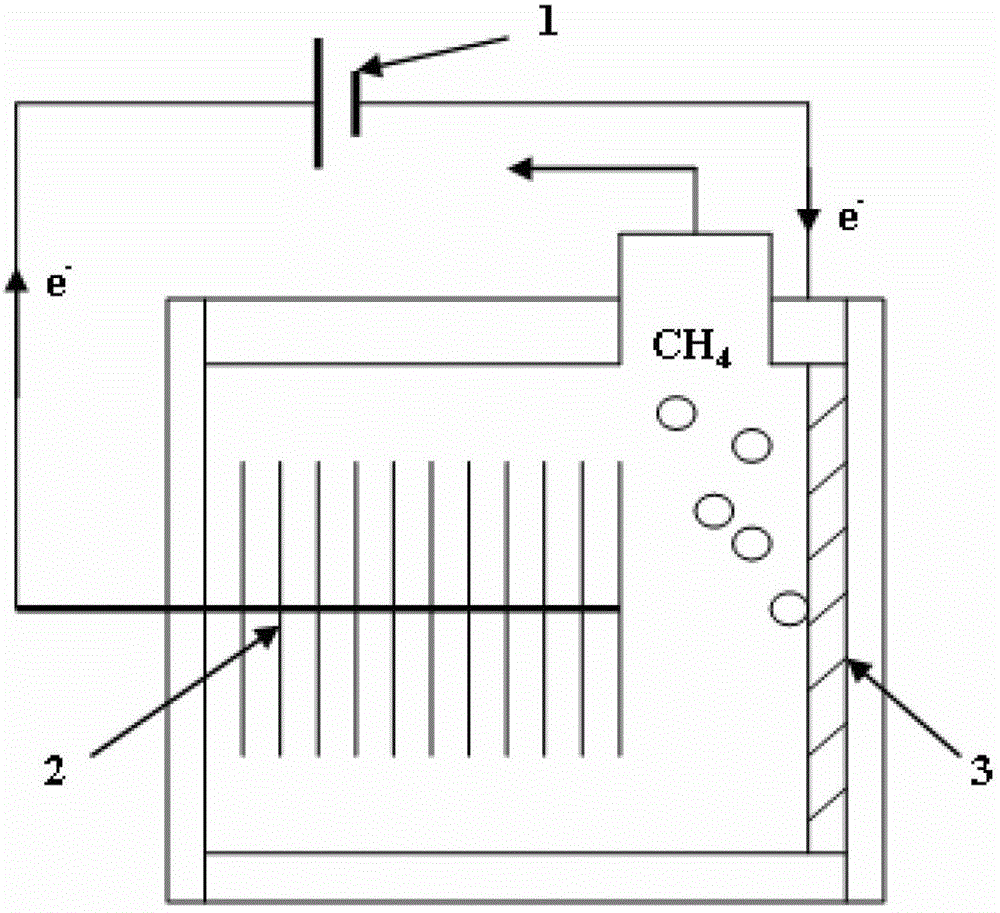
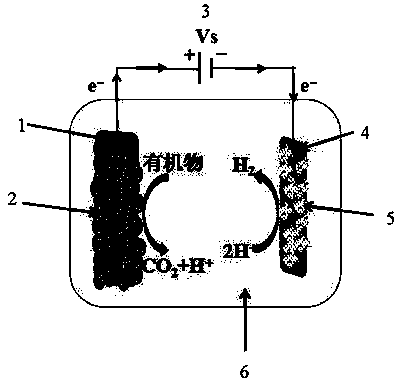
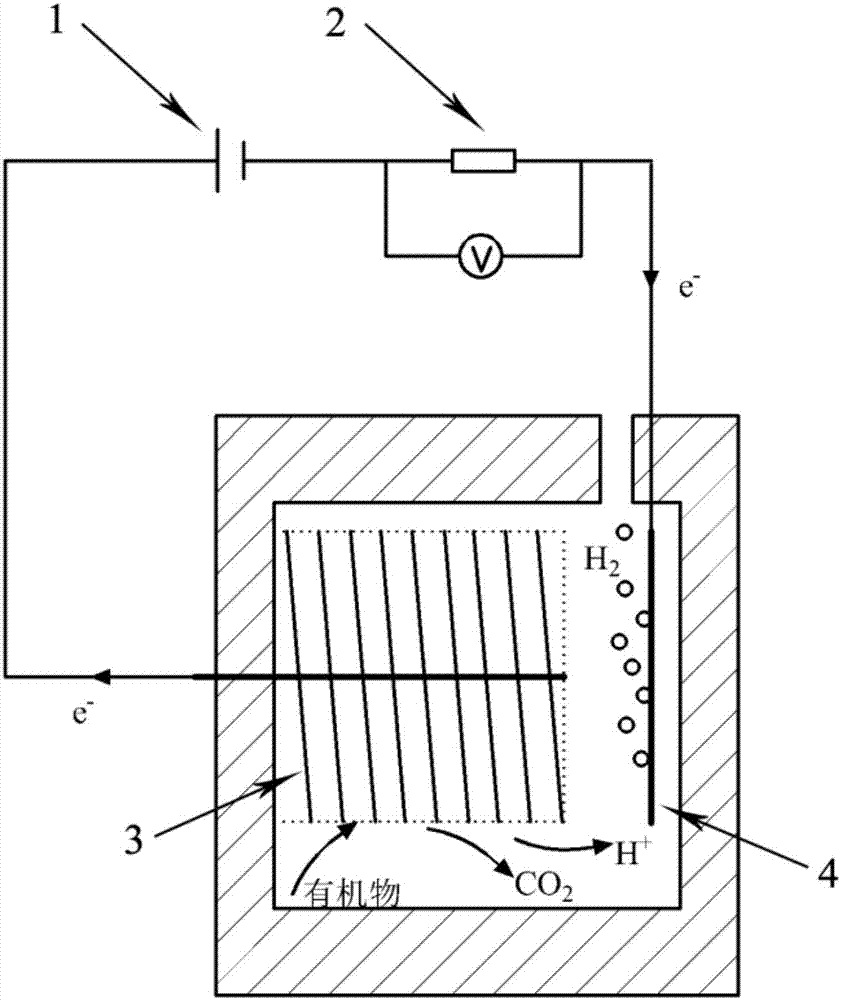
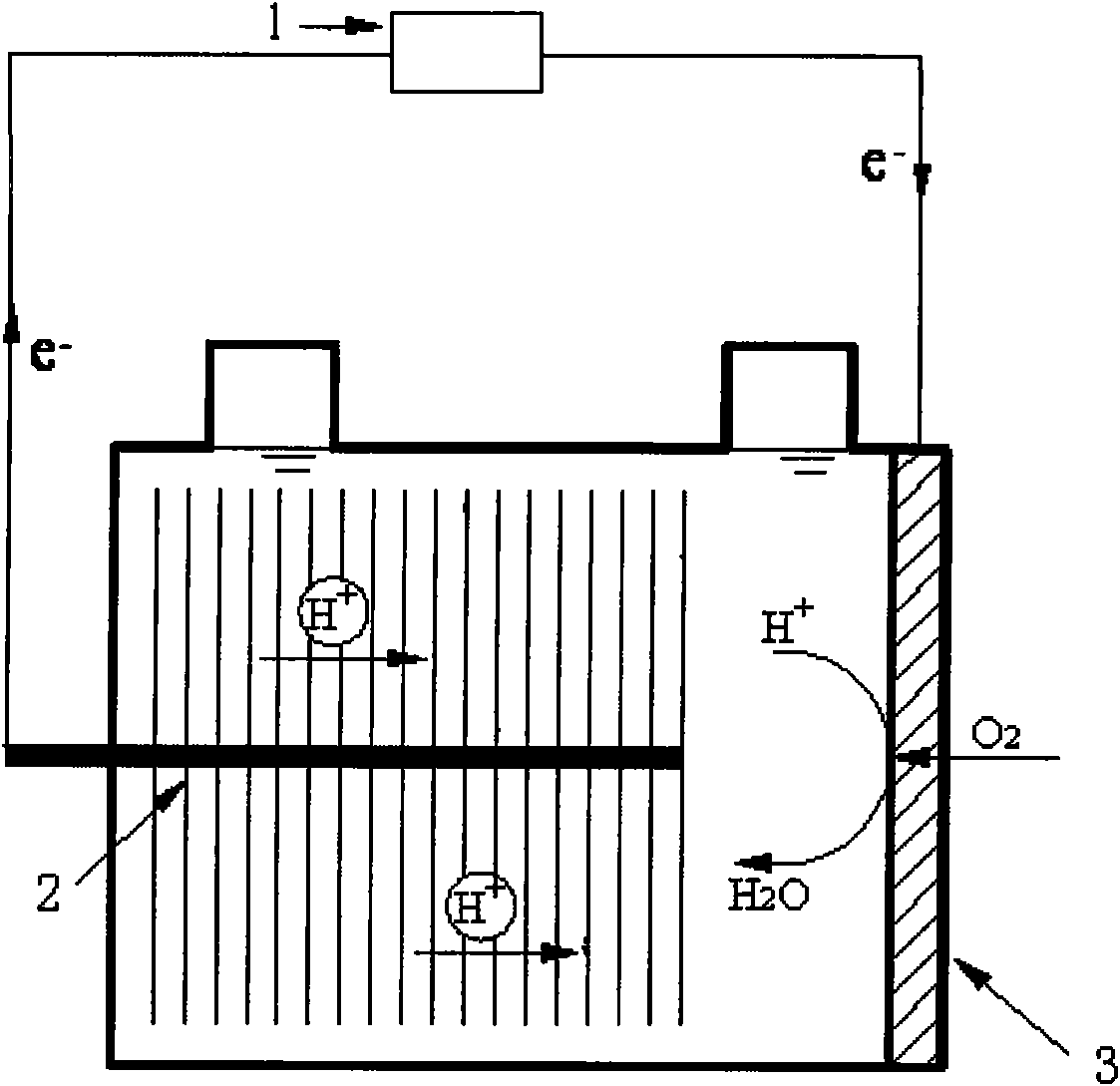
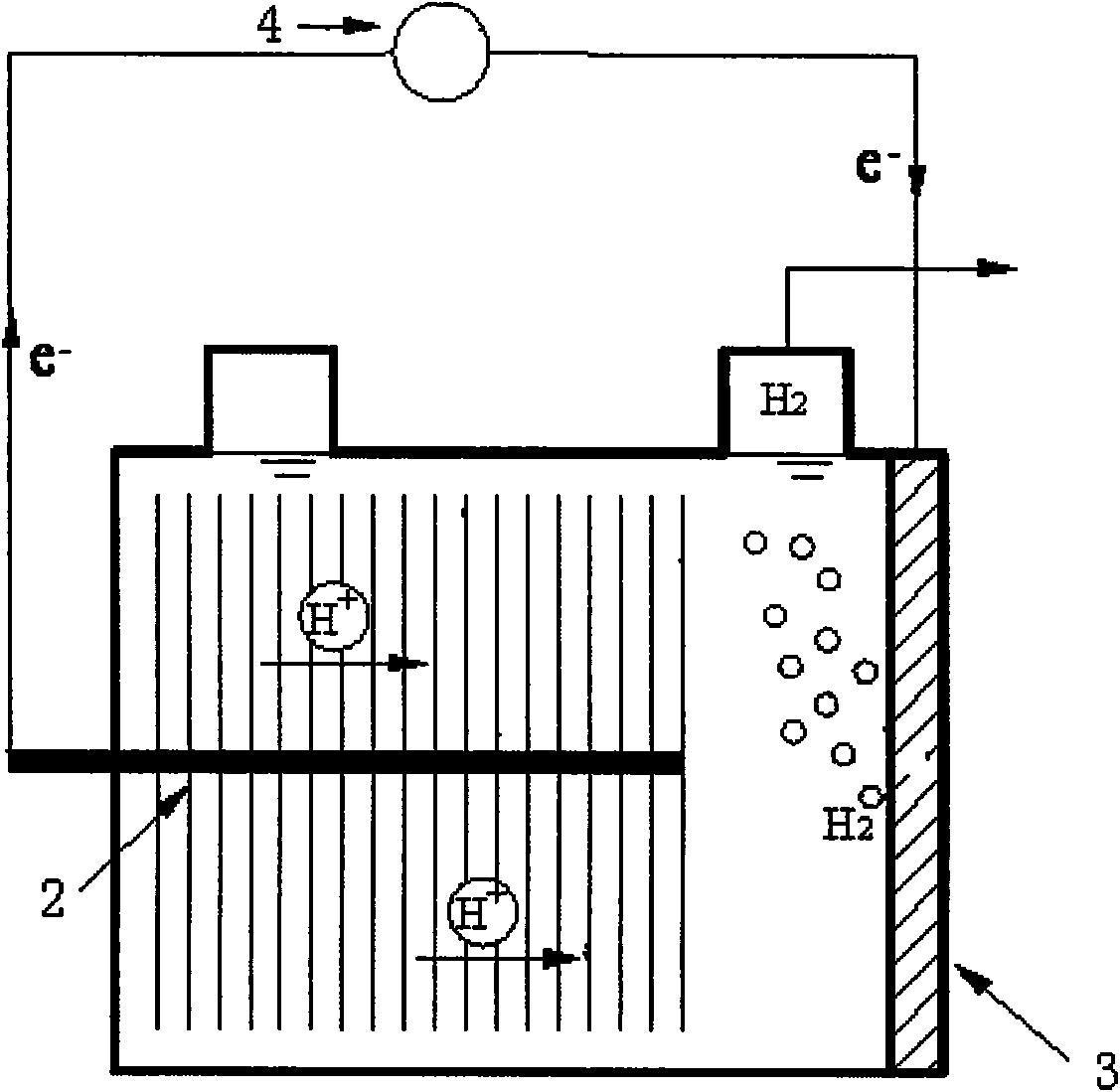
A microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) is a technology related to Microbial fuel cells (MFC). Whilst MFCs produce an electric current from the microbial decomposition of organic compounds, MECs partially reverse the process to generate hydrogen or methane from organic material by applying an electric current. The electric current would ideally be produced by a renewable source of power. The hydrogen or methane produced can be used to produce electricity by means of an additional PEM fuel cell or internal combustion engine.
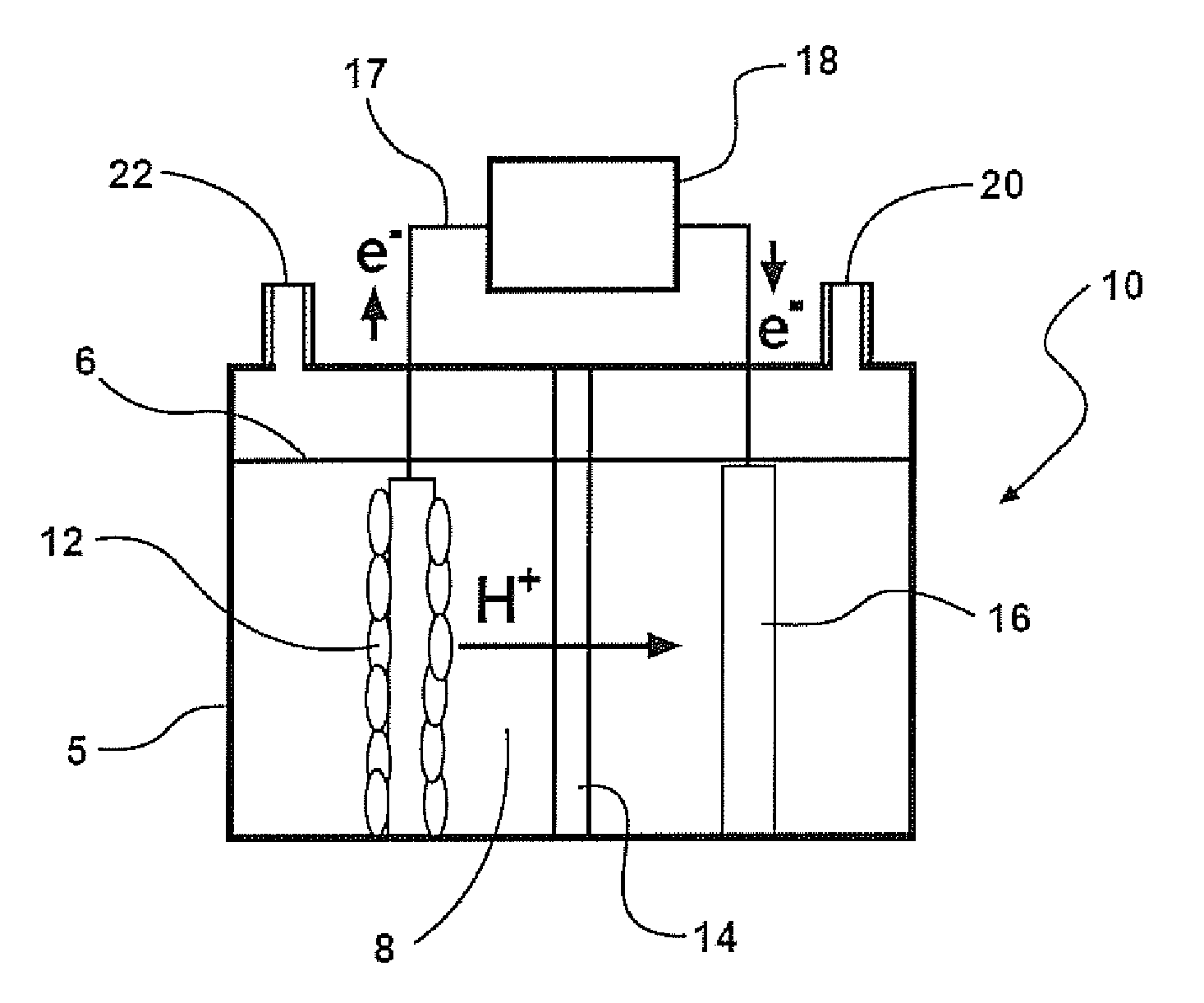
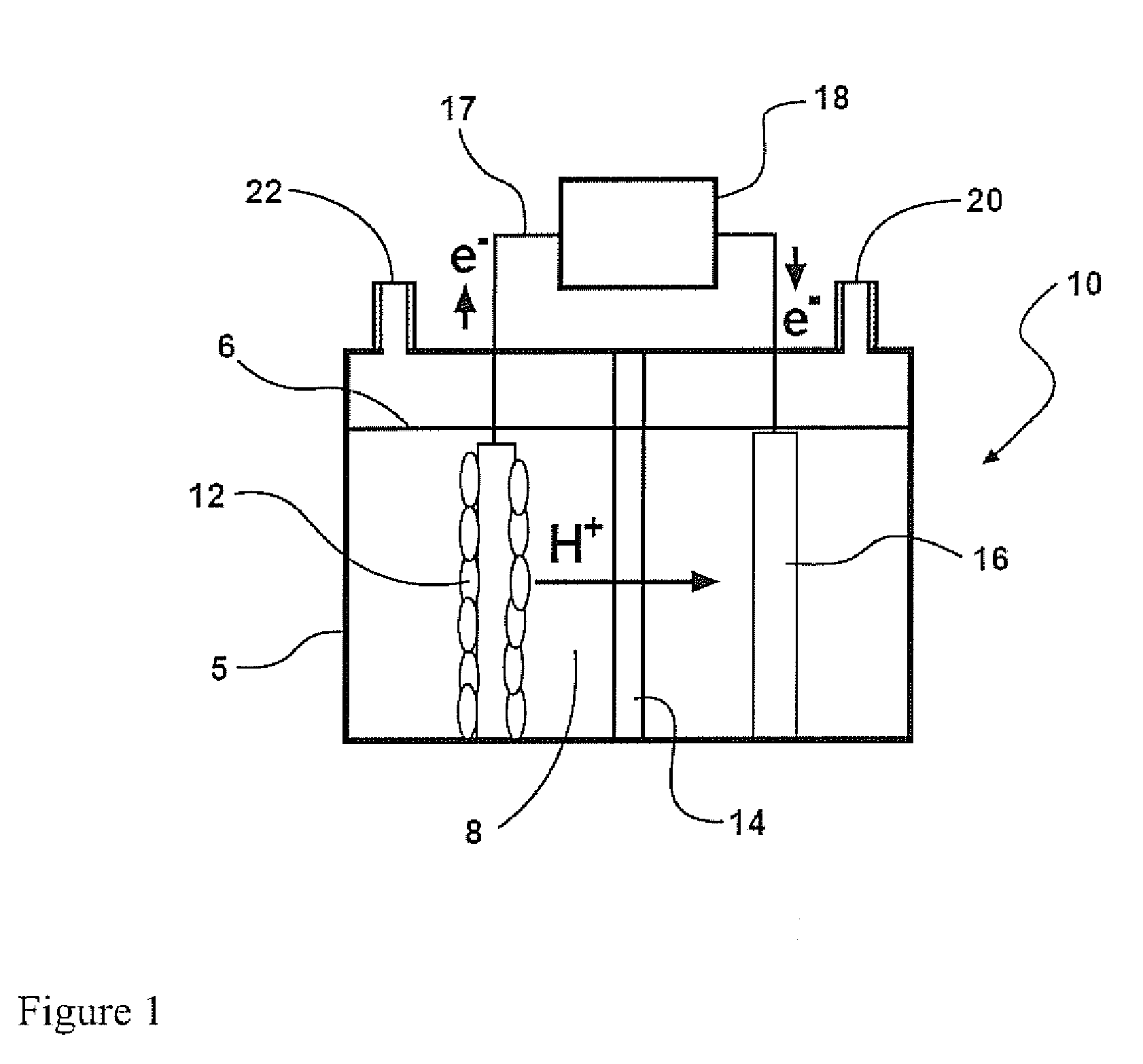
Cathodes for microbial electrolysis cells and microbial fuel cells
An apparatus is provided according to embodiments of the present invention which includes a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reaction chamber and an exterior of the reaction chamber; exoelectrogenic bacteria disposed in the interior of the reaction chamber; an aqueous medium having a pH in the range of 3-9, inclusive, the aqueous medium including an organic substrate oxidizable by exoelectrogenic bacteria and the medium disposed in the interior of the reaction chamber. An inventive apparatus further includes an anode at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber; and a brush or mesh cathode including stainless steel, nickel or titanium, the cathode at least partially contained within the interior of the reaction chamber.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
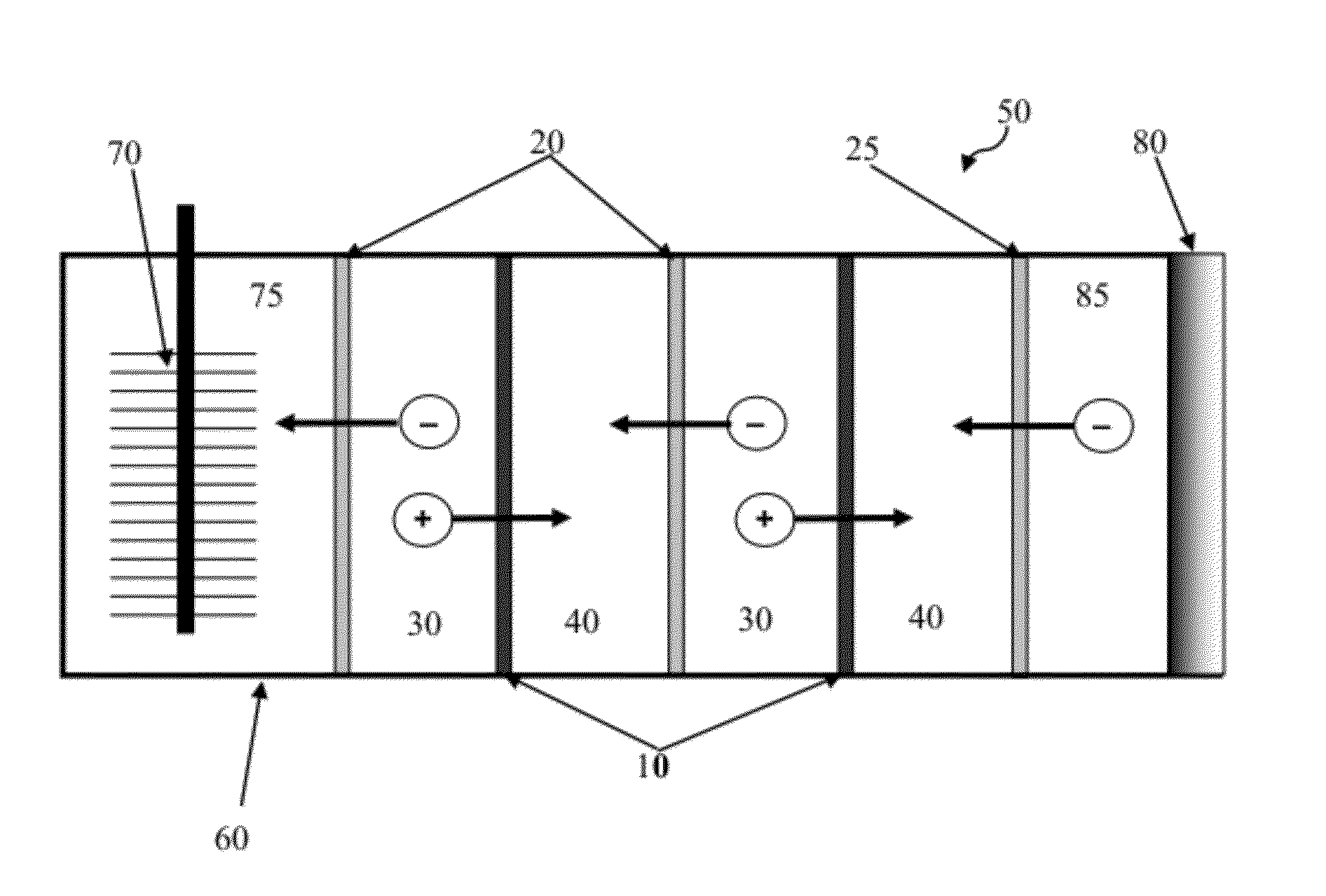
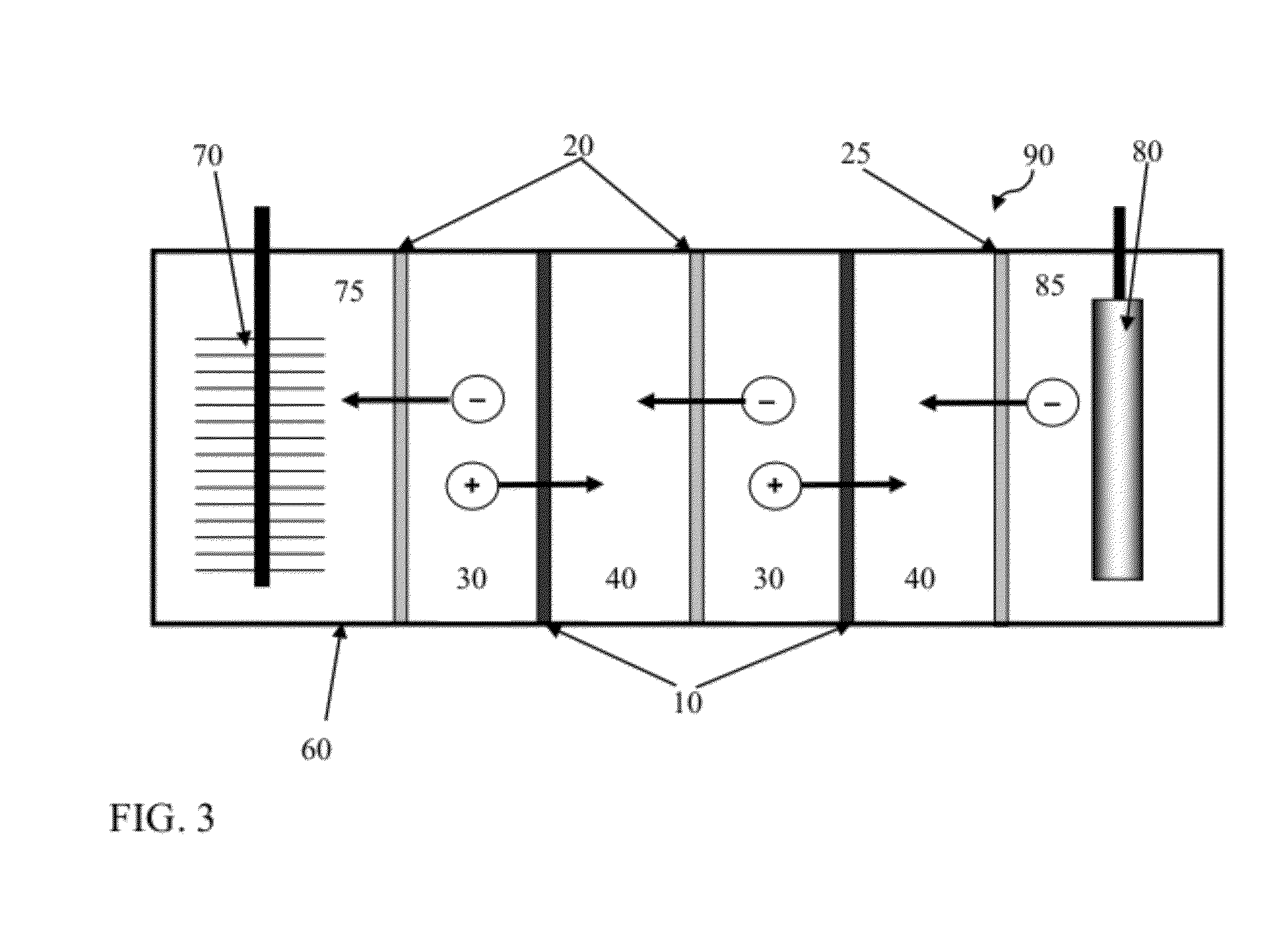
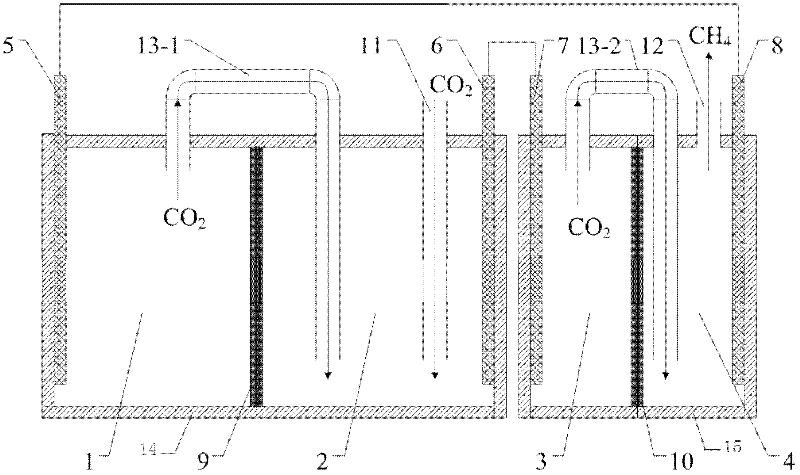
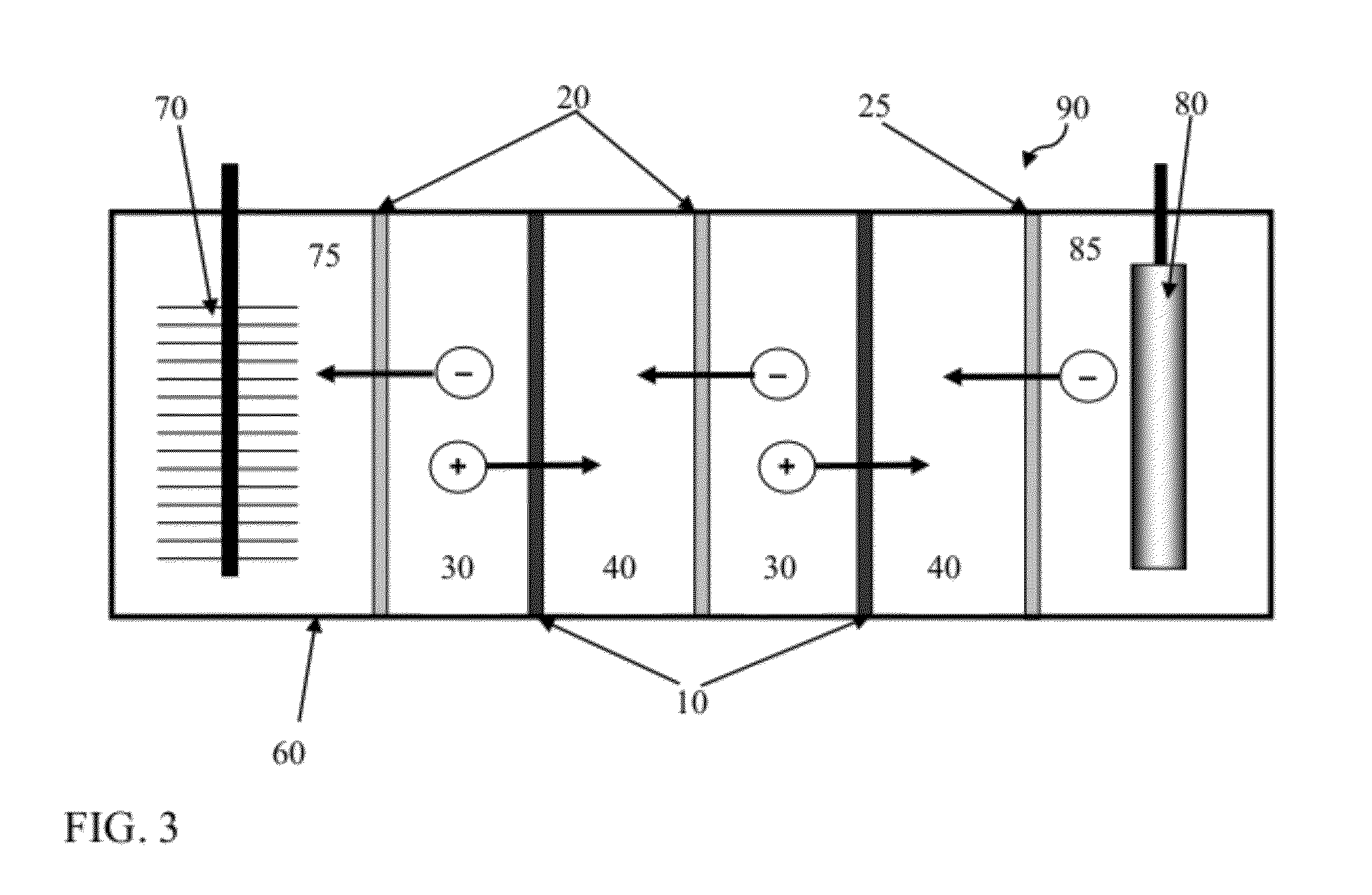
Reverse electrodialysis supported microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells
ActiveUS20120292187A1Raise the potentialSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrobiological ProcessesElectron
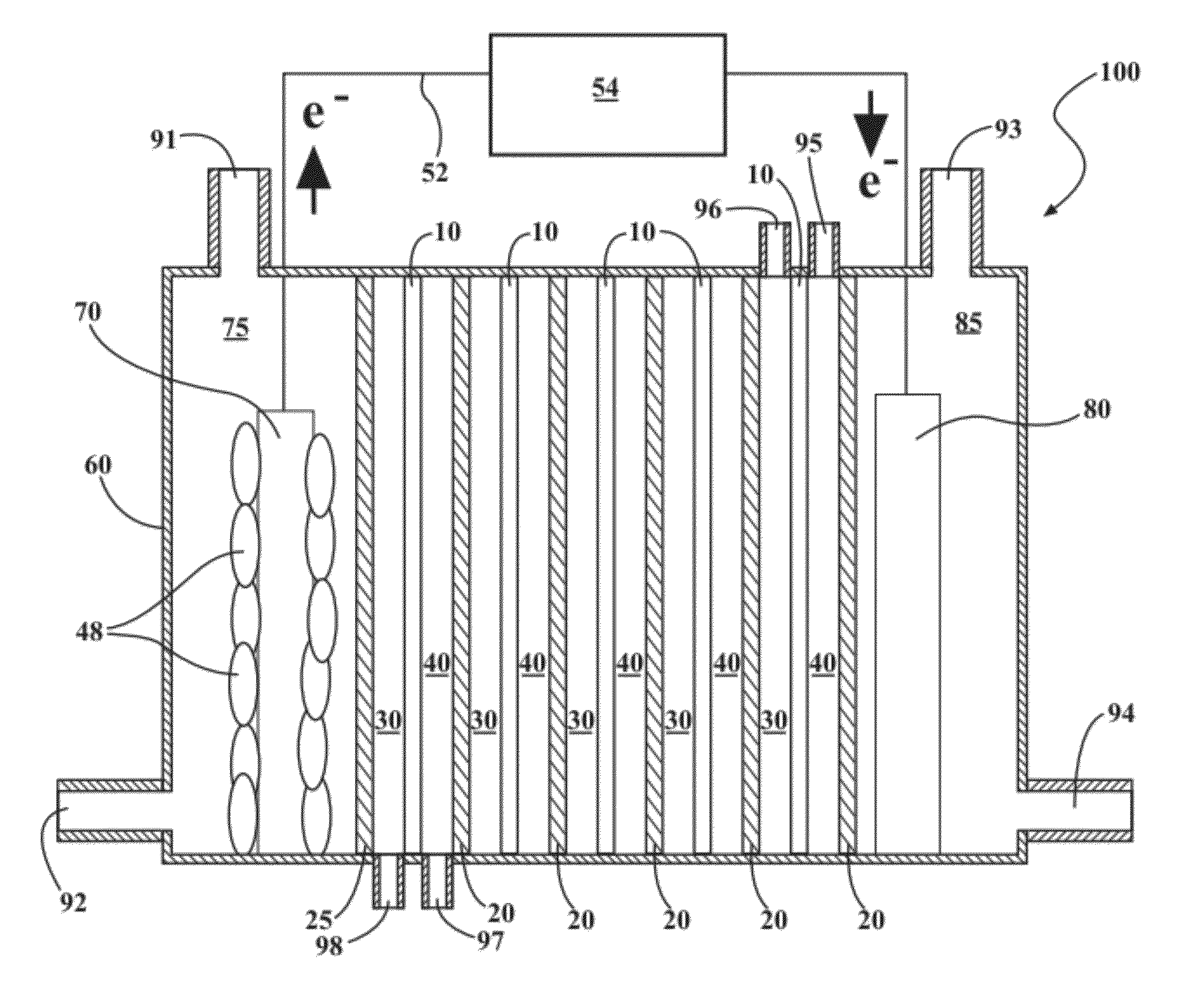
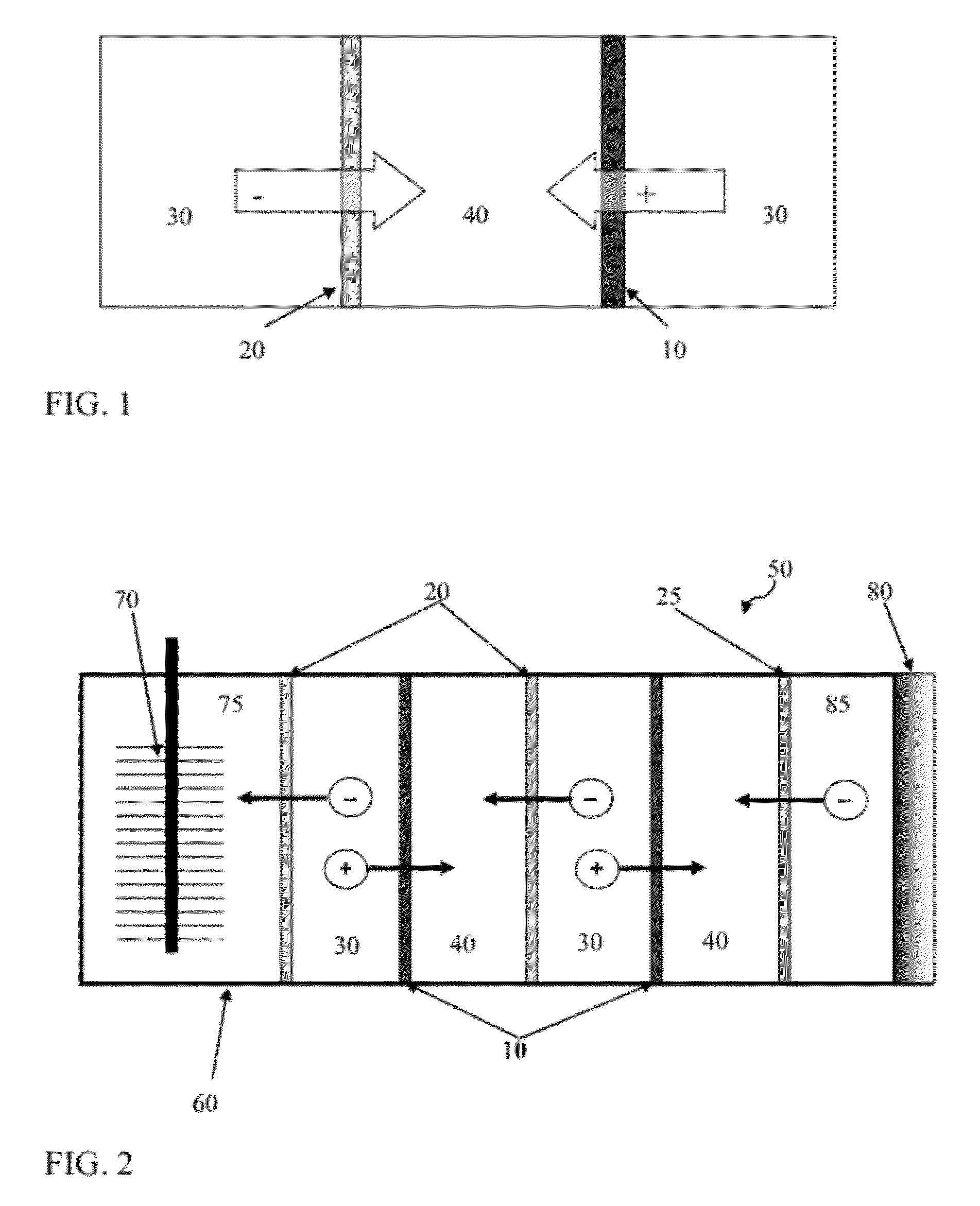
Systems and methods for microbial processes of generating products such as electrical power, hydrogen gas and methane, are provided according to aspects of the present invention which include a reaction chamber having a wall defining an interior of the reaction chamber and an exterior of the reaction chamber; an anode at least partially contained within an anode compartment of the reaction chamber; a plurality of exoelectrogenic microorganisms disposed in the anode compartment; a cathode at least partially contained within a cathode compartment of the reaction chamber; a conductive conduit for electrons in electrical communication with the anode and the cathode; and a reverse electrodialysis stack comprising a plurality of plurality of alternating anion selective barriers and cation selective barriers disposed between the anode and the cathode defining one or more saline material compartments and one or more lower-saline material compartments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
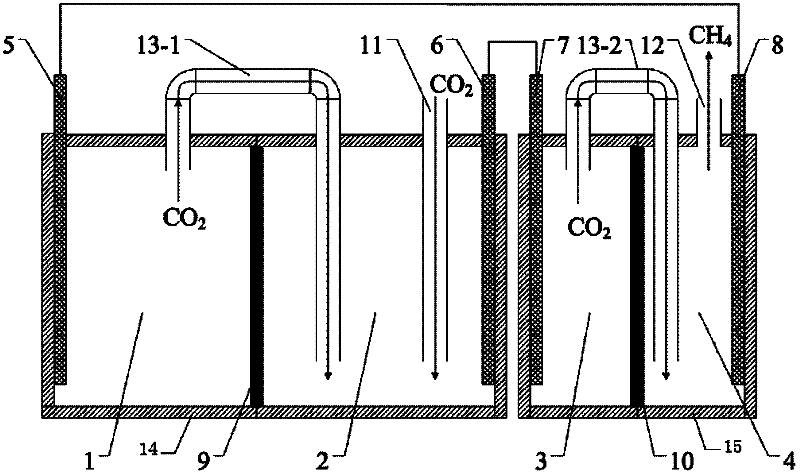
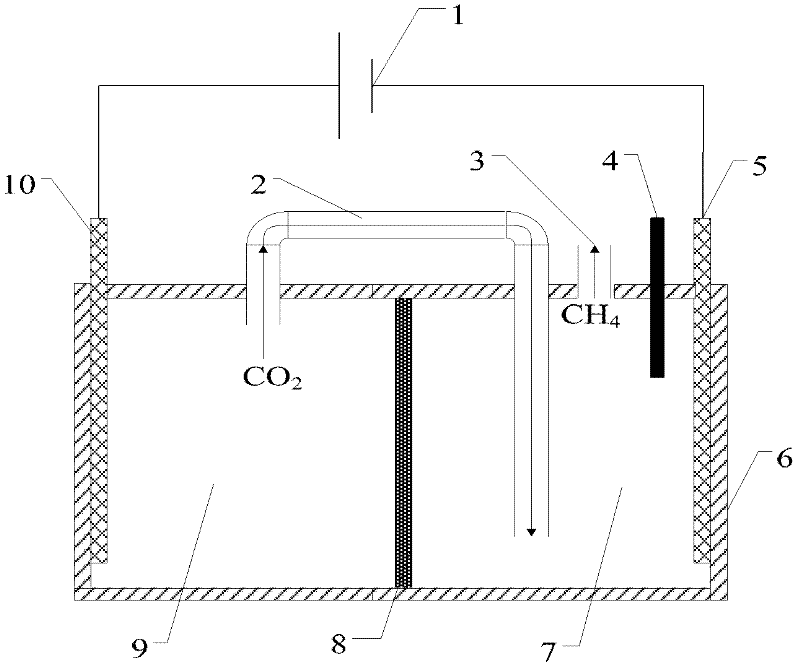
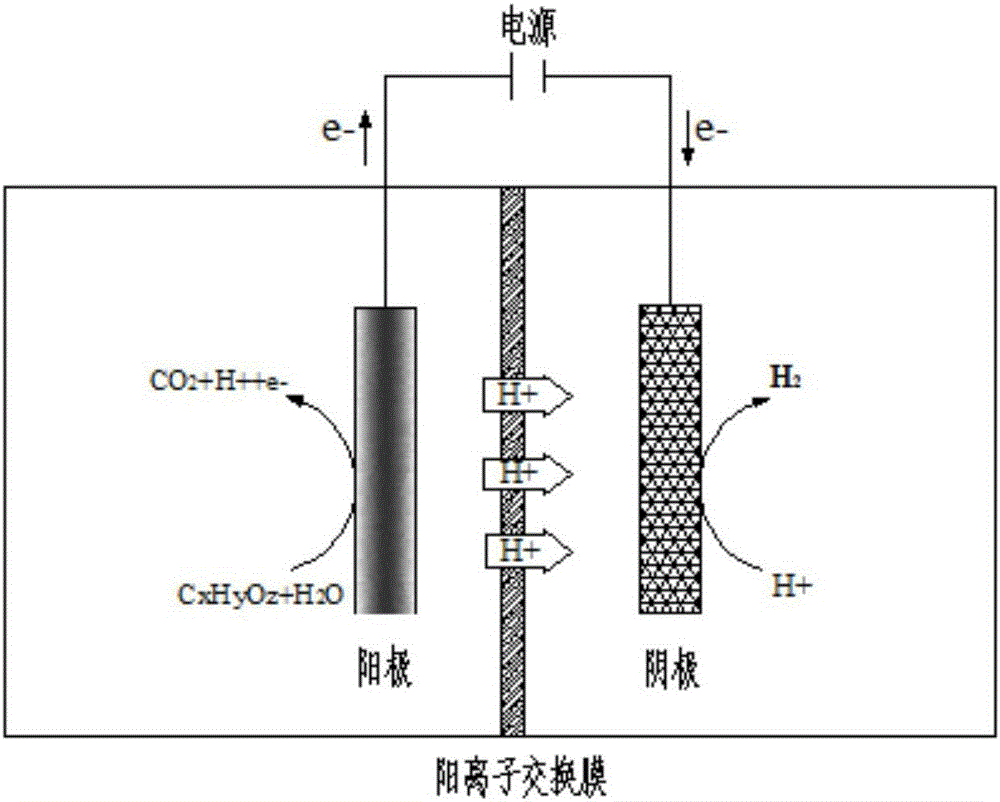
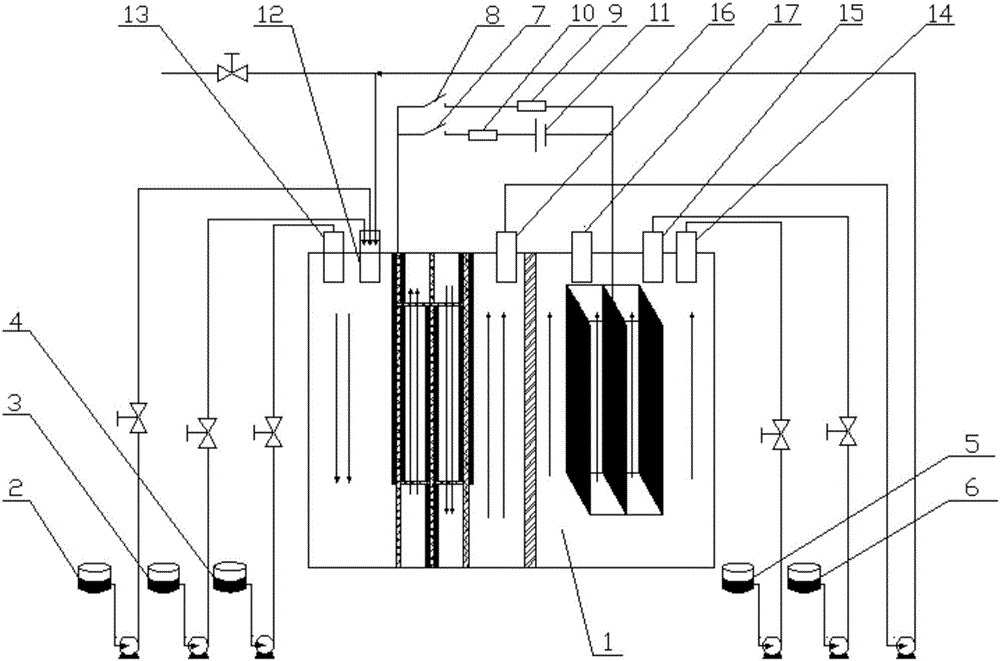
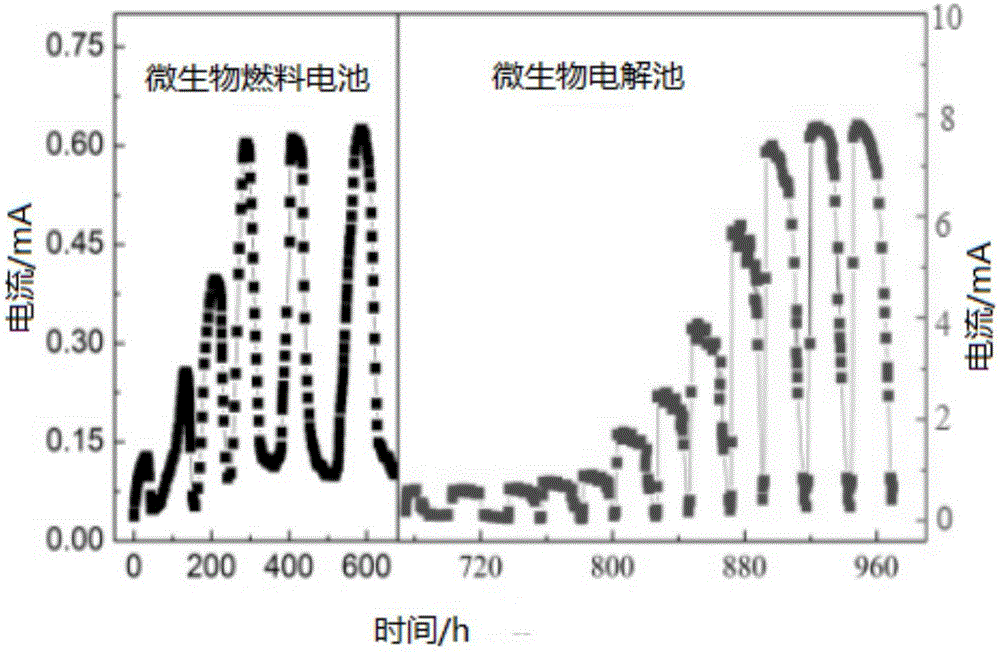
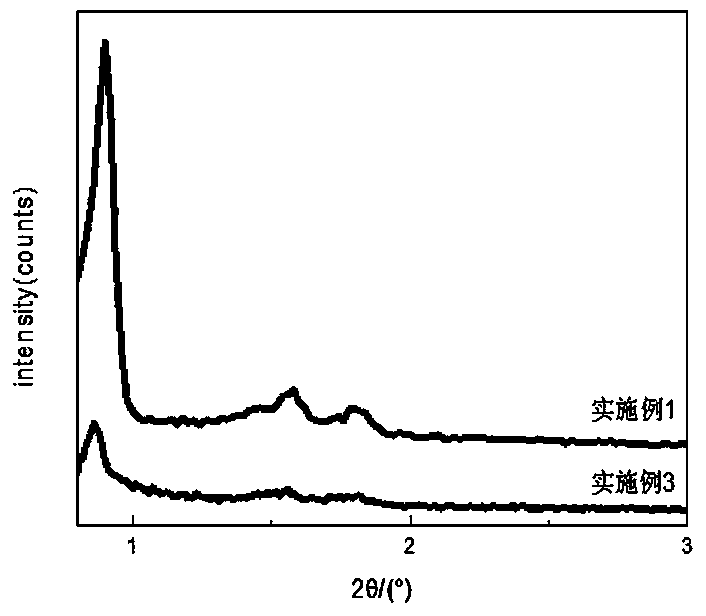
Microbial electrochemical CO2 capture system
InactiveCN102351310ARealize processingEasy to implementElectrolysis componentsChemical industryFuel cellsWastewater
The invention relates to a microbial electrochemical CO2 capture system. The system comprises a microbial fuel cell and a microbial electrolytic tank, wherein the microbial electrolytic tank comprises an electrolytic tank shell; an ion exchange membrane for dividing the electrolytic tank shell into an electrolytic tank anode chamber and an electrolytic tank cathode chamber is arranged in the electrolytic tank shell; an electrolytic tank anode electrode and an electrolytic tank cathode electrode which are connected with the microbial fuel cell are arranged in the electrolytic tank anode chamber and the electrolytic tank cathode chamber which accommodate sewage to be treated; the upper end of the electrolytic tank cathode chamber is provided with a gas outlet; and the electrolytic tank anode chamber is communicated with the electrolytic tank cathode chamber through an electrolytic tank gas guide tube. Sewage treatment is performed by taking organic wastewater as a microbial nutrient source; and the problems of sewage treatment, energy recovery and the like are solved while CO2 is captured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
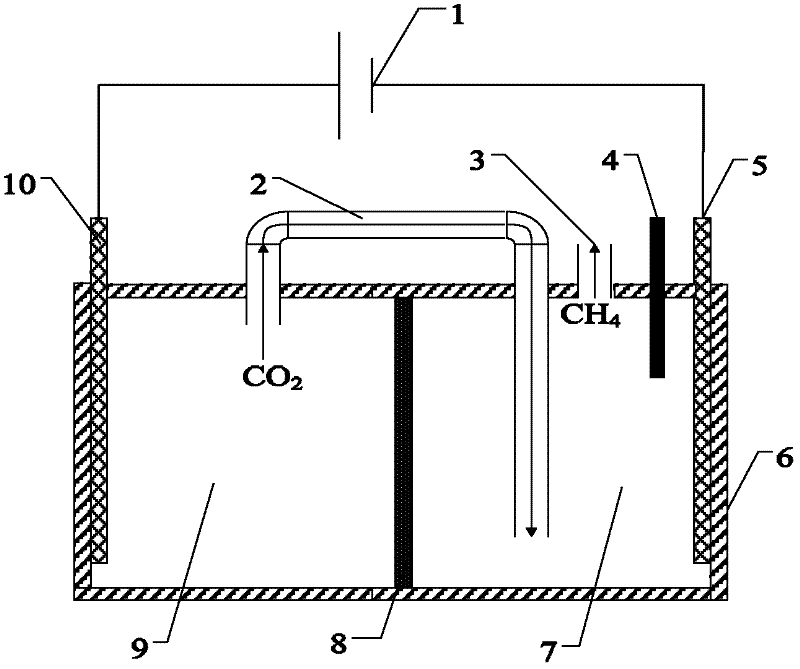
Microbial electrolysis cell integrating functions of CO2 conversion and sewage treatment
InactiveCN102408155AEasy to implementEasy to operateElectrolysis componentsWaste based fuelGuide tubeNutrient
The invention discloses a microbial electrolysis cell integrating functions of CO2 conversion and sewage treatment, which comprises a microbial electrolysis cell shell, the inside of the microbial electrolysis cell shell is provided with an anion / cation exchange membrane for dividing the microbial electrolysis cell shell into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, the insides of the anode chamber and the cathode chamber for accommodating to-be-treated sewage are respectively provided with an anode and a cathode which are connected with an external power supply, the inside of the cathode chamber is also provided with a reference electrode for controlling the electric potential of the cathode, the upper end of the cathode chamber is provided with a cathode product outlet, and the anode chamber is communicated with the cathode chamber by an air-guide tube. In the invention, sewage is fed into the anode chamber and used as a nutrient source for the growth of various microbes, and at room temperature, the microbes carry out catabolism on organic matters in the sewage so as to achieve a wastewater treatment process. In the CO2 capturing and conversion process, CO2 released by the anode is fed into the cathode chamber by the air-guide tube, then under the catalytic action of bacteria in the cathode chamber, an effect of CO2 capturing and an effect of converting the CO2 into CH4 are achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for promoting anaerobic digestion of residual activated sludge to generate methane by pretreatment combined electrochemical technology
InactiveCN105621826AImprove biodegradabilityAchieve reductionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSpecific water treatment objectivesHydrogenResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for promoting anaerobic digestion of residual activated sludge to generate methane by a pretreatment combined electrochemical technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) concentration treatment of sludge; 2) combined pretreatment of sludge: performing ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge and alkaline pretreatment to obtain pretreated sludge; and 3) microbial electrolysis cell coupling with anaerobic digestion of sludge to generate methane: feeding the sludge after the combined pretreatment into a MEC-AD coupling reactor and fermenting to generate methane. In the method, the pretreatment combined microbial electrolysis cell hydrogen generation technology is used for the first time, and the reduction and resource utilization of the sludge from a municipal sewage treatment plant are realized.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for producing hydrogen by alkalescent microbe electrolysis
InactiveCN102400169AInhibitionReduce methane contentWater/sewage treatmentEnergy based wastewater treatmentGeneration rateBatch operation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe electrochemistry and aims to provide a method for producing hydrogen by alkalescent microbe electrolysis. The method comprises steps of: (1) starting an electrolytic bath under a microbiological fuel cell mode: accessing a resistor in a closed-loop of a system and replacing a solution in the electrolytic bath when a voltage is low; continuing to replace until voltages at two ends of the resistor are higher than 500mV to finish anode starting; (2) producing hydrogen under a microbe electrolytic bath mode: replacing a cathode in the started electrolytic bath with stainless steel net or foamed nickel, keeping solution in the whole electrolytic bath in a anaerobic state and applying 0.4-0.8 V voltage at two ends of the cathode and the anode by using direct-current power supply and realizing hydrogen production of the electrolytic bath at 20-35 DEG C. The invention can effectively inhibit generation of methane, realize long time continuous operation or multiple batch operation and generate gas with low methane content; the method has a low cost and can obtain high hydrogen generation rate; utilization rate of organic matter under an alkalescent environment is increased, and hydrogen generation stability of the system is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hydrogen-producing microbial electrolytic cell and biological cathode domestication method
A biological cathode domestication method for a biological cathode-type hydrogen-producing microbial electrolytic cell is provided by the invention, and is characterized by comprising: A) culturing an anode electrogenic microbial population under a microbial fuel cell mode; B) domesticating an anode hydrogen-consuming microbial population under a microbial electrolytic cell hydrogen-producing mode; C) carrying out domestication culturing of a cathode hydrogen-producing microbe under a three-electrode mode. On the basis of a further aspect of the invention, a biological cathode-type microbial electrolytic cell (400) is formed by combination of the biological anode obtained by the step A) and the biological cathode obtained by domestication culturing in the step C). The invention also provides the biological cathode-type hydrogen-producing microbial electrolytic cell, and the microbial electrolytic cell comprises the biological anode obtained by the step A) and the biological cathode obtained by domestication culturing in the step C).
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
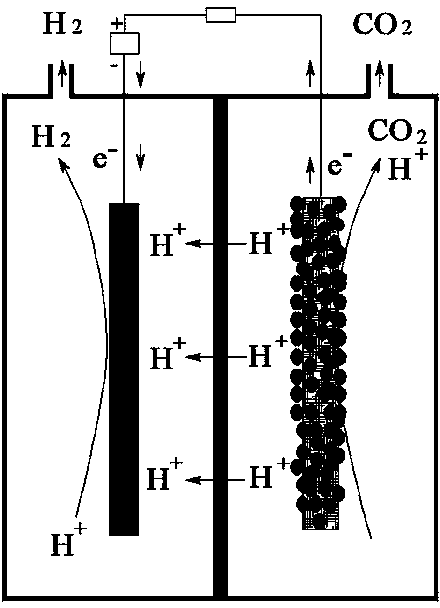
Method of preparing methanol by sewage treatment and carbon dioxide reduction
InactiveCN103922487ASolve the problem of energy consumptionSolve efficiency problemsElectrolysis componentsMicroorganism based processesElectronEnergy conservation
The invention provides a method of preparing methanol by sewage treatment and carbon dioxide reduction by means of a microbial electrolytic tank. The method comprises the following steps: after removing oxygen in organic sewage, injecting the organic sewage into the microbial electrolytic tank as a nutritional source for growing anode electrogenesis microorganisms which disassimilate organic matters in sewage to generate CO2, H+ and electrons; under the effect of an electronic assistant and cathode biocatalyst, reducing the generated H+ and electrons as well as CO2 on the surface of the cathode to methanol. The method provided by the invention is free from expensive catalysts, low in cost and low in energy consumption, and the speed of treating the organic sewage and generating methanol by reducing carbon dioxide is relatively high, so that the problems that conventional organic sewage bio-treatment is high in energy consumption and conventional electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to prepare methanol is high in energy consumption and low in efficiency of a cathode catalyst are solved, thereby providing a novel path to resourceful utilization of the organic sewage and carbon dioxide. The method is of important meanings to energy conservation and emission reduction and environmental management.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Microbial electrochemical apparatus and method for restoring nitrate-polluted underground water
ActiveCN104377378APromote enrichmentImprove removal efficiencyFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesGroundwater nitrateEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of environment protection, and especially relates to a microbial electrochemical apparatus and a method for in-situ restoring of nitrate-polluted underground water. The apparatus is composed of an electrode restoration system, an electrode control system, an electrode liquid circulating system and a temperature control / adjusting system; through the electrode control system, the electrode restoration system is capable of intermittently at a microbe electrolysis cell state (MEC), a microbe fuel cell state (MFC) and an open-circuit state; through the electrode liquid circulating system, an electrolyte is controlled to be circulated between a cathode chamber and an anode chamber and is continuously updated; and the temperature control / adjusting system is capable of controlling the temperature of the electrode in the two electrode chambers and promoting metabolism of microbes. The advantages comprise that by employing in-situ restoration for underground water, underground water does not need pumping out, the restoration efficiency is high, the energy utilization rate is high, secondary pollution does not exist, the restoration apparatus is strong in adaptability, the restoration apparatus and the restoration process are simple, and industrial production and operation are facilitated.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
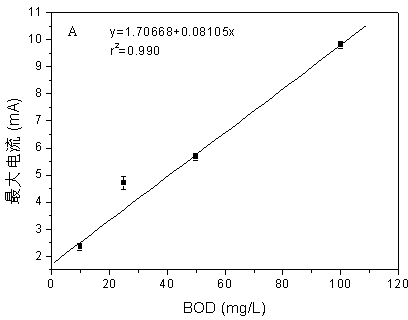
Device and method for quickly measuring BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) based on microbial electrolysis cell technology
InactiveCN103364469AImprove stabilityLow maintenanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData acquisitionBiology
The invention discloses a device and method for quickly measuring a BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) based on a microbial electrolysis cell technology. The device adopts a microbial electrolysis cell structure and comprises a microbial electrolysis cell, a data acquisition system and a record cell, wherein the microbial electrolysis cell takes conductive inert materials as an anode electrode and a cathode electrode which are connected with each other through a titanium wire, a potentiostat and a resistor; the data acquisition system is connected in parallel with the resistor; the record cell is connected with the data acquisition system. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a BOD contained sample into the microbial electrolysis cell; measuring electrochemical signals generated by the microbial electrolysis cell; and determining the BOD of the sample according to the relation between the BOD concentration and the size of the electrochemical signals (indicating the maximum current and coulomb quantity) generated by the microbial electrolysis cell. The device and the method have the advantages of high sensitivity, wide linearity range, short detection time, and the like, can be used for measuring the BOD of sewage in an on-line or off-line manner.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
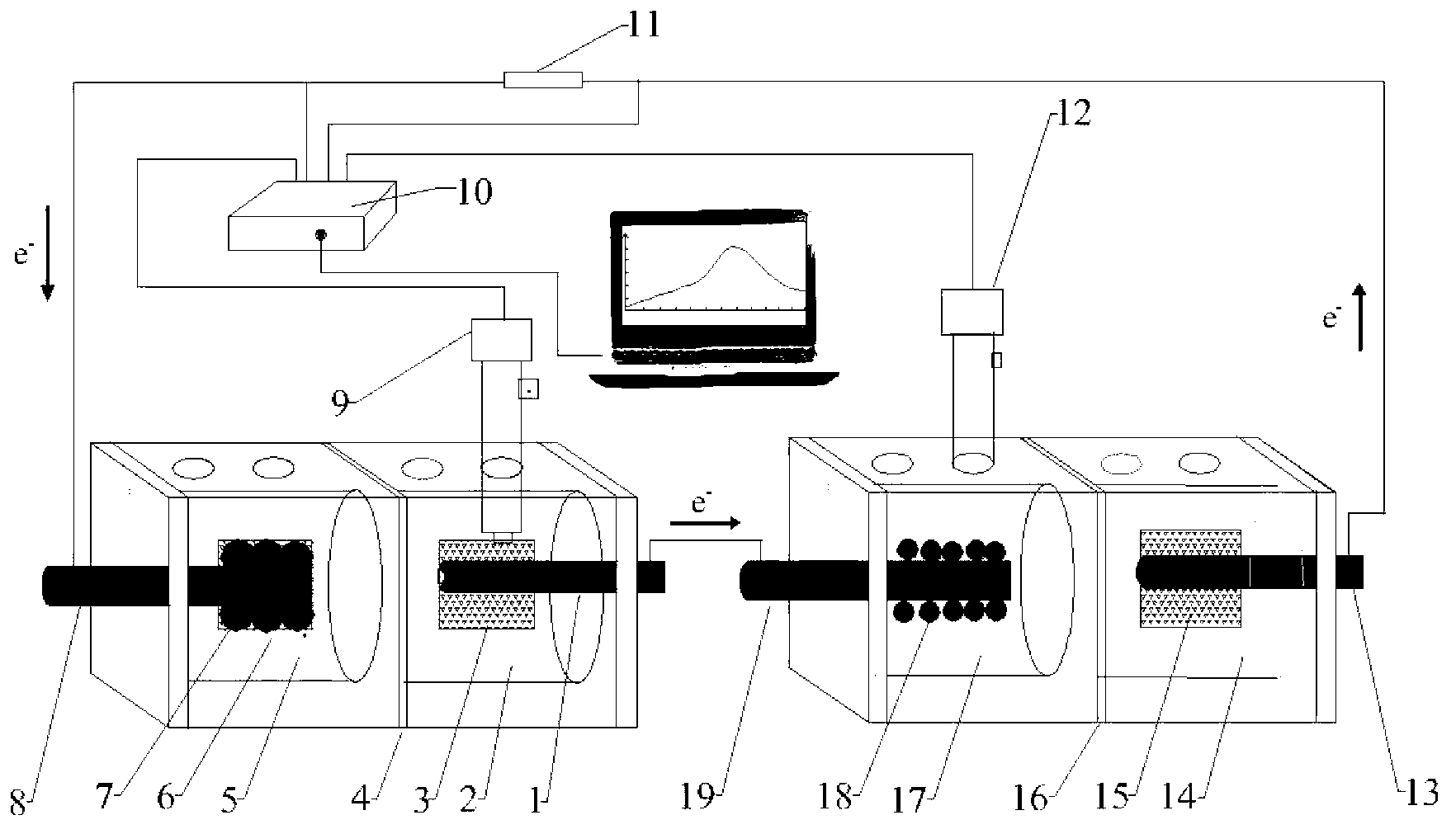
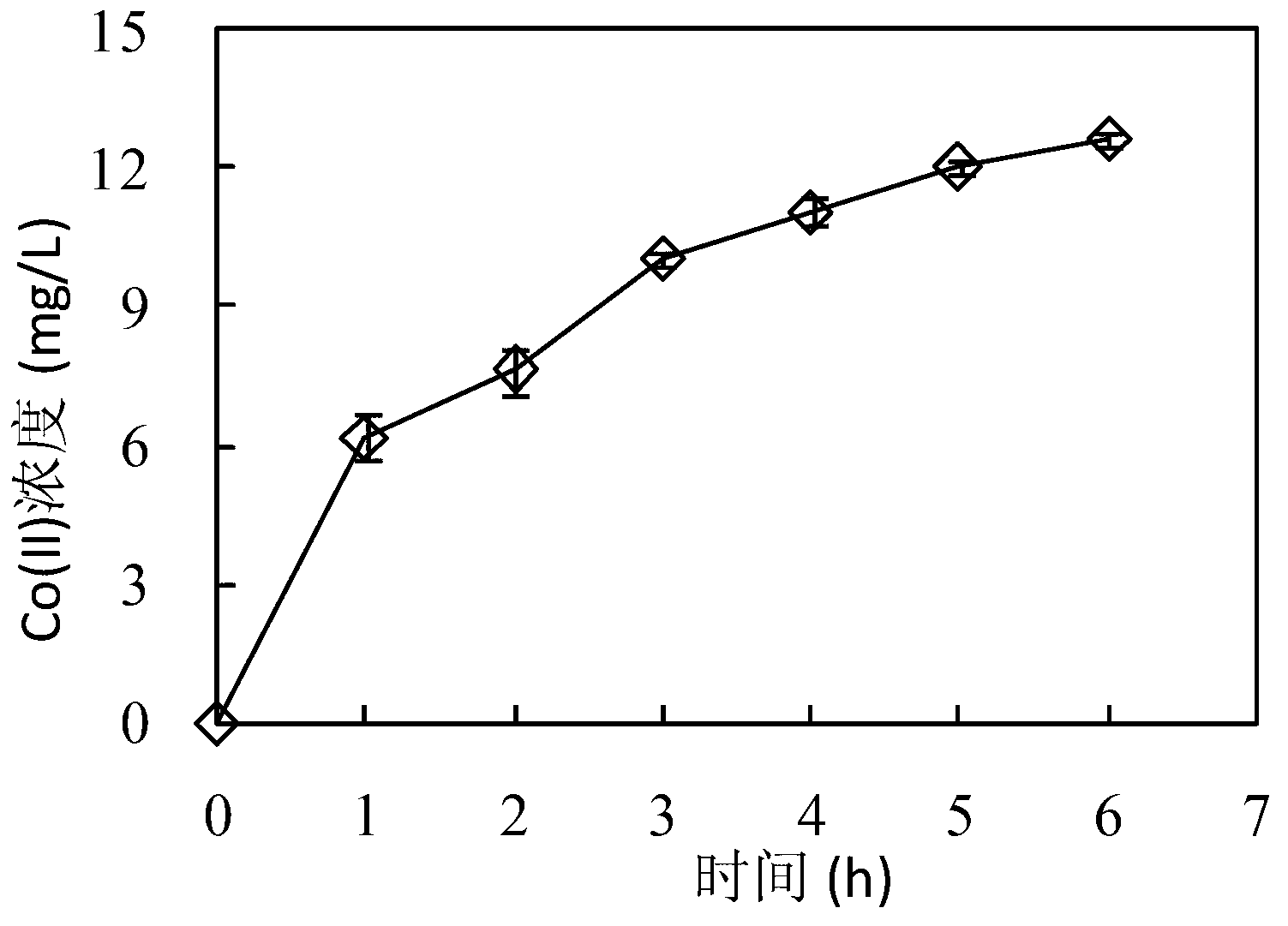
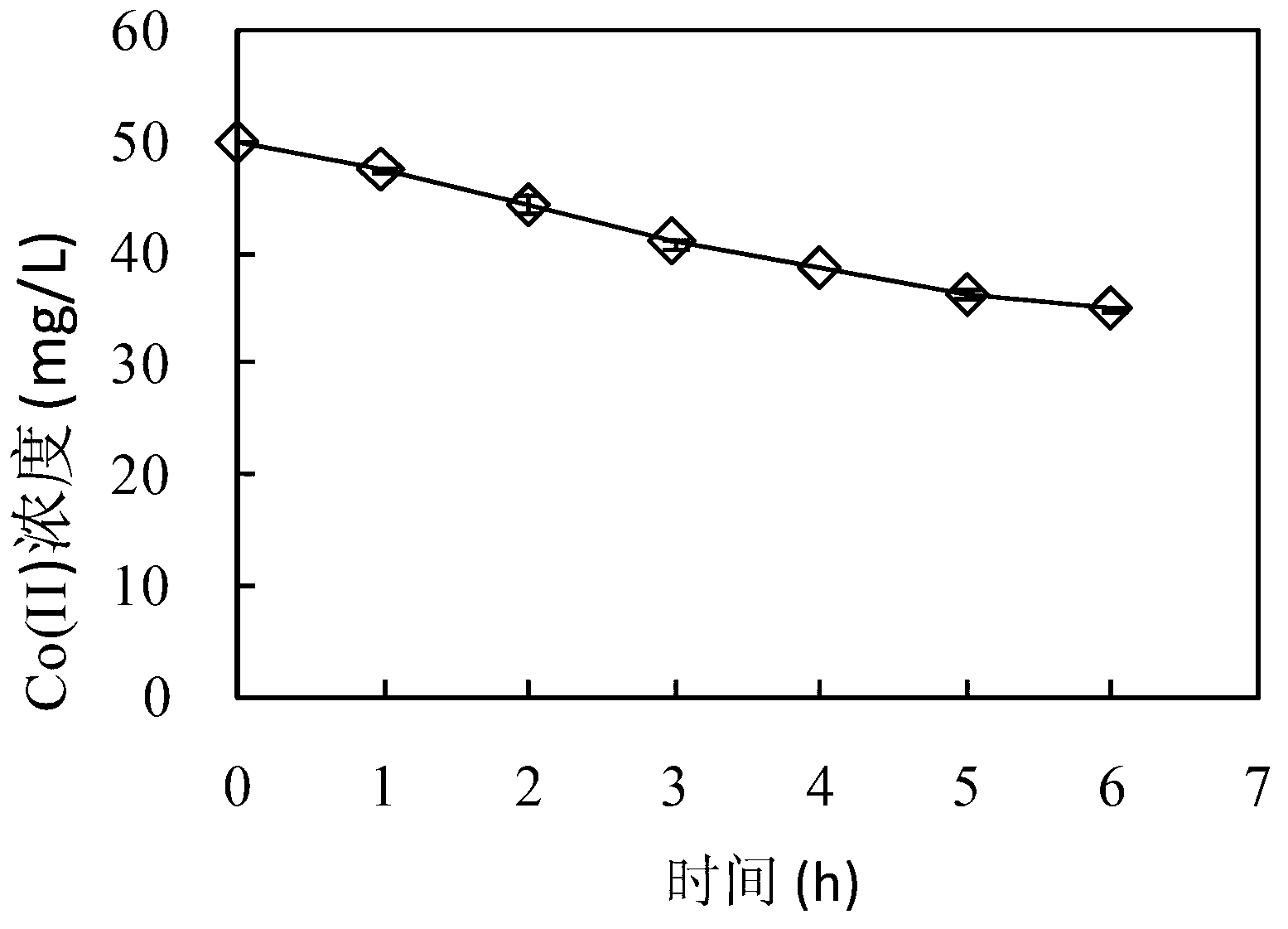
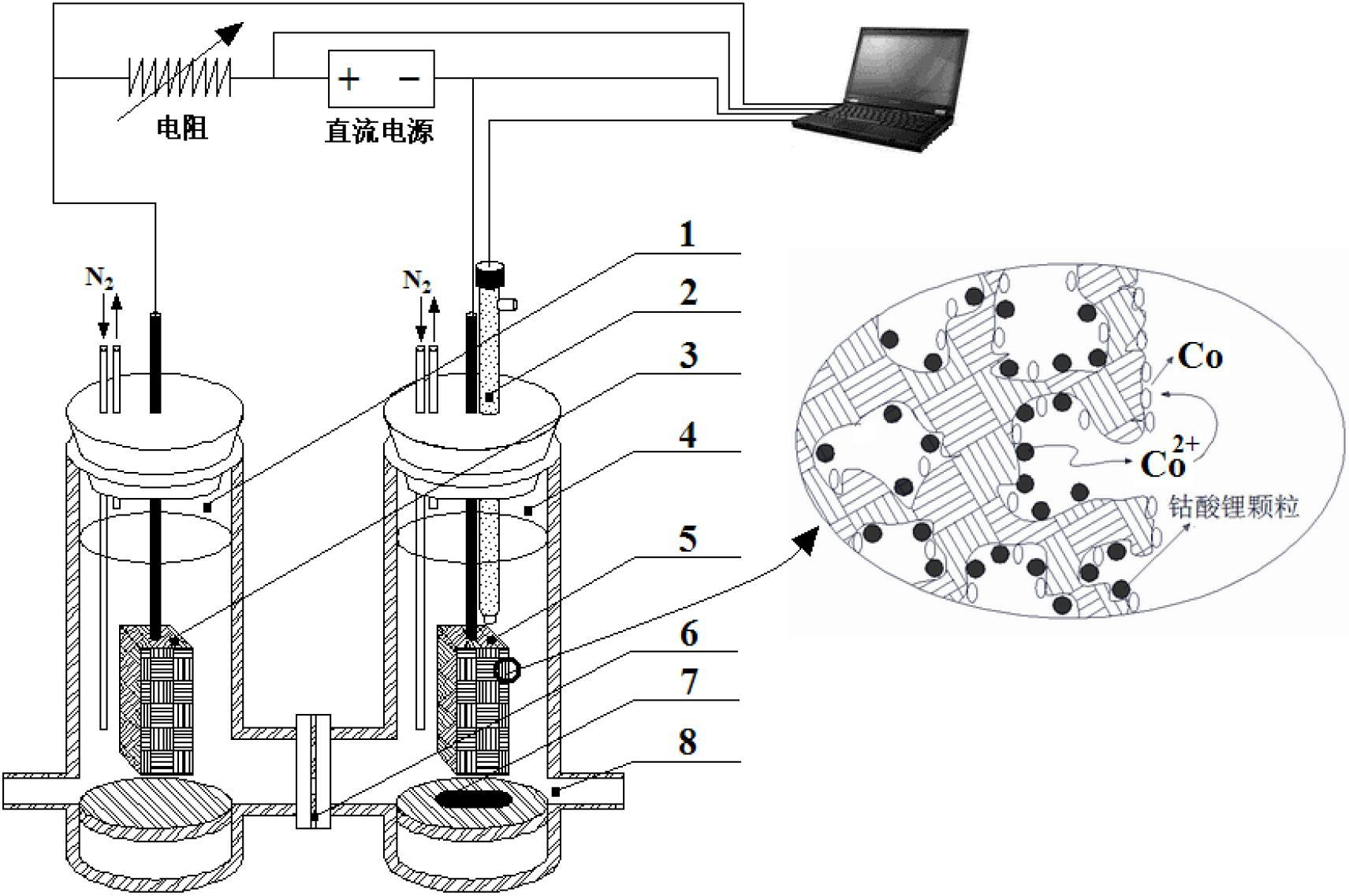
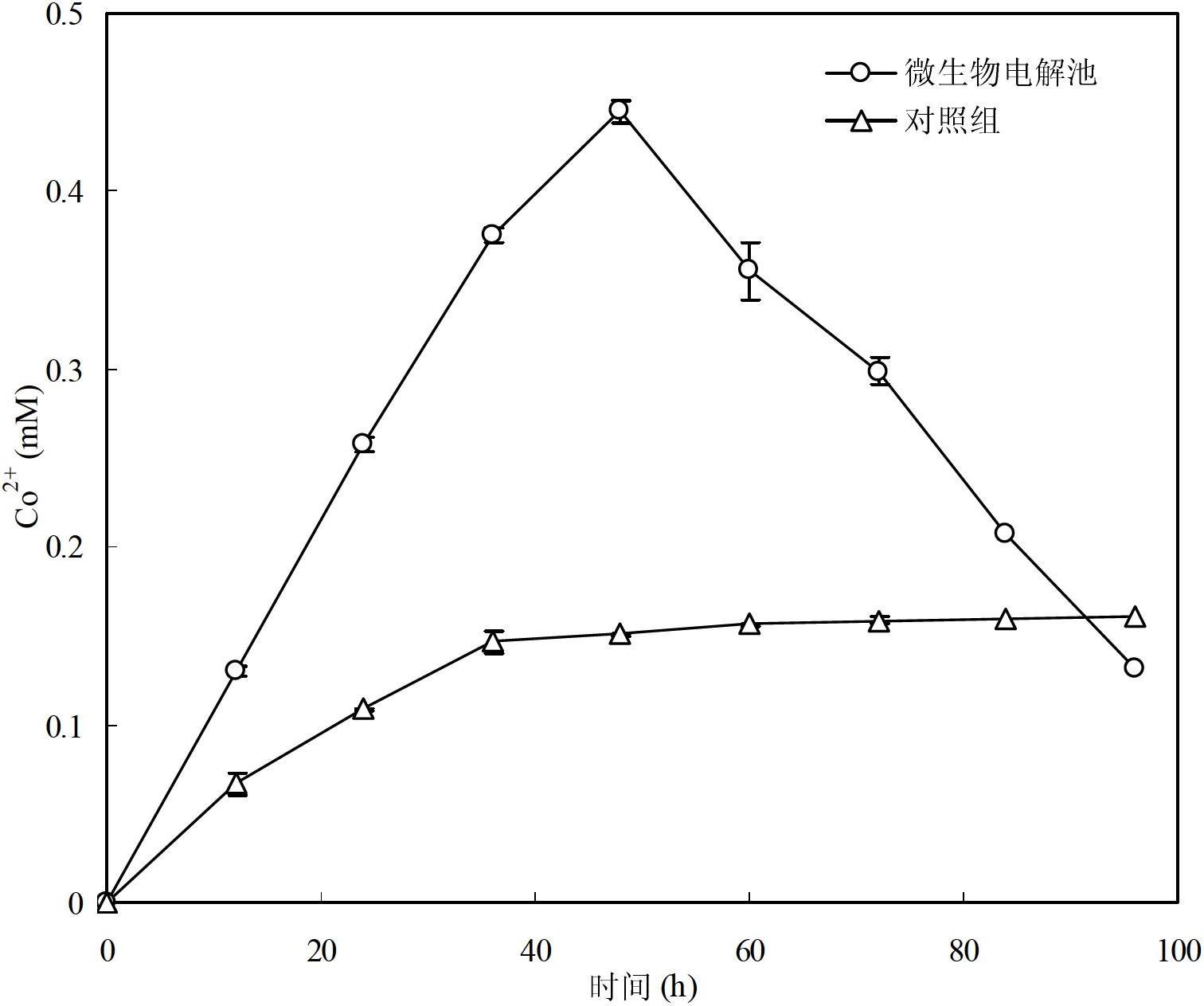
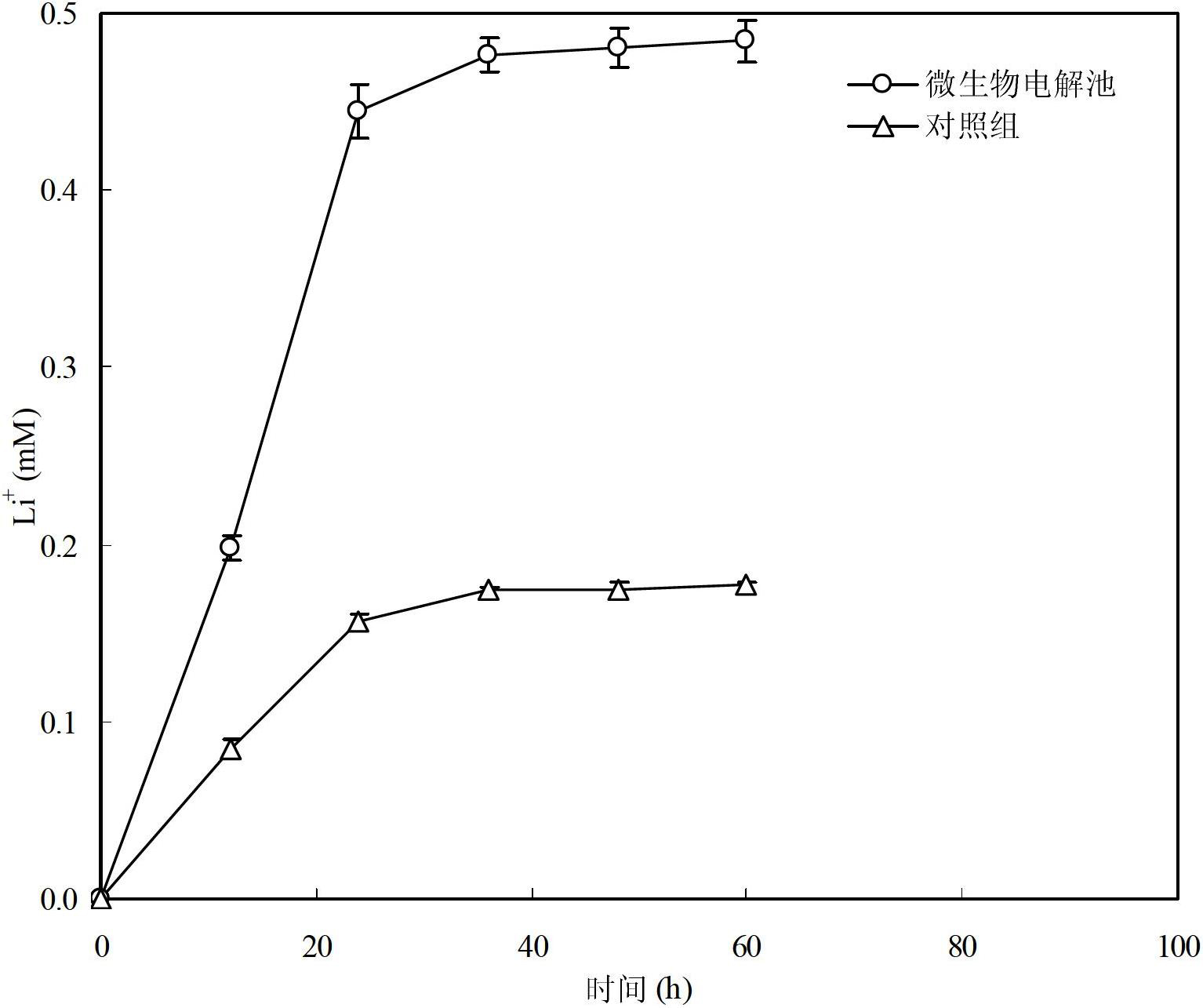
Method for recovery of elemental cobalt from lithium cobaltate by microbial fuel cell (MFC) self-driven microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) coupled system
The invention discloses a method for recovery of elemental cobalt from lithium cobaltate by a microbial fuel cell (MFC) self-driven microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) coupled system. The method is characterized in that an MFC anode is directly connected to an MEC cathode; an MFC cathode is connected to an MEC anode by a resistance; an MFC cathode chamber is filled with a cathode liquid and lithium cobaltate particles; an MFC anode chamber is inoculated with sludge as an electrochemical activity microbe source in a clarification pool of a sewage treatment plant, an MEC cathode chamber is filled with a Co(II)-containing aqueous solution; an MEC anode chamber is inoculated with the sludge as an electrochemical activity microbe source in a clarification pool of a sewage treatment plant; and anode and cathode materials are graphite materials. The method provides an effective approach for in-situ utilization of MFC output electric energy and provides a wide space for extra electric energy input-free and cathode liquid acidity limit-free MEC application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system
ActiveCN105906051AEfficient couplingAccelerate reaction mass transfer efficiencyTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsSmall footprintElectrochemistry
The invention discloses an electrochemical microorganism autotrophic nitrogen removal sewage treatment method and system. The system comprises a microorganism electrolytic tank shell, a sealed cover, a microorganism positive electrode, a microorganism negative electrode and a power supply, wherein the sealed cover covers the microorganism electrolytic tank shell to form a closed space; the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode are connected with a negative electrode and a positive electrode of the power supply respectively, a short-distance nitrification microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism positive electrode, and denitrification methane anaerobic oxidation microorganisms are enriched on the microorganism negative electrode; the side, close to the microorganism positive electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water inlet, and the side, close to the microorganism negative electrode, of the microorganism electrolytic tank shell is provided with a water outlet. An inorganic carbon source put-in opening is formed in the position, close to the microorganism negative electrode, between the microorganism positive electrode and the microorganism negative electrode. By means of one electrolytic tank, short-distance nitrification, electrochemical methane production and methane anaerobic oxidation are effectively coupled, reaction mass transfer efficiency is accelerated, occupied area is small, and capital construction investment is small.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
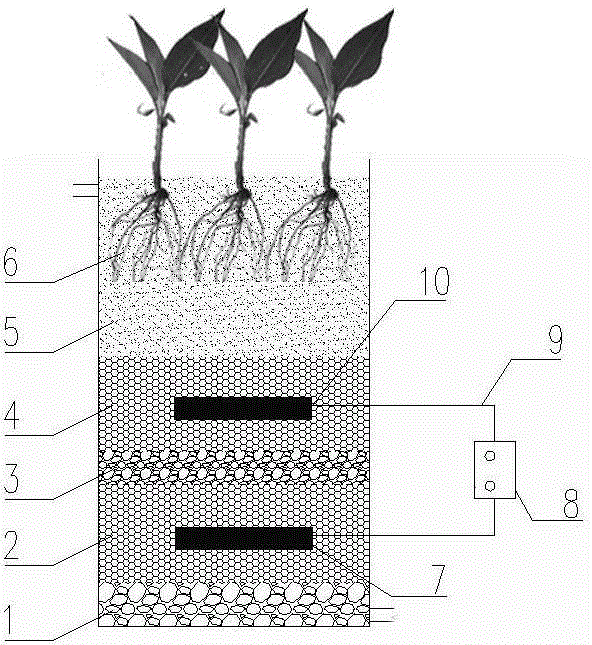
Enhanced denitrification method and device for coupled microorganism electrolytic tank of downstream vertical flow artificial wetland
ActiveCN105217796AImprove removal efficiencyImprove total nitrogen removal effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentWastewaterWater flow
The invention discloses an enhanced denitrification method and device for a coupled microorganism electrolytic tank of a downstream vertical flow artificial wetland. The enhanced denitrification method comprises the following steps: (A) water is uniformly distributed on the top of a system, and waste water firstly flows into an upper non-conductive filler layer; (B) waste water flows into an anodic conductive filler layer, and unoxidized organic matters are removed in the anodic conductive filler layer; (C) then waste water flows into a non-conductive filler isolating layer which is a separator between a cathodic conductive filler layer and the anodic conductive filler layer; (D) waste water flows into the cathodic conductive filler layer to generate an autotrophic denitrification process; and (E) waste water is drained through a bottom draining pipe. The anodic conductive filler layer is connected with the bottom communication filler layer and the non-conductive filler isolating layer, respectively, the anodic conductive filler layer is connected with the non-conductive filler isolating layer and the upper non-conductive filler layer, respectively, and cathodic and anodic collector electrodes are respectively placed in the cathodic conductive filler layer and the anodic conductive filler layer. The enhanced denitrification method has the beneficial effects that the operation is simple, and the removal efficacy of the downstream vertical flow artificial wetland to low-carbon and high-nitrogen wastewater is substantially improved.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
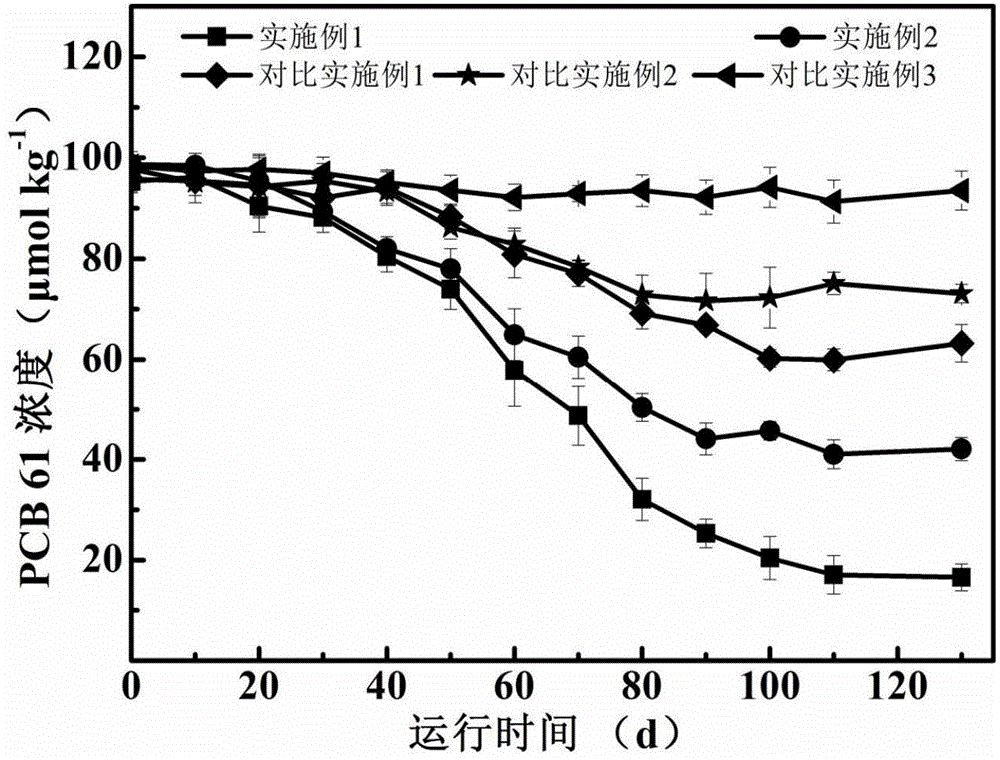
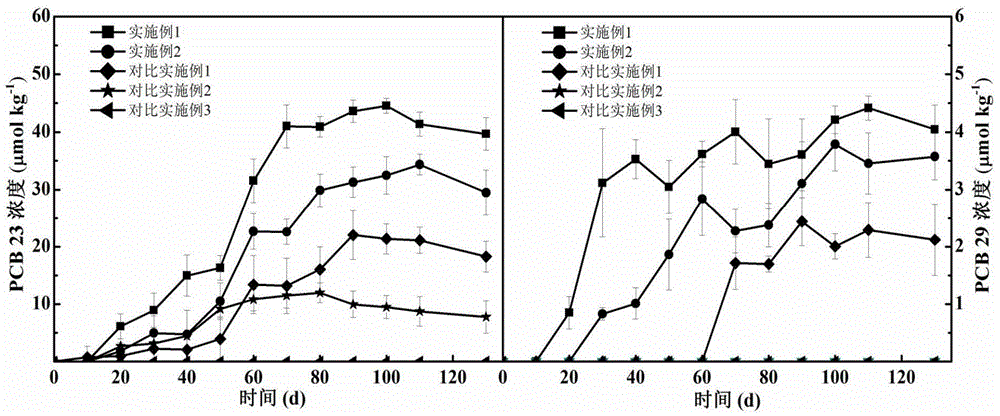
Device and method for removing polychlorinated biphenyl in bottom mud through microorganism electrolytic tank
ActiveCN104984994AAchieving Reductive RemovalImplement pollution remediationContaminated soil reclamationToxicity reductionPolychlorinated biphenyl
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil restoration and discloses a device and method for removing polychlorinated biphenyl in bottom mud through a microorganism electrolytic tank. The microorganism electrolytic tank is established, hybrid electrochemical activity bacteria and perchlorate domesticated bacteria are inoculated to an anode chamber, soil polluted by polychlorinated biphenyl is added, a nutrient solution is supplemented to the rest part, the water phase-bottom mud anode chamber is formed, anode potential is controlled to be kept constant through an electrochemical work station, growth and propagation of the hybrid electrochemical activity bacteria and the perchlorate domesticated bacteria can be promoted, dechloridation efficiency can be greatly improved, and constant bioelectric currents can be generated. By the adoption of the device and method, natural restoration and toxicity reduction can be conducted on the polluted soil, and good environmental protection benefits are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
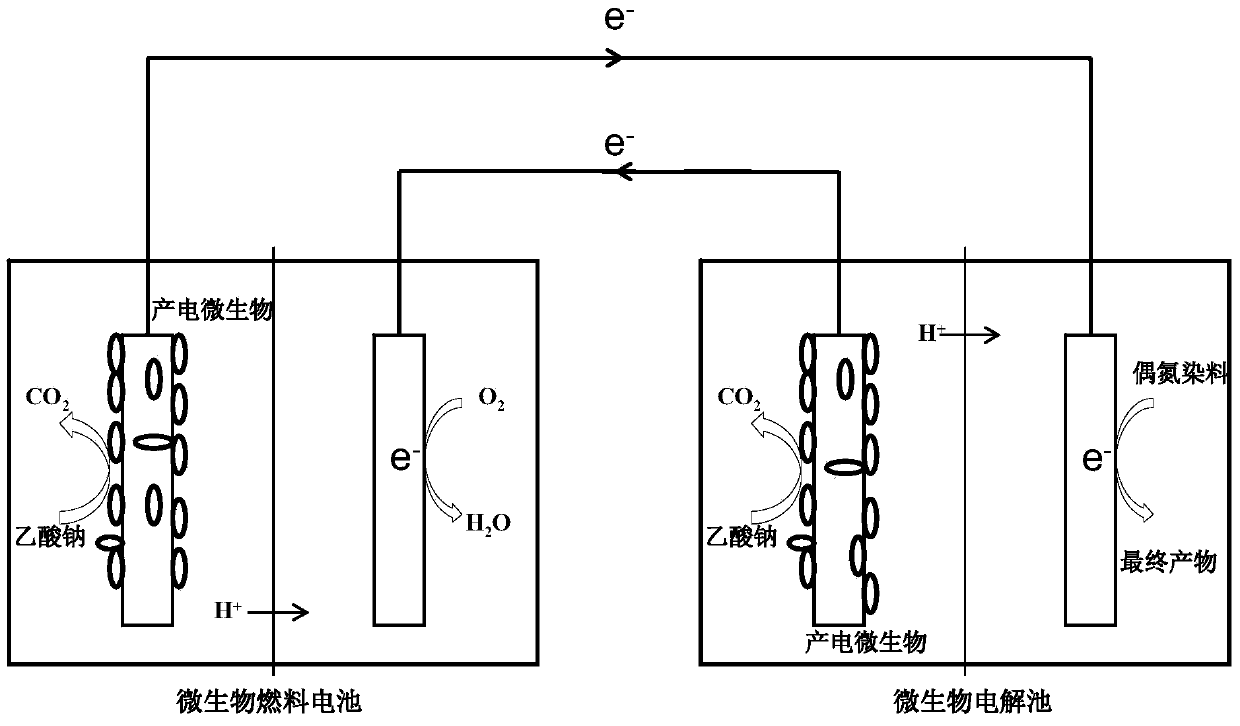
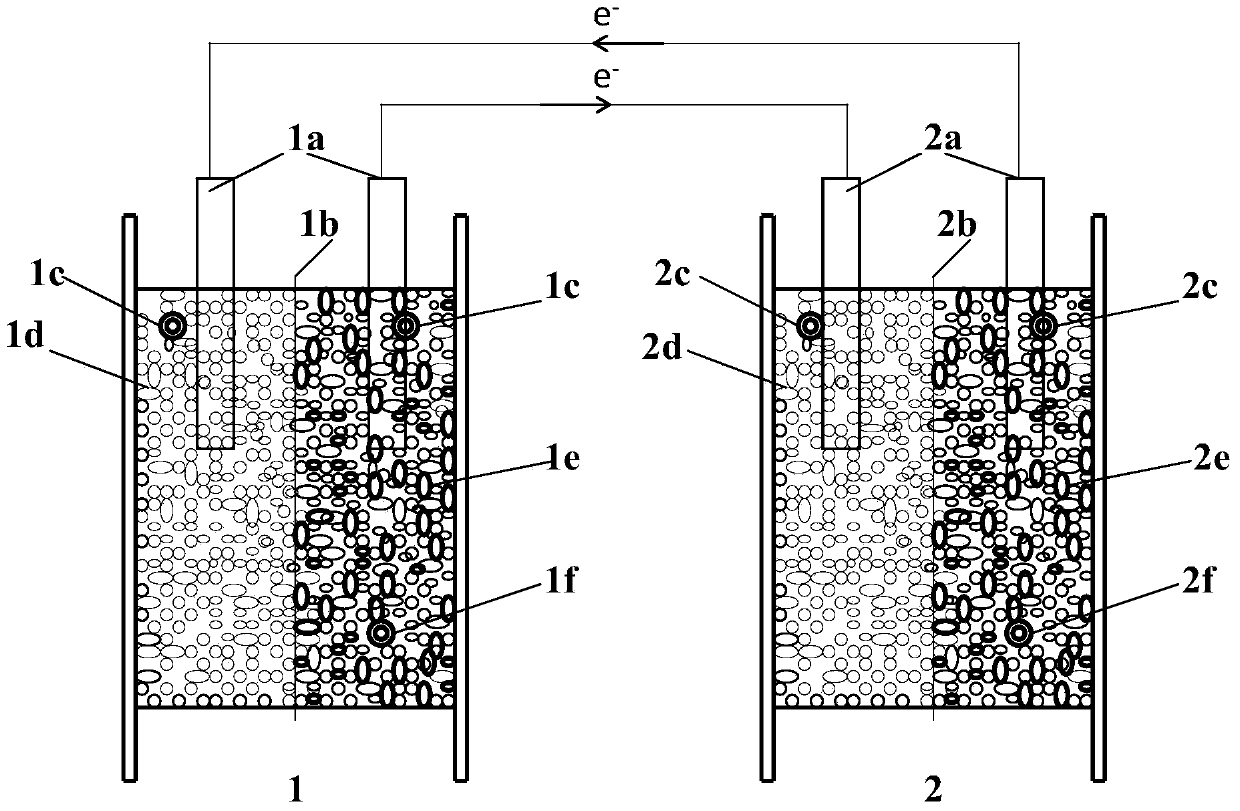
Treatment method for dyeing wastewater
ActiveCN103588307AImprove degradation efficiencySave energyBiochemical fuel cellsWaste water treatment from textile industryFuel cellsCoupling system
The invention discloses a treatment method for dyeing wastewater. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: configuring a microbial electrochemical coupling system which couples a microbial fuel cell (MFC) and a microbial electrolysis cell (MEC); and adding dyeing wastewater to be treated into the cathode chamber of the MEC for degradation. According to the method, the MFC and the MEC are connected in series, the MFC supplies the MEC with electric energy used for degrading the dyeing wastewater, supply of extra voltage to the MEC for improvement of degradation efficiency of the dyeing wastewater is not needed, so energy is saved; combination of the MFC and the MEC improves efficiency of the individual MFC in degradation of the dyeing wastewater.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
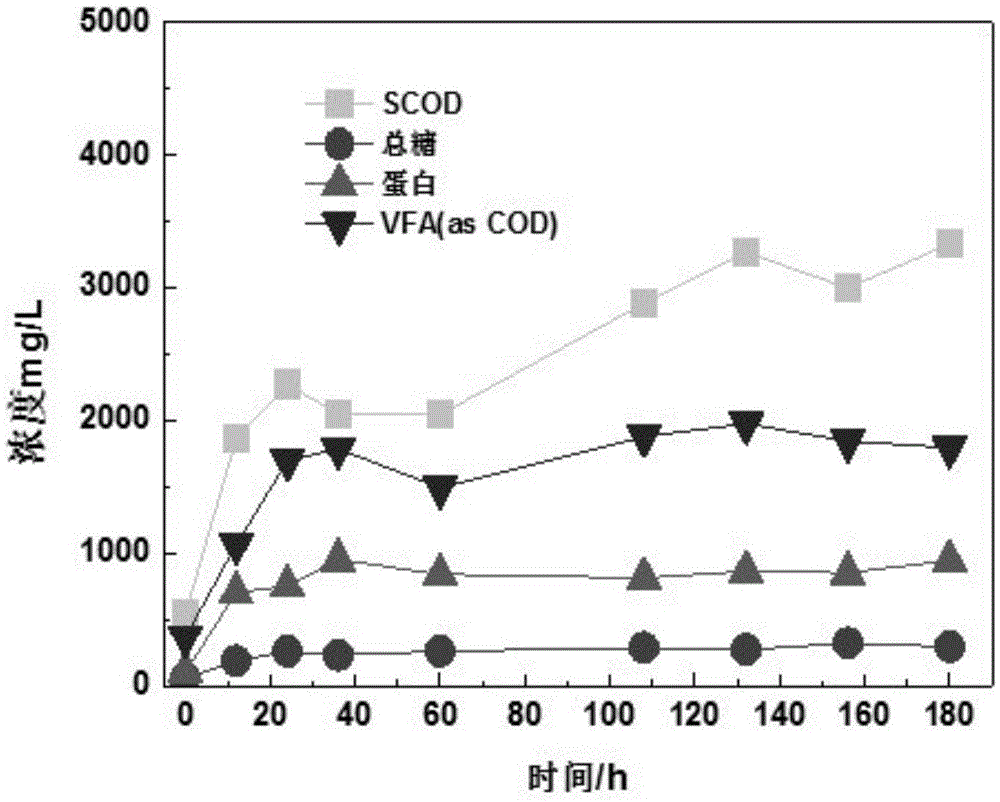
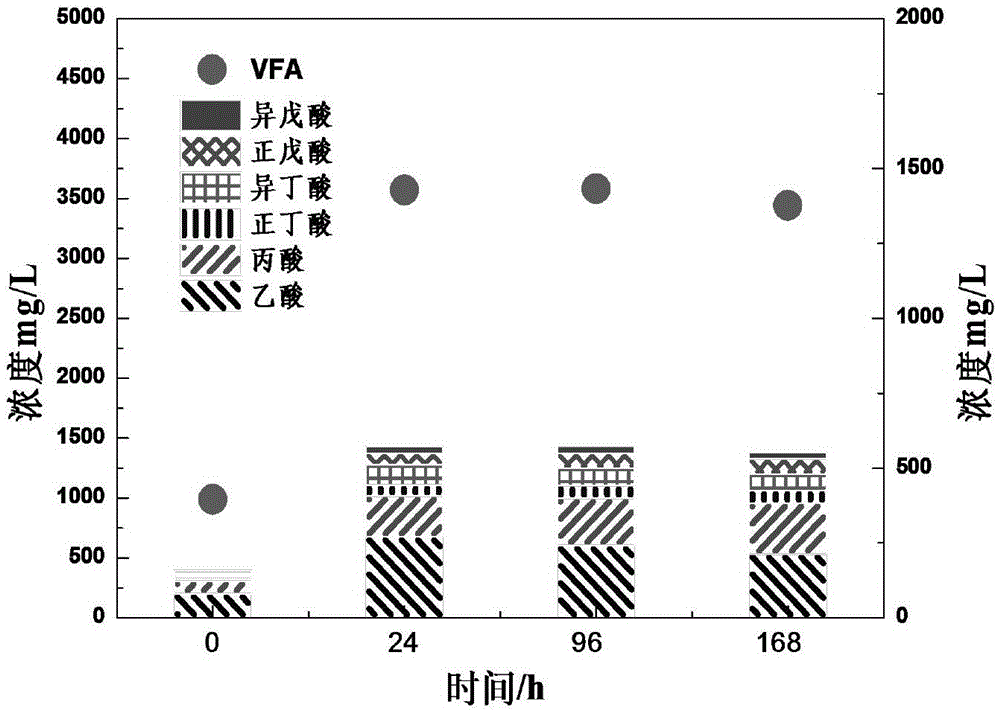
Method for producing hydrogen from residual sludge by anaerobic fermentation and microbial electrolysis cell coupling
ActiveCN106011176AAchieve stabilizationFully degradedSludge treatmentSpecific water treatment objectivesSludgeVolatile fatty acids
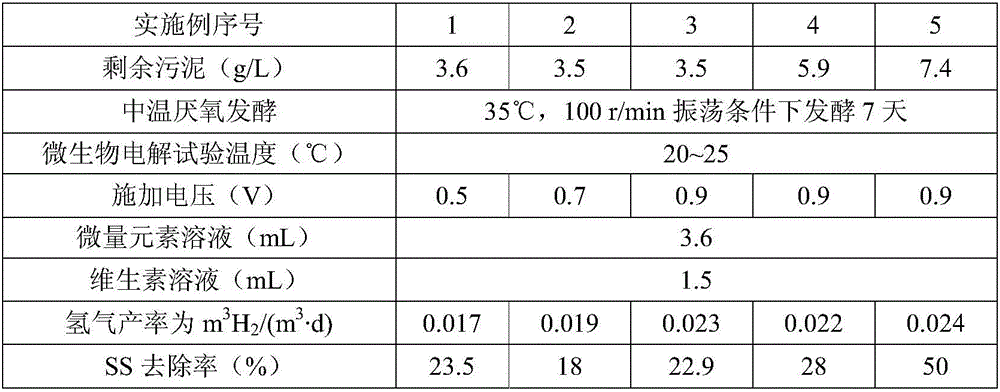
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen from residual sludge by anaerobic fermentation and microbial electrolysis cell coupling. The method comprises the following steps: S1, enriching anode electricity production bacteria by taking the residual sludge as an inoculums and using a double-chamber microbial fuel cell at the temperature of 20 to 25 DEG C, wherein when an external resistance voltage value of the microbial fuel cell tends to be stable and at least three cycles recur, enrichment of anode microorganisms is completed; S2, performing anaerobic fermentation on the residual sludge at the temperature of 35 DEG C under an oscillation condition for 7 days, to obtain residual sludge pretreated by medium-temperature anaerobic fermentation; S3, operating a single-chamber microbial electrolysis cell by taking the pretreated residual sludge as a substrate at the temperature of 20 to 25 DEG C under external voltage of 0.5 to 0.9 V, to produce hydrogen from the residual sludge. According to the method, products, such as volatile fatty acid, a carbohydrate and proteins, obtained by anaerobic fermentation of the residual sludge and a microbial electrolysis technology are used to produce hydrogen from small-molecule organic matters in fermentation supernate, so that reutilization of fermentation final products is realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for recovering multiple metals through driving microbial electrolysis cells by microbial fuel cells
InactiveCN103966626AImprove pollutionResource optimizationPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementCarbon feltPrinted circuit board
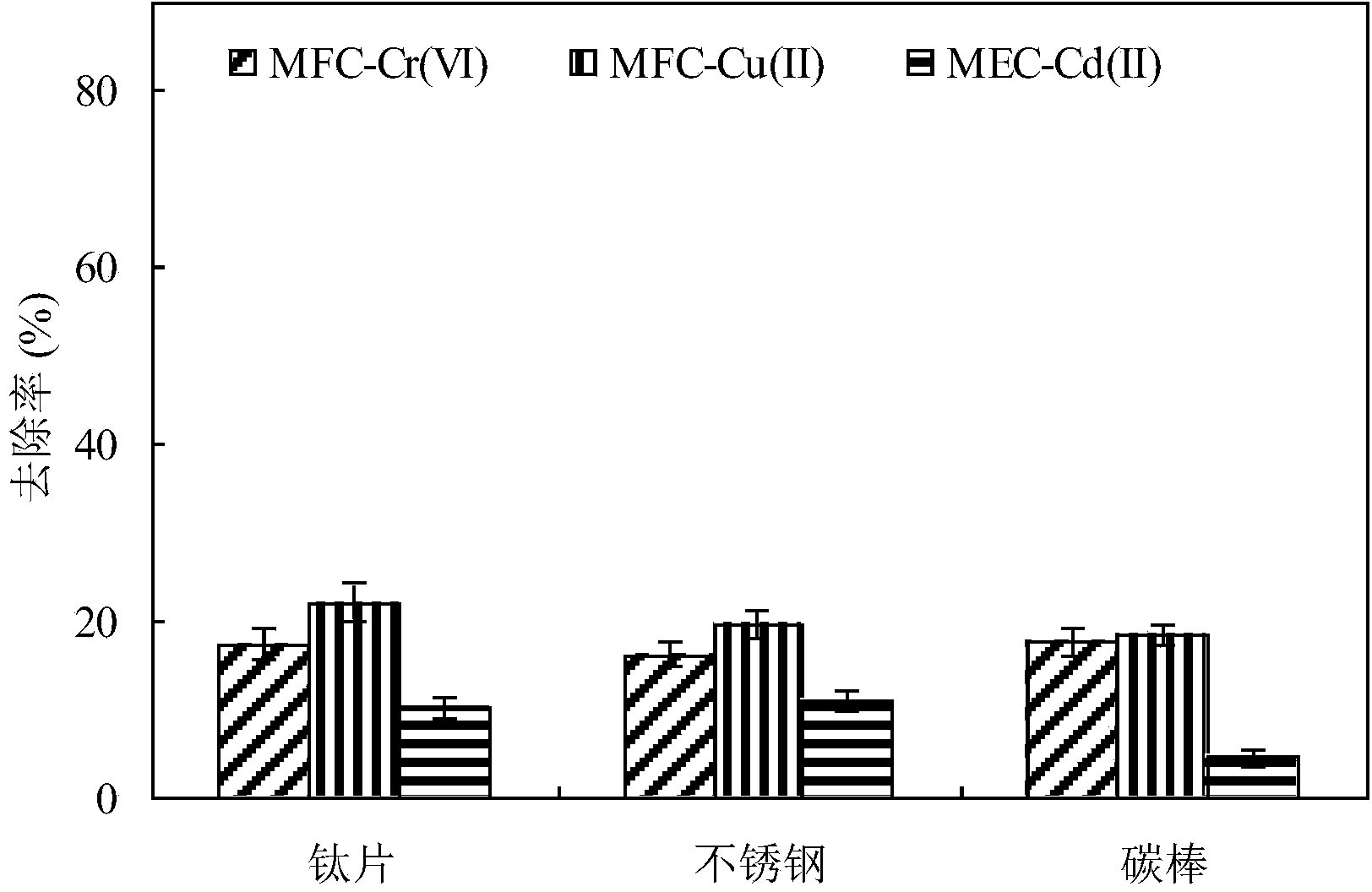
The invention relates to a method for recovering multiple metals through driving microbial electrolysis cells by microbial fuel cells, and belongs to the field of heavy metal recovery treatment. The method comprises the following steps: MFCsCr and MFCCu which adopt Cr(VI) and Cu(II) as cathode electron acceptors respectively are connected in series, the anodes of MFCsCr and MFCCu after series connection are connected with the cathode of MECsCd adopting Cd(II) as a cathode electron acceptor, the cathodes of the MFCsCr and MFCCu after series connection are connected with the anode of MECsCd through a series resistor, the cathodes of MFCsCr and MFCCu are carbon rods, the cathode of MECsCd is a stainless steel wire or a titanium sheet, and the anodes of MFCsCr, MFCCu and MECsCd are carbon felts or carbon rods. Through the adoption of the method, organic sewage such as electroplating wastewater, printed circuit board etching wastewater and municipal wastewater can be treated, and Cr metal, Cu metal and Cd metal are recovered, and broad space is provided for expanding the application field and the use range of an electrochemical system by MFCs output electric energy in situ.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Reverse electrodialysis supported microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells
ActiveUS9112217B2Raise the potentialSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicrobiological ProcessesElectron
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for realizing methanogenesis with surplus sludge by utilizing microbial electrolytic tank
ActiveCN102718381AHigh removal rateReduce pollutionWaste based fuelBiological sludge treatmentMicroorganismChemical oxygen demand
The invention provides a method for realizing methanogenesis with surplus sludge by utilizing a microbial electrolytic tank, relates to a method for methanogenesis, and aims at solving the problems that a conventional fermentation method cannot completely utilize surplus sludge and is longer in time. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking surplus sludge as a substrate for acclimatization of anode functional microorganism and starting a microbial electrolytic tank reactor; and secondly, under the condition that the electrolytic tank is stable, taking the surplus sludge as the substrate for methanogenesis. The method completely utilizes the surplus sludge, and is short in reaction time; the methanogenesis rate is 0.10-0.25m<3>H2 / m<3>.d; and the protein removal rate is as high as 38%-58%, and the COD (chemical oxygen demand) removal rate is up to 38%-55%. Due to the higher removal rates of the protein and COD, the method for treating surplus sludge through the microbial electrolytic tank technology and recycling the energy product methane with higher economic value has the characteristic of combining productivity with reduction of environmental pollution.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
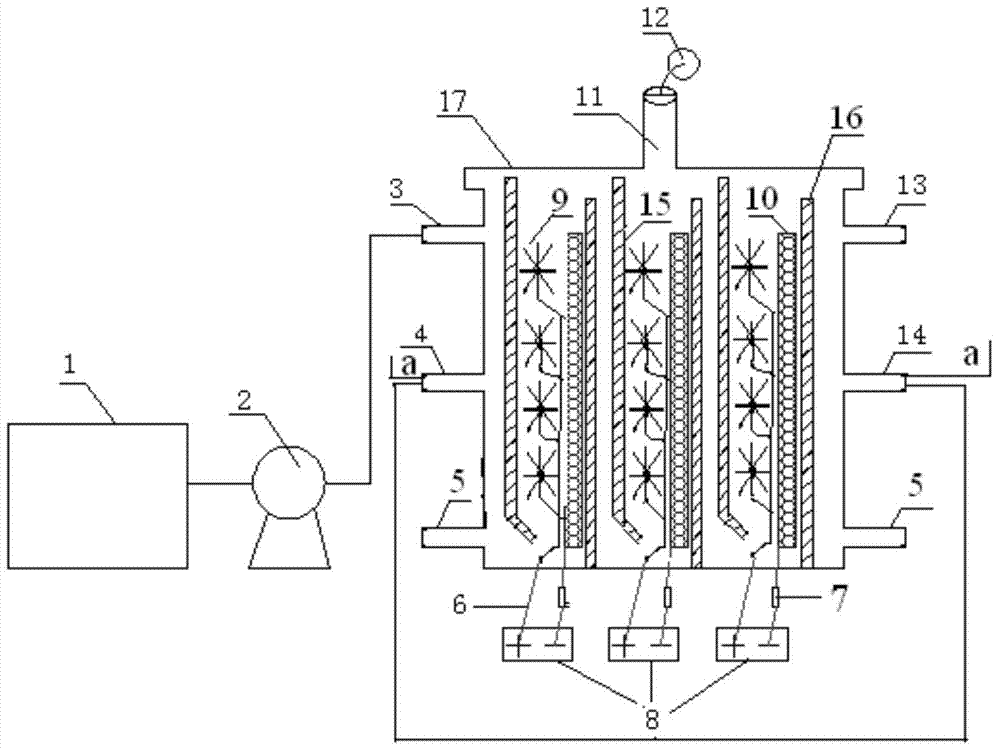
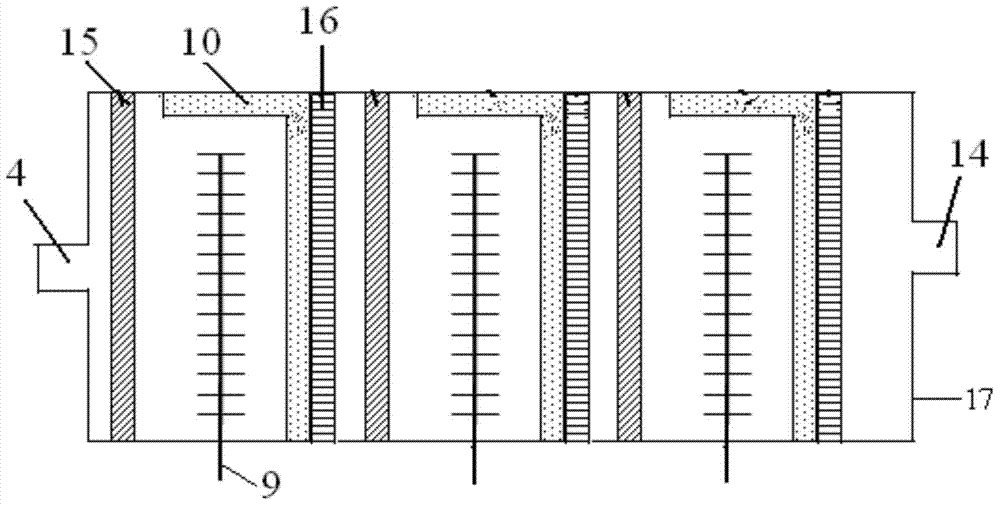
Guide-plate microbial electrolysis cell embedded with multi-electrode system and use method thereof
ActiveCN103668305AReduce construction costsSuitable for industrial development researchCellsBiological sludge treatmentFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a guide-plate microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) embedded with a multi-electrode system and a use method thereof, and relates to an MEC and a use method thereof. The invention aims to solve the technical problems of low yields of hydrogen and methane, limits on development and difficulty in realizing scale development due to high costs of anode materials and catalysts in the conventional MEC system and small size of the MEC system. The microbial electrolysis cell comprises anode carbon fibers, a cathode steel mesh and a baffle plate tank body, wherein a plurality of anode carbon fiber brushes and one cathode steel mesh are arranged in grids of the baffle plate tank body; the cathode steel mesh is folded into two rectangular steel meshes of which surfaces are vertical to each other; the anode carbon fiber brushes are arranged from top to bottom; the two faces of the cathode steel mesh are 2-4 centimeters away from the anode carbon fiber brushes. The use method of the MEC disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: I, enriching microorganisms on an anode; II, collecting gas in the MEC. The guide-plate MEC is applied to the field of MECs.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for recovering elementary-substance cobalt from lithium cobaltate in one step by utilizing microbial electrolysis cell
InactiveCN102650063AEasy to handleResource optimizationPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSludgeElectrochemistry
The invention relates to a method for recovering elementary-substance cobalt from lithium cobaltate in one step by utilizing a microbial electrolysis cell. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting a resistor between the anode and the cathode of the microbial electrolysis cell, and applying voltage; filling electrochemical active microorganisms and anode liquor in an anode chamber of the microbial electrolysis cell; filling cathode liquor and lithium cobaltate particles in a cathode chamber of the microbial electrolysis cell; and inoculating the anode chamber by the clarifier sludge of a sewage treatment plant, wherein the clarifier sludge is used as the electrochemical active microorganisms, the cathode liquor is an inorganic acid solution, and a cathode electrode and an anode electrode are respectively made of a graphite material. The method for recovering the elementary-substance cobalt from the lithium cobaltate in one step by utilizing the microbial electrolysis cell is clean and efficient in process, is simple, is low in cost and is very good in application prospect of treating waste lithium ion batteries and recovering cobalt metal in the waste lithium ion batteries.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
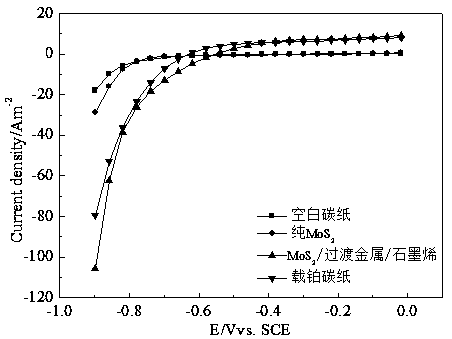
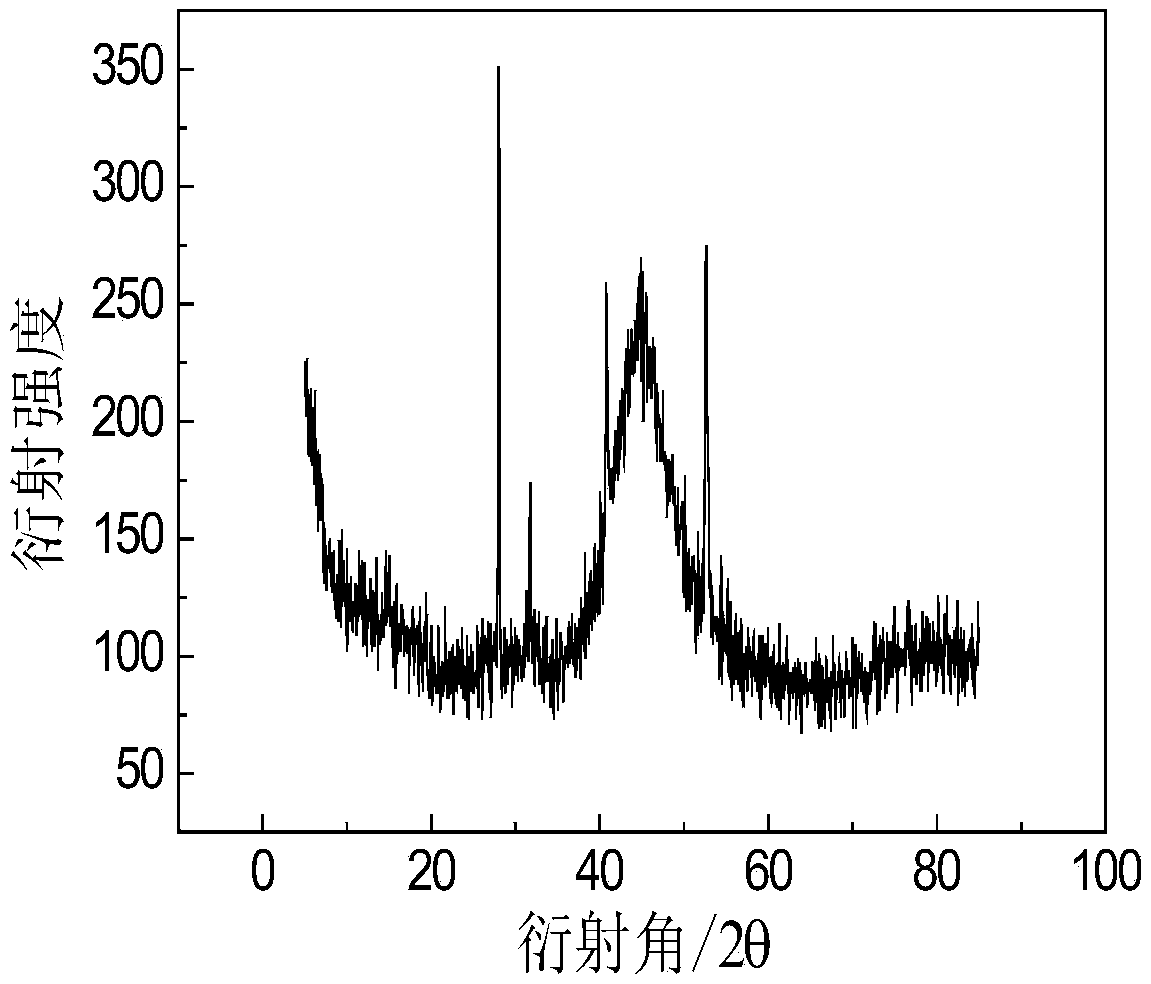
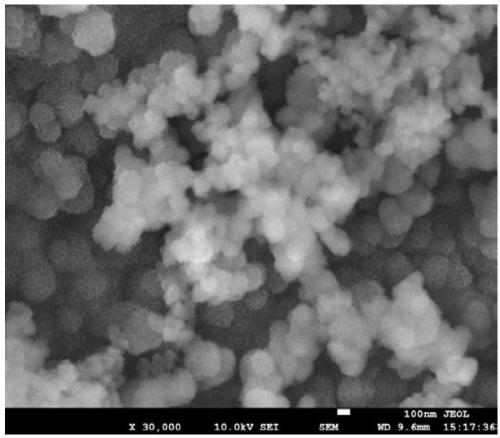
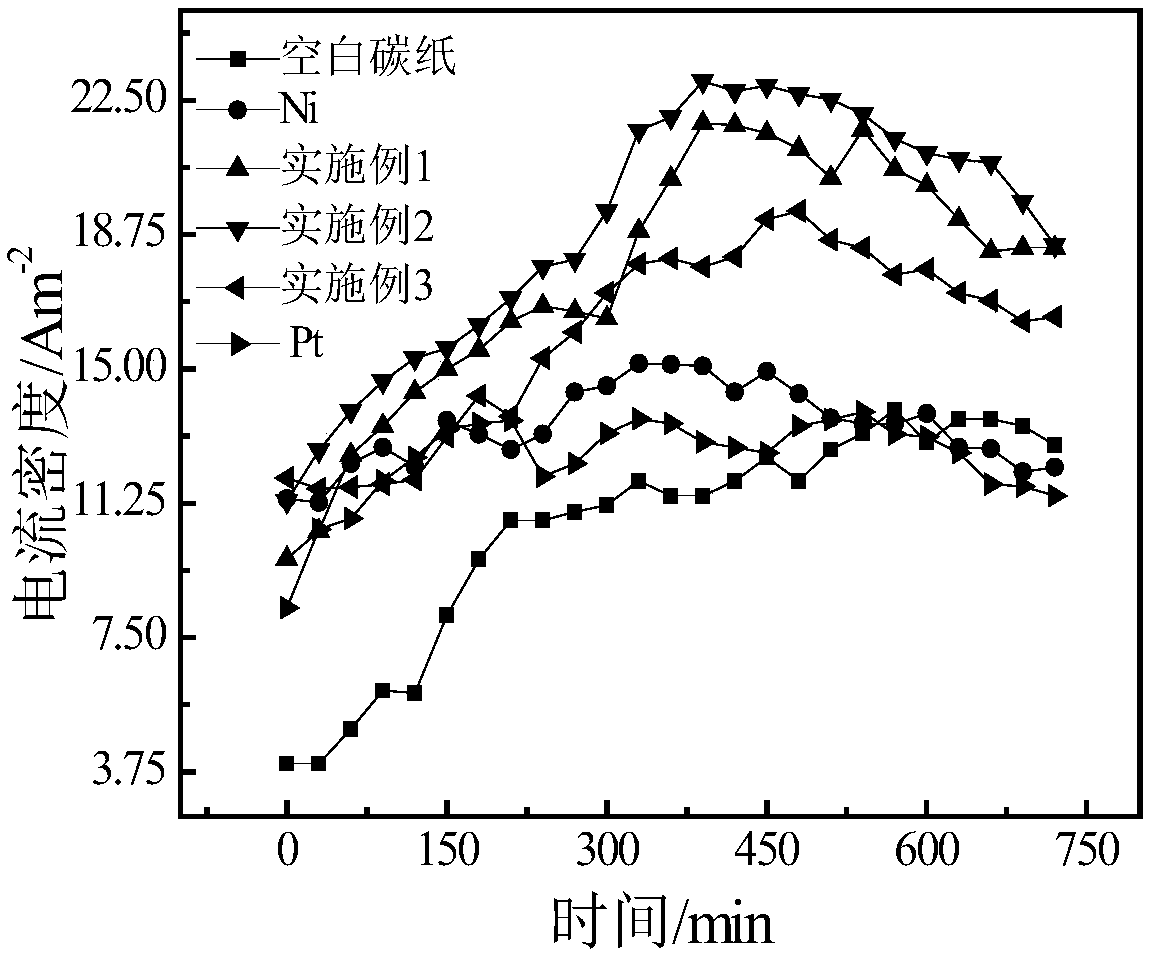
Preparation method and application of MoS2/transition metal/graphene composite hydrogen dissociation electrode in microbial electrolytic tank
InactiveCN108191075AEasy to makeReduce energy consumptionWater treatment parameter controlWaste water treatment from animal processingPollutionReducing agent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an MoS2 / transition metal / graphene composite hydrogen dissociation electrode in a microbial electrolytic tank. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving graphene oxide with deionized water, performing ultrasonic peeling to obtain a graphene oxide solution, then, adding ammonium tetrathiomolybdate, a salt compound of transition metal and a reducing agent in sequence, and dispersing uniformly to obtain a mixed solution; (2) transferring the mixed solution into a reaction kettle, preserving heat for 10 to 12hours at 170 to 200 DEG C, and centrifuging, washing and drying a product to obtain the MoS2 / transition metal / graphene composite hydrogen dissociation catalyst; (3) uniformly loading an electrode material with the MoS2 / transition metal / graphene composite hydrogen dissociation catalyst to obtain the hydrogen dissociation electrode. According to the preparation method and the application of the MoS2 / transition metal / graphene composite hydrogen dissociation electrode in the microbial electrolytic tank, a reaction system is uniform; the production cost is low; the MoS2 / transition metal / graphene composite hydrogen dissociation electrode has good electrochemical performance, has a good catalytic hydrogen production effect, and can achieve double effects of treating pollution and producing energy.
Owner:太原学院
Mo/Ni/Co/P/C composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109136983ALow priceLow hydrogen evolution overpotentialTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesElectrodesAuxiliary electrodeWorkstation
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite materials, and particularly relates to an Mo / Ni / Co / P / C composite material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The material is prepared with the following method: in a three-electrode system, a carbon-based substrate taken as a working electrode, a platinum net taken as an auxiliary electrode and Ag / AgCl taken as a reference electrode are connected with an electrochemical workstation, potentiostatic deposition is conducted in a mixed solution of nickel sulfate with concentration of 30-70 g / L, sodium hypophosphitewith concentration of 20-40 g / L, nickel chloride with concentration of 10-20 g / L, boric acid with concentration of 30-35 g / L, cobalt chloride with concentration of 30-50 g / L and sodium molybdate withconcentration of 40-50 g / L, magnetic stirring is conducted throughout the deposition process, initial potential set on the working electrode during electroplating is (-1.5)V-(-1)V, electroplating timeis 5-30 min, electroplating temperature is set to be 25-35 DEG C, a power supply is turned off finally, and the Mo / Ni / Co / P / C composite material is prepared. The Mo / Ni / Co / P / C composite material is taken as a cathode material of a microbial electrolytic cell to treat coking wastewater and produce hydrogen synchronously, waste is changed into treasure, and a new idea and a new perspective are provided for impending coking wastewater treatment.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization
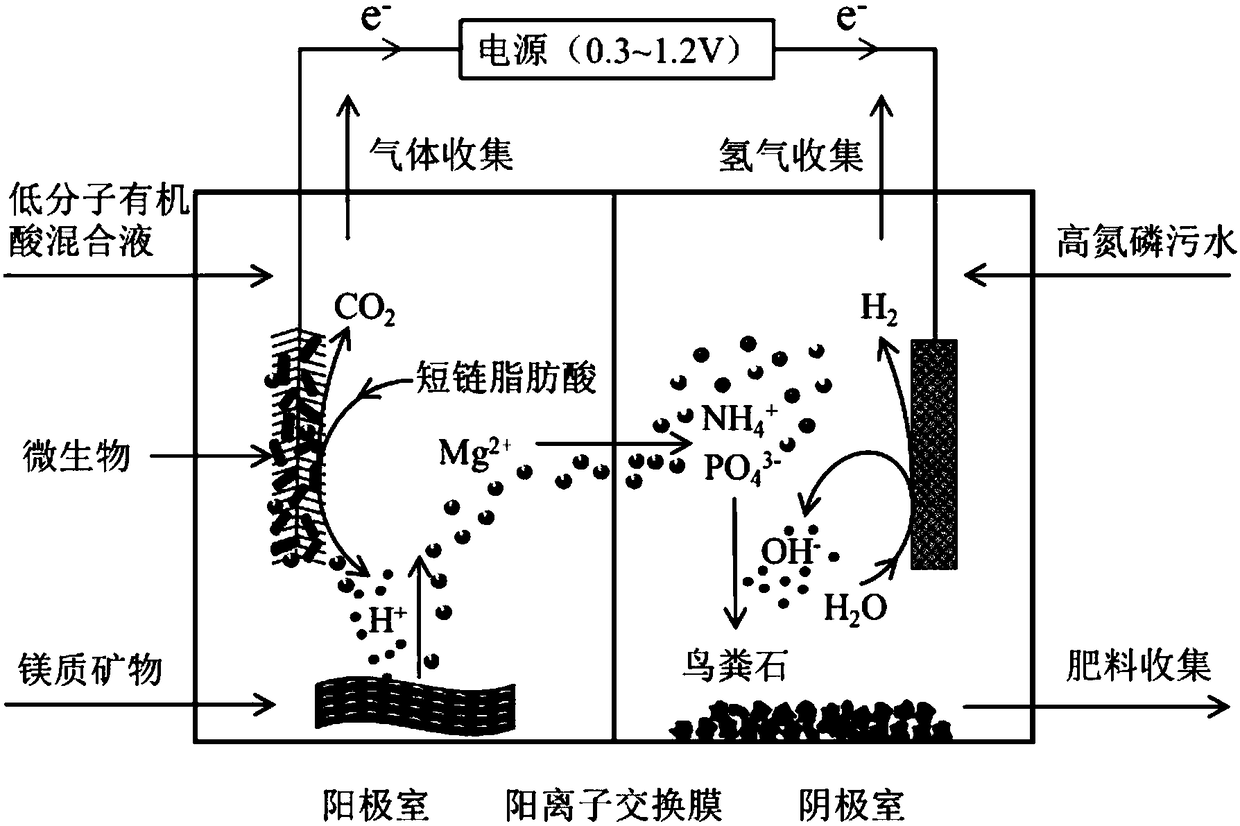
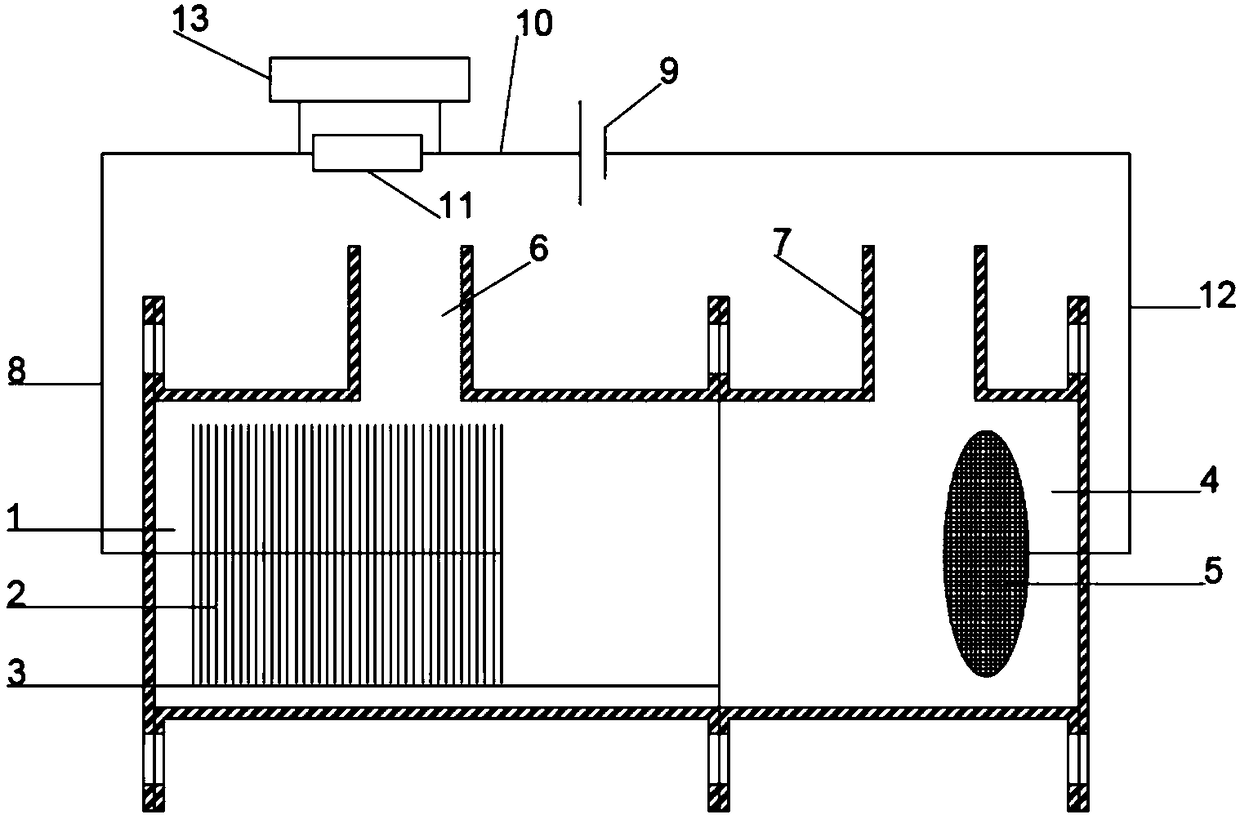
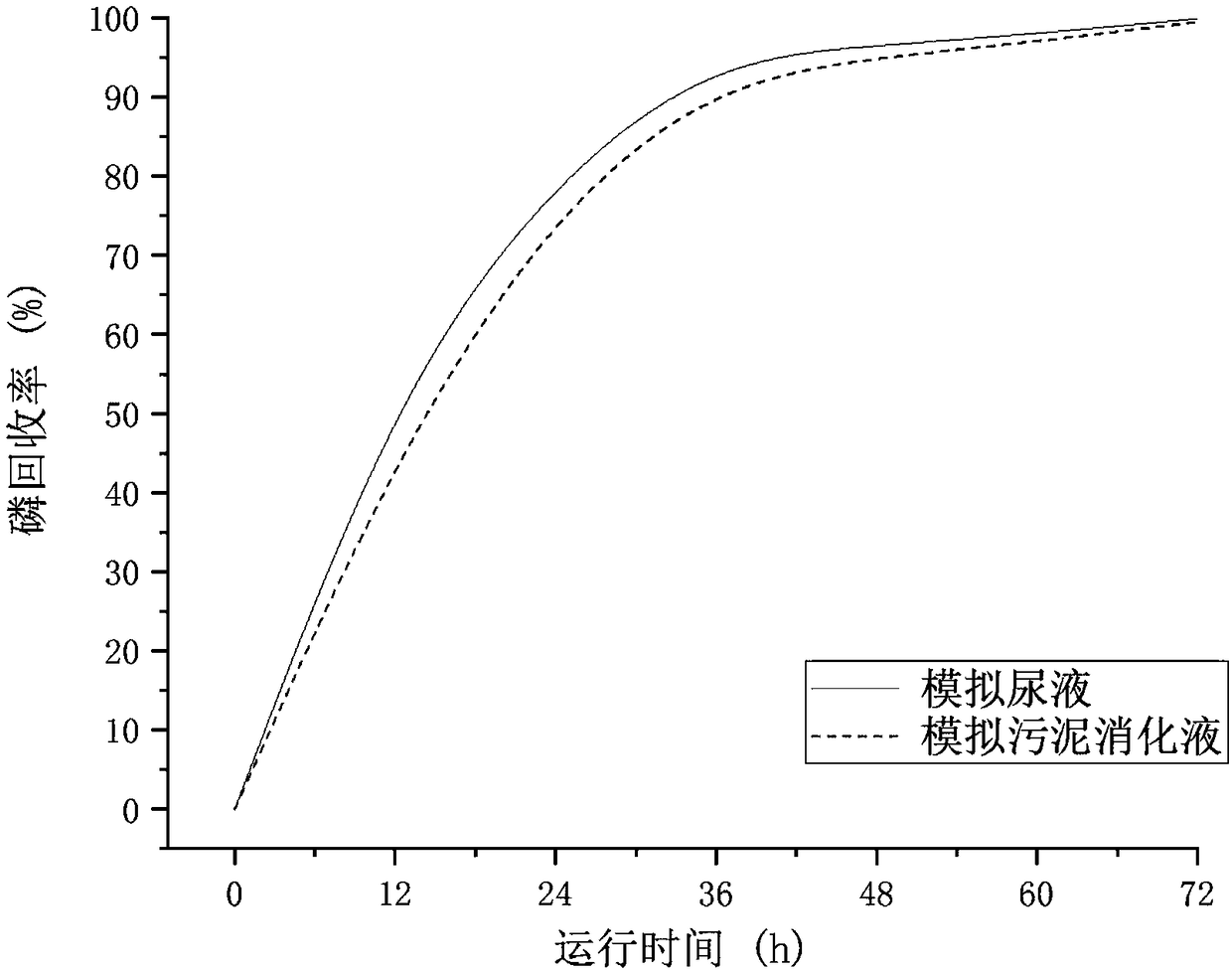
ActiveCN108660475APromote acidolysisCrystallize fastCellsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesOverpotentialMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization. The method aims to solve the problems that in existing recycling of phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization, an anode liquid is acidized, the overpotential is large, the magnesium source cost is high, and the like. Cheap magnesium ores are subjected to acidolysis in the anode liquid, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the overpotential is remarkably reduced, and the magnesium source cost is lowered. According to the method, based on a bichamber microbial electrolysis pool, under an extremely low externally applied voltage (0.3-1.2 V), an electrode reaction is performed to form conditions for acidification of the anode liquid and acidification of a cathode liquid; the crushed magnesium ores are added to an anode chamber, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the pH of the anode liquid is stabilized, and microorganisms are promoted to continuously degrade organic matter to generate power; and magnesium ions released through acidolysis of the magnesian cores move to an cathode through a cation exchange membrane under the drive of the electric filed force and has a crystallization reaction with ammonium radials and phosphate radicals under an alkaline condition, struvite deposits are formed, the pH of the cathode liquid is stabilized, and the purposes of removing and recycling the phosphorus from sewage are realized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and apparatus for intensifying denitrification in coupling microorganism electrolytic tank of upstream vertical flow artificial wetland
ActiveCN105236584AImprove removal efficiencyImprove total nitrogen removal effectWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMicroorganismNitrate nitrogen
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for intensifying denitrification in a coupling microorganism electrolytic tank of an upstream vertical flow artificial wetland. The method comprises the following steps: A, uniformly distributing water at the bottom of a system, raising waste water in a pushing flow manner along a bottom non-conducting filler layer firstly; B, enabling the waste water to flow in an anode conducting filler layer; C, then enabling the waste water to flow in a non-conducting filler isolated layer which is a separator between a cathode conducting filler layer and the anode conducting filler layer; D, enabling the waste water to flow in the cathode conducting filler layer, and carrying out autotrophic denitrification removal on nitrate nitrogen; and E, enabling the waste water to flow out of a drain pipe in the upper non-conducting filler layer. The anode conducting filler layer is connected with the non-conducting filler isolated layer and the bottom non-conducting filler layer respectively, the cathode conducting filler layer is connected with the upper non-conducting filler layer and the non-conducting filler isolated layer respectively, and a cathode collector and an anode collector are placed in the cathode conducting filler layer and the anode conducting filler layer respectively. The operation is simple, and the removal capability of the upstream vertical flow artificial wetland for the waste water containing low carbon and high nitrate nitrogen is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Method and device for treating coking wastewater and producing hydrogen gas by microbial electrolysis cell
InactiveCN106630177ASignificant progressSignificant positive effectBiochemical fuel cellsBiological water/sewage treatmentHazardous substanceToxic material
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment methods and devices, and particularly relates to a method and a device for treating coking wastewater and producing hydrogen gas by a microbial electrolysis cell. According to the method, coking bacteria are used as a biocatalyst; the microbial electrolysis cell is used for degrading toxic substances in the coking wastewater and producing the hydrogen gas. A microbial fuel cell is built through coding wastewater bacterium activation, anode electrode carbon felt and cathode electrode Pt-loaded carbon cloth treatment; after current reaches a stable highest value, the microbial fuel cell is converted into the microbial electrolysis cell; identically, after the current reaches the stable highest value, a dilution method is used for performing anti-toxic domestication on a biological membrane of the microbial electrolysis cell; then, the coking wastewater can be directly treated, and harmful substances in the coding wastewater are eliminated. By using the method and the device for removing the harmful substances from the coding wastewater, the harmful substance removal rate of 90 percent or more can be achieved only through 72h; the good economic benefits and environment-friendly benefits are realized.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of ordered mesopore cathode composite of MEC
InactiveCN107740136AReduce dependenceEasy to prepareWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectrode shape/formsMesoporous silicaElectron transfer
The invention relates to the field of microorganism electrolytic tank cathode materials, in particular to a preparation method of an ordered mesopore cathode composite of MEC. P123 is adopted as a template agent, tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) is adopted as a silicone source, and a mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 is obtained through synthesis. Mesoporous silica SBA-15 is adopted as a hard template, the hard template is filled with a precursor nickel source and a cobalt source different in molar ratio through the nanometer casting technology, after roasting at different temperatures, a catalyst isput in alkali liquor to be stirred to remove the template, and metal oxide with an ordered mesopore structure is prepared. The preparation method is simple, operation is easy, cost is low, dependencyon precious metal Pt is greatly reduced, and wide application prospects are achieved in the field such as microorganism electrolytic tank waste water treatment. The mesopore metal oxide NiCo2O4 is adopted as a cathode catalyst of the MEC, the specific surface area of an electrode is increased, an ordered mesopore channel is formed, the chemocatalysis function can be achieved synchronously, and electron transfer can be accelerated.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
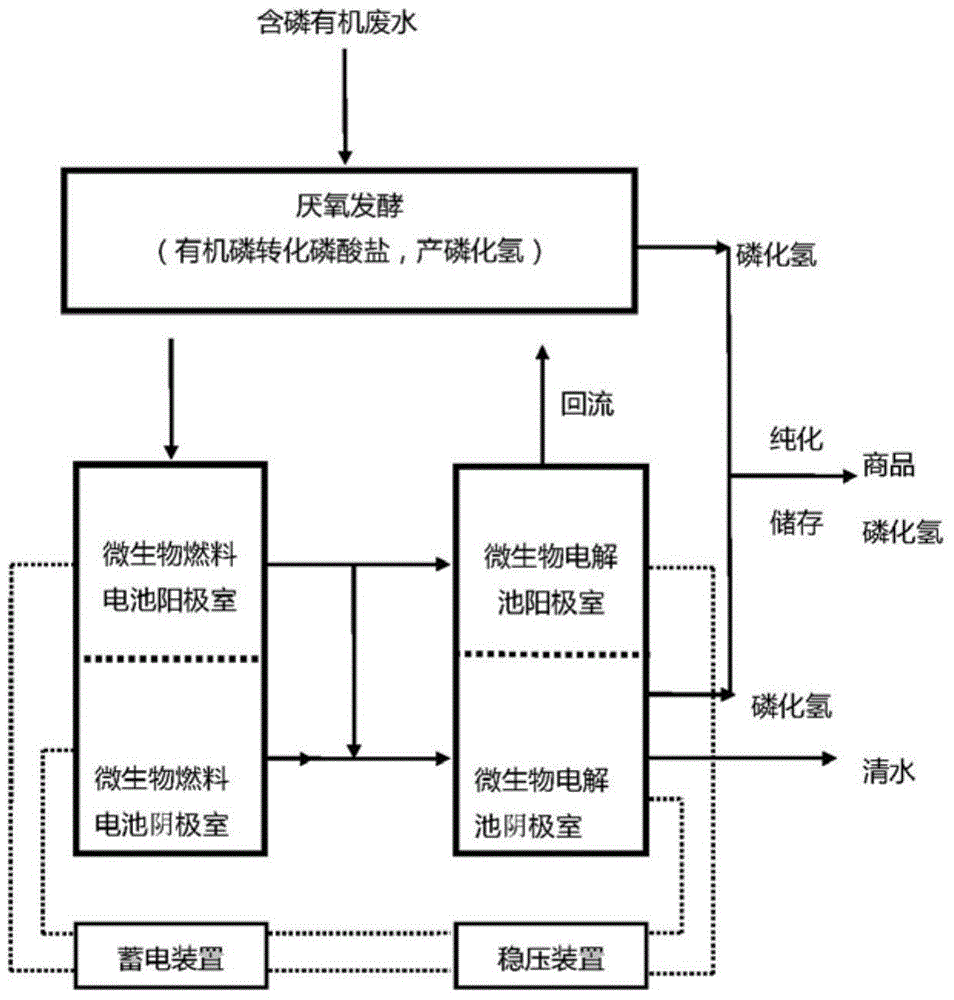
Device for removing phosphor from phosphor-containing organic wastewater and producing hydrogen phosphide
ActiveCN104828938AAvoid the problem of low phosphorus removal efficiencyHigh purityWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSequencing batch reactorElectricity
The invention discloses a device for removing phosphor from phosphor-containing organic wastewater and producing hydrogen phosphide. The device comprises an anaerobic reactor, a microbial fuel cell and a microbial electrolytic bath; the water outlet pipe of the anaerobic reactor is connected to the anode water inlet pipe of the microbial fuel cell; the anode water outlet pipe of the microbial fuel cell is connected to the water inlet pipe of the microbial electrolytic bath; and the electricity output terminal of the microbial fuel cell is connected to the power supply port of the microbial electrolytic bath. The organic wastewater is introduced into the anaerobic sequencing batch reactor, the organic phosphor and occluded phosphor in organic wastewater are converted into phosphate through the metabolism of microbes, and then the wastewater is processed by the microbial fuel cell and microbial electrolytic bath. In the prior art, the phosphor removing efficiency is very low because the microbial anaerobic process is taken as the main process of hydrogen phosphide production, and the provided device solve the problem mentioned above.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for promoting electrolysis of sludge microorganisms for hydrogen production by joint use of ultrasound and alkali
InactiveCN107204479AIncrease the rate of hydrolysisImprove utilization efficiencyBiochemical fuel cellsElectrodesSludgeCell wall
The invention discloses a method for promoting electrolysis of sludge microorganisms for hydrogen production by joint use of ultrasound and alkali. The method comprises the following steps: by taking residual sludge of a municipal wastewater treatment plant as an inoculants, enriching electrochemically active microorganisms of a cathode through utilizing a two-chamber MFC (microbial fuel cell), and transferring the cathode as a cathode of a single-chamber MEC (microbial electrolysis cell); regulating the residual sludge to be alkaline, and performing ultrasound irradiation to obtain a mixed solution D; connecting an external circuit in series with a resistor at room temperature, and running the MEC to realize hydrogen production by taking the sludge subjected to ultrasound and alkali treatment as a substrate. According to the method, joint ultrasound and alkali treatment is performed on the residual sludge to damage flocs and the cell structure of the sludge to release most of organic substances wrapped with cell walls in the sludge into the liquid phase of the sludge and accelerate hydrolysis of the residual sludge, and the hydrogen production efficiency of the MEC is improved by organic matters dissolved after the sludge is disintegrated; stable, reduction and resourceful treatment of the residual sludge of the municipal wastewater treatment plant is successfully realized, and the method is simple in principle, convenient to operate, less in equipment and apparatus investment and high in practicability and applicability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for generating hydrogen in microorganism electrolysis cell with protein
InactiveCN101550551AIncrease profitHigh economic valueElectrolysis componentsWater/sewage treatmentFermentationPollution
A method for generating hydrogen in microorganism electrolysis cell with protein relates to a hydrogen generation method. The invention settles a problem that the prior fermentation method can not use protein for generating hydrogen. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1. actuating a reactor when the electrolysis cell is in a power generation mode; 2. using the protein as zymolyte for domesticating the functional microorganism of anode; and 3. using the protein as zymolyte for generating hydrogen when the electrolysis cell is in a hydrogen generation mode. The invention uses a microorganism electrolysis cell technique for directly preparing hydrogen from protein. The method of the invention has the advantages of high utilization factor of protein and high removal rate to COD, and can be used for treating the organic waster water and organic solid waste which are rich in protein and can be simultaneously used for recycling the energy product of hydrogen gas with higher economic value. The method has a characteristic of combing pollution control and energy production.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com