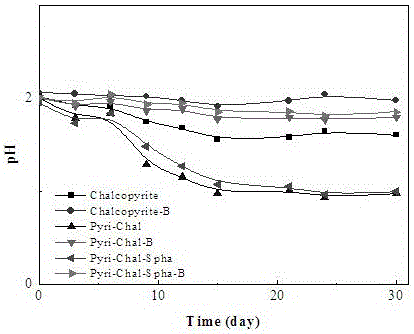
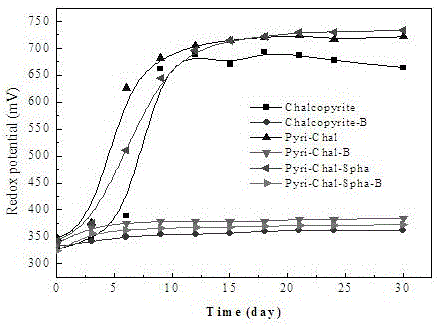
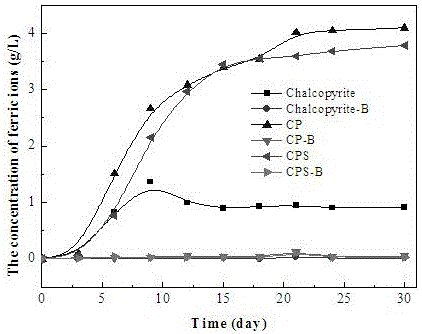
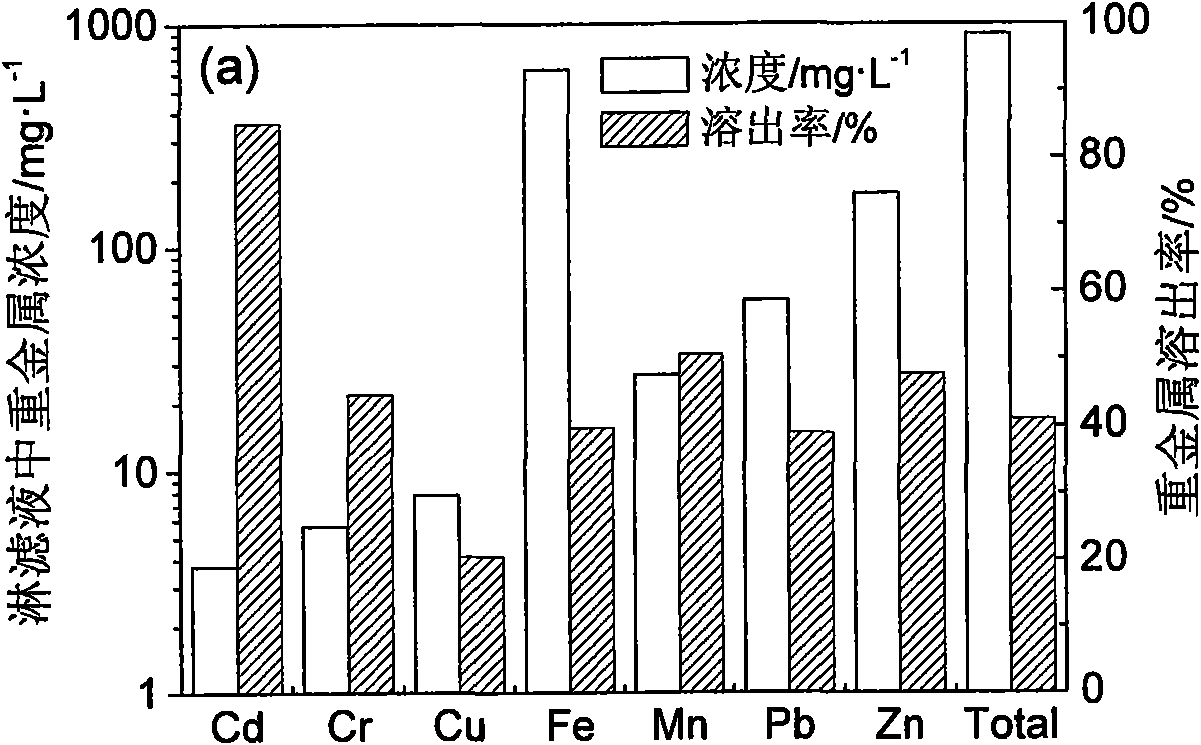
Patents
Literature
207 results about "Bioleaching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioleaching is the extraction of metals from their ores through the use of living organisms. This is much cleaner than the traditional heap leaching using cyanide. Bioleaching is one of several applications within biohydrometallurgy and several methods are used to recover copper, zinc, lead, arsenic, antimony, nickel, molybdenum, gold, silver, and cobalt.
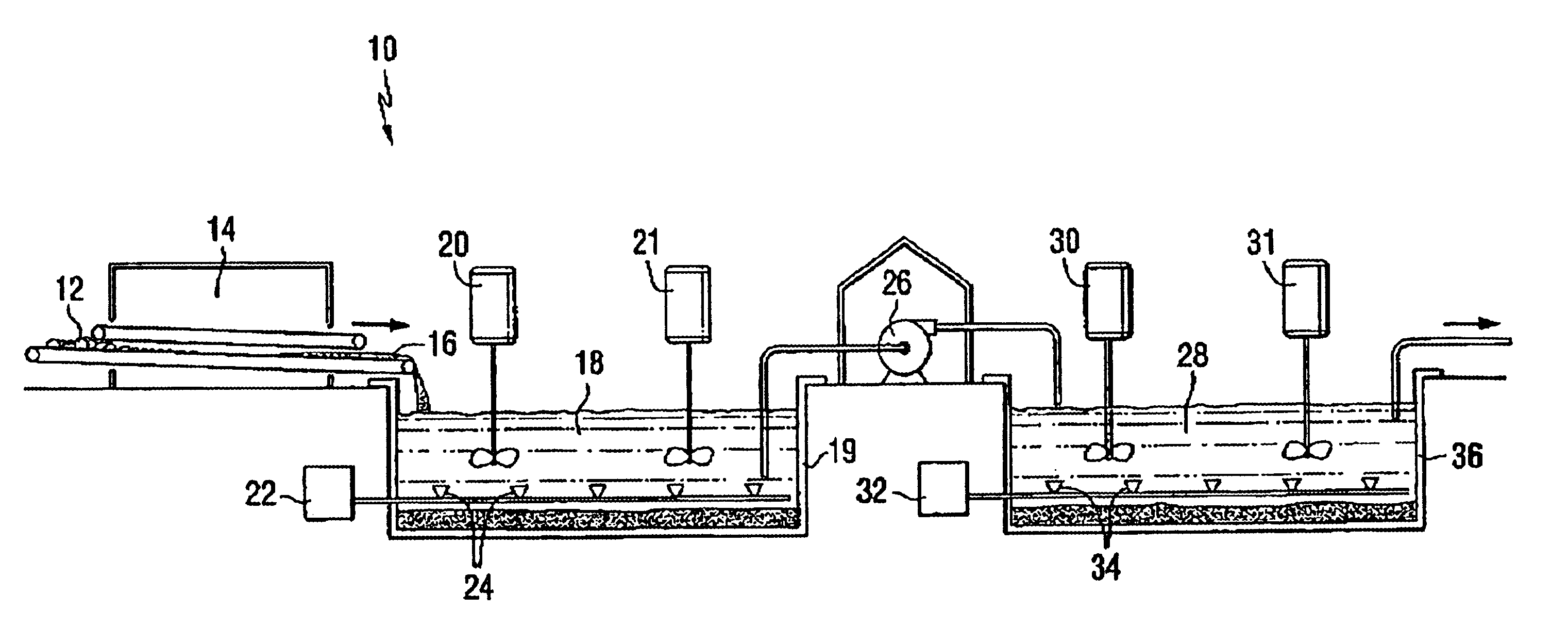
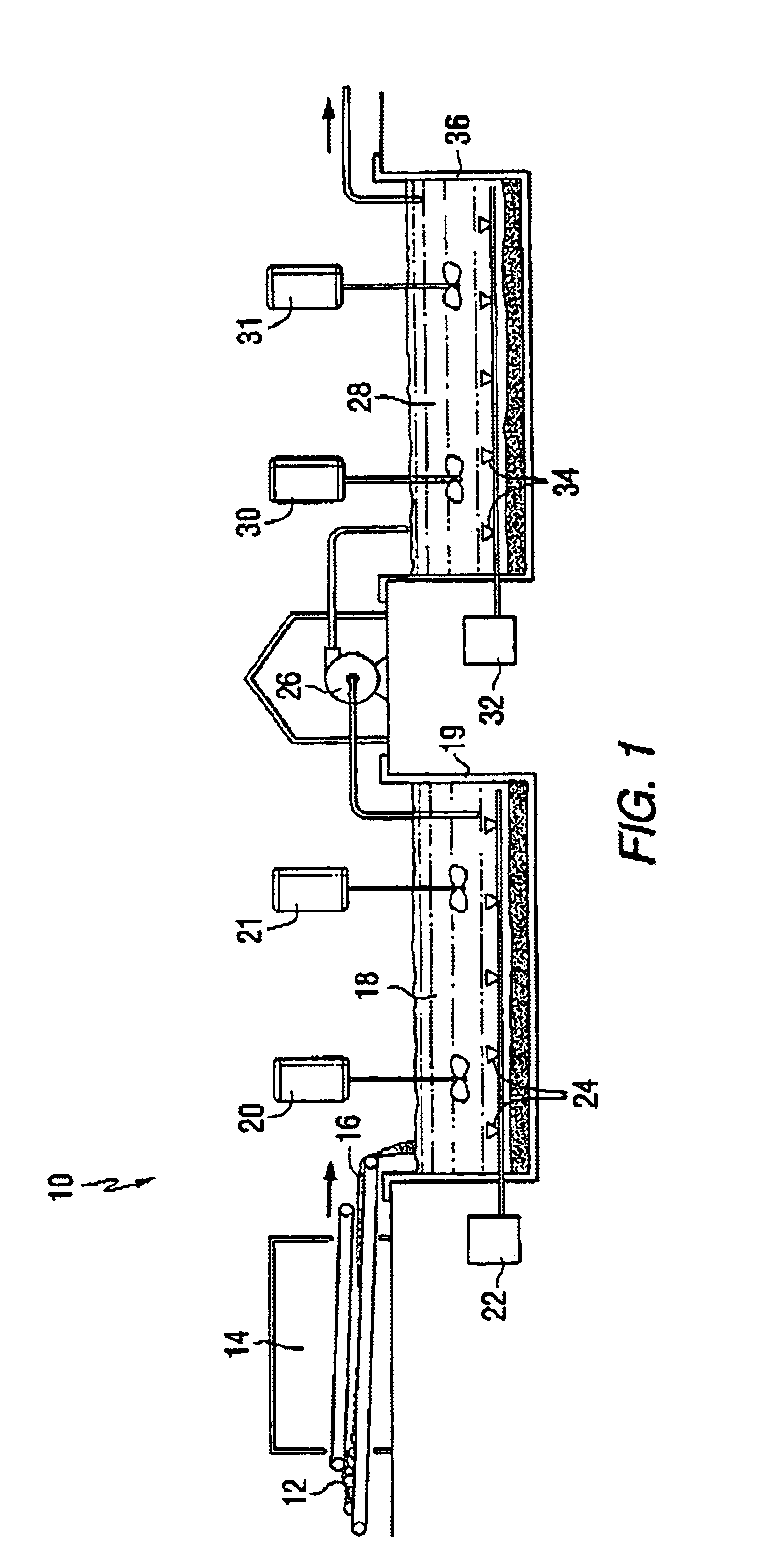
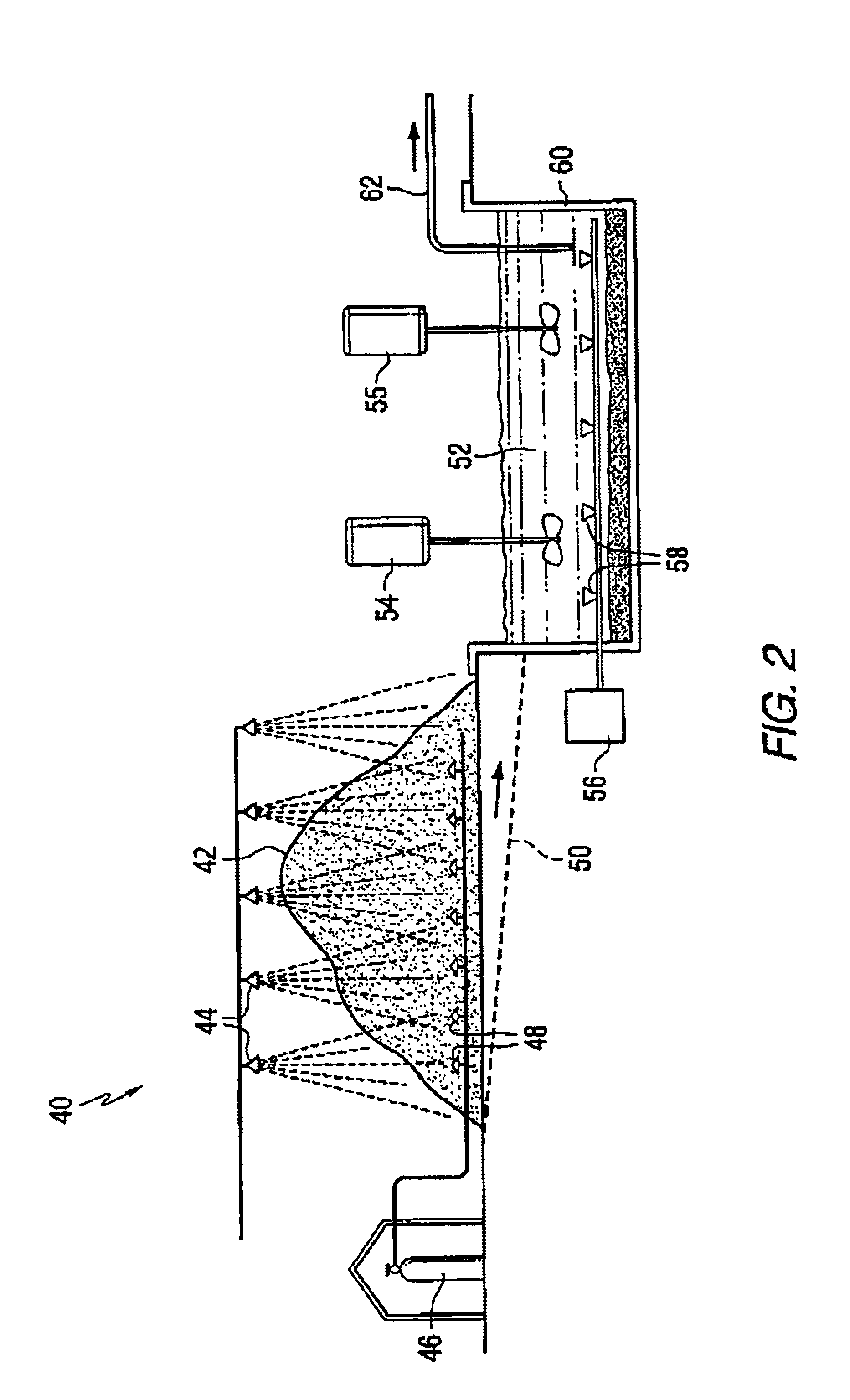
Method and apparatus for recovery of metals with hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6875356B2Treatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSprinkler systemBioleaching
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
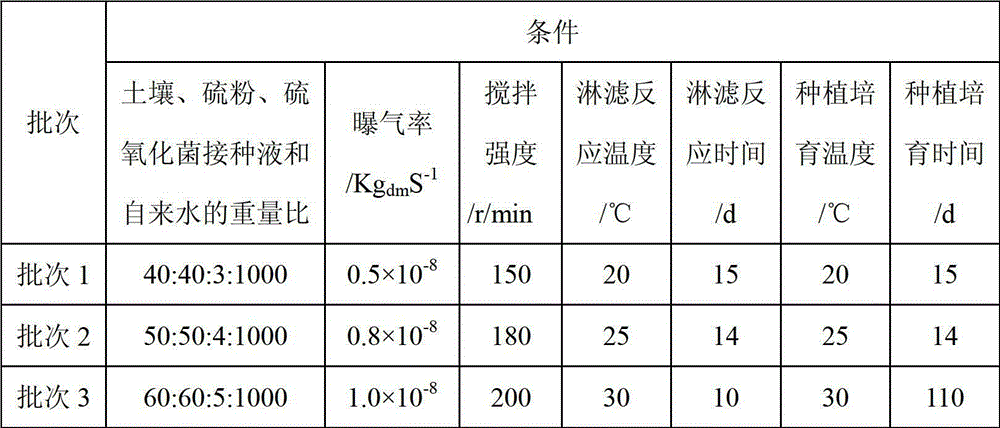
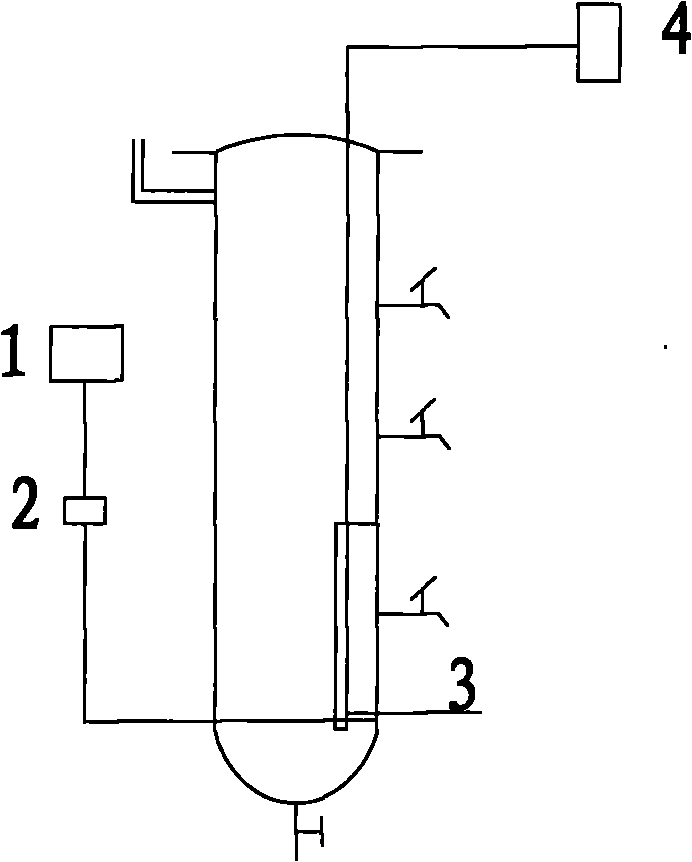
Plug flow type bioleaching process and apparatus for sludge treatment
InactiveCN101503269AStable productionLow investment costSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge processingFluid phaseSludge
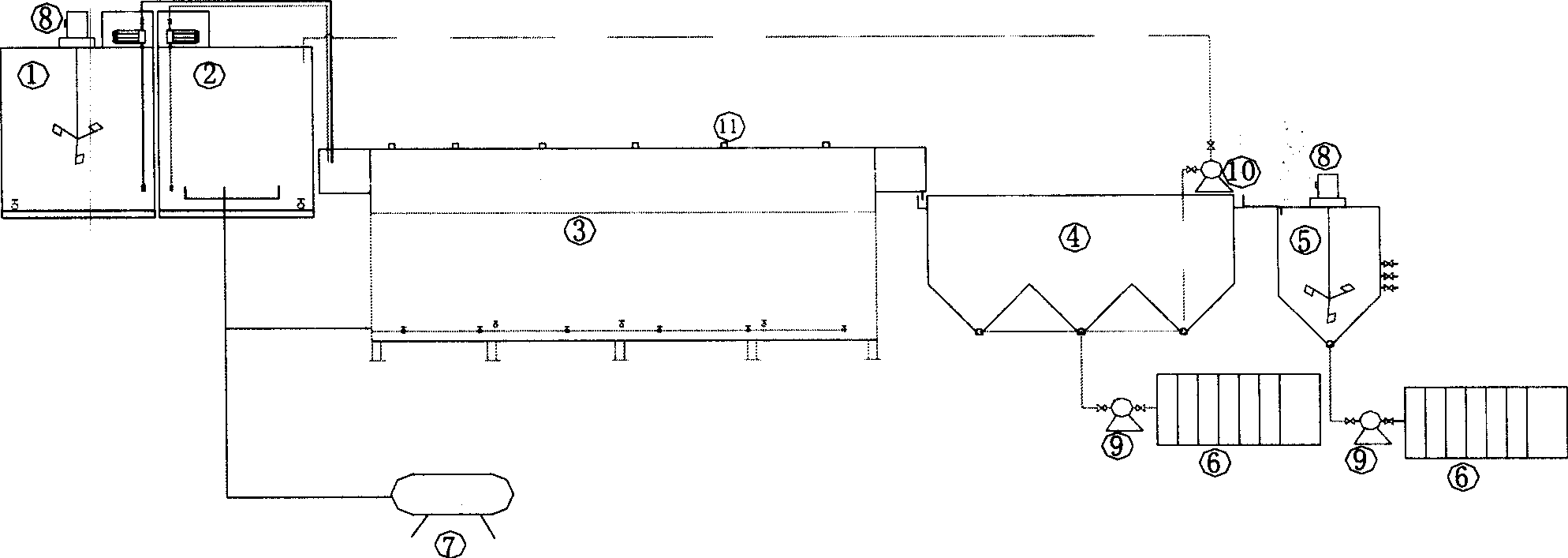
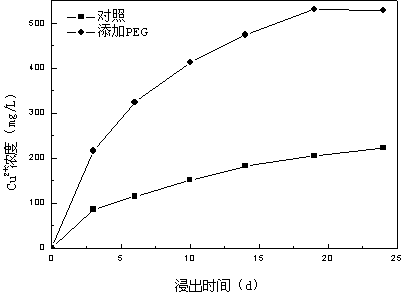
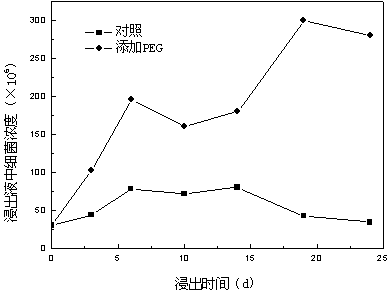
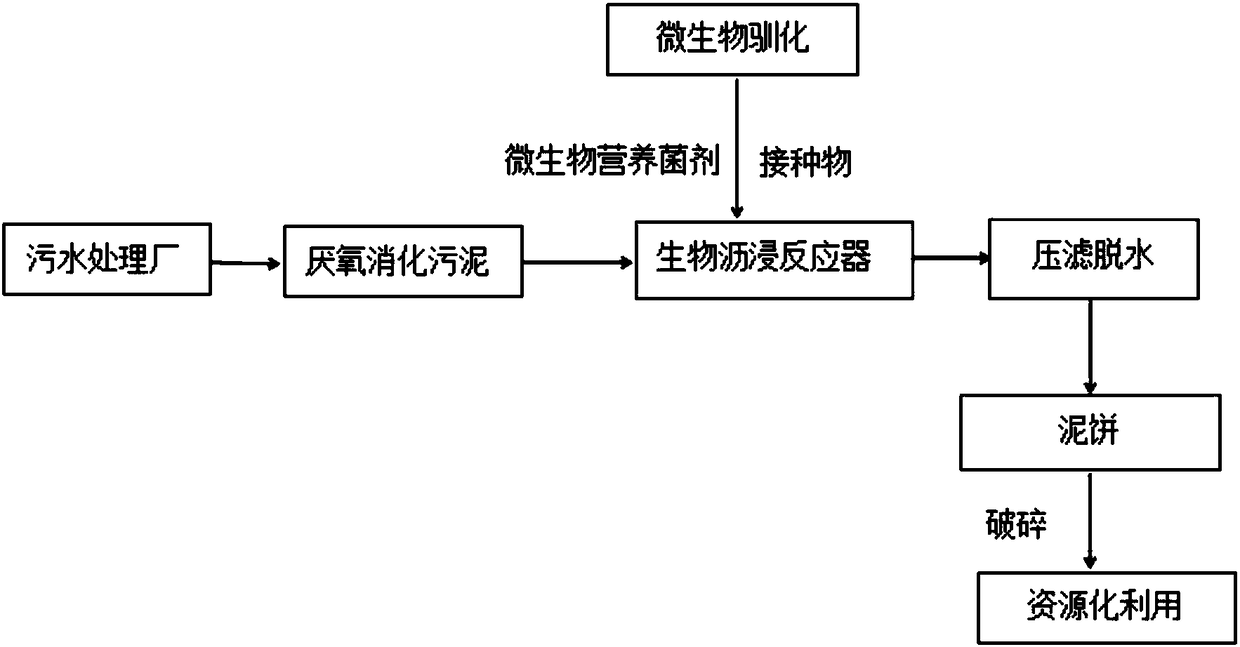
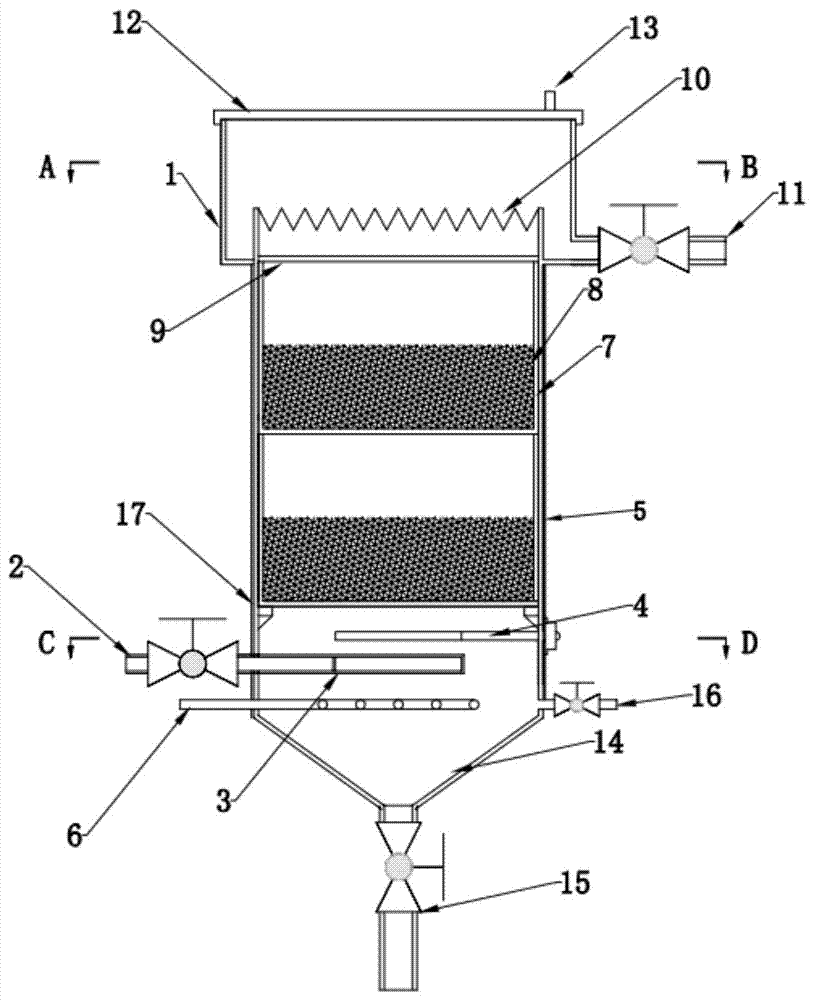
The invention provides a plug-flow type bioleaching treatment process for sludge treatment and equipment thereof. The equipment comprises a sludge regulating reservoir, an activating tank, a plug-flow type bioleaching reactor, an advection type sludge concentrated tank, a heavy metal recovery pond and other facilities, an aeration device, a heating device, a dehydration device, a stirring device and other devices. The process comprises the following steps that: a sludge system is acidified by a composite bacterium consisting of a thiobacillus and an acid resistant heterotrophic bacterium under conditions of aerobism and existence of sulfur powder and other composite nutriments, heavy metal in the sludge is massively dissolved in liquid phase, the sludge is regulated at the same time so as to facilitate sedimentation and dehydration; the sludge stays in the reactor for 2 to 4 days; discharged treated sludge enters the concentrated tank to be subjected to gravity thickening; 20 to 50 percent of concentrated bioleaching sludge flows back to the reactor, and the rest sludge is subjected to chamber filtration and dehydration without adding any flocculating agent until the water ratio is below 60 percent; and the heavy metal in the water is recycled by an alkali precipitation method. The method can remove massive heavy metals of the sludge, has over 99 percent of sludge pathogen kill ratio, and ensures that the treated sludge does not have malodor and is in khaki color, thereby realizing the aims of innoxiousness and minimization of the sludge.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bioreactor for continuous production of bioleaching solutions for inoculation and irrigation of sulfide-ore bioleaching heaps and dumps
InactiveUS20110045581A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWaste Dump SitesCulture mediums
The invention discloses an air-lift bioreactor, with internal recirculation, for producing sulfide-ore and minerals bioleaching solutions, with a phase-separating and solids-recirculation system without needing to impel the suspension containing the solids to the bioreactor by means of pumps, using diatomaceous earth and / or ferric precipitates as solid support to immobilize iron and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms. Specifically speaking, the invention describes a bioreactor that continuously produces bioleaching solutions containing microorganisms for inoculation and irrigation of sulfide-ore heaps and dumps processed by bioleaching. The bioreactor is stirred pneumatically, and is generally made up of an air diffuser, a reaction zone, a de-gasification zone, a solids separation zone, a culture media inlet, and a bioleaching solution outlet. Depending on the source of energy supplied for the growth of microorganisms, the bioreactor can produce a solution concentrated in ferric ions, iron-oxidizing bacteria and reduced-sulfur-compound-oxidizing bacteria.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
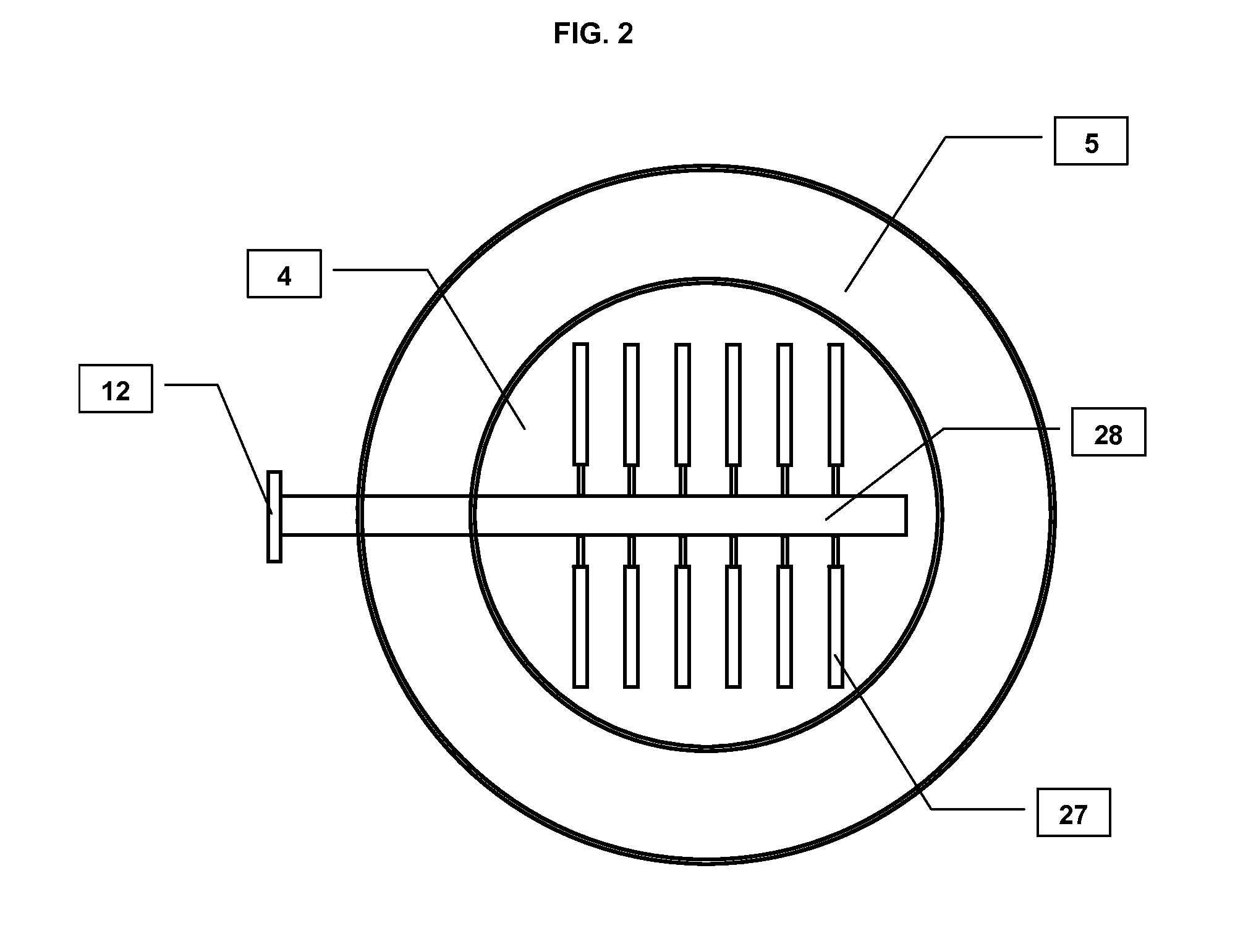
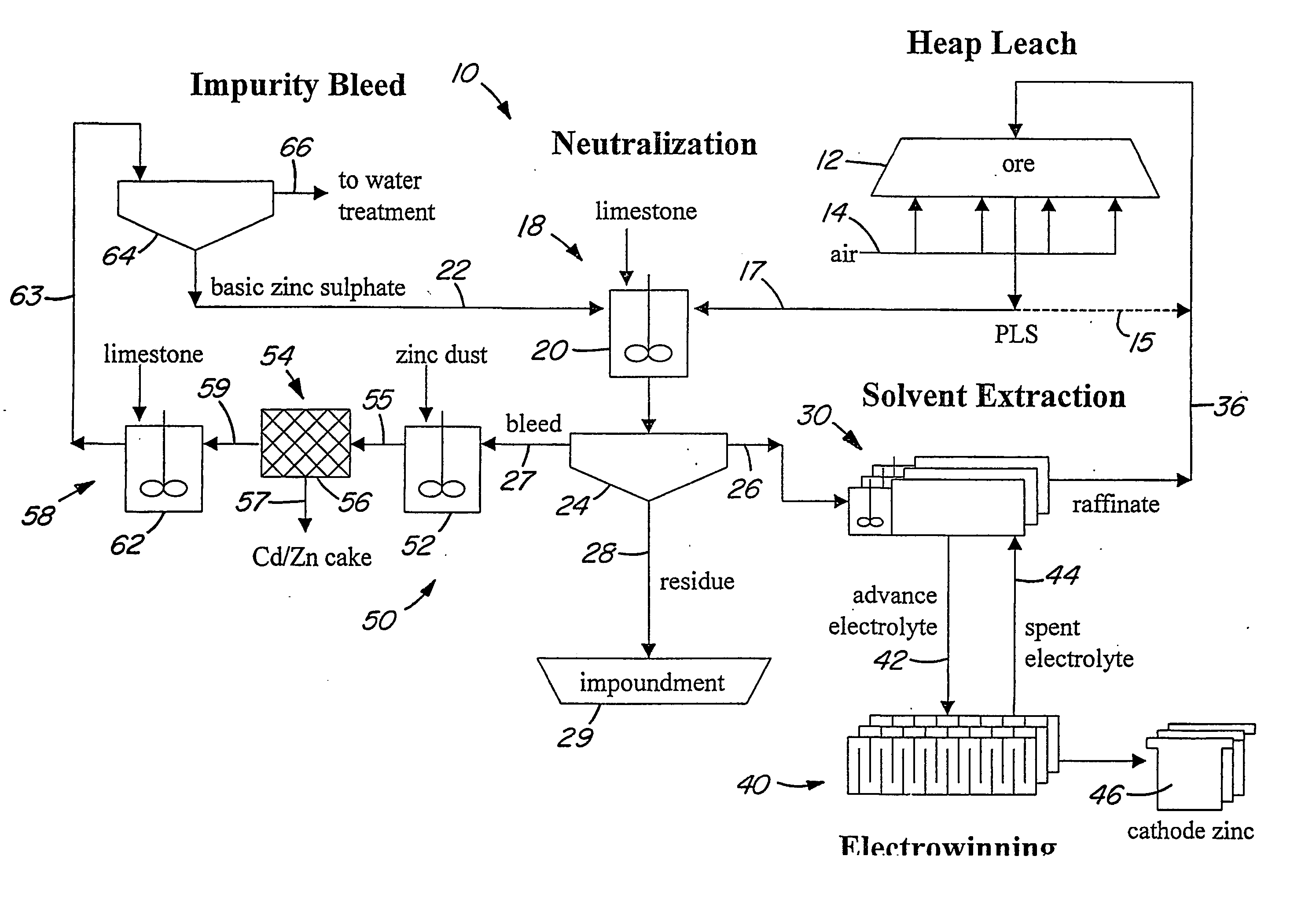
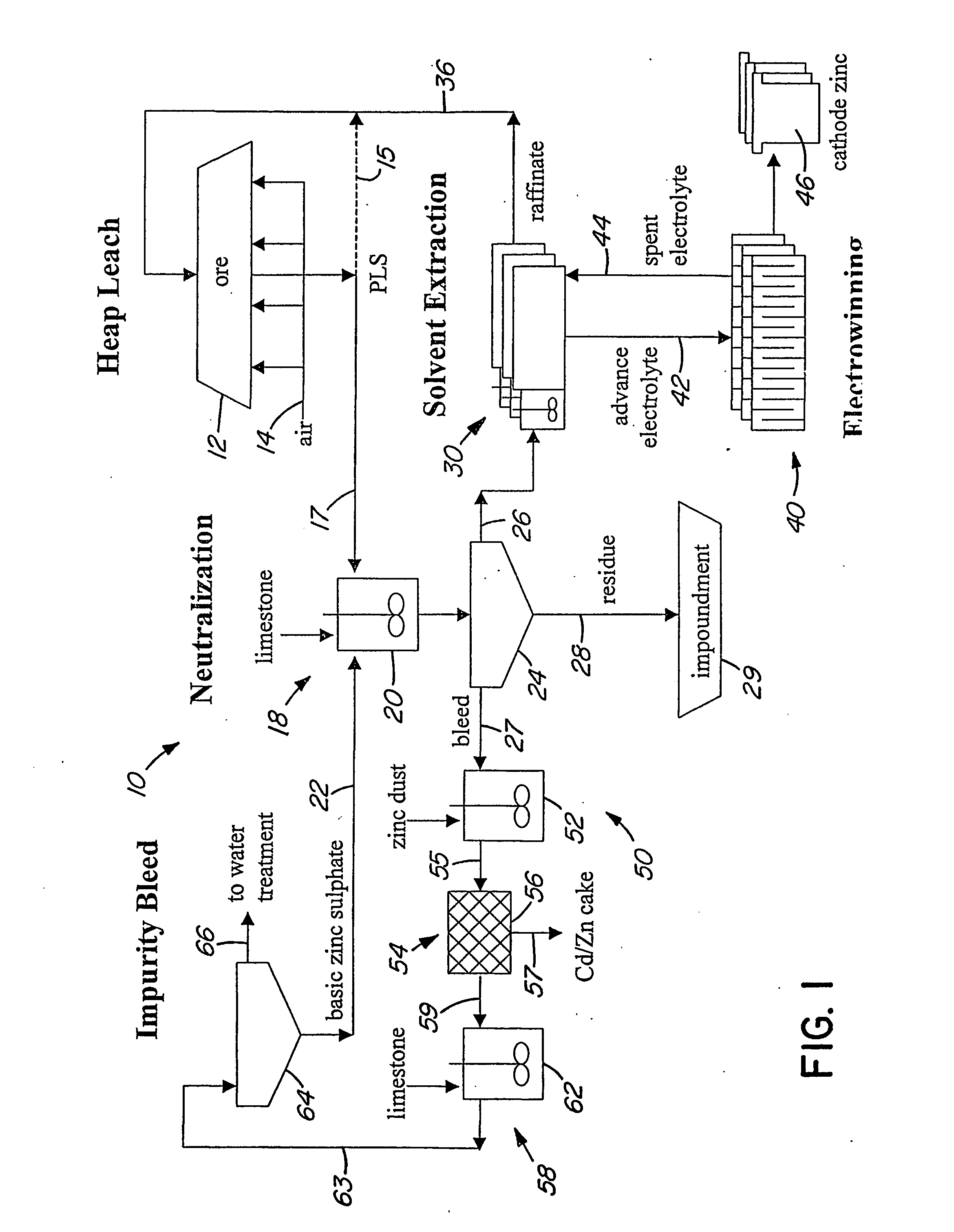
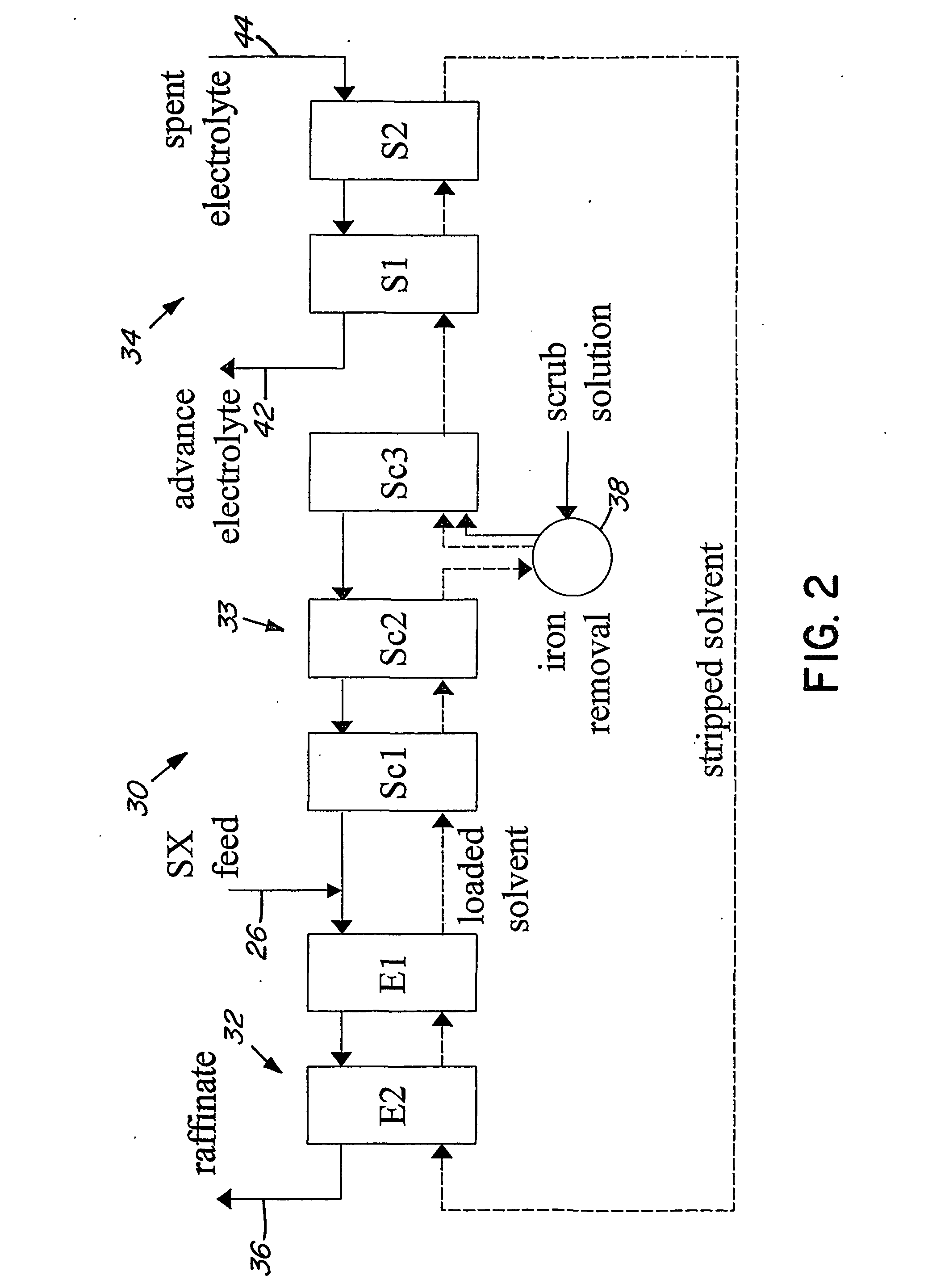
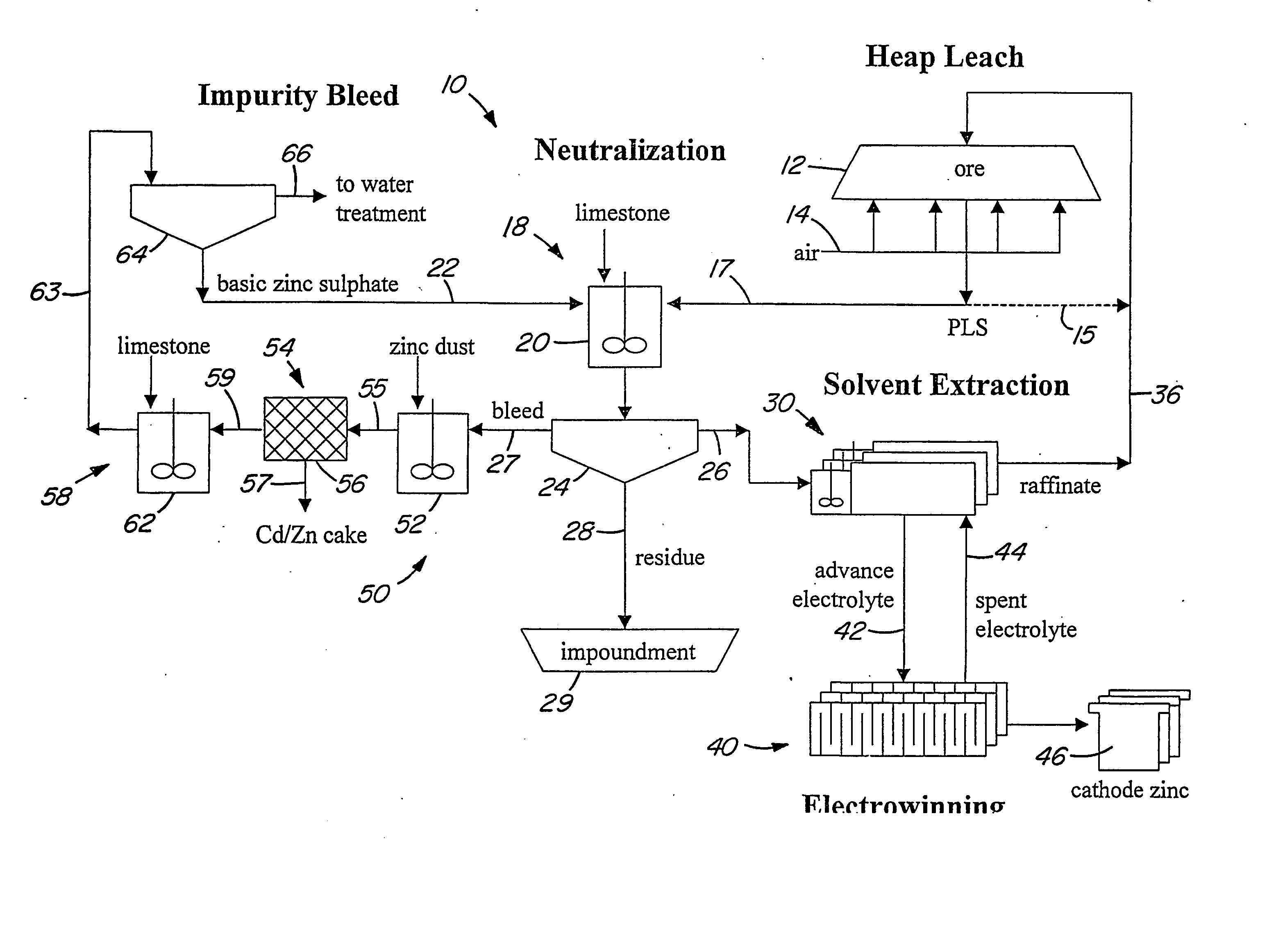
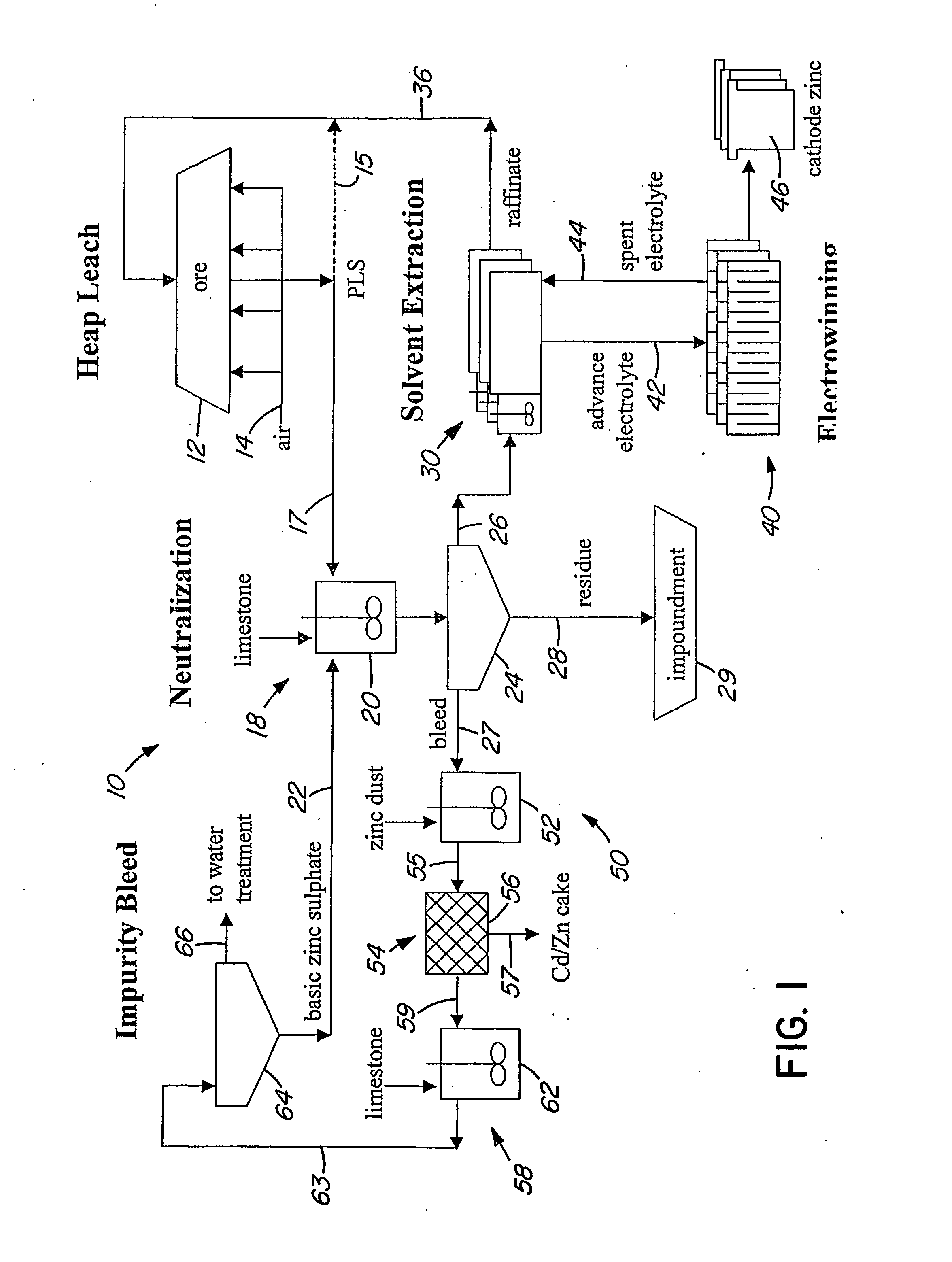
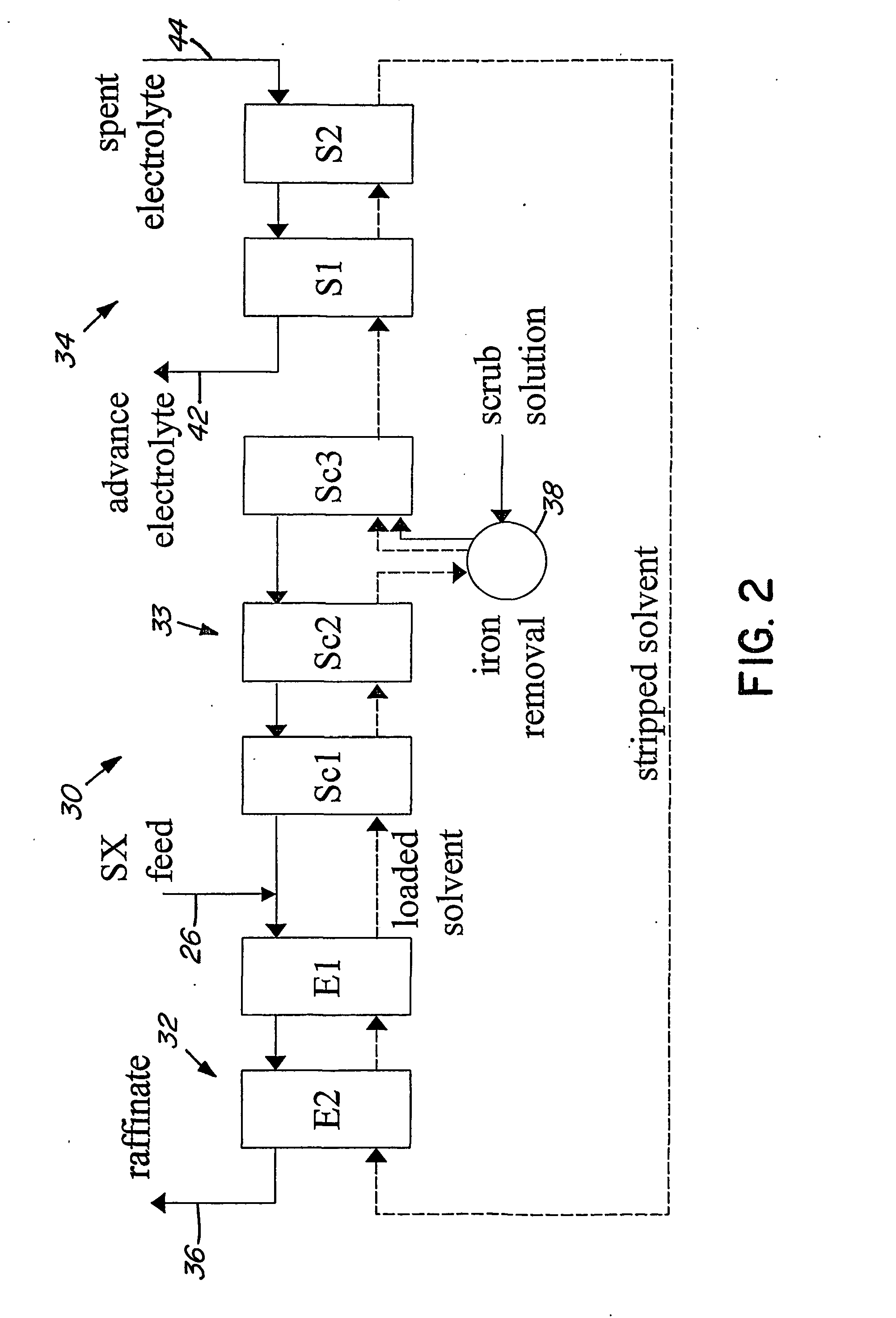
Heap bioleaching process for the extraction of zinc
InactiveUS20050066773A1Sufficient acid contentPrevent precipitationProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionZinc compounds
A method of extracting zinc from a sulphidic ore is provided which comprises bioleaching the ore in a heap with acidophilic microorganisms to produce a pregnant leach solution which is recovered from the bottom of the heap. An integrated process which comprises subjecting the pregnant leach solution to neutralization and solvent extraction to produce a concentrated zinc solution is also provided. Zinc may be recovered from the concentrated solution by means of electrowinning, either in the absence or presence of manganese. Alternatively zinc may be recovered in the form of a zinc compound.
Owner:TECK METALS
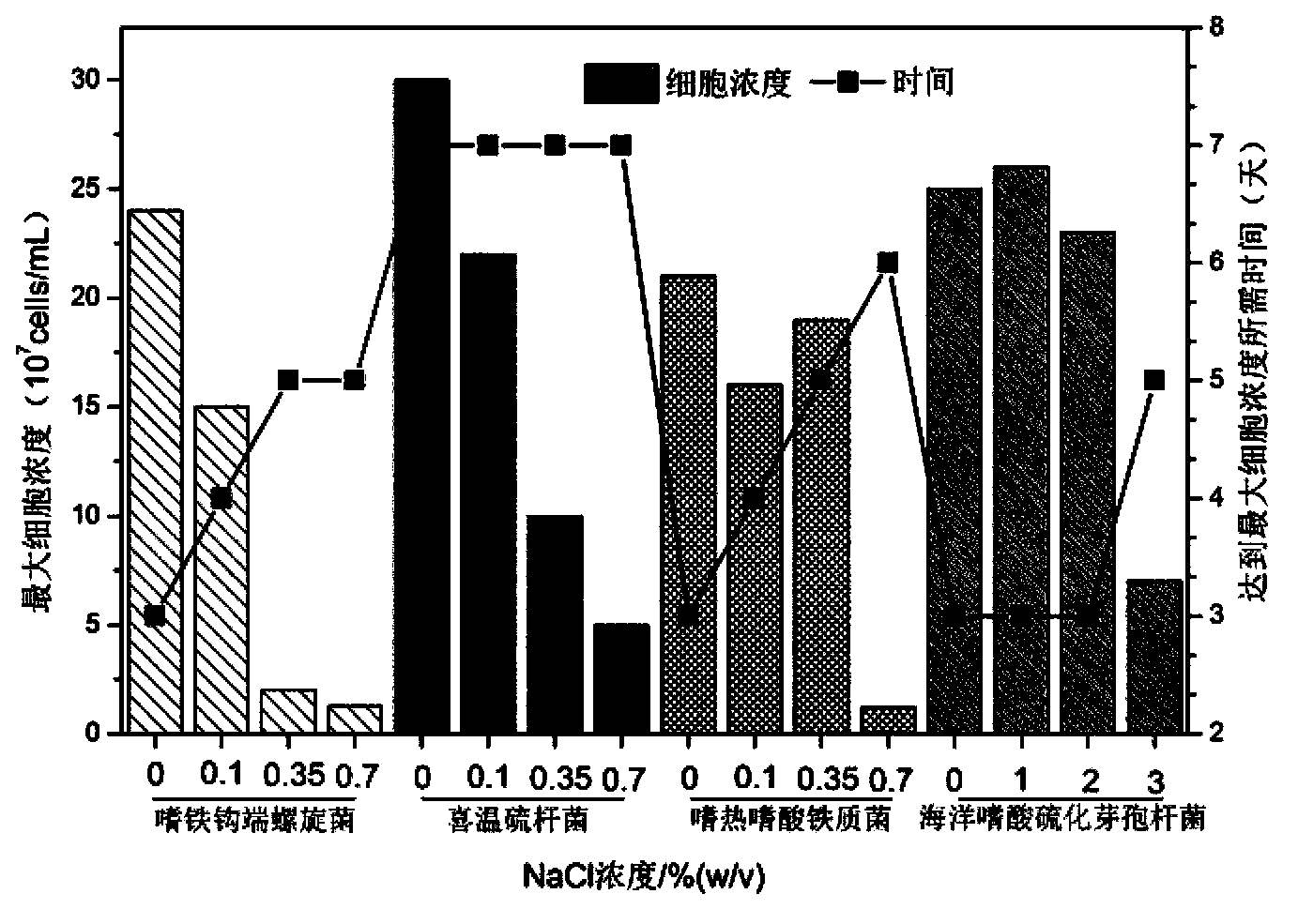
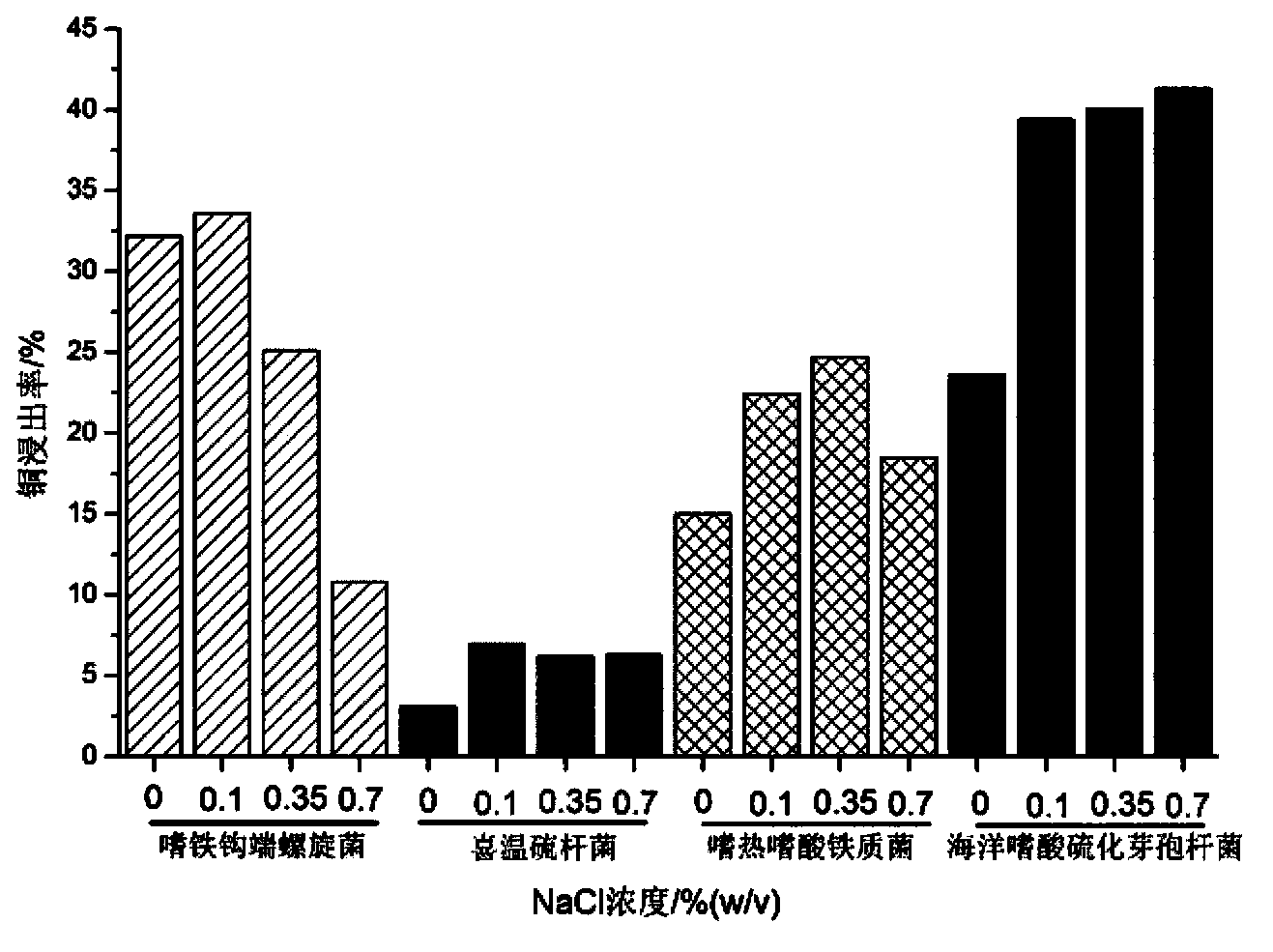
Compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching sulphide ore, and compounding method and application method thereof
ActiveCN103396964AIncrease resistanceImprove leaching efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical reactionEngineering
The invention discloses a compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching a sulphide ore, and a compounding method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of wet-process metallurgy. Aiming at a biological leaching mechanism of the sulphide ore and the physiological-biochemical characteristics of microorganisms, a community capable of efficiently leaching the sulphide ore is compounded by a plurality of mineral leaching microorganisms, wherein the mineral leaching microorganisms comprise marine bacteria which come from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and are capable of enduring high concentration sodium chloride, sulfur-oxidized bacteria, iron-oxidized bacteria and archaea which are from a freshwater environment, autotrophic bacteria and facultative heterotrophic bacteria. Not only can the difficult problem that the mineral leaching microorganisms from the freshwater environment are intolerance of sodium chloride be solved, but also microorganisms required by oxidation and dissolution of the sulphide ore and diversity of chemical reactions are guaranteed. The compound bacterium community can obviously increase leaching efficiency and leaching rate of the sulphide ore such as copper pyrites and can be applied in a leaching process and a dump leaching process of a stirring tank. A certain basis for popularization and application of biological metallurgy of the sulphide ore is provided by the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Process for removing heavy metal from sludge of sewage treatment plants
InactiveCN101913745AIncrease growth activityReduce dehydration costsClimate change adaptationWater contaminantsFlocculationSludge compost
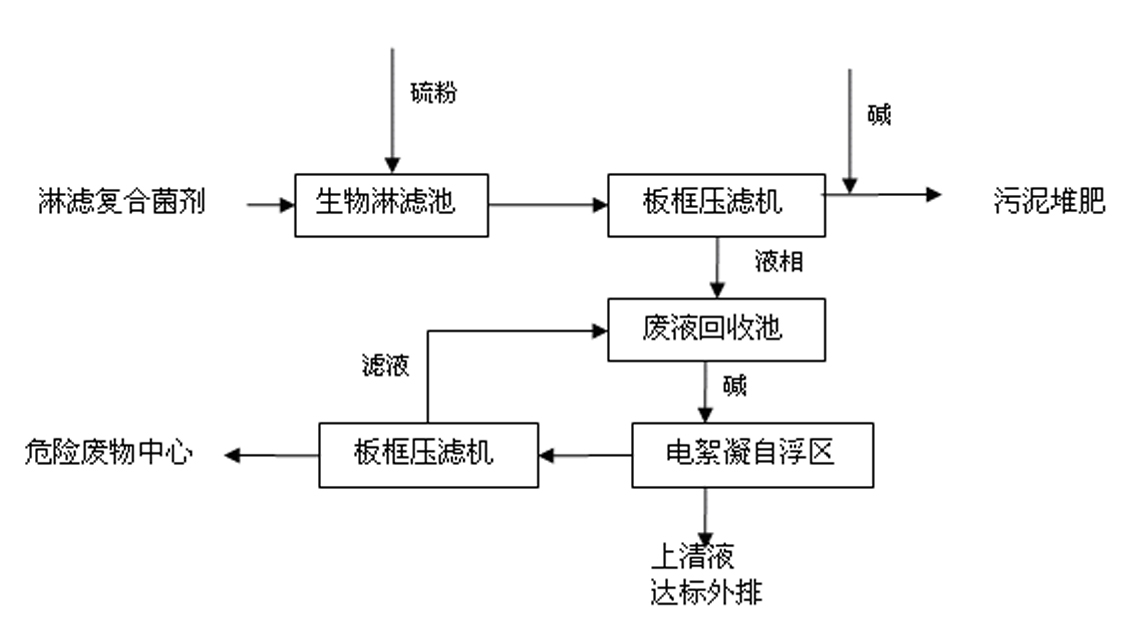
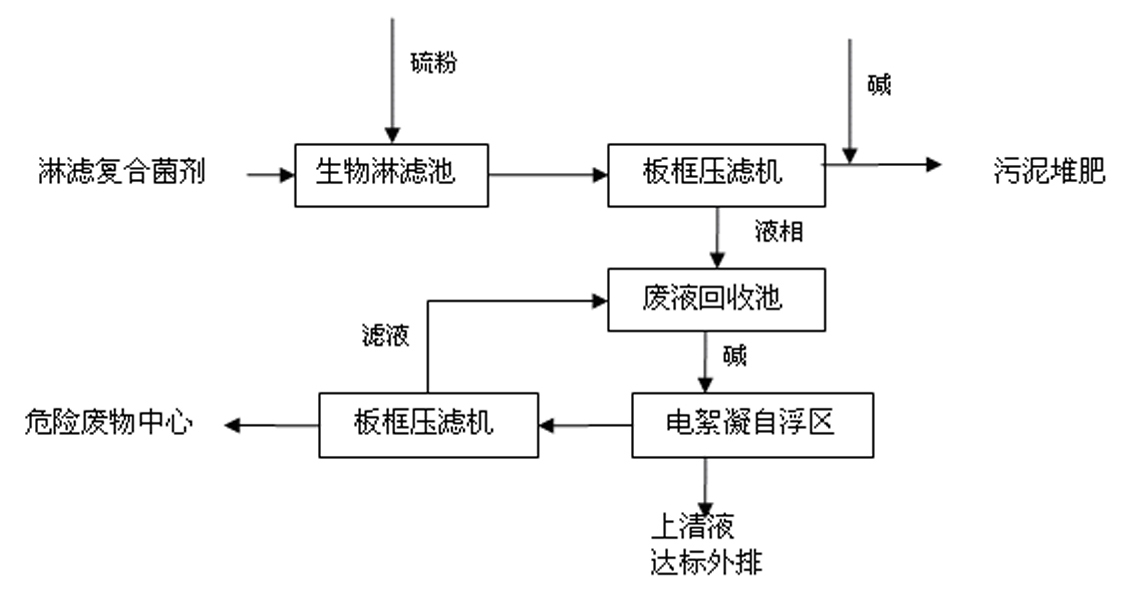
The invention discloses a process for removing heavy metals from sludge of sewage treatment plants. The process comprises the following steps of: adding 0.5 to 30g of elemental sulfur in each litre of sludge in a bioleaching tank, respectively inoculating 1 to 5 percent of thiobacilli and 1 to 3 percent of acidophilus moulds in the bioleaching tank, carrying out aerated bioleaching on the obtained sludge for 2 to 6 days until the pH value of the obtained sludge in the bioleaching tank is less than 2, and pumping the sludge subjected to bioleaching treatment in a plate-and-frame filter press by using a pump to carry out filter press separation so as to obtain sludge from which heavy metal is removed and sewage containing the heavy metal; adding alkali into the sludge from which heavy metal is removed to neutralize the sludge and then transporting the sludge to a sludge composting plant for composting; adding alkali into the sewage containing the heavy metal until the pH value of the sewage is about 7, then putting the sewage into an electrolytic flocculation floatation device to carry out electrolytic flocculation and self-floatation treatments on the sewage, and after the obtained liquid supernatant reaches the standard, draining the liquid supernatant; and pumping the flocculated scum of the pollutant in water into the plate-and-frame filter press for separation to obtain corresponding filter liquor and sludge, wherein the filter liquor is drained to a waste liquor recovery tank, and the sludge is transported to a hazardous waste disposal center for treatment. The process of the invention has the advantages of shortening the lixiviation period, improving the lixiviation efficiency and the variety of lixiviated heavy metal, ensuring the stability of removing heavy metal, and saving equipment investment.
Owner:湖南德施普生物科技有限公司
Method for removing heavy metals in excess sludge by bioleaching-similar Fenton oxidative coupling
InactiveCN101891358AReduce processing costsImprove processing efficiencySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationActivated sludgeOxygen
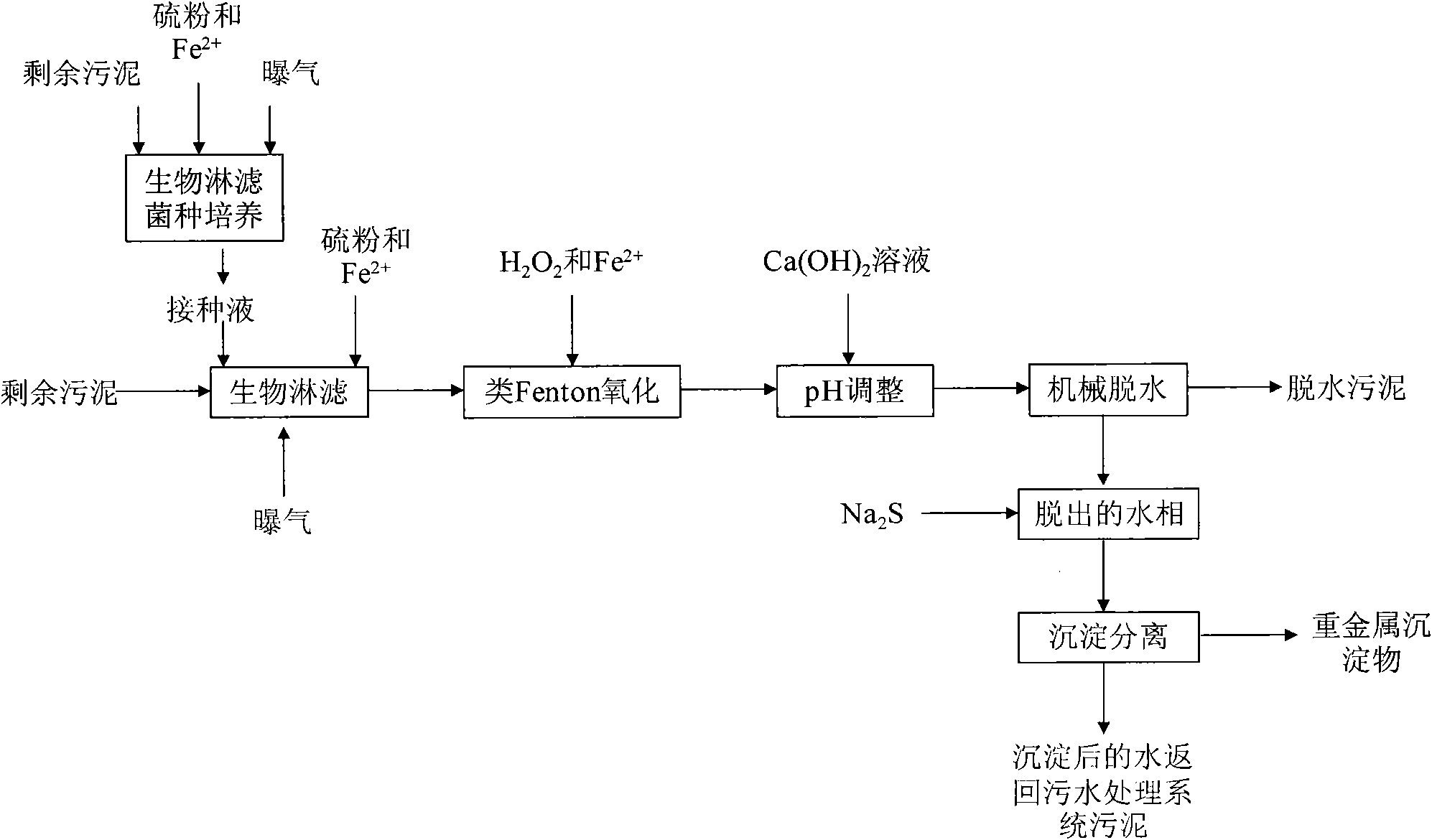
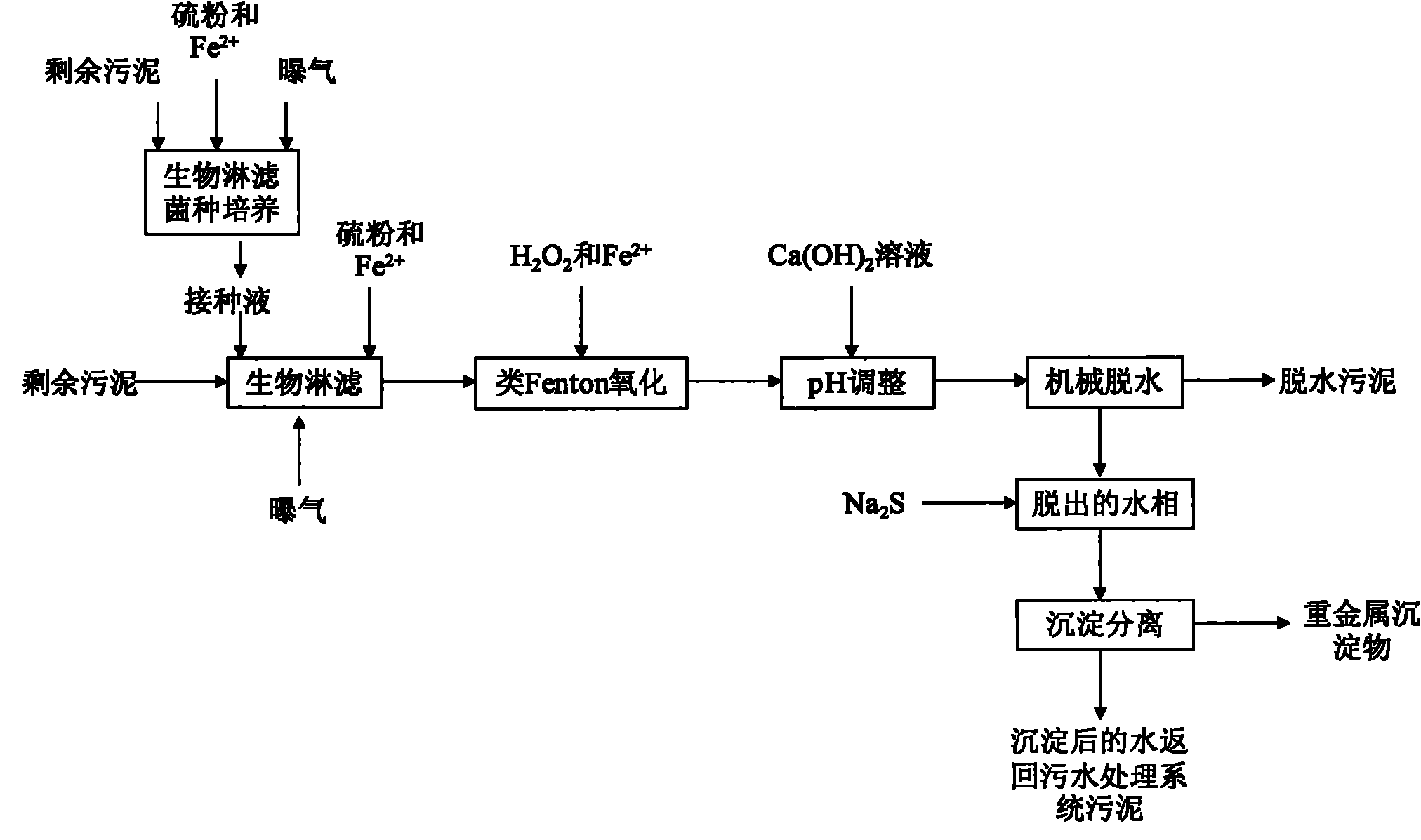
The invention relates to a method for removing heavy metals in excess sludge by bioleaching-similar Fenton oxidative coupling and belongs to the technical field of sewage and sludge treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing domesticated autochthonous bioleaching bacteria serving as inoculation liquid in the sludge under the condition that enough substrate is added; adding the inoculation liquid into the excess sludge and bioleaching the sludge under the condition that oxygen exists, stirring is performed and an appropriate amount of substrate is added until the pH of the sludge is between 2 and 3; allowing H2O2 to produce strong oxidizing free radicals and the like to oxidizing the sludge under the catalytic action of Fe<2+> and Fe<3+>; adding solution of Ca(OH)2 into the treated sludge and adjusting the pH of the sludge to be between 6 and 7; and dehydrating the treated sludge by a plate and frame filter pressing or centrifugal dehydration method to obtain the dehydrated sludge of which the water content is between 65 and 75 percent. After the sludge bioleaching-similar Fenton oxidative coupling is performed, the dissolution rates of cadmium, mercury, lead, chromium, arsenic, nickel, zinc and copper in the sludge are up to 50 to 65 percent, 50 to 70 percent, 15 to 35 percent, 55 to 70 percent, 70 to 80 percent, 65 to 80 percent, 60 to 85 percent and 60 to 80 percent respectively. The heavy metal content of the sludge is lower than the requirements of The Disposal of Sludge from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant: Control Standards for Agricultural Use of the State Criteria of the People's Republic of China (CJT309-2009) and The Disposal of Sewage Sludge from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Quality for Afforestation in Gardens or Forests (GB / T 23486-2009).
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Biological potassic fertilizer produced by using low-grade potassium-bearing rocks and production method thereof
InactiveCN101229984AImprove fertilityIncrease contentBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationPotassiumDrug biotransformation
The invention provides biological potassium fertilizer produced by using low taste rock containing potassium and a production method for the fertilizer. The biological potassium fertilizer is prepared through the following steps of solid state fermentation treatment of the low taste rock containing potassium, processing waste of agricultural byproducts, water, earthworm and complex bacteria, biotransformation under the effect of the earthworm and housefly larvae as well as the bioleaching. On the basis of the two-step transformation method (the solid state fermentation and the bioleaching) for producing biological potassium fertilizer, the biotransformation step is added in the invention. After the solid state fermentation, biology with biotransformation function is inoculated. The conversion of the potassium in the low taste rock containing potassium is improved; therefore, the rock powder containing the potassium and agriculture waste are turned into good organic fertilizer through a plurality of transmission ways. The contents of other trace elements in the potassium fertilizer are increased. Therefore, the invention has a good market promotion prospect with an economical and practical advantage and good fertility of the potassium fertilizer.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for bioleaching a metal present in a material
InactiveUS20160138128A1Less exposedIncrease cell densityProcess efficiency improvementBiological water/sewage treatmentBioleachingFerric ion
The invention relates to a method for recovering at least one metal present within a material, said material possibly including iron, said method including a step of supplying a ferrous ion, a step of supplying a ferric ion, and a step of bioleaching at least one metal present in the material by the ferric ions, each one of the steps being implemented by a particular bacterial population.
Owner:MEURICE RECH & DEVEMENT
Bacillus and method for bio-leaching of scandium from scandium-containing minerals by virtue of bacillus
ActiveCN105886425AReduce manufacturing costSimple processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to a bacillus and a method for bio-leaching of scandium from scandium-containing minerals by virtue of the bacillus. The method comprises the following steps: crushing the scandium-containing minerals and grinding the scandium-containing minerals until grain size is 0.037-0.074mm, adding obtained scandium-containing mineral powder to a microorganism-containing culture solution, controlling a pulp concentration as 1-10%, and conducting bio-leaching for 7-15 days, wherein a leaching rate is 20-50%; and centrifuging or settling-separating a leached pulp, so that a scandium-containing solution is obtained, and conducting extracting, conducting washing and conducting reverse-extracting as conventional means, so that a scandium primary concentrate is obtained. The method disclosed by the invention, which is free from the addition of acid during leaching, can reduce production cost and achieve green scandium leaching, without pollution to environment; and the scandium in a leachate can be enriched by virtue of a conventional method. The biological method is green and environment-friendly, simple in process and easy for popularization.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI +1
Method for leaching metal from metallic ores and special strain in same
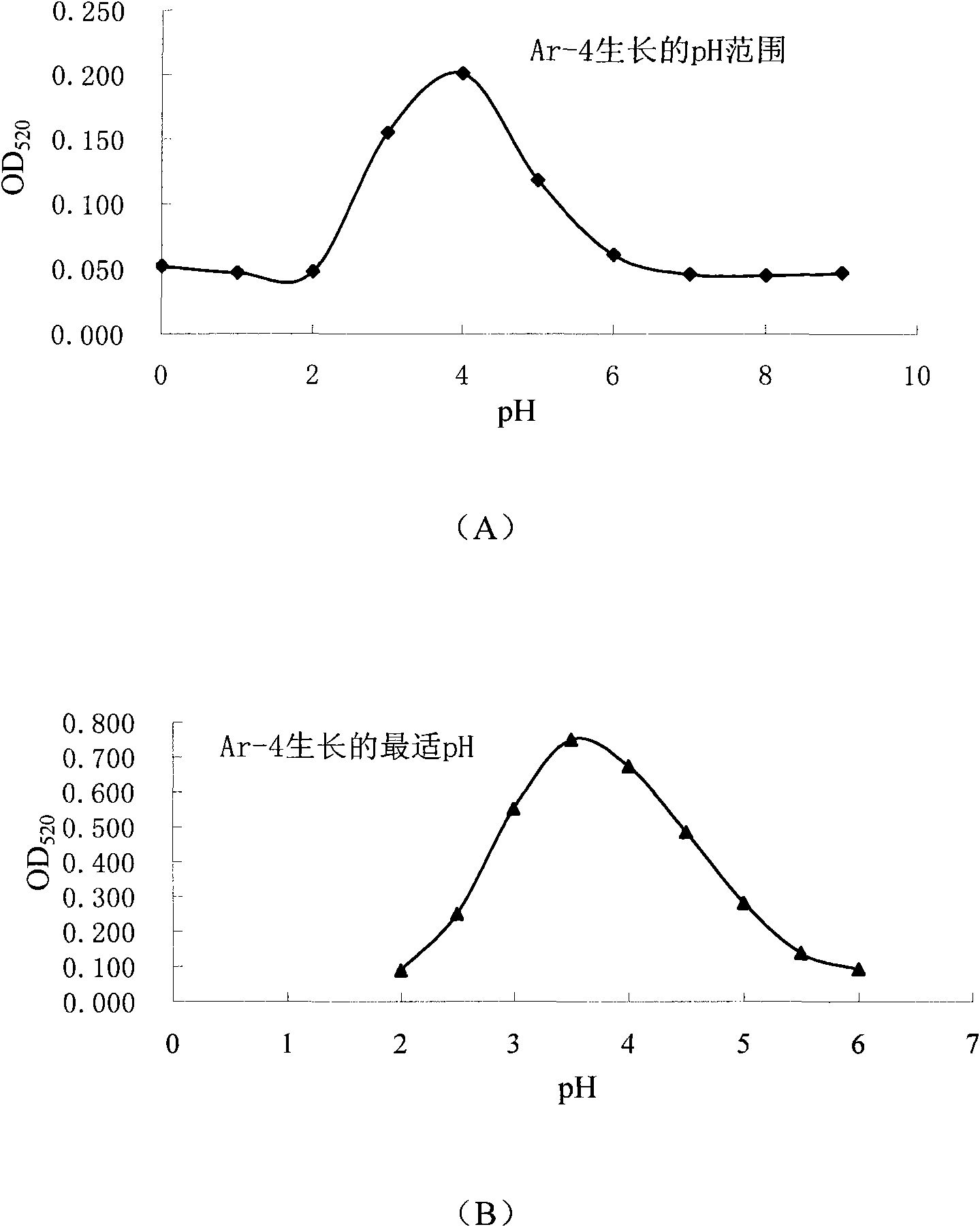
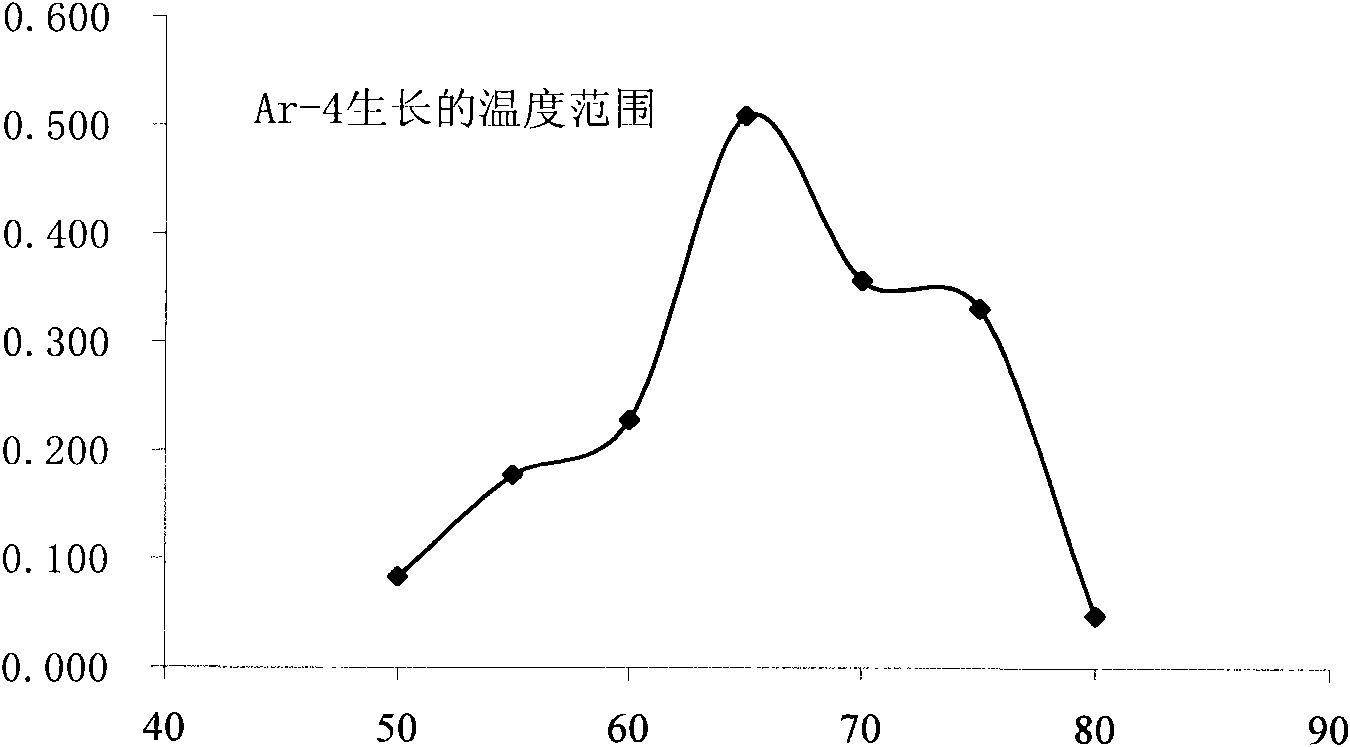
The invention discloses a method for leaching metal from metallic ores and a special strain in the same. The strain is metallosphaera sp. Ar-4, with the collection number being CGMCC NO.3402. Experiments prove that the strain can grow under the environment of low pH value, high temperature and hypersalinity, can be used for leaching copper ions from the copper pyrite, with leaching rate of 10.6%, and can be also used for leaching iron ions from the pyrite (sulfur concentrate), with leaching rate of 2.9%. The high temperature ore-leaching strain improves the oxidation efficiency of the sulfide from at least two aspects as follows: first, with temperature rise, the reaction rate is increased; and second, temperature rise can expand the range of extraction of metal from a few minerals, thus marking up for the defects of unsuccessful leaching of a few minerals by the mesophilic strain, high investment, low efficiency and the like. The strain is especially suitable for the minerals with low leaching efficiency, such as copper pyrite. In addition, the strain has superstrong acid resistance; therefore, generated acidity can not affect the effects of the strain in the bioleaching process and can further improve the leaching efficiency.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
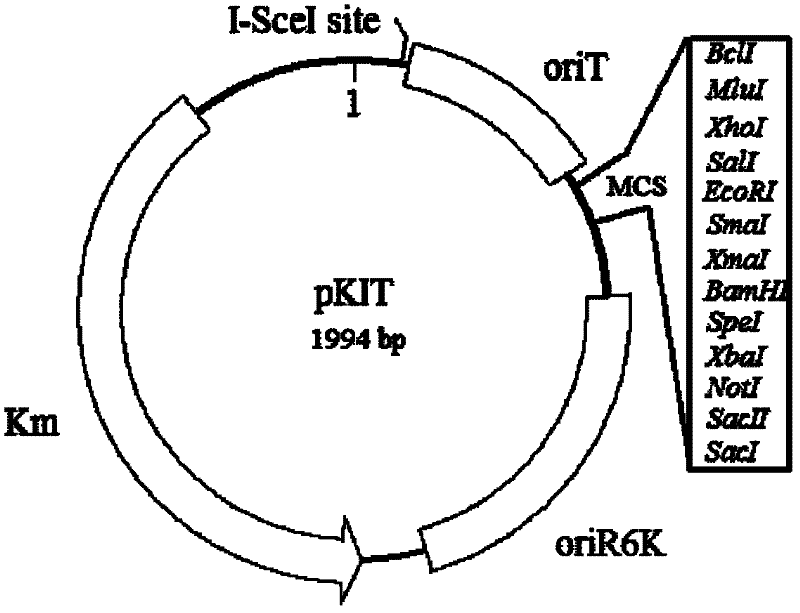
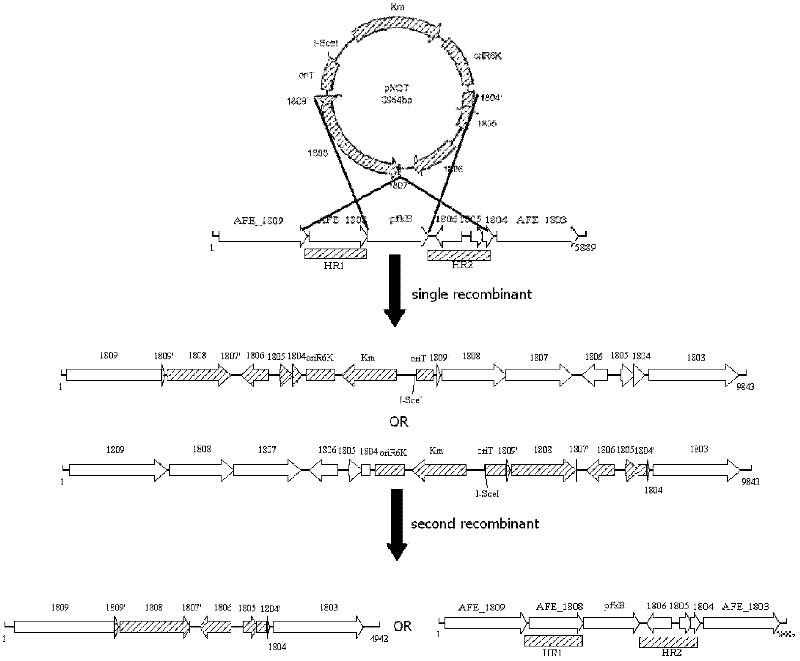
A marker-free gene knockout method for extreme acidophilic Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
ActiveCN102260699ARapid knockoutEfficient knockoutMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionThiobacillus ferrooxidansBiotechnology
The invention discloses an unmarked gene knock-out method of extremely acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans based on the principle of homologous recombination. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing initial plasmids, suicide plasmids containing homologous fragments at upstream and downstream parts of target genes to be knocked out, and induction plasmids containing yeast endonuclease I-SceI genes; jointing and transferring the suicide plasmids and the induction plasmids to acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans; and screening and identifying single commutators generating homologous recombination for the first time and double-exchange mutant strains generating homologous recombination for the second time. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the unmarked gene knock-out of acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans for the first time, can realize the purpose of quickly, stably and efficiently knocking out the genes of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, and can be used for researching the functional and metabolic mechanisms of the genes of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, improving the genetic characters and constructing efficient bioleaching engineering bacteria; and moreover, the obtained mutant strain does not carry any resistance gene, thus the obtained mutant strain not only can be used as an original strain to knock out and improve genes in subsequent different sites, but also can be safely used for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
New alicyclobacillus strain and application thereof in bioleaching
InactiveCN102161977AImprove leaching rateShort leaching timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlicyclobacillusBioleaching
The invention relates to a new alicyclobacillus strain and an application thereof in bioleaching. The conservation number of the screened alicyclobacillus strain is CGMCC 4500; and the strain is cultured at the temperature of 25-35 DEG C and grows within the pH range of 1.5-5.0. The strain can be applied in the bioleaching field such as pyrite leaching. The alicyclobacillus strain has an acidophilic character, and can grow by taking ferrous ions as an energy matrix and fixed CO2 as a carbon source and meanwhile can rapidly grow by virtue of organicnutrition, thus the strain is suitable for large-scale amplification culture so as to be applied in the bioleaching field. Studies show that the new alicyclobacillus strain has the advantages of high leaching rate, short leaching time, no environmental pollution and the like, and metal ions therein have high tolerance and are free from inhibition of organic matters in the system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for reinforcing leaching of chalcopyrite microorganisms
InactiveCN105861823AHigh static potentialImprove solubilityProcess efficiency improvementMicroorganismChalcopyrite
The invention discloses a method for reinforcing leaching of chalcopyrite microorganisms. The method comprises the steps that (1) a chalcopyrite sample, a pyrite sample and a blende sample are crushed into particles; (2) a culture medium, chalcopyrite, blende to be added and / or pyrites to be added are subjected to high-temperature and high-pressure sterilization; (3) the sterilized samples are put into a shake flask with the culture medium according to the requirement, and the microorganisms in bioleaching are inoculated; (4) the shake flask in the step (3) is placed in a constant-temperature shaking table to be cultured; and (5) the leaching efficiency of copper in the leaching process is measured. By adding the pyrites and the blende in a chalcopyrite microorganism leaching system, pH of a solution is low, the concentration of iron ions and the redox potential are high, oxygenolysis of the chalcopyrite is reinforced under the synergistic effect of biological, physical and chemical factors, and the leaching rate of the copper is increased. Compared with microorganism leaching results obtained without adding any minerals, the leaching rate of the copper is increased by 5.0%-5.5%. The method provides technological guidance for efficient leaching of the chalcopyrite.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
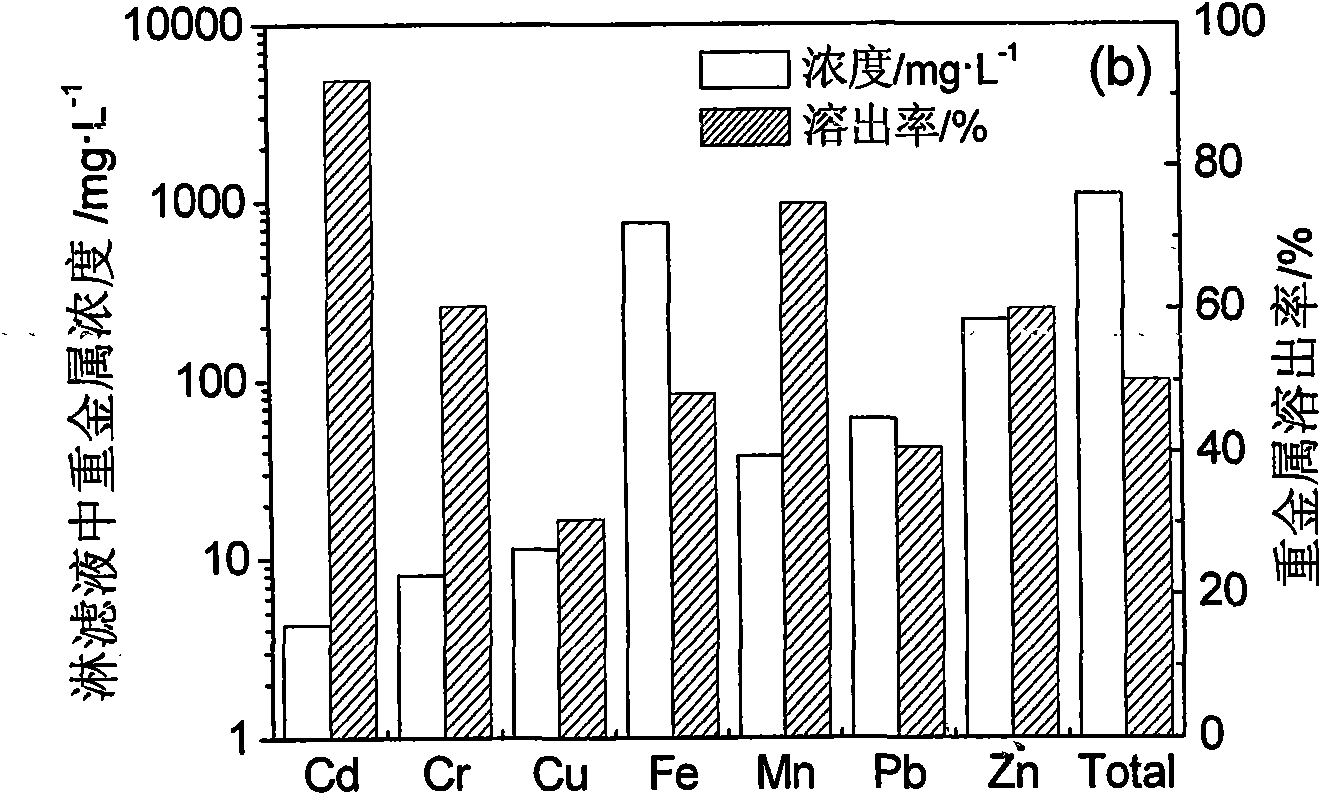
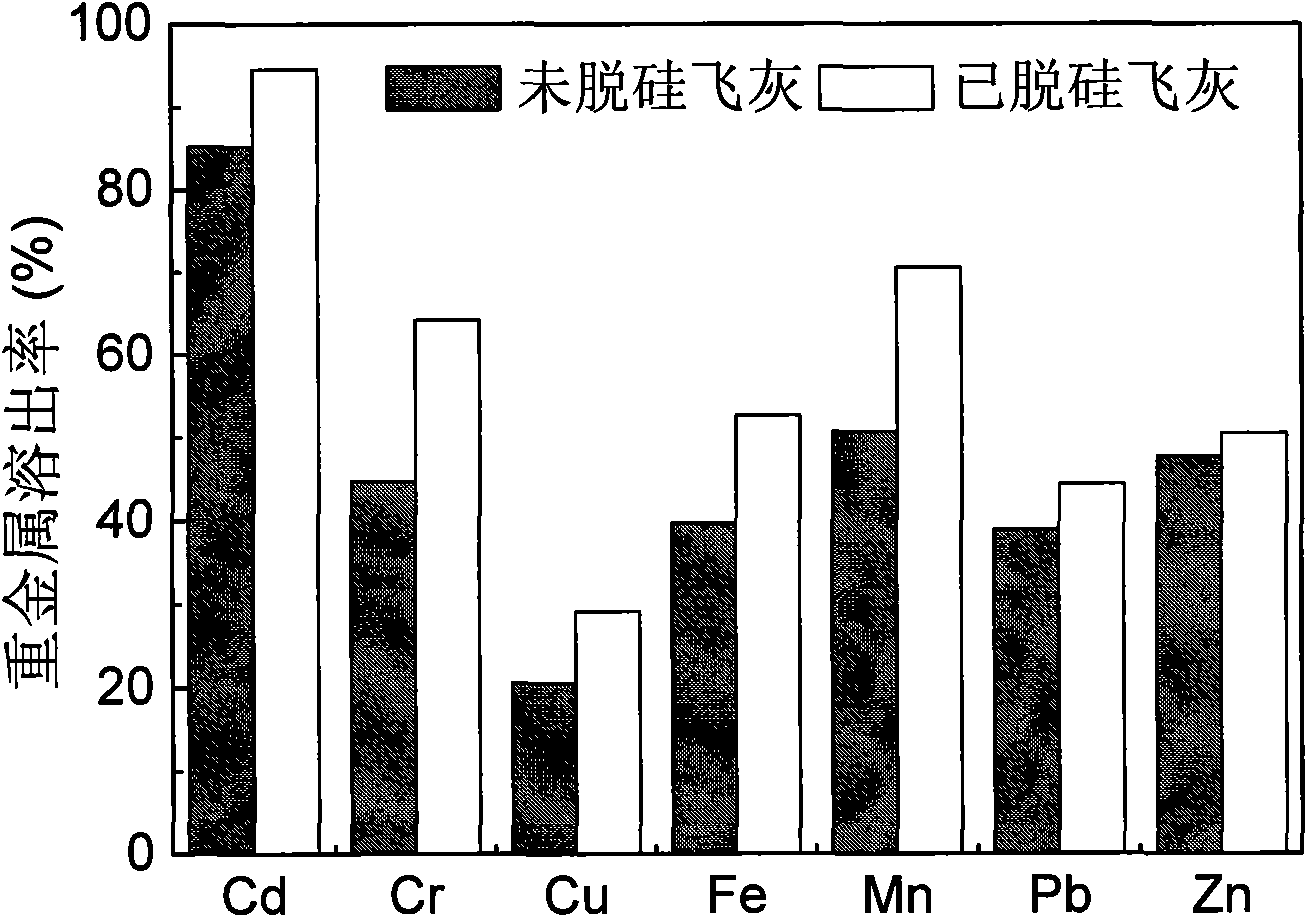
Method for improving bioleaching effect of municipal solid waste incineration flying ash
InactiveCN101555548AEfficient removalHigh dissolution rateFungiBacteriaAspergillus nigerContact reaction
A method for improving bioleaching effect of municipal solid waste incineration flying ash relates to a method for leaching the heavy metal in the waste incineration flying ash by the combination of biological desiliconization and bioleaching. The specific steps include: using silicate bacteria to conduct biological desiliconization treatment on the flying ash and damaging the mineral crystal lattice in the flying ash to release more metal oxide; and using Aspergillus niger to conduct bioleaching on the flying ash after the desiliconization treatment, thus remarkably improving the leaching effect of heavy metal in the bioleaching process due to the full contact reaction between more heavy metal oxide and the organic acid generated by the Aspergillus niger. The method is simple and convenient in operation, high in efficiency, economical and feasible and safe, is an environment-friendly effective method for removing the heavy metal in waste incineration flying ash; and leaching toxicity thereof is far lower than the authentication standard of hazardous wastes and the flying ash can enter a landfill yard or is prepared for further resource recycling.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Heavy metal polluted soil remediation device and method
ActiveCN102974602ASimple structureEasy to useContaminated soil reclamationPeristaltic pumpSoil remediation
The invention provides a heavy metal polluted soil remediation device. The device comprises a peristaltic pump, a bioleaching reactor, a micro-pore filtering column, an adjusting groove and a plant processing groove, which are sequentially connected with one another through a communication pipeline to form a ring, wherein a sample feeding opening is arranged at the top of the bioleaching reactor; an agitator is arranged inside the bioleaching reactor; an aeration device is arranged on the outer wall of the bioleaching reactor; a sample discharging opening is arranged at the bottom of the bioleaching reactor; an air outlet of the aeration device is arranged inside the bioleaching reactor; a first control valve is arranged between the bioleaching reactor and the micro-pore filtering column; a second control valve is arranged between the adjusting groove and the plant processing groove; and a third control valve is arranged at the bottom of the plant processing groove. The invention further provides a method for processing heavy metal polluted soil by the device. The device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience for use, low utilization cost, high processing efficiency and good processing effect.
Owner:北京亿利生物科技有限公司
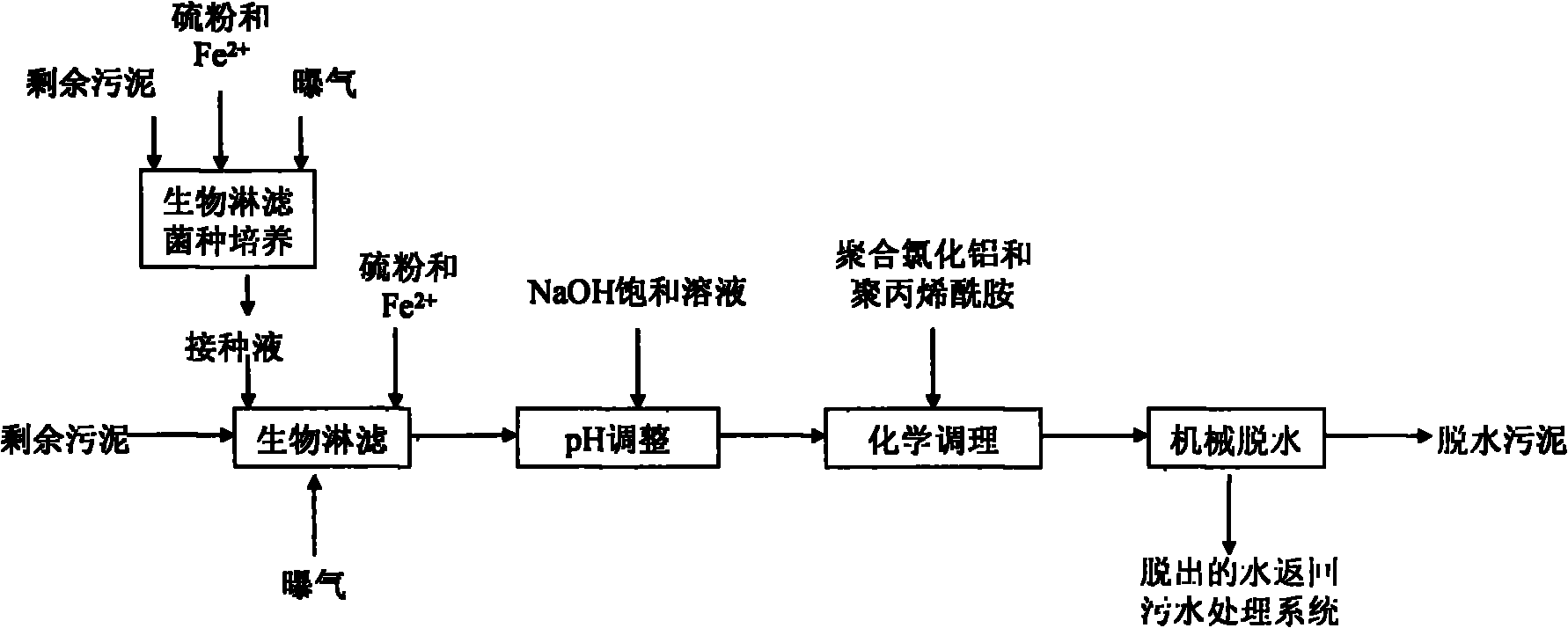
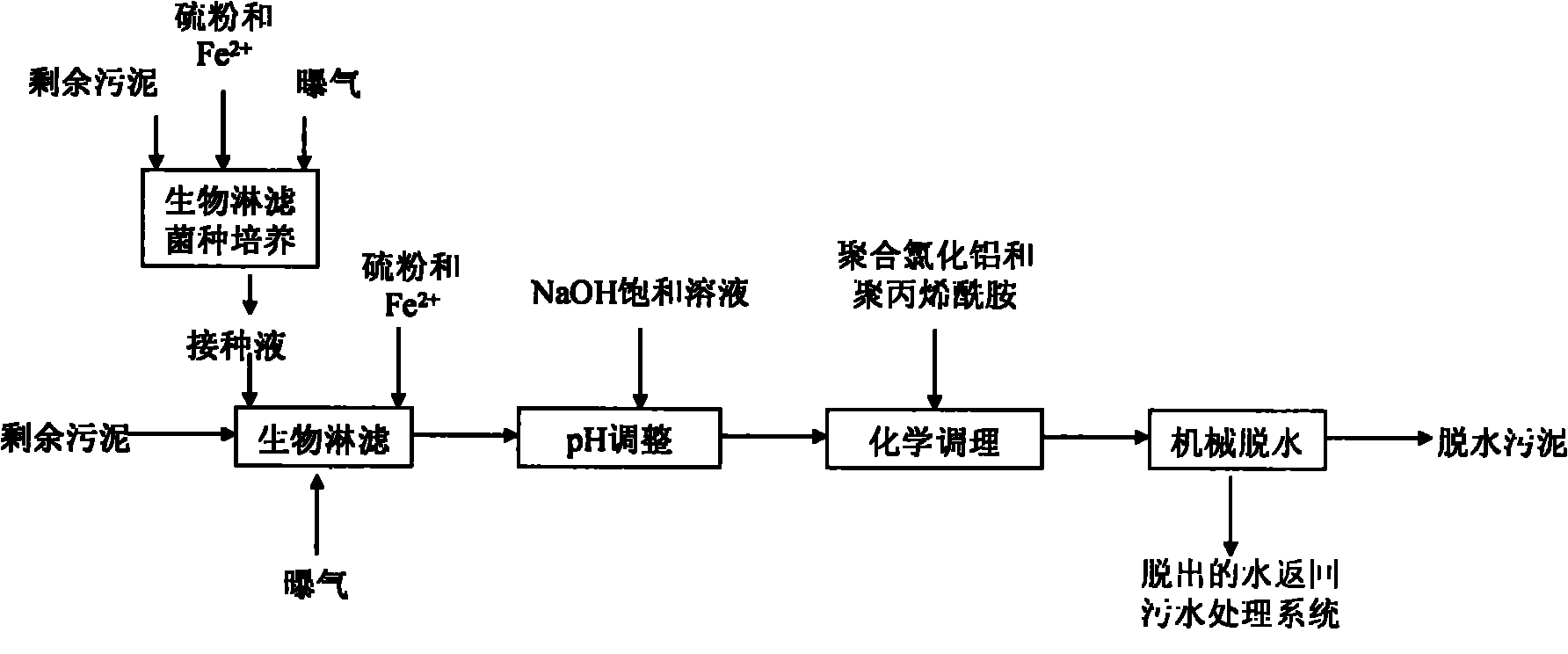
Method for improving sludge dewatering performance by combining bioleaching and dual conditioners
InactiveCN101863612AImprove dehydration effectLower specific resistanceSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningAluminium chlorohydrateBioleaching
The invention relates to a method for improving sludge dewatering performance by combining bioleaching and dual conditioners, and belongs to the technical field of sludge treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: under the condition of adding sufficient substrates, culturing and domesticating autochthonous bacteria in sludge, and using the autochthonous bacteria as inoculum; adding the inoculums into the residual sludge, and performing bioleaching on the sludge under the conditions of aerob, stirring and proper substrate until the pH of the sludge is about 2; adding saturated NaOH solution into the leached sludge to adjust the pH of the sludge to between 6 and 7; adding aluminium polychlorid and polyacrylamide into the sludge to condition the sludge; and performing mechanical dewatering on the treated sludge by a plate-and-frame filter pressing or centrifugal dewatering method to obtain the dewatered sludge with the moisture content between 65 and 75 percent. The bio-acidification and the dual conditioners are combined to improve the sludge dewatering performance, so the reaction efficiency can be improved, the reaction time can be shortened, the treatment capacity can be improved, and the sludge treatment cost can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Recovery of precious metal from sulphide minerals by bioleaching
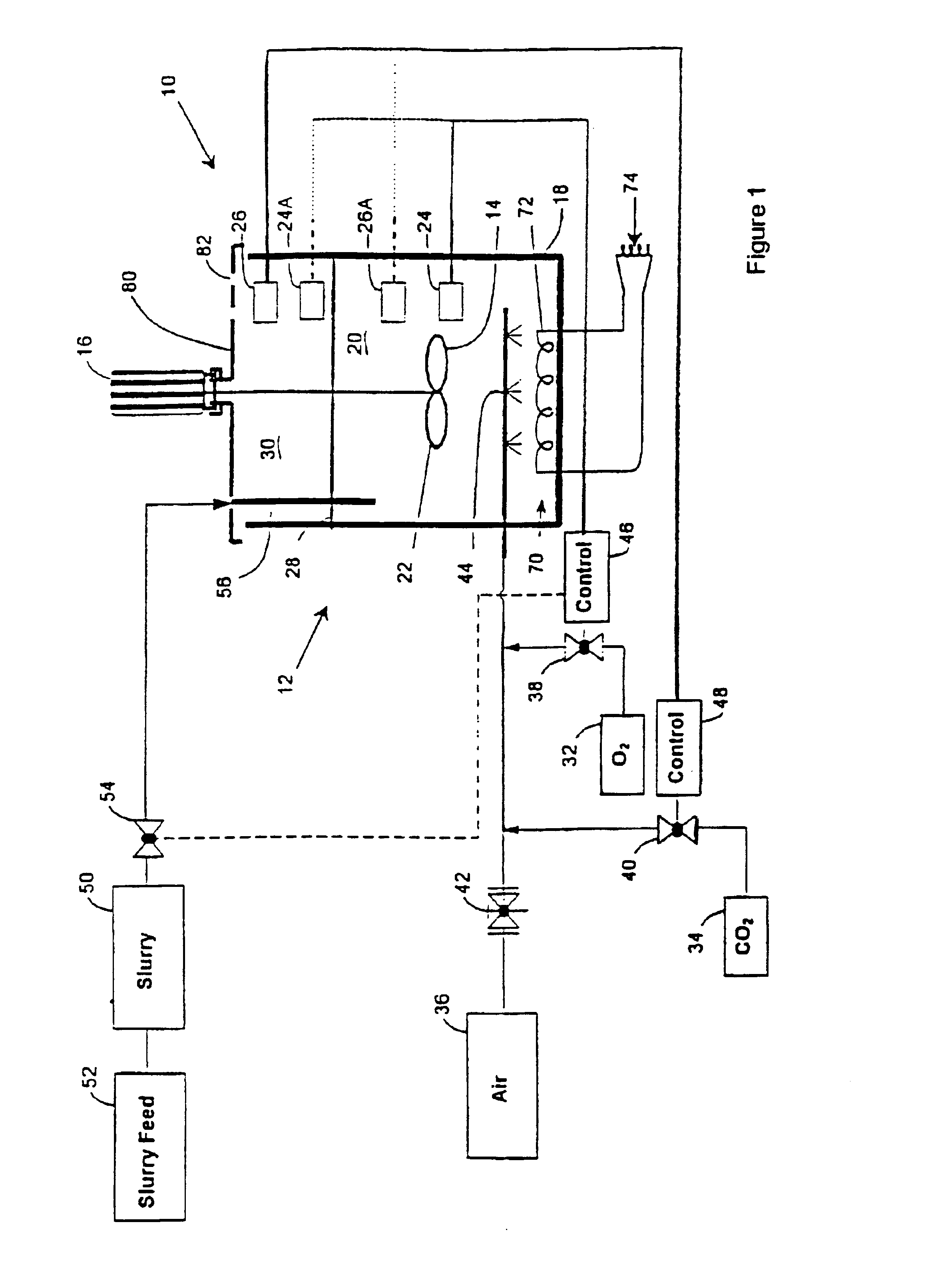
InactiveUS6860919B1Solve the low leaching rateReduced Power RequirementsInorganic chemistryBlast furnace detailsBioleachingSlurry
A method of recovering a precious metal from a sulphide mineral slurry which contains the precious metal which includes the steps of subjecting the slurry to a bioleaching process, supplying a feed gas which contains in excess of 21% oxygen by volume to the slurry, and recovering precious metal from a bioleach residue of the bioleaching process.
Owner:BILLITON INTPROP
Method for removing heavy metal Cr from sludge by bioleaching
The invention provides a method for removing a heavy metal Cr from sludge by bioleaching, relates to technology for processing municipal solid waste, and aims to solve the problem of restriction on recycling the sludge, which contains higher heavy metal Cr content, of municipal sewage plants in agriculture and forestry. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a proper amount of cultured and domesticated inoculating solution in a reaction system, wherein the ratio of the substrate concentration to the sludge quantity (dry weight) is controlled to be 0.5-0.8; the sludge concentration is 15-25 g / L; the dissolved oxygen concentration is 7.5-9.0 mg / L; the reflux ratio of the sludge is 10-20 percent; and the temperature is controlled to be 25-30 DEG C; and supplementing water which is evaporated in a reactor regularly. By using the method, the removal rate of the heavy metal Cr reaches 45-55 percent through the bioleaching period.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Novel method for processing heavy metal in sludge through bioleaching
InactiveCN102424509AMeet the requirements of agricultural heavy metal contentNo need for secondary cultureBiological sludge treatmentSludgeReaction temperature
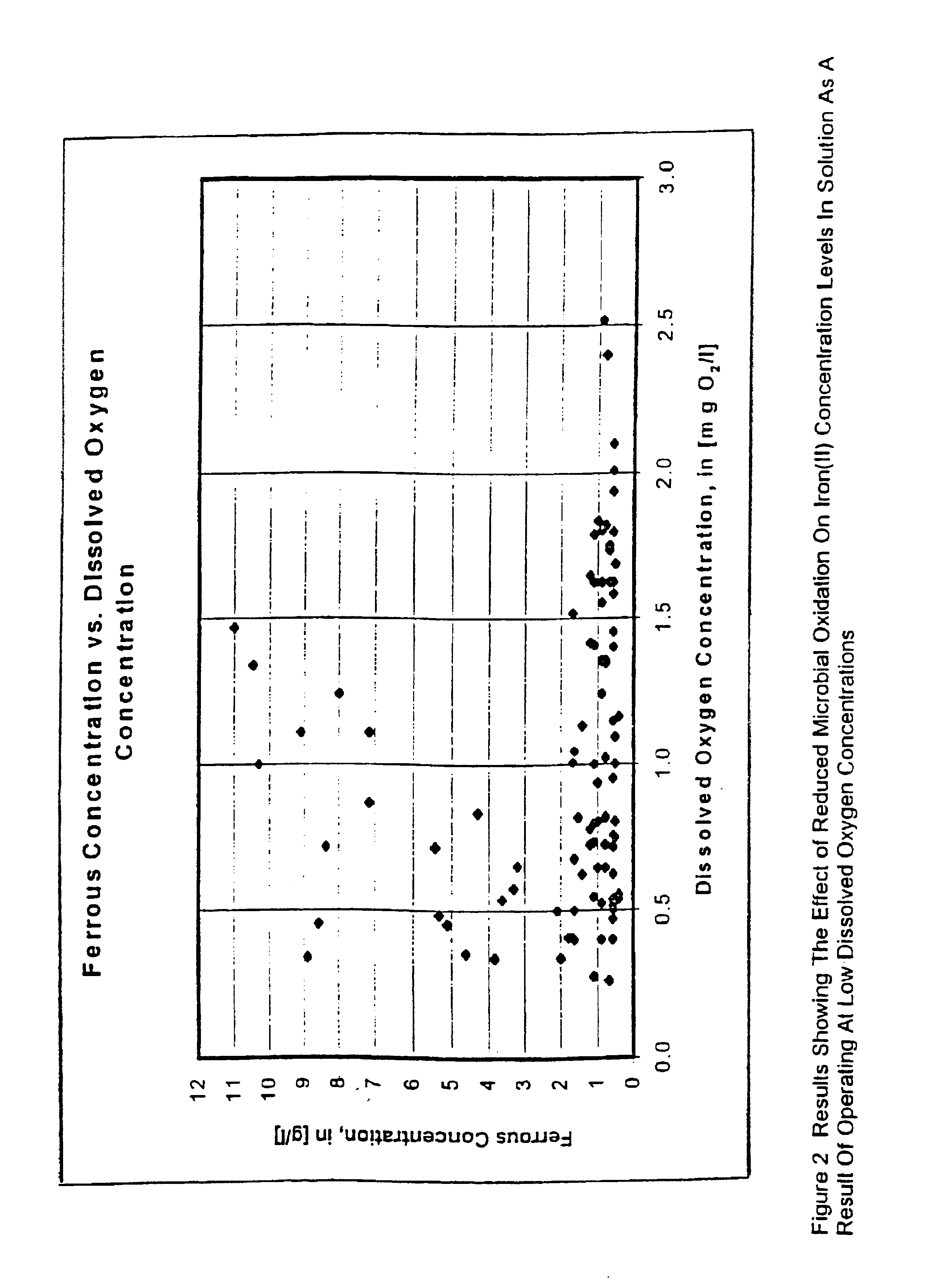
The invention relates to a method for processing heavy metal in sludge, particularly a method for removing heavy metal in sludge by recycling residual sludge after leaching and needing no additional strains. In the process of sludge reaction, by controlling the reaction temperature to 28-35 DEG C, the pH value to 2-2.5, and the dissolved oxygen to 2-3 mg / L, the effect of removing heavy metal in sludge is guaranteed. Compared with the techniques of processing heavy metal in sludge in the prior art, especially a traditional bioleaching method, the use of the method disclosed herein saves the culture time of strains, and reduces the difficulties of operators for operation management. According to the invention, the invention guarantees that improved strains have strong activity in every processing stage, residual partial sludge after processing is used as the strain, thus the reaction of removing heavy metal in sludge through a biological method can be guaranteed to carry out. The method has the advantages of simple structure, convenient operation management, low production cost and the like, and has good supporting effect of processing and utilizing urban sludge.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
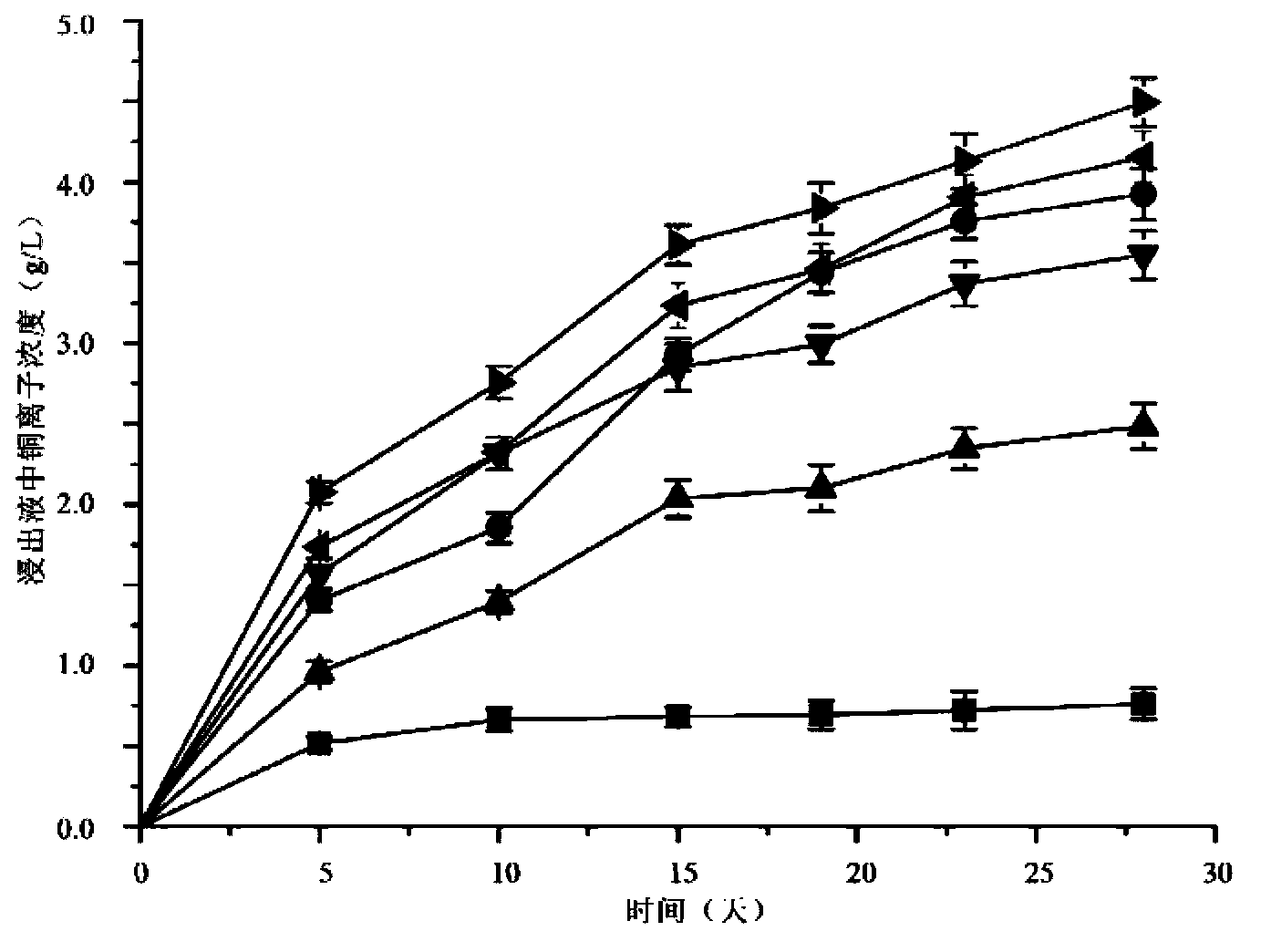
Method for removing heavy metal Cu in sludge of urban sewage treatment plant in bioleaching mode
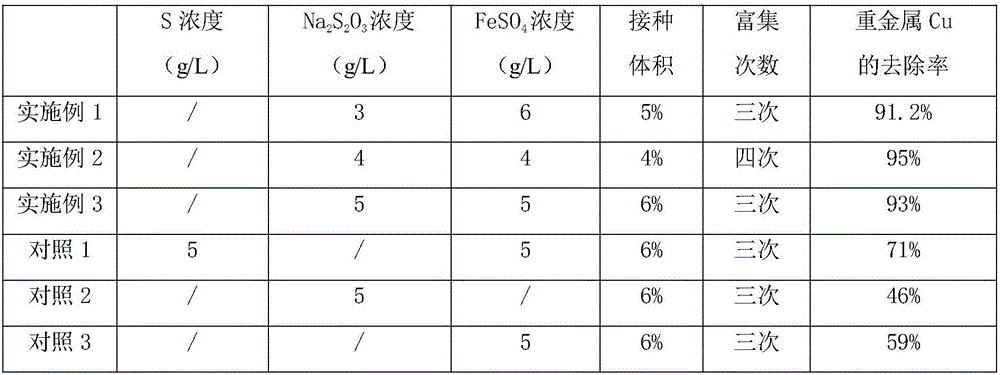
ActiveCN105776788ASmall amount of inoculumImprove the growing environmentSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsThiobacillusMunicipal sewage
The invention discloses a method for removing heavy metal Cu in sludge of an urban sewage treatment plant in a bioleaching mode, by means of the method, the problem that sludge of the urban sewage treatment plant contains much heavy metal Cu is solved, and the treated sludge can serve as fertilizer for agricultural utilization. The method includes the following specific steps that original thiobacillus in the sludge is enriched and cultured, acclimated sludge is obtained, the acclimated sludge serves as the inoculum and is added to raw sludge, Na2S2O3 and FeSO4 substrates are fed, the feeding amount of Na2S2O3 is controlled to be 3-5 g / L, the feeding amount of FeSO4 is controlled to be 4-6 g / L, air is blown into the sludge at the speed of 1.0-1.5 L / (min-L), stirring is conducted at a certain rotation speed, the temperature is controlled to be 20-30 DEG C, and the sludge is subjected to bioleaching; after bioleaching is conducted for 3-4 days, the removal rate of the heavy metal Cu reaches 90% or above. The method is reasonable in design and high in practicability.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
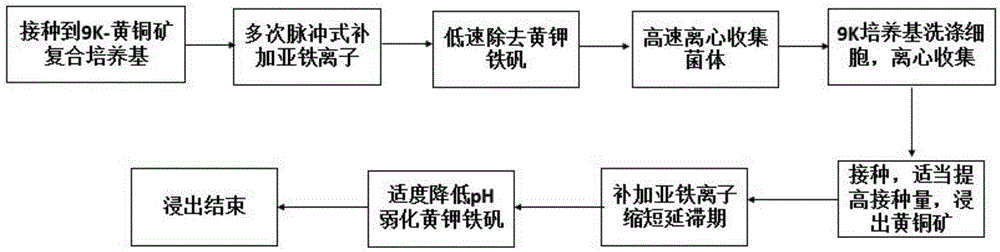
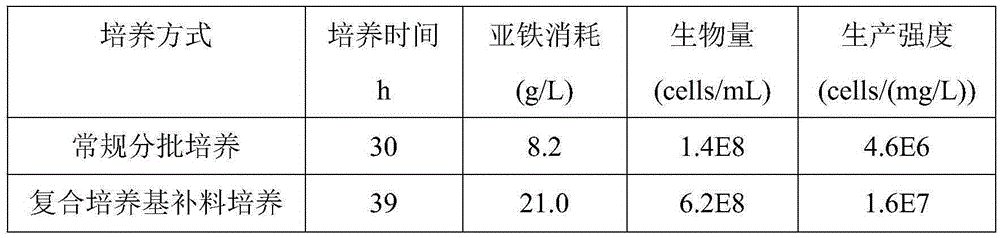
Method for leaching chalcopyrite through reinforced iron oxidized culture
ActiveCN105256133AIncrease cell concentrationImprove leaching efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementChalcopyriteHigh density
The invention discloses a method for leaching chalcopyrite through a reinforced iron oxidized culture and belongs to the technical field of bioleaching. The method includes the steps that on the basis of a 9K-chalcopyrite complex medium, a ferrous energy substrate is added through an impulse type supplementary material in the middle and later periods of cultivation, and ferric oxide thiobacillus is cultured at high density; centrifugal operation and suspended elution cells of the 9K medium are adopted for removing jarosite, the cells not containing jarosite are adopted for inoculation, the inoculation size is increased properly, and meanwhile ferrous ions are supplemented and included to shorten a lag phase; and the pH of lixivium is lowered level by level in the later leaching period, accumulation of the jarosite is reduced, and the leaching effect of the chalcopyrite is improved in the whole process. By the adoption of the method, the iron oxidized culture can be more efficiently cultured, the lag phase can be shortened, the passivation effect caused by accumulation of the jarosite can be weakened, the leaching process of the chalcopyrite is improved while iron metabolism is reinforced, operation is easy and feasible, and the method is suitable for being applied and popularized on a large scale.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
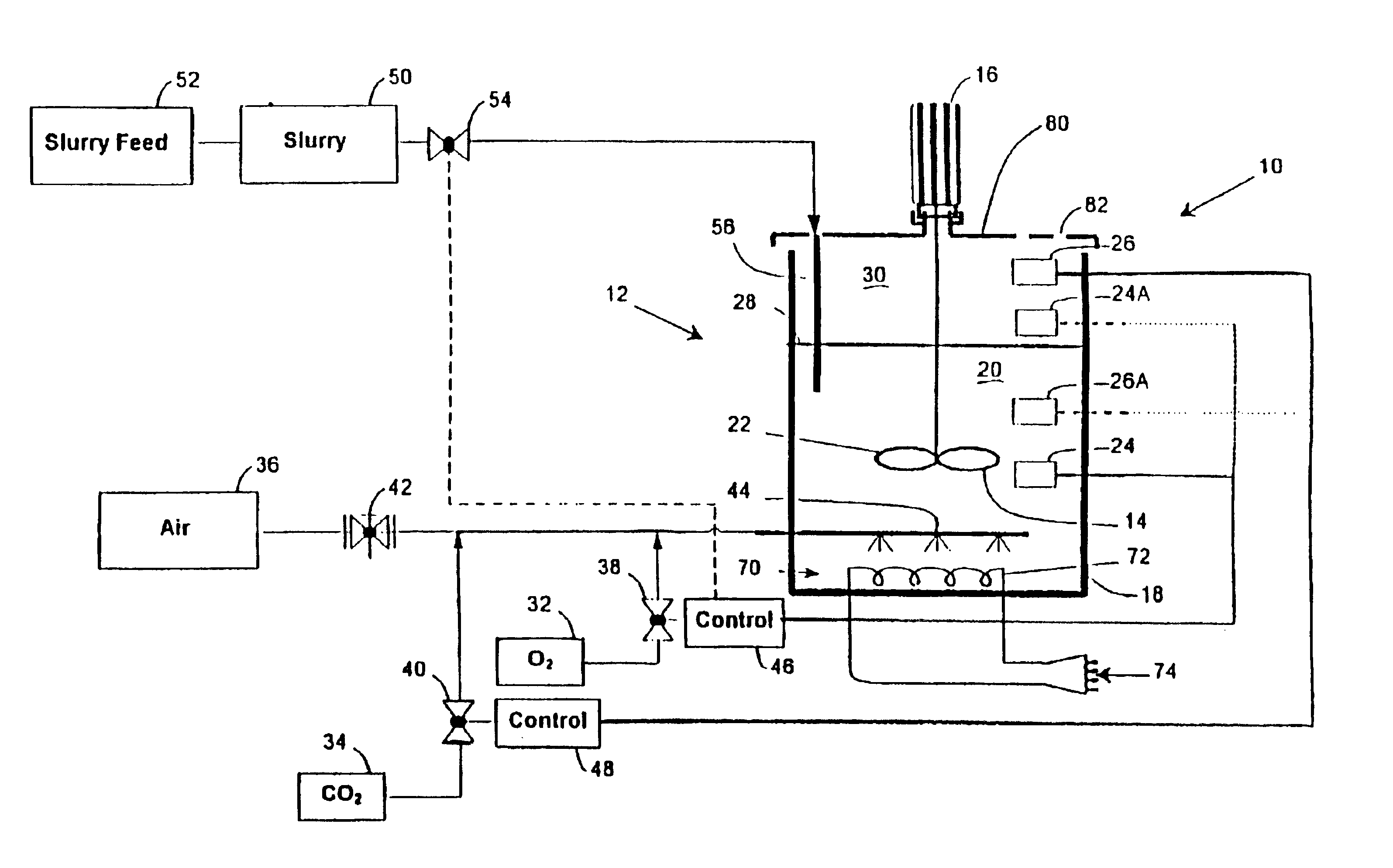
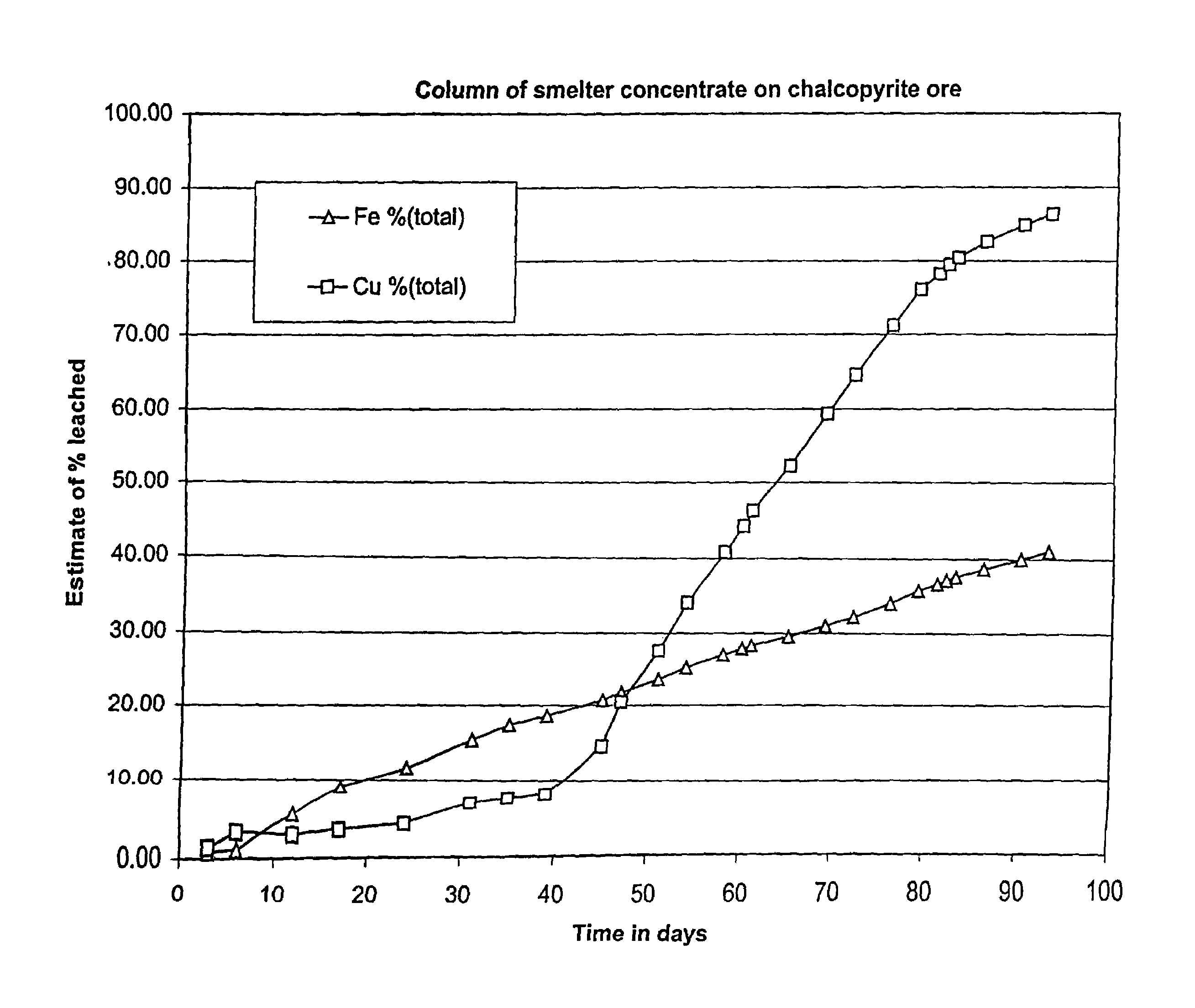
High temperature heap bioleaching process
A heap is constructed with hypogenic copper sulfide bearing ore to include exposed sulfide mineral particles at least 25 weight % of which are hypogenic copper sulfides. The concentration of the exposed sulfide mineral particles is such that the heap includes at least 10 Kg of exposed sulfide sulfur per tonne of solids in the heap. At least 50% of the total copper in the heap is in the form of hypogenic copper sulfides. A substantial portion of the heap is heated to at least 50° C. The heap is inoculated with a thermophilic microorganism, and bioleaching is carried out so that sufficient sulfide mineral particles in the heap are biooxidized to oxidize at least 10 Kg of sulfide sulfur per tonne of solids in the heap and to cause the dissolution of at least 50% of the copper in the heap in a relatively short period of time.
Owner:BUSHNELL +9
Efficient separation and purification process for bioleaching solution with low-content nickel and cobalt
InactiveCN106811598AAchieve separationTo achieve the purpose of purification, separation and purificationProcess efficiency improvementIon exchangeGradient elution
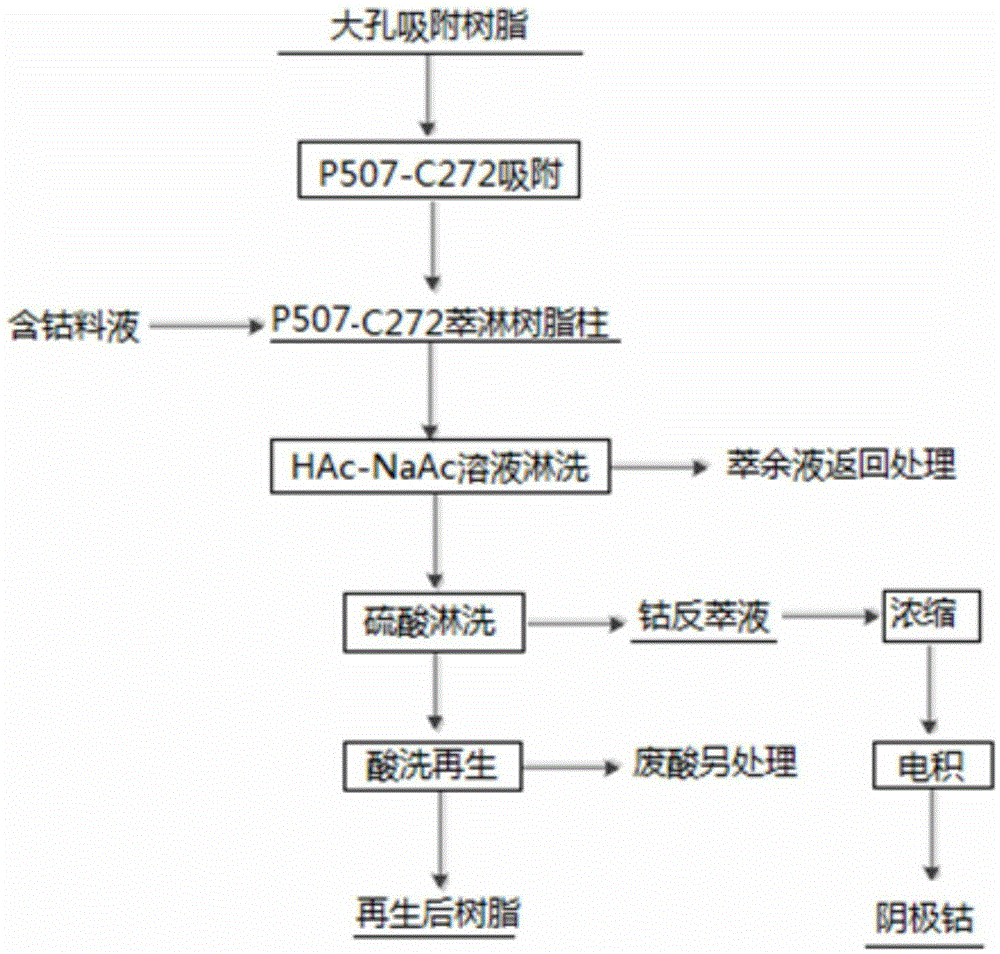
The invention discloses an efficient separation and purification process for a bioleaching solution with low-content nickel and cobalt. The efficient separation and purification process comprises the following steps: (1) taking a macroporous adsorption resin as a supporter, taking the saponified P507-Cyanex272 double-extraction agent as an active component of an extraction-elution resin, taking ethyl alcohol or petroleum ether as a diluent, and preparing an extraction-elution resin with the double-extraction agent; (2) filling an extraction-elution resin column with the prepared extraction-elution resin, adjusting the pH value of the bioleaching solution with nickel and cobalt to be in a range from 3.5 to 5.0, and eluting the extraction-elution resin column to carry out charging; (3) carrying out gradient elution on the extraction-elution resin column, and carrying out two-section gradient elution by virtue of an HAc-NaAc buffer solution with a pH value of 3.0-5.5 and sulphuric acid with a pH value of 1.0-3.5 separately; and (4) concentrating the eluted cobalt back-extraction solution, and then carrying out electrolytic deposition to obtain a cathode cobalt product. Compared with a conventional extraction separation method or ion exchange method, the efficient separation and purification process disclosed by the invention is multistage and efficient, and further has the advantages of being high in selectivity, good in mass transfer effect and the like, increases the separation and purification efficiency of the cobalt solution, and is simple in flow, easy to operate and low in environmental pollution.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Selective bioleaching process of high-sulphur/copper ratio secondary copper sulphide ore
ActiveCN101805829AIncrease geometryReduce mass transfer intensityProcess efficiency improvementSelective leachingResource utilization
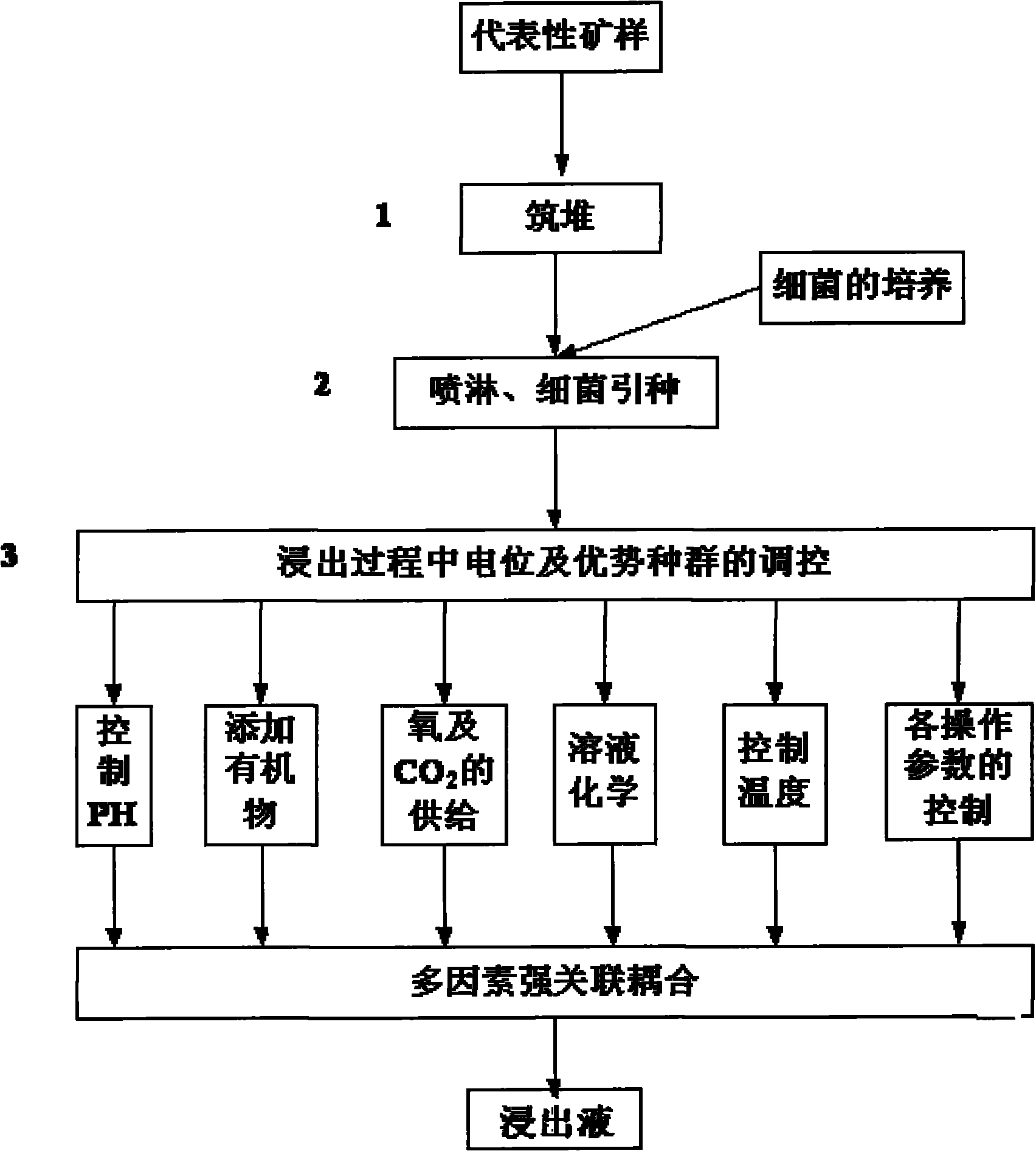
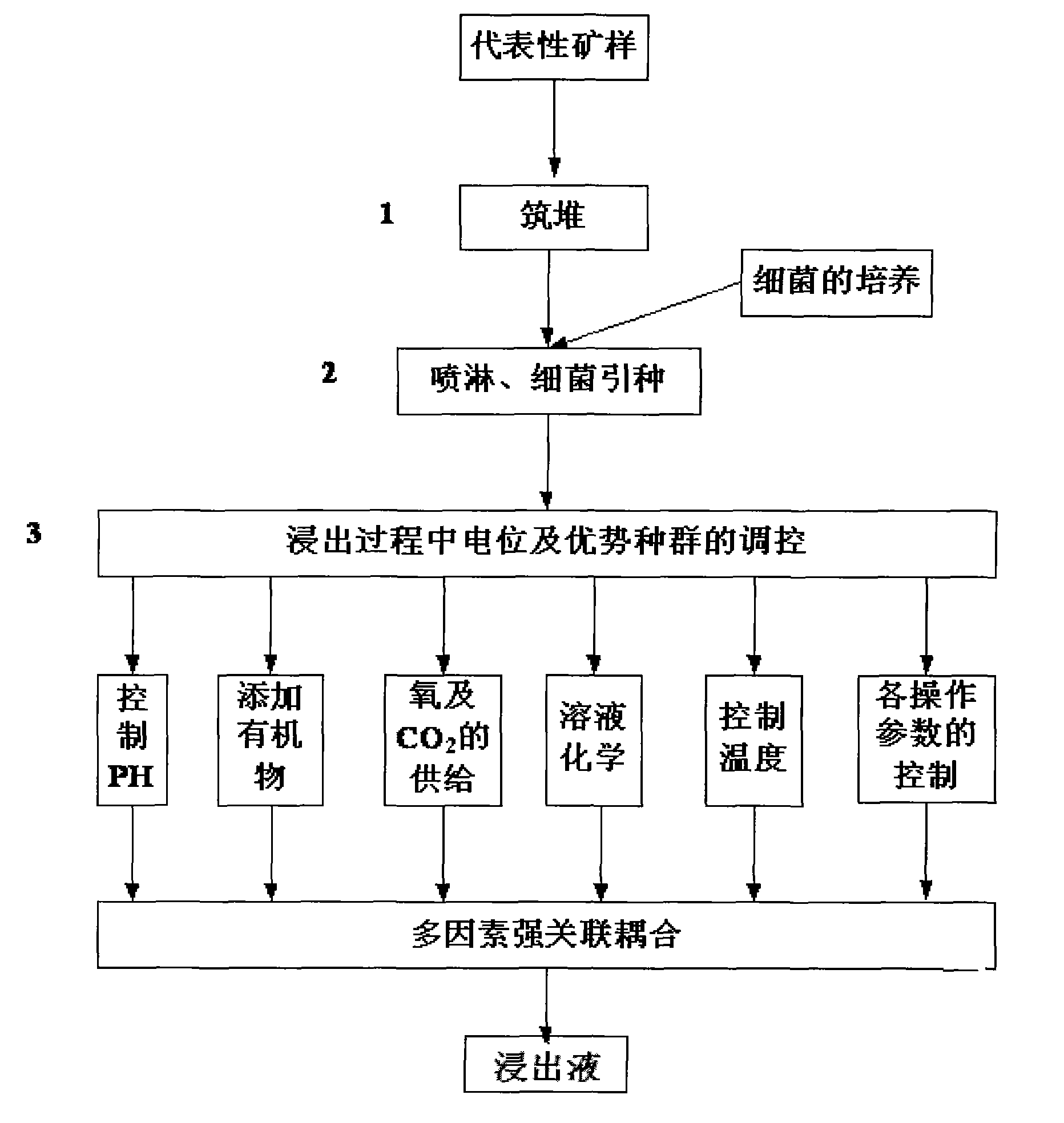
The invention relates to a selective bioleaching process of a high-sulphur / copper ratio secondary copper sulphide ore. In the process, microorganisms are utilized to leach the high-S / Cu ratio low-grade secondary copper sulphide ore, and the oxidation-reduction potential in the leaching process is controlled through the measures of regulating the pH, the dripping intensity, the fallow system, the air permeability, the breeding of dominant species, and the like so as to realize the selective leaching of the secondary copper sulphide ore. The process has short flow, simple equipment, low investment, low cost, no pollution, high recovery rate and adjustable production scale, can treat low-grade copper ore resources which cannot be treated by using the traditional selecting and smelting process, the resource utilization range is enlarged, and the comprehensive recovery level of copper metal is improved.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Heap bioleaching process for the extraction of zinc
InactiveUS20070193413A9Assists leaching processProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionZinc compounds
A method of extracting zinc from a sulphidic ore is provided which comprises bioleaching the ore in a heap with acidophilic microorganisms to produce a pregnant leach solution which is recovered from the bottom of the heap. An integrated process which comprises subjecting the pregnant leach solution to neutralization and solvent extraction to produce a concentrated zinc solution is also provided. Zinc may be recovered from the concentrated solution by means of electrowinning, either in the absence or presence of manganese. Alternatively zinc may be recovered in the form of a zinc compound.
Owner:TECK METALS
Method of promoting bioleaching of copper pyrites by adding nonionic surfactant
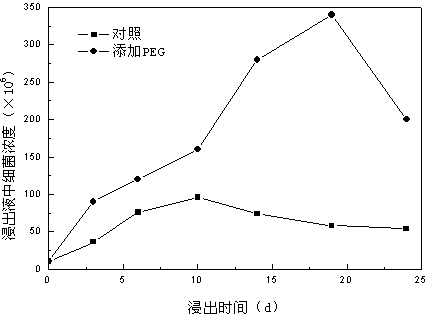
ActiveCN103993171AImproved bioleachingIncrease speedProcess efficiency improvementIron(II) oxideUltraviolet lights
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy and particularly relates to a method of promoting bioleaching of copper pyrites by adding a nonionic surfactant. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding a copper pyrites sample and sterilizing the sample by ultraviolet light to obtain a product as a leaching sample; putting the leaching sample in a 9L basic salt solution sterilized; inoculating ferrous oxide thiobacillus; then, adding polyethylene glycol, wherein the addition of polyethylene glycol is 30-90mg / L; adjusting the initial leaching pH to 1.8-3.5 by using dilute sulphuric acid; under the condition of 25-35 DEG C and 150-180r / min, oscillating and leaching for 18-25 days; and adding polyethylene glycol to at least increase the leaching ratio of copper pyrites by 1.36 times. The invention provides a novel path for increasing the bioleaching rate of low-grade copper pyrites and is of important meaning to promote large-scale industrial application of a low-grade copper pyrite bioleaching process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Compound microbial liquid for treating anaerobic digested sludge and novel bioleaching method
ActiveCN108083597AGuaranteed dehydration efficiencyDetox inhibitionFungiSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBiologyWater content
The invention discloses a bioleaching method for anaerobic digested sludge and belongs to the technical field of sludge treatment. Bioleaching work flora is compounded by introducing new microbial strains, continuous domestication is performed, an inoculum obtained through domestication is mixed with the anaerobic digested sludge for bioleaching treatment, the new microbial strains are used for degrading small-molecular organic acids and secreting surface active materials to rapidly remove EPSs (extracellular polymeric substances) wrapping surfaces of sludge cells, bioleaching reaction time isshortened to 12-24 h, the sludge obtained after bioleaching directly enters a plate-and-frame filter press for dehydration, and a mud cake with water content lower than 60% is obtained. The method adopts simple process, no chemical reagent is needed due to complete dependence on action of microbes, and the method has the advantages of high dehydration efficiency, low operation cost and low technological operation difficulty.
Owner:南京贝克特环保科技有限公司
Continuous enlarging cultivation device and method for mineral-bioleaching microorganisms
ActiveCN107881081ACompact structureImprove cultivation efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses a continuous enlarging cultivation device for mineral-bioleaching microorganisms. The cultivation device comprises a cylinder which is formed by sequentially connecting an upper cylinder body, a middle cylinder body and a lower cylinder body, wherein the upper cylinder body can collect feed liquid which is discharged due to overflowing, the middle cylinder body can continuously cultivate the microorganisms in an enlarged mode, and the lower cylinder body can collect discharged precipitates. A detachable multi-layer filler assembly is arranged in the middle cylinder body, the multi-layer filler assembly is composed of a multi-layer filler box and filler which is arranged in the filler box, a heater, a nutrient solution distributing plate and an aeration device are arranged below the multi-layer filler assembly, and the aeration device is arranged below the nutrient solution distributing plate. The cultivation device is simple in design, continuous cultivation canbe achieved, the concentration of the microorganisms in a mature bacteria solution can be improved, and while continuous production of the high-concentration bacteria solution is maintained, the problem about the loss of strains in a reactor is effectively eased. The cultivation efficiency of the mineral-bioleaching microorganisms is improved, and the device has the advantages of being safe, efficient, low in space occupation, low in power consumption, simple and easy in operation and capable of achieving combined cultivation of a plurality of cultivation devices.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
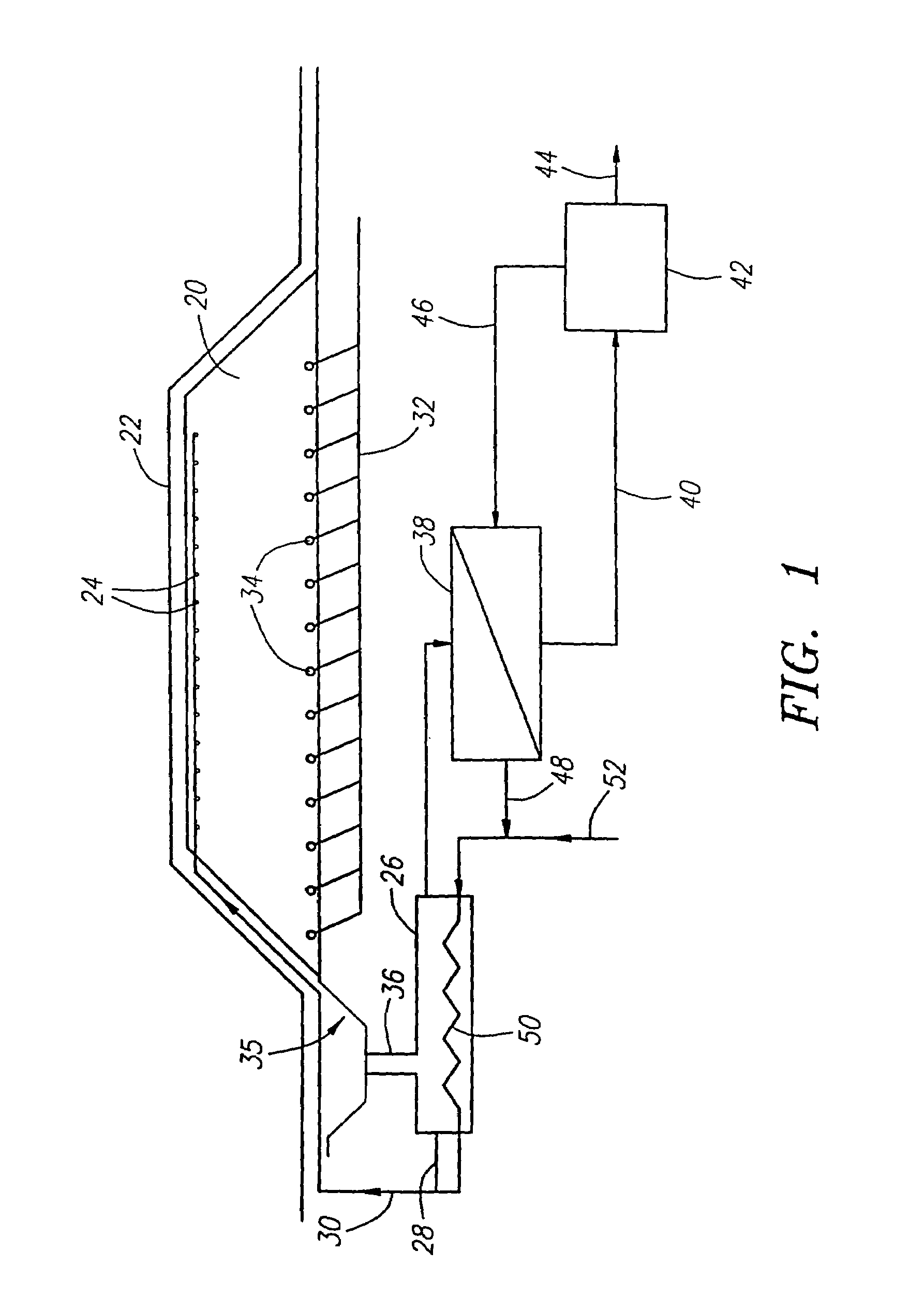
Column reactor for testing and evaluating refractory ores
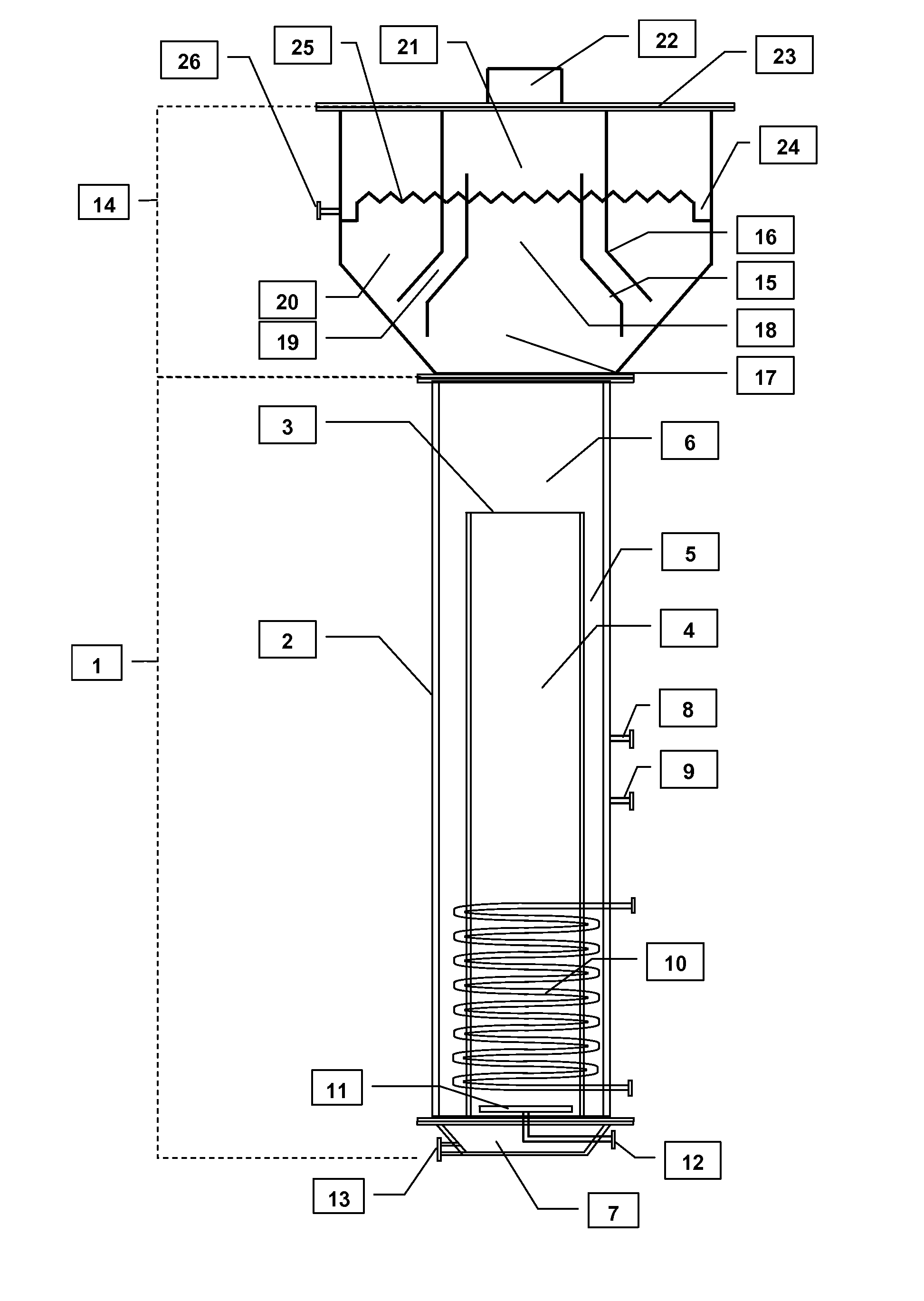
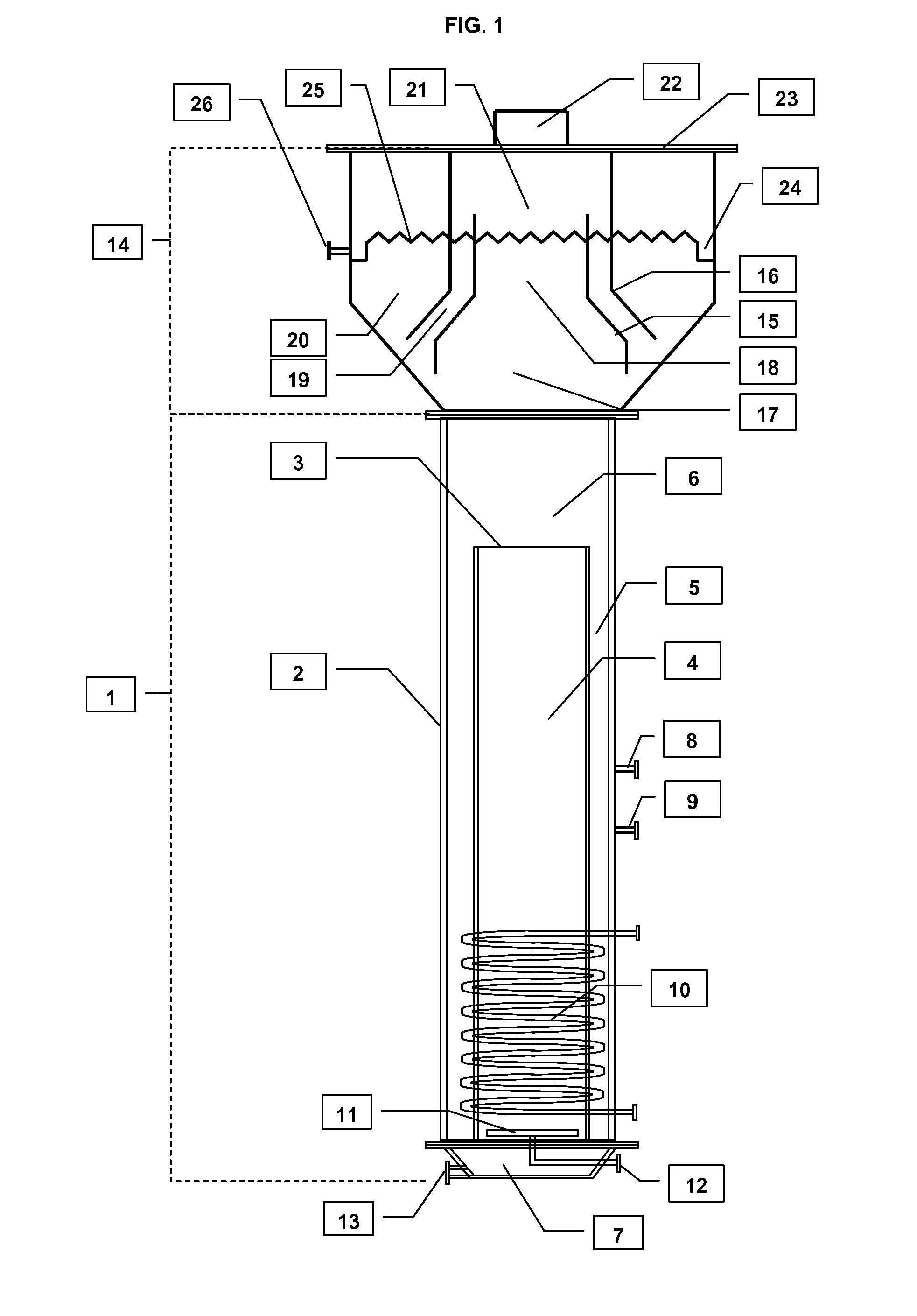
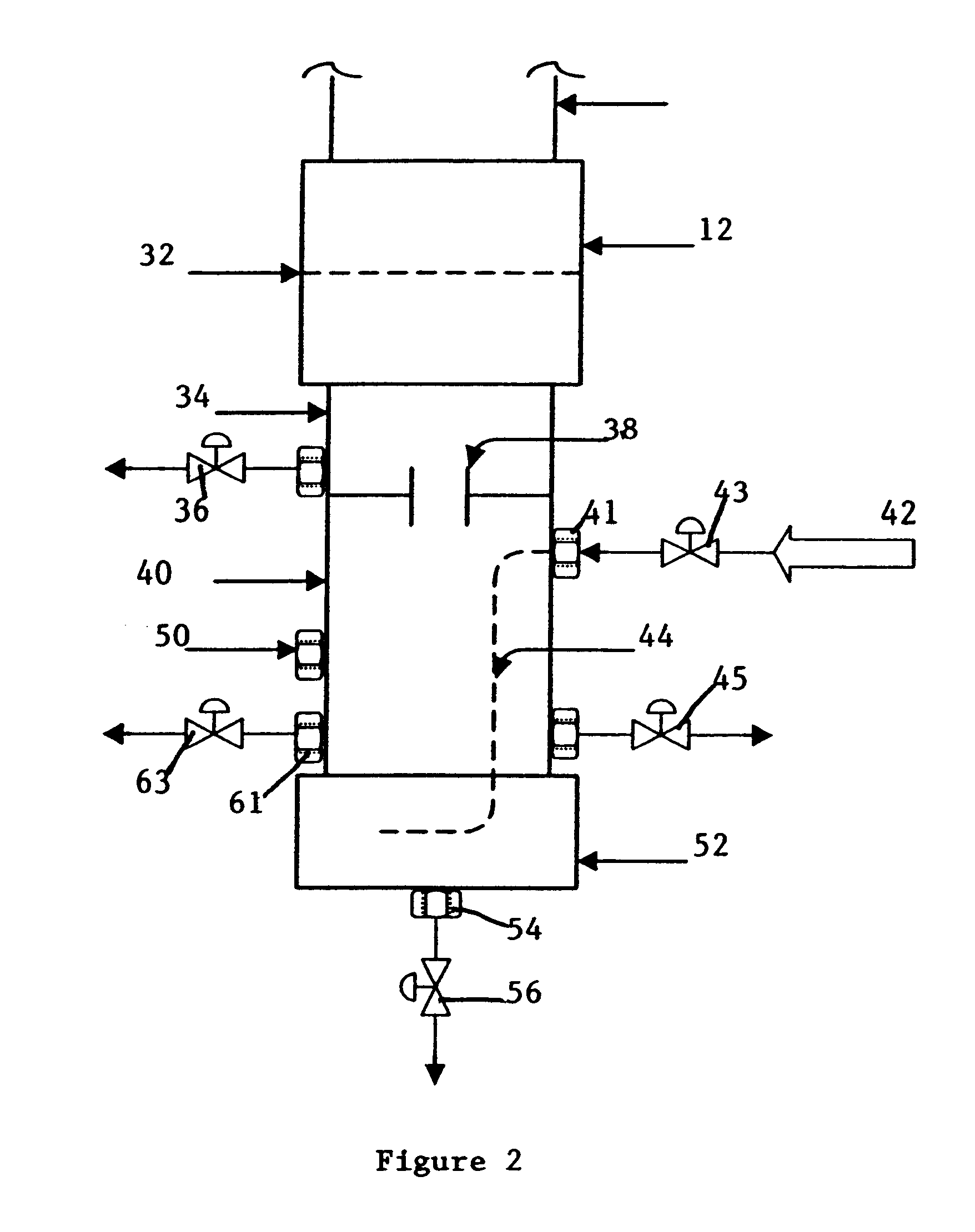
InactiveUS6498031B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVulcanizationBioleaching
The present invention is directed to microbiological processes for the oxidative treatment of refractory gold and base metal ores and concentrates, and particularly, an apparatus for testing refractory gold and sulfidic base metal ores for their suitability to heap biooxidation or bioleaching processes. The invention can be used to simulate heap biooxidation. This apparatus incorporates features of heap biooxidation and may be used to generate engineering data for creating detailed process and engineering designs. The invention can be used to develop a select population of bacteria geared to optimize biooxidation of a specific refractory ore.
Owner:OXIDOR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com