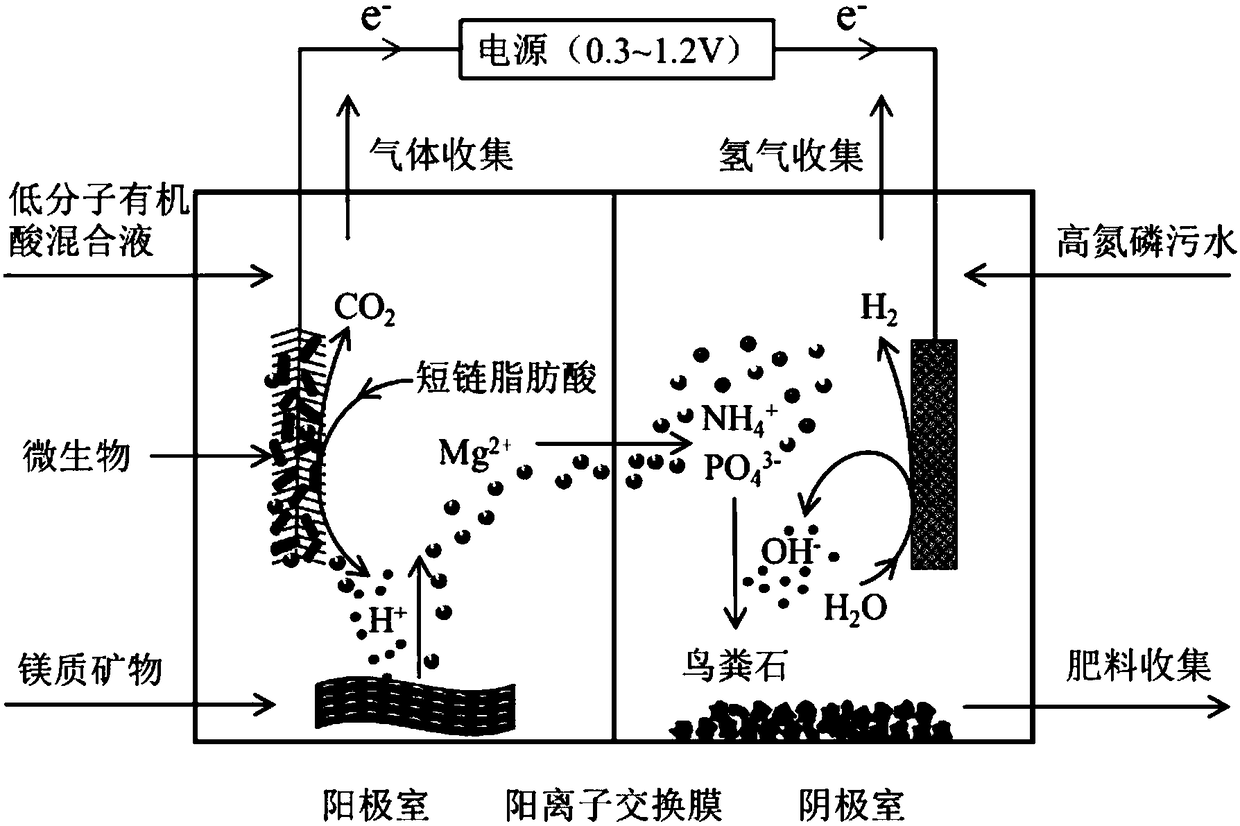
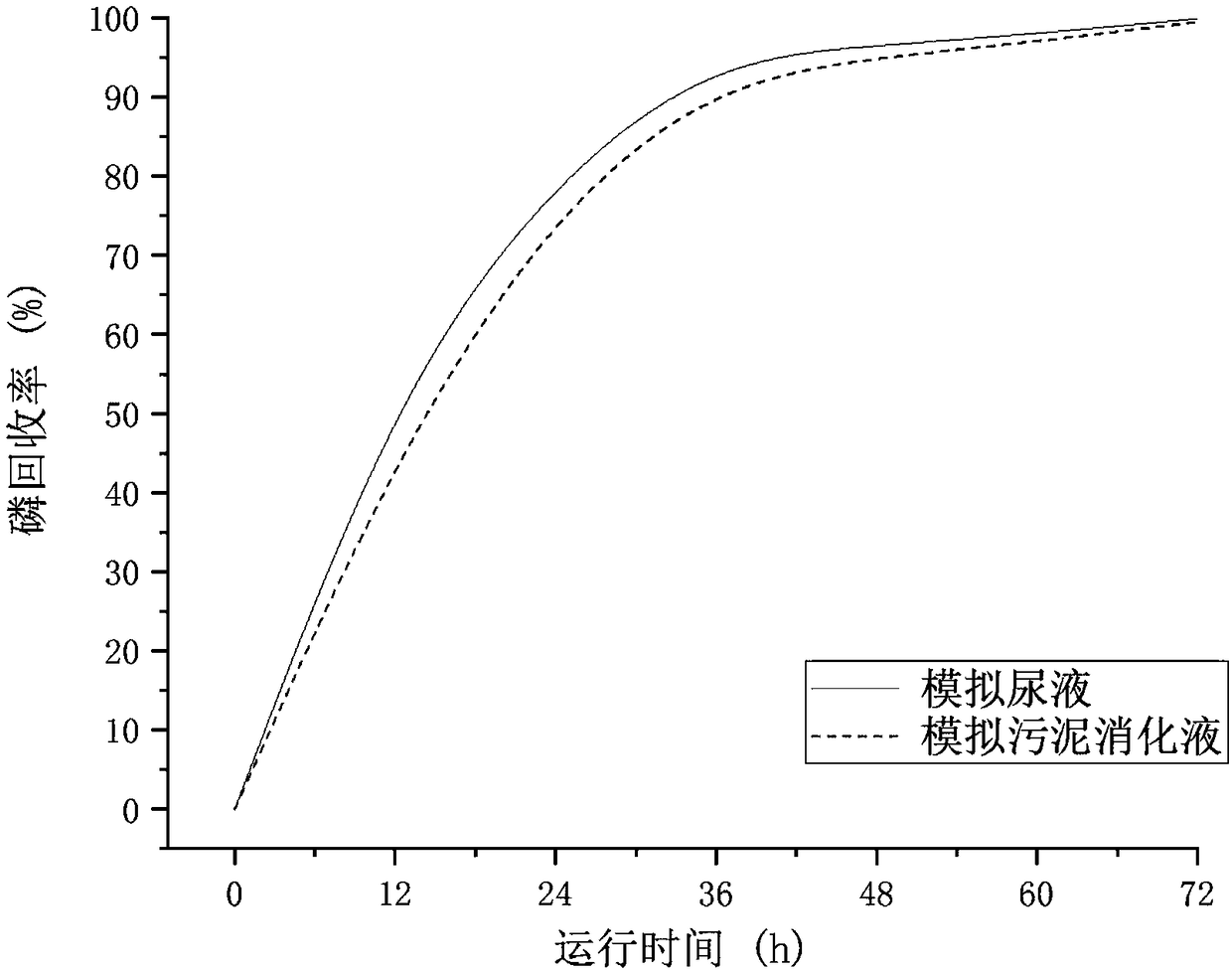
Method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization
A bioelectrochemical and struvite technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, electrochemical biocombination treatment, etc., can solve problems such as system performance degradation, damage to the activity of electrogenic bacteria, and potential increase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Applied to sludge digestion liquid, the process flow is as follows:
[0033] 1. Construction of double-chamber microbial electrolytic cell:
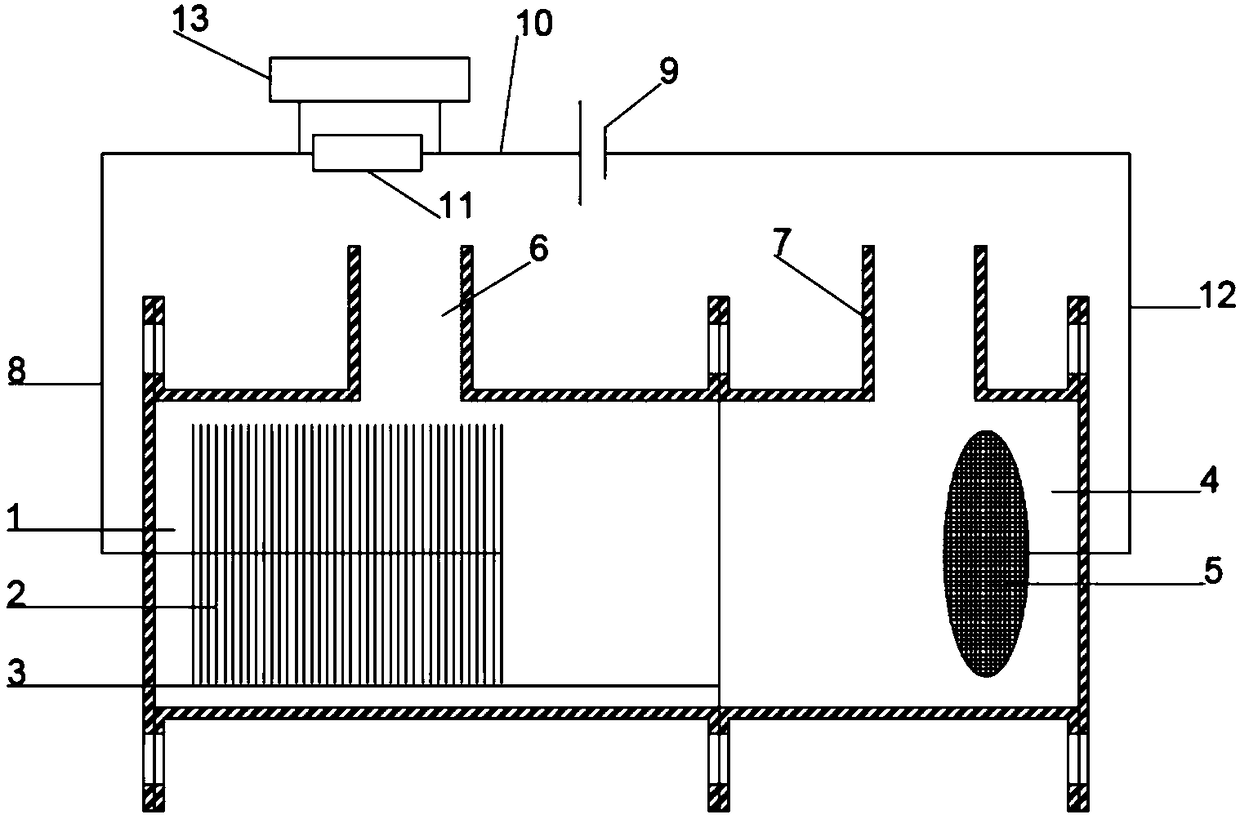
[0034] The structure of the double-chamber microbial electrolytic cell is as follows: figure 2 As shown, including: 1 anode chamber, 2 carbon brush anode electrode, 3 cation exchange membrane, 4 cathode chamber, 5 stainless steel mesh cathode electrode, 6 anode chamber inlet, 7 cathode chamber inlet / gas collection port, 8 wires, 9 potentiostat, 10 wire, 11 high-precision resistor, 12 titanium wire, 13 data acquisition system.
[0035] The anode chamber 1 and the cathode chamber 4 of the dual-chamber microbial electrolysis cell are separated by a cation exchange membrane 3 (CMI-7000, Membrane International). Before the carbon brush anode is used, clean the impurities on the carbon fiber with deionized water, and heat it at 450°C for 30 minutes in a muffle furnace to facilitate the attachment of microorganisms. Before using the ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Applied to urine, the technological process is as follows:
[0043] 1. Construction of double-chamber microbial electrolytic cell:
[0044] The structure of the double-chamber microbial electrolytic cell is as follows: figure 2 As shown, including: 1 anode chamber, 2 carbon brush anode electrode, 3 cation exchange membrane, 4 cathode chamber, 5 stainless steel mesh cathode electrode, 6 anode chamber inlet, 7 cathode chamber inlet / gas collection port, 8 wires, 9 potentiostat, 10 wire, 11 high-precision resistor, 12 titanium wire, 13 data acquisition system.
[0045] The anode chamber 1 and the cathode chamber 4 of the dual-chamber microbial electrolysis cell are separated by a cation exchange membrane 3 (CMI-7000, Membrane International). Before the carbon brush anode is used, clean the impurities on the carbon fiber with deionized water, and heat it at 450°C for 30 minutes in a muffle furnace to facilitate the attachment of microorganisms. Before using the stainless...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com