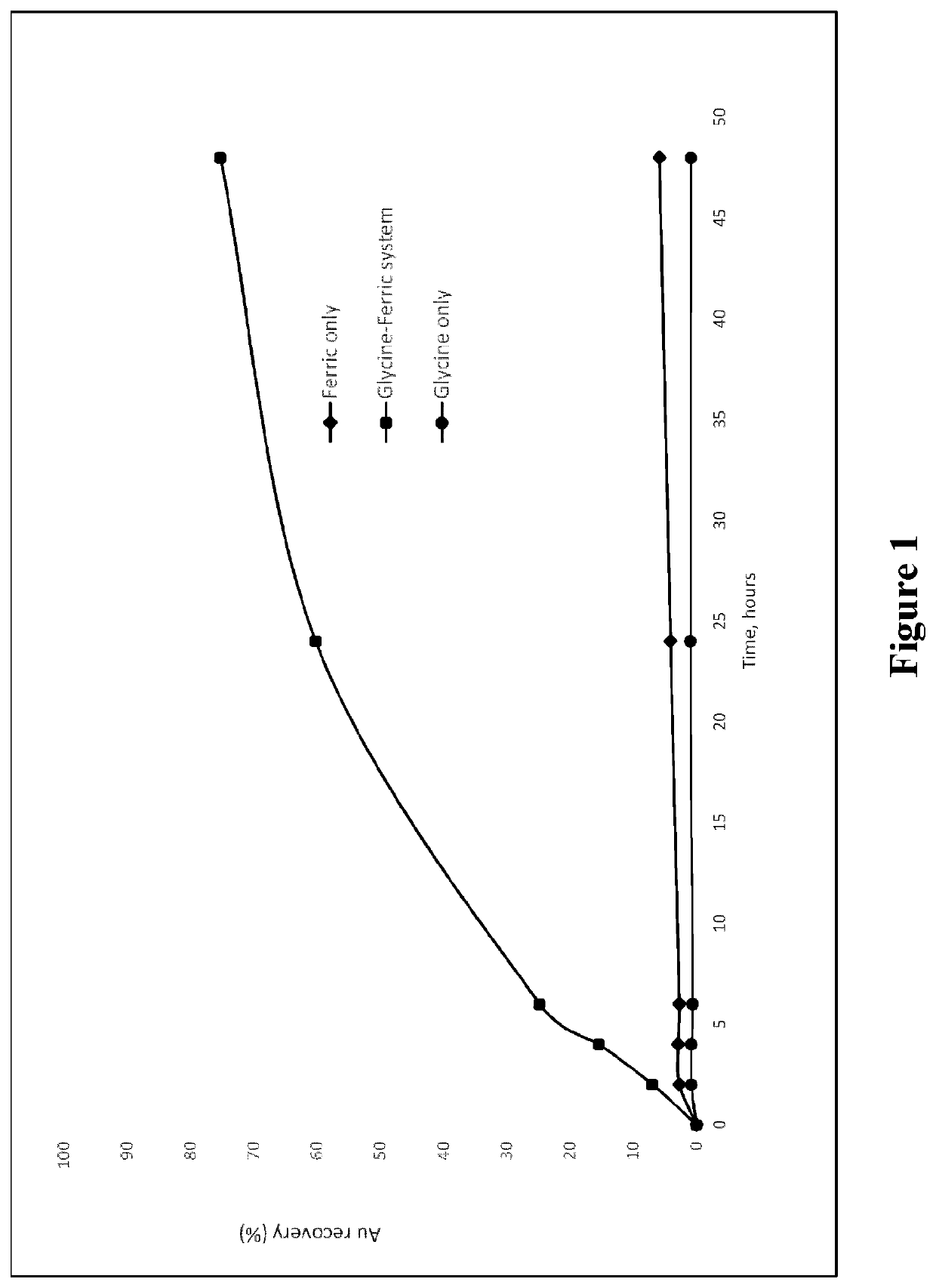
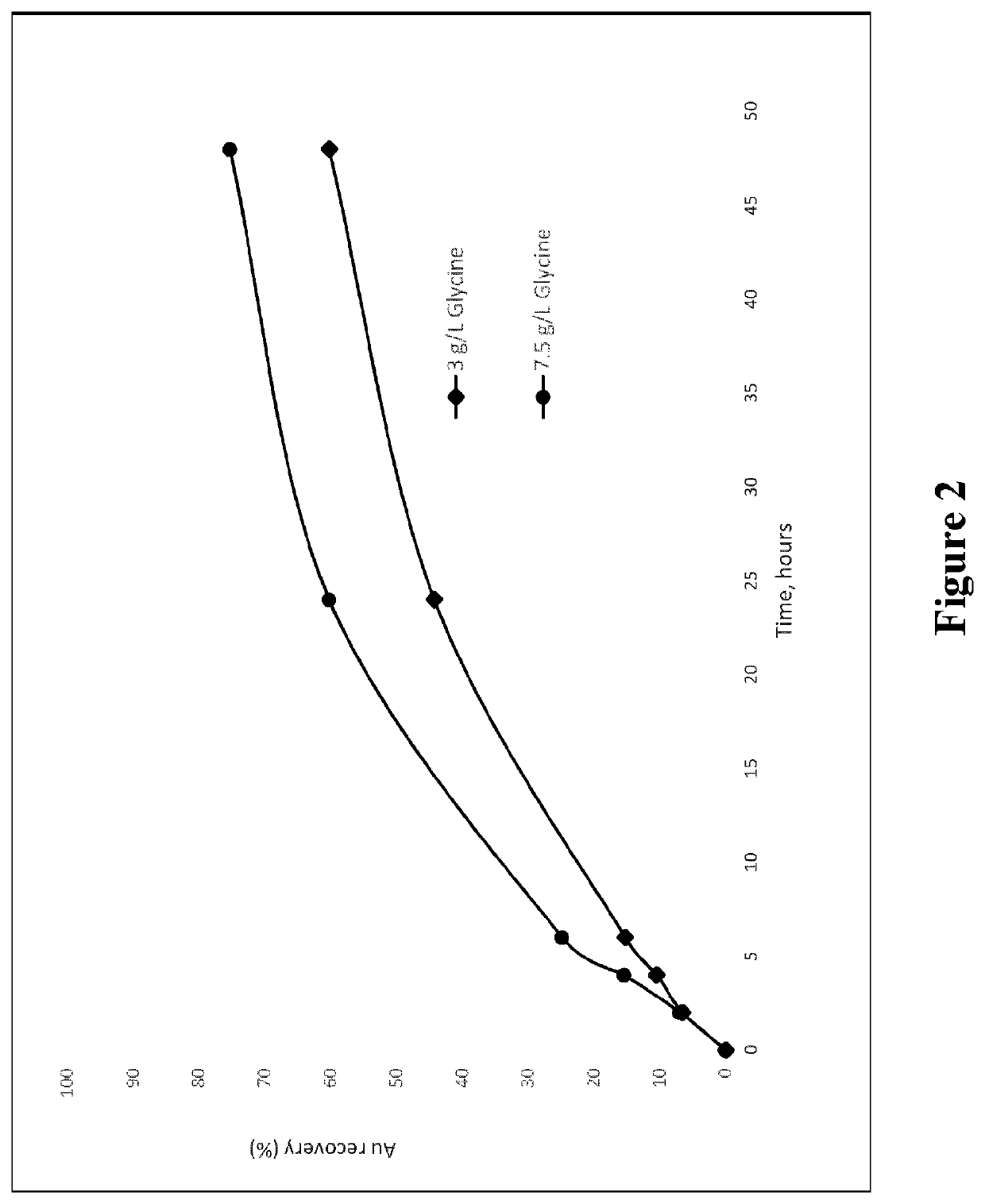
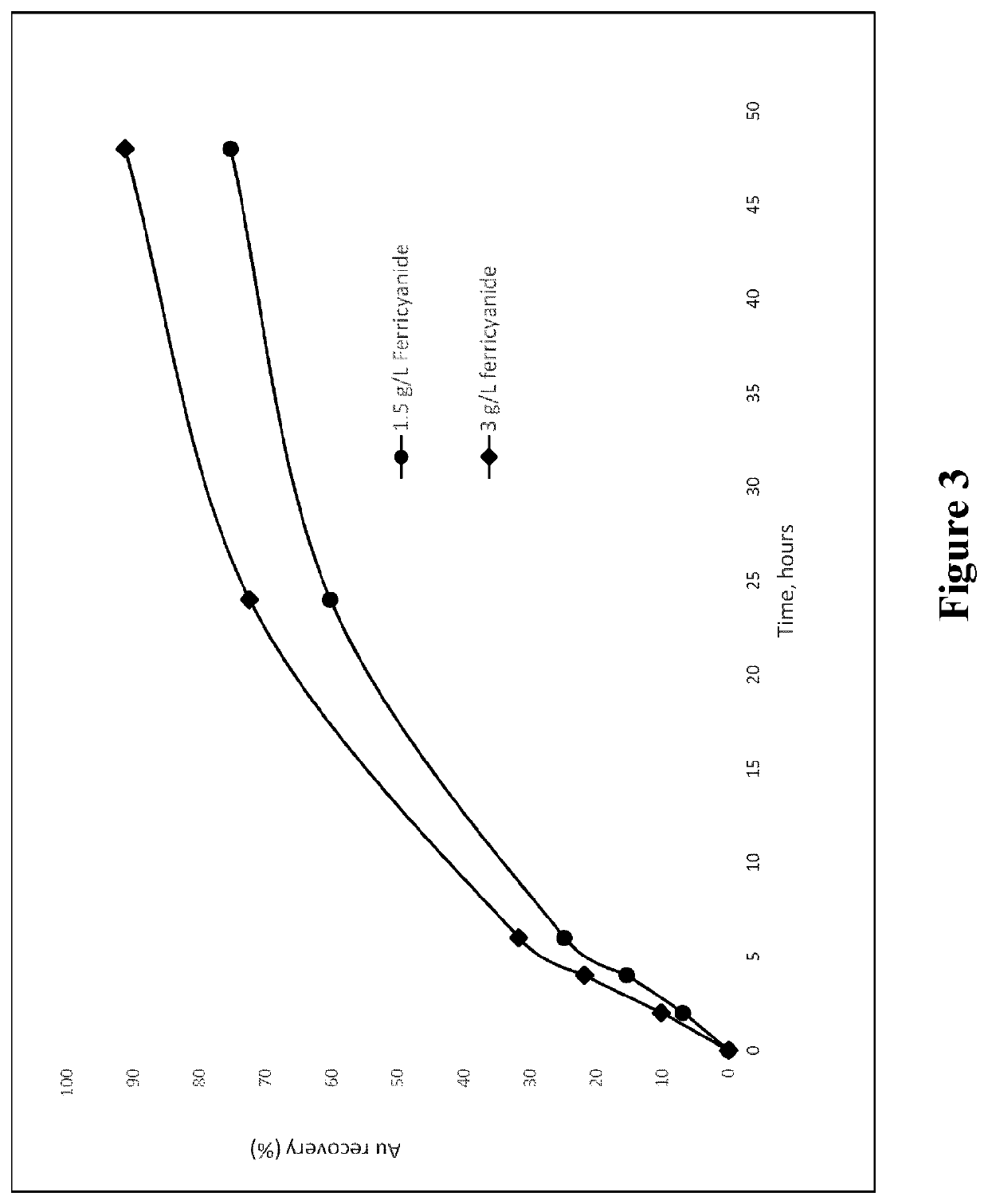
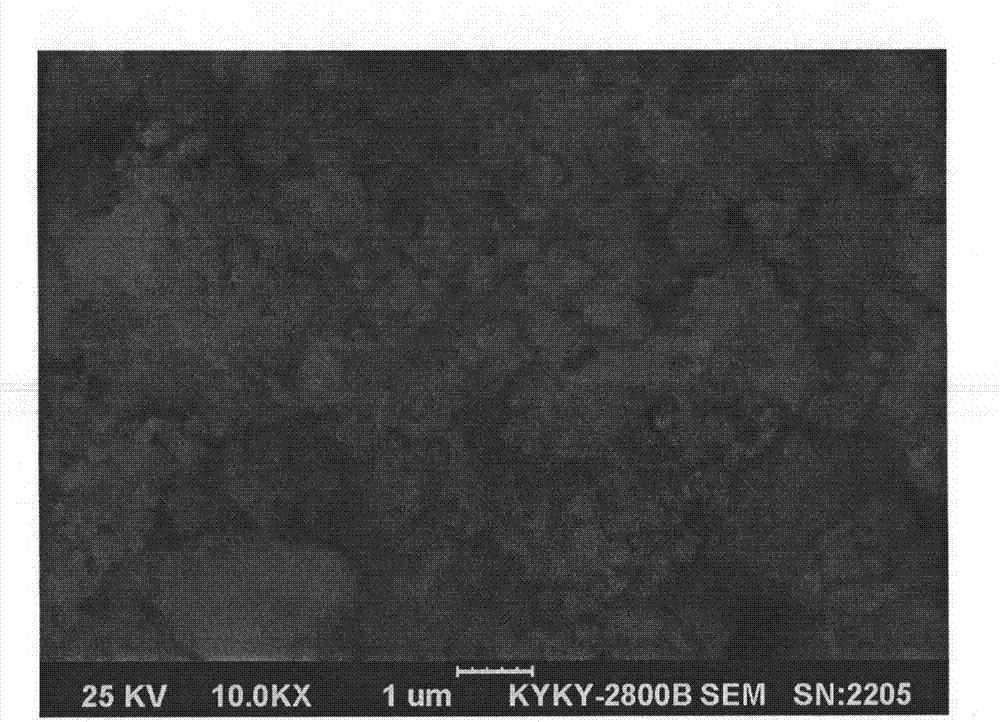
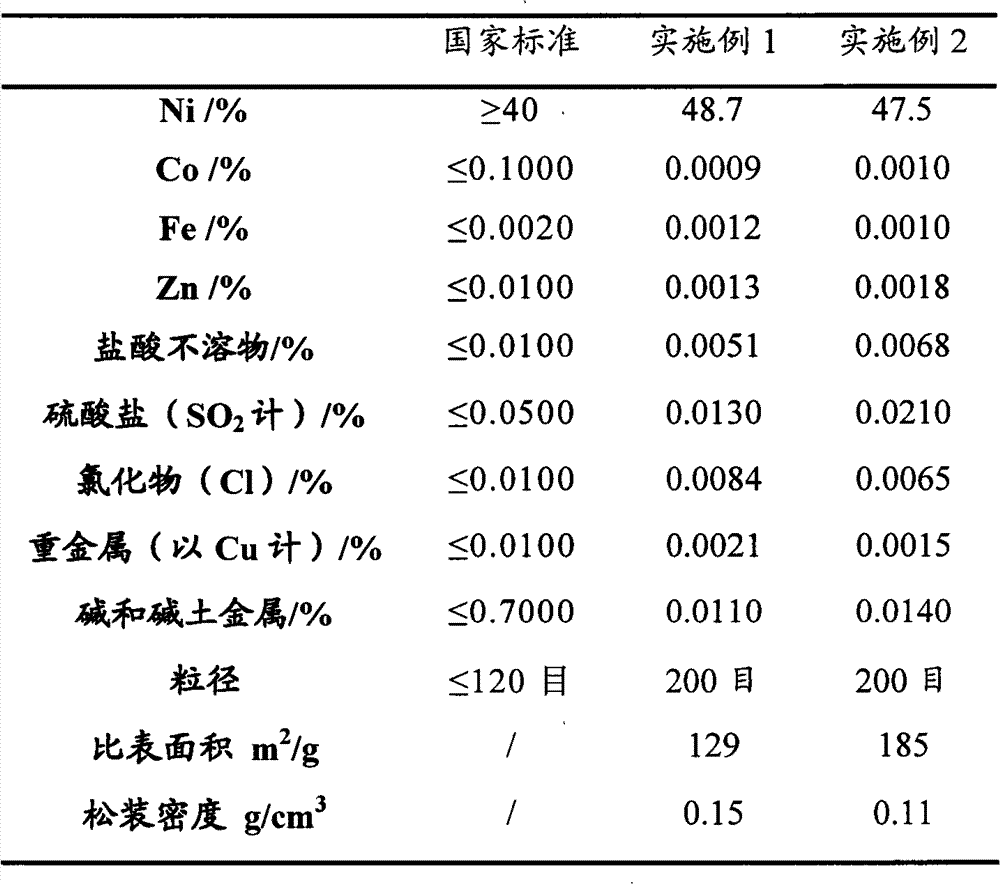
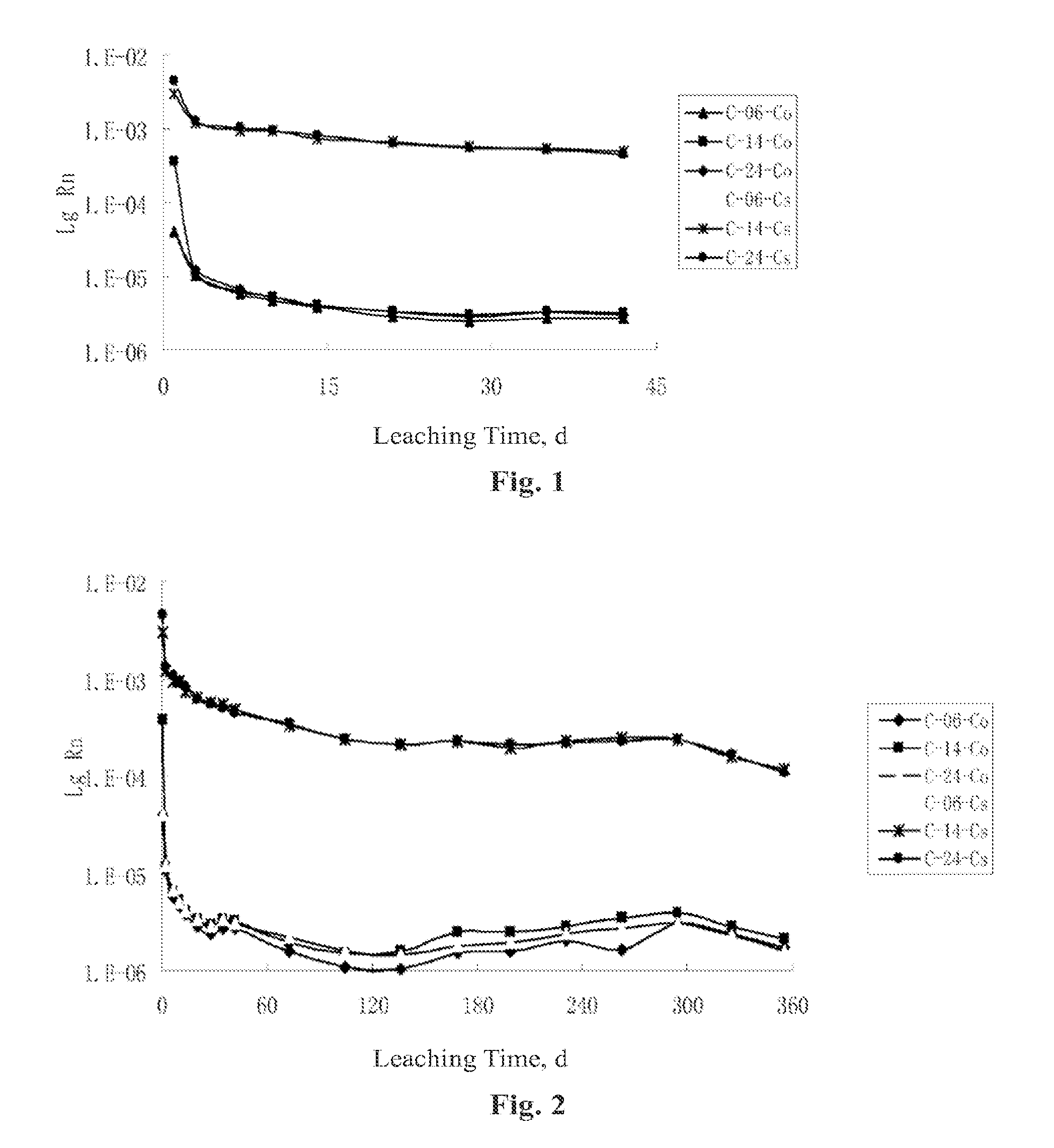
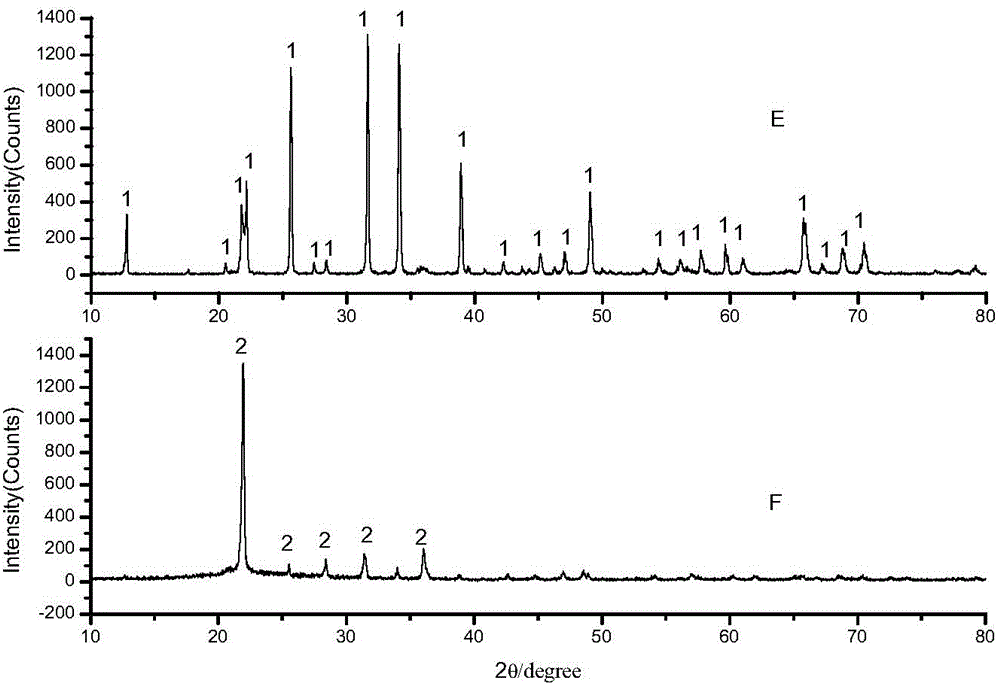
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Solve the low leaching rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for removing lead in heavy metal polluted soil by utilizing nanometer zero-valent iron and citric acid for combined elution
InactiveCN103599923AEasy to operateGood rinse effectContaminated soil reclamationFiltrationPrecipitation
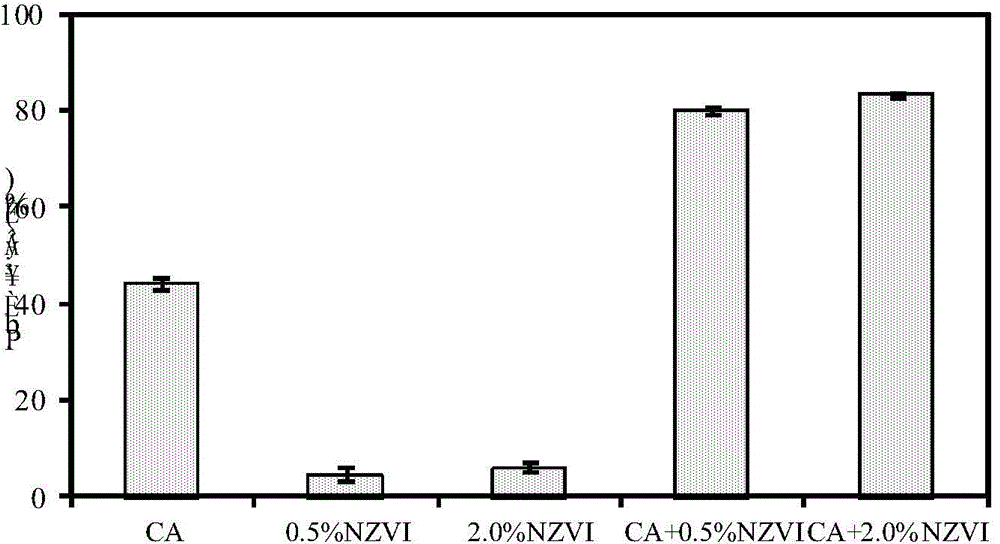
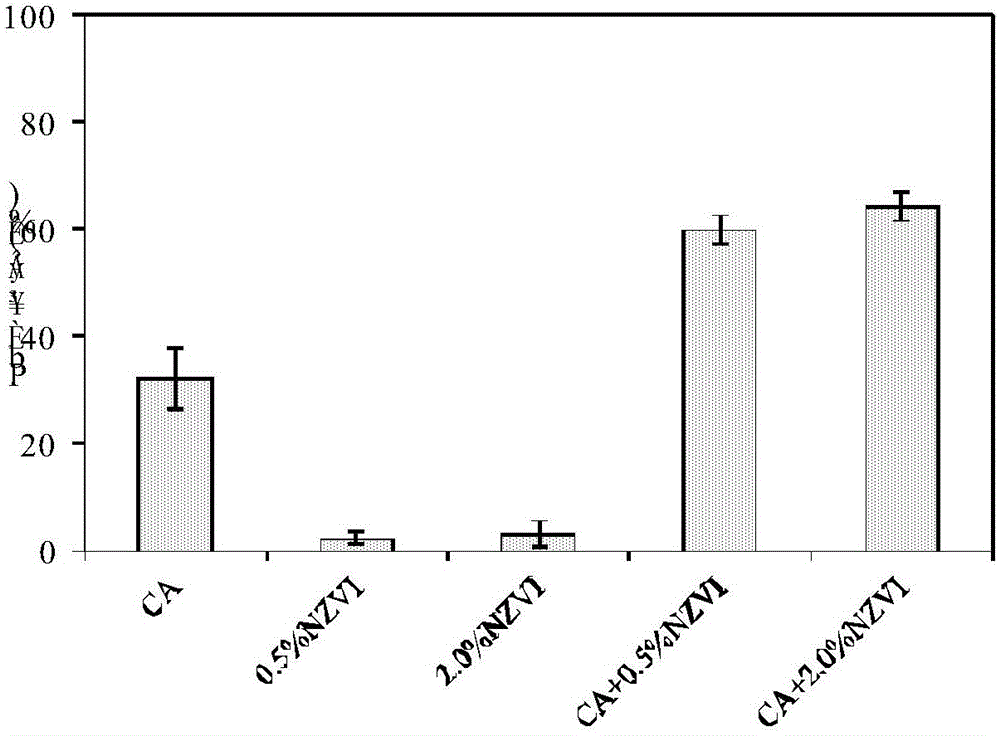
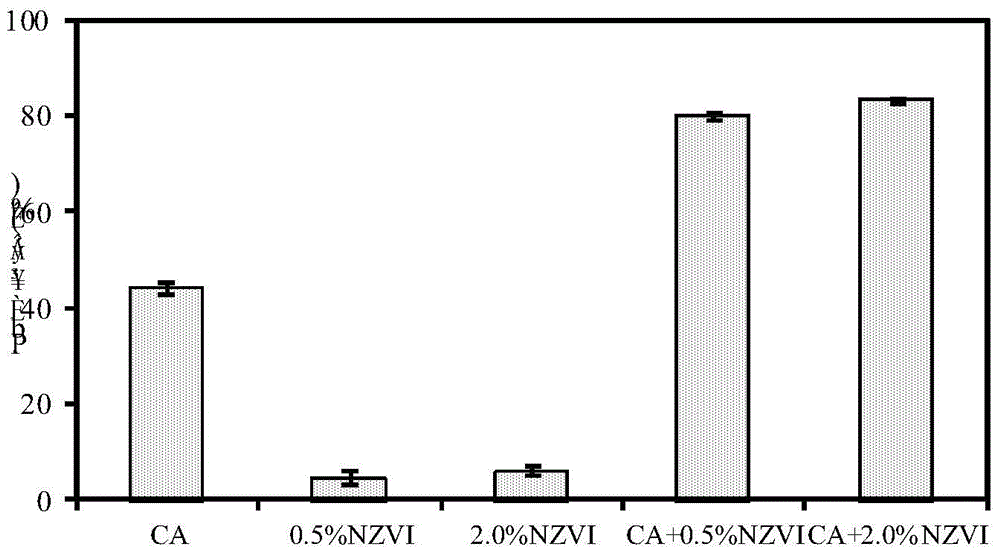
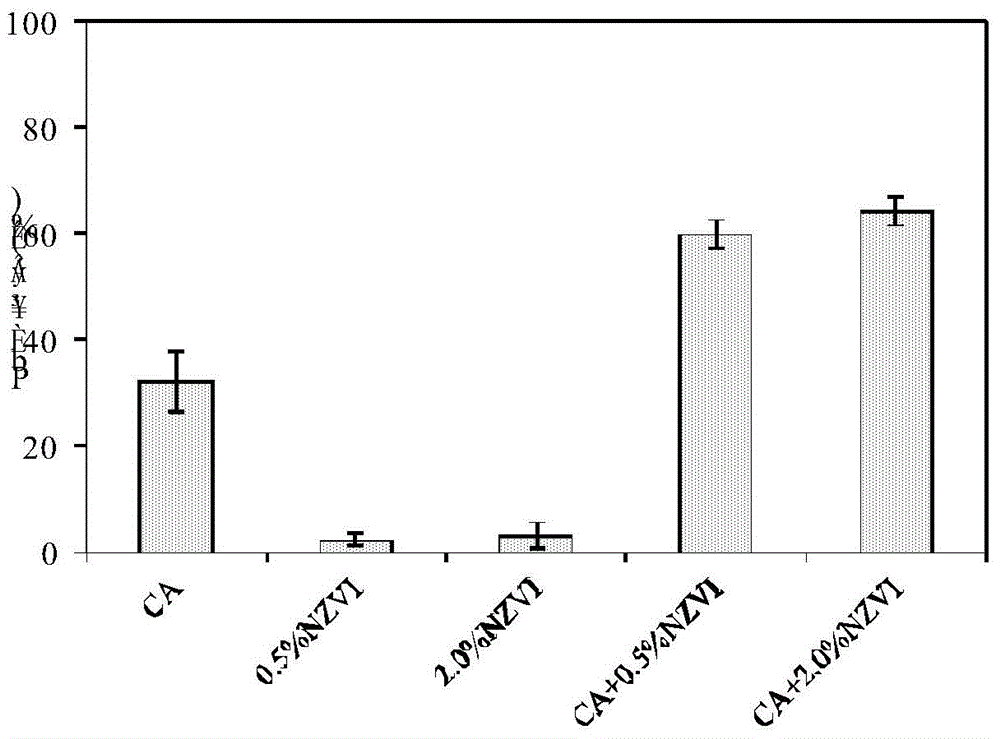
The invention discloses a method for removing lead in heavy metal polluted soil by utilizing nanometer zero-valent iron and citric acid for combined elution. The method comprises: adding nanometer zero-valent iron into a citric acid solution to prepare a nanometer zero-valent iron and critic acid composite solution, adding the composite solution into lead polluted soil, performing oscillation, elution and centrifuging at room temperature, then performing membrane filtration and collecting filtrate. The eluent is simple to prepare, strong in operationality and substantial in elution effect, and has the elution rate on lead of 83.08%; the lead content of eluted soil accords with soil environmental quality standards; lead in eluate can be recovered by chemical precipitation, biological adsorption and the like, and the eluate reaches discharging standards and does not cause secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Lead and zinc tailing recycling method
ActiveCN102776368AReduce recycling costsSolve the low leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementChemistryLead zinc
The invention relates to a lead and zinc tailing recovery technique, in particular to a lead and zinc tailing recycling method, which solves the problems that the leaching efficiency is low and the recovery cost is high when the existing lead and zinc tailing recovery technique is adopted. The lead and zinc tailing recycling method is realized through the following steps of: 1) mixing concentrated sulfuric acid with saturated sodium chloride solution to obtain leaching solution; 2) placing lead and zinc tailing slag in an agitating tank, adding the leaching solution into the agitating tank and fully agitating at 5-20DEG C to leach lead ions, zinc ions and silver ions contained in the lead and zinc tailing slag; 3) adding sodium sulfide solution into the agitating tank and fully agitating at 5-20DEG C; and 4) adding ammonium hydrogen carbonate solution into filtrate containing the zinc ions and fully agitating at 5-30DEG C. The lead and zinc tailing recycling method effectively solves the problems that the leaching efficiency is low and the recovery cost is high when the existing lead and zinc tailing recovery technology is adopted, and is suitable for recovery of lead and zinc tailing.
Owner:深圳市日昇生态科技股份有限公司
Recovery of precious metal from sulphide minerals by bioleaching
InactiveUS6860919B1Solve the low leaching rateReduced Power RequirementsInorganic chemistryBlast furnace detailsBioleachingSlurry
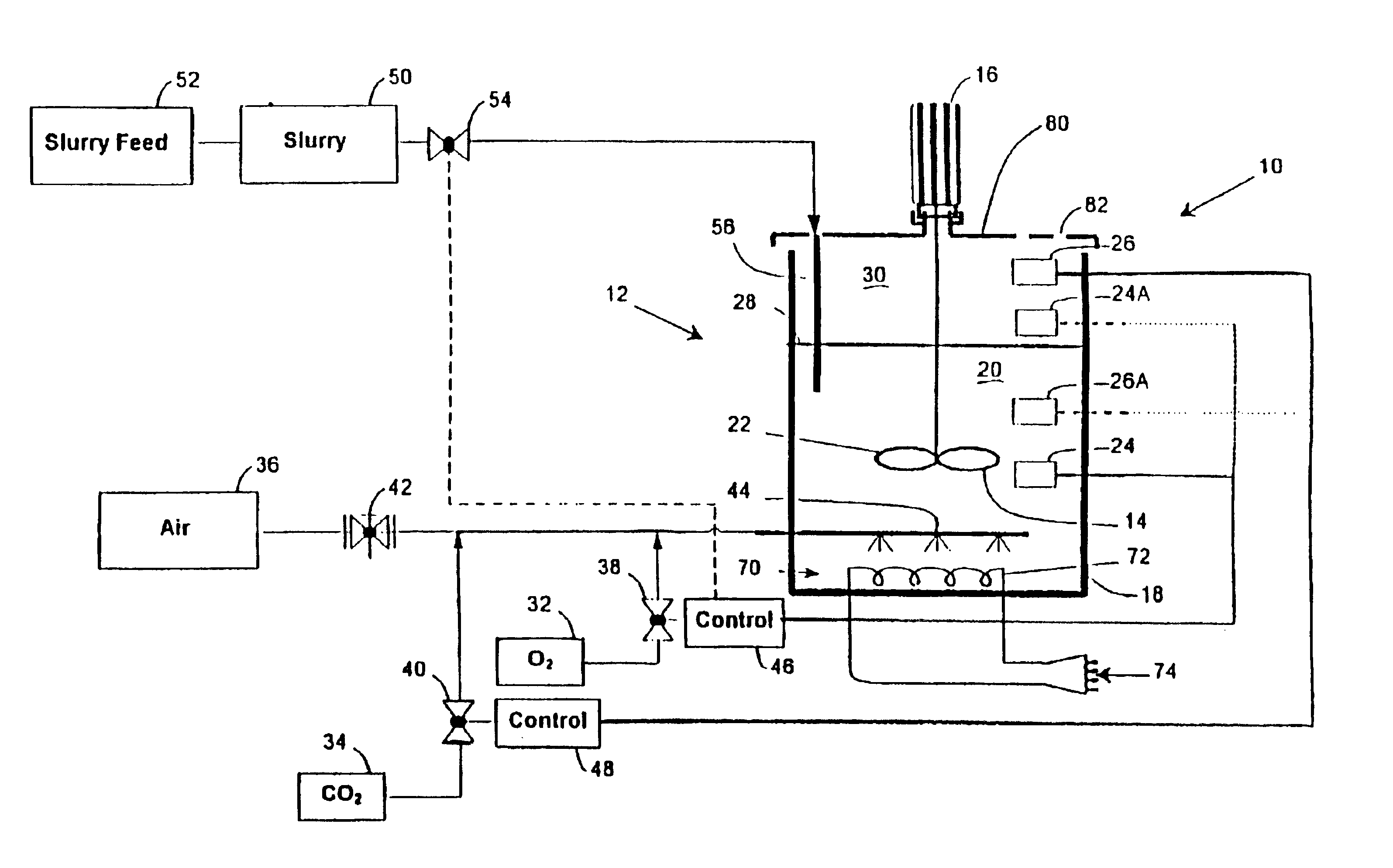
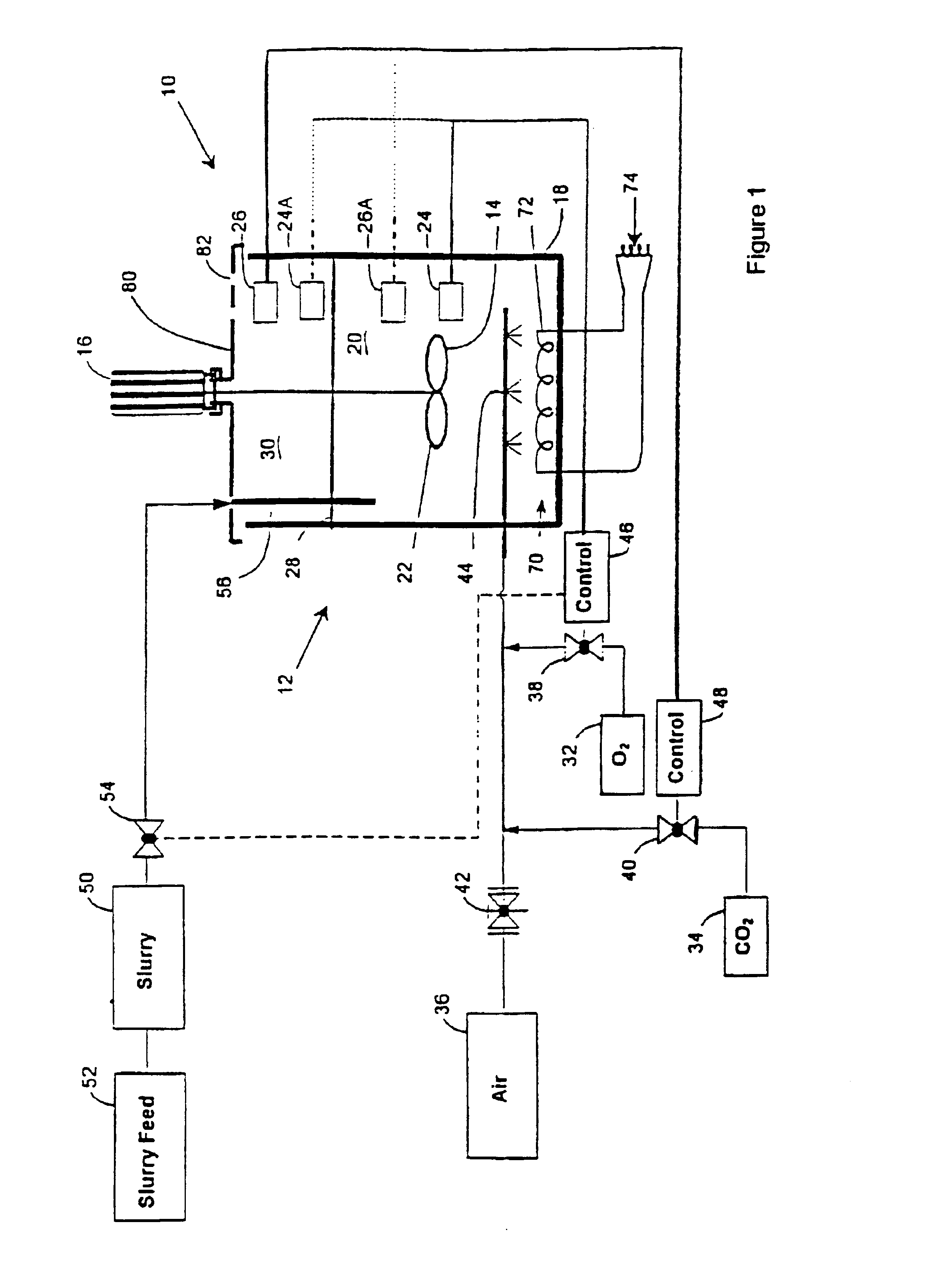
A method of recovering a precious metal from a sulphide mineral slurry which contains the precious metal which includes the steps of subjecting the slurry to a bioleaching process, supplying a feed gas which contains in excess of 21% oxygen by volume to the slurry, and recovering precious metal from a bioleach residue of the bioleaching process.
Owner:BILLITON INTPROP
Method for recovering indium from indium-containing material
ActiveCN106319221ASolve the low leaching rateSolve the problem of low extraction rateProcess efficiency improvementIndiumIron powder
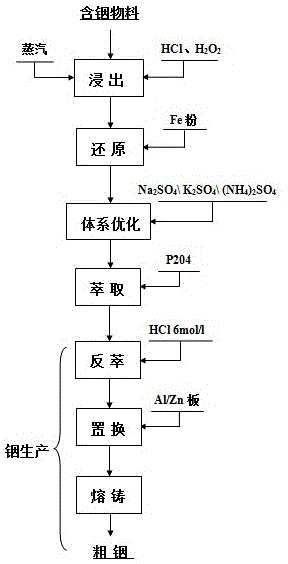
The invention discloses a method for recovering indium from an indium-containing material. The method comprises the following steps: (a) leaching: leaching the indium-containing material with hydrochloric acid under a heating condition by adding an oxidizing agent, and after leaching, adding a flocculant to clarify the precipitate and obtain a supernatant; (b) reduction: adding iron powder to the supernatant to reduce Fe<3+> in the supernatant; (c) system optimizing: adding a sufficient amount of a sulfate ion-containing reagent into the reduced indium-containing solution, so that the reduced indium-containing solution is optimized from a hydrochloric acid system into a sulfuric acid system; (d) extraction: extracting the indium-containing solution subjected to the system optimizing with a P204-containing organic phase to obtain an indium-containing organic phase; and (e) indium production: conducting reverse extraction and displacement on the indium-containing organic phase to obtain sponge indium, and conducting melt casting on the sponge indium to obtain crude indium. Due to adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, not only the high leaching rate in the leaching process, but also the extraction rate and the product quality of indium can be ensured.
Owner:HANERGY MOBILE ENERGY HLDG GRP CO LTD
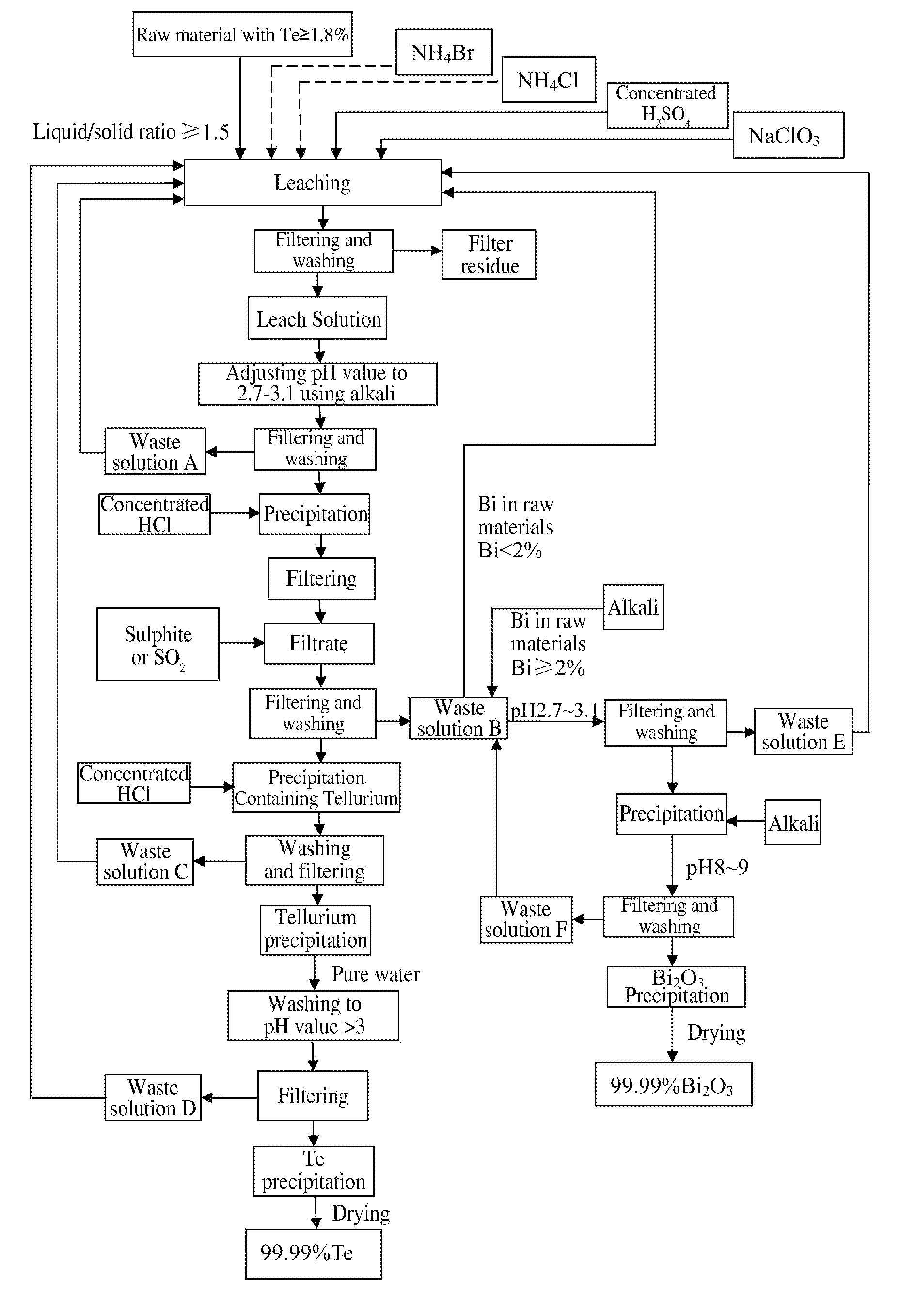
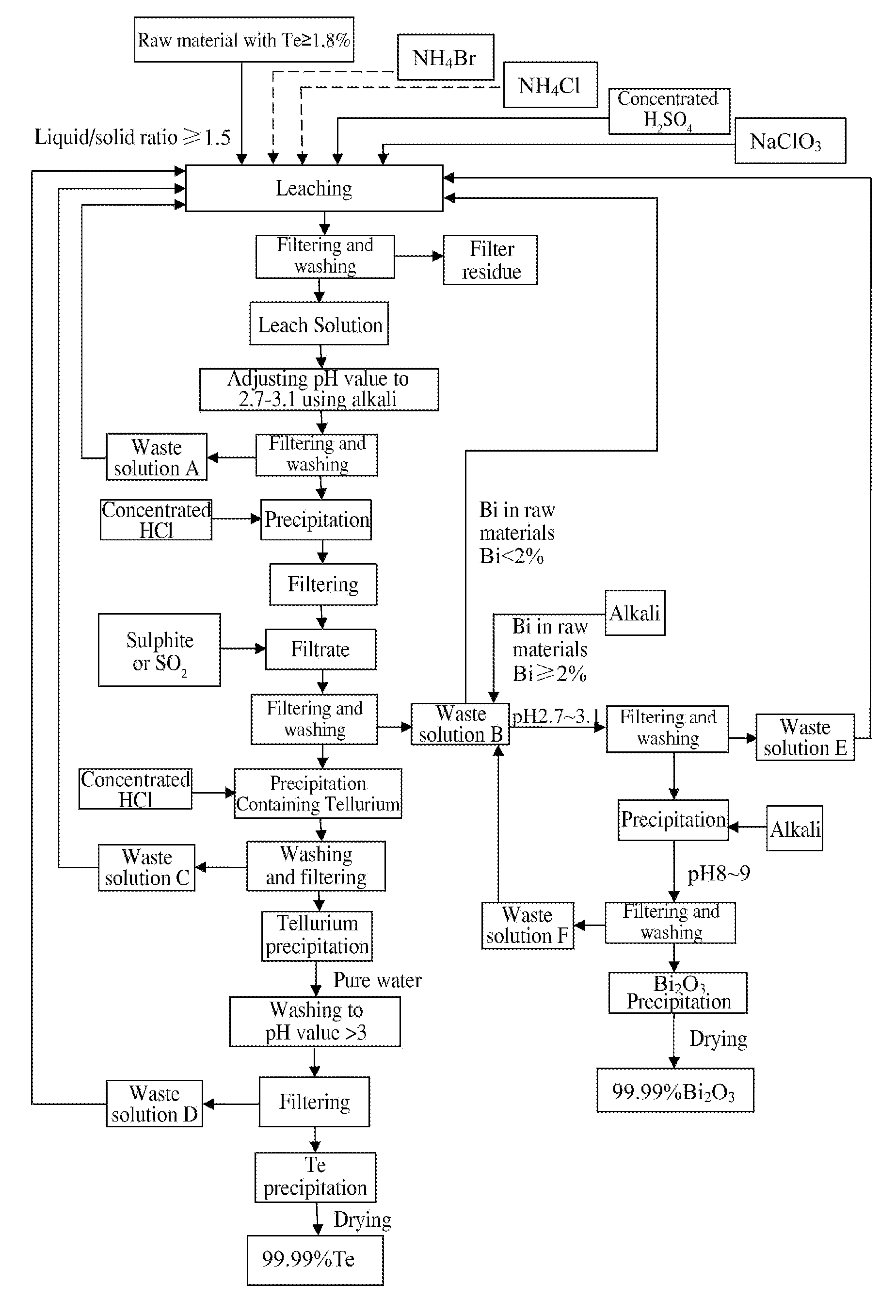
Method of Extracting Te and Bismuth Oxide and Recovering Byproducts
InactiveUS20110076208A1Improve leaching rateShorten the leaching timeSolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsBismuthImpurity
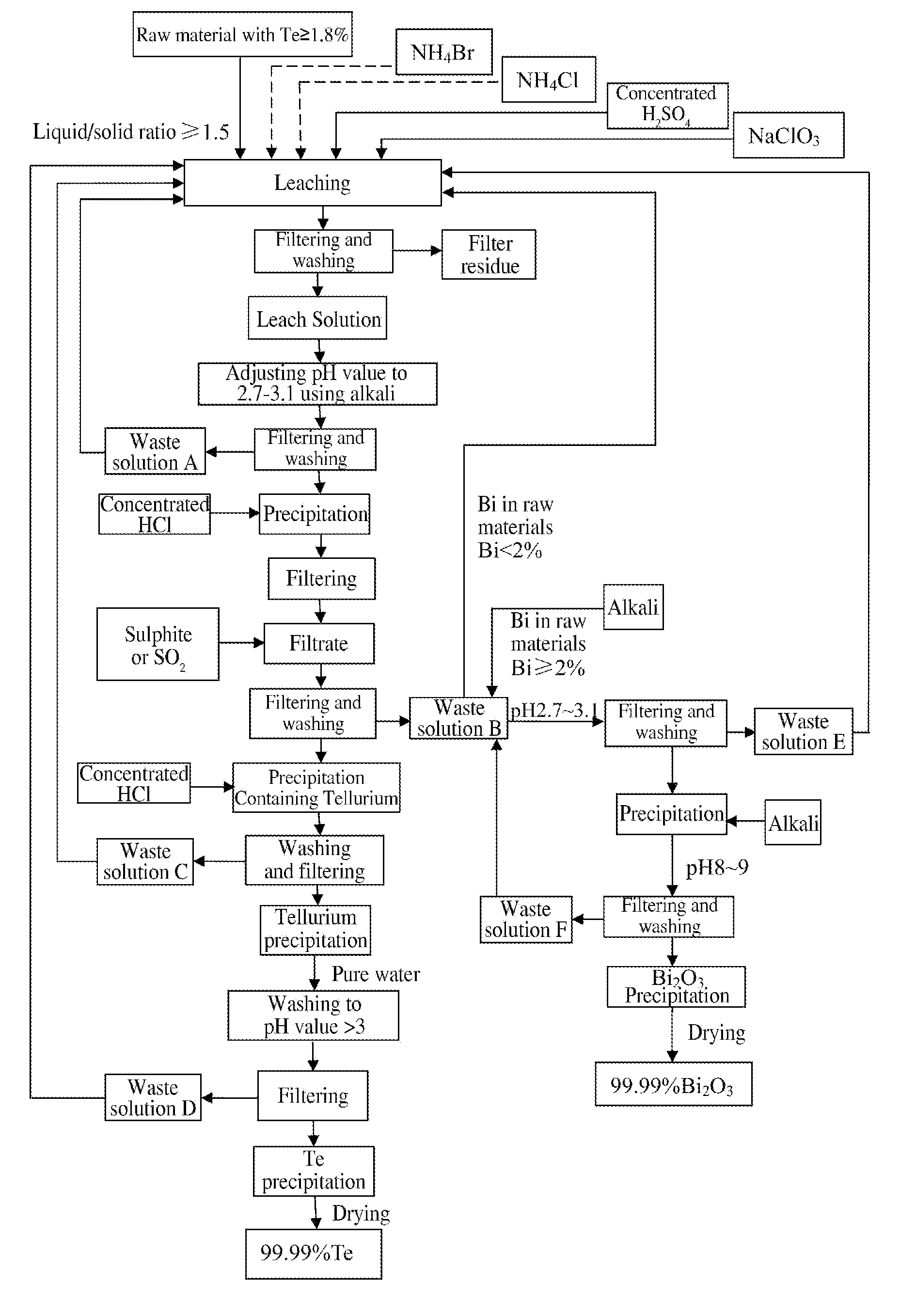
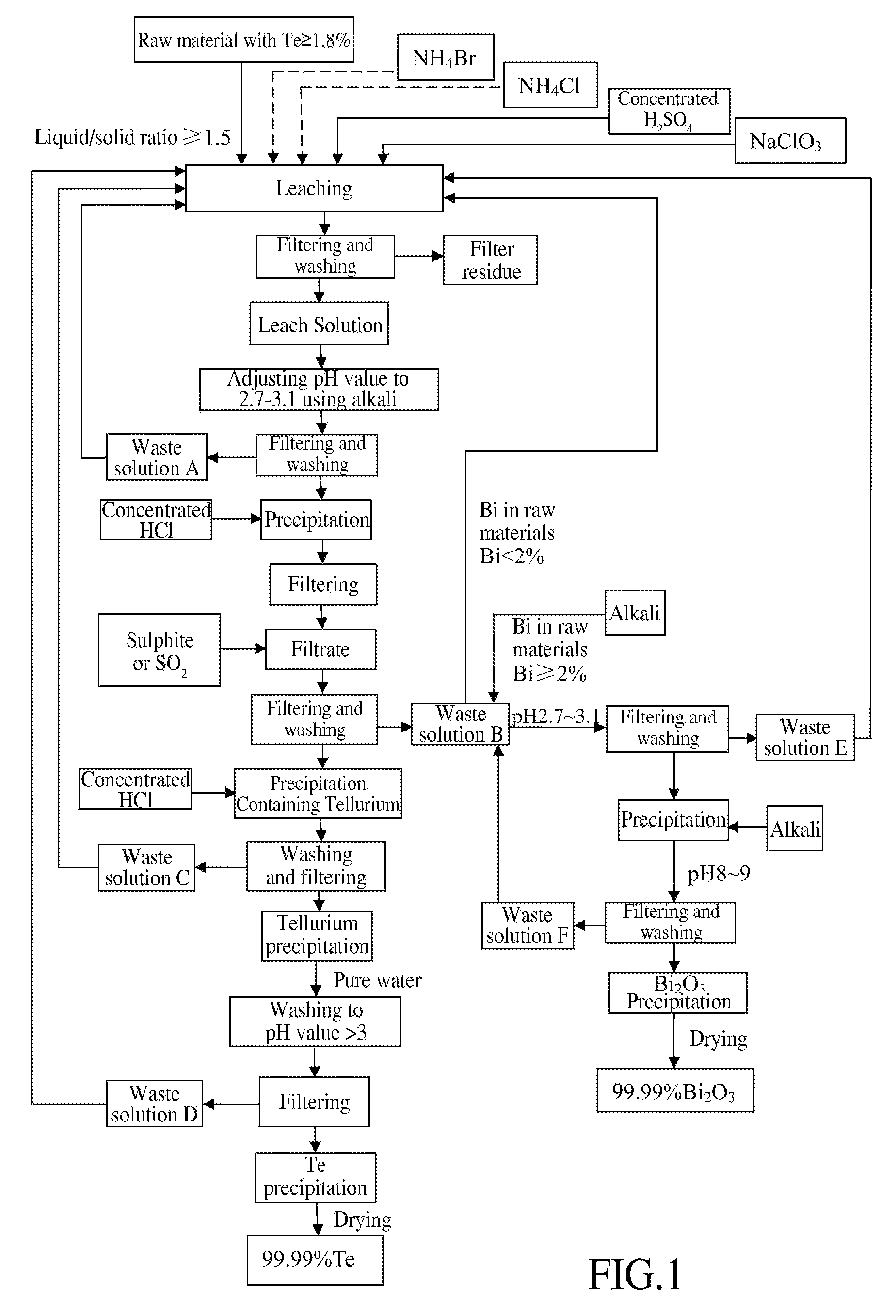
A method of extracting Te and bismuth oxide and recovering byproduct comprises: leaching raw materials with a Te content of ≧1.8% by utilizing a leaching system containing H2SO4, Cl−, Br−, NH4+ and NaClO3, reducing leach solution with SO2 gas by precipitation method after separating impurities from it, washing with concentrated hydrochloric acid to obtain tellurium precipitation (18), purifying to obtain Te with a purity of higher than 99.99%. The filtrate produced is used for extracting Bi2O3 with a purity of higher than 99.99% when Bi content in the raw material is ≧2%. Acidic waste solution produced during the process could be returned to the leaching step for recycle.
Owner:WANG JUN
Comprehensive recovery method of waste electrolyte containing lithium and aluminum
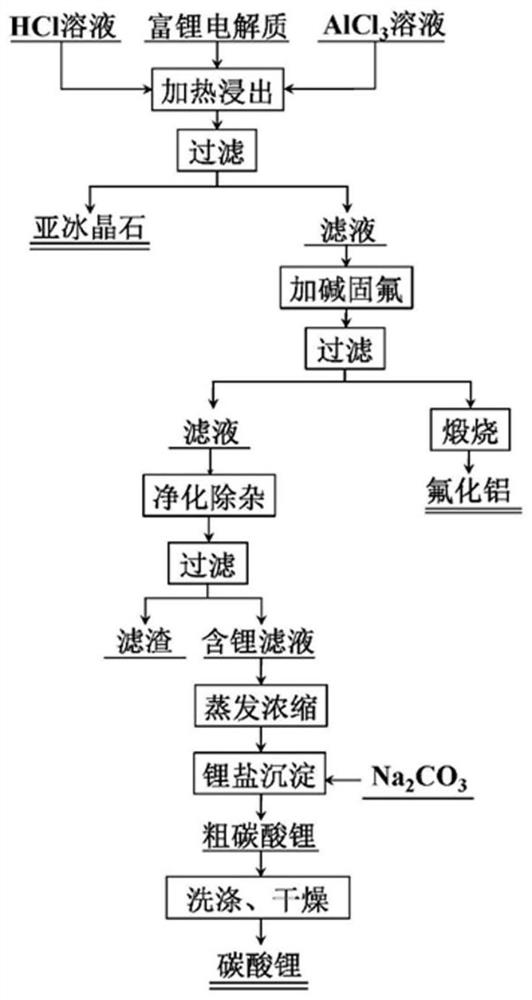
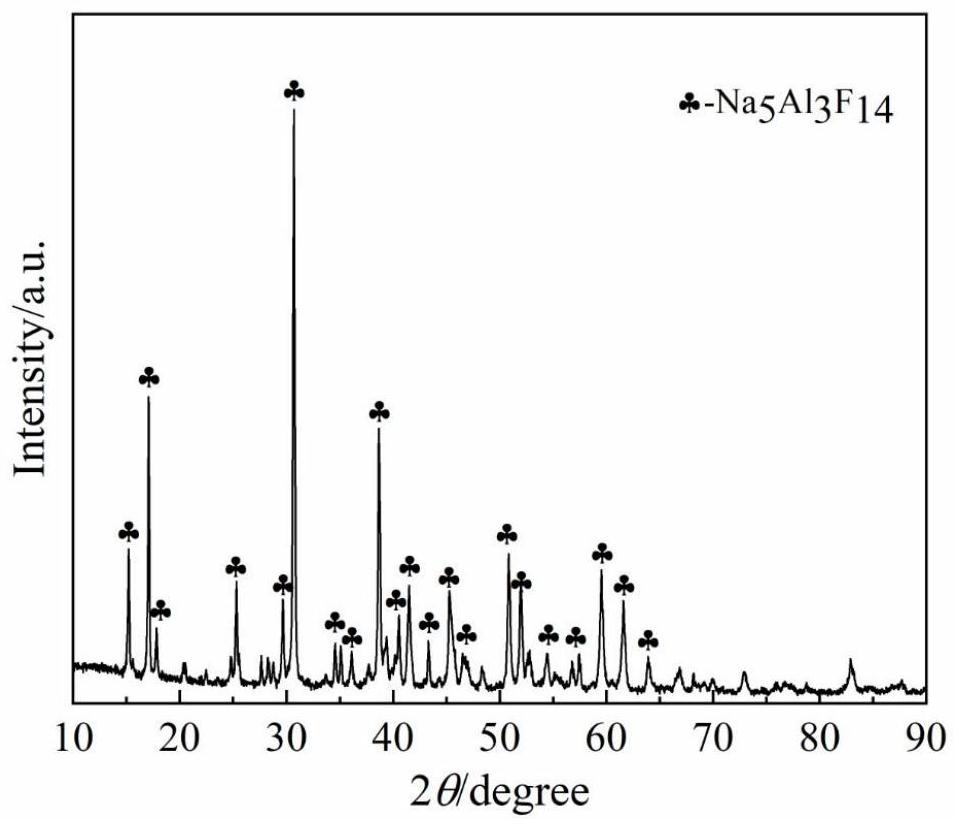
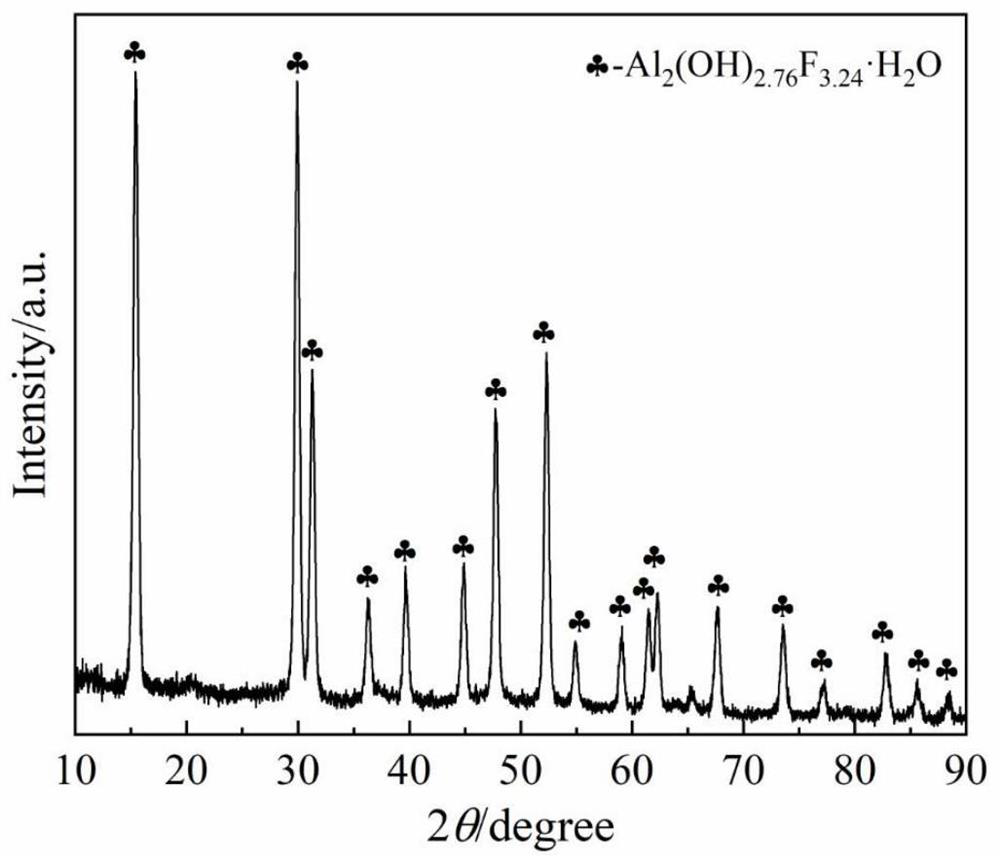
ActiveCN114438329AGuaranteed uptimeHarmlessAluminium fluoridesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesAluminum fluorideSocial benefits
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of waste electrolyte containing lithium and aluminum. The method comprises the following steps: crushing and finely grinding the waste lithium-aluminum-containing electrolyte into electrolyte powder; preparing an acid solution, and adding a leaching enhancer; then adding the electrolyte powder into an acid solution for leaching, and filtering to obtain a filter residue A and a filtrate A; washing and drying the filter residue A to obtain a subcryolite product; adding alkali liquor into the filtrate A for adjustment to generate crystal precipitates, and filtering to obtain filter residues B and filtrate B; drying and calcining the filter residue B to obtain an aluminum fluoride product; adding sulfate into the filtrate B for reaction to generate precipitate, and filtering to obtain filtrate C; evaporating and concentrating the filtrate C to separate out solid substances, filtering to obtain sodium salt and a concentrated solution D, adding carbonate into the concentrated solution D to react, and filtering and drying after reaction to obtain a lithium carbonate product. The storage problem of the waste aluminum electrolyte can be effectively solved, harmlessness and recycling of the waste electrolyte are achieved, and environmental protection is facilitated. Therefore, the method has remarkable economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
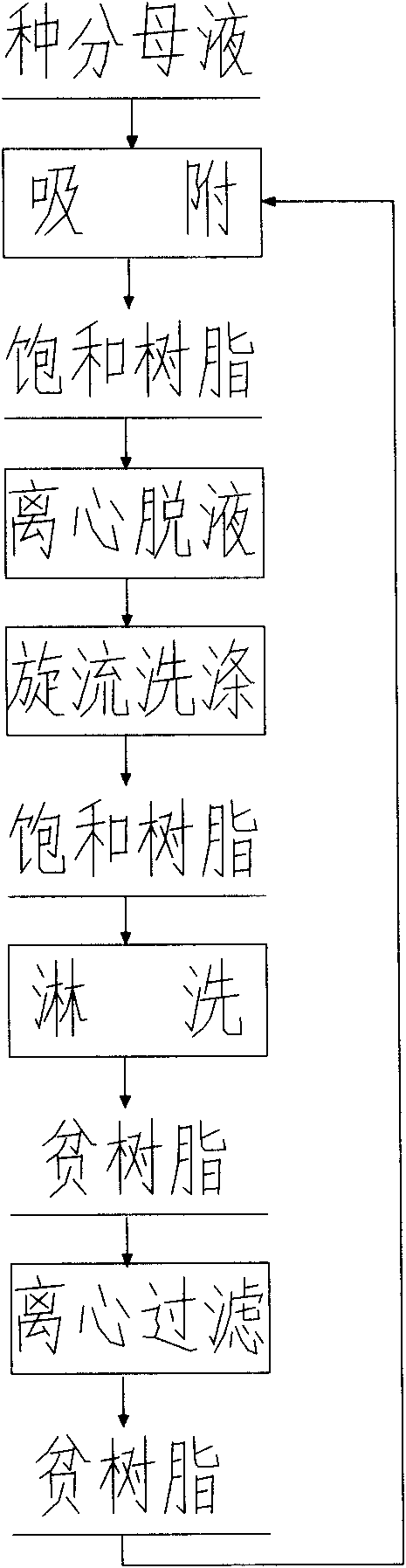
Ion exchange method for extracting gallium from seed separation mother liquid
InactiveCN101597699AImprove the washing methodIncrease rinsing rateProcess efficiency improvementIonIon exchange
The invention relates to an ion exchange method for extracting gallium from seed separation mother liquid, which is characterized in that gallium is extracted from seed separation mother liquid for producing alumina by different ion exchange equipment and ion exchange methods, namely the ion exchange method comprising the following steps: connecting a plurality of fixed beds in parallel to adsorb the seed separation mother liquid; removing the mother liquid by a centrifugal machine and then washing impurities in rotating flow; connecting the fixed beds in series to leach the impurities; and removing leaching agent by the centrifugal machine. Compared with the prior moving bed, ISEP technology and complete counter-flow mixed bed ion exchange, the technical method has the advantages of low production cost, simple technical equipment, convenient operation, easy automation realization, and the like.
Owner:冯峰
Recovery of precious and chalcophile metals
ActiveUS20200172994A1Limit its contamination in downstream processingPrevent copper contaminationProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPhysical chemistry
A process for recovery of one or more elements, selected from precious metals and chalcophile metals, as herein defined, from materials containing precious and / or chalcophile metal / s, said process including: (i) contacting the material with an alkaline solution containing a lixiviant comprising an amino acid, or derivative thereof, and an alkali stable transition metal complex in order to form a leachate containing the precious metal and / or chalcophile metal; and (ii) recovering the precious metal and / or chalcophile metal from the leachate.
Owner:MINING & PROCESS SOLUTIONS PTY LTD
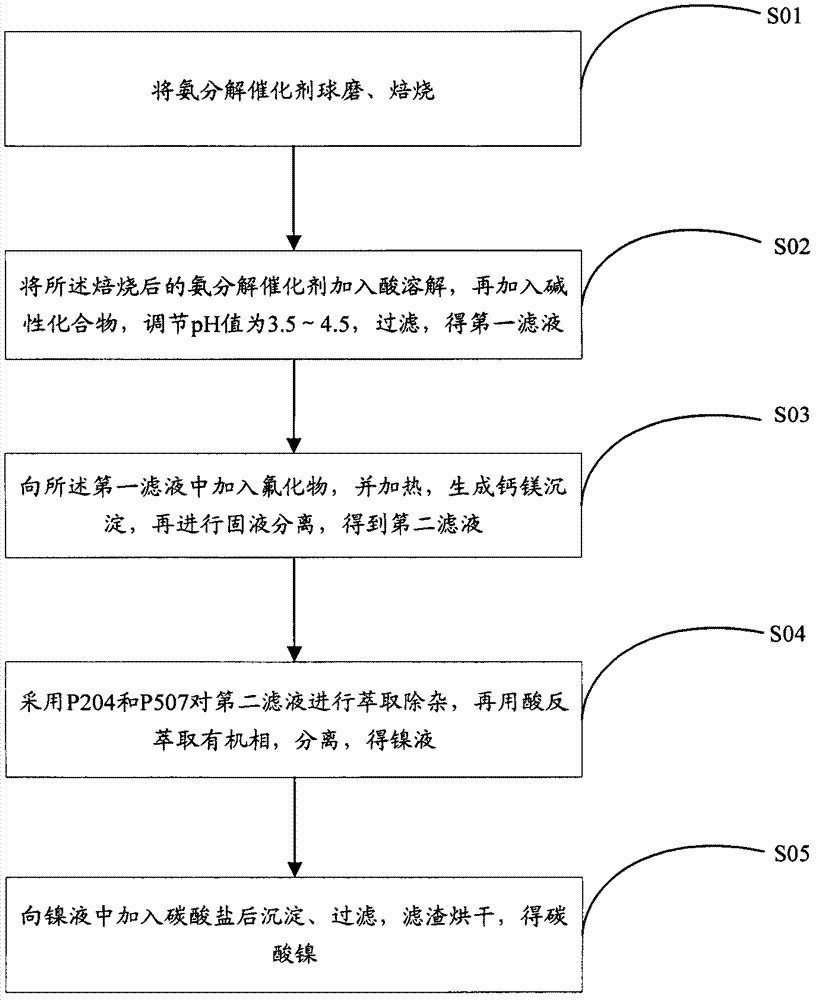
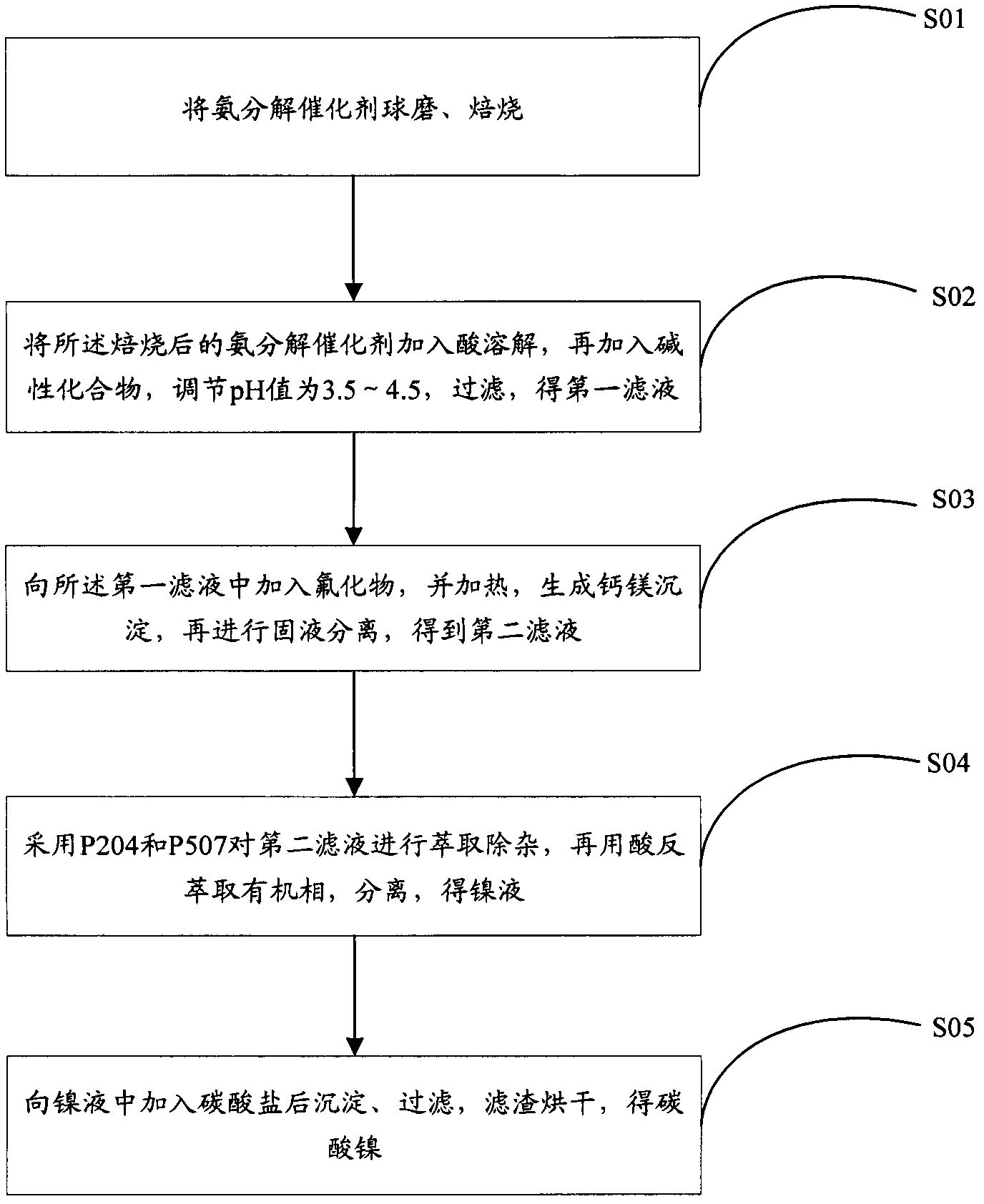
Method for preparing nickelous carbonate by utilization of waste ammonia decomposition catalyst
ActiveCN102765762ASolve the low leaching rateReduce lossNickel carbonatesDecompositionMaterials processing
The invention relates to the technical field of non-ferrous metal material processing and preparation and provides a method for preparing nickelous carbonate by the utilization of a waste ammonia decomposition catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out ball milling on an ammonia decomposition catalyst, roasting, dissolving the roasted ammonia decomposition catalyst by the addition of an acid, adding an alkaline compound, adjusting pH value to 3.5-4.5, and filtering to obtain a first filtrate; adding fluoride into the first filtrate, heating to generate calcium and magnesium precipitates, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a second filtrate; carrying out extraction and impurity removal on the second filtrate by the use of P204 and P507, carrying out back extraction on an organic phase by the use of an acid, and separating to obtain a nickel liquid; adding carbonate into the nickel liquid, precipitating, filtering, and drying filter residue to obtain nickelous carbonate. According to the method, by the adoption of multiple steps of oxidation-assisted leaching, extraction separation and carbonate precipitating nickel, nickel dipping has high yield and low loss, and the product has high purity, small particle size and high activity.
Owner:GEM CO LTD +1
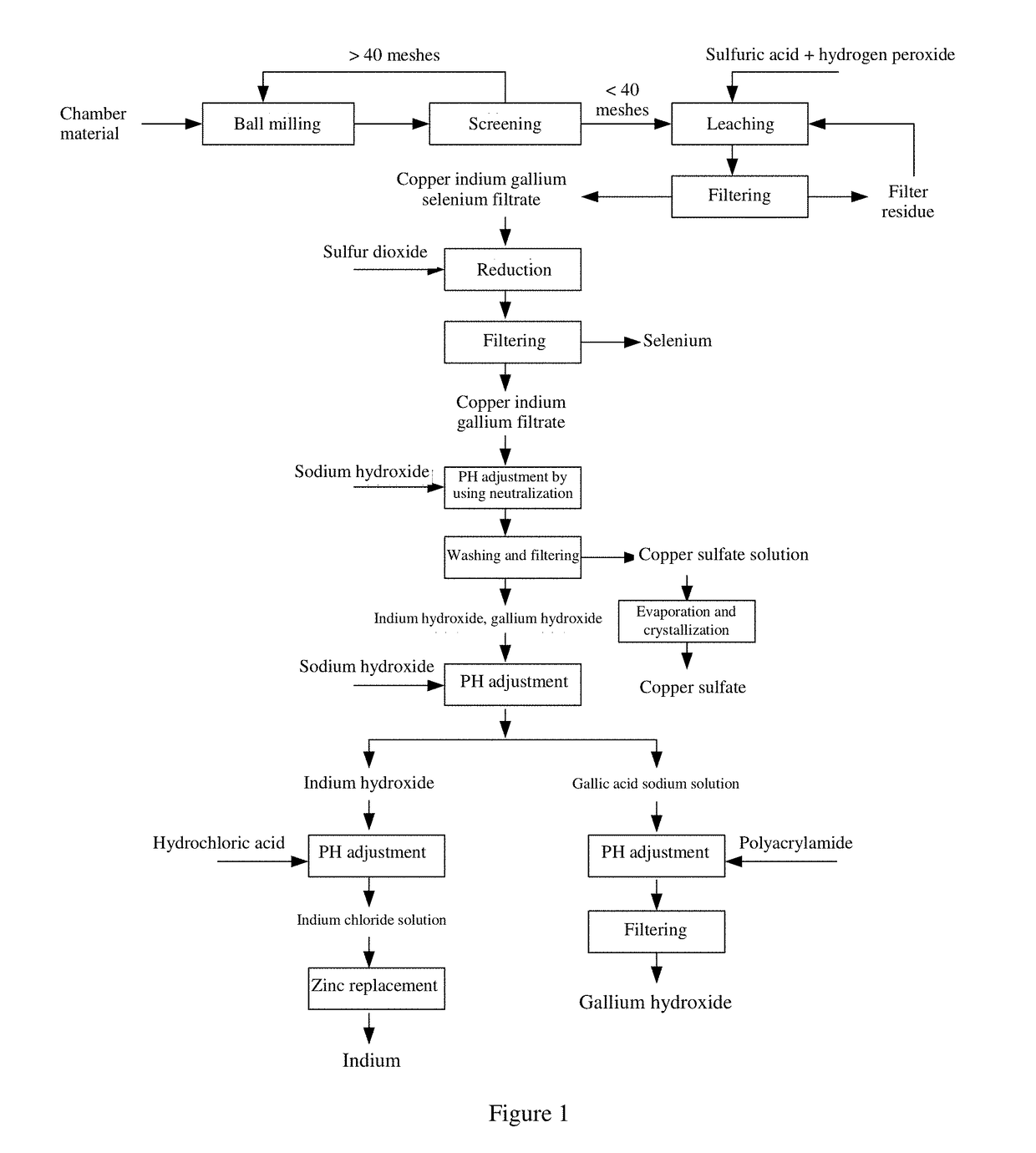
Method for recycling copper indium gallium selenium materials
InactiveUS20190010578A1Reduce environmental pollutionHigh recovery rateGallium/indium/thallium compoundsProcess efficiency improvementIndiumCell separation
A method for recycling copper indium gallium selenium materials comprises the steps of leaching by using sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide, reduction of selenium by using sulfur dioxide, separation of copper by using hydrolysis, alkali separation of indium and gallium, replacement of indium, hydrolysis of gallium, and the like. Leaching is carried out by using sulfuric acid in cooperation with hydrogen peroxide, so that the leaching rate is greatly improved, and acid gas pollution is reduced; PH differential copper is separated by using metal ion hydrolysis, so that costs are low; and in addition, alkali separation of gallium is carried out, separation between indium and gallium can be implemented by merely adjusting the PH of a solution, the separation effect is good, the purities of obtained indium and gallium products are high.
Owner:HANERGY NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Cement curing formulation and method for high-level radioactive boron waste resins from nuclear reactor
ActiveUS9443628B2Reduce intensitySolve the low leaching rateSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A cement curing formulation and curing method for high-level radioactive boron waste resins from a nuclear reactor. The curing formulation comprises the following raw materials: cement, lime, water, curing aids and additives. The curing method comprises: (1) weighing the raw materials and the high-level radioactive boron waste resins, and adding lime into a curing container; (2) then adding the high-level radioactive boron waste resins; (3) feeding other raw materials under stirring; (4) adding the cement and supplementing water depending on the moisture state of the cement, and stirring until uniform; and (5) standing and maintaining after stirring until uniform. The curing formulation has the features of a high curing containment rate, high strength of the cured body, better water resistance, better freeze-thaw resistance, and low radioactive leakage.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +3
A method for removing lead in heavy metal polluted soil by combined leaching of nanometer zero-valent iron and citric acid
InactiveCN103599923BEasy to operateGood rinse effectContaminated soil reclamationEmission standardContamination
The invention discloses a method for removing lead in heavy metal polluted soil by combined leaching of nanometer zero-valent iron and citric acid. The method is to add nanometer zero-valent iron to citric acid solution to make nanometer zerovalent iron-citric acid composite solution, then add the composite solution into lead-contaminated soil, vibrate at room temperature, rinse, centrifuge, and then filter membrane and collect the filtrate. The leach solution of the present invention is simple to prepare, has strong operability, and remarkable leaching effect, and the leaching rate of lead reaches 83.08%; the lead content in the soil after leaching meets the soil environmental quality standard, and the lead in the leach solution can pass Recycling by means of chemical precipitation, biological adsorption and other methods, the eluent meets the discharge standard and will not cause secondary pollution to the environment.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Valuable metal leaching method, and valuable metal collection method employing the leaching method
ActiveUS9068242B2Solve the low leaching rateEfficiently leached outCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingMetal leachingHydrogen
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Method for roasting vanadium-containing material by using chain grate machine and rotary kiln
InactiveCN110878388ASolve cohesionSolve the conversion rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionProcess engineering
The invention relates to the field of chemical methods for extracting vanadium, and in particular relates to a method capable of greatly improving the conversion rate and leaching rate of vanadium forroasting a vanadium-containing material by using a chain grate machine and a rotary kiln. The method comprises the following steps: a, crushing the vanadium-containing material to a required particlesize, mixing the crushed particles and additives, and performing mechanical activation to obtain a mixture; b, uniformly arranging the formed material in the chain grate machine by using a roll screening machine, and performing drying, curing and strengthening in the chain grate machine; and c, allowing the formed material to enter the rotary kiln for concentrated high-temperature roasting, performing discharge to obtain a vanadium-containing formed clinker, crushing the vanadium-containing formed clinker to a required particle size, and performing water leaching or acid leaching to obtain avanadium-containing leaching solution, wherein the vanadium-containing leaching solution is used for subsequent vanadium precipitation. The method uses the chain grate machine and the rotary kiln to roast the vanadium-containing material, has the technical advantages of a simple and easy process, low requirements for equipment, convenient operation, a wide application range and low costs, and is particularly suitable for the vanadium-containing material roasting process.
Owner:四川大裂谷钒业有限公司
Method of extracting Te and bismuth oxide and recovering byproducts
InactiveUS8277772B2Low leaching rateLow recovery rateSolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsTe elementImpurity
Owner:WANG JUN
Method for selectively leaching zinc in complex zinc oxide materials at high temperature by adopting ammonium chloride solution
InactiveCN104928470APromote leachingSolve the low leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium hydroxideSilica gel
The invention discloses a method for selectively leaching zinc in complex zinc oxide materials at high temperature by adopting an ammonium chloride solution. According to the method, the zinc in the complex zinc oxide materials is selectively leached at the high temperature by taking the neutral ammonium chloride solution as a leaching agent in a sealed container; the zinc in the complex zinc oxide materials can be selectively leached, the zinc leaching rate is higher than 90 percent, and the effective separation of the zinc from impurity elements such as silicon, iron, calcium and magnesium is achieved; the problems that silica gel is prone to being generated and the acid consumption is large in the traditional acid leaching process of the complex zinc oxide materials are solved; the problem that the zinc leaching rate is low when an ammonium hydroxide and ammonia-ammonium salt method is used to leach complex zinc oxide ore especially containing ore phases such as willemite, hemimorphite and iron-zinc ore is solved; the method is specially suitable for processing the complex zinc oxide materials containing high silicon, the calcium, the magnesium and the iron.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Ion exchanging method for extracting gallium from alumina production process
ActiveCN100510125COne charge reductionGuaranteed adsorption conditionsProcess efficiency improvementFixed bedIon exchange
Owner:冯峰 +1
Method for leaching, enriching and reclaiming indium from lead-zinc smelting by-product zinc oxide
ActiveCN100537796CSolve the low leaching rateSolve the problem of how to dispose ofProcess efficiency improvementIndiumStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for leaching, enriching and recovering indium from zinc oxide byproduct in the lead and zinc smelting process. The invention is implemented by the following technical proposal: by using three-step leaching process and adding oxidizing agent in the leached slurry, the problem of low indium leaching rate is solved; intermittent slag feeding mode is used to prevent the over-high acidity due to the leached strong acids and the excessive iron production and thus to avoid the production of indium-conjugated jarosite in the next preneutralization process, which may influence the recovery of indium; the high-acidity solution is neutralized with a neutralizer such as zinc oxide or zinc calcine, so that the problem of high-acidity solution disposal is solved; when the low-acidity and high-acidity leach slurry are fed into the concentration machine, the compound flocculant is added to solve the technical problems of difficulty in settlement clarification of ore slurry, poor fluidity of thickened underflow and serious hardening. With this method, the indium leaching rate is increased up to 70-80 percent and the recovery rates of indium and zinc are also increased. Additionally, the method allows the disposal of lead-containing materials (lead slag) in the lead system and helps to reduce the discharge of waste slag, gas and water, protecting the environment.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
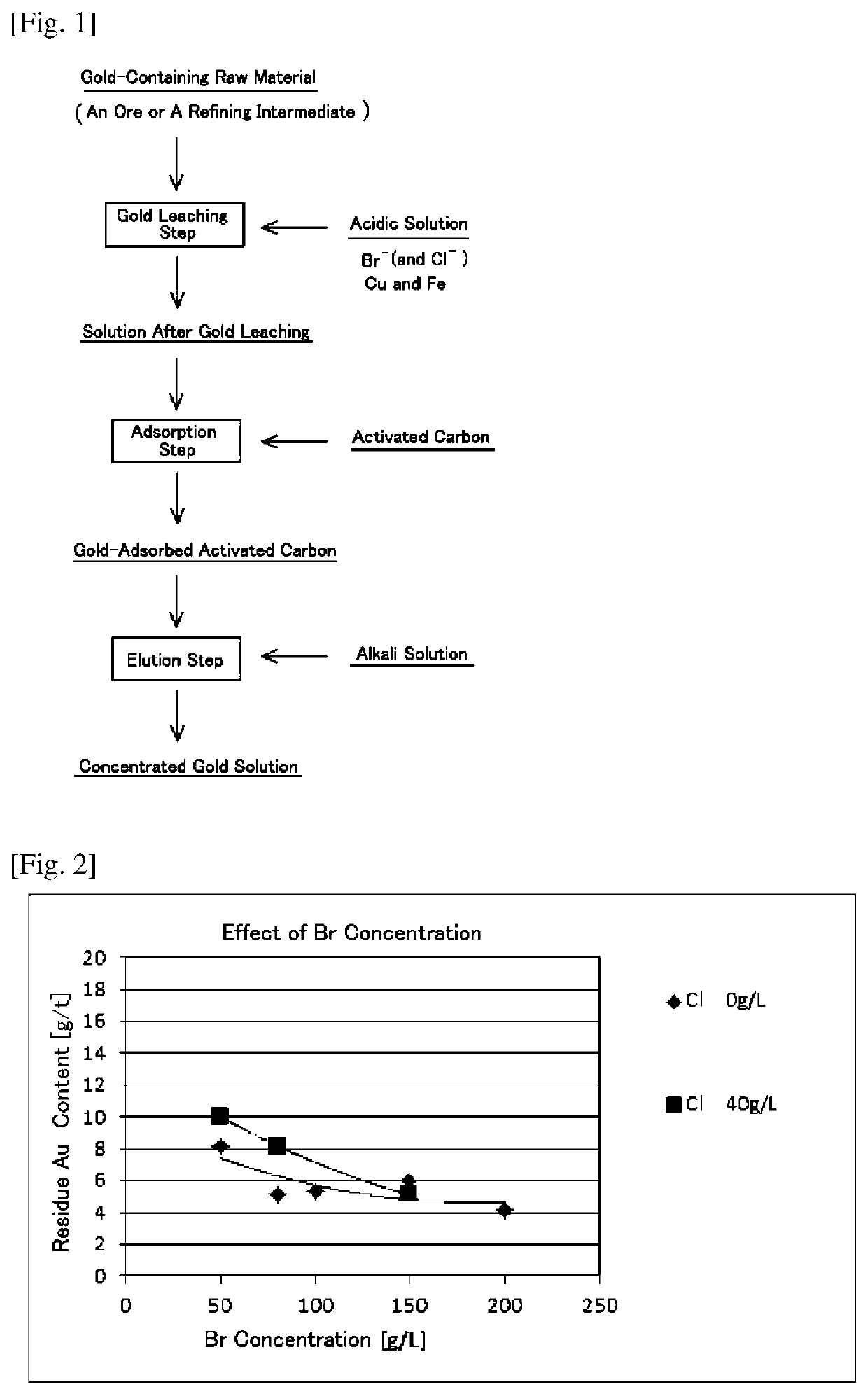
Method for recovering gold from an ore or a refining intermediate containing gold
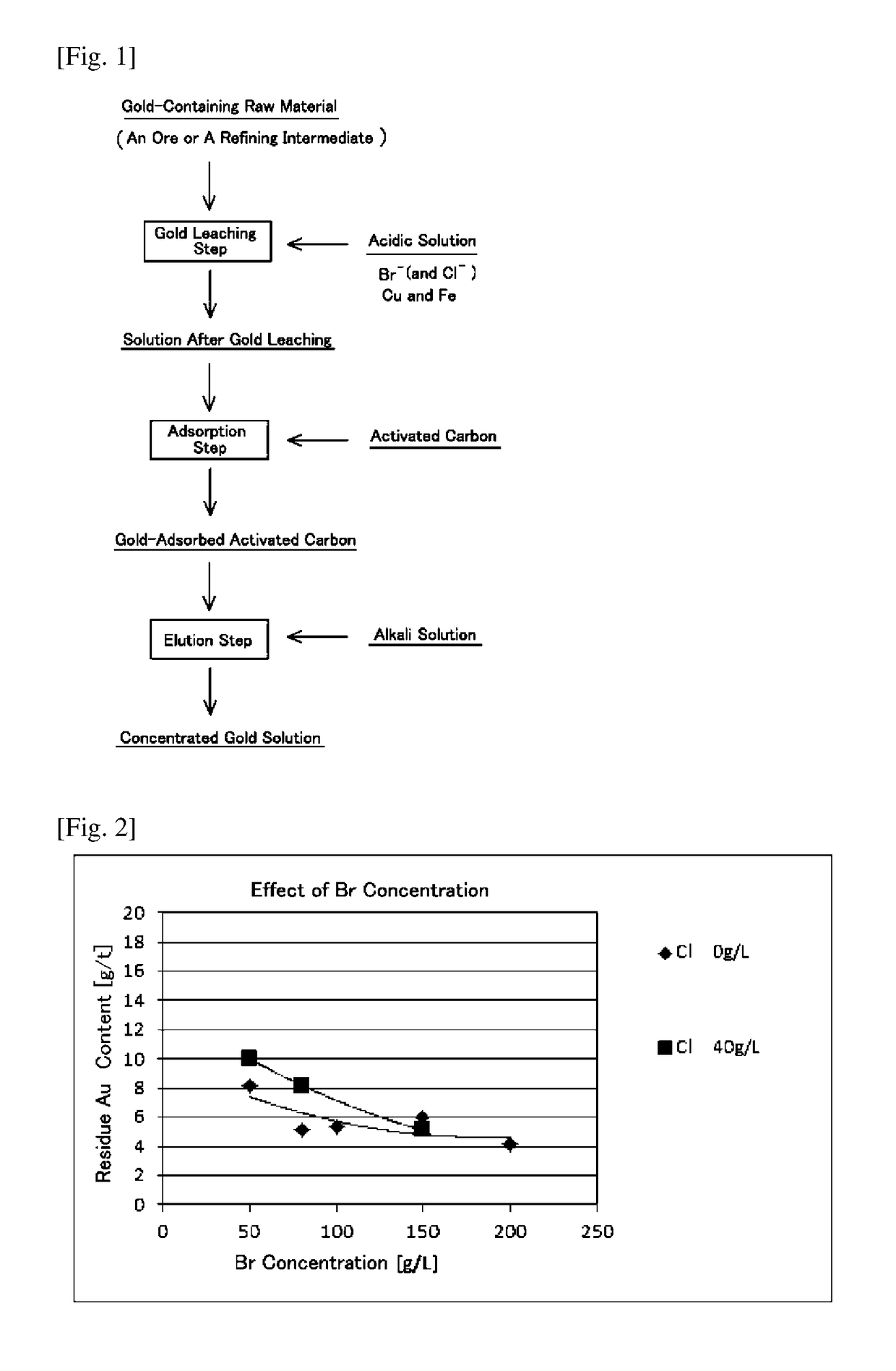
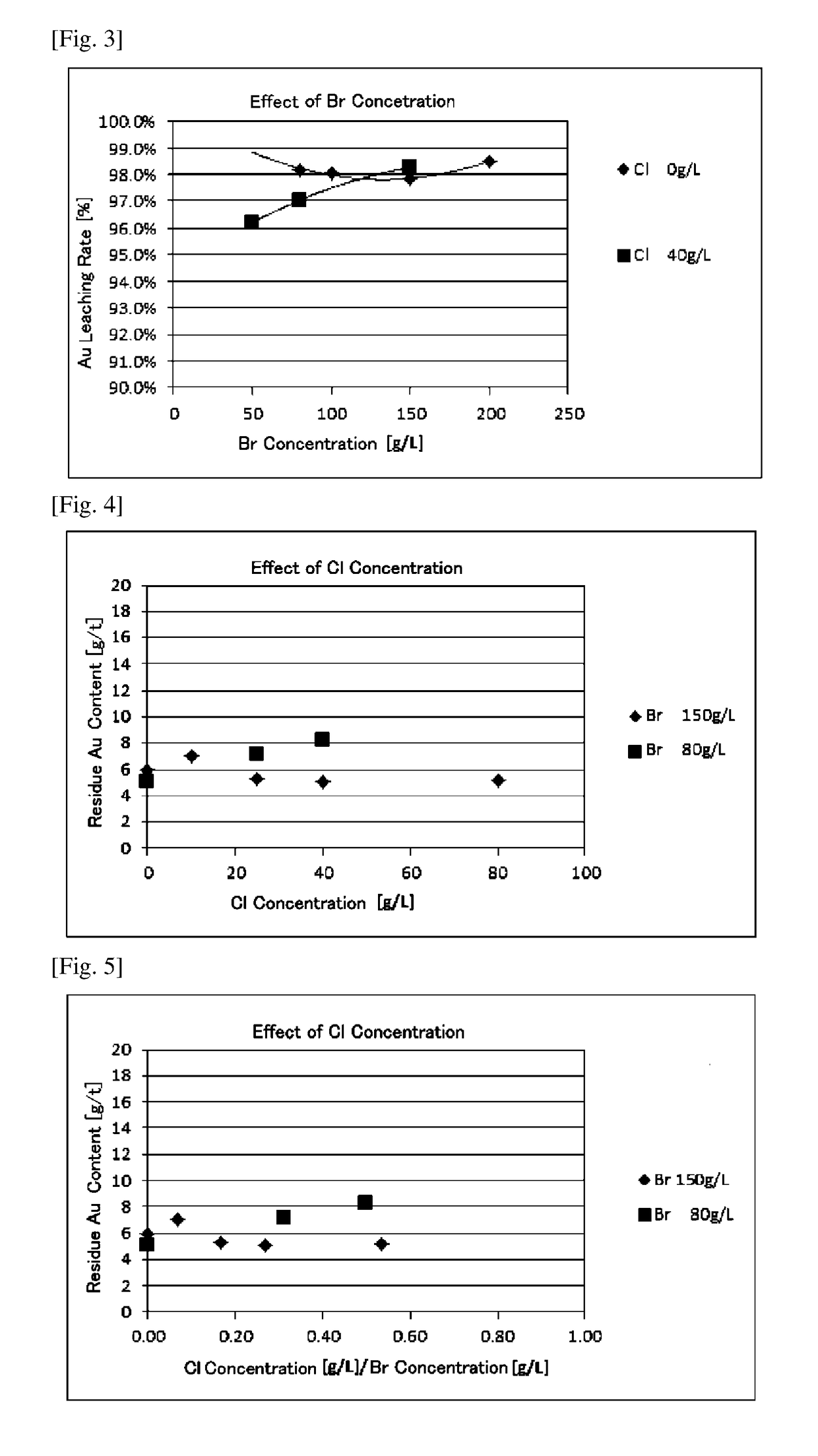
ActiveUS10883155B2Solve the low leaching ratePromote recoveryProcess efficiency improvementCu2 ionsPhysical chemistry
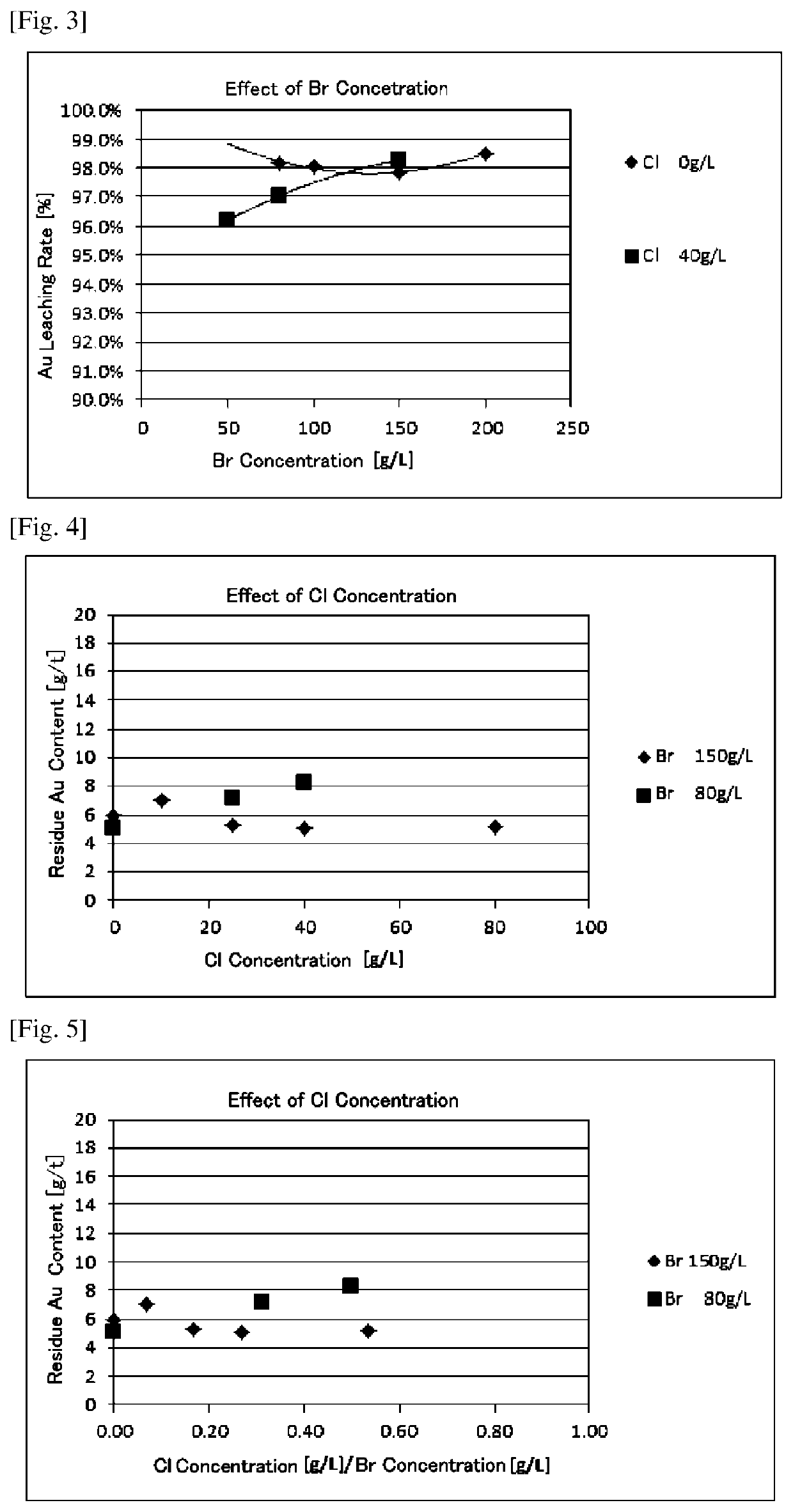
A method for recovering gold from an ore or a refining intermediate containing gold, comprising a step of contacting a gold-containing raw material obtained from the ore or the refining intermediate with an acidic solution containing a copper ion, an iron ion and a halide ion while supplying an oxidizing agent to leach the gold component in the raw material. The halide ion in the acidic solution is only a bromide ion, wherein the concentration of the bromide ion in the acidic solution is 100 g / L or more or the concentration of the bromide ion in the acidic solution is less than 100 g / L. When the concentration of the bromide ion is less than 100 g / L, a concentration ratio of the halide ion in the acidic solution is such that a ratio of the concentration of the chloride ion to the concentration of the bromide ion is ⅓ or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Method for recovering indium from indium-contained sulfuric acid solution and copper ash
ActiveCN103031444BSolve the low leaching rateLittle impact on extractionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionIndium
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
A kind of method utilizing Bacillus subtilis fermentation to prepare tailings eluent
InactiveCN106734140BLow costImprove rinsing efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationPulp and paper industryBacillus subtilis
The invention discloses a method for preparing tailing leacheate through fermentation of bacillus subtilis. The method comprises the following steps that beans or bean pulp is smashed till the grain size is 2-3 mm, water is added and mixed with the smashed beans or bean pulp, and then high-temperature sterilization is carried out; bacillus subtilis powder is added after the mixture is cooled to the room temperature, the new mixture is put on a constant temperature shaking table to be cultivated for 48-72 hours, and mixed fermentation liquor is obtained; and after the mixed fermentation liquor settles completely through standing, supernatant is fetched, and thus the tailing leacheate is obtained. According to the method, raw materials are easily available, the preparation process is simple, the preparation cost is greatly reduced, and no secondary pollution is caused to tailing treatment.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
Cement curing formulation and method for high-level radioactive boron waste resins from nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20140336437A1Low strengthHigh leaching rateSolid waste managementTransportation and packagingFreeze thaw resistanceNuclear reactor
A cement curing formulation and curing method for high-level radioactive boron waste resins from a nuclear reactor. The curing formulation comprises the following raw materials: cement, lime, water, curing aids and additives. The curing method comprises: (1) weighing the raw materials and the high-level radioactive boron waste resins, and adding lime into a curing container; (2) then adding the high-level radioactive boron waste resins; (3) feeding other raw materials under stirring; (4) adding the cement and supplementing water depending on the moisture state of the cement, and stirring until uniform; and (5) standing and maintaining after stirring until uniform. The curing formulation has the features of a high curing containment rate, high strength of the cured body, better water resistance, better freeze-thaw resistance, and low radioactive leakage.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +3
A kind of preparation method of compound leaching agent for chromium polluted soil
InactiveCN104492806BSolve the low leaching rateClean thoroughlyContaminated soil reclamationChromium CompoundsLotion
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite leaching agent for chromium-contaminated soil, which comprises the following steps: taking an inclined-plane PDA containing Aspergillus niger, washing the surface of the inclined-plane PDA with sterile water to obtain a first mixed material, and dissolving the first mixture The material is placed in a sterile Erlenmeyer flask, shaken and cultured for 11-13h to obtain the Aspergillus niger liquid; crush the saponins shell until the particle size is 2-3mm, add water and mix it, then sterilize it at high temperature, add the Aspergillus niger liquid after cooling to room temperature, Place it on a constant temperature shaker and cultivate it for 115-125 hours to obtain the second mixed material; after the second mixed material is left to settle completely, take the upper liquid and add it to citric acid and mix evenly to obtain a chromium-contaminated soil eluent. The raw material of the invention is simple and easy to obtain, the preparation process is simple, the preparation cost is greatly reduced, the leaching rate of chromium in the soil is high, and the remediation soil will not bring secondary pollution.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
A kind of preparation method of heavy metal lead polluted soil leachate
InactiveCN104479682BSolve the low leaching rateClean thoroughlyContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersAspergillus nigerPollution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a heavy metal lead-contaminated soil leachate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking inclined PDA containing aspergillus niger, rinsing the surface of the inclined PDA with sterile water to obtain a first mixture material, placing the first mixture material into a sterile conical flask, and performing shake cultivation for 11-13h to obtain an aspergillus niger solution; smashing tea seed cake to particle size of 2-3mm, adding water and mixing and then performing high-temperature sterilization, cooling to room temperature and then adding the aspergillus niger solution, culturing for 115-125h on a constant-temperature shaking table to obtain a second mixture material; thoroughly standing and precipitating the second mixture material, taking and adding supernatant liquid into lactic acid and evenly mixing to obtain the heavy metal lead-contaminated soil leachate. According to the preparation method, the raw materials are simply available, the preparation technology is simple, the preparation cost is greatly lowered, the leaching rate of lead in soil is high, and no secondary pollution to remedied soil exists.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
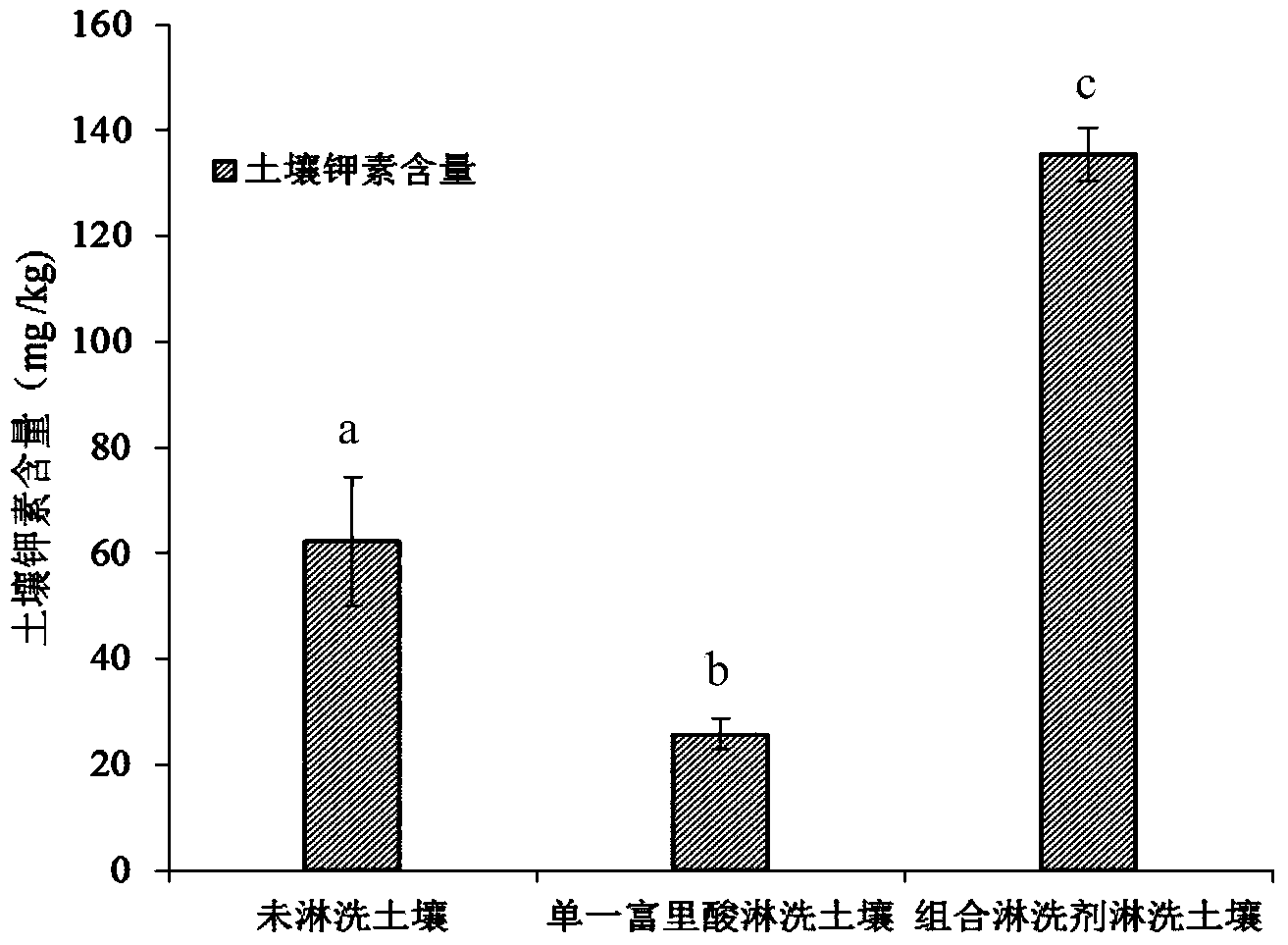
Fulvic acid-potassium chloride combined eluant, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a fulvic acid-potassium chloride combined eluant, and a preparation method and application thereof, relating to the technical field of restoration of heavy metal pollution in soil. According to the invention, humic acids with different qualities for restoring heavy metal cadmium polluted soil are dissolved in a 0.1m / L potassium chloride solution, a 0.1m / L sodium hydroxide solution is utilized to regulate the pH value to 11 or so to prepare a 0.05-1.00% humic acid solution, centrifugation is performed, and the separated solution is a fulvic acid-potassium chloride mixed solution; and the fulvic acid-potassium chloride mixed solution can be used as a combined eluant to elute the cadmium polluted soil. The chemical eluant used in the invention has the advantages of simple formula, obvious effect, strong operability, low application cost, high elution rate and high removal effect for cadmium ions in soil. The test indicates that the elution rate is optimal when the concentration of the eluate is 0.05%, the pH value is 4, the volume ratio of the eluant to the cadmium polluted soil is 10:1 and the elution time is 2 hours; and the eluate can not generate secondary pollution to the soil, and has an obvious supplementation action on potassium lost in the elution process.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Calcium aluminate slag containing sodium oxide and titanium oxide
InactiveCN102730729BSolve the low leaching rateImprove leaching rateAlkaline-earth metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationAluminateSlag
The invention relates to a calcium aluminate slag containing sodium oxide and titanium oxide which has a high alumina leaching rate. The slag comprises the following proportioning materials, by mass, 1.5% to 4% of Na2O, 23.5% to 6% of TiO, 54 to 57% of CaO, 17 to 21% of SiO2, 16 to 20% of Al2O3 and the total of 100%. The mass ratio of Al2O3 to SiO2 in the materials is 0.8 to 1.0. The total amount of CaO meets the following three requirements: the first requirement that CaO reacts with SiO2 to produce 2CaO. SiO2 is met; the second requirement of needed CaO amount to produce 12CaO. 7Al2O3 by reacting with Al2O3 is met; and the third requirement of needed CaO amount to have a molar ratio of 0.5 to 1.25 with TiO2 on the basis of the Na2O and TiO2 content in the slag is met. The alumina leaching rate of the slag increases to more than 83% compared with the initial 78%.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering gold from an ore or a refining intermediate containing gold
ActiveUS20180298465A1Solve the low leaching rateImprovement of gold recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementBromineConcentration ratio
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for recovering gold in an ore or a refining intermediate by sufficiently leaching gold in a raw material resulting from the ore or the refining intermediate in an acidic solution containing a copper ion, an iron ion and a halide ion, which can contribute to improve the recovery rate of gold. Provided is a method for recovering gold from an ore or a refining intermediate containing gold, the method comprising a step of contacting a gold-containing raw material obtained from the ore or the refining intermediate with an acidic solution containing a copper ion, an iron ion and a halide ion while supplying an oxidizing agent to leach the gold component in the raw material, and the halide ion in the acidic solution comprising at least a bromide ion, wherein the concentration of the bromide ion in the acidic solution is 100 g / L or more or the concentration of the bromide ion in the acidic solution is less than 100 g / L, and wherein when the concentration of the bromide ion is less than 100 g / L, a concentration ratio of the halide ions in the acidic solution is such that a ratio of the concentration of the chloride ion to the concentration of the bromide ion (a Cl / Br concentration ratio) is ⅓ or less.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method for preparing nickelous carbonate by utilization of waste ammonia decomposition catalyst
ActiveCN102765762BSolve the low leaching rateReduce lossNickel carbonatesDecompositionMetallic materials
The invention relates to the technical field of non-ferrous metal material processing and preparation and provides a method for preparing nickelous carbonate by the utilization of a waste ammonia decomposition catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out ball milling on an ammonia decomposition catalyst, roasting, dissolving the roasted ammonia decomposition catalyst by the addition of an acid, adding an alkaline compound, adjusting pH value to 3.5-4.5, and filtering to obtain a first filtrate; adding fluoride into the first filtrate, heating to generate calcium and magnesium precipitates, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a second filtrate; carrying out extraction and impurity removal on the second filtrate by the use of P204 and P507, carrying out back extraction on an organic phase by the use of an acid, and separating to obtain a nickel liquid; adding carbonate into the nickel liquid, precipitating, filtering, and drying filter residue to obtain nickelous carbonate. According to the method, by the adoption of multiple steps of oxidation-assisted leaching, extraction separation and carbonate precipitating nickel, nickel dipping has high yield and low loss, and the product has high purity, small particle size and high activity.
Owner:GEM CO LTD +1
Method for whole component microwave fast digestion and precious metal extraction from ionic liquid of waste circuit board
ActiveUS20220267879A1Add additional massRaise transfer toProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHydrometallurgy
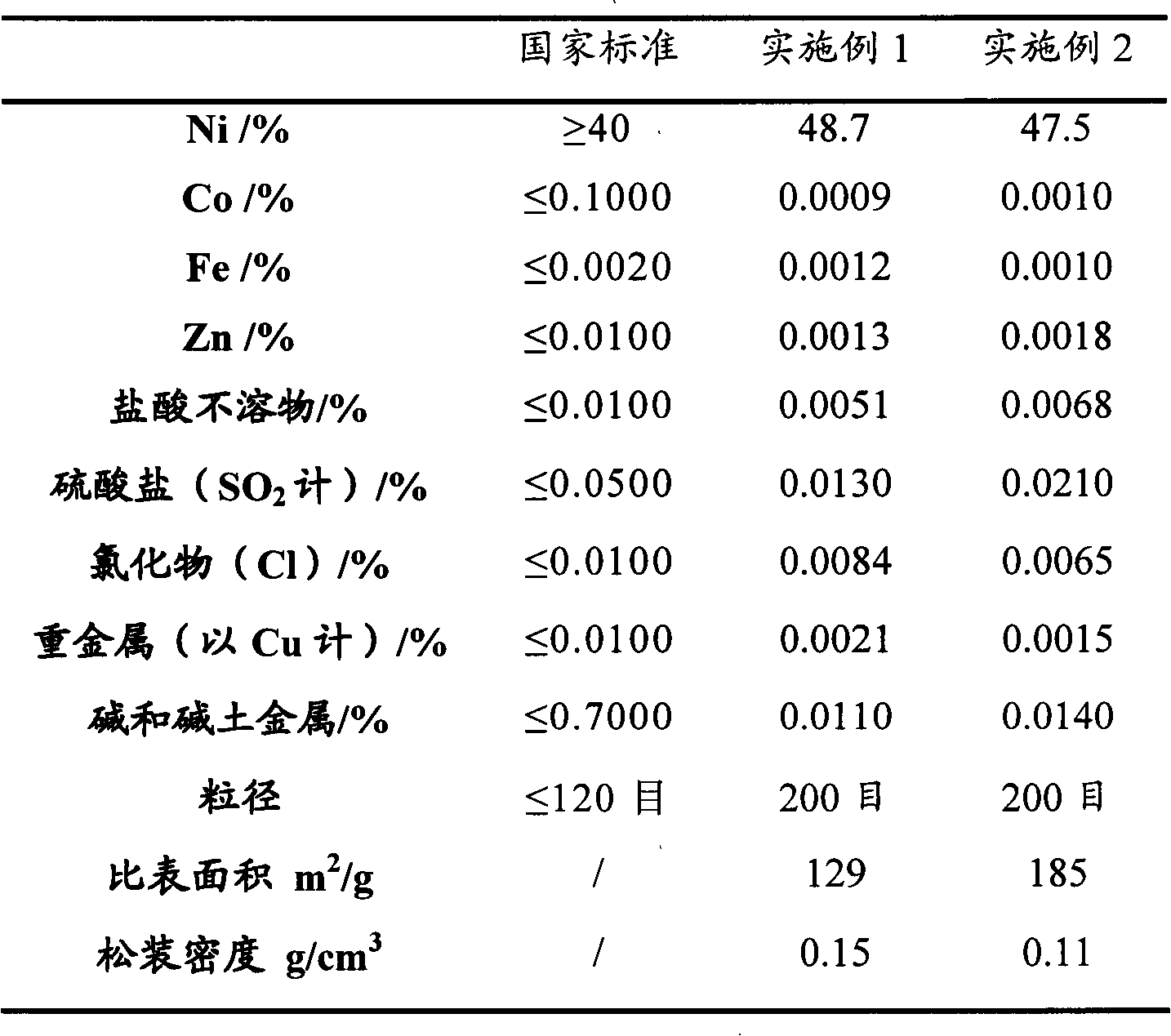
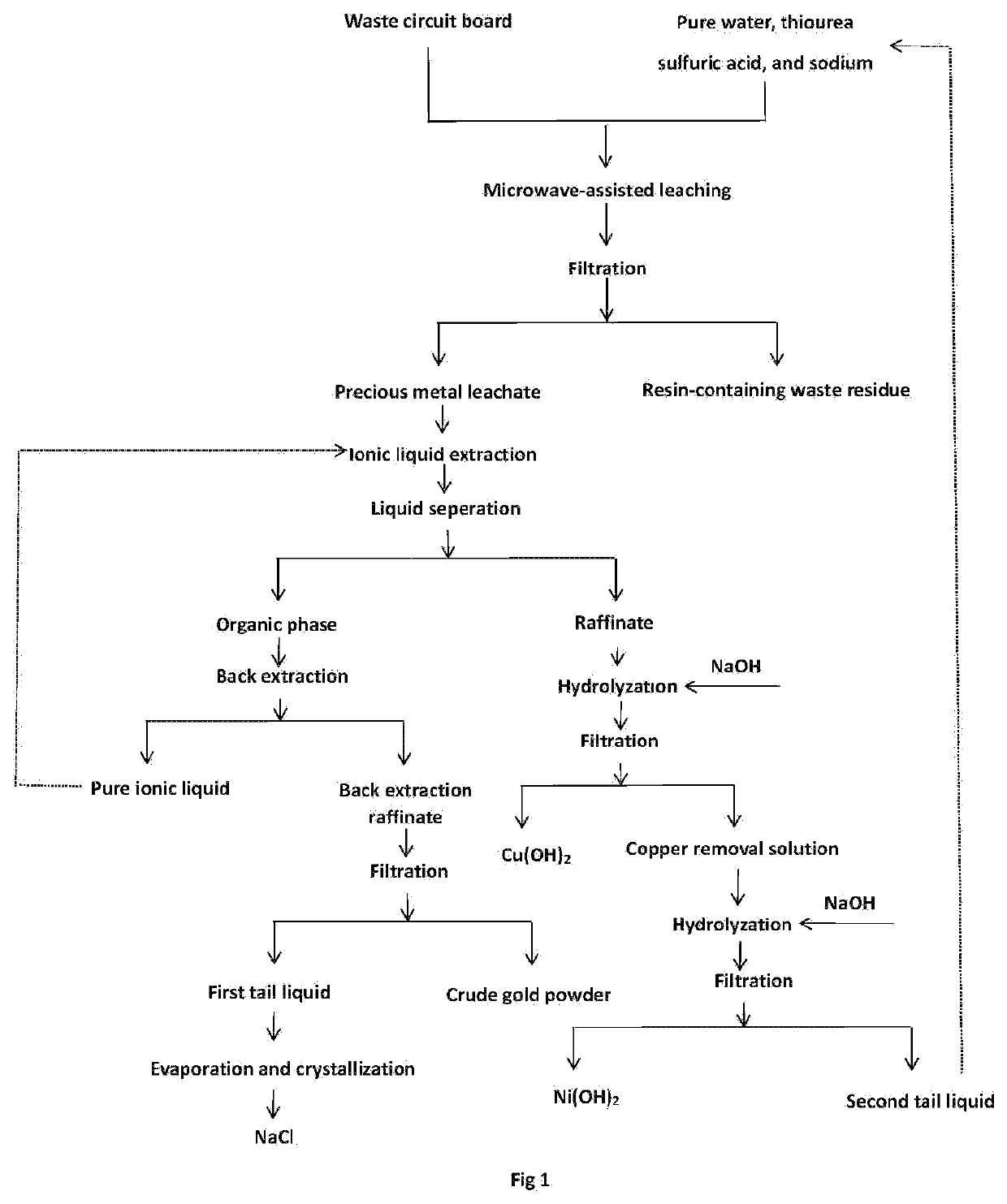
The invention discloses Method for whole component microwave fast digestion and precious metal extraction from ionic liquid of waste circuit board, and belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy. Based on the theory that microwaves can directly penetrate through a leaching medium to directly heat a circuit board, microwave-assisted leaching can reinforce mass transfer and heat transfer in the traditional leaching process, the leaching time is greatly shortened, and the leaching efficiency is improved. Before leaching, a waste circuit board does not need to be smashed, and environmental protection is achieved while energy is saved. The temperature rising process and reaction time of the reaction can be controlled, the whole process is conducted under the airtight condition, heat loss in the leaching process is avoided, the valuable leaching rate is high, the selectivity is high, and efficient leaching of valuable metal can be achieved. Precious metal leachate is extracted through imidazolium ionic liquid, the selectivity of the imidazolium ionic liquid to gold is high, and the co-extraction phenomenon of gold, nickel, copper and other ions is avoided. The method for extracting the precious metal leachate through ionic liquid is a green and clean recycling method, and the overall recycling rate of gold, nickel and copper can reach 99% or above
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Functional ionic liquid and preparation method thereof as well as method for ultrasonic intensified leaching of Cd in soil and recycling method
InactiveCN109180541AIncrease distribution rateIncrease rinsing rateOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acids salts preparationIonSodium succinate
The invention relates to a functional ionic liquid and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for ultrasonic intensified leaching of Cd in soil and a recycling method. The functional ionic liquid is bi(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinic acid tetrabutyl ammonium chloride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving bi(2-ethylhexyl) sulfo sodium succinate and tetrabutyl ammonium chloride in trichloromethane, stirring and performing refluxing reaction for 20-30h at 45-55 DEG C, so as to obtain a crude product; washing the crude product until no chloride ion is detected ina water phase; removing trichloromethane from the obtained product, and drying to obtain the functional ionic liquid. The method for leaching Cd in soil comprises the following steps: mixing soil, thefunctional ionic liquid and water, ultrasonically leaching heavy metal Cd in the soil; performing centrifugal separation after leaching is ended, so as to remove ionic liquid and water, and washing and drying the obtained soil. According to the invention, Cd in the soil can be effectively leached, the leaching time is short, and the functional ionic liquid can be recycled, thus being green and environment-friendly.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com