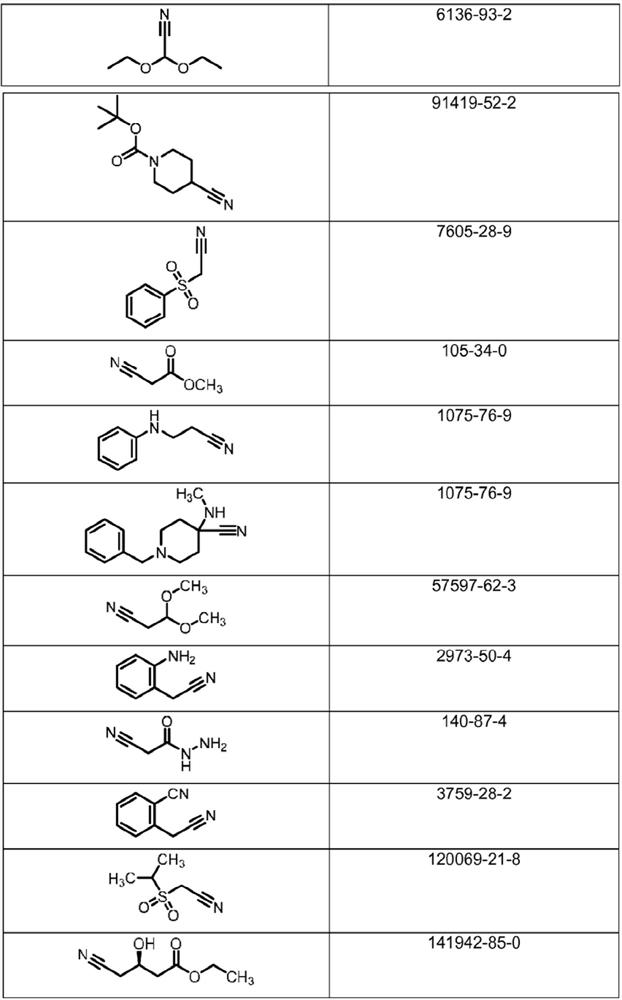
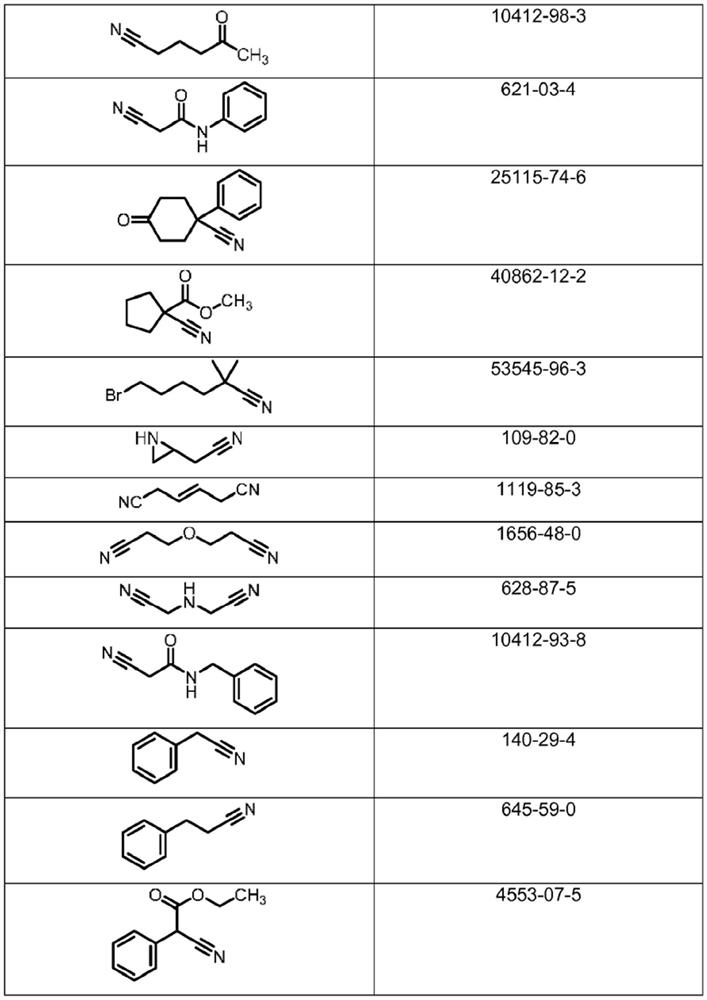
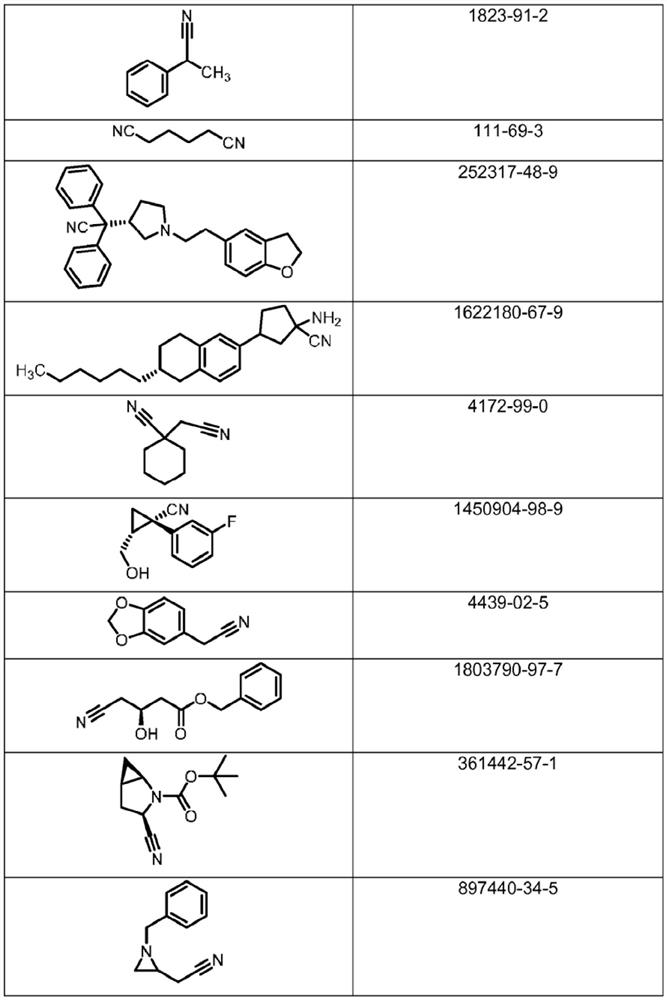
Microbiological process for the preparation of amides
A technology of microbiology and microbial strains, applied in the field of amide preparation, which can solve problems such as inability to apply chemically specific substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] 2-Chloroacetamide
[0064] NHase was ground in a mortar and added to potassium phosphate buffer (10 mM, pH=7.4) (9 mL) in a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The suspension was mixed by vortexing, and 2-chloroacetonitrile (38 mg, 0.5 mmol) was added to the suspension dissolved in MeOH (1 mL). The reaction was stirred by rotary shaking at 25°C and 250 rpm. After the reaction 1 H-NMR. Samples (1 mL) were analyzed after 1.5, 2.5, 4 and 7 hours. The sample was mixed with MeOH (2 mL), filtered and evaporated under vacuum. After 1.5 hours, complete conversion to 2-chloroacetamide was observed.
[0065] 1 H-NMR (CD 3 OD, 300.13MHz): 4.05-4.83 (s, 2H), comparable to commercially available 2-chloroacetamide samples.
Embodiment 2
[0067] 2,2-diethoxyacetamide
[0068] NHase was ground in a mortar and added to potassium phosphate buffer (10 mM, pH=7.4) (9 mL) in a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The suspension was mixed by vortexing, and 2,2-diethoxyacetonitrile (65 mg, 0.5 mmol) was added to the suspension dissolved in MeOH (1 mL). The reaction was stirred by rotary shaking at 25°C and 250 rpm. After the reaction 1 H-NMR. Samples (1 mL) were analyzed after 1.5, 2.5, 4 and 7 hours. The sample was mixed with MeOH (2 mL), filtered and evaporated under vacuum. After 1.5 hours, complete conversion to 2,2-diethoxyacetamide was observed.
[0069] 1 H-NMR (CD 3 OD, 300.13MHz): 1.44(t, 6H, 3 J HH =6.0Hz), 3.61-3.70 (m, 4H), 4.81 (s, 1H), comparable to commercially available 2,2-diethoxyacetamide samples.
Embodiment 3
[0071] tert-Butyl 4-carbamoylpiperidine-1-carboxylate
[0072] NHase was ground in a mortar and added to potassium phosphate buffer (10 mM, pH=7.4) (9 mL) in a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The suspension was mixed by vortexing, and tert-butyl 4-cyanopiperidine-1-carboxylate (105 mg, 0.5 mmol) was added to the suspension dissolved in MeOH (1 mL). The reaction was stirred by rotary shaking at 25°C and 250 rpm. HPLC-MS was performed after the reaction. Samples (1 mL) were analyzed after 1.5, 2.5, 4 and 7 hours. Samples were mixed with MeOH (2 mL), filtered and injected directly into HPLC. After 7 hours, 40% conversion to tert-butyl 4-carbamoylpiperidine-1-carboxylate was observed.
[0073] MS (ES + ): m / z: 173.0 [M-55]. MS (ES - ): m / z: 227.0 [M-1].
[0074] The HPLC chromatogram is comparable to a synthetic sample of tert-butyl 4-carbamoylpiperidine-1-carboxylate. RRT 3 = 1, RRT 3a = 0.87.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com